The world s groundwater resources Contribution to Chapter 4 of WWDR-2 (Draft)
|
|
|
- Wesley Simon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The world s groundwater resources Contribution to Chapter 4 of WWDR-2 (Draft) Dr Jaroslav Vrba Jac van der Gun (coordinator) Utrecht December 2004 Report Nr IP
2 Table of contents 1 Importance of groundwater Occurrence Natural groundwater quality Non-renewable groundwater Impact of abstraction Monitoring and management Figures Fig Mean groundwater abstraction rates (mm/a) (IGRAC, 2004)...2 Fig Groundwater abstraction by water use sectors (proportions) (IGRAC, 2004)...2 Fig Global groundwater regions: predominant mode of groundwater occurrence and mean rate of renewal (IGRAC, 2004)...3 Fig WHYMAP The world s Groundwater Resources (simplified after the 1: scale version of the map; source: BGR, Hannover)...4 Fig Typical groundwater flow, age and hydrochemical patterns in basin settings (adapted from British Geological Survey)...5 Fig Arsenic in shallow wells (<150 m) in Bangladesh (source: MML/BGS project Groundwater Studies for Arsenic Contamination in Bangladesh )...6 Fig Aquifer-wide groundwater level declines in Yemen...8 Fig Land subsidence in Shanghai arising from groundwater abstraction...8 Tables Table Natural groundwater quality hazards: contents observed in some case studies...6 Table Selected large aquifer systems with non-renewable groundwater resources...7 Boxes Box The 10 countries with largest groundwater abstraction...1 i
3 1 Importance of groundwater Groundwater systems are replenished by precipitation and surface water and discharge into surface waters, the ocean or by evapotranspiration back in the atmosphere. Groundwater circulation globally is less than atmospheric and surface waters but what is stored beneath the earth s surface is orders of magnitude larger. Its total volume represents 96% of all earth s unfrozen fresh water 1.Without groundwater, the face of the earth would look different. Groundwater feeds springs and streams, supports wetlands, maintains land surface stability in areas of unstable ground and overall is a critical water resource serving mankind s water needs 2.For example, it meets over 75% of the water needs in Estonia, Iceland, Russian Federation, Jamaica, Saudi Arabia, Georgia, Swaziland, Mongolia, Libya and Lithuania. Figure reflects intensity of groundwater abstraction in different countries: particularly high (per km 2) groundwater abstractions occur in Bahrain, Taiwan, Mauritius, Malta, Pakistan, Bangladesh, India and Israel. Figure shows the extent groundwater is allocated to agricultural, domestic and industrial use. Box lists the 10 countries in the world with largest groundwater abstraction. About 60% of groundwater withdrawn is used by agriculture; the rest is almost equally divided between the domestic and industrial sectors. The predominant use is agriculture in many countries where arid and semi-arid climates prevail 3. Predominantly industrial sector use is in a few countries only. In many nations, more than half of the withdrawn groundwater is for domestic water supplies and globally it provides 25 to 40 % of the world s drinking water 4. Today, half the world s megacities and hundreds of other major cities on all continents rely upon or make significant use of groundwater. Small towns and rural communities particularly rely on it for domestic supplies. Even where groundwater provides lower percentages of total water used, it still may serve local areas where otherwise no other accessible supply exists and it usually does so with relatively low cost and good water quality. Finally, groundwater bridges water supply gaps during long dry seasons and during droughts. Box The 10 countries with largest groundwater abstraction Country Groundwater abstraction (km 3 /yr) reference year Main use (main sector) % of main sector demands covered by groundwater India Agriculture 53 USA Agriculture 42 China Agriculture 18 Pakistan Agriculture 34 Iran Agriculture 50 Mexico Agriculture 30 Russ. Federation Domestic 80 Saudi Arabia Agriculture 96 Italy Agriculture Japan Industry 35 Sources: FAO/AQUASTAT; UNEP/GEO-3; FAO, 1997;FAO, 2000; USGS, 2004 (personal communication). 1 Shiklomanov, I.A., and J.C. Rodda, World Water Resources at the Beginning of the 21 st Century. UNESCO/IHP Int. Hydrology Series, Cambridge University Press. 2 See e.g. the databases of FAO (AQUASTAT - UNEP (GEO-3 Data Compendium - and IGRAC (GGIS /Global Overview - and FAO s Water Reports no s 7 (1995), 9 (1997) and 20 (2000). 3 See IGRAC s GGIS database and UNEP s GEO-3 database. 4 UNEP, 2003: Groundwater and its Susceptibility to Degradation. UNEP/DEWA, Nairobi. 1
4 Fig Mean groundwater abstraction rates (mm/a) (IGRAC, 2004) Fig Groundwater abstraction by water use sectors (proportions) (IGRAC, 2004) 2
5 2 Occurrence As recent UNESCO supported activities show 5, large variations in groundwater exist in terms of its occurrence, rate of renewal and volume stored. Geological setting is an important factor. Shallow basement aquifers with limited storage are contrasting with large volumes of groundwater stored in thick sedimentary basins, aquifers in folded mountain zones tend to be fragmented and variable, while volcanic rock environments create special hydraulic and water quality conditions. Fig shows the world divided into 36 Global Groundwater Regions and gives an idea of their predominant hydrogeological setting by classifying them into four categories: Basement, Sedimentary Basin, High- Relief Folded Mountain and Volcanic regions.. Shallow aquifer systems with near-surface water tables are present in most regions. Unlike deep groundwater, shallow groundwater is strongly linked to surface waters in a hydraulic sense. Variations of mean groundwater renewal rates between regions are reflected in the map by variation of colour intensities, with low colour intensity in regions with predominantly arid climates or with permafrost. In some arid zone areas, limited groundwater renewals contrast with large groundwater reserves created mainly during past pluvial periods of the Pleistocene (hatched zones in Fig 4-9-3). Fig Global groundwater regions: predominant mode of groundwater occurrence and mean rate of renewal (IGRAC, 2004) Small-scale world map on the basis of 36 Global Groundwater Regions depicting the predominant hydrogeological setting (Basement (red), Sedimentary Basin (yellow), High-Relief Folded Mountain (green) and Volcanic (blue). Higher groundwater renewal rates, as averaged over each of the mentioned Global Groundwater Regions, are reflected in Fig by higher colour intensities. 5 Zekster and Everett, Groundwater Resources of the World and their Use. UNESCO, IHP-VI Series in Groundwater No 6. WHYMAP, Groundwater Resources of the World. Map 1: 50 M. Special Edition, August 2004, BGR Hannover/ UNESCO, Paris. IGRAC, Global Groundwater Information System ( 3
6 Fig WHYMAP The world s Groundwater Resources (simplified after the 1: scale version of the map; source: BGR, Hannover) The map intends primarily to give an overall picture of the more and less favourably groundwater endowed zones on the globe. 4
7 3 Natural groundwater quality A groundwaters natural geochemistry reflects its host-rock or soil composition/minerals, its solubility and the rate at which water passes through it basically its residence and surface contact time within a given geologic material. Within single groundwater systems, total dissolved solids content (TDS) and chemical composition change measurably over distance along the flow path as in-situ processes interact (Fig 4-9-5). Most renewable groundwater supplies commonly have a natural quality that is adequate for domestic, irrigation and other uses. However, examples of higher than desired levels 6 of constituents such as iron, manganese, fluoride, arsenic (Fig 4-9-6) and other constituents can restrict its untreated suitability and some hazardous concentrations constituents which have been noted in groundwater are summarized in Table Saline conditions developing in soil and groundwater occur both naturally and from man s actions in coastal aquifers as sea water intrudes when freshwater levels are lowered 7 ; in arid and semi-arid regions with extensive high evapotranspiration rates 8 ; as concentrated brines migrate 14 or where sediments contained high salt content during their deposition 9. A specific category forms groundwater high in minerals, gas and temperature, which is mostly connected with past and present volcanic activities. Fig Typical groundwater flow, age and hydrochemical patterns in basin settings (adapted from British Geological Survey). Groundwater in recharge areas and near-surface aquifers usually has low TDS levels (with bicarbonate the dominant anion) which reflect short contact times between water and rocks (usually tens of years). Down the flow direction, groundwater TDS increases, as gradual changes occur in the proportions of the major ions according to longer contact times and more reaction with the minerals in the rocks takes place. Commonly there is gradual transition along the flow paths from fresh bicarbonate groundwater through sulphate water to heavily mineralised chloride water. Part of this evolution is observed in most large groundwater basins, but the complete sequence is seldomly present Matthess, 1982 and Edmunds and Smedley, 1996) 7 Chapman, D. (editor), Water quality assessments. Chapman and Hall, Cambridge. 8 Matthess, G., The properties of groundwater. A Wiley-Interscience Publication, New York. 9 Morgan, K. and J. Jankowski, Origin of salts in a fractured bedrock aquifer in the Central West Region, NSW Australia. In: Proceedings Int. Conf. on Groundwater in fractured rocks, pp , UNESCO Series on Groundwater No.7, Paris. 10 Domenico, P., Concepts and models in Groundwater Hydrology. McGraw-Hill, Inc. 5
8 Fig Arsenic in shallow wells (<150 m) in Bangladesh (source: MML/BGS project Groundwater Studies for Arsenic Contamination in Bangladesh ) Table Natural groundwater quality hazards: contents observed in some case studies country chemical content drinking water origin constituents (mg/l) standards (mg/l) India, Bangladesh arsenic arsenic bearing minerals 1 Czech Republic, India fluorine fluorine bearing minerals 2,3 China chloride sea water intrusion 4 Australia chloride connate salts 5 USA sodium salt bearing strata 6 USA aluminium marine argillaceous rocks 7 China, India ph acid mine water 8 1 Chakraborti (2002), 2 Hercik at al. (2003), 3 Singhal and Gupta (1999), 4 Guanghui and Yuhong (2004), 5 Morgan and Jankowski (2003), 6,7 Matthess (1982), 8 Singhal and Gupta (1999). 6
9 4 Non-renewable groundwater Groundwater as a resource can be characterized by two main variables - its rate of renewal (groundwater recharge rate indicator see Table 4-3-2) and its volume in storage. Groundwater is renewed globally at a rate about equal to 30% of the rate of renewal of surface water. However, in terms of volume stored, there is approximately one hundred times more groundwater than surface water stored on the globe 11. Where present-day annual groundwater renewal is negligible compared with the stored volumes, most of the groundwater stored is not related to contemporaneous recharge but to recharge events which took place in the remote past. Such groundwater is called non-renewable groundwater or groundwater reserves. Its exploitation cannot be balanced by recharge of groundwater today, but will cause a steady reduction of the stored volume. The world s largest nonrenewable groundwater systems (Table 4-9-2) are located in arid zones of Northern Africa, the Arabian Peninsula and Australia, and under the permafrost in Western Siberia. Some of these reserves are large enough to maintain sizeable abstraction rates for many tens to hundreds of years. Sustainable groundwater development commonly is understood as exploiting the resource in dynamic equilibrium, leaving reserves, on average, undiminished. Where renewable water resources are scarce and groundwater non-renewable reserves are large, however, it may be justified to exploit the reserves when this would not produce undesired side-effects 12. Table Selected large aquifer systems with non-renewable groundwater resources 13 (simplified after UNESCO Working Group on Non-Renewable Groundwater Resources, 2004) Countries Aquifer System Area (km 2 ) Estimated total volume (km 3 ) Egypt, Libya, Sudan, Chad Algeria, Libya, Tunisia Nubian Sandstone Aquifer System NW Sahara Aquifer System Estimated exploitable volume (km 3 ) Estimate d annual recharge (km 3 ) Estimated annual abstraction (km 3 ) 2,200, ,000 > 6, to 457,000 1,000,000 60,000 1, Algeria, Libya, Niger Murzuk Basin 450,000 > 4,800 > 60 to Mali, Niger, Nigeria Iullemeden Aquifer 500,000 10, to to 80 System to 15,000 Niger, Nigeria, Chad, Cameroon Chad Basin Aquifer 600,000 >170 to 350 S.Arabia, UAR, Multilayer Aquifer 250, ? Bahrain, Qatar Arabian Platform Australia Great Artesian Basin 1,700,000 20, Russia West Siberian Artesian Basin 3,200,000 1,000, FAO, Aquastat ( Shiklomanov, I.A., and J.C. Rodda, World Water Resources at the Beginning of the 21 st Century. UNESCO/IHP Int. Hydrology Series, Cambridge University Press. Abderrahman, W. A., Should intensive use of non-renewable groundwater resources always be rejected? In: Llamas & Custodio: Intensive Use of Groundwater Challenges and Opportunities, Balkema, Lisse, The Netherlands. Two criteria have to be satisfied by such aquifers: (a) stored volume of groundwater at least 100 times greater than current annual recharge; and (b) the exploitation of non-renewable resources should not have a significant impact on recharged water bodies. 7
10 5 Impact of abstraction Groundwater abstraction has increased dramatically during the second half of the twentieth century, producing important benefits, as well as negative side-effects 14. The benefits are beyond any doubt, as already. An impressive example is India, where the area of irrigated land approximately has doubled during the mentioned period, mainly as a consequence of groundwater development. But there are unintended negative impacts as well, because intensive exploitation of the resource causes significant changes to the local water regime: groundwater levels decline; yields of springs, contributions to baseflow and other natural groundwater outflows are reduced; the intrusion of saline water or other water of allochtonous quality may be triggered. These changes have many practical consequences: wells and qanats become less productive and eventually run dry; groundwater becomes more expensive; aquifers may become exhausted; spring and baseflow users will lose part or all of their water; groundwater quality may deteriorate; ecosystems related to groundwater may be affected; and environmental impacts produced. Examples are storage depletion in Yemen 15 (Fig 4-9-7), land subsidence in Shanghai 16 (Fig 4-9-8); and degradation of the Tablas de Daimiel national park in Spain 17. Intensive exploitation is producing particular stress on the sustainability of groundwater systems in arid countries of the Middle East and North Africa and in Pakistan (Figure 4-9-9), and also in several parts of India, US and other countries where aridity and high population density occur. Shallow aquifers with limited storage capacity are particularly vulnerable to droughts and are more quickly exhausted by intensive abstraction than thick aquifers with large groundwater volumes in storage. Other factors play a role in the case of impacts on ecosystems or the environment, e.g. the link with surface water systems (in the case of wetlands) or the presence of compressible layers (in the case of land subsidence). Groundwater level (m-surface level) Continous regional groundwater level declines have forced many small farmers already to abandon irrigated agriculture (e.g. in Sadah area) Sadah Plain Sana'a Plain Rada Plain Marib Plain Wadi Hadramawt Tihama cumulative subsidence (cm) From 1965 onwards, progressive land subsidence was stopped effectively by reducing and 50 relocating groundwater withdrawal (since 1964) and by 100 initiating massive artificial recharge (since 1965) O-282 O-301 O-283 O-293 O-264 Fig Aquifer-wide groundwater level declines in Yemen Fig Land subsidence in Shanghai arising from groundwater abstraction Llamas and Custodio (editors), Intensive Use of Groundwater Challenges and Opportunities. Balkema, Lisse, The Netherlands. UNEP, Groundwater and its Susceptibility to Degradation. UNEP/DEWA, Nairobi. FAO, Groundwater Management. FAO Water Report no. 25, Rome. Burke, J., and M. Moench, Groundwater and Society. United Nations publication, New York. Van der Gun, J.A.M. and A.A. Ahmed, The Water Resources of Yemen. Report WRAY-35, TNO Delft/MOMR Sana a. Shanghai Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, China. Introduction about the preventive effect of Shanghai land subsidence (China). Unpublished report, Shanghai Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. Llamas, R., Wetlands: an important issue in hydrogeology. In: Selected Papers on Aquifer Overexploitation, IAH, Volume 3, p.p
11 Fig Groundwater development indicator: abstraction rate as a percentage of mean recharge rate (IGRAC, 2004). Low percentages indicate underdeveloped groundwater resources, high percentages point to development stress or eventually overexploitation. 9
12 6 Monitoring and management Groundwater resources management requires strategic planning and makes use of a wide range of instruments and measures, such as technical measures, incentives, legally enforced measures and sanctions, public awareness raising, etc 18. Adequate legal and institutional frameworks are crucial for implementing effective management measures, preferably done as part of integrated water resources management. Assessment and monitoring are indispensable for the development of a management plan, valuing the water appropriately may strengthen the plan, stakeholder participation may be crucial for its acceptance. While groundwater is less vulnerable to human impacts than surface water, once groundwater is polluted, remediation can be relatively long term (years), technically demanding and costly 19. Vulnerability assessments have been developed as part of management strategies for groundwater resources 20. The results are typically portrayed on maps now being used to plan, regulate, manage and take decisions when combined with land use, hydrogeological and other environmental maps. Large scale maps have been compiled in e.g. France, Germany, Spain, Italy, The Czech Republic, Poland, Russia, Australia where they serve as guidelines for land use zoning on the national or regional level, to identify areas susceptible to human impacts and to support policy and strategy for groundwater resources protection and water quality conservation. Groundwater monitoring programmes operate variably at national, regional or local levels. Water levels are the most observed parameter, with widespread and continuous water quality and natural groundwater discharge and abstraction networks operational in only a few countries 21. Several largescale efforts are underway to upgrade networks, e.g. in Europe (initiated by the EU Water Framework Directive 22 ) and in India (Hydrology Project 23 ). Countries concerned and financed adequately to carry out these programs understand how crucial credible, reliable and readily accessible groundwater monitoring data are to best plan and use their water resources. However, groundwater assessment, monitoring and data management activities are minimal or ineffective in many developing countries and are being downsized and reduced in comprehensiveness in several developed counties. The resulting lack of data will certainly make adequate groundwater management more difficult. Groundwater does not respect administrative boundaries. Most of the large groundwater reserves listed in Table are shared between countries, but there are numerous smaller transboundary aquifers as well scattered all over the world. Attention for internationally shared groundwater resources management is increasing, with strong support of several international organizations (GEF, UNESCO, IAH/ISARM, OAS, OSS, etc.) Foster, S., and K. Kemper, 2003: Sustainable Groundwater Management: Concepts and Tools. World Bank GW-Mate. UNEP, Groundwater and its Susceptibility to Degradation. UNEP/DEWA, Nairobi. FAO, Groundwater Management. FAO Water Report no. 25, Rome. Burke, J., and M. Moench, Groundwater and Society. United Nations publication, New York. Vrba, J., Impact of domestic and industrial wastes and agricultural activities on groundwater quality. In: Hydrogeology in the service of man, Vol. XVIII, Part I, pp , IAH Memoires of the 18 th Congress, Cambridge J. Vrba and A. Zaporozec, editors, (1994). Guidebook on mapping groundwater vulnerability. Vol. 16, IHP-IAH International contribution to hydrogeology, Verlag H. Heise, Germany. See See ~theSitePK:4607,00.html See e.g. 10
GWES. Groundwater for Emergency Situations. Jaroslav Vrba and Jan Šilar
 GWES Groundwater for Emergency Situations Jaroslav Vrba and Jan Šilar IHP VI Theme 2, Focal Area 2.2 Identification and management of strategic groundwater bodies to be used for emergency situations as
GWES Groundwater for Emergency Situations Jaroslav Vrba and Jan Šilar IHP VI Theme 2, Focal Area 2.2 Identification and management of strategic groundwater bodies to be used for emergency situations as
H 2 O know-how. by Pradeep Aggarwal & Ali Boussaha
 H 2 O know-how by Pradeep Aggarwal & Ali Boussaha 38 IAEA BULLETIN 47/1 September 2005 The IAEA spreads the science for harnessing the world s aquifers. We know water is essential for life. Less known
H 2 O know-how by Pradeep Aggarwal & Ali Boussaha 38 IAEA BULLETIN 47/1 September 2005 The IAEA spreads the science for harnessing the world s aquifers. We know water is essential for life. Less known
NON-RENEWABLE GROUNDWATER RESOURCES
 UNESCO IHP VI NON-RENEWABLE GROUNDWATER RESOURCES basic concepts & management approaches DR STEPHEN FOSTER GW-MATE Director (IAH President) a GWP Associate Program NON-RENEWABLE GROUNDWATER RESOURCES relative
UNESCO IHP VI NON-RENEWABLE GROUNDWATER RESOURCES basic concepts & management approaches DR STEPHEN FOSTER GW-MATE Director (IAH President) a GWP Associate Program NON-RENEWABLE GROUNDWATER RESOURCES relative
The International Hydrological Programme (IHP) Intergovernmental programme on Water Resources of UNESCO
 The International Hydrological Programme (IHP) Intergovernmental programme on Water Resources of UNESCO 160 Countries established National Committees and jointly formulate regional and global water strategies
The International Hydrological Programme (IHP) Intergovernmental programme on Water Resources of UNESCO 160 Countries established National Committees and jointly formulate regional and global water strategies
AS127 - Wasia-Biyadh-Aruma Aquifer System (North): Sakaka-Rutba
 Geography Total area TBA (km 2 ): 84 000 No. countries sharing: 2 Countries sharing: Iraq, Saudi Arabia Population: 560 000 Climate zone: Arid Rainfall (mm/yr): 87 Hydrogeology Aquifer type: Multiple 4-layered,
Geography Total area TBA (km 2 ): 84 000 No. countries sharing: 2 Countries sharing: Iraq, Saudi Arabia Population: 560 000 Climate zone: Arid Rainfall (mm/yr): 87 Hydrogeology Aquifer type: Multiple 4-layered,
Groundwater in the Santa Rosa Plain
 . Groundwater in the Santa Rosa Plain Marcus Trotta, PG, CHg Principal Hydrogeologist Sonoma County Water Agency Santa Rosa Plain Groundwater Sustainability Agency October 12, 2017 www.sonomacountywater.org
. Groundwater in the Santa Rosa Plain Marcus Trotta, PG, CHg Principal Hydrogeologist Sonoma County Water Agency Santa Rosa Plain Groundwater Sustainability Agency October 12, 2017 www.sonomacountywater.org
GWES Groundwater for Emergency Situations - Project of IHP VI. Jaroslav Vrba GWES Project Coordinator UNESCO Senior Consultant
 GWES Groundwater for Emergency Situations - Project of IHP VI Jaroslav Vrba GWES Project Coordinator UNESCO Senior Consultant Resolution of the International Conference on Freshwater (Bonn, 2001) The world
GWES Groundwater for Emergency Situations - Project of IHP VI Jaroslav Vrba GWES Project Coordinator UNESCO Senior Consultant Resolution of the International Conference on Freshwater (Bonn, 2001) The world
International Shared Aquifers in the Arab Region
 International Shared Aquifers in the Arab Region Chahra Ksia - Amb Chief of the Center of water Studies and Arab water Security, League of Arab States ABSTRACT The Arab countries are sharing many aquifers,
International Shared Aquifers in the Arab Region Chahra Ksia - Amb Chief of the Center of water Studies and Arab water Security, League of Arab States ABSTRACT The Arab countries are sharing many aquifers,
Groundwater Resource Management an introduction to its scope and practice
 Sustainable Groundwater Management: Concepts and Tools Sustainable Groundwater Management Concepts & Tools Briefing Note Series Note 1 Groundwater Resource Management an introduction to its scope and practice
Sustainable Groundwater Management: Concepts and Tools Sustainable Groundwater Management Concepts & Tools Briefing Note Series Note 1 Groundwater Resource Management an introduction to its scope and practice
AS139 - Wasia-Biyadh-Aruma Aquifer System (South): Tawila- Mahra/Cretaceous Sands
 Geography Total area TBA (km 2 ): 160 000 No. countries sharing: 2 Countries sharing: Saudi Arabia, Yemen Population: 870 000 Climate zone: Arid Rainfall (mm/yr): 61 Hydrogeology Aquifer type: 2-layered,
Geography Total area TBA (km 2 ): 160 000 No. countries sharing: 2 Countries sharing: Saudi Arabia, Yemen Population: 870 000 Climate zone: Arid Rainfall (mm/yr): 61 Hydrogeology Aquifer type: 2-layered,
AS141 - Umm er Radhuma-Dammam Aquifer System (South): Rub' al Khali
 Geography Total area TBA (km 2 ): 670 000 No. countries sharing: 4 Countries sharing: Oman, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Yemen Population: 4 200 000 Climate zone: Arid Rainfall (mm/yr): 57 Hydrogeology
Geography Total area TBA (km 2 ): 670 000 No. countries sharing: 4 Countries sharing: Oman, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Yemen Population: 4 200 000 Climate zone: Arid Rainfall (mm/yr): 57 Hydrogeology
6. Hydrogeological zones and groundwater resources balance baseflow map of the Czech Republic. Jiri Sima
 6. Hydrogeological zones and groundwater resources balance baseflow map of the Czech Republic Jiri Sima General content Regional hydrogeological units Groundwater resources assessment Water balancing background
6. Hydrogeological zones and groundwater resources balance baseflow map of the Czech Republic Jiri Sima General content Regional hydrogeological units Groundwater resources assessment Water balancing background
UNESCO International Hydrological Programme (IHP)
 UNESCO International Hydrological Programme (IHP) Activities related to Groundwater Resources Management in the Sahel Zone International Hydrological Programme The only global intergovernmental scientific
UNESCO International Hydrological Programme (IHP) Activities related to Groundwater Resources Management in the Sahel Zone International Hydrological Programme The only global intergovernmental scientific
Global Assessment of Transboundary Aquifers. ISARM and GEF TWAP
 Global Assessment of Transboundary Aquifers ISARM and GEF TWAP Holger Treidel UNESCO, International Hydrological Programme (IHP) ISARM Programme The worldwide ISARM (Internationally Shared Aquifer Resources
Global Assessment of Transboundary Aquifers ISARM and GEF TWAP Holger Treidel UNESCO, International Hydrological Programme (IHP) ISARM Programme The worldwide ISARM (Internationally Shared Aquifer Resources
Circum Saharan Transboundary Aquifers: Inventory and challenges for Management
 Circum Saharan Transboundary Aquifers: Inventory and challenges for Management UNESCO-IAH-UNDP conference, Paris, 6-8 December 2010 A. Mamou 1 (1) Sahara and Sahel Observatory- BP 31 1080 Charguia-Tunis.
Circum Saharan Transboundary Aquifers: Inventory and challenges for Management UNESCO-IAH-UNDP conference, Paris, 6-8 December 2010 A. Mamou 1 (1) Sahara and Sahel Observatory- BP 31 1080 Charguia-Tunis.
General Groundwater Concepts
 General Groundwater Concepts Hydrologic Cycle All water on the surface of the earth and underground are part of the hydrologic cycle (Figure 1), driven by natural processes that constantly transform water
General Groundwater Concepts Hydrologic Cycle All water on the surface of the earth and underground are part of the hydrologic cycle (Figure 1), driven by natural processes that constantly transform water
Reclaimed Wastewater as Ground Water Recharge. Dr. Mo ayyad Shawaqfah Al al-bayt University
 Reclaimed Wastewater as Ground Water Recharge Dr. Mo ayyad Shawaqfah Al al-bayt University Groundwater as a Resource Large Regional Flow Systems Well Yield Analysis Artificial Recharge Conjunctive Use
Reclaimed Wastewater as Ground Water Recharge Dr. Mo ayyad Shawaqfah Al al-bayt University Groundwater as a Resource Large Regional Flow Systems Well Yield Analysis Artificial Recharge Conjunctive Use
Indicator Fact Sheet (WQ01c) Water exploitation index
 Indicator Fact Sheet (WQ01c) Water exploitation index Authors: Conchita Marcuello and Concha Lallana, CEDEX EEA project manager: Niels Thyssen version 01.10.03 Key message 18% of Europe s population live
Indicator Fact Sheet (WQ01c) Water exploitation index Authors: Conchita Marcuello and Concha Lallana, CEDEX EEA project manager: Niels Thyssen version 01.10.03 Key message 18% of Europe s population live
Inventory of African transboundary aquifer systems
 Inventory of African transboundary aquifer systems B. Appelgren UNESCO/ISARM 1 Outline Part I. African TBA Inventory: aspirations and objectives Part II. ISARM 2002/2004 Inventory Part III. Conclude 2
Inventory of African transboundary aquifer systems B. Appelgren UNESCO/ISARM 1 Outline Part I. African TBA Inventory: aspirations and objectives Part II. ISARM 2002/2004 Inventory Part III. Conclude 2
FOOD SECURITY & GROUNDWATER
 International Association of Hydrogeologists Strategic Overview Series FOOD SECURITY & GROUNDWATER KEY MESSAGES food production requires large quantities of water, with groundwater resources providing
International Association of Hydrogeologists Strategic Overview Series FOOD SECURITY & GROUNDWATER KEY MESSAGES food production requires large quantities of water, with groundwater resources providing
Water Resources on PEI: an overview and brief discussion of challenges
 Water Resources on PEI: an overview and brief discussion of challenges Components: Components and links Atmospheric water Surface water (including glacial water) Groundwater Links: Precipitation (atm(
Water Resources on PEI: an overview and brief discussion of challenges Components: Components and links Atmospheric water Surface water (including glacial water) Groundwater Links: Precipitation (atm(
Executive summary. Pressures
 6 Groundwater quality and quantity in Europe Executive summary Groundwater is a major source of drinking water all over Europe, and thus the state of groundwater in terms of quality and quantity is of
6 Groundwater quality and quantity in Europe Executive summary Groundwater is a major source of drinking water all over Europe, and thus the state of groundwater in terms of quality and quantity is of
2 Groundwater. indicators 2.1 GENERAL
 2 Groundwater indicators 2.1 GENERAL The International Hydrological Programme (IHP) and The World Water Assessment Programme (WWAP) both recognized the role of groundwater in the overall assessment of
2 Groundwater indicators 2.1 GENERAL The International Hydrological Programme (IHP) and The World Water Assessment Programme (WWAP) both recognized the role of groundwater in the overall assessment of
Human impacts on groundwater resources in Iran
 Man's Influence on Freshwater Ecosystems and Water Use (Proceedings of a Boulder Symposium, July 1995). IAHS Publ. no. 230, 1995. 141 Human impacts on groundwater resources in Iran ALI VALI-KHODJEINI Irrigation
Man's Influence on Freshwater Ecosystems and Water Use (Proceedings of a Boulder Symposium, July 1995). IAHS Publ. no. 230, 1995. 141 Human impacts on groundwater resources in Iran ALI VALI-KHODJEINI Irrigation
Groundwater and risk management Las aguas subterráneas y el manejo de riesgos
 Groundwater and risk management Las aguas subterráneas y el manejo de riesgos Jac van der Gun IGRAC 4 th World Water Forum, Mexico, 21 March 2006 Session Groundwater and risk management: coping with water
Groundwater and risk management Las aguas subterráneas y el manejo de riesgos Jac van der Gun IGRAC 4 th World Water Forum, Mexico, 21 March 2006 Session Groundwater and risk management: coping with water
NEC - Element 5 - Control of contamination of water sources July Copyright RMS. Copyright RMS. Copyright RMS
 NEC - Element 5 - Control of July 2014 Learning outcomes NEBOSH Certificate in Environmental Management 5.1 Outline the importance of the quality of water for life 5.2 Outline the main sources of water
NEC - Element 5 - Control of July 2014 Learning outcomes NEBOSH Certificate in Environmental Management 5.1 Outline the importance of the quality of water for life 5.2 Outline the main sources of water
POSSIBILITIES FOR GROUNDWATER DEVELOPMENT FOR THE CITY OF JAKARTA, INDONESIA
 Hydrological Processes and Water Management in Urban Areas (Proceedings of the Duisberg Symposium, April 1988). IAHS Publ. no. 198, 1990. POSSIBILITIES FOR GROUNDWATER DEVELOPMENT FOR THE CITY OF JAKARTA,
Hydrological Processes and Water Management in Urban Areas (Proceedings of the Duisberg Symposium, April 1988). IAHS Publ. no. 198, 1990. POSSIBILITIES FOR GROUNDWATER DEVELOPMENT FOR THE CITY OF JAKARTA,
Urban Groundwater Scenario. M. S. Mohan Kumar. Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore
 Urban Groundwater Scenario M. S. Mohan Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Global Water Scarcity Increased global water stress Groundwater Groundwater is the largest
Urban Groundwater Scenario M. S. Mohan Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore Global Water Scarcity Increased global water stress Groundwater Groundwater is the largest
Water Security for Sustainable Development: The challenge of Scarcity in the Middle East & North Africa
 Water Security for Sustainable Development: The challenge of Scarcity in the Middle East & North Africa Shawki Barghouti Director General International Center for Biosaline Agriculture 1 water scarcity
Water Security for Sustainable Development: The challenge of Scarcity in the Middle East & North Africa Shawki Barghouti Director General International Center for Biosaline Agriculture 1 water scarcity
Challenges for the sustainable management of urban water supply and sanitation systems Case of the Thiaroye aquifer
 Challenges for the sustainable management of urban water supply and sanitation systems Case of the Thiaroye aquifer Prof. Cheikh B. Gaye G-WADI Global Conference G-WADI more than a decade enhancing water
Challenges for the sustainable management of urban water supply and sanitation systems Case of the Thiaroye aquifer Prof. Cheikh B. Gaye G-WADI Global Conference G-WADI more than a decade enhancing water
Grounding Water: An Exploration of the Unseen World Beneath Our Feet
 1 Grounding Water: An Exploration of the Unseen World Beneath Our Feet Kerry Schwartz, Director, Arizona Project WET Protect Your Groundwater Day: Tuesday, September 9, 2014 What I Hope to Convey Groundwater
1 Grounding Water: An Exploration of the Unseen World Beneath Our Feet Kerry Schwartz, Director, Arizona Project WET Protect Your Groundwater Day: Tuesday, September 9, 2014 What I Hope to Convey Groundwater
UNESCO s action for Groundwater Governance in Africa
 AFRICA Focus- Groundwater governance and institutional management UNESCO s action for Groundwater Governance in Africa Dr. Alice Aureli PhD Chief of the Section Groundwater Systems and HumanSettlements
AFRICA Focus- Groundwater governance and institutional management UNESCO s action for Groundwater Governance in Africa Dr. Alice Aureli PhD Chief of the Section Groundwater Systems and HumanSettlements
Water Resources Data APPENDIX 1. Actual Renewable Water Resources per Capita, by Region. Actual Renewable Water Resources per Capita, by Region
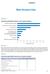 APPENDIX 1 Water Resources Data FIGURE A1.1 Actual Renewable Water Resources per Capita, by Region Australia and New Zealand Latin America and the Caribbean North America Europe and Central Asia Sub-Saharan
APPENDIX 1 Water Resources Data FIGURE A1.1 Actual Renewable Water Resources per Capita, by Region Australia and New Zealand Latin America and the Caribbean North America Europe and Central Asia Sub-Saharan
WATER FROM THE CLOUDS
 WATER FROM THE CLOUDS 814 mm per year on land or 110 000 km 3 56% is evapotranspirated by forests and natural landscapes 5% is evapotranspirated by rainfed agriculture 39% available for human uses (irrigation,
WATER FROM THE CLOUDS 814 mm per year on land or 110 000 km 3 56% is evapotranspirated by forests and natural landscapes 5% is evapotranspirated by rainfed agriculture 39% available for human uses (irrigation,
Natural Gas Facts & Figures. New Approach & Proposal
 Natural Gas Facts & Figures New Approach & Proposal 1. Production and reserves Sources : Total G&P, WOC1, IEA, IHS Cera, Resources- Reserves o Conventional o Unconventional : types and reserves Countries,
Natural Gas Facts & Figures New Approach & Proposal 1. Production and reserves Sources : Total G&P, WOC1, IEA, IHS Cera, Resources- Reserves o Conventional o Unconventional : types and reserves Countries,
Characterization of Deep Groundwater: A Conference Report. William M. Alley, Michael Wireman, Mary Musick 2014 GWPC Annual Forum
 Characterization of Deep Groundwater: A Conference Report William M. Alley, Michael Wireman, Mary Musick 2014 GWPC Annual Forum Topical Discussions Analysis of data and information to characterize hydrogeologic
Characterization of Deep Groundwater: A Conference Report William M. Alley, Michael Wireman, Mary Musick 2014 GWPC Annual Forum Topical Discussions Analysis of data and information to characterize hydrogeologic
MODULE 5. Groundwater Quality Assessment and Protection
 MODULE 5 Groundwater Quality Assessment and Protection Why do groundwater merit protection? Groundwater provides a potable water supply for vast population Often unprotected Pollution threats are increasing
MODULE 5 Groundwater Quality Assessment and Protection Why do groundwater merit protection? Groundwater provides a potable water supply for vast population Often unprotected Pollution threats are increasing
GIS APPLICATION IN GROUNDWATER QUALITY ESTIMATION
 GIS APPLICATION IN GROUNDWATER QUALITY ESTIMATION CRP 514 Term Paper Hatim H. Gazaz 5/18/2013 ID #: 200903270 Table of Contents GIS Application in Groundwater Quality Estimation 2013 TABLE OF CONTENTS...
GIS APPLICATION IN GROUNDWATER QUALITY ESTIMATION CRP 514 Term Paper Hatim H. Gazaz 5/18/2013 ID #: 200903270 Table of Contents GIS Application in Groundwater Quality Estimation 2013 TABLE OF CONTENTS...
Robert W. Buddemeier*, Hillel Rubin**, and David P. Young *
 PROTECTING URBAN WATER SUPPLIES IN SOUTH-CENTRAL KANSAS BY INTEGRATED GROUNDWATER-SURFACE WATER MANAGEMENT TO MEET MUNICIPAL, AGRICULTURAL AND ECOSYSTEM WATER NEEDS Robert W. Buddemeier*, Hillel Rubin**,
PROTECTING URBAN WATER SUPPLIES IN SOUTH-CENTRAL KANSAS BY INTEGRATED GROUNDWATER-SURFACE WATER MANAGEMENT TO MEET MUNICIPAL, AGRICULTURAL AND ECOSYSTEM WATER NEEDS Robert W. Buddemeier*, Hillel Rubin**,
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Grotzinger Jordan. Understanding Earth. Sixth Edition
 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 17: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE AND GROUNDWATER 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 17 The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater 1 About the Hydrologic
Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 17: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE AND GROUNDWATER 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 17 The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater 1 About the Hydrologic
GROUNDWATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN TANZANIA BY MR. LISTER R.E. KONGOLA ASSISTANT DIRECTOR WATER RESOURCES DIVISION
 GROUNDWATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN TANZANIA BY MR. LISTER R.E. KONGOLA ASSISTANT DIRECTOR WATER RESOURCES DIVISION BACKGROUND Basic facts Location: Tanzania is located on the east coast of Africa and
GROUNDWATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN TANZANIA BY MR. LISTER R.E. KONGOLA ASSISTANT DIRECTOR WATER RESOURCES DIVISION BACKGROUND Basic facts Location: Tanzania is located on the east coast of Africa and
5. Basin Evaluation Salt and Nitrate Balance
 SNMP Attachment B, Section B.2.1.3 (originally Section 5 in CV-SALTS Phase 2 Conceptual Model Task 5 deliverables) 5. As part of the evaluation of water quality the SNMP requires loading estimates and
SNMP Attachment B, Section B.2.1.3 (originally Section 5 in CV-SALTS Phase 2 Conceptual Model Task 5 deliverables) 5. As part of the evaluation of water quality the SNMP requires loading estimates and
The effect of Hilti / Salahi Recharge Dam in Batineh Area, Sultanate of Oman on the Quality of Groundwater Using GIS
 The effect of Hilti / Salahi Recharge Dam in Batineh Area, Sultanate of Oman on the Quality of Groundwater Using GIS William Bajjali University of Wisconsin Superior, Department of Biology & Earth Sciences,
The effect of Hilti / Salahi Recharge Dam in Batineh Area, Sultanate of Oman on the Quality of Groundwater Using GIS William Bajjali University of Wisconsin Superior, Department of Biology & Earth Sciences,
A International Conference on Hydrology and Meteorology. Presented By
 A International Conference on Hydrology and Meteorology On Presented By (Research Scholar) Department of Environmental Science & Engineering Indian School of Mines, Dhanbad, Jharkhand INTRODUCTION Groundwater
A International Conference on Hydrology and Meteorology On Presented By (Research Scholar) Department of Environmental Science & Engineering Indian School of Mines, Dhanbad, Jharkhand INTRODUCTION Groundwater
The role of dams in securing the surface water in the northern and eastern parts of the United Arab Emirates (UAE)
 Changes in Water Resources Systems: Methodologies to Maintain Water Security and Ensure Integrated Management (Proceedings of Symposium HS at IUGG, Perugia, July ). IAHS Publ.,. The role of dams in securing
Changes in Water Resources Systems: Methodologies to Maintain Water Security and Ensure Integrated Management (Proceedings of Symposium HS at IUGG, Perugia, July ). IAHS Publ.,. The role of dams in securing
Groundwater Resource Management
 GW MATE Briefing Note Series Sustainable Groundwater Management: Concepts and Tools Briefing Note 1 Groundwater Resource Management an introduction to its scope and practice Authors (GW MATE Core Group)
GW MATE Briefing Note Series Sustainable Groundwater Management: Concepts and Tools Briefing Note 1 Groundwater Resource Management an introduction to its scope and practice Authors (GW MATE Core Group)
N. Africa & S.W. Asia
 N. Africa & S.W. Asia CHAPTER #8, SECTION #1 Identifying Boundaries Three Regions North Africa (Border Mediterranean and Red Seas) Morocco, Western Sahara, Algeria, Egypt, Sudan, Tunisia, & Libya Southwest
N. Africa & S.W. Asia CHAPTER #8, SECTION #1 Identifying Boundaries Three Regions North Africa (Border Mediterranean and Red Seas) Morocco, Western Sahara, Algeria, Egypt, Sudan, Tunisia, & Libya Southwest
Prof. Harvey Shear Department of Geography University of Toronto Mississauga. February 5, 2013
 Prof. Harvey Shear Department of Geography University of Toronto Mississauga February 5, 2013 Water, water, everywhere, And all the boards did shrink; Water, water, everywhere, Nor any drop to drink. Rime
Prof. Harvey Shear Department of Geography University of Toronto Mississauga February 5, 2013 Water, water, everywhere, And all the boards did shrink; Water, water, everywhere, Nor any drop to drink. Rime
UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS Office of Institutional Research and Planning
 10/13 TABLE 4-170 FALL - TOTAL 1,624 1,740 1,926 2,135 2,134 2,138 2,246 Male 927 968 1,076 1,191 1,188 1,179 1,262 Female 697 772 850 944 946 959 984 Undergraduate 685 791 974 1,181 1,189 1,217 1,281
10/13 TABLE 4-170 FALL - TOTAL 1,624 1,740 1,926 2,135 2,134 2,138 2,246 Male 927 968 1,076 1,191 1,188 1,179 1,262 Female 697 772 850 944 946 959 984 Undergraduate 685 791 974 1,181 1,189 1,217 1,281
Cool waters and atmospheric high pressure
 QU: How does human activity contribute to drought risk? AIM: To evaluate the human influence of drought events in Africa's Sahel region. ST: What part of the ENSO cycle is at work here? What does it mean
QU: How does human activity contribute to drought risk? AIM: To evaluate the human influence of drought events in Africa's Sahel region. ST: What part of the ENSO cycle is at work here? What does it mean
Office of Land and Water Evaluations of Groundwater Resources of Southern Mississippi
 Office of Land and Water Evaluations of Groundwater Resources of Southern Mississippi Virtually all of the water used for public and domestic drinking water supplies in southern Mississippi is derived
Office of Land and Water Evaluations of Groundwater Resources of Southern Mississippi Virtually all of the water used for public and domestic drinking water supplies in southern Mississippi is derived
Water Quality Index For Assessment Of Water Quality In South Chennai Coastal Aquifer, Tamil Nadu, India
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.4, No.4, pp 1582-1588, Oct-Dec 2012 Water Quality Index For Assessment Of Water Quality In South Chennai Coastal Aquifer,
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN( USA): IJCRGG ISSN : 0974-4290 Vol.4, No.4, pp 1582-1588, Oct-Dec 2012 Water Quality Index For Assessment Of Water Quality In South Chennai Coastal Aquifer,
ASSESSMENT OF GROUND WATER QUALITY STUDIES AT KALBADEVI ESTUARY AND ADJOINING AREA OF RATNAGIRI TAHSIL, MAHARASHTRA.
 ASSESSMENT OF GROUND WATER QUALITY STUDIES AT KALBADEVI ESTUARY AND ADJOINING AREA OF RATNAGIRI TAHSIL, MAHARASHTRA. Patil Padurang Y*. Department of Environmental Science, University of Mumbai, Ratnagiri
ASSESSMENT OF GROUND WATER QUALITY STUDIES AT KALBADEVI ESTUARY AND ADJOINING AREA OF RATNAGIRI TAHSIL, MAHARASHTRA. Patil Padurang Y*. Department of Environmental Science, University of Mumbai, Ratnagiri
Water Resources Management from a Nexus perspective
 Water Resources Management from a Nexus perspective Dr. Mari Ito Academic Officer Water Resources Management Photo: MHE Photo: Jungmann Water Resources Management from a Nexus perspective - This presentation
Water Resources Management from a Nexus perspective Dr. Mari Ito Academic Officer Water Resources Management Photo: MHE Photo: Jungmann Water Resources Management from a Nexus perspective - This presentation
Groundwater and Surface Water Overview of the Lochend Area, Alberta
 Groundwater and Surface Water Overview of the Lochend Area, Alberta The Lochend Industry Producers Group (LIPG) conducted a hydrogeological / hydrological study in the Lochend operating field. The objectives
Groundwater and Surface Water Overview of the Lochend Area, Alberta The Lochend Industry Producers Group (LIPG) conducted a hydrogeological / hydrological study in the Lochend operating field. The objectives
The state of the world s land and water resources: A summary
 The state of the world s land and water resources: A summary Jean- Marc Faurès and Chris White Food and Agriculture Organisation, Italy and Australian National University, Australia Discussion Paper 1106
The state of the world s land and water resources: A summary Jean- Marc Faurès and Chris White Food and Agriculture Organisation, Italy and Australian National University, Australia Discussion Paper 1106
CHAPTER 13 OUTLINE The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater. Hydrologic cycle. Hydrologic cycle cont.
 CHAPTER 13 OUTLINE The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. Hydrologic cycle The hydrologic cycle is
CHAPTER 13 OUTLINE The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. Hydrologic cycle The hydrologic cycle is
WATER AND THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE
 WATER AND THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE Summary Water is essential for the support of life and can be considered as a fundamental environmental good. Water is needed to support human habitation, grow crops and
WATER AND THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE Summary Water is essential for the support of life and can be considered as a fundamental environmental good. Water is needed to support human habitation, grow crops and
Isotope hydrology and water resources management in Africa
 Isotope hydrology and water resources management in Africa Current status and challenges Cheikh B. Gaye International initiatives At the Millennium Summit in 2000 and during the 2002 World Summit on Sustainable
Isotope hydrology and water resources management in Africa Current status and challenges Cheikh B. Gaye International initiatives At the Millennium Summit in 2000 and during the 2002 World Summit on Sustainable
Spirax SafeBloc TM. double block and bleed bellows sealed stop valve
 Spirax SafeBloc TM double block and bleed bellows sealed stop Spirax SafeBloc TM a single solution for safe double isolation The Spirax SafeBloc TM is a safe isolation solution, with a unique space-saving
Spirax SafeBloc TM double block and bleed bellows sealed stop Spirax SafeBloc TM a single solution for safe double isolation The Spirax SafeBloc TM is a safe isolation solution, with a unique space-saving
Linking science and development: Experience from groundwater work in Asia and Africa
 Linking science and development: Experience from groundwater work in Asia and Africa Karen G. Villholth Senior Researcher, Groundwater Management, IWMI-Southern Africa Chair, Danish Chapter of IAH ATV-IAH
Linking science and development: Experience from groundwater work in Asia and Africa Karen G. Villholth Senior Researcher, Groundwater Management, IWMI-Southern Africa Chair, Danish Chapter of IAH ATV-IAH
CHAPTER 9 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 CHAPTER 9 TABLE OF CONTENTS Chapter 9 Table of Contents... i Chapter 9 List of Tables... i Chapter 9 List of Figures... i Chapter 9. GROUNDWATER STORAGE IN SANA'A BASIN... 504 Executive summary... 504
CHAPTER 9 TABLE OF CONTENTS Chapter 9 Table of Contents... i Chapter 9 List of Tables... i Chapter 9 List of Figures... i Chapter 9. GROUNDWATER STORAGE IN SANA'A BASIN... 504 Executive summary... 504
The social and economic aspects of groundwater. indicator. 3.1 SOCIAL AND ECONOMIC RELEVANCE OF GROUNDWATER INDICATORS
 3 The social and economic aspects of groundwater indicators This chapter explores the key social and economic aspects of the proposed groundwater resources sustainability indicators. The aim of the chapter
3 The social and economic aspects of groundwater indicators This chapter explores the key social and economic aspects of the proposed groundwater resources sustainability indicators. The aim of the chapter
Water Resources. The Water Cycle. Section 1. Key Terms surface water river system watershed groundwater aquifer porosity permeability recharge zone
 Water Resources The next time you drink a glass of water, think about where the water came from. Did you know that some of the water in your glass may have been part of a rainstorm that pounded Earth long
Water Resources The next time you drink a glass of water, think about where the water came from. Did you know that some of the water in your glass may have been part of a rainstorm that pounded Earth long
Problems of groundwater quality related to the urban environment in Greater Cairo
 Impacts of Urban Growth on Surface Water and Groundwater Quality (Proceedings of IUGG 99 Symposium HS5, Birmingham, July 1999). IAHS Publ. no. 259, 1999. 29 Problems of groundwater quality related to the
Impacts of Urban Growth on Surface Water and Groundwater Quality (Proceedings of IUGG 99 Symposium HS5, Birmingham, July 1999). IAHS Publ. no. 259, 1999. 29 Problems of groundwater quality related to the
12/11/2014. Provided by Thomas Harter, UC Davis RAIN. How much groundwater is in an aquifer?
 12/11/2014 Drought Effects on Groundwater Management: Understanding Groundwater, Drought, and Streams Overview 1. Differences in aquifer characteristics across California ag areas (capacity, material,
12/11/2014 Drought Effects on Groundwater Management: Understanding Groundwater, Drought, and Streams Overview 1. Differences in aquifer characteristics across California ag areas (capacity, material,
The Effects of Water Table Decline on the Groundwater Quality in Aquifer of Torbat Jam Plain, Northeast Iran
 Int. J. Emerg. Sci., 1(2), 153-163, June 2011 ISSN: 2222-4254 IJES The Effects of Water Table Decline on the Groundwater Quality in Aquifer of Torbat Jam Plain, Northeast Iran G.R. Lashkaripour, M. Ghafoori
Int. J. Emerg. Sci., 1(2), 153-163, June 2011 ISSN: 2222-4254 IJES The Effects of Water Table Decline on the Groundwater Quality in Aquifer of Torbat Jam Plain, Northeast Iran G.R. Lashkaripour, M. Ghafoori
Water. a shared responsibility. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2 BERGHAHN BOOKS
 Water a shared responsibility The United Nations World Water Development Report 2 BERGHAHN BOOKS Part 1. Global Hydrology and Water Resources...121 1a. The driving forces and pressures on our water resources...121
Water a shared responsibility The United Nations World Water Development Report 2 BERGHAHN BOOKS Part 1. Global Hydrology and Water Resources...121 1a. The driving forces and pressures on our water resources...121
Renewable Energy Conference
 SANA'A CITY WATER SITUATION The Second Middle East and North Africa Renewable Energy Conference Amman, May, 9 11, 2005 Prof. Dr. Towfick Sufian (Vice Rector) Sana a University Republic of Yemen 1 Introduction
SANA'A CITY WATER SITUATION The Second Middle East and North Africa Renewable Energy Conference Amman, May, 9 11, 2005 Prof. Dr. Towfick Sufian (Vice Rector) Sana a University Republic of Yemen 1 Introduction
GROUNDWATER DISCHARGE INTO THE WORLD OCEAN. Zektser I.S. Water Problems Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia
 GROUNDWATER DISCHARGE INTO THE WORLD OCEAN Zektser I.S. Water Problems Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia Keywords: groundwater discharge, water balance, salt balance, hydrological
GROUNDWATER DISCHARGE INTO THE WORLD OCEAN Zektser I.S. Water Problems Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia Keywords: groundwater discharge, water balance, salt balance, hydrological
WATER AS A SCARCE. Manuel Sapiano Regulation Unit Malta Resources Authority
 WATER AS A SCARCE NATIONAL RESOURCE Manuel Sapiano Regulation Unit Malta Resources Authority Introduction (1) WATER SCARCITY a situation where insufficient water resources are available to satisfy long-term
WATER AS A SCARCE NATIONAL RESOURCE Manuel Sapiano Regulation Unit Malta Resources Authority Introduction (1) WATER SCARCITY a situation where insufficient water resources are available to satisfy long-term
12th Session of the Commission on Sustainable Development. Statement By Christophe Yvetot International Atomic Energy Agency
 12th Session of the Commission on Sustainable Development Statement By Christophe Yvetot International Atomic Energy Agency Thursday, 29 April 2004 UNHQ, New York Mr. Chairman, Excellencies, distinguished
12th Session of the Commission on Sustainable Development Statement By Christophe Yvetot International Atomic Energy Agency Thursday, 29 April 2004 UNHQ, New York Mr. Chairman, Excellencies, distinguished
A d i l N a j a m Pardee Center for the study of the Longer-Term Future B o s t o n U n i v e r s i t y
 A d i l N a j a m The Fredrick S. Pardee Chair for Global Public Policy Pardee Center for the study of the Longer-Term Future B o s t o n U n i v e r s i t y How can ECOSOC and AMR foster integration of
A d i l N a j a m The Fredrick S. Pardee Chair for Global Public Policy Pardee Center for the study of the Longer-Term Future B o s t o n U n i v e r s i t y How can ECOSOC and AMR foster integration of
Overview of Water Resources (Part 2): Groundwater in Sonoma Valley
 . Overview of Water Resources (Part 2): Groundwater in Sonoma Valley Marcus Trotta, PG, CHg Principal Hydrogeologist Sonoma County Water Agency Sonoma Valley Groundwater Sustainability Agency October 23,
. Overview of Water Resources (Part 2): Groundwater in Sonoma Valley Marcus Trotta, PG, CHg Principal Hydrogeologist Sonoma County Water Agency Sonoma Valley Groundwater Sustainability Agency October 23,
Investigation of sustainable development potential for Ulubey Aquifer System, Turkey
 doi:10.5194/piahs-364-513-2014 Evolving Water Resources Systems: Understanding, Predicting and Managing Water Society Interactions Proceedings of ICWRS2014, Bologna, Italy, June 2014 (IAHS Publ. 364, 2014).
doi:10.5194/piahs-364-513-2014 Evolving Water Resources Systems: Understanding, Predicting and Managing Water Society Interactions Proceedings of ICWRS2014, Bologna, Italy, June 2014 (IAHS Publ. 364, 2014).
Groundwater Management in Urban Area
 Groundwater Management in Urban Area N.Dörfliger of Changsha, May 2014 ASEM Seminar on Sustainable Management of Water resources in the context of urbanization Urban water cycle - facts > Outline Urban
Groundwater Management in Urban Area N.Dörfliger of Changsha, May 2014 ASEM Seminar on Sustainable Management of Water resources in the context of urbanization Urban water cycle - facts > Outline Urban
groundwater. Because watersheds are complex systems, each tends to respond differently to natural or human activities.
 The private development of Altos del María is located at an altitude between 550 and 1,000 meters above sea level in the environmentally sensitive Cordillera Central of Panama that separates the Pacific
The private development of Altos del María is located at an altitude between 550 and 1,000 meters above sea level in the environmentally sensitive Cordillera Central of Panama that separates the Pacific
Ingress of salinity in coastal area
 Ingress of salinity in coastal area P re p a re d B y : - Patel Hardik P. Patel Dax S. Patel Sapana S. Patel Hiral J. (En No.110780106034) (En No.110780106026) (EnNo.110780106011) (En No.110780106023)
Ingress of salinity in coastal area P re p a re d B y : - Patel Hardik P. Patel Dax S. Patel Sapana S. Patel Hiral J. (En No.110780106034) (En No.110780106026) (EnNo.110780106011) (En No.110780106023)
East Maui Watershed Partnership Adapted from Utah State University and University of Wisconsin Ground Water Project Ages 7 th -Adult
 INTRODUCTION What is groundwater? Water contained in saturated soil and rock materials below the surface of the earth. It is not NEW water, but is recycled water through the hydraulic cycle. The source
INTRODUCTION What is groundwater? Water contained in saturated soil and rock materials below the surface of the earth. It is not NEW water, but is recycled water through the hydraulic cycle. The source
Joint Spain-Algeria Initiative for Water Strategy in the Western Mediterranean Basin
 Joint Spain-Algeria Initiative for Water Strategy in the Western Mediterranean Basin Spain and Algeria are active members of the United Nations, the Union for the Mediterranean and the 5+5 Dialogue for
Joint Spain-Algeria Initiative for Water Strategy in the Western Mediterranean Basin Spain and Algeria are active members of the United Nations, the Union for the Mediterranean and the 5+5 Dialogue for
ScienceDirect. Identification of saltwater intrusion/assessment scheme in groundwater using the role of empirical knowledge
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Environmental Sciences 30 (2015 ) 291 296 International Conference on Environmental Forensics 2015 (ienforce2015) Identification of saltwater
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Environmental Sciences 30 (2015 ) 291 296 International Conference on Environmental Forensics 2015 (ienforce2015) Identification of saltwater
Coachella Valley Regional Water Management Group (CVRWMG)
 April 13, 2015 SNMP Overview Introduction Regulatory Framework Water Quality Objectives Basin Characterization Ambient Water Quality and Assimilative Capacity Estimate of Future Water Quality Salt and
April 13, 2015 SNMP Overview Introduction Regulatory Framework Water Quality Objectives Basin Characterization Ambient Water Quality and Assimilative Capacity Estimate of Future Water Quality Salt and
SIXTH INTERNATIONAL GROUNDWATER CONFERENCE (IGWC-2015)
 SIXTH INTERNATIONAL GROUNDWATER CONFERENCE (IGWC-2015) on Exploration, Assessment and Management of Groundwater Resources in Arid and Semi-Arid regions December 09-11, 2015 Organized jointly by Department
SIXTH INTERNATIONAL GROUNDWATER CONFERENCE (IGWC-2015) on Exploration, Assessment and Management of Groundwater Resources in Arid and Semi-Arid regions December 09-11, 2015 Organized jointly by Department
Renewable Energies in the MENA Region. Potential for Sustainable Energy Provision and Export to Europe
 MED-CSP TRANS-CSP AQUA-CSP : Potential for Sustainable Energy Provision and Export to Europe and Franz Trieb Institute of Technical Thermodynamics, German Aerospace Center (DLR) Project Partners German
MED-CSP TRANS-CSP AQUA-CSP : Potential for Sustainable Energy Provision and Export to Europe and Franz Trieb Institute of Technical Thermodynamics, German Aerospace Center (DLR) Project Partners German
IMPO P RT R AN A C N E C E O F G RO R UN U D N W
 Introduction IMPORTANCE OF GROUNDWATER Global Groundwater Situation ACWADAM s database Sources for presentation CGWB, various publications FAO-database Various United Nations publications. UN World Water
Introduction IMPORTANCE OF GROUNDWATER Global Groundwater Situation ACWADAM s database Sources for presentation CGWB, various publications FAO-database Various United Nations publications. UN World Water
Global Groundwater Withdrawal
 Global Groundwater Withdrawal Large withdrawals in North India, Western US, Middle East, Spain Global total ~630 km 3 More than 90% is used for irrigation Reported: Wada et al., 010 (IGRAC) Results agree
Global Groundwater Withdrawal Large withdrawals in North India, Western US, Middle East, Spain Global total ~630 km 3 More than 90% is used for irrigation Reported: Wada et al., 010 (IGRAC) Results agree
Groundwater quality in Hungary a general view
 Freshwater Contamination (Proceedings of Rabat Symposium S4, April-May 1997). IAHS Publ. no. 243, 1997 227 Groundwater quality in Hungary a general view EVA DESEO Institute for Environmental Management
Freshwater Contamination (Proceedings of Rabat Symposium S4, April-May 1997). IAHS Publ. no. 243, 1997 227 Groundwater quality in Hungary a general view EVA DESEO Institute for Environmental Management
4. Pressures on groundwater quantity
 Pressures on groundwater quantity 39 4. Pressures on groundwater quantity 4.1 Groundwater abstraction 4.1.1 Geographical situation The vulnerability of an aquifer to overexploitation depends on its type,
Pressures on groundwater quantity 39 4. Pressures on groundwater quantity 4.1 Groundwater abstraction 4.1.1 Geographical situation The vulnerability of an aquifer to overexploitation depends on its type,
Management of aquifer recharge and discharge processes and aquifer storage equilibrium
 A Global Framework for Action GEF-FAO Governance Project A Global Framework for Country Action Digest 1 of Thematic Paper 4: Management of aquifer recharge and discharge processes and aquifer storage equilibrium
A Global Framework for Action GEF-FAO Governance Project A Global Framework for Country Action Digest 1 of Thematic Paper 4: Management of aquifer recharge and discharge processes and aquifer storage equilibrium
TSUNAMI DISASTER AND GROUNDWATER RESOURCES: THE SOUTHEASTERN COAST OF INDIA. Bhanu Neupane Regional Hydrologist, UNESCO
 TSUNAMI DISASTER AND GROUNDWATER RESOURCES: THE SOUTHEASTERN COAST OF INDIA Bhanu Neupane Regional Hydrologist, UNESCO Background On December 26, 2004, Tsunami waves struck the coast of the Indian subcontinent
TSUNAMI DISASTER AND GROUNDWATER RESOURCES: THE SOUTHEASTERN COAST OF INDIA Bhanu Neupane Regional Hydrologist, UNESCO Background On December 26, 2004, Tsunami waves struck the coast of the Indian subcontinent
Water Availability and Use Science Program. WestFAST September 24, 2015
 Water Availability and Use Science Program WestFAST September 24, 2015 WAUSP Objective To place technical information and tools in the hands of stakeholders, allowing them to answer questions they face
Water Availability and Use Science Program WestFAST September 24, 2015 WAUSP Objective To place technical information and tools in the hands of stakeholders, allowing them to answer questions they face
Isotope hydrology: Stable isotopes in water resources assessment IAEA International Atomic Energy Agency
 Isotope hydrology: Stable isotopes in water resources assessment Luis Araguás Workshop on Flow-path characterization, Munich, 29 June 2010 International Atomic Energy Agency Isotope Hydrology Section Outline
Isotope hydrology: Stable isotopes in water resources assessment Luis Araguás Workshop on Flow-path characterization, Munich, 29 June 2010 International Atomic Energy Agency Isotope Hydrology Section Outline
International Association of Hydrogeologists
 International Association of Hydrogeologists Teodóra Szőcs International Association of Hydrogeologists Mining and Geological Survey of Hungary KINDRA Final Conference MAKING GROUNDWATER VISIBLE, ACCESSIBLE
International Association of Hydrogeologists Teodóra Szőcs International Association of Hydrogeologists Mining and Geological Survey of Hungary KINDRA Final Conference MAKING GROUNDWATER VISIBLE, ACCESSIBLE
Water ressources in Tunisiaare limitedand characterised by high spatial disparities.
 Tunisia ranks in the category of countries with the least resources water in the Mediterranean. For a population of 11 million, the total renewable water resources per capita is estimated to 415 m 3 (2014)
Tunisia ranks in the category of countries with the least resources water in the Mediterranean. For a population of 11 million, the total renewable water resources per capita is estimated to 415 m 3 (2014)
Groundwater in the Mekong Region Transboundary Aquifers
 Groundwater in the Mekong Region Transboundary Aquifers Felix Seebacher, PhD Information and Knowledge Management Programme Mekong River Commission Secretariat International Conference on Cooperation for
Groundwater in the Mekong Region Transboundary Aquifers Felix Seebacher, PhD Information and Knowledge Management Programme Mekong River Commission Secretariat International Conference on Cooperation for
The Hydrologic Cycle (with emphasis on groundwater)
 The Hydrologic Cycle (with emphasis on groundwater) The Hydrologic Cycle (viewed in series of steps) 1. Water evaporates from bodies of surface water and from land 2. As moist air is lifted, it cools and
The Hydrologic Cycle (with emphasis on groundwater) The Hydrologic Cycle (viewed in series of steps) 1. Water evaporates from bodies of surface water and from land 2. As moist air is lifted, it cools and
Groundwater Governance in Lebanon for Sustainable Development. Talal Darwish, Amin Shaban and Mouin Hamze
 Groundwater Governance in Lebanon for Sustainable Development Talal Darwish, Amin Shaban and Mouin Hamze National Council for Scientific Research, Beirut, Lebanon 1. Introduction Lebanon was described
Groundwater Governance in Lebanon for Sustainable Development Talal Darwish, Amin Shaban and Mouin Hamze National Council for Scientific Research, Beirut, Lebanon 1. Introduction Lebanon was described
MODELLING THE GROUNDWATER FLOW FOR ESTIMATING THE PUMPING COST OF IRRIGATION IN THE AQUIFER OF N. MOUDANIA, GREECE
 Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 MODELLING THE GROUNDWATER FLOW FOR ESTIMATING THE PUMPING COST OF IRRIGATION
Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 MODELLING THE GROUNDWATER FLOW FOR ESTIMATING THE PUMPING COST OF IRRIGATION
USE OF ISOTOPE HYDROLOGY FOR WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT. Report by the Director General
 International Atomic Energy Agency BOARD OF GOVERNORS GENERAL CONFERENCE Sub-Item 17(b) of the Conference s provisional agenda (GC(45)/1) B GC GOV/2001/33-GC(45)/16 14 August 2001 GENERAL Distr. Original:
International Atomic Energy Agency BOARD OF GOVERNORS GENERAL CONFERENCE Sub-Item 17(b) of the Conference s provisional agenda (GC(45)/1) B GC GOV/2001/33-GC(45)/16 14 August 2001 GENERAL Distr. Original:
D.G.S.W. Pitakumbura Manager (Groundwater Studies) Groundwater Section NWS&DB. Groundwater recharge or deep drainage or
 Groundwater Recharge and Extraction Techniques D.G.S.W. Pitakumbura Manager (Groundwater Studies) Groundwater Section NWS&DB What is Groundwater Recharge Groundwater recharge or deep drainage or deep percolation
Groundwater Recharge and Extraction Techniques D.G.S.W. Pitakumbura Manager (Groundwater Studies) Groundwater Section NWS&DB What is Groundwater Recharge Groundwater recharge or deep drainage or deep percolation
