Friday 9.15 Due: Assignment 1 Topics: Before the Constitution: The Colonial and Revolutionary Experiences Homework: Assignment 2
|
|
|
- Harold Leonard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AP U.S. Government & Politics Unit 2: Constitutional Underpinnings Readings: Chapters 2 and 3, pp Wednesday 9.13 In Class: Getting to know your Constitution! Homework: Assignment 1 Friday 9.15 Due: Assignment 1 Topics: Before the Constitution: The Colonial and Revolutionary Experiences Homework: Assignment 2 Tuesday 9.19 Due: Assignment 2 Topics: Negotiating toward a Constitution Homework: Assignment 3 Thursday 9.21 Monday 9.25 Due: Assignment 3 Analysis of Federalist papers An Actual Quiz Topics: Democratic principles and constitutional practices Homework: Assignment 4 Due: Assignment 4 Analysis of Federalist Papers and Anti-Federalist papers Federalism Homework: Assignment 5 Wednesday 9.27 Due: Assignment 5 Federalism Homework: Debate Friday! Friday 9.29 Tuesday 10.3 In Class: Debate Friday! Homework: Study for objective and short answer question test Test - Objective and short answer questions Please take the time to read The Declaration of Independence and The Constitution of the United States of America found in your textbook on pages Please take notes on the chapter using the headings as organization. No google doc in classroom; just you and your computer or pen and paper. Assignment 1: Due Friday 9.15 A little bit of U.S. history 1. Please read Chapter 2, pages 25-32, and From An Economic Interpretation of the Constitution of the United States, Charles Beard, and From Charles Beard and the Constitution: A Critical Analysis of 'An Economic Interpretation of the Constitution,'" Robert E. Brown. 2. There are two questions at the end of the readings that I would like you to read and be able to answer/discuss in class. 1
2 Consider the following questions to gain a better understanding of the history (not to be handed in for credit): 1. Make a detailed list of the weaknesses in the Articles of Confederation. 2. What was Shays's Rebellion and what role did it play in the push for changing the Articles of Confederation? 3. What specific events, besides Shays's Rebellion, were considered part of the "perceived overall decline in societal order and republican virtue" that increasingly convinced political and economic elites of the need for change in the 1780s? 4. The major principles of American government are: federalism, separation of powers, checks and balances, limited government, and judicial review. Write definitions for each one and give an example for each. 5. What is the social contract? In what ways was John Lock's political theory used by the Founding Fathers? 6. Explain the meaning of "inalienable rights," both in theory and in practice. Assignment 2: Due Tuesday 9.19 Actual word-processed work to hand in!! 1. Please read Chapter 2, pages and Federalist #10, and Federalist #23 2. Please take notes on the chapter using the headings as organization. Analysis of some of the key documents related to the ratification of the U.S. Constitution. Federalist Papers give us insight into the men who wrote the Constitution, and understanding of what they meant in the words they chose. Fabulous readings! Word-processed Work to hand in: Work should be word processed and shared with me through the google wormhole and google docs. Please remember to follow those rules of grammar and include complete sentences, proper punctuation and capitalization for credit. Federalist #10, and Federalist #23: You will find the Federalist papers at "The Library of Congress" web page: Answer the following questions: Federalist #10 James Madison 1. Define faction. In your own words, explain why Madison considers factions to be dangerous to republican government. 2. In paragraphs 3 through 6, Madison presents a number of "straw arguments." These are arguments that are given and then dismissed. What are the two ways in which factions can be cured? 3. What is the most common cause for the development of factions? Is it eliminable? 4. Summarize Madison's four arguments as to why it is not possible to remove the causes of factions. 5. Why do you think Federalist #10 is considered one of the most important documents in U.S. History? Federalist #23 Alexander Hamilton 1. According to Hamilton, what are the main purposes of forming a Union under the Constitution? Make a list in your own words. 2. Do the majority of Hamilton's purposes relate to domestic or to foreign affairs? (Common defense and authority to act indicates that it relates to foreign affairs.) 2
3 Please use U.S. Constitution Questions and chart on compromises for your understanding of the history and to begin to learn the Constitution, as well as the following questions: 1. What was the political significance of the "three-fifths compromise?" 2. What are the specific checks and balances of the three branches of government? 3. In the Constitution, what is the relationship between the nation, state, and local governments? 4. How does the Constitution establish property, commerce, and a strong national government? Why are these important? How do they compare to the ideals of the Declaration of Independence? Assignment 3: Due Thursday 9.21 More and last word-processed work Please read Chapter 2, pages and Federalist #39, Federalist #51, Federalist #70, and Anti-Federalist #38. Please take notes on the chapter using the headings as organization. Word-processed work to hand in: Federalist #39 1. How does Madison define a republic? 2. Why does he think it important to show that the Constitution provides for a republican form of government? 3. What is meant by the federal form of government? What is meant by the national form of government? Federalist #51 1. What is the "great difficulty" with government? Why? 2. What does Madison mean by the statement, "ambition must be made to counteract ambition."? 3. Which branch of government is the strongest? Why? What steps were taken to prevent it from becoming too strong? Federalist #70 1. What is Hamilton's argument against a plural executive? 2. What does he write that a strong executive need? (What is he talking about? Examples?) 3. Try it: What is Hamilton referring to when he writes of the "energy" needed in the executive? Anti-Federalist # How does the author respond to the claim that the men who wrote the Constitution were "an illustrious band of patriots" who spent a long time thinking about and drafting the Constitution? 2. How does the writer respond to the claim that the Constitution must be adopted because the country is in danger of falling into anarchy? 3. What does the writer say about self-interest? Assignment 4: Due Monday Federalism 1. Please read Chapter 3, pages 57-71, "Learning Objectives" handout, as well as the Supreme Court decisions. 2. Don't forget to take notes! Use the "Learning Objectives" to assist you in understanding the principles of federalism as well as the application of it. 3
4 3. As you read each Supreme Court decisions, be sure to understand take the relationship between each Court decision and federalism as it has existed in our political history. Bring your questions to class. Does the Court support the federal government or the state government? Why? When? How? Connect congressional, executive, and judicial actions to constitutional powers (expressed, implied, necessary and proper, and reserved) Assignment 5: Due Wednesday Please read Chapter 3, pages and The Thread of Federalism in the Fabric of American National Government." 2. Please take notes on the chapter using the headings as organization. 3. Look at the chart and fill in with specific programs or evidence from the text. Connect congressional, executive, and judicial actions to constitutional powers (expressed, implied, necessary and proper, and reserved). 4. Read, and in your mind, summarize Sheffield's paper. 5. Find specific examples of "full faith and credit" among specific state actions. 6. Pay attention to current political events, and bring questions to class about your analysis of the use of federal power. Terms: Bicameral Implied powers Full faith and credit clause Privileges and immunities clause Expressed powers Necessary and proper clause Judicial review Supremacy clause Bill of Rights Federalism Reserved power Police power Concurrent powers Constitutionalism Dual federalism Commerce clause Cooperative federalism Grants-in-aid Categorical grants-in-aid Project grants Formula grants Regulated federalism New Federalism Unfunded mandates Devolution States' rights Block Grants 4
5 State sovereignty immunity Legislative supremacy Divided government Executive privilege Writ of habeas corpus AP U.S. Government: Philosophical Foundations Philosophers Hobbes, Locke, Rousseau and Montesquieu all served as influences for the founding fathers of the U.S. Constitution. Remembering their philosophies puts today s issues in perspective with a greater political philosophy. Thomas Hobbes (author, Leviathan) Hobbes believed that the state of nature is chaotic, and in it life is nasty, brutish, and short. In a state of nature, everyone is afraid of everyone else and people are very uncooperative in communal efforts. He believed that the state of nature is so crazy because human nature is to be greedy, selfish, and vain. Hobbes thought men are motivated toward war out of competition and mistrust of other people, but at the same time, desire peace and hope for safety. Hobbes and a Sovereign Ruler The reason we want to leave this state of nature, Hobbes would say, is out of a fear of a violent death and a desire for security. Once we leave the state of nature, the only way to ensure security is to give lots of power to a sovereign. This sovereign keeps things peaceful by making people too afraid of repercussions of disrupting the peace to start any conflicts. John Locke (author, Second Treatise) In contrast, philosopher John Locke is much more optimistic about people than Thomas Hobbes. Locke saw the state of nature as cooperative, and saw people as interested in their own needs, but were not necessarily as war-driven as Hobbes thought. People banded together to get rid of degenerates and were able to mostly keep their own peace. Thus, Locke s reasoning of why we leave the state of nature is based more around the lack of politics rather than a lack of security. Like Hobbes, Locke assumed that the sole right to defend in the state of nature was not enough, so people established a civil society to resolve conflicts in a civil way with help from government in a state of society. Locke advocated governmental separation of powers and believed that revolution is not only a right but also an obligation in some circumstances. He also clearly advocated for a separation of church and state. Checks and Balances Locke thought everyone needed to form a society together where there is a system of checks and balances. The main problem in the state of nature, Locke would say, is that there aren t any impartial judges and there s no clear interpretation of law. Creating a society solves these problems. He also felt that the people should elect a series of representatives to keep things in order, not place all the power in the hands of one. 5
6 Jean-Jacques Rousseau (author, Social Contract) According to Rousseau, a society is legitimate if it is freer than it was in a state of nature. Morality proper, i.e., selfrestraint, can only develop through careful education in a civil state. Humans "in a state of Nature" may act with all of the ferocity of an animal. He believed that everyone is enslaved to each other under the original contracts and everyone is also a slave to acquisition and protection of private property. Since labor as a commodity and the right to private property don t really exist in a state of nature, people are freer without it. Rousseau believed we d all be freer if we didn t own property and if we decided what rules we wanted to follow based on a consensus. Rousseau on Locke and the Social Contract Rousseau felt Locke s idea of a representative democracy doesn t work because the representatives only represent their own experiences and interests, not the common good of all society. He felt the best social contract is one in which everyone participates in politics. Summary, Hobbes, Locke and Rousseau Rousseau s ideas for a legitimate society are liberty and the common good. Locke s test for legitimacy is to make sure that individual interests are protected with a heavy emphasis on property. And Hobbes felt that a good society is ruled by one person who instills enough fear in citizens to keep them from breaking rules. Baron de Montesquieu, Charles-Louis de Secondat (author, The Spirit of the Laws) He saw despotism, in particular, as a standing danger for any government not already despotic, and argued that it could best be prevented by a system in which different bodies exercised legislative, executive, and judicial power, and in which all those bodies were bound by the rule of law. This theory of the separation of powers had an enormous impact on liberal political theory, and on the framers of the constitution of the United States of America. 6
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1
 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Define government and the basic powers every government holds. 2. Describe the four defining characteristics of a state. 3. Identify four theories
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Define government and the basic powers every government holds. 2. Describe the four defining characteristics of a state. 3. Identify four theories
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1
 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Basic Types of Government In a dictatorship, all powers are held by one person or group. In a democracy, authority lies with the people. The U.S. government
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Basic Types of Government In a dictatorship, all powers are held by one person or group. In a democracy, authority lies with the people. The U.S. government
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution What is a government? A government is a person, or group, who has the power to provide law, order, services, and security within a country. Government gives organization and structure
Creating the Constitution What is a government? A government is a person, or group, who has the power to provide law, order, services, and security within a country. Government gives organization and structure
Chapter 1 Constitutional Democracy. Constitutional Democracy. Constitutional Democracy. The peaceful transfer of political power through elections
 Chapter 1 A student from Chicago casts an early vote in the 2008 Illinois presidential primary. The peaceful transfer of political power through elections In 2000, Democrat Al Gore won the popular vote,
Chapter 1 A student from Chicago casts an early vote in the 2008 Illinois presidential primary. The peaceful transfer of political power through elections In 2000, Democrat Al Gore won the popular vote,
Writing the Constitution
 Writing the Constitution Backwards Planning Curriculum Units Michael Hutchison, Writer Dr. Aaron Willis, Project Coordinator Justin Coffey, Editor Kerry Gordonson, Editor Social Studies School Service
Writing the Constitution Backwards Planning Curriculum Units Michael Hutchison, Writer Dr. Aaron Willis, Project Coordinator Justin Coffey, Editor Kerry Gordonson, Editor Social Studies School Service
In framing a government which is to be administrated by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to
 In framing a government which is to be administrated by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to control the governed; and in the next place oblige it to
In framing a government which is to be administrated by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to control the governed; and in the next place oblige it to
Field 050: Social Studies Government and Citizenship Assessment Blueprint
 Field 050: Social Studies Government and Citizenship Assessment Blueprint Domain I Political Science Concepts and Systems 0001 Political Science Concepts and Skills (Standard 9) 0002 Purposes, Forms, and
Field 050: Social Studies Government and Citizenship Assessment Blueprint Domain I Political Science Concepts and Systems 0001 Political Science Concepts and Skills (Standard 9) 0002 Purposes, Forms, and
AP Exam Review. Chapter 3-4
 AP Exam Review Chapter 3-4 Chapter 3 The Constitution Colonies Declaration from the British (chapter 3) The British was imposing taxes on the colonies Boston Tea Party Video (schoolhouse rock boston tea
AP Exam Review Chapter 3-4 Chapter 3 The Constitution Colonies Declaration from the British (chapter 3) The British was imposing taxes on the colonies Boston Tea Party Video (schoolhouse rock boston tea
Name: FEDERALISM. Unit No.3. AP Government & Politics Timpanogos High School
 Name: FEDERALISM Unit No.3 AP Government & Politics Timpanogos High School STUDY GUIDE - Federalism READING... Herzog Ch.3 TARGETS... 3.1 American Federalism 3.2 Constitutional Basis 3.3 Evolution of Federalism
Name: FEDERALISM Unit No.3 AP Government & Politics Timpanogos High School STUDY GUIDE - Federalism READING... Herzog Ch.3 TARGETS... 3.1 American Federalism 3.2 Constitutional Basis 3.3 Evolution of Federalism
Key areas to pay attention to for the CBA 2
 Sequencing Key areas to pay attention to for the CBA 2 There are four fundamental documents that are created in America and that lead to our system of government now. In sequential order they are Fundamental
Sequencing Key areas to pay attention to for the CBA 2 There are four fundamental documents that are created in America and that lead to our system of government now. In sequential order they are Fundamental
CHAPTER 3: Federalism
 Name CHAPTER 3: Federalism CHAPTER OUTLINE I. Politics in Action: Aiding Disaster Victims (pp. 71 72) A. The government response to Hurricane Katrina illustrates the importance of understanding American
Name CHAPTER 3: Federalism CHAPTER OUTLINE I. Politics in Action: Aiding Disaster Victims (pp. 71 72) A. The government response to Hurricane Katrina illustrates the importance of understanding American
Government: Definition, Forms, and Purpose.
 Government: Definition, Forms, and Purpose. SS6CG4 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and
Government: Definition, Forms, and Purpose. SS6CG4 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and
DRAFT SOCIAL SCIENCES STANDARDS: CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT
 DRAFT SOCIAL SCIENCES STANDARDS: CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT CORE STANDARDS Civics and Government 10. Examine the relationship between government and citizens to distinguish and evaluate the ways that civic
DRAFT SOCIAL SCIENCES STANDARDS: CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT CORE STANDARDS Civics and Government 10. Examine the relationship between government and citizens to distinguish and evaluate the ways that civic
Month of Instruction Title of Unit Big Idea Standards. Challenge Conflict Cooperation Democracy Diversity Tyranny Liberty Justice
 Month of Instruction Title of Unit Big Idea Standards August-September (1st Foundations of American Semester) Government January-February (2nd Semester) Conflict Tyranny Justice 5.1.9.B, 5.1.9.C,5.1.9.D,
Month of Instruction Title of Unit Big Idea Standards August-September (1st Foundations of American Semester) Government January-February (2nd Semester) Conflict Tyranny Justice 5.1.9.B, 5.1.9.C,5.1.9.D,
CHAPTER 1: FOUNDATIONS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: THE PURPOSE OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 2: FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 3: DEMOCRACY IN THE UNITED STATES
 CHAPTER 1: FOUNDATIONS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: THE PURPOSE OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 2: FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 3: DEMOCRACY IN THE UNITED STATES SECTION 1: THE PURPOSES OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: FOCUS
CHAPTER 1: FOUNDATIONS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: THE PURPOSE OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 2: FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 3: DEMOCRACY IN THE UNITED STATES SECTION 1: THE PURPOSES OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: FOCUS
Monday, January 23 rd
 Monday, January 23 rd For help with lecture, readings, help with essays, and test preparation, visit 173A SWKT (The American Heritage Review Room. It is open from 9:00 am to 4:00 pm, Monday through Friday.
Monday, January 23 rd For help with lecture, readings, help with essays, and test preparation, visit 173A SWKT (The American Heritage Review Room. It is open from 9:00 am to 4:00 pm, Monday through Friday.
AP COMPARATIVE GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS 2011 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP COMPARATIVE GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS 2011 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 2 3 points One point is earned for a description of a major function of the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom. Major functions
AP COMPARATIVE GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS 2011 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 2 3 points One point is earned for a description of a major function of the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom. Major functions
Introductory Paragraph
 Name: Lit-Based Essay Outline Learning Target: I can defend a thesis in a five-paragraph essay that uses facts and direct details to support my points. My Essay must: Include the following terms: three
Name: Lit-Based Essay Outline Learning Target: I can defend a thesis in a five-paragraph essay that uses facts and direct details to support my points. My Essay must: Include the following terms: three
5. Revolutions A: English Civil War, Absolutism, Scientific Rev and Enlightenment
 5. Revolutions A: English Civil War, Absolutism, Scientific Rev and Enlightenment Study online at quizlet.com/_2rq93a 1. Absolutism 5. Cardinal Richelieu When kings and queens have complete control over
5. Revolutions A: English Civil War, Absolutism, Scientific Rev and Enlightenment Study online at quizlet.com/_2rq93a 1. Absolutism 5. Cardinal Richelieu When kings and queens have complete control over
CIVIC VALUES AND SKILLS
 CIVIC VALUES AND SKILLS Compromise Compromise means looking for solutions to problems that allow all to benefit, even if it requires setting aside one s own personal interests. Citizens compromise in politics
CIVIC VALUES AND SKILLS Compromise Compromise means looking for solutions to problems that allow all to benefit, even if it requires setting aside one s own personal interests. Citizens compromise in politics
Handout D: The Bill of Rights 1 per student. Unit IV: Rights and Responsibilities LESSON 2: MR. MADISON NEEDS SOME HELP. Overview
 Unit IV: Rights and Responsibilities LESSON 2: MR. MADISON NEEDS SOME HELP OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Explain why the Bill of Rights was added to the Constitution. Identify rights they have learned
Unit IV: Rights and Responsibilities LESSON 2: MR. MADISON NEEDS SOME HELP OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Explain why the Bill of Rights was added to the Constitution. Identify rights they have learned
Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy
 Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy FOQ #1: Did the English Civil War help or hurt Democracy? Explain. FOQ #2: What were the causes of the American Revolutionary War? How did it end? FOQ #3: What were the
Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy FOQ #1: Did the English Civil War help or hurt Democracy? Explain. FOQ #2: What were the causes of the American Revolutionary War? How did it end? FOQ #3: What were the
America: Republic vs. Democracy
 America: Republic vs. Democracy By Frank Li, Ph.D. Founder & President, West-East International, Inc. January 11, 2013 In my book Saving America, Chinese Style, I fundamentally questioned democracy as
America: Republic vs. Democracy By Frank Li, Ph.D. Founder & President, West-East International, Inc. January 11, 2013 In my book Saving America, Chinese Style, I fundamentally questioned democracy as
THE STRENGTH OF AMERICAN FEDERAL DEMOCRACY by Roger Myerson
 THE STRENGTH OF AMERICAN FEDERAL DEMOCRACY by Roger Myerson http://home.uchicago.edu/~rmyerson/research/amerfed.pdf The institutions received from England were admirably calculated to lay the foundation
THE STRENGTH OF AMERICAN FEDERAL DEMOCRACY by Roger Myerson http://home.uchicago.edu/~rmyerson/research/amerfed.pdf The institutions received from England were admirably calculated to lay the foundation
1. Constitutional Law Based on the constitution Sets out how power is divided between governments Limits the powers of government Any other law that
 Where do laws come from? There are three sources of law: 1. Canadian Constitution (constitutional law, over-rides all other laws) 2. Statute Law - passed by governments (over-rides common law) 3. Common
Where do laws come from? There are three sources of law: 1. Canadian Constitution (constitutional law, over-rides all other laws) 2. Statute Law - passed by governments (over-rides common law) 3. Common
We the People Lesson 1
 We the People Lesson 1 1. What is the purpose of government according to the natural rights philosophers? The main purpose of government should be to protect people s natural rights. 2. Where does government
We the People Lesson 1 1. What is the purpose of government according to the natural rights philosophers? The main purpose of government should be to protect people s natural rights. 2. Where does government
Civics EOC Review 1. Enlightenment SS.7.C.1.1 Founding Documents SS.7.C.1.2 Rule of Law SS.7.C.1.9 Citizenship SS.7.C.2.1 and 2.2
 Civics EOC Review 1 Enlightenment SS.7.C.1.1 Founding Documents SS.7.C.1.2 Rule of Law SS.7.C.1.9 Citizenship SS.7.C.2.1 and 2.2 Enlightenment SS.7.C.1.1 Recognize how Enlightenment ideas including Montesquieu
Civics EOC Review 1 Enlightenment SS.7.C.1.1 Founding Documents SS.7.C.1.2 Rule of Law SS.7.C.1.9 Citizenship SS.7.C.2.1 and 2.2 Enlightenment SS.7.C.1.1 Recognize how Enlightenment ideas including Montesquieu
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 15, you should be able to: 1. Describe the bureaucrats who they are, how they got there, and what they do. 2. Discuss how the federal bureaucracy is organized.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 15, you should be able to: 1. Describe the bureaucrats who they are, how they got there, and what they do. 2. Discuss how the federal bureaucracy is organized.
The Federalists Paper #51
 The Federalists Paper #51 There were no notes taken at the Constitutional Convention in 1787. The members thought it wise to not allow members to take notes and to meet in complete secrecy in order to
The Federalists Paper #51 There were no notes taken at the Constitutional Convention in 1787. The members thought it wise to not allow members to take notes and to meet in complete secrecy in order to
AUTOCRACY. SS.7.C.3.1 Forms of Government
 AUTOCRACY An autocracy is a form of government where one person has unlimited power. One form of an autocracy is a dictatorship where a military leader secures power often through violent means. Another
AUTOCRACY An autocracy is a form of government where one person has unlimited power. One form of an autocracy is a dictatorship where a military leader secures power often through violent means. Another
December 1, 2015: Warm Up 1. The gov't collects taxes from both businesses and individuals in economic flow. 2. The gov't uses what they collect to
 December 1, 2015: Warm Up 1. The gov't collects taxes from both businesses and individuals in economic flow. 2. The gov't uses what they collect to create public goods and services. 3. Businesses and households
December 1, 2015: Warm Up 1. The gov't collects taxes from both businesses and individuals in economic flow. 2. The gov't uses what they collect to create public goods and services. 3. Businesses and households
SS.7.C.2.1 Citizenship
 SS.7.C.2.1 Citizenship ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Define citizenship as stated in the 14 th Amendment Describe the process of becoming a naturalized citizen Evaluate
SS.7.C.2.1 Citizenship ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Define citizenship as stated in the 14 th Amendment Describe the process of becoming a naturalized citizen Evaluate
U.S. Presidents...79
 Table of Contents Introduction... 4 The Basics of Government Government in Your Life...5 What Is Government?...6 Authority vs. Power...7 Why Do We Need Government?...8 What Does Government Do?...9 Limited
Table of Contents Introduction... 4 The Basics of Government Government in Your Life...5 What Is Government?...6 Authority vs. Power...7 Why Do We Need Government?...8 What Does Government Do?...9 Limited
Life in the Colonies. Chapter 4, Section 1
 Life in the Colonies Chapter 4, Section 1 All English colonies shared a common English heritage, and that heritage included the idea that citizens had political rights. England also promoted the theory
Life in the Colonies Chapter 4, Section 1 All English colonies shared a common English heritage, and that heritage included the idea that citizens had political rights. England also promoted the theory
BUSINESS LAW Chapter 1 PowerPoint Notes & Assignment Ethics and the Law
 BUSINESS LAW Chapter 1 PowerPoint Notes & Assignment Ethics and the Law SECTION 1.1- DEFINING ETHICS How Ethical Decisions Are Made Determining the difference between and can be difficult. Individuals
BUSINESS LAW Chapter 1 PowerPoint Notes & Assignment Ethics and the Law SECTION 1.1- DEFINING ETHICS How Ethical Decisions Are Made Determining the difference between and can be difficult. Individuals
ALIGNMENT DOCUMENT Ultimate Civics Activating My Democracy LESSON 1: What Can We Do Now? (How to move ideas into action)
 ALIGNMENT DOCUMENT LESSON 1: What Can We Do Now? (How to move ideas into action) EALR 1: CIVICS The student understands and applies knowledge of government, law, COMPONENT 1.4: Understands civic involvement.
ALIGNMENT DOCUMENT LESSON 1: What Can We Do Now? (How to move ideas into action) EALR 1: CIVICS The student understands and applies knowledge of government, law, COMPONENT 1.4: Understands civic involvement.
Government in Athens
 SECTION 2 Government in Athens What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. Aristocrats and tyrants ruled early Athens. 2. Athens created the world s first democracy. 3. Ancient democracy was different than modern
SECTION 2 Government in Athens What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. Aristocrats and tyrants ruled early Athens. 2. Athens created the world s first democracy. 3. Ancient democracy was different than modern
Chapter 7 Bureaucracy and the Executive Branch. AP Government
 Chapter 7 Bureaucracy and the Executive Branch AP Government The Paradoxes of Bureaucratic Politics Americans generally have negative views of bureaucracy, and we tend only to focus on bureaucracy when
Chapter 7 Bureaucracy and the Executive Branch AP Government The Paradoxes of Bureaucratic Politics Americans generally have negative views of bureaucracy, and we tend only to focus on bureaucracy when
Course Civics and Economics
 Leandro v. State of North Carolina A Deliberation on School Funding in North Carolina Overview Should North Carolina s public schools be funded locally? Through a structured small-group deliberation process,
Leandro v. State of North Carolina A Deliberation on School Funding in North Carolina Overview Should North Carolina s public schools be funded locally? Through a structured small-group deliberation process,
OTTAWA ONLINE OAD Compensation and Benefits
 OTTAWA ONLINE OAD-41564 Compensation and Benefits Course Description Examines human resource functions of salary administration, job evaluation, compensation, legal requirements, and benefit designs (including
OTTAWA ONLINE OAD-41564 Compensation and Benefits Course Description Examines human resource functions of salary administration, job evaluation, compensation, legal requirements, and benefit designs (including
Formulation and Enforcement of Socio-Economic Rights
 United Nations Assistance Mission for Iraq (UNAMI) Baghdad-Iraq Office of Constitutional Support Formulation and Enforcement of Socio-Economic Rights United Nations Multiparty Dialogue on the Enforcement
United Nations Assistance Mission for Iraq (UNAMI) Baghdad-Iraq Office of Constitutional Support Formulation and Enforcement of Socio-Economic Rights United Nations Multiparty Dialogue on the Enforcement
Huntsville City Schools Pacing Guide Course: Civics Grade: 7 First 9 Weeks
 Huntsville City Schools 2017-18 Pacing Guide Course: Civics Grade: 7 First 9 Weeks Civics Fall 2017 General Resources The State of Alabama is now requiring that all students pass a Civics test to receive
Huntsville City Schools 2017-18 Pacing Guide Course: Civics Grade: 7 First 9 Weeks Civics Fall 2017 General Resources The State of Alabama is now requiring that all students pass a Civics test to receive
Ulrich Karpen, University of Hamburg
 Subnational Constitutionalism in Germany Ulrich Karpen, University of Hamburg 1. The Basic Law, Germany s constitution, came into force on May 23 rd, 1949, established the federal system as an integrative
Subnational Constitutionalism in Germany Ulrich Karpen, University of Hamburg 1. The Basic Law, Germany s constitution, came into force on May 23 rd, 1949, established the federal system as an integrative
GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE
 TYPES OF GOVERNMENT GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE CITIZEN A LEGAL MEMBER OF A COUNTRY CONSTITUTION A WRITTEN PLAN
TYPES OF GOVERNMENT GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE CITIZEN A LEGAL MEMBER OF A COUNTRY CONSTITUTION A WRITTEN PLAN
STREET LAW - CURRICULUM MAP
 WHAT IS LAW? *Reasons for having laws *Laws are a reflection of economic, moral, political, and social values *Incorporating human rights in written laws *In the United States, the relation between rights
WHAT IS LAW? *Reasons for having laws *Laws are a reflection of economic, moral, political, and social values *Incorporating human rights in written laws *In the United States, the relation between rights
Supplementary Texts: How Do They Shed Light on the Primary Text?
 Study Guide The Purpose of the American Union--1 The Purpose of the American Union Fragment on the Constitution and Union (1861) Essential Question: Illustrate how the principles of the Declaration represent
Study Guide The Purpose of the American Union--1 The Purpose of the American Union Fragment on the Constitution and Union (1861) Essential Question: Illustrate how the principles of the Declaration represent
BREXIT Challenge: European Union Citizenship
 BREXIT Challenge: European Union Citizenship Speaker: Tom Muirhead. Event: Public Meeting on EU Citizenship. Links: www.shru.org Location: Hillhead Library, Glasgow. Date: 24 th November 2016 at 18:30
BREXIT Challenge: European Union Citizenship Speaker: Tom Muirhead. Event: Public Meeting on EU Citizenship. Links: www.shru.org Location: Hillhead Library, Glasgow. Date: 24 th November 2016 at 18:30
Do you think studying the ideas above was a reason why we declared our independence from Britain? Why or why not?
 Benchmark SS.7.C.1.1 Recognize how Enlightenment ideas including Montesquieu s view of separation of power and John Locke s theories related to natural law and how Locke s social contract influenced the
Benchmark SS.7.C.1.1 Recognize how Enlightenment ideas including Montesquieu s view of separation of power and John Locke s theories related to natural law and how Locke s social contract influenced the
DECLARATION ON PRINCIPLES OF INTERNATIONAL LAW FRIENDLY RELATIONS AND CO-OPERATION AMONG STATES IN ACCORDANCE WITH THE CHARTER OF THE UNITED NATIONS
 DECLARATION ON PRINCIPLES OF INTERNATIONAL LAW FRIENDLY RELATIONS AND CO-OPERATION AMONG STATES IN ACCORDANCE WITH THE CHARTER OF THE UNITED NATIONS The General Assembly, Recalling its resolutions 1815
DECLARATION ON PRINCIPLES OF INTERNATIONAL LAW FRIENDLY RELATIONS AND CO-OPERATION AMONG STATES IN ACCORDANCE WITH THE CHARTER OF THE UNITED NATIONS The General Assembly, Recalling its resolutions 1815
UBC POLI 101 Canadian Politics. The Federal System. Federalism
 UBC POLI 101 Canadian Politics The Federal System (not Constitutional Mega-Politics) http://www.politics.ubc.ca/fcutler/teaching/poli101 1 Federalism Separate orders of government defined by the Constitution
UBC POLI 101 Canadian Politics The Federal System (not Constitutional Mega-Politics) http://www.politics.ubc.ca/fcutler/teaching/poli101 1 Federalism Separate orders of government defined by the Constitution
Grade 8 History Teacher s Guide Confederation
 Grade 8 History Teacher s Guide Confederation Overall Expectations Describe the internal and external political factors, key personalities, significant events, and geographical realities that led to the
Grade 8 History Teacher s Guide Confederation Overall Expectations Describe the internal and external political factors, key personalities, significant events, and geographical realities that led to the
SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government.
 SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government. 1a. Determine how governments differ in geographic distribution of power, particularly unitary, confederal, and federal types of government. Unitary
SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government. 1a. Determine how governments differ in geographic distribution of power, particularly unitary, confederal, and federal types of government. Unitary
bureaucracy cabinet civil service independent agencies
 Purpose Departments, agencies, and bureaus that administer laws (bureaucracy) touch every aspect of American life. This lesson examines the role of administrative departments and agencies in America s
Purpose Departments, agencies, and bureaus that administer laws (bureaucracy) touch every aspect of American life. This lesson examines the role of administrative departments and agencies in America s
Wednesday March 22, 2017
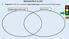 Wednesday March 22, 2017 1. Assignment 3. Open your workbook to page 8 (blank page), and draw the Venn Diagram below. dictatorship (autocracy) democracy What are you expected to do with these forms of
Wednesday March 22, 2017 1. Assignment 3. Open your workbook to page 8 (blank page), and draw the Venn Diagram below. dictatorship (autocracy) democracy What are you expected to do with these forms of
Federalism and The Modern Presidency From Eisenhower to Obama: If All Men Were Angels
 Trinity College Trinity College Digital Repository Senior Theses and Projects Student Works 5-1-2013 Federalism and The Modern Presidency From Eisenhower to Obama: If All Men Were Angels Daisy Chastain
Trinity College Trinity College Digital Repository Senior Theses and Projects Student Works 5-1-2013 Federalism and The Modern Presidency From Eisenhower to Obama: If All Men Were Angels Daisy Chastain
It is envisaged that students will have a better-than-basic knowledge of their own country s legal and constitutional system.
 The English Constitution teacher s notes By Nigel Haines As most countries have a written constitution, the English example is usually particularly curious to foreign students. This lesson explores the
The English Constitution teacher s notes By Nigel Haines As most countries have a written constitution, the English example is usually particularly curious to foreign students. This lesson explores the
first Vice-President, in charge of Better Regulation, Inter-Institutional Relations, the Rule of Law and the Charter of Fundamental Rights
 Jean-Claude Juncker, President-elect of the European Commission Mission letter Brussels, 10 September 2014 Frans Timmermans First Vice-President, in charge of Better Regulation, Inter-Institutional Relations,
Jean-Claude Juncker, President-elect of the European Commission Mission letter Brussels, 10 September 2014 Frans Timmermans First Vice-President, in charge of Better Regulation, Inter-Institutional Relations,
POPULAR SOVEREIGNTY. The Constitution and Popular Sovereignty. Use the Information above to explain the MAIN IDEA about popular sovereignty
 POPULAR SOVEREIGNTY The Constitution and Popular Sovereignty In the United States, all political power lives within in the people. The people are sovereign. They are the only source for any and all governmental
POPULAR SOVEREIGNTY The Constitution and Popular Sovereignty In the United States, all political power lives within in the people. The people are sovereign. They are the only source for any and all governmental
AMERICAN POLITICAL THEORY II: THE LINCOLN/DOUGLAS DEBATES Graduate Program Fall 2005
 AMERICAN POLITICAL THEORY II: THE LINCOLN/DOUGLAS DEBATES Graduate Program Fall 2005 Professor Sheehan Phone: 519-7421 Office Hours: Mondays: 2-3 and 4:15-5:15 Office: 254 SAC I. COURSE DESCRIPTION This
AMERICAN POLITICAL THEORY II: THE LINCOLN/DOUGLAS DEBATES Graduate Program Fall 2005 Professor Sheehan Phone: 519-7421 Office Hours: Mondays: 2-3 and 4:15-5:15 Office: 254 SAC I. COURSE DESCRIPTION This
LIBYA CONSTITUTION 1969
 LIBYA CONSTITUTION 1969 PREAMBLE The Revolutionary Command Council, in the name of the Arab people in Libya, who pledged to restore their freedom, enjoy the wealth of their land, live in a society in which
LIBYA CONSTITUTION 1969 PREAMBLE The Revolutionary Command Council, in the name of the Arab people in Libya, who pledged to restore their freedom, enjoy the wealth of their land, live in a society in which
HOW TO WRITE A WINNING PROPOSAL
 HOW TO WRITE A WINNING PROPOSAL WHAT IS A PROPOSAL? A proposal is a picture of a project, it is NOT the project. In that sense, it is based on your project plan but may be quite different from the Project
HOW TO WRITE A WINNING PROPOSAL WHAT IS A PROPOSAL? A proposal is a picture of a project, it is NOT the project. In that sense, it is based on your project plan but may be quite different from the Project
Discuss questions on each slide in small groups and be ready to share your answers with whole class.
 Big Picture Question About the US & End of WWI Why did the US fail to Ratify the Versailles Treaty and how did this impact on US Foreign Policy? Directions: See pages 678-681 in text as well as internet
Big Picture Question About the US & End of WWI Why did the US fail to Ratify the Versailles Treaty and how did this impact on US Foreign Policy? Directions: See pages 678-681 in text as well as internet
3. According to the text. Europe invented sovereignty. Therefore, using this as context, sovereignty can be defined as:
 Name AP Comparative Government Directions: Use the readings from your summer assignment packet on the European Union, and your own knowledge in order to answer the following questions. These questions
Name AP Comparative Government Directions: Use the readings from your summer assignment packet on the European Union, and your own knowledge in order to answer the following questions. These questions
Chapter 22: Comparative Political Systems Section 4
 Chapter 22: Comparative Political Systems Section 4 Objectives 1. Examine elements of the United Kingdom s parliamentary democracy. 2. Describe regional and local government in the United Kingdom. 3. Analyze
Chapter 22: Comparative Political Systems Section 4 Objectives 1. Examine elements of the United Kingdom s parliamentary democracy. 2. Describe regional and local government in the United Kingdom. 3. Analyze
STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth,
 STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries by c) assessing the impacts
STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries by c) assessing the impacts
EU Charter of Fundamental Rights
 EU Charter of Fundamental Rights A5-0064/2000 European Parliament resolution on the drafting of a European Union Charter of Fundamental Rights (C5-0058/1999 1999/2064(COS)) The European Parliament, - having
EU Charter of Fundamental Rights A5-0064/2000 European Parliament resolution on the drafting of a European Union Charter of Fundamental Rights (C5-0058/1999 1999/2064(COS)) The European Parliament, - having
Breaking with Britain. Part I
 Breaking with Britain Part I Monday, February 6 th COMING SOON: Open Lab Test Review on Saturday, February 11 th from 10:00 am to 2:00 pm in 173A, 240, and 270 SWKT Midterm #1: February 14th 17th Tuesday,
Breaking with Britain Part I Monday, February 6 th COMING SOON: Open Lab Test Review on Saturday, February 11 th from 10:00 am to 2:00 pm in 173A, 240, and 270 SWKT Midterm #1: February 14th 17th Tuesday,
Copyright 2002 The Bureau of National Affairs, Inc. International Environment Reporter Current Report, January 16, Vol. 25, No. 2; Pg.
 LENGTH: 2915 words Copyright 2002 The Bureau of National Affairs, Inc. International Environment Reporter Current Report, January 16, 2002 Vol. 25, No. 2; Pg. 86 SECTION: ANALYSIS & PERSPECTIVE: Kyoto
LENGTH: 2915 words Copyright 2002 The Bureau of National Affairs, Inc. International Environment Reporter Current Report, January 16, 2002 Vol. 25, No. 2; Pg. 86 SECTION: ANALYSIS & PERSPECTIVE: Kyoto
Part I. The Evolution of English Constitutional Government
 Part I The Evolution of English Constitutional Government Preface Why Begin a Study of Christianity in America With an Overview of English Political and Religious History? (1)We cannot learn history in
Part I The Evolution of English Constitutional Government Preface Why Begin a Study of Christianity in America With an Overview of English Political and Religious History? (1)We cannot learn history in
Irish Politics PO3630 Julie Kolding Olsen Student number: xxxxxx
 'Given the serious problem of democratic accountability in Ireland brought about by EU membership, it is not surprising that there was a majority No vote in the Lisbon Treaty referendum in June 2008, and
'Given the serious problem of democratic accountability in Ireland brought about by EU membership, it is not surprising that there was a majority No vote in the Lisbon Treaty referendum in June 2008, and
Syllabus: Human Resource Management
 Syllabus: Human Resource Management MGMT 440 02 Spring Semester T H 2:00 3:15 MH 208 Paul L. Schumann, Ph.D. Department of Management College of Business Minnesota State University Mankato Key Information
Syllabus: Human Resource Management MGMT 440 02 Spring Semester T H 2:00 3:15 MH 208 Paul L. Schumann, Ph.D. Department of Management College of Business Minnesota State University Mankato Key Information
CONCEPTS AND SKILLS. MASSACHUSETTS HISTORY & SOCIAL SCIENCE LEARNING STANDARDS Grades 8 1 2
 Prentice Hall Civics: Government and Economics In Action 2005 Massachusetts History and Social Science Curriculum Framework Learning Standards, Economics and American Government (Grades 9-12) Grades 8
Prentice Hall Civics: Government and Economics In Action 2005 Massachusetts History and Social Science Curriculum Framework Learning Standards, Economics and American Government (Grades 9-12) Grades 8
Public Faith in Democracy. The Maturing of a (Skeptical) Democratic Culture in Taiwan
 Public Faith in Democracy The Maturing of a (Skeptical) Democratic Culture in Taiwan REASONABLY HIGH SUPPORT FOR DEMOCRACY Measuring Democratic Legitimacy in the Asian Barometer Support for Democracy (average
Public Faith in Democracy The Maturing of a (Skeptical) Democratic Culture in Taiwan REASONABLY HIGH SUPPORT FOR DEMOCRACY Measuring Democratic Legitimacy in the Asian Barometer Support for Democracy (average
Grade 10. Duration 30 min. for lesson and activity description Additional time for resume completion, resume reviewing, and class election
 North Carolina s Council of State Overview Students will learn about the members of North Carolina s Council of State and their roles within state government. Grade 10 NC Essential Standards for 10 th
North Carolina s Council of State Overview Students will learn about the members of North Carolina s Council of State and their roles within state government. Grade 10 NC Essential Standards for 10 th
PA 6603 Economics for Public Management Course Description: An introduction to economic theory emphasizing the application of microeconomic and
 Core Course Descriptions, Objectives, and Competencies for the Master of Public Administration Program February 16, 2007 (Revised: November 11, 2007, February 18, 2008 and June 23, 2008) PA 6601 Research
Core Course Descriptions, Objectives, and Competencies for the Master of Public Administration Program February 16, 2007 (Revised: November 11, 2007, February 18, 2008 and June 23, 2008) PA 6601 Research
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1
 Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. 2. Explain the influence of three landmark English documents.
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. 2. Explain the influence of three landmark English documents.
Athenian Democracy. To what extent was Athenian democracy an incomplete and restricted form of political suffrage? DISSECTING DEMOCRACY PLII001
 Athenian Democracy To what extent was Athenian democracy an incomplete and restricted form of political suffrage? DISSECTING DEMOCRACY PLII001 1 To what extent was Athenian democracy an incomplete and
Athenian Democracy To what extent was Athenian democracy an incomplete and restricted form of political suffrage? DISSECTING DEMOCRACY PLII001 1 To what extent was Athenian democracy an incomplete and
Sometimes public means open as opposed to closed a public place, public behavior, published work as opposed to private homes or diaries.
 OUTLINE Privatization: Some Theoretical Considerations Much of this material comes from The Meaning of Privatization, by Paul Starr (Yale Law and Policy Review, 1988), but I have added other material and
OUTLINE Privatization: Some Theoretical Considerations Much of this material comes from The Meaning of Privatization, by Paul Starr (Yale Law and Policy Review, 1988), but I have added other material and
KALAMAZOO VALLEY COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE ASSIGNMENT SCHEDULE LEN 101 INTRODUCTION TO LAW ENFORCEMENT AND CRIMINAL JUSTICE
 KALAMAZOO VALLEY COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE ASSIGNMENT SCHEDULE LEN 101 INTRODUCTION TO LAW ENFORCEMENT AND CRIMINAL JUSTICE Instructor: Nicholas Meier, J.D. Office: 7353 Phone: 488-4295 e-mail: nmeier@kvcc.edu
KALAMAZOO VALLEY COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE ASSIGNMENT SCHEDULE LEN 101 INTRODUCTION TO LAW ENFORCEMENT AND CRIMINAL JUSTICE Instructor: Nicholas Meier, J.D. Office: 7353 Phone: 488-4295 e-mail: nmeier@kvcc.edu
TEXTS ADOPTED. having regard to the Treaties, and in particular to Articles 2, 3, 4 and 6 of the Treaty on European Union (TEU),
 European Parliament 2014-2019 TEXTS ADOPTED P8_TA(2016)0344 Recent developments in Poland and their impact on fundamental rights as laid down in the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union
European Parliament 2014-2019 TEXTS ADOPTED P8_TA(2016)0344 Recent developments in Poland and their impact on fundamental rights as laid down in the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union
Political Science: International Relations
 Political Science: International Relations Table of Contents You know the major European organizations... 2 You know the current situation with regard to membership in European organizations... 2 You know
Political Science: International Relations Table of Contents You know the major European organizations... 2 You know the current situation with regard to membership in European organizations... 2 You know
Collective-Action Problems and Other Types of Collective Dilemmas
 Collective-Action Problems and Other Types of Collective Dilemmas Ryan D. Williamson University of Georgia Ryan D. Williamson Collective Dilemmas 1 / 26 Agenda Attendance Discuss Collective Dilemmas Readings
Collective-Action Problems and Other Types of Collective Dilemmas Ryan D. Williamson University of Georgia Ryan D. Williamson Collective Dilemmas 1 / 26 Agenda Attendance Discuss Collective Dilemmas Readings
The Fundamentals of Australian Constitutional Law. A Constitutional Road Map: Some Basic Principles & Ideas
 The Fundamentals of Australian Constitutional Law What is Constitutional Law? The rules that constitute the state. All constitutions with same purpose whether for businesses or nations. It is both a legal
The Fundamentals of Australian Constitutional Law What is Constitutional Law? The rules that constitute the state. All constitutions with same purpose whether for businesses or nations. It is both a legal
Impossible demands made of government, which, if granted, would mean its end. Unsuccessful gov t attempts to suppress the revolutionaries
 Stages of Crane Brinton Impossible demands made of government, which, if granted, would mean its end Unsuccessful gov t attempts to suppress the revolutionaries Revolutions gain power and seem united.
Stages of Crane Brinton Impossible demands made of government, which, if granted, would mean its end Unsuccessful gov t attempts to suppress the revolutionaries Revolutions gain power and seem united.
4. EU Charter of Fundamental Rights
 C 377/329 58. Calls on the Commission to submit the proposals referred to above and to inform Parliament of the progress of the legislative programme and of any changes or delays, in order to improve both
C 377/329 58. Calls on the Commission to submit the proposals referred to above and to inform Parliament of the progress of the legislative programme and of any changes or delays, in order to improve both
REPUBLIC OF ALBANIA THE ASSEMBLY LAW. No. 154/2014 ORGANIZATION AND FUNCTIONING OF STATE SUPREME AUDIT INSTITUTION
 REPUBLIC OF ALBANIA THE ASSEMBLY LAW No. 154/2014 ORGANIZATION AND FUNCTIONING OF STATE SUPREME AUDIT INSTITUTION In accordance with Articles 81, 83 and 162-165 of the Constitution, with the proposal of
REPUBLIC OF ALBANIA THE ASSEMBLY LAW No. 154/2014 ORGANIZATION AND FUNCTIONING OF STATE SUPREME AUDIT INSTITUTION In accordance with Articles 81, 83 and 162-165 of the Constitution, with the proposal of
Assessing the Situation
 Assessing the Situation Table of Materials 1. Introduction Purpose of a Situation Assessment When is a Consensus Process Most Likely to be Appropriate: Reasons to Participate in a Consensus Process When
Assessing the Situation Table of Materials 1. Introduction Purpose of a Situation Assessment When is a Consensus Process Most Likely to be Appropriate: Reasons to Participate in a Consensus Process When
Luxembourg: Parliament abolishes royal confirmation of laws. 1. The history of the Luxembourg royal assent
 Luxembourg: Parliament abolishes royal confirmation of laws Luc Frieden * Law concerning royal assent royal sanction of laws royal accountability in a constitutional monarchy A major constitutional reform
Luxembourg: Parliament abolishes royal confirmation of laws Luc Frieden * Law concerning royal assent royal sanction of laws royal accountability in a constitutional monarchy A major constitutional reform
During the decade of the 50 s, the national territories were made into provinces and 8 new provinces were admitted: Chaco, Chubut, Formosa, La Pampa,
 CONSIDERATION OF SUBNATIONAL CONSTITUTIONS IN ARGENTINA By ANTONIO M. HERNANDEZ, Professor in Constitutional Law and Professor in State Constitutional Law and Municipal Law at the National University of
CONSIDERATION OF SUBNATIONAL CONSTITUTIONS IN ARGENTINA By ANTONIO M. HERNANDEZ, Professor in Constitutional Law and Professor in State Constitutional Law and Municipal Law at the National University of
Why Does Sovereignty Matter to America?
 Why Does Sovereignty Matter to America? Steven Groves Why Does Sovereignty Matter to America? The United States is a sovereign nation. Sovereignty is a simple idea: the United States is an independent
Why Does Sovereignty Matter to America? Steven Groves Why Does Sovereignty Matter to America? The United States is a sovereign nation. Sovereignty is a simple idea: the United States is an independent
PREAMBLE AND THE SALIENT FEATURES OF THE CONSTITUTION OF INDIA
 MODULE - 2 Political Science 5 PREAMBLE AND THE SALIENT FEATURES OF THE CONSTITUTION OF INDIA T he was framed by a Constituent Assembly. This Assembly was an indirectly elected body. It had laid down certain
MODULE - 2 Political Science 5 PREAMBLE AND THE SALIENT FEATURES OF THE CONSTITUTION OF INDIA T he was framed by a Constituent Assembly. This Assembly was an indirectly elected body. It had laid down certain
TTUISD - TEKS Tracker
 uthor Todd McKay TTUISD - TEKS Tracker Evaluator Evaluation Date TEKS Requirement (Secondary) Submission Date / / / / TTUISD: Economics with Emphasis on the Free Enterprise System and its Benefits (ECO
uthor Todd McKay TTUISD - TEKS Tracker Evaluator Evaluation Date TEKS Requirement (Secondary) Submission Date / / / / TTUISD: Economics with Emphasis on the Free Enterprise System and its Benefits (ECO
LAW 1504 PRINCIPLES OF PUBLIC LAW. Final Exam Notes
 LAW 1504 PRINCIPLES OF PUBLIC LAW Final Exam Notes Week 1 Constitutionalism & the Australian Constitution Constitutionalism Function of Constitutions: Mechanism devised to address the problem of unlimited
LAW 1504 PRINCIPLES OF PUBLIC LAW Final Exam Notes Week 1 Constitutionalism & the Australian Constitution Constitutionalism Function of Constitutions: Mechanism devised to address the problem of unlimited
The Future of the Nineveh Plain: A Proposal from Chaldean/Syriac/Assyrian Political Parties
 The Future of the Nineveh Plain: A Proposal from Chaldean/Syriac/Assyrian Political Parties Further to the unified work paper signed by the Chaldean/Syriac political parties on March 6-7, 2017, we stress
The Future of the Nineveh Plain: A Proposal from Chaldean/Syriac/Assyrian Political Parties Further to the unified work paper signed by the Chaldean/Syriac political parties on March 6-7, 2017, we stress
ALMA MATER SOCIETY OF QUEEN S UNIVERSITY INCORPORATED AMS Board of Directors Open Session Minutes
 ALMA MATER SOCIETY OF QUEEN S UNIVERSITY INCORPORATED 2015-2016 AMS Board of Directors Open Session Minutes November 26 th 2015, 2015 at 6:00PM AMS Board Room, John Deutsch University Centre, Kingston,
ALMA MATER SOCIETY OF QUEEN S UNIVERSITY INCORPORATED 2015-2016 AMS Board of Directors Open Session Minutes November 26 th 2015, 2015 at 6:00PM AMS Board Room, John Deutsch University Centre, Kingston,
Commissioner for International Cooperation and Development
 Jean-Claude Juncker, President-elect of the European Commission Mission letter Brussels, 10 September 2014 Neven Mimica Commissioner for International Cooperation and Development Dear Neven, You are becoming
Jean-Claude Juncker, President-elect of the European Commission Mission letter Brussels, 10 September 2014 Neven Mimica Commissioner for International Cooperation and Development Dear Neven, You are becoming
Constitutional Charter of the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro
 Constitutional Charter of the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro Proceeding from the equality of the two member states, the state of Montenegro and the state of Serbia which includes the Autonomous Province
Constitutional Charter of the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro Proceeding from the equality of the two member states, the state of Montenegro and the state of Serbia which includes the Autonomous Province
INFORMAL EUROPEAN COUNCIL 16 April 2003 Athens
 DIRECTORATE FOR THE PLANNING OF PARLIAMENTARY BUSINESS INFORMAL EUROPEAN COUNCIL 16 April 2003 Athens SPEECH BY THE PRESIDENT, MR PAT COX 03/S-2003 EN Directorate-General for the Presidency EN (Intranet)
DIRECTORATE FOR THE PLANNING OF PARLIAMENTARY BUSINESS INFORMAL EUROPEAN COUNCIL 16 April 2003 Athens SPEECH BY THE PRESIDENT, MR PAT COX 03/S-2003 EN Directorate-General for the Presidency EN (Intranet)
LAW ON THE ASSEMBLY OF THE REPUBLIC OF MACEDONIA
 1 LAW ON THE ASSEMBLY OF THE REPUBLIC OF MACEDONIA 1. BASIC PROVISIONS Article 1 (1) This law shall regulate certain aspects of the functioning of the Assembly of the Republic of Macedonia (hereafter:
1 LAW ON THE ASSEMBLY OF THE REPUBLIC OF MACEDONIA 1. BASIC PROVISIONS Article 1 (1) This law shall regulate certain aspects of the functioning of the Assembly of the Republic of Macedonia (hereafter:
Meet & Confer: Run & Hide, or Get Prepared?
 Meet & Confer: Run & Hide, or Get Prepared? Presented by: Elizabeth M. Provencio Denton, Navarro, Rocha & Bernal, P. C. elizabeth.provencio@rampage-sa.com 2517 North Main, San Antonio, Texas 78212 (210)227-3243
Meet & Confer: Run & Hide, or Get Prepared? Presented by: Elizabeth M. Provencio Denton, Navarro, Rocha & Bernal, P. C. elizabeth.provencio@rampage-sa.com 2517 North Main, San Antonio, Texas 78212 (210)227-3243
