Overexpression of DEAD box protein pmss116 promotes ATP-dependent splicing of a yeast group intron in vitro
|
|
|
- Hollie Floyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nulei Aids Reserh, 1995, Vol. 23, No. 15 Overexpression of DEAD ox protein pmss116 promotes ATP-dependent spliing of yest group intron in vitro sell Niemer, Crlo Shmelzer nd G. Vlentin Borner* nstitut fur Genetik und Mikroiologie, Universitt Miinhen, Mri-Wrd-Strsse 1, D Munhen, Germny Reeived April 1, 1995; Revised nd Aepted June 19, 1995 ABSTRACT The group intron l1, the first intron of the mltohondril ytohrome gene in yest is self-spliing n vitro. Geneti evidene suggests tht frns-ting ftors re required for in vivo spliing of this intron. n ordne with these findings, we present in vitro dt showing tht spliing of h under physiologil onditions depends upon the presene of proteins of mitohondril lyste. ATP is n essentil omponent in this retion. Overexpression of the nulerenoded DEAD ox protein pmss116 results in mrked inrese in the ATP-dependent spliing tivity of the extrt, suggesting tht pmss116 my ply n importnt role in spliing of l1. NTRODUCTON n orgnisms with split genes the introns re removed from the primry trnsript y RNA spliing. Spliing of nuler premrna introns tkes ple on the splieosome, omplex ontining numerous proteins nd five smll nuler rionuleoprotein prtiles (snrnps). Notly, severl of the proteins prtiipting in splieosome ssemly or the two trnsesterifitions require ATP hydrolysis. Yet, for the hemil retion itself energy input is dispensile, s group introns undergo self-spliing without ATP (reviewed in 1). n ontrst, protein-independent utotlyti spliing of some group nd group introns hs een shown in vitro (2-5). Two lines of evidene, however, hve led to the view tht speifi fr/w-ting ftors, presumly proteins, re essentil for in vivo spliing of most, if not ll, group nd group introns (reviewed in 6). First, self-spliing n only proeed under reltively non-physiologil onditions, e.g. 60 mm Mg 2+ nd 45 C (2,5). Seond, geneti nlysis of spliing in fungl mitohondri hs resulted in the hrteriztion of numerous nuler s well s orgnellr frnj-ting mutnts tht impir spliing of one or more mitohondril introns. Two lsses of proteins tht prtiipte in spliing of orgnellr introns hve een identified y their different pttern of inheritene. Mturses re enoded y open reding frmes loted in the intron tht they help to exise. Thus their synthesis is dependent upon mitohondril trnsltion (6-9). A seond lss of muttions tht ffets spliing of orgnellr introns is loted on nuler genes whose produts re presumly imported into the mitohondri where they ssist spliing. These genes inlude, for exmple, CBP2, MSS18 nd MSS116 in yest or yt-18 in Neurospor (10-13). The nuler yest gene MSS116 ws initilly isolted vi geneti sreenrevelingtht this gene n omplement nuler mutnt defetive in spliing of severl group nd possily group introns (12). nterestingly, the sequene of MSSJ16 shows remrkle degree of sequene homology with new fmily of proteins, the DEAD ox proteins, so lled euse they shre the highly onserved motif Asp-Glu Al-Asp, together with six other onserved elements (14). Memers of this nd the relted DEAH sugroup prtiipte in vriety of RNA-ssoited funtions, e.g. initition of trnsltion, splieosoml spliing nd riosome ssemly (15-19). Some memers of the DEAD ox fmily hve een shown to possess n ATP-dependent RNA unwinding tivitiy (20-22). Most of the orgnellr spliing ftors hrterized to dte re essentil for exision of only one or of few introns nd exhiit no ovious sequene homologies mongst eh other. This speifiity of ftors for their respetive introns distinguishes orgnellr from splieosoml spliing, where roughly the sme set of ftors proess the mjority of mrnas. Consequently, it is widely elieved tht ll introns with onserved seondry strutures were originlly self-spliing. Aording to this hypothesis, it ws only lter in evolution tht protein-ssisted spliing developed independently for eh of these introns (6). Although numerous trns-ting ftors ffeting spliing of group nd group introns hve een defined y muttions in mitohondril systems, iohemil evidene for suh prtiiption is still sre nd hs een suessfully demonstrted only for some proteins involved in group intron spliing. One exmple is the CYT-18 protein in Neurospor, whih is identil to mitohondril tyrosyl-trna synthetse. The purified protein CYT-18 hs een shown to filitte spliing of the mitohondril lrge rrna intron (13,23). We were interested in identifying the trns-ting ftors tht promote spliing of group intron l 1, the first intron of the ytohrome gene in yest mitohondri. The development of n ssy omprising proteins of mitohondril lyste mde it possile to demonstrte protein-ssisted in vitro spliing of group intron. This retion is ATP-dependent. One protein involved in spliing of ll is enoded y the nuler gene *To whom orrespondene should e ddressed t present ddress: Zoologishes nstitut, UrriversitSt MUnhen, Luisenstrsse 14, D Miinhen, Germny
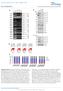
2 Nulei Aids Reserh, 1995, Vol. 23, No MSS116. Overexpression of this gene inreses the ATP-dependent spliing tivity of the extrt Prmeters of pmss116-promoted spliing of l 1 hve een hrterized. MATERALS AND METHODS Strins of Shromyes erevisie, growth onditions nd preprtion of mitohondri! mtrix proteins The wild-type strin used in this study ws S.erevisie A237 (MAT, trpl, ur3-52, rho + ), whih is devoid of mitohondril DNse nd RNse NUC1 (24). The host strin for trnsformtions ws A237, onstruting A237/pGU (ontining plsmid pgu) nd the AfSS//6-overexpressing strin A237/pGU:MSS116 (ontining MSS116 in plsmid pgu). Cultures of A237 were grown t 30 C in YP medium supplemented with 3% glyerol. Strins ontining the pgu plsmid or derivtive thereof were grown in miniml medium supplemented with essentil mino ids t 30 C. For preprtion of mitohondril mtrix proteins ells were grown to log phse nd hrvested t titer of 10 7 ells/ml. Mitohondri were prepred from spheroplsts y osmoti lysis nd purified y differentil entrifugtion. Mtrix proteins were otined y sonition of the orgnelles nd susequent entrifugtion t g nd g to remove mitohondril memrnes nd riosomes, respetively. The olleted extrt (S100) ws dilyzed nd stored t-70 C in 20% glyerol, 0.1 mm EDTA, 1 mm PMSF, 1 mm DTT, 20 mm HEPES-KOH, ph 7.4, 100 mm NCl. Preprtion of RNA Trnsripts were synthesized y in vitro trnsription with T3 RNA polymerse. Trnsription ssys were rried out in 20 u.1 retion ontining 5 \xg templte DNA, 40 U enzyme, 40 mm Tris-HCl, ph 7.5,6 mm MgCl 2,10 mm DTT, 4 mm spermidine, 500 nm eh rntp for 2 h t 37 C. For genertion of internlly leled trnsripts 10 u.ci [ 32 P]UTP were dded to the ssy. Following trnsription prernas were eletrophoresed on 5% polyrylmide-8 M ure gels, utordiogrphed, extrted from the gel nd purified. Templtes for synthesis of prerna were plsmid BS/l 1/5+24 (25), whih hrors the omplete intron ll, 35 nt of the 5' exon nd 238 nt of the 3' exon, nd plsmid BS/5 (26), respetively. n vitro spliing ssys n vitro self-spliing ws performed in 20 u,l Tris-HCl, ph 7.5, 60 mm MgCl 2, 2mM spermidine, 500 mm NH4C t 45 C for 15 min. The retion ws stopped y ethnol preipittion. The resulting pellet ws wshed with 70% ethnol nd dried under vuum. Protein-dependent in vitro spliing ws performed in 40 il 10 mm HEPES-KOH, ph 7.5, 10 mm Tris-HCl, ph 7.5, 100 mm NCl, 10 mm MgCl 2, 2 mm DTT, 2 mm ATP, 10 ig Esherihi oli trna nd 10 U RNse inhiitor t 28 C for vrious times. The retion ws stopped with 60 u.150 mm NA, ph 5.2, 50 mm EDTA, 0.1% SDS, 2.5 u.1 proteinse K (20 mg/ml). After phenol/hloroform extrtion the retion produts were preipitted with ethnol nd the resulting pellet wshed nd dried. The ssys were done in the presene of u.g mitohondri] mtrix proteins nd in the presene of extrts previously digested with proteinse Krespetively.The produts of in vitro spliing retions were seprted y eletrophoresis on denturing 5% polyrylmide gels. Constrution of plsmid pgv:mss116 Plsmid CA7 (27) ontins the omplete sequene of MSS116 with n dditionl 5' 600 nt nd 3' 350 nt s genomi HindB frgment. The Hindlll frgment of CA7 ws loned into Bluesript SK (Strtgene). The 5' non-oding region of the MSS116 sequene ws then shortened to 60 nt yrestritionof the plsmid with Bll nd Sml. Restrition of the resulting plsmid with BmH nd Sil yielded frgment ontining the MSS116 gene with 5' nd 3' non-oding regions nd djent Bluesript polylinker sequenes. This frgment ws loned into the multiopy yest 2(i plsmid pgu nd the resulting plsmid designted pgv:mss116. pgu ws derived from plsmid pgl (28) y repling the TRP1 mrker gene with the URA3 mrker gene derived from puc19. Trnsformtion of A237 ws rried out ording to Klee et l. (29). Trnsformnts were seleted on syntheti omplete medium without uril. soltion of S.erevisie RNA nd Northern nlysis Cells were hrvested in log phse, wshed one in H 2 O nd the pellet frozen in liquid nitrogen. The pellet ws resuspended in extrtion uffer (0.15 M NCl, 50 mm Tris-HCl, ph 7.5,5 mm EDTA, 5% SDS). Cells were roken y vortexing with glss eds nd phenol/hloroform for 5 min. Nulei ids were extrted three times with phenol/hloroform nd preipitted from the liquid phse with ethnol, 0.3 M NA. nution for 3 h in 10 mm Tris-HCl, ph 8.0, 1 mm EDTA, 3 M LiCl preipitted the RNA. Whole-ell RNA ws seprted on formldehyde-grose gels nd trnsferred to nylon memrnes (Amershm). DNA proes were 32 P-leled y nik trnsltion (30). The nik-trnslted hyridiztion proe for detetion of MSS116 sequenes ws the desried HindlW frgment of plsmid CA7 (27). Anlysis of pmss116 protein Rit ntiodies were rised ginst 14 mino id domin derived from mino id positions of pmss 116 (sequene S-R-P-R-T-R-S-R-E-D-D-D-E-V). SDS-PAGE ws rried out y the method of Lemmli (31), using 5% stking gel nd 12% seprting gel. Eh lne ws loded with 30 Xg mitohondril proteins. After trnsferring the seprted proteins to n mmoilon P memrne (Millipore) the produts ould e proed with ntiserum P, direted ginst the ove-desried mino id domin. mmunolots were stined with ECL (Amershm). RESULTS Protein-dependent spliing of ll depends on ATP The group intron ll hs previously een shown to undergo self-spliing in vitro, retion identil with splieosoml spliing in mehnism,resultingin the exision of n intron lrit vi two susequent trnsesterifitions (5). Yet effiient selfspliing of ll requires high slt onentrtions nd high temperture, suggesting tht /r/w-ting ftors re essentil for the in vivo exision of this intron. n order to hrterize suh ftors, we estlished n in vitro system whih llowed us to ssy for protein-dependent spliing.
3 2968 Nulei Aids Reserh, 1995, Vol. 23, No min M 30min 60 min 120 min mmatp M L-3'E _ L «P 5E-3E ^. Figure 2. ATP dependene of spliing of l 1. Spliing ssys in the presene of ntive mitohondril proteins were erned out s desried (see Mterils nd Methods) with inresing onentrtions of ATP (0-10 mm). Figure 1. Protein-dependent spliing of ll in the presene of mitohondril SlOO extrt 32P-Leled l/5+24 RNA ('prerna') ws inuted for vrious times in the presene of 15 ig mitohondri] mtrix proteins pretreted with proteinse K (), 15 ig ntive proteins () nd in the sene of proteins (). The produts were gel eletrophoresed on 5% denturing polyrylmide gels. Lne M shows the produts of n utotjyti retion of prerna. L-3'E, lrit with ovlenuy ound 3' exon; L, lrit; P, prerna; 1, liner intron, 5'E-3'E, ligted exons. An internlly 32P-leled trnsript hroring l 1 ws inuted under vrious onditions with n SlOO extrt prepred from rude mitohondril lyste. To minimize non-speifi endogeneous nulese tivity, mitohondri were isolted from yest strin A237, whih is defiient in the extremely tive mitohondri] NUCl exo-endonulese (24). After inution of the trnsript with the mitohondril SlOO extrt under onditions resemling the physiologil stte nd in the presene of ATP the RNA ws nlyzed y polyrylmide gel eletrophoresis. To monitor the effiieny of spliing we sreened for the presene of n intron lrit, whih is esy to detet due to its low eletrophoreti moility. As n e inferred from the time ourse shown in Figure 1, spliing under physiologil onditions only proeeded in the presene of mitohondril SlOO extrt (lnes ), wheres no lrit ws formed if the RNA ws inuted in retion uffer lone (lnes ). Preinution with proteinse K resulted in mrked redution in spliing tivity, inditing the prtiiption of proteins in the retion (lnes ). The time ourse shows tht spliing inreses linerly for 2 h nd lrit formtion plteus t ~5% of the input prerna (Fig. 1). n omprison with optimized in vitro self-spliing, where >50% of the intron ws exised from the preursor fter 30 min (see lne M in Fig. 1), the protein-dependent in vitro retion is reltively slow. Lyste-dependent spliing of group intron ll n only proeed in the presene of ATP nd Mg 2+. Aording to the experiment shown in Figure 2, there is n optimum spliing tivity t 2 mm ATP. This tivity drops t higher ATP onentrtions, however, when the Mg2+ onentrtion is inresed onomitntly with ATP, protein-dependent spliing tivity remins unhnged (not shown). The pprent deline in spliing tivity t higher ATP onentrtions thus seems to e due to the omplexing of ATP with Mg 2+, rther thn to n inhiitory effet of high ATP onentrtions. As Mg 2+ onentrtions >10 mm lso promote utotlyti spliing, ll susequent experiments were rried out t 10 mm Mg 2+ nd 2 mm ATP. The ATP dependene of the spliing tivity oserved in these experiments with mitohondril lystes lerly distinguishes protein-dependent spliing of ll from utotlyti spliing of group introns, pthwy tht hs een shown to e intrinsilly independent of nuleotide o-ftor (3-5). Overexpression of MSS116 Hving estlished tht protein-ssisted spliing of l 1 depends on ATP, we further investigted the nture of this spliing tivity. As shown in lnes of Figure 1, preinution of the extrt with proteinse K resulted in ler redution in spliing tivity. The fint nd in lnes fter 60 nd 120 min respetively ould e due to inomplete digestion of lyste proteins y proteinse K. Another possile explntion ould e tht proteinse K-generted peptide frgments my hve ertin stilizing effet on the tlytilly ompetent onformtion of this group intron. Peptides with high positive hrge hve previously een shown to stimulte tlysis of the hmmerhed riozyme (40). n ontrst, spliing tivity proved insensitive to mirool nulese nd thus seems to onsist of one or severl protein omponent(s) lking n essentil RNA omponent (not shown). At the time of our initil experiments it ws shown tht the yest gene MSS116 n omplement nuler mutnt defiient in spliing of l 1, nother group intron nd possily severl group introns in yest mitohondri (12). n the sme study the gene MSS116 ws shown to e loted on 2.9 k genomi Hin&\\\ frgment with n ORF oding for protein with 664 mino ids.
4 Nulei Aids Reserh, 1995, Vol. 23, No The derived protein sequene of pmss 116 shres remrkle homology with memers of the DEAD/H ox fmily, protein fmily some memers of whih hve demonstrted ATPpGU MSS pgu MSS dependent RNA unwinding tivity (14,20-22). Compred with the prototypes of this fmily, p68 nd ef4, pmssl 16 possesses 97,4 n dditionl streth of 30 minly positively hrged mino ids t its N-teiminus, s expeted of presequene required for 4.4 trgeting proteins into mitohondri (12,32). 72 kd 69 We inferred tht the gene produt of MSS116 ould e possile MSS116 ndidte for the ATP-dependent spliing tivity oserved in 2,4 mitohondril lystes. Therefore, we hve ompred the spliing 2.1 kb tivity of n extrt from n MS577<5-overexpressing strin with tht of strin rrying the hromosoml opy of this gene only MSS116 ws overexpressed under trnsriptionl ontrol of the onstitutive GPD promotor (33). To remove possile endogeneous expression signls, the sequene 5' of the MSS116 initition odon ws shortened to length of 60 nt The resulting 2.3 k frgment C ontining MSS116 flnked y some non-oding sequenes ws inserted into the 2u. plsmid pgu ehind the GPD promotor. Vetor pgu MSS K pgu is derived from pgl (28) y repling the seletion mrker t TRP1 with URA3. Susequendy the onstrut pg\j:mss116 ws trnsformed into yest strin A237. As negtive ontrol we used extrts from wild-type strin A237, whih ontins single opy of MSS116 ompred with the overexpressing strin. To ensure 97,4 similr growth onditions A237 ws trnsformed with plsmid pgu lking the MSSU6 insert (A237/pGU). -72kD Anlysis of the expression levels of MSS116 ws performed y 69 MSS116 Northern nd Western lots of A237/pGU:MS5776 nd A237/pGU respetively. A RNA lot proed with n A/SS776~-speifi DNA frgment showed signl of 2.1 k tht ws present in A237/pGU:MSSJ16 t high onentrtion, while the trnsript from the hromosoml gene ws hrdly detetle 46 in A237/pGU (Fig. 3). Thus MSS116 is trnsried with high effiieny into stle mrna in the overexpressing strin. As next step n ntiody ws rised ginst the 14mer peptide P Figure 3. Overexpression of MSS 116 in yest strin trnsformed with plsmid (S-R-P-R-T-R-S-R-E-D-D-D-E-V), representing n N-terminl pgumss116. () Northern nlysis of whole-ell RNA from A237/pGU pmss 116 epitope (mino id positions 67-80) of potentilly (pglf) ompred with RNA from A237/pGU:W55//6 (MSS). The RNA ws seprted on formldehyde grose gel, trnsferred to nylon memrne nd high immunodominne s predited y the progrm DNA STAR proed with nik-trnslted M55//6-speifi DNA frgment. The hyridiz(34,35). The nti-pi serum, ut not pre-immune serum, reogtion proe detets 2.1 k trnsript, speifilly overexpressed in nized protein in the mitohondril lyste with n pprent A237/pGU:MSS//6. () mmunolot nlysis of mitohondril proteins. moleulr weight of 72 kd. This oinides with the size Mitohondri] mtrix proteins from the strins indited were seprted on 12% SDS polyrylmide gels with 5% slking gel. n the immunolot shown predited for pmss 116 lking the ~30 mino ids of puttive nti-pmssl 16 ntiserum P ws used for deortion. The moleulr weight of import sequene t its N-terminus (Fig. 3). While the silver pmss16 ws estimted from omprison with stndrd protein mrker, stined SDS-PAGE gel showed no differene in the expression indited on the left side of the lot () mmunolot nlysis of proteins shows pttern of mitohondri! proteins etween A237/pGU.MSSl16 the loliztion of pmss 116 in the mitohondril mtrix. dentil mounts of nd A237/pGU (not shown), the Western lot in Figure 3 proteins (20 ig) were seprted y SDS-PAGE nd deorted ording to (). Mtrix proteins re from A237/pGU (pgu) nd A237/pGU:MSSl 16 (MSS). reveled tht the onentrtion of protein pmss116 is t lest Lne K shows mitohondril memrne proteins from A237/pGU:MSS 116 for 30-fold higher in A237/pGU:AfSS776 thn in A237/pGU. The omprison. ellulr loliztion of pmss116 ws determined y immunodeortion of the mitohondril mtrix frtion, s ompred with the memrne frtion. Anti-Pi only reognized nd in Figure 4, the level of lrit formtion ws signifintly inresed the mtrix frtion. This experiment onfirmed umultion of in the A231/pGV:MSS116 extrt (lnes ) ompred with the pmss116 in the mitohondril mtrix (Fig. 3). A237/pGU extrt (lnes ). The differene in spliing tivities is espeilly pprent fter 60 min nd orreltes roughly with the level of overexpression oserved in the Western lot. Aording n vitro spliing of ll is promoted y overexpression of to the experiment shown in Figure 4, lrit formtion seems to MSS116 hve lg period in the lyste from the overexpressing strin. However, this oservtion ws not onsistent nd ws not n order to investigte whether the level of MSS116 expression investigted further. We lso oserved tht extrts from strin orreltes with the spliing tivity found in mitohondri! A237/pGU exhiited redued spliing tivity thn those from lystes we inuted l 1/8+24 prerna (25) with the two non-trnsformed A237. This is proly due to the differene in respetive extrts. As n e seen in the time ourse shown in
5 2970 Nulei Aids Reserh, 1995, Vol. 23, No min 30 min Control 60 min M G A M L Figure 4. Enhned spliing tivity of extrts derived from A237/pGU:AfSS//6 ompred with A237/pGU. Spliing ssys were performed s desried (see Mterils nd Methods) in the sene of proteins (), in the presene of mitohondri] proteins from A237/pGU () nd in the presene of mitohondril proteins from A237/pGU:MS5//6 (). pgu U C G A U C MSS r G A U C - i Figure 5. The spliing retion speifilly requires ATP. Spliing ssys were rried out in the sene of proteins (ontrol), with A237/pGU extrts (pgu) nd with protein extrts from A237/pGU:A/SS//<5 (MSS). Where indited, 2 mm ATP in the retion uffer ws sustituted y 2 mm GTP (G), CTP (C) or UTP (U) respetively. nution ws performed for 45 min. DSCUSSON growth medium (A237/pGU ws grown on seletive miniml medium). n prllel preprtions from A237/pGU nd A237/pGU:M55776, however, extrts from A237/pGU:A/SS7/6~ lwys exhiited higher spliing tivity thn A237/pGU. Our results thus demonstrte tht overexpression of nuler gene MSS 116 lone is suffiient to inrese ATP-dependent spliing of group intron l 1 in mitohondri] lyste. n order to eluidte this proess further, the speifiity of pmss 116-promoted spliing with respet to o-ftors nd the RNA sustrte ws investigted. Aording to the results shown in Figure 5, pmssl 16-promoted spliing of ll proeeds only in the presene of ATP, while none of the other stndrd rntps n e used. A similir speifiity for ATP hs lso een shown for other DEAD ox porteins, inluding DpA (19) nd ef4 (21). To lern more out the sustrte speifiity of pmssl 16promoted spliing we tested whether A231/pG\J:MSS116 lyste n lso enhne spliing of other group introns. ntron 5, the lst intron of the oxl gene in yest mitohondri is losely relted to l 1 in seondry struture nd primry sequene, oth introns elonging to the sme sugroup of group introns (36). n vitro self-spliing of!5 hs een oserved under onditions similir to those of l 1 (3,4). However, neither the extrt from A237/pGU nor tht from A237/pGU:A/55/76 hd ny detetle effet on spliing of 5, i.e. no lrit formtion ould e oserved under onditions optimized for ll spliing (not shown). Our findings re onsistent with results from the geneti sreen, showing tht MSS116 is not essentil for in vivo exision of 5 (12). The oservtion tht overexpression of MSS 116 is not suffiient to generlly enhne spliing of group introns seems to indite tht pmss 116 does not ffet l 1 spliing s sequene-non-speifi RNA helise, n tivity oserved for some DEAD ox proteins (20-22). n this work we hve nlyzed protein-dependent spliing of mitohondril yest intron ll, n in vitro utotlyti group intron. We estlished n in vitro system tht llows spliing of l 1 prerna only in the presene of mitohondril S100 extrt ATP is n essentil omponent in this retion. The ft tht the spliing tivity of the extrt is signifintly inresed y overexpression of DEAD ox protein pmss 116 suggests tht this protein my ply n importnt role in spliing of l 1. n vitro spliing of ll under physiologil onditions depends on protein lyste nd ATP Spliing of group introns proeeds vi two trnsesterifitions, resulting in the exision of rnhed struture, the intron lrit (3-5). Extensive reserh with mutnts of utotlyti group introns hs provided reltively ler onept of the funtion of onserved seondry struture domins 1-6 for the spliing retion (36,37). These dt imply tht ll tlyti tivities required for spliing re inherent in the onserved struture of the intron RNA. However, t physiologil Mg 2+ onentrtions nd t low temperture no utotlyti tivity ould e oserved. Our results show tht under these onditions effiient lrit formtion (nd onsequently formtion of the funtionl mrna) depends upon the presene of one or severl protein(s) from mitohondril S100 extrt. This finding supports the hypothesis tht the utotlyti retion, whih is hrdly detetle under physiologil in vitro onditions, n e enhned onsiderly y the tion of trns-ting ftors. The oservtion tht proteinse K, ut not mirool nulese, redues spliing nd tht ATP is n essentil oftor, whih nnot e sustituted y other rionuleotide triphosphtes, suggests tht DEAD ox protein pmss 116 ould e the ndidte protein. The speifiity for ATP is mjor hrteristi of the DEAD ox proteins investigted
6 Nulei Aids Reserh, 1995, Vol. 23, No to dte (19-21). The dependene on ATP distinguishes the protein-dependent pthwy from in vitro self-spliing of group introns, whih does not require n externl energy soure. n oth the protein-dependent nd the utotlyti pthwys the intron is exised s lrit. t therefore seems resonle to ssume tht protein-dependent nd utotlyti spliing of ll proeed vi the sme mehnism, despite the ft tht protein-dependent spliing relies on the presene of ATP. The role of pmss116 in spliing of ll A geneti pproh hs previously shown tht ll nnot e exised from the primry trnsript in yest strins rrying muttion in the nuler gene MSSJ16(\2). We hve onstruted strin tht overexpresses DEAD ox protein pmss116. Northern nlysis shows tht this gene is trnsried in strin A237/pG\J:MSS116 with onsiderle effiieny into stle mrna. t seems, therefore, tht the low undne of MSS116 mrna in the wild-type is due to low level of trnsription, rther thn to the instility of the trnsript, s disussed erlier (27). The trnsltion produt pmss116 is present in the mitohondril mtrix of strin A237/pGU:A/55//6 s solule ompound t onsiderly inresed onentrtion s ompred with the wild-type strin. Dt from our in vitro spliing ssy show tht overexpression of MSS116 signifintly enhnes protein-dependent spliing of l 1. As in the wild-type lyste, the retion is dependent on ATP. A plusile interprettion of these results is tht the ATPdependent spliing tivity n e ttriuted to DEAD ox protein pmss116. This is supported y t lest two lines of evidene. First, the spliing tivity present in mitohondril extrts exhiits ll the iohemil hrteristis oserved for DEAD ox proteins, nmely dependene on ATP nd Mg 2+ (17-20). Seondly, Western nlysis hs provided evidene tht overexpressed pmss116 is umulted in the mitohondri] mtrix, s lredy suggested y die puttive import sequene t the N-terminus of the protein (12). An indiret influene of pmss116 on ll spliing vi mitohondril trnsltion n e exluded, sine spliing of l 1 does not require mitohondrilly enoded mturse (38). Our results, of ourse, do not prelude the possiility tht pmss116 ould possily e ytoplsmi trnsltion ftor tht indues the synthesis of spliing ftor speifi for l 1 nd other mitohondril introns. Thus we would like to emphsize tht onlusive eluidtion of the role of pmss116 in spliing of ll will require purifition of this protein. Addition of the purified omponent to the mitohondril lyste should promote spliing of l 1 similrly to the overexpression desried in this work. A model for the intertion etween pmss116 nd ll Apprently, fter trnsription only ertin suset of prerna moleules hs the proper tertiry struture required for RNA tlyzed spliing. t hs een speulted tht severl yles of unfolding nd refolding promoted y n RNA helise tivity ould inrese the proportion of retive prerna moleules nd therey the effiieny of the overll retion. A previous model suggested tht pmss 116 might promote spliing of, t lest, three mitohondril group nd group introns vi suh n RNA unwinding tivity (12). Unwinding of syntheti RNA sustrtes hs een oserved for severl DEAD ox proteins (20-22). However, no inresed RNA helise tivity ould e deteted in extrt A231/pGU:MSS116 s ompred with A237/pGU using onditions under whih p68 unwinds smll syntheti RNA moleules (dt not shown). t thus seems unlikely tht pmss 116 hs sequene-non-speifi RNA unwinding tivity. Further exmintion of the model inluded testing die effet of MSS116 overexpression on in vitro spliing of group intron 5. This intron is losely relted to ll nd requires lmost identil onditions for self-spliing. Yet we ould not detet ny effet of pmss116 overexpression on in vitro spliing of 5. This result, whih is onsistent with the geneti dt (12), my provide some insight into the mehnism of pmss 116-dependent spliing. Although group F introns ll nd 5 hve very similir seondry (nd mye tertiry) struture, this ommon feture is oviously not suffiient for intertion with pmss116, s n e onluded from our experimentl results. One rther unlikely explntion ould e tht pmss116 ts s n RNA helise speifi for the unwinding of n unknown sudomin of l 1. Suh primry trget would hve to e ommon to ll group nd group introns whih nnot splie in n MSS116 mutnt (12), ut sent from 5. Thus more plusile model would e tht pmss 116 n only intert with its RNA sustrte(s) due to essory ftors speifi for therespetiveintrons. This would e onsistent with the hypothesis of n independent development of protein-ssisted spliing in different group introns. Evolutionry implitions Spliing of group F introns nd splieosoml spliing proeed vi the sme moleulr mehnism. This oservtion hs prompted speultion tht group introns my e the evolutionry nestors of splieosoml introns. Aording to this model, splieosoml introns grdully developed from group introns y: (i) eoming inresingly dependent upon trns-txng protein ftors; (ii) trnsposition of severl formerly w-ting RNA strutures into fr/u-ting snrnas (39). Until now no similrities with respet to trns-ting ftors hve een desried. Our results show tht spliing of group intron depends on ATP nd t lest one protein elonging to the DEAD ox fmily. While splieosoml spliing my require fr more ftors thn group intron spliing, future nlysis will nswer the intriguing question of whether pmss116 nd PRP proteins elonging to the DEAD/H ox fmily shre similir funtion in group nd splieosoml spliing, respetively. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thnk T. H. Chng for his friendly gift of CA7 (MSS116), H. P. Zssenhus for strin A237, W.Horz for vetor pgl nd Tois Shlpp for rising ntiser. Brr Gelhus is knowledged for her expert tehnil ssistne nd H. Ulrih Goringer, Louis Fleishmn, Tony Mihelson-Yetes nd Hendrik Poinr for ritil reding of the mnusript This work ws supported y SFB 184 of the Deutshe Forshungsgemeinshft. REFERENCES 1 Guthrie.C. (1991) Siene, 253, CehJ.R., Zug^J. nd Growski^J. (1981) Cell, 27, 487^96. 3 Vn der Veen,R., AmergAC, Vn der Horet,G., BonenX-, TtJl.F. nd Grivell,L. A. (1986) Cell, 44, Peeles.CL., Perlmn^.S., Meklenurg,K.L., Petrillo,M.L., Jrreu,K.A. nd Cheng,H.L. (1986) Cell, 44, Shmelzer.C. nd ShweyenR. (1986) Cell, 46,
7 2972 Nulei Aids Reserh, 1995, Vol. 23, No LmowitzAM. nd PerlmnJ>.S. (\990) Trends Biohem. Si., 15, LzowskJ., Jq.C. nd SlonimskiJ'.P. (1980) Cell, 22, Bonitz,G., Homison,G., Thlenfeld^B.E., TzgolofTA nd NoregJ.G. (1982;/. BioL Chem., 257, De L Slle,H., Jq.C. nd Slonimski^J. (1982) Cell, 28, GmpelA. Nishikimi,M. nd TzgoloffA (1989) MoL Cell BioL, 9, Serphin3., Simonjvl. nd Fye.G. (1988) EMBO /., 7, S<Srphin,B., SimoivM., BouletA nd Fye.G. (1989) Nture, 337, AkinsJtA nd LmowitzAM. (.1987) Cell, 50, Linder,P., Lsko,P.F., Leroy.R, NielsenJU., Nishi.K., ShnierJ. nd Slonimski^.P. (1989) Nture, 337, Ry3K., Lwson,T.G., KrmerJ.C. QdrsJ^.H., GrifoJ.A., ArmsonJ^D., Merrik,W.C. nd ThlvR.T. (1985) /. BioL Chem., 260, Compny^., Arens J. nd AelsonJ. (1991) Nture, 349,487^ Shwer3- nd Guthri.C. (1991) Nture, 349, KimS.-H., SmithJ., CludeA nd Lin,R.-J. (1992) EMBO J., 11, Fuller-PeJ'.V., Niol^.M., ReidA-D. nd Lne.D.P. (1993) EMBO J., 12, Hii1ing,H., Sheffiierjvl., Testle.T. nd SthU. (1989) Nture, 339, Rozen,F., EderyJ., Meerovith.K., Dever.T.E., Merrik,W.C. nd SonenergJ>f. (1990) MoL Cell Biol., 10, GururjiuR., Mthews,L., Longo^J. nd Weeks,D.L. (1994) Pro. NtL Ad. SL USA, 91, MjumderAL., Akins,RA, WilkinsonJ.G., KelleyJl.L., SnooltAJ. nd LmowitzAM. (1989) MoL Cell BioL, 9, Zssenhus,H.P., Hofmnn,TJ.,Uthyshnker,R., Vinent,R.D. nd ZOTULM- (1988) Nulei Aids Res., 16, M6ri,M. nd Shmelzer.C. (1990) Cell, 60, MUUei\M.W., ShweyenJlJ. nd Shmelzer.C. (1988) Nulei Aids Res., 16, Chng,T.-H., ArensJ. nd AelsonJ. (1990) Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA, X, Shenjd. nd Ymmoto,K.R. (1988) Siene, 241, KleRJ., HrrissJ.V., ShrpZD. nd DouglsJvl.G. (1983) Gene, 25, Rigy,P.W., Diekmnn,M., Rhodes.C. nd Berg.P. (1977) /. Mol. BioL, 113, Lemmli.U.K. (1970) Nture, 227, RoiseJD. nd Shtz,G. (1988)7. BioL Chem., 263, Bitter.GA nd Egn.lCM (1984) Gene, 32, Hopp.TP. nd Woods,K.R. (1981) Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA, 78, KyteJ. nd Doolittle.R.F. (1982) J. Mol. BioL, 157, Mihel J 3., Umesono.K. nd Ozeki.H. (1989) Gene, 82, BhlJ. nd Shmelzer.C. (1990)/ MoL BioL, 212, HensgensJLA.M., AmergAC, Roosendl^E., Vn der Horst,G., Vn der Veen.R., Vn Ommen.GJ.B. nd Grivell,LA (1983) /. MoL BioL, 164, SuhyJVi. nd Shmelzer.C. (1991) / Mol. BioL, 222, Hershlg.D., Khosljd., TsuhihshiZ nd Krpel.R.L. (1994) EMBO /., 13,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture10924 no tg Lsm1-my Lsm2-my Lsm5-my Lsm6-my Lsm7-my Lsm8-my no tg Lsm1-my Lsm2-my Lsm5-my Lsm6-my Lsm7-my Lsm8-my kd 220 120 100 80 60 50 40 30 20 SeeBlue Mrker Mgi Mrk no tg Sm1-my Smd3-my
doi:10.1038/nture10924 no tg Lsm1-my Lsm2-my Lsm5-my Lsm6-my Lsm7-my Lsm8-my no tg Lsm1-my Lsm2-my Lsm5-my Lsm6-my Lsm7-my Lsm8-my kd 220 120 100 80 60 50 40 30 20 SeeBlue Mrker Mgi Mrk no tg Sm1-my Smd3-my
sensitive VBSs Vh subdomains EF EF
 Tlin- Tlin-EGFP-His 2 3 2 3 ABD Mehno- ABD2 ABD3 sensitive VBSs DD 6xHis EGFP Vh sudomins EGFP-Vinulin EGFP 2 3 4 Vt EGFP-Vh EGFP 2 3 4 -tinin- CH CH2 SP SP SP SP EF EF mcherry--tinin- mcherry CH CH2 SP
Tlin- Tlin-EGFP-His 2 3 2 3 ABD Mehno- ABD2 ABD3 sensitive VBSs DD 6xHis EGFP Vh sudomins EGFP-Vinulin EGFP 2 3 4 Vt EGFP-Vh EGFP 2 3 4 -tinin- CH CH2 SP SP SP SP EF EF mcherry--tinin- mcherry CH CH2 SP
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n74 In the formt provided y the uthors nd unedited. d 331p 637p 9p 394p 48p 467p 22p 23p 489p 419p 3p 493p 332p 53p 39p 1 G1: 16.4% S: 73.1% G2/M: 1.5% 2 1 2 E-KO G1: 2.2% S: 7.7% G2/M: 9.1%
DOI: 1.138/n74 In the formt provided y the uthors nd unedited. d 331p 637p 9p 394p 48p 467p 22p 23p 489p 419p 3p 493p 332p 53p 39p 1 G1: 16.4% S: 73.1% G2/M: 1.5% 2 1 2 E-KO G1: 2.2% S: 7.7% G2/M: 9.1%
iaspp oncoprotein is a key inhibitor of p53 conserved from worm to human 12.5 no irradiation +100 J/m 2 UV germ-cell corpses / gonad arm
 onoprotein is key inhiitor of onserved from worm to humn 23 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Dniele Bergmshi 1 *, Yrden Smuels 1 *, Nigel J. O Neil 2 *, Giuseppe Triginte 1, Tim Crook
onoprotein is key inhiitor of onserved from worm to humn 23 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Dniele Bergmshi 1 *, Yrden Smuels 1 *, Nigel J. O Neil 2 *, Giuseppe Triginte 1, Tim Crook
HeLa. CaSki. Supplementary Figure 1. Validation of the NKX6.1 expression in mrna level and
 Supplementry Figure. Li et l. Reltive expression ( / GAPDH ) 6 5 4 3 2 5 Reltive expression ( / GAPDH ) 4 3 2 Reltive expression ( / GAPDH ) 4 3 2 Reltive expression ( / GAPDH ) 4 3 2 Ve S Ve S2 S S2 Ve
Supplementry Figure. Li et l. Reltive expression ( / GAPDH ) 6 5 4 3 2 5 Reltive expression ( / GAPDH ) 4 3 2 Reltive expression ( / GAPDH ) 4 3 2 Reltive expression ( / GAPDH ) 4 3 2 Ve S Ve S2 S S2 Ve
Gan et al., Supplemental Figure 1
 Gn et l., Supplementl Figure IB: DU45 Unp IB: py-68 IB: perk IB: ERK IB: Akt Unp DU45 DU45 ErB2 - EGF - EGF ErB2 75 75 Supplementl Figure. DU45 nd ells predominntly express nd re highly responsive to EGF.
Gn et l., Supplementl Figure IB: DU45 Unp IB: py-68 IB: perk IB: ERK IB: Akt Unp DU45 DU45 ErB2 - EGF - EGF ErB2 75 75 Supplementl Figure. DU45 nd ells predominntly express nd re highly responsive to EGF.
Crop Rotations, Reduced Tillage and N Fertilization Effects on Corn Yields And Aflatoxin Levels
 Crop Rottions, Redued Tillge nd N Fertiliztion Effets on Corn Yields And Afltoxin Levels J.E. Mtoh nd M. Rihrdson Texs AgriLife Reserh nd Extension Center Stte Hwy Corpus Christi, TX 78- jmtoh@g.tmu.edu
Crop Rottions, Redued Tillge nd N Fertiliztion Effets on Corn Yields And Afltoxin Levels J.E. Mtoh nd M. Rihrdson Texs AgriLife Reserh nd Extension Center Stte Hwy Corpus Christi, TX 78- jmtoh@g.tmu.edu
TTT DIAGRAM OF A NEWLY DEVELOPED NICKEL-BASE SUPERALLOY ALLVAC 718PLUS
 Superlloys 718, 625, 706 nd Derivtives 2005 Edited y E.A. Lori TMS (The Minerls, Metls & Mterils Soiety), 2005 TTT DIAGRAM OF A NEWLY DEVELOPED NICKEL-BASE SUPERALLOY ALLVAC 718PLUS Xishn Xie 1, Chunmei
Superlloys 718, 625, 706 nd Derivtives 2005 Edited y E.A. Lori TMS (The Minerls, Metls & Mterils Soiety), 2005 TTT DIAGRAM OF A NEWLY DEVELOPED NICKEL-BASE SUPERALLOY ALLVAC 718PLUS Xishn Xie 1, Chunmei
THE INFLUENCE OF THERMOMECHANICAL TREATMENT AND CHEMICAL COMPOSITION ON RECRYSTALLIZATION OF Al-Mg ALLOYS
 Assoition of Metllurgil Engineers of Seri Sientifi pper AMES UDC:669.715 721.065.53.040.2-174=20 THE INFLUENCE OF THERMOMECHANICAL TREATMENT AND CHEMICAL COMPOSITION ON RECRYSTALLIZATION OF Al-Mg ALLOYS
Assoition of Metllurgil Engineers of Seri Sientifi pper AMES UDC:669.715 721.065.53.040.2-174=20 THE INFLUENCE OF THERMOMECHANICAL TREATMENT AND CHEMICAL COMPOSITION ON RECRYSTALLIZATION OF Al-Mg ALLOYS
Figure S1. Characterization of sirna uptake in HeLa cells.
 Supplementry Informtion The Rough Endoplsmti Retiulum is Centrl Nuletion Site of sirna-medited RNA Silening Luks Stlder, Wolf Heusermnn, Len Sokol, Domini Trojer, Joel Wirz, Justin Hen, Anj Fritzshe, Florin
Supplementry Informtion The Rough Endoplsmti Retiulum is Centrl Nuletion Site of sirna-medited RNA Silening Luks Stlder, Wolf Heusermnn, Len Sokol, Domini Trojer, Joel Wirz, Justin Hen, Anj Fritzshe, Florin
Isolation of human DNA sequences that bind to nuclear factor I, host protein involved in adenovirus DNA replication
 Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA Vol. 81, pp. 413-417, July 1984 Biohemistry Isoltion of humn DNA sequenes tht bind to nuler ftor I, host protein involved in denovirus DNA replition (protein-medited seletion/origins
Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA Vol. 81, pp. 413-417, July 1984 Biohemistry Isoltion of humn DNA sequenes tht bind to nuler ftor I, host protein involved in denovirus DNA replition (protein-medited seletion/origins
*** supplementary information. axon growth (µm/1h) 5 ng/ml NGF. 150 ng/ml NGF. 20 ng/ml NGF. n.s. n.s. n.s. DOI: /ncb1916
 DOI: 1.138/n1916 25 xon growth (µm/1h) 2 15 1 5 ng/ml NGF 5 ng/ml NGF 2 ng/ml NGF 1 ng/ml NGF 15 ng/ml NGF Figure S1 () Doseresponse urve for xon outgrowth in response to NGF. Speifi tivities of NGF from
DOI: 1.138/n1916 25 xon growth (µm/1h) 2 15 1 5 ng/ml NGF 5 ng/ml NGF 2 ng/ml NGF 1 ng/ml NGF 15 ng/ml NGF Figure S1 () Doseresponse urve for xon outgrowth in response to NGF. Speifi tivities of NGF from
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SI Fig. PrpS is single copy gene k 3. 9... EcoRV EcoRV k 5 BmH Pst c well k HindIII HindIII HindIII.3.5 3.. Southern lots of Ppver genomic DNA from plnts with SS8 hplotypes, hyridized with PrpS proe..
SI Fig. PrpS is single copy gene k 3. 9... EcoRV EcoRV k 5 BmH Pst c well k HindIII HindIII HindIII.3.5 3.. Southern lots of Ppver genomic DNA from plnts with SS8 hplotypes, hyridized with PrpS proe..
Supplementary Figure S1. Akaike et al.
 reltive expression of HIPK2 (HIPK2/GAPDH) Supplementry Figure S1. Akike et l. 1.25 ontrol HIPK2 #1 1 HIPK2 #2 HIPK2 3 U 0.75 0.5 0.25 0 ontrol : + + - HIPK2 #1: - - - + + - - - - HIPK2 #2: - - - - + +
reltive expression of HIPK2 (HIPK2/GAPDH) Supplementry Figure S1. Akike et l. 1.25 ontrol HIPK2 #1 1 HIPK2 #2 HIPK2 3 U 0.75 0.5 0.25 0 ontrol : + + - HIPK2 #1: - - - + + - - - - HIPK2 #2: - - - - + +
scientificreport ATM-mediated phosphorylation of SOG1 is essential for the DNA damage response in Arabidopsis scientific report
 sientifireport is essentil for the DNA dmge response in Aridopsis Koru O. Yoshiym 1,2+,JunyKoyshi 3,NouoOgit 1,MinkoUed 1,SeisukeKimur 2, Hisji Mki 1 & Mski Umed 1,4++ 1 Grdute Shool of Biologil Sienes,
sientifireport is essentil for the DNA dmge response in Aridopsis Koru O. Yoshiym 1,2+,JunyKoyshi 3,NouoOgit 1,MinkoUed 1,SeisukeKimur 2, Hisji Mki 1 & Mski Umed 1,4++ 1 Grdute Shool of Biologil Sienes,
Broken rice facts. Physical and Functional Characteristics of Broken Rice Kernels. Parboiling Process. May 23, Production of broken rice 14-10%
 My 23, 218 Physil nd Funtionl Chrteristis of Broken Rie Kernels Broken rie fts Redued eonomi vlue Undesirle Inevitle Ree M. Brue University of Arknss Advisor: Dr. Griffiths G. Atungulu Inexpensive Affets
My 23, 218 Physil nd Funtionl Chrteristis of Broken Rie Kernels Broken rie fts Redued eonomi vlue Undesirle Inevitle Ree M. Brue University of Arknss Advisor: Dr. Griffiths G. Atungulu Inexpensive Affets
Heat-shock protein 70 inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment of procaspase-9 to the Apaf-1 apoptosome
 Het-shok protein 7 inhiits poptosis y preventing reruitment of prospse-9 to the poptosome Helen M. Beere*, Beni B. Wolf*, Kelvin Cin, Dik D. Mosser, Artin Mhoui*, Tomomi Kuwn*, Pnkj Tilor, Rihrd I. Morimoto,
Het-shok protein 7 inhiits poptosis y preventing reruitment of prospse-9 to the poptosome Helen M. Beere*, Beni B. Wolf*, Kelvin Cin, Dik D. Mosser, Artin Mhoui*, Tomomi Kuwn*, Pnkj Tilor, Rihrd I. Morimoto,
Nucleosome dynamics regulates DNA processing
 r t i l e s Nuleosome dynmis regultes proessing Nihols L Adkins 1, Hengyo Niu 2, Ptrik Sung 2 & Crig L Peterson 1 npg 213 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. The repir of doule-strnd reks (DSBs) is ritil
r t i l e s Nuleosome dynmis regultes proessing Nihols L Adkins 1, Hengyo Niu 2, Ptrik Sung 2 & Crig L Peterson 1 npg 213 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. The repir of doule-strnd reks (DSBs) is ritil
Atypical RNA polymerase subunits required for RNA-directed DNA methylation
 Atypil RNA polymerse suunits required for RNA-direted DNA methyltion tsuo Knno 1, Bruno Huettel 1, M Florin Mette 1,3, Werner Aufstz 1, Estelle Jligot 1, Lui Dxinger 1, Dvid P Kreil 2, Mrjori Mtzke 1 &
Atypil RNA polymerse suunits required for RNA-direted DNA methyltion tsuo Knno 1, Bruno Huettel 1, M Florin Mette 1,3, Werner Aufstz 1, Estelle Jligot 1, Lui Dxinger 1, Dvid P Kreil 2, Mrjori Mtzke 1 &
Mammalian Sprouty4 suppresses Ras-independent ERK activation by binding to Raf1
 Mmmlin suppresses Rs-independent ERK tivtion y inding to Rf1 letters Atsuo Sski*, Tkhru Tketomi*, Reiko Kto*, Kzuko Seki*, Atsushi Nonmi*, Mik Sski*, Msmitsu Kuriym, Noki Sito, Msumi Shiuy nd Akihiko Yoshimur*
Mmmlin suppresses Rs-independent ERK tivtion y inding to Rf1 letters Atsuo Sski*, Tkhru Tketomi*, Reiko Kto*, Kzuko Seki*, Atsushi Nonmi*, Mik Sski*, Msmitsu Kuriym, Noki Sito, Msumi Shiuy nd Akihiko Yoshimur*
Interplay between NS3 protease and human La protein---- by Ray and Das Supplementary fig 1. NS3 pro
 Interply etween tese nd humn L protein---- y Ry nd Ds Supplementry fig 1 1 2 3 4 UV crosslinking ssy: α[ 32 P]UTP leled HCV IRES RNA ws UV-crosslinked to incresing concentrtions (0.1, 0.2 nd 0.4µM) in
Interply etween tese nd humn L protein---- y Ry nd Ds Supplementry fig 1 1 2 3 4 UV crosslinking ssy: α[ 32 P]UTP leled HCV IRES RNA ws UV-crosslinked to incresing concentrtions (0.1, 0.2 nd 0.4µM) in
A Fast Heuristic Scheduling Algorithm for Periodic ConcurrenC Models
 A Fst Heuristi Sheduling Algorithm for Periodi ConurrenC Models Weiwei Chen nd Riner Doemer Center for Emedded Computer Systems University of Cliforni, Irvine Outline Introdution nd Relted Work ConurrenC
A Fst Heuristi Sheduling Algorithm for Periodi ConurrenC Models Weiwei Chen nd Riner Doemer Center for Emedded Computer Systems University of Cliforni, Irvine Outline Introdution nd Relted Work ConurrenC
Arabidopsis HT1 kinase controls stomatal movements in response to CO 2
 Aridopsis kinse ontrols stomtl movements in response to Mimi Hshimoto, Juntro Negi, Jred Young 2, Mri Isrelsson 2, Julin I. Shroeder 2 nd Koh I,3 Gurd ells, whih form stomt in lef epidermes, sense multitude
Aridopsis kinse ontrols stomtl movements in response to Mimi Hshimoto, Juntro Negi, Jred Young 2, Mri Isrelsson 2, Julin I. Shroeder 2 nd Koh I,3 Gurd ells, whih form stomt in lef epidermes, sense multitude
LETTERS. Histone modifications at human enhancers reflect global cell-type-specific gene expression
 Vol 59 7 My 29 doi:1.138/nture7829 Histone modifitions t humn enhners reflet glol ell-type-speifi gene expression Nthniel D. Heintzmn 1,2 *, Gry C. Hon 1,3 *, R. Dvid Hwkins 1 *, Pouy Kherdpour 5, Alexnder
Vol 59 7 My 29 doi:1.138/nture7829 Histone modifitions t humn enhners reflet glol ell-type-speifi gene expression Nthniel D. Heintzmn 1,2 *, Gry C. Hon 1,3 *, R. Dvid Hwkins 1 *, Pouy Kherdpour 5, Alexnder
Electrostatic vs covalent bond in modified Jeffamine: effect on the phase behaviour and on the templating of mesoporous silica
 Eletroni upplementry Mteril (EI) for oft Mtter This journl is The Royl oiety of Chemistry 3 upporting Informtion Eletrostti vs ovlent ond in modified Jeffmine: effet on the phse ehviour nd on the templting
Eletroni upplementry Mteril (EI) for oft Mtter This journl is The Royl oiety of Chemistry 3 upporting Informtion Eletrostti vs ovlent ond in modified Jeffmine: effet on the phse ehviour nd on the templting
JBC Papers in Press. Published on June 2, 2010 as Manuscript M Mbnl1 binds to IR intronic enhancer
 JBC Ppers in Press. Pulished on June 2, 2010 s Mnusript M109.095224 The ltest version is t http://www.j.org/gi/doi/10.1074/j.m109.095224 Mnl1 inds to IR introni enhner MUSCLEBLIND-LIKE 1 (MBNL1) PROMOTES
JBC Ppers in Press. Pulished on June 2, 2010 s Mnusript M109.095224 The ltest version is t http://www.j.org/gi/doi/10.1074/j.m109.095224 Mnl1 inds to IR introni enhner MUSCLEBLIND-LIKE 1 (MBNL1) PROMOTES
Initiation complex dynamics direct the transitions between distinct phases of early HIV reverse transcription
 Initition omplex dynmis diret the trnsitions etween distint phses of erly IV reverse trnsription Shixin Liu 1,6, Bryn T rd 2,6, Jennifer T Miller 3, Sturt J Le rie 3 & Xiowei Zhung 1,4,5 21 Nture meri,
Initition omplex dynmis diret the trnsitions etween distint phses of erly IV reverse trnsription Shixin Liu 1,6, Bryn T rd 2,6, Jennifer T Miller 3, Sturt J Le rie 3 & Xiowei Zhung 1,4,5 21 Nture meri,
The gene defective in leukocyte adhesion deficiency II encodes a putative GDP-fucose transporter
 letter The gene defetive in leukoyte dhesion defiieny II enodes puttive GDP-fuose trnsporter Kerstin Lühn 1 *, Mrtin K. Wild 1 *, Mtthis Ekhrdt 2, Rit Gerrdy-Shhn 3 & Dietmr Vestweer 1 *These uthors ontriuted
letter The gene defetive in leukoyte dhesion defiieny II enodes puttive GDP-fuose trnsporter Kerstin Lühn 1 *, Mrtin K. Wild 1 *, Mtthis Ekhrdt 2, Rit Gerrdy-Shhn 3 & Dietmr Vestweer 1 *These uthors ontriuted
NATURE STRUCTURAL & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 Communition etween nd during sustrte proessing nd degrdtion Shilp A Joshi 1, Greg L Hersh 1, Tni A Bker 1,2 & Roert T Suer 1 In the P omprtmentl protese, ring hexmers of the AAA + ATPse ind, denture nd
Communition etween nd during sustrte proessing nd degrdtion Shilp A Joshi 1, Greg L Hersh 1, Tni A Bker 1,2 & Roert T Suer 1 In the P omprtmentl protese, ring hexmers of the AAA + ATPse ind, denture nd
Evidence for an instructive mechanism of de novo methylation in cancer cells
 26 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Evidene for n instrutive mehnism of de novo methyltion in ner ells Iln Keshet, Yeshyhu Shlesinger, Shlomit Frksh, Eyl Rnd, Merv Heht, Ern Segl,
26 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Evidene for n instrutive mehnism of de novo methyltion in ner ells Iln Keshet, Yeshyhu Shlesinger, Shlomit Frksh, Eyl Rnd, Merv Heht, Ern Segl,
Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus
 Exon-intron irulr RNAs regulte trnsription in the nuleus Zhoyong Li 1,2,7, Chun Hung 1,7, Chun Bo 1,3,4,7, Ling Chen 1, Mei Lin 1, Xiolin Wng 1, Guolin Zhong 1, Bin Yu 1, Wnhen Hu 1, Limin Di 1, Pengfei
Exon-intron irulr RNAs regulte trnsription in the nuleus Zhoyong Li 1,2,7, Chun Hung 1,7, Chun Bo 1,3,4,7, Ling Chen 1, Mei Lin 1, Xiolin Wng 1, Guolin Zhong 1, Bin Yu 1, Wnhen Hu 1, Limin Di 1, Pengfei
Supplementary Figure 1. Zhang et al.
 Supplementry Figure 1. Zhng et l. T30-SurA: GGCAGTTTCATCATGAATGTGCAGGAGCTTGCAACAATTAAGGTGGAGAATCTCCC T30-SurB: GGCAGTTTCATCATGAATGTGCAGGAGCTAGCAACTATTAAGGTGGAGAATCTCCC T41-SurA: ACTGAATAATCAACACTTGGGAATGGTGGTTCAATGGGAGGATCGGTTCTAT
Supplementry Figure 1. Zhng et l. T30-SurA: GGCAGTTTCATCATGAATGTGCAGGAGCTTGCAACAATTAAGGTGGAGAATCTCCC T30-SurB: GGCAGTTTCATCATGAATGTGCAGGAGCTAGCAACTATTAAGGTGGAGAATCTCCC T41-SurA: ACTGAATAATCAACACTTGGGAATGGTGGTTCAATGGGAGGATCGGTTCTAT
Atmospheric leaching of EAF dust with diluted sulphuric acid
 Hydrometllurgy 77 (5) 1 5 www.elsevier.om/lote/hydromet Atmospheri lehing of EAF dust with diluted sulphuri id Toms Hvlik, *, Mrtin Turzkov, Sreko Stopi, Bernd Friedrih Deprtment of Non-ferrous Metls nd
Hydrometllurgy 77 (5) 1 5 www.elsevier.om/lote/hydromet Atmospheri lehing of EAF dust with diluted sulphuri id Toms Hvlik, *, Mrtin Turzkov, Sreko Stopi, Bernd Friedrih Deprtment of Non-ferrous Metls nd
MED18 interaction with distinct transcription factors regulates multiple plant functions
 Reeived 13 Aug 213 Aepted 4 De 213 Pulished 23 Jn 214 DOI: 1.138/nomms464 MED18 intertion with distint trnsription ftors regultes multiple plnt funtions Zhiing Li 1, Crig M. Shluttenhofer 1,w, Ketki Bhide
Reeived 13 Aug 213 Aepted 4 De 213 Pulished 23 Jn 214 DOI: 1.138/nomms464 MED18 intertion with distint trnsription ftors regultes multiple plnt funtions Zhiing Li 1, Crig M. Shluttenhofer 1,w, Ketki Bhide
Regulation of microrna-mediated gene silencing by microrna precursors
 Regultion of mirorna-medited gene silening y mirorna preursors Biswjoy Roy-Chudhuri 1,2, Pul N Vldmnis 1,2, Yue Zhng 1,2, Qing Wng 1,2, Qing-Jun Luo 1,2 & Mrk A Ky 1,2 Proessing of mirornas (mirnas) from
Regultion of mirorna-medited gene silening y mirorna preursors Biswjoy Roy-Chudhuri 1,2, Pul N Vldmnis 1,2, Yue Zhng 1,2, Qing Wng 1,2, Qing-Jun Luo 1,2 & Mrk A Ky 1,2 Proessing of mirornas (mirnas) from
Meganuclease-mediated Virus Self-cleavage Facilitates Tumor-specific Virus Replication
 originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Megnulese-medited Virus Self-levge Filittes Tumor-speifi Virus Replition Engin Gürlevik 1, Peter Shhe 1, Anneliese Goez 1, Arnold Kloos 1, Normn Woller
originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Megnulese-medited Virus Self-levge Filittes Tumor-speifi Virus Replition Engin Gürlevik 1, Peter Shhe 1, Anneliese Goez 1, Arnold Kloos 1, Normn Woller
ROLAND V. RALLOS* Agriculture Research Section Philippine Nuclear Research Institute
 Influene of Potssium Soluilizing Bteri on Growth nd Rdioesium Aumultion of Brssi rp L. vr. perviridis grown in Cs-Contminted Fukushim Soils ROLAND V. RALLOS* Agriulture Reserh Setion Philippine Nuler Reserh
Influene of Potssium Soluilizing Bteri on Growth nd Rdioesium Aumultion of Brssi rp L. vr. perviridis grown in Cs-Contminted Fukushim Soils ROLAND V. RALLOS* Agriulture Reserh Setion Philippine Nuler Reserh
1999 Nature America Inc. Tsix, a gene antisense to Xist at the X-inactivation centre
 Tsix, gene ntisense to Xist t the X-intivtion entre Jennie T. Lee, Lne S. Dvidow & Dvid Wrshwsky In mmmls, dosge ompenstion is hieved y X intivtion 1 nd is regulted in is y the X-intivtion entre 2 (Xi)
Tsix, gene ntisense to Xist t the X-intivtion entre Jennie T. Lee, Lne S. Dvidow & Dvid Wrshwsky In mmmls, dosge ompenstion is hieved y X intivtion 1 nd is regulted in is y the X-intivtion entre 2 (Xi)
Modelling and Prediction of NOx emissions from coal fired boilers: Case study
 Interntionl Reserh Journl of Engineering nd Tehnology (IRJET) e-issn: 9 - Volume: Issue: June- www.irjet.net p-issn: 9-7 Modelling nd redition of NO emissions from ol fired boilers: se study Vineeth Morris
Interntionl Reserh Journl of Engineering nd Tehnology (IRJET) e-issn: 9 - Volume: Issue: June- www.irjet.net p-issn: 9-7 Modelling nd redition of NO emissions from ol fired boilers: se study Vineeth Morris
Rap1 Activation in Collagen Phagocytosis Is Dependent on Nonmuscle Myosin II-A
 Moleulr Biology of the ell Vol. 19, 532 546, Deemer 28 tivtion in ollgen Phgoytosis Is Dependent on Nonmusle Myosin II- Pmel D. ror,* Mry nne onti, Shoshn Rvid, Dvid B. Sks, ndrs Kpus, Roert S. delstein,
Moleulr Biology of the ell Vol. 19, 532 546, Deemer 28 tivtion in ollgen Phgoytosis Is Dependent on Nonmusle Myosin II- Pmel D. ror,* Mry nne onti, Shoshn Rvid, Dvid B. Sks, ndrs Kpus, Roert S. delstein,
EXPLORING BIOFUMIGATIONAL POTENTIAL OF MUSTARDS
 EXPLORING BIOFUMIGATIONAL POTENTIAL OF MUSTARDS Oleg Dugovish*, (University of Cliforni Coopertive Extension - Ventur County), Jmes Downer nd Ole Beker (University of Cliforni Coopertive Extension -Ventur
EXPLORING BIOFUMIGATIONAL POTENTIAL OF MUSTARDS Oleg Dugovish*, (University of Cliforni Coopertive Extension - Ventur County), Jmes Downer nd Ole Beker (University of Cliforni Coopertive Extension -Ventur
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nture598 SUPPLEMETARY IFORMATIO + + + + + + + + + rit TRIC-A: M------ELLSALSLGELALSFSRVPLFPVFDLSYFIVSILYLKYEPG--AVELSRRHPVASWLCAMLHCFGSYILADLLLGEPLIDYFSSSI 87 mouse TRIC-A: M------DLMSALSLGELALSFSRVPLFPVFDLSYFIVSIIYLKYEPG--AVELSRRHPVASWLCAMLHCFGSYILADLLLGEPIIDYFSSSSI
doi:.38/nture598 SUPPLEMETARY IFORMATIO + + + + + + + + + rit TRIC-A: M------ELLSALSLGELALSFSRVPLFPVFDLSYFIVSILYLKYEPG--AVELSRRHPVASWLCAMLHCFGSYILADLLLGEPLIDYFSSSI 87 mouse TRIC-A: M------DLMSALSLGELALSFSRVPLFPVFDLSYFIVSIIYLKYEPG--AVELSRRHPVASWLCAMLHCFGSYILADLLLGEPIIDYFSSSSI
2000 Nature America Inc.
 Quntittive expression of Ot-3/4 defines differentition, dedifferentition or self-renewl of ES ells Hitoshi Niw 1,2, Jun-ihi Miyzki 2 & Austin G. Smith 1 Cell fte during development is defined y trnsription
Quntittive expression of Ot-3/4 defines differentition, dedifferentition or self-renewl of ES ells Hitoshi Niw 1,2, Jun-ihi Miyzki 2 & Austin G. Smith 1 Cell fte during development is defined y trnsription
Enzyme Triggered Cascade Reactions and Assembly of Abiotic Block Copolymers into Micellar Nanostructures
 Enzyme Triggered Csde Retions nd Assemly of Aioti Blok Copolymers into Miellr Nnostrutures Jingyi Ro, Christine Hottinger, nd Anzr Khn Deprtment of Mterils, ETH-Zürih, Switzerlnd nzr@mt.ethz.h Styrene,
Enzyme Triggered Csde Retions nd Assemly of Aioti Blok Copolymers into Miellr Nnostrutures Jingyi Ro, Christine Hottinger, nd Anzr Khn Deprtment of Mterils, ETH-Zürih, Switzerlnd nzr@mt.ethz.h Styrene,
Regulatory activity revealed by dynamic correlations in gene expression noise
 28 Nture Pulishing Group http://wwwntureom/nturegenetis Regultory tivity reveled y dynmi orreltions in gene expression Mry J Dunlop, Roert Sidney Cox III 2, Joseph H Levine, Rihrd M Murry & Mihel Elowitz
28 Nture Pulishing Group http://wwwntureom/nturegenetis Regultory tivity reveled y dynmi orreltions in gene expression Mry J Dunlop, Roert Sidney Cox III 2, Joseph H Levine, Rihrd M Murry & Mihel Elowitz
Changes in trehalose content, enzyme activity and gene expression related to trehalose metabolism in Flammulina velutipes under heat shock
 Miroiology (2016), 162, 1274 1285 DOI 10.1099/mi.0.000324 Chnges in trehlose ontent, enzyme tivity nd gene expression relted to trehlose metolism in Flmmulin velutipes under het shok Jin-hui Liu, Xio-dong
Miroiology (2016), 162, 1274 1285 DOI 10.1099/mi.0.000324 Chnges in trehlose ontent, enzyme tivity nd gene expression relted to trehlose metolism in Flmmulin velutipes under het shok Jin-hui Liu, Xio-dong
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Pulldown HeL lyste lyste lyste 25 5 75 5 5kD 37 25 5 MDDIFTQCREGNAVAVRLWLDNTENDLNQGDDHGFSPLHWACREGRSAVVEMLIMRGARINVMNRGDDTP LHLAASHGHRDIVQKLLQYKADINAVNEHGNVPLHYACFWGQDQVAEDLVANGALVSICNKYGEMPVDKA KAPLRELLRERAEKMGQNLNRIPYKDTFWKGTTRTRPRNGTLNKHSGIDFKQLNFLTKLNENHSGELWKG
Pulldown HeL lyste lyste lyste 25 5 75 5 5kD 37 25 5 MDDIFTQCREGNAVAVRLWLDNTENDLNQGDDHGFSPLHWACREGRSAVVEMLIMRGARINVMNRGDDTP LHLAASHGHRDIVQKLLQYKADINAVNEHGNVPLHYACFWGQDQVAEDLVANGALVSICNKYGEMPVDKA KAPLRELLRERAEKMGQNLNRIPYKDTFWKGTTRTRPRNGTLNKHSGIDFKQLNFLTKLNENHSGELWKG
Theoretical Analysis of Electronic Structure for the Chemical Bonding of Pu and Am in MgO
 Journl of Nuler nd Rdiohemil Sienes, Vol. 5, No.2, pp. 27-31, 2004 Review Theoretil Anlysis of Eletroni Struture for the Chemil Bonding of Pu nd Am in MgO Kumiko Tnk,*,, Msru Hirt, nd Rik Sekine Deprtment
Journl of Nuler nd Rdiohemil Sienes, Vol. 5, No.2, pp. 27-31, 2004 Review Theoretil Anlysis of Eletroni Struture for the Chemil Bonding of Pu nd Am in MgO Kumiko Tnk,*,, Msru Hirt, nd Rik Sekine Deprtment
I n all metazoans, programmed cell death, or apoptosis, is essential
 Regultion of Drosophil IAP1 degrdtion nd poptosis y reper nd ud1 f Hyung Don Ryoo*, Andres Bergmnn, Hedv Gonen, Aron Ciehnover nd Hermnn Steller* *Howrd Hughes Medil Institute, Strng Lortory of Cner Reserh,
Regultion of Drosophil IAP1 degrdtion nd poptosis y reper nd ud1 f Hyung Don Ryoo*, Andres Bergmnn, Hedv Gonen, Aron Ciehnover nd Hermnn Steller* *Howrd Hughes Medil Institute, Strng Lortory of Cner Reserh,
Rockefeller University, New York, New York Correspondence should be addressed to L.T.
 26 ture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nsm Moleulr sis for the inhiition of humn MPRTse, novel trget for ntiner gents Jved A Khn 1, Xio To 1,2 & Ling Tong 1 iotinmide phosphoriosyltrnsferse (MPRTse)
26 ture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nsm Moleulr sis for the inhiition of humn MPRTse, novel trget for ntiner gents Jved A Khn 1, Xio To 1,2 & Ling Tong 1 iotinmide phosphoriosyltrnsferse (MPRTse)
Research Article Identification of Differential Expression Genes in Leaves of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Response to Heat Stress by cdna-aflp Analysis
 BioMed Reserh Interntionl Volume 213, Artile ID 576189, 11 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/576189 Reserh Artile Identifition of Differentil Expression Genes in Leves of Rie (Oryz stiv L.) in Response
BioMed Reserh Interntionl Volume 213, Artile ID 576189, 11 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/576189 Reserh Artile Identifition of Differentil Expression Genes in Leves of Rie (Oryz stiv L.) in Response
Arabidopsis thaliana class-ii TGA transcription factors are essential activators of jasmonic acid/ethylene-induced defense responses
 Pulished in "The Plnt Journl 6(2): 2-2, 2" whih should e ited to refer to this work. Aridopsis thlin lss-ii TGA trnsription ftors re essentil tivtors of jsmoni id/ethylene-indued defense responses Mrk
Pulished in "The Plnt Journl 6(2): 2-2, 2" whih should e ited to refer to this work. Aridopsis thlin lss-ii TGA trnsription ftors re essentil tivtors of jsmoni id/ethylene-indued defense responses Mrk
Research. Tongjun Sun 1, Lucas Busta 2, Qian Zhang 1, Pingtao Ding 1, Reinhard Jetter 1,2 and Yuelin Zhang 1. Summary.
 Reserh TGACG-BINDING FACTOR (TGA) nd TGA regulte sliyli id nd pipeoli id iosynthesis y modulting the expression of SYSTEMIC ACQUIRED RESISTANCE DEFICIENT (SARD) nd CALMODULIN-BINDING PROTEIN g (CBPg) Tongjun
Reserh TGACG-BINDING FACTOR (TGA) nd TGA regulte sliyli id nd pipeoli id iosynthesis y modulting the expression of SYSTEMIC ACQUIRED RESISTANCE DEFICIENT (SARD) nd CALMODULIN-BINDING PROTEIN g (CBPg) Tongjun
Comparative transcription of right- and left-handed poly[d(g-c)] by
![Comparative transcription of right- and left-handed poly[d(g-c)] by Comparative transcription of right- and left-handed poly[d(g-c)] by](/thumbs/75/72112352.jpg) The MBO Journl Vol.2 No.1 pp.177 1714, 1983 omprtive trnsription of right nd lefthnded poly[d(g)] by whet germ RN polymerse II Robert Durnd, ludette Job, Dvid.Zrling1, Mrel Teissere, Thoms M.Jovinl* nd
The MBO Journl Vol.2 No.1 pp.177 1714, 1983 omprtive trnsription of right nd lefthnded poly[d(g)] by whet germ RN polymerse II Robert Durnd, ludette Job, Dvid.Zrling1, Mrel Teissere, Thoms M.Jovinl* nd
A gene expression map of Arabidopsis thaliana development
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis A gene expression mp of Aridopsis thlin development Mrkus Shmid, Timothy S Dvison,2, Stefn R Henz, Utz J Ppe 3, Monik Demr, Mrtin Vingron 3, Bernhrd
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis A gene expression mp of Aridopsis thlin development Mrkus Shmid, Timothy S Dvison,2, Stefn R Henz, Utz J Ppe 3, Monik Demr, Mrtin Vingron 3, Bernhrd
Technology & Prod uct Reports Does Amendment of Soak Solution with Sucrose and Urea Increase Production of Shiitake Mushrooms on Sawdust Blocks?
 Tehnology & Prod ut Reports Does Amendment of Sok Solution with Surose nd Ure Inrese Prodution of Shiitke Mushrooms on Swdust Bloks? Cthy Sot, Cul Beyl, nd Gokul Ghle ADDITIONAL INDEX WORDS. iologil effiieny,
Tehnology & Prod ut Reports Does Amendment of Sok Solution with Surose nd Ure Inrese Prodution of Shiitke Mushrooms on Swdust Bloks? Cthy Sot, Cul Beyl, nd Gokul Ghle ADDITIONAL INDEX WORDS. iologil effiieny,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2885 kd M ΔNZipA 66.4 55.6 ZipA 42.7 34.6 6x His NiNTA 27.0 c 1.,, 2. evnescent field supported memrne Supplementry Figure 1 Experimentl ssy. () Illustrtion of protein interctions (dpted
DOI: 10.1038/nc2885 kd M ΔNZipA 66.4 55.6 ZipA 42.7 34.6 6x His NiNTA 27.0 c 1.,, 2. evnescent field supported memrne Supplementry Figure 1 Experimentl ssy. () Illustrtion of protein interctions (dpted
Unprecedented inhibition of tubulin polymerization directed by gold nanoparticles inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
 Eletroni supplementry informtion (ESI) for Nnosle Unpreedented inhiition of tuulin polymeriztion direted y gold nnoprtiles induing ell yle rrest nd poptosis Diptimn Choudhury,,e, Pulrjpilli Lourdu Xvier,,
Eletroni supplementry informtion (ESI) for Nnosle Unpreedented inhiition of tuulin polymeriztion direted y gold nnoprtiles induing ell yle rrest nd poptosis Diptimn Choudhury,,e, Pulrjpilli Lourdu Xvier,,
Physiological effects of mechanized harvesting and ways to minimize its impacts
 8/3/218 Physiologil effets of mehnized hrvesting nd wys to minimize its impts S.R.W. Pthirnge 1, M.A. Wijertne 1 nd W.A.J.M. De Cost 2 1 Agronomy Division, Te Reserh Institute of Sri Lnk 2 Fulty of Agriulture,
8/3/218 Physiologil effets of mehnized hrvesting nd wys to minimize its impts S.R.W. Pthirnge 1, M.A. Wijertne 1 nd W.A.J.M. De Cost 2 1 Agronomy Division, Te Reserh Institute of Sri Lnk 2 Fulty of Agriulture,
PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF SILICON CARBIDE FIBER FROM ACTIVATED CARBON FIBERS
 PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF SILICON CARBIDE FIBER FROM ACTIVATED CARBON FIBERS Zhenyu Ryu, Jingtng Zheng, Mozhng Wng nd Bijing Zhng Institute of Col Chemistry, Chinese Ademy of Sienes, P. O. Box
PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF SILICON CARBIDE FIBER FROM ACTIVATED CARBON FIBERS Zhenyu Ryu, Jingtng Zheng, Mozhng Wng nd Bijing Zhng Institute of Col Chemistry, Chinese Ademy of Sienes, P. O. Box
Effect of Dispersed Phase Particle Dispersion on the Thermal Stability of Recycled Poly(ethylene terephthalate)/polypropylene Blend
 Effet of Dispersed Phse Prtile Dispersion on the Therml Stility of Reyled Poly(ethylene terephthlte)/polypropylene Blend Yew Wei Leong 1*, Hiroyuki Inoy 2, Supphorn Thumsorn 1 nd Hiroyuki Hmd 1 1 Deprtment
Effet of Dispersed Phse Prtile Dispersion on the Therml Stility of Reyled Poly(ethylene terephthlte)/polypropylene Blend Yew Wei Leong 1*, Hiroyuki Inoy 2, Supphorn Thumsorn 1 nd Hiroyuki Hmd 1 1 Deprtment
LETTERS. A regulatory circuit for piwi by the large Maf gene traffic jam in Drosophila
 Vol 461 29 Otoer 29 doi:1.138/nture851 LETTERS A regultory iruit for piwi y the lrge Mf gene trffi jm in Drosophil Kuniki Sito 1, Shi Ingki 1, Touti Mituym 2, Yoshinori Kwmur 1,3, Yukiteru Ono 4, Eri Skot
Vol 461 29 Otoer 29 doi:1.138/nture851 LETTERS A regultory iruit for piwi y the lrge Mf gene trffi jm in Drosophil Kuniki Sito 1, Shi Ingki 1, Touti Mituym 2, Yoshinori Kwmur 1,3, Yukiteru Ono 4, Eri Skot
Dual control of nuclear EIN3 by bifurcate MAPK cascades in C 2 H 4 signalling
 Vol 51 1 Ferury doi:1.13/nture653 ARTICLES Dul ontrol of nuler y ifurte MAPK sdes in C H signlling Sng-Dong Yoo 1, Young-Hee Cho 1, Guillume Ten 1, Yn Xiong 1 & Jen Sheen 1 A prinipl question in MAP kinse
Vol 51 1 Ferury doi:1.13/nture653 ARTICLES Dul ontrol of nuler y ifurte MAPK sdes in C H signlling Sng-Dong Yoo 1, Young-Hee Cho 1, Guillume Ten 1, Yn Xiong 1 & Jen Sheen 1 A prinipl question in MAP kinse
Cysteine methylation disrupts ubiquitin-chain sensing in NF-kB activation. NF-κB activation (fold change) NleE TRAF p-ikk /β.
 doi:10.1038/nture10690 Cysteine methyltion disrupts uiquitin-hin sensing in NF-kB tivtion Li Zhng 1,2, Xiojun Ding 2, Jixin Cui 2,HoXu 2, Jing Chen 2, Yi-Nn Gong 2, Liyn Hu 2, Yn Zhou 2, Jinning Ge 2,
doi:10.1038/nture10690 Cysteine methyltion disrupts uiquitin-hin sensing in NF-kB tivtion Li Zhng 1,2, Xiojun Ding 2, Jixin Cui 2,HoXu 2, Jing Chen 2, Yi-Nn Gong 2, Liyn Hu 2, Yn Zhou 2, Jinning Ge 2,
2014. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd The Journal of Experimental Biology (2014) 217, doi: /jeb
 2014. Pulished y The Compny of Biologists Ltd The Journl of Experimentl Biology (2014) 217, 1392-1401 doi:10.1242/je.092288 RESEARCH ARTICLE Regultion of the Rn sylvti revinin-1sy ntimiroil peptide during
2014. Pulished y The Compny of Biologists Ltd The Journl of Experimentl Biology (2014) 217, 1392-1401 doi:10.1242/je.092288 RESEARCH ARTICLE Regultion of the Rn sylvti revinin-1sy ntimiroil peptide during
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion Polypurine reverse-hoogsteen (PPRH) oligonucleotides cn form triplexes with their trget sequences even under conditions where they fold into G-qudruplexes. Ann Solé, Emmnuelle Delgoutte,
Supplementry Informtion Polypurine reverse-hoogsteen (PPRH) oligonucleotides cn form triplexes with their trget sequences even under conditions where they fold into G-qudruplexes. Ann Solé, Emmnuelle Delgoutte,
PRODUCTION METHOD. contact sulphuric acid plant, various kind of waste gases).
 "POL" PHOSPHATE FERTLZER DRY AND WASTE-FREE PRODUCTON METHOD / The elborted fertilizer prodution tehnology nd POL -phosphte fertilizer, re originl hievements dpted to present hnges in the rw-mteril nd
"POL" PHOSPHATE FERTLZER DRY AND WASTE-FREE PRODUCTON METHOD / The elborted fertilizer prodution tehnology nd POL -phosphte fertilizer, re originl hievements dpted to present hnges in the rw-mteril nd
EFECT OF CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE ALLOY ON ALUMINIUM/CARBON FIBRES COMPOSITE STRUCTURE
 18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS EFECT OF CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE ALLOY ON ALUMINIUM/CARBON FIBRES COMPOSITE STRUCTURE A. Dolt-Grosz 1 *, M. Dyzi 1 J. lezion 1 1 Deprtment of Mterils
18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS EFECT OF CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF THE ALLOY ON ALUMINIUM/CARBON FIBRES COMPOSITE STRUCTURE A. Dolt-Grosz 1 *, M. Dyzi 1 J. lezion 1 1 Deprtment of Mterils
Ezh2 controls B cell development through histone H3 methylation and Igh rearrangement
 Ezh2 ontrols B ell development through histone H3 methyltion nd Igh rerrngement I-hsin Su 1,Ashwin Bsvrj 1,Andrew N. Kruthinsky 2, Oliver Hoert 3,Axel Ullrih 4, Brin T. Chit 2 nd Alexnder Trkhovsky 1 Pulished
Ezh2 ontrols B ell development through histone H3 methyltion nd Igh rerrngement I-hsin Su 1,Ashwin Bsvrj 1,Andrew N. Kruthinsky 2, Oliver Hoert 3,Axel Ullrih 4, Brin T. Chit 2 nd Alexnder Trkhovsky 1 Pulished
A conserved PUF Ago eef1a complex attenuates translation elongation
 A onserved PUFAgoeEFA omplex ttenutes trnsltion elongtion Kyle Friend, Zhry T Cmpell, Amy Cooke,, Peggy Kroll-Conner, Mrvin P Wikens, & Judith Kimle Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. PUF (Pumilio/FBF)
A onserved PUFAgoeEFA omplex ttenutes trnsltion elongtion Kyle Friend, Zhry T Cmpell, Amy Cooke,, Peggy Kroll-Conner, Mrvin P Wikens, & Judith Kimle Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. PUF (Pumilio/FBF)
EVALUATION OF ALTERNATIVE FUNGICIDES FOR CONTROL OF CERCOSPORA SPOT ON FUERTE
 Proeedings V World Avodo Congress (Ats V Congreso Mundil del Agute) 23. pp. 579-583. EVALUATION OF ALTERNATIVE FUNGICIDES FOR CONTROL OF CERCOSPORA SPOT ON FUERTE A Willis nd JA Duvenhge Merensky Tehnologil
Proeedings V World Avodo Congress (Ats V Congreso Mundil del Agute) 23. pp. 579-583. EVALUATION OF ALTERNATIVE FUNGICIDES FOR CONTROL OF CERCOSPORA SPOT ON FUERTE A Willis nd JA Duvenhge Merensky Tehnologil
Genome Degradation is an Ongoing Process in Rickettsia
 Genome Degrdtion is n Ongoing Proess in Rikettsi Jn O. Andersson nd Siv G. E. Andersson Deprtment of Moleulr Evolution, Uppsl University, Uppsl, Sweden To study redutive evolutionry proesses in teril genomes,
Genome Degrdtion is n Ongoing Proess in Rikettsi Jn O. Andersson nd Siv G. E. Andersson Deprtment of Moleulr Evolution, Uppsl University, Uppsl, Sweden To study redutive evolutionry proesses in teril genomes,
Protein sliding and DNA denaturation are essential for DNA organization by human mitochondrial transcription factor A
 Reeived 2 Jul 212 Aepted 1 Jul 212 Pulished 21 Aug 212 DOI: 1.138/nomms21 Protein sliding nd DNA denturtion re essentil for DNA orgniztion y humn mitohondril trnsription ftor A Gérldine Frge 1, *, Niels
Reeived 2 Jul 212 Aepted 1 Jul 212 Pulished 21 Aug 212 DOI: 1.138/nomms21 Protein sliding nd DNA denturtion re essentil for DNA orgniztion y humn mitohondril trnsription ftor A Gérldine Frge 1, *, Niels
LETTER. Coordination of DNA replication and histone modification by the Rik1 Dos2 complex
 oi:1.138/nture1161 Coorintion of DNA replition n histone moifition y the Rik1 Dos2 omplex Fei Li 1, Ro Mrtienssen 2 & W. Zheus Cne 3 Histone moifition mrks hve n importnt role in mny hromtin proesses 1,2.
oi:1.138/nture1161 Coorintion of DNA replition n histone moifition y the Rik1 Dos2 omplex Fei Li 1, Ro Mrtienssen 2 & W. Zheus Cne 3 Histone moifition mrks hve n importnt role in mny hromtin proesses 1,2.
than 1 week at -90, were resuspended by gentle homogenization
 Pro. Nti. Ad. Si. USA Vol. 74, No. 11, pp. 4881-4885, November 1977 Biohemistry Role of nuleotides in tubulin polymeriztion: Effet of gunylyl 5'-methylenediphosphonte (mirotubules/gunosine nuleotides/high
Pro. Nti. Ad. Si. USA Vol. 74, No. 11, pp. 4881-4885, November 1977 Biohemistry Role of nuleotides in tubulin polymeriztion: Effet of gunylyl 5'-methylenediphosphonte (mirotubules/gunosine nuleotides/high
PP100 N ABSOLUTE DEPTH FILTER ELEMENTS FEATURES & BENEFITS. Process Filtration
 PP100 N ABSOLUTE DEPTH FILTER ELEMENTS Proess Filtrtion Donldson LifeTe PP100 N filters re solute rted depth type filters onstruted of 100% polypropylene. They ontin grded density polypropylene mirofier
PP100 N ABSOLUTE DEPTH FILTER ELEMENTS Proess Filtrtion Donldson LifeTe PP100 N filters re solute rted depth type filters onstruted of 100% polypropylene. They ontin grded density polypropylene mirofier
Assembly-driven activation of the AIM2 foreign-dsdna sensor provides a polymerization template for downstream ASC
 Reeived 21 Jn 2015 Aepted 16 Jun 2015 Pulished 22 Jul 2015 DOI: 10.1038/nomms8827 Assemly-driven tivtion of the AIM2 foreign- sensor provides polymeriztion templte for downstrem ASC Semus R. Morrone 1,
Reeived 21 Jn 2015 Aepted 16 Jun 2015 Pulished 22 Jul 2015 DOI: 10.1038/nomms8827 Assemly-driven tivtion of the AIM2 foreign- sensor provides polymeriztion templte for downstrem ASC Semus R. Morrone 1,
acj mutants in which it is affected (olfaction/behavior genetics/sensory system/brain/antennae)
 Pro. Nti. Ad. Si. USA Vol. 86, pp. 8118-8122, Otoer 1989 Neuroiology A simple hemosensory response in Drosophil nd the isoltion of j mutnts in whih it is ffeted (olftion/ehvior genetis/sensory system/rin/ntenne)
Pro. Nti. Ad. Si. USA Vol. 86, pp. 8118-8122, Otoer 1989 Neuroiology A simple hemosensory response in Drosophil nd the isoltion of j mutnts in whih it is ffeted (olftion/ehvior genetis/sensory system/rin/ntenne)
PML regulates p53 stability by sequestering Mdm2 to the nucleolus
 regultes stility y sequestering to the nuleolus Ros Bernrdi 1,Pier Polo Sglioni 1,3,Stephn Bergmnn 1,3,Henning F. Horn 2,Kren H. Vousden 2 nd Pier Polo Pndolfi 1,4 The promyeloyti leukemi () tumour-suppressor
regultes stility y sequestering to the nuleolus Ros Bernrdi 1,Pier Polo Sglioni 1,3,Stephn Bergmnn 1,3,Henning F. Horn 2,Kren H. Vousden 2 nd Pier Polo Pndolfi 1,4 The promyeloyti leukemi () tumour-suppressor
Total Rewards: Vacation, Sick and Personal Leave for Full Time Employees
 POLICY: 6Hx28:3D-03 Responsible Exeutive: Vie President, Orgniztionl Development & Humn Resoures Poliy Contts: Diretor, HR Poliy nd Compline Progrms Speifi Authority: 1001.61, F.S. Lw Implemented: 1001.64,
POLICY: 6Hx28:3D-03 Responsible Exeutive: Vie President, Orgniztionl Development & Humn Resoures Poliy Contts: Diretor, HR Poliy nd Compline Progrms Speifi Authority: 1001.61, F.S. Lw Implemented: 1001.64,
Steels used in braking systems
 Steels use in rking systems A report A mterils engineer is require to prepre report on the seletion of plin ron steels for use in the proution of vrious omponents for rke mnufturing ompny. Portions of
Steels use in rking systems A report A mterils engineer is require to prepre report on the seletion of plin ron steels for use in the proution of vrious omponents for rke mnufturing ompny. Portions of
Effect of AtNRT2.1 transgene on HATS nitrate uptake in transgenic Nicotiana plumbaginifolia
 Progress in Biologil Sienes Vol. 1, No.1, 1-9, Winter/Spring 11 Effet of AtNRT2.1 trnsgene on HATS nitrte uptke in trnsgeni Niotin plumginifoli Przhk Zoufn 2 nd Mnsour Shriti 1 * 1 Deprtment of Biology,
Progress in Biologil Sienes Vol. 1, No.1, 1-9, Winter/Spring 11 Effet of AtNRT2.1 trnsgene on HATS nitrte uptke in trnsgeni Niotin plumginifoli Przhk Zoufn 2 nd Mnsour Shriti 1 * 1 Deprtment of Biology,
Supplementary Figure S1. MKRN1 depletion induces apoptosis via the caspase-8 pathway. kda h 72h 96h 6.8 % 22.5 % 21.
 Supplementry Figure S1. depletion indues poptosis vi the spse-8 pthwy. Atin 61.5 46.2 48h 72h 96h zvad 96h 5. % 6.8 % 8.7 % 4.3% simk1#5 9.5 % 22.5 % 39.6 % 11.8 % simk1#6 8. % 21.7 % 33.5 % 11. % 48h
Supplementry Figure S1. depletion indues poptosis vi the spse-8 pthwy. Atin 61.5 46.2 48h 72h 96h zvad 96h 5. % 6.8 % 8.7 % 4.3% simk1#5 9.5 % 22.5 % 39.6 % 11.8 % simk1#6 8. % 21.7 % 33.5 % 11. % 48h
Functional analysis of the Landsberg erecta allele of FRIGIDA
 Shmlenh et l. BMC Plnt Biology 214, 14:218 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Funtionl nlysis of the Lndserg eret llele of FRIGIDA Ing Shmlenh 1, Lei Zhng 1, Mlgorzt Ryngjllo 1 nd José M Jiménez-Gómez 1,2* Astrt
Shmlenh et l. BMC Plnt Biology 214, 14:218 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Funtionl nlysis of the Lndserg eret llele of FRIGIDA Ing Shmlenh 1, Lei Zhng 1, Mlgorzt Ryngjllo 1 nd José M Jiménez-Gómez 1,2* Astrt
LETTERS. A fast, robust and tunable synthetic gene oscillator
 Vol 456 27 Novemer 28 doi:1.138/nture7389 A fst, roust nd tunle syntheti gene osilltor Jesse Striker 1 *, Sott Cookson 1 *, Mtthew R. Bennett 1,2 *, Willim H. Mther 1, Lev S. Tsimring 2 & Jeff Hsty 1,2
Vol 456 27 Novemer 28 doi:1.138/nture7389 A fst, roust nd tunle syntheti gene osilltor Jesse Striker 1 *, Sott Cookson 1 *, Mtthew R. Bennett 1,2 *, Willim H. Mther 1, Lev S. Tsimring 2 & Jeff Hsty 1,2
WesternBright TM MCF and MCF-IR
 WesternBright TM MCF nd MCF-IR Quntittive, multi-color fluorescent Western lotting kits WesternBright MCF visile nd ner infrred (IR) fluorescent Western lotting kits llow the ssy of two proteins t once,
WesternBright TM MCF nd MCF-IR Quntittive, multi-color fluorescent Western lotting kits WesternBright MCF visile nd ner infrred (IR) fluorescent Western lotting kits llow the ssy of two proteins t once,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTRY INFORMTION DOI:./n7 d Tm d- d- Frequeny, e+ e+ kp e+ e+.e+ Ctegory # peks % peks % genome Fold Enrihment k upstrem TSS.7 9..77 Exon..7. ' UTR...7 ' UTR... Intron 79.
SUPPLEMENTRY INFORMTION DOI:./n7 d Tm d- d- Frequeny, e+ e+ kp e+ e+.e+ Ctegory # peks % peks % genome Fold Enrihment k upstrem TSS.7 9..77 Exon..7. ' UTR...7 ' UTR... Intron 79.
PF-PT N MEMBRANE FILTER ELEMENTS FEATURES & BENEFITS. Compressed Air & Process Filtration PF-PT N
 PF-PT N MEMBRANE FILTER ELEMENTS Compressed Air & Proess Filtrtion The Donldson LifeTe PF-PT N filter element is sterile grde, pleted high performne PTFE memrne filter. It provides the gretest ssurne of
PF-PT N MEMBRANE FILTER ELEMENTS Compressed Air & Proess Filtrtion The Donldson LifeTe PF-PT N filter element is sterile grde, pleted high performne PTFE memrne filter. It provides the gretest ssurne of
letters Crystal structure of an RNA tertiary domain essential to HCV IRES-mediated translation initiation III
 letters Crystl struture of n RN tertiry domin essentil to HCV IRES-medited trnsltion initition Jeffrey S. Kieft 1,2, Kihong Zhou 1,2, ngie Greh 1, Ronld Juin nd Jennifer. Doudn 1,2 1 Deprtment of Moleulr
letters Crystl struture of n RN tertiry domin essentil to HCV IRES-medited trnsltion initition Jeffrey S. Kieft 1,2, Kihong Zhou 1,2, ngie Greh 1, Ronld Juin nd Jennifer. Doudn 1,2 1 Deprtment of Moleulr
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture10970 I. GN directly grown on the h-bn relese lyer Figure S1 shows X-ry diffrction with the 2θ/ω configurtion nd n opticl microscopy imge for the GN directly grown on the h-bn relese lyer.
doi:10.1038/nture10970 I. GN directly grown on the h-bn relese lyer Figure S1 shows X-ry diffrction with the 2θ/ω configurtion nd n opticl microscopy imge for the GN directly grown on the h-bn relese lyer.
Synapsis, Strand Scission, and Strand Exchange Induced by the
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Sept. 1991, p. 4497-4508 0270-7306/91/094497-12$02.00/0 Copyright C) 1991, Americn Society for Microiology Vol. 11, No. 9 Synpsis, Strnd Scission, nd Strnd Exchnge Induced
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Sept. 1991, p. 4497-4508 0270-7306/91/094497-12$02.00/0 Copyright C) 1991, Americn Society for Microiology Vol. 11, No. 9 Synpsis, Strnd Scission, nd Strnd Exchnge Induced
Job Description. Senior Lecturer. Electronic & Electrical Engineering. Education and Research. Head of Department/Group. Any research staff/students
 Jo Desription Jo title Deprtment/Shool Jo fmily Senior Leturer Eletroni & Eletril Engineering Edution nd Reserh Grde 9 Reporting to Responsile for Lotion Hed of Deprtment/Group Any reserh stff/students
Jo Desription Jo title Deprtment/Shool Jo fmily Senior Leturer Eletroni & Eletril Engineering Edution nd Reserh Grde 9 Reporting to Responsile for Lotion Hed of Deprtment/Group Any reserh stff/students
Virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS)-mediated functional characterization of two genes involved in lignocellulosic secondary cell wall formation
 Plnt Cell Rep DOI 1.17/s299-16-239-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Virus-indued gene silening (VIGS)-medited funtionl hrteriztion of two genes involved in lignoellulosi seondry ell wll formtion Shshnk K. Pndey 1 Akul
Plnt Cell Rep DOI 1.17/s299-16-239-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Virus-indued gene silening (VIGS)-medited funtionl hrteriztion of two genes involved in lignoellulosi seondry ell wll formtion Shshnk K. Pndey 1 Akul
Negative regulation of TLR4 via targeting of the proinflammatory tumor suppressor PDCD4 by the microrna mir-21
 Negtive regultion of TLR vi trgeting of the proinflmmtory tumor suppressor y the mirorna mir-1 Frederik J Sheedy 1, Ev Plsson-MDermott 1, Elizeth J Hennessy 1, Cr Mrtin,, John J O Lery,, Qingguo Run, Derek
Negtive regultion of TLR vi trgeting of the proinflmmtory tumor suppressor y the mirorna mir-1 Frederik J Sheedy 1, Ev Plsson-MDermott 1, Elizeth J Hennessy 1, Cr Mrtin,, John J O Lery,, Qingguo Run, Derek
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 BRC repet RPA DSB RAD52 DSB Repir doi:1.138/nture9399 Gp Repir ssdna/dsdna junction ssdna/dsdna junction RPA Binding Resection RPA Binding Filment Formtion or or Filment Formtion DNA Piring DNA Piring
BRC repet RPA DSB RAD52 DSB Repir doi:1.138/nture9399 Gp Repir ssdna/dsdna junction ssdna/dsdna junction RPA Binding Resection RPA Binding Filment Formtion or or Filment Formtion DNA Piring DNA Piring
Comparative Study of Weldline Strength in Conventional Injection Molding and Rapid Heat Cycle Molding
 Comprtive Study of Weldline Strength in Conventionl Injetion Molding nd Rpid Het Cyle Molding JIQUAN LI 1,2, SHAOGUANG YANG 1, LIH-SHENG TURNG 2, ZUOJIAN XIE 1, SHAOFEI JIANG 1 * 1 College of Mehnil Engineering,
Comprtive Study of Weldline Strength in Conventionl Injetion Molding nd Rpid Het Cyle Molding JIQUAN LI 1,2, SHAOGUANG YANG 1, LIH-SHENG TURNG 2, ZUOJIAN XIE 1, SHAOFEI JIANG 1 * 1 College of Mehnil Engineering,
Effect of Microstructure on Mechanical Properties of Friction-Welded Joints between Ti and AISI 321 Stainless Steel
 Mterils Trnstions, Vol. 45, No. 9 (4) pp. 2805 to 2811 #4 The Jpn Institute of Metls Effet of Mirostruture on Mehnil Properties of Frition-Welded Joints etween nd AISI 321 Stinless Steel Won-Be Lee* 1
Mterils Trnstions, Vol. 45, No. 9 (4) pp. 2805 to 2811 #4 The Jpn Institute of Metls Effet of Mirostruture on Mehnil Properties of Frition-Welded Joints etween nd AISI 321 Stinless Steel Won-Be Lee* 1
PCR primers and functional probes for amplification and detection of bacterial genes for extracellular peptidases in single strains and in soil
 Ž. Journl of Miroiologil Methods 44 2001 173 182 www.elsevier.omrloterjmimeth PCR primers nd funtionl proes for mplifition nd detetion of teril genes for extrellulr peptidses in single strins nd in soil
Ž. Journl of Miroiologil Methods 44 2001 173 182 www.elsevier.omrloterjmimeth PCR primers nd funtionl proes for mplifition nd detetion of teril genes for extrellulr peptidses in single strins nd in soil
