Nuclear Organization and Gene Expression Dr. David L. Spector
|
|
|
- Marshall Crawford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NUCLEAR ORGANIZATION AND GENE EXPRESSION David L. Spector, Ph.D. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory One Bungtown Road Cold Spring Harbor, New York Visit our website at 1 Orphanides and Reinberg (2002) Cell 108, Spector, D.L. (2001) J. Cell Sci. 114, The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 1
2 Chromosomes are arranged in territories in the interphase nucleus 4 Bolzer et al. (2005) PLoS Biology 3, Visualizing gene expression in living cells 5 Characterization of the U2OS stable cell line Southern Northern Western 3.4 kb 2.8 kb 6 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 2
3 The locus is stably integrated in a euchromatic region of chromosome 1p hours post-transfection (-) Dox CFP-lac repressor MS2 binding protein-yfp hours post-transfection hours after the addition of Dox MS2 binding protein-yfp 9 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 3
4 RNA is present at the focal concentration of MS2 binding protein-yfp CFP-lac repressor MS2 binding protein-yfp Intron probe 10 MS2 binding protein-yfp msec exposure every 2.5 min for 4.5 hrs YFP-MS2 0 min (-) dox 5 min (+) dox 7.5 min 17.5 min 130 min 12 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 4
5 3-D organization of gene expression 2 hours after initiation 13 Nuclear mrnp dynamics is consistent with a diffusion based mechanism msec exposure for 30 sec Shav-Tal et al. (2004) Science 304, mrnp particle tracking Simple diffusion Corralled diffusion 60% 40% Average diffusion coefficient 0.04 µm 2 /sec 15 Shav-Tal et al. (2004) Science 304, The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 5
6 Tet-ON-VP16-YFP is present at the locus 5 min after the addition of Dox Tet-ON-VP16-YFP rtetr VP16 YFP 16 Tet-ON-VP16-YFP is increasingly recruited to the locus over time (15 min after the addition of Dox) Tet-ON-VP16-YFP rtetr VP16 YFP 17 The RNA polymerase II large subunit is recruited to the active locus YFP-RNA pol II 18 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 6
7 The pre-mrna splicing factor, SF2/ASF, is recruited to the active locus YFP-SF2/ASF 19 CstF-64 is recruited to the active locus YFP-lac repressor CstF Active Chromatin Repressed Chromatin Adapted from: Kouzarides, 21 T. The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 7
8 HP1α, β and γ are enriched at the inactive locus YFP-HP1α YFP-HP1β YFP-HP1γ 22 Histone H3 tri-methylated at Lysine 9 is enriched at the inactive locus 0 min (-) Dox 2.5 hrs (+) Dox YFP-lac repressor Histone H3 trimethyl-k9 23 The Suv39h1 and G9a-L histone methyltransferases localize at the inactive locus YFP-Suv39h1 YFP-G9a-L 24 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 8
9 HP1α clears from the locus upon transcriptional induction 0 min (-) Dox 2.5 hr (+) Dox YFP-HP1α 25 YFP-HP1α 100 msec exposure every 2.5 min for 3 hrs 26 0 min 17.5 min 30 min 50 min 27 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 9
10 Histone H3 and the H3.3 variant Deposition Replication coupled Replication coupled and independent S31 Histone Fold Domain A31 S87 V89 M90 A87 I89 G90 Ahmad and Henikoff (2002) Mol. Cell 9, ; PNAS 99, pseudo-colored red H3.3-YFP Exposure every 2.5 min for 5 hrs 16 min 29 H3.3-YFP 0 min (-) dox 7.5 min (+) dox 40 min 75 min 180 min 30 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 10
11 Summary (1) The cell nucleus is an organized cellular compartment containing chromosome territories and numerous nuclear compartments which may play a role in sequestering and releasing factors as well as function in their modification and assembly. Using an inducible system we have been able to directly visualize a genetic locus as well as its RNA and protein products in living mammalian cells. Nascent RNA can be detected within 5-8 min after induction, while dramatic changes in chromatin structure are seen by min. Factors from various nucleoplasmic regions are recruited to the locus in a transcription-dependent manner. 31 Summary (2) mrnp nuclear dynamics is consistent with a diffusion based mechanism. HP1α, β and γ, histone H3 tri-methyl K9, and several HMTases are enriched at the inactive locus. HP1α clears from the locus as it decondenses and is not detected at the locus ~ 50 min after transcriptional activation. Histone H3.3 is enriched at the transcriptionally active locus. 32 Acknowledgements Cold Spring Harbor Susan Janicki Prasanth Kannanganattu Himeji Inst. Tech. Toshiro Tsukamoto NIH/NCI Thomas Ried Fred Hutchinson Kami Ahmad Steven Henikoff University of Illinois Andrew Belmont Albert Einstein College of Medicine Yaron Shav-Tal Robert Singer CNRS - Montpellier Edouard Bertrand Visit our web site at 33 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 11
CHAPTERS , 17: Eukaryotic Genetics
 CHAPTERS 14.1 14.6, 17: Eukaryotic Genetics 1. Review the levels of DNA packing within the eukaryote nucleus. Label each level. (A similar diagram is on pg 188 of your textbook.) 2. How do the coding regions
CHAPTERS 14.1 14.6, 17: Eukaryotic Genetics 1. Review the levels of DNA packing within the eukaryote nucleus. Label each level. (A similar diagram is on pg 188 of your textbook.) 2. How do the coding regions
Chapter 13. The Nucleus. The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus".
 Chapter 13 The Nucleus The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus". Fig.13.1. The EM of the Nucleus of a Eukaryotic Cell 13.1. The Nuclear Envelope
Chapter 13 The Nucleus The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus". Fig.13.1. The EM of the Nucleus of a Eukaryotic Cell 13.1. The Nuclear Envelope
Lecture 21: Epigenetics Nurture or Nature? Chromatin DNA methylation Histone Code Twin study X-chromosome inactivation Environemnt and epigenetics
 Lecture 21: Epigenetics Nurture or Nature? Chromatin DNA methylation Histone Code Twin study X-chromosome inactivation Environemnt and epigenetics Epigenetics represents the science for the studying heritable
Lecture 21: Epigenetics Nurture or Nature? Chromatin DNA methylation Histone Code Twin study X-chromosome inactivation Environemnt and epigenetics Epigenetics represents the science for the studying heritable
The life of an mrna in space and time
 Research Article 1761 The life of an mrna in space and time Ya ara Ben-Ari 1, *, Yehuda Brody 1, *, Noa Kinor 1, Amir Mor 1, Toshiro Tsukamoto 2, David L. Spector 3, Robert H. Singer 4 and Yaron Shav-Tal
Research Article 1761 The life of an mrna in space and time Ya ara Ben-Ari 1, *, Yehuda Brody 1, *, Noa Kinor 1, Amir Mor 1, Toshiro Tsukamoto 2, David L. Spector 3, Robert H. Singer 4 and Yaron Shav-Tal
Epigenetics. Medical studies in English, Lecture # 12,
 Epigenetics Medical studies in English, 2018. Lecture # 12, Epigenetics Regulation of gene activity in eukaryotes Correlation of chromatin structure with transcription stably heritable phenotype resulting
Epigenetics Medical studies in English, 2018. Lecture # 12, Epigenetics Regulation of gene activity in eukaryotes Correlation of chromatin structure with transcription stably heritable phenotype resulting
GENE REGULATION slide shows by Kim Foglia modified Slides with blue edges are Kim s
 GENE REGULATION slide shows by Kim Foglia modified Slides with blue edges are Kim s 2007-2008 Bacterial metabolism Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment STOP GO if they have
GENE REGULATION slide shows by Kim Foglia modified Slides with blue edges are Kim s 2007-2008 Bacterial metabolism Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment STOP GO if they have
NUCLEUS. Fig. 2. Various stages in the condensation of chromatin
 NUCLEUS Animal cells contain DNA in nucleus (contains ~ 98% of cell DNA) and mitochondrion. Both compartments are surrounded by an envelope (double membrane). Nuclear DNA represents some linear molecules
NUCLEUS Animal cells contain DNA in nucleus (contains ~ 98% of cell DNA) and mitochondrion. Both compartments are surrounded by an envelope (double membrane). Nuclear DNA represents some linear molecules
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
WORKSHOP. Transcriptional circuitry and the regulatory conformation of the genome. Ofir Hakim Faculty of Life Sciences
 WORKSHOP Transcriptional circuitry and the regulatory conformation of the genome Ofir Hakim Faculty of Life Sciences Chromosome conformation capture (3C) Most GR Binding Sites Are Distant From Regulated
WORKSHOP Transcriptional circuitry and the regulatory conformation of the genome Ofir Hakim Faculty of Life Sciences Chromosome conformation capture (3C) Most GR Binding Sites Are Distant From Regulated
Chapter 5 DNA and Chromosomes
 Chapter 5 DNA and Chromosomes DNA as the genetic material Heat-killed bacteria can transform living cells S Smooth R Rough Fred Griffith, 1920 DNA is the genetic material Oswald Avery Colin MacLeod Maclyn
Chapter 5 DNA and Chromosomes DNA as the genetic material Heat-killed bacteria can transform living cells S Smooth R Rough Fred Griffith, 1920 DNA is the genetic material Oswald Avery Colin MacLeod Maclyn
REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. II. Eukaryotes
 REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS II. Eukaryotes Complexities of eukaryotic gene expression! Several steps needed for synthesis of mrna! Separation in space of transcription and translation! Compartmentation
REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS II. Eukaryotes Complexities of eukaryotic gene expression! Several steps needed for synthesis of mrna! Separation in space of transcription and translation! Compartmentation
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 18, 2009 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 18, 2009 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes 2007-2008 The BIG Questions n How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? n How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Control of Eukaryotic Genes 2007-2008 The BIG Questions n How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? n How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
BIOLOGY. Chapter 16 GenesExpression
 BIOLOGY Chapter 16 GenesExpression CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 18 Gene Expression 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 16.1 Differential Gene Expression results
BIOLOGY Chapter 16 GenesExpression CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 18 Gene Expression 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 16.1 Differential Gene Expression results
Chromatin and Transcription
 Chromatin and Transcription Chromatin Structure Chromatin Represses Transcription Nucleosome Positioning Histone Acetylation Chromatin Remodeling Histone Methylation CHIP Analysis Chromatin and Elongation
Chromatin and Transcription Chromatin Structure Chromatin Represses Transcription Nucleosome Positioning Histone Acetylation Chromatin Remodeling Histone Methylation CHIP Analysis Chromatin and Elongation
AP Biology Gene Expression/Biotechnology REVIEW
 AP Biology Gene Expression/Biotechnology REVIEW Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Gene expression can be a. regulated before transcription.
AP Biology Gene Expression/Biotechnology REVIEW Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Gene expression can be a. regulated before transcription.
Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression. 1. Gene Regulation in Bacteria 2. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes 3. Gene Regulation & Cancer
 Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression 1. Gene Regulation in Bacteria 2. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes 3. Gene Regulation & Cancer Gene Regulation Gene regulation refers to all aspects of controlling
Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression 1. Gene Regulation in Bacteria 2. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes 3. Gene Regulation & Cancer Gene Regulation Gene regulation refers to all aspects of controlling
Transcription in Eukaryotes
 Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline. Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics
 Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers
 Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that usually extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated the (#1) of transcription
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that usually extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated the (#1) of transcription
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins. The Central Dogma
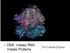 DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
Correction: The Leukemia-Associated Mllt10/ Af10-Dot1l Are Tcf4/β-Catenin Coactivators Essential for Intestinal Homeostasis
 CORRECTION Correction: The Leukemia-Associated Mllt10/ Af10-Dot1l Are Tcf4/β-Catenin Coactivators Essential for Intestinal Homeostasis Tokameh Mahmoudi, Sylvia F. Boj, Pantelis Hatzis, Vivian S. W. Li,
CORRECTION Correction: The Leukemia-Associated Mllt10/ Af10-Dot1l Are Tcf4/β-Catenin Coactivators Essential for Intestinal Homeostasis Tokameh Mahmoudi, Sylvia F. Boj, Pantelis Hatzis, Vivian S. W. Li,
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA
 TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE SLIDES
 CHAPTER 13 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
DNA: The Genetic Material. Chapter 10
 DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 10 DNA as the Genetic Material DNA was first extracted from nuclei in 1870 named nuclein after their source. Chemical analysis determined that DNA was a weak acid rich
DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 10 DNA as the Genetic Material DNA was first extracted from nuclei in 1870 named nuclein after their source. Chemical analysis determined that DNA was a weak acid rich
Regulation of Gene Expression
 Slide 1 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Slide 1 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Le proteine regolative variano nei vari tipi cellulari e in funzione degli stimoli ambientali
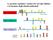 Le proteine regolative variano nei vari tipi cellulari e in funzione degli stimoli ambientali Tipo cellulare 1 Tipo cellulare 2 Tipo cellulare 3 DNA-protein Crosslink Lisi Frammentazione Immunopurificazione
Le proteine regolative variano nei vari tipi cellulari e in funzione degli stimoli ambientali Tipo cellulare 1 Tipo cellulare 2 Tipo cellulare 3 DNA-protein Crosslink Lisi Frammentazione Immunopurificazione
Gene Expression: Transcription
 Gene Expression: Transcription The majority of genes are expressed as the proteins they encode. The process occurs in two steps: Transcription = DNA RNA Translation = RNA protein Taken together, they make
Gene Expression: Transcription The majority of genes are expressed as the proteins they encode. The process occurs in two steps: Transcription = DNA RNA Translation = RNA protein Taken together, they make
Lecture 9 Controlling gene expression
 Lecture 9 Controlling gene expression BIOLOGY Campbell, Reece and Mitchell Chapter 18 334- (352-356) Every cell in your body contains the same number of genes approximately 35, 000 DNA is wound around
Lecture 9 Controlling gene expression BIOLOGY Campbell, Reece and Mitchell Chapter 18 334- (352-356) Every cell in your body contains the same number of genes approximately 35, 000 DNA is wound around
Chapter 16: Gene Expression from Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license.
 Chapter 16: Gene Expression from Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license. 2013, Rice University. CHAPTER 16 GENE EXPRESSION 429 16 GENE EXPRESSION
Chapter 16: Gene Expression from Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license. 2013, Rice University. CHAPTER 16 GENE EXPRESSION 429 16 GENE EXPRESSION
Prokaryotic Transcription
 Prokaryotic Transcription Transcription Basics DNA is the genetic material Nucleic acid Capable of self-replication and synthesis of RNA RNA is the middle man Nucleic acid Structure and base sequence are
Prokaryotic Transcription Transcription Basics DNA is the genetic material Nucleic acid Capable of self-replication and synthesis of RNA RNA is the middle man Nucleic acid Structure and base sequence are
Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of..
 Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription
 Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription Epigenetics 2014 by Nigel Atkinson The University of Texas at Austin From Weaver 4th edition and Armstrong 1st edition What is the point? DNA is not
Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription Epigenetics 2014 by Nigel Atkinson The University of Texas at Austin From Weaver 4th edition and Armstrong 1st edition What is the point? DNA is not
M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION
 M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION Chapter 7 Microbial Genetics Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, University of Tennessee, Knoxville The Structure and Replication
M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION Chapter 7 Microbial Genetics Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, University of Tennessee, Knoxville The Structure and Replication
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells
 Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
8/21/2014. From Gene to Protein
 From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
Decoding Chromatin States with Epigenome Data Advanced Topics in Computa8onal Genomics
 Decoding Chromatin States with Epigenome Data 02-715 Advanced Topics in Computa8onal Genomics HMMs for Decoding Chromatin States Epigene8c modifica8ons of the genome have been associated with Establishing
Decoding Chromatin States with Epigenome Data 02-715 Advanced Topics in Computa8onal Genomics HMMs for Decoding Chromatin States Epigene8c modifica8ons of the genome have been associated with Establishing
RNA-Guided Gene Activation by CRISPR-Cas9-Based Transcription Factors
 Supplementary Information RNA-Guided Gene Activation by CRISPR-Cas9-Based Transcription Factors Pablo Perez-Pinera 1, Daniel D. Kocak 1, Christopher M. Vockley 2,3, Andrew F. Adler 1, Ami M. Kabadi 1,
Supplementary Information RNA-Guided Gene Activation by CRISPR-Cas9-Based Transcription Factors Pablo Perez-Pinera 1, Daniel D. Kocak 1, Christopher M. Vockley 2,3, Andrew F. Adler 1, Ami M. Kabadi 1,
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process.
 Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Eukaryotic Transcription
 Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
Bioinformatics of Transcriptional Regulation
 Bioinformatics of Transcriptional Regulation Carl Herrmann IPMB & DKFZ c.herrmann@dkfz.de Wechselwirkung von Maßnahmen und Auswirkungen Einflussmöglichkeiten in einem Dialog From genes to active compounds
Bioinformatics of Transcriptional Regulation Carl Herrmann IPMB & DKFZ c.herrmann@dkfz.de Wechselwirkung von Maßnahmen und Auswirkungen Einflussmöglichkeiten in einem Dialog From genes to active compounds
Regulation of gene expression. (Lehninger pg )
 Regulation of gene expression (Lehninger pg. 1072-1085) Today s lecture Gene expression Constitutive, inducible, repressible genes Specificity factors, activators, repressors Negative and positive gene
Regulation of gene expression (Lehninger pg. 1072-1085) Today s lecture Gene expression Constitutive, inducible, repressible genes Specificity factors, activators, repressors Negative and positive gene
Gene Expression and Heritable Phenotype. CBS520 Eric Nabity
 Gene Expression and Heritable Phenotype CBS520 Eric Nabity DNA is Just the Beginning DNA was determined to be the genetic material, and the structure was identified as a (double stranded) double helix.
Gene Expression and Heritable Phenotype CBS520 Eric Nabity DNA is Just the Beginning DNA was determined to be the genetic material, and the structure was identified as a (double stranded) double helix.
Einführung in die Genetik
 Einführung in die Genetik Prof. Dr. Kay Schneitz (EBio Pflanzen) http://plantdev.bio.wzw.tum.de schneitz@wzw.tum.de Twitter: @PlantDevTUM, #genetiktum FB: Plant Development TUM Prof. Dr. Claus Schwechheimer
Einführung in die Genetik Prof. Dr. Kay Schneitz (EBio Pflanzen) http://plantdev.bio.wzw.tum.de schneitz@wzw.tum.de Twitter: @PlantDevTUM, #genetiktum FB: Plant Development TUM Prof. Dr. Claus Schwechheimer
What we ll do today. Types of stem cells. Do engineered ips and ES cells have. What genes are special in stem cells?
 Do engineered ips and ES cells have similar molecular signatures? What we ll do today Research questions in stem cell biology Comparing expression and epigenetics in stem cells asuring gene expression
Do engineered ips and ES cells have similar molecular signatures? What we ll do today Research questions in stem cell biology Comparing expression and epigenetics in stem cells asuring gene expression
Chapter 31. Transcription and RNA processing
 Chapter 31 Transcription and RNA processing RNA polymerase (RNAP) E. coli promoters Components of E. coli RNA Polymerase Holoenzyme (α 2 ββ'ωσ) Structure of prokaryotic RNAP The closed and open state of
Chapter 31 Transcription and RNA processing RNA polymerase (RNAP) E. coli promoters Components of E. coli RNA Polymerase Holoenzyme (α 2 ββ'ωσ) Structure of prokaryotic RNAP The closed and open state of
Do engineered ips and ES cells have similar molecular signatures?
 Do engineered ips and ES cells have similar molecular signatures? Comparing expression and epigenetics in stem cells George Bell, Ph.D. Bioinformatics and Research Computing 2012 Spring Lecture Series
Do engineered ips and ES cells have similar molecular signatures? Comparing expression and epigenetics in stem cells George Bell, Ph.D. Bioinformatics and Research Computing 2012 Spring Lecture Series
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 12 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes WORKING WITH THE FIGURES 1. In Figure 12-4, certain mutations decrease the relative transcription rate of the -globin gene. Where are these mutations located,
12 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes WORKING WITH THE FIGURES 1. In Figure 12-4, certain mutations decrease the relative transcription rate of the -globin gene. Where are these mutations located,
Nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ribonucleic acid (RNA) nucleotide
 Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
I. Prokaryotic Gene Regulation. Figure 1: Operon. Operon:
 I. Prokaryotic Gene Regulation Figure 1: Operon Operon: a) Regulatory Elements consist of an Operator that serves as the on-off switch for the genes of the operon. Also contains a promoter for the Structural
I. Prokaryotic Gene Regulation Figure 1: Operon Operon: a) Regulatory Elements consist of an Operator that serves as the on-off switch for the genes of the operon. Also contains a promoter for the Structural
Protein Synthesis & Gene Expression
 DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictates the order of amino acids that
DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictates the order of amino acids that
Fig Ch 17: From Gene to Protein
 Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Supplemental Data. Regulating Gene Expression. through RNA Nuclear Retention
 Supplemental Data Regulating Gene Expression through RNA Nuclear Retention Kannanganattu V. Prasanth, Supriya G. Prasanth, Zhenyu Xuan, Stephen Hearn, Susan M. Freier, C. Frank Bennett, Michael Q. Zhang,
Supplemental Data Regulating Gene Expression through RNA Nuclear Retention Kannanganattu V. Prasanth, Supriya G. Prasanth, Zhenyu Xuan, Stephen Hearn, Susan M. Freier, C. Frank Bennett, Michael Q. Zhang,
7.1 The lac Operon 7-1
 7.1 The lac Operon The lac operon was the first operon discovered It contains 3 genes coding for E. coli proteins that permit the bacteria to use the sugar lactose Galactoside permease (lacy) which transports
7.1 The lac Operon The lac operon was the first operon discovered It contains 3 genes coding for E. coli proteins that permit the bacteria to use the sugar lactose Galactoside permease (lacy) which transports
Tumor Growth Suppression Through the Activation of p21, a Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor
 Tumor Growth Suppression Through the Activation of p21, a Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor Nicholas Love 11/28/01 A. What is p21? Introduction - p21 is a gene found on chromosome 6 at 6p21.2 - this gene
Tumor Growth Suppression Through the Activation of p21, a Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor Nicholas Love 11/28/01 A. What is p21? Introduction - p21 is a gene found on chromosome 6 at 6p21.2 - this gene
TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA TRANSCRIPTION. Umm AL Qura University. Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose. Bases AUCG ATCG. Strand length Short Long
 Umm AL Qura University TRANSCRIPTION Dr Neda Bogari TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA RNA DNA Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose Bases AUCG ATCG Strand length Short Long No. strands One Two Helix Single Double
Umm AL Qura University TRANSCRIPTION Dr Neda Bogari TRANSCRIPTION COMPARISON OF DNA & RNA RNA DNA Sugar Ribose Deoxyribose Bases AUCG ATCG Strand length Short Long No. strands One Two Helix Single Double
Transcription in Prokaryotes. Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone:
 Transcription in Prokaryotes Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone: 352-273-8098 Email: jbungert@ufl.edu Objectives Understand the basic mechanism of transcription. Know the function of promoter elements and associating
Transcription in Prokaryotes Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone: 352-273-8098 Email: jbungert@ufl.edu Objectives Understand the basic mechanism of transcription. Know the function of promoter elements and associating
Establishing epigenetic domains via chromatin-bound histone modifiers
 Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. ISSN 0077-8923 ANNALS OF THE NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Issue: Evolutionary Dynamics and Information Hierarchies in Biological Systems Establishing epigenetic domains via chromatin-bound
Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. ISSN 0077-8923 ANNALS OF THE NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Issue: Evolutionary Dynamics and Information Hierarchies in Biological Systems Establishing epigenetic domains via chromatin-bound
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
Chromatin. Structure and modification of chromatin. Chromatin domains
 Chromatin Structure and modification of chromatin Chromatin domains 2 DNA consensus 5 3 3 DNA DNA 4 RNA 5 ss RNA forms secondary structures with ds hairpins ds forms 6 of nucleic acids Form coiling bp/turn
Chromatin Structure and modification of chromatin Chromatin domains 2 DNA consensus 5 3 3 DNA DNA 4 RNA 5 ss RNA forms secondary structures with ds hairpins ds forms 6 of nucleic acids Form coiling bp/turn
Einführung in die Genetik
 Einführung in die Genetik Prof. Dr. Kay Schneitz (EBio Pflanzen) http://plantdev.bio.wzw.tum.de schneitz@wzw.tum.de Prof. Dr. Claus Schwechheimer (PlaSysBiol) http://wzw.tum.de/sysbiol claus.schwechheimer@wzw.tum.de
Einführung in die Genetik Prof. Dr. Kay Schneitz (EBio Pflanzen) http://plantdev.bio.wzw.tum.de schneitz@wzw.tum.de Prof. Dr. Claus Schwechheimer (PlaSysBiol) http://wzw.tum.de/sysbiol claus.schwechheimer@wzw.tum.de
BEADLE & TATUM EXPERIMENT
 FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE OBJECTIVES What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? How Does Information Flow from Genes to Proteins? How Is the Information Content in
FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE OBJECTIVES What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? How Does Information Flow from Genes to Proteins? How Is the Information Content in
Chapter 13. From DNA to Protein
 Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes
 Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes Concepts, Strategies, and Techniques Michael Carey Stephen T. Smale COLD SPRING HARBOR LABORATORY PRESS NEW YORK 2000 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 0-87969-537-4
Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes Concepts, Strategies, and Techniques Michael Carey Stephen T. Smale COLD SPRING HARBOR LABORATORY PRESS NEW YORK 2000 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 0-87969-537-4
Themes: RNA and RNA Processing. Messenger RNA (mrna) What is a gene? RNA is very versatile! RNA-RNA interactions are very important!
 Themes: RNA is very versatile! RNA and RNA Processing Chapter 14 RNA-RNA interactions are very important! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have many important differences. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries genetic
Themes: RNA is very versatile! RNA and RNA Processing Chapter 14 RNA-RNA interactions are very important! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have many important differences. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries genetic
CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION PART B: CONTROL IN EUKARYOTES
 CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION PART B: CONTROL IN EUKARYOTES I. Introduction A. No operon structures in eukaryotes B. Regulation of gene expression is frequently tissue specific.
CHAPTER 18 LECTURE NOTES: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION PART B: CONTROL IN EUKARYOTES I. Introduction A. No operon structures in eukaryotes B. Regulation of gene expression is frequently tissue specific.
Biology Lecture 2 Genes
 Genes Definitions o Gene: DNA that codes for a single polypeptide/mrna/rrna/trna o Euchromatin: region of DNA containing genes being actively transcribed o Heterochromatin: region of DNA containing genes
Genes Definitions o Gene: DNA that codes for a single polypeptide/mrna/rrna/trna o Euchromatin: region of DNA containing genes being actively transcribed o Heterochromatin: region of DNA containing genes
Ch. 10 Notes DNA: Transcription and Translation
 Ch. 10 Notes DNA: Transcription and Translation GOALS Compare the structure of RNA with that of DNA Summarize the process of transcription Relate the role of codons to the sequence of amino acids that
Ch. 10 Notes DNA: Transcription and Translation GOALS Compare the structure of RNA with that of DNA Summarize the process of transcription Relate the role of codons to the sequence of amino acids that
GENE REGULATION IN PROKARYOTES
 GENE REGULATION IN PROKARYOTES Prepared by Brenda Leady, University of Toledo Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gene regulation refers to
GENE REGULATION IN PROKARYOTES Prepared by Brenda Leady, University of Toledo Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gene regulation refers to
CLASS 3.5: 03/29/07 EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION I: PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS
 CLASS 3.5: 03/29/07 EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION I: PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS A. Promoters and Polymerases (RNA pols): 1. General characteristics - Initiation of transcription requires a. Transcription factors
CLASS 3.5: 03/29/07 EUKARYOTIC TRANSCRIPTION I: PROMOTERS AND ENHANCERS A. Promoters and Polymerases (RNA pols): 1. General characteristics - Initiation of transcription requires a. Transcription factors
DNA Transcription. Dr Aliwaini
 DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis
 Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis 1. Describe how genetic information is transcribed into sequences of bases in RNA molecules and is finally translated into sequences of amino
Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis 1. Describe how genetic information is transcribed into sequences of bases in RNA molecules and is finally translated into sequences of amino
Synthetic Biology. Sustainable Energy. Therapeutics Industrial Enzymes. Agriculture. Accelerating Discoveries, Expanding Possibilities. Design.
 Synthetic Biology Accelerating Discoveries, Expanding Possibilities Sustainable Energy Therapeutics Industrial Enzymes Agriculture Design Build Generate Solutions to Advance Synthetic Biology Research
Synthetic Biology Accelerating Discoveries, Expanding Possibilities Sustainable Energy Therapeutics Industrial Enzymes Agriculture Design Build Generate Solutions to Advance Synthetic Biology Research
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN. Section C: The Synthesis of Protein
 CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section C: The Synthesis of Protein 1. Translation is the RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide: a closer look 2. Signal peptides target some eukaryotic polypeptides to
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section C: The Synthesis of Protein 1. Translation is the RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide: a closer look 2. Signal peptides target some eukaryotic polypeptides to
DNA Structure and Analysis. Chapter 4: Background
 DNA Structure and Analysis Chapter 4: Background Molecular Biology Three main disciplines of biotechnology Biochemistry Genetics Molecular Biology # Biotechnology: A Laboratory Skills Course explorer.bio-rad.com
DNA Structure and Analysis Chapter 4: Background Molecular Biology Three main disciplines of biotechnology Biochemistry Genetics Molecular Biology # Biotechnology: A Laboratory Skills Course explorer.bio-rad.com
Genes - DNA - Chromosome. Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology
 Genes - DNA - Chromosome Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology DNA Cellular DNA contains genes and intragenic regions both of which may
Genes - DNA - Chromosome Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology DNA Cellular DNA contains genes and intragenic regions both of which may
RNA : functional role
 RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
Bundle 5 Test Review
 Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins
 PHRM 836 September 22, 2015 Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins Devlin Chapter 8.8-9 u General description of transcription factors (TFs) u Sequence-specific interactions between DNA
PHRM 836 September 22, 2015 Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins Devlin Chapter 8.8-9 u General description of transcription factors (TFs) u Sequence-specific interactions between DNA
Classes of eukaryotic cellular RNAs
 Classes of eukaryotic cellular RNAs ribosomal RNA (rrna) 18S (small subunit) 28S (large subunit) 5.8S (large subunit) 5S (large subunit) transfer RNA (trna) messenger RNA (mrna) heterogeneous nuclear RNA
Classes of eukaryotic cellular RNAs ribosomal RNA (rrna) 18S (small subunit) 28S (large subunit) 5.8S (large subunit) 5S (large subunit) transfer RNA (trna) messenger RNA (mrna) heterogeneous nuclear RNA
DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES-
 DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES- THE COMPONENTS AND STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA is made up of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of three basic components:, called deoxyribose in DNA In DNA, there
DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES- THE COMPONENTS AND STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA is made up of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of three basic components:, called deoxyribose in DNA In DNA, there
Functional Genomics Overview RORY STARK PRINCIPAL BIOINFORMATICS ANALYST CRUK CAMBRIDGE INSTITUTE 18 SEPTEMBER 2017
 Functional Genomics Overview RORY STARK PRINCIPAL BIOINFORMATICS ANALYST CRUK CAMBRIDGE INSTITUTE 18 SEPTEMBER 2017 Agenda What is Functional Genomics? RNA Transcription/Gene Expression Measuring Gene
Functional Genomics Overview RORY STARK PRINCIPAL BIOINFORMATICS ANALYST CRUK CAMBRIDGE INSTITUTE 18 SEPTEMBER 2017 Agenda What is Functional Genomics? RNA Transcription/Gene Expression Measuring Gene
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra
 Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy
 Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 7 Cellular differentiation and the regulation of gene expression. In this lecture we looked at two main questions: How is gene expression regulated? (revision
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 7 Cellular differentiation and the regulation of gene expression. In this lecture we looked at two main questions: How is gene expression regulated? (revision
DNA Structure and Properties Basic Properties Predicting Melting Temperature. Dinesh Yadav
 DNA Structure and Properties Basic Properties Predicting Melting Temperature Dinesh Yadav Nucleic Acid Structure Question: Is this RNA or DNA? Molecules of Life, pp. 15 2 Nucleic Acid Bases Molecules of
DNA Structure and Properties Basic Properties Predicting Melting Temperature Dinesh Yadav Nucleic Acid Structure Question: Is this RNA or DNA? Molecules of Life, pp. 15 2 Nucleic Acid Bases Molecules of
EUKARYOTIC REGULATION C H A P T E R 1 3
 EUKARYOTIC REGULATION C H A P T E R 1 3 EUKARYOTIC REGULATION Every cell in an organism contains a complete set of DNA. But it doesn t use all of the DNA it receives Each cell chooses different DNA sequences
EUKARYOTIC REGULATION C H A P T E R 1 3 EUKARYOTIC REGULATION Every cell in an organism contains a complete set of DNA. But it doesn t use all of the DNA it receives Each cell chooses different DNA sequences
Learning Objectives. Define RNA interference. Define basic terminology. Describe molecular mechanism. Define VSP and relevance
 Learning Objectives Define RNA interference Define basic terminology Describe molecular mechanism Define VSP and relevance Describe role of RNAi in antigenic variation A Nobel Way to Regulate Gene Expression
Learning Objectives Define RNA interference Define basic terminology Describe molecular mechanism Define VSP and relevance Describe role of RNAi in antigenic variation A Nobel Way to Regulate Gene Expression
REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION
 REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION Each cell of a living organism contains thousands of genes. But all genes do not function at a time. Genes function according to requirements of the cell. Genes control the
REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION Each cell of a living organism contains thousands of genes. But all genes do not function at a time. Genes function according to requirements of the cell. Genes control the
Protein Synthesis Notes
 Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
2054, Chap. 14, page 1
 2054, Chap. 14, page 1 I. Recombinant DNA technology (Chapter 14) A. recombinant DNA technology = collection of methods used to perform genetic engineering 1. genetic engineering = deliberate modification
2054, Chap. 14, page 1 I. Recombinant DNA technology (Chapter 14) A. recombinant DNA technology = collection of methods used to perform genetic engineering 1. genetic engineering = deliberate modification
Alteration of Large-Scale Chromatin Structure by Estrogen Receptor
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, May 2002, p. 3437 3449 Vol. 22, No. 10 0270-7306/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.10.3437 3449.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, May 2002, p. 3437 3449 Vol. 22, No. 10 0270-7306/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.10.3437 3449.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
CHAPTER 21 LECTURE SLIDES
 CHAPTER 21 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
CHAPTER 21 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
Eukaryotic Gene Structure
 Eukaryotic Gene Structure Terminology Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Gene Basic physical and
Eukaryotic Gene Structure Terminology Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Gene Basic physical and
MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
 CHAPTER 6 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE POINTS TO REMEMBER Anticodon : A sequence of three nitrogenous bases on trna which is complementary to the codon on mrna. Transformation : The phenomenon by which
CHAPTER 6 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE POINTS TO REMEMBER Anticodon : A sequence of three nitrogenous bases on trna which is complementary to the codon on mrna. Transformation : The phenomenon by which
Chromosomes. Chromosomes. Genes. Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce
 Chromosomes Chromosomes Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce Genes Segments of DNA that specify how to build a protein genes may specify more than one
Chromosomes Chromosomes Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce Genes Segments of DNA that specify how to build a protein genes may specify more than one
Transcription & post transcriptional modification
 Transcription & post transcriptional modification Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be transferred from DNA to RNA Similarity
Transcription & post transcriptional modification Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be transferred from DNA to RNA Similarity
The information provided below may be useful in answering some questions.
 Molecular Exam 1 More Tutorial at www.dumblittledoctor.com The information provided below may be useful in answering some questions. INFORMATION ON COMPONENTS OF RIBOSOMES I. Prokaryotes (e.g. E. coli)
Molecular Exam 1 More Tutorial at www.dumblittledoctor.com The information provided below may be useful in answering some questions. INFORMATION ON COMPONENTS OF RIBOSOMES I. Prokaryotes (e.g. E. coli)
Figure S1: NUN preparation yields nascent, unadenylated RNA with a different profile from Total RNA.
 Summary of Supplemental Information Figure S1: NUN preparation yields nascent, unadenylated RNA with a different profile from Total RNA. Figure S2: rrna removal procedure is effective for clearing out
Summary of Supplemental Information Figure S1: NUN preparation yields nascent, unadenylated RNA with a different profile from Total RNA. Figure S2: rrna removal procedure is effective for clearing out
