Directed Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. into Fallopian Tube Epithelium
|
|
|
- Sibyl Watkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Directed Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells into Fallopian Tube Epithelium Nur Yucer 1,2, Marie Holzapfel 2, Tilley Jenkins Vogel 2, Lindsay Lenaeus 1, Loren Ornelas 1, Anna Laury 3, Dhruv Sareen 1, Robert Barrett 1, Beth Y. Karlan 2,4,* and Clive N. Svendsen 1,4,*
2 Supplementary Figure 1: Characterization of ipsc lines. All characterized ipsc lines (87iCTR-n3, 01iMEC-n4 and 14iCTR-n6) express pluripotent stem cell markers a) Alkaline Phosphatase (AP) and b) for OCT4, NANOG, SOX2, TRA160, TRA181, SSEA4 based on immunocytochemistry, as well as c) exhibit a normal karyotype based on Gband analysis.
3 Supplementary Figure 2: IM differentiation efficiency for established protocols. Expression kinetics of mesoderm markers a) MIXL1- and b) BRACHYURY during the 6- day differentiation course of ipsc lines 87iCTR-n3, 01iMEC-n4 and 14iCTR-n6 using protocols from Xia et. al. (2013), Mae et. al. (2013), Takasato et. al. (2014)
4 Supplementary Figure 3: Substitution to Mae et al. protocol with BMP4 from BMP7. a) Expression kinetics of mesoderm markers MIXL1- and BRACHYURY during differentiation with BMP4 vs BMP7 treatment for 87iCTR-n3 ipsc line. b) Expression of intermediate mesoderm marker, PAX2, during the 6-day differentiation course of ipsc lines 87iCTR-n3, 01iMEC-n4 and 14iCTR-n6 using protocols from Xia et. al. (2013) and Mae et. al. (2013) c) Expression kinetics of ectoderm marker NCAM and endoderm marker SOX17 during differentiation with BMP4 vs BMP7 treatment for 87iCTR-n3 ipsc line.
5 Supplementary Fig 4. PAX8 expression pattern during the course of differentiation: a) qpcr quantification of gene expression kinetics for PAX8 in response to Müllerian (WNT4, black bars) vs nephric duct (WNT3a, gray bars) differentiation. b) Immunocytochemistry demonstrating PAX8 expression during Müllerian duct differentiation. c) Immunocytochemistry demonstrating protein production and localization of PAX8 during nephric duct differentiation. d) Immunocytochemistry for PAX8 at FTE organoid culture day, day 30 and human fallopian tube tissue. e) Gene expression of PAX8 at organoids culture day 45, human fallopian tube and kidney. The color matrix of the heat map represents the log2(ratio) of PAX8 to its expression at the ipsc stage. Relative gene expression to ipsc stage (day 0) was calculated using DDCt method and normalized to endogenous GAPDH level for 87iCTR-n3 ipsc line.
6 Supplementary Figure 5: Immunocytochemistry analysis throughout the Müllerian duct differentiation for production of a) gut marker CDX2 and b) lung marker NKX2.1.
7 Supplementary Figure 6: Expression kinetics of a,b) early mesonephric duct markers HOXB7 and GATA3, c,d) Müllerian duct markers WT1 and OVGP1 and e,f) kidney markers SIX2 and FOXD1 with WNT4/CHIR99021 treatment of the 87iCTR-n3 ipsc line.
8 Supplementary Figure 7: Bright field image of Müllerian duct differentiation in monolayer culture for 6 days. Red arrow indicates the epithelial bud formation at day4.
9 Supplementary Figure 8: Bright field image of 3D structure of FTE organoid at day 14 in a) Matrigel with Phenol Red vs b) Matrigel without Phenol Red.
10 Supplementary Figure 9: Immunocytochemistry analysis of day 21 organoid for kidney marker SIX2 with a) WNT3A treatment as a positive control for kidney differentiation compared with b) WNT4 treatment for Müllerian duct differentiation.
11 Supplementary Figure 10: a) Bright field image of 3D structure of FTE organoid from 01iMEC-n4 ipsc lines at day 30 in. b) H&E staining of FTE organoid from 01iMEC-n4 ipsc lines at day 30. (c-e) Immunocytochemistry for FTE markers TUBB4A and PAX8, and epithelial marker CDH1 (E-Cadherin) at organoid culture day 30, 87CTR-n3 ipsc, 01iMEC-n4 ipsc biological replicate1 and 01iMEC-n4 ipsc biological replicate2 respectively.
12 Supplementary Figure 11. Development and Characterization of an ipsc-derived Fallopian Tube Organoid. Immunocytochemistry for FTE markers TUBB4A and OVGP1 at FTE organoid culture day 45, along with human fallopian tube tissue in high magnification. Cell ID Parent Tissue Biopsy Gender Karyotype 87iCTR-n3 EBV B-Cell Blood Female Normal 01iMEC-n4 Mammary Epithelial Cells Mammary Epithelial Female Normal 14iCTR-n6 Fibroblast Skin Female Normal Supplementary Table 1. Cell background information. Cell line description, parent tissue, biopsy, gender, and karyotype.
13 Primer Forward Reverse BRACHYURY FOXD1 FOXJ1 GCTGTGACAGGTACCCAACC GACTCTGCACCAAGGGACTG GGGGTGGGAGCAACTTCT CATGCAGGTGAGTTGTCAGAA CAATTGGAAATCCTAGCAGTAAAGT CCTCCTCCGAATAAGTATGTGGT GAPDH GTGGACCTGACCTGCCGTCT GGAGGAGTGGGTGTCGCTGT GATA3 CTCATTAAGCCCAAGCGAAG GTCTGACAGTTCGCACAGGA HOXB7 CCGAGAGTAACTTCCGGATCTA CGTCAGGTAGCGATTGTAGTGA MIXL1 GGTACCCCGACATCCACTT GCCTGTTCTGGAACCATACCT NCAM GATTCCTCCTCCACCCTCAC CAATATTCTGCCTGGCCTGG NKX2.1 TCATTTGTTGGCGACTGG TGCTTTGGACTCATCGACAT OSR1 GGACCTCTGCGGAACAAG TGCAGGGAAGGGTGGATA OVGP1 AAGCTGTTGCTGTGGGTTG TGTGCCCAGTTGGTGAAAT OVGP1-2 AATTCTCTACCCAGAGTTCAACAAA CCGATGGACAGTAGTGTTTTCA PAX2 GAAGTGCCCCCTTGTGTG TCGTTGTAGGCCGTGTACTG POU5F1 ACCCACACTGCAGCAGATCA CCACACTCGGACCACATCC SALL1 ATTGCAGCCTAGCCAAAAAG ACCAGCTGAGCAGAAAGGTC SIX2 SOX17 CAGGTCAGCAACTGGTTCAA ACGCCGAGTTGAGCAAGA AGCTGCCTAACACCGACTTG TCTGCCTCCTCCACGAAG SOX2 GGGGGAATGGACCTTGTATAG GCAAAGCTCCTACCGTACCA TDGF1 AGGGAACAATGACAGAGTGTGA CCCGAGATGGACGAGCAAAT TNFaIP2 GAGCCACGGCTTTGACAC GTGCGTGAACCTCTTGAACA WT1 GAATGCATGACCTGGAATCA TCTGCCCTTCTGTCCATTTC Supplementary Table 2: Primers List
14 Supplementary Table 3 and 4: Statistical Analysis Provided as Excel File
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Quantification of western blot analysis of fibroblasts (related to Figure 1) (A-F) Quantification of western blot analysis for control and IR-Mut fibroblasts. Data are expressed
Supplementary Figure 1. Quantification of western blot analysis of fibroblasts (related to Figure 1) (A-F) Quantification of western blot analysis for control and IR-Mut fibroblasts. Data are expressed
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/11/e1701679/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells to blood-brain barrier endothelial cells Tongcheng Qian,
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/11/e1701679/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells to blood-brain barrier endothelial cells Tongcheng Qian,
HUMAN EMBRYONIC STEM CELL (hesc) ASSESSMENT BY REAL-TIME POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION (PCR)
 HUMAN EMBRYONIC STEM CELL (hesc) ASSESSMENT BY REAL-TIME POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION (PCR) OBJECTIVE: is performed to analyze gene expression of human Embryonic Stem Cells (hescs) in culture. Real-Time PCR
HUMAN EMBRYONIC STEM CELL (hesc) ASSESSMENT BY REAL-TIME POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION (PCR) OBJECTIVE: is performed to analyze gene expression of human Embryonic Stem Cells (hescs) in culture. Real-Time PCR
Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured
 Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured in 90-Pa 3D fibrin gels for 5 days in the presence
Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured in 90-Pa 3D fibrin gels for 5 days in the presence
Supplementary Data. Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells Mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (ipscs) were cultured
Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells Mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (ipscs) were cultured
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assays of hepatocyte-like cells induced from H1 hescs (a) P450 and AAT staining, PAS staining, LDL uptake assay, and ICG uptake and release assay
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assays of hepatocyte-like cells induced from H1 hescs (a) P450 and AAT staining, PAS staining, LDL uptake assay, and ICG uptake and release assay
A Novel Platform to Enable the High-Throughput Derivation and Characterization of Feeder-Free Human ipscs
 Supplementary Information A Novel Platform to Enable the High-Throughput Derivation and Characterization of Feeder-Free Human ipscs Bahram Valamehr, Ramzey Abujarour, Megan Robinson, Thuy Le, David Robbins,
Supplementary Information A Novel Platform to Enable the High-Throughput Derivation and Characterization of Feeder-Free Human ipscs Bahram Valamehr, Ramzey Abujarour, Megan Robinson, Thuy Le, David Robbins,
Disease Clinical features Genotype
 Disease Clinical features Genotype Alpha 1 Antitrypsin deficiency (A1ATD) Patient 1 65 year old caucasian male, liver transplant recipient, explant biopsy confirmed A1ATD induced liver cirrhosis Patient
Disease Clinical features Genotype Alpha 1 Antitrypsin deficiency (A1ATD) Patient 1 65 year old caucasian male, liver transplant recipient, explant biopsy confirmed A1ATD induced liver cirrhosis Patient
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1259; doi: /ijms
 S1 of S5 Supplementary Materials: Fibroblast-Derived Extracellular Matrix Induces Chondrogenic Differentiation in Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells in Vitro Kevin Dzobo, Taegyn Turnley,
S1 of S5 Supplementary Materials: Fibroblast-Derived Extracellular Matrix Induces Chondrogenic Differentiation in Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells in Vitro Kevin Dzobo, Taegyn Turnley,
Sundari Chetty, Felicia Walton Pagliuca, Christian Honore, Anastasie Kweudjeu, Alireza Rezania, and Douglas A. Melton
 A simple tool to improve pluripotent stem cell differentiation Sundari Chetty, Felicia Walton Pagliuca, Christian Honore, Anastasie Kweudjeu, Alireza Rezania, and Douglas A. Melton Supplementary Information
A simple tool to improve pluripotent stem cell differentiation Sundari Chetty, Felicia Walton Pagliuca, Christian Honore, Anastasie Kweudjeu, Alireza Rezania, and Douglas A. Melton Supplementary Information
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2239 Hepatocytes (Endoderm) Foreskin fibroblasts (Mesoderm) Melanocytes (Ectoderm) +Dox rtta TetO CMV O,S,M,K & N H1 hes H7 hes H9 hes H1 hes-derived EBs H7 hes-derived EBs H9 hes-derived
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2239 Hepatocytes (Endoderm) Foreskin fibroblasts (Mesoderm) Melanocytes (Ectoderm) +Dox rtta TetO CMV O,S,M,K & N H1 hes H7 hes H9 hes H1 hes-derived EBs H7 hes-derived EBs H9 hes-derived
Supplementary Data. In Vivo Bone Formation by impcs Materials and methods. Results. Conclusions
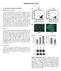 Supplementary Data In Vivo Bone Formation by impcs Materials and methods Induced pluripotent stem cell (ipsc)-derived mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-like progenitor cells (impcs) (1 10 6 M-iMPC-GMs in 10
Supplementary Data In Vivo Bone Formation by impcs Materials and methods Induced pluripotent stem cell (ipsc)-derived mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-like progenitor cells (impcs) (1 10 6 M-iMPC-GMs in 10
produced in this study characterized using 3-8 % gradient SDS-PAGE under reducing
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterisation of newly produced laminins. Human recombinant LN-521 produced in this study characterized using 3-8 % gradient SDS-PAGE under reducing 1 and non-reducing conditions.
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterisation of newly produced laminins. Human recombinant LN-521 produced in this study characterized using 3-8 % gradient SDS-PAGE under reducing 1 and non-reducing conditions.
Gene name forward primer 5->3 reverse primer 5->3 product GCCCATA. Nfatc1 AGGTGCAGCCCAAGTCTCAC GTGGCCATCTGGAGCCTTC CTGT GATGC GCT ACCAA
 Supplementary able 1 is presenting the PCR primer list used. ene name forward primer 5->3 reverse primer 5->3 product size cdna VE-Cadherin AACCCAAAAA CACCCCAAAAC 260bp CCA CCCAA PECAM-1 CACCACAA CCCCCACC
Supplementary able 1 is presenting the PCR primer list used. ene name forward primer 5->3 reverse primer 5->3 product size cdna VE-Cadherin AACCCAAAAA CACCCCAAAAC 260bp CCA CCCAA PECAM-1 CACCACAA CCCCCACC
Isolation of human ips cells using EOS lentiviral vectors to select for pluripotency
 nature methods Isolation of human ips cells using EOS lentiviral vectors to select for pluripotency Akitsu Hotta, Aaron Y L Cheung, Natalie Farra, Kausalia Vijayaragavan, Cheryle A Séguin, Jonathan S Draper,
nature methods Isolation of human ips cells using EOS lentiviral vectors to select for pluripotency Akitsu Hotta, Aaron Y L Cheung, Natalie Farra, Kausalia Vijayaragavan, Cheryle A Séguin, Jonathan S Draper,
Assuring Pluripotency of ESC and ipsc Lines
 Assuring Pluripotency of ESC and ipsc Lines Introduction Compared to other cell types, stem cells have the unique ability to self-renew their populations by dividing into identical daughter stem cells
Assuring Pluripotency of ESC and ipsc Lines Introduction Compared to other cell types, stem cells have the unique ability to self-renew their populations by dividing into identical daughter stem cells
Electromagnetic Fields Mediate Efficient Cell Reprogramming Into a Pluripotent State
 Electromagnetic Fields Mediate Efficient Cell Reprogramming Into a Pluripotent State Soonbong Baek, 1 Xiaoyuan Quan, 1 Soochan Kim, 2 Christopher Lengner, 3 Jung- Keug Park, 4 and Jongpil Kim 1* 1 Lab
Electromagnetic Fields Mediate Efficient Cell Reprogramming Into a Pluripotent State Soonbong Baek, 1 Xiaoyuan Quan, 1 Soochan Kim, 2 Christopher Lengner, 3 Jung- Keug Park, 4 and Jongpil Kim 1* 1 Lab
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of hipscs derived from primary human fibroblasts. a,b. Morphology of hipscs. hipscs exhibit hesc-like
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of hipscs derived from primary human fibroblasts. a,b. Morphology of hipscs. hipscs exhibit hesc-like morphology in co-culture with mouse embryonic feeder fibroblasts
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of hipscs derived from primary human fibroblasts. a,b. Morphology of hipscs. hipscs exhibit hesc-like morphology in co-culture with mouse embryonic feeder fibroblasts
Protocol Using the Reprogramming Ecotropic Retrovirus Set: Mouse OSKM to Reprogram MEFs into ips Cells
 STEMGENT Page 1 OVERVIEW The following protocol describes the reprogramming of one well of mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) cells into induced pluripotent stem (ips) cells in a 6-well format. Transduction
STEMGENT Page 1 OVERVIEW The following protocol describes the reprogramming of one well of mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) cells into induced pluripotent stem (ips) cells in a 6-well format. Transduction
hipscs were derived from human skin fibroblasts (CRL-2097) by ectopic
 Generation and characterization of hipscs hipscs were derived from human skin fibroblasts (CRL-2097) by ectopic expression of OCT4, SOX2, KLF4, and C-MYC as previously described 1. hipscs showed typical
Generation and characterization of hipscs hipscs were derived from human skin fibroblasts (CRL-2097) by ectopic expression of OCT4, SOX2, KLF4, and C-MYC as previously described 1. hipscs showed typical
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of NSCs from hpscs in SDC medium.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of NSCs from hpscs in SDC medium. (a) Q-PCR of pluripotent markers (OCT4, NANOG), neural markers (SOX1, PAX6, N-Cadherin), markers for the other germ layers (T, EOMES,
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of NSCs from hpscs in SDC medium. (a) Q-PCR of pluripotent markers (OCT4, NANOG), neural markers (SOX1, PAX6, N-Cadherin), markers for the other germ layers (T, EOMES,
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S9. Morphology and DNA staining of cipsc-differentiated trophoblast cell-like cell. Scale bar: 100 mm. SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S10.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Lentivirus-infected canine fibroblasts show YFP expression. (A, B) Uninfected canine skin fibroblasts (CSFs); (C, D) infected CSFs; (E, F) uninfected CTFs; (G,
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Lentivirus-infected canine fibroblasts show YFP expression. (A, B) Uninfected canine skin fibroblasts (CSFs); (C, D) infected CSFs; (E, F) uninfected CTFs; (G,
Supplemental Information. Tissue Mechanics Orchestrate Wnt-Dependent. Human Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 19 Supplemental Information Tissue Mechanics Orchestrate Wnt-Dependent Human Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation Laralynne Przybyla, Johnathon N. Lakins, and Valerie M. Weaver Supplemental
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 19 Supplemental Information Tissue Mechanics Orchestrate Wnt-Dependent Human Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation Laralynne Przybyla, Johnathon N. Lakins, and Valerie M. Weaver Supplemental
INTESTINAL ORGANOIDS. IntestiCult and STEMdiff Media for Intestinal Organoid Culture. Scientists Helping Scientists
 INTESTINAL ORGANOIDS IntestiCult and STEMdiff Media for Intestinal Organoid Culture Scientists Helping Scientists WWW.STEMCELL.COM CULTURING INTESTINAL ORGANOIDS TABLE OF CONTENTS 3 Introduction 4 IntestiCult
INTESTINAL ORGANOIDS IntestiCult and STEMdiff Media for Intestinal Organoid Culture Scientists Helping Scientists WWW.STEMCELL.COM CULTURING INTESTINAL ORGANOIDS TABLE OF CONTENTS 3 Introduction 4 IntestiCult
Human induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (ipsc) Line: GM23225*B
 Certificate of Analysis NIGMS Human tic Cell Repository Human induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (ipsc) Line: GM23225*B Diagnosis Mutation Reprogramming method Publication(s) describing ipsc line establishment
Certificate of Analysis NIGMS Human tic Cell Repository Human induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (ipsc) Line: GM23225*B Diagnosis Mutation Reprogramming method Publication(s) describing ipsc line establishment
Xeno-Free Systems for hesc & hipsc. Facilitating the shift from Stem Cell Research to Clinical Applications
 Xeno-Free Systems for hesc & hipsc Facilitating the shift from Stem Cell Research to Clinical Applications NutriStem Defined, xeno-free (XF), serum-free media (SFM) specially formulated for growth and
Xeno-Free Systems for hesc & hipsc Facilitating the shift from Stem Cell Research to Clinical Applications NutriStem Defined, xeno-free (XF), serum-free media (SFM) specially formulated for growth and
Markers of genitourinary tract in NordiQC assessments. Jan Klos, MD Stavanger University Hospital Stavanger, Norway
 Markers of genitourinary tract in NordiQC assessments Jan Klos, MD Stavanger University Hospital Stavanger, Norway 2004-2017 PSA, PAP, PROSTEIN, NKX3.1, AMACR/P504S P63, p40, HMWCK PAX8 (PAX2) GATA3 PLAP,
Markers of genitourinary tract in NordiQC assessments Jan Klos, MD Stavanger University Hospital Stavanger, Norway 2004-2017 PSA, PAP, PROSTEIN, NKX3.1, AMACR/P504S P63, p40, HMWCK PAX8 (PAX2) GATA3 PLAP,
NIA Aging Cell Repository
 Certificate of Analysis NIA Aging Cell Repository Human induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (ipsc) Line: AG25370*B Diagnosis Alzheimer Disease, Familial, Type 4 Mutation Reprogramming method Publication(s) describing
Certificate of Analysis NIA Aging Cell Repository Human induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (ipsc) Line: AG25370*B Diagnosis Alzheimer Disease, Familial, Type 4 Mutation Reprogramming method Publication(s) describing
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of timing of DE dissociation and RA concentration on lung field specification in hpscs. (a) Effect of duration of endoderm induction on expression of
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of timing of DE dissociation and RA concentration on lung field specification in hpscs. (a) Effect of duration of endoderm induction on expression of
Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
 Applied StemCell, Inc. (866) 497-4180 www.appliedstemcell.com Datasheet Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Product Information Catalog Number Description Tissue Age Sex Race Clinical information Quantity
Applied StemCell, Inc. (866) 497-4180 www.appliedstemcell.com Datasheet Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Product Information Catalog Number Description Tissue Age Sex Race Clinical information Quantity
PI3K/mTORC2 regulates TGFβ/Activin signalling by modulating Smad2/3
 Supplementary Information PI3K/mTORC2 regulates TGFβ/Activin signalling by modulating Smad2/3 activity via linker phosphorylation Jason S.L. Yu, 1 Thamil Selvee Ramasamy, 1,2 Nick Murphy, 1 Marie Holt,
Supplementary Information PI3K/mTORC2 regulates TGFβ/Activin signalling by modulating Smad2/3 activity via linker phosphorylation Jason S.L. Yu, 1 Thamil Selvee Ramasamy, 1,2 Nick Murphy, 1 Marie Holt,
Development 142: doi: /dev : Supplementary Material
 Development 142: doi:1.42/dev.11687: Supplementary Material Figure S1 - Relative expression of lineage markers in single ES cell and cardiomyocyte by real-time quantitative PCR analysis. Single ES cell
Development 142: doi:1.42/dev.11687: Supplementary Material Figure S1 - Relative expression of lineage markers in single ES cell and cardiomyocyte by real-time quantitative PCR analysis. Single ES cell
T-iPSC. Gra-iPSC. B-iPSC. TTF-iPSC. Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.1667
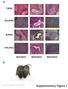 a T-iPSC Gra-iPSC B-iPSC TTF-iPSC Ectoderm Endoderm Mesoderm b Nature Biotechnology: doi:.38/nbt.667 Supplementary Figure Klf4 transgene expression Oct4 transgene expression.7 Fold GAPDH.6.5.4.3 Fold GAPDH
a T-iPSC Gra-iPSC B-iPSC TTF-iPSC Ectoderm Endoderm Mesoderm b Nature Biotechnology: doi:.38/nbt.667 Supplementary Figure Klf4 transgene expression Oct4 transgene expression.7 Fold GAPDH.6.5.4.3 Fold GAPDH
Stem Cells in Kidney Disease: Where Are We Now?
 Stem Cells in Kidney Disease: Where Are We Now? Berliner Dialyseseminar 5. Dezember 2015 Albert Q. Lam, MD Associate Physician Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Cell
Stem Cells in Kidney Disease: Where Are We Now? Berliner Dialyseseminar 5. Dezember 2015 Albert Q. Lam, MD Associate Physician Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Cell
Gene Expression in Stem Cells Featured scientist: Adam Heck from Colorado State University
 Gene Expression in Stem Cells Featured scientist: Adam Heck from Colorado State University Research Background: Every cell in your body contains the same DNA. How is it that genetically identical skin,
Gene Expression in Stem Cells Featured scientist: Adam Heck from Colorado State University Research Background: Every cell in your body contains the same DNA. How is it that genetically identical skin,
Supplementary Figure 1. Differentiation of human ESC into definitive endoderm.
 87.5 Supplementary Figure. Differentiation of human ESC into definitive endoderm. a-c. Human ESC treated with Activin A and WNT3a for 4 days and seeded onto collagen Type IV matrix generated stable and
87.5 Supplementary Figure. Differentiation of human ESC into definitive endoderm. a-c. Human ESC treated with Activin A and WNT3a for 4 days and seeded onto collagen Type IV matrix generated stable and
Supplementary Data. Supplementary Table S1.
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Table S1. Primer Sequences for Real-Time Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction Gene Forward 5?3 Reverse 3?5 Housekeeping gene 36B4 TCCAGGCTTTGGGCATCA CTTTATCAGCTGCACATCACTCAGA
Supplementary Data Supplementary Table S1. Primer Sequences for Real-Time Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction Gene Forward 5?3 Reverse 3?5 Housekeeping gene 36B4 TCCAGGCTTTGGGCATCA CTTTATCAGCTGCACATCACTCAGA
Figure S1. Phenotypic characterization of AND-1_WASKO cell lines. AND- 1_WASKO_C1.1 (WASKO_C1.1) and AND-1_WASKO_C1.2 (WASKO_C1.
 LEGENDS TO SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Phenotypic characterization of AND-1_WASKO cell lines. AND- 1_WASKO_C1.1 (WASKO_C1.1) and AND-1_WASKO_C1.2 (WASKO_C1.2) were stained with the antibodies oct3/4
LEGENDS TO SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Phenotypic characterization of AND-1_WASKO cell lines. AND- 1_WASKO_C1.1 (WASKO_C1.1) and AND-1_WASKO_C1.2 (WASKO_C1.2) were stained with the antibodies oct3/4
Electronic Supplementary Information (Table S1 and Figures S1-S4)
 Electronic Supplementary Information (Table S1 and igures S1-S4) One-Step Microfluidic Generation of Pre-Hatching Embryo-Like Core-Shell Microcapsules for Miniaturized 3D Culture of Pluripotent Stem Cells
Electronic Supplementary Information (Table S1 and igures S1-S4) One-Step Microfluidic Generation of Pre-Hatching Embryo-Like Core-Shell Microcapsules for Miniaturized 3D Culture of Pluripotent Stem Cells
Biology Open (2015): doi: /bio : Supplementary information
 Fig. S1. Verification of optimal conditions for the generation of LIF-dependent inscs Representative images (from five repeat experiments) of human primary fibroblasts undergoing reprogramming for 21 days
Fig. S1. Verification of optimal conditions for the generation of LIF-dependent inscs Representative images (from five repeat experiments) of human primary fibroblasts undergoing reprogramming for 21 days
hpsc Growth Medium DXF Dr. Lorna Whyte
 hpsc Growth Medium DXF Dr. Lorna Whyte 27.06.2014 Training from Heidelberg Overview Background: Stem Cells Introduction: Human Pluripotent Stem Cells (hpsc) vs. Adult Stem Cells Promise of PSC Research
hpsc Growth Medium DXF Dr. Lorna Whyte 27.06.2014 Training from Heidelberg Overview Background: Stem Cells Introduction: Human Pluripotent Stem Cells (hpsc) vs. Adult Stem Cells Promise of PSC Research
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. (A) UCSC Genome Browser view of region immediately downstream of the NEUROG3 start codon. All candidate grna target sites which meet the G(N 19 )NGG constraint are aligned to illustrate
Supplementary Figure 1. (A) UCSC Genome Browser view of region immediately downstream of the NEUROG3 start codon. All candidate grna target sites which meet the G(N 19 )NGG constraint are aligned to illustrate
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Extrinsic Signaling during Reprogramming.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Extrinsic Signaling during Reprogramming. a, In human pluripotent stem cells, exogenously- (medium) and endogenously-promoted (cell-secreted) FGF and TGF- pathways sustain the master
Supplementary Figure 1 Extrinsic Signaling during Reprogramming. a, In human pluripotent stem cells, exogenously- (medium) and endogenously-promoted (cell-secreted) FGF and TGF- pathways sustain the master
Supplementary Fig. 1. A, Upper panel shows schematic molecular representation of mutation- and SNP-replacement with FANCA-c-HDAdV in FANCA-corrected
 Supplementary Fig. 1. A, Upper panel shows schematic molecular representation of mutation- and SNP-replacement with FANCA-c-HDAdV in FANCA-corrected FA-iPSC line (C-FA-iPSCs). Lower panels show the sequencing
Supplementary Fig. 1. A, Upper panel shows schematic molecular representation of mutation- and SNP-replacement with FANCA-c-HDAdV in FANCA-corrected FA-iPSC line (C-FA-iPSCs). Lower panels show the sequencing
Anexo a la solicitud de depósito de la línea celular. Annexes to the deposited cell line. RP1-FiPS4F1
 Anexo a la solicitud de depósito de la línea celular Annexes to the deposited cell line RP1-FiPS4F1 1 Marcadores de pluripotencia/ Pluripotency markers i) In situ staining for TRA-1-81 (bright field BF
Anexo a la solicitud de depósito de la línea celular Annexes to the deposited cell line RP1-FiPS4F1 1 Marcadores de pluripotencia/ Pluripotency markers i) In situ staining for TRA-1-81 (bright field BF
Best Practices Maintaining Pluripotency. Anne R. Greenlee, PhD
 Best Practices Maintaining Pluripotency Anne R. Greenlee, PhD HESI-Workshop Cary, NC 27 Feb 2007 OHSU La Grande Campus Research Directions Past Fertility Risk Factor Study Pesticide effects on embryo development
Best Practices Maintaining Pluripotency Anne R. Greenlee, PhD HESI-Workshop Cary, NC 27 Feb 2007 OHSU La Grande Campus Research Directions Past Fertility Risk Factor Study Pesticide effects on embryo development
Comparative study of human induced pluripotent stem cells derived from bone marrow cells, hair keratinocytes and skin fibroblasts
 ESC CONGRESS 2012, Munich Comparative study of human induced pluripotent stem cells derived from bone marrow cells, hair keratinocytes and skin fibroblasts I have no financial relationships to disclose
ESC CONGRESS 2012, Munich Comparative study of human induced pluripotent stem cells derived from bone marrow cells, hair keratinocytes and skin fibroblasts I have no financial relationships to disclose
A cost-effective system for differentiation of intestinal epithelium from human induced pluripotent stem cells
 A cost-effective system for differentiation of intestinal epithelium from human induced pluripotent stem cells Soichiro Ogaki 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, *, ayu orooka 1,*, Kaito Otera 1, 1, 3 and Shoen Kume Supplementary
A cost-effective system for differentiation of intestinal epithelium from human induced pluripotent stem cells Soichiro Ogaki 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, *, ayu orooka 1,*, Kaito Otera 1, 1, 3 and Shoen Kume Supplementary
Embryonic germ cell formation. Maintainance of pluripotency
 hvasa 2.5 kb promoter egfp 3 UTR(1kb) 1. Stable integration of germ cell reporter into hescs 2. Adherent differentiation and FACS isolation for VASA:GFP+ cells 4. Silencing or overexpression of the human
hvasa 2.5 kb promoter egfp 3 UTR(1kb) 1. Stable integration of germ cell reporter into hescs 2. Adherent differentiation and FACS isolation for VASA:GFP+ cells 4. Silencing or overexpression of the human
Directed differentiation of human embryonic stem cells
 Directed differentiation of human embryonic stem cells TECAN Symposium 2008 Biologics - From Benchtop to Production Wednesday 17 September 2008 Andrew Elefanty Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation Laboratory,
Directed differentiation of human embryonic stem cells TECAN Symposium 2008 Biologics - From Benchtop to Production Wednesday 17 September 2008 Andrew Elefanty Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation Laboratory,
Supplementary figures (Zhang)
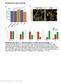 Supplementary figures (Zhang) Supplementary figure 1. Characterization of hesc-derived astroglia. (a) Treatment of astroglia with LIF and CNTF increases the proportion of GFAP+ cells, whereas the percentage
Supplementary figures (Zhang) Supplementary figure 1. Characterization of hesc-derived astroglia. (a) Treatment of astroglia with LIF and CNTF increases the proportion of GFAP+ cells, whereas the percentage
Chemically defined conditions for human ipsc derivation and culture
 Nature Methods Chemically defined conditions for human ipsc derivation and culture Guokai Chen, Daniel R Gulbranson, Zhonggang Hou, Jennifer M Bolin, Victor Ruotti, Mitchell D Probasco, Kimberly Smuga-Otto,
Nature Methods Chemically defined conditions for human ipsc derivation and culture Guokai Chen, Daniel R Gulbranson, Zhonggang Hou, Jennifer M Bolin, Victor Ruotti, Mitchell D Probasco, Kimberly Smuga-Otto,
Day AP2a FOXG1 PAX6 SOX10 OCT4 OCT4 SIX6 PAX7 NES NES NES CD146 CD146 CD93 CD146 CD31 CD31. Flk1 CD34 CD34 CD34 CD34 CD34 CD43 CD43 DES
 Endoderm Mesoderm Ectoderm OCT4 T CXCR4 FOXA2 SOX17 OCT4 CD34 CXCR4 FOXA2 AP2a SOX10 NES CD93 Flk1 CD34 CD43 DES TAL1 HNF4α C/EBPα FOXA2 AAT NES CD146 CD31 CD34 DES HNF4α C/EBPα LGR5 CK19 Fib AAT C/EBPα
Endoderm Mesoderm Ectoderm OCT4 T CXCR4 FOXA2 SOX17 OCT4 CD34 CXCR4 FOXA2 AP2a SOX10 NES CD93 Flk1 CD34 CD43 DES TAL1 HNF4α C/EBPα FOXA2 AAT NES CD146 CD31 CD34 DES HNF4α C/EBPα LGR5 CK19 Fib AAT C/EBPα
Protocol Reprogramming Human Fibroblasts into ips Cells using the Stemgent Reprogramming Lentivirus Set: Human OKSM
 STEMGENT Page 1 Reprogramming Lentivirus Set: Human OKSM OVERVIEW The following procedure describes the reprogramming of BJ Human Fibroblasts (BJ cells) to induced pluripotent stem (ips) cells using the
STEMGENT Page 1 Reprogramming Lentivirus Set: Human OKSM OVERVIEW The following procedure describes the reprogramming of BJ Human Fibroblasts (BJ cells) to induced pluripotent stem (ips) cells using the
Multicolor flow cytometry analysis of human pluripotent stem cell cultures
 Multicolor flow cytometry analysis of human pluripotent stem cell cultures ackground Thorough characterization of pluripotency is mandatory during the establishment of newly derived human embryonic or
Multicolor flow cytometry analysis of human pluripotent stem cell cultures ackground Thorough characterization of pluripotency is mandatory during the establishment of newly derived human embryonic or
Guided differentiation of ES cell into mesenchymal stem cell
 Guided differentiation of ES cell into mesenchymal stem cell Takumi Era Division of Molecular Neurobiology Institute of Molecular Embryology and Genetics, Kumamoto University Differentiation pathways of
Guided differentiation of ES cell into mesenchymal stem cell Takumi Era Division of Molecular Neurobiology Institute of Molecular Embryology and Genetics, Kumamoto University Differentiation pathways of
Protocol Reprogramming MEFs using the Dox Inducible Reprogramming Lentivirus Set: Mouse OKSM
 STEMGENT Page 1 OVERVIEW The following protocol describes the reprogramming of one well of mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) into induced pluripotent stem (ips) cells in a 6-well format. Transduction
STEMGENT Page 1 OVERVIEW The following protocol describes the reprogramming of one well of mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) into induced pluripotent stem (ips) cells in a 6-well format. Transduction
CULTURE ENGINEERING DIFFERENTIATION CHARACTERIZATION. Stem Cell Research Solutions Promotional offers
 CULTURE ENGINEERING DIFFERENTIATION CHARACTERIZATION Stem Cell Research Solutions Promotional offers Stem Cell research products For more than a decade, we have provided you with key tools to address challenges
CULTURE ENGINEERING DIFFERENTIATION CHARACTERIZATION Stem Cell Research Solutions Promotional offers Stem Cell research products For more than a decade, we have provided you with key tools to address challenges
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic and results of screening the combinatorial antibody library for Sox2 replacement activity. A single batch of MEFs were plated and transduced with doxycycline inducible
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic and results of screening the combinatorial antibody library for Sox2 replacement activity. A single batch of MEFs were plated and transduced with doxycycline inducible
Supplementary Figure 1. Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings.
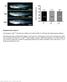 Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
Supplementary Information. Conversion of vascular endothelial cells into multipotent stem-like cells
 Supplementary Information Conversion of vascular endothelial cells into multipotent stem-like cells Damian Medici 1, Eileen M. Shore 2,3,4, Vitali Y. Lounev 2,4, Frederick S. Kaplan 2,4,5, Raghu Kalluri
Supplementary Information Conversion of vascular endothelial cells into multipotent stem-like cells Damian Medici 1, Eileen M. Shore 2,3,4, Vitali Y. Lounev 2,4, Frederick S. Kaplan 2,4,5, Raghu Kalluri
mrna for Integration- free Cell Fate Manipulation BRAD HAMILTON ISSCR 2012 YOKOHAMA, JAPAN JUNE 13 TH, 2012
 mrna for Integration- free Cell Fate Manipulation BRAD HAMILTON ISSCR 2012 YOKOHAMA, JAPAN JUNE 13 TH, 2012 Presentation Outline mrna Reprogramming System mirna Enhanced mrna Reprogramming mrna for Differentiation
mrna for Integration- free Cell Fate Manipulation BRAD HAMILTON ISSCR 2012 YOKOHAMA, JAPAN JUNE 13 TH, 2012 Presentation Outline mrna Reprogramming System mirna Enhanced mrna Reprogramming mrna for Differentiation
Naked Mole Rat Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells and Their Contribution
 Stem Cell eports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information Naked Mole at Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells and Their Contribution to Interspecific Chimera Sang-Goo Lee, Aleksei E. Mikhalchenko, Sun Hee Yim, Alexei
Stem Cell eports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information Naked Mole at Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells and Their Contribution to Interspecific Chimera Sang-Goo Lee, Aleksei E. Mikhalchenko, Sun Hee Yim, Alexei
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.4166
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION Figure 1. METHODS ipsc culture ATCC No. Initial Cell Type Description Reprogramming Method Table 1.
 THE ESSENTIALS OF LIFE SCIENCE RESEARCH GLOBALLY DELIVERED DIRECTED DIFFERENTIATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL EPITHELIAL ORGANOIDS USING ATCC CELLMATRIX BASEMENT MEMBRANE FROM MULTIPLE HUMAN ATCC ipsc LINES
THE ESSENTIALS OF LIFE SCIENCE RESEARCH GLOBALLY DELIVERED DIRECTED DIFFERENTIATION OF GASTROINTESTINAL EPITHELIAL ORGANOIDS USING ATCC CELLMATRIX BASEMENT MEMBRANE FROM MULTIPLE HUMAN ATCC ipsc LINES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure S1 Colony-forming efficiencies using transposition of inducible mouse factors. (a) Morphologically distinct growth foci appeared from rtta-mefs 6-8 days following PB-TET-mFx cocktail
Supplementary Figure S1 Colony-forming efficiencies using transposition of inducible mouse factors. (a) Morphologically distinct growth foci appeared from rtta-mefs 6-8 days following PB-TET-mFx cocktail
Induced Stem Cells in Research and Therapy of Neuropsychiatric Disorders
 Berlin-Brandenburg Center for Regenerative Therapies Induced Stem Cells in Research and Therapy of Neuropsychiatric Disorders Josef Priller Department of Neuropsychiatry Laboratory of Molecular Psychiatry
Berlin-Brandenburg Center for Regenerative Therapies Induced Stem Cells in Research and Therapy of Neuropsychiatric Disorders Josef Priller Department of Neuropsychiatry Laboratory of Molecular Psychiatry
Supplementary Information to Accompany. Precision Modulation of Neurodegenerative Disease-Related Gene Expression in Human ipsc-derived Neurons
 Supplementary Information to Accompany Precision Modulation of Neurodegenerative Disease-Related Gene Expression in Human ipsc-derived Neurons Sabrina Mahalia Heman-Ackah 1,2,3,*, Andrew Roger Bassett
Supplementary Information to Accompany Precision Modulation of Neurodegenerative Disease-Related Gene Expression in Human ipsc-derived Neurons Sabrina Mahalia Heman-Ackah 1,2,3,*, Andrew Roger Bassett
TITLE: Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells as Potential Therapeutic Agents in NF1
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0181 TITLE: Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells as Potential Therapeutic Agents in NF1 PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jonathan Chernoff, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Institute
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0181 TITLE: Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells as Potential Therapeutic Agents in NF1 PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jonathan Chernoff, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Institute
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTRY INFORMTION DOI:.38/ncb Kdmb locus kb Long isoform Short isoform Long isoform Jmj XX PHD F-box LRR Short isoform XX PHD F-box LRR Target Vector 3xFlag Left H Neo Right H TK LoxP LoxP Kdmb Locus
SUPPLEMENTRY INFORMTION DOI:.38/ncb Kdmb locus kb Long isoform Short isoform Long isoform Jmj XX PHD F-box LRR Short isoform XX PHD F-box LRR Target Vector 3xFlag Left H Neo Right H TK LoxP LoxP Kdmb Locus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature08267 Figure S: Karyotype analysis of ips cell line One hundred individual chromosomal spreads were counted for each of the ips samples. Shown here is an spread at passage 5, predominantly
doi:.38/nature08267 Figure S: Karyotype analysis of ips cell line One hundred individual chromosomal spreads were counted for each of the ips samples. Shown here is an spread at passage 5, predominantly
New Technique for Differentiation Monitoring using Supernatant. Dojindo EU GmbH Takatoshi EZOE
 New Technique for Differentiation Monitoring using Supernatant Dojindo EU GmbH Takatoshi EZOE Jun/26/2013 1 Culturing Process from ES/iPS to Organs ES / ips Cells Activin Endoderm Intestine Pancreas Liver
New Technique for Differentiation Monitoring using Supernatant Dojindo EU GmbH Takatoshi EZOE Jun/26/2013 1 Culturing Process from ES/iPS to Organs ES / ips Cells Activin Endoderm Intestine Pancreas Liver
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Workflow for multimodal analysis using sc-gem on a programmable microfluidic device (Fluidigm). 1) Cells are captured and lysed, 2) RNA from lysed single cell is reverse-transcribed
Supplementary Figure 1 Workflow for multimodal analysis using sc-gem on a programmable microfluidic device (Fluidigm). 1) Cells are captured and lysed, 2) RNA from lysed single cell is reverse-transcribed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NMAT3777 Biophysical regulation of epigenetic state and cell reprogramming Authors: Timothy L. Downing 1,2, Jennifer Soto 1,2, Constant Morez 2,3,, Timothee Houssin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NMAT3777 Biophysical regulation of epigenetic state and cell reprogramming Authors: Timothy L. Downing 1,2, Jennifer Soto 1,2, Constant Morez 2,3,, Timothee Houssin
First xeno-free serum replacement for pluripotent stem cells
 Stem Cell Research First xeno-free serum replacement for pluripotent stem cells KnockOut SR XenoFree Stem Cell Research New, xeno-free growth and expansion of hescs and human ipscs KnockOut SR XenoFree
Stem Cell Research First xeno-free serum replacement for pluripotent stem cells KnockOut SR XenoFree Stem Cell Research New, xeno-free growth and expansion of hescs and human ipscs KnockOut SR XenoFree
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of OKSM-iNSCs
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of OKSM-iNSCs (A) Gene expression levels of Sox1 and Sox2 in the indicated cell types by microarray gene expression analysis. (B) Dendrogram cluster analysis of
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of OKSM-iNSCs (A) Gene expression levels of Sox1 and Sox2 in the indicated cell types by microarray gene expression analysis. (B) Dendrogram cluster analysis of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Correction notice Disease-corrected haematopoietic progenitors from Fanconi anaemia induced pluripotent stem cells Ángel Raya, Ignasi Rodríguez-Pizà, Guillermo Guenechea, Rita Vassena, Susana Navarro,
Correction notice Disease-corrected haematopoietic progenitors from Fanconi anaemia induced pluripotent stem cells Ángel Raya, Ignasi Rodríguez-Pizà, Guillermo Guenechea, Rita Vassena, Susana Navarro,
Lineage-specific Reporter Knock-in ipscs: MAP2-Nanoluc-Halotag ipsc (Heterozygous)
 Lineage-specific Reporter Knock-in ipscs: MAP2-Nanoluc-Halotag ipsc (Heterozygous) Applied StemCell, Inc. (866) 497-4180 www.appliedstemcell.com Datasheet Product Information Catalog Number Description
Lineage-specific Reporter Knock-in ipscs: MAP2-Nanoluc-Halotag ipsc (Heterozygous) Applied StemCell, Inc. (866) 497-4180 www.appliedstemcell.com Datasheet Product Information Catalog Number Description
Lineage-specific Reporter Knock-in ipscs: MAP2-Nanoluc-Halotag ipsc (Heterozygous)
 Lineage-specific Reporter Knock-in ipscs: MAP2-Nanoluc-Halotag ipsc (Heterozygous) Applied StemCell, Inc. (866) 497-4180 www.appliedstemcell.com Datasheet Product Information Catalog Number Description
Lineage-specific Reporter Knock-in ipscs: MAP2-Nanoluc-Halotag ipsc (Heterozygous) Applied StemCell, Inc. (866) 497-4180 www.appliedstemcell.com Datasheet Product Information Catalog Number Description
Accelerating skin wound healing by M-CSF through generating SSEA-1 and -3 stem cells. in the injured sites
 Accelerating skin wound healing by M-CSF through generating SSEA-1 and -3 stem cells in the injured sites Yunyuan Li, Reza Baradar Jalili, Aziz Ghahary Department of Surgery, University of British Columbia,
Accelerating skin wound healing by M-CSF through generating SSEA-1 and -3 stem cells in the injured sites Yunyuan Li, Reza Baradar Jalili, Aziz Ghahary Department of Surgery, University of British Columbia,
Cell therapies to treat haematopoietic disorders
 Cell therapies to treat haematopoietic disorders Haematopoietic Stem Cells (CD34) RBCs Platelets Limitations A donor required for each treatment Transfusion-transmitted infection Immunological (HLA/AB0)
Cell therapies to treat haematopoietic disorders Haematopoietic Stem Cells (CD34) RBCs Platelets Limitations A donor required for each treatment Transfusion-transmitted infection Immunological (HLA/AB0)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11435 Supplementary Figures Figure S1. The scheme of androgenetic haploid embryonic stem (ahes) cells derivation. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S2.
doi:10.1038/nature11435 Supplementary Figures Figure S1. The scheme of androgenetic haploid embryonic stem (ahes) cells derivation. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S2.
Supplemental Figure 1
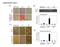 Supplemental Figure 1 A B 50 * 40 30 20 10 0 NeurofilamentM/βactin Relative expression control D neurogenic cond. PPARγ/ Relative expression C PPARγ Hprt OilRedO adipogenic cond. control 125 * 100 75 50
Supplemental Figure 1 A B 50 * 40 30 20 10 0 NeurofilamentM/βactin Relative expression control D neurogenic cond. PPARγ/ Relative expression C PPARγ Hprt OilRedO adipogenic cond. control 125 * 100 75 50
Supplementary Figure 1. Wnt10a mutation causes aberrant molar tooth development and formation of an ectopic M4 molar. (a,b) Smaller molar teeth with
 Supplementary Figure 1. Wnt10a mutation causes aberrant molar tooth development and formation of an ectopic M4 molar. (a,b) Smaller molar teeth with blunted cusp formation, and presence of an ectopic molar
Supplementary Figure 1. Wnt10a mutation causes aberrant molar tooth development and formation of an ectopic M4 molar. (a,b) Smaller molar teeth with blunted cusp formation, and presence of an ectopic molar
Plates available individually or as a set of 6. Each set contains 84 unique gene primer pairs deposited in one 96-well plate.
 Product Data Sheet ExProfile TM Human Embryonic Stem Cells Related Gene qpcr Array For focused group profiling of human embryonic stem cells genes expression Cat. No. QG016-A (1 x 96-well plate, Format
Product Data Sheet ExProfile TM Human Embryonic Stem Cells Related Gene qpcr Array For focused group profiling of human embryonic stem cells genes expression Cat. No. QG016-A (1 x 96-well plate, Format
TITLE: Identification of different mechanisms leading to PAX6 down-regulation, as potential
 TITLE: Identification of different mechanisms leading to PAX6 down-regulation, as potential events contributing to the onset of Hirschsprung disease AUTHOR: María Valle Enguix-Riego 1,2,#, Ana Torroglosa
TITLE: Identification of different mechanisms leading to PAX6 down-regulation, as potential events contributing to the onset of Hirschsprung disease AUTHOR: María Valle Enguix-Riego 1,2,#, Ana Torroglosa
(51) Int Cl.: C12N 5/07 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _Z49 B_T (11) EP 2 3 492 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 22.07.1 Bulletin 1/ (21) Application number: 09774297.7 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ _Z49 B_T (11) EP 2 3 492 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 22.07.1 Bulletin 1/ (21) Application number: 09774297.7 (22) Date
Isolation, culture, and transfection of primary mammary epithelial organoids
 Supplementary Experimental Procedures Isolation, culture, and transfection of primary mammary epithelial organoids Primary mammary epithelial organoids were prepared from 8-week-old CD1 mice (Charles River)
Supplementary Experimental Procedures Isolation, culture, and transfection of primary mammary epithelial organoids Primary mammary epithelial organoids were prepared from 8-week-old CD1 mice (Charles River)
Protocol Reprogramming Human Fibriblasts using the Dox Inducible Reprogramming Polycistronic Lentivirus Set: Human 4F2A LoxP
 STEMGENT Page 1 OVERVIEW The following protocol describes the reprogramming of one well of BJ Human Fibroblasts (BJ cells) into induced pluripotent stem (ips) cells in a 6-well format. Transduction efficiency
STEMGENT Page 1 OVERVIEW The following protocol describes the reprogramming of one well of BJ Human Fibroblasts (BJ cells) into induced pluripotent stem (ips) cells in a 6-well format. Transduction efficiency
Electronic Supplementary Information (Table S1 and Figures S1-S5)
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Integrative Biology. This journal is The oyal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information (Table S1 and igures S1-S5) Coaxial electrospray
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Integrative Biology. This journal is The oyal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information (Table S1 and igures S1-S5) Coaxial electrospray
Matrices sourcebook. Your guide to Gibco extracellular matrices products
 Matrices sourcebook Your guide to Gibco extracellular matrices products Introduction Gibco products, including extracellular matrices, 3D scaffolds, and attachment proteins, are essential tools for providing
Matrices sourcebook Your guide to Gibco extracellular matrices products Introduction Gibco products, including extracellular matrices, 3D scaffolds, and attachment proteins, are essential tools for providing
Single cell transcriptional profiling reveals heterogeneity of human induced pluripotent stem cells
 Brief report Single cell transcriptional profiling reveals heterogeneity of human induced pluripotent stem cells Kazim H. Narsinh, 1,2,3 Ning Sun, 1,2 Veronica Sanchez-Freire, 1,2 Andrew S. Lee, 1,2 Patricia
Brief report Single cell transcriptional profiling reveals heterogeneity of human induced pluripotent stem cells Kazim H. Narsinh, 1,2,3 Ning Sun, 1,2 Veronica Sanchez-Freire, 1,2 Andrew S. Lee, 1,2 Patricia
EQA of gynecological cancer markers The NordiQC experience. Rasmus Røge Scheme Organizer, NordiQC Aalborg University Hospital
 EQA of gynecological cancer markers The NordiQC experience Rasmus Røge Scheme Organizer, NordiQC Aalborg University Hospital Markers WT1 Discussed by prof. Mogens Vyberg prev. ER Discussion by Søren Nielsen:
EQA of gynecological cancer markers The NordiQC experience Rasmus Røge Scheme Organizer, NordiQC Aalborg University Hospital Markers WT1 Discussed by prof. Mogens Vyberg prev. ER Discussion by Søren Nielsen:
A simple choice. Essential 8 Media
 A simple choice Essential 8 Media Your stem cells thrive with the essentials Gibco Essential 8 Medium is a feeder-free, xeno-free medium originally developed in the laboratory of stem cell research pioneer
A simple choice Essential 8 Media Your stem cells thrive with the essentials Gibco Essential 8 Medium is a feeder-free, xeno-free medium originally developed in the laboratory of stem cell research pioneer
Derivation of UCSFB lines from biopsied blastomeres of cleavage-stage human. Spare embryos were obtained through the UCSF IVF Tissue Bank from donors
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Derivation of UCSFB lines from biopsied blastomeres of cleavage-stage human embryos Spare embryos were obtained through the UCSF IVF Tissue Bank from donors undergoing
Supplementary Materials and Methods Derivation of UCSFB lines from biopsied blastomeres of cleavage-stage human embryos Spare embryos were obtained through the UCSF IVF Tissue Bank from donors undergoing
Supplementary Figure 1, related to Figure 1. GAS5 is highly expressed in the cytoplasm of hescs, and positively correlates with pluripotency.
 Supplementary Figure 1, related to Figure 1. GAS5 is highly expressed in the cytoplasm of hescs, and positively correlates with pluripotency. (a) Transfection of different concentration of GAS5-overexpressing
Supplementary Figure 1, related to Figure 1. GAS5 is highly expressed in the cytoplasm of hescs, and positively correlates with pluripotency. (a) Transfection of different concentration of GAS5-overexpressing
Supplementary Data. Supplementary Figures. (A) Mock BV (B) (C) Transduction efficiency (%)
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Figures (A) Mock BV (B) Transduction efficiency (%) 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Mock BV (C) Transduction efficiency (%) 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 100 MOI 250 500 Fig. S1. BV
Supplementary Data Supplementary Figures (A) Mock BV (B) Transduction efficiency (%) 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Mock BV (C) Transduction efficiency (%) 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 100 MOI 250 500 Fig. S1. BV
Supplemental Information. A Mesenchymal-to-Epithelial Transition. Initiates and Is Required for the Nuclear. Reprogramming of Mouse Fibroblasts
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information A Mesenchymal-to-Epithelial Transition Initiates and Is Required for the Nuclear Reprogramming of Mouse Fibroblasts Ronghui Li, Jialiang Liang, Su Ni,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information A Mesenchymal-to-Epithelial Transition Initiates and Is Required for the Nuclear Reprogramming of Mouse Fibroblasts Ronghui Li, Jialiang Liang, Su Ni,
Spironolactone ameliorates PIT1-dependent vascular osteoinduction in klotho-hypomorphic mice
 Spironolactone ameliorates PIT1-dependent vascular osteoinduction in klotho-hypomorphic mice Supplementary Material Supplementary Methods Materials Spironolactone, aldosterone and β-glycerophosphate were
Spironolactone ameliorates PIT1-dependent vascular osteoinduction in klotho-hypomorphic mice Supplementary Material Supplementary Methods Materials Spironolactone, aldosterone and β-glycerophosphate were
PluriQ TM Serum Replacement (PluriQ TM SR)
 PluriQ TM Serum Replacement (PluriQ TM SR) (PluriQ SR) is a defined, serum-free supplement formulated as a direct replacement for FBS (fetal bovine serum) used in the growth and maintenance of undifferentiated
PluriQ TM Serum Replacement (PluriQ TM SR) (PluriQ SR) is a defined, serum-free supplement formulated as a direct replacement for FBS (fetal bovine serum) used in the growth and maintenance of undifferentiated
