Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
|
|
|
- Arnold Preston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure 1 Ihh interacts preferentially with its upstream neighboring gene Nhej1. Genes are indicated by gray lines, and Ihh and Nhej1 are highlighted in blue. 4C seq performed in E14.5 limbs using the Ihh promoter as the viewpoint is shown below. Note the increased interactions with intron 3 of the adjacent Nhej1 gene. The gray line indicates the zoomed region displayed in Figure 1. Black bars indicate the size and position of human duplications converted to mouse genome coordinates that overlap with the regulatory landscape of Ihh. Below, Capture-C data from Andrey et al. (2017) at different developmental time points. Chromatin organization is maintained during limb development.
2 Supplementary Figure 2 Conservation of the IHH locus between mouse and human. The upper panel shows a representation of the mouse locus with positions indicated for the genes and regulatory elements investigated (blue and gray ovals). Below, ChIP seq tracks for CTCF with corresponding motif orientation as well as ChIP seq tracks for active enhancer elements (H3K4me1 and H3K27ac); all experiments were performed in developing limbs at E14.5 (ENCODE). The equivalent positions of human pathogenic duplications are shown at the bottom. The lower panel shows a representation of the human locus with the positions of genes and equivalent positions of the regulatory elements investigated in mouse (blue and gray ovals). Below, ChIP seq tracks for CTCF with corresponding motif orientation as well as ChIP seq tracks for active enhancer elements (H3K4me1 and H3K27ac); all are ENCODE data sets for osteoblasts. Note that the convergent orientation of CTCF at the locus is conserved between mouse and human, as well as the presence of active enhancers. The equivalent positions of human pathogenic duplications are shown at the bottom.
3 Supplementary Figure 3 Transgenic reporter assay (LacZ) of elements positive at E17.5. Each element displays a lateral view of the embryo at E14.5 (scale bar, 2,000 m), a dorsal view of the forelimbs (scale bar, 1,000 m) and a top view of the skull at 17.5 (scale bar, 2,000 m) together with tissue specificity scoring (bottom). All tested elements appear positive at E17.5 but not at E14.5 and are marked in Figure 1 in gray. An arrowhead indicates positive staining in the skull. The regulatory activity of the region as indicated by the inserted lacz reporter (SB; black outline) is also displayed.
4 Supplementary Figure 4 Nhej1-knockout mice have normal skulls. µct analysis of adult skulls. The red square indicates enlargement of the metopic suture region, shown on the right. An enlargement of the corresponding cross-section (red arrow) of the metopic sutures is shown below. Note the normal development of sutures in Nhej1- knockout mice as compared to wild-type controls.
5 Supplementary Figure 5 Quantitative expression analysis (qpcr) of mutants at different tissues and stages. (a) Expression analysis of Nhej1. Note that manipulations of the intronic region of the Nhej1 gene do not cause alterations in expression levels overall. (b) Expression analysis of Cnppd1 and Fam134a. Note that the increased contacts observed in 4C seq experiments for Dup(syn) mutants (Fig. 4b, asterisk) do not cause any alteration in the expression levels of the genes. Bars represent the mean of n = 3 different individuals (circles). Two-sided Student's t test, *P < 0.05; ns, not significant.
6 Supplementary Figure 6 Enhancer deletions result in delayed skull ossification and reduced bone length. Left, CT scan of wild-type mouse forelimb and skull displaying the different regions used for measurement. Right, bone measurements for Del(4 6) and Del(7 9) mutants and wild-type age-matched controls (P70). Note the reduction in ulna and nasal suture length for Del(4 6). Del(4 6) shows a more severe effect on digit length than that observed in Del(7 9) mutants. Bars represent the mean of n = 3 different individuals (circles). Two-sided Student's t test, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < ; ns, not significant.
7 Supplementary Figure 7 Expression analysis of genes involved in syndactyly/interdigital cell death. In situ hybridization analysis were performed in E14.5 forelimbs from Dup(syn)/+ mutants and corresponding wt controls. Note increased expression for Bmp4 and Nog as well as expansion of Bmp4 expression in the interdigital space (arrows). Bars represent 200µm.
8 Supplementary Figure 8 Pathogenic structural variants associated to the Ihh locus. Schematic of the mouse locus with coordinates of structural variants indicated by colored bars and associated phenotypes. Positions of human duplications were transformed to the mouse genome. Enhancer elements are displayed with ovals. Duplications are depicted in green and deletions in red. All human variants are heterozygous, all mouse variants are homozygous.
9 Supplementary Figure 9 Limb abnormalities of Dup(syn) mice do not result from increased copies of Ihh gene. (A) Forelimb morphology of duplications. Dup(syn)/+ mice (3 copies of Ihh gene) display 2/5 syndactyly. Skeletal stainings (right) show short and broad terminal phalanges. Dup(syn) mice were crossed to Del(2-9) or Ihh ko in order to have only 2 functional copies of Ihh, both in the duplicated allele. In both cases compound heterozygous displayed the same phenotypical effects. Bars represent 1000µm for P7 and 500µm for E17.5 autopods. (B) CT analysis of wt mouse forelimb at P70 displaying the different regions used for measurement. None of the mutant mice displayed alterations in bone length. Bars represent mean of n 3 different individuals (circles). Two-sided Student's t test, *P< 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < ; ns, not significant.
10 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Construct E14.5 E17.5 Embryos analysed Fingertips Digits Embryos analysed Skulls Growth Plates i i i i i i i i i Supplementary Table 1: Tissue-specific activity of enhancer elements. Each stage shows total number of embryos analyzed for each construct as well as those displaying positive staining for the corresponding tissue. Positive scoring is indicated in bold.
11 Construct Genomic Position Size Guide Sequence Del(2-9), Dup(int) Chr1:75,015,710-75,091,187 75kb N2-L1 gagacacgtggagaattcgc-agg N2-R1 gttacccacactactacgtt-agg Del(4-6) Chr1:75,050,992-75,063,567 13kb N4-L2 ggacacgactttcataacac-tgg N4-R2 aatttcgggtagggcgttgg-agg Del(7-9) Chr1:75,063,567-75,091,187 24kb N4-R2 aatttcgggtagggcgttgg-agg N2-R1 gttacccacactactacgtt-agg Del(4-9) Chr1:75,050,992-75,091,187 37kb N4-L2 ggacacgactttcataacac-tgg N2-R1 gttacccacactactacgtt-agg Dup(syn) Chr1:74,989,792-75,055,634 65kb N9-L9 agcgtggggcttttaaccgt-ggg N9-R6 ttagacacaccagtatacgg-agg Dup(csp) Chr1:75,005,921-75,060,430 54kb N10-L4 ggggcaatctgatatagtgg-ggg N10-R5 tggcccctgacccgtaggat-tgg Supplementary Table 2: Genomic rearrangements generated using CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing. Two sgrnas flanking the target region were used to generate the genomic rearrangement.
12 Construct Genomic Position Size Primer Sequence centromeric homologous arm SB-HR-L1 Chr1:75,055,877-75,058,875 3kb HR3a1-f-SalI tatagtcgaccaaagtccttgtaaggaacagcagt HR3a1-r-ClaI tataatcgatgacatgcctctgctgtacatagttt SB-HR-L2 Chr1:75,058,877-75,060,875 2kb HR3a2-f-F3-ClaI tataatcgattacaagctttacgaagttcctattcttcaaatagtat aggaacttcagcaactcaggaagaattcctaacac HR3a2-r-F3-SacII tataccgcgggtagaagttcctatactatttgaagaataggaactt cttgcagccctcctatagaaaatgga telomeric homologous arm SB-HR-R Chr1:75,060,877-75,063,875 3kb HR3b-f-XhoI tatactcgagtctataagaacacacaacaatgtgccag HR3b-r-NotI tatagcggccgcactgttctgggtgaaccagaaatctt Supplementary Table 3: Homologous arms cloned for the insertion of the SB cassette. Cloning of the centromeric arm (total size 5kb) was performed in two steps (constructs SB-HR-L1 and SB-HR-L2). Restrictions sites are shown in italic/bold.
13 Element Vista ID Primer forward, reverse Genomic Position (mm9) Size (bp) i1 mm1142 ctcagtgtctcaaccacttgaa, chr1:75,008,008-75,012, ctctgccatgacttcttgtgta i2 mm1143 ggtgggattaatctctcgactg, chr1:75,023,290-75,026, ggtgatgaacagcagtatggaa i3 mm1148 tctcccagaccaaaatgcttat, chr1:75,046,263-75,049, aaccttgccctcatgaagttta i4 mm1144 cagactggagttcacagagtgc, chr1:75,051,762-75,053, actcaggcacaagtctagcaca i5 cctctgtgctcttgagttagactac, chr1:75,053,880-75,055,928 cctccttgctagttcttacctaaaga 2045 i6 mm1145 tccttgagagactccagaaagg, chr1:75,059,085-75,064, tcccccatatcagatgtttacc i7 mm1146 gtactgggaaaaatggcaagag, chr1:75,068,299-75,072, ctgaaagggggttagaaggact i8 ttgaggcagaaggattgtcata, chr1:75,075,786-75,080, agccagaggtcaacatttgagt i9 mm1439 gctgagatgaatgacagtgagg, gtcacacctgatgatctgcatt chr1:75,085,302-75,089, Supplementary Table 4: Genomic regions tested for enhancer activity.
14 Primer Gapdh-F Gapdh-R Ihh-F Ihh-R Nhej1-F (exon3+4) Nhej1-R (exon3+4) Nhej1-F (exon2+3) Nhej1-R (exon2+3) Cnppd1-F Cnppd1-R Fam134a-F Fam134a-R Sequence GGGAAGCCCATCACCATCTT CGGCCTCACCCCATTTG GCCGACCGCCTCATGAC CATGACAGAGATGGCCAGTGA TGAAGACAGAGCCATTTGAAGA GCTTTCCATCACCAACAGCA CATTGCTTCGGATGAAGGACC TCAATCGACTTCGGCTCAG CCTATTCGCCGACTCCAGAAA CATTCGTCATTGAAGACCTCCTC CACAAACATGACAAGAGAAAGCG AGCTCAGAGTCTGTAATAGCCA Supplementary Table 5: qpcr primer sequences.
15 Viewpoint 1 st primer (5 3 ) Genomic Position 2 nd primer (5 3 ) Genomic Position Ihh promoter ACAGCTGGGGACCCTATAC chr1:74,998,765-74,998,783 CCCGTCAGGAGGACAATC chr1:75,059,837-75,059,854 Supplementary Table 6: 4C-seq primer sequences. For reference, the mm9 mouse genome was used.
Generation of App knock-in mice reveals deletion mutations protective against Alzheimer s. disease-like pathology. Nagata et al.
 Generation of App knock-in mice reveals deletion mutations protective against Alzheimer s disease-like pathology Nagata et al. Supplementary Fig 1. Previous App knock-in model did not show Aβ accumulation
Generation of App knock-in mice reveals deletion mutations protective against Alzheimer s disease-like pathology Nagata et al. Supplementary Fig 1. Previous App knock-in model did not show Aβ accumulation
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Gómez-Marín et al. 10.1073/pnas.1505463112 SI Materials and Methods Generation of BAC DK74B2-six2a::GFP-six3a::mCherry-iTol2. BAC clone (number 74B2) from DanioKey zebrafish BAC
Supporting Information Gómez-Marín et al. 10.1073/pnas.1505463112 SI Materials and Methods Generation of BAC DK74B2-six2a::GFP-six3a::mCherry-iTol2. BAC clone (number 74B2) from DanioKey zebrafish BAC
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.4166
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Supplementary Information. Optimization of the production of knock-in alleles by CRISPR/Cas9 microinjection into the mouse zygote
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures S1 to S5 and Tables S1 to S3. Optimization of the production of knock-in alleles by CRISPR/Cas9 microinjection into the mouse zygote Aurélien Raveux, Sandrine
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures S1 to S5 and Tables S1 to S3. Optimization of the production of knock-in alleles by CRISPR/Cas9 microinjection into the mouse zygote Aurélien Raveux, Sandrine
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Gene replacements and insertions in rice by intron targeting using CRISPR Cas9 Table of Contents Supplementary Figure 1. sgrna-induced targeted mutations in the OsEPSPS gene in rice protoplasts. Supplementary
Gene replacements and insertions in rice by intron targeting using CRISPR Cas9 Table of Contents Supplementary Figure 1. sgrna-induced targeted mutations in the OsEPSPS gene in rice protoplasts. Supplementary
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3556 INTEGRATED SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE TEMPLATE. Supplementary Figure 1
 INTEGRATED SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE TEMPLATE Supplementary Figure 1 REF6 expression in transgenic lines. (a,b) Expression of REF6 in REF6-HA ref6 and REF6ΔZnF-HA ref6 plants detected by RT qpcr (a) and immunoblot
INTEGRATED SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE TEMPLATE Supplementary Figure 1 REF6 expression in transgenic lines. (a,b) Expression of REF6 in REF6-HA ref6 and REF6ΔZnF-HA ref6 plants detected by RT qpcr (a) and immunoblot
Easi CRISPR for conditional and insertional alleles
 Easi CRISPR for conditional and insertional alleles C.B Gurumurthy, University Of Nebraska Medical Center Omaha, NE cgurumurthy@unmc.edu Types of Genome edits Gene disruption/inactivation Types of Genome
Easi CRISPR for conditional and insertional alleles C.B Gurumurthy, University Of Nebraska Medical Center Omaha, NE cgurumurthy@unmc.edu Types of Genome edits Gene disruption/inactivation Types of Genome
Supplementary Figure 1 Activities of ABEs using extended sgrnas in HEK293T cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activities of ABEs using extended sgrnas in HEK293T cells. Base editing efficiencies of ABEs with extended sgrnas at Site 18 (a), Site 19 (b), the HBB-E2 site (c), and the HBB-E3
Supplementary Figure 1 Activities of ABEs using extended sgrnas in HEK293T cells. Base editing efficiencies of ABEs with extended sgrnas at Site 18 (a), Site 19 (b), the HBB-E2 site (c), and the HBB-E3
Revised: RG-RV2 by Fukuhara et al.
 Supplemental Figure 1 The generation of Spns2 conditional knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the wild type Spns2 locus (Spns2 + ), the targeted allele, the floxed allele (Spns2 f ) and the
Supplemental Figure 1 The generation of Spns2 conditional knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the wild type Spns2 locus (Spns2 + ), the targeted allele, the floxed allele (Spns2 f ) and the
You use the UCSC Genome Browser (www.genome.ucsc.edu) to assess the exonintron structure of each gene. You use four tracks to show each gene:
 CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing Part 1: You would like to rapidly generate two different knockout mice using CRISPR-Cas9. The genes to be knocked out are Pcsk9 and Apoc3, both involved in lipid metabolism.
CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing Part 1: You would like to rapidly generate two different knockout mice using CRISPR-Cas9. The genes to be knocked out are Pcsk9 and Apoc3, both involved in lipid metabolism.
Supplemental Data. Zhou et al. (2016). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Confirmation of mutant mapping results. (A) Complementation assay with stably transformed genomic fragments (ComN-N) (2 kb upstream of TSS and 1.5 kb downstream of TES) and CaMV
Supplemental Figure 1. Confirmation of mutant mapping results. (A) Complementation assay with stably transformed genomic fragments (ComN-N) (2 kb upstream of TSS and 1.5 kb downstream of TES) and CaMV
PIE1 ARP6 SWC6 KU70 ARP6 PIE1. HSA SNF2_N HELICc SANT. pie1-3 A1,A2 K1,K2 K1,K3 K3,LB2 A3, A4 A3,LB1 A1,A2 K1,K2 K1,K3. swc6-1 A3,A4.
 A B N-terminal SWC2 H2A.Z SWC6 ARP6 PIE1 HSA SNF2_N HELICc SANT C pie1-3 D PIE1 ARP6 5 Kb A1 200 bp A3 A2 LB1 arp6-3 A4 E A1,A2 A3, A4 A3,LB1 K1,K2 K1,K3 K3,LB2 SWC6 swc6-1 A1,A2 A3,A4 K1,K2 K1,K3 100
A B N-terminal SWC2 H2A.Z SWC6 ARP6 PIE1 HSA SNF2_N HELICc SANT C pie1-3 D PIE1 ARP6 5 Kb A1 200 bp A3 A2 LB1 arp6-3 A4 E A1,A2 A3, A4 A3,LB1 K1,K2 K1,K3 K3,LB2 SWC6 swc6-1 A1,A2 A3,A4 K1,K2 K1,K3 100
Ramp1 EPD0843_4_B11. EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping
 EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping Introduction The majority of animals produced from the EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD ES cell resource contain the Knockout-First-Reporter Tagged Insertion allele. As well as
EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping Introduction The majority of animals produced from the EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD ES cell resource contain the Knockout-First-Reporter Tagged Insertion allele. As well as
Usp14 EPD0582_2_G09. EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping
 EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping Introduction The majority of animals produced from the EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD ES cell resource contain the Knockout-First-Reporter Tagged Insertion allele. As well as
EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping Introduction The majority of animals produced from the EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD ES cell resource contain the Knockout-First-Reporter Tagged Insertion allele. As well as
Optimizing Cas9 and sgrna concentrations for increasing mutation efficiency. Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.3360
 Supplementary Figure 1 Optimizing Cas9 and sgrna concentrations for increasing mutation efficiency. (a) Wild-type, 2-dpf slc24a5 b1 embryos and a series of slc24a5 CRISPR-injected embryos; anterior is
Supplementary Figure 1 Optimizing Cas9 and sgrna concentrations for increasing mutation efficiency. (a) Wild-type, 2-dpf slc24a5 b1 embryos and a series of slc24a5 CRISPR-injected embryos; anterior is
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Super-resolution imaging of fluorescently labeled, endogenous RNA Polymerase II in living cells with CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing Won-Ki Cho 1, Namrata Jayanth 1, Susan Mullen
Supplementary Information Super-resolution imaging of fluorescently labeled, endogenous RNA Polymerase II in living cells with CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing Won-Ki Cho 1, Namrata Jayanth 1, Susan Mullen
Supplemental Figure 1.
 Supplemental Data. Charron et al. Dynamic landscapes of four histone modifications during de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell (2009). 10.1105/tpc.109.066845 Supplemental Figure 1. Immunodetection
Supplemental Data. Charron et al. Dynamic landscapes of four histone modifications during de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell (2009). 10.1105/tpc.109.066845 Supplemental Figure 1. Immunodetection
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information MicroRNA-212/132 family is required for epithelial stromal interactions necessary for mouse mammary gland development Ahmet Ucar, Vida Vafaizadeh, Hubertus Jarry, Jan Fiedler,
Supplementary Information MicroRNA-212/132 family is required for epithelial stromal interactions necessary for mouse mammary gland development Ahmet Ucar, Vida Vafaizadeh, Hubertus Jarry, Jan Fiedler,
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Reverse transcribed Quantitative PCR. Total RNA was isolated from bone marrow derived macrophages using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), DNase-treated (Promega RQ1), and reverse transcribed
Supplementary Methods Reverse transcribed Quantitative PCR. Total RNA was isolated from bone marrow derived macrophages using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), DNase-treated (Promega RQ1), and reverse transcribed
Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 )
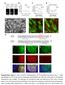 Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 ) homologous recombination arm (left) and of the right (3 )
Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 ) homologous recombination arm (left) and of the right (3 )
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary figures and supplementary tables. File name: Peer review file Description:
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary figures and supplementary tables. File name: Peer review file Description: Supplementary Figure 1. dcas9-mq1 fusion protein induces de novo
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary figures and supplementary tables. File name: Peer review file Description: Supplementary Figure 1. dcas9-mq1 fusion protein induces de novo
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. ChIP-seq genome browser views of BRM occupancy at previously identified BRM targets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ChIP-seq genome browser views of BRM occupancy at previously identified BRM targets. Gene structures are shown underneath each panel. Supplementary Figure 2 pref6::ref6-gfp complements
Supplementary Figure 1 ChIP-seq genome browser views of BRM occupancy at previously identified BRM targets. Gene structures are shown underneath each panel. Supplementary Figure 2 pref6::ref6-gfp complements
CRISPR/Cas9 Mouse Production
 CRISPR/Cas9 Mouse Production Emory Transgenic and Gene Targeting Core http://cores.emory.edu/tmc Tamara Caspary, Ph.D. Scientific Director Teresa Quackenbush --- Lab Operations and Communications Coordinator
CRISPR/Cas9 Mouse Production Emory Transgenic and Gene Targeting Core http://cores.emory.edu/tmc Tamara Caspary, Ph.D. Scientific Director Teresa Quackenbush --- Lab Operations and Communications Coordinator
SUPPLEMENT MATERIALS FOR CURTIN,
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 SUPPLEMENT MATERIALS FOR CURTIN, et al. Validating genome-wide association candidates: Selecting, testing, and characterizing
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 SUPPLEMENT MATERIALS FOR CURTIN, et al. Validating genome-wide association candidates: Selecting, testing, and characterizing
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Liz/Zdbf2 dynamics in vivo and in vitro.
 Supplementary igure 1 Liz/Zdbf2 dynamics in vivo and in vitro. (a) Schematic of Liz/Zdbf2 regulation during early development. Summary from Duffié et al. 18. Liz transcript initiates from the unmethylated
Supplementary igure 1 Liz/Zdbf2 dynamics in vivo and in vitro. (a) Schematic of Liz/Zdbf2 regulation during early development. Summary from Duffié et al. 18. Liz transcript initiates from the unmethylated
Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified
 Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified by primers used for mrna expression analysis. Gray
Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified by primers used for mrna expression analysis. Gray
Supplemental Information. Autoregulatory Feedback Controls. Sequential Action of cis-regulatory Modules. at the brinker Locus
 Developmental Cell, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Autoregulatory Feedback Controls Sequential Action of cis-regulatory Modules at the brinker Locus Leslie Dunipace, Abbie Saunders, Hilary L. Ashe,
Developmental Cell, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Autoregulatory Feedback Controls Sequential Action of cis-regulatory Modules at the brinker Locus Leslie Dunipace, Abbie Saunders, Hilary L. Ashe,
Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Supplementary Information. Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish
 Supplementary Information Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish Hagen R. Witzel 1, Sirisha Cheedipudi 1, Rui Gao 1, Didier Y.R. Stainier 2 and Gergana D. Dobreva 1,3* 1 Origin
Supplementary Information Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish Hagen R. Witzel 1, Sirisha Cheedipudi 1, Rui Gao 1, Didier Y.R. Stainier 2 and Gergana D. Dobreva 1,3* 1 Origin
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3494
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
A CRISPR/Cas9 Vector System for Tissue-Specific Gene Disruption in Zebrafish
 Developmental Cell Supplemental Information A CRISPR/Cas9 Vector System for Tissue-Specific Gene Disruption in Zebrafish Julien Ablain, Ellen M. Durand, Song Yang, Yi Zhou, and Leonard I. Zon % larvae
Developmental Cell Supplemental Information A CRISPR/Cas9 Vector System for Tissue-Specific Gene Disruption in Zebrafish Julien Ablain, Ellen M. Durand, Song Yang, Yi Zhou, and Leonard I. Zon % larvae
Zhang et al., RepID facilitates replication Initiation. Supplemental Information:
 Supplemental Information: a b 1 Supplementary Figure 1 (a) DNA sequence of all the oligonucleotides used in this study. Only one strand is shown. The unshaded nucleotide sequences show changes from the
Supplemental Information: a b 1 Supplementary Figure 1 (a) DNA sequence of all the oligonucleotides used in this study. Only one strand is shown. The unshaded nucleotide sequences show changes from the
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous gene tagging to study subcellular localization and chromatin binding. a, b, Schematic of experimental set-up to endogenously tag RNAi factors using the CRISPR Cas9 technology,
Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous gene tagging to study subcellular localization and chromatin binding. a, b, Schematic of experimental set-up to endogenously tag RNAi factors using the CRISPR Cas9 technology,
TALEN mediated targeted editing of GM2/GD2-synthase gene modulates anchorage independent growth by reducing anoikis resistance in mouse tumor cells
 Supplementary Information for TALEN mediated targeted editing of GM2/GD2-synthase gene modulates anchorage independent growth by reducing anoikis resistance in mouse tumor cells Barun Mahata 1, Avisek
Supplementary Information for TALEN mediated targeted editing of GM2/GD2-synthase gene modulates anchorage independent growth by reducing anoikis resistance in mouse tumor cells Barun Mahata 1, Avisek
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1 shrna mediated knockdown of ZRSR2 in K562 and 293T cells. (a) ZRSR2 transcript levels in stably transduced K562 cells were determined using qrt-pcr. GAPDH was
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1 shrna mediated knockdown of ZRSR2 in K562 and 293T cells. (a) ZRSR2 transcript levels in stably transduced K562 cells were determined using qrt-pcr. GAPDH was
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. (A) UCSC Genome Browser view of region immediately downstream of the NEUROG3 start codon. All candidate grna target sites which meet the G(N 19 )NGG constraint are aligned to illustrate
Supplementary Figure 1. (A) UCSC Genome Browser view of region immediately downstream of the NEUROG3 start codon. All candidate grna target sites which meet the G(N 19 )NGG constraint are aligned to illustrate
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 AS-NMD modulates FLM-dependent thermosensory flowering response in Arabidopsis NATURE PLANTS www.nature.com/natureplants 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Genomic sequence of FLM along with the splice sites. Sequencing
AS-NMD modulates FLM-dependent thermosensory flowering response in Arabidopsis NATURE PLANTS www.nature.com/natureplants 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Genomic sequence of FLM along with the splice sites. Sequencing
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS
 SUPPLEMENL MERILS Eh-seq: RISPR epitope tagging hip-seq of DN-binding proteins Daniel Savic, E. hristopher Partridge, Kimberly M. Newberry, Sophia. Smith, Sarah K. Meadows, rian S. Roberts, Mark Mackiewicz,
SUPPLEMENL MERILS Eh-seq: RISPR epitope tagging hip-seq of DN-binding proteins Daniel Savic, E. hristopher Partridge, Kimberly M. Newberry, Sophia. Smith, Sarah K. Meadows, rian S. Roberts, Mark Mackiewicz,
Supplementary Fig. 1
 a FL (1-2266) NL (1-1190) CL (1191-2266) HA-ICE1: - HA-ICE1: - - - FLAG-ICE2: + + + + FLAG-ELL: + + + + + + IP: anti-ha FLAG-ICE2 HA-ICE1-FL HA-ICE1-NL HA-ICE1-CL FLAG-ICE2 b IP: anti-ha FL (1-2266) NL
a FL (1-2266) NL (1-1190) CL (1191-2266) HA-ICE1: - HA-ICE1: - - - FLAG-ICE2: + + + + FLAG-ELL: + + + + + + IP: anti-ha FLAG-ICE2 HA-ICE1-FL HA-ICE1-NL HA-ICE1-CL FLAG-ICE2 b IP: anti-ha FL (1-2266) NL
Map-Based Cloning of Qualitative Plant Genes
 Map-Based Cloning of Qualitative Plant Genes Map-based cloning using the genetic relationship between a gene and a marker as the basis for beginning a search for a gene Chromosome walking moving toward
Map-Based Cloning of Qualitative Plant Genes Map-based cloning using the genetic relationship between a gene and a marker as the basis for beginning a search for a gene Chromosome walking moving toward
Supplementary Table 3d: PCR primers for genomic sequencing-based phasereconstruction
 Supplementary Table 3: Detailed lists of grnas, primers, donor constructs, antibodies, Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) identifiers for Chip-seq and DHSs datasets and CRISPR/Cas9 genome edited cell lines
Supplementary Table 3: Detailed lists of grnas, primers, donor constructs, antibodies, Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) identifiers for Chip-seq and DHSs datasets and CRISPR/Cas9 genome edited cell lines
Supplementary Figure 1. Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings.
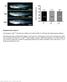 Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
Identification and characterization of a pathogenicity-related gene VdCYP1 from Verticillium dahliae
 Identification and characterization of a pathogenicity-related gene VdCYP1 from Verticillium dahliae Dan-Dan Zhang*, Xin-Yan Wang*, Jie-Yin Chen*, Zhi-Qiang Kong, Yue-Jing Gui, Nan-Yang Li, Yu-Ming Bao,
Identification and characterization of a pathogenicity-related gene VdCYP1 from Verticillium dahliae Dan-Dan Zhang*, Xin-Yan Wang*, Jie-Yin Chen*, Zhi-Qiang Kong, Yue-Jing Gui, Nan-Yang Li, Yu-Ming Bao,
Supplemental Figure 1 A
 Supplemental Figure 1 A Supplemental Data. Han et al. (2016). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.15.00997 BamHI -1616 bp SINE repeats SalI ATG SacI +1653 bp HindIII LB HYG p35s pfwa LUC Tnos RB pfwa-bamhi-f: CGGGATCCCGCCTTTCTCTTCCTCATCTGC
Supplemental Figure 1 A Supplemental Data. Han et al. (2016). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.15.00997 BamHI -1616 bp SINE repeats SalI ATG SacI +1653 bp HindIII LB HYG p35s pfwa LUC Tnos RB pfwa-bamhi-f: CGGGATCCCGCCTTTCTCTTCCTCATCTGC
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Product purity of cytosine base editing for the wheat genomic loci tested. Product distributions and indels frequencies at four representative wheat genomic DNA sites in wheat protoplasts
Supplementary Figure 1 Product purity of cytosine base editing for the wheat genomic loci tested. Product distributions and indels frequencies at four representative wheat genomic DNA sites in wheat protoplasts
(a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of Diaph3 ko mice. (a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for different regions of Diaph3 mrna from WT, heterozygote
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of Diaph3 ko mice. (a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for different regions of Diaph3 mrna from WT, heterozygote
Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably expressing shrna sequences against TRF2 were examined by western blotting. shcon, shrna
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably expressing shrna sequences against TRF2 were examined by western blotting. shcon, shrna
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fujii et al. 10.1073/pnas.1217563110 A Human Cen chromosome 4q ART3 NUP54 SCARB2 FAM47E CCDC8 Tel B Bac clones RP11-54D17 RP11-628A4 Exon 1 2 34 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 5 3 PCR region
Supporting Information Fujii et al. 10.1073/pnas.1217563110 A Human Cen chromosome 4q ART3 NUP54 SCARB2 FAM47E CCDC8 Tel B Bac clones RP11-54D17 RP11-628A4 Exon 1 2 34 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 5 3 PCR region
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS. -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells. - Two methods to produce transgenic animals:
 TRANSGENIC ANIMALS -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection - random insertion 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated gene
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection - random insertion 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated gene
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
GENOME 371, Problem Set 6
 GENOME 371, Problem Set 6 1. S. pombe is a distant relative of baker s yeast (which you used in quiz section). Wild type S. pombe can grow on plates lacking tryptophan (-trp plates). A mutant has been
GENOME 371, Problem Set 6 1. S. pombe is a distant relative of baker s yeast (which you used in quiz section). Wild type S. pombe can grow on plates lacking tryptophan (-trp plates). A mutant has been
A novel tool for monitoring endogenous alpha-synuclein transcription by NanoLuciferase
 A novel tool for monitoring endogenous alpha-synuclein transcription by NanoLuciferase tag insertion at the 3 end using CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing technique Sambuddha Basu 1, 3, Levi Adams 1, 3, Subhrangshu
A novel tool for monitoring endogenous alpha-synuclein transcription by NanoLuciferase tag insertion at the 3 end using CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing technique Sambuddha Basu 1, 3, Levi Adams 1, 3, Subhrangshu
Supplementary Figures and Figure legends
 Supplementary Figures and Figure legends 3 Supplementary Figure 1. Conditional targeting construct for the murine Satb1 locus with a modified FLEX switch. Schematic of the wild type Satb1 locus; the conditional
Supplementary Figures and Figure legends 3 Supplementary Figure 1. Conditional targeting construct for the murine Satb1 locus with a modified FLEX switch. Schematic of the wild type Satb1 locus; the conditional
Supplemental Data. Guo et al. (2015). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. The Mutant exb1-d Displayed Pleiotropic Phenotypes and Produced Branches in the Axils of Cotyledons. (A) Branches were developed in exb1-d but not in wild-type plants. (B) and (C)
Supplemental Figure 1. The Mutant exb1-d Displayed Pleiotropic Phenotypes and Produced Branches in the Axils of Cotyledons. (A) Branches were developed in exb1-d but not in wild-type plants. (B) and (C)
Jung-Nam Cho, Jee-Youn Ryu, Young-Min Jeong, Jihye Park, Ji-Joon Song, Richard M. Amasino, Bosl Noh, and Yoo-Sun Noh
 Developmental Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Control of Seed Germination by Light-Induced Histone Arginine Demethylation Activity Jung-Nam Cho, Jee-Youn Ryu, Young-Min Jeong, Jihye Park, Ji-Joon
Developmental Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Control of Seed Germination by Light-Induced Histone Arginine Demethylation Activity Jung-Nam Cho, Jee-Youn Ryu, Young-Min Jeong, Jihye Park, Ji-Joon
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature09861 & &' -(' ()*+ ')(+,,(','-*+,&,,+ ',+' ' 23,45/0*6787*9:./09 ;78?4?@*+A786?B- &' )*+*(,-* -(' ()*+ ')(+,,(','-*+,&,,+ ',+'./)*+*(,-*..)*+*(,-*./)*+*(,-*.0)*+*(,-*..)*+*(,-*
doi:10.1038/nature09861 & &' -(' ()*+ ')(+,,(','-*+,&,,+ ',+' ' 23,45/0*6787*9:./09 ;78?4?@*+A786?B- &' )*+*(,-* -(' ()*+ ')(+,,(','-*+,&,,+ ',+'./)*+*(,-*..)*+*(,-*./)*+*(,-*.0)*+*(,-*..)*+*(,-*
Genome-wide genetic screening with chemically-mutagenized haploid embryonic stem cells
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Supplementary Information Genome-wide genetic screening with chemically-mutagenized haploid embryonic stem cells Josep V. Forment 1,2, Mareike Herzog
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Supplementary Information Genome-wide genetic screening with chemically-mutagenized haploid embryonic stem cells Josep V. Forment 1,2, Mareike Herzog
Supplementary Fig. 1 Generation and genotyping of ThPOK / mice
 Supplementary Fig. 1 Generation and genotyping of ThPOK / mice (a). The strategy used to target the ThPOK locus is schematically depicted. A targeting construct was generated by inserting a loxp site (filled
Supplementary Fig. 1 Generation and genotyping of ThPOK / mice (a). The strategy used to target the ThPOK locus is schematically depicted. A targeting construct was generated by inserting a loxp site (filled
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Synthetic annealed poly(ra):poly(dt) hybrid induces type I interferon response. a) Bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) were transfected with or without
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Synthetic annealed poly(ra):poly(dt) hybrid induces type I interferon response. a) Bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) were transfected with or without
Table 1.C.1 Example of Hazardous Materials Identification System. Name of chemical. Personal protection equipment. Table 1.C.2 Example NFPA table.
 Table 1.C.1 Example of Hazardous Materials Identification System. Name of chemical Health Flammability Reactivity Personal protection equipment Table 1.C.2 Example NFPA table. Fire Health Reactivity Specific
Table 1.C.1 Example of Hazardous Materials Identification System. Name of chemical Health Flammability Reactivity Personal protection equipment Table 1.C.2 Example NFPA table. Fire Health Reactivity Specific
 Figure S1. Generation of HspA4 -/- mice. (A) Structures of the wild-type (Wt) HspA4 -/- allele, targeting vector and targeted allele are shown together with the relevant restriction sites. The filled rectangles
Figure S1. Generation of HspA4 -/- mice. (A) Structures of the wild-type (Wt) HspA4 -/- allele, targeting vector and targeted allele are shown together with the relevant restriction sites. The filled rectangles
Supplementary Figures Montero et al._supplementary Figure 1
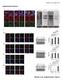 Montero et al_suppl. Info 1 Supplementary Figures Montero et al._supplementary Figure 1 Montero et al_suppl. Info 2 Supplementary Figure 1. Transcripts arising from the structurally conserved subtelomeres
Montero et al_suppl. Info 1 Supplementary Figures Montero et al._supplementary Figure 1 Montero et al_suppl. Info 2 Supplementary Figure 1. Transcripts arising from the structurally conserved subtelomeres
Trasposable elements: Uses of P elements Problem set B at the end
 Trasposable elements: Uses of P elements Problem set B at the end P-elements have revolutionized the way Drosophila geneticists conduct their research. Here, we will discuss just a few of the approaches
Trasposable elements: Uses of P elements Problem set B at the end P-elements have revolutionized the way Drosophila geneticists conduct their research. Here, we will discuss just a few of the approaches
(i) A trp1 mutant cell took up a plasmid containing the wild type TRP1 gene, which allowed that cell to multiply and form a colony
 1. S. pombe is a distant relative of baker s yeast (which you used in quiz section). Wild type S. pombe can grow on plates lacking tryptophan (-trp plates). A mutant has been isolated that cannot grow
1. S. pombe is a distant relative of baker s yeast (which you used in quiz section). Wild type S. pombe can grow on plates lacking tryptophan (-trp plates). A mutant has been isolated that cannot grow
Rassf1a -/- Sav1 +/- mice. Supplementary Figures:
 1 Supplementary Figures: Figure S1: Genotyping of Rassf1a and Sav1 mutant mice. A. Rassf1a knockout mice lack exon 1 of the Rassf1 gene. A diagram and typical PCR genotyping of wildtype and Rassf1a -/-
1 Supplementary Figures: Figure S1: Genotyping of Rassf1a and Sav1 mutant mice. A. Rassf1a knockout mice lack exon 1 of the Rassf1 gene. A diagram and typical PCR genotyping of wildtype and Rassf1a -/-
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
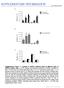 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12474 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of mtdna mutation loads in different types of mtdna mutator mice. a, PCR, cloning, and sequencing analysis of mtdna mutations
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12474 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of mtdna mutation loads in different types of mtdna mutator mice. a, PCR, cloning, and sequencing analysis of mtdna mutations
LRBA is Essential for Allogeneic Responses in Bone Marrow Transplantation
 LRBA is Essential for Allogeneic Responses in Bone Marrow Transplantation Mi Young Park, 1# Raki Sudan, 1# Neetu Srivastava, 1 Sudha Neelam, 1 Christie Youngs, 1 Jia- Wang Wang, 4 Robert W. Engelman, 5,6,7
LRBA is Essential for Allogeneic Responses in Bone Marrow Transplantation Mi Young Park, 1# Raki Sudan, 1# Neetu Srivastava, 1 Sudha Neelam, 1 Christie Youngs, 1 Jia- Wang Wang, 4 Robert W. Engelman, 5,6,7
Figure S1. Figure S2. Figure S3 HB Anti-FSP27 (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab. Anti-GST-FSP27(45-127) Ab.
 / 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
/ 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
A Naturally Occurring Epiallele associates with Leaf Senescence and Local Climate Adaptation in Arabidopsis accessions He et al.
 A Naturally Occurring Epiallele associates with Leaf Senescence and Local Climate Adaptation in Arabidopsis accessions He et al. Supplementary Notes Origin of NMR19 elements Because there are two copies
A Naturally Occurring Epiallele associates with Leaf Senescence and Local Climate Adaptation in Arabidopsis accessions He et al. Supplementary Notes Origin of NMR19 elements Because there are two copies
A Low salt diet. C Low salt diet + mf4-31c1 3. D High salt diet + mf4-31c1 3. B High salt diet
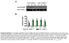 A Low salt diet GV [AU]:. [mmhg]: 0..... 09 9 7 B High salt diet GV [AU]:. [mmhg]: 7 8...0. 7.8 8.. 0 8 7 C Low salt diet + mf-c GV [AU]:. [mmhg]:.0.9 8.7.7. 7 8 0 D High salt diet + mf-c E Lymph capillary
A Low salt diet GV [AU]:. [mmhg]: 0..... 09 9 7 B High salt diet GV [AU]:. [mmhg]: 7 8...0. 7.8 8.. 0 8 7 C Low salt diet + mf-c GV [AU]:. [mmhg]:.0.9 8.7.7. 7 8 0 D High salt diet + mf-c E Lymph capillary
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of Hi-C/CHi-C dynamics and enhancer identification. (a) Scatterplot of Hi-C read counts supporting contacts between domain boundaries. Contacts enclosing domains
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of Hi-C/CHi-C dynamics and enhancer identification. (a) Scatterplot of Hi-C read counts supporting contacts between domain boundaries. Contacts enclosing domains
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of migg1-yf mice. (A) Targeting strategy. Upper panel: schematic organization of the murine ɣ1 immunoglobulin
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of migg1-yf mice. (A) Targeting strategy. Upper panel: schematic organization of the murine ɣ1 immunoglobulin locus. The EcoRI restriction site between exons M1 and M2
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of migg1-yf mice. (A) Targeting strategy. Upper panel: schematic organization of the murine ɣ1 immunoglobulin locus. The EcoRI restriction site between exons M1 and M2
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.2949
 Supplementary Figure 1. Abnormal differentiation in vivo and colony growth in vitro of B cells with triplication of chr.21 orthologs. (a) (Top) B220 and CD43 staining of bone marrow from Ts1Rhr and wild-type
Supplementary Figure 1. Abnormal differentiation in vivo and colony growth in vitro of B cells with triplication of chr.21 orthologs. (a) (Top) B220 and CD43 staining of bone marrow from Ts1Rhr and wild-type
Supplemental Data. Jing et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Characterization of epp1 Mutants. (A) Cotyledon angles of 5-d-old Col wild-type (gray bars) and epp1-1 (black bars) seedlings under red (R), far-red (FR) and blue (BL) light conditions,
Supplemental Figure 1. Characterization of epp1 Mutants. (A) Cotyledon angles of 5-d-old Col wild-type (gray bars) and epp1-1 (black bars) seedlings under red (R), far-red (FR) and blue (BL) light conditions,
Erhard et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. c1-hbr allele structure. Diagram of the c1-hbr allele found in stocks segregating 1:1 for rpd1-1 and rpd1-2 homozygous mutants showing the presence of a 363 base pair (bp) Heartbreaker
Supplemental Figure 1. c1-hbr allele structure. Diagram of the c1-hbr allele found in stocks segregating 1:1 for rpd1-1 and rpd1-2 homozygous mutants showing the presence of a 363 base pair (bp) Heartbreaker
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of inducible BICD2 knock-out mice. A) The mouse BICD2 locus and gene targeting constructs. To generate an inducible Bicd2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of inducible BICD2 knock-out mice. A) The mouse BICD2 locus and gene targeting constructs. To generate an inducible Bicd2
sides of the aleurone (Al) but it is excluded from the basal endosperm transfer layer
 Supplemental Data. Gómez et al. (2009). The maize transcription factor MRP-1 (Myb-Related-Protein-1) is a key regulator of the differentiation of transfer cells. Supplemental Figure 1. Expression analyses
Supplemental Data. Gómez et al. (2009). The maize transcription factor MRP-1 (Myb-Related-Protein-1) is a key regulator of the differentiation of transfer cells. Supplemental Figure 1. Expression analyses
NAME TA SEC Problem Set 4 FRIDAY October 15, Answers to this problem set must be inserted into the box outside
 MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel NAME TA SEC 7.012 Problem Set 4 FRIDAY October 15,
MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel NAME TA SEC 7.012 Problem Set 4 FRIDAY October 15,
Supplementary Tables. Primers and probes. Target Primer / probe sequences Chemistry Human HBB F: AACTGTGTTCACTAGCAACCTCAAA
 Supplementary Tables Primers and probes Target Primer / probe sequences Chemistry H F: AACTGTGTTCACTAGCAACCTCAAA promoter R: ACAGGGCAGTAACGGCAGACT H Downstream Actb alpha (162) alpha (162.) (Pro) (16)
Supplementary Tables Primers and probes Target Primer / probe sequences Chemistry H F: AACTGTGTTCACTAGCAACCTCAAA promoter R: ACAGGGCAGTAACGGCAGACT H Downstream Actb alpha (162) alpha (162.) (Pro) (16)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature875 a promoter firefly luciferase CNS b Supplementary Figure 1. Dual luciferase assays on enhancer activity of CNS1, 2, and 3. a. promoter sequence was inserted upstream of firefly luciferase
doi: 1.138/nature875 a promoter firefly luciferase CNS b Supplementary Figure 1. Dual luciferase assays on enhancer activity of CNS1, 2, and 3. a. promoter sequence was inserted upstream of firefly luciferase
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Negative selection analysis of sgrnas targeting all Brd4 exons comparing day 2 to day 10 time points. Systematic evaluation of 64 Brd4 sgrnas in negative selection experiments, targeting
Supplementary Figure 1 Negative selection analysis of sgrnas targeting all Brd4 exons comparing day 2 to day 10 time points. Systematic evaluation of 64 Brd4 sgrnas in negative selection experiments, targeting
Growth factor, augmenter of liver regeneration
 Supplemental Table 1: Human and mouse PC1 sequence equivalencies Human Mouse Domain Clinical significance; Score* PolyPhen prediction; PSIC score difference C210G C210G WSC Highly likely pathogenic; 15
Supplemental Table 1: Human and mouse PC1 sequence equivalencies Human Mouse Domain Clinical significance; Score* PolyPhen prediction; PSIC score difference C210G C210G WSC Highly likely pathogenic; 15
Supplementary Figure 1. CRISPR/Cas9-induced targeted mutations in TaGASR7, TaDEP1, TaNAC2, TaPIN1, TaLOX2 and TaGW2 genes in wheat protoplasts.
 Supplementary Figure 1. CRISPR/Cas9-induced targeted mutations in TaGASR7, TaDEP1, TaNAC2, TaPIN1, TaLOX2 and TaGW2 genes in wheat protoplasts. Lanes 1 and 2: digested CRISPR/Cas9-transformed protoplasts;
Supplementary Figure 1. CRISPR/Cas9-induced targeted mutations in TaGASR7, TaDEP1, TaNAC2, TaPIN1, TaLOX2 and TaGW2 genes in wheat protoplasts. Lanes 1 and 2: digested CRISPR/Cas9-transformed protoplasts;
Sperm cells are passive cargo of the pollen tube in plant fertilization
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 3 ARTICLE NUMBER: 17079 Sperm cells are passive cargo of the pollen tube in plant fertilization Jun Zhang 1, Qingpei
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 3 ARTICLE NUMBER: 17079 Sperm cells are passive cargo of the pollen tube in plant fertilization Jun Zhang 1, Qingpei
A) (5 points) As the starting step isolate genomic DNA from
 GS Final Exam Spring 00 NAME. bub ts is a recessive temperature sensitive mutation in yeast. At º C bub ts cells grow normally, but at º C they die. Use the information below to clone the wild-type BUB
GS Final Exam Spring 00 NAME. bub ts is a recessive temperature sensitive mutation in yeast. At º C bub ts cells grow normally, but at º C they die. Use the information below to clone the wild-type BUB
6/256 1/256 0/256 1/256 2/256 7/256 10/256. At3g06290 (SAC3B)
 Chr.III M 5M 1M 15M 2M 23M BAC clones F22F7 F1A16 F24F17 F24P17 T8E24 F17A9 F21O3 F17A17 F18C1 F2O1 F28L1 F5E6 F3E22 T1B9 MLP3 Number of recombinants 6/256 1/256 /256 1/256 2/256 7/256 1/256 At3g629 (SAC3B)
Chr.III M 5M 1M 15M 2M 23M BAC clones F22F7 F1A16 F24F17 F24P17 T8E24 F17A9 F21O3 F17A17 F18C1 F2O1 F28L1 F5E6 F3E22 T1B9 MLP3 Number of recombinants 6/256 1/256 /256 1/256 2/256 7/256 1/256 At3g629 (SAC3B)
Pei et al. Supplementary Figure S1
 Pei et al. Supplementary Figure S1 C H-CUL9: + + + + + Myc-ROC1: - - + + + U2OS/pcDN3 U2OS/H-CUL9 U2OS/ + H-CUL9 IP: -H -myc input -H -myc 1 2 3 4 5 H-CUL9 Myc-ROC1 -H -H -H -H H-CUL9: wt RR myc-roc1:
Pei et al. Supplementary Figure S1 C H-CUL9: + + + + + Myc-ROC1: - - + + + U2OS/pcDN3 U2OS/H-CUL9 U2OS/ + H-CUL9 IP: -H -myc input -H -myc 1 2 3 4 5 H-CUL9 Myc-ROC1 -H -H -H -H H-CUL9: wt RR myc-roc1:
Supplementary Fig. S1. Building a training set of cardiac enhancers. (A-E) Empirical validation of candidate enhancers containing matches to Twi and
 Supplementary Fig. S1. Building a training set of cardiac enhancers. (A-E) Empirical validation of candidate enhancers containing matches to Twi and Tin TFBS motifs and located in the flanking or intronic
Supplementary Fig. S1. Building a training set of cardiac enhancers. (A-E) Empirical validation of candidate enhancers containing matches to Twi and Tin TFBS motifs and located in the flanking or intronic
Supplementary Table S1
 Primers used in RT-qPCR, ChIP and Bisulphite-Sequencing. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR primers Supplementary Table S1 gene Forward primer sequence Reverse primer sequence Product TRAIL CAACTCCGTCAGCTCGTTAGAAAG
Primers used in RT-qPCR, ChIP and Bisulphite-Sequencing. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR primers Supplementary Table S1 gene Forward primer sequence Reverse primer sequence Product TRAIL CAACTCCGTCAGCTCGTTAGAAAG
Supplementary information, Figure S1
 Supplementary information, Figure S1 (A) Schematic diagram of the sgrna and hspcas9 expression cassettes in a single binary vector designed for Agrobacterium-mediated stable transformation of Arabidopsis
Supplementary information, Figure S1 (A) Schematic diagram of the sgrna and hspcas9 expression cassettes in a single binary vector designed for Agrobacterium-mediated stable transformation of Arabidopsis
Analysis of gene function
 Genome 371, 22 February 2010, Lecture 12 Analysis of gene function Gene knockouts PHASE TWO: INTERPRETATION I THINK I FOUND A CORNER PIECE. 3 BILLION PIECES Analysis of a disease gene Gene knockout or
Genome 371, 22 February 2010, Lecture 12 Analysis of gene function Gene knockouts PHASE TWO: INTERPRETATION I THINK I FOUND A CORNER PIECE. 3 BILLION PIECES Analysis of a disease gene Gene knockout or
A Nucleus-Encoded Chloroplast Protein YL1 Is Involved in Chloroplast. Development and Efficient Biogenesis of Chloroplast ATP Synthase in Rice
 A Nucleus-Encoded Chloroplast Protein YL1 Is Involved in Chloroplast Development and Efficient Biogenesis of Chloroplast ATP Synthase in Rice Fei Chen 1,*, Guojun Dong 2,*, Limin Wu 1, Fang Wang 3, Xingzheng
A Nucleus-Encoded Chloroplast Protein YL1 Is Involved in Chloroplast Development and Efficient Biogenesis of Chloroplast ATP Synthase in Rice Fei Chen 1,*, Guojun Dong 2,*, Limin Wu 1, Fang Wang 3, Xingzheng
S156AT168AY175A (AAA) were purified as GST-fusion proteins and incubated with GSTfused
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Supplemental Materials Supplemental Figure S1 (a) Phenotype of the wild type and grik1-2 grik2-1 plants after 8 days in darkness.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Supplemental Materials Supplemental Figure S1 (a) Phenotype of the wild type and grik1-2 grik2-1 plants after 8 days in darkness.
Table S1. Primers used in the study
 Table S1. Primers used in the study Primer name Application Sequence I1F16 Genotyping GGCAAGTGAGTGAGTGCCTA I1R11 Genotyping CCCACTCGTATTGACGCTCT V19 Genotyping GGGTCTCAAAGTCAGGGTCA D18Mit184-F Genotyping
Table S1. Primers used in the study Primer name Application Sequence I1F16 Genotyping GGCAAGTGAGTGAGTGCCTA I1R11 Genotyping CCCACTCGTATTGACGCTCT V19 Genotyping GGGTCTCAAAGTCAGGGTCA D18Mit184-F Genotyping
Theoretical cloning project
 Theoretical cloning project Needed to get credits Make it up yourself, don't copy Possible to do in groups of 2-4 students If you need help or an idea, ask! If you have no idea what to clone, I can give
Theoretical cloning project Needed to get credits Make it up yourself, don't copy Possible to do in groups of 2-4 students If you need help or an idea, ask! If you have no idea what to clone, I can give
b number of motif occurrences
 supplementary information DOI: 1.138/ncb194 a b number of motif occurrences number of motif occurrences number of motif occurrences I II III IV V X TTGGTCAGTGCA 3 8 23 4 13 239 TTGGTCAGTGCT 7 5 8 1 3 83
supplementary information DOI: 1.138/ncb194 a b number of motif occurrences number of motif occurrences number of motif occurrences I II III IV V X TTGGTCAGTGCA 3 8 23 4 13 239 TTGGTCAGTGCT 7 5 8 1 3 83
Alternative Cleavage and Polyadenylation of RNA
 Developmental Cell 18 Supplemental Information The Spen Family Protein FPA Controls Alternative Cleavage and Polyadenylation of RNA Csaba Hornyik, Lionel C. Terzi, and Gordon G. Simpson Figure S1, related
Developmental Cell 18 Supplemental Information The Spen Family Protein FPA Controls Alternative Cleavage and Polyadenylation of RNA Csaba Hornyik, Lionel C. Terzi, and Gordon G. Simpson Figure S1, related
Supplemental Data. Borg et al. Plant Cell (2014) /tpc
 Supplementary Figure 1 - Alignment of selected angiosperm DAZ1 and DAZ2 homologs Multiple sequence alignment of selected DAZ1 and DAZ2 homologs. A consensus sequence built using default parameters is shown
Supplementary Figure 1 - Alignment of selected angiosperm DAZ1 and DAZ2 homologs Multiple sequence alignment of selected DAZ1 and DAZ2 homologs. A consensus sequence built using default parameters is shown
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09937 a Name Position Primersets 1a 1b 2 3 4 b2 Phenotype Genotype b Primerset 1a D T C R I E 10000 8000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 800 Donor (D)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09937 a Name Position Primersets 1a 1b 2 3 4 b2 Phenotype Genotype b Primerset 1a D T C R I E 10000 8000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 800 Donor (D)
