Answers. Unit 2 Nature s chemistry. Chapter 8 Fuels and energy 1: Fuels. Activity 8.1. Activity 8.2. Activity 8.3
|
|
|
- Harvey Blair
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NATURE S EMISTRY Answers Unit 2 Nature s chemistry hapter 8 Fuels and energy 1: Fuels Activity (a) Fossil fuels (b) ydrocarbons (c) Oxygen (d) arbon dioxide (e) Use p paper to test the p of droplets condensing on the test tube; the p should be 7. Use cobalt chloride paper which will turn from blue to pink in the presence of water. Activity (a) burned (b) energy (c) rude (d) coal (e) fossil (f) fuels (g) carbon (h) water (i) vegetable (j) proteins 2. (a) Oxygen (b) (i) To cool the tube and condense water vapour (ii) The limewater will turn milky. (c) food + oxygen carbon dioxide + water 3. All the foods produced carbon dioxide and water. 4. You should find that foods with a high fat/oil content burn well and give the most energy. The table below gives the actual energy released by 100 g of the foods you might have tested. Food tested Energy (kilojoules per 100 g) peanut 2370 potato crisps 2170 biscuit (digestive) 2014 sugar 1620 bread 1110 Activity (a) Alcohol molecules are not hydrocarbons because they also contain oxygen atoms. (b) alcohol + oxygen carbon dioxide + water 20
2 FUELS AND ENERGY 2: ONTROLLING FIRES hapter 9 Fuels and energy 2: ontrolling fires Activity (a) Fuel, oxygen and heat (b) The fire triangle Activity (a) (i) On burning solids such as wood, paper, cloth (ii) eat (b) Dry powder and carbon dioxide (c) Foam and carbon dioxide 2. Oxygen 3. Using foam (i) removes heat, cooling the fire, and (ii) prevents oxygen getting to the fire. 4. Putting a fire blanket or towel soaked in water over a burning chip pan. This stops oxygen getting to the burning oil. Also switch off heat source. 5. Using water or a foam that contains water on an electrical fire can lead to electrocution as water can conduct electricity. 6. Ask your teacher to give feedback on your leaflet. Activity The carbon dioxide acts like a blanket and stops oxygen in the air getting to the burning candle. 2. (a) arbon dioxide (b) The foam from the extinguisher stops oxygen getting to the tea light. 21
3 NATURE S EMISTRY hapter 10 Fuels 1: Fossil fuels Activity (a) hlorophyll (b) Oxygen (c) The energy is stored in bonds holding the atoms in sugar and starch compounds together. Activity A fossil fuel is a fuel that has been formed from the decaying remains of ancient plants and animals. 2. (a) Some of the things the same are: coal and oil were formed millions of years ago they were formed from living things that had died and were decaying they were covered over by mud and sand which squashed them and buried them deeper heat from within the Earth helped change the decaying plants and animals into coal and oil. (b) Things that were different are: coal was made from plant material such as trees oil was made from tiny sea creatures oil is trapped below impermeable rock. 3. Your flow charts will not look exactly like these but should describe the same stages. (a) Formation of coal energy from Sun helps plants to grow 300 million years ago, dead plants and trees fall into swampy water dead plants and trees are covered by mud, which stops them from decaying combination of layers of mud and heat from underground rocks causes plant remains to be squashed after millions of years of heat and pressure, the remains of the dead plants turn into coal 22
4 FUELS 1: FOSSIL FUELS (b) Formation of oil and natural gas energy from Sun helps microscopic sea creatures to grow, and be consumed by sea creatures millions of years ago, the sea creatures died and were covered by mud and sand, which stops them from decaying combination of layers of mud and heat from underground rocks causes remains of sea creatures to be squashed after millions of years of heat and pressure, the remains of the sea creatures turn into oil and natural gas Activity 10.3 Arguments for fracking include: creates jobs provides a new domestic energy source makes the country less reliant on imports extends the time before supplies run out. Arguments against fracking include: may cause minor earthquakes can pollute water supplies may have impacts on health such as asthma levels in children undermines efforts to tackle climate change. 23
5 NATURE S EMISTRY Activity (a) Supplies of fossil fuels will eventually run out. When they are used up, they cannot be replaced. (b) Fracking and deep-water drilling 2. (a) 35 (billion barrels) (b) 2008 (c) New discoveries of reserves 3. Information likely to be included in your report is: the Deepwater orizon was a drilling rig operated by British Petroleum (BP) in the Gulf of Mexico on 20 April 2010 a leak developed and a blowout preventer which would have sealed the well failed. The flow of oil and gas couldn t be controlled. These caught fire and caused several explosions on the rig. It took 5 months to finally seal the well there was lots of damage to the marine environment with the deaths of many fish, sea turtles and dolphins hundreds of miles of coastline were badly polluted by oil the disaster has cost BP more than $44 billion in fines, compensation and clean-up costs. 4. (a) Gas reserves (trillion cubic feet) Year (b) From 1970 until 1990 gas reserves fell as the amount of gas used was greater than new discoveries. From 1995 until 2015 gas reserves rose as the amount of new gas discoveries was greater than the amount being used. 24
6 FUELS 1: FOSSIL FUELS Activity (a) ydrocarbons (b) arbon dioxide and water (c) (i) arbon and carbon monoxide (ii) Incomplete combustion 2. (a) (i) Oxidation (ii) omplete combustion (b) Exothermic 3. atalytic converters are used to reduce emissions of poisonous carbon monoxide and oxides of nitrogen which causes acid rain. Activity (a) 38 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 5 (3O2 have 6 oxygen atoms, 42O have 4 oxygen atoms, giving a total of 10 oxygen atoms; dividing by 2 gives 5 molecules of oxygen, O2) (e) + propane + oxygen carbon + carbon dioxide hydrogen + water oxygen The number of each type of atom is the same on both sides of the equation. No mass has been gained or lost. Therefore this demonstrates the law of conservation of mass S1-N4 hemistry SB_Unit 2_Answers.indd 25 12/08/17 11:23 AM
7 NATURE S EMISTRY hapter 11 Fuels and energy 3: The problems with using fossil fuels Activity (a) A mixture of smoke and fog which is dangerous to health (b) Reduce use of coal; close coal-fired power stations; shut polluting factories; phase out polluting vehicles (c) To stop breathing in fine soot particles that are given out by car exhausts (d) Breathing problems and heart problems 2. Answers will vary but ideas for your poster could include: a graphic of a cyclist with a mask, statistics on death rates due to air pollution and different types of air pollution or a before cartoon of one cyclist with a mask and one without, and an after cartoon with one looking happy and one coughing and wheezing, with a caption wear a mask. 1. Activity Individual/household emissions ousing Transport Food onsumption Other Emissions (%) Theme (a) Methods include: insulating, draught proofing and double glazing, turning down the heating and hot-water thermostats, reducing the time the heating is on, using energyefficient heating systems and microgeneration technologies. (b) Using energy-efficient light bulbs and appliances; washing clothes at a lower temperature (c) Walking; cycling; using car share; using public transport (d) Sustainable: able to be done in a way that meets present needs without making it difficult for future generations to meet their needs because we have used up the resources. Seasonal: available according to local growing conditions (not imported). Eating a sustainable and healthy diet will reduce greenhouse gas emissions because food isn t grown out of season in heated greenhouses or transported from other countries, both of which use energy.
8 FUELS AND ENERGY 4: MEETING ENERGY NEEDS IN TE FUTURE 3. (a) Greenhouse gases (b) Using electric power packs instead of diesel engines to power the buses (c) 18% (d) (i) 50% (half) of all buses to be low emission by 2032 (ii) Because the graph is nearly a straight line which is steadily increasing, it is hoped that this will increase steadily from 2017 to 2032, by replacing diesel buses with low-emission vehicles hapter 12 Fuels and energy 4: Meeting energy needs in the future Activity Biomass 2. Biodiesel; bioethanol; biogas (biomethane) 3. They release the same amount of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere when they burn as was absorbed by the plants that produced them. 4. (a) Sugarcane and sugar beet (b) Biodiesel (c) Biomethane 5. (a) Type of climate Yield Sugar content (%) required (tonnes per hectare) Sugarcane tropical Sugar beet temperate (b) (i) It was too labour intensive, making it uneconomic. (ii) Bioethanol Biofuel Number of plants Total capacity (million litres) Feedstocks biodiesel used cooking oils; waste oils; tallow; sewage grease bioethanol wheat; sugar beet biomethane 1 5 municipal (town) solid waste 27
9 NATURE S EMISTRY Activity Scotland relies on a mix of energy sources. These include nuclear, hydroelectric, wind, and wave and tidal energy. Peterhead power station is the only power station that still uses fossil fuels. 2. (a) (i) Finite (ii) Renewable (iii) Nuclear (b) Solar (c) Biomass (d) Geothermal 3. Any two from: buses powered by hydrogen fuel cells only emit water/don t emit carbon dioxide; don t cause air pollution; are quieter and smoother running. 4. (a) Scotland has mountains and fast-flowing rivers. (b) During periods of low electricity demand, excess electricity is used to pump water from the loch into a dam high above the power station. At periods of high electricity demand, the water from the dam is allowed to flow down through the turbines, generating electricity. Activity (a) (i) An energy source whose present-day use does not affect future use. (ii) Sustainable energy sources reduce greenhouse gas emissions. (b) Any two from: risk of accidents; high cost of construction; high decommissioning costs; difficulty of dealing with radioactive waste. (c) ydroelectric power stations can be switched on and off quickly. (d) Tides are predictable, whereas wind and solar are not. 2. Answers may vary but should include an overview of the potential energy sources that could be used to meet Scotland s future energy needs and your own ideas about which are most suitable. hapter 13 Fuels 2: Solutions to fossil fuel problems Activity (a) (i) Respiration (ii) Photosynthesis (iii) Respiration (b) Burning fossil fuels is increasing the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. 28
10 FUELS 2: SOLUTIONS TO FOSSIL FUEL PROBLEMS Activity Planting forests and regenerating peat bogs 2. Growing trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. 3. A lack of oxygen in the water slows the decay process. Activity Step 1: Remove the carbon dioxide from the gases being emitted to the atmosphere Step 2: ompress the gas Step 3: Inject the carbon dioxide into suitable rocks deep in the Earth s crust Activity Biofuels only release the carbon dioxide that the plants used to make the biofuel, absorbed from the atmosphere during their growing cycle. Activity Report Answers will vary but should include conclusions about which type of biomass produces biogas most quickly and which type produces most biogas. The results depend on what you used. The mixture of cow manure + other biomass material, such as vegetable peelings, should produce much more biogas than the cow manure on its own. Your graph will look similar to the one shown, but details will vary depending on the actual cow dung + biomass conditions. The rate at which cow dung produces biogas is faster at the start than the cow dung + biomass mixture. 40 g of cow dung can produce about 800 cm 3 cow dung of biogas. Also state any two ways of making your experiment fair from: the same mass of biomass was used in each case the bottles were filled to the same level with distilled water the bottles were kept in the same conditions Biogas may be given off at different rates when Time (days) different types of biomass are heated. ircumference of balloon (cm) 29
11 NATURE S EMISTRY Activity The mass (weight) of seeds or nuts used must be the same in each case. 3. Biomass is material that can be obtained from living things and burned to produce energy. Three biofuels that can be obtained from biomass are biogas from decomposing waste, bioethanol made by fermenting sugar, and biodiesel that can be made from used cooking oil. Purified biogas that is suitable for injecting into the national gas grid is known as liquid biomethane. Activity Wind farms and solar panel sites. 2. Risk of injury to birds, bats and marine life 3. Decaying plants can release greenhouse gases 4. Release of hydrogen sulfide, which smells, and release of trapped greenhouse gases Activity Wind turbines 2. (a) 0.7 arbon dioxide emissions (kg of O 2 per kilowatt hour of electricity produced) Natural gas oal Solar cells Wind turbine Geothermal Wave/Tidal ydroelectricity Power generation source (b) Using sustainable energy sources instead of fossil fuels means that less carbon dioxide will be released into the atmosphere. This will slow the rise in (stabilise/decrease) the concentration of O 2 in the atmosphere. 30
12 FUELS 3: YDROARBONS hapter 14 Fuels 3: ydrocarbons Activity (a) Fractional distillation (b) Molecules made up of only carbon and hydrogen atoms. (c) Fractions 2. (a) Fraction A (b) Fraction B (c) Fraction A (d) Fraction A 3. (a) Gasoline (b) Gasoline (c) (i) Petrol (ii) Diesel (d) Paraffin or aircraft fuel Activity (a) A formula that shows the number of atoms of each type that are in the molecule (b) A formula that shows how the atoms are joined together in a molecule 2. (a) You should be able to build models of the alkanes named in the table. (b) See column 3 of the table below. (c) Alkane name Number of carbons Number of hydrogens Molecular formula Full structural formula methane ethane propane (continued) 31
13 32 Activity (a) pentene hexene heptene octene propene butene ethene NATURE S EMISTRY butane pentane hexane heptane octane (d) Pent- indicates the number of carbons (five); -ane indicates it is an alkane with single carbon-to-carbon bonds. (e) It can form four bonds, so it can bond to itself to form long chains, and also to other atoms.
14 33 FUELS 3: YDROARBONS (b) 2. There are always twice as many hydrogens as carbons in the molecules. 3. (a) Alkenes (b) It indicates that the molecules of the compound contain a carbon-to-carbon double bond. 4. Add bromine solution to samples of each and shake. The alkene will decolourise the bromine solution immediately, but the alkane will not. Alkene name Number of carbons Number of hydrogens Molecular formula Full structural formula propene pentene hexene heptene octene Activity (c) (d)
15 NATURE S EMISTRY 2. (a) 7 16 (b) (i) + (ii) There is not a great demand for heavy fractions. racking breaks the large molecules in unwanted heavy fractions into smaller, more useful molecules. 4. (a) atalytic cracking (b) (i) 3 6 (ii) Octane; ethene; propene 5. (a) (i) The alkane molecules in liquid paraffin are very large. (ii) The bromine solution will not be decolourised. (b) (i) The gas consists of hydrocarbons. (ii) Because the product is a gas, the molecules must be small. Because the bromine solution is decolourised immediately, the molecules must be alkene molecules. (c) The delivery tube must be removed from the water to prevent suck-back. hapter 15 Everyday consumer products 1: Plants for food Activity Food arbohydrate Sugars Starch Fats and oils Protein bread Brazil nut apple breakfast cereal pasta 34
16 EVERYDAY ONSUMER PRODUTS 1: PLANTS FOR FOOD Activity Plants are a vital source of nutrients. The foods we obtain from plants include proteins, carbohydrates, fats and oils, vitamins and minerals. 2. Starch and sugars 3. Proteins 4. Starch and sugar 5. Protein 6. arbohydrates: provide the body with energy. Proteins: needed for growth and repair of body tissue. Fats and oils: provide the body with energy and act as an insulator against cold. Vitamins: needed for normal growth, to repair tissue, to fight infection and to prevent diseases. Minerals and trace elements: for example, calcium is needed for healthy bones and teeth, iron is needed for healthy blood. Activity (a) Obesity (b) arbohydrates, and fats and oils. (c) (i) 28 (kg/m 2 ) (ii) overweight 2. Their diet does not contain enough vitamins and minerals. Scurvy is caused by a lack of vitamin in the diet. Rickets is caused by a lack of vitamin D. 3. Essential fatty acids 4. Any one from: lower body weight; lower blood pressure; reduced cholesterol; reduced risk of heart disease, stroke and cancers. 5. Disease/condition Vitamin/mineral deficiency Plant source of vitamin/mineral scurvy vitamin red pepper, curly kale, kiwi fruit rickets vitamin D no significant plant source anaemia iron (Fe) spinach, oatmeal, sunflower seeds and soya beans beriberi vitamin B1 spinach and sunflower seeds pellagra vitamin B3 oatmeal 35
17 NATURE S EMISTRY Activity (a) Sugars (carbohydrates) (b) Fermentation (c) The wine could be distilled. The wine would be heated producing vapours with a high alcohol content. These would be condensed and collected, producing brandy. 2. (a) 5.6 units ( ) (b) A bottle of strong beer and a whisky (3 units) would have less alcohol than two glasses of wine (at least 4 units). (c) Ensuring labels on alcoholic drinks show units of alcohol and recommending maximum and low-risk levels of drinking for men and women Activity In your experiment you should observe: yellowing of leaves for mung beans grown in culture medium lacking nitrogen stunted growth for mung beans grown in culture medium lacking potassium poor root development for mung beans grown in culture medium lacking phosphorus. 2. In your experiment you should observe that fertiliser improves the development of roots and leaves. Activity hemical symbol Element hemical symbol Element N nitrogen Mn manganese P phosphorus Fe iron K potassium Zn zinc S sulfur u copper a calcium Mo molybdenum Mg magnesium carbon B boron hydrogen l chlorine O oxygen 36
18 EVERYDAY ONSUMER PRODUTS 2: OSMETI PRODUTS 2. (a) Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium (b) (i) To increase the yield of crops for food, or for other purposes such as making alcohol (ii) Growing crops absorb nutrients from the soil. ropping removes the nutrients. Fertilisers are used to replace the nutrients. hapter 16 Everyday consumer products 2: osmetic products Activity (a) cosmetics (b) carbohydrates (c) Fats (d) oils Activity Essential oils are responsible for the distinctive aroma of plants and can be extracted by steam distillation. 2. Lavender has calming effects on the body. 3. Spearmint and peppermint 4. As muscle pain relief 5. They might feel energised. 6. Any of the oils that have memory-boosting capacity (basil, cypress, lemon, peppermint, rosemary) 7. You should be able to detect a very small quantity of essential oil by visual inspection or by smell. Activity (d) Over the period of time, the strength of the smell should decrease gradually from strong to very faint. (e) (i) A simple Eau de ologne-type fragrance can be made by dissolving a few drops of essential oil in a water and alcohol mixture. (ii) Molecules of the essential oils evaporate from the skin. When there are fewer essential oil molecules on the skin, the scent will only be detected faintly. 2. You may be able to detect a range of different essential oils, distinguishing between them by smell. 37
19 NATURE S EMISTRY 3. Answers will vary but should consist of a list of essential oils and the products that contain them. 4. (a) 41.6% ( ) (b) 2.25 billion 5. (a) Steam distillation (b) The liquid that was distilled would have a scent of rosemary and there may be evidence of a small amount of oil on the surface of the water in the flask. (c) Roots: ginger; flowers: lavender; peel: orange; wood: sandalwood; stem (and leaves): peppermint 6. (a) Orange (b) Floral (c) (i) Patchouli and vetiver are classed as base notes because their scents last a long time on the skin/take a long time to evaporate from the skin. (ii) A woody scent (d) The perfume has all three types of notes and can, therefore, be described as balanced. hapter 17 Everyday consumer products 3: Plants for energy Activity arbohydrates and oils can be burned. 1. B Activity (a) 6 12 O 6 (b) (i) It is made of many glucose molecules joined together in a long chain. (ii) Because it is made of many glucose molecules (compared with simple carbohydrates such as glucose, fructose, maltose and sucrose). 3. (a) When glucose is heated with Benedict s solution the blue solution turns brick-red. (b) Starch gives a blue black colour with iodine solution. Activity When iodine is added to a sample of the water surrounding the visking tubing containing the starch it doesn t give a blue black colour. The starch molecules are too large to pass through the visking tubing into the water. When the water surrounding the visking tubing containing the glucose solution is tested with Benedict s solution, a brick-red colour is produced. Glucose molecules are small enough to pass through the visking tubing into the water. 38
20 EVERYDAY ONSUMER PRODUTS 3: PLANTS FOR ENERGY Activity (a) Starch gives a blue black colour with iodine. (b) Amylase is an enzyme. (c) eat a sample of the solution with Benedict s solution. A brick-red colour is produced in the presence of glucose. 2. (a) As time passes, there is less starch present, because the starch is being broken down by the amylase. (b) Benedict s solution gives a brick-red colour because starch has been broken down to produce glucose. Activity Answers will vary but should contain reference to the froth on the top of the liquid, which shows that a gas is being produced, and that limewater turns milky because carbon dioxide is produced. Activity (a) The enzymes stop working because the yeast cells die when the alcohol percentage becomes too high. (b) Spirits have a much higher alcohol content than the percentage alcohol at which yeast enzymes will work, so spirits cannot be produced by fermentation alone. Distillation is needed to increase the percentage alcohol content. 2. Answers will vary but should cover these facts: Barley is malted to produce sugars. Enzymes in the barley break starch down to simple sugars. The malted barley is then allowed to ferment. Enzymes break the sugars down, producing alcohol (ethanol). The percentage of alcohol is increased by distillation. The distilled spirit is allowed to mature in wooden barrels to produce whisky. 3. Any two from: cider (from apples), rum (from sugarcane) and vodka (from potatoes). 4. (a) Volume of alcohol = = 280 cm Units of alcohol = 280 = 28 units 10 (b) Volume of alcohol = units 10 = = 16 cm 3 39
21 NATURE S EMISTRY Activity (a) Biological catalysts (b) arbon dioxide (c) (i) p of 8 ( ) (ii) Temperature 2. You should find that amylase works well at temperatures around 40 and at p 7 (neutral). hapter 18 Plants to products Activity You will be able to dye fabrics with vegetable colours. You should find that using a mordant improves the dyeing process and that the p of the dye solution can influence colour. 2. (a) Indigo (b) The roots (c) Mordant Activity (a) Morphine or codeine (b) eroin or opium (c) Any one from: can be addictive; can cause harm to users; can cause harm to society. Activity (a) Active compound (b) To improve the taste and appearance of a medicine or to improve the shelf-life of a medicine. 2. (a) (i) 2.5 ml (cm 3 ) (ii) To ensure that a fever due to serious infection can be diagnosed quickly (b) 4 3. Answers may vary but should include information from various medicine packaging, showing what the medicines contain, how they should be stored, what they can be used for and how they should be used. 40
22 UNIT 2 PRATIE ASSESSMENT Unit 2 practice assessment National 3 1. (a) Fuels 1 (b) A compound made of only hydrogen and carbon atoms 1 (c) (i) Water 1 (ii) Limewater turns milky/cloudy 1 2. (a) Fuel, oxygen and heat 1 (b) Risk of electrocution 1 3. (a) Fossil fuels are a finite resource or Using sustainable sources reduces greenhouse gas/carbon dioxide emissions. 1 (b) When demand for electricity is low, surplus electricity from other sources is used to pump water into a reservoir higher in the hills 1 and At times of high electricity demand, water is released from the reservoir and used to produce electricity. 1 (c) Low/no generation of electricity when wind speed is very low. 1 (d) Wood or crop waste, etc 1 (e) Sugar beet could be processed to give biofuels/bioethanol (a) They replace the nutrients that plants need which cropping removes from the soil. 1 (b) arbohydrates provide the body with energy. 1 (c) Fermentation 1 (d) million tonnes 1 5. (a) Steam distillation 1 (b) Smell of essential oil or essential oil floating on top of the water 1 (c) Spearmint or peppermint 1 (d) Base note 1 6. (a) The plant material should be chopped finely or crushed 1 and The plant material should be heated in water or other solvent. 1 (b) Dyeing fabrics or as a food colouring 1 7. Willow or meadowsweet 1 Total 24 41
23 NATURE S EMISTRY National 4 1. rude oil is formed from the decaying remains of small sea creatures 1 and Over a long period of time, temperature and pressure change the remains into crude oil (a) ombustion or oxidation 1 (b) Exothermic 1 (c) Any from: carbon monoxide, carbon (soot). 1 (d) arbon dioxide produced by burning the fossil fuels is separated from the gases released to the atmosphere 1 and The carbon dioxide (is liquefied and) stored in rock formations Foam from the extinguisher cuts off the supply of oxygen to the burning fuel (a) MW 1 (b) Any from: biogas, biomethane, (bio)ethanol, biodiesel (a) The hydrocarbons in each fraction have similar boiling points. 1 (b) 1 (c) (i) (ii) or Both of these are acceptable structural formulae; the formula showing bonds is termed a full structural formula, and the other is described as a shortened structural formula. 6. (a) Alkanes 1 (b) racking produces unsaturated compounds or racking produces alkenes or racking produces molecules containing double bonds. 1 (c) (a) Iodine solution will produce a blue black colour. 1 (b) Enzymes are biological catalysts. 1 (c) The formula contains, and O and the : ratio is 2 : 1 1 (d) 28 ± 1 1 (e) Distillation 1 8. (a) As time passes the rate at which caffeine is extracted from the tea bag decreases. 1 (b) 225 mg 1 9. (a) Active ingredient 1 (b) Morphine or heroin 1 1 Total 26 42
National 4 Chemistry. Unit 2 Nature s Chemistry Summary Notes
 National 4 Chemistry Unit 2 Nature s Chemistry Summary Notes Success Criteria I am confident that I understand this and I can apply this to problems? I have some understanding but I need to revise this
National 4 Chemistry Unit 2 Nature s Chemistry Summary Notes Success Criteria I am confident that I understand this and I can apply this to problems? I have some understanding but I need to revise this
NATIONAL 4 CHEMISTRY
 Farr High School NATIONAL 4 CHEMISTRY Unit 2 Nature s Chemistry Question Booklet 1 Fuels 1. What is meant by the word fuel? 2. Give three ways in which the formation of coal and oil are similar. 3. We
Farr High School NATIONAL 4 CHEMISTRY Unit 2 Nature s Chemistry Question Booklet 1 Fuels 1. What is meant by the word fuel? 2. Give three ways in which the formation of coal and oil are similar. 3. We
Topic 6 National Chemistry Summary Notes. Fuels. Fuels and Combustion
 Topic 6 National Chemistry Summary Notes Fuels LI 1 Fuels and Combustion Coal, oil, gas and wood can all be used as fuels. These fuels have energy-rich chemical bonds which were created using the energy
Topic 6 National Chemistry Summary Notes Fuels LI 1 Fuels and Combustion Coal, oil, gas and wood can all be used as fuels. These fuels have energy-rich chemical bonds which were created using the energy
The names and formulae of three hydrocarbons in the same homologous series are: Which homologous series contains ethane, propane and butane?
 Q1.This question is about hydrocarbons. (a) The names and formulae of three hydrocarbons in the same homologous series are: Ethane C 2 H 6 Propane C 3 H 8 Butane C 4 H 10 The next member in the series
Q1.This question is about hydrocarbons. (a) The names and formulae of three hydrocarbons in the same homologous series are: Ethane C 2 H 6 Propane C 3 H 8 Butane C 4 H 10 The next member in the series
Crude Oil National 4
 Fuels National 4 A fuel is a chemical which burns to give out energy. When a fuel burns the chemical reaction is known as combustion. When combustion takes place the fuel is reacting with oxygen from the
Fuels National 4 A fuel is a chemical which burns to give out energy. When a fuel burns the chemical reaction is known as combustion. When combustion takes place the fuel is reacting with oxygen from the
Fuels. N4 & N5 Homework Questions
 St Peter the Apostle High school Chemistry Department Fuels N4 & N5 Homework Questions Answer questions as directed by your teacher. National 4 level questions are first followed by National 5 level questions.
St Peter the Apostle High school Chemistry Department Fuels N4 & N5 Homework Questions Answer questions as directed by your teacher. National 4 level questions are first followed by National 5 level questions.
Page 2. Q1.Greenhouse gases affect the temperature of the Earth. Which gas is a greenhouse gas? Tick one box. Argon. Methane. Nitrogen.
 Q1.Greenhouse gases affect the temperature of the Earth. (a) Which gas is a greenhouse gas? Tick one box. Argon Methane Nitrogen Oxygen (b) An increase in global temperature will cause climate change.
Q1.Greenhouse gases affect the temperature of the Earth. (a) Which gas is a greenhouse gas? Tick one box. Argon Methane Nitrogen Oxygen (b) An increase in global temperature will cause climate change.
Unit C1, C1.4 and C1.5
 rude oil, fuels and other useful substances from crude oil 1. rude oil is a resource from which fuels can be separated. (a) The name of the main fuel fractions and one of the hydrocarbons in each fraction
rude oil, fuels and other useful substances from crude oil 1. rude oil is a resource from which fuels can be separated. (a) The name of the main fuel fractions and one of the hydrocarbons in each fraction
How can hydrocarbons be broken down into smaller molecules? What is an alkane? Give an example and draw it
 How can hydrocarbons be broken down into smaller molecules? What is an alkane? Give an example and draw it What kind of reaction happens when large hydrocarbons are broken down? What is the general formula
How can hydrocarbons be broken down into smaller molecules? What is an alkane? Give an example and draw it What kind of reaction happens when large hydrocarbons are broken down? What is the general formula
Name: Organic chemistry. Class: Foundation revision questions. Date: 67 minutes. Time: 67 marks. Marks: Comments: Page 1 of 27
 Organic chemistry Foundation revision questions Name: Class: Date: Time: 67 minutes Marks: 67 marks Comments: Page of 27 Barbecues are heated by burning charcoal or burning hydrocarbons. (a) Use the Chemistry
Organic chemistry Foundation revision questions Name: Class: Date: Time: 67 minutes Marks: 67 marks Comments: Page of 27 Barbecues are heated by burning charcoal or burning hydrocarbons. (a) Use the Chemistry
Questions Q1. (b) Molecules of two compounds W and X are shown. (i) Compound W is an alkane. Explain what is meant by the term alkane.
 Questions Q1. (a) Crude oil is separated into useful fractions by fractional distillation. Diesel oil and kerosene are two of these fractions. Draw one straight line from each of these fractions to a use
Questions Q1. (a) Crude oil is separated into useful fractions by fractional distillation. Diesel oil and kerosene are two of these fractions. Draw one straight line from each of these fractions to a use
C7 Quick Revision Questions
 C7 Quick Revision Questions H = Higher tier only SS = Separate science only Question 1... of 50 What does a finite resource mean? Answer 1... of 50 A resource that is being used up quicker than it is being
C7 Quick Revision Questions H = Higher tier only SS = Separate science only Question 1... of 50 What does a finite resource mean? Answer 1... of 50 A resource that is being used up quicker than it is being
SUBJECT: Integrated Science TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: GRADE: 7 DURATION: 2 wks GENERAL TOPIC: The Sun As The Main Source Of Energy / Fuels and
 SUBJECT: Integrated Science TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: GRADE: 7 DURATION: 2 wks GENERAL TOPIC: The Sun As The Main Source Of Energy / Fuels and their uses in the home. The Sun As The Main Source Of
SUBJECT: Integrated Science TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: GRADE: 7 DURATION: 2 wks GENERAL TOPIC: The Sun As The Main Source Of Energy / Fuels and their uses in the home. The Sun As The Main Source Of
4th Grade. Energy and Natural Resources.
 1 4th Grade Energy and Natural Resources 2015 11 18 www.njctl.org 2 Energy and Natural Resources Human Energy Use Click on the topic to go to that section Renewable Energy Non Renewable Energy Environmental
1 4th Grade Energy and Natural Resources 2015 11 18 www.njctl.org 2 Energy and Natural Resources Human Energy Use Click on the topic to go to that section Renewable Energy Non Renewable Energy Environmental
Chapter: Conserving Resources
 Table of Contents Chapter: Conserving Resources Section 1: Resources Section 2: Pollution Section 3: The Three Rs of Conservation *Problems related to the use of Fossil Fuels Limited availability Pollution
Table of Contents Chapter: Conserving Resources Section 1: Resources Section 2: Pollution Section 3: The Three Rs of Conservation *Problems related to the use of Fossil Fuels Limited availability Pollution
We are covering. 1 of 27 Boardworks Ltd From C1 Limestone Extracting Metals Crude Oil Alkanes Alkenes
 We are covering 1 of 27 Boardworks Ltd 2006 From C1 Limestone Extracting Metals Crude Oil Alkanes Alkenes Where do building materials come from? 2 of 27 Boardworks Ltd 2006 Buildings are constructed using
We are covering 1 of 27 Boardworks Ltd 2006 From C1 Limestone Extracting Metals Crude Oil Alkanes Alkenes Where do building materials come from? 2 of 27 Boardworks Ltd 2006 Buildings are constructed using
Chapter 13 The Earths Atmosphere
 Chapter 3 The Earths Atmosphere Name: Class: Date: Time: 79 minutes Marks: 79 marks Comments: Page of 28 The bar chart shows some of the gases in the atmospheres of Earth today and Mars today. (b) Complete
Chapter 3 The Earths Atmosphere Name: Class: Date: Time: 79 minutes Marks: 79 marks Comments: Page of 28 The bar chart shows some of the gases in the atmospheres of Earth today and Mars today. (b) Complete
C1 The Essential Questions
 C1 The Essential Questions Name... Fundamental ideas (12 marks) ALWAYS ON THE EXAM 1. Complete the sentences: (i) The atomic number of an atom is the number of... (ii) The mass number of an atom is the
C1 The Essential Questions Name... Fundamental ideas (12 marks) ALWAYS ON THE EXAM 1. Complete the sentences: (i) The atomic number of an atom is the number of... (ii) The mass number of an atom is the
CHAPTER - 14 SOURCES OF ENERGY
 CHAPTER - 14 SOURCES OF ENERGY PREPARED BY NIKHIL V JONES 1) Characteristics of a good source of fuel :- i) It should have a high energy output per unit mass or volume. ii) It should be easily available.
CHAPTER - 14 SOURCES OF ENERGY PREPARED BY NIKHIL V JONES 1) Characteristics of a good source of fuel :- i) It should have a high energy output per unit mass or volume. ii) It should be easily available.
Unit 2 Lesson 4 Effects of Energy Transfer. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Check the Source! How do people use energy? Energy is the capacity to do work. People use energy to heat and cool their homes, provide light, manufacture goods, produce and prepare food, and move vehicles.
Check the Source! How do people use energy? Energy is the capacity to do work. People use energy to heat and cool their homes, provide light, manufacture goods, produce and prepare food, and move vehicles.
CHY1H (JUN08CHY1H01) General Certifi cate of Secondary Education June Unit Chemistry C1. CHEMISTRY Unit Chemistry C1.
 Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certifi cate of Secondary Education June 2008 SCIENCE B Unit Chemistry C1 CHEMISTRY Unit Chemistry C1 CHY1H
Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certifi cate of Secondary Education June 2008 SCIENCE B Unit Chemistry C1 CHEMISTRY Unit Chemistry C1 CHY1H
The equation for one of the reactions in the blast furnace is: + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO 2. Oxygen is removed from iron oxide in the blast furnace.
 Q1. Iron is extracted from iron oxide in the blast furnace. (a) The equation for one of the reactions in the blast furnace is: Fe 2 O 3 + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO 2 Complete the word equation for this reaction. iron
Q1. Iron is extracted from iron oxide in the blast furnace. (a) The equation for one of the reactions in the blast furnace is: Fe 2 O 3 + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO 2 Complete the word equation for this reaction. iron
Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete each sentence.
 1 Fossil fuels contain carbon. The figure below represents a carbon atom. Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete each sentence. (i) The name of the particle with a positive charge is an electron.
1 Fossil fuels contain carbon. The figure below represents a carbon atom. Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete each sentence. (i) The name of the particle with a positive charge is an electron.
OC22 Show that approximately one fifth of the air is oxygen; show that there is CO 2 and water vapour in air
 Chemistry: 10. Air and Oxygen Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OC21 Understand that air is a mixture of gases, and state
Chemistry: 10. Air and Oxygen Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OC21 Understand that air is a mixture of gases, and state
State one factor that makes a good fuel. (1) (b) Bioethanol is a fuel that can be obtained from the plant, sugar beet.
 1 (a) Some fuels are better fuels than others. State one factor that makes a good fuel....... (b) Bioethanol is a fuel that can be obtained from the plant, sugar beet. (i) Bioethanol and petrol can both
1 (a) Some fuels are better fuels than others. State one factor that makes a good fuel....... (b) Bioethanol is a fuel that can be obtained from the plant, sugar beet. (i) Bioethanol and petrol can both
Ethene is used as a starting material for the production of many other substances, including ethanol.
 Organic Chemistry Part 2 Q1. Ethene is used as a starting material for the production of many other substances, including ethanol. Ethene is produced when hydrocarbons are cracked. To do this hydrocarbons
Organic Chemistry Part 2 Q1. Ethene is used as a starting material for the production of many other substances, including ethanol. Ethene is produced when hydrocarbons are cracked. To do this hydrocarbons
Chapter: Conserving Resources
 Table of Contents Chapter: Conserving Resources Section 1: Resources Section 2: Pollution Section 3: The Three Rs of Conservation Chapter 19 Section 1- Natural Resources What are fossil fuels? *Fossil
Table of Contents Chapter: Conserving Resources Section 1: Resources Section 2: Pollution Section 3: The Three Rs of Conservation Chapter 19 Section 1- Natural Resources What are fossil fuels? *Fossil
Period 26 Solutions: Using Energy Wisely
 Period 26 Solutions: Using Energy Wisely Activity 26.1: Comparison of Energy Sources for Generating Electricity 1) Comparison of energy sources a) Fill in the table below to describe the advantages and
Period 26 Solutions: Using Energy Wisely Activity 26.1: Comparison of Energy Sources for Generating Electricity 1) Comparison of energy sources a) Fill in the table below to describe the advantages and
yr 11 paper 2 Feb half term
 yr paper 2 Feb half term Chemistry Higher Name: Class: Date: Time: 79 minutes Marks: 77 marks Comments: Multiple choice questions: Structured questions: Page Q.A student investigated the rate of reaction
yr paper 2 Feb half term Chemistry Higher Name: Class: Date: Time: 79 minutes Marks: 77 marks Comments: Multiple choice questions: Structured questions: Page Q.A student investigated the rate of reaction
Hydrocarbons contain the elements... and... only. (1) H 6. Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence.
 Q. Alkanes are hydrocarbons found in crude oil. (a) (i) Complete the sentence. Hydrocarbons contain the elements... and... only. () Ethane is an alkane with the formula C H 6 Draw a ring around the correct
Q. Alkanes are hydrocarbons found in crude oil. (a) (i) Complete the sentence. Hydrocarbons contain the elements... and... only. () Ethane is an alkane with the formula C H 6 Draw a ring around the correct
Biobased Product Testing
 Biobased Product Testing Analytical Background: The Carbon Cycle The carbon cycle is a biogeochemical system or cycle through which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere
Biobased Product Testing Analytical Background: The Carbon Cycle The carbon cycle is a biogeochemical system or cycle through which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere
Q1. The equation below shows the cracking of a hydrocarbon compound into two different compounds, A and B.
 Q1. The equation below shows the cracking of a hydrocarbon compound into two different compounds, A and B. State two differences between the structures of compounds A and B............. (b) Why is compound
Q1. The equation below shows the cracking of a hydrocarbon compound into two different compounds, A and B. State two differences between the structures of compounds A and B............. (b) Why is compound
A student did an experiment to find the energy released when propane is burned. heated the water by burning propane for 1 minute
 Chemistry of the atmosphere part 2 Q1. A camping stove uses propane gas. (a) A student did an experiment to find the energy released when propane is burned. The student: put 500 g water into a beaker measured
Chemistry of the atmosphere part 2 Q1. A camping stove uses propane gas. (a) A student did an experiment to find the energy released when propane is burned. The student: put 500 g water into a beaker measured
Environmental Resources: Renewable & Non-Renewable Resources & Energy
 Directions: Fill in the blanks. Renewable Resources & Energy Segment 1. Renewable Resources Are significant resources which can be replenished and reused to reduce negative environmental Are used as a
Directions: Fill in the blanks. Renewable Resources & Energy Segment 1. Renewable Resources Are significant resources which can be replenished and reused to reduce negative environmental Are used as a
Oxygen Formula: O 2 Bonding: covalent Appearance: colourless gas. Oxygen is one of the two main gases in our atmosphere, the other being nitrogen.
 Composition of the air Air is a mixture of gases. The approximate amount if each gas in dry air is shown in the pie chart (right), but you should be aware that air also contains a variable amount of water
Composition of the air Air is a mixture of gases. The approximate amount if each gas in dry air is shown in the pie chart (right), but you should be aware that air also contains a variable amount of water
Alternative Fuels, How to improve air quality
 Alternative Fuels, How to improve air quality 1 1 1 1 1 1 Introduction Nearly one-fifth of pollution in the USA is caused by cars and trucks. Fossil fuel-powered transportation is the primary contributor
Alternative Fuels, How to improve air quality 1 1 1 1 1 1 Introduction Nearly one-fifth of pollution in the USA is caused by cars and trucks. Fossil fuel-powered transportation is the primary contributor
RENEWABLE ENERGY NON-RENEWABLE ENERGY
 Hydro Solar Biomass RENEWABLE ENERGY The motion associated with rapidly falling water, waves and tidal currents can be harnessed to drive turbines and generate electricity. RENEWABLE ENERGY Energy from
Hydro Solar Biomass RENEWABLE ENERGY The motion associated with rapidly falling water, waves and tidal currents can be harnessed to drive turbines and generate electricity. RENEWABLE ENERGY Energy from
Renewable Energy Alternatives
 Renewable Energy Alternatives Reasons for Alternative Energy Fossil fuels won t last forever Renewable unlikely to run out Decrease air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions Less dependent on other nations
Renewable Energy Alternatives Reasons for Alternative Energy Fossil fuels won t last forever Renewable unlikely to run out Decrease air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions Less dependent on other nations
Power Technologies. Question. Answer. Energy is the ability to do work or change the system. Answer. Question. What are the various sources of energy?
 What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work or change the system. What are the various sources of energy? Fossil fuels Oil (Petroleum) Propane Natural gas Coal Alternative fuels Nuclear Wind Solar
What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work or change the system. What are the various sources of energy? Fossil fuels Oil (Petroleum) Propane Natural gas Coal Alternative fuels Nuclear Wind Solar
Plastic bags are used to carry, protect and store food. Plastic bags are made from polymers.
 Q1. Polymers are used to make many materials that people need. (a) Plastic bags are used to carry, protect and store food. Plastic bags are made from polymers. Ethene is the small molecule (the monomer)
Q1. Polymers are used to make many materials that people need. (a) Plastic bags are used to carry, protect and store food. Plastic bags are made from polymers. Ethene is the small molecule (the monomer)
Introduction to Energy
 Introduction to Energy Get Energized! What are two types of energy? Energy is the ability to cause change. Energy takes many different forms and causes many different effects. There are two general types
Introduction to Energy Get Energized! What are two types of energy? Energy is the ability to cause change. Energy takes many different forms and causes many different effects. There are two general types
UNIT 5. Biomass energy
 UNIT 5 1 Biomass energy SYLLABUS 5.1 Types of Biomass Energy Sources 5.2 Energy content in biomass of different types 5.3 Types of Biomass conversion processes 5.4 Biogas production 2 WHAT IS BIOMASS?
UNIT 5 1 Biomass energy SYLLABUS 5.1 Types of Biomass Energy Sources 5.2 Energy content in biomass of different types 5.3 Types of Biomass conversion processes 5.4 Biogas production 2 WHAT IS BIOMASS?
RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES
 RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES State of Renewable Energy Only 6% of energy used in U.S.; 18% of world s energy use Why so low, if most renewable energies are environmentally friendly and potentially limitless?
RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES State of Renewable Energy Only 6% of energy used in U.S.; 18% of world s energy use Why so low, if most renewable energies are environmentally friendly and potentially limitless?
Name Date Class. How do fuels provide energy? What are the three major fossil fuels? Why are fossil fuels considered nonrenewable resources?
 Chapter 12 Energy and Material Resources Section 1 Summary Fossil Fuels How do fuels provide energy? What are the three major fossil fuels? Why are fossil fuels considered nonrenewable resources? A fuel
Chapter 12 Energy and Material Resources Section 1 Summary Fossil Fuels How do fuels provide energy? What are the three major fossil fuels? Why are fossil fuels considered nonrenewable resources? A fuel
Chemistry CH1HP. (Jan13CH1Hp01) General Certificate of Secondary Education Higher Tier January Unit Chemistry C1. Unit Chemistry C1 TOTAL
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Science A Unit Chemistry C1 Chemistry Unit Chemistry C1 Monday 14 January 2013 For this paper
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Science A Unit Chemistry C1 Chemistry Unit Chemistry C1 Monday 14 January 2013 For this paper
Biomass. Coal. 10 Intermediate Energy Infobook Activities. Description of biomass: Renewable or nonrenewable: Description of photosynthesis:
 Biomass Description of biomass: Description of photosynthesis: Ways we turn biomass into energy we can use: Who uses biomass and for what purposes: Effect of using biomass on the environment: Important
Biomass Description of biomass: Description of photosynthesis: Ways we turn biomass into energy we can use: Who uses biomass and for what purposes: Effect of using biomass on the environment: Important
Renewable Energy Today
 Chapter 18 Renewable Energy Today Renewable Energy energy from a source that is constantly being reformed. Many governments are planning to increase their use of renewable energy resources. This will reduce
Chapter 18 Renewable Energy Today Renewable Energy energy from a source that is constantly being reformed. Many governments are planning to increase their use of renewable energy resources. This will reduce
Human Dependence on Natural Resources
 You use Earth s resources every day. When you eat cereal with milk for breakfast, you use resources from plants and animals. When you ride the bus to school, you use energy (fuel) resources. When you take
You use Earth s resources every day. When you eat cereal with milk for breakfast, you use resources from plants and animals. When you ride the bus to school, you use energy (fuel) resources. When you take
Chapter 18 Renewable Energy
 Chapter 18 Renewable Energy MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Habitat loss, soil erosion, and air pollution are disadvantages of which renewable energy source? a. solar c. biomass fuel b. wind d. moving water C DIF:
Chapter 18 Renewable Energy MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Habitat loss, soil erosion, and air pollution are disadvantages of which renewable energy source? a. solar c. biomass fuel b. wind d. moving water C DIF:
GCSE SCIENCE A CHEMISTRY
 Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature GCSE SCIENCE A CHEMISTRY Higher Tier Unit Chemistry C1 H Thursday 19 May 2016 Morning Time
Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature GCSE SCIENCE A CHEMISTRY Higher Tier Unit Chemistry C1 H Thursday 19 May 2016 Morning Time
A is any natural material that is used by humans.
 Chapter 5 Notes Energy Resources Section 1 Natural Resources Describe how humans use natural resources. Compare renewable resources with nonrenewable resources. Explain three ways that humans can conserve
Chapter 5 Notes Energy Resources Section 1 Natural Resources Describe how humans use natural resources. Compare renewable resources with nonrenewable resources. Explain three ways that humans can conserve
Energy: Conservation and Transfer
 Energy: Conservation and Transfer Energy: Conservation and Transfer 8.P.2 Explain the environmental implications associated with the various methods of obtaining, managing and using energy resources. 8.P.2.1
Energy: Conservation and Transfer Energy: Conservation and Transfer 8.P.2 Explain the environmental implications associated with the various methods of obtaining, managing and using energy resources. 8.P.2.1
Alternative Energy Resources. Environmental Earth Science Rev 2018, Spds 2011
 Alternative Energy Resources Environmental Earth Science Rev 2018, Spds 2011 Energy Sources Sun is the ultimate source of most energy on Earth. The Sun s energy is transferred from photosynthetic organisms
Alternative Energy Resources Environmental Earth Science Rev 2018, Spds 2011 Energy Sources Sun is the ultimate source of most energy on Earth. The Sun s energy is transferred from photosynthetic organisms
complex systems many different variables many alternative theories 1
 M.(a) any one from: complex systems many different variables many alternative theories (b) carbon dioxide allows short wavelength radiation to pass through allow greenhouse gas(es) for carbon dioxide the
M.(a) any one from: complex systems many different variables many alternative theories (b) carbon dioxide allows short wavelength radiation to pass through allow greenhouse gas(es) for carbon dioxide the
FOSSIL FUEL COMBUSTION:
 Science 30 Unit B Chemistry and the Environment Outcome 1: Students will analyze the sources of acids and bases and their effects on the environment. Specific Outcome 1.8: Outline the chemical reactions
Science 30 Unit B Chemistry and the Environment Outcome 1: Students will analyze the sources of acids and bases and their effects on the environment. Specific Outcome 1.8: Outline the chemical reactions
Earth Systems and Interactions
 CHAPTER The Earth System Earth Systems and Interactions What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
CHAPTER The Earth System Earth Systems and Interactions What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
4-9 Chemistry/5-9 Trilogy Chemistry of the atmosphere
 4-9 Chemistry/5-9 Trilogy Chemistry of the atmosphere.0 This question is about fuels.. There are two main types of diesel fuel used for cars: biodiesel, made from vegetable oils petroleum diesel, made
4-9 Chemistry/5-9 Trilogy Chemistry of the atmosphere.0 This question is about fuels.. There are two main types of diesel fuel used for cars: biodiesel, made from vegetable oils petroleum diesel, made
Name Class Date. Conventional Energy Resources
 Energy Resources SECTION 25.1 Conventional Energy Resources In your textbook, read about energy resources on Earth. For each statement below, write true or false. 1. The Sun is the ultimate source of most
Energy Resources SECTION 25.1 Conventional Energy Resources In your textbook, read about energy resources on Earth. For each statement below, write true or false. 1. The Sun is the ultimate source of most
The GHG Club. Water vapour
 Trace gases in our atmosphere act like the glass in a greenhouse. These trace gases trap much of the heat from the sun close to earth at night. These gases are called Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) and they help
Trace gases in our atmosphere act like the glass in a greenhouse. These trace gases trap much of the heat from the sun close to earth at night. These gases are called Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) and they help
BIOMASS AS A FUEL A Lesson Plan developed for Teachers of Agriculture This lesson plan is designed to assist teachers in guiding the learning process
 BIOMASS AS A FUEL A Lesson Plan developed for Teachers of Agriculture This lesson plan is designed to assist teachers in guiding the learning process in students as they learn more about biomass as an
BIOMASS AS A FUEL A Lesson Plan developed for Teachers of Agriculture This lesson plan is designed to assist teachers in guiding the learning process in students as they learn more about biomass as an
Generating Electricity
 Worksheet 3 Generating Electricity In most power stations, electricity is generated by burning fuels. Coal, oil and natural gas are the common fuels for generating electricity. Major parts of a power station
Worksheet 3 Generating Electricity In most power stations, electricity is generated by burning fuels. Coal, oil and natural gas are the common fuels for generating electricity. Major parts of a power station
Name Class Date. The statements below are false. For each statement, replace the underlined term to make a true statement.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS The statements below are false. For each statement, replace the underlined term to make a true statement. 1. A liquid mixture of complex hydrocarbon compounds
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS The statements below are false. For each statement, replace the underlined term to make a true statement. 1. A liquid mixture of complex hydrocarbon compounds
ANSWERS AND MARK SCHEMES
 GSE EMISTRY PRODUTS FROM OIL ANSWERS AND MARK SEMES QUESTIONSEET (a) Any three from: bodies of sea creatures that died millions of years ago decayed anaerobically under high temperature and pressure 3
GSE EMISTRY PRODUTS FROM OIL ANSWERS AND MARK SEMES QUESTIONSEET (a) Any three from: bodies of sea creatures that died millions of years ago decayed anaerobically under high temperature and pressure 3
THE COMBUSTION OF HYDROCARBONS. I love the smell of napalm in the morning smells like victory!
 THE COMBUSTION OF HYDROCARBONS I love the smell of napalm in the morning smells like victory! Carbon monoxide is a toxic gas that can be produced during the combustion of a carbon-based fuel such as propane.
THE COMBUSTION OF HYDROCARBONS I love the smell of napalm in the morning smells like victory! Carbon monoxide is a toxic gas that can be produced during the combustion of a carbon-based fuel such as propane.
Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources
 9 9 Table of Contents Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources Chapter 9: Energy Sources 9.1: Fossil Fuels 9.2: Nuclear Energy 9.3: Renewable Energy Sources Fossil Fuels 9.1 Using Energy You can see energy
9 9 Table of Contents Unit 2: Electricity and Energy Resources Chapter 9: Energy Sources 9.1: Fossil Fuels 9.2: Nuclear Energy 9.3: Renewable Energy Sources Fossil Fuels 9.1 Using Energy You can see energy
4/30/12. Chapter: Energy Sources
 Table of Contents Chapter: Energy Sources Section: Section : Section : Using Energy You can see energy being used in many ways, throughout the day. Furnaces and stoves use thermal energy to heat buildings
Table of Contents Chapter: Energy Sources Section: Section : Section : Using Energy You can see energy being used in many ways, throughout the day. Furnaces and stoves use thermal energy to heat buildings
The rest of this article describes four biogeochemical cycles: the water cycle, carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, and phosphorous cycle.
 BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES The chemical elements and water that are needed by living things keep recycling over and over on Earth. These cycles are called biogeochemical cycles. They pass back and forth through
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES The chemical elements and water that are needed by living things keep recycling over and over on Earth. These cycles are called biogeochemical cycles. They pass back and forth through
B1 Biogeochemical Systems
 B1 Biogeochemical Systems Carbon Cycle What elements makes life possible? Carbon based life Key component of all known naturally occurring life on Earth Unique properties make it ideal for construction
B1 Biogeochemical Systems Carbon Cycle What elements makes life possible? Carbon based life Key component of all known naturally occurring life on Earth Unique properties make it ideal for construction
Introduction to Bioenergy
 1 Introduction to Bioenergy 1. Global Warming and Carbon Cycle Carbon Cycle Carbon cycle Carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere,
1 Introduction to Bioenergy 1. Global Warming and Carbon Cycle Carbon Cycle Carbon cycle Carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere,
6. What are the two main components of our environment? Answer. 7. Why are green plants called producers? Answer.
 Question Bank Our Environment 1. (a) What is environmental pollution? (b) Distinguish between biodegradable and non-biodegradable pollutants. (c) Choose the biodegradable pollutants from the list given
Question Bank Our Environment 1. (a) What is environmental pollution? (b) Distinguish between biodegradable and non-biodegradable pollutants. (c) Choose the biodegradable pollutants from the list given
Iron filings (Fe) 56g IRON + SULPHUR IRON SULPHIDE
 W.S.51. Chemical reactions. All of the different materials around us have been formed by chemical reactions from about one hundred simple elements. The diagram below shows a chemical reaction between the
W.S.51. Chemical reactions. All of the different materials around us have been formed by chemical reactions from about one hundred simple elements. The diagram below shows a chemical reaction between the
Ch. 9 RTB - Energy Sources & Conversions
 Ch. 9 RTB - Energy Sources & Conversions A. Types of Energy Sources 1. There are many different types of sources for energy 2. Energy comes from plants & Animals when living & Digested by another life
Ch. 9 RTB - Energy Sources & Conversions A. Types of Energy Sources 1. There are many different types of sources for energy 2. Energy comes from plants & Animals when living & Digested by another life
SAMPLE COURSE OUTLINE CHEMISTRY GENERAL YEAR 12
 SAMPLE COURSE OUTLINE CHEMISTRY GENERAL YEAR 12 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2015 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it may be freely copied,
SAMPLE COURSE OUTLINE CHEMISTRY GENERAL YEAR 12 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2015 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it may be freely copied,
ENERGY 1: RESOURCES. Ppt. by Robin D. Seamon
 ENERGY 1: RESOURCES Ppt. by Robin D. Seamon Types of Energy Energy: the ability to do work (joules) (amt. of E to lift an apple 1m) Energy comes in many forms. FORMS of ENERGY: Thermal energy: energy from
ENERGY 1: RESOURCES Ppt. by Robin D. Seamon Types of Energy Energy: the ability to do work (joules) (amt. of E to lift an apple 1m) Energy comes in many forms. FORMS of ENERGY: Thermal energy: energy from
ENVI.5720 Energy and Environment
 ENVI.5720 Energy and Environment British thermal unit (Btu) = amount of heat needed to raise one pound of water at maximum density through one degree Fahrenheit. 1Btu = 1.055 10 3 joules tonne of oil
ENVI.5720 Energy and Environment British thermal unit (Btu) = amount of heat needed to raise one pound of water at maximum density through one degree Fahrenheit. 1Btu = 1.055 10 3 joules tonne of oil
ENERGY FORMS & CONVERSION
 1 ENERGY FORMS & CONVERSION 1.1 Energy sources and forms 1.2 Energy conversion 1.3 Energy storage and conservation Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: Knowledge, Understanding and Application
1 ENERGY FORMS & CONVERSION 1.1 Energy sources and forms 1.2 Energy conversion 1.3 Energy storage and conservation Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: Knowledge, Understanding and Application
Answer Acceptable answers Mark. Answer Acceptable answers Mark
 1(a) burns easily / produces little ash / produces little smoke / produces high heat energy (per unit mass) / easy to {store / transport} 'renewable' / few pollutants / few emissions / easy to ignite /
1(a) burns easily / produces little ash / produces little smoke / produces high heat energy (per unit mass) / easy to {store / transport} 'renewable' / few pollutants / few emissions / easy to ignite /
GTL. and Edited and Revised 2016 by H M Fahmy
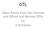 GTL Taken Partly from the Internet and Edited and Revised 2016 by H M Fahmy STEPS TO GET OIL FROM SEA OR EARTH SEISMIC SHOOTING SEISMIC INTERPRETATION ANALYSIS OF SAMPLES PREPARATION OF RIG DRILLING OIL
GTL Taken Partly from the Internet and Edited and Revised 2016 by H M Fahmy STEPS TO GET OIL FROM SEA OR EARTH SEISMIC SHOOTING SEISMIC INTERPRETATION ANALYSIS OF SAMPLES PREPARATION OF RIG DRILLING OIL
Solar panels The Fizzics Organisation
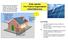 Most solar panels installed on houses in the last few years convert the energy of sunlight directly into electrical energy. These are photovoltaic cells. Solar panels 3 This electricity can be used around
Most solar panels installed on houses in the last few years convert the energy of sunlight directly into electrical energy. These are photovoltaic cells. Solar panels 3 This electricity can be used around
Activity 3 Information sheet
 Activity 3 Information sheet Type of energy Solar Where is it from Energy from sunlight is caught in solar panels and turned into electricity. Advantages The sun will always be there during our lifetime.
Activity 3 Information sheet Type of energy Solar Where is it from Energy from sunlight is caught in solar panels and turned into electricity. Advantages The sun will always be there during our lifetime.
CHY1F (JUN08CHY1F01) General Certifi cate of Secondary Education June Unit Chemistry C1. CHEMISTRY Unit Chemistry C1.
 Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certifi cate of Secondary Education June 2008 SCIENCE B Unit Chemistry C1 CHEMISTRY Unit Chemistry C1 CHY1F
Surname Other Names For Examiner s Use Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certifi cate of Secondary Education June 2008 SCIENCE B Unit Chemistry C1 CHEMISTRY Unit Chemistry C1 CHY1F
Fossil Fuels. Coal. Natural Gas. Petroleum Oil. Propane
 Fossil Fuels Coal Natural Gas Petroleum Oil Propane Conservation of Energy Your parents may tell you to conserve energy. Turn off the lights, they say. To scientists, energy conservation is not just about
Fossil Fuels Coal Natural Gas Petroleum Oil Propane Conservation of Energy Your parents may tell you to conserve energy. Turn off the lights, they say. To scientists, energy conservation is not just about
succeeding in the vce, 2017
 Unit 3 Chemistry succeeding in the vce, 2017 extract from the master class teaching materials Our Master Classes form a component of a highly specialised weekly program, which is designed to ensure that
Unit 3 Chemistry succeeding in the vce, 2017 extract from the master class teaching materials Our Master Classes form a component of a highly specialised weekly program, which is designed to ensure that
ESA Study Guide Year 10 Science
 Then and now 1. Complete the following sentence: Questions from page 76 of ESA Study Guide Year 10 Science Fuels are substances that, when burned, turn chemical a. b. and light. energy into useful 2. What
Then and now 1. Complete the following sentence: Questions from page 76 of ESA Study Guide Year 10 Science Fuels are substances that, when burned, turn chemical a. b. and light. energy into useful 2. What
ANSWERS: Combustion. 2C3H8(g) + 7O2(g) 6CO(g) + 8H2O(g)
 ANSWERS: Combustion organic molecule methane equation for complete combustion CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) equation for incomplete combustion 4CH4(g) + 5O2(g) 2CO(g) + 2C(s) + 8H2O(g) methanol 2CH3OH(l)
ANSWERS: Combustion organic molecule methane equation for complete combustion CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) equation for incomplete combustion 4CH4(g) + 5O2(g) 2CO(g) + 2C(s) + 8H2O(g) methanol 2CH3OH(l)
CHEMISTRY- AIR AND ATMOSPHERE CLASS VII
 CHEMISTRY- AIR AND ATMOSPHERE CLASS VII Q1. Explain the following terms. 1. Catalyst: A catalyst is a chemical substance that alters the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any chemical change
CHEMISTRY- AIR AND ATMOSPHERE CLASS VII Q1. Explain the following terms. 1. Catalyst: A catalyst is a chemical substance that alters the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any chemical change
SCB1FP. (Jun15SCB1FP01) General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier June 2015 TOTAL. Time allowed 1 hour
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Science B General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier June 2015
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Science B General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier June 2015
LESSON 3 OTHER LAND RESOURCES C H A P T E R 6, C O N S E R V I N G O U R R E S O U R C E S
 LESSON 3 OTHER LAND RESOURCES C H A P T E R 6, C O N S E R V I N G O U R R E S O U R C E S OBJECTIVES Compare renewable and nonrenewable resources. Describe how human activities affect the environment.
LESSON 3 OTHER LAND RESOURCES C H A P T E R 6, C O N S E R V I N G O U R R E S O U R C E S OBJECTIVES Compare renewable and nonrenewable resources. Describe how human activities affect the environment.
C9 CHEMISTRY OF THE ATMOSPHERE
 C9 CHEMISTRY OF THE ATMOSPHERE Question Practice Name: Class: Date: Time: 94 minutes Marks: 92 marks Comments: HIGHER TIER Page of 66 Oxides of nitrogen are produced when fuels are burnt. (a) Write a balanced
C9 CHEMISTRY OF THE ATMOSPHERE Question Practice Name: Class: Date: Time: 94 minutes Marks: 92 marks Comments: HIGHER TIER Page of 66 Oxides of nitrogen are produced when fuels are burnt. (a) Write a balanced
Biomass Energy Slide Index Slide 2: Biomass Energy: What is Biomass? Slide 3: Biomass Energy: Resources Primary biomass Secondary biomass
 Biomass Energy Slide Index 1 Introduction 2 3 Biomass Energy: 2 What is Biomass? 3 Resources 4 9 Uses of Biomass: 4 Schematic Representation 5 Combustion (Heating & Cooking) 6 Combustion (Electricity)
Biomass Energy Slide Index 1 Introduction 2 3 Biomass Energy: 2 What is Biomass? 3 Resources 4 9 Uses of Biomass: 4 Schematic Representation 5 Combustion (Heating & Cooking) 6 Combustion (Electricity)
Biomass. The latter is not a new concept, homes and industries were, at one time, heated and powered by wood.
 Biomass Energy Content Biomass Conversion of Biomass in Energy Thermochemical Processes Extraction Processes Biological Processes Waste to Energy Mechanical Biological Treatment (MBT) Biofuels Biomass
Biomass Energy Content Biomass Conversion of Biomass in Energy Thermochemical Processes Extraction Processes Biological Processes Waste to Energy Mechanical Biological Treatment (MBT) Biofuels Biomass
Lesson Overview. Cycles of Matter. Lesson Overview. 3.4 Cycles of Matter
 Lesson Overview 3.4 THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them up, so where do essential
Lesson Overview 3.4 THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these elements and do not use them up, so where do essential
Matter Cycles How are nutrients recycled through ecosystems?
 9. In order to continually use the same area of land for agriculture, some farmers apply fertilizers to improve the level of nitrates in the soil. An alternative to this intensive use of fertilizer is
9. In order to continually use the same area of land for agriculture, some farmers apply fertilizers to improve the level of nitrates in the soil. An alternative to this intensive use of fertilizer is
Lesson 2.4 Biogeochemical Cycles
 Lesson 2.4 Biogeochemical Cycles A carbon atom in your body today may have been part of a blade of grass last year, or a dinosaur bone millions of years ago. Fossilized bones in a Colorado dig. Lesson
Lesson 2.4 Biogeochemical Cycles A carbon atom in your body today may have been part of a blade of grass last year, or a dinosaur bone millions of years ago. Fossilized bones in a Colorado dig. Lesson
Fossil Fuels, Fossil Rules and Fossil Fools
 Name: Date: Fossil Fuels, Fossil Rules and Fossil Fools You ve probably heard the term fossil fuels before. Maybe you already know all about fossil fuels. Maybe you stopped and wondered: What are fossil
Name: Date: Fossil Fuels, Fossil Rules and Fossil Fools You ve probably heard the term fossil fuels before. Maybe you already know all about fossil fuels. Maybe you stopped and wondered: What are fossil
Supported by. A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science.
 Supported by A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science. Energy is the ability to do work. Light Motion (kinetic) Heat Electrical Energy can be found in different forms. Chemical Sound
Supported by A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science. Energy is the ability to do work. Light Motion (kinetic) Heat Electrical Energy can be found in different forms. Chemical Sound
Cycles of Ma,er. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 3.4 Cycles of Matter
 Lesson Overview Cycles of Ma,er Lesson Overview 3.4 Cycles of Matter THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these
Lesson Overview Cycles of Ma,er Lesson Overview 3.4 Cycles of Matter THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these
WHY DO WE NEED NITROGEN?? Nitrogen is needed to make up DNA and protein!
 Nitrogen Cycle 2.2 WHY DO WE NEED NITROGEN?? Nitrogen is needed to make up DNA and protein! In animals, proteins are vital for muscle function. In plants, nitrogen is important for growth. NITROGEN Nitrogen
Nitrogen Cycle 2.2 WHY DO WE NEED NITROGEN?? Nitrogen is needed to make up DNA and protein! In animals, proteins are vital for muscle function. In plants, nitrogen is important for growth. NITROGEN Nitrogen
Carbon dioxide and methane
 arbon dioxide and Question Paper Level IGSE Subject hemistry (060/097) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic ir and Water Sub-Topic arbon dioxide and ooklet Question Paper Time llowed:
arbon dioxide and Question Paper Level IGSE Subject hemistry (060/097) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic ir and Water Sub-Topic arbon dioxide and ooklet Question Paper Time llowed:
The modern atmosphere
 The modern atmosphere Heat can be transferred from place to place by conduction, convection and radiation. Dark matt surfaces are better at absorbing heat energy than light shiny surfaces. Heat energy
The modern atmosphere Heat can be transferred from place to place by conduction, convection and radiation. Dark matt surfaces are better at absorbing heat energy than light shiny surfaces. Heat energy
