Climate Change and the Water Sector
|
|
|
- Rolf Harmon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 National Issues Paper on Climate Change and the Water Sector in Saint Lucia April 2009
2 1.0 Why water is a key sector for Saint Lucia Saint Lucia has a fragile economy which has been evolving over the years from one being heavily dependent on Agriculture specifically banana production to one which is dependent on Tourism and Other Services (80% GDP), Agriculture (5% GDP) and Industry (15% GDP). Freshwater is a fragile, finite and vulnerable resource vital to human, economic and environmental sustainability and influences national prosperity and quality of life. The water sector is a cross cutting sector and plays an important role in all sectors in Saint Lucia and therefore any impact of climate change on the water sector could have far reaching repercussions on the economy of the country and affect life in general, being a catalyst for economic development and a vehicle for empowerment and poverty alleviation. Over the years there has been a significant focus on the water sector in Saint Lucia with the government initiating a reform of the sector in 1999 which is still ongoing. It is clear that significant investments are required to bring the sector to the level required to meet the current demand and future needs. Water demand continues to change rapidly in certain areas, for example the extreme north due to high infra structural development and migration of people into areas in the north and other major centers of commercial activity in the south. In general there is water supply versus demand deficit, island wide, and this is affected directly by rainfall distribution. Although there have been continuous improvements, the potable water supply, has in recent years, been severely affected by pressures of increased demand as a result of socio -economic development, destruction of upper watersheds, increasing exploitation of the rivers and wetlands, and an inefficient, inadequate and aging water distribution network. The ability of the Water and Sewerage Company (WASCO) to meet the current demand for water, island wide is as a result of a combination of marginal river base flows experienced during the dry season and high turbidity during the rainy season. It is widely suggested that present water demand is exceeding the available supply and that the potential increase in future demand can only serve to exacerbate this deficit. While the available data does not allow for an exact determination of supply/demand dynamics, data of the potential supply/demand situation within various sectors and zones and for the island as a whole point more to a suppressed demand than a real deficit [AGRICO, 2001]. Freshwater supplies are highly susceptible to normal climate variability. This results in periods of excess rainfall which can lead to flooding as well as periods of below normal rainfall which leads to drought conditions. During such periods of heavy rainfall watercourses are susceptible to siltation which impacts significantly on raw water quality. In addition there are a number of anthropogenic activities currently affecting the quality of Saint Lucia s rivers and freshwater systems. These include: housing, agriculture, water abstraction, sewage disposal, solid waste disposal, tourism, fishing, river sand mining, manufacturing, river bathing and picnicking, and river alteration. Page 2
3 Although it is suggested that the island currently has sufficient freshwater to meet all demands, a key concern is that the resources are unevenly distributed temporally and spatially. Therefore it is absolutely necessary that an Integrated Water Resources Assessment be conducted to ascertain the actual available water resources as well as the water resource potential. The need for an implemented Integrated Water Resource Management Plan cannot be overstated. 2.0 Key Aspects of the Water Sector Saint Lucia is a small island developing country and experiences year round warm, humid conditions associated with the tropical marine climate which can be attributed to its location. The geographical location of the island results in the occurrence of tropical storms and hurricanes during the rainy season. The island s weather is influenced by the Atlantic High Pressure system, surface, mid and upper level troughs/lows, the Inter Tropical Convergence Zone, tropical waves and cyclones and the occasional frontal system. The island experiences wet (June November) and dry (December May) rainfall seasons annually. In the wet season the quantity of rainfall is influenced primarily by the frequency and intensity of tropical waves, depressions, storms and hurricanes. Saint Lucia is a volcanic island and is geologically composed of impermeable rock. Therefore movement of water into underground reserves is very limited. Water resources are as a result from surface sources in rivers, wetlands, streams and springs. There are thirty-seven (37) main sources of surface run-off (figure 1) and few groundwater sources. Surface water catchments are relatively small, with steep slopes on which run-off occurs fairly rapidly. Surface water yields for potable water purposes vary due to increased abstraction and in some cases soil and chemical contamination. Surface water is heavily exploited for municipal and agricultural purposes. The island s freshwater requirements are met through an integrated network of river intakes, treatment plants, transmission pipelines and distribution systems. These system components are under operation and control of the Water and Sewerage Company (WASCO). With respect to the potable water supply there are four (4) major water supply systems in the country: North - Roseau Dam and Hill 20, South - Grace and Beausejour. The supply to the treatment plants is from water streams through both gravity and pumped conveyance systems. The above mentioned systems treat the raw water in filtration plants and then disinfect. There are approximately 56,000 customers (households and commercial establishments) served by the system, distributed between the networks in the north and south [WASCO, 2009]. As noted earlier there are a number of challenges to WASCO in the provision of an adequate water supply island wide. Page 3
4 Figure 1 : Watersheds in Saint Lucia Inter annual variability in the Southern Caribbean climate is influenced strongly the El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO). El Niño episodes bring warmer and drier than average conditions between June and August and La Niña episodes bring colder and wetter conditions at this time [Saint Lucia Hires Report]. Observational records and climate projections provide abundant evidence that freshwater resources are vulnerable and have the potential to be strongly impacted by climate change, with wide-ranging consequences for human societies and ecosystems [IPCC, Special Report on Climate Change & Water]. A thorough understanding and response to climate change is critical for small island developing states (SIDS) like Saint Lucia. Despite the fact that Saint Lucia s contribution to the source of this anthropogenic change is minimal, by virtue of inherent characteristics such as geographic location, small land mass with high proportion of low lying coastal Page 4
5 areas, the island is rendered vulnerable to the anticipated impacts of climate change on the water sector. It is expected that climate change will result in impacts on water resources sources as follows, through : 1. Changes in surface and groundwater systems 2. Changes in water quality 3. Increased flooding 4. Increased droughts 5. Changes in water temperature 6. Changes in water chemistry 7. Increased water erosion and sedimentation 8. Decreased freshwater availability due to saltwater intrusion Table 1 below highlights the anticipated impacts on the Fresh Water Resources as indicated in the Government of Saint Lucia First National Communication on Climate Change. IMPACTS Table 1 : Anticipated Impacts on the Fresh Water Resources [Source: CC FNC, GOSL] IMPLICATIONS Climate Change Factor: Sea Level Rise Sea level rise may precipitate the intrusion of salt water into fresh water lenses, particularly in low- lying coastal areas. While there is little use of ground water in Saint Lucia, saline intrusions will reduce the quantity and quality of potential source of potable water. Irrigation with brackish water will most often destroy crops and ruin soils. Climate Change Factor: Tropical Storm Activity Destruction and/or modification of existing aquatic ecosystems caused by the increased frequency and intensity of precipitation. Soil erosion resulting from increased surface run off on exposed soils. Siltation of river systems during periods of increased rainfall. Temporary increase in water supply. Damage to water intakes, dams and reservoirs leaving settlements without water or providing poor water quality. Increased social and economic cost to ensure that these facilities are maintained. Degradation of the habitats of species of flora and fauna which occupy the aquatic ecosystems, leading to a loss of biodiversity. Page 5
6 IMPACTS Climate Change Factor: Precipitation Decreased precipitation: Periods of low precipitation are likely to be accompanied by extended dry periods. Increased frequency & Intensity of precipitation: Destruction and/or modification of existing aquatic ecosystems. Siltation of river systems. Increased incidence of flooding. The likelihood of cross contamination from leaching of pit latrines into flood plains increases during flooding. Climate Change Factor: Temperature Possibility of excessive evapo-transpiration associated with the level of temperature increases of the high precipitation scenario. Municipal demands are likely to increase as higher temperatures lead to increased water consumption. IMPLICATIONS Extended periods of drought leading to decreases in water supply for domestic and other use. Consumers who normally maximize rainwater stores may need to increase consumption of treated water to meet domestic needs. The elevation of water rates to discourage wastage and greater efficiency of production may be another necessary option. Temporary increase in water supply. Damage to water intakes, dams and reservoirs and/or pollution of water sources leaving settlements without water or providing poor water quality. Increased social and economic cost to ensure that these facilities are maintained. Degradation of the habitats of species of flora and fauna, which occupy the aquatic ecosystems leading to a loss of biodiversity. Loss of livestock and crops Increased freshwater outflows will reduce the salinity of coastal waters with consequences for fisheries, as coral reefs and sea grass beds no longer support their normal biodiversity. Loss of soil moisture, which will impact on crop production. Dwindling basal flows may alter the biophysical parameters of rivers and wetlands sufficiently to affect breeding cycles, offspring and parent fecundity, offspring survival and overall species resistance to environmental stresses such as disease and fishing effort. Page 6
7 3.0 Adaptation Options for the Water Sector The Climate Change First National Communication [CCFNC] for Saint Lucia indicated that adaptation involves developing and institutionalizing various levels of capacity, as well as developing expertise and building knowledge through research and monitoring. Such adaptation measures are most effective if implemented early while the various systems are still intact. It is suggested that anticipatory approaches can also greatly mitigate the need for forced ad hoc responses at a subsequent date when loss of resources and poorly planned developments will likely limit the range of adaptation options available [CCFNC]. The Climate Change First National Communication [CCFNC] highlighted the following as select adaptation options for Saint Lucia for the Water Sector: 1. Reductions in line losses 2. Accurately reflecting costs of water supply 3. Restoration of riverbanks and wetlands 4. Water conservation 5. Public awareness 6. Improved management of forest resources including private forests 7. Strengthening data collection 8. Development of a national water management plan To this end the Government of Saint Lucia in recognition of the potential implications of the impacts of climate change on water resources remains committed to addressing these issues as indicated in The Saint Lucia National Climate Change Policy and Adaptation Plan (2003). The following articulates the government s commitment as stated in the plan [GOSL, CCPAP] : In addressing these and other related issues, the Government of Saint Lucia, in collaboration with other relevant entities, will: 1. Develop or improve the basis for sound decision making by promoting and fostering the developing of capacity to undertake research into and analysis of the relevant climate change processes (including forecasting and data collection). 2. Undertake a comprehensive inventory of all water resources including surface and ground water. 3. Promote the strengthening of national water management agencies to ensure the sound management of the island s water resources. 4. Develop a long-term national water management plan which incorporates and addresses Climate Change concerns including catchment and watershed protection and saltwater intrusion. Page 7
8 5. Undertake reforestation and other measures to increase the resilience of watersheds and catchments to maximize water availability and to reduce soil erosion and sedimentation. 6. Assess and address needs for water storage and distribution infrastructure to ensure water availability during drought periods. 7. Promote initiatives to identify and, where necessary, exploit non-traditional water sources such as groundwater. 3.1 Additional Considerations : - Adaptation Measures Beyond the areas highlighted by Government in the Climate Change Policy and Adaptation Plan the following needs to be considered: 1. The Water Sector Reform process when concluded this year will result in a new company to manage the provision of services to the sector as well as regulatory environment. This is critical as investments under this program are key to the water security of the country and by extension result in a reduced vulnerability of the sector. 2. Map areas susceptible to saline intrusions and develop alternative sources of water supply. Also explore the use of desalination techniques for saline tainted water source. 3. It is important not only to consider supplying water demand from conventional sources such as rivers but also look at alternatives to these sources. The following are sources that can be used to augment the supply to facilitate long term, sustainability of the water resources. Wastewater Reuse : - Waste water can be reused depending on its origin and the purpose for which it is required. Domestic wastewater is perhaps a better choice of wastewater over industrial wastewater but of course this depends on the nature of the industry. Domestic wastewater for example can be used for irrigation of golf courses in the hotel sector. Hotels tend to consume a significant amount of fresh water at the expense of local consumers. This option can allow a reduction in the potable water demand of hotels. Storm Water Collection & Use : - This is an option that is worth looking into in more detail. It is evident in Saint Lucia that a significant amount of water is wasted and simply flows into the sea during and after periods of rainfall. If this water is collected and treated it could be used for normal consumption. Ground Water : - Due to the general impervious nature of the volcanic bedrock very little water that fall as precipitation is stored as ground water. As indicated previously the reserves are inadequate for major consumptive purposes. However Page 8
9 in recent times there has been exploration of deep groundwater reserves. It is worth pursuing further. Desalination : - In this case the seawater resource is abundant but all factors need to be considered to ascertain the economic feasibility. This can be used as a last resort due to the high cost associated with the process. It should be noted that due to improved technology some desalination plants prove to be comparable in terms of cost but this is dependent on the specific situation and the cost of the options available. One option is the utilization of brackish water or slightly saline water from waters contaminated by salt water intrusions. Rainwater Harvesting: - This is the collection and concentration of rainwater and runoff for irrigation of annual crops, pastures and trees, domestic consumption and livestock consumption. Catchment areas for rainwater harvesting are roof tops, small ground surfaces, courtyards, streets, public squares, slopes and large catchment areas feeding seasonal rivers. Storage mediums consist of : underground soil, sediment, cisterns; above ground tanks and jars, ponds, reservoirs. Roof top rainwater harvesting is already being explored in some areas in Saint Lucia with domestic water supply problems. In recent times there have been a number of projects supported by the European Union, Government of Saint Lucia, Caribbean Environmental Health Institute (GEF funded) promoting the widespread reintroduction of rainwater harvesting. 3.2 Adaptation Measures under consideration and implementation Further to the identification of adaptation measures listed previously, the following highlights initiatives being pursued : 1. Water Sector Reform Process to address the following: a. Regulation and Management of Water Resources to include the development of an Integrated Water Resources Management Plan, identification of alternative sources of water (groundwater or desalination), promote water conservation, establish system and sustain collection of water resources data. b. Regulation and Management of Provision of Services to include the establishment of a new company to facilitate installation and maintenance of new infrastructure and maintenance of old infrastructure and systems. 2. Water Conservation and Demand Management : a. Introduction of rainwater harvesting schemes. b. Promotion of water conservation in the dry season. c. Promotion of the use of water conservation devices. d. Wastewater reuse. e. Water demand reduction. Page 9
10 4.0 Key issues in Assessing Investment and Financial Flows In assessing investment and financial flows when dealing with climate change adaptation in the water sector a number of issues need to be considered. Water Resource Management encompasses a wide range of sectors and is impacted by areas such as agriculture, forestry, urban environment, reservoir development, wetlands, groundwater reserves. Some of the major issues which must be considered are as follows: 1. Inadequate Natural and Water Resource Management. 2. Water Resource Availability and Quality There is a water supply deficit island wide based on the supply and demand of the various water systems. This is particularly acute in the dry season. Poor raw & treated water quality is an issue in some areas. It is necessary to assess the impact of agricultural intensification as well as deforestation on water quality and availability. Soil erosion, land degradation, sedimentation, poor land drainage, uncontrolled rural development, are issues that require consideration. 3. Current State of the Water Sector i.e. Investments required to ensure the sustainability of the sector with normal variability and no climate change. Currently the Water Supply Infrastructure is inadequate. 4. Inadequate Data availability Current & Historic Rainfall, Stream Flow, Runoff, Water Demand & Supply. 5. Absence of Implemented the Water & Land Use Policy as it relates to Water Resource Management. 6. Inadequate Institutional and Regulatory Capacity. 7. The extent to which non action in relation to the water sector investments will exacerbate the climate change impacts. 8. How does one apportion the adaptation costs to climate change. It is clear that climate change will have impacts on the availability of water for the potable water supply. Even without the effects of climate change and variability there are significant challenges to the sector. It should be noted that the First National Communication [FNC] was based on expert judgment and included a situational analysis of the sector. It did not contain detailed analyses based on scenario generation and modeling of climate change conditions and impacts. The Second National Communication is currently ongoing and the Vulnerability and Adaptation component which has not yet been untaken is expected to produce a more detailed data collection and analysis of the sector resulting in scenario generation and a quantitative determination of the vulnerabilities and associated costs of adaptation. Page 10
11 4.1 Constraints In the assessment of climate change impacts on the water sector, one of the major issues is quantifying the resource. It is clear that if you cannot measure, it you cannot manage it. It is necessary that the availability of the resource be measured. Only then can one clearly determine the extent to which climate change will have adverse effects on the resource and the extent to which the adaptation measures need to be effective. It should be noted that the major issues emanating from this analysis are issues that exist even with the potential effects of climate change. It is there difficult to apportion costs of adaptation measures for climate change impacts as most of these investments were required anyway to deal with existing challenges to the sector. There are a number of constraints in this sector: Data availability there is a paucity of data. It is necessary to have well established records of Current & Historic Rainfall, Stream Flow, Runoff, Water Demand & Supply. The data available is insufficient to facilitate proper planning and as such the establishment of a system of continuous collection of data is important. (Legal Responsibility of the Water Resources Management Agency (WRMA). Inadequate Water Supply Infrastructure the infrastructure is over 50 years old and is in dire need of replacement. (Legal Responsibility of the Water Company (WASCO/ NewCo). Absence of implemented water & land use policy as it relates to water resource management and inadequate natural and water resource management. (Legal Responsibility of the Water Resource Management Agency (WRMA)). Inadequate Institutional and Regulatory Capacity absence of a functional Water Resources Management Agency and National Water and Sewerage Commission as mandate by law. It should be noted the above mentioned constraints will be dealt with through the establishment and operationalization of the Water Resource Management Agency (WRMA) and the Water and Sewerage Commission (WSC) and the New Water Company (NewCo) which is expected within the next 3 months. 4.2 Modeling and Scenario Limitations and/or Assumptions It should be noted that there are a number of limitations as it relates to monitoring and scenario generation as follows: 1. Availability of data required to develop models based on various scenarios. 2. Inadequate national capacity to develop the required models for the region. It is therefore necessary to seek relevant expertise in countries where English is not the Page 11
12 primary language. As a result the language barrier poses challenges with respect to capacity building. 3. Inability to purchase relevant models and modeling software. 4. Due to differences in models for various regions, technology transfer is limited. 5. Application of available models to the local situation is limited and also inability to select appropriate models. 6. Models utilized for local application are scaled down from global models and as such the accuracy of models and scenario generation is assumed. 7. Ability to communicate to policy makers information arising from models. It should be noted the climate change timelines are long term (30, 50, 100 years etc). There is a challenge to convince the policy makers of the need to act now and address such a long term phenomena in the short to medium term within their shorter political term of office. It should be noted that based on the above, a key approach developed to move forward especially with respect to completion of the Second National Communication s, Vulnerability and Adaptation Assessment is as follows: 1. Utilize the Climate Change expertise in the region from Cuba, Jamaica and Barbados. This will deal with the language barrier as well as ensure that the most appropriate models are selected and modified for Saint Lucia since these countries possess the expertise required. 2. This assessment has a strong capacity building component and as such the local expertise involved will be trained where necessary to ensure the country is capable of conducting future assessments. 5.0 Assessment of Investment and Financial Flows 5.1 Proposed Methodological Approach in Assessing Investment and Financial Flows The following highlights the approach being proposed to assess investment and financial flows: 1. Development and application of appropriate models to clearly articulate anticipated climate change scenarios and the effects on the sector. It should be noted that the First National Communication did not utilized models. It is expected that models will be used for the Second National Communication. It is expected that a combination of global and regional models will be utilized in the SNC Vulnerability and Adaptation Assessment including the use of the PRECIS model and a compatible global model. Page 12
13 2. Situation Analysis using a basic scenario with or without climate change. In assessing impacts and costs associated with climate change adaptations it is necessary to assess the situation with and without climate change. There are a number of interventions that are required even without climate change being an issue. It should be noted however that if these issues are not addressed on their own merit, the effect of climate change will only exacerbate the situation. 3. Assessment of costs anticipated with the existing challenges without the application of climate change scenarios. 4. Assessment of costs associated with climate change. This is expected to be initiated during the preparation of the Second National Communication for the Vulnerability and Adaptation Assessment. It should be noted that the water sector reform process has generated costs associated with the improvement in the level of service of the sector including critical investments in areas of water supply and sewerage services required to sustain the sector. This figure has been estimated to be EC$1.7 billion over a 30 year period [Stone & Webster, 2004]. This does not take into consideration adaptation options. 5. Comparison of implementation timeline of normal development objectives in the sector. Determination of extent to which climate change impacts would have an effect in advance of the normal development commitments. 6. Establishment of a system for allocating investments and financial flows to climate change adaptation. This is expected to be initiated during the preparation of the Second National Communication for the Vulnerability and Adaptation Assessment. 5.2 Institutional Arrangements and Key Stakeholders There are a number of legal instruments and stakeholders as it relates to the water sector in Saint Lucia. Figure 2 below highlights the key players in the sector as well as the relevant legal instruments. The key players in the sector are the Water Resource Management Agency (in embryonic stage), National Water and Sewerage Commission and Water Company (new company to be formed soon), Ministry of Health Public Health Department. Page 13
14 Figure 2 : Saint Lucia Water Cycle, Associated Legal Instruments and Main Actors [Source : CANARI, T. Geoghegan, 2002] 5.3 National Sources of Finance and Investment for the Sector To date water sector reform initiatives have been financially supported by the following : Government of Saint Lucia, World Bank, Caribbean Development Bank, European Union, Government of France (AFD). It is expected that there will continue to be donor support for the sector. As well, with the new regime of private sector involvement it is expected that much needed investments will also be met by private sector interests. Since 1998, Government of Saint Lucia recognized the need for reforming the Water Sector. The major reasons being the poor performance, unreliability of supply, low coverage of sewerage, poor financial performance and low level of capital investment faced by the then Water Company. The Water Sector Reform Project (funded by the Caribbean Development Bank, the World Bank, WASCO and the Government of Saint Lucia, EC$ 24 million) aimed to prepare an adequate legal and regulatory framework for the private delivery of water and sanitation services throughout Saint Lucia. The project s objective was to prepare the Water Company for the transition from a publicly managed utility, to a privately managed and operated company. Additionally, the Page 14
15 project aims to safeguard the integrity of the critical water supply and wastewater services infrastructure through the implementation of urgently needed capital works in the region of EC$ 1.7 billion over a period of 30 years. Table 2 illustrates some critical investments anticipated in the short to medium term financed by the new water company, the Government of Saint Lucia, and various lending institutions and aid agencies. One of the major components of the Project was the strengthening of the Legal and Regulatory Framework. To this end Government focused on drafting the necessary laws, regulations and licenses for the sector. This is expected to facilitate significant and sustainable private sector participation in the water and sewerage sector while protecting the interests of Saint Lucia s consumers. Another component was the strengthening of the Environmental and Water Resource Management Framework. This is intended to create an enabling environment and water resource management framework for the delivery of sustainable water supply and sewerage services and to integrate water supply needs with environmental management. An Institutional Strengthening Program within the Water Company aimed to enhance the capacity of the company, with a view to improving the delivery of reliable and responsive service to its customers in the short to medium term. This involves the development and application of relevant industry accepted technical, financial, accounting and commercial information systems and procedures and appropriate staff training in key operational areas to upgrade their skills. The implementation of a critical capital works program was another aspect of the project. Due to the age of the system components, many facilities are approaching or reaching the end of their operating life. The objective of the program is to prevent further deterioration of the water supply and sewerage system, through the implementation of critical capital works to impact positively on the reliability and quality of service in the short term. The rehabilitation works that are planned under the project are those urgently needed to enhance the reliability of the system and to ensure that the improvements to these systems redound to the benefit of the population. Additionally, the improved systems are more likely to attract private sector capital, to fund further expansion and upgrading of the water supply and sewerage networks. The projects currently being implemented in the sector are critical to mitigate against the problems resulting from the inadequate water supply systems island wide. It is therefore important these be taken into consideration as any scheme of adaptation options should be in synergy with each other and benefit from each other. It is further suggested that a scheme be devised to apportion cost to climate change adaptation as some of the recommendations are required without any climate change impacts. Page 15
16 Table 2 : Schedule of Investments (Short to Medium Term) [Source : Diagnostic of the Utility, Santander Investment Services, February 2006] INVESTMENT SCHEDULE Millions US$ NORTH AND SOUTH SERVICES Hydrological study of the watersheds Study of new water sources Geographic Information System Commercial Information & Billing System Administration Systems Offices Office Equipment and Miscellaneous Vehicles and Mobile Equipment NORTHERN REGION Physical Losses Reduction Meters Normalisation & renovation of existing connections Commercial System (collection improvement) Bulk Metering Installations modification for better operation Treatment Plants Improvement Pumping Stations Improvement Reservoirs improvement Sewer Treatment Plant Sewer Network Extension Roseau Upgrade SOUTHERN REGION Dennery Micoud Vieux Fort Choiseul Soufriere Canaries Physical Losses Reduction Renovation and Normalisation of existing connections Commercial System (collection improvement) Meters Installations modification for better operation Troumasse River Intake TOTAL INVESTMENTS Page 16
17 6.0 Conclusion Saint Lucia s Climate Change Adaptation Policy & Strategy [2003] is premised on an acceptance that climate change is happening and it will continue to occur even if immediate steps are taken to reduce global warming. Also accepted is the fact that the effects thereof are more than likely to have a profound, and in sum, adverse, impact on the economic, social, and environmental aspects of life in the country. The water service provider (Water and Sewerage Company Inc) has the responsibility to supply consumers with potable water; however the Government and People of the country being the custodians of the water resources of the country bear responsibility for water resource management through a recently established Water Resource Management Agency. Due to the fragile nature of the water resource it is necessary to promote a joint responsibility of its management and promotion of adaption measures to deal with climate change. All citizens have to play a part from a domestic level to a commercial and industrial level. Such effects on water resources will have far reaching consequences on all sectors, domestic consumers, commercial consumers, tourism plants, industrial consumers, the agricultural sector, the health sector. It is clear that Water is Life. Inadequate supply of water for all sectors can result in a collapse of the economy as there are very few options to do otherwise. 7.0 Bibliography & References: 1. National Climate Change Adaptation Policy, 2003, Government of Saint Lucia. 2. Saint Lucia s Initial National Communication on Climate Change, Climate Change and Water, IPCC Technical Paper VI, June Saint Lucia Hires Report, UNDP Climate Change Country Profile. 5. Saint Lucia Water Policy, Report on National Water Situation and Assessment of National Water Profile prepared by AGRICO Ltd. December Incentives for Watershed Management in Saint Lucia : Results of a Brief Diagnostic, CANARI, T. Geoghegan, August Investment Feasibility and Financial Strategy for PSP in Saint Lucia, Technical Assessment and Operational Efficiency Report, Stone and Webster, October Page 17
18 9. Diagnostic of the Utility, Transaction in St. Lucia s Water Utility, Santander Investment Services S.A. - Société des Eaux de Marseille, February, Page 18
Rashid Ali Khan, FAO (Ret.) Gurgaon, Haryana
 Sustainability and Water Conservation mentioned in the draft strategic plan of DDWS was not provided adequate coverage, though important for improving the supply. In view of the unpredictable rainfall,
Sustainability and Water Conservation mentioned in the draft strategic plan of DDWS was not provided adequate coverage, though important for improving the supply. In view of the unpredictable rainfall,
Prepared by: Hopeton Peterson & Doneika Simms of the The Planning Institute of Jamaica (PIOJ) May 10, 2012
 Prepared by: Hopeton Peterson & Doneika Simms of the The Planning Institute of Jamaica (PIOJ) May 10, 2012 Objectives Highlight expected climate risks and discuss how they will affect Jamaica s rural areas
Prepared by: Hopeton Peterson & Doneika Simms of the The Planning Institute of Jamaica (PIOJ) May 10, 2012 Objectives Highlight expected climate risks and discuss how they will affect Jamaica s rural areas
Lecture 1 Integrated water resources management and wetlands
 Wetlands and Poverty Reduction Project (WPRP) Training module on Wetlands and Water Resources Management Lecture 1 Integrated water resources management and wetlands 1 Water resources and use The hydrological
Wetlands and Poverty Reduction Project (WPRP) Training module on Wetlands and Water Resources Management Lecture 1 Integrated water resources management and wetlands 1 Water resources and use The hydrological
5 th World Water Forum
 5 th World Water Forum Istanbul Water Consensus For Local and Regional Authorities As Mayors and local/regional elected representatives from different parts of the world, meeting in Istanbul in March 2009,
5 th World Water Forum Istanbul Water Consensus For Local and Regional Authorities As Mayors and local/regional elected representatives from different parts of the world, meeting in Istanbul in March 2009,
Climate Change & Small Island Developing States
 Climate Change & Small Island Developing States 49th Session of United Nations Statistical Commission 7 March 2018 Statistical Institute of Jamaica Contents What is climate change? Small island developing
Climate Change & Small Island Developing States 49th Session of United Nations Statistical Commission 7 March 2018 Statistical Institute of Jamaica Contents What is climate change? Small island developing
2. Irrigation and Drainage Sub-sector. Guideline:
 Sub-sector Guideline: (1) Irrigation (Adaptation Project) (2) Irrigation (BAU Development with Adaptation Options) (3) Drainage (Adaptation Project) (4) Drainage (BAU Development with Adaptation Options)
Sub-sector Guideline: (1) Irrigation (Adaptation Project) (2) Irrigation (BAU Development with Adaptation Options) (3) Drainage (Adaptation Project) (4) Drainage (BAU Development with Adaptation Options)
Susan P. Abano Engineer IV Policy and Program Division
 National Water Resources Board Integrated Water Resources Management Susan P. Abano Engineer IV Policy and Program Division National Water Resources Board Outline Philippines Water Resources Situationer
National Water Resources Board Integrated Water Resources Management Susan P. Abano Engineer IV Policy and Program Division National Water Resources Board Outline Philippines Water Resources Situationer
Fisheries and Aquaculture in a Changing Climate
 Fisheries and Aquaculture in a Changing Climate Climate change impacts such as more frequent and severe floods and droughts will affect the food and water security of many people. The impact of climate
Fisheries and Aquaculture in a Changing Climate Climate change impacts such as more frequent and severe floods and droughts will affect the food and water security of many people. The impact of climate
CYPRUS REPORT FOR COMBATING DESERTIFICATION
 CYPRUS REPORT FOR COMBATING DESERTIFICATION CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 2 INTRODUCTION 3 DESERTIFICATION FACTORS IN CYPRUS CLIMATE 5 SOIL 5 WATER MANAGEMENT 5 ANTHROPOGENIC FACTORS 6 GENERAL MEASURES TO
CYPRUS REPORT FOR COMBATING DESERTIFICATION CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 2 INTRODUCTION 3 DESERTIFICATION FACTORS IN CYPRUS CLIMATE 5 SOIL 5 WATER MANAGEMENT 5 ANTHROPOGENIC FACTORS 6 GENERAL MEASURES TO
Presenter: Farzana Yusuf-Leon Water Resource Specialist Water Resource Management Agency, Ministry of Sustainable Development, Energy, Science and
 Presenter: Farzana Yusuf-Leon Water Resource Specialist Water Resource Management Agency, Ministry of Sustainable Development, Energy, Science and Technology Saint Lucia Overview Water Resources of Saint
Presenter: Farzana Yusuf-Leon Water Resource Specialist Water Resource Management Agency, Ministry of Sustainable Development, Energy, Science and Technology Saint Lucia Overview Water Resources of Saint
National Ecosystems and Landscapes Restoration Program of El Salvador
 National Ecosystems and Landscapes Restoration Program of El Salvador Rationale/Background Ecosystem restoration and degraded lands rehabilitation are necessary measures to reverse the high degree of environmental
National Ecosystems and Landscapes Restoration Program of El Salvador Rationale/Background Ecosystem restoration and degraded lands rehabilitation are necessary measures to reverse the high degree of environmental
Overview of the Issues Relevant to the Impacts Associated with Slow Onset Events for SIDS
 Overview of the Issues Relevant to the Impacts Associated with Slow Onset Events for SIDS Dr Murray C. Simpson Chief Executive Officer, The CARIBSAVE Partnership and INTASAVE Senior Research Associate,
Overview of the Issues Relevant to the Impacts Associated with Slow Onset Events for SIDS Dr Murray C. Simpson Chief Executive Officer, The CARIBSAVE Partnership and INTASAVE Senior Research Associate,
GREEN DEVELOPMENT POLICY
 GREEN DEVELOPMENT POLICY 1. A NEED AND JUSTIFICATION FOR THE TRANSITION TO GREEN DEVELOPMENT 1.1. Global Perspective Climate change, rapid economic and population growth, the sharp increase in consumption
GREEN DEVELOPMENT POLICY 1. A NEED AND JUSTIFICATION FOR THE TRANSITION TO GREEN DEVELOPMENT 1.1. Global Perspective Climate change, rapid economic and population growth, the sharp increase in consumption
Princess Ramada Hotel Paramaribo, Suriname September11, /14/2015 1
 Princess Ramada Hotel Paramaribo, Suriname September11, 2015 9/14/2015 1 The First National Climate Outlook Forum (NCOF) The First National Climate Outlook Forum (NCOF) will function as an important platform
Princess Ramada Hotel Paramaribo, Suriname September11, 2015 9/14/2015 1 The First National Climate Outlook Forum (NCOF) The First National Climate Outlook Forum (NCOF) will function as an important platform
Surface Water. Solutions for a better world
 1 Surface Water Solutions for a better world Our Surface Water Services Expertise Growing worldwide awareness of water scarcity has encouraged water preservation programs, better irrigation techniques
1 Surface Water Solutions for a better world Our Surface Water Services Expertise Growing worldwide awareness of water scarcity has encouraged water preservation programs, better irrigation techniques
Presentation on community-based adaptation approaches in the Pacific Island Countries.
 Presentation on community-based adaptation approaches in the Pacific Island Countries. The presentation will focus on adaptation activities undertaken in the Pacific and on community based involvement
Presentation on community-based adaptation approaches in the Pacific Island Countries. The presentation will focus on adaptation activities undertaken in the Pacific and on community based involvement
Linking the FDES and Climate Change Statistics
 Linking the FDES and Climate Change Statistics Fifth Meeting of the Expert Group on Environment Statistics 16 18 May 2018 Statistical Institute of Jamaica Contents What is climate change? Small island
Linking the FDES and Climate Change Statistics Fifth Meeting of the Expert Group on Environment Statistics 16 18 May 2018 Statistical Institute of Jamaica Contents What is climate change? Small island
Strategic Initiative on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Development in Mountain Regions. Presentation of the Position Paper.
 Strategic Initiative on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Development in Mountain Regions Presentation of the Position Paper Riad BALAGHI FAO consultant National Agricultural Research Institute of
Strategic Initiative on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Development in Mountain Regions Presentation of the Position Paper Riad BALAGHI FAO consultant National Agricultural Research Institute of
Management of Water Resources in Cyprus
 Management of Water Resources in Cyprus CHARLES DEMETRIOU Hydrologist Water Development Department Ministry of Agriculture, Natural Resources & Environment 9 July, 2012 OUTLINE Mission of the Water Development
Management of Water Resources in Cyprus CHARLES DEMETRIOU Hydrologist Water Development Department Ministry of Agriculture, Natural Resources & Environment 9 July, 2012 OUTLINE Mission of the Water Development
Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR) Practical Techniques for the Caribbean
 Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR) Practical Techniques for the Caribbean Scope of Presentation What is MAR? Antigua and Barbuda water resources issues Why promote MAR? MAR: Techniques MAR: Design criteria
Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR) Practical Techniques for the Caribbean Scope of Presentation What is MAR? Antigua and Barbuda water resources issues Why promote MAR? MAR: Techniques MAR: Design criteria
Experiences from the Caribbean
 Experiences from the Caribbean TEC Thematic Dialogue on Enablers and Barriers to South South Cooperation on Technologies for Adaptation Carlos Fuller International and Regional Liaison Officer Vulnerability
Experiences from the Caribbean TEC Thematic Dialogue on Enablers and Barriers to South South Cooperation on Technologies for Adaptation Carlos Fuller International and Regional Liaison Officer Vulnerability
Experiences from the Caribbean
 Experiences from the Caribbean TEC Thematic Dialogue on Enablers and Barriers to South-South Cooperation on Technologies for Adaptation Carlos Fuller International and Regional Liaison Officer Vulnerability
Experiences from the Caribbean TEC Thematic Dialogue on Enablers and Barriers to South-South Cooperation on Technologies for Adaptation Carlos Fuller International and Regional Liaison Officer Vulnerability
A 25 Year Strategic Plan
 A 25 Year Strategic Plan The challenges which face the provision of water services are identified as: Meeting Customer Needs at an Affordable Cost Providing Safe Water Supplies Managing Wastewater Protecting
A 25 Year Strategic Plan The challenges which face the provision of water services are identified as: Meeting Customer Needs at an Affordable Cost Providing Safe Water Supplies Managing Wastewater Protecting
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY solid waste, agricultural waste, manufacturing industrial waste potable generally more than adequate to satisfy the demands
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The risk for future generations of Dominicans lies in under-valuing the country s remarkable, common resource base and, by doing so, inadvertently allowing it to deteriorate and devolve
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The risk for future generations of Dominicans lies in under-valuing the country s remarkable, common resource base and, by doing so, inadvertently allowing it to deteriorate and devolve
RESEARCH PRIORITIES FOR 2016
 National Environmental Science Programme RESEARCH PRIORITIES FOR 2016 Note that bolded dot points are considered high priority. CLEAN AIR AND URBAN LANDSCAPES: RESEARCH PRIORITIES Increasing our understanding
National Environmental Science Programme RESEARCH PRIORITIES FOR 2016 Note that bolded dot points are considered high priority. CLEAN AIR AND URBAN LANDSCAPES: RESEARCH PRIORITIES Increasing our understanding
CYPRUS NATIONAL REPORT
 Convention on Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes SEMINAR ON THE ROLE OF ECOSYSTEMS AS WATER SUPPLIERS (Geneva, 13-14 December 2004) CYPRUS NATIONAL REPORT Water Management
Convention on Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes SEMINAR ON THE ROLE OF ECOSYSTEMS AS WATER SUPPLIERS (Geneva, 13-14 December 2004) CYPRUS NATIONAL REPORT Water Management
(1) Coastal Protection (Adaptation Project) (2) Coastal Protection (BAU Development with Adaptation Options)
 Sub-sector Guideline: (1) Coastal Protection (Adaptation Project) (2) Coastal Protection (BAU Development with Adaptation Options) Basic Concept A. General Concept B. Vulnerability Climate change will
Sub-sector Guideline: (1) Coastal Protection (Adaptation Project) (2) Coastal Protection (BAU Development with Adaptation Options) Basic Concept A. General Concept B. Vulnerability Climate change will
AN ASSESSMENT OF THE IMPACT OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON THE WATER SECTOR IN THE CARIBBEAN
 11 TH ANNUAL CWWA CONFERNECE in conjunction with the 1 ST CARIBBEAN ENVIRONMENTAL FORUM AND EXHIBITION Sandals Grande St Lucian Resort Pigeon Island Causeway, St Lucia 7-11 October 2002 AN ASSESSMENT OF
11 TH ANNUAL CWWA CONFERNECE in conjunction with the 1 ST CARIBBEAN ENVIRONMENTAL FORUM AND EXHIBITION Sandals Grande St Lucian Resort Pigeon Island Causeway, St Lucia 7-11 October 2002 AN ASSESSMENT OF
Expert Meeting on Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation FAO Headquarters, Rome, 5-7 March Options for Decision Makers
 Expert Meeting on Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation FAO Headquarters, Rome, 5-7 March 2008 Options for Decision Makers Introduction Climate change will compound existing food insecurity and vulnerability
Expert Meeting on Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation FAO Headquarters, Rome, 5-7 March 2008 Options for Decision Makers Introduction Climate change will compound existing food insecurity and vulnerability
Water and Climate Change. David Coates Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity Montreal Canada
 Water and Climate Change David Coates Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity Montreal Canada Water and climate change How important is water? What do ecosystems have to do with it? How important
Water and Climate Change David Coates Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity Montreal Canada Water and climate change How important is water? What do ecosystems have to do with it? How important
LAW OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA NUMBER 7 OF 2004 REGARDING WATER RESOURCES
 LAW OF NUMBER 7 OF 2004 REGARDING WATER RESOURCES BY THE GRACE OF THE ALMIGHTY GOD, THE PRESIDENT OF Considering : a. that water resources is the gift of the Almighty God which gives benefits for the realization
LAW OF NUMBER 7 OF 2004 REGARDING WATER RESOURCES BY THE GRACE OF THE ALMIGHTY GOD, THE PRESIDENT OF Considering : a. that water resources is the gift of the Almighty God which gives benefits for the realization
11th International Riversymposium,
 Climate change impacts on fisheries production in Land-Water interface by Yemi Akegbejo-Samsons University of Agriculture Dept of Aquaculture & Fish Mgt Abeokuta, Nigeria Major Environmental Challenges
Climate change impacts on fisheries production in Land-Water interface by Yemi Akegbejo-Samsons University of Agriculture Dept of Aquaculture & Fish Mgt Abeokuta, Nigeria Major Environmental Challenges
Fresh Water Treaty. International Setting and Issues in Water, Environment and Development
 Fresh Water Treaty Preamble International Setting and Issues in Water, Environment and Development 1. In recent years most countries have faced a grave economic crisis which generated a great decrease
Fresh Water Treaty Preamble International Setting and Issues in Water, Environment and Development 1. In recent years most countries have faced a grave economic crisis which generated a great decrease
WASA Quiz Review. Chapter 2
 WASA Quiz Review Chapter 2 Question#1 What is surface runoff? part of the water cycle that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed into groundwater or evaporating Question #2 What are
WASA Quiz Review Chapter 2 Question#1 What is surface runoff? part of the water cycle that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed into groundwater or evaporating Question #2 What are
Groundwater Training Course SOPAC, April Island Groundwater Resources
 Groundwater Training Course SOPAC, April 2005 Island Groundwater Resources Outline of Presentation Freshwater resources of islands Water use Factors affecting freshwater resources Water resource management
Groundwater Training Course SOPAC, April 2005 Island Groundwater Resources Outline of Presentation Freshwater resources of islands Water use Factors affecting freshwater resources Water resource management
SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): AGRICULTURE, NATURAL RESOURCES, and RUDAL DEVELOPMENT. 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities
 Pehur High Level Canal Extension Project (RRP PAK 47024) SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): AGRICULTURE, NATURAL RESOURCES, and RUDAL DEVELOPMENT Sector Road Map 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities
Pehur High Level Canal Extension Project (RRP PAK 47024) SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): AGRICULTURE, NATURAL RESOURCES, and RUDAL DEVELOPMENT Sector Road Map 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities
Climate change Adaptation in South Asia
 Climate change Adaptation in South Asia SREEJA NAIR TERI South Asia Climate Change Focal Points and Experts Consultation Meeting, Thimphu, 16-17 November 2011 Global mean temperatures rising faster with
Climate change Adaptation in South Asia SREEJA NAIR TERI South Asia Climate Change Focal Points and Experts Consultation Meeting, Thimphu, 16-17 November 2011 Global mean temperatures rising faster with
National Water Policy for Palestine
 Palestinian National Authority Palestinian Water Authority National Water Policy for Palestine Final Draft Water Policy 2013-2032 1 1. Background 1.1 National Water Policy The purpose of this document
Palestinian National Authority Palestinian Water Authority National Water Policy for Palestine Final Draft Water Policy 2013-2032 1 1. Background 1.1 National Water Policy The purpose of this document
THREATS AND OPPORTUNITIES
 CLIMATE CHANGE AND TOURISM IN THE CARIBBEAN THREATS AND OPPORTUNITIES CARIBBEAN TOURISM ORGANISATION 9 TH Annual conference on Sustainable Tourism Development Grand Cayman, B.W. I U. O Trotz Caribbean
CLIMATE CHANGE AND TOURISM IN THE CARIBBEAN THREATS AND OPPORTUNITIES CARIBBEAN TOURISM ORGANISATION 9 TH Annual conference on Sustainable Tourism Development Grand Cayman, B.W. I U. O Trotz Caribbean
Open Working Group, February 2014: Australia, the Netherlands, United Kingdom Constituency Statement. Oceans and Seas, Forests and Biodiversity
 Open Working Group, February 2014: Australia, the Netherlands, United Kingdom Constituency Statement Oceans and Seas, Forests and Biodiversity Healthy ecosystems, biological diversity (biodiversity) and
Open Working Group, February 2014: Australia, the Netherlands, United Kingdom Constituency Statement Oceans and Seas, Forests and Biodiversity Healthy ecosystems, biological diversity (biodiversity) and
Challenges and Opportunities
 The 18th Asia-Pacific Seminar on Climate Change 2 3 March 2009, Hanoi, Viet Nam Viet Nam-Climate Change Adaptation: Challenges and Opportunities Nguyen Mong Cuong Task Leader, Vulnerability and Adaptation
The 18th Asia-Pacific Seminar on Climate Change 2 3 March 2009, Hanoi, Viet Nam Viet Nam-Climate Change Adaptation: Challenges and Opportunities Nguyen Mong Cuong Task Leader, Vulnerability and Adaptation
Hydrogeology and Water Related Issues in Hawaii and the Pacific
 Hydrogeology and Water Related Issues in Hawaii and the Pacific Stephen Anthony U.S. Geological Survey Honolulu, Hawaii U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey Presentation Overview Natural
Hydrogeology and Water Related Issues in Hawaii and the Pacific Stephen Anthony U.S. Geological Survey Honolulu, Hawaii U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey Presentation Overview Natural
Drought conditions and management strategies in Iran
 Drought conditions and management strategies in Iran Parviz Garshasbi Deputy head of watershed management forest, range and watershed management organization, Jihad-agriculture ministry p.garsh@yahoo.com
Drought conditions and management strategies in Iran Parviz Garshasbi Deputy head of watershed management forest, range and watershed management organization, Jihad-agriculture ministry p.garsh@yahoo.com
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience Project (PPCR) Saint Lucia
 Pilot Program for Climate Resilience Project (PPCR) Saint Lucia Neranda Maurice Sustainable Development & Environment Section Ministry of Physical Development & the Environment Government of Saint Lucia
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience Project (PPCR) Saint Lucia Neranda Maurice Sustainable Development & Environment Section Ministry of Physical Development & the Environment Government of Saint Lucia
Components, sub-components and statistical topics of the FDES 2013
 Environment Statistics Section, United Nations Statistics Division Components, sub-components and statistical topics of the FDES 2013 Component 1: Environmental conditions and quality 6. Environment Protection,
Environment Statistics Section, United Nations Statistics Division Components, sub-components and statistical topics of the FDES 2013 Component 1: Environmental conditions and quality 6. Environment Protection,
WATER AND THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE
 WATER AND THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE Summary Water is essential for the support of life and can be considered as a fundamental environmental good. Water is needed to support human habitation, grow crops and
WATER AND THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE Summary Water is essential for the support of life and can be considered as a fundamental environmental good. Water is needed to support human habitation, grow crops and
Santa Clara Valley Water District 2017 Water Supply Master Plan Planning Objectives
 Santa Clara Valley Water District 2017 Water Supply Master Plan Planning Objectives The purpose of the Water Supply Master Plan (Water Master Plan) is to present the District s strategy for ensuring a
Santa Clara Valley Water District 2017 Water Supply Master Plan Planning Objectives The purpose of the Water Supply Master Plan (Water Master Plan) is to present the District s strategy for ensuring a
UN-GGIM: Europe Work Group A «Core Data» SDG related use cases
 UN-GGIM: Europe Work Group A «Core Data» SDG related use cases Risk 1.5 Build the resilience of the poor and those in vulnerable situations and reduce their exposure and vulnerability to climate-related
UN-GGIM: Europe Work Group A «Core Data» SDG related use cases Risk 1.5 Build the resilience of the poor and those in vulnerable situations and reduce their exposure and vulnerability to climate-related
UNEP/AEO/ NEPAD Lead Indicators Change in incident of water borne diseases. UNSD suggestions. Population connected to public water supply
 Session 4: for the ECOWAS countries: level (based on research of official government websites), Questionnaire, NEPAD, (22 February 2005) Environmental health Environmentally related diseases: malaria,
Session 4: for the ECOWAS countries: level (based on research of official government websites), Questionnaire, NEPAD, (22 February 2005) Environmental health Environmentally related diseases: malaria,
2.4.0 CLIMATE CHANGE, EXPOSURE & RISK. Contents of Set : Guide 2.4.1: Activity : Activity : Activity 3 IN THIS SET YOU WILL:
 2.4.0 SERIES 2 Understanding Vulnerability & Risk CLIMATE CHANGE, EXPOSURE & RISK Contents of Set 2.4.0: Guide 2.4.1: Activity 1 2.4.2: Activity 2 2.4.3: Activity 3 One component of vulnerability to climate
2.4.0 SERIES 2 Understanding Vulnerability & Risk CLIMATE CHANGE, EXPOSURE & RISK Contents of Set 2.4.0: Guide 2.4.1: Activity 1 2.4.2: Activity 2 2.4.3: Activity 3 One component of vulnerability to climate
Chapter 4 - Changes in Impacts of Climate Extremes: Human Systems and Ecosystems
 to Advance Climate Change Adaptation (SREX) Chapter 4 - Changes in Impacts of Climate Extremes: Human Systems and Ecosystems Pascal Peduzzi 30 March 2012 Assesses exposure, vulnerability and impacts by
to Advance Climate Change Adaptation (SREX) Chapter 4 - Changes in Impacts of Climate Extremes: Human Systems and Ecosystems Pascal Peduzzi 30 March 2012 Assesses exposure, vulnerability and impacts by
National Water Demand Management Policy
 National Water Demand Management Policy Introduction In 1997, the Ministry of Water and Irrigation developed Jordan s Water Strategy and the following four policies, which include: Water Utility Policy;
National Water Demand Management Policy Introduction In 1997, the Ministry of Water and Irrigation developed Jordan s Water Strategy and the following four policies, which include: Water Utility Policy;
Title: Protection and Management of Shallow Groundwater Sources for South Tarawa
 Integrated Water Resources Management Demonstration Project Country: Republic of Kiribati Title: Protection and Management of Shallow Groundwater Sources for South Tarawa A. Executing Agency The Ministry
Integrated Water Resources Management Demonstration Project Country: Republic of Kiribati Title: Protection and Management of Shallow Groundwater Sources for South Tarawa A. Executing Agency The Ministry
SOUTHEAST FLORIDA S RESILIENT WATER RESOURCES INCLUDING A CASE STUDY FOR THE CITY OF POMPANO BEACH
 SOUTHEAST FLORIDA S RESILIENT WATER RESOURCES INCLUDING A CASE STUDY FOR THE CITY OF POMPANO BEACH SOUTHEAST FLORIDA S WATER INFRASTRUCTURE IS VULNERABLE TO CLIMATE CHANGE THE WATER INFRASTRUCTURE IN FLORIDA
SOUTHEAST FLORIDA S RESILIENT WATER RESOURCES INCLUDING A CASE STUDY FOR THE CITY OF POMPANO BEACH SOUTHEAST FLORIDA S WATER INFRASTRUCTURE IS VULNERABLE TO CLIMATE CHANGE THE WATER INFRASTRUCTURE IN FLORIDA
Water and agriculture
 Rural Development and Agriculture Briefing Note Water and agriculture Background According to the International Water Management Institute, 56% of global precipitation evaporates from forests, savannahs
Rural Development and Agriculture Briefing Note Water and agriculture Background According to the International Water Management Institute, 56% of global precipitation evaporates from forests, savannahs
8. Water Resources, Forests, and Their Related Issues in Japan
 8. Water Resources, Forests, and Their Related Issues in Japan Hideji MAITA 1 1. INTRODUCTION Water management in Japan has traditionally focused on manipulating the country s abundant supplies of freshwater
8. Water Resources, Forests, and Their Related Issues in Japan Hideji MAITA 1 1. INTRODUCTION Water management in Japan has traditionally focused on manipulating the country s abundant supplies of freshwater
Adaptation Strategy of the Slovak Republic on Adverse Impacts of Climate Change Overview: Executive Summary
 Adaptation Strategy of the Slovak Republic on Adverse Impacts of Climate Change Overview: Executive Summary Ministry of Environment of the Slovak Republic December 2016 Climate change has caused a wide
Adaptation Strategy of the Slovak Republic on Adverse Impacts of Climate Change Overview: Executive Summary Ministry of Environment of the Slovak Republic December 2016 Climate change has caused a wide
The Water Cycle and Water Insecurity
 The Water Cycle and Water Insecurity EQ1: What are the processes operating within the hydrological cycle from global to local scale? 6 & 8 markers = AO1. 12 & 20 markers = AO1 and AO2 larger weighting
The Water Cycle and Water Insecurity EQ1: What are the processes operating within the hydrological cycle from global to local scale? 6 & 8 markers = AO1. 12 & 20 markers = AO1 and AO2 larger weighting
Integrated Water Resource Management in Refugee Hosting Catchments
 Integrated Water Resource Management in Refugee Hosting Catchments Dr. Callist Tindimugaya Commissioner, Water Resources Planning and Regulation Ministry of Water and Environment 1 Introduction- water
Integrated Water Resource Management in Refugee Hosting Catchments Dr. Callist Tindimugaya Commissioner, Water Resources Planning and Regulation Ministry of Water and Environment 1 Introduction- water
Climate Change Country Profile: Viet Nam
 Climate Change Country Profile: Viet Nam 1. Country description 1.1 Geography Located in South-East Asia Borders China, Lao People s Democratic Republic, Cambodia and East Sea Coastline: 3260 km Total
Climate Change Country Profile: Viet Nam 1. Country description 1.1 Geography Located in South-East Asia Borders China, Lao People s Democratic Republic, Cambodia and East Sea Coastline: 3260 km Total
Land Degradation, Desertification Most Critical Challenges in West Asia, as Rolling Conflicts Damage Environment, Human Health
 Land Degradation, Desertification Most Critical Challenges in West Asia, as Rolling Conflicts Damage Environment, Human Health Land degradation and desertification The spread of land degradation and desertification
Land Degradation, Desertification Most Critical Challenges in West Asia, as Rolling Conflicts Damage Environment, Human Health Land degradation and desertification The spread of land degradation and desertification
IWRM And Water Planning in Gurara River Basin Engr. Abdul-Qadir D. Aliyu
 IWRM And Water Planning in Gurara River Basin Engr. Abdul-Qadir D. Aliyu National Water Resources Institute, Kaduna Nigeria. Outline Introduction IWRM Water Planning and Allocation Background Study Area
IWRM And Water Planning in Gurara River Basin Engr. Abdul-Qadir D. Aliyu National Water Resources Institute, Kaduna Nigeria. Outline Introduction IWRM Water Planning and Allocation Background Study Area
Testimony of Shari T. Wilson, Secretary Maryland Department of the Environment. Before. The Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works
 Testimony of Shari T. Wilson, Secretary Maryland Department of the Environment Before The Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works The Clean Energy Jobs and American Power Act (S. 1733) Wednesday,
Testimony of Shari T. Wilson, Secretary Maryland Department of the Environment Before The Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works The Clean Energy Jobs and American Power Act (S. 1733) Wednesday,
A Path to Resilient Water Resources
 Water Resources Management A Path to Resilient Water Resources Jason M. Bird CH2M August 17, 2017 (8:30-9:30 am) Tampa Convention Center Tampa, Florida About Presenter Jason Bird - Principal Technologist
Water Resources Management A Path to Resilient Water Resources Jason M. Bird CH2M August 17, 2017 (8:30-9:30 am) Tampa Convention Center Tampa, Florida About Presenter Jason Bird - Principal Technologist
BELIZE (INDC) Submitted to the UNFCCC on 1 October, 2015
 BELIZE (INDC) Submitted to the UNFCCC on 1 October, 2015 1. National Context Belize is a small country with relatively minor contributions to global greenhouse gas emissions and has limited capacity to
BELIZE (INDC) Submitted to the UNFCCC on 1 October, 2015 1. National Context Belize is a small country with relatively minor contributions to global greenhouse gas emissions and has limited capacity to
LINKAGES BETWEEN WOMEN, LIVELIHOODS & ENVIRONMENTAL SECURITY
 Nigeria in Focus LINKAGES BETWEEN WOMEN, LIVELIHOODS & ENVIRONMENTAL SECURITY Panel Discussion by George Akor Program Manager, Women Environmental Programme (WEP), Nigeria Key Messages Progress in human
Nigeria in Focus LINKAGES BETWEEN WOMEN, LIVELIHOODS & ENVIRONMENTAL SECURITY Panel Discussion by George Akor Program Manager, Women Environmental Programme (WEP), Nigeria Key Messages Progress in human
Agriculture and Climate Change Rural Urban Linkages. Erick Fernandes, Adviser, Agriculture & Rural Development
 Agriculture and Climate Change Rural Urban Linkages Erick Fernandes, Adviser, Agriculture & Rural Development 75% of the world s poor are rural and most are involved in farming In the 21st century, agriculture
Agriculture and Climate Change Rural Urban Linkages Erick Fernandes, Adviser, Agriculture & Rural Development 75% of the world s poor are rural and most are involved in farming In the 21st century, agriculture
SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): AGRICULTURE, NATURAL RESOURCES, AND RURAL DEVELOPMENT 1
 Country Partnership Strategy: People s Republic of China, 2016 2020 SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): AGRICULTURE, NATURAL RESOURCES, AND RURAL DEVELOPMENT 1 Sector Road Map A. Sector Performance, Problems,
Country Partnership Strategy: People s Republic of China, 2016 2020 SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): AGRICULTURE, NATURAL RESOURCES, AND RURAL DEVELOPMENT 1 Sector Road Map A. Sector Performance, Problems,
Integrated Water Management Developer Guidance
 WESTERN WATER Western Water Whole-of-water-cycle Strategy Integrated Water Management Developer Guidance Edition 1, 2018 For more information call 1300 650 422 or visit us at WesternWater.com.au Development
WESTERN WATER Western Water Whole-of-water-cycle Strategy Integrated Water Management Developer Guidance Edition 1, 2018 For more information call 1300 650 422 or visit us at WesternWater.com.au Development
Adaptation to climate change: key concepts
 LIFE08 ENV/IT/436 Adaptation to climate change: key concepts Domenico Gaudioso ISPRA Institute for Environmental Protection and Research Structure of the presentation Definitions Key concepts Types of
LIFE08 ENV/IT/436 Adaptation to climate change: key concepts Domenico Gaudioso ISPRA Institute for Environmental Protection and Research Structure of the presentation Definitions Key concepts Types of
Impact of Climate Change
 Impact of Climate Change Water resources Impact of Climate Change Agriculture and food security Forest Coastal areas > Temperature increase > Sea level rise > More rain Species and natural areas Human
Impact of Climate Change Water resources Impact of Climate Change Agriculture and food security Forest Coastal areas > Temperature increase > Sea level rise > More rain Species and natural areas Human
DEFINITION OF TERMS AND ACRONYMS 31 TAC EFFECTIVE DECEMBER 8, 2016
 DEFINITION OF TERMS AND ACRONYMS 31 TAC 357.10 EFFECTIVE DECEMBER 8, 2016 The terms and acronyms used in this guidance document as defined in 31 TAC 357.10 have the following meanings: 1. Agricultural
DEFINITION OF TERMS AND ACRONYMS 31 TAC 357.10 EFFECTIVE DECEMBER 8, 2016 The terms and acronyms used in this guidance document as defined in 31 TAC 357.10 have the following meanings: 1. Agricultural
LIST OF POSSIBLE APPLICATIONS OF DECADAL PREDICTION
 LIST OF POSSIBLE APPLICATIONS OF DECADAL PREDICTION Document prepared for CLIVAR Pacific Panel by: William Crawford, Rodney Martinez and Toshio Suga. October 2006 The decadal time period falls between
LIST OF POSSIBLE APPLICATIONS OF DECADAL PREDICTION Document prepared for CLIVAR Pacific Panel by: William Crawford, Rodney Martinez and Toshio Suga. October 2006 The decadal time period falls between
Water Resources. Chapter 13
 Water Resources Chapter 13 Freshwater Is an Irreplaceable Resource That We Are Managing Poorly Why is water so important? Health we are made up of 60% water, supplies us with food, shelter Sculpts earth
Water Resources Chapter 13 Freshwater Is an Irreplaceable Resource That We Are Managing Poorly Why is water so important? Health we are made up of 60% water, supplies us with food, shelter Sculpts earth
September 2016 ID Competency Statement Type
 September 06 Ensures that the impact assessment scope, criteria and conditions (geographic, environmental, economic, social, and cultural) are defined adequately. Develops a project management plan for
September 06 Ensures that the impact assessment scope, criteria and conditions (geographic, environmental, economic, social, and cultural) are defined adequately. Develops a project management plan for
Palestinian Water Sector Capacity Building
 Palestinian Water Sector Capacity Building By Khairy Al-Jamal Senior Infrastructure Specialist World Bank, MNSSD International Conference -Sustainable Development and Management of Water in Palestine-
Palestinian Water Sector Capacity Building By Khairy Al-Jamal Senior Infrastructure Specialist World Bank, MNSSD International Conference -Sustainable Development and Management of Water in Palestine-
Climate Change, Climate variability and Water Management
 Climate Change, Climate variability and Water Management Ainun Nishat Ph.D. Country Representative, Bangladesh IUCN, the International Union for Conservation of Nature From Water and Climate Change: IPCC
Climate Change, Climate variability and Water Management Ainun Nishat Ph.D. Country Representative, Bangladesh IUCN, the International Union for Conservation of Nature From Water and Climate Change: IPCC
Water Security for Sustainable Development: The challenge of Scarcity in the Middle East & North Africa
 Water Security for Sustainable Development: The challenge of Scarcity in the Middle East & North Africa Shawki Barghouti Director General International Center for Biosaline Agriculture 1 water scarcity
Water Security for Sustainable Development: The challenge of Scarcity in the Middle East & North Africa Shawki Barghouti Director General International Center for Biosaline Agriculture 1 water scarcity
Climate Change Research in support of Government Policy Implementation
 Climate Change Research in support of Government Policy Implementation Chris Moseki, Water Research Commission (WRC) of SA Public Hearing on Climate Change Parliament, Cape Town 18 November 2009 Pavel
Climate Change Research in support of Government Policy Implementation Chris Moseki, Water Research Commission (WRC) of SA Public Hearing on Climate Change Parliament, Cape Town 18 November 2009 Pavel
13 Water: A Limited Resource
 13 Water: A Limited Resource Overview of Chapter 13 Importance of Water Water Use and Resource Problems Water Problems in U.S. and Canada Global Water Problems Water Management Water Conservation Water
13 Water: A Limited Resource Overview of Chapter 13 Importance of Water Water Use and Resource Problems Water Problems in U.S. and Canada Global Water Problems Water Management Water Conservation Water
CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS IN GHANA
 CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS IN GHANA OPPONG-BOADI KYEKYEKU PRINCIPAL PROGRAMME OFFICER, ENERGY RESOURCES AND CLIMATE CHANGE UNIT, ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY ACCRA, GHANA. 1 INTRODUCTION Climate change
CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS IN GHANA OPPONG-BOADI KYEKYEKU PRINCIPAL PROGRAMME OFFICER, ENERGY RESOURCES AND CLIMATE CHANGE UNIT, ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY ACCRA, GHANA. 1 INTRODUCTION Climate change
DRAINAGE WATER REUSE STRATEGIC OPTIONS AND MEASURES TO ALLEVIATE RISK OF FAILURE (EGYPT)
 International Commission on Irrigation and Drainage 26 th Euro-mediterranean Regional Conference and Workshops «Innovate to improve Irrigation performances» WORKSHOP : FUTURE OF DRAINAGE UNDER ENVIRONMENTAL
International Commission on Irrigation and Drainage 26 th Euro-mediterranean Regional Conference and Workshops «Innovate to improve Irrigation performances» WORKSHOP : FUTURE OF DRAINAGE UNDER ENVIRONMENTAL
Domestic adaptation to climate change in Rwanda
 Annex I Expert Global Forum on Sustainable Development: Key Issues for the Post-2012 Climate Change Framework OECD, Paris 4-5 March 2009 Domestic adaptation to climate change in Rwanda By URAMUTSE Charles
Annex I Expert Global Forum on Sustainable Development: Key Issues for the Post-2012 Climate Change Framework OECD, Paris 4-5 March 2009 Domestic adaptation to climate change in Rwanda By URAMUTSE Charles
Directorate of Climate Change Department of Adaptation Training Workshop on National Adaptation Plans (NAPs) 4 to 7 September 2017 San Jose Costa Rica
 Directorate of Climate Change Department of Adaptation Training Workshop on National Adaptation Plans (NAPs) 4 to 7 September 2017 San Jose Costa Rica Questions and Answers Requested to Dominican Republic
Directorate of Climate Change Department of Adaptation Training Workshop on National Adaptation Plans (NAPs) 4 to 7 September 2017 San Jose Costa Rica Questions and Answers Requested to Dominican Republic
Lecture 14. Water: A Limited Resource. Lecture 14
 Lecture 14 Water: A Limited Resource Lecture 14 1. Importance of Water 2. Water Use and Resource Problems 3. Water Problems in U.S. and Canada 4. Global Water Problems 5. Water Management 6. Water Conservation
Lecture 14 Water: A Limited Resource Lecture 14 1. Importance of Water 2. Water Use and Resource Problems 3. Water Problems in U.S. and Canada 4. Global Water Problems 5. Water Management 6. Water Conservation
Palestinian Hydrology Group
 Palestinian Hydrology Group Identifying Vulnerabilities and Climate Risks; Climate Change Adaptation / Implementation in Palestine Dr. Ayman Rabi Palestinian National Workshop on Climate Change 26-28 January,
Palestinian Hydrology Group Identifying Vulnerabilities and Climate Risks; Climate Change Adaptation / Implementation in Palestine Dr. Ayman Rabi Palestinian National Workshop on Climate Change 26-28 January,
3. Present Situation of Environmental Problems
 3. Present Situation of Environmental Problems 3.1 Natural Environment The goals, issues and programmes regarding the natural environment of the Ten Year Perspective Development Plan 2001-2011 are shown
3. Present Situation of Environmental Problems 3.1 Natural Environment The goals, issues and programmes regarding the natural environment of the Ten Year Perspective Development Plan 2001-2011 are shown
VEGETATIVE, WATER, FISH AND WILDLIFE RESOURCES POLICIES
 VEGETATIVE, WATER, FISH AND WILDLIFE RESOURCES POLICIES The County will: GOALS AND OBJECTIVES 1.1 Conserve, Enhance, Protect, Maintain and Manage Vegetative, Water, Fish and Wildlife Resources Promote
VEGETATIVE, WATER, FISH AND WILDLIFE RESOURCES POLICIES The County will: GOALS AND OBJECTIVES 1.1 Conserve, Enhance, Protect, Maintain and Manage Vegetative, Water, Fish and Wildlife Resources Promote
Third Session: Small island developing States: Transport and trade logistics challenges. Ecosystems Based Adaptation for SIDS
 Multi-year Expert Meeting on Transport, Trade Logistics and Trade Facilitation Third Session: Small island developing States: Transport and trade logistics challenges 24 26 November 2014 Ecosystems Based
Multi-year Expert Meeting on Transport, Trade Logistics and Trade Facilitation Third Session: Small island developing States: Transport and trade logistics challenges 24 26 November 2014 Ecosystems Based
Integrated Water Resource Management: Water Security
 Integrated Water Resource Management: Water Security Asma Younas, PhD Principal Scientific Officer, UNESCO Chair on Knowledge Systems for IWRM, Pakistan July 10, 2017 Overview Water Security An Emerging
Integrated Water Resource Management: Water Security Asma Younas, PhD Principal Scientific Officer, UNESCO Chair on Knowledge Systems for IWRM, Pakistan July 10, 2017 Overview Water Security An Emerging
MINISTÈRE DES AFFAIRES ÉTRANGÈRES ET EUROPÉENNES 20 December /5 6th World Water Forum Ministerial Process Draft document
 MINISTÈRE DES AFFAIRES ÉTRANGÈRES ET EUROPÉENNES 20 December 2011 1/5 6th World Water Forum Ministerial Process Draft document 1. We the Ministers and Heads of Delegations assembled in Marseille, France,
MINISTÈRE DES AFFAIRES ÉTRANGÈRES ET EUROPÉENNES 20 December 2011 1/5 6th World Water Forum Ministerial Process Draft document 1. We the Ministers and Heads of Delegations assembled in Marseille, France,
Module 7 GROUNDWATER AND CLIMATE CHANGE
 Module 7 GROUNDWATER AND CLIMATE CHANGE Learning Objectives To become familiar with the basic concepts of the impacts of climate change on groundwater To explore the link between climate change impacts
Module 7 GROUNDWATER AND CLIMATE CHANGE Learning Objectives To become familiar with the basic concepts of the impacts of climate change on groundwater To explore the link between climate change impacts
SPATE IRRIGATION IN MALAWI: STATUS, POTENTIAL AND CHALLENGES.
 SPATE IRRIGATION IN MALAWI: STATUS, POTENTIAL AND CHALLENGES. Authors; Introduction Henry Njoloma (PhD) The Greenbelt Initiative, Office of President and Cabinet. Chairman, Rainwater Harvesting Association
SPATE IRRIGATION IN MALAWI: STATUS, POTENTIAL AND CHALLENGES. Authors; Introduction Henry Njoloma (PhD) The Greenbelt Initiative, Office of President and Cabinet. Chairman, Rainwater Harvesting Association
Climate Change (CC) Impacts & Adaptation
 Analysis for ENPI countries of Social and Economic Benefits of Enhanced Environmental Protection EuropeAid DCI-ENV/2009/225-962 Climate Change (CC) Impacts & Adaptation Alistair Hunt Department of Economics
Analysis for ENPI countries of Social and Economic Benefits of Enhanced Environmental Protection EuropeAid DCI-ENV/2009/225-962 Climate Change (CC) Impacts & Adaptation Alistair Hunt Department of Economics
PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE. Report No.: AB2140 Project Name
 PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Report No.: AB2140 Project Name Design and Implementation of Pilot Climate Change Adaptation Measures Region LATIN AMERICA AND CARIBBEAN Sector General
PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Report No.: AB2140 Project Name Design and Implementation of Pilot Climate Change Adaptation Measures Region LATIN AMERICA AND CARIBBEAN Sector General
HYDRAULICS DIVISION. Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mustafa ERGİL. Assoc. Prof. Dr. Umut TÜRKER
 HYDRAULICS DIVISION Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mustafa ERGİL Assoc. Prof. Dr. Umut TÜRKER HYDRAULICS AND C.E. Civil Engineers plan, design and construct: new harbors and waterways, pipelines, irrigation and drainage
HYDRAULICS DIVISION Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mustafa ERGİL Assoc. Prof. Dr. Umut TÜRKER HYDRAULICS AND C.E. Civil Engineers plan, design and construct: new harbors and waterways, pipelines, irrigation and drainage
DRAINAGE AND NATURAL AQUIFER GROUNDWATER RECHARGE ELEMENT
 Goal 7.0. To optimize integrated stormwater management in order to reduce damage and impacts from sea level rise and flooding, promotes recharge to the Surficial Aquifer System (SAS), improve and protect
Goal 7.0. To optimize integrated stormwater management in order to reduce damage and impacts from sea level rise and flooding, promotes recharge to the Surficial Aquifer System (SAS), improve and protect
Climate Change and Adaptation in Asia: Key Findings of the IPCC 5 th Assessment Report
 1 Climate Change and Adaptation in Asia: Key Findings of the IPCC 5 th Assessment Report Juan M. Pulhin, Professor and Dean College of Forestry and Natural Resources University of the Philippines Los Baños
1 Climate Change and Adaptation in Asia: Key Findings of the IPCC 5 th Assessment Report Juan M. Pulhin, Professor and Dean College of Forestry and Natural Resources University of the Philippines Los Baños
Cool waters and atmospheric high pressure
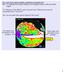 QU: How does human activity contribute to drought risk? AIM: To evaluate the human influence of drought events in Africa's Sahel region. ST: What part of the ENSO cycle is at work here? What does it mean
QU: How does human activity contribute to drought risk? AIM: To evaluate the human influence of drought events in Africa's Sahel region. ST: What part of the ENSO cycle is at work here? What does it mean
Water Resources on PEI: an overview and brief discussion of challenges
 Water Resources on PEI: an overview and brief discussion of challenges Components: Components and links Atmospheric water Surface water (including glacial water) Groundwater Links: Precipitation (atm(
Water Resources on PEI: an overview and brief discussion of challenges Components: Components and links Atmospheric water Surface water (including glacial water) Groundwater Links: Precipitation (atm(
