Supplemental Information. Pacemaker and Plateau Potentials. Shape Output of a Developing. Locomotor Network. Current Biology, Volume 22
|
|
|
- Nathan Price
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Current Biology, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Pacemaker and Plateau Potentials Shape Output of a Developing Locomotor Network Huaxia Tong and Jonathan Robert McDearmid SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Animals and preparation for in vivo recording Zebrafish were maintained according to established procedures [1] and all experiments carried out in compliance with the Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act, Embryo staging was performed in accordance with Kimmel et al. [2] and animals were prepared for patch clamp electrophysiology as previously described [3]. Briefly, embryos or larvae were anesthetised and pinned into a Sylgardlined dish containing % tricaine (MS-222) dissolved in Evans solution (constituents in mm: 134 NaCl, 2.9 KCl, 2.1 CaCl 2, 1.2 MgCl 2, 10 HEPES, and 10 glucose, osmolarity mosm, ph 7.8 adjusted with NaOH). The skin overlying myotomal tissue was removed with fine forceps. In most experiments, tricaine was subsequently replaced with Evans containing the neuromuscular blocker D- tubocurarine (10 µm) to ensure muscle paralysis during experiments. However, during recordings of neuromuscular activity, embryos were partially paralysed via exposure to reduced D-tubocurarine concentrations (3 µm). Fish were then transferred to the patch clamp microscope (Nikon FN-1) and muscle fibres removed from a two to four somite region via aspiration with a broken patch pipette. Recordings were made between somites 4 to 9 as rostral spinal regions have previously been shown to be critical for generation of SNA. Patch clamp electrophysiology Patch pipettes were pulled from filamented borosilicate glass (GC150F-10, Harvard Apparatus, Edenbridge, UK) using a P-80 micropipette puller (Sutter Instrument, Novato, CA, USA). Pipettes with resistance ranging between 3-5 MΩ and 3-10 MΩ were used for voltage and current clamp recordings respectively. Depending on the experiment, pipettes were filled with one of three recording solutions: a potassium-based internal solution, containing (mm): K-Gluconate 126, KCl 6, NaCl 10, HEPES 10, EGTA 10, MgCl 2 2, ph to 7.2); a caesium-based recording solution, where K-gluconate (126 mm) and KCl (6 mm) were substituted with CsCl (132 mm) or; when examining locomotor drive, a low chloride solution containing (mm): 125 K-gluconate, 2.5 MgCl 2, 10 EGTA, 10 HEPES. In voltage clamp and some, but not all, current clamp experiments 1 mm Mg-ATP and 0.1 mm Na-GTP were included in the patch pipette. As these reagents had no detectable effects on physiological properties of embryonic neurons, data was pooled with experiments in which these reagents were not included. For experiments in which sodium channels were blocked in the recorded cell, QX-314 (4 mm) was added to the pipette solution. Sulforhodamine B was routinely included in the patch pipette solution to facilitate visualization of neurons under fluorescence. Neurons were classified in accordance with previously established morphological criteria [4-7]. Recordings were amplified with a Multiclamp 700B (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) or an RK-400 (BioLogic, Claix, France) amplifier. Data were digitised with an Axon Digidata 1440 A (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) A-D converter connected to a PC running either pclamp 10 (Molecular Devices) or WinEDR ( Raw signals were acquired at 10-20kHz and low-pass filtered at 5-10kHz. For voltage-clamp, series resistance was routinely compensated by 70-80%. All traces were compensated for a junction potential of 13.7 mv. 1
2 During initial voltage-current (V-I) experiments in which I NaP was studied we used conditions designed to minimize contamination from calcium and potassium channels. Specifically we used a caesium chloride based pipette solution (to minimise potassium currents) and Evans extracellular saline containing µm cadmium chloride (to minimise calcium currents). In subsequent experiments where I NaP was examined under more physiological conditions, a potassium-based internal solution (see above) was used and cadmium was excluded from the extracellular saline. In both scenarios linear 55 mv/s ramps were used so that transient sodium currents were inactivated and thus did not contaminate ramp traces. Pharmacological isolation of I NaP was achieved by application of VGSC blockers tetrodotoxin (TTX, µm) or riluzole (5-10 µm). For Boltzmann analysis individual current traces were leak subtracted prior to averaging. Estimates of membrane resistance were calculated by determining the slope of the V-I relationship in ohmic regions of the curve (ca. -80 mv). To monitor chloride and cation currents during locomotor activity, reversal potential of ionic species was determined experimentally by monitoring spontaneous currents at various holding potentials prior to stimulation of motor activity. Current-clamp recordings were carried out to study spontaneous network activity, neuronal firing properties and locomotor drive. Prior to recordings, neurons were routinely bridge-balanced using the electronic features of the amplifier. When studying neuronal firing properties, the synaptic blockers strychnine (1 µm), bicuculline (10 µm) and kynurenic acid (2-4 mm) were included in the extracellular saline. To study rheobase (measured as the amount of injected current at action potential threshold), a small amount of holding current was injected into neurons to maintain a membrane potential of ca mv. From this potential depolarising current steps, ranging between -20 pa to 100 pa, were applied. For experiments in which firing properties of coiling stage embryos were examined, we used hpf embryos as in earlier embryos neurons received regular driving inputs from gap junction coupled neighbours. As gap junctions are resistant to pharmacological blockade [9, 10] (H. Tong, unpublished observations), it was difficult synaptically isolate neurons and thus separate intrinsic activity from network-driven events. This problem was ameliorated by recording from late stage coiling fish (26 29 hpf) as here network activity is infrequent. Simultaneous patch clamp recordings were performed as previously described [3, 8]. Briefly recordings were obtained from an IC cell in the rostral spinal cord and an ipsilateral CPG neuron located 1 3 spinal segments caudal to it. Upon completion of experiments neuronal identities were determined via fluorescence detection of sulforhodamine labelling. During experiments in which fictive swimming was monitored, locomotion was triggered via application of a small amount of current delivered to the tail skin using a stimulating electrode connected to a stimulus isolation unit (Digitimer, UK). Drugs All drugs were obtained from Sigma (UK) with the exception of TTX, riluzole, apamin, ZD7288 and kynurenic acid which were obtained from Ascent Scientific (UK). Stock solutions were made in water or DMSO and diluted in Evans to final working concentrations. To study pharmacology of network activity, drugs were added directly to the perfusion saline. During voltage and current clamp studies of cellular currents and firing properties, drugs were applied focally using a gravity-fed VC3-4 perfusion system (ALA Scientific). Electrophysiological analysis PD durations were assessed from the average of consecutive events obtained from each experiment. The difference between resting membrane potential and steady stage voltage at PD peak was used to assess amplitudes. To determine PD frequencies the number of events that occurred over a 100 s was calculated. Estimates of baseline membrane potential were derived from quiescent periods of recordings. However, in instances where SNA was high, this value was determined after silencing of network activity with 1 µm TTX. EPSP parameters were determined from the average of events obtained from each locomotor-related episode and amplitude of tonic depolarisation was measured as the mean steady-state depolarisation from each recorded swim episode. Because I NaP appeared identical in all recorded cells, voltage clamp data was combined for generation of mean IV and conductance plots. Persistent sodium conductances were calculated from averaged 2
3 I NaP by taking account of the driving forces, and fitted with a Boltzmann function; g/gmax = (1+exp(V- V1/2/K))-1 where g and gmax are conductances at membrane potential (V) and the maximum conductance, respectively, V1/2 is the half-activation voltage and K is the slope factor. Behavioural analysis To assess the effects of ion channel blockers on coiling, hpf embryos were embedded in an agarose-lined dish containing egg water. Their tails were cut free and, with the exception of riluzole which was added directly to the egg water, the desired drug or control saline was injected into the yolk sac using a fine glass needle. After a 90 min incubation, 1 minute sequences of activity were filmed with a video camera (Basler, Germany; acquisition rate of 210 Hz) connected to a PC running VirtualDub ( Sequential frames were montaged or stacked in ImageJ for presentation. To assess the effects of dopamine on swimming, control saline or dopamine (100 µm) was injected into the yolk sac of 42 hpf embryos which were then left to recover for 60 min. Then fish were transferred to a 35 mm Petri dish and free-swimming responses evoked by sensory stimuli (touching of the tail with a pair of fine forceps) were recorded as described above. Statistics All data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. and statistical significance determined using two-tailed Student's t tests. A p value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. 3
4 Figure S1. Role of Calcium during SNA, Related to Figure 2 (A,B) Representative voltage traces depicting effects of efonidipine (100 µm, A), low calcium (0.5 mm) saline (B) and apamin (40 nm, C) on SNA. Recordings were obtained from Mns (A,B) and VeLD interneurons (C) at 24, 25 and 24 hpf respectively. Arrows and asterisks show PD and SB, respectively. (D) Bar charts depicting effects of Efonid, low calcium saline (0.5 1 mm; Low Ca) and apamin on mean PD amplitude (left hand panel), width (middle panel) and frequency (right hand panel). Note that low calcium saline significantly increased PD duration (control saline = 0.86±0.10 s cf. low Ca saline = 1.64 ± 0.3 s, n = 8, *p = 0.009) and PD frequency (control saline = 0.12±0.01 Hz cf. low Ca saline = 1.04 ± 0.42 Hz, *p = 0.046) whilst apamin significantly increased PD duration (control = 1.49 ± 0.13 s cf. apamin 2.18 ± 0.19 s, *p = 4.5x10-3 ). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. 4
5 Figure S2. Effects of Riluzole on Action Potential Properties, Related to Figure 3 (A) Representative voltage recordings of Mn action potentials (APs) at 22 hpf, evoked by threshold current injection in control and in the presence of 5 µm and 10 µm riluzole respectively. (B) Bar chart depicting effects of riluzole on membrane voltage at peak AP amplitude. 5 µm riluzole (n=20) did not affect peak AP amplitude (p = 0.97) but 10 µm riluzole significantly reduced this parameter (n = 13 *p = 0.03). (C) Neither 5 µm (n = 20, p = 0.33) nor 10 µm (n = 13, p = 0.12) riluzole affected rheobase (i.e. current threshold for AP firing). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. 5
6 Figure S3. I NaP Underpins IC Cell Oscillations at the Coiling Stage, Related to Figure 4 (A,B) Raw V-I traces (55mV/s ramps) of derived from an IC cell (A) and Mn (B) in control saline (black) and after addition of 1µM TTX (grey). Perfusion of TTX blocked inward rectification in the IC cell (A) and increased outward rectification in the Mn (B). Red traces depict TTX-sensitive subtraction current (sub). (C) Sample voltage recordings of each cell class at hpf showing differences between PD amplitude and baseline membrane potential. (D) IC cell oscillations were conditional on depolarising input and terminated immediately upon release of command current. (E) Oscillation frequency was dependent on magnitude of current injection. 20 pa depolarising current evoked 1.5 Hz oscillations (left hand panel) whilst 60 pa evoked 2.2 Hz oscillations (right hand panel). Traces in D-E are derived from separate current clamp recordings at 28 and 27 hpf respectively. 6
7 Figure S4. IC Cells and Sustained Bursts at the Early Swimming Stage, Related to Figure 5 (A) At early swimming stages IC cells often generated repetitive bursts in response to prolonged depolarising steps. (B) IC cell bursts were conditional on depolarising input because neurons immediately returned to rest upon termination of the current command. (C) During IC cell recordings, bath perfusion of TTX (1 µm) abolished both action potential generation and sustained bursts. Traces in A-C derived from separate current clamp recordings spanning hpf. Current commands are depicted by grey traces. 7
8 Figure S5. IC Cell Locomotor Drive during Early Swimming Periods, Related to Figure 6 (A) Left-hand panel: paired voltage recording of an IC cell and a VeLD interneuron 31 hpf. Right hand panel: Expanded sweep taken from corresponding episode showing rhythmic IC cell bursting occurring in register with rhythmic EPSPs in VeLD interneurons. Note that small spikelets (arrows) were often observed at the peak of IC cell bursts. (B) (a) IC cell current responses to a voltage waveform derived from an IC cell during fictive locomotion. Upper trace: command waveform. Middle trace: current response in control saline. Lower trace: current response after 8 min perfusion of TTX (1 µm). (b) Sodium current flow (upper trace, isolated by subtraction of current response in TTX from current response in control saline) during the voltage command (lower trace). Note that the TTX sensitive current comprises cyclically active persistent currents (presumably I NaP ) and large, transient currents (presumably I NaT ). I NaT peaks in a,b have been cropped (oblique lines). 8
9 Figure S6. Effects of Riluzole, Dopamine and Hyperpolarisation on IC cells, Related to Figure 7 (A) Effects of riluzole on EPSP frequency during locomotor episodes recorded from primary Mns at hpf. (B) Voltage responses (upper traces) to a family of current pulses (lower traces) recorded from a primary neuron at 38 hpf in control saline and after 10 min exposure to riluzole (5 µm). Note that riluzole abolishes repetitive spike capability in this cell. (C) Effects of dopamine (DA) on rheobase current of the four primary neurons studied. Dopamine increased IC cell firing threshold (control = ± 1.54 pa cf. DA = ± 2.77 pa, *p = 2x10-3 ) and decreased VeLD threshold (control = 29.3 ± 5.7 cf. DA = 25 ± 4.6, *p = 0.048) but had no effect on other cell classes (D). 9
10 Changes in resting membrane potential of each primary neuron following dopamine (DA) perfusion. Dopamine hyperpolarised resting potential of IC cells (*p = 2x10-4 ) but had no effect on other cell classes Data in C,D obtained from embryos at hpf. (E) Effects of dopamine (DA) on EPSP frequency during locomotor episodes recorded from primary Mns at hpf. (F) Simultaneous recording of an IC cell (upper trace) and Mn (lower trace) during locomotor activity. Injecting the IC cell with a hyperpolarising current step (middle trace) does not impair Mn activity. Data in A,C-E represented as mean ± SEM. 10
11 SUPPLEMENTAL REFERENCES 1. Westerfield, M. (1994). The Zebrafish Book: a Guide to the Laboratory Use of the Zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio), 2.1 Edition, (University of Oregon Press, Eugene, OR). 2. Kimmel, C.B., Ballard, W.W., Kimmel, S.R., Ullmann, B., and Schilling, T.F. (1995). Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Developmental Dynamics 203, Drapeau, P., Ali, D.W., Buss, R.R., and Saint-Amant, L. (1999). In vivo recording from identifiable neurons of the locomotor network in the developing zebrafish. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 88, Mendelson, B. (1986). Development of reticulospinal neurons of the zebrafish. II. Early axonal outgrowth and cell body position. Journal of Comparative Neurology 251, Myers, P.Z., Eisen, J.S., and Westerfield, M. (1986). Development and axonal outgrowth of identified motoneurons in the zebrafish. Journal of Neuroscience 6, Kuwada, J.Y., and Bernhardt, R.R. (1990). Axonal outgrowth by identified neurons in the spinal cord of zebrafish embryos. Experimental Neurology 109, Bernhardt, R.R., Chitnis, A.B., Lindamer, L., and Kuwada, J.Y. (1990). Identification of spinal neurons in the embryonic and larval zebrafish. Journal of Comparative Neurology 302, Saint-Amant, L., and Drapeau, P. (2003). Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings from identified spinal neurons in the zebrafish embryo. Methods in Cell Science 25,
Voltage clamp and patch-clamp techniques
 Voltage clamp and patch-clamp techniques Dr. Nilofar Khan Objectives Historical background Voltage Clamp Theory Variations of voltage clamp Patch-clamp Principal Patch-clamp configurations Applications
Voltage clamp and patch-clamp techniques Dr. Nilofar Khan Objectives Historical background Voltage Clamp Theory Variations of voltage clamp Patch-clamp Principal Patch-clamp configurations Applications
11 Loose-Patch-Clamp Method
 11 Loose-Patch-Clamp Method Hector G. Marrero and José R. Lemos 1. Introduction ne of the basic tenets of experimental science has been the search for techniques that give relevant information from intact
11 Loose-Patch-Clamp Method Hector G. Marrero and José R. Lemos 1. Introduction ne of the basic tenets of experimental science has been the search for techniques that give relevant information from intact
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION Recombinant HEK293 cell line expressing the four subunits α1, β1, δ and ε of the human nicotinic acetylcholine receptor type I.
 PRODUCT DATASHEET PrecisION hnachr α1/β1/δ/ε-hek Recombinant Cell Line Catalog Number: CYL3052 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION Recombinant HEK293 cell line expressing the four subunits α1, β1, δ and ε of the human
PRODUCT DATASHEET PrecisION hnachr α1/β1/δ/ε-hek Recombinant Cell Line Catalog Number: CYL3052 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION Recombinant HEK293 cell line expressing the four subunits α1, β1, δ and ε of the human
SI8000 Live Cell Imaging System
 SI8000 Live Cell Imaging System Sony Biotechnology Inc. SI8000 Cell Motion Imaging System The Sony SI8000 Live Cell Imaging System detects and quantifies cellular motion using proprietary video processing
SI8000 Live Cell Imaging System Sony Biotechnology Inc. SI8000 Cell Motion Imaging System The Sony SI8000 Live Cell Imaging System detects and quantifies cellular motion using proprietary video processing
CytoPatch Study: Effect of Cisapride, (d-l)-sotalol and Terfenadine on herg channel currents of transfected CHO cells
 CytoPatch Study: Effect of Cisapride, (d-l)-sotalol and Terfenadine on herg channel currents of transfected CHO cells 1. Conclusion In this study, the operating efficiency of the CytoPatch instrument was
CytoPatch Study: Effect of Cisapride, (d-l)-sotalol and Terfenadine on herg channel currents of transfected CHO cells 1. Conclusion In this study, the operating efficiency of the CytoPatch instrument was
Implantable Microelectronic Devices
 ECE 8803/4803 Implantable Microelectronic Devices Fall - 2015 Maysam Ghovanloo (mgh@gatech.edu) School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology 2015 Maysam Ghovanloo 1 Outline
ECE 8803/4803 Implantable Microelectronic Devices Fall - 2015 Maysam Ghovanloo (mgh@gatech.edu) School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology 2015 Maysam Ghovanloo 1 Outline
High-Speed, Random-Access Fluorescence Microscopy: II. Fast Quantitative Measurements With Voltage-Sensitive Dyes
 2272 Biophysical Journal Volume 76 April 1999 2272 2287 High-Speed, Random-Access Fluorescence Microscopy: II. Fast Quantitative Measurements With Voltage-Sensitive Dyes A. Bullen* # and P. Saggau* *Division
2272 Biophysical Journal Volume 76 April 1999 2272 2287 High-Speed, Random-Access Fluorescence Microscopy: II. Fast Quantitative Measurements With Voltage-Sensitive Dyes A. Bullen* # and P. Saggau* *Division
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Materials and Methods Circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. Far ultraviolet (UV) CD spectra of apo- and holo- CaM and the CaM mutants were recorded on a Jasco J-715 spectropolarimeter
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Materials and Methods Circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. Far ultraviolet (UV) CD spectra of apo- and holo- CaM and the CaM mutants were recorded on a Jasco J-715 spectropolarimeter
The capsaicin receptor: a heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway
 The capsaicin receptor: a heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway Michael J. Caterina*, Mark A. Schumacher k, Makoto Tominaga*k, Tobias A. Rosen*, Jon D. Levine & David Julius* Departments of *
The capsaicin receptor: a heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway Michael J. Caterina*, Mark A. Schumacher k, Makoto Tominaga*k, Tobias A. Rosen*, Jon D. Levine & David Julius* Departments of *
Mechanical stimulation of Piezo1 receptors depends on extracellular matrix proteins and directionality of force. Supporting Information
 Mechanical stimulation of Piezo1 receptors depends on extracellular matrix proteins and directionality of force Benjamin M. Gaub and Daniel J. Müller Supporting Information Supporting Information Note
Mechanical stimulation of Piezo1 receptors depends on extracellular matrix proteins and directionality of force Benjamin M. Gaub and Daniel J. Müller Supporting Information Supporting Information Note
Cellular adhesion and neuronal excitability on functionalised diamond surfaces
 Cellular adhesion and neuronal excitability on functionalised diamond surfaces P. Ariano 1,2, P. Baldelli 1,3, E. Carbone1,3, A. Gilardino1,2, A. Lo Giudice1,4, D. Lovisolo1,2, C. Manfredotti1,4, M. Novara1,3,
Cellular adhesion and neuronal excitability on functionalised diamond surfaces P. Ariano 1,2, P. Baldelli 1,3, E. Carbone1,3, A. Gilardino1,2, A. Lo Giudice1,4, D. Lovisolo1,2, C. Manfredotti1,4, M. Novara1,3,
Calcium Assay Kit. Technical Data Sheet. Product Information. Description. Storage. Materials not included
 BD Technical Data Sheet Calcium Assay Kit Product Information Catalog Number: 640176 Size Reagents for 10 plates Components: Calcium Indicator, 1 vial, lyophilized 10X Signal Enhancer, 10 ml 1X Calcium
BD Technical Data Sheet Calcium Assay Kit Product Information Catalog Number: 640176 Size Reagents for 10 plates Components: Calcium Indicator, 1 vial, lyophilized 10X Signal Enhancer, 10 ml 1X Calcium
DNAse I qualification and sample treatment
 DNA Application Note DNAse I qualification and sample treatment INTRODUCTION The Threshold Total DNA Assay quantitates contaminant DNA in biopharmaceutical drugs. DNase I can be used in conjunction with
DNA Application Note DNAse I qualification and sample treatment INTRODUCTION The Threshold Total DNA Assay quantitates contaminant DNA in biopharmaceutical drugs. DNase I can be used in conjunction with
icell DopaNeurons Application Protocol
 icell DopaNeurons Application Protocol Measuring Synchronous Neuronal Activity on the Maestro Multielectrode Array Introduction icell DopaNeurons, human induced pluripotent stem cell (ipsc)-derived neurons,
icell DopaNeurons Application Protocol Measuring Synchronous Neuronal Activity on the Maestro Multielectrode Array Introduction icell DopaNeurons, human induced pluripotent stem cell (ipsc)-derived neurons,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 PCR-genotyping of the three mouse models used in this study and controls for behavioral experiments after semi-chronic Pten inhibition. a-c. DNA from App/Psen1 (a), Pten tg (b) and
Supplementary Figure 1 PCR-genotyping of the three mouse models used in this study and controls for behavioral experiments after semi-chronic Pten inhibition. a-c. DNA from App/Psen1 (a), Pten tg (b) and
PI3 Kinase Assay Kit. Catalog Number KA assays Version: 05. Intended for research use only.
 PI3 Kinase Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0904 400 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials Supplied...
PI3 Kinase Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0904 400 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials Supplied...
QUANTITATIVE RT-PCR PROTOCOL (SYBR Green I) (Last Revised: April, 2007)
 QUANTITATIVE RT-PCR PROTOCOL (SYBR Green I) (Last Revised: April, 007) Please contact Center for Plant Genomics (CPG) facility manager Hailing Jin (hljin@iastate.edu) regarding questions or corrections.
QUANTITATIVE RT-PCR PROTOCOL (SYBR Green I) (Last Revised: April, 007) Please contact Center for Plant Genomics (CPG) facility manager Hailing Jin (hljin@iastate.edu) regarding questions or corrections.
Peri.4U TM Application Protocol Multiwell-MEA
 Peri.4U TM Application Protocol Multiwell-MEA Measuring Neuronal Electrical Activity of Peri.4U TM (Axiogenesis AG) on the 24-well Multiwell-MEA System (Multi Channel Systems MCS GmbH). Version 1.0: July
Peri.4U TM Application Protocol Multiwell-MEA Measuring Neuronal Electrical Activity of Peri.4U TM (Axiogenesis AG) on the 24-well Multiwell-MEA System (Multi Channel Systems MCS GmbH). Version 1.0: July
Histological preparation of embryonic and adult zebrafish eyes
 Histological preparation of embryonic and adult zebrafish eyes Richard J. Nuckels 1 and Jeffrey M. Gross 1,2,3 1 Section of Molecular Cell and Developmental Biology 2 Institute of Cell and Molecular Biology
Histological preparation of embryonic and adult zebrafish eyes Richard J. Nuckels 1 and Jeffrey M. Gross 1,2,3 1 Section of Molecular Cell and Developmental Biology 2 Institute of Cell and Molecular Biology
A Fluorescence-Based High-Throughput Screening Assay for the Identification of T-Type Calcium Channel Blockers
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Fluorescence-Based High-Throughput Screening Assay for the Identification of T-Type Calcium Channel Blockers Francesco Belardetti, 1, * Elizabeth Tringham, 1 Cyrus Eduljee, 1 Xinpo Jiang,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Fluorescence-Based High-Throughput Screening Assay for the Identification of T-Type Calcium Channel Blockers Francesco Belardetti, 1, * Elizabeth Tringham, 1 Cyrus Eduljee, 1 Xinpo Jiang,
Improved Monitoring of P. aeruginosa on Agar Plates
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analytical Methods. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Improved Monitoring of P. aeruginosa on Agar Plates SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION T. A. Webster,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analytical Methods. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Improved Monitoring of P. aeruginosa on Agar Plates SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION T. A. Webster,
acid; RF-amide, arginine-phenylalanine-amide.
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 283, NO. 4, pp. 1818 1830, January 25, 2008 2008 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in the U.S.A. Endogenous Arginine-Phenylalanine-Amide-related
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 283, NO. 4, pp. 1818 1830, January 25, 2008 2008 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in the U.S.A. Endogenous Arginine-Phenylalanine-Amide-related
VDL106.3 LARGE-SCALE AMPLIFICATION AND PURIFICATION OF ADENOVIRAL VECTOR
 1. Purpose 1.1. The purpose of this protocol is to amplify an adenoviral vector from a crude lysate (final product in SOP:VDL105.2 Preparation of Adenoviral Vector Lysate) for production of high titer
1. Purpose 1.1. The purpose of this protocol is to amplify an adenoviral vector from a crude lysate (final product in SOP:VDL105.2 Preparation of Adenoviral Vector Lysate) for production of high titer
HTS of Ca 2+ Transients in Human ips-derived Cardiomyocytes as a Predictive and Cost Effective Assay Early on in Drug Development
 Use our discoveries to advance yours HTS of Ca 2+ Transients in Human ips-derived Cardiomyocytes as a Predictive and Cost Effective Assay Early on in Drug Development Dr. Ralf Kettenhofen! Axiogenesis
Use our discoveries to advance yours HTS of Ca 2+ Transients in Human ips-derived Cardiomyocytes as a Predictive and Cost Effective Assay Early on in Drug Development Dr. Ralf Kettenhofen! Axiogenesis
NEURONAL CELL CULTURE MATRIX FOR BETTER MAINTENANCE AND SURVIVAL OF NEURONAL CELL CULTURES IN TISSUE CULTURE.
 NEURONAL CELL CULTURE MATRIX FOR BETTER MAINTENANCE AND SURVIVAL OF NEURONAL CELL CULTURES IN TISSUE CULTURE. D. R. Aguirre, N. DiMassa, Chrystal Johnson, H. Eran, R. Perez, C.V.R. Sharma, M.V.R. Sharma,
NEURONAL CELL CULTURE MATRIX FOR BETTER MAINTENANCE AND SURVIVAL OF NEURONAL CELL CULTURES IN TISSUE CULTURE. D. R. Aguirre, N. DiMassa, Chrystal Johnson, H. Eran, R. Perez, C.V.R. Sharma, M.V.R. Sharma,
Genetically targeted all-optical electrophysiology with a transgenic Credependent
 Genetically targeted all-optical electrophysiology with a transgenic Credependent Optopatch mouse Short title: Transgenic Optopatch mouse Shan Lou 1, Yoav Adam 1, Eli N. Weinstein 1,4, Erika Williams 2,
Genetically targeted all-optical electrophysiology with a transgenic Credependent Optopatch mouse Short title: Transgenic Optopatch mouse Shan Lou 1, Yoav Adam 1, Eli N. Weinstein 1,4, Erika Williams 2,
Supplemental Information. Spatial and Temporal Regulation of Receptor. Endocytosis in Neuronal Dendrites Revealed
 Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Spatial and Temporal Regulation of Receptor Endocytosis in Neuronal Dendrites Revealed by Imaging of Single Vesicle Formation Morgane Rosendale, Damien
Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Spatial and Temporal Regulation of Receptor Endocytosis in Neuronal Dendrites Revealed by Imaging of Single Vesicle Formation Morgane Rosendale, Damien
Modeling Cardiac Hypertrophy: Endothelin-1 Induction with qrt-pcr Analysis
 icell Cardiomyocytes Application Protocol Modeling Cardiac Hypertrophy: Endothelin-1 Induction with qrt-pcr Analysis Introduction Cardiac hypertrophy is characterized by several different cellular changes,
icell Cardiomyocytes Application Protocol Modeling Cardiac Hypertrophy: Endothelin-1 Induction with qrt-pcr Analysis Introduction Cardiac hypertrophy is characterized by several different cellular changes,
Lab 1 Microdissection 1. Microdissection
 Lab 1 Microdissection 1 Lab 1. Microdissection The goal of this techniques lab is to understand how to dissect and process tissues that have been incubated in bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU). BrdU is a synthetic
Lab 1 Microdissection 1 Lab 1. Microdissection The goal of this techniques lab is to understand how to dissect and process tissues that have been incubated in bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU). BrdU is a synthetic
Gary L. Moulder, MS. Director, CVRI Zebrafish Shared Facility at UCSF
 Hatching Fish When should animal tracking begin? Gary L. Moulder, MS. Director, CVRI Zebrafish Shared Facility at UCSF Abstract The National Institutes of Health: Final Report to Office of Laboratory Animal
Hatching Fish When should animal tracking begin? Gary L. Moulder, MS. Director, CVRI Zebrafish Shared Facility at UCSF Abstract The National Institutes of Health: Final Report to Office of Laboratory Animal
Application Note. Author. Abstract. Biopharmaceuticals. Verified for Agilent 1260 Infinity II LC Bio-inert System. Sonja Schneider
 Combining small-scale purification and analysis of monoclonal antibodies on one instrument Protein purification with high-volume injection using the Agilent 126 Infinity Bio-inert Quaternary LC System
Combining small-scale purification and analysis of monoclonal antibodies on one instrument Protein purification with high-volume injection using the Agilent 126 Infinity Bio-inert Quaternary LC System
Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for BRAF V599E
 Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for BRAF V599E Overview This protocol describes how to develop a LanthaScreen kinase assay designed to detect and characterize inhibitors of BRAF V599E using
Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for BRAF V599E Overview This protocol describes how to develop a LanthaScreen kinase assay designed to detect and characterize inhibitors of BRAF V599E using
Roche Molecular Biochemicals Technical Note No. LC 10/2000
 Roche Molecular Biochemicals Technical Note No. LC 10/2000 LightCycler Overview of LightCycler Quantification Methods 1. General Introduction Introduction Content Definitions This Technical Note will introduce
Roche Molecular Biochemicals Technical Note No. LC 10/2000 LightCycler Overview of LightCycler Quantification Methods 1. General Introduction Introduction Content Definitions This Technical Note will introduce
OPTICAL CONTROL OF TUMOR INDUCTION IN THE ZEBRAFISH
 OPTICAL CONTROL OF TUMOR INDUCTION IN THE ZEBRAFISH Zhiping Feng, 1,12 Suzy Nam, 2 Fatima Hamouri, 3,4 Isabelle Aujard, 5,6 Bertrand Ducos, 3,4 Sophie Vriz, 7,8 Michel Volovitch, 7,9 Ludovic Jullien, 5,6
OPTICAL CONTROL OF TUMOR INDUCTION IN THE ZEBRAFISH Zhiping Feng, 1,12 Suzy Nam, 2 Fatima Hamouri, 3,4 Isabelle Aujard, 5,6 Bertrand Ducos, 3,4 Sophie Vriz, 7,8 Michel Volovitch, 7,9 Ludovic Jullien, 5,6
QS S Assist STK_FP Kit
 QS S Assist STK_FP Kit Description STK FP kit is designed for use in pharmacological assays for STK based on fluorescence polarization. The kit includes assay buffer, human protein kinase, ATP/fluorescence-
QS S Assist STK_FP Kit Description STK FP kit is designed for use in pharmacological assays for STK based on fluorescence polarization. The kit includes assay buffer, human protein kinase, ATP/fluorescence-
Zhang et al., Supplemental information, 1
 Zhang et al., Supplemental information, 1 Zhang et al., Supplemental information, 2 Figure S1: Electrophysiological properties of layer V pyramidal cells and PVINs in normal and SNI mice (relates to Figure
Zhang et al., Supplemental information, 1 Zhang et al., Supplemental information, 2 Figure S1: Electrophysiological properties of layer V pyramidal cells and PVINs in normal and SNI mice (relates to Figure
Masayoshi Honda, Jeehae Park, Robert A. Pugh, Taekjip Ha, and Maria Spies
 Molecular Cell, Volume 35 Supplemental Data Single-Molecule Analysis Reveals Differential Effect of ssdna-binding Proteins on DNA Translocation by XPD Helicase Masayoshi Honda, Jeehae Park, Robert A. Pugh,
Molecular Cell, Volume 35 Supplemental Data Single-Molecule Analysis Reveals Differential Effect of ssdna-binding Proteins on DNA Translocation by XPD Helicase Masayoshi Honda, Jeehae Park, Robert A. Pugh,
Packaging Commercial CMOS Chips for Lab on a Chip Integration
 Supporting Information for Packaging Commercial CMOS Chips for Lab on a Chip Integration by Timir Datta-Chaudhuri, Pamela Abshire, and Elisabeth Smela Biocompatibility Although the supplier s instructions
Supporting Information for Packaging Commercial CMOS Chips for Lab on a Chip Integration by Timir Datta-Chaudhuri, Pamela Abshire, and Elisabeth Smela Biocompatibility Although the supplier s instructions
 Microarray protocol Emmanuela Marchi PhD Dept. Pharmacology UFIR - Comparative nutritional systems biology Focus Team Post-doc emanuela.marchi@unifi.it 16 April 2009 When citing this SOP you should acknowledge
Microarray protocol Emmanuela Marchi PhD Dept. Pharmacology UFIR - Comparative nutritional systems biology Focus Team Post-doc emanuela.marchi@unifi.it 16 April 2009 When citing this SOP you should acknowledge
GM130 Is Required for Compartmental Organization of Dendritic Golgi Outposts
 Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information GM130 Is Required for Compartmental Organization of Dendritic Golgi Outposts Wei Zhou, Jin Chang, Xin Wang, Masha G. Savelieff, Yinyin Zhao, Shanshan
Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information GM130 Is Required for Compartmental Organization of Dendritic Golgi Outposts Wei Zhou, Jin Chang, Xin Wang, Masha G. Savelieff, Yinyin Zhao, Shanshan
QS S Assist KINASE_MSA Kit
 QS S Assist KINASE_MSA Kit Description KINASE MSA Kit is designed for use in pharmacological assays for KINASE based on Off-chip mobility shift assay (MSA). This kit includes Assay Buffer, Termination
QS S Assist KINASE_MSA Kit Description KINASE MSA Kit is designed for use in pharmacological assays for KINASE based on Off-chip mobility shift assay (MSA). This kit includes Assay Buffer, Termination
Modern Physics/Biophysics Laboratory
 Overview of Physics 173/ BGGN 266 - Prof. David Kleinfeld Modern Physics/Biophysics Laboratory This laboratory course consists of table-top experiments in biological and solid state physics, with an emphasis
Overview of Physics 173/ BGGN 266 - Prof. David Kleinfeld Modern Physics/Biophysics Laboratory This laboratory course consists of table-top experiments in biological and solid state physics, with an emphasis
Manuscript JN R1 in press Journal of Neurophysiology
 1 Manuscript JN-01168-2005-R1 in press Journal of Neurophysiology Electrical stimulation of mammalian retinal ganglion cells with multi-electrode arrays Chris Sekirnjak 1, Pawel Hottowy 2, Alexander Sher
1 Manuscript JN-01168-2005-R1 in press Journal of Neurophysiology Electrical stimulation of mammalian retinal ganglion cells with multi-electrode arrays Chris Sekirnjak 1, Pawel Hottowy 2, Alexander Sher
Specificity of cold thermotransduction is determined by differential ionic channel expression 2002 Nature Publishing Group
 Specificity of cold thermotransduction is determined by differential ionic channel expression 22 Nature Publishing Group http://neurosci.nature.com Félix Viana*, Elvira de la Peña and Carlos Belmonte Instituto
Specificity of cold thermotransduction is determined by differential ionic channel expression 22 Nature Publishing Group http://neurosci.nature.com Félix Viana*, Elvira de la Peña and Carlos Belmonte Instituto
RECOMMENDED CULTURE CONDITIONS Recommended culture conditions and standard operating procedure are provided with the product.
 PRODUCT DATASHEET PrecisION hnav1.5-hek Recombinant Cell Line Catalog Number: CYL3004 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION Recombinant HEK293 cell line expressing the human Nav1.5 (type V voltage-gated sodium channel alpha
PRODUCT DATASHEET PrecisION hnav1.5-hek Recombinant Cell Line Catalog Number: CYL3004 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION Recombinant HEK293 cell line expressing the human Nav1.5 (type V voltage-gated sodium channel alpha
CENTER FOR BRAIN EXPERIMENT
 CENTER FOR BRAIN EXPERIMENT Section of Brain Structure Associate Professor: ARII, Tatsuo, PhD 1967 Graduated from Tohoku University, Faculty of Science. Completed the doctoral course in Engineering, Nagoya
CENTER FOR BRAIN EXPERIMENT Section of Brain Structure Associate Professor: ARII, Tatsuo, PhD 1967 Graduated from Tohoku University, Faculty of Science. Completed the doctoral course in Engineering, Nagoya
HEPARIN CALCIUM. Heparinum calcicum
 Pharmeuropa 25.1 1 Reference: PA/PH/Exp. 6/T (12) 38 ANP NOTE ON THE MONOGRAPH Definition. It is proposed to restrict the scope to heparin material of porcine origin since some of the latest requirements
Pharmeuropa 25.1 1 Reference: PA/PH/Exp. 6/T (12) 38 ANP NOTE ON THE MONOGRAPH Definition. It is proposed to restrict the scope to heparin material of porcine origin since some of the latest requirements
Final exam. Please write your name on the exam and keep an ID card ready.
 Biophysics of Macromolecules Prof. R. Jungmann and Prof. J. Lipfert SS 2017 Final exam Final exam First name: Last name: Student number ( Matrikelnummer ): Please write your name on the exam and keep an
Biophysics of Macromolecules Prof. R. Jungmann and Prof. J. Lipfert SS 2017 Final exam Final exam First name: Last name: Student number ( Matrikelnummer ): Please write your name on the exam and keep an
The Touch and Zap Method for In Vivo Whole-Cell Patch Recording of Intrinsic and Visual Responses of Cortical Neurons and Glial Cells
 The Touch and Zap Method for In Vivo Whole-Cell Patch Recording of Intrinsic and Visual Responses of Cortical Neurons and Glial Cells Adrien E. Schramm a, Daniele Marinazzo b, Thomas Gener c, Lyle J. Graham*
The Touch and Zap Method for In Vivo Whole-Cell Patch Recording of Intrinsic and Visual Responses of Cortical Neurons and Glial Cells Adrien E. Schramm a, Daniele Marinazzo b, Thomas Gener c, Lyle J. Graham*
SCIEX Anion Analysis Kit For P/ACE MDQ and P/ACE MDQ plus Capillary Electrophoresis Systems. Instruction Guide
 For P/ACE MDQ and P/ACE MDQ plus Capillary Electrophoresis Systems A49108AE May 2015 AB Sciex Pte. Ltd and its affiliates disclaims all warranties with respect to this document, expressed or implied, including
For P/ACE MDQ and P/ACE MDQ plus Capillary Electrophoresis Systems A49108AE May 2015 AB Sciex Pte. Ltd and its affiliates disclaims all warranties with respect to this document, expressed or implied, including
Supplementary Information and Figures
 Supplementary Information and Figures Multicolor two-photon imaging of endogenous fluorophores in living tissues by wavelength mixing Chiara Stringari 1, Lamiae Abdeladim 1, Guy Malkinson 1, Pierre Mahou
Supplementary Information and Figures Multicolor two-photon imaging of endogenous fluorophores in living tissues by wavelength mixing Chiara Stringari 1, Lamiae Abdeladim 1, Guy Malkinson 1, Pierre Mahou
! #!!! % &!! %! (! ) +,,. / 0 1 & ! , 106, ,
 ! #!!! % &!! %! (! ) +,,. / 0 1 & 2 3 2 0 3 4! + 5. 6, 106,+ 7884 +90+, : promoting access to White Rose research papers Universities of Leeds, Sheffield and York http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/ White
! #!!! % &!! %! (! ) +,,. / 0 1 & 2 3 2 0 3 4! + 5. 6, 106,+ 7884 +90+, : promoting access to White Rose research papers Universities of Leeds, Sheffield and York http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/ White
Scientists have successfully used stem cells to reverse this paralysis. Magnification 0.02
 1 The photograph below shows an X-ray of a dachshund. The dachshund is a breed of dog that is at higher risk of paralysis due to spinal injury. Scientists have successfully used stem cells to reverse this
1 The photograph below shows an X-ray of a dachshund. The dachshund is a breed of dog that is at higher risk of paralysis due to spinal injury. Scientists have successfully used stem cells to reverse this
Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion
 Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion Tissues are made of cells and materials secreted by cells that occupy the spaces between the individual cells. This material outside of cells is called the Extracellular Matrix
Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion Tissues are made of cells and materials secreted by cells that occupy the spaces between the individual cells. This material outside of cells is called the Extracellular Matrix
Electrodes: »3 types. Types: Micro electrode Depth & needle electrodes Surface electrodes
 Electrodes: Types:»3 types Micro electrode Depth & needle electrodes Surface electrodes Micro electrodes: Intra cellular electrodes Used to measure the potential near or within cell Features: Types: Smaller
Electrodes: Types:»3 types Micro electrode Depth & needle electrodes Surface electrodes Micro electrodes: Intra cellular electrodes Used to measure the potential near or within cell Features: Types: Smaller
In Vitro Angiogenesis Assay Kit
 In Vitro Angiogenesis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1323 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
In Vitro Angiogenesis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1323 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
GUS Assays. 1. Label all tubes. Prepare solutions and have ready at hand.
 GUS Assays I. Protein isolation A. Method for ~1g or more of tissue. 1. Label all tubes. Prepare solutions and have ready at hand. 2. Remove the tissue from the 80 o C freezer and thaw on ice. If the tissue
GUS Assays I. Protein isolation A. Method for ~1g or more of tissue. 1. Label all tubes. Prepare solutions and have ready at hand. 2. Remove the tissue from the 80 o C freezer and thaw on ice. If the tissue
Manual patch clamp evaluation of herg channel 37 C and next steps
 Manual patch clamp evaluation of herg channel pharmacology @ 37 C and next steps Wendy Wu, Ph.D. Division of Applied Regulatory Science Office of Clinical Pharmacology Office of Translational Sciences
Manual patch clamp evaluation of herg channel pharmacology @ 37 C and next steps Wendy Wu, Ph.D. Division of Applied Regulatory Science Office of Clinical Pharmacology Office of Translational Sciences
Lars Funke, PhD Thesis Material and Methods. Phosphorylated and PAGE purified shrna oligonucleotides were inserted
 DNA Constructs Phosphorylated and PAGE purified shrna oligonucleotides were inserted into pllox3.7 at HpaI and XhoI restriction sites. In short, Oligonucleotides are diluted to 3µg/µl and 1µl each is added
DNA Constructs Phosphorylated and PAGE purified shrna oligonucleotides were inserted into pllox3.7 at HpaI and XhoI restriction sites. In short, Oligonucleotides are diluted to 3µg/µl and 1µl each is added
Normalization of Agilent Seahorse XF Data by In-situ Cell Counting Using a BioTek Cytation 5
 Normalization of Agilent Seahorse XF Data by In-situ Cell Counting Using a BioTek Cytation Application Note Authors Yoonseok Kam 1, Ned Jastromb 1, Joe Clayton, Paul Held, and Brian P. Dranka 1 1 Agilent
Normalization of Agilent Seahorse XF Data by In-situ Cell Counting Using a BioTek Cytation Application Note Authors Yoonseok Kam 1, Ned Jastromb 1, Joe Clayton, Paul Held, and Brian P. Dranka 1 1 Agilent
Construction of Improved HT-PEM MEAs and Stacks for Long Term Stable Modular CHP Units. NEXT ENERGY EWE Forschungszentrum für Energietechnologie e.v.
 FCH JU Grant Agreement number: 325262 Project acronym: CISTEM Project title: Construction of Improved HT-PEM MEAs and Stacks for Long Term Stable Modular CHP Units Work package: 2 - Materials beyond State
FCH JU Grant Agreement number: 325262 Project acronym: CISTEM Project title: Construction of Improved HT-PEM MEAs and Stacks for Long Term Stable Modular CHP Units Work package: 2 - Materials beyond State
Fluo-2 MA Brighter, Faster, Cheaper
 Fluo-2 MA Brighter, Faster, Cheaper Fluo-2 MA Essentials A direct substitute for Fluo-3 and Fluo-4 The same molecule as Fluo-8 Nearly twice as bright as Fluo-4 Nearly four times as bright as Fluo-3 AM
Fluo-2 MA Brighter, Faster, Cheaper Fluo-2 MA Essentials A direct substitute for Fluo-3 and Fluo-4 The same molecule as Fluo-8 Nearly twice as bright as Fluo-4 Nearly four times as bright as Fluo-3 AM
Acid-Sensing Ion Channels
 Acid-Sensing Ion Channels Properties of the H + -activated channel. a. Examples of ion currents at 70 mv caused by a rapid change from ph 7.4 to 6.0. b. ph response curves showing current change normalized
Acid-Sensing Ion Channels Properties of the H + -activated channel. a. Examples of ion currents at 70 mv caused by a rapid change from ph 7.4 to 6.0. b. ph response curves showing current change normalized
A Dendritic Model of Coincidence Detection in the Avian Brainstem Jonathan Z. Simon 1
 A Dendritic Model of Coincidence Detection in the Avian Brainstem Jonathan Z. Simon 1 Catherine E. Carr 2 Shihab A. Shamma 1,3 1 2 Department of Biology 3 Department of Electrical Engineering Supported
A Dendritic Model of Coincidence Detection in the Avian Brainstem Jonathan Z. Simon 1 Catherine E. Carr 2 Shihab A. Shamma 1,3 1 2 Department of Biology 3 Department of Electrical Engineering Supported
For Safe and Delicious Water
 RESIDUAL CHLORINE ANALYZER 400G NON-REAGENT FREE CHLORINE ANALYZER FC400G 400G RESIDUAL CHLORINE ANALYZER FC400G NON-REAGENT FREE CHLORINE ANALYZER Bulletin 12F01A01-01E www.yokogawa.com/an/ For Safe and
RESIDUAL CHLORINE ANALYZER 400G NON-REAGENT FREE CHLORINE ANALYZER FC400G 400G RESIDUAL CHLORINE ANALYZER FC400G NON-REAGENT FREE CHLORINE ANALYZER Bulletin 12F01A01-01E www.yokogawa.com/an/ For Safe and
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Real-Time PCR Detection Kit for detection of Histomonas meleagridis.
 For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Real-Time PCR Detection Kit for detection of Histomonas meleagridis www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Art. No. 31416/31417 Kylt Histomonas meleagridis Real-Time PCR
For in vitro Veterinary Diagnostics only. Real-Time PCR Detection Kit for detection of Histomonas meleagridis www.kylt.eu DIRECTION FOR USE Art. No. 31416/31417 Kylt Histomonas meleagridis Real-Time PCR
ab83355 ATP Assay Kit (Colorimetric/ Fluorometric)
 Version 18 Last updated 2 January 2018 ab83355 ATP Assay Kit (Colorimetric/ Fluorometric) For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of ATP in a variety of samples. This product is for research
Version 18 Last updated 2 January 2018 ab83355 ATP Assay Kit (Colorimetric/ Fluorometric) For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of ATP in a variety of samples. This product is for research
A Discovery Laboratory Investigating Bacterial Gene Regulation
 Chapter 8 A Discovery Laboratory Investigating Bacterial Gene Regulation Robert Moss Wofford College 429 N. Church Street Spartanburg, SC 29307 mosssre@wofford.edu Bob Moss is an Associate Professor of
Chapter 8 A Discovery Laboratory Investigating Bacterial Gene Regulation Robert Moss Wofford College 429 N. Church Street Spartanburg, SC 29307 mosssre@wofford.edu Bob Moss is an Associate Professor of
Tissue Engineering and the Brain. Susan Perry Bioengineering Program Lehigh University
 Tissue Engineering and the Brain Susan Perry Bioengineering Program Lehigh University ...all the most acute, most powerful, and most deadly diseases, and those which are most difficult to be understood
Tissue Engineering and the Brain Susan Perry Bioengineering Program Lehigh University ...all the most acute, most powerful, and most deadly diseases, and those which are most difficult to be understood
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Retention of RNA with LabelX.
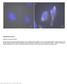 Supplementary Figure 1 Retention of RNA with LabelX. (a) Epi-fluorescence image of single molecule FISH (smfish) against GAPDH on HeLa cells expanded without LabelX treatment. (b) Epi-fluorescence image
Supplementary Figure 1 Retention of RNA with LabelX. (a) Epi-fluorescence image of single molecule FISH (smfish) against GAPDH on HeLa cells expanded without LabelX treatment. (b) Epi-fluorescence image
Cadmium Testing and On Site Calibration for Water Testing Detection Range: ppm
 Document: AND016 04 2014 Cadmium Testing and On Site Calibration for Water Testing Detection Range: 0.1 1.0ppm April, 2014 Edition 3 ANDalyze, Inc., 2012. All rights reserved. Printed in USA. Table of
Document: AND016 04 2014 Cadmium Testing and On Site Calibration for Water Testing Detection Range: 0.1 1.0ppm April, 2014 Edition 3 ANDalyze, Inc., 2012. All rights reserved. Printed in USA. Table of
Voltage-gated K + currents in mouse articular chondrocytes regulate membrane potential
 Channels ISSN: 1933-6950 (Print) 1933-6969 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/kchl20 Voltage-gated K + currents in mouse articular chondrocytes regulate membrane potential Robert
Channels ISSN: 1933-6950 (Print) 1933-6969 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/kchl20 Voltage-gated K + currents in mouse articular chondrocytes regulate membrane potential Robert
Zona glomerulosa cells of the mouse adrenal cortex are intrinsic electrical oscillators
 Research article Zona glomerulosa cells of the mouse adrenal cortex are intrinsic electrical oscillators Changlong Hu, 1,2 Craig G. Rusin, 3 Zhiyong Tan, 2 Nick A. Guagliardo, 2 and Paula Q. Barrett 2
Research article Zona glomerulosa cells of the mouse adrenal cortex are intrinsic electrical oscillators Changlong Hu, 1,2 Craig G. Rusin, 3 Zhiyong Tan, 2 Nick A. Guagliardo, 2 and Paula Q. Barrett 2
A CRISPR/Cas9 Vector System for Tissue-Specific Gene Disruption in Zebrafish
 Developmental Cell Supplemental Information A CRISPR/Cas9 Vector System for Tissue-Specific Gene Disruption in Zebrafish Julien Ablain, Ellen M. Durand, Song Yang, Yi Zhou, and Leonard I. Zon % larvae
Developmental Cell Supplemental Information A CRISPR/Cas9 Vector System for Tissue-Specific Gene Disruption in Zebrafish Julien Ablain, Ellen M. Durand, Song Yang, Yi Zhou, and Leonard I. Zon % larvae
ARTICLE Recording Field Potentials From Zebrafish Larvae During Escape Responses
 ARTICLE Recording Field Potentials From Zebrafish Larvae During Escape Responses Bryan D. Monesson-Olson, Eileen L. Troconis, & Josef G. Trapani Biology Department and Neuroscience Program, Amherst College,
ARTICLE Recording Field Potentials From Zebrafish Larvae During Escape Responses Bryan D. Monesson-Olson, Eileen L. Troconis, & Josef G. Trapani Biology Department and Neuroscience Program, Amherst College,
PROTOCOL TO PREPARE PLANTAR FOOTSKIN FOR MORPHOMETRY. I. Removal and Fixation of Plantar Skin (see video)
 PROTOCOL TO PREPARE PLANTAR FOOTSKIN FOR MORPHOMETRY I. Removal and Fixation of Plantar Skin (see video) 1. Sacrifice the animal a. Anaesthetize the animal by placing in a closed chamber with isoflurane.
PROTOCOL TO PREPARE PLANTAR FOOTSKIN FOR MORPHOMETRY I. Removal and Fixation of Plantar Skin (see video) 1. Sacrifice the animal a. Anaesthetize the animal by placing in a closed chamber with isoflurane.
Relevance of Exocytotic Glutamate Release from Retinal Glia
 Neuron, Volume 74 Supplemental Information Relevance of Exocytotic Glutamate Release from Retinal Glia Michal Slezak, Antje Grosche, Aurore Niemiec, Naoyuki Tanimoto, Thomas Pannicke, Thomas A. Münch,
Neuron, Volume 74 Supplemental Information Relevance of Exocytotic Glutamate Release from Retinal Glia Michal Slezak, Antje Grosche, Aurore Niemiec, Naoyuki Tanimoto, Thomas Pannicke, Thomas A. Münch,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2013
 Sodium-ion battery based on ion exchange membranes as electrolyte and separator Chengying Cao, Weiwei Liu, Lei Tan, Xiaozhen Liao and Lei Li* School of Chemical and Chemistry Engineering, Shanghai Jiaotong
Sodium-ion battery based on ion exchange membranes as electrolyte and separator Chengying Cao, Weiwei Liu, Lei Tan, Xiaozhen Liao and Lei Li* School of Chemical and Chemistry Engineering, Shanghai Jiaotong
Role of automated patch-clamp systems in drug research and development
 Role of automated patch-clamp systems in drug research and development Péter Orvos, M.Sc. Ph.D. Thesis Szeged, Hungary 216 Role of automated patch-clamp systems in drug research and development Péter Orvos,
Role of automated patch-clamp systems in drug research and development Péter Orvos, M.Sc. Ph.D. Thesis Szeged, Hungary 216 Role of automated patch-clamp systems in drug research and development Péter Orvos,
AFFINITY HIS-TAG PURIFICATION
 DESCRIPTION Nickel NTA Agarose Cartridges 5ml are used for purification of histidine-tagged proteins in native or denaturing conditions. This cartridge can be used with an automated chromatography system,
DESCRIPTION Nickel NTA Agarose Cartridges 5ml are used for purification of histidine-tagged proteins in native or denaturing conditions. This cartridge can be used with an automated chromatography system,
S everal studies have been devoted to the introduction of in-vitro 3D neuronal systems but the use of such
 OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS NETWORK MODELS Received 28 August 2013 Accepted 11 June 2014 Published 30 June 2014 Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to S.M. (sergio.
OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS NETWORK MODELS Received 28 August 2013 Accepted 11 June 2014 Published 30 June 2014 Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to S.M. (sergio.
National Food Safety Standard
 National standard of People s Republic of China GB 5413.21 2010 National Food Safety Standard Determination of calcium, iron, zinc, sodium, potassium, magnesium, copper and manganese in foods for infants
National standard of People s Republic of China GB 5413.21 2010 National Food Safety Standard Determination of calcium, iron, zinc, sodium, potassium, magnesium, copper and manganese in foods for infants
Determination of Oxalate and Other Anions in Bayer Liquor Using Ion Chromatography
 Application Note 206 Determination of Oxalate and Other Anions in Bayer Liquor Using Ion Chromatography Introduction The Bayer Process is used to isolate alumina (Al 2 O ) from bauxite. In this process,
Application Note 206 Determination of Oxalate and Other Anions in Bayer Liquor Using Ion Chromatography Introduction The Bayer Process is used to isolate alumina (Al 2 O ) from bauxite. In this process,
Axol Guide to Culturing Axol human Neural Progenitor Cells (hnpcs) on Axion BioSystems Microelectrode Arrays. Application Protocol Version 2.
 Axol Guide to Culturing Axol human Neural Progenitor Cells (hnpcs) on Axion BioSystems Microelectrode Arrays Application Protocol Version 2.1 Table of Contents Before You Begin 3 Required Materials 4 Preparing
Axol Guide to Culturing Axol human Neural Progenitor Cells (hnpcs) on Axion BioSystems Microelectrode Arrays Application Protocol Version 2.1 Table of Contents Before You Begin 3 Required Materials 4 Preparing
Human alpha-galactosidase A / GLA ELISA Pair Set
 Human alpha-galactosidase A / GLA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK12078 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Human alpha-galactosidase A / GLA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK12078 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Lab module 6b Receptor-mediated endocytosis
 Goal for the module Lab module 6b Receptor-mediated endocytosis To follow the movement of a degraded ligand, LDL, and a recycled ligand, transferrin, as they undergo endocytic processing. Pre-lab homework
Goal for the module Lab module 6b Receptor-mediated endocytosis To follow the movement of a degraded ligand, LDL, and a recycled ligand, transferrin, as they undergo endocytic processing. Pre-lab homework
CULTURING OF LEECH NEURONS AND FORMING SYNAPSES IN VITRO. Italy
 CULTURING OF LEECH NEURONS AND FORMING SYNAPSES IN VITRO Josh Titlow 1, Zana R. Majeed 1,2, John G. Nicholls 3 and Robin L. Cooper 1 1 Department of Biology, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY 40506,
CULTURING OF LEECH NEURONS AND FORMING SYNAPSES IN VITRO Josh Titlow 1, Zana R. Majeed 1,2, John G. Nicholls 3 and Robin L. Cooper 1 1 Department of Biology, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY 40506,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Copper and zinc ions specifically promote non-amyloid aggregation of the highly stable human γ-d crystallin Liliana Quintanar, 1,* José A. Domínguez-Calva, 1 Eugene Serebryany, 2
Supporting Information Copper and zinc ions specifically promote non-amyloid aggregation of the highly stable human γ-d crystallin Liliana Quintanar, 1,* José A. Domínguez-Calva, 1 Eugene Serebryany, 2
DEPArray Technology. Sorting and Recovery of Rare Cells
 DEPArray Technology Sorting and Recovery of Rare Cells Delivering pure, single, viable cells The DEPArray system from Silicon Biosystems is the only automated instrument that can identify, quantify, and
DEPArray Technology Sorting and Recovery of Rare Cells Delivering pure, single, viable cells The DEPArray system from Silicon Biosystems is the only automated instrument that can identify, quantify, and
Corrosion Rate Measurement on C-Steel
 Measurements of corrosion rate on Carbon-steel using Electrochemical (potentiodynamic Polarization, EIS etc.) technique. Corrosion Rate Measurement on C-Steel Abdullah Al Ashraf 1. Introduction: The degradation
Measurements of corrosion rate on Carbon-steel using Electrochemical (potentiodynamic Polarization, EIS etc.) technique. Corrosion Rate Measurement on C-Steel Abdullah Al Ashraf 1. Introduction: The degradation
ab MDR Assay Kit (Fluorometric)
 ab112142 MDR Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Instructions for Use For detecting MDR pump activities in cells using our proprietary fluorescence probe. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab112142 MDR Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Instructions for Use For detecting MDR pump activities in cells using our proprietary fluorescence probe. This product is for research use only and is not intended
Simple, intuitive and accessible MRI solution for preclinical research. M-Series Compact MRI Systems
 Simple, intuitive and accessible MRI solution for preclinical research M-Series Compact MRI Systems Application Oriented Imaging Anatomy and Morphology In vivo soft tissue imaging for morphological characterization.
Simple, intuitive and accessible MRI solution for preclinical research M-Series Compact MRI Systems Application Oriented Imaging Anatomy and Morphology In vivo soft tissue imaging for morphological characterization.
Separation of Recombinant Human Erythropoietin (rhepo) using the European Pharmacopoeia Method on the PA 800 plus Pharmaceutical Analysis System
 Separation of Recombinant Human Erythropoietin (rhepo) using the European Pharmacopoeia Method on the PA 800 plus Pharmaceutical Analysis System Marcia R Santos Global Tactical Marketing, Beckman Coulter
Separation of Recombinant Human Erythropoietin (rhepo) using the European Pharmacopoeia Method on the PA 800 plus Pharmaceutical Analysis System Marcia R Santos Global Tactical Marketing, Beckman Coulter
Syringe Pumps. Please contact us for help in selecting the best pump for your application and a free quote.
 Syringe Pumps Microfluidic Pumps! We are proud to offer select Harvard Apparatus syringe pumps for use with SynVivo biochips. These high quality pumps have been extensively tested and offer a feature rich
Syringe Pumps Microfluidic Pumps! We are proud to offer select Harvard Apparatus syringe pumps for use with SynVivo biochips. These high quality pumps have been extensively tested and offer a feature rich
An in silico canine cardiac midmyocardial action potential duration model as a tool for early drug safety assessment
 Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 302: H1466 H1480, 2012. First published December 23, 2011; doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00808.2011. An in silico canine cardiac midmyocardial action potential duration model as
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 302: H1466 H1480, 2012. First published December 23, 2011; doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00808.2011. An in silico canine cardiac midmyocardial action potential duration model as
Culturing Protocol for JM8.N4 ES Cell Clones Revised July 2014
 Culturing Protocol for JM8.N4 ES Cell Clones Revised July 2014 Cell Line Information The JM8.N4 subline is derived from the JM8 parental line and are considered to be feeder independent. These cells are
Culturing Protocol for JM8.N4 ES Cell Clones Revised July 2014 Cell Line Information The JM8.N4 subline is derived from the JM8 parental line and are considered to be feeder independent. These cells are
Oscillating Channels and Sensors ONR/DARPA Julie E. M. McGeoch and Guido Guidotti 1998
 Oscillating Channels and Sensors ONR/DARPA Julie E. M. McGeoch and Guido Guidotti 1998 Impact New biological-electronic interface. Compact, rapid sensor of agents. Protection of personnel. Detection of
Oscillating Channels and Sensors ONR/DARPA Julie E. M. McGeoch and Guido Guidotti 1998 Impact New biological-electronic interface. Compact, rapid sensor of agents. Protection of personnel. Detection of
The image part with relationship ID rid4 was not found in the file. Welcome
 The image part with relationship ID rid4 was not found in the file. Welcome Trace Metals Analysis: Impurity Determinations By Thomas Kozikowski Chemist, R&D at Inorganic Ventures Key Considerations What
The image part with relationship ID rid4 was not found in the file. Welcome Trace Metals Analysis: Impurity Determinations By Thomas Kozikowski Chemist, R&D at Inorganic Ventures Key Considerations What
Cycles of vascular plexus formation within the nephrogenic zone of the developing mouse kidney
 1 Supplementary text and data for: 2 3 4 5 Cycles of vascular plexus formation within the nephrogenic zone of the developing mouse kidney Authors: David A. D. Munro 1*, Peter Hohenstein 2, and Jamie A.
1 Supplementary text and data for: 2 3 4 5 Cycles of vascular plexus formation within the nephrogenic zone of the developing mouse kidney Authors: David A. D. Munro 1*, Peter Hohenstein 2, and Jamie A.
64 CuCl 2 in 50 µl 0.1N NaOAc buffer, and 20 µg of each DOTA-antibody conjugate in 40 µl
 Number of DOTA per antibody The average number of DOTA chelators per antibody was measured using a reported procedure with modifications (1,2). Briefly, nonradioactive CuCl 2 (80-fold excess of DOTA antibodies)
Number of DOTA per antibody The average number of DOTA chelators per antibody was measured using a reported procedure with modifications (1,2). Briefly, nonradioactive CuCl 2 (80-fold excess of DOTA antibodies)
