A CRISPR/Cas9 Vector System for Tissue-Specific Gene Disruption in Zebrafish
|
|
|
- Janel Knight
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Developmental Cell Supplemental Information A CRISPR/Cas9 Vector System for Tissue-Specific Gene Disruption in Zebrafish Julien Ablain, Ellen M. Durand, Song Yang, Yi Zhou, and Leonard I. Zon
2 % larvae per phenotype Supplemental Data A urod p53 Target sequences #1: AGTTCAGGGAATCACGGGCA #2: AGATCCTCAGGCTCCTTCAG GGTGGGAGAGTGGATGGCTG B grna p53 grna urod # bp 500 bp C 100 WT Mild Intermediate Strong D Cas9 mrna + grna urod 80 * phenotype: WT Mild Int Strong bp 20 0 Ø * urod wt mrna urod yq mrna Cas9 mrna + grna urod E Cas9 mrna + grna p53 Cas9 mrna + grna urod 50 hpf 300 µm Figure S1. CRISPR targeting of urod, but not p53, elicits a fluorescent phenotype in zebrafish embryos (related to Figure 1)
3 (A) CRISPR target sequences used to knockout the urod and p53 zebrafish genes. (B) T7E1 mutagenesis assay at the p53 CRISPR target site (left) and at the second urod site (right). The assay was performed on genomic DNA from 2 dpf embryos injected at the one-cell stage with Cas9 mrna and either the grna against p53 or the grna against urod. Arrows point to cleavage bands. (C) Quantification of the fluorescent phenotype obtained after co-injection of Cas9 mrna and a grna against urod ± wt urod mrna (urod wt ) or yquem urod mrna (urod mrna bearing the inactivating mutation found in the yquem mutant, urod yq ). WT: no fluorescent blood cell. Mild: <10 fluorescent blood cells. Intermediate: <50 fluorescent blood cells. Strong: >50 fluorescent blood cells. Data represented as mean percentage ± SD of 3 independent experiments. *: p<0.05, paired t-test. (D) T7E1 mutagenesis assay at the CRISPR target site in the urod gene. AB embryos were injected at the one-cell stage with Cas9 mrna and a grna against urod, and sorted into 4 groups (WT, mild, intermediate, high) according to their fluorescent phenotypes (see Figure S1C). The assay was performed on genomic DNA from 8 embryos from each group at 2 dpf. Arrows point to cleavage bands. (E) Confocal images at 50 hpf of embryos injected at the one-cell stage with Cas9 mrna and either the grna against p53 (negative control) or a grna against urod.
4 A GCGTCTTTTGTTCTGGTCATCAAGGAGGGGGGAATGTTCTGCGCATGCCTGTGGGGGAGGGAGAAGGA CACGTCACTGAAAACGTCCCTGCATCACACCGAGACACCCAATCACTCAAGCCGAGACCAGATAATTTT GCATATGCTTTACAGTTTGAAAAATACCACGGTAAACCCTCACACAAACTCTGGATTTGAGATCTTTCAGG TTTTATCAGTTTGCAGGTTTATGTCACCATGATATAGGGTCAGACTTGATCTAAGGGAGCTGAATAAGTG GTTTAGTCACTCACCACCTCCCAAAAACATACCCAGAAGTCCCTGGTATATATAGCTCTCCCTCCAGCTC TTGGTTCGCATATGACTCCTCAGTGACGAGGAGTCAGTAGCGTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGCAAGTTAAAA TAAGGCTAGTCCGTTATCAACTTGAAAAAGTGGCACCGAGTCGGTGCTTTTTT B U6-3 promoter BseRI sites grna scaffold uninjected Cas9 WISH ubi:cas9 48 hpf gata1:cas9 mylz2:cas9 C grna: urod p53 p53 urod E D Blood pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA, gata1:cas9 p53 locus pcmlc2:gfp U6:gRNA urod urod locus D urod target locus AACAGAGTTCAGGGAATCACGGGCAGGGAAAGATT WT AACAGAGTTCAGGGAA AGATT -14 AACAGAGTTCAGGGAATCACGGGC del AACAGAGTTCAGGGAATCAC GGGAAAGATT -5 AACAGAGTTCAGGGAATCACGG CAGGGAAAGATT -1 AACAGAGTTCAGGGAATCACGGG GAAAGATT -4 AACAGAGTTCAGGGAATCA GGGAAAGATT -6 AACAGAGTTCAGGGAATCACGG AAAGATT -6 p53 target locus ATGTTGGTGGGAGAGTGGATGGCTGAGGCTGTTCT WT ctrl mylz2 gata1:cas9 ATGTTGGTGGGAGAGTGGATGGCTG del GCTGAGGCTGTTCT del CTGAGGCTGTTCT del ATGTTGGTGGGAGAGTGGATG AGGCTGTTCT -4 ATGTTGGTGGGAGAGTGGATGGCTG TTCT -6 Sorted muscle Figure S2. Tissue-specific expression of Cas9 and gene targeting with the CRISPR vector (related to Figure 2).
5 (A) Sequence of the portion of the vector presented in Figure 2A encompassing the U6 promoter and the grna scaffold. (B) Representative images of whole mount in situ hybridization (WISH) using an antisense RNA probe against Cas9 mrna in 48 hpf embryos injected with Tol2 mrna and the pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA vectors expressing Cas9 under the control of the indicated promoters. (C) T7E1 mutagenesis assay at the CRISPR target sites in the p53 or urod genes. The assay was performed on genomic DNA from the blood of 2 dpf embryos injected at the one-cell stage with Tol2 mrna and the pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA, gata1:cas9 vectors containing a grna against p53 or urod. Arrows point to cleavage bands. (D) Most frequent (>2%) mutant urod and p53 alleles found by deep-sequencing in the blood of embryos injected with Tol2 mrna and the pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA, gata1:cas9 vectors containing grnas against urod and p53 respectively. The CRISPR target sequence is in green, mutations in red. The type of mutation is indicated (del: large deletion). (E) T7E1 mutagenesis assay at the CRISPR target site in the urod gene. The assay was performed on genomic DNA from sorted mcherry-positive cells from 2 dpf Tg(mylz2:mCherry) embryos injected at the one-cell stage with Tol2 mrna and the pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA urod, mylz2:cas9 or pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA urod, gata1:cas9 vectors.
6 % larvae per phenotype A pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA urod, ubi:cas9 pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA urod, gata1:cas9 50 hpf pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA urod, mylz2:cas9 pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA p53, gata1:cas9 300 µm B 100 WT Mild Intermediate Strong ubi:cas9 gata1:cas9 mylz2:cas9 pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA urod C D pa2 U6:gRNA urod gata1:cas9- T2A-GFP Figure S3. Fluorescent phenotype induced by CRISPR vectors targeting urod (related to Figure 3).
7 (A) Confocal images of 50 hpf embryos injected with Tol2 mrna and pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA urod vectors expressing Cas9 under the control of the indicated promoters. (B) Quantification of the fluorescent phenotype presented in Figure 3A. WT: no fluorescent blood cell. Mild: <10 fluorescent blood cells. Intermediate: <50 fluorescent blood cells. Strong: >50 fluorescent blood cells. Ubi:Cas9 (n=61), gata1:cas9 (n=51), mylz2:cas9 (n=43). (C) Schematic representation of a variant tissue-specific CRISPR vector. Gata1 promoter (Pgata1) drives both Cas9 and GFP expression through a self-cleaving T2A peptide. Any grna of interest can be produced ubiquitously off the U6 promoter. Tol2 indicates transposition sites for the Tol2 transposase. pa: SV40 polya sequence. (D) Confocal images of the yolk region of 30 hpf embryos injected with Tol2 mrna and the pa2, U6:gRNA urod, gata1:cas9-t2a-gfp vector. Arrows point to cells that are both green and red. Scale bar: 20 µm. Note the small size of red-only cells.
8 Relative Cas9 expression (ΔΔCt) pcmlc2:gfp U6:gRNA urod gata1:cas9 % larvae per phenotype WT siblings A pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA urod, gata1:cas9 F1 pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA urod, mylz2:cas9 50 hpf 300 µm B F1, 36 hpf C Blood GFP in the heart - + E D 14 mutant alleles out of 20 sequenced alleles CAGAGTTCAGGGAATCACGGGCA GGGAAAGATT WT x6 CAGAGTTCAGGGAATCACGG CAGGGAAAGATT -1 x4 CAGAGTTCAGGGAATCAC GGGAAAGATT -5 x2 CAGAGTTCAG CAGGGAAAGATT -11 x2 CAGAGTTCAGGGAA AGATT -14 CAGAGTTCAGGGAATCAC AGGGAAAGATT -4 CAGAGTTCAGGGAATCACGGGC del CAGAGTTCAGGGAATCACG CAGGGAAAGATT -2 CAGAGTTCAGGGAATCACGG AAAGATT -6 CAGAGTTCAGGGAAT A GAAAGATT -10;+1 F ,5 2 1,5 1 0,5 0-0,5 ubi:cas9 gata1:cas9 Mild Full p = Mild Full Figure S4. Analysis of the urod phenotype in stable F1 embryos (related to Figure 4).
9 (A) Confocal images of 50 hpf embryos from the F1 generation of fish stably expressing the indicated vectors. (B) FACS analysis of the blood of 36 hpf F1 embryos stably expressing the pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA urod, gata1:cas9 vector (bottom panels). Blood from F1 siblings not presenting green hearts was used as a negative control (top panels). Red fluorescence due to urod inactivation was detected in the PE-Cy5 channel (right panels). Cytox blue was used to mark dead or dying cells (left panels). (C) T7E1 mutagenesis assay at the CRISPR target site in the urod gene. The assay was performed on genomic DNA from the blood of 2 dpf F1 embryos stably expressing the pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA urod, gata1:cas9 vector. Blood from F1 siblings not presenting green hearts was used as a negative control. (D) Sequences of the mutant urod alleles found in the blood of embryos stably expressing the pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA urod, gata1:cas9 vector. The CRISPR target sequence is in green, mutations in red. The type of mutation and the associated number of detected alleles are indicated. (E) Quantification of the fluorescent phenotype observed in F1 embryos. Mild: <10 fluorescent blood cells. Full denotes a number of fluorescent cells comparable to that observed in age-matched LCR:GFP embryos. Ubi:Cas9 (n=37), gata1:cas9 (n=80). (F) qpcr analysis of Cas9 expression in F1 embryos stably expressing pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA urod, ubi:cas9 vector. Four embryos showing no or few fluorescent cells (mild) and four embryos showing a full phenotype were compared. Data represented as mean ± SD.
10 Mutation index F0 ubi promoter (whole embryos) F0 gata1 promoter (blood) F1 ubi promoter (whole embryos) F1 gata1 promoter (blood) Deep-sequencing 36% 25% NA NA TA cloning 40% 33% 82% 70% Table S1. Mutation indexes for the pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA urod, ubi:cas9 and pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA urod, gata1:cas9 vectors (related to Figure 4). The index was calculated as the number of mutated alleles over the total number of sequenced alleles using either of two methods: deep-sequencing or TA cloning followed by Sanger sequencing of PCR amplicons around the CRISPR target site in the urod gene. Mutation indexes for both injected F0 and stable F1 embryos are indicated. Movie S1. Circulating fluorescent erythrocytes after tissue-specific urod targeting (related to Figure 3). Live confocal imaging of a 50 hpf embryo injected with Tol2 mrna and the pcmlc2:gfp, U6:gRNA urod, gata1:cas9 vector at the one-cell stage.
embryos. Asterisk represents loss of or reduced expression. Brackets represent
 Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1. tfec expression is highly enriched in tail endothelial cells (A- B) ISH of tfec at 15 and 16hpf in WT embryos. (C- D) ISH of tfec at 36 and 38hpf in WT embryos.
Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1. tfec expression is highly enriched in tail endothelial cells (A- B) ISH of tfec at 15 and 16hpf in WT embryos. (C- D) ISH of tfec at 36 and 38hpf in WT embryos.
Protocol for tissue-specific gene disruption in zebrafish
 Protocol for tissue-specific gene disruption in zebrafish Overview This protocol describes a method to inactivate genes in zebrafish in a tissue-specific manner. It can be used to analyze mosaic loss-of-function
Protocol for tissue-specific gene disruption in zebrafish Overview This protocol describes a method to inactivate genes in zebrafish in a tissue-specific manner. It can be used to analyze mosaic loss-of-function
A CRISPR/Cas9 Vector System for Tissue-Specific Gene Disruption in Zebrafish
 Resource A CRISPR/Cas9 Vector System for Tissue-Specific Gene Disruption in Zebrafish Graphical Abstract Authors Julien Ablain, Ellen M. Durand,..., Yi Zhou, Leonard I. Zon Correspondence zon@enders.tch.harvard.edu
Resource A CRISPR/Cas9 Vector System for Tissue-Specific Gene Disruption in Zebrafish Graphical Abstract Authors Julien Ablain, Ellen M. Durand,..., Yi Zhou, Leonard I. Zon Correspondence zon@enders.tch.harvard.edu
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.4166
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Supplementary Figure 1. Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings.
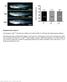 Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3494
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
Figure S1a. The modular dcas9 fusion system works efficiently to suppress and activate endogenous gene expression in C. elegans
 Figure S1a. The modular dcas9 fusion system works efficiently to suppress and activate endogenous gene expression in C. elegans A, a normal wild-type hermaphrodite N2 is shown. B, a dpy-5-supressed F1
Figure S1a. The modular dcas9 fusion system works efficiently to suppress and activate endogenous gene expression in C. elegans A, a normal wild-type hermaphrodite N2 is shown. B, a dpy-5-supressed F1
Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably expressing shrna sequences against TRF2 were examined by western blotting. shcon, shrna
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably expressing shrna sequences against TRF2 were examined by western blotting. shcon, shrna
Aquatic Vertebrates Platform Services (See services description below, page 3)
 Aquatic Vertebrates Platform Services (See services description below, page 3) Services 1. Micro-injection of DNA, morpholino or mrna in zebrafish and medaka embryos. 2. Generation of stable zebrafish
Aquatic Vertebrates Platform Services (See services description below, page 3) Services 1. Micro-injection of DNA, morpholino or mrna in zebrafish and medaka embryos. 2. Generation of stable zebrafish
To assess the localization of Citrine fusion proteins, we performed antibody staining to
 Trinh et al 1 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL FlipTraps recapitulate endogenous protein localization To assess the localization of Citrine fusion proteins, we performed antibody staining to compare the expression
Trinh et al 1 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL FlipTraps recapitulate endogenous protein localization To assess the localization of Citrine fusion proteins, we performed antibody staining to compare the expression
Protocol for Genome Editing via the RNA-guided Cas9 Nuclease in. Zebrafish Embryos 1
 Protocol for Genome Editing via the RNA-guided Cas9 Nuclease in Zebrafish Embryos 1 1. In vitro synthesis of capped Cas9 mrna The full length of humanized Cas9 cdnas with double NLS were cloned into pxt7
Protocol for Genome Editing via the RNA-guided Cas9 Nuclease in Zebrafish Embryos 1 1. In vitro synthesis of capped Cas9 mrna The full length of humanized Cas9 cdnas with double NLS were cloned into pxt7
Zebrafish, a model of choice for biomedical research. Yoav Gothilf Dept. Neurobiology, Tel Aviv University
 Zebrafish, a model of choice for biomedical research Yoav Gothilf Dept. Neurobiology, Tel Aviv University yoavgothilf@gmail.com https://youtu.be/4c-kw4timva Zebrafish Vertebrate External fertilization
Zebrafish, a model of choice for biomedical research Yoav Gothilf Dept. Neurobiology, Tel Aviv University yoavgothilf@gmail.com https://youtu.be/4c-kw4timva Zebrafish Vertebrate External fertilization
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Super-resolution imaging of fluorescently labeled, endogenous RNA Polymerase II in living cells with CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing Won-Ki Cho 1, Namrata Jayanth 1, Susan Mullen
Supplementary Information Super-resolution imaging of fluorescently labeled, endogenous RNA Polymerase II in living cells with CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing Won-Ki Cho 1, Namrata Jayanth 1, Susan Mullen
SUPPLEMENT MATERIALS FOR CURTIN,
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 SUPPLEMENT MATERIALS FOR CURTIN, et al. Validating genome-wide association candidates: Selecting, testing, and characterizing
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 SUPPLEMENT MATERIALS FOR CURTIN, et al. Validating genome-wide association candidates: Selecting, testing, and characterizing
Supplementary Information. Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish
 Supplementary Information Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish Hagen R. Witzel 1, Sirisha Cheedipudi 1, Rui Gao 1, Didier Y.R. Stainier 2 and Gergana D. Dobreva 1,3* 1 Origin
Supplementary Information Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish Hagen R. Witzel 1, Sirisha Cheedipudi 1, Rui Gao 1, Didier Y.R. Stainier 2 and Gergana D. Dobreva 1,3* 1 Origin
Revised: RG-RV2 by Fukuhara et al.
 Supplemental Figure 1 The generation of Spns2 conditional knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the wild type Spns2 locus (Spns2 + ), the targeted allele, the floxed allele (Spns2 f ) and the
Supplemental Figure 1 The generation of Spns2 conditional knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the wild type Spns2 locus (Spns2 + ), the targeted allele, the floxed allele (Spns2 f ) and the
Supplemental Data. Na Xu et al. (2016). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. The weak fluorescence phenotype is not caused by the mutation in At3g60240. (A) A mutation mapped to the gene At3g60240. Map-based cloning strategy was used to map the mutated site
Supplemental Figure 1. The weak fluorescence phenotype is not caused by the mutation in At3g60240. (A) A mutation mapped to the gene At3g60240. Map-based cloning strategy was used to map the mutated site
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Ihh interacts preferentially with its upstream neighboring gene Nhej1. Genes are indicated by gray lines, and Ihh and Nhej1 are highlighted in blue. 4C seq performed in E14.5 limbs
Supplementary Figure 1 Ihh interacts preferentially with its upstream neighboring gene Nhej1. Genes are indicated by gray lines, and Ihh and Nhej1 are highlighted in blue. 4C seq performed in E14.5 limbs
Supplemental Information. Kinesin 1 Drives Autolysosome Tubulation
 Developmental Cell, Volume 37 Supplemental Information Kinesin 1 Drives Autolysosome Tubulation Wanqing Du, Qian Peter Su, Yang Chen, Yueyao Zhu, Dong Jiang, Yueguang Rong, Senyan Zhang, Yixiao Zhang,
Developmental Cell, Volume 37 Supplemental Information Kinesin 1 Drives Autolysosome Tubulation Wanqing Du, Qian Peter Su, Yang Chen, Yueyao Zhu, Dong Jiang, Yueguang Rong, Senyan Zhang, Yixiao Zhang,
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary figures and supplementary tables. File name: Peer review file Description:
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary figures and supplementary tables. File name: Peer review file Description: Supplementary Figure 1. dcas9-mq1 fusion protein induces de novo
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary figures and supplementary tables. File name: Peer review file Description: Supplementary Figure 1. dcas9-mq1 fusion protein induces de novo
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
Supplementary Figures Montero et al._supplementary Figure 1
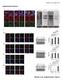 Montero et al_suppl. Info 1 Supplementary Figures Montero et al._supplementary Figure 1 Montero et al_suppl. Info 2 Supplementary Figure 1. Transcripts arising from the structurally conserved subtelomeres
Montero et al_suppl. Info 1 Supplementary Figures Montero et al._supplementary Figure 1 Montero et al_suppl. Info 2 Supplementary Figure 1. Transcripts arising from the structurally conserved subtelomeres
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary figure 1: List of primers/oligonucleotides used in this study. 1 Supplementary figure 2: Sequences and mirna-targets of i) mcherry expresses in transgenic fish used
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary figure 1: List of primers/oligonucleotides used in this study. 1 Supplementary figure 2: Sequences and mirna-targets of i) mcherry expresses in transgenic fish used
Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms
 Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms No. 1 of 10 1. The mouse gene knockout is based on. (A) Homologous recombination (B) Site-specific recombination
Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms No. 1 of 10 1. The mouse gene knockout is based on. (A) Homologous recombination (B) Site-specific recombination
Optimizing Cas9 and sgrna concentrations for increasing mutation efficiency. Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.3360
 Supplementary Figure 1 Optimizing Cas9 and sgrna concentrations for increasing mutation efficiency. (a) Wild-type, 2-dpf slc24a5 b1 embryos and a series of slc24a5 CRISPR-injected embryos; anterior is
Supplementary Figure 1 Optimizing Cas9 and sgrna concentrations for increasing mutation efficiency. (a) Wild-type, 2-dpf slc24a5 b1 embryos and a series of slc24a5 CRISPR-injected embryos; anterior is
CRISPR RNA-guided activation of endogenous human genes
 CRISPR RNA-guided activation of endogenous human genes Morgan L Maeder, Samantha J Linder, Vincent M Cascio, Yanfang Fu, Quan H Ho, J Keith Joung Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of VEGF activation induced
CRISPR RNA-guided activation of endogenous human genes Morgan L Maeder, Samantha J Linder, Vincent M Cascio, Yanfang Fu, Quan H Ho, J Keith Joung Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of VEGF activation induced
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS. -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells. - Two methods to produce transgenic animals:
 TRANSGENIC ANIMALS -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection - random insertion 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated gene
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection - random insertion 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated gene
Surrogate reporter-based enrichment of cells containing RNA-guided Cas9 nucleaseinduced
 Supplementary Data Surrogate reporter-based enrichment of cells containing RNA-guided Cas9 nucleaseinduced mutations Suresh Ramakrishna 1, Seung Woo Cho 2, Sojung Kim 2, Myungjae Song 1, Ramu Gopalappa
Supplementary Data Surrogate reporter-based enrichment of cells containing RNA-guided Cas9 nucleaseinduced mutations Suresh Ramakrishna 1, Seung Woo Cho 2, Sojung Kim 2, Myungjae Song 1, Ramu Gopalappa
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information This Supplementary Information file contains the following contents: Supplementary Methods, Supplementary Discussion, Supplementary Figures (S1~S9), Supplementary Tables (1~3)
Supplementary Information This Supplementary Information file contains the following contents: Supplementary Methods, Supplementary Discussion, Supplementary Figures (S1~S9), Supplementary Tables (1~3)
- 1 - Supplemental Data
 - 1-1 Supplemental Data 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Supplemental Figure S1. Differential expression of AtPIP Genes in DC3000-inoculated plants. Gene expression in leaves was analyzed by real-time RT-PCR and expression
- 1-1 Supplemental Data 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Supplemental Figure S1. Differential expression of AtPIP Genes in DC3000-inoculated plants. Gene expression in leaves was analyzed by real-time RT-PCR and expression
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. (A) UCSC Genome Browser view of region immediately downstream of the NEUROG3 start codon. All candidate grna target sites which meet the G(N 19 )NGG constraint are aligned to illustrate
Supplementary Figure 1. (A) UCSC Genome Browser view of region immediately downstream of the NEUROG3 start codon. All candidate grna target sites which meet the G(N 19 )NGG constraint are aligned to illustrate
CRISPR Ribonucleoprotein (RNP) User Manual
 CRISPR Ribonucleoprotein (RNP) User Manual Description This user manual describes how to use GenScript s CRISPR Ribonucleoprotein (RNP) products for targeted genome editing. The RNP system is comprised
CRISPR Ribonucleoprotein (RNP) User Manual Description This user manual describes how to use GenScript s CRISPR Ribonucleoprotein (RNP) products for targeted genome editing. The RNP system is comprised
Supplementary Figure 1 Activities of ABEs using extended sgrnas in HEK293T cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activities of ABEs using extended sgrnas in HEK293T cells. Base editing efficiencies of ABEs with extended sgrnas at Site 18 (a), Site 19 (b), the HBB-E2 site (c), and the HBB-E3
Supplementary Figure 1 Activities of ABEs using extended sgrnas in HEK293T cells. Base editing efficiencies of ABEs with extended sgrnas at Site 18 (a), Site 19 (b), the HBB-E2 site (c), and the HBB-E3
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09937 a Name Position Primersets 1a 1b 2 3 4 b2 Phenotype Genotype b Primerset 1a D T C R I E 10000 8000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 800 Donor (D)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09937 a Name Position Primersets 1a 1b 2 3 4 b2 Phenotype Genotype b Primerset 1a D T C R I E 10000 8000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 800 Donor (D)
Chapter 20 Biotechnology
 Chapter 20 Biotechnology Manipulation of DNA In 2007, the first entire human genome had been sequenced. The ability to sequence an organisms genomes were made possible by advances in biotechnology, (the
Chapter 20 Biotechnology Manipulation of DNA In 2007, the first entire human genome had been sequenced. The ability to sequence an organisms genomes were made possible by advances in biotechnology, (the
i-stop codon positions in the mcherry gene
 Supplementary Figure 1 i-stop codon positions in the mcherry gene The grnas (green) that can potentially generate stop codons from Trp (63 th and 98 th aa, upper panel) and Gln (47 th and 114 th aa, bottom
Supplementary Figure 1 i-stop codon positions in the mcherry gene The grnas (green) that can potentially generate stop codons from Trp (63 th and 98 th aa, upper panel) and Gln (47 th and 114 th aa, bottom
Applicazioni biotecnologiche
 Applicazioni biotecnologiche Analisi forense Sintesi di proteine ricombinanti Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Polymorphism (more fully genetic polymorphism) refers to the simultaneous occurrence
Applicazioni biotecnologiche Analisi forense Sintesi di proteine ricombinanti Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Polymorphism (more fully genetic polymorphism) refers to the simultaneous occurrence
Biotechnology. Chapter 20. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 20 Biotechnology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Chapter 20 Biotechnology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Supplementary Figure 1 An overview of pirna biogenesis during fetal mouse reprogramming. (a) (b)
 Supplementary Figure 1 An overview of pirna biogenesis during fetal mouse reprogramming. (a) A schematic overview of the production and amplification of a single pirna from a transposon transcript. The
Supplementary Figure 1 An overview of pirna biogenesis during fetal mouse reprogramming. (a) A schematic overview of the production and amplification of a single pirna from a transposon transcript. The
Recent technology allow production of microarrays composed of 70-mers (essentially a hybrid of the two techniques)
 Microarrays and Transcript Profiling Gene expression patterns are traditionally studied using Northern blots (DNA-RNA hybridization assays). This approach involves separation of total or polya + RNA on
Microarrays and Transcript Profiling Gene expression patterns are traditionally studied using Northern blots (DNA-RNA hybridization assays). This approach involves separation of total or polya + RNA on
Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Lu et al. 10.1073/pnas.1106801108 Fig. S1. Analysis of spatial localization of mrnas coding for 23 zebrafish Wnt genes by whole mount in situ hybridization to identify those present
Supporting Information Lu et al. 10.1073/pnas.1106801108 Fig. S1. Analysis of spatial localization of mrnas coding for 23 zebrafish Wnt genes by whole mount in situ hybridization to identify those present
Incorporating SeqStudio Genetic Analyzer and Sanger sequencing into genome editing workflows
 Incorporating SeqStudio Genetic Analyzer and Sanger sequencing into genome editing workflows Stephen Jackson, Ph.D 27 May 2017 The world leader in serving science Key Applications for Genome Editing Research
Incorporating SeqStudio Genetic Analyzer and Sanger sequencing into genome editing workflows Stephen Jackson, Ph.D 27 May 2017 The world leader in serving science Key Applications for Genome Editing Research
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 AS-NMD modulates FLM-dependent thermosensory flowering response in Arabidopsis NATURE PLANTS www.nature.com/natureplants 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Genomic sequence of FLM along with the splice sites. Sequencing
AS-NMD modulates FLM-dependent thermosensory flowering response in Arabidopsis NATURE PLANTS www.nature.com/natureplants 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Genomic sequence of FLM along with the splice sites. Sequencing
Mitotic cell rounding and epithelial thinning regulate lumen
 Mitotic cell rounding and epithelial thinning regulate lumen growth and shape Esteban Hoijman, Davide Rubbini, Julien Colombelli and Berta Alsina SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1 (a-c) Localization
Mitotic cell rounding and epithelial thinning regulate lumen growth and shape Esteban Hoijman, Davide Rubbini, Julien Colombelli and Berta Alsina SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1 (a-c) Localization
Alternative Cleavage and Polyadenylation of RNA
 Developmental Cell 18 Supplemental Information The Spen Family Protein FPA Controls Alternative Cleavage and Polyadenylation of RNA Csaba Hornyik, Lionel C. Terzi, and Gordon G. Simpson Figure S1, related
Developmental Cell 18 Supplemental Information The Spen Family Protein FPA Controls Alternative Cleavage and Polyadenylation of RNA Csaba Hornyik, Lionel C. Terzi, and Gordon G. Simpson Figure S1, related
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
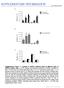 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12474 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of mtdna mutation loads in different types of mtdna mutator mice. a, PCR, cloning, and sequencing analysis of mtdna mutations
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12474 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of mtdna mutation loads in different types of mtdna mutator mice. a, PCR, cloning, and sequencing analysis of mtdna mutations
CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing Tools
 CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing Tools - Guide-it Products for Successful CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing - Why choose Guide-it products? Optimized methods designed for speed and ease of use Complete kits that don t
CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing Tools - Guide-it Products for Successful CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing - Why choose Guide-it products? Optimized methods designed for speed and ease of use Complete kits that don t
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Park et al. 10.1073/pnas.1410555111 5 -TCAAGTCCATCTACATGGCC-3 5 -CAGCTGCCCGGCTACTACTA-3 5 -TGCAGCTGCCCGGCTACTAC-3 5 -AAGCTGGACATCACCTCCCA-3 5 -TGACAGGAACACCTACAAGT-3 5 -AAGGCACCTTTCTGTCTCCA-3
Supporting Information Park et al. 10.1073/pnas.1410555111 5 -TCAAGTCCATCTACATGGCC-3 5 -CAGCTGCCCGGCTACTACTA-3 5 -TGCAGCTGCCCGGCTACTAC-3 5 -AAGCTGGACATCACCTCCCA-3 5 -TGACAGGAACACCTACAAGT-3 5 -AAGGCACCTTTCTGTCTCCA-3
Supplementary Information. Optimization of the production of knock-in alleles by CRISPR/Cas9 microinjection into the mouse zygote
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures S1 to S5 and Tables S1 to S3. Optimization of the production of knock-in alleles by CRISPR/Cas9 microinjection into the mouse zygote Aurélien Raveux, Sandrine
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures S1 to S5 and Tables S1 to S3. Optimization of the production of knock-in alleles by CRISPR/Cas9 microinjection into the mouse zygote Aurélien Raveux, Sandrine
Easi CRISPR for conditional and insertional alleles
 Easi CRISPR for conditional and insertional alleles C.B Gurumurthy, University Of Nebraska Medical Center Omaha, NE cgurumurthy@unmc.edu Types of Genome edits Gene disruption/inactivation Types of Genome
Easi CRISPR for conditional and insertional alleles C.B Gurumurthy, University Of Nebraska Medical Center Omaha, NE cgurumurthy@unmc.edu Types of Genome edits Gene disruption/inactivation Types of Genome
Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified
 Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified by primers used for mrna expression analysis. Gray
Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified by primers used for mrna expression analysis. Gray
Protocols for cell lines using CRISPR/CAS
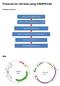 Protocols for cell lines using CRISPR/CAS Procedure overview Map Preparation of CRISPR/CAS plasmids Expression vectors for guide RNA (U6-gRNA) and Cas9 gene (CMV-p-Cas9) are ampicillin-resist ant and stable
Protocols for cell lines using CRISPR/CAS Procedure overview Map Preparation of CRISPR/CAS plasmids Expression vectors for guide RNA (U6-gRNA) and Cas9 gene (CMV-p-Cas9) are ampicillin-resist ant and stable
Zebrafish (Daniorerio)
 Zebrafish (Daniorerio) Connecting genotype to phenotype Photo credit: Robert Tanguay Somefactsaboutzebrafish Originate from North India(Ganges), slow streams Freshwaterfish, tolerate12-39 C (optimal25
Zebrafish (Daniorerio) Connecting genotype to phenotype Photo credit: Robert Tanguay Somefactsaboutzebrafish Originate from North India(Ganges), slow streams Freshwaterfish, tolerate12-39 C (optimal25
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Gómez-Marín et al. 10.1073/pnas.1505463112 SI Materials and Methods Generation of BAC DK74B2-six2a::GFP-six3a::mCherry-iTol2. BAC clone (number 74B2) from DanioKey zebrafish BAC
Supporting Information Gómez-Marín et al. 10.1073/pnas.1505463112 SI Materials and Methods Generation of BAC DK74B2-six2a::GFP-six3a::mCherry-iTol2. BAC clone (number 74B2) from DanioKey zebrafish BAC
Supplemental Data. Li et al. (2015). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1: Characterization of asr3 T-DNA knockout lines and complementation transgenic lines. (A) The scheme of At2G33550 (ASR3) with gray boxes indicating exons and dash
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1: Characterization of asr3 T-DNA knockout lines and complementation transgenic lines. (A) The scheme of At2G33550 (ASR3) with gray boxes indicating exons and dash
A novel tool for monitoring endogenous alpha-synuclein transcription by NanoLuciferase
 A novel tool for monitoring endogenous alpha-synuclein transcription by NanoLuciferase tag insertion at the 3 end using CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing technique Sambuddha Basu 1, 3, Levi Adams 1, 3, Subhrangshu
A novel tool for monitoring endogenous alpha-synuclein transcription by NanoLuciferase tag insertion at the 3 end using CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing technique Sambuddha Basu 1, 3, Levi Adams 1, 3, Subhrangshu
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Secondary mutations as a mechanism of cisplatin resistance in BRCA2-mutated cancers Wataru Sakai, Elizabeth M. Swisher, Beth Y. Karlan, Mukesh K. Agarwal, Jake Higgins, Cynthia Friedman, Emily Villegas,
Secondary mutations as a mechanism of cisplatin resistance in BRCA2-mutated cancers Wataru Sakai, Elizabeth M. Swisher, Beth Y. Karlan, Mukesh K. Agarwal, Jake Higgins, Cynthia Friedman, Emily Villegas,
High-throughput genotyping of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutants using fluorescent
 High-throughput genotyping of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutants using fluorescent PCR-capillary gel electrophoresis Muhammad Khairul RAMLEE, Tingdong YAN, Alice M. S. CHEUNG, Charles CHUAH, Shang LI Figure
High-throughput genotyping of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutants using fluorescent PCR-capillary gel electrophoresis Muhammad Khairul RAMLEE, Tingdong YAN, Alice M. S. CHEUNG, Charles CHUAH, Shang LI Figure
Cell line CDH1 mrna AS-paRNA S-paRNA
 a b Cell line mrna AS-paRNA S-paRNA HCT116 P53 +/+ 39.47 + + HCT116 P53 -/- 35.36 + + LNCAP 1562.4 + - MCF7 C1 1864.76 + - MCF7 C2 1812.81 + - Supplementary Figure 1. Promoter-associated transcripts at
a b Cell line mrna AS-paRNA S-paRNA HCT116 P53 +/+ 39.47 + + HCT116 P53 -/- 35.36 + + LNCAP 1562.4 + - MCF7 C1 1864.76 + - MCF7 C2 1812.81 + - Supplementary Figure 1. Promoter-associated transcripts at
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Methods Supplementary Discussion Supplementary Figure 1 Calculated frequencies of embryo cells bearing bi-allelic alterations. Targeted indel mutations induced by
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Methods Supplementary Discussion Supplementary Figure 1 Calculated frequencies of embryo cells bearing bi-allelic alterations. Targeted indel mutations induced by
Improving CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Knockout with a Validated Guide RNA Algorithm
 Improving CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Knockout with a Validated Guide RNA Algorithm Anja Smith Director R&D Dharmacon, part of GE Healthcare Imagination at work crrna:tracrrna program Cas9 nuclease Active crrna is
Improving CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Knockout with a Validated Guide RNA Algorithm Anja Smith Director R&D Dharmacon, part of GE Healthcare Imagination at work crrna:tracrrna program Cas9 nuclease Active crrna is
sides of the aleurone (Al) but it is excluded from the basal endosperm transfer layer
 Supplemental Data. Gómez et al. (2009). The maize transcription factor MRP-1 (Myb-Related-Protein-1) is a key regulator of the differentiation of transfer cells. Supplemental Figure 1. Expression analyses
Supplemental Data. Gómez et al. (2009). The maize transcription factor MRP-1 (Myb-Related-Protein-1) is a key regulator of the differentiation of transfer cells. Supplemental Figure 1. Expression analyses
Supplemental Data. Borg et al. Plant Cell (2014) /tpc
 Supplementary Figure 1 - Alignment of selected angiosperm DAZ1 and DAZ2 homologs Multiple sequence alignment of selected DAZ1 and DAZ2 homologs. A consensus sequence built using default parameters is shown
Supplementary Figure 1 - Alignment of selected angiosperm DAZ1 and DAZ2 homologs Multiple sequence alignment of selected DAZ1 and DAZ2 homologs. A consensus sequence built using default parameters is shown
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Gene replacements and insertions in rice by intron targeting using CRISPR Cas9 Table of Contents Supplementary Figure 1. sgrna-induced targeted mutations in the OsEPSPS gene in rice protoplasts. Supplementary
Gene replacements and insertions in rice by intron targeting using CRISPR Cas9 Table of Contents Supplementary Figure 1. sgrna-induced targeted mutations in the OsEPSPS gene in rice protoplasts. Supplementary
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.15 GENOMES AND GENOMICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF GENOMICS Genomics is the study of genomes in their entirety Bioinformatics is the analysis of the information content of genomes - Genes, regulatory sequences,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF GENOMICS Genomics is the study of genomes in their entirety Bioinformatics is the analysis of the information content of genomes - Genes, regulatory sequences,
Allele-specific locus binding and genome editing by CRISPR at the
 Supplementary Information Allele-specific locus binding and genome editing by CRISPR at the p6ink4a locus Toshitsugu Fujita, Miyuki Yuno, and Hodaka Fujii Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Information Allele-specific locus binding and genome editing by CRISPR at the p6ink4a locus Toshitsugu Fujita, Miyuki Yuno, and Hodaka Fujii Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/4/e1602814/dc1 Supplementary Materials for CRISPR-Cpf1 correction of muscular dystrophy mutations in human cardiomyocytes and mice Yu Zhang, Chengzu Long, Hui
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/4/e1602814/dc1 Supplementary Materials for CRISPR-Cpf1 correction of muscular dystrophy mutations in human cardiomyocytes and mice Yu Zhang, Chengzu Long, Hui
Reprogramming MHC specificity by CRISPR-Cas9-assisted cassette exchange
 1 Supplementary Materials Reprogramming MHC specificity by CRISPR-Cas9-assisted cassette exchange 3 4 5 6 Authors William Kelton 1, Ann Cathrin Waindok 1, Theresa Pesch 1, Mark Pogson 1, Kyle Ford 1, Cristina
1 Supplementary Materials Reprogramming MHC specificity by CRISPR-Cas9-assisted cassette exchange 3 4 5 6 Authors William Kelton 1, Ann Cathrin Waindok 1, Theresa Pesch 1, Mark Pogson 1, Kyle Ford 1, Cristina
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. In vitro validation of OTC sgrnas and donor template.
 Supplementary Figure 1 In vitro validation of OTC sgrnas and donor template. (a) In vitro validation of sgrnas targeted to OTC in the MC57G mouse cell line by transient transfection followed by 4-day puromycin
Supplementary Figure 1 In vitro validation of OTC sgrnas and donor template. (a) In vitro validation of sgrnas targeted to OTC in the MC57G mouse cell line by transient transfection followed by 4-day puromycin
You use the UCSC Genome Browser (www.genome.ucsc.edu) to assess the exonintron structure of each gene. You use four tracks to show each gene:
 CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing Part 1: You would like to rapidly generate two different knockout mice using CRISPR-Cas9. The genes to be knocked out are Pcsk9 and Apoc3, both involved in lipid metabolism.
CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing Part 1: You would like to rapidly generate two different knockout mice using CRISPR-Cas9. The genes to be knocked out are Pcsk9 and Apoc3, both involved in lipid metabolism.
CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing Tools
 CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing Tools - Separations Simply Spectacular INDELS Identify indels Determine if one or both copies of your gene have indels The Guide-it Genotype Confirmation Kit: Simple detection
CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing Tools - Separations Simply Spectacular INDELS Identify indels Determine if one or both copies of your gene have indels The Guide-it Genotype Confirmation Kit: Simple detection
Non-coding Function & Variation, MPRAs II. Mike White Bio /5/18
 Non-coding Function & Variation, MPRAs II Mike White Bio 5488 3/5/18 MPRA Review Problem 1: Where does your CRE DNA come from? DNA synthesis Genomic fragments Targeted regulome capture Problem 2: How do
Non-coding Function & Variation, MPRAs II Mike White Bio 5488 3/5/18 MPRA Review Problem 1: Where does your CRE DNA come from? DNA synthesis Genomic fragments Targeted regulome capture Problem 2: How do
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 ATP1A1 variants with in-frame deletions are enriched in ouabain-resistant cell populations. (a) Total editing efficacy along with spectrum and frequency of individual indels as determined
Supplementary Figure 1 ATP1A1 variants with in-frame deletions are enriched in ouabain-resistant cell populations. (a) Total editing efficacy along with spectrum and frequency of individual indels as determined
Applications of Cas9 nickases for genome engineering
 application note genome editing Applications of Cas9 nickases for genome engineering Shuqi Yan, Mollie Schubert, Maureen Young, Brian Wang Integrated DNA Technologies, 17 Commercial Park, Coralville, IA,
application note genome editing Applications of Cas9 nickases for genome engineering Shuqi Yan, Mollie Schubert, Maureen Young, Brian Wang Integrated DNA Technologies, 17 Commercial Park, Coralville, IA,
Inhibition of HSV-1 Replication by Gene Editing Strategy. Running Title: Targeting HSV-1 Infection by CRISPR/Cas9
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS 2/4/16 Inhibition of HSV-1 Replication by Gene Editing Strategy Running Title: Targeting HSV-1 Infection by CRISPR/Cas9 Pamela C. Roehm 1,2,3*, Masoud Shekarabi 1, Hassen Wollebo
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS 2/4/16 Inhibition of HSV-1 Replication by Gene Editing Strategy Running Title: Targeting HSV-1 Infection by CRISPR/Cas9 Pamela C. Roehm 1,2,3*, Masoud Shekarabi 1, Hassen Wollebo
Figure S1 Glucocorticoid receptor-green fluorescent protein (GR-GFP) reporter construct.
 Figure S1 Glucocorticoid receptor-green fluorescent protein (GR-GFP) reporter construct. (A) Schematic display of the construct is presented detailing binding sites and regions of interest within the GR
Figure S1 Glucocorticoid receptor-green fluorescent protein (GR-GFP) reporter construct. (A) Schematic display of the construct is presented detailing binding sites and regions of interest within the GR
Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Isolation of single-base genome-edited human ips cells without
 Nature Methods Isolation of single-base genome-edited human ips cells without antibiotic selection Yuichiro Miyaoka, Amanda H. Chan, Luke M. Judge, Jennie Yoo, Miller Huang, Trieu D. Nguyen, Paweena P.
Nature Methods Isolation of single-base genome-edited human ips cells without antibiotic selection Yuichiro Miyaoka, Amanda H. Chan, Luke M. Judge, Jennie Yoo, Miller Huang, Trieu D. Nguyen, Paweena P.
Return to Web Version
 Page 1 of 7 Page 1 of 7 Return to Web Version ZFN Technology Biowire Volume 10 Article 1 Have your genomic work cut out for you The genomes of several organisms, including humans, have been sequenced,
Page 1 of 7 Page 1 of 7 Return to Web Version ZFN Technology Biowire Volume 10 Article 1 Have your genomic work cut out for you The genomes of several organisms, including humans, have been sequenced,
Gene editing in cereals
 University of Minnesota Gene editing in cereals Mick Ayliffe The importance of cereals in Australian agriculture VALUE OF AGRICULTURAL COMMODITIES PRODUCED IN Australia (year ended 30 June 2016) Gene editing
University of Minnesota Gene editing in cereals Mick Ayliffe The importance of cereals in Australian agriculture VALUE OF AGRICULTURAL COMMODITIES PRODUCED IN Australia (year ended 30 June 2016) Gene editing
Chapter 13: Biotechnology
 Chapter Review 1. Explain why the brewing of beer is considered to be biotechnology. The United Nations defines biotechnology as any technological application that uses biological system, living organism,
Chapter Review 1. Explain why the brewing of beer is considered to be biotechnology. The United Nations defines biotechnology as any technological application that uses biological system, living organism,
Bootcamp: Molecular Biology Techniques and Interpretation
 Bootcamp: Molecular Biology Techniques and Interpretation Bi8 Winter 2016 Today s outline Detecting and quantifying nucleic acids and proteins: Basic nucleic acid properties Hybridization PCR and Designing
Bootcamp: Molecular Biology Techniques and Interpretation Bi8 Winter 2016 Today s outline Detecting and quantifying nucleic acids and proteins: Basic nucleic acid properties Hybridization PCR and Designing
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature09861 & &' -(' ()*+ ')(+,,(','-*+,&,,+ ',+' ' 23,45/0*6787*9:./09 ;78?4?@*+A786?B- &' )*+*(,-* -(' ()*+ ')(+,,(','-*+,&,,+ ',+'./)*+*(,-*..)*+*(,-*./)*+*(,-*.0)*+*(,-*..)*+*(,-*
doi:10.1038/nature09861 & &' -(' ()*+ ')(+,,(','-*+,&,,+ ',+' ' 23,45/0*6787*9:./09 ;78?4?@*+A786?B- &' )*+*(,-* -(' ()*+ ')(+,,(','-*+,&,,+ ',+'./)*+*(,-*..)*+*(,-*./)*+*(,-*.0)*+*(,-*..)*+*(,-*
Simple protocol for gene editing using GenCrisprTM Cas9 nuclease
 Simple protocol for gene editing using GenCrisprTM Cas9 nuclease Contents Protocol Step 1: Choose the target DNA sequence Step 2: Design sgrna Step 3: Preparation for sgrna 3.1 In vitro transcription of
Simple protocol for gene editing using GenCrisprTM Cas9 nuclease Contents Protocol Step 1: Choose the target DNA sequence Step 2: Design sgrna Step 3: Preparation for sgrna 3.1 In vitro transcription of
A Guide to CRISPR/Cas9
 Genome editing and beyond freepik A Guide to CRISPR/Cas9 The latest advance in genomic DNA editing is the Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat (CRISPR)/Cas9 system. This simple-touse
Genome editing and beyond freepik A Guide to CRISPR/Cas9 The latest advance in genomic DNA editing is the Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat (CRISPR)/Cas9 system. This simple-touse
Gene Expression Technology
 Gene Expression Technology Bing Zhang Department of Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University bing.zhang@vanderbilt.edu Gene expression Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene
Gene Expression Technology Bing Zhang Department of Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University bing.zhang@vanderbilt.edu Gene expression Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene
Supplemental Data. Liu et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. The GFP Tag Does Not Disturb the Physiological Functions of WDL3. (A) RT-PCR analysis of WDL3 expression in wild-type, WDL3-GFP, and WDL3 (without the GFP tag) transgenic seedlings.
Supplemental Figure 1. The GFP Tag Does Not Disturb the Physiological Functions of WDL3. (A) RT-PCR analysis of WDL3 expression in wild-type, WDL3-GFP, and WDL3 (without the GFP tag) transgenic seedlings.
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Reverse transcribed Quantitative PCR. Total RNA was isolated from bone marrow derived macrophages using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), DNase-treated (Promega RQ1), and reverse transcribed
Supplementary Methods Reverse transcribed Quantitative PCR. Total RNA was isolated from bone marrow derived macrophages using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), DNase-treated (Promega RQ1), and reverse transcribed
SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector
 SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector Richard J. Wall 1,#, Magali Roques 1,+, Nicholas J. Katris
SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector Richard J. Wall 1,#, Magali Roques 1,+, Nicholas J. Katris
Using CRISPR for genetic alteration
 Using CRISPR for genetic alteration Joffrey Mianné. j.mianne@har.mrc.ac.uk Mary Lyon Centre, MRC Harwell. CRISPR/Cas origins Origin of the CRISPR/Cas system: Clustered-Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic
Using CRISPR for genetic alteration Joffrey Mianné. j.mianne@har.mrc.ac.uk Mary Lyon Centre, MRC Harwell. CRISPR/Cas origins Origin of the CRISPR/Cas system: Clustered-Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic
Supplementary Figure 1: sgrna library generation and the length of sgrnas for the functional screen. (a) A diagram of the retroviral vector for sgrna
 Supplementary Figure 1: sgrna library generation and the length of sgrnas for the functional screen. (a) A diagram of the retroviral vector for sgrna expression. It contains a U6-promoter-driven sgrna
Supplementary Figure 1: sgrna library generation and the length of sgrnas for the functional screen. (a) A diagram of the retroviral vector for sgrna expression. It contains a U6-promoter-driven sgrna
Supplemental data. Zhao et al. (2009). The Wuschel-related homeobox gene WOX11 is required to activate shoot-borne crown root development in rice.
 Supplemental data. Zhao et al. (2009). The Wuschel-related homeobox gene WOX11 is required to activate shoot-borne crown root development in rice. A B Supplemental Figure 1. Expression of WOX11p-GUS WOX11-GFP
Supplemental data. Zhao et al. (2009). The Wuschel-related homeobox gene WOX11 is required to activate shoot-borne crown root development in rice. A B Supplemental Figure 1. Expression of WOX11p-GUS WOX11-GFP
Test Bank for Molecular Cell Biology 7th Edition by Lodish
 Test Bank for Molecular Cell Biology 7th Edition by Lodish Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-formolecular-cell-biology-7th-edition-by-lodish/ Chapter 5 Molecular Genetic Techniques
Test Bank for Molecular Cell Biology 7th Edition by Lodish Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-formolecular-cell-biology-7th-edition-by-lodish/ Chapter 5 Molecular Genetic Techniques
Genome research in eukaryotes
 Functional Genomics Genome and EST sequencing can tell us how many POTENTIAL genes are present in the genome Proteomics can tell us about proteins and their interactions The goal of functional genomics
Functional Genomics Genome and EST sequencing can tell us how many POTENTIAL genes are present in the genome Proteomics can tell us about proteins and their interactions The goal of functional genomics
Bart Williams, PhD Van Andel Research Center
 A History of Genome Editing in the Laboratory Implications for Translational Applications Bart Williams, PhD Van Andel Research Center Introduction by Matthew Denenberg, MD DeVos Childrens Hospital Disclosures:
A History of Genome Editing in the Laboratory Implications for Translational Applications Bart Williams, PhD Van Andel Research Center Introduction by Matthew Denenberg, MD DeVos Childrens Hospital Disclosures:
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. ChIP-seq genome browser views of BRM occupancy at previously identified BRM targets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ChIP-seq genome browser views of BRM occupancy at previously identified BRM targets. Gene structures are shown underneath each panel. Supplementary Figure 2 pref6::ref6-gfp complements
Supplementary Figure 1 ChIP-seq genome browser views of BRM occupancy at previously identified BRM targets. Gene structures are shown underneath each panel. Supplementary Figure 2 pref6::ref6-gfp complements
Site directed mutagenesis, Insertional and Deletion Mutagenesis. Mitesh Shrestha
 Site directed mutagenesis, Insertional and Deletion Mutagenesis Mitesh Shrestha Mutagenesis Mutagenesis (the creation or formation of a mutation) can be used as a powerful genetic tool. By inducing mutations
Site directed mutagenesis, Insertional and Deletion Mutagenesis Mitesh Shrestha Mutagenesis Mutagenesis (the creation or formation of a mutation) can be used as a powerful genetic tool. By inducing mutations
Supplemental Data. Zhou et al. (2016). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Confirmation of mutant mapping results. (A) Complementation assay with stably transformed genomic fragments (ComN-N) (2 kb upstream of TSS and 1.5 kb downstream of TES) and CaMV
Supplemental Figure 1. Confirmation of mutant mapping results. (A) Complementation assay with stably transformed genomic fragments (ComN-N) (2 kb upstream of TSS and 1.5 kb downstream of TES) and CaMV
