Cell isn't defenseless against DNA damage, not to mention mistakes it makes during replication. Has a variety of repair systems to limit mutations.
|
|
|
- Augustine Randall
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture Outline I. Spontaneous mutation II. Induced mutation III. Repair A. Mismatch repair B. Oxidative damage repair C. SOS response III. DNA repair Cell isn't defenseless against DNA damage, not to mention mistakes it makes during replication. Has a variety of repair systems to limit mutations. How to identify repair functions genetically? isolate mutants not doing it right- PHENOTYPE? Higher mutation frequency- mutators Already discussed one type- what is? Replication proofreading exonuclease minus- doesn't catch polymerization mistakes BOARD - screen for mutator mutants (as in experiment 3) How to identify Start with cells that are laci - lacz - lacy + Plate on minimal glucose + lactose (or Phenyl galactoside (PG)) + Xgal go through papillation assay Once get, test other gene to be sure GENERAL MUTATOR A. Mismatch repair- common write: muts muth mutl- all required for mismatch repair Genetic evidence that work together- all show similar spectrum, including hotspots-
2 idea that some sites in DNA are more prone to replication mismatch errors than others and these are normally repaired by MM repair- even though not clear why some more prone to mm error Draw on OH of mismatch being corrected in either of two directions: Main purpose- to catch replication errors that DNA polymerase proofreading misses. Works by identifying mismatches, excising them and repolymerizing in correct base So mismatch repair won't help if random! Need way to distinguish which base in mismatch is wrong!! Logic used by the cell: assumes that recently polymerized of two mismatched bases is wrong one How to tell which one is recently polymerized? Relative age is ascertained by methylation state of the DNA after replication- DNA methylated on A's by DNA adenine methylase (DAM Methylase)- not all A's, just GATC- DONT CONFUSE WITH CYTOSINE METHYLATION! replication CTA G + GA TC dam methylation dam methylation Note: time lag after replication before methylation- newly made strand is transiently undermethylated- this is how relative age is determined Mechanism muts binds to mismatch muth, L recognize nearby methyl site in DNA, cleave unmethylated strand at the site then 3 >5 exonuclease removes, polymerase and ligase act phenotype of Dam- mutants (mutator)- same spectrum as others
3 phenotype if overproduce dam methylase- also mutator, not enough time to distinguish strands Draw on OH=> Mismatch-stimulated killing Dam- is hypersensitive to 2-aminopurine. Idea is that 2AP is normally incorporated but causes buldge (opposite either T or C) that is recognized by mm repair. If no dam function, get cleavage at random and sites close together give fragmentation of genome. Isolate additional mutations not showing sensitivitiyfind in muthsl so donʼt get cleavage. After killing, cells lose DNA FUNCTION ERROR RATE DNA polymerizing >5 proofreading 10-4 mismatch repair 10-1 Think about the mutational behavior of different single vs double mutants. For the following, mutations complete nulls except for proofreading exonuclease mutant. Mutations affect components of same repair system Mutant Mutation frequency None (wild-type) MutS (MM repair) MutH (MM repair) MutS MutH double Ask = Mutations affect components of repair systems acting on different types of damage (replication mismatches vs cytosine deamination products) Mutant Mutation frequency None (wild-type) MutS (MM repair) Uracil N glycosylase 10 9 (10 X increase) MutS Uracil N glycosylase double 2 X 10 9 (20X increase) Mutations affect components of different repair systems acting on same damage (mismatched bases arising in replication) Mutant Mutation frequency None (wild-type) 10 10
4 MutS (MM repair) Proofreading (partial) MutS Proofreading double Ask =10 8 (100X increase) Other role for mismatch repair (HSL) in blocking recombination between homeologous sequences. (=similar but not identical sequences) interferes with formation of Holiday intermediate Oxidative damage oxidants from normal metabolism- usually fairly efficient conversion of O 2 to H 2 0, but some of the reactive intermediates are inevitable byproducts (all organisms). OH-reduction of oxygen to water e e e e O 2 ---> O 2 ---> H 2 O 2 ---> OH ---> H 2 O The most important nucleotide change is formation of 8-oxoguanine (= GO ) /genome/replication Guanine 8-oxo guanine Can occur either in free nucleotide or DNA
5 Problem: can base pair with A as well as C! Figure 1 showing- GO tends to flip around into syn isomer but most of the time pairs like G OH- Multiple lines of defense- write on OH as say 1. mutt Fig. - cleaves OG triphosphate (DEOXY) before can be incorporated into DNA; monophosphate is further degraded 2. mutm- Figs 3and -removes GO from GO:C mismatch -Doesn't remove GO from GO:A mismatch- Why? Make 100% mutants. If replicate, have chance to rep right 3. muty- Figs and -removes A from GO:A mismatch - If replaces A with C, mutm can correct (then it's GO:C) mutant specificities: mutt: A:T >C:G mutm: G:C >T:A muty: G:C >T:A Although both mutm and muty help avoid same type of damage, they function largely independently (redundant). Can see this in comparing single and double mutants BOARD: freq. Rif R (X10-8 ) mutm+ muty+ 5 (1X)
6 mutm- muty+ 151 (30X) mutm+ muty- mutm- muty- 290 (58X) 8200 (1640X)
September 19, synthesized DNA. Label all of the DNA strands with 5 and 3 labels, and clearly show which strand(s) contain methyl groups.
 KEY DNA Replication and Mutation September 19, 2011 1. Below is a short DNA sequence located on the E. coli chromosome. In class we talked about how during the process of DNA replication, an enzyme adds
KEY DNA Replication and Mutation September 19, 2011 1. Below is a short DNA sequence located on the E. coli chromosome. In class we talked about how during the process of DNA replication, an enzyme adds
DNA metabolism. DNA Replication DNA Repair DNA Recombination
 DNA metabolism DNA Replication DNA Repair DNA Recombination Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology Central Dogma or Flow of genetic information
DNA metabolism DNA Replication DNA Repair DNA Recombination Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology Central Dogma or Flow of genetic information
LECTURE 26. a) A light-independent repair mechanism that involves three steps:
 LECTURE 26 DNA REPAIR A. The capability for repair of damaged DNA is found in one form or another in all organisms. Prokaryotes (e.g., E. coli) have five repair systems, whereas higher organisms (e.g.,
LECTURE 26 DNA REPAIR A. The capability for repair of damaged DNA is found in one form or another in all organisms. Prokaryotes (e.g., E. coli) have five repair systems, whereas higher organisms (e.g.,
Peter Pristas. Mutations and DNA repair
 Peter Pristas BNK1 Mutations and DNA repair The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology The DNA molecule is a single biopolymer in the cell which is repaired All other uncorrectly synthetised biopolymers (RNA,
Peter Pristas BNK1 Mutations and DNA repair The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology The DNA molecule is a single biopolymer in the cell which is repaired All other uncorrectly synthetised biopolymers (RNA,
MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: I 32 II 33 III 24 IV 30 V
 MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 32 II 33 III 24 IV 30 V 31 150 Please write your name/student ID number on each of the following five pages. This exam must be written
MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 32 II 33 III 24 IV 30 V 31 150 Please write your name/student ID number on each of the following five pages. This exam must be written
DNA Repair Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm January 31, 2005
 DNA Repair Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 31, 2005 Summary of types of DNA damage Depurination Deamination Alkylation UV photoproducts Oxidation (maybe most important) ROS, reactive oxygen species (H
DNA Repair Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 31, 2005 Summary of types of DNA damage Depurination Deamination Alkylation UV photoproducts Oxidation (maybe most important) ROS, reactive oxygen species (H
DNA replication. - proteins for initiation of replication; - proteins for polymerization of nucleotides.
 DNA replication Replication represents the duplication of the genetic information encoded in DNA that is the crucial step in the reproduction of living organisms and the growth of multicellular organisms.
DNA replication Replication represents the duplication of the genetic information encoded in DNA that is the crucial step in the reproduction of living organisms and the growth of multicellular organisms.
Bacterial Genetics, BIO 4443/6443 Fall Semester 2002 Exam I. Name Answer Key
 Name Answer Key Student pid# Bacterial Genetics, BIO 4443/6443 Fall Semester 2002 Exam I 1.) What is a sigma factor? Why does the cell contain multiple sigma factors? (5pts) Sigma Is a subunit of the RNA
Name Answer Key Student pid# Bacterial Genetics, BIO 4443/6443 Fall Semester 2002 Exam I 1.) What is a sigma factor? Why does the cell contain multiple sigma factors? (5pts) Sigma Is a subunit of the RNA
Some types of Mutagenesis
 Mutagenesis What Is a Mutation? Genetic information is encoded by the sequence of the nucleotide bases in DNA of the gene. The four nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine
Mutagenesis What Is a Mutation? Genetic information is encoded by the sequence of the nucleotide bases in DNA of the gene. The four nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine
DNA Replication III & DNA Damage/Modification Biochemistry 302. January 27, 2006
 DNA Replication III & DNA Damage/Modification Biochemistry 302 January 27, 2006 Bacterial replication organized into a membrane-bound replication factory Two replisomes do not travel away from one another
DNA Replication III & DNA Damage/Modification Biochemistry 302 January 27, 2006 Bacterial replication organized into a membrane-bound replication factory Two replisomes do not travel away from one another
Chapter 30. Replication. Meselson Stahl Experiment. BCH 4054 Chapter 30 Lecture Notes. Slide 1. Slide 2 Conceptual Mechanism of.
 BCH 4054 Chapter 30 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 30 DNA Replication and Repair 2 Conceptual Mechanism of Replication Strand separation, with copying of each strand by Watson-Crick base pairing Fig 30.2 Three
BCH 4054 Chapter 30 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 30 DNA Replication and Repair 2 Conceptual Mechanism of Replication Strand separation, with copying of each strand by Watson-Crick base pairing Fig 30.2 Three
4) separates the DNA strands during replication a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E. 5) covalently connects segments of DNA a. A b. B c. C d. D e.
 1) Chargaff's analysis of the relative base composition of DNA was significant because he was able to show that a. the relative proportion of each of the four bases differs from species to species. b.
1) Chargaff's analysis of the relative base composition of DNA was significant because he was able to show that a. the relative proportion of each of the four bases differs from species to species. b.
Department. Zoology & Biotechnology QUESTION BANK BIOTECHNOLOGY SEMESTER-V
 Department of Zoology & Biotechnology QUESTION BANK BIOTECHNOLOGY SEMESTER-V Unit-1 Genetic Material Different forms of DNA(DNA topology):- B-form, Z-form, D-form; Gene structure-introns,exaons and pseudogenes:
Department of Zoology & Biotechnology QUESTION BANK BIOTECHNOLOGY SEMESTER-V Unit-1 Genetic Material Different forms of DNA(DNA topology):- B-form, Z-form, D-form; Gene structure-introns,exaons and pseudogenes:
Bundle 5 Test Review
 Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle.
 Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
Read the question carefully before answering. Think before you write. If I can not read your handwriting, I will count the question wrong.
 Name KEY Note Total points added up to only 98 points so everyone received 2 free points to make total points 100. Biology 201 (Genetics) Exam #3 23 November 2004 Read the question carefully before answering.
Name KEY Note Total points added up to only 98 points so everyone received 2 free points to make total points 100. Biology 201 (Genetics) Exam #3 23 November 2004 Read the question carefully before answering.
4000/ Sal I. Eco RI and Sma I/Probe 1 Bam HI and Sma I/Probe 2. Increasing Shape. Increasing Shape
 MIT Department of Biology 7.28, Spring 2005 - Molecular Biology 7.28 Spring 2005 Name Exam One Question 1 (28 Points). Your lab is studying a novel thermophilic eukaryote called S. mokin that has an optimum
MIT Department of Biology 7.28, Spring 2005 - Molecular Biology 7.28 Spring 2005 Name Exam One Question 1 (28 Points). Your lab is studying a novel thermophilic eukaryote called S. mokin that has an optimum
DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork
 DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork Tw 1) T w : # of turns around the central axis 2) W r : # of times the double helix crosses itself 3) Linking Number: L k = T w + W
DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork Tw 1) T w : # of turns around the central axis 2) W r : # of times the double helix crosses itself 3) Linking Number: L k = T w + W
BCMB Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair
 BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
BCMB 3100 - Chapters 34 & 35 DNA Replication and Repair Semi-conservative DNA replication DNA polymerase DNA replication Replication fork; Okazaki fragments Sanger method for DNA sequencing DNA repair
Spring 2006 Biochemistry 302 Exam 1
 1 Name Spring 2006 Biochemistry 302 Exam 1 Directions: This exam has 36 questions/problems totaling 90 points. Check to make sure you have all six pages. Some questions have multiple parts so read each
1 Name Spring 2006 Biochemistry 302 Exam 1 Directions: This exam has 36 questions/problems totaling 90 points. Check to make sure you have all six pages. Some questions have multiple parts so read each
M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION
 M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION Chapter 7 Microbial Genetics Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, University of Tennessee, Knoxville The Structure and Replication
M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION Chapter 7 Microbial Genetics Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, University of Tennessee, Knoxville The Structure and Replication
DNA REPLICATION. Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari»
 DNA REPLICATION Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari» Learning objectives 1. Understand the basic rules governing DNA replication 2. Understand the function of key proteins involved in a generalised replication
DNA REPLICATION Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari» Learning objectives 1. Understand the basic rules governing DNA replication 2. Understand the function of key proteins involved in a generalised replication
Fig. 16-7a. 5 end Hydrogen bond 3 end. 1 nm. 3.4 nm nm
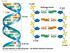 Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
DNA replication. Begins at specific sites on a double helix. Proceeds in both directions. Is initiated at many points in eukaryotic chromosomes.
 DNA replication Begins at specific sites on a double helix. Proceeds in both directions. Is initiated at many points in eukaryotic chromosomes. Figure 10.8 http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/media/ DNAi_replication_schematic-lg.mov
DNA replication Begins at specific sites on a double helix. Proceeds in both directions. Is initiated at many points in eukaryotic chromosomes. Figure 10.8 http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/media/ DNAi_replication_schematic-lg.mov
Genetics Final Exam Summer 2012 VERSION B. Multiple Choice (50 pts. possible) IF you completed the in-class workshop put a CHECK MARK HERE --->
 enetics Final Exam Summer 2012 VERSION B Name Multiple hoice (50 pts. possible) Problems (50 points possible) Total (100 points possible) KEY IF you completed the in-class workshop put a HEK MRK HERE --->
enetics Final Exam Summer 2012 VERSION B Name Multiple hoice (50 pts. possible) Problems (50 points possible) Total (100 points possible) KEY IF you completed the in-class workshop put a HEK MRK HERE --->
Molecular Biology (Continued)
 The Central Dogma Molecular Biology (Continued) Chapter 6: DNA mutation, damage, and repair Chapter 7: Gene regulation in prokaryotes Chapter 8: Gene regulation in eukaryotes Chapter 9: Techniques in molecular
The Central Dogma Molecular Biology (Continued) Chapter 6: DNA mutation, damage, and repair Chapter 7: Gene regulation in prokaryotes Chapter 8: Gene regulation in eukaryotes Chapter 9: Techniques in molecular
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.
Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 AP Biology Reading Guide Name Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Concept 16.1 DNA is the genetic material 1. What are the two chemical components of chromosomes? 2. The search for identifying
AP Biology Reading Guide Name Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Concept 16.1 DNA is the genetic material 1. What are the two chemical components of chromosomes? 2. The search for identifying
The Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression
 The Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression Constitutive genes are expressed at a fixed rate Other genes are expressed only as needed Inducible genes Repressible genes Catabolite repression Pre-transcriptional
The Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression Constitutive genes are expressed at a fixed rate Other genes are expressed only as needed Inducible genes Repressible genes Catabolite repression Pre-transcriptional
The structure, type and functions of a cell are all determined by chromosomes:
 DNA Basics The structure, type and functions of a cell are all determined by chromosomes: They are found in the nucleus of a cell. These chromosomes are composed of DNA, the acronym for deoxyribonucleic
DNA Basics The structure, type and functions of a cell are all determined by chromosomes: They are found in the nucleus of a cell. These chromosomes are composed of DNA, the acronym for deoxyribonucleic
DNA Structure & the Genome. Bio160 General Biology
 DNA Structure & the Genome Bio160 General Biology Lecture Outline I. DNA A nucleic acid II. Chromosome Structure III. Chromosomes and Genes IV. DNA vs. RNA I. DNA A Nucleic Acid Structure of DNA: Remember:
DNA Structure & the Genome Bio160 General Biology Lecture Outline I. DNA A nucleic acid II. Chromosome Structure III. Chromosomes and Genes IV. DNA vs. RNA I. DNA A Nucleic Acid Structure of DNA: Remember:
Genetics Lecture Notes Lectures 17 19
 Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 17 19 Lecture 17 Gene Regulation We are now going to look at ways that genetics can be used to study gene regulation. The issue is how cells adjust the expression
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 17 19 Lecture 17 Gene Regulation We are now going to look at ways that genetics can be used to study gene regulation. The issue is how cells adjust the expression
DNA and Its Role in Heredity. DNA and Its Role in Heredity. A. DNA: The Genetic Material. A. DNA: The Genetic Material.
 DNA and Its Role in Heredity A. DNA: The Genetic Material Lecture Series 8 DNA and Its Role in Heredity B. The Structure of DNA C. DNA E. DNA Proofreading and Repair F. Practical Applications of DNA A.
DNA and Its Role in Heredity A. DNA: The Genetic Material Lecture Series 8 DNA and Its Role in Heredity B. The Structure of DNA C. DNA E. DNA Proofreading and Repair F. Practical Applications of DNA A.
The Double Helix. DNA and RNA, part 2. Part A. Hint 1. The difference between purines and pyrimidines. Hint 2. Distinguish purines from pyrimidines
 DNA and RNA, part 2 Due: 3:00pm on Wednesday, September 24, 2014 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due. Grading Policy The Double Helix DNA, or deoxyribonucleic
DNA and RNA, part 2 Due: 3:00pm on Wednesday, September 24, 2014 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due. Grading Policy The Double Helix DNA, or deoxyribonucleic
Molecular Biology, Lecture 3 DNA Replication
 Molecular Biology, Lecture 3 DNA Replication We will continue talking about DNA replication. We have previously t discussed the structure of DNA. DNA replication is the copying of the whole DNA content
Molecular Biology, Lecture 3 DNA Replication We will continue talking about DNA replication. We have previously t discussed the structure of DNA. DNA replication is the copying of the whole DNA content
Bio 105/Summer Mutation and Repair 8/13/ Mutations: Primary Tools of genetic Analysis p. 200
 Reading: 7.1 Mutations: Primary Tools of genetic Analysis p. 200 Suggested Problems: Solved Problem I: 12, 13. Also work the practice problems following these lecture notes. 7.1.1 Mutations are heritable
Reading: 7.1 Mutations: Primary Tools of genetic Analysis p. 200 Suggested Problems: Solved Problem I: 12, 13. Also work the practice problems following these lecture notes. 7.1.1 Mutations are heritable
MMG 301, Lec. 25 Mutations and Bacteriophage
 MMG 301, Lec. 25 Mutations and Bacteriophage Questions for today: 1. What are mutations and how do they form? 2. How are mutant bacteria used in research? 3. What are the general properties of bacteriophage
MMG 301, Lec. 25 Mutations and Bacteriophage Questions for today: 1. What are mutations and how do they form? 2. How are mutant bacteria used in research? 3. What are the general properties of bacteriophage
Gene Mutation, DNA Repair, and Transposition
 Gene Mutation, DNA Repair, and Transposition Mutations Are Classified in Various Ways Spontaneous mutations happen naturally and randomly and are usually linked to normal biological or chemical processes
Gene Mutation, DNA Repair, and Transposition Mutations Are Classified in Various Ways Spontaneous mutations happen naturally and randomly and are usually linked to normal biological or chemical processes
DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA
 DNA Replication DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA molecule can assume different structures
DNA Replication DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA molecule can assume different structures
Link between iron homeostasis, oxidative mutagenesis and antibiotic resistance evolution
 Thesis of the PhD dissertation Link between iron homeostasis, oxidative mutagenesis and antibiotic resistance evolution Orsolya Katinka Méhi Supervisor: Dr. Csaba Pál, senior research associate PhD School
Thesis of the PhD dissertation Link between iron homeostasis, oxidative mutagenesis and antibiotic resistance evolution Orsolya Katinka Méhi Supervisor: Dr. Csaba Pál, senior research associate PhD School
Genetic material must be able to:
 Genetic material must be able to: Contain the information necessary to construct an entire organism Pass from parent to offspring and from cell to cell during cell division Be accurately copied Account
Genetic material must be able to: Contain the information necessary to construct an entire organism Pass from parent to offspring and from cell to cell during cell division Be accurately copied Account
DNA is the genetic material. DNA structure. Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test
 DNA is the genetic material Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test Dr. Amy Rogers Bio 139 General Microbiology Hereditary information is carried by DNA Griffith/Avery
DNA is the genetic material Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test Dr. Amy Rogers Bio 139 General Microbiology Hereditary information is carried by DNA Griffith/Avery
Chapter 10. DNA: The Molecule of Heredity. Lectures by Gregory Ahearn. University of North Florida. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 DNA: The Molecule of Heredity Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 10.1 What Is The Structure Of DNA? Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is
Chapter 10 DNA: The Molecule of Heredity Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 10.1 What Is The Structure Of DNA? Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 article in Nature Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 article in Nature Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible
Lecture for Wednesday. Dr. Prince BIOL 1408
 Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ribonucleic acid (RNA) nucleotide
 Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
DNA Replication semiconservative replication conservative replication dispersive replication DNA polymerase
 DNA Replication DNA Strands are templates for DNA synthesis: Watson and Crick suggested that the existing strands of DNA served as a template for the producing of new strands, with bases being added to
DNA Replication DNA Strands are templates for DNA synthesis: Watson and Crick suggested that the existing strands of DNA served as a template for the producing of new strands, with bases being added to
Lecture #18 10/17/01 Dr. Wormington
 Lecture #18 10/17/01 Dr. Wormington DNA Replication The Story So Far Semiconservative Hydrolysis of 5' dntp 3' HO N 4 pn 3 pn 2 pn 1 p5'... + PP i 2P i Provides Energy for Phosphodiester Bond Formation
Lecture #18 10/17/01 Dr. Wormington DNA Replication The Story So Far Semiconservative Hydrolysis of 5' dntp 3' HO N 4 pn 3 pn 2 pn 1 p5'... + PP i 2P i Provides Energy for Phosphodiester Bond Formation
DNA Structure and Replication, and Virus Structure and Replication Test Review
 DNA Structure and Replication, and Virus Structure and Replication Test Review What does DNA stand for? Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA is what type of macromolecule? DNA is a nucleic acid The building blocks
DNA Structure and Replication, and Virus Structure and Replication Test Review What does DNA stand for? Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA is what type of macromolecule? DNA is a nucleic acid The building blocks
encodes a sigma factor to modify the recognition of the E.coli RNA polymerase (Several other answers would also be acceptable for each phage)
 Name Student ID# Bacterial Genetics, BIO 4443/6443 Spring Semester 2001 Final Exam 1.) Different bacteriophage utilize different mechanisms to ensure that their own genes (and not host s genes) are transcribed
Name Student ID# Bacterial Genetics, BIO 4443/6443 Spring Semester 2001 Final Exam 1.) Different bacteriophage utilize different mechanisms to ensure that their own genes (and not host s genes) are transcribed
Genetic variations and Gene Rearrangements. Mutation
 Genetic variations and Gene Rearrangements Mutation Def.: It is a physical change of one or more nucleotide pairs in the DNA of a cell. The change is inherited by every descendant of the mutant cell. Classification:
Genetic variations and Gene Rearrangements Mutation Def.: It is a physical change of one or more nucleotide pairs in the DNA of a cell. The change is inherited by every descendant of the mutant cell. Classification:
DNA REPAIR Introduction
 DNA REPAIR Introduction The integrity of DNA is vital to the survival of the cell. Therefore, efficient mechanisms have evolved to correct mistakes that occur during replication. As we have seen, proofreading
DNA REPAIR Introduction The integrity of DNA is vital to the survival of the cell. Therefore, efficient mechanisms have evolved to correct mistakes that occur during replication. As we have seen, proofreading
Astronomy picture of the day (4/21/08)
 Biol 205 Spring 2008 Astronomy picture of the day (4/21/08) http://antwrp.gsfc.nasa.gov/apod/ap080421.html Are viruses alive? http://serc.carleton.edu/microbelife/yellowstone/viruslive.html 1 Week 3 Lecture
Biol 205 Spring 2008 Astronomy picture of the day (4/21/08) http://antwrp.gsfc.nasa.gov/apod/ap080421.html Are viruses alive? http://serc.carleton.edu/microbelife/yellowstone/viruslive.html 1 Week 3 Lecture
Storage and Expression of Genetic Information
 Storage and Expression of Genetic Information 29. DNA structure, Replication and Repair ->Ch 25. DNA metabolism 30. RNA Structure, Synthesis and Processing ->Ch 26. RNA metabolism 31. Protein Synthesis
Storage and Expression of Genetic Information 29. DNA structure, Replication and Repair ->Ch 25. DNA metabolism 30. RNA Structure, Synthesis and Processing ->Ch 26. RNA metabolism 31. Protein Synthesis
Chapter 4: How Cells Work
 Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: l l l l l Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription:
Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: l l l l l Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription:
Site-directed Mutagenesis
 Site-directed Mutagenesis Applications Subtilisin (Met à Ala mutation resistant to oxidation) Fluorescent proteins Protein structure-function Substrate trapping mutants Identify regulatory regions/sequences
Site-directed Mutagenesis Applications Subtilisin (Met à Ala mutation resistant to oxidation) Fluorescent proteins Protein structure-function Substrate trapping mutants Identify regulatory regions/sequences
CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
 CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE DNA as genetic material? Deducted that DNA is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE DNA as genetic material? Deducted that DNA is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
DNA The Genetic Material
 DNA The Genetic Material 2006-2007 Chromosomes related to phenotype T.H. Morgan working with Drosophila fruit flies associated phenotype with specific chromosome white-eyed male had specific X chromosome
DNA The Genetic Material 2006-2007 Chromosomes related to phenotype T.H. Morgan working with Drosophila fruit flies associated phenotype with specific chromosome white-eyed male had specific X chromosome
Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene For Next Week Lab -Hand in questions from 4 and 5 by TUES in my mailbox (Biology Office) -Do questions for Lab 6 for next week -Lab practical next week Lecture Read
Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene For Next Week Lab -Hand in questions from 4 and 5 by TUES in my mailbox (Biology Office) -Do questions for Lab 6 for next week -Lab practical next week Lecture Read
Wednesday, April 9 th. DNA The Genetic Material Replication. Chapter 16
 Wednesday, April 9 th DNA The Genetic Material Replication Chapter 16 Modified from Kim Foglia Scientific History The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick
Wednesday, April 9 th DNA The Genetic Material Replication Chapter 16 Modified from Kim Foglia Scientific History The march to understanding that DNA is the genetic material T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick
Ch. 10 Notes DNA: Transcription and Translation
 Ch. 10 Notes DNA: Transcription and Translation GOALS Compare the structure of RNA with that of DNA Summarize the process of transcription Relate the role of codons to the sequence of amino acids that
Ch. 10 Notes DNA: Transcription and Translation GOALS Compare the structure of RNA with that of DNA Summarize the process of transcription Relate the role of codons to the sequence of amino acids that
Chromosomes. Chromosomes. Genes. Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce
 Chromosomes Chromosomes Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce Genes Segments of DNA that specify how to build a protein genes may specify more than one
Chromosomes Chromosomes Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce Genes Segments of DNA that specify how to build a protein genes may specify more than one
What can you tell me about DNA? copyright cmassengale 1
 What can you tell me about DNA? copyright cmassengale 1 DNA and Replication copyright cmassengale 2 Credit for discovery of DNA is given to Watson & Crick 1 DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid
What can you tell me about DNA? copyright cmassengale 1 DNA and Replication copyright cmassengale 2 Credit for discovery of DNA is given to Watson & Crick 1 DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid
The Molecul Chapter ar Basis 16: The M of olecular Inheritance Basis of Inheritance Fig. 16-1
 he Chapter Molecular 16: he Basis Molecular of Inheritance Basis of Inheritance Fig. 16-1 dditional Evidence hat DN Is the Genetic Material It was known that DN is a polymer of nucleotides, each consisting
he Chapter Molecular 16: he Basis Molecular of Inheritance Basis of Inheritance Fig. 16-1 dditional Evidence hat DN Is the Genetic Material It was known that DN is a polymer of nucleotides, each consisting
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA
 Chapter 8: DNA and RNA Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 8-1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins Proteins play
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 8-1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins Proteins play
Protein Synthesis
 HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
Review Quizzes Chapters 11-16
 Review Quizzes Chapters 11-16 1. In pea plants, the allele for smooth seeds (S) is dominant over the allele for wrinkled seeds (s). In an experiment, when two hybrids are crossed, what percent of the offspring
Review Quizzes Chapters 11-16 1. In pea plants, the allele for smooth seeds (S) is dominant over the allele for wrinkled seeds (s). In an experiment, when two hybrids are crossed, what percent of the offspring
Double helix structure of DNA
 Replication Double helix structure of It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material. Watson & Crick
Replication Double helix structure of It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material. Watson & Crick
Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation
 Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are the workhorses but contain no information THUS Information in DNA must
Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are the workhorses but contain no information THUS Information in DNA must
Independent Study Guide The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to Protein (Chapter 7)
 Independent Study Guide The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to Protein (Chapter 7) I. General Principles (Chapter 7 introduction) a. Morse code distinct series of dots and dashes encode the 26 letters of the
Independent Study Guide The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to Protein (Chapter 7) I. General Principles (Chapter 7 introduction) a. Morse code distinct series of dots and dashes encode the 26 letters of the
FROM MOLECULES TO LIFE
 Chapter 7 (Strickberger) FROM MOLECULES TO LIFE Organisms depended on processes that transformed materials available outside of the cell into metabolic products necessary for cellular life. These processes
Chapter 7 (Strickberger) FROM MOLECULES TO LIFE Organisms depended on processes that transformed materials available outside of the cell into metabolic products necessary for cellular life. These processes
Microbiology: The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to protein
 Microbiology: The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to protein I. Overview A. DNA ultimately determines every aspect of a cell from shape to function 1. DNA = 2. Nucleotides of DNA have three units a. A nitrogen-containing
Microbiology: The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to protein I. Overview A. DNA ultimately determines every aspect of a cell from shape to function 1. DNA = 2. Nucleotides of DNA have three units a. A nitrogen-containing
Mutagenesis. Classification of mutation. Spontaneous Base Substitution. Molecular Mutagenesis. Limits to DNA Pol Fidelity.
 Mutagenesis 1. Classification of mutation 2. Base Substitution 3. Insertion Deletion 4. s 5. Chromosomal Aberration 6. Repair Mechanisms Classification of mutation 1. Definition heritable change in DNA
Mutagenesis 1. Classification of mutation 2. Base Substitution 3. Insertion Deletion 4. s 5. Chromosomal Aberration 6. Repair Mechanisms Classification of mutation 1. Definition heritable change in DNA
MCB 421 First Exam October 4, 2004
 1. (10 pts). An E. coli strain (strain A) that lacks an inducing prophage and carries the F factor is heavily irradiated with UV light and then mixed 1:1 with a second E. coli strain (strain B) that carries
1. (10 pts). An E. coli strain (strain A) that lacks an inducing prophage and carries the F factor is heavily irradiated with UV light and then mixed 1:1 with a second E. coli strain (strain B) that carries
Brief History. Many people contributed to our understanding of DNA
 DNA (Ch. 16) Brief History Many people contributed to our understanding of DNA T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944) Erwin Chargaff (1947) Hershey & Chase (1952)
DNA (Ch. 16) Brief History Many people contributed to our understanding of DNA T.H. Morgan (1908) Frederick Griffith (1928) Avery, McCarty & MacLeod (1944) Erwin Chargaff (1947) Hershey & Chase (1952)
DNA Structure and Replication
 Name: DNA Structure and Replication 1. DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid a. Credit for discovery is given to Watson & Crick b. DNA stands for c. This chemical substance is present in the of all cells in all living
Name: DNA Structure and Replication 1. DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid a. Credit for discovery is given to Watson & Crick b. DNA stands for c. This chemical substance is present in the of all cells in all living
MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE C H A P T E R 1 6 as genetic material? Deducted that is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE C H A P T E R 1 6 as genetic material? Deducted that is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
The Mosaic Nature of Genomes
 The Mosaic Nature of Genomes n DNA sequence is not static Mutations of single bases Large deletions Large insertions of sequence n Transferred from other species n New functions useful in particular situations
The Mosaic Nature of Genomes n DNA sequence is not static Mutations of single bases Large deletions Large insertions of sequence n Transferred from other species n New functions useful in particular situations
From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype
 12 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype 12.1 What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? The gene-enzyme relationship is one-gene, one-polypeptide relationship. Example: In hemoglobin, each
12 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype 12.1 What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? The gene-enzyme relationship is one-gene, one-polypeptide relationship. Example: In hemoglobin, each
DNA, Genes and Chromosomes. Vocabulary
 Vocabulary Big Ideas Heredity and Reproduction Understand and explain that every organism requires a set of instructions that specifies its traits, that this hereditary information (DNA) contains genes
Vocabulary Big Ideas Heredity and Reproduction Understand and explain that every organism requires a set of instructions that specifies its traits, that this hereditary information (DNA) contains genes
DNA, Replication and RNA
 DNA, Replication and RNA The structure of DNA DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, is the blue prints for building all of life. DNA is a long molecule made up of units called NUCLEOTIDES. Each nucleotide is
DNA, Replication and RNA The structure of DNA DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, is the blue prints for building all of life. DNA is a long molecule made up of units called NUCLEOTIDES. Each nucleotide is
NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses)
 NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses) Consist of chemically linked sequences of nucleotides Nitrogenous base Pentose-
NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses) Consist of chemically linked sequences of nucleotides Nitrogenous base Pentose-
DNA is a functional genetic material as it:
 DNA DNA is a functional genetic material as it: varies between species and individuals can store information remains constant within a species Replicates undergoes mutations 1 `It has not escaped our notice
DNA DNA is a functional genetic material as it: varies between species and individuals can store information remains constant within a species Replicates undergoes mutations 1 `It has not escaped our notice
14 DNA STRUCTURE, REPLICATION, AND ORGANIZATION
 14 DNA STRUCTURE, REPLICATION, AND ORGANIZATION Chapter Outline 14.1 ESTABLISHING DNA AS THE HEREDITARY MOLECULE Experiments began when Griffith found a substance that could genetically transform pneumonia
14 DNA STRUCTURE, REPLICATION, AND ORGANIZATION Chapter Outline 14.1 ESTABLISHING DNA AS THE HEREDITARY MOLECULE Experiments began when Griffith found a substance that could genetically transform pneumonia
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE SLIDES
 CHAPTER 13 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
Design and application of DGGE-based mutation detection systems for genes involved in HNPCC Wu, Ying
 University of Groningen Design and application of DGGE-based mutation detection systems for genes involved in HNPCC Wu, Ying IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
University of Groningen Design and application of DGGE-based mutation detection systems for genes involved in HNPCC Wu, Ying IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
3 Designing Primers for Site-Directed Mutagenesis
 3 Designing Primers for Site-Directed Mutagenesis 3.1 Learning Objectives During the next two labs you will learn the basics of site-directed mutagenesis: you will design primers for the mutants you designed
3 Designing Primers for Site-Directed Mutagenesis 3.1 Learning Objectives During the next two labs you will learn the basics of site-directed mutagenesis: you will design primers for the mutants you designed
Confirming the Phenotypes of E. coli Strains
 Confirming the Phenotypes of E. coli Strains INTRODUCTION Before undertaking any experiments, we need to confirm that the phenotypes of the E. coli strains we intend to use in the planned experiments correspond
Confirming the Phenotypes of E. coli Strains INTRODUCTION Before undertaking any experiments, we need to confirm that the phenotypes of the E. coli strains we intend to use in the planned experiments correspond
Molecular Genetics I DNA
 Molecular Genetics I DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid is the molecule that encodes the characteristics of living things. It is the molecule that is passed from a mother cell to daughter cells, and the molecule
Molecular Genetics I DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid is the molecule that encodes the characteristics of living things. It is the molecule that is passed from a mother cell to daughter cells, and the molecule
Replication. Obaidur Rahman
 Replication Obaidur Rahman DIRCTION OF DNA SYNTHESIS How many reactions can a DNA polymerase catalyze? So how many reactions can it catalyze? So 4 is one answer, right, 1 for each nucleotide. But what
Replication Obaidur Rahman DIRCTION OF DNA SYNTHESIS How many reactions can a DNA polymerase catalyze? So how many reactions can it catalyze? So 4 is one answer, right, 1 for each nucleotide. But what
By the end of today, you will have an answer to: How can 1 strand of DNA serve as a template for replication?
 Name: Period: Date: KIPP NYC College Prep Genetics and Biotech UNIT 9: Introduction to DNA Lecture 4: DNA Modeling and Intro to Replication By the end of today, you will have an answer to: How can 1 strand
Name: Period: Date: KIPP NYC College Prep Genetics and Biotech UNIT 9: Introduction to DNA Lecture 4: DNA Modeling and Intro to Replication By the end of today, you will have an answer to: How can 1 strand
DNA REPLICATION & REPAIR
 DNA REPLICATION & REPAIR Table of contents 1. DNA Replication Model 2. DNA Replication Mechanism 3. DNA Repair: Proofreading 1. DNA Replication Model Replication in the cell cycle 3 models of DNA replication
DNA REPLICATION & REPAIR Table of contents 1. DNA Replication Model 2. DNA Replication Mechanism 3. DNA Repair: Proofreading 1. DNA Replication Model Replication in the cell cycle 3 models of DNA replication
CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis. General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith
 CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis General, rganic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis Learning bjectives: q Nucleosides & Nucleo@des:
CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis General, rganic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 22: Nucleic Acids & Protein Synthesis Learning bjectives: q Nucleosides & Nucleo@des:
Lecture 15: 05/24/16. DNA: Molecular basis of Inheritance
 Lecture 15: 05/24/16 DN: Molecular basis of Inheritance 1 DN Double Helix 2 3 DN: Molecular basis of Inheritance Historical Overview! First Isolation of DN DN as genetic material ransformation change in
Lecture 15: 05/24/16 DN: Molecular basis of Inheritance 1 DN Double Helix 2 3 DN: Molecular basis of Inheritance Historical Overview! First Isolation of DN DN as genetic material ransformation change in
AP2013-DNAPacket-II. Use the list of choices below for the following questions:
 Class: Date: AP2013-DNAPacket-II Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the list of choices below for the following questions: I. helicase II.
Class: Date: AP2013-DNAPacket-II Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the list of choices below for the following questions: I. helicase II.
Nucleic Acids: Structure and Function
 ucleic Acids: Structure and Function Components of ucleotides The building blocks (monomers) of the nucleic acids are called nucleotides. ucleotides are made up of: phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar, and
ucleic Acids: Structure and Function Components of ucleotides The building blocks (monomers) of the nucleic acids are called nucleotides. ucleotides are made up of: phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar, and
What happens after DNA Replication??? Transcription, translation, gene expression/protein synthesis!!!!
 What happens after DNA Replication??? Transcription, translation, gene expression/protein synthesis!!!! Protein Synthesis/Gene Expression Why do we need to make proteins? To build parts for our body as
What happens after DNA Replication??? Transcription, translation, gene expression/protein synthesis!!!! Protein Synthesis/Gene Expression Why do we need to make proteins? To build parts for our body as
DNA Replication. Packet #17 Chapter #16
 DNA Replication Packet #17 Chapter #16 1 HISTORICAL FACTS ABOUT DNA 2 Historical DNA Discoveries 1928 Frederick Griffith finds a substance in heat-killed bacteria that transforms living bacteria 1944 Oswald
DNA Replication Packet #17 Chapter #16 1 HISTORICAL FACTS ABOUT DNA 2 Historical DNA Discoveries 1928 Frederick Griffith finds a substance in heat-killed bacteria that transforms living bacteria 1944 Oswald
