Biochemistry 111. Carl Parker x A Braun
|
|
|
- Godwin Fleming
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biochemistry 111 Carl Parker x A Braun
2 Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
3 DNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Requires a DNA Template Synthesizes RNA in a 5 to 3 direction Requires ribonucleoside tri-phosphates rntps Requires a divalent cation Mg The enzyme is very large with 4 subunits (bacterial enzyme)
4 Structure of E. coli RNAP
5 6.1 RNA Polymerase Structure By 1969 SDS-PAGE of RNA polymerase from E. coli had shown several subunits 2 very large subunits are β (150 kd) and β (160 kd) Sigma (σ) at 70 kd Alpha (α) at 40 kd 2 copies present in holoenzyme Omega (w) at 10 kd Was not clearly visible in SDS-PAGE, but seen in other experiments Not required for cell viability or in vivo enzyme activity Appears to play a role in enzyme assembly 6-5
6 Activity of core vs holoenzyme.
7 Eσ and Ecore have different properties Both will transcribe a heterogenous sheared DNA template Only the holoenzyme can transcribe an intact specific template Ecore has the catalytic activity The sigma subunit plays a role in template selection
8 Binding of RNA Polymerase to Promoters How tightly does core enzyme v. holoenzyme bind DNA? Experiment measures binding of DNA to enzyme using nitrocellulose filters Holoenzyme binds filters tightly Core enzyme binding is more transient 6-8
9 Sigma forces rapid dissociation and facilitates stable complex
10 Results of Hinkle and Chamberlain s experiment E/DNA Ratio % stable # stable complexes % loose # loose complexes total 8/ / /
11 Closed and Open Promoter Complexes
12 Shapes of E.coli RNAP core (a) holoenzyme (b)
13 Model for RNAP interaction with promoter DNA
14 Summary The σ-factor allows initiation of transcription by causing the RNA polymerase holoenzyme to bind tightly to a promoter This tight binding depends on local melting of the DNA to form an open promoter complex and is stimulated by σ The σ-factor can therefore select which genes will be transcribed 6-14
15 Core Promoter Elements There is a region common to bacterial promoters described as 6-7 bp centered about 10 bp upstream of the start of transcription = -10 box Another short sequence centered 35 bp upstream is known as the -35 box Comparison of thousands of promoters has produced a consensus sequence (or most common sequence) for each of these boxes 6-15
16 Promoter Strength Consensus sequences: -10 box sequence approximates TATAAT -35 box sequence approximates TTGACA Mutations that weaken promoter binding: Down mutations Increase deviation from the consensus sequence Mutations that strengthen promoter binding: Up mutations Decrease deviation from the consensus sequence 6-16
17 UP Element The UP element is upstream of the core promoter, stimulating transcription by a factor of 30 UP is associated with 3 Fis sites which are binding sites for the transcription-activator protein Fis, not for the polymerase itself 6-17
18 The rrn P1 Promoter
19 6.3 Transcription Initiation Transcription initiation was assumed to end as RNA polymerase formed 1 st phosphodiester bond Carpousis and Gralla found that very small oligonucleotides (2-6 nt long) are made without RNA polymerase leaving the DNA Abortive transcripts such as these have been found up to 10 nt 6-19
20 Synthesis of short transcripts by RNAP bound to a promoter
21 Stages of Transcription Initiation
22 Sigma Stimulates Initiation of Transcription In this first experiment stimulation by σ appears to cause both initiation and elongation Or stimulating initiation by σ provides more initiated chains for core polymerase to elongate Further experiments by the same group proved that σ does not stimulate elongation 6-22
23 Reuse of σ During initiation σ can be recycled for additional use with a new core polymerase The core enzyme can release σ which is then free to associate with another core enzyme 6-23
24 Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer The σ-factor changes its relationship to the core polymerase during elongation It may not dissociate from the core but actually shift position and become more loosely bound to core To answer this question Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) was used as it relies on two fluorescent molecules that are close enough together to engage in transfer of resonance energy FRET allows the position of σ relative to a site on the DNA to be measured without using separation techniques that might displace σ from the core enzyme 6-24
25 FRET Assay for σ Movement Relative to DNA 6-25
26 Models for the σ-cycle The obligate release version of the σ-cycle model arose from experiments performed by Travers and Burgess that proposed the dissociation of σ from core as polymerase undergoes promoter clearance and switches from initiation to elongation mode The stochastic release model proposes that σ is indeed released from the core polymerase but that there is no discrete point of release during transcription and that the release occurs at random - a preponderance of evidence favors this model 6-26
27 Structure and Function of σ Genes encoding a variety of σ-factors have been cloned and sequenced There are striking similarities in amino acid sequence clustered in 4 regions Conservation of sequence in these regions suggests important function All of the 4 sequences are involved in binding to core and DNA 6-27
28 Homologous Regions in Bacterial σ Factors 6-28
29 E. coli σ 70 Four regions of high sequence similarity are indicated Specific areas that recognize the core promoter elements are the -10 box and 35 box 6-29
30 Region 1 Role of region 1 appears to be in preventing σ from binding to DNA by itself This is important as σ binding to promoters could inhibit holoenzyme binding and thereby inhibit transcription Region 2 This region is the most highly conserved of the four There are four subregions 2.1 to recognizes the promoter s -10 box The 2.4 region appears to be α-helix 6-30
31 Regions 3 and 4 Region 3 is involved in both core and DNA binding Region 4 is divided into 2 subregions This region seems to have a key role in promoter recognition Subregion 4.2 contains a helix-turn-helix DNAbinding domain and appears to govern binding to the -35 box of the promoter 6-31
32 Specific interactions between the sigma subunit and promoter elements
33 Role of α-subunit in UP Element Recognition RNA polymerase itself can recognize an upstream promoter element, UP element While σ-factor recognizes the core promoter elements, what recognizes the UP element? It appears to be the α-subunit of the core polymerase 6-33
34 Modeling the Function of the C-Terminal Domain RNA polymerase binds to a core promoter via its σ-factor, no help from C-terminal domain of α-subunit Binds to a promoter with an UP element using σ plus the α- subunit C-terminal domains (CTD) Results in very strong interaction between polymerase and promoter This produces a high level of transcription 6-34
35 The Elongation Complex
36 6.5 Termination of Transcription When the polymerase reaches a terminator at the end of a gene it falls off the template and releases the RNA There are 2 main types of terminators Intrinsic terminators function with the RNA polymerase by itself without help from other proteins Other type depends on auxiliary factor called rho (ρ), these are rho or ρ-dependent terminators 6-36
37 Inverted Repeats and Hairpins The repeat at right is symmetrical around its center shown with a dot A transcript of this sequence is selfcomplementary Bases can pair up to form a hairpin as seen in the lower panel 6-37
38 Model of Intrinsic Termination Bacterial terminators act by: Base-pairing of the transcript to destabilize RNA-DNA hybrid Causes hairpin to form This causes transcription to pause a string of U s incorporated just downstream of hairpin to destabilize the hybrid and the RNA falls off the DNA template 6-38
39 Rho-Dependent Termination Rho caused depression of the ability of RNA polymerase to transcribe phage DNAs in vitro This depression was due to termination of transcription After termination, polymerase must reinitiate to begin transcribing again 6-39
40 Rho Affects Chain Elongation There is little effect of rho or ρ on transcription initiation, if anything it is increased The effect of rho or ρ on total RNA synthesis is a significant decrease This is consistent with action of rho or ρ to terminate transcription forcing time-consuming reinitiation 6-40
41 Mechanism of Rho No string of T s in the ρ- dependent terminator, just inverted repeat to hairpin Binding to the growing transcript, ρ follows the RNA polymerase It catches the polymerase as it pauses at the hairpin Releases transcript from the DNA-polymerase complex by unwinding the RNA-DNA hybrid 6-41
42 Summary Using the trp attenuator as a model rho-independet terminator revealed two important features: 1 - an inverted repeat that allows a hairpin to for at the end of the transcript 2 - a string of T s in the nontemplate strand that results in a string of weak ru-da base pairs holding the transcript to the template strand Rho-dependent terminators consist of an inverted repeat, which can cause a hairpin to form in the transcript but no string of T s 6-42
43 Rho-independent termination
44 Rho-dependent termination
RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA
 RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA that it has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position of the
RNA Expression of the information in a gene generally involves production of an RNA molecule transcribed from a DNA template. RNA differs from DNA that it has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position of the
RNA synthesis/transcription I Biochemistry 302. February 6, 2004 Bob Kelm
 RNA synthesis/transcription I Biochemistry 302 February 6, 2004 Bob Kelm Overview of RNA classes Messenger RNA (mrna) Encodes protein Relatively short half-life ( 3 min in E. coli, 30 min in eukaryotic
RNA synthesis/transcription I Biochemistry 302 February 6, 2004 Bob Kelm Overview of RNA classes Messenger RNA (mrna) Encodes protein Relatively short half-life ( 3 min in E. coli, 30 min in eukaryotic
Expression of the genome. Books: 1. Molecular biology of the gene: Watson et al 2. Genetics: Peter J. Russell
 Expression of the genome Books: 1. Molecular biology of the gene: Watson et al 2. Genetics: Peter J. Russell 1 Transcription 1. Francis Crick (1956) named the flow of information from DNA RNA protein the
Expression of the genome Books: 1. Molecular biology of the gene: Watson et al 2. Genetics: Peter J. Russell 1 Transcription 1. Francis Crick (1956) named the flow of information from DNA RNA protein the
DNA Transcription. Dr Aliwaini
 DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
Transcription in Prokaryotes. Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone:
 Transcription in Prokaryotes Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone: 352-273-8098 Email: jbungert@ufl.edu Objectives Understand the basic mechanism of transcription. Know the function of promoter elements and associating
Transcription in Prokaryotes Jörg Bungert, PhD Phone: 352-273-8098 Email: jbungert@ufl.edu Objectives Understand the basic mechanism of transcription. Know the function of promoter elements and associating
Basi s c i Fea e tu t re r s s of f R NA N Sy S nth t esi s s i s
 Transcription Dr.H.B.Mahesha, Yuvaraja s College, University of Mysore, Mysuru. It is the process of transcribing or making a copy of Genetic information stored in a DNA strand into a Complementary strand
Transcription Dr.H.B.Mahesha, Yuvaraja s College, University of Mysore, Mysuru. It is the process of transcribing or making a copy of Genetic information stored in a DNA strand into a Complementary strand
Transcription is the first step of gene expression, in which a particular segment of DNA is copied into RNA by the enzyme, RNA polymerase.
 Transcription in Bacteria Transcription in Bacteria Transcription in Bacteria Transcription is the first step of gene expression, in which a particular segment of DNA is copied into RNA by the enzyme,
Transcription in Bacteria Transcription in Bacteria Transcription in Bacteria Transcription is the first step of gene expression, in which a particular segment of DNA is copied into RNA by the enzyme,
Transcription. By : Lucia Dhiantika Witasari M.Biotech., Apt
 Transcription By : Lucia Dhiantika Witasari M.Biotech., Apt REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION 11/26/2010 2 RNA Messenger RNAs (mrnas) encode the amino acid sequence of one or more polypeptides specified by
Transcription By : Lucia Dhiantika Witasari M.Biotech., Apt REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION 11/26/2010 2 RNA Messenger RNAs (mrnas) encode the amino acid sequence of one or more polypeptides specified by
We can now identify three major pathways of information flow in the cell (in replication, information passes from one DNA molecule to other DNA
 1 We can now identify three major pathways of information flow in the cell (in replication, information passes from one DNA molecule to other DNA molecules; in transcription, information passes from DNA
1 We can now identify three major pathways of information flow in the cell (in replication, information passes from one DNA molecule to other DNA molecules; in transcription, information passes from DNA
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW. Overview of Biomolecules. Chapter 12 Transcription
 BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 12 Transcription 2 3 4 5 Are You Getting It?? Which are general characteristics of transcription? (multiple answers) a) An entire DNA molecule is transcribed
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 12 Transcription 2 3 4 5 Are You Getting It?? Which are general characteristics of transcription? (multiple answers) a) An entire DNA molecule is transcribed
Chapters 31-32: Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
 Chapters 31-32: Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Short segments from the transcription, processing and translation sections of each chapter Slide 1 RNA In comparison with DNA RNA utilizes uracil in place of thymine
Chapters 31-32: Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Short segments from the transcription, processing and translation sections of each chapter Slide 1 RNA In comparison with DNA RNA utilizes uracil in place of thymine
SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat
 SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat TRANSCRIPTION: AN OVERVIEW Transcription: the synthesis of a single-stranded RNA from a doublestranded DNA template.
SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat TRANSCRIPTION: AN OVERVIEW Transcription: the synthesis of a single-stranded RNA from a doublestranded DNA template.
DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork
 DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork Tw 1) T w : # of turns around the central axis 2) W r : # of times the double helix crosses itself 3) Linking Number: L k = T w + W
DNA Topoisomerases relieve the supercoiling stress ahead of the fork Tw 1) T w : # of turns around the central axis 2) W r : # of times the double helix crosses itself 3) Linking Number: L k = T w + W
30 Gene expression: Transcription
 30 Gene expression: Transcription Gene structure. o Exons coding region of DNA. o Introns non-coding region of DNA. o Introns are interspersed between exons of a single gene. o Promoter region helps enzymes
30 Gene expression: Transcription Gene structure. o Exons coding region of DNA. o Introns non-coding region of DNA. o Introns are interspersed between exons of a single gene. o Promoter region helps enzymes
The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function
 Central Dogma The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function! Fundamental observations in genetics!! Genes are located in nuclei (in eukaryotes)!! Polypeptides are synthesised in
Central Dogma The discovery of the role of RNA RNA structure, synthesis and function! Fundamental observations in genetics!! Genes are located in nuclei (in eukaryotes)!! Polypeptides are synthesised in
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II.
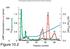 Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
DNA RNA. Protein. Enzymes in the central dogma. Cellular enzymes (Mostly) RNA virus enzymes. DNA polymerase. Reverse transcriptase.
 Enzymes in the central dogma Cellular enzymes (Mostly) RNA virus enzymes DNA DNA polymerase Reverse transcriptase RNA polymerase RNA-dependent RNA polymerase RNA Ribosome Protein The process of transcription
Enzymes in the central dogma Cellular enzymes (Mostly) RNA virus enzymes DNA DNA polymerase Reverse transcriptase RNA polymerase RNA-dependent RNA polymerase RNA Ribosome Protein The process of transcription
Feedback D. Incorrect! No, although this is a correct characteristic of RNA, this is not the best response to the questions.
 Biochemistry - Problem Drill 23: RNA No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements best describes the structural highlights of RNA? (A) RNA can be single or double stranded. (B) G-C pairs have 3 hydrogen
Biochemistry - Problem Drill 23: RNA No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements best describes the structural highlights of RNA? (A) RNA can be single or double stranded. (B) G-C pairs have 3 hydrogen
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes
 Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
RNA: Structure & Synthesis. Amr S. Moustafa, M.D.; Ph.D.
 RNA: Structure & Synthesis By Amr S. Moustafa, M.D.; Ph.D. Objectives The differences between DNA and RNA The structure and functions of RNAs RNA synthesis (Transcription) Post-transcriptional events (modifications)
RNA: Structure & Synthesis By Amr S. Moustafa, M.D.; Ph.D. Objectives The differences between DNA and RNA The structure and functions of RNAs RNA synthesis (Transcription) Post-transcriptional events (modifications)
Answers to Module 1. An obligate aerobe is an organism that has an absolute requirement of oxygen for growth.
 Answers to Module 1 Short Answers 1) What is an obligate aerobe? An obligate aerobe is an organism that has an absolute requirement of oxygen for growth. What about facultative anaerobe? 2) Distinguish
Answers to Module 1 Short Answers 1) What is an obligate aerobe? An obligate aerobe is an organism that has an absolute requirement of oxygen for growth. What about facultative anaerobe? 2) Distinguish
Chapter 11. Transcription. The biochemistry and molecular biology department of CMU
 Chapter 11 Transcription The biochemistry and molecular biology department of CMU Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be
Chapter 11 Transcription The biochemistry and molecular biology department of CMU Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be
Transcription. Manzur Ali PP, DBT,M.E.S College,Marampally
 Transcription Manzur Ali PP, DBT,M.E.S College,Marampally manzursir@gmail.com RNA transcription is actively regulated Not all DNA is transcribed in a given cell (less than 50% even in prokaryotes) For
Transcription Manzur Ali PP, DBT,M.E.S College,Marampally manzursir@gmail.com RNA transcription is actively regulated Not all DNA is transcribed in a given cell (less than 50% even in prokaryotes) For
Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
 Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis 4. Transcription Gene Expression Regulatory region (promoter) 5 flanking region Upstream region Coding region 3 flanking region Downstream region Transcription
Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis 4. Transcription Gene Expression Regulatory region (promoter) 5 flanking region Upstream region Coding region 3 flanking region Downstream region Transcription
DNA Transcription. Visualizing Transcription. The Transcription Process
 DNA Transcription By: Suzanne Clancy, Ph.D. 2008 Nature Education Citation: Clancy, S. (2008) DNA transcription. Nature Education 1(1) If DNA is a book, then how is it read? Learn more about the DNA transcription
DNA Transcription By: Suzanne Clancy, Ph.D. 2008 Nature Education Citation: Clancy, S. (2008) DNA transcription. Nature Education 1(1) If DNA is a book, then how is it read? Learn more about the DNA transcription
Transcription & post transcriptional modification
 Transcription & post transcriptional modification Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be transferred from DNA to RNA Similarity
Transcription & post transcriptional modification Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be transferred from DNA to RNA Similarity
M1 - Biochemistry. Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I
 M1 - Biochemistry Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I PH Ratz, PhD (Resources: Lehninger et al., 5th ed., Chapters 8, 24 & 26) 1 Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I Learning Objectives: 1.
M1 - Biochemistry Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I PH Ratz, PhD (Resources: Lehninger et al., 5th ed., Chapters 8, 24 & 26) 1 Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I Learning Objectives: 1.
Mechanisms of Transcription. School of Life Science Shandong University
 Mechanisms of Transcription School of Life Science Shandong University Ch 12: Mechanisms of Transcription 1. RNA polymerase and the transcription cycle 2. The transcription cycle in bacteria 3. Transcription
Mechanisms of Transcription School of Life Science Shandong University Ch 12: Mechanisms of Transcription 1. RNA polymerase and the transcription cycle 2. The transcription cycle in bacteria 3. Transcription
Chapter 11 Part A: Metabolism: The synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins
 Chapter 11 Part A: Metabolism: The synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins I. Synthesis of DNA = REPLICATION A. Components of DNA (Fig. 11-1) 1. Composed of 4 different nucleotides that are joined by the
Chapter 11 Part A: Metabolism: The synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins I. Synthesis of DNA = REPLICATION A. Components of DNA (Fig. 11-1) 1. Composed of 4 different nucleotides that are joined by the
Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code
 Lecture 28-29 Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code Central dogma of molecular biology During transcription, the information in a DNA sequence (a gene) is copied into a
Lecture 28-29 Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code Central dogma of molecular biology During transcription, the information in a DNA sequence (a gene) is copied into a
Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination
 Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination Copyright Copyright 2009 Pearson 2009 Pearson Education, Education, Inc. Inc. 11.1 DNA is reproduced by Semiconservative Replication The complementarity of
Chapter 11 DNA Replication and Recombination Copyright Copyright 2009 Pearson 2009 Pearson Education, Education, Inc. Inc. 11.1 DNA is reproduced by Semiconservative Replication The complementarity of
RNA POLYMERASE FUNCTIONS E-BOOK
 08 March, 2018 RNA POLYMERASE 1 2 3 FUNCTIONS E-BOOK Document Filetype: PDF 431.06 KB 0 RNA POLYMERASE 1 2 3 FUNCTIONS E-BOOK It catalyzes the transcription of DNA to synthesize precursors of mrna and
08 March, 2018 RNA POLYMERASE 1 2 3 FUNCTIONS E-BOOK Document Filetype: PDF 431.06 KB 0 RNA POLYMERASE 1 2 3 FUNCTIONS E-BOOK It catalyzes the transcription of DNA to synthesize precursors of mrna and
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.17 - GENE EXPRESSION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: GENES Beadle and Tatum develop the one gene one enzyme hypothesis through their work with Neurospora (bread mold). This idea was later revised as the one gene one polypeptide
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: GENES Beadle and Tatum develop the one gene one enzyme hypothesis through their work with Neurospora (bread mold). This idea was later revised as the one gene one polypeptide
I. Gene Expression Figure 1: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
 I. Gene Expression Figure 1: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Central Dogma: Gene Expression: RNA Structure RNA nucleotides contain the pentose sugar Ribose instead of deoxyribose. Contain the bases
I. Gene Expression Figure 1: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Central Dogma: Gene Expression: RNA Structure RNA nucleotides contain the pentose sugar Ribose instead of deoxyribose. Contain the bases
Bi 8 Lecture 10. Ellen Rothenberg 4 February 2016
 Bi 8 Lecture 10 Bacterial regulation, II Ellen Rothenberg 4 February 2016 Not all bacterial promoters use the same σ factors, and this provides added regulation capability Most sigma factors are related
Bi 8 Lecture 10 Bacterial regulation, II Ellen Rothenberg 4 February 2016 Not all bacterial promoters use the same σ factors, and this provides added regulation capability Most sigma factors are related
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription. RNA polymerases
 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY. Transcription
 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Transcription U. N. Dwivedi Department of Biochemistry University of Lucknow, Lucknow-226007 and Smita Rastogi Department of Biotechnology, Integral University, Lucknow 20-Jul-2006 (Revised
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Transcription U. N. Dwivedi Department of Biochemistry University of Lucknow, Lucknow-226007 and Smita Rastogi Department of Biotechnology, Integral University, Lucknow 20-Jul-2006 (Revised
7.1 The lac Operon 7-1
 7.1 The lac Operon The lac operon was the first operon discovered It contains 3 genes coding for E. coli proteins that permit the bacteria to use the sugar lactose Galactoside permease (lacy) which transports
7.1 The lac Operon The lac operon was the first operon discovered It contains 3 genes coding for E. coli proteins that permit the bacteria to use the sugar lactose Galactoside permease (lacy) which transports
IN E. COLI WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF DNA POLYMERASE III
 10 January, 2018 IN E. COLI WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF DNA POLYMERASE III Document Filetype: PDF 312 KB 0 IN E. COLI WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF DNA POLYMERASE III The actual replication enzyme in E. Both will
10 January, 2018 IN E. COLI WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF DNA POLYMERASE III Document Filetype: PDF 312 KB 0 IN E. COLI WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF DNA POLYMERASE III The actual replication enzyme in E. Both will
BS1940 Course Topics Fall 2001 Drs. Hatfull and Arndt
 BS1940 Course Topics Fall 2001 Drs. Hatfull and Arndt Introduction to molecular biology Combining genetics, biochemistry, structural chemistry Information flow in biological systems: The Central Dogma
BS1940 Course Topics Fall 2001 Drs. Hatfull and Arndt Introduction to molecular biology Combining genetics, biochemistry, structural chemistry Information flow in biological systems: The Central Dogma
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.10 TRANSCRIPTION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF TRANSCRIPTION Transcription is the process of using DNA as a template to RNA RNA polymerase is the enzyme that transcribes DNA - There are many different types
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF TRANSCRIPTION Transcription is the process of using DNA as a template to RNA RNA polymerase is the enzyme that transcribes DNA - There are many different types
Genetic Parts in Bacterial Gene Expression
 Genetic Parts in Bacterial Gene Expression The Focus Promoters Operators Transcription Factors Transcriptional Terminators Ribosome Binding Sites An Abstract Annotation We ll Pay Particular Attention To:
Genetic Parts in Bacterial Gene Expression The Focus Promoters Operators Transcription Factors Transcriptional Terminators Ribosome Binding Sites An Abstract Annotation We ll Pay Particular Attention To:
Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription
 Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription Cis-acting sequences Distance-independent cis-acting elements Dissecting regulatory elements Transcription factors Overview transcriptional regulation Transcription
Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription Cis-acting sequences Distance-independent cis-acting elements Dissecting regulatory elements Transcription factors Overview transcriptional regulation Transcription
In Chapter 3 we learned that transcription
 C H P T E R 6 The Mechanism of Transcription in Bacteria Colorized scanning electron micrograph of bacterial cells (Staphylococcus aureus). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention In Chapter 3 we learned
C H P T E R 6 The Mechanism of Transcription in Bacteria Colorized scanning electron micrograph of bacterial cells (Staphylococcus aureus). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention In Chapter 3 we learned
Overview of Transcription
 Overview of Transcription The general process is similar in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Three phases: - Initiation The word gene was coined in 1909 (W. Johannsen). The central dogma (1950s). - Elongation
Overview of Transcription The general process is similar in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Three phases: - Initiation The word gene was coined in 1909 (W. Johannsen). The central dogma (1950s). - Elongation
Transcription & RNA Processing
 Chapter 10. Transcription & RNA Processing 1. Transfer of Genetic Information: the Central Dogma 2. The Process of Gene Expression 3. Transcription & RNA Processing in Eukaryotes 4. Interrupted Genes in
Chapter 10. Transcription & RNA Processing 1. Transfer of Genetic Information: the Central Dogma 2. The Process of Gene Expression 3. Transcription & RNA Processing in Eukaryotes 4. Interrupted Genes in
Module 3. Lecture 5. Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes
 Module 3 Lecture 5 Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes Recap So far, we have looked at prokaryotic gene regulation using 3 operon models. lac: a catabolic operon which displays induction via negative
Module 3 Lecture 5 Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes Recap So far, we have looked at prokaryotic gene regulation using 3 operon models. lac: a catabolic operon which displays induction via negative
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline. Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics
 Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Transcription. The sugar molecule found in RNA is ribose, rather than the deoxyribose found in DNA.
 Transcription RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a key intermediary between a DNA sequence and a polypeptide. RNA is an informational polynucleotide similar to DNA, but it differs from DNA in three ways: RNA generally
Transcription RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a key intermediary between a DNA sequence and a polypeptide. RNA is an informational polynucleotide similar to DNA, but it differs from DNA in three ways: RNA generally
Prokaryotic Physiology. March 3, 2017
 1. (10 pts) Explain the replication of both strands of DNA in prokaryotes. At a minimum explain the direction of synthesis, synthesis of the leading and lagging strand, separation of the strands and the
1. (10 pts) Explain the replication of both strands of DNA in prokaryotes. At a minimum explain the direction of synthesis, synthesis of the leading and lagging strand, separation of the strands and the
Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis
 Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis 1. Describe how genetic information is transcribed into sequences of bases in RNA molecules and is finally translated into sequences of amino
Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis 1. Describe how genetic information is transcribed into sequences of bases in RNA molecules and is finally translated into sequences of amino
Principle 2. Overview of Central. 3. Nucleic Acid Structure 4. The Organization of
 Central dogma I and II the flow of genetic information 1. The Transforming Principle 2. Overview of Central Dogma 3. Nucleic Acid Structure 4. The Organization of DNA in Cells 5. DNA Replication 6. Gene
Central dogma I and II the flow of genetic information 1. The Transforming Principle 2. Overview of Central Dogma 3. Nucleic Acid Structure 4. The Organization of DNA in Cells 5. DNA Replication 6. Gene
SCBC203 Gene Expression. Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science PR318
 SCBC203 Gene Expression Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science PR318 Rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th 1 Gene Expression Gene expression is a process where by the genetic
SCBC203 Gene Expression Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science PR318 Rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th 1 Gene Expression Gene expression is a process where by the genetic
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells
 Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Proofreading, post-replication modification of DNA. Mitesh Shrestha
 Proofreading, post-replication modification of DNA Mitesh Shrestha Proofreading During DNA replication (copying), most DNA polymerases can check their work with each base that they add. This process is
Proofreading, post-replication modification of DNA Mitesh Shrestha Proofreading During DNA replication (copying), most DNA polymerases can check their work with each base that they add. This process is
Transcription steps. Transcription steps. Eukaryote RNA processing
 Transcription steps Initiation at 5 end of gene binding of RNA polymerase to promoter unwinding of DNA Elongation addition of nucleotides to 3 end rules of base pairing requires Mg 2+ energy from NTP substrates
Transcription steps Initiation at 5 end of gene binding of RNA polymerase to promoter unwinding of DNA Elongation addition of nucleotides to 3 end rules of base pairing requires Mg 2+ energy from NTP substrates
Class XII Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Biology
 Question 1: Group the following as nitrogenous bases and nucleosides: Adenine, Cytidine, Thymine, Guanosine, Uracil and Cytosine. Nitrogenous bases present in the list are adenine, thymine, uracil, and
Question 1: Group the following as nitrogenous bases and nucleosides: Adenine, Cytidine, Thymine, Guanosine, Uracil and Cytosine. Nitrogenous bases present in the list are adenine, thymine, uracil, and
Bis2A 12.0 Transcription *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m56068 1 Bis2A 12.0 Transcription * Mitch Singer Based on Transcription by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
OpenStax-CNX module: m56068 1 Bis2A 12.0 Transcription * Mitch Singer Based on Transcription by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins. From DNA to RNA
 From DNA to RNA Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins I. After the discovery of the structure of DNA, the major question remaining was how does the stored in the 4 letter code of DNA direct the and of
From DNA to RNA Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins I. After the discovery of the structure of DNA, the major question remaining was how does the stored in the 4 letter code of DNA direct the and of
5. Which of the following enzymes catalyze the attachment of an amino acid to trna in the formation of aminoacyl trna?
 Sample Examination Questions for Exam 3 Material Biology 3300 / Dr. Jerald Hendrix Warning! These questions are posted solely to provide examples of past test questions. There is no guarantee that any
Sample Examination Questions for Exam 3 Material Biology 3300 / Dr. Jerald Hendrix Warning! These questions are posted solely to provide examples of past test questions. There is no guarantee that any
Transcription is the first stage of gene expression
 Transcription is the first stage of gene expression RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and hooks together the RNA nucleotides The RNA is complementary to the
Transcription is the first stage of gene expression RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and hooks together the RNA nucleotides The RNA is complementary to the
Independent Study Guide The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to Protein (Chapter 7)
 Independent Study Guide The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to Protein (Chapter 7) I. General Principles (Chapter 7 introduction) a. Morse code distinct series of dots and dashes encode the 26 letters of the
Independent Study Guide The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to Protein (Chapter 7) I. General Principles (Chapter 7 introduction) a. Morse code distinct series of dots and dashes encode the 26 letters of the
Transcription: Synthesis of RNA
 Transcription: Synthesis of RNA The flow of information in the cells (the central dogma of molecular biology): Transcription = RNA synthesis on a DNA template. The mrna will provide the information for
Transcription: Synthesis of RNA The flow of information in the cells (the central dogma of molecular biology): Transcription = RNA synthesis on a DNA template. The mrna will provide the information for
Nucleic Acid Structure:
 Nucleic Acid Structure: Purine and Pyrimidine nucleotides can be combined to form nucleic acids: 1. Deoxyribonucliec acid (DNA) is composed of deoxyribonucleosides of! Adenine! Guanine! Cytosine! Thymine
Nucleic Acid Structure: Purine and Pyrimidine nucleotides can be combined to form nucleic acids: 1. Deoxyribonucliec acid (DNA) is composed of deoxyribonucleosides of! Adenine! Guanine! Cytosine! Thymine
Transcription. Dr. Mahesha H B Associate Professor and Head Department of Sericulture Yuvaraja scollege University of Mysore, Mysuru, India
 Transcription Dr. Mahesha H B Associate Professor and Head Department of Sericulture Yuvaraja scollege University of Mysore, Mysuru, India 3 September 2017 www.hbmahesh.weebly.com 1 Transcription It is
Transcription Dr. Mahesha H B Associate Professor and Head Department of Sericulture Yuvaraja scollege University of Mysore, Mysuru, India 3 September 2017 www.hbmahesh.weebly.com 1 Transcription It is
Gene function at the level of traits Gene function at the molecular level
 Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function at the molecular level Two levels tied together since the molecular level affects the structure and function of cells which determines
Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function at the molecular level Two levels tied together since the molecular level affects the structure and function of cells which determines
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process.
 Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
3.1 Storing Information. Polypeptides. Protein Structure. Helical Secondary Structure. Types of Protein Structure. Molecular Biology Fourth Edition
 Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Molecular Biology Fourth Edition Robert F. Weaver Chapter 3 An Introduction to Gene Function 3.1 Storing Information Producing a protein from DNA information involves both
Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Molecular Biology Fourth Edition Robert F. Weaver Chapter 3 An Introduction to Gene Function 3.1 Storing Information Producing a protein from DNA information involves both
However, only a fraction of these genes are transcribed in an individual cell at any given time.
 All cells in an organism contain the same set of genes. However, only a fraction of these genes are transcribed in an individual cell at any given time. It is the pattern of gene expression that determines
All cells in an organism contain the same set of genes. However, only a fraction of these genes are transcribed in an individual cell at any given time. It is the pattern of gene expression that determines
Protein Synthesis Notes
 Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Molecular Basis of Inheritance Question 1: Group the following as nitrogenous bases and nucleosides: Adenine, Cytidine, Thymine, Guanosine, Uracil and Cytosine. Answer Nitrogenous bases present in the
Molecular Basis of Inheritance Question 1: Group the following as nitrogenous bases and nucleosides: Adenine, Cytidine, Thymine, Guanosine, Uracil and Cytosine. Answer Nitrogenous bases present in the
Genes and How They Work. Chapter 15
 Genes and How They Work Chapter 15 The Nature of Genes They proposed the one gene one enzyme hypothesis. Today we know this as the one gene one polypeptide hypothesis. 2 The Nature of Genes The central
Genes and How They Work Chapter 15 The Nature of Genes They proposed the one gene one enzyme hypothesis. Today we know this as the one gene one polypeptide hypothesis. 2 The Nature of Genes The central
Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4)
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4) Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression I Flow of information: DNA to polypeptide DNA Start Exon1 Intron Exon2 Termination
Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4) Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression I Flow of information: DNA to polypeptide DNA Start Exon1 Intron Exon2 Termination
Replication Review. 1. What is DNA Replication? 2. Where does DNA Replication take place in eukaryotic cells?
 Replication Review 1. What is DNA Replication? 2. Where does DNA Replication take place in eukaryotic cells? 3. Where does DNA Replication take place in the cell cycle? 4. 4. What guides DNA Replication?
Replication Review 1. What is DNA Replication? 2. Where does DNA Replication take place in eukaryotic cells? 3. Where does DNA Replication take place in the cell cycle? 4. 4. What guides DNA Replication?
Transcription and Translation. DANILO V. ROGAYAN JR. Faculty, Department of Natural Sciences
 Transcription and Translation DANILO V. ROGAYAN JR. Faculty, Department of Natural Sciences Protein Structure Made up of amino acids Polypeptide- string of amino acids 20 amino acids are arranged in different
Transcription and Translation DANILO V. ROGAYAN JR. Faculty, Department of Natural Sciences Protein Structure Made up of amino acids Polypeptide- string of amino acids 20 amino acids are arranged in different
 The replication of DNA Kornberg 1957 Meselson and Stahl 1958 Cairns 1963 Okazaki 1968 DNA Replication The driving force for DNA synthesis. The addition of a nucleotide to a growing polynucleotide
The replication of DNA Kornberg 1957 Meselson and Stahl 1958 Cairns 1963 Okazaki 1968 DNA Replication The driving force for DNA synthesis. The addition of a nucleotide to a growing polynucleotide
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA
 TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra
 Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
7.05 Recitation Schedule
 7.05 Spring 004 February 13, 004 7.05 Recitation Schedule Contact Information TA: Victor Sai Recitation: Friday, 3-4pm, -13 E-mail: sai@mit.edu ffice ours: Friday, 4-5pm, -13 Spring 004 Calendar Sun Monday
7.05 Spring 004 February 13, 004 7.05 Recitation Schedule Contact Information TA: Victor Sai Recitation: Friday, 3-4pm, -13 E-mail: sai@mit.edu ffice ours: Friday, 4-5pm, -13 Spring 004 Calendar Sun Monday
Chapter 3 An Introduction to Gene Function 3.1 Storing Information 3.2 Replication 3.3 Mutation
 Chapter 3 An Introduction to Gene Function 3.1 Storing Information 3.2 Replication 3.3 Mutation 3.1 Storing Information [Central Dogma] Producing a protein from DNA => by transcription and translation
Chapter 3 An Introduction to Gene Function 3.1 Storing Information 3.2 Replication 3.3 Mutation 3.1 Storing Information [Central Dogma] Producing a protein from DNA => by transcription and translation
2. From the first paragraph in this section, find three ways in which RNA differs from DNA.
 Name Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein Begin reading at page 328 Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours
Name Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein Begin reading at page 328 Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours
DNA. Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses.
 Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
7 Synthesizing the ykkcd Mutant Toxin Sensor RNA in vitro
 7 Synthesizing the ykkcd Mutant Toxin Sensor RNA in vitro 7.1 Learning Objective In the quest toward understanding how the ykkcd toxin sensor recognizes the antibiotic tetracycline you thus far designed
7 Synthesizing the ykkcd Mutant Toxin Sensor RNA in vitro 7.1 Learning Objective In the quest toward understanding how the ykkcd toxin sensor recognizes the antibiotic tetracycline you thus far designed
Videos. Lesson Overview. Fermentation
 Lesson Overview Fermentation Videos Bozeman Transcription and Translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Drawing transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/6yqplgnjr4q Objectives 29a) I can contrast
Lesson Overview Fermentation Videos Bozeman Transcription and Translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Drawing transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/6yqplgnjr4q Objectives 29a) I can contrast
The Structure of RNA. The Central Dogma
 12-3 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis The Structure of RNA The Central Dogma Phenotype A gene is a SEQUENCE of DNA that codes for a protein (or functional RNA). Phenotype is the individual s observable trait
12-3 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis The Structure of RNA The Central Dogma Phenotype A gene is a SEQUENCE of DNA that codes for a protein (or functional RNA). Phenotype is the individual s observable trait
DNA, RNA, Replication and Transcription
 Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College DNA, RNA, Replication and Transcription The metabolic processes described earlier (glycolysis, cellular respiration, photophosphorylation,
Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College DNA, RNA, Replication and Transcription The metabolic processes described earlier (glycolysis, cellular respiration, photophosphorylation,
Fig Ch 17: From Gene to Protein
 Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Storage and Expression of Genetic Information
 Storage and Expression of Genetic Information 29. DNA structure, Replication and Repair ->Ch 25. DNA metabolism 30. RNA Structure, Synthesis and Processing ->Ch 26. RNA metabolism 31. Protein Synthesis
Storage and Expression of Genetic Information 29. DNA structure, Replication and Repair ->Ch 25. DNA metabolism 30. RNA Structure, Synthesis and Processing ->Ch 26. RNA metabolism 31. Protein Synthesis
The Stringent Response
 The Stringent Response When amino acids are limiting a response is triggered to shut down a wide range of biosynthetic processes This process is called the Stringent Response It results in the synthesis
The Stringent Response When amino acids are limiting a response is triggered to shut down a wide range of biosynthetic processes This process is called the Stringent Response It results in the synthesis
Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology
 Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated
Unit II Problem 3 Genetics: Summary of Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated
Transcription. DNA to RNA
 Transcription from DNA to RNA The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology replication DNA RNA Protein transcription translation Why call it transcription and translation? transcription is such a direct copy
Transcription from DNA to RNA The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology replication DNA RNA Protein transcription translation Why call it transcription and translation? transcription is such a direct copy
Section 3: DNA Replication
 Section 3: DNA Replication Main Idea: Replication- process by which DNA is copied during the cell cycle DNA Polymerase- a group of enzymes that bond the new nucleotides together 1 DNA Replication Replication
Section 3: DNA Replication Main Idea: Replication- process by which DNA is copied during the cell cycle DNA Polymerase- a group of enzymes that bond the new nucleotides together 1 DNA Replication Replication
Module 7: The Central Dogma. CSE590: Molecular programming and neural computation. All slides by Eric Klavins.
 Module 7: The Central Dogma CSE590: Molecular programming and neural computation. All slides by Eric Klavins. 1 The Central Dogma RNA Polymerase The Ribosome m Note: We will look mainly at prokaryo=c (e.g.
Module 7: The Central Dogma CSE590: Molecular programming and neural computation. All slides by Eric Klavins. 1 The Central Dogma RNA Polymerase The Ribosome m Note: We will look mainly at prokaryo=c (e.g.
CH 17 :From Gene to Protein
 CH 17 :From Gene to Protein Defining a gene gene gene Defining a gene is problematic because one gene can code for several protein products, some genes code only for RNA, two genes can overlap, and there
CH 17 :From Gene to Protein Defining a gene gene gene Defining a gene is problematic because one gene can code for several protein products, some genes code only for RNA, two genes can overlap, and there
Chapter 31. Transcription and RNA processing
 Chapter 31 Transcription and RNA processing RNA polymerase (RNAP) E. coli promoters Components of E. coli RNA Polymerase Holoenzyme (α 2 ββ'ωσ) Structure of prokaryotic RNAP The closed and open state of
Chapter 31 Transcription and RNA processing RNA polymerase (RNAP) E. coli promoters Components of E. coli RNA Polymerase Holoenzyme (α 2 ββ'ωσ) Structure of prokaryotic RNAP The closed and open state of
Chapter Fundamental Molecular Genetic Mechanisms
 Chapter 5-1 - Fundamental Molecular Genetic Mechanisms 5.1 Structure of Nucleic Acids 5.2 Transcription of Protein-Coding Genes and Formation of Functional mrna 5.3 The Decoding of mrna by trnas 5.4 Stepwise
Chapter 5-1 - Fundamental Molecular Genetic Mechanisms 5.1 Structure of Nucleic Acids 5.2 Transcription of Protein-Coding Genes and Formation of Functional mrna 5.3 The Decoding of mrna by trnas 5.4 Stepwise
Biochemistry Eukaryotic Transcription
 1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 1. Understand and have an overview of eucaryotic transcriptional regulation. 2. Explain
1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 1. Understand and have an overview of eucaryotic transcriptional regulation. 2. Explain
Lecture Summary: Regulation of transcription. General mechanisms-what are the major regulatory points?
 BCH 401G Lecture 37 Andres Lecture Summary: Regulation of transcription. General mechanisms-what are the major regulatory points? RNA processing: Capping, polyadenylation, splicing. Why process mammalian
BCH 401G Lecture 37 Andres Lecture Summary: Regulation of transcription. General mechanisms-what are the major regulatory points? RNA processing: Capping, polyadenylation, splicing. Why process mammalian
Bis2A 12.2 Eukaryotic Transcription
 OpenStax-CNX module: m56061 1 Bis2A 12.2 Eukaryotic Transcription Mitch Singer Based on Eukaryotic Transcription by OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
OpenStax-CNX module: m56061 1 Bis2A 12.2 Eukaryotic Transcription Mitch Singer Based on Eukaryotic Transcription by OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
DNA replication: Enzymes link the aligned nucleotides by phosphodiester bonds to form a continuous strand.
 DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
