Sigma receptors were originally described in brain tissue, Sigma Receptor Antagonists Inhibit Human Lens Cell Growth and Induce Pigmentation
|
|
|
- Karin Crawford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sigma Receptor Antagonists Inhibit Human Lens Cell Growth and Induce Pigmentation Lixin Wang, 1 Alan R. Prescott, 2 Barbara A. Spruce, 3 Julie Sanderson, 1 and George Duncan 1 From the 1 School of Biological Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich, United Kingdom; the 2 Centre for High-Resolution Imaging (CHIPs), School of Life Sciences, and the 3 Department of Surgery and Molecular Oncology, Ninewells Hospital and Medical School, University of Dundee, Dundee, Scotland, United Kingdom. Supported by The Humane Research Trust, The Royal Society, Fight for Sight, and The Wellcome Trust. Submitted for publication October 12, 2004; revised December 17, 2004; accepted January 7, Disclosure: L. Wang, None; A.R. Prescott, None; B.A. Spruce, None; J. Sanderson, None; G. Duncan, None The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. This article must therefore be marked advertisement in accordance with 18 U.S.C solely to indicate this fact. Corresponding author: George Duncan, School of Biological Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich NR4 7TJ, UK; g.duncan@uea.ac.uk. PURPOSE. The expression of the Sigma 1 receptor and the ability of receptor antagonists to inhibit growth and induce pigment formation were investigated in human lens epithelial cells. METHODS. Capsular bags were formed for experimental purposes by performing sham cataract operations on donor lenses. The resultant bags were cultured in Eagle s minimum essential medium (EMEM) alone or supplemented with the Sigma receptor antagonists rimcazole (3 M) and BD1047 (10 M). Cell growth was monitored by phase microscopy. Tyrosine incorporation was quantified by culturing in the presence of 14-C tyrosine for 24 hours. At the end of the culture period, some bags were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for electron microscopy, and others were plunged into liquid nitrogen for later immunoblot and PCR analyses. Protein levels of tyrosinase (TYR), tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TYRP1), and tyrosinaserelated protein 2 (TYRP2) were quantified by Western blot analysis. The presence of pigment granules within epithelial cells were monitored by phase and electron microscopy techniques. RESULTS. The Sigma-1 receptor was expressed in native human lens cells and in cultured capsular bag cells. The Sigma receptor antagonists BD1047 and rimcazole inhibited lens cell growth and, surprisingly, lens cells accumulated pigment granules in the presence of the antagonists. The antagonists raised preexisting levels of TYR and TYRP1, whereas there was no change in TYRP2. CONCLUSIONS. The human lens normally expresses components of the melanin synthesis pathway, and this suggests a possible origin for the pigment granules that have been observed under certain conditions in the human lens. Exposure of lens cells to Sigma receptor antagonists leads to growth inhibition and pigment granule production. (Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005; 46: ) DOI: /iovs Sigma receptors were originally described in brain tissue, and Sigma ligands were developed to treat certain psychiatric disorders. 1 More recently, however, Sigma receptor antagonists have been shown to inhibit proliferation in mammary and colon carcinoma cell lines. 2 This has led to the development of specific Sigma ligands for diagnostic tumor imaging 3,4 and specific Sigma antagonists to control tumor growth. 5 A striking characteristic of the human lens is that it continues to grow throughout life by the division of cells in the equatorial region and the consequential production of fully differentiated fiber cells. 6 The robust growth of lens cells becomes clinically significant in the events that follow cataract surgery where a capsular bag is formed to hold the implanted intraocular lens. The ability of lens epithelial cells to colonize the posterior capsule after surgery provides the basis for posterior capsule opacification (PCO), which can induce a marked deterioration in vision for a significant proportion of patients with cataract. 7 Spruce et al. 5 have recently shown that primary cultures of bovine lens cells are unusually sensitive to Sigma receptor antagonists, compared with most other normal, untransformed cells and the Sigma-1 receptor has been reported to be present in the lens epithelium of mice. 8 In this study, we evaluated the potential of Sigma antagonists to inhibit lens epithelial cell growth in our human capsular bag model. 9 The results show that not only is messenger RNA for the Sigma-1 receptor expressed in human lens cells, but growth is indeed inhibited by Sigma antagonists. Exposure to the antagonists also induced pigmentation of the epithelial cells and, intriguingly, pigment granules of unknown origin have been reported to be present in certain cataracts and aged human lenses. 10 Cell pigmentation is critically important in the eye where, for example, oculocutaneous albinism leads to a loss of visual acuity and in extreme cases, blindness. 11 The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is heavily pigmented and a major function of melanin is to protect the retina by absorbing stray light. 12 There is also evidence that melanin has an antioxidant and free radical scavenging ability, and this is important in a number of cell types. 13 The synthesis of pigment by certain cell types is of great importance, not only in terms of protective mechanisms, but also in the acquisition of an aggressive cell phenotype, for example, in malignant melanomas. 14 The mechanisms underlying pigment dynamics are not well understood, partly because of the complexity of the control processes, but also because of the lack of availability of a suitable model system that does not normally pigment, but can be made to produce fully formed pigment granules. We propose that the normally optically clear lens provides an excellent model system for studying the molecular mechanisms of pigment granule formation. METHODS Preparation and Culture of Capsular Bags Human eye tissue donated for research was obtained from the East Anglian Eye Bank, and usage was in accordance with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Most eyes contained whole lenses, but four globes were also obtained from donors who had undergone cataract surgery. The resultant ex vivo capsular bag was dissected and used for RNA extraction. As previously described, 15 a sham cataract operation was performed on donor eyes, and the resultant capsular bag and anterior Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, April 2005, Vol. 46, No. 4 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology 1403
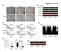
2 1404 Wang et al. IOVS, April 2005, Vol. 46, No. 4 epithelium were secured separately on PMMA dishes. Bags were maintained in EMEM alone 9 or EMEM supplemented with either 3 M rimcazole dihydrochloride (rimcazole), 10 M ( )-SK&F hydrochloride (SKF), and 3 or 10 M BD1047 dihydrochloride (BD1047) and incubated at 35 C in a 5% CO 2 atmosphere. Ongoing cell observations were performed with a phase-contrast microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) and images captured with a digital camera (Coolpix 950; Nikon) with associated software. Western Blot Analyses After dissection, epithelial preparations were maintained in EMEM, with or without 3 M rimcazole for 5 days. Cells were then lysed on ice in buffer: 50 mm HEPES (ph 7.5), 150 mm NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, 1 mm EDTA, 10% glycerol, 10 mm sodium pyrophosphate, 2 mm sodium orthovanadate, 10 mm sodium fluoride, 1 mm phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), and 10 g/ml aprotinin. Lysates were precleared by centrifuging at 13,000 rpm 4 C for 10 minutes, 16 and the protein content of the soluble fraction assayed (Pierce, Rockford, IL). Equal amounts of protein from each sample were loaded onto 10% SDS-PAGE gels for electrophoresis and transfer onto polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane (NEN Life Science Products, Boston, MA) with a semidry transfer cell (Trans-Blot; Bio-Rad, Herts, UK). Proteins were detected using a chemiluminescent blot analysis system (ECL ; Amersham Biosciences, Amersham, UK) with anti-tyr (Upstate Biotechnology, Lake Placid, NY), anti-tyrp1, anti-tyrp2, and anti-actin. The latter three were from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc. Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction After dissection, epithelial preparations, including ex vivo capsular bags, were washed in serum-free EMEM, and RNA was collected from the cells by using a mini kit (RNeasy; Qiagen, Ltd., Crawley, UK). RNA (250 ng) was reverse transcribed in a 20- L reaction mixture (Superscript II RT; Invitrogen, Ltd., Paisley, UK). cdna (1 L; diluted 1:5 in sterile double distilled water) was amplified by PCR in a 20- L reaction buffer in the following conditions: 0.5 M each primer (Invitrogen, Ltd.), 0.8 mm deoxy-nucleoside trisphosphate mixture (Bioline Ltd., London, UK), 10 mm Tris-HCl, 1.5 mm MgCl 2, 50 mm KCl, and 2.5 U TaqDNA polymerase (Roche Diagnostics, Lewes, UK). PCR was performed by using the following program with a thermal controller (MJ Research Inc., Reno, NV): initial denaturation 94 C for 2 minutes, denaturation at 94 C for 40 seconds, annealing at 50 C for 30 seconds, and extension at 72 C for 40 seconds. Steps 2 through 4 were cycled 27 times (GAPDH); 36 cycles (Sigma-1 receptor) with a final extension at 72 C for 10 minutes. The oligonucleotide primer (5 3 ) sequences specific for the genes examined were as follows: GAPDH: ACCA- CAGTCCATGCCATCAC (sense) and TCCACCACCCTGTTGCTGTA (anti-sense); Sigma 1 receptor: 5 -AGCGCGAAGAGATAGC-3 (sense) and 5 -AGCATAGGAGCGAAGAGT-3 (anti-sense). 8 PCR products, together with the 100-bp DNA markers (Invitrogen-Life Technologies), were run on a 1% agarose gel, and images were captured and analyzed (1D system; Eastman Kodak, Rochester, NY). 14 C-Tyrosine Uptake Capsular bags were maintained in EMEM or EMEM supplemented with 3 M rimcazole for 7 days (when the pigment granules could be observed in cells). Then, 2 Ci/mL of 14 C-tyrosine (Amersham Biosciences) was then added to each dish for an additional 24 hours. The bags were washed briefly twice with fresh EMEM, and the medium was then replaced with 1 ml of ice-cold 5% trichloroacetic acid (TCA). After 30 minutes, the TCA was removed from each well to determine cytosolic tyrosine levels. Then, 1 ml of 250 mm NaOH was added to each dish to digest the preparation and determine the radioisotope levels in the remaining fraction. Ten milliliters of scintillation fluid (HiSafe Supermix; PerkinElmer Life Sciences, Wellesley, MA) were then added to each scintillation vial and the samples assayed with a scintillation counter (PerkinElmer Life Sciences). Transmission Electron Microscopy The anterior epithelium and capsular bag specimens were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde while they were attached to the Petri dish. They were then postfixed for 1 hour in 1% glutaraldehyde and for 30 minutes in osmium tetroxide (OsO 4 ) in PBS, washed in PBS and dehydrated through graded alcohols, and soaked in propylene oxide (two times for 15 minutes each) before overnight infiltration in resin (Durcupan; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) and propylene oxide (1:1) followed by resin. Sections of 70-nm thickness were mounted onto copper grids and stained with 1% uranyl acetate and lead citrate before viewing in a transmission electron microscope (Tecnai 12; FEI, Hillsboro, OR) equipped with plates (model FDL5000; Fuji, Tokyo, Japan) which were scanned digitally (Ditabis, Pforzheim, Germany). Statistical Analysis All results are expressed as mean SEM. All experiments were performed on a matched-pair basis, with one donor eye serving as the control and the other eye from the same donor as the tested eye. Data were analyzed by a two-tailed t-test assuming equal variance. The level of significance was set as P RESULTS The data in Figure 1A show that messenger RNA for the Sigma-1 receptor was expressed in native human anterior and equatorial epithelial lens cells and expression was also retained in cells from a capsular bag recovered from a donor who had undergone cataract surgery (ex vivo bag). The growth of cells within the capsular bag cultured in vitro (Figs. 1B, 1C, 1D) shows the same pattern as found in vivo; in both cases, the posterior capsule was covered by a single monolayer of epithelial cells within approximately 14 days. The robust nature of this growth is shown by the fact that cell coverage occurred in vitro without the addition of serum or added growth factors. This robust growth was inhibited by the relatively nonselective Sigma antagonist rimcazole (Fig. 1B), and we have further shown that the Sigma-1 selective antagonist BD (10 M) also inhibited growth (Fig. 1C). Although the Sigma-2 receptor plays an important role in cell survival and growth in several systems, 18 the sensitivity of lens cells to BD1047 indicates that the Sigma-1 receptor may play the more important role in lens cells. The Sigma receptor agonist ( )-SKF had no significant effect on growth when added alone (Fig. 1D). Cell growth in human lens cells can be entirely suppressed and cell death induced by inactivating the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) calcium store, 19 and it is interesting that the Sigma-1 receptor appears to be located primarily in this compartment. 20,21 In fact, Sigma receptor agonists and antagonists have a profound, but complex, effect on calcium signaling, 4,5,20,22 which could help to explain why growth ultimately ceased and cells on the posterior capsule regressed when exposed to rimcazole or BD1047 for long periods (data not shown). Consistent with a role for calcium in Sigma-antagonist mediated lens cell growth inhibition, we have recently found that rimcazole empties the ER store in human lens cells (Collison DJ, Wang L, Duncan G, unpublished data, 2003). In addition, Sigma-1 receptor stimulation appears to be anti-apoptotic, 5 and antagonists such as BD1047 would therefore be expected ultimately to induce cell death. The retardation of growth on the posterior capsule generally took 7 days to become apparent, and during that time the cells became increasingly pigmented (Fig. 2A). Control cells, on the contrary, remained quite clear. Confluent anterior cells and actively growing posterior cells both underwent pigmentation. When the antagonist-treated cells were viewed using the transmission electron microscope (Fig. 2B), the pigment was seen to be packaged in vesicles and appeared to follow the
3 IOVS, April 2005, Vol. 46, No. 4 Sigma 1 Receptor and Lens Cell Growth Inhibition 1405 appear to have associated higher molecular weight species that probably reflect posttranslational modification of the original proteins. It should be noted that Zhao and Overbeek 25 failed to detect mrna transcripts for TYRP2 in the developing murine lens. This discrepancy may reflect species differences or indeed a low level of gene activity relative to protein levels. FIGURE 1. Sigma-1 receptor expression and growth control. (A) Expression of Sigma-1 receptor mrna in lens central epithelium (CE), equatorial epithelium (EE), and in vivo capsular bags (CB). (B, C) Effect of the antagonists rimcazole and BD1047 on the growth of cells across the posterior capsule. (D) Effect of the Sigma agonist SKF10047 on cell cover. (B D) 100% represents cell confluence on the posterior capsule. The data at each time point are expressed as mean SE (n 4). same developmental progression (stages 1 1V) as in MNT-1 melanoma cells (Fig. 2C). 23 The first stages of melanin synthesis involve the incorporation of tyrosine into the cell, and whereas rimcazole had no effect on uptake of labeled tyrosine into the freely exchanging pool (data not shown), it induced a significant increase in incorporation into the TCA precipitable fraction of matchpaired capsular bags (Fig. 3B), indicating that it may be incorporated into melanin. We therefore investigated the expression of other critical components of the tyrosine-melanin pathway (Fig. 3A) 24 specifically, TYR, TYRP1, and TYRP2. Surprising in an optically clear tissue such as the lens was that all three components were found to be present. Figure 3C gives the comparison of the expression of these proteins with two heavily pigmented cell types: human RPE cells (lane 2) and the melanoma cell line A2508 (lane 3). The non lens cells FIGURE 2. Sigma-1 receptor and pigmentation of lens cells. (A) Phase micrographs of cultured human lens cells on central anterior and posterior capsule, respectively. The capsular bags were maintained in serum-free or supplemented (3 M rimcazole) medium for 1 week, and at this time dark pigmented areas (arrowheads) were apparent in the treated bags. (B, C) Electron micrographs of cells on the posterior capsule. (B) Cross-sections of human lens epithelial cells grown (Ba) in control medium and (Bb) in the presence of 3 M BD1047. (C) Different stages of pigment granule formation (I IV) as defined in MNT-1 melanoma cells by Seiji et al. 23
4 1406 Wang et al. IOVS, April 2005, Vol. 46, No. 4 FIGURE 3. Effect of Sigma-1 receptor antagonism on components of the melanin synthesis pathway. (A) The melanin synthesis pathway. The critical steps involving tyrosine, TYR, TYRP1, and TYRP2 are indicated. (B) The effect of 3 M rimcazole on 14 C-tyrosine incorporation into protein in human lens epithelial cells over 24 hours. Data are expressed as a percentage of control incorporation and are given as mean SEM (n 6). *P 0.05; t-test. (C) Immunoblots giving the expression of TYR, TYRP1, and TYRP2 in (lane 1) freshly-isolated native human lens cells, (lane 2) freshly isolated RPE cells, and (lane 3) the melanoma cell line A2508. Numbers to the left indicate the molecular size (in kilodaltons) of the protein marker. (D) The effect of 3 M rimcazole on the expression of TYR, TYRP1, and TYRP2 in human lens epithelial cells by Western blot. Pooled data are given as the mean SEM (n 4). *P 0.05; paired t-test. Representative immunoblots for TYR, TYRP1, TYRP2, and -actin are also shown.
5 IOVS, April 2005, Vol. 46, No. 4 Sigma 1 Receptor and Lens Cell Growth Inhibition 1407 Pigment granules are present in capsular bag cells after 5 days of exposure to 3 M rimcazole and the protein expression data obtained at this time reveal a significant upregulation of TYR and TYRP1 (Fig. 3D). In these experiments, it was invaluable to be able to carry them out in a matched paired format. Although there was variation from donor to donor, the immunoblots from the rimcazole-treated epithelia for TYR and TYRP1 always gave a higher absorbance value than those from the control samples. DISCUSSION The growth data in Figure 1 confirm the conclusions of Spruce et al., 5 drawn from experiments on cultured bovine cells, that the lens is unusually sensitive to Sigma receptor antagonism. Untransformed cells are not usually influenced by these antagonists, and Spruce et al. 5 ascribed the sensitivity of lens and microvascular endothelial cells to their self-reliant, autocrine mode of survival. We have recently shown that human lens cells grown on the posterior capsule not only survive but actively proliferate in growth-factor free EMEM. 9 The molecular mechanisms for the growth inhibition are unknown, but they are believed to involve calcium signaling, channel modulation, and eventual apoptosis. 2,5,26 Although human lens cells exposed to rimcazole for prolonged periods ultimately die, they appear to undergo all the normal processes of melanin production 23,27 before they do so. Stage 1 is initiated in the ER, 28 and the progression to the fibrillar stage appears to involve both TYRP1 and -2. Once the fibrillar matrix has been generated, melanin synthesis is initiated and electron-dense pigment becomes deposited on the fibrils. TYR plays a critical role at this time. The availability of tyrosine itself is also important, and there is evidence that tyrosine levels can control the proliferative activity of pigmented cells. 29 High levels of tyrosine inhibit proliferation and increase the proportion of pigmented, highly differentiated cells. It should be noted that Spruce et al. 5 failed to report a similar pigmentation in bovine cells exposed to rimcazole, but they used higher concentrations of rimcazole, inducing rapid cell death and did not perform the detailed phase and EM studies necessary to establish the presence of pigment granules. It is now accepted that several factors increase pigmentation of melanoma cells, and these include an upregulation of TYR and the tyrosine-related proteins. 14,27 Conversely, oculocutaneous albinism, an ER retention disease, involves mutations of either TYR or TYRP1. 11 Human lens cells not only express TYR, TYRP1, and TYRP2, but the Sigma antagonist rimcazole significantly increased the expression of two of these. Furthermore, both Sigma antagonists increased pigment granule production in capsular bag cells. The human lens, therefore, has the potential, throughout life, to produce pigment granules but does not except under certain special circumstances. The data presented herein, suggest that one function of Sigma receptors could be to modulate pigment formation. Their location in the ER and their possible role in protein trafficking 20 indicate that they could control both proliferation, which in the human lens is critically dependent on a functional calcium store 19 and also melanin production, which initiates in the ER. 28 Iris pigmentation is increased on exposure to PGF2 ligands, 30 and tyrosinase expression is upregulated in cultures of iris cells exposed to latanoprost, a PGF2 receptor agonist. 31 Furthermore, this receptor signals by releasing calcium from the ER. The question remains as to why the lens expresses elements of the potentially damaging melanin biosynthesis pathway. In fact, the original investigators of both cataracta nigra (Fig. 4) and age-related axial pigmentation of the human lens suggested FIGURE 4. Section through a cataracta nigra lens removed by cryoprobe attached to the anterior surface (uppermost) followed by intracapsular extraction. The lens (1.1 cm in diameter) was frozen at 20 C immediately after surgery and later bisected, thawed at ambient temperature (18 C), and photographed. This lens was in fact processed as part of a past comparative cataract study involving the photography of lenses in vivo and in vitro. 32 The data were not used, as the patient could not focus for comparative in vivo photography. a possible explanation. 10 Although they did not know the source of the pigment granules they identified, the authors proposed that it might be within the lens itself and argued that, if this were the case, the lens must possess at least some of the enzymes involved in melanin synthesis (Fig. 3A). They also pointed out that most of the melanin precursors are actually powerful antioxidants 10 and so could play a protecting role. In this context, it is known that skin or RPE cells respond to photo-oxidation insults by increasing melanin production. 13 The cataracta nigra lens illustrated in Figure 4 shows that the black pigmentation of the anterior portion of the lens accompanies a dense brunescent nuclear cataract. In nuclear cataract, the central regions of the lens have a high concentration of oxidized methionine and glutathione, as well as protein-mixed disulfides, all indicating prolonged oxidative insults to the lens. 33 The lens becomes increasingly brunescent with age and browning via the Maillard reaction, 34 and tryptophan oxidation 6 undoubtedly contributes to this process, which is accelerated in nuclear cataract. 34 Intriguingly, the melanin synthesis pathway can also produce brunescent products in the presence of free sulfhydryl groups. 35 Pirie 36 has pointed out that exposure of lens proteins to oxidized tyrosine itself can produce brunescent products. An increasing activation of the tyrosine-melanin synthesis pathway has thus the potential to explain not only cataracta nigra, but also the brunescent pigmentation in the much more common age-related nuclear cataract. 10,34,36 Sigma receptors of different subtypes appear to act in opposite ways to regulate apoptosis. Sigma-1 receptors appear to be antiapoptotic, whereas Sigma-2 receptors are proapoptotic, 5,18 and Sigma-1 receptors may also be involved in neuroprotection. 37 The Sigma-1 knockout mouse shows no abnormal phenotype and behaves in a manner similar to their control littermates. However, they show different physiological responses when stressed, 38 and this may also be critical in the lack of induction in lens changes. We cannot unequivocally propose a Sigma-1-specific role for the antagonist effects that we observe, as we cannot exclude that the Sigma-2 receptor may be present in the human lens. Until this receptor is cloned and sequenced and the appropriate reagents are available this, will have to remain unresolved. However, we have established the presence of Sigma-1 and have found that the Sigma-1- specific antagonist BD1047 induces pigmentation. We there-
6 1408 Wang et al. IOVS, April 2005, Vol. 46, No. 4 fore suggest that the Sigma-1 receptor has an important protective role in minimizing the harmful effects of photooxidation. In cells where the melanin pathway has been upregulated, it is crucial to distribute correctly the enzyme components if full melanin synthesis is not to be the result. Sigma-1 ligands are known to disrupt the dynamic relationship of the receptor with the ER, 20 and this we propose links the unscheduled production of pigment granules with inhibition of cell growth. Acknowledgments The authors thank Michael Wormstone for helpful discussions on all aspects of the work, Ian Clark for providing the melanoma cell line (A2058), and John James (Centre for High-resolution Imaging; CHIPS) for technical assistance. References 1. Quirion R, Bowen WD, Itzhak Y, et al. A proposal for the classification of sigma binding sites. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992;13: Brent PJ, Pang GT. Sigma binding site ligands inhibit cell proliferation in mammary and colon carcinoma cell lines and melanoma cells in culture. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995;278: John CS, Vilner BJ, Geyer BC, Moody T, Bowen WD. Targeting Sigma receptor-binding benzamides as in vivo diagnostic and therapeutic agents for human prostate tumors. Cancer Res. 1999;59: Brent PJ, Herd L, Saunders H, Sim AT, Dunkley PR. Protein phosphorylation and calcium uptake into rat forebrain synaptosomes: modulation by the sigma ligand, 1,3-ditolylguanidine. J Neurochem. 1997;68: Spruce BA, Campbell LA, McTavish N, et al. Small molecule antagonists of the -1 receptor cause selective release of the death program in tumor and self-reliant cells and inhibit tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 2004;64: Harding J. Cataract. London: Chapman & Hall; Wormstone IM. Posterior capsule opacification: a cell biological perspective. Exp Eye Res. 2002;74: Shamsul Ola M, Moore P, El-Sherbeny A, et al. Expression pattern of sigma receptor 1 mrna and protein in mammalian retina. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2001;95: Wormstone IM, Liu CS, Rakic JM, Marcantonio JM, Vrensen GF, Duncan G. Human lens epithelial cell proliferation in a protein-free medium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997;38: Duke-Elder S. Diseases of the lens and vitreous. London: H Kimpton; System of Ophthalmology; Vol Toyofuku K, Wada I, Valencia JC, Kushimoto T, Ferrans VJ, Hearing VJ. Oculocutaneous albinism types 1 and 3 are ER retention diseases: mutation of tyrosinase or Tyrp1 can affect the processing of both mutant and wild-type proteins. FASEB J. 2001;15: Forrester JV, Dick AD, McMenamin PG, Lee WR. The Eye. 2nd ed. New York: Saunders, Elsevier Science Ltd.; Hirobe T, Kawa Y, Mizoguchi M, Ito S, Wakamatsu K. Effects of genic substitution at the pink-eyed dilution locus on the proliferation and differentiation of mouse epidermal melanocytes in vivo and in vitro. J Exp Zool. 2002;292: Hochberg M, Lotem M, Gimon Z, Shiloni E, Enk CD. Expression of tyrosinase, MIA and MART-1 in sentinel lymph nodes of patients with malignant melanoma. Br J Dermatol. 2002;146: Liu CS, Wormstone IM, Duncan G, Marcantonio JM, Webb SF, Davies PD. A study of human lens cell growth in vitro: a model for posterior capsule opacification. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1996; 37: Maidment JM, Duncan G, Tamiya S, Collison DJ, Wang L, Wormstone IM. Regional differences in tyrosine kinase receptor signaling components determine differential growth patterns in the human lens. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2004;45: Matsumoto RR, Bowen WD, Tom MA, Vo VN, Truong DD, De Costa BR. Characterization of two novel sigma receptor ligands: antidystonic effects in rats suggest sigma receptor antagonism. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995;280: Crawford KW, Bowen WD. Sigma-2 receptor agonists activate a novel apoptotic pathway and potentiate antineoplastic drugs in breast tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 2002;62: Duncan G, Wormstone IM, Liu CS, Marcantonio JM, Davies PD. Thapsigargin-coated intraocular lenses inhibit human lens cell growth. Nat Med. 1997;3: Hayashi T, Su TP. Regulating ankyrin dynamics: roles of sigma-1 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98: Hanner M, Moebius FF, Flandorfer A, et al. Purification, molecular cloning, and expression of the mammalian sigma1-binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93: Hayashi T, Kagaya A, Takebayashi M, et al. Modulation by sigma ligands of intracellular free Ca mobilization by N-methyl-Daspartate in primary culture of rat frontal cortical neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995;275: Seiji M, Iwashita S. On the site of melanin formation in melanocytes. J Biochem (Tokyo). 1963;54: Korner A, Pawelek J. Mammalian tyrosinase catalyzes three reactions in the biosynthesis of melanin. Science. 1982;217: Zhao S, Overbeek PA. Tyrosinase-related protein 2 promoter targets transgene expression to ocular and neural crest-derived tissues. Dev Biol. 1999;216: Aydar E, Palmer CP, Djamgoz MB. Sigma receptors and cancer: possible involvement of ion channels. Cancer Res. 2004;64: Watabe H, Valencia JC, Yasumoto K, et al. Regulation of tyrosinase processing and trafficking by organellar ph and by proteasome activity. J Biol Chem. 2004;279: Kushimoto T, Valencia JC, Costin GE, et al. The Seiji memorial lecture: the melanosome: an ideal model to study cellular differentiation. Pigment Cell Res. 2003;16: Schwahn DJ, Xu W, Herrin AB, Bales ES, Medrano EE. Tyrosine levels regulate the melanogenic response to alpha-melanocytestimulating hormone in human melanocytes: implications for pigmentation and proliferation. Pigment Cell Res. 2001;14: Drago F, Marino A, La Manna C. alpha-methyl-p-tyrosine inhibits latanoprost-induced melanogenesis in vitro. Exp Eye Res. 1999;68: Lindsey JD, Jones HL, Hewitt EG, Angert M, Weinreb RN. Induction of tyrosinase gene transcription in human iris organ cultures exposed to latanoprost. Arch Ophthalmol. 2001;119: Marcantonio JM, Duncan G, Davies PD, Bushell AR. Classification of human senile cataracts by nuclear colour and sodium content. Exp Eye Res. 1980;31: Truscott RJ, Augusteyn RC. Oxidative changes in human lens proteins during senile nuclear cataract formation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977;492: Monnier VM, Kohn RR, Cerami A. Accelerated age-related browning of human collagen in diabetes mellitus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1984;81: Barsh GS. What controls variation in human skin color? Public Library of Science Biology. 2003;1: Pirie A. Reaction of tyrosine oxidation products with proteins of the lens. Biochem J. 1968;109: Martin PM, Ola MS, Agarwal N, Ganapathy V, Smith SB. The sigma receptor ligand ( )-pentazocine prevents apoptotic retinal ganglion cell death induced in vitro by homocysteine and glutamate. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004;123: Langa F, Codony X, Tovar V, et al. Generation and phenotypic analysis of sigma receptor type I (sigma 1) knockout mice. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;18:
Apoptosis And Anti-tumor Effect Induced By Mtor Inhibitor And Autophagy Inhibitor In Human Osteosarcoma Cells
 Apoptosis And Anti-tumor Effect Induced By Mtor Inhibitor And Autophagy Inhibitor In Human Osteosarcoma Cells Ryosuke Horie. Kagawa University of medecine, Kita-gun, Japan. Disclosures: R. Horie: None.
Apoptosis And Anti-tumor Effect Induced By Mtor Inhibitor And Autophagy Inhibitor In Human Osteosarcoma Cells Ryosuke Horie. Kagawa University of medecine, Kita-gun, Japan. Disclosures: R. Horie: None.
Gα 13 Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Gα 13 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 80401 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 Table of Content Product
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Gα 13 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 80401 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 Table of Content Product
RNA was isolated using NucleoSpin RNA II (Macherey-Nagel, Bethlehem, PA) according to the
 Supplementary Methods RT-PCR and real-time PCR analysis RNA was isolated using NucleoSpin RNA II (Macherey-Nagel, Bethlehem, PA) according to the manufacturer s protocol and quantified by measuring the
Supplementary Methods RT-PCR and real-time PCR analysis RNA was isolated using NucleoSpin RNA II (Macherey-Nagel, Bethlehem, PA) according to the manufacturer s protocol and quantified by measuring the
Gα i Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Gα i Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number 80301 20 assays NewEast Biosciences, Inc 1 Table of Content Product
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Gα i Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number 80301 20 assays NewEast Biosciences, Inc 1 Table of Content Product
Supplemental methods:
 Supplemental methods: ASC-J9 treatment ASC-J9 was patented by the University of Rochester, the University of North Carolina, and AndroScience Corp., and then licensed to AndroScience Corp. Both the University
Supplemental methods: ASC-J9 treatment ASC-J9 was patented by the University of Rochester, the University of North Carolina, and AndroScience Corp., and then licensed to AndroScience Corp. Both the University
Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg
![Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg](/thumbs/84/90687567.jpg) Supplementary information Supplementary methods PCNA antibody and immunodepletion Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg extracts, one volume of protein
Supplementary information Supplementary methods PCNA antibody and immunodepletion Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg extracts, one volume of protein
Site directed mutagenesis, Insertional and Deletion Mutagenesis. Mitesh Shrestha
 Site directed mutagenesis, Insertional and Deletion Mutagenesis Mitesh Shrestha Mutagenesis Mutagenesis (the creation or formation of a mutation) can be used as a powerful genetic tool. By inducing mutations
Site directed mutagenesis, Insertional and Deletion Mutagenesis Mitesh Shrestha Mutagenesis Mutagenesis (the creation or formation of a mutation) can be used as a powerful genetic tool. By inducing mutations
supplementary information
 DOI: 1.138/ncb1839 a b Control 1 2 3 Control 1 2 3 Fbw7 Smad3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 c d IGF-1 IGF-1Rβ IGF-1Rβ-P Control / 1 2 3 4 Real-time RT-PCR Relative quantity (IGF-1/ mrna) 2 1 IGF-1 1 2 3 4 Control /
DOI: 1.138/ncb1839 a b Control 1 2 3 Control 1 2 3 Fbw7 Smad3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 c d IGF-1 IGF-1Rβ IGF-1Rβ-P Control / 1 2 3 4 Real-time RT-PCR Relative quantity (IGF-1/ mrna) 2 1 IGF-1 1 2 3 4 Control /
B. ADM: C. D. Apoptosis: 1.68% 2.99% 1.31% Figure.S1,Li et al. number. invaded cells. HuH7 BxPC-3 DLD-1.
 A. - Figure.S1,Li et al. B. : - + - + - + E-cadherin CK19 α-sma vimentin β -actin C. D. Apoptosis: 1.68% 2.99% 1.31% - : - + - + - + Apoptosis: 48.33% 45.32% 44.59% E. invaded cells number 400 300 200
A. - Figure.S1,Li et al. B. : - + - + - + E-cadherin CK19 α-sma vimentin β -actin C. D. Apoptosis: 1.68% 2.99% 1.31% - : - + - + - + Apoptosis: 48.33% 45.32% 44.59% E. invaded cells number 400 300 200
Cdc42 Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Cdc42 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 80701 20 assays 1 Table of Content Product Description 3 Assay
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Cdc42 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 80701 20 assays 1 Table of Content Product Description 3 Assay
MeCP2. MeCP2/α-tubulin. GFP mir1-1 mir132
 Conservation Figure S1. Schematic showing 3 UTR (top; thick black line), mir132 MRE (arrow) and nucleotide sequence conservation (vertical black lines; http://genome.ucsc.edu). a GFP mir1-1 mir132 b GFP
Conservation Figure S1. Schematic showing 3 UTR (top; thick black line), mir132 MRE (arrow) and nucleotide sequence conservation (vertical black lines; http://genome.ucsc.edu). a GFP mir1-1 mir132 b GFP
Analysing protein protein interactions using a GST-fusion protein to pull down the interacting target from the cell lysate Hong Wang and Xin Zeng
 Analysing protein protein interactions using a GST-fusion protein to pull down the interacting target from the cell lysate Hong Wang and Xin Zeng Department of Molecular Genetics, Biochemistry and Microbiology,
Analysing protein protein interactions using a GST-fusion protein to pull down the interacting target from the cell lysate Hong Wang and Xin Zeng Department of Molecular Genetics, Biochemistry and Microbiology,
The Wnt-5a-derived hexapeptide Foxy-5 inhibits breast cancer. metastasis in vivo by targeting cell motility
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL: The Wnt-5a-derived hexapeptide Foxy-5 inhibits breast cancer metastasis in vivo by targeting cell motility Annette Säfholm, Johanna Tuomela, Jeanette Rosenkvist, Janna Dejmek, Pirkko
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL: The Wnt-5a-derived hexapeptide Foxy-5 inhibits breast cancer metastasis in vivo by targeting cell motility Annette Säfholm, Johanna Tuomela, Jeanette Rosenkvist, Janna Dejmek, Pirkko
Fig. S1. Effect of p120-catenin overexpression on the interaction of SCUBE2 with E-cadherin. The expression plasmid encoding FLAG.
 Fig. S1. Effect of p120-catenin overexpression on the interaction of SCUBE2 with E-cadherin. The expression plasmid encoding FLAG.SCUBE2, E-cadherin.Myc, or HA.p120-catenin was transfected in a combination
Fig. S1. Effect of p120-catenin overexpression on the interaction of SCUBE2 with E-cadherin. The expression plasmid encoding FLAG.SCUBE2, E-cadherin.Myc, or HA.p120-catenin was transfected in a combination
RheB Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based RheB Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 81201 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 FAX: 610-945-2008 Table
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based RheB Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 81201 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 FAX: 610-945-2008 Table
Arf6 Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Arf6 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 82401 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 Table of Content Product
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Arf6 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 82401 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 Table of Content Product
Non-Organic-Based Isolation of Mammalian microrna using Norgen s microrna Purification Kit
 Application Note 13 RNA Sample Preparation Non-Organic-Based Isolation of Mammalian microrna using Norgen s microrna Purification Kit B. Lam, PhD 1, P. Roberts, MSc 1 Y. Haj-Ahmad, M.Sc., Ph.D 1,2 1 Norgen
Application Note 13 RNA Sample Preparation Non-Organic-Based Isolation of Mammalian microrna using Norgen s microrna Purification Kit B. Lam, PhD 1, P. Roberts, MSc 1 Y. Haj-Ahmad, M.Sc., Ph.D 1,2 1 Norgen
Rat Neurotrophin-3 ELISA Kit (rnt-3-elisa)
 Rat Neurotrophin-3 ELISA Kit (rnt-3-elisa) Cat. No. EK0474 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) is a new member of the nerve growth factor gene family which plays an important
Rat Neurotrophin-3 ELISA Kit (rnt-3-elisa) Cat. No. EK0474 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) is a new member of the nerve growth factor gene family which plays an important
Supplementary data. sienigma. F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM. a-p53
 Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
Rab5 Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Rab5 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 83701 20 assays 24 Whitewoods Lane 1 Table of Content Product
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Rab5 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 83701 20 assays 24 Whitewoods Lane 1 Table of Content Product
Data Sheet IDO2 - HEK293 Recombinant Cell Line Cat #: 60533
 Data Sheet IDO2 - HEK293 Recombinant Cell Line Cat #: 60533 Description Recombinant HEK293 cell line expressing tetracycline-inducible human indoleamine 2,3- dioxygenase (IDO2), Genbank accession number
Data Sheet IDO2 - HEK293 Recombinant Cell Line Cat #: 60533 Description Recombinant HEK293 cell line expressing tetracycline-inducible human indoleamine 2,3- dioxygenase (IDO2), Genbank accession number
EpiQuik Methyl-CpG Binding Domain Protein 2 ChIP Kit
 EpiQuik Methyl-CpG Binding Domain Protein 2 ChIP Kit Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Methyl-CpG Binding Domain Protein 2 ChIP Kit is suitable for combining the
EpiQuik Methyl-CpG Binding Domain Protein 2 ChIP Kit Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Methyl-CpG Binding Domain Protein 2 ChIP Kit is suitable for combining the
Anti-CLOCK (Mouse) mab
 Page 1 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Anti-CLOCK (Mouse) mab CODE No. D349-3 CLONALITY CLONE ISOTYPE QUANTITY SOURCE IMMUNOGEN FORMURATION STORAGE Monoclonal CLSP4 Mouse IgG1
Page 1 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Anti-CLOCK (Mouse) mab CODE No. D349-3 CLONALITY CLONE ISOTYPE QUANTITY SOURCE IMMUNOGEN FORMURATION STORAGE Monoclonal CLSP4 Mouse IgG1
EZ-Zyme Chromatin Prep Kit
 Instruction Manual for EZ-Zyme Chromatin Prep Kit Catalog # 17 375 Sufficient reagents for 22 enzymatic chromatin preparations per kit. Contents Page I. INTRODUCTION 2 II. EZ-Zyme KIT COMPONENTS 3 A. Provided
Instruction Manual for EZ-Zyme Chromatin Prep Kit Catalog # 17 375 Sufficient reagents for 22 enzymatic chromatin preparations per kit. Contents Page I. INTRODUCTION 2 II. EZ-Zyme KIT COMPONENTS 3 A. Provided
Heparan Sulphate in Breast Cancer Low, Y.L.A 1 and Yip, C.W.G 2
 Heparan Sulphate in Breast Cancer Low, Y.L.A 1 and Yip, C.W.G 2 Department of Anatomy, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore MD10, 4 Medical Drive, Singapore 117597 ABSTRACT
Heparan Sulphate in Breast Cancer Low, Y.L.A 1 and Yip, C.W.G 2 Department of Anatomy, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore MD10, 4 Medical Drive, Singapore 117597 ABSTRACT
EPIGENTEK. EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit. Base Catalog # P-2002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE
 EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity of
EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity of
RNP-IP (Modified Method)-Getting Majority RNA from RNA Binding Protein in the Cytoplasm Fengzhi Liu *
 RNP-IP (Modified Method)-Getting Majority RNA from RNA Binding Protein in the Cytoplasm Fengzhi Liu * School of Biomedical Sciences, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, USA *For correspondence:
RNP-IP (Modified Method)-Getting Majority RNA from RNA Binding Protein in the Cytoplasm Fengzhi Liu * School of Biomedical Sciences, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, USA *For correspondence:
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Anti-NRF2 mab
 Page 1 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Anti-NRF2 mab CODE No. M200-3 CLONALITY CLONE ISOTYPE QUANTITY SOURCE IMMUNOGEN FORMURATION STORAGE Monoclonal 1F2 Mouse IgG1 100 L,
Page 1 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Anti-NRF2 mab CODE No. M200-3 CLONALITY CLONE ISOTYPE QUANTITY SOURCE IMMUNOGEN FORMURATION STORAGE Monoclonal 1F2 Mouse IgG1 100 L,
Tumor tissues or cells were homogenized and proteins were extracted using
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Western Blotting Tumor tissues or cells were homogenized and proteins were extracted using T-PER tissue protein extraction buffer. Protein concentrations were determined
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Western Blotting Tumor tissues or cells were homogenized and proteins were extracted using T-PER tissue protein extraction buffer. Protein concentrations were determined
INVESTIGATION OF THE BINDING SPECIFICITY OF IGF-IR USING MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES
 INVESTIGATION OF THE BINDING SPECIFICITY OF IGF-IR USING MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES By Mehrnaz Keyhanfar, Pharm.D. A thesis submitted to the University of Adelaide, South Australia in fulfilment of the requirements
INVESTIGATION OF THE BINDING SPECIFICITY OF IGF-IR USING MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES By Mehrnaz Keyhanfar, Pharm.D. A thesis submitted to the University of Adelaide, South Australia in fulfilment of the requirements
Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Fluorometric)
 Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Fluorometric) Catalog Number KA1539 48 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use...
Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Fluorometric) Catalog Number KA1539 48 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use...
NEBNext RNase III RNA Fragmentation Module
 SAMPLE PREPARATION NEBNext RNase III RNA Fragmentation Module Instruction Manual NEB #E6146S 100 reactions NEBNext RNase III RNA Fragmentation Module Table of Contents: Description....2 Applications....2
SAMPLE PREPARATION NEBNext RNase III RNA Fragmentation Module Instruction Manual NEB #E6146S 100 reactions NEBNext RNase III RNA Fragmentation Module Table of Contents: Description....2 Applications....2
HCV Genotype Primer Kit
 Instruction Manual for HCV Genotype Primer Kit HCV Genotype Determination Kit for Research Purpose Thoroughly read this instruction manual before use of this kit Background Study of nucleotide sequence
Instruction Manual for HCV Genotype Primer Kit HCV Genotype Determination Kit for Research Purpose Thoroughly read this instruction manual before use of this kit Background Study of nucleotide sequence
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods sirna sequences used in this study The sequences of Stealth Select RNAi for ALK and FLOT-1 were as follows: ALK sense no.1 (ALK): 5 -AAUACUGACAGCCACAGGCAAUGUC-3 ; ALK
Supplementary Materials and Methods sirna sequences used in this study The sequences of Stealth Select RNAi for ALK and FLOT-1 were as follows: ALK sense no.1 (ALK): 5 -AAUACUGACAGCCACAGGCAAUGUC-3 ; ALK
Fisher (Fairlawn, NJ) and Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO) and were used without further. (Promega) and DpnI (New England Biolabs, Beverly, MA).
 175 Appendix III Chapter 4 Methods General. Unless otherwise noted, reagents were purchased from the commercial suppliers Fisher (Fairlawn, NJ) and Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO) and were used without further
175 Appendix III Chapter 4 Methods General. Unless otherwise noted, reagents were purchased from the commercial suppliers Fisher (Fairlawn, NJ) and Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO) and were used without further
Mice TRAMP mice were maintained in a C57BL/6J background. Syngeneic UBI-GFP/BL6 mice were used for bone marrow engraftment. 2
 Antibodies Chicken IgY polyclonal α-gfp antibodies were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, MA) and were detected using α-chicken IgY-FITC or α-chicken-hrp (also purchased from Abcam). The CD31-PE, CD11b-PE,
Antibodies Chicken IgY polyclonal α-gfp antibodies were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, MA) and were detected using α-chicken IgY-FITC or α-chicken-hrp (also purchased from Abcam). The CD31-PE, CD11b-PE,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Tal et al. 10.1073/pnas.0807694106 SI Materials and Methods VSV Infection and Quantification. Infection was carried out by seeding 5 10 5 MEF cells per well in a 6-well plate and
Supporting Information Tal et al. 10.1073/pnas.0807694106 SI Materials and Methods VSV Infection and Quantification. Infection was carried out by seeding 5 10 5 MEF cells per well in a 6-well plate and
Apoptosis assay: Apoptotic cells were identified by Annexin V-Alexa Fluor 488 and Propidium
 Apoptosis assay: Apoptotic cells were identified by Annexin V-Alexa Fluor 488 and Propidium Iodide (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) staining. Briefly, 2x10 5 cells were washed once in cold PBS and resuspended
Apoptosis assay: Apoptotic cells were identified by Annexin V-Alexa Fluor 488 and Propidium Iodide (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) staining. Briefly, 2x10 5 cells were washed once in cold PBS and resuspended
Flow cytometric determination of apoptosis by annexin V/propidium iodide double staining.
 Supplementary materials and methods Flow cytometric determination of apoptosis by annexin V/propidium iodide double staining. Cells were analyzed for phosphatidylserine exposure by an annexin-v FITC/propidium
Supplementary materials and methods Flow cytometric determination of apoptosis by annexin V/propidium iodide double staining. Cells were analyzed for phosphatidylserine exposure by an annexin-v FITC/propidium
Supplemental Online Material. The mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line #10 derived from β-arrestin1 -/- -β-arrestin2 -/-
 #1074683s 1 Supplemental Online Material Materials and Methods Cell lines and tissue culture The mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line #10 derived from β-arrestin1 -/- -β-arrestin2 -/- knock-out animals
#1074683s 1 Supplemental Online Material Materials and Methods Cell lines and tissue culture The mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line #10 derived from β-arrestin1 -/- -β-arrestin2 -/- knock-out animals
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit
 HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
Supplementary material and methods
 Inhibitory effect of caffeic acid on ADP-induced thrombus formation and platelet activation involves mitogen-activated protein kinases Yu Lu 1,2,3,#, Quan Li 3,4,#, Yu-Ying Liu 3,4, Kai Sun 3,4, Jing-Yu
Inhibitory effect of caffeic acid on ADP-induced thrombus formation and platelet activation involves mitogen-activated protein kinases Yu Lu 1,2,3,#, Quan Li 3,4,#, Yu-Ying Liu 3,4, Kai Sun 3,4, Jing-Yu
CHAPTER 5 PTP-1B CLONING AND RECOMBINANT PROTEIN EXPRESSION. Recombinant DNA technology has revolutionized molecular biology and
 204 CHAPTER 5 PTP-1B CLONING AND RECOMBINANT PROTEIN EXPRESSION SUMMARY Recombinant DNA technology has revolutionized molecular biology and genetics. Today, virtually any segment of DNA, the genetic material
204 CHAPTER 5 PTP-1B CLONING AND RECOMBINANT PROTEIN EXPRESSION SUMMARY Recombinant DNA technology has revolutionized molecular biology and genetics. Today, virtually any segment of DNA, the genetic material
Solid Phase cdna Synthesis Kit
 #6123 v.02.09 Table of Contents I. Description... 2 II. Kit components... 2 III. Storage... 2 IV. Principle... 3 V. Protocol V-1. Preparation of immobilized mrna... 4 Protocol A: Starting from Tissue or
#6123 v.02.09 Table of Contents I. Description... 2 II. Kit components... 2 III. Storage... 2 IV. Principle... 3 V. Protocol V-1. Preparation of immobilized mrna... 4 Protocol A: Starting from Tissue or
Supplementary Figure 1. Co-localization of GLUT1 and DNAL4 in BeWo cells cultured
 Supplementary Figure 1. Co-localization of GLUT1 and DNAL4 in BeWo cells cultured under static conditions. Cells were seeded in the chamber area of the device and cultured overnight without medium perfusion.
Supplementary Figure 1. Co-localization of GLUT1 and DNAL4 in BeWo cells cultured under static conditions. Cells were seeded in the chamber area of the device and cultured overnight without medium perfusion.
. Viability of colonies was then assessed using the WST-1 reagent as described above, and normalized relative to untreated controls.
 Cell viability analysis in the absence of disaggregation To assess cell viability in the absence of disaggregation, quintuplicate samples of cells at 5 x 1 5 /ml were treated with mab (1 µg/ml) for 24
Cell viability analysis in the absence of disaggregation To assess cell viability in the absence of disaggregation, quintuplicate samples of cells at 5 x 1 5 /ml were treated with mab (1 µg/ml) for 24
Online Supporting Material for. The Bisecting GlcNAc on N-Glycans Inhibits Growth. Factor Signaling and Retards Mammary Tumor
 Online Supporting Material for The Bisecting GlcNAc on N-Glycans Inhibits Growth Factor Signaling and Retards Mammary Tumor Progression Yinghui Song 1, Jason A. Aglipay 1, Joshua D. Bernstein 2, Sumanta
Online Supporting Material for The Bisecting GlcNAc on N-Glycans Inhibits Growth Factor Signaling and Retards Mammary Tumor Progression Yinghui Song 1, Jason A. Aglipay 1, Joshua D. Bernstein 2, Sumanta
Sarker et al. Supplementary Material. Subcellular Fractionation
 Supplementary Material Subcellular Fractionation Transfected 293T cells were harvested with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and centrifuged at 2000 rpm (500g) for 3 min. The pellet was washed, re-centrifuged
Supplementary Material Subcellular Fractionation Transfected 293T cells were harvested with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and centrifuged at 2000 rpm (500g) for 3 min. The pellet was washed, re-centrifuged
ProtoScript. First Strand cdna Synthesis Kit DNA AMPLIFICATION & PCR. Instruction Manual. NEB #E6300S/L 30/150 reactions Version 2.
 DNA AMPLIFICATION & PCR ProtoScript First Strand cdna Synthesis Kit Instruction Manual NEB #E6300S/L 30/150 reactions Version 2.2 11/16 be INSPIRED drive DISCOVERY stay GENUINE This product is intended
DNA AMPLIFICATION & PCR ProtoScript First Strand cdna Synthesis Kit Instruction Manual NEB #E6300S/L 30/150 reactions Version 2.2 11/16 be INSPIRED drive DISCOVERY stay GENUINE This product is intended
Fig. S1 TGF RI inhibitor SB effectively blocks phosphorylation of Smad2 induced by TGF. FET cells were treated with TGF in the presence of
 Fig. S1 TGF RI inhibitor SB525334 effectively blocks phosphorylation of Smad2 induced by TGF. FET cells were treated with TGF in the presence of different concentrations of SB525334. Cells were lysed and
Fig. S1 TGF RI inhibitor SB525334 effectively blocks phosphorylation of Smad2 induced by TGF. FET cells were treated with TGF in the presence of different concentrations of SB525334. Cells were lysed and
EPIGENTEK. EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit. Base Catalog # P-2003 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE
 EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2003 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity
EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2003 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity
Supplemental Table 1: Sequences of real time PCR primers. Primers were intronspanning
 Symbol Accession Number Sense-primer (5-3 ) Antisense-primer (5-3 ) T a C ACTB NM_001101.3 CCAGAGGCGTACAGGGATAG CCAACCGCGAGAAGATGA 57 HSD3B2 NM_000198.3 CTTGGACAAGGCCTTCAGAC TCAAGTACAGTCAGCTTGGTCCT 60
Symbol Accession Number Sense-primer (5-3 ) Antisense-primer (5-3 ) T a C ACTB NM_001101.3 CCAGAGGCGTACAGGGATAG CCAACCGCGAGAAGATGA 57 HSD3B2 NM_000198.3 CTTGGACAAGGCCTTCAGAC TCAAGTACAGTCAGCTTGGTCCT 60
Data Sheet. TCR activator / PD-L1 - CHO Recombinant Cell line Cat. #: 60536
 Data Sheet TCR activator / PD-L1 - CHO Recombinant Cell line Cat. #: 60536 Product Description Recombinant CHO-K1 cells constitutively expressing human PD-L1 (Programmed Cell Death 1 Ligand 1, CD274, B7
Data Sheet TCR activator / PD-L1 - CHO Recombinant Cell line Cat. #: 60536 Product Description Recombinant CHO-K1 cells constitutively expressing human PD-L1 (Programmed Cell Death 1 Ligand 1, CD274, B7
WesternMAX Alkaline Phosphatase Chemiluminescent Detection Kits
 WesternMAX Alkaline Phosphatase Chemiluminescent Detection Kits Code N221-KIT N220-KIT Description WesternMAX Chemiluminescent AP Kit, Anti-Mouse Includes: Alkaline Phosphatase (AP) Conjugated Anti-Mouse
WesternMAX Alkaline Phosphatase Chemiluminescent Detection Kits Code N221-KIT N220-KIT Description WesternMAX Chemiluminescent AP Kit, Anti-Mouse Includes: Alkaline Phosphatase (AP) Conjugated Anti-Mouse
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SIRTUIN 1 PROMOTES HYPEROXIA-INDUCED LUNG EPITHELIAL DEATH INDEPENDENT OF NRF2 ACTIVATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SIRTUIN PROMOTES HYPEROXIA-INDUCED LUNG EPITHELIAL DEATH INDEPENDENT OF NRF ACTIVATION Haranatha R. Potteti*, Subbiah Rajasekaran*, Senthilkumar B. Rajamohan*, Chandramohan R. Tamatam,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SIRTUIN PROMOTES HYPEROXIA-INDUCED LUNG EPITHELIAL DEATH INDEPENDENT OF NRF ACTIVATION Haranatha R. Potteti*, Subbiah Rajasekaran*, Senthilkumar B. Rajamohan*, Chandramohan R. Tamatam,
sirna Transfection Into Primary Neurons Using Fuse-It-siRNA
 sirna Transfection Into Primary Neurons Using Fuse-It-siRNA This Application Note describes a protocol for sirna transfection into sensitive, primary cortical neurons using Fuse-It-siRNA. This innovative
sirna Transfection Into Primary Neurons Using Fuse-It-siRNA This Application Note describes a protocol for sirna transfection into sensitive, primary cortical neurons using Fuse-It-siRNA. This innovative
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Intrinsic protein-protein interaction mediated and chaperonin assisted sequential assembly of a stable Bardet Biedl syndome protein complex, the BBSome * Qihong Zhang 1#, Dahai
Supplemental Information Intrinsic protein-protein interaction mediated and chaperonin assisted sequential assembly of a stable Bardet Biedl syndome protein complex, the BBSome * Qihong Zhang 1#, Dahai
EpiQuik Tissue Methyl-CpG Binding Domain Protein 2 ChIP Kit
 EpiQuik Tissue Methyl-CpG Binding Domain Protein 2 ChIP Kit Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Tissue Methyl-CpG Binding Domain Protein 2 ChIP Kit is suitable for
EpiQuik Tissue Methyl-CpG Binding Domain Protein 2 ChIP Kit Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Tissue Methyl-CpG Binding Domain Protein 2 ChIP Kit is suitable for
Data Sheet. Hippo Pathway TEAD Reporter MCF7 Cell Line Catalog #: 60618
 Data Sheet Hippo Pathway TEAD Reporter MCF7 Cell Line Catalog #: 6618 Background The Hippo pathway regulates cell proliferation and cell death. It is activated by high cell density and cell stress to stop
Data Sheet Hippo Pathway TEAD Reporter MCF7 Cell Line Catalog #: 6618 Background The Hippo pathway regulates cell proliferation and cell death. It is activated by high cell density and cell stress to stop
ENDEXT Technology. Instruction manual for protein synthesis. with wheat germ cell-free system
 ENDEXT Technology Instruction manual for protein synthesis with wheat germ cell-free system 1 Protocol Overview Plasmid DNA construction (see Section 3.1) Preparation of plasmid DNA for transcription (see
ENDEXT Technology Instruction manual for protein synthesis with wheat germ cell-free system 1 Protocol Overview Plasmid DNA construction (see Section 3.1) Preparation of plasmid DNA for transcription (see
Roche Molecular Biochemicals Technical Note No. LC 12/2000
 Roche Molecular Biochemicals Technical Note No. LC 12/2000 LightCycler Absolute Quantification with External Standards and an Internal Control 1. General Introduction Purpose of this Note Overview of Method
Roche Molecular Biochemicals Technical Note No. LC 12/2000 LightCycler Absolute Quantification with External Standards and an Internal Control 1. General Introduction Purpose of this Note Overview of Method
Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy
 Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy HL-6 and cells were cultured and cytospun onto glass slides. The cells were double immunofluorescence stained for Mt NPM1 and fibrillarin (nucleolar marker). Briefly,
Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy HL-6 and cells were cultured and cytospun onto glass slides. The cells were double immunofluorescence stained for Mt NPM1 and fibrillarin (nucleolar marker). Briefly,
Supplementary Information: Materials and Methods. Immunoblot and immunoprecipitation. Cells were washed in phosphate buffered
 Supplementary Information: Materials and Methods Immunoblot and immunoprecipitation. Cells were washed in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and lysed in TNN lysis buffer (50mM Tris at ph 8.0, 120mM NaCl
Supplementary Information: Materials and Methods Immunoblot and immunoprecipitation. Cells were washed in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and lysed in TNN lysis buffer (50mM Tris at ph 8.0, 120mM NaCl
For quantitative detection of mouse IGF-1 in serum, body fluids, tissue lysates or cell culture supernatants.
 Mouse IGF-1 ELISA Kit (migf-1-elisa) Cat. No. EK0378 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also known as somatomedin C, is a polypeptide protein hormone similar
Mouse IGF-1 ELISA Kit (migf-1-elisa) Cat. No. EK0378 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also known as somatomedin C, is a polypeptide protein hormone similar
Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT - Reporter - Jurkat Recombinant Cell Line Catalog #: 60535
 Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT - Reporter - Jurkat Recombinant Cell Line Catalog #: 60535 Product Description Recombinant Jurkat T cell expressing firefly luciferase gene under the control of NFAT response elements
Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT - Reporter - Jurkat Recombinant Cell Line Catalog #: 60535 Product Description Recombinant Jurkat T cell expressing firefly luciferase gene under the control of NFAT response elements
of the Triphosphate of ATP
 A Small Aptamer with Strong and Specific Recognition of the Triphosphate of Peter L. Sazani, Rosa Larralde and Jack W. Szostak Howard Hughes Medical Institute, and Department of Molecular Biology, Massachusetts
A Small Aptamer with Strong and Specific Recognition of the Triphosphate of Peter L. Sazani, Rosa Larralde and Jack W. Szostak Howard Hughes Medical Institute, and Department of Molecular Biology, Massachusetts
Rat IGF-1 ELISA Kit (rigf-1-elisa)
 Rat IGF-1 ELISA Kit (rigf-1-elisa) Cat. No. EK0377 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also known as somatomedin C, is a polypeptide protein hormone similar
Rat IGF-1 ELISA Kit (rigf-1-elisa) Cat. No. EK0377 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also known as somatomedin C, is a polypeptide protein hormone similar
ProductInformation TECHNICAL BULLETIN MULTIPLE TISSUE NORTHERN BLOT, MOUSE. Product No. BLOT-2 Technical Bulletin No. MB-865 February 2000
 MULTIPLE TISSUE NORTHERN BLOT, MOUSE Product No. BLOT-2 Technical Bulletin No. MB-865 February 2000 ProductInformation TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description Sigma s Mouse Multiple Tissue Northern Blot
MULTIPLE TISSUE NORTHERN BLOT, MOUSE Product No. BLOT-2 Technical Bulletin No. MB-865 February 2000 ProductInformation TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description Sigma s Mouse Multiple Tissue Northern Blot
HLA-DR TYPING OF GENOMIC DNA
 HLA-DR TYPING OF GENOMIC DNA Zofia SZCZERKOWSKA, Joanna WYSOCKA Institute of Forensic Medicine, Medical University, Gdañsk, Poland ABSTRACT: Advances in molecular biology techniques allowed for introduction
HLA-DR TYPING OF GENOMIC DNA Zofia SZCZERKOWSKA, Joanna WYSOCKA Institute of Forensic Medicine, Medical University, Gdañsk, Poland ABSTRACT: Advances in molecular biology techniques allowed for introduction
Combining Techniques to Answer Molecular Questions
 Combining Techniques to Answer Molecular Questions UNIT FM02 How to cite this article: Curr. Protoc. Essential Lab. Tech. 9:FM02.1-FM02.5. doi: 10.1002/9780470089941.etfm02s9 INTRODUCTION This manual is
Combining Techniques to Answer Molecular Questions UNIT FM02 How to cite this article: Curr. Protoc. Essential Lab. Tech. 9:FM02.1-FM02.5. doi: 10.1002/9780470089941.etfm02s9 INTRODUCTION This manual is
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA). Nuclear extracts were. oligonucleotide spanning the NF-kB site (5 -GATCC-
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA). Nuclear extracts were prepared as previously described. (1) A [ 32 P] datp-labeled doublestranded oligonucleotide spanning
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA). Nuclear extracts were prepared as previously described. (1) A [ 32 P] datp-labeled doublestranded oligonucleotide spanning
Generation of Non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae Directed Gene Deletion Mutants Jeroen D. Langereis *
 Generation of Non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae Directed Gene Deletion Mutants Jeroen D. Langereis * Laboratory of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, Department of Pediatrics and Laboratory of Medical Immunology,
Generation of Non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae Directed Gene Deletion Mutants Jeroen D. Langereis * Laboratory of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, Department of Pediatrics and Laboratory of Medical Immunology,
Supplementary Figure 1 - Characterization of rbag3 binding on macrophages cell surface.
 Supplementary Figure 1 - Characterization of rbag3 binding on macrophages cell surface. (a) Human PDAC cell lines were treated as indicated in Figure 1 panel F. Cells were analyzed for FITC-rBAG3 binding
Supplementary Figure 1 - Characterization of rbag3 binding on macrophages cell surface. (a) Human PDAC cell lines were treated as indicated in Figure 1 panel F. Cells were analyzed for FITC-rBAG3 binding
Checkpoint Kinase Activity Immunoblot Kit
 Product Manual Checkpoint Kinase Activity Immunoblot Kit Catalog Number STA- 413 20 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cdc25C is a protein phosphatase responsible
Product Manual Checkpoint Kinase Activity Immunoblot Kit Catalog Number STA- 413 20 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cdc25C is a protein phosphatase responsible
DNA Microarray Technology
 CHAPTER 1 DNA Microarray Technology All living organisms are composed of cells. As a functional unit, each cell can make copies of itself, and this process depends on a proper replication of the genetic
CHAPTER 1 DNA Microarray Technology All living organisms are composed of cells. As a functional unit, each cell can make copies of itself, and this process depends on a proper replication of the genetic
High Pure RNA Isolation Kit for isolation of total RNA from 50 samples Cat. No
 for isolation of total RNA from 50 samples Cat. No. 1 88 665 Principle A single reagent lyses the sample lysis and inactivates RNase. In the presence of a chaotropic salt (guanidine HCl), the released
for isolation of total RNA from 50 samples Cat. No. 1 88 665 Principle A single reagent lyses the sample lysis and inactivates RNase. In the presence of a chaotropic salt (guanidine HCl), the released
At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
To determine the effect of N1IC in the susceptibility of T cells to the tolerogenic effect of tumorassociated
 Supplementary Methods Tolerogenic effect of MDSC To determine the effect of N1IC in the susceptibility of T cells to the tolerogenic effect of tumorassociated MDSC in vivo, we used a model described previously
Supplementary Methods Tolerogenic effect of MDSC To determine the effect of N1IC in the susceptibility of T cells to the tolerogenic effect of tumorassociated MDSC in vivo, we used a model described previously
FIVEphoton Biochemicals
 Human Cyclophilin B (CYPB) ELISA Kit Protocol Protocol for other species is identical except for dilutions of species specific standard. Use the protocol shipped with the kit for your experiment. FIVEphoton
Human Cyclophilin B (CYPB) ELISA Kit Protocol Protocol for other species is identical except for dilutions of species specific standard. Use the protocol shipped with the kit for your experiment. FIVEphoton
Data Sheet CD137/NF-κB Reporter - HEK293 Recombinant Cell Line Catalog # 79289
 Data Sheet CD137/NF-κB Reporter - HEK293 Recombinant Cell Line Catalog # 79289 Background Human CD137 (4-1BB; TNFRS9) is an inducible co-stimulatory molecule that activates T cells. CD137:CD137L-mediated
Data Sheet CD137/NF-κB Reporter - HEK293 Recombinant Cell Line Catalog # 79289 Background Human CD137 (4-1BB; TNFRS9) is an inducible co-stimulatory molecule that activates T cells. CD137:CD137L-mediated
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Study of mgtl translation in vitro. (A) Detection of 5 LR RNA using wild-type and anti-sd (91-95) substituted templates in a transcription-translation
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Study of mgtl translation in vitro. (A) Detection of 5 LR RNA using wild-type and anti-sd (91-95) substituted templates in a transcription-translation
EpiQuik Global Histone H3 Phosphorylation (Ser28) Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
 EpiQuik Global Histone H3 Phosphorylation (Ser28) Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Global Histone H3 Phosphorylation (Ser28) Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
EpiQuik Global Histone H3 Phosphorylation (Ser28) Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Global Histone H3 Phosphorylation (Ser28) Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
ReliaBLOT TM. IP/Western Blot Reagents Cat. No. WB120, rabbit
 ReliaBLOT TM Introduction: IP/Western Blot Reagents Cat. No. WB120, rabbit ReliaBLOT TM IP/Western Blot Reagents and Procedures (patent pending) provide an improved method for the detection of immunoprecipitated
ReliaBLOT TM Introduction: IP/Western Blot Reagents Cat. No. WB120, rabbit ReliaBLOT TM IP/Western Blot Reagents and Procedures (patent pending) provide an improved method for the detection of immunoprecipitated
Human skin punch biopsies were obtained under informed consent from normal healthy
 SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Acquisition of human skin specimens. Human skin punch biopsies were obtained under informed consent from normal healthy volunteers (n = 30) and psoriasis patients (n = 45) under a
SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Acquisition of human skin specimens. Human skin punch biopsies were obtained under informed consent from normal healthy volunteers (n = 30) and psoriasis patients (n = 45) under a
5.36 Biochemistry Laboratory Spring 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.36 Biochemistry Laboratory Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Laboratory Manual for URIECA
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.36 Biochemistry Laboratory Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Laboratory Manual for URIECA
RNA oligonucleotides and 2 -O-methylated oligonucleotides were synthesized by. 5 AGACACAAACACCAUUGUCACACUCCACAGC; Rand-2 OMe,
 Materials and methods Oligonucleotides and DNA constructs RNA oligonucleotides and 2 -O-methylated oligonucleotides were synthesized by Dharmacon Inc. (Lafayette, CO). The sequences were: 122-2 OMe, 5
Materials and methods Oligonucleotides and DNA constructs RNA oligonucleotides and 2 -O-methylated oligonucleotides were synthesized by Dharmacon Inc. (Lafayette, CO). The sequences were: 122-2 OMe, 5
Data Sheet. Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Gli Reporter NIH3T3 Cell Line Catalog #: 60409
 Data Sheet Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Gli Reporter NIH3T3 Cell Line Catalog #: 60409 Product Description The Gli Reporter NIH3T3 Cell Line is designed for monitoring the activity of the hedgehog signaling
Data Sheet Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Gli Reporter NIH3T3 Cell Line Catalog #: 60409 Product Description The Gli Reporter NIH3T3 Cell Line is designed for monitoring the activity of the hedgehog signaling
Human Neurotrophin-3 ELISA Kit
 Human Neurotrophin-3 ELISA Kit CATALOG NO: IRKTAH5200 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE For quantitative detection of human Neurotrophin-3 in cell culture supernates and serum. BACKGROUND Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3)
Human Neurotrophin-3 ELISA Kit CATALOG NO: IRKTAH5200 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE For quantitative detection of human Neurotrophin-3 in cell culture supernates and serum. BACKGROUND Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3)
Human Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) ELISA Kit
 Human Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) ELISA Kit Catalog No: IRKTAH2579 Lot No: SAMPLE INTRODUCTION Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) is a 70 amino acid polypeptide protein hormone with molecular
Human Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) ELISA Kit Catalog No: IRKTAH2579 Lot No: SAMPLE INTRODUCTION Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) is a 70 amino acid polypeptide protein hormone with molecular
RNA Blue REAGENT FOR RAPID ISOLATION OF PURE AND INTACT RNA (Cat. No. R011, R012, R013)
 RNA Blue REAGENT FOR RAPID ISOLATION OF PURE AND INTACT RNA (Cat. No. R011, R012, R013) WARNING: RNA Blue contains phenol and some other toxic components. After contact with skin, wash immediately with
RNA Blue REAGENT FOR RAPID ISOLATION OF PURE AND INTACT RNA (Cat. No. R011, R012, R013) WARNING: RNA Blue contains phenol and some other toxic components. After contact with skin, wash immediately with
Thermo Scientific GeneJET Whole Blood RNA Purification Mini Kit #K0761
 PRODUCT INFORMATION Thermo Scientific GeneJET Whole Blood RNA Purification Mini Kit #K0761 www.thermoscientific.com/onebio #K0761 Lot Exp. CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS Thermo Scientific GeneJET Whole Blood
PRODUCT INFORMATION Thermo Scientific GeneJET Whole Blood RNA Purification Mini Kit #K0761 www.thermoscientific.com/onebio #K0761 Lot Exp. CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS Thermo Scientific GeneJET Whole Blood
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Taylor et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201403021/dc1 Figure S1. Representative images of Cav 1a -YFP mutants with and without LMB treatment.
Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Taylor et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201403021/dc1 Figure S1. Representative images of Cav 1a -YFP mutants with and without LMB treatment.
Cytotoxicity of Botulinum Neurotoxins Reveals a Direct Role of
 Supplementary Information Cytotoxicity of Botulinum Neurotoxins Reveals a Direct Role of Syntaxin 1 and SNAP-25 in Neuron Survival Lisheng Peng, Huisheng Liu, Hongyu Ruan, William H. Tepp, William H. Stoothoff,
Supplementary Information Cytotoxicity of Botulinum Neurotoxins Reveals a Direct Role of Syntaxin 1 and SNAP-25 in Neuron Survival Lisheng Peng, Huisheng Liu, Hongyu Ruan, William H. Tepp, William H. Stoothoff,
FMF NIRCA PROTOCOL STEP 1.
 FMF NIRCA PROTOCOL STEP 1. After you have isolated patient s DNA and DNA from a healthy donor (wild type), you perform a nested PCR. The primers used to amplify exon 2 and exon 10 of the mefv gene are
FMF NIRCA PROTOCOL STEP 1. After you have isolated patient s DNA and DNA from a healthy donor (wild type), you perform a nested PCR. The primers used to amplify exon 2 and exon 10 of the mefv gene are
ProductInformation. Genomic DNA Isolation Kit. Product No. GDI-3 Technical Bulletin No. MB-275 May 2000 TECHNICAL BULLETIN
 Genomic DNA Isolation Kit Product No. GDI-3 Technical Bulletin No. MB-275 May 2000 TECHNICAL BULLETIN ProductInformation Product Description Sigma s Genomic DNA Isolation Kit isolates genomic DNA from
Genomic DNA Isolation Kit Product No. GDI-3 Technical Bulletin No. MB-275 May 2000 TECHNICAL BULLETIN ProductInformation Product Description Sigma s Genomic DNA Isolation Kit isolates genomic DNA from
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
Supplemental Data. Noncoding Transcription by RNA Polymerase Pol IVb/Pol V Mediates Transcriptional Silencing of Overlapping and Adjacent Genes
 Cell, Volume 135 Supplemental Data Noncoding Transcription by RNA Polymerase Pol IVb/Pol V Mediates Transcriptional Silencing of Overlapping and Adjacent Genes Andrzej T. Wierzbicki, Jeremy R. Haag, and
Cell, Volume 135 Supplemental Data Noncoding Transcription by RNA Polymerase Pol IVb/Pol V Mediates Transcriptional Silencing of Overlapping and Adjacent Genes Andrzej T. Wierzbicki, Jeremy R. Haag, and
Page 1 of 5. Product Name Label Quantity Product No. Cy 3 10 µg (~0.75 nmol) MIR Cy µg (~7.5 nmol) MIR 7901
 Page 1 of 5 Label IT RNAi Delivery Control Product Name Label Quantity Product No. Cy 3 10 µg (~0.75 nmol) MIR 7900 Label IT RNAi Delivery Control Cy 3 100 µg (~7.5 nmol) MIR 7901 Fluorescein 10 µg (~0.75
Page 1 of 5 Label IT RNAi Delivery Control Product Name Label Quantity Product No. Cy 3 10 µg (~0.75 nmol) MIR 7900 Label IT RNAi Delivery Control Cy 3 100 µg (~7.5 nmol) MIR 7901 Fluorescein 10 µg (~0.75
RhoC Activation Assay Kit
 Product Manual RhoC Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number STA-403-C 20 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Small GTP-binding proteins (or GTPases) are a family
Product Manual RhoC Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number STA-403-C 20 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Small GTP-binding proteins (or GTPases) are a family
MATERIAL DATA SHEET. NOTE: Kit contains reagents sufficient for 10 x 30 μl reactions and 5 Western Blots (mini-gel format). Reagents Provided in Kit
 Lot # XXXXX MuRF1/S5a Ubiquitination Kit Cat. # K-102 MATERIAL DATA SHEET MuRF1 (Muscle-specific RING-finger protein 1) is a RING-finger E3 ligase found in striated muscle (heart and skeletal) and iris
Lot # XXXXX MuRF1/S5a Ubiquitination Kit Cat. # K-102 MATERIAL DATA SHEET MuRF1 (Muscle-specific RING-finger protein 1) is a RING-finger E3 ligase found in striated muscle (heart and skeletal) and iris
