NREM 407/507 WATERSHED MANAGEMENT
|
|
|
- Oscar Ramsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NREM 407/507 WATERSHED MANAGEMENT Please pick up Syllabus, Reading Material & Today s Lab on the Table in the Front Dick Schultz Instructor Sara Berges Teaching Assistant
2 January 13, Conduct Get To Know Each Other Exercises 2. Organize into Base Groups. 3. Review class syllabus. 4. Identify where water is located globally. 5. Determine how much water we use. 6. Discuss world water problems. 7. Begin discussion of hydrologic cycle 8. Please read pages 1-40 in Introduction-Weather-Climate Reading Material Handout and Chapters 1, 2, 3 in Rivers Run Dry
3 Activity 1 What did you do over Break? Take sheet with list of numerous activities & go around the room to find individuals who did them over break Have individuals sign the activity One person can sign your sheet only once Astana, Kazakhstan Shamsha Mashtaeva
4
5
6 Eurasian National University
7 Why Kazakhstan? Study Abroad Trips Summer 2009 China/Yangtze 40 N 20 N Three Gorges Dam
8 2009 Study Abroad Uganda School Gardens Food Security
9 Activity 1 What did you do over Break? Take sheet with list of numerous activities & go around the room to find individuals who did them over break Have individuals sign the activity One person can sign your sheet only once
10 Organize into Groups - Seating Plan Front of Room 233 Group 1 Group 5 Group 9 Group 2 Group 6 Group 10 Door Group 3 Group 4 Group 7 Group 8 Group 11 Group 12 Door
11 Activity 2 Team Tower Building You have 6 large marsh mellows, a cup of small ones and 20 toothpicks to build a tower. This is a nonverbal activity (no talking among team members or between teams will be allowed) Team members can move around the room to look at other team s creations but the whole exercise will only last 12 minutes. The team that builds the best tower will win the exercise. The whole class will vote on the best tower based on the following criteria: height, strength, beauty and creativity
12 Activity 2 Team Tower Building WOW! 2008 FIRST PLACE WINNERS
13 Activity 3 Three Facts and a Lie Team Building We would like each of you to share 4 things about yourself with you team members (things that they probably do not know) 3 should be truthful and 1 should be a lie Please write these on a piece of paper Then have a group go-around with each person sharing their four items and the others guessing which item is a lie Keep track of who correctly identifies the lies
14 Water Movement - The Hydrologic Cycle
15 How Much Precipitation Ends Up As Evaporation/Transpiration & Streamflow? Streamflow = Precipitation Evaporation/Transpiration + Soil Water Storage How much Precipitation in Iowa? ~ 34 in How much Evaporation/Transpriation? 2/3 P = 23 inches How much Streamflow? = 11 inches
16 Precipitation In Iowa 34 inches per year (38 inches in SE to 26 inches in NW) - Ave snowfall = 32 inches per year (40 in NE to 20 in in SE) Cold Arctic Air Mass Warm Air Mass 8 pm Last Night
17 How does water move through the landscape? 1 1 Watershed the land area that contributes water to a given point in a stream or river Watersheds vary in size depending on the size of stream. Stream orders The Small Order Streams Are In Closest Contact With The Land Most Influenced By Land Uses
18 Most watersheds are part of larger watersheds College Creek Squaw Creek Skunk River Mississippi River
19 Page 18 & 19 Introduction Global Cycle 97% in Oceans 3% Fresh Water Where is all the water on the planet? Team Activity Organize the list of fresh water sources from largest to smallest & make an estimate of the % of fresh water in each. Of the Fresh Water (100%) Largest Atmosphere Glaciers Rivers Soil Moisture Groundwater Lakes Biosphere (plants & animals) Smallest
20 Where is all the fresh water on the planet? Global Cycle 97% in Oceans 3% Fresh Water Of the Fresh Water (100%) 0.06% Soil Moisture 69% Glaciers 0.04% Atmosphere 30% Groundwater 0.006% Rivers 0.3% Lakes 0.003% Biosphere (plants & animals)
21 NREM 407/507 WATERSHED MANAGEMENT Laboratory Review Syllabus Brief review of class discussion Hydrologic Cycle Terms, pathways & sinks Dick Schultz Instructor Sara Berges Teaching Assistant
22 Water Movement - The Hydrologic Cycle
23 How Much Precipitation Ends Up As Evaporation/Transpiration & Streamflow? Streamflow = Precipitation Evaporation/Transpiration + Soil Water Storage How much Precipitation in Iowa? ~ 34 in How much Evaporation/Transpriation? 2/3 P = 23 inches How much Streamflow? = 11 inches
24 Precipitation In Iowa 34 inches per year (38 inches in SE to 26 inches in NW) - Ave snowfall = 32 inches per year (40 in NE to 20 in in SE) Cold Arctic Air Mass Warm Air Mass 8 pm Last Night
25 How does water move through the landscape? 1 1 Watershed the land area that contributes water to a given point in a stream or river Watersheds vary in size depending on the size of stream. Stream orders The Small Order Streams Are In Closest Contact With The Land Most Influenced By Land Uses
26 Most watersheds are part of larger watersheds College Creek Squaw Creek Skunk River Mississippi River
27 Where is all the fresh water on the planet? Global Cycle 97% in Oceans 3% Fresh Water Of the Fresh Water (100%) 0.06% Soil Moisture 69% Glaciers 0.04% Atmosphere 30% Groundwater 0.006% Rivers 0.3% Lakes 0.003% Biosphere (plants & animals)
28 Page 17 Introduction Handout
29 Today s Laboratory Exercise How Does Water Move Through a Watershed? What pathways does it follow? What are the major storage sinks for water? Be able to use hydrologic & watershed terms to describe pathways & sinks for water Give reasonable definitions for 50% of terms by the end of today & all terms by the end of two weeks. Work comfortably & supportively with your team North Platte River Wyoming
30 What paths can a raindrop take before reaching a stream?
31 Pathways Above the Soil Through Watersheds Precipitation Canopy Interception Throughfall Stemflow Litter Interception Water Entering Soil Channel Interception Plant material protects the soil! (Living or Dead)
32 Corn transpires 4,000 gal/acre/day 140 day growing season ~ 500,000 gal/ac/year Forest transpires 200,000 1 million gallons/acre/year Water lost from forests in US = 3 X the amount of water used by people This water critical to producing rainfall to redistribute water around the globe
33 Forests of US receive ½ of precip & produce 2/3 of streamflow (90% in west)
34 If soil is exposed no perennial plants (forest/prairie) or litter layer Water erosion & transport can occur Streams carry excess sediment reduced water quality & disturbed aquatic habitat
35 Infiltration vs Runoff Infiltration rates crop fields: inches/hr Natural prairies & forests: 3 5 inches/hr
36 Movement of Water to Streams
37 ET Atmospheric Sink (Storage) Input (Rain, Snow, Condensation) Sinks/Sources Pathways WT Losing Stream Plant Storage Bed Load Plant Canopy Storage Suspended Load Healthy Watershed Hydrologic Cycle Gaining Stream Surface Interception Surface/Depression Storage Return flow Soil Water Storage Detention/Retention Capillary Fringe Water Table Sheet, rill Gully flow Infiltration Groundwater Storage Seepage Percolation Liquid Watershed Output Subsurface Flow Subsurface Storm flow Stream Channel Storage Bank Storage Page 36 Reading
38 Group I precipitation interception interception storage (identify sink) depression storage surface storage (identify sink) channel interception channel storage(identify sink) Group 2 stemflow throughfall infiltration Percolation Group 3 surface runoff /overland flow sheet flow rill flow gully flow suspended sediment Sedimentation Group 4 plant uptake plant storage (identify sink) transpiration evaporation Evapotranspiration Page 6 of Lab Team Vocabulary Responsibilities Be prepared to describe & discuss assigned terms Terms described starting page 3 of Reading Guide Group 5 subsurface flow/interflow soil macro/micropores detention storage (identify sink) retention storage (identify sink) Group 6 soil water storage (identify sink) antecedent soil moisture return flow /exfiltration saturated overland flow subsurface stormflow Group 7 water table capillary fringe shallow groundwater storage (identify sink) unconfined aquifer confined aquifer Group 8 ephemeral channel intermittent channel perennial channel Group 9 bank storage (identify sink) influent (losing) stream (be able to draw) effluent (gaining) stream (be able to draw) Group 10 dissolved load suspended load bed load stormflow baseflow Group 11 vadose zone interflow hyphoreic zone NPSP TSS Invertebrates Group 12 watershed sub-watershed ecosystem riparian area
39 Sinks/Sources Pathways Lab Action 1 Fill in the blanks & learn what is going on Healthy Watershed Hydrologic Cycle Liquid Watershed Output
40 ET Atmospheric Sink (Storage) Input (Rain, Snow, Condensation) Sinks/Sources Pathways WT Losing Stream Plant Storage Bed Load Plant Canopy Storage Suspended Load Surface Interception Surface/Depression Storage Return flow Soil Water Storage Detention/Retention Capillary Fringe Water Table Sheet, rill Gully flow Infiltration Groundwater Storage Seepage Percolation Liquid Watershed Output Subsurface Flow Subsurface Storm flow Stream Channel Storage Bank Storage Page 36 Introduction Handout
41 Compare Water Movement Between Disturbed & Undisturbed Watersheds
42 Water Movement In Disturbed & Undisturbed Watersheds Crop Field Native Forest or Prairie Precipitation Interception Precipitation Interception Evapotranspiration Evapotranspiration Stemflow Throughfall Stemflow Throughfall Infiltration Infiltration Percolation Water Table Unconfined Aquifer Surface Runoff Groundwater Plant Uptake Subsurface flow Confined Aquifer Surface Runoff Plant Uptake Groundwater Percolation Water Table
43 Water Movement In Disturbed & Undisturbed Watersheds Crop Field Native Forest or Prairie Precipitation Interception Precipitation Interception Evapotranspiration Evapotranspiration Stemflow Throughfall Stemflow Throughfall Infiltration Infiltration Percolation Water Table Unconfined Aquifer Surface Runoff Groundwater Plant Uptake Subsurface flow Confined Aquifer Surface Runoff Plant Uptake Groundwater Percolation Water Table
NREM 407/507 WATERSHED MANAGEMENT Day 2
 NREM 407/507 WATERSHED MANAGEMENT 1-15-09 - Day 2 1. Review Hydrologic Cycle Terminology/Model 2. Summarize Differences Cropfield vs Perennial Watershed 3. Tues Lab Develop International River PPT bring
NREM 407/507 WATERSHED MANAGEMENT 1-15-09 - Day 2 1. Review Hydrologic Cycle Terminology/Model 2. Summarize Differences Cropfield vs Perennial Watershed 3. Tues Lab Develop International River PPT bring
Introduction. Welcome to the Belgium Study Abroad Program. Courses:
 Introduction Welcome to the Belgium Study Abroad Program Courses: AGSM 335: Soil and Water Management BAEN 460: Principals of Environmental Hydrology BAEN 460 / AGSM 335 Combined lecture and HW sessions
Introduction Welcome to the Belgium Study Abroad Program Courses: AGSM 335: Soil and Water Management BAEN 460: Principals of Environmental Hydrology BAEN 460 / AGSM 335 Combined lecture and HW sessions
Hydrologic cycle, runoff process
 Hydrologic cycle, runoff process Motivation of hydrological modelling What happens at the catchment and in the stream when it rains? How does the increased/decreased runoff affect (not only) the landowners
Hydrologic cycle, runoff process Motivation of hydrological modelling What happens at the catchment and in the stream when it rains? How does the increased/decreased runoff affect (not only) the landowners
BAEN 673 / February 18, 2016 Hydrologic Processes
 BAEN 673 / February 18, 2016 Hydrologic Processes Assignment: HW#7 Next class lecture in AEPM 104 Today s topics SWAT exercise #2 The SWAT model review paper Hydrologic processes The Hydrologic Processes
BAEN 673 / February 18, 2016 Hydrologic Processes Assignment: HW#7 Next class lecture in AEPM 104 Today s topics SWAT exercise #2 The SWAT model review paper Hydrologic processes The Hydrologic Processes
Welcome to the MWON Advanced Webinar Series
 Welcome to the MWON Advanced Webinar Series Today s presentation: The Importance of Forests to Streams and Groundwater You will need to have speakers attached to your computer to hear the presenter. You
Welcome to the MWON Advanced Webinar Series Today s presentation: The Importance of Forests to Streams and Groundwater You will need to have speakers attached to your computer to hear the presenter. You
Unit 2: Weather Dynamics Chapter 1: Hydrological Cycle
 UNIT 2 Chapter 1: Inquiring about Weather Unit 2: Weather Dynamics Chapter 1: Hydrological Cycle Science 10 Mrs. Purba Importance of H 2 O From the beginning of time when water first appeared, it has been
UNIT 2 Chapter 1: Inquiring about Weather Unit 2: Weather Dynamics Chapter 1: Hydrological Cycle Science 10 Mrs. Purba Importance of H 2 O From the beginning of time when water first appeared, it has been
DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY POST GRADUATE GOVT. COLLEGE FOR GIRLS.SECTOR-11 CHANDIGARH CLASS-B.A.II PAPER-A RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT: WORLD PATTERNS
 DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY POST GRADUATE GOVT. COLLEGE FOR GIRLS.SECTOR-11 CHANDIGARH CLASS-B.A.II PAPER-A RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT: WORLD PATTERNS Hydrological cycle The sun, which drives the water cycle,
DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY POST GRADUATE GOVT. COLLEGE FOR GIRLS.SECTOR-11 CHANDIGARH CLASS-B.A.II PAPER-A RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT: WORLD PATTERNS Hydrological cycle The sun, which drives the water cycle,
Single most important determinant of the establishment and maintenance of specific types of wetlands & wetland processes
 Wetland Ecology Lectures 12 & 13 Wetland Hydrology Hydrology Single most important determinant of the establishment and maintenance of specific types of wetlands & wetland processes Starting point of hydrological
Wetland Ecology Lectures 12 & 13 Wetland Hydrology Hydrology Single most important determinant of the establishment and maintenance of specific types of wetlands & wetland processes Starting point of hydrological
CHAPTER ONE : INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER ONE : INTRODUCTION WHAT IS THE HYDROLOGY? The Hydrology means the science of water. It is the science that deals with the occurrence, circulation and distribution of water of the earth and earth
CHAPTER ONE : INTRODUCTION WHAT IS THE HYDROLOGY? The Hydrology means the science of water. It is the science that deals with the occurrence, circulation and distribution of water of the earth and earth
Lecture 11: Water Flow; Soils and the Hydrologic Cycle
 Lecture 11: Water Flow; Soils and the Hydrologic Cycle Water Flow in Soils Types of Water Flow in Soil Saturated flow: Soil pores completely filled with water; controlled by the hydrostatic potential After
Lecture 11: Water Flow; Soils and the Hydrologic Cycle Water Flow in Soils Types of Water Flow in Soil Saturated flow: Soil pores completely filled with water; controlled by the hydrostatic potential After
The Hydrological Cycle. Hydrological Cycle. Definition of Terms. Soils and Water, Spring Lecture 7, The Hydrological Cycle 1
 The Hydrological Cycle Water vapor helps warm up the earth Evaporation+Transpiration Chemical Spill Runoff To Oceans Water potential, atmosphere Hydrological Cycle Transpiration, T Atmospheric pool Interception
The Hydrological Cycle Water vapor helps warm up the earth Evaporation+Transpiration Chemical Spill Runoff To Oceans Water potential, atmosphere Hydrological Cycle Transpiration, T Atmospheric pool Interception
Topic 5. Water in the Atmosphere, Surface, and Subsurface. Unique Properties of Water Heat Properties 10/24/2017. Phase Changes
 Topic 5 Water in the Atmosphere, Surface, and Subsurface Properties of Water Omit Humidity and Atmospheric Moisture Distribution of Water The Hydrologic Cycle The Water Balance Concept Groundwater Characteristics
Topic 5 Water in the Atmosphere, Surface, and Subsurface Properties of Water Omit Humidity and Atmospheric Moisture Distribution of Water The Hydrologic Cycle The Water Balance Concept Groundwater Characteristics
Hydrology 101. Impacts of the Urban Environment. Nokomis Knolls Pond Summer June 2008
 Hydrology 101 Nokomis Knolls Pond Summer 2002 Impacts of the Urban Environment Hydrologic Cycle; What is it? Geography, Topography, Geology, Land Cover and Climate determine the Amount and Behavior of
Hydrology 101 Nokomis Knolls Pond Summer 2002 Impacts of the Urban Environment Hydrologic Cycle; What is it? Geography, Topography, Geology, Land Cover and Climate determine the Amount and Behavior of
Hydrologic Cycle. Rain Shadow:
 Hydrologic Cycle The cyclical movement of water from the ocean to the atmosphere by evaporation, to the surface through precipitation, to streams through runoff and groundwater, and back to the ocean.
Hydrologic Cycle The cyclical movement of water from the ocean to the atmosphere by evaporation, to the surface through precipitation, to streams through runoff and groundwater, and back to the ocean.
Inputs. Outputs. Component/store. Section of a system where material or energy is held. Something that enters the system (material or energy)
 .. Inputs Something that enters the system (material or energy) Outputs Something that leaves the system (material or energy) Component/store Section of a system where material or energy is held Transfer/flow
.. Inputs Something that enters the system (material or energy) Outputs Something that leaves the system (material or energy) Component/store Section of a system where material or energy is held Transfer/flow
WASA Quiz Review. Chapter 2
 WASA Quiz Review Chapter 2 Question#1 What is surface runoff? part of the water cycle that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed into groundwater or evaporating Question #2 What are
WASA Quiz Review Chapter 2 Question#1 What is surface runoff? part of the water cycle that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed into groundwater or evaporating Question #2 What are
4.2 The Water Cycle. Recycling water. Sharing water with the dinosaurs. The Sun drives the water cycle. Wind and weather. Gravity
 4.2 The Water Cycle The Sun keeps water moving through the hydrosphere by providing energy. In this section, you will learn about the water cycle and where water goes so that it is available for people,
4.2 The Water Cycle The Sun keeps water moving through the hydrosphere by providing energy. In this section, you will learn about the water cycle and where water goes so that it is available for people,
What is a Watershed? Understanding Surface Runoff. Controlling Erosion and Sediment.
 What is a Watershed? Understanding Surface Runoff. Controlling Erosion and Sediment. Aleksey Sheshukov Assistant Professor and Water-Quality Specialist Biological & Agricultural Engineering ashesh@ksu.edu,
What is a Watershed? Understanding Surface Runoff. Controlling Erosion and Sediment. Aleksey Sheshukov Assistant Professor and Water-Quality Specialist Biological & Agricultural Engineering ashesh@ksu.edu,
Module 8: Weathering, Erosion, and Groundwater Topic 5 Content: The Water Cycle Presentation Notes. The Water Cycle
 The Water Cycle 1 Imagine taking a trip around the water cycle as a single drop of water. This cycle has no beginning or ending point, so it does not matter where the trip starts. Since over 70% of the
The Water Cycle 1 Imagine taking a trip around the water cycle as a single drop of water. This cycle has no beginning or ending point, so it does not matter where the trip starts. Since over 70% of the
Physically-based Distributed Hydrologic Modeling
 Physically-based Distributed Hydrologic Modeling Goal of Phys.-based Distrib. Hydrologic Modeling To date we have learned about: Key forcings at land surface (precipitation/net radiation) Physical processes
Physically-based Distributed Hydrologic Modeling Goal of Phys.-based Distrib. Hydrologic Modeling To date we have learned about: Key forcings at land surface (precipitation/net radiation) Physical processes
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Engineering Hydrology Chapter 1 Introduction 2016-2017 Hydrologic Cycle Hydrologic Cycle Processes Processes Precipitation Atmospheric water Evaporation Infiltration Surface Runoff Land Surface Soil water
Engineering Hydrology Chapter 1 Introduction 2016-2017 Hydrologic Cycle Hydrologic Cycle Processes Processes Precipitation Atmospheric water Evaporation Infiltration Surface Runoff Land Surface Soil water
Hydrologic Cycle. Water Availabilty. Surface Water. Groundwater
 Hydrologic Cycle Hydrologic ydoogccyce cycle Surface Water Groundwater Water Availabilty 1 Hydrologic Cycle Constant movement of water above, on, and, below the earth s surface (Heath) Endless circulation
Hydrologic Cycle Hydrologic ydoogccyce cycle Surface Water Groundwater Water Availabilty 1 Hydrologic Cycle Constant movement of water above, on, and, below the earth s surface (Heath) Endless circulation
Hydrology Review, New paradigms, and Challenges
 Hydrology Review, New paradigms, and Challenges Intent quick introduction with emphasis on aspects related to watershed hydrochemistry and new paradigms Watershed / Catchment Definition Portion of landscape
Hydrology Review, New paradigms, and Challenges Intent quick introduction with emphasis on aspects related to watershed hydrochemistry and new paradigms Watershed / Catchment Definition Portion of landscape
THE IMPORTANCE OF NATURAL WATERSHED HYDROLOGY AND HOW TO ADVANCE IT IN URBAN AREAS
 THE IMPORTANCE OF NATURAL WATERSHED HYDROLOGY AND HOW TO ADVANCE IT IN URBAN AREAS Pacific Northwest Forest Hydrology Surface runoff rare, slow sheet flow when it occurs Trees Intercept rainfall, evaporate
THE IMPORTANCE OF NATURAL WATERSHED HYDROLOGY AND HOW TO ADVANCE IT IN URBAN AREAS Pacific Northwest Forest Hydrology Surface runoff rare, slow sheet flow when it occurs Trees Intercept rainfall, evaporate
Workshop 1 Our Groundwater and Surfacewaters are Connected and We are What We Drink Hosted by: Lackawanna County Conservation District
 Workshop 1 Our Groundwater and Surfacewaters are Connected and We are What We Drink Hosted by: Lackawanna County Conservation District Sponsored by: Pocono Northeast RC&D Council Through the C-SAW C Program
Workshop 1 Our Groundwater and Surfacewaters are Connected and We are What We Drink Hosted by: Lackawanna County Conservation District Sponsored by: Pocono Northeast RC&D Council Through the C-SAW C Program
4. Ponds and infiltration BMPs can achieve 60 to 100% removal efficiencies for sediment.
 Landscape BMPs For the purposes of this project, preventive measures have been categorized into two categories: landscape BMPs and source prevention BMPs. Landscape BMPs includes both vegetative practices
Landscape BMPs For the purposes of this project, preventive measures have been categorized into two categories: landscape BMPs and source prevention BMPs. Landscape BMPs includes both vegetative practices
KARTIK SHARMA LECT. IN CIVIL ENGINEERING GGSGP CHEEKA
 The Hydrological Cycle KARTIK SHARMA LECT. IN CIVIL ENGINEERING GGSGP CHEEKA The Hydrological Cycle What you need to know: Be able to draw a diagram of the hydrological cycle. Describe its main elements.
The Hydrological Cycle KARTIK SHARMA LECT. IN CIVIL ENGINEERING GGSGP CHEEKA The Hydrological Cycle What you need to know: Be able to draw a diagram of the hydrological cycle. Describe its main elements.
WATER AND THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE
 WATER AND THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE Summary Water is essential for the support of life and can be considered as a fundamental environmental good. Water is needed to support human habitation, grow crops and
WATER AND THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE Summary Water is essential for the support of life and can be considered as a fundamental environmental good. Water is needed to support human habitation, grow crops and
Timing Key Narrative Snapshots a) 00:44 How does groundwater recharge occur? How do streams form?
 Module 4 Narration: Runoff and Recharge Timing Key Narrative Snapshots a) 00:44 How does groundwater recharge occur? How do streams form? These processes are closely linked. Lets first investigate how
Module 4 Narration: Runoff and Recharge Timing Key Narrative Snapshots a) 00:44 How does groundwater recharge occur? How do streams form? These processes are closely linked. Lets first investigate how
Hydrology and Water Management. Dr. Mujahid Khan, UET Peshawar
 Hydrology and Water Management Dr. Mujahid Khan, UET Peshawar Course Outline Hydrologic Cycle and its Processes Water Balance Approach Estimation and Analysis of Precipitation Data Infiltration and Runoff
Hydrology and Water Management Dr. Mujahid Khan, UET Peshawar Course Outline Hydrologic Cycle and its Processes Water Balance Approach Estimation and Analysis of Precipitation Data Infiltration and Runoff
River Channel Characteristics
 River Channel Characteristics Storages and Transfers in Drainage Basins Precipitation Evapotranspiration SURFACE STORAGE INTERCEPTION STORAGE CHANNEL STORAGE Soil Moisture Storage Aeration Zone Storage
River Channel Characteristics Storages and Transfers in Drainage Basins Precipitation Evapotranspiration SURFACE STORAGE INTERCEPTION STORAGE CHANNEL STORAGE Soil Moisture Storage Aeration Zone Storage
2.A Hydrologic and Hydraulic Processes 2.B Geomorphic Processes 2.C Chemical Processes 2.D Biological Processes
 2.A Hydrologic and Hydraulic Processes Where does stream flow come from? What processes affect or are involved with stream flow? How fast, how much, how deep, how often and when does water flow? How is
2.A Hydrologic and Hydraulic Processes Where does stream flow come from? What processes affect or are involved with stream flow? How fast, how much, how deep, how often and when does water flow? How is
CEE6400 Physical Hydrology
 CEE6400 Physical Hydrology Midterm Review Learning Objectives (what you should be able to do) Hydrologic data, the hydrologic cycle and water balance (HW 1) Work with hydrologic data, quantify uncertainty
CEE6400 Physical Hydrology Midterm Review Learning Objectives (what you should be able to do) Hydrologic data, the hydrologic cycle and water balance (HW 1) Work with hydrologic data, quantify uncertainty
Rangeland Watersheds. Maintenance and provision of genetic resources Maintenance and regeneration of habitat Provision of shade and shelter
 Rangeland Watersheds What is a Watershed? A surface water designation The area that flows into a distinct drainage (i.e., stream, river, creek, pond) Separated from other watershed by ridge-top boundaries.
Rangeland Watersheds What is a Watershed? A surface water designation The area that flows into a distinct drainage (i.e., stream, river, creek, pond) Separated from other watershed by ridge-top boundaries.
NREM 301 Forest Ecology & Soils
 NREM 301 Forest Ecology & Soils Instructor: Dick Schultz WELCOME! Day 1 Please Pick Up Papers at Back of Room Objectives: Get to know each other Set up groups & conduct team building activity Introduction
NREM 301 Forest Ecology & Soils Instructor: Dick Schultz WELCOME! Day 1 Please Pick Up Papers at Back of Room Objectives: Get to know each other Set up groups & conduct team building activity Introduction
Stormwater Management in Your Backyard: Stormwater 101
 Stormwater Management in Your Backyard: Stormwater 101 Gregory Rusciano Program Associate, Water Resources Rutgers Cooperative Extension New Jersey Sea Grant Extension Program How much water do we have?
Stormwater Management in Your Backyard: Stormwater 101 Gregory Rusciano Program Associate, Water Resources Rutgers Cooperative Extension New Jersey Sea Grant Extension Program How much water do we have?
CHAPTER FIVE Runoff. Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) Instructors: Dr. Yunes Mogheir Dr. Ramadan Al Khatib. Overland flow interflow
 Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) CHAPTER FIVE Runoff Instructors: Dr. Yunes Mogheir Dr. Ramadan Al Khatib Overland flow interflow Base flow Saturated overland flow ١ ٢ 5.1 Introduction To Runoff Runoff
Engineering Hydrology (ECIV 4323) CHAPTER FIVE Runoff Instructors: Dr. Yunes Mogheir Dr. Ramadan Al Khatib Overland flow interflow Base flow Saturated overland flow ١ ٢ 5.1 Introduction To Runoff Runoff
Black River Watershed Management Plan Plan
 Black River Watershed Management Plan Plan Final Report Part II: Appendices May 2010 This watershed management plan was prepared for the New York State Department of State Division of Coastal Resources
Black River Watershed Management Plan Plan Final Report Part II: Appendices May 2010 This watershed management plan was prepared for the New York State Department of State Division of Coastal Resources
General Groundwater Concepts
 General Groundwater Concepts Hydrologic Cycle All water on the surface of the earth and underground are part of the hydrologic cycle (Figure 1), driven by natural processes that constantly transform water
General Groundwater Concepts Hydrologic Cycle All water on the surface of the earth and underground are part of the hydrologic cycle (Figure 1), driven by natural processes that constantly transform water
W A T E R F O R L I F E
 Module 4 The Hydrological Cycle Disclaimer: The contents of this presentation include original content as well as items compiled from a variety of sources. Though the sources are not attributed individually,
Module 4 The Hydrological Cycle Disclaimer: The contents of this presentation include original content as well as items compiled from a variety of sources. Though the sources are not attributed individually,
THE WATER CYCLE IN GREATER VICTORIA
 THE WATER CYCLE IN GREATER VICTORIA KEY CONCEPTS THE GREATER VICTORIA DRINKING WATER SUPPLY SYSTEM IS DEPENDENT ON ANNUAL PRECIPITATION, WHICH FALLS MOSTLY AS RAIN. RESPONSIBILITY FOR WATER IS EVERYONE
THE WATER CYCLE IN GREATER VICTORIA KEY CONCEPTS THE GREATER VICTORIA DRINKING WATER SUPPLY SYSTEM IS DEPENDENT ON ANNUAL PRECIPITATION, WHICH FALLS MOSTLY AS RAIN. RESPONSIBILITY FOR WATER IS EVERYONE
Runoff Processes. Daene C. McKinney
 CE 374 K Hydrology Runoff Processes Daene C. McKinney Watershed Watershed Area draining to a stream Streamflow generated by water entering surface channels Affected by Physical, vegetative, and climatic
CE 374 K Hydrology Runoff Processes Daene C. McKinney Watershed Watershed Area draining to a stream Streamflow generated by water entering surface channels Affected by Physical, vegetative, and climatic
Review of the Hydrologic Cycle & Streamflow Generation
 Quantitative Elements of Physical Hydrology Review of the Hydrologic Cycle & Streamflow Generation (Review) Contact information: Jack Hermance Environmental Geophysics/Hydrology Department of Geological
Quantitative Elements of Physical Hydrology Review of the Hydrologic Cycle & Streamflow Generation (Review) Contact information: Jack Hermance Environmental Geophysics/Hydrology Department of Geological
Watershed Health and Water Management in the Porcupine Hills
 Watershed Health and Water Management in the Porcupine Hills In Alberta, our quality of life is tied to healthy and sustainable water supplies for the environment, for our communities, and for our economic
Watershed Health and Water Management in the Porcupine Hills In Alberta, our quality of life is tied to healthy and sustainable water supplies for the environment, for our communities, and for our economic
56 JOURNAL OF THE ALABAMA ACADEMY OF SCIENCE
 Reprinted from the Journal of the Alabama. Academy of Science, Volume 29. October 1, 1957. SECTION IV EFFECTS OF LAND USE ON STREAMFLOW By DONALD E. WHELAN Coweeta Hydrologic Laboratory, Dillard, Georgia
Reprinted from the Journal of the Alabama. Academy of Science, Volume 29. October 1, 1957. SECTION IV EFFECTS OF LAND USE ON STREAMFLOW By DONALD E. WHELAN Coweeta Hydrologic Laboratory, Dillard, Georgia
Water Asset Account in Physical Terms
 Water Asset Account in Physical Terms Regional Training Workshop on the System of Environmental-Economic Accounting with a Focus on Water Accounting September 26-30, 2016 Putrajaya, Malaysia François Soulard
Water Asset Account in Physical Terms Regional Training Workshop on the System of Environmental-Economic Accounting with a Focus on Water Accounting September 26-30, 2016 Putrajaya, Malaysia François Soulard
How could we possibly change the Hydrologic Cycle on an Island as big as Vancouver Island?
 How could we possibly change the Hydrologic Cycle on an Island as big as Vancouver Island? Do you think for a moment that humans altering the Hydrologic Cycle would also change the Weather? Precipitation
How could we possibly change the Hydrologic Cycle on an Island as big as Vancouver Island? Do you think for a moment that humans altering the Hydrologic Cycle would also change the Weather? Precipitation
TB pg Liquid. Ice. Vapour. Surface water Underground water. Poles Icebergs Permafrost. Atmosphere
 The Hydrosphere TB pg. 227 Liquid Surface water Underground water Ice Poles Icebergs Permafrost Vapour Atmosphere TB pg. 228 Living organisms depend on it. Bodily structure of living organisms (cells,
The Hydrosphere TB pg. 227 Liquid Surface water Underground water Ice Poles Icebergs Permafrost Vapour Atmosphere TB pg. 228 Living organisms depend on it. Bodily structure of living organisms (cells,
The Hydrosphere. Introduction To Surface Water. What Do You Think?
 Introduction To Surface Water Unit Essential Questions: How does the Earth cycle its water through its major reservoirs? How does society s use of resources affect water quality? Presentation Objectives:
Introduction To Surface Water Unit Essential Questions: How does the Earth cycle its water through its major reservoirs? How does society s use of resources affect water quality? Presentation Objectives:
are sufficiently different that his models are not useful to us at this stage. We anticipate, however, that he can provide submodels
 INTERNAL REPORT 20 HYDROLOGIC MODEL FOR WATERSHED 10, ANDREWS EXPERIMENTAL FOREST Round 1 George Brown, Dick Fredriksen, and Scott Overton School of Forestry, Oregon State University BACKGROUND Watershed
INTERNAL REPORT 20 HYDROLOGIC MODEL FOR WATERSHED 10, ANDREWS EXPERIMENTAL FOREST Round 1 George Brown, Dick Fredriksen, and Scott Overton School of Forestry, Oregon State University BACKGROUND Watershed
The Water Cycle and Water Insecurity
 The Water Cycle and Water Insecurity EQ1: What are the processes operating within the hydrological cycle from global to local scale? 6 & 8 markers = AO1. 12 & 20 markers = AO1 and AO2 larger weighting
The Water Cycle and Water Insecurity EQ1: What are the processes operating within the hydrological cycle from global to local scale? 6 & 8 markers = AO1. 12 & 20 markers = AO1 and AO2 larger weighting
3F. Hydrology and Water Quality
 This section provides an analysis of potential hydrological and water quality impacts associated with implementation of the proposed project. The section also evaluates and describes the potential impacts
This section provides an analysis of potential hydrological and water quality impacts associated with implementation of the proposed project. The section also evaluates and describes the potential impacts
Estimating Groundwater Recharge within Wisconsin s Central Sands
 Estimating Groundwater Recharge within Wisconsin s Central Sands Adam Freihoefer and Robert Smail Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources [study objective] Identify a defensible approach to quantify
Estimating Groundwater Recharge within Wisconsin s Central Sands Adam Freihoefer and Robert Smail Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources [study objective] Identify a defensible approach to quantify
Aquatic Science Unit 1. Introduction to Freshwater Ecology
 Aquatic Science Unit 1 Introduction to Freshwater Ecology Water is essential to life Water is essential to the survival of all living things No living organism can survive without water Humans cannot go
Aquatic Science Unit 1 Introduction to Freshwater Ecology Water is essential to life Water is essential to the survival of all living things No living organism can survive without water Humans cannot go
Hydrogeology of Prince Edward Island
 Hydrogeology of Prince Edward Island General Characteristics and Groundwater on Prince Edward Island General Characteristics and Key Issues Issues PEI Dept. of Environment, Energy and Forestry 9/29/2009
Hydrogeology of Prince Edward Island General Characteristics and Groundwater on Prince Edward Island General Characteristics and Key Issues Issues PEI Dept. of Environment, Energy and Forestry 9/29/2009
Overview of the Surface Hydrology of Hawai i Watersheds. Ali Fares Associate Professor of Hydrology NREM-CTAHR
 Overview of the Surface Hydrology of Hawai i Watersheds Ali Fares Associate Professor of Hydrology NREM-CTAHR 5/23/2008 Watershed Hydrology Lab 1 What is Hydrology? Hydrology is the water science that
Overview of the Surface Hydrology of Hawai i Watersheds Ali Fares Associate Professor of Hydrology NREM-CTAHR 5/23/2008 Watershed Hydrology Lab 1 What is Hydrology? Hydrology is the water science that
Unit 5 Lesson 1 What Is the Water Cycle? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Water on the Move warm up 1 Water on the Move About three-fourths of Earth s surface is covered by water. Water on the Move Video!!! Water on the Move Water moves between Earth s surface and the atmosphere
Water on the Move warm up 1 Water on the Move About three-fourths of Earth s surface is covered by water. Water on the Move Video!!! Water on the Move Water moves between Earth s surface and the atmosphere
Understanding Environmental Impacts of Horticulture
 Lesson A1 3 Understanding Environmental Impacts of Horticulture Unit A. Horticultural Science Problem Area 1. Exploring the Horticulture Industry Lesson 3. Understanding Environmental Impacts of Horticulture
Lesson A1 3 Understanding Environmental Impacts of Horticulture Unit A. Horticultural Science Problem Area 1. Exploring the Horticulture Industry Lesson 3. Understanding Environmental Impacts of Horticulture
Water Resources on PEI: an overview and brief discussion of challenges
 Water Resources on PEI: an overview and brief discussion of challenges Components: Components and links Atmospheric water Surface water (including glacial water) Groundwater Links: Precipitation (atm(
Water Resources on PEI: an overview and brief discussion of challenges Components: Components and links Atmospheric water Surface water (including glacial water) Groundwater Links: Precipitation (atm(
Forests and Water in the Sierra Nevada. Roger Bales, Sierra Nevada Research Institute, UC Merced
 Forests and Water in the Sierra Nevada Roger Bales, Sierra Nevada Research Institute, UC Merced Some motivating points Water is the highest-value ecosystem service associated with Sierra Nevada conifer
Forests and Water in the Sierra Nevada Roger Bales, Sierra Nevada Research Institute, UC Merced Some motivating points Water is the highest-value ecosystem service associated with Sierra Nevada conifer
M.L. Kavvas, Z. Q. Chen, M. Anderson, L. Liang, N. Ohara Hydrologic Research Laboratory, Civil and Environmental Engineering, UC Davis
 Assessment of the Restoration Activities on Water Balance and Water Quality at Last Chance Creek Watershed Using Watershed Environmental Hydrology (WEHY) Model M.L. Kavvas, Z. Q. Chen, M. Anderson, L.
Assessment of the Restoration Activities on Water Balance and Water Quality at Last Chance Creek Watershed Using Watershed Environmental Hydrology (WEHY) Model M.L. Kavvas, Z. Q. Chen, M. Anderson, L.
Water Science and the Environment HWRS 201
 Water Science and the Environment HWRS 201 Dr. Mr. Ghasemian 2015 Office hours and contact information Office hours MWF - or by appointment Starting Harshbarger 3 Contact 621- r @.arizona.edu D2L site
Water Science and the Environment HWRS 201 Dr. Mr. Ghasemian 2015 Office hours and contact information Office hours MWF - or by appointment Starting Harshbarger 3 Contact 621- r @.arizona.edu D2L site
Lesson 1.2 Recycling Matter
 Lesson 1.2 Recycling Matter Lesson Objectives Define biogeochemical cycles. Describe the water cycle and its processes. Give an overview of the carbon cycle. Outline the steps of the nitrogen cycle. Lesson
Lesson 1.2 Recycling Matter Lesson Objectives Define biogeochemical cycles. Describe the water cycle and its processes. Give an overview of the carbon cycle. Outline the steps of the nitrogen cycle. Lesson
NREM 301 Forest Ecology & Soils
 NREM 301 Forest Ecology & Soils Instructors: Dick Schultz/Leigh Ann Long TA: Nick Ohde Today s Objectives: Day 1 Please Pick Up Papers at Back of Room Get to know each other Set up groups & conduct team
NREM 301 Forest Ecology & Soils Instructors: Dick Schultz/Leigh Ann Long TA: Nick Ohde Today s Objectives: Day 1 Please Pick Up Papers at Back of Room Get to know each other Set up groups & conduct team
1.6 Influence of Human Activities and Land use Changes on Hydrologic Cycle
 1.6 Influence of Human Activities and Land use Changes on Hydrologic Cycle Watersheds are subjected to many types of changes, major or minor, for various reasons. Some of these are natural changes and
1.6 Influence of Human Activities and Land use Changes on Hydrologic Cycle Watersheds are subjected to many types of changes, major or minor, for various reasons. Some of these are natural changes and
CHAPTER 13 OUTLINE The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater. Hydrologic cycle. Hydrologic cycle cont.
 CHAPTER 13 OUTLINE The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. Hydrologic cycle The hydrologic cycle is
CHAPTER 13 OUTLINE The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. Hydrologic cycle The hydrologic cycle is
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition
 Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 17: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE AND GROUNDWATER Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors, Department of Geology, FUM Copyright 2007
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 17: THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE AND GROUNDWATER Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors, Department of Geology, FUM Copyright 2007
The Hydrologic Cycle. Floods 3 5. Flood Science LESSON PLAN 1. Key Terms and Concepts. Purposes. Objectives
 LESSON PLAN 1 The Hydrologic Cycle Floods It is important for children to understand the hydrologic cycle in preparation for learning the science behind floods and flash floods. Key Terms and Concepts
LESSON PLAN 1 The Hydrologic Cycle Floods It is important for children to understand the hydrologic cycle in preparation for learning the science behind floods and flash floods. Key Terms and Concepts
Hydrology Attribute 1/15/2016. California Rapid Assessment Method for Wetlands. Hydrology. Precipitation Increases the Extent of Wetlands
 California Rapid Assessment Method for Wetlands Hydrology Attribute Hydrology Determines existence of wetlands, drives primary physical and ecological processes: Establishment of reducing conditions Nutrient
California Rapid Assessment Method for Wetlands Hydrology Attribute Hydrology Determines existence of wetlands, drives primary physical and ecological processes: Establishment of reducing conditions Nutrient
Water Distribution Rivers
 Water Distribution Rivers Question 1 One of the main issues concerning fresh water is that most of it is found where? A. Glaciers and Icecaps B. Aquifers C. Underground D. Oceans Question 2 How does water
Water Distribution Rivers Question 1 One of the main issues concerning fresh water is that most of it is found where? A. Glaciers and Icecaps B. Aquifers C. Underground D. Oceans Question 2 How does water
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS
 Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS
 Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
Thanks to Bill Elliot, Research Leader U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service
 Thanks to Bill Elliot, Research Leader U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service To present an overview Forest Soil Erosion Processes 2 Precipitation or melting snow Evapotranspiration Infiltration
Thanks to Bill Elliot, Research Leader U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service To present an overview Forest Soil Erosion Processes 2 Precipitation or melting snow Evapotranspiration Infiltration
Precipitation Surface Cover Topography Soil Properties
 Precipitation Surface Cover Topography Soil Properties Intrinsic capacity of rainfall to cause erosion Influenced by Amount, intensity, terminal velocity, drop size and drop size distribution of rain.
Precipitation Surface Cover Topography Soil Properties Intrinsic capacity of rainfall to cause erosion Influenced by Amount, intensity, terminal velocity, drop size and drop size distribution of rain.
Watersheds and the Hydrologic Cycle
 Watersheds and the Hydrologic Cycle The Global Hydrologic Cycle Water Cycle in Florida Florida Water Facts Surface Area = 170,452 km 2 Average Rainfall = 140 cm (55 ) Total Annual Rain = 238 billion m
Watersheds and the Hydrologic Cycle The Global Hydrologic Cycle Water Cycle in Florida Florida Water Facts Surface Area = 170,452 km 2 Average Rainfall = 140 cm (55 ) Total Annual Rain = 238 billion m
Working with the Water Balance
 Working with the Water Balance Forest Hydrology and Land Use Change Paul K. Barten, Ph.D. Professor of Forestry and Hydrology Department of Environmental Conservation www.forest-to-faucet.org The Living
Working with the Water Balance Forest Hydrology and Land Use Change Paul K. Barten, Ph.D. Professor of Forestry and Hydrology Department of Environmental Conservation www.forest-to-faucet.org The Living
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS
 Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
CENTRAL COAST POST-CONSTRUCTION REQUIREMENTS IMPLEMENTATION GUIDANCE SERIES 1
 CENTRAL COAST POST-CONSTRUCTION REQUIREMENTS IMPLEMENTATION GUIDANCE SERIES 1 SERIES ISSUE #2: DECENTRALIZED STORMWATER MANAGEMENT TO COMPLY WITH RUNOFF RETENTION POST-CONSTRUCTION STORMWATER CONTROL REQUIREMENTS
CENTRAL COAST POST-CONSTRUCTION REQUIREMENTS IMPLEMENTATION GUIDANCE SERIES 1 SERIES ISSUE #2: DECENTRALIZED STORMWATER MANAGEMENT TO COMPLY WITH RUNOFF RETENTION POST-CONSTRUCTION STORMWATER CONTROL REQUIREMENTS
Water for Life Lesson
 Water for Life Lesson 1 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Objectives The student will be able to do the following: Explain
Water for Life Lesson 1 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Objectives The student will be able to do the following: Explain
This PowerPoint presentation can be downloaded from Ditch_10.asp. Slide 1. Slide 2
 Slide 1 This PowerPoint presentation can be downloaded from http://ei.cornell.edu/watersheds/ditches/ Ditch_10.asp. Roadside Ditches A Watershed Curriculum Module Rebecca Schneider, Nancy Trautmann, &
Slide 1 This PowerPoint presentation can be downloaded from http://ei.cornell.edu/watersheds/ditches/ Ditch_10.asp. Roadside Ditches A Watershed Curriculum Module Rebecca Schneider, Nancy Trautmann, &
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS
 Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
Nitrates and Row Cropping
 Nitrates and Row Cropping Matthew Helmers Dean s Professor, College of Ag. & Life Sciences Professor, Dept. of Ag. and Biosystems Eng. Iowa State University Corn Grain Harvest (~100 lbs N/acre/year) Corn
Nitrates and Row Cropping Matthew Helmers Dean s Professor, College of Ag. & Life Sciences Professor, Dept. of Ag. and Biosystems Eng. Iowa State University Corn Grain Harvest (~100 lbs N/acre/year) Corn
Lecture 1 Integrated water resources management and wetlands
 Wetlands and Poverty Reduction Project (WPRP) Training module on Wetlands and Water Resources Management Lecture 1 Integrated water resources management and wetlands 1 Water resources and use The hydrological
Wetlands and Poverty Reduction Project (WPRP) Training module on Wetlands and Water Resources Management Lecture 1 Integrated water resources management and wetlands 1 Water resources and use The hydrological
Computation of excess stormflow at the basin scale. Prof. Pierluigi Claps. Dept. DIATI, Politecnico di Torino
 Computation of excess stormflow at the basin scale Prof. Pierluigi Claps Dept. DIATI, Politecnico di Torino Pierluigi.claps@polito.it losses include: interception, evapotranspiration, storage infiltration,
Computation of excess stormflow at the basin scale Prof. Pierluigi Claps Dept. DIATI, Politecnico di Torino Pierluigi.claps@polito.it losses include: interception, evapotranspiration, storage infiltration,
1 INTRODUCTION. 1.1 Definition of Hydrology and Hydrometry
 INTRODUCTION 1 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Definition of Hydrology and Hydrometry Hydrology is a multidisciplinary subject that deals with the occurrence, circulation and distribution of the waters of the Earth.
INTRODUCTION 1 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Definition of Hydrology and Hydrometry Hydrology is a multidisciplinary subject that deals with the occurrence, circulation and distribution of the waters of the Earth.
HYDROLOGY WORKSHEET 1 PRECIPITATION
 HYDROLOGY WORKSHEET 1 PRECIPITATION A watershed is an area of land that captures rainfall and other precipitation and funnels it to a lake or stream or wetland. The area within the watershed where the
HYDROLOGY WORKSHEET 1 PRECIPITATION A watershed is an area of land that captures rainfall and other precipitation and funnels it to a lake or stream or wetland. The area within the watershed where the
Watersheds and the Hydrologic Cycle
 Watersheds and the Hydrologic Cycle The Global Hydrologic Cycle Water Cycle in Florida Florida Water Facts Surface Area = 170,452 km 2 Average Rainfall = 140 cm (55 ) Total Annual Rain = 238 billion m
Watersheds and the Hydrologic Cycle The Global Hydrologic Cycle Water Cycle in Florida Florida Water Facts Surface Area = 170,452 km 2 Average Rainfall = 140 cm (55 ) Total Annual Rain = 238 billion m
Watersheds & Water Pollution
 Watersheds & Water Pollution Runoff What is runoff? Review: When rain or snow falls onto the earth, it just doesn't sit there, it starts moving according to the laws of gravity. A portion of the precipitation
Watersheds & Water Pollution Runoff What is runoff? Review: When rain or snow falls onto the earth, it just doesn't sit there, it starts moving according to the laws of gravity. A portion of the precipitation
M.L. Kavvas, Z. Q. Chen, M. Anderson, L. Liang, N. Ohara Hydrologic Research Laboratory, Civil and Environmental Engineering, UC Davis
 Assessment of the Restoration Activities on Water Balance and Water Quality at Last Chance Creek Watershed Using Watershed Environmental Hydrology (WEHY) Model M.L. Kavvas, Z. Q. Chen, M. Anderson, L.
Assessment of the Restoration Activities on Water Balance and Water Quality at Last Chance Creek Watershed Using Watershed Environmental Hydrology (WEHY) Model M.L. Kavvas, Z. Q. Chen, M. Anderson, L.
Stream Hydrology. Watershed 8/29/13. Area that contributes water to a point on a stream Scale is user-defined Other names: Catchment Drainage basin
 Stream Hydrology Watershed Area that contributes water to a point on a stream Scale is user-defined Other names: Catchment Drainage basin http://warnercnr.colostate.edu/geo/front_range/poudre.php# 1 Basics
Stream Hydrology Watershed Area that contributes water to a point on a stream Scale is user-defined Other names: Catchment Drainage basin http://warnercnr.colostate.edu/geo/front_range/poudre.php# 1 Basics
East Maui Watershed Partnership Adapted from Utah State University and University of Wisconsin Ground Water Project Ages 7 th -Adult
 INTRODUCTION What is groundwater? Water contained in saturated soil and rock materials below the surface of the earth. It is not NEW water, but is recycled water through the hydraulic cycle. The source
INTRODUCTION What is groundwater? Water contained in saturated soil and rock materials below the surface of the earth. It is not NEW water, but is recycled water through the hydraulic cycle. The source
Ch 18. Hydrologic Cycle and streams. Tom Bean
 Ch 18. Hydrologic Cycle and streams Tom Bean Wednesday s outline 1. the hydrologic cycle reservoirs cycling between them Evaporation and the atmosphere 2. Surface hydrology infiltration and soil moisture
Ch 18. Hydrologic Cycle and streams Tom Bean Wednesday s outline 1. the hydrologic cycle reservoirs cycling between them Evaporation and the atmosphere 2. Surface hydrology infiltration and soil moisture
Effect of forest management on water yields & other ecosystem services in Sierra Nevada forests UCB/UC Merced/UCANR project
 Effect of forest management on water yields & other ecosystem services in Sierra Nevada forests UCB/UC Merced/UCANR project Some motivating points Water is the highest-value ecosystem service associated
Effect of forest management on water yields & other ecosystem services in Sierra Nevada forests UCB/UC Merced/UCANR project Some motivating points Water is the highest-value ecosystem service associated
Unit 2: Geomorphologic and Hydrologic Characteristics of Watersheds. ENVS 435: Watershed Management INSTR.: Dr. R.M. Bajracharya
 Unit 2: Geomorphologic and Hydrologic Characteristics of Watersheds ENVS 435: Watershed Management INSTR.: Dr. R.M. Bajracharya Watersheds are hydro-geologic units Water flow and cycling are basic and
Unit 2: Geomorphologic and Hydrologic Characteristics of Watersheds ENVS 435: Watershed Management INSTR.: Dr. R.M. Bajracharya Watersheds are hydro-geologic units Water flow and cycling are basic and
River Talk Patterns. Student Copy Page PART I (1 of 1) 3. Human nervous system. Waters and drainage patterns. Road system.
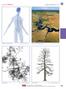 River Talk Patterns Student Copy Page PART I (1 of 1) 3 Human nervous system photo credit: Hemera Thinkstock Photos Waters and drainage patterns photo credit: Comstock Getty Images Road system photo credit:
River Talk Patterns Student Copy Page PART I (1 of 1) 3 Human nervous system photo credit: Hemera Thinkstock Photos Waters and drainage patterns photo credit: Comstock Getty Images Road system photo credit:
Air & Water Lesson 2. Chapter 6 Conserving Our Resources
 Air & Water Lesson 2 Chapter 6 Conserving Our Resources Objectives Summarize the importance of air. Describe the water cycle. Main Idea Living things use air and water to carry out their life processes.
Air & Water Lesson 2 Chapter 6 Conserving Our Resources Objectives Summarize the importance of air. Describe the water cycle. Main Idea Living things use air and water to carry out their life processes.
Term Info Picture. The process by which liquid water changes to gas. The process by which water vapor changes in to liquid water.
 Water Cycle S6E3. Obtain, evaluate and communicate information to recognize the significant role of water in Earth s processes. A. Ask questions to determine where water is located on Earth s surface (oceans,
Water Cycle S6E3. Obtain, evaluate and communicate information to recognize the significant role of water in Earth s processes. A. Ask questions to determine where water is located on Earth s surface (oceans,
UCS Mi-STAR Science 7 Semester 1 Midterm Exam Review Guide
 Name Date Hour 2018-2019 UCS Mi-STAR Science 7 Semester 1 Midterm Exam Review Guide Question How does cold air compare to warm air? Cold air weighs more than hot air. When a 9-centimeter balloon is filled
Name Date Hour 2018-2019 UCS Mi-STAR Science 7 Semester 1 Midterm Exam Review Guide Question How does cold air compare to warm air? Cold air weighs more than hot air. When a 9-centimeter balloon is filled
Effect of Land Surface on Runoff Generation
 Effect of Land Surface on Runoff Generation Context: Hydrologic Cycle Runoff vs Infiltration Infiltration: Process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil Runoff: Water (from rain, snowmelt,
Effect of Land Surface on Runoff Generation Context: Hydrologic Cycle Runoff vs Infiltration Infiltration: Process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil Runoff: Water (from rain, snowmelt,
Issue paper: Aquifer Water Balance
 Issue paper: Aquifer Water Balance 1. Introduction And Background 1.1. Purpose and Scope The population in Kitsap County has grown rapidly in recent years and is expected to increase substantially in the
Issue paper: Aquifer Water Balance 1. Introduction And Background 1.1. Purpose and Scope The population in Kitsap County has grown rapidly in recent years and is expected to increase substantially in the
