DEVELOPMENT OF AQUIFER TESTING PLANS. Brent Bauman, P.G. / Erin Lynam, Aquatic Biologist
|
|
|
- Noah Bond
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DEVELOPMENT OF AQUIFER TESTING PLANS Brent Bauman, P.G. / Erin Lynam, Aquatic Biologist
2 DEVELOPMENT OF AQUIFER TESTING PLANS Goals of Aquifer Testing What questions are we trying to answer Staff review and approval of Aquifer Test Plans Commission Aquifer Testing Guidance Components of a successful plan
3 CONSTANT-RATE AQUIFER TESTING Pumping a production well at a rate greater than or equal to the desired rate of withdrawal and observing the induced changes in groundwater levels, surface water bodies, and wetlands. The constant-rate test allows the evaluation of the aquifer, the local groundwater basin, and the proposed production well to supply the requested quantity of water and the potential impact of the proposed withdrawal on existing water supplies and environmental resources.
4 Required under 18 CFR AQUIFER TESTING PLANS The project sponsor shall prepare a constant-rate aquifer test plan for prior review and approval by Commission staff before testing is undertaken. What questions are we trying to answer Sustainability of the withdrawal Impacts to competing groundwater or surface water users Impacts to the Environment
5 COMPONENTS OF AN AQUIFER TESTING PLAN A. Hydrogeologic Description B. Groundwater Availability C. Aquifer Testing Procedures D. Step Testing E. Background Monitoring F. Constant-Rate Aquifer Test G. Recovery Testing H. General Performance Requirements *SRBC Aquifer Testing Guidance
6 Geologic setting HYDROGEOLOGIC DESCRIPTION Site Conceptual model Local vs. Regional Flow Systems Formation(s), field measurements, boundary conditions Figures / Maps Well Logs Geologic Maps Contour Maps X-Sections
7 SITE CONCEPTUAL MODEL LOCAL V. REGIONAL FLOW SYSTEMS Groundwater flow path vary greatly in length, depth, and travel-time from the points of recharge to the points of discharge in the groundwater flow system
8 WELL LOGS Commission Guidance requests: A scaled diagram showing well construction and geology. The geologic description should include lithology, lithologic contacts, and the depth, yield, and lithologic characterization of water-bearing zones (fractures, conduits, clay seams, gravel beds, etc.). A textural and mineralogic description of the unconsolidated and weathered materials.
9 WELL LOGS For existing wells, detailed well logs may not be available. Acceptable well log varies depending on what is being requested: For existing well with no requested increase, historic use demonstrating the requested rate, and/or historic water level data, less information may be required. For existing well with a requested increase, the project sponsor should provide as many details as possible.
10 GEOLOGIC MAPS A geologic map is a textbook on one sheet of paper. In its cryptic manner its codes of color and sign-it reflects (or should reflect) all the important research that has been done on any geologic topic within its boundaries. From broad formational measurements down to patterns in the fabric of the rock, a map should serve as an epitome of what is known and not known about a region, up to date. Annals of The Former World by John McPhee
11 Geologic structure HYDROGEOLOGIC CROSS SECTION Potentiometric surface Surface water features and wetlands Aquifers, aquitards, and hydrogeologic boundaries Top of rock; Unconsolidated deposits thickness and extent Well bore, casing, pump intake, and water-bearing zones, or screened intervals; Monitoring Locations (GW, SW, Wetlands) Scale: 1:1 to 5:1 (adjust dip projections to account for VE) Tan(dip) =VE*Tan(dip)
12 HYDROGEOLOGIC CROSS SECTION
13 PLAN-SPECIFIC MAPS Contributing geology within the area of contribution of the proposed well. Location(s) of recorded field measurements (water elevations, structural geologic features, lithologic changes, etc.). Locations of surface water features. Fracture traces. Contributing aquifer(s) and the presence of any aquitards. Boundary conditions. Hydrogeologic cross section transects. Groundwater Contours Estimated Zone of Influence Proposed Discharge Location
14 ESTIMATED AREA OF INFLUENCE AOI should be based upon aquifer properties including: dominant types of permeability and their spatial characteristics such as bedding and fracture orientations, anisotropy, etc. topography, hydraulic gradient, groundwater flow directions, recharge boundaries, confining boundaries, etc. Mapping should depict the aquifer properties (bedding strike, fracture traces, joints, etc.) used to determine the area of influence.
15 GROUNDWATER AVAILABILITY Project Hydro should evaluate prior to well siting 18 CFR (b) Requires completion of a groundwater availability analysis using 1-in-10 year recurrence interval (drought conditions). The Commission considers the cumulative effects of existing and proposed withdrawals within a watershed, and can limit approvals to ensure the sustainability of the stream/aquifer system based on this standard. GW Availability Analysis Steps Select applicable recharge rate; Delineate GW recharge basin; Calculate Unit Area Recharge Complete Phase I Analysis; and Phase II Analysis, if necessary.
16 SELECTION OF RECHARGE RATE Provide reference and rationale for chosen recharge rate Do not select the highest rate available, unless it can be demonstrated that the highest rate is the most appropriate rate Do not average recharge rates: select a source and justify that selection Water Resource Report 70 (Reese and Risser) is a good starting point. Commission does not approve recharge rates or groundwater availability analyses
17 STAFF REVIEW OF RECHARGE RATE Staff evaluate numerous gauges reference reports to determine appropriate recharge rate List of commonly used recharge references included with CD handout.
18 GROUNDWATER BASIN MAP Topographic map with contributing geology Potential hydrogeologic boundaries (divides, discharge areas or points [springs], dikes, sharp permeability changes). Production wells within the contributing recharge area of the proposed pumping well (residential, municipal, industrial, irrigation, etc.). Surface water withdrawals.
19 PHASE I GROUNDWATER AVAILABILITY
20 PHASE II GROUNDWATER AVAILABILITY ANALYSIS Required where utilization exceeds 50% Considers: Impervious cover (land development) NPDES discharges Surface water withdrawals Contributions to aquifer from surface water (setting dependent)
21 AQUIFER TEST MONITORING LOCATIONS Monitoring should be: Focused on the AOI, especially along high permeability trends, generally in the up-dip or k-max direction, where impacts are most likely to occur. Selected to adequately characterize impacts in the k-max and k-min directions. Coordinated with member jurisdiction agencies to ensure monitoring meets all requirements
22 GROUNDWATER MONITORING Observation well selection should be based on the expected area of influence, and the distribution and construction of existing wells. It may be necessary to monitor wells outside the anticipated area of influence due to impact sensitivity or uncertainty in the estimated area of influence or area of contribution. All observation points should be monitored with digital data loggers. Staff recommend the collection of back up manual water levels.
23 SURFACE WATER MONITORING Surface water monitoring locations should be selected to adequately characterize surface water impacts. These will generally be in the k-max or up-dip direction(s) and in the proximity of the well being tested. The location of high permeability features should be taken into consideration (fracture trends, gravel beds, etc.) that likely have an efficient hydraulic connection to the well being tested.
24 SURFACE WATER MONITORING HEADWATER SETTINGS (AQUATIC RESOURCE CLASS [ARC] 1) For streams, springs and other surface water feature with channelized flowing water: 1. Monitor water levels. SRBC has zero de minimis standard for withdrawals in headwaters; includes groundwater withdrawals that show connection to headwaters (e.g., a pass/fail standard). Connection to headwaters could result in passby flow or some other required protective flow condition. 2. Monitor flow to quantify impact/interception of flow, which will assist in any considered mitigation options, if warranted.
25 SURFACE WATER MONITORING ALL OTHER SETTINGS Use best professional judgment, based on operational goals; Quantifying flow impacts can yield a stronger argument about impact and required mitigation, but can be difficult in larger streams; whereas monitoring water level changes precludes a discussion of how much mitigation should occur beyond modeled flows; staff would rely on policy standards in decision-making about protective conditions.
26 WETLAND MONITORING Monitoring important for assessing water level drawdown, particularly important in exceptional value wetlands. Wetlands have specific hydrology that support vegetation and ecosystem functions. Impacts to that hydrology, especially during the growing season, could result in significant adverse impacts to wetland plant diversity, quality, and eventual ecosystem functions. Nested piezometers should be designed so that the shallow PZ targets wetland roots zone (0-18 ) bgs; deep PZ targets are project specific.
27 POND/LAKE MONITORING Monitoring is important for assessing potential water level drawdown and reduction in outflow (if present). Water level drawdown could result in adverse impacts to connected wetlands, reduction in quality of in-pond aquatic communities, diminution of flow to downstream surface waters/wetlands, or limitations to a user s ability to recreate in the system. Ponds and wetlands without flow monitor using nested piezometers Ponds and wetlands with flow monitor flow using an instrumented weir or flume, as appropriate
28 PRECIPITATION MONITORING Precipitation should be monitored (on-site) on a 12-hour interval through the background, pumping, and recovery phases of testing. Liquid precipitation should be recorded to the nearest 0.1 inch. Precipitation as snow should be reported in a liquid equivalent. An attempt should be made to note the duration (i.e., the start and stop times) of any precipitation events that occur during the aquifer testing.
29 ENVIRONMENTAL REVIEW AQUIFER TESTING PLAN
30 SRBC ENVIRONMENTAL REVIEW INFORMED BY: (b)(2) Standards for Water Withdrawals
31 ENVIRONMENTAL REVIEW AQUIFER TESTING PLAN 1. Desktop environmental screening to assess mapped natural resources & review proposed monitoring network. 2. Site visit to assess on-the-ground natural resources & proposed monitoring network, as needed. 3. Both efforts inform final monitoring network for the aquifer test so that sensitive natural resources, that could potentially be impacted by the withdrawal, are properly monitored. This may include coordination with partner resource agencies.
32 ENVIRONMENTAL SCREENING Desktop Review GIS based Identify nearby SW classifications Identify mapped wetlands Coordinate with resource agencies re: rare, threatened, endangered species Review monitoring network where potential for impact to streams/wetlands is possible
33 ENVIRONMENTAL SCREENING Assists in desktop review of proposed monitoring locations. Does the proposed area of influence include any? Headwater streams Exceptional value or high quality wetlands or streams Naturally reproducing trout streams Rare species or sensitive settings Coordinate with member jurisdiction agencies about monitoring locations (PFBC, DCNR, PADEP, NYDEC, etc) There are protective conditions that may be assigned if impacts are detected in any of the settings listed above; emphasizes importance of appropriate monitoring network.
34 SITE VISIT SRBC biologist may attend field visit to meet project sponsor and go over proposed monitoring locations based on results from desktop environmental screening. This effort works to ensure streams, wetlands, and/or sensitive natural features are included in the aquifer testing plan monitoring network. Results from these monitoring points can be used to inform docket conditions during the Groundwater Withdrawal Application phase.
35 AQUIFER TEST PROCEDURES The aquifer test is comprised of four parts: Step test; Background monitoring (48 hours); Constant-rate aquifer test (72 hours); and Recovery monitoring (24 hours or 90 percent recovery).
36 STEP TESTING AND SELECTING A FLOW RATE Usually not required, but a good idea If the proposed production well is to be used as one of the two monitoring points in a distance-drawdown analysis, then a step test is necessary to provide information on the efficiency of the well. Used to select appropriate rate for constant-rate test Steps of equal duration First step 25% of blown yield; increase by 25% blown yield Target 5 steps (until water level in well does not equilibrate during test period)
37 STEP TESTING AND SELECTING A FLOW RATE
38 BACKGROUND MONITORING Begins after 90% recovery from step test At least 48 hours (72-hours in PADEP guidance) Demonstrate asymptotic recessional trends in surface water and ground water monitoring network prior to starting test Additional background monitoring may be required for some projects (e.g. projects with other pumping wells) No pumping of test well during background period.
39 CONSTANT-RATE AQUIFER TESTING Immediately follows Background Monitoring Period The duration of pumping should be sufficiently long to establish the hydrologic changes and trend characteristics of the proposed production well operation, aquifer, and groundwater basin (recommended 72 hours). The consultant should be the expert on the site
40 RECOVERY TESTING The recovery test immediately follows the constant-rate test and consists of monitoring the recovery of water levels and flow rates at all of the monitoring locations, following pump shutoff. Duration is a minimum of 24-hours or until aquifer has recovered to at least 90% of pretest levels, minus groundwater recession The measurement interval for the first 15 minutes of recovery should be 1 minute or less.
41 GENERAL PERFORMANCE REQUIREMENTS Appropriate Testing Conditions: The background, pumping, and recovery phases of aquifer testing must be conducted during a period of asymptotic groundwater and surface water recession (base flow). The test should not be conducted during or shortly after a precipitation event that could result in a rapid change of water level or flow.
42 GENERAL PERFORMANCE REQUIREMENTS Tested Rate: The test well may be pumped at any rate desired, but must be pumped at a constant rate for the test duration. The Commission will not approve the well for operation at a rate higher than the average tested rate. Maintaining a Constant Rate: The tested rate must be monitored and maintained to within 5 percent of the target flow rate for the duration of the test or the test will likely not qualify as a constant-rate test and may have to be rerun. Flow Rate Adjustments: All flow rate adjustments must be documented with a measurement of flow before and after adjustment, the time at which the adjustments were made, and a rationale for the adjustment. This information must be included in the hydrogeologic report.
43 GENERAL PERFORMANCE REQUIREMENTS Test Discharge: Discharge from the test well must be routed such that recirculation does not occur. This typically results in a discharge point 300 to 500 feet down dip (bedding, schistosity, etc.) from the proposed pumping well, but may be 2,000 feet or more in karst or unconsolidated aquifers. Discharge Approval: Contact member jurisdiction agencies to determine if a temporary discharge approval is required.
44 WATER CHEMISTRY During the constant-rate testing, temperature, conductivity, turbidity, and any other agreed-upon chemistry measurements should be collected from the well being tested at a minimum of every 2 hours. Temperature and conductivity must be collected from all surface water features (streams, ponds, springs, and wetlands) being monitored at the start and end of the constant-rate test. Commission does not require laboratory analysis of water samples to evaluate water quality in relation to drinking water standards Coordinate with member jurisdiction agencies PADEP - New source sampling requirements and field measurements
45 SYSTEM OPERATION DURING TESTING Operations of systems during testing can be challenging Goal is to isolate impacts as a result of pumping the test well Extended background periods may be needed to establish steady-state or near steady-state conditions (especially for existing production wells) In some cases, it may be necessary to provide operational plans during the testing periods Discuss how other on-site or system wells will operate to meet system/ facility demands during testing Minimize interference during testing Use of test Discharge In certain cases, test discharge water can be used by the project sponsor (renewal of approved source, or new source with member jurisdiction agency approval).
46 QUESTIONS
AQUIFER TEST IMPLEMENTATION BILL MILLER, P.G. SUSQUEHANNA RIVER BASIN COMMISSION
 AQUIFER TEST IMPLEMENTATION BILL MILLER, P.G. SUSQUEHANNA RIVER BASIN COMMISSION AQUIFER TEST IMPLEMENTATION Once your Aquifer Test Plan is approved Usually two years to complete the aquifer test The majority
AQUIFER TEST IMPLEMENTATION BILL MILLER, P.G. SUSQUEHANNA RIVER BASIN COMMISSION AQUIFER TEST IMPLEMENTATION Once your Aquifer Test Plan is approved Usually two years to complete the aquifer test The majority
Predicting Groundwater Sustainability: What Tools, Models and Data are Available?
 Predicting Groundwater Sustainability: What Tools, Models and Data are Available? Ray Wuolo Barr Engineering Company Assessing Sustainability is All About: Predicting (or describing) how potentiometric
Predicting Groundwater Sustainability: What Tools, Models and Data are Available? Ray Wuolo Barr Engineering Company Assessing Sustainability is All About: Predicting (or describing) how potentiometric
AQUIFER TESTING WAIVER REQUESTS. Brent Bauman, P.G.
 AQUIFER TESTING WAIVER REQUESTS Brent Bauman, P.G. AQUIFER TESTING WAIVER REQUESTS A project sponsor may request a waiver of any requirement, provided the request and explanation is made in writing at
AQUIFER TESTING WAIVER REQUESTS Brent Bauman, P.G. AQUIFER TESTING WAIVER REQUESTS A project sponsor may request a waiver of any requirement, provided the request and explanation is made in writing at
Aquifer Science Staff, January 2007
 Guidelines for Hydrogeologic Reports and Aquifer Tests Conducted Within the Jurisdictional Boundaries of the Barton Springs / Edwards Aquifer Conservation District I. Introduction Aquifer Science Staff,
Guidelines for Hydrogeologic Reports and Aquifer Tests Conducted Within the Jurisdictional Boundaries of the Barton Springs / Edwards Aquifer Conservation District I. Introduction Aquifer Science Staff,
Surface Water Impacts from Groundwater Withdrawals. Presented by: Al Pratt Steve Howe
 Surface Water Impacts from Groundwater Withdrawals Presented by: Al Pratt Steve Howe New Hampshire Water and Watershed Conference March 25, 2011 Why should we care? Groundwater withdrawals have the potential
Surface Water Impacts from Groundwater Withdrawals Presented by: Al Pratt Steve Howe New Hampshire Water and Watershed Conference March 25, 2011 Why should we care? Groundwater withdrawals have the potential
Recharge Lake/Wetland: Generalized Monitoring Strategy
 General Hydrologic Characteristics of Recharge Lakes & Wetlands The primary sources of water for recharge lakes and wetlands are direct precipitation and surface runoff. The lake stage of a recharge lake
General Hydrologic Characteristics of Recharge Lakes & Wetlands The primary sources of water for recharge lakes and wetlands are direct precipitation and surface runoff. The lake stage of a recharge lake
Information Requirements Table for Liquid Waste
 Applicant Summary Tracking # Authorization # Applicant / Facility Name Ministry of Environment Prepared by: Title Date The Information Requirements Table (IRT) for Liquid Waste is a tool used by Ministry
Applicant Summary Tracking # Authorization # Applicant / Facility Name Ministry of Environment Prepared by: Title Date The Information Requirements Table (IRT) for Liquid Waste is a tool used by Ministry
Gaining Stream: Generalized Monitoring Strategy
 General Hydrologic Characteristics of Gaining Streams Most stream reaches in the metro area are gaining reaches (i.e. the stream flow increases in the downstream direction due to inflow of groundwater).
General Hydrologic Characteristics of Gaining Streams Most stream reaches in the metro area are gaining reaches (i.e. the stream flow increases in the downstream direction due to inflow of groundwater).
General Groundwater Concepts
 General Groundwater Concepts Hydrologic Cycle All water on the surface of the earth and underground are part of the hydrologic cycle (Figure 1), driven by natural processes that constantly transform water
General Groundwater Concepts Hydrologic Cycle All water on the surface of the earth and underground are part of the hydrologic cycle (Figure 1), driven by natural processes that constantly transform water
Flow-Through Lake/Wetland: Generalized Monitoring Strategy
 General Hydrologic Characteristics of Flow-Through Lakes & Wetlands Flow-through lakes are surface expressions of the water table and are in direct hydraulic connection with the water-table aquifer. They
General Hydrologic Characteristics of Flow-Through Lakes & Wetlands Flow-through lakes are surface expressions of the water table and are in direct hydraulic connection with the water-table aquifer. They
OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION
 GROUNDWATER?? OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION What is groundwater? Geologic investigation Definitions: aquifer and aquitard, unconfined and semi-confined Water level and interpretation of water level data Well
GROUNDWATER?? OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION What is groundwater? Geologic investigation Definitions: aquifer and aquitard, unconfined and semi-confined Water level and interpretation of water level data Well
WELLHEAD PROTECTION DELINEATION REPORT FOR THE VILLAGE OF BEAR LAKE DECEMBER 2002
 WELLHEAD PROTECTION DELINEATION REPORT FOR THE VILLAGE OF BEAR LAKE DECEMBER 2002 Prepared by: Gosling Czubak Engineering Sciences, Inc. 1280 Business Park Drive Traverse City, Michigan 48686 Telephone:
WELLHEAD PROTECTION DELINEATION REPORT FOR THE VILLAGE OF BEAR LAKE DECEMBER 2002 Prepared by: Gosling Czubak Engineering Sciences, Inc. 1280 Business Park Drive Traverse City, Michigan 48686 Telephone:
STANDARDS AND GUIDELINES FOR MUNICIPAL WATERWORKS, WASTEWATER AND STORM DRAINAGE SYSTEMS
 STANDARDS AND GUIDELINES FOR MUNICIPAL WATERWORKS, WASTEWATER AND STORM DRAINAGE SYSTEMS January 2006 Drinking Water Branch Environmental Policy Branch Environmental Assurance Division Pub. No.: T/840
STANDARDS AND GUIDELINES FOR MUNICIPAL WATERWORKS, WASTEWATER AND STORM DRAINAGE SYSTEMS January 2006 Drinking Water Branch Environmental Policy Branch Environmental Assurance Division Pub. No.: T/840
Groundwater Investigations for CCR Landfills in Karst Terrain
 Groundwater Investigations for CCR Landfills in Karst Terrain Justin Brown, RG, GeoEngineers, Inc. Chris Hickman, PG, Jacobs Engineering Coal Ash Regulatory History 1978: Fossil fuel combustion waste was
Groundwater Investigations for CCR Landfills in Karst Terrain Justin Brown, RG, GeoEngineers, Inc. Chris Hickman, PG, Jacobs Engineering Coal Ash Regulatory History 1978: Fossil fuel combustion waste was
Category 1 Waste Rock Stockpile Groundwater Containment System
 Memorandum To: Jennifer Saran, Poly Met Mining Inc. Project: 23690862.00-042-008 1.0 Introduction The Co-Lead Agencies have requested a summary of the four containment systems that are planned for the
Memorandum To: Jennifer Saran, Poly Met Mining Inc. Project: 23690862.00-042-008 1.0 Introduction The Co-Lead Agencies have requested a summary of the four containment systems that are planned for the
Hydrogeology 101 3/7/2011
 Hydrogeology 101 W. Richard Laton, Ph.D., PG, CPG Associate Professor of Hydrogeology California State University, Fullerton Department of Geological Sciences 1 Hydrogeology 101 The objective is to obtain
Hydrogeology 101 W. Richard Laton, Ph.D., PG, CPG Associate Professor of Hydrogeology California State University, Fullerton Department of Geological Sciences 1 Hydrogeology 101 The objective is to obtain
NEW BRUNSWICK DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENT AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT. Environmental Impact Assessment WATER SUPPLY SOURCE ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES
 NEW BRUNSWICK DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENT AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT Environmental Impact Assessment WATER SUPPLY SOURCE ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES Department of Environment and Local Government January 2012 Table
NEW BRUNSWICK DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENT AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT Environmental Impact Assessment WATER SUPPLY SOURCE ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES Department of Environment and Local Government January 2012 Table
Grounding Water: An Exploration of the Unseen World Beneath Our Feet
 1 Grounding Water: An Exploration of the Unseen World Beneath Our Feet Kerry Schwartz, Director, Arizona Project WET Protect Your Groundwater Day: Tuesday, September 9, 2014 What I Hope to Convey Groundwater
1 Grounding Water: An Exploration of the Unseen World Beneath Our Feet Kerry Schwartz, Director, Arizona Project WET Protect Your Groundwater Day: Tuesday, September 9, 2014 What I Hope to Convey Groundwater
NEW BRUNSWICK DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENT AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT. Environmental Impact Assessment WATER SUPPLY SOURCE ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES
 NEW BRUNSWICK DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENT AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT Environmental Impact Assessment WATER SUPPLY SOURCE ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES Department of Environment and Local Government April 2017 Table of
NEW BRUNSWICK DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENT AND LOCAL GOVERNMENT Environmental Impact Assessment WATER SUPPLY SOURCE ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES Department of Environment and Local Government April 2017 Table of
RIDDICK ASSOCIATES, P.C.
 RIDDICK ASSOCIATES, P.C. CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERS 139 LAFAYETTE AVENUE SUFFERN, NEW YORK 10901 845 357-7238 FAX 845 357-7267 NORMAN L. LINDSAY DENNIS G. LINDSAY ---------------------------- SEAN
RIDDICK ASSOCIATES, P.C. CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERS 139 LAFAYETTE AVENUE SUFFERN, NEW YORK 10901 845 357-7238 FAX 845 357-7267 NORMAN L. LINDSAY DENNIS G. LINDSAY ---------------------------- SEAN
Groundwater in the Santa Rosa Plain
 . Groundwater in the Santa Rosa Plain Marcus Trotta, PG, CHg Principal Hydrogeologist Sonoma County Water Agency Santa Rosa Plain Groundwater Sustainability Agency October 12, 2017 www.sonomacountywater.org
. Groundwater in the Santa Rosa Plain Marcus Trotta, PG, CHg Principal Hydrogeologist Sonoma County Water Agency Santa Rosa Plain Groundwater Sustainability Agency October 12, 2017 www.sonomacountywater.org
Karst Spring: Generalized Monitoring Strategy
 General Hydrologic Characteristics of Karst Springs Karst spring means a location of concentrated groundwater discharge from conduits in bedrock (predominantly solution enhanced conduits or zones in carbonate
General Hydrologic Characteristics of Karst Springs Karst spring means a location of concentrated groundwater discharge from conduits in bedrock (predominantly solution enhanced conduits or zones in carbonate
Discharge Lake/Wetland: Generalized Monitoring Strategy
 Discharge Lake/Wetland: Generalized Monitoring Strategy General Hydrologic Characteristics of Discharge Lakes & Wetlands Discharge lakes and wetlands are in direct hydraulic connection with the water-table
Discharge Lake/Wetland: Generalized Monitoring Strategy General Hydrologic Characteristics of Discharge Lakes & Wetlands Discharge lakes and wetlands are in direct hydraulic connection with the water-table
Groundwater Level and Movement
 Groundwater Level and Movement Infiltration and Recharge Infiltration Entry of rain water into the ground. Recharge Addition of infiltrated water to the aquifer. Two types of Recharge- 1. Natural 2. Artificial
Groundwater Level and Movement Infiltration and Recharge Infiltration Entry of rain water into the ground. Recharge Addition of infiltrated water to the aquifer. Two types of Recharge- 1. Natural 2. Artificial
East Maui Watershed Partnership Adapted from Utah State University and University of Wisconsin Ground Water Project Ages 7 th -Adult
 INTRODUCTION What is groundwater? Water contained in saturated soil and rock materials below the surface of the earth. It is not NEW water, but is recycled water through the hydraulic cycle. The source
INTRODUCTION What is groundwater? Water contained in saturated soil and rock materials below the surface of the earth. It is not NEW water, but is recycled water through the hydraulic cycle. The source
Reference Guideline #1. Hydrogeological Impact Assessment
 Reference Guideline #1 Hydrogeological Impact Assessment Reference Guideline #1 Hydrogeological Impact Assessment Hydrogeological assessments are required for some subdivision applications when triggered
Reference Guideline #1 Hydrogeological Impact Assessment Reference Guideline #1 Hydrogeological Impact Assessment Hydrogeological assessments are required for some subdivision applications when triggered
GUIDE TO THE DEVELOPMENT OF A MINING AND RECLAMATION PLAN IN NEW BRUNSWICK
 PROVINCE OF NEW BRUNSWICK DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY AND RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT Minerals and Petroleum Development Branch GUIDE TO THE DEVELOPMENT OF A MINING AND RECLAMATION PLAN IN NEW BRUNSWICK Guide to the
PROVINCE OF NEW BRUNSWICK DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY AND RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT Minerals and Petroleum Development Branch GUIDE TO THE DEVELOPMENT OF A MINING AND RECLAMATION PLAN IN NEW BRUNSWICK Guide to the
Water Availability Study Safe Yield Analysis. Lori A. Burkert, P.G
 Water Availability Study Safe Yield Analysis Lori A. Burkert, P.G. lburkert@entecheng.com 610-373-6667 Inflow vs Outflow What is Safe Yield? Maintainable yield of water from a surface or groundwater source
Water Availability Study Safe Yield Analysis Lori A. Burkert, P.G. lburkert@entecheng.com 610-373-6667 Inflow vs Outflow What is Safe Yield? Maintainable yield of water from a surface or groundwater source
San Benito County Water District Groundwater Sustainability Agency. Community Workshop. November 14, 2018
 San Benito County Water District Groundwater Sustainability Agency Community Workshop November 14, 2018 Introduction to SGMA and the GSAs Sustainable Groundwater Management Act (SGMA) Landmark legislation
San Benito County Water District Groundwater Sustainability Agency Community Workshop November 14, 2018 Introduction to SGMA and the GSAs Sustainable Groundwater Management Act (SGMA) Landmark legislation
DYNFLOW accepts various types of boundary conditions on the groundwater flow system including:
 Section 6 Groundwater Flow Model A groundwater flow model was developed to evaluate groundwater flow patterns in the site area and to provide a basis for contaminant transport modeling. 6.1 Model Code
Section 6 Groundwater Flow Model A groundwater flow model was developed to evaluate groundwater flow patterns in the site area and to provide a basis for contaminant transport modeling. 6.1 Model Code
CHAPTER 7 GROUNDWATER FLOW MODELING
 148 CHAPTER 7 GROUNDWATER FLOW MODELING 7.1 GENERAL In reality, it is not possible to see into the sub-surface and observe the geological structure and the groundwater flow processes. It is for this reason
148 CHAPTER 7 GROUNDWATER FLOW MODELING 7.1 GENERAL In reality, it is not possible to see into the sub-surface and observe the geological structure and the groundwater flow processes. It is for this reason
Groundwater Flow Demonstration Model Activities for grades 4-12
 Groundwater Flow Demonstration Model Activities for grades 4-12 NR/WQ/2012-5 SET-UP Please allow time to practice using the groundwater model before conducting demonstrations. 1. Remove the groundwater
Groundwater Flow Demonstration Model Activities for grades 4-12 NR/WQ/2012-5 SET-UP Please allow time to practice using the groundwater model before conducting demonstrations. 1. Remove the groundwater
PIMA COUNTY COMPREHENSIVE PLAN CO PIMA COUNTY REGIONAL COMPREHENSIVE PLAN POLICY MAJOR PLAN AMENDMENT
 PIMA COUNTY COMPREHENSIVE PLAN CO7-07-04 PIMA COUNTY REGIONAL COMPREHENSIVE PLAN POLICY MAJOR PLAN AMENDMENT Arizona law [A.R.S. 11-821(C)(3)] requires: Planning for water resources that addresses: a)
PIMA COUNTY COMPREHENSIVE PLAN CO7-07-04 PIMA COUNTY REGIONAL COMPREHENSIVE PLAN POLICY MAJOR PLAN AMENDMENT Arizona law [A.R.S. 11-821(C)(3)] requires: Planning for water resources that addresses: a)
Groundwater basics. Groundwater and surface water: a single resource. Pore Spaces. Simplified View
 Groundwater and surface water: a single resource Santa Cruz River, Tucson Groundwater basics Groundwater is water found within the pore spaces of geologic material beneath the surface of the Earth. It
Groundwater and surface water: a single resource Santa Cruz River, Tucson Groundwater basics Groundwater is water found within the pore spaces of geologic material beneath the surface of the Earth. It
Municipal Groundwater Flow Modelling Study. Town of Torbay, NL
 Municipal Groundwater Flow Modelling Study Town of Torbay, NL October 19, 2015 Agenda 1 Purpose 2 What is a Groundwater Model 3 Approach 4 Conceptual Model & GW Flow Model Construction 5 Model Predictions
Municipal Groundwater Flow Modelling Study Town of Torbay, NL October 19, 2015 Agenda 1 Purpose 2 What is a Groundwater Model 3 Approach 4 Conceptual Model & GW Flow Model Construction 5 Model Predictions
The DNR is charged with managing waters resources to assure an adequate and sustainable supply for multiple uses.
 The DNR is charged with managing waters resources to assure an adequate and sustainable supply for multiple uses. Minnesota Laws 2015, chapter 4, article 4, directed the Department of Natural Resources
The DNR is charged with managing waters resources to assure an adequate and sustainable supply for multiple uses. Minnesota Laws 2015, chapter 4, article 4, directed the Department of Natural Resources
Groundwater level fluctuations caused by surface hydrologic pulsing of a wetland
 Groundwater 53 Groundwater level fluctuations caused by surface hydrologic pulsing of a wetland Bo Zhang and Frank W. Schwartz Department of Geological Sciences, The Ohio State University Introduction
Groundwater 53 Groundwater level fluctuations caused by surface hydrologic pulsing of a wetland Bo Zhang and Frank W. Schwartz Department of Geological Sciences, The Ohio State University Introduction
Groundwater and surface water: a single resource. Santa Cruz River, Tucson
 Groundwater and surface water: a single resource Santa Cruz River, Tucson 1942 1989 1 Groundwater basics Groundwater is water found within the pore spaces of geologic material beneath the surface of the
Groundwater and surface water: a single resource Santa Cruz River, Tucson 1942 1989 1 Groundwater basics Groundwater is water found within the pore spaces of geologic material beneath the surface of the
Environmental Resource Inventories. What are ERIs? Significance of information How to use them
 Environmental Resource Inventories What are ERIs? Significance of information How to use them Environmental Resource Inventory - ERI Compiled by the environmental commission Information about the natural
Environmental Resource Inventories What are ERIs? Significance of information How to use them Environmental Resource Inventory - ERI Compiled by the environmental commission Information about the natural
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS GUELPH/GUELPH-ERAMOSA TIER 3 WATER BUDGET AND LOCAL AREA RISK ASSESSMENT STUDY
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS GUELPH/GUELPH-ERAMOSA TIER 3 WATER BUDGET AND LOCAL AREA RISK ASSESSMENT STUDY Contents Overview... 3 1. What is a Tier 3 Water Budget Study?... 3 2. How does a Tier 3 Water
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS GUELPH/GUELPH-ERAMOSA TIER 3 WATER BUDGET AND LOCAL AREA RISK ASSESSMENT STUDY Contents Overview... 3 1. What is a Tier 3 Water Budget Study?... 3 2. How does a Tier 3 Water
4 DETERMINATION OF WELLHEAD PROTECTION AREAS
 4 DETERMINATION OF WELLHEAD PROTECTION AREAS A wellhead protection area is defined as the surface and subsurface area surrounding a well, wellfield or spring that supplies a public water supply through
4 DETERMINATION OF WELLHEAD PROTECTION AREAS A wellhead protection area is defined as the surface and subsurface area surrounding a well, wellfield or spring that supplies a public water supply through
A. Growth management, resource land conservation, and critical areas protection share problems related to governmental costs and efficiency.
 CITY OF MOSES LAKE MUNICIPAL CODE CHAPTER 19.03 CLASSIFICATION AND DESIGNATION OF RESOURCE LANDS AND CRITICAL AREAS AND REGULATIONS FOR THE CONSERVATION AND PROTECTION OF RESOURCE LANDS AND CRITICAL AREAS
CITY OF MOSES LAKE MUNICIPAL CODE CHAPTER 19.03 CLASSIFICATION AND DESIGNATION OF RESOURCE LANDS AND CRITICAL AREAS AND REGULATIONS FOR THE CONSERVATION AND PROTECTION OF RESOURCE LANDS AND CRITICAL AREAS
Supplemental Guide II-Delineations
 Supplemental Guide II-Delineations Contents Source Water Protection Area Delineation... 1 Delineation Criteria for Systems Using Groundwater Sources... 2 Time of Travel... 4 Flow Boundaries... 4 Delineation
Supplemental Guide II-Delineations Contents Source Water Protection Area Delineation... 1 Delineation Criteria for Systems Using Groundwater Sources... 2 Time of Travel... 4 Flow Boundaries... 4 Delineation
Current Applicant s Handbook Wetland Criteria No Harm Standards. Narrative Standard All categories. Assessment
 District 40X-2.301 Exclusions SFWMD SJRWMD harm to s or waters; harmful 1) Isolated s ½ acre or less (some caveats) 2) Wetlands be impacts by an ERP or SWM; 3) constructed waterbodies 4) s & waters that
District 40X-2.301 Exclusions SFWMD SJRWMD harm to s or waters; harmful 1) Isolated s ½ acre or less (some caveats) 2) Wetlands be impacts by an ERP or SWM; 3) constructed waterbodies 4) s & waters that
OVERVIEW. Report Summary CUMULATIVE WATER USE AND AVAILABILITY STUDY. for the Susquehanna River Basin
 No. 303 August 2016 Report Summary CUMULATIVE WATER USE AND AVAILABILITY STUDY for the Susquehanna River Basin OVERVIEW The Cumulative Water Use and Availability Study (CWUAS) represents the Susquehanna
No. 303 August 2016 Report Summary CUMULATIVE WATER USE AND AVAILABILITY STUDY for the Susquehanna River Basin OVERVIEW The Cumulative Water Use and Availability Study (CWUAS) represents the Susquehanna
1.0 INTRODUCTION. 28 th November Hawke s Bay Project Management Limited 1139 Maraekakaho Road RD5 Hastings, 4175.
 28 th November 2016 Hawke s Bay Project Management Limited 1139 Maraekakaho Road RD5 Hastings, 4175 Attn: John Roil RE: IRONGATE INDUSTRIAL AREA WATER SUPPLY 1.0 INTRODUCTION Industrial development is
28 th November 2016 Hawke s Bay Project Management Limited 1139 Maraekakaho Road RD5 Hastings, 4175 Attn: John Roil RE: IRONGATE INDUSTRIAL AREA WATER SUPPLY 1.0 INTRODUCTION Industrial development is
REGION OF PEEL PUBLIC WORKS DESIGN, SPECIFICATIONS & PROCEDURES MANUAL LINEAR INFRASTRUCTURE
 REGION OF PEEL PUBLIC WORKS DESIGN, SPECIFICATIONS & PROCEDURES MANUAL LINEAR INFRASTRUCTURE GUIDELINES FOR HYDROGEOLOGIC ASSESSMENT AND REPORTING REQUIREMENTS NEW DEVELOPMENTS ON MUNICIPAL SERVICES REVISED
REGION OF PEEL PUBLIC WORKS DESIGN, SPECIFICATIONS & PROCEDURES MANUAL LINEAR INFRASTRUCTURE GUIDELINES FOR HYDROGEOLOGIC ASSESSMENT AND REPORTING REQUIREMENTS NEW DEVELOPMENTS ON MUNICIPAL SERVICES REVISED
Report on Effects of Groundwater Withdrawal from the Doghouse Meadow, Yosemite National Park
 Report on Effects of Groundwater Withdrawal from the Doghouse Meadow, Yosemite National Park William E. Sanford Department of Geosciences Colorado State University 03 March 2006 1 Purpose The purpose of
Report on Effects of Groundwater Withdrawal from the Doghouse Meadow, Yosemite National Park William E. Sanford Department of Geosciences Colorado State University 03 March 2006 1 Purpose The purpose of
ENVIRONET Conceptual Site Model
 ENVIRONET Conceptual Site Model Peter Booth Senior Technical Director 17/04/2012 Definition The conceptual site model (CSM) can be seen as; A representation which sets out the critical pollutant linkages
ENVIRONET Conceptual Site Model Peter Booth Senior Technical Director 17/04/2012 Definition The conceptual site model (CSM) can be seen as; A representation which sets out the critical pollutant linkages
Investigation of a Floodplain Pond to Improve Alluvial Aquifer Sustainability: A Quantity and Quality Report
 Investigation of a Floodplain Pond to Improve Alluvial Aquifer Sustainability: A Quantity and Quality Report Water Resources Investigation Report 16 i P a g e Investigation of a Floodplain Pond to Improve
Investigation of a Floodplain Pond to Improve Alluvial Aquifer Sustainability: A Quantity and Quality Report Water Resources Investigation Report 16 i P a g e Investigation of a Floodplain Pond to Improve
1 THE USGS MODULAR MODELING SYSTEM MODEL OF THE UPPER COSUMNES RIVER
 1 THE USGS MODULAR MODELING SYSTEM MODEL OF THE UPPER COSUMNES RIVER 1.1 Introduction The Hydrologic Model of the Upper Cosumnes River Basin (HMCRB) under the USGS Modular Modeling System (MMS) uses a
1 THE USGS MODULAR MODELING SYSTEM MODEL OF THE UPPER COSUMNES RIVER 1.1 Introduction The Hydrologic Model of the Upper Cosumnes River Basin (HMCRB) under the USGS Modular Modeling System (MMS) uses a
KARST GEOLOGY, VAPOR INTRUSION, AND HUMAN HEALTH RISK ASSESSMENT. Fundamental Issues to Consider
 KARST GEOLOGY, VAPOR INTRUSION, AND HUMAN HEALTH RISK ASSESSMENT Fundamental Issues to Consider Introduction 2 Development of property with karst features Standard geologic investigation methods to determine
KARST GEOLOGY, VAPOR INTRUSION, AND HUMAN HEALTH RISK ASSESSMENT Fundamental Issues to Consider Introduction 2 Development of property with karst features Standard geologic investigation methods to determine
STORMWATER MANAGEMENT. 158 Attachment 2. Borough of Perkasie
 158 Attachment 2 Borough of Perkasie Appendix B Site Soil Evaluation and Soil Infiltration Testing Source: Pennsylvania Stormwater Best Management Practice Manual, December 2006. SITE SOIL EVALUATION AND
158 Attachment 2 Borough of Perkasie Appendix B Site Soil Evaluation and Soil Infiltration Testing Source: Pennsylvania Stormwater Best Management Practice Manual, December 2006. SITE SOIL EVALUATION AND
Calcareous Fen: Generalized Monitoring Strategy
 Calcareous Fen: Generalized Monitoring Strategy General Hydrologic Characteristics of Trout Streams Fens are wetlands fed by groundwater. Calcareous fens are wetlands fed by groundwater containing high
Calcareous Fen: Generalized Monitoring Strategy General Hydrologic Characteristics of Trout Streams Fens are wetlands fed by groundwater. Calcareous fens are wetlands fed by groundwater containing high
Assessing Water Use and Availability Trends in New Hampshire
 Assessing Water Use and Availability Trends in New Hampshire Brandon Kernen, PG NH Department of Environmental Services (603) 271-0660/Brandon.Kernen@des.nh.gov Existing Groundwater Use and Availability
Assessing Water Use and Availability Trends in New Hampshire Brandon Kernen, PG NH Department of Environmental Services (603) 271-0660/Brandon.Kernen@des.nh.gov Existing Groundwater Use and Availability
RESPONSIBLE PLANNING FOR FUTURE GROUND WATER USE FROM THE GREAT FLATS AQUIFER : TWO CASE STUDIES: THE GEP ENERGY
 RESPONSIBLE PLANNING FOR FUTURE GROUND WATER USE FROM THE GREAT FLATS AQUIFER : TWO CASE STUDIES: THE GEP ENERGY Introduction PROJECT AND THE SI GREEN FUELS BOILER PROJECT Thomas M. Johnson Hydrogeologist,
RESPONSIBLE PLANNING FOR FUTURE GROUND WATER USE FROM THE GREAT FLATS AQUIFER : TWO CASE STUDIES: THE GEP ENERGY Introduction PROJECT AND THE SI GREEN FUELS BOILER PROJECT Thomas M. Johnson Hydrogeologist,
Task 4.2 Technical Memorandum on Pumping Impacts on Squaw Creek
 Task 4.2 Technical Memorandum on Pumping Impacts on Squaw Creek Aquifer Test 1 Aquifer Test 2 Prepared for: Squaw Valley Public Service District April 2013 Prepared by: This page left intentionally blank
Task 4.2 Technical Memorandum on Pumping Impacts on Squaw Creek Aquifer Test 1 Aquifer Test 2 Prepared for: Squaw Valley Public Service District April 2013 Prepared by: This page left intentionally blank
BAEN 673 / February 18, 2016 Hydrologic Processes
 BAEN 673 / February 18, 2016 Hydrologic Processes Assignment: HW#7 Next class lecture in AEPM 104 Today s topics SWAT exercise #2 The SWAT model review paper Hydrologic processes The Hydrologic Processes
BAEN 673 / February 18, 2016 Hydrologic Processes Assignment: HW#7 Next class lecture in AEPM 104 Today s topics SWAT exercise #2 The SWAT model review paper Hydrologic processes The Hydrologic Processes
Developing a Technically Sound Aquifer Test Plan that Meets the Requirements of the Susquehanna River Basin Commission
 Developing a Technically Sound Aquifer Test Plan that Meets the Requirements of the Susquehanna River Basin Commission NY PA Brooks G. Abeln, P.G. Hydrogeologist, Project Review September 24, 2012 MD Susquehanna
Developing a Technically Sound Aquifer Test Plan that Meets the Requirements of the Susquehanna River Basin Commission NY PA Brooks G. Abeln, P.G. Hydrogeologist, Project Review September 24, 2012 MD Susquehanna
Evolving Conceptual Models and Monitoring Well Reconstruction in the Passaic Formation in New Jersey Abstract
 Evolving Conceptual Models and Monitoring Well Reconstruction in the Passaic Formation in New Jersey John N. Dougherty and Andrea Soo, CDM. Robert M. Alvey, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Abstract
Evolving Conceptual Models and Monitoring Well Reconstruction in the Passaic Formation in New Jersey John N. Dougherty and Andrea Soo, CDM. Robert M. Alvey, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Abstract
A-2. Soils. Soil Media. Chapter Contents. Soil Media In-situ Soil Testing Separation from Seasonal High Water Table (SHWT)
 A-2. Soils Chapter Contents Soil Media In-situ Soil Testing Separation from Seasonal High Water Table (SHWT) Importance of Soil Composition in SCMs The soil composition of many stormwater SCMs also is
A-2. Soils Chapter Contents Soil Media In-situ Soil Testing Separation from Seasonal High Water Table (SHWT) Importance of Soil Composition in SCMs The soil composition of many stormwater SCMs also is
Potential effects evaluation of dewatering an underground mine on surface water and groundwater located in a rural area
 Potential effects evaluation of dewatering an underground mine on surface water and groundwater located in a rural area ITRODUCTIO Michel Mailloux* Eng. M.Sc, Vincent Boisvert, M.Sc, Denis Millette, Eng.,
Potential effects evaluation of dewatering an underground mine on surface water and groundwater located in a rural area ITRODUCTIO Michel Mailloux* Eng. M.Sc, Vincent Boisvert, M.Sc, Denis Millette, Eng.,
15A NCAC 02C.0225 GROUNDWATER REMEDIATION WELLS (a) Groundwater Remediation Wells are used to inject additives, treated groundwater, or ambient air
 15A NCAC 02C.0225 GROUNDWATER REMEDIATION WELLS (a) Groundwater Remediation Wells are used to inject additives, treated groundwater, or ambient air for the treatment of contaminated soil or groundwater.
15A NCAC 02C.0225 GROUNDWATER REMEDIATION WELLS (a) Groundwater Remediation Wells are used to inject additives, treated groundwater, or ambient air for the treatment of contaminated soil or groundwater.
Groundwater Models as Inputs into Ecosystem Services Models Evaluating Uncertainty
 Groundwater Models as Inputs into Ecosystem Services Models Evaluating Uncertainty Ray Wuolo Barr Engineering Co. modeling surface-water groundwater interaction feels like WATER LEVELS Kx swimming in a
Groundwater Models as Inputs into Ecosystem Services Models Evaluating Uncertainty Ray Wuolo Barr Engineering Co. modeling surface-water groundwater interaction feels like WATER LEVELS Kx swimming in a
Guidelines for Preparing an Alternatives Analysis
 Policy Number: Policy No. 2017-01 Title: Guidelines for Preparing an Alternatives Analysis Effective Date: September 7, 2017 Authority: Policy: Public Law 91-575, 84 Stat. 1509 et seq., Sections 3.1, 3.4(2),
Policy Number: Policy No. 2017-01 Title: Guidelines for Preparing an Alternatives Analysis Effective Date: September 7, 2017 Authority: Policy: Public Law 91-575, 84 Stat. 1509 et seq., Sections 3.1, 3.4(2),
Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR) Practical Techniques for the Caribbean
 Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR) Practical Techniques for the Caribbean Scope of Presentation What is MAR? Antigua and Barbuda water resources issues Why promote MAR? MAR: Techniques MAR: Design criteria
Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR) Practical Techniques for the Caribbean Scope of Presentation What is MAR? Antigua and Barbuda water resources issues Why promote MAR? MAR: Techniques MAR: Design criteria
Water for All, Now and Into the Future: Water Quantity in Wisconsin. A report by the Sierra Club-John Muir Chapter
 Water for All, Now and Into the Future: Water Quantity in Wisconsin A report by the Sierra Club-John Muir Chapter Table of Contents Background The Importance of Water Quantity Water Use in Wisconsin Excessive
Water for All, Now and Into the Future: Water Quantity in Wisconsin A report by the Sierra Club-John Muir Chapter Table of Contents Background The Importance of Water Quantity Water Use in Wisconsin Excessive
MEMORANDUM. RAI Responses Related to East Lake Road Wellfield Drawdown Analysis, WUP No SDI Project No. PCF-180.
 SDI Environmental Services, Inc. 13911 N. Dale Mabry Hwy. Suite 201, Tampa, FL 33618; (813) 961-1935 MEMORANDUM TO: FROM: SUBJECT: Dave Slonena, P.G., Pinellas County Cathleen Beaudoin Jonas RAI Responses
SDI Environmental Services, Inc. 13911 N. Dale Mabry Hwy. Suite 201, Tampa, FL 33618; (813) 961-1935 MEMORANDUM TO: FROM: SUBJECT: Dave Slonena, P.G., Pinellas County Cathleen Beaudoin Jonas RAI Responses
Oversized quarry sumps can be used to store run-off during
 Oversized quarry sumps can be used to store run-off during large events Paved quarry yard with channels routing run-off to attenuation 3 The Hydrogeology of Quarry Dewatering Extraction below the water
Oversized quarry sumps can be used to store run-off during large events Paved quarry yard with channels routing run-off to attenuation 3 The Hydrogeology of Quarry Dewatering Extraction below the water
The Corning Primary Aquifer -One of 18. NYSDEC Primary Aquifers in New York
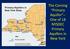 The Corning Primary Aquifer -One of 18 NYSDEC Primary Aquifers in New York NYSDEC Primary and Principal Aquifers PRIMARY AQUIFERS (18) Highly productive aquifers presently being utilized by major municipal
The Corning Primary Aquifer -One of 18 NYSDEC Primary Aquifers in New York NYSDEC Primary and Principal Aquifers PRIMARY AQUIFERS (18) Highly productive aquifers presently being utilized by major municipal
Lab #12: Groundwater (GetWET Field Trip)
 Lab #12: Groundwater (GetWET Field Trip) GEOL121 Introductory Geology Lab Name: TA and Section: Assignment Part 1: Well installation and core descriptions 1. Watch the movie clip of the GetWET well installation
Lab #12: Groundwater (GetWET Field Trip) GEOL121 Introductory Geology Lab Name: TA and Section: Assignment Part 1: Well installation and core descriptions 1. Watch the movie clip of the GetWET well installation
2.3 Water Budget Data In Ontario
 2.3 Water Budget Data In Ontario Water budget data available for Ontario includes meteorologic data, hydrometric data and groundwater data. Geological and physiographical data provide information to describe
2.3 Water Budget Data In Ontario Water budget data available for Ontario includes meteorologic data, hydrometric data and groundwater data. Geological and physiographical data provide information to describe
Strength. Performance. Passion. Paris Pit CAP. April 30, Permit To Take Water Application Holcim (Canada) Inc.
 Strength. Performance. Passion. Paris Pit CAP April 30, 2013 Permit To Take Water Application 2012 Holcim (Canada) Inc. Agenda Welcome Minutes from Last Meeting Dufferin Paris Pit - General Update Review
Strength. Performance. Passion. Paris Pit CAP April 30, 2013 Permit To Take Water Application 2012 Holcim (Canada) Inc. Agenda Welcome Minutes from Last Meeting Dufferin Paris Pit - General Update Review
Chapter 2: Aquifers and groundwater
 Chapter 2: Aquifers and groundwater Groundwater movement through aquifers is driven by differences in groundwater levels or pressure and is controlled by how porous the material is that it passes through.
Chapter 2: Aquifers and groundwater Groundwater movement through aquifers is driven by differences in groundwater levels or pressure and is controlled by how porous the material is that it passes through.
KINGWOOD TOWNSHIP THREE PART PUMP TEST CHECKLIST. APPLICANT: Road Name: TAX MAP Sheet/Block/Lot Date Submitted: Name of Project (If Any):
 APPLICANT: Road Name: TAX MAP Sheet/Block/Lot Date Submitted: Name of Project (If Any): Signature of Applicant: 1 2 Supervision. All well tests shall be conducted under the supervision of a Certified Well
APPLICANT: Road Name: TAX MAP Sheet/Block/Lot Date Submitted: Name of Project (If Any): Signature of Applicant: 1 2 Supervision. All well tests shall be conducted under the supervision of a Certified Well
ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY
 ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY Prof. Rajesh Bhagat Asst. Professor Civil Engineering Department Yeshwantrao Chavan College Of Engineering Nagpur B. E. (Civil Engg.) M. Tech. (Enviro. Engg.) GCOE, Amravati VNIT,
ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY Prof. Rajesh Bhagat Asst. Professor Civil Engineering Department Yeshwantrao Chavan College Of Engineering Nagpur B. E. (Civil Engg.) M. Tech. (Enviro. Engg.) GCOE, Amravati VNIT,
William Wilmot Matrix Solutions Inc. 118, Avenue S.W., Calgary, Alberta, Canada
 Hydrogeologic Assessment in Support of the Development of the Peace River Oil Sands Deposit: A Case Study Concerning a Pilot-Scale in-situ SAGD Operation William Wilmot Matrix Solutions Inc. 118, 319-2
Hydrogeologic Assessment in Support of the Development of the Peace River Oil Sands Deposit: A Case Study Concerning a Pilot-Scale in-situ SAGD Operation William Wilmot Matrix Solutions Inc. 118, 319-2
MODELLING THE GROUNDWATER FLOW FOR ESTIMATING THE PUMPING COST OF IRRIGATION IN THE AQUIFER OF N. MOUDANIA, GREECE
 Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 MODELLING THE GROUNDWATER FLOW FOR ESTIMATING THE PUMPING COST OF IRRIGATION
Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 MODELLING THE GROUNDWATER FLOW FOR ESTIMATING THE PUMPING COST OF IRRIGATION
Groundwater 3/16/2010. GG22A: GEOSPHERE & HYDROSPHERE Hydrology
 GG22A: GEOSPHERE & HYDROSPHERE Hydrology Definitions Groundwater Subsurface water in soil or rock that is fully saturated. Aquifer Contains enough saturated material to yield significant quantities of
GG22A: GEOSPHERE & HYDROSPHERE Hydrology Definitions Groundwater Subsurface water in soil or rock that is fully saturated. Aquifer Contains enough saturated material to yield significant quantities of
EFFECTS OF WATERSHED TOPOGRAPHY, SOILS, LAND USE, AND CLIMATE ON BASEFLOW HYDROLOGY IN HUMID REGIONS: A REVIEW
 PROGRESS IN PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY EFFECTS OF WATERSHED TOPOGRAPHY, SOILS, LAND USE, AND CLIMATE ON BASEFLOW HYDROLOGY IN HUMID REGIONS: A REVIEW KATIE PRICE 2011 Presented by: Jordan Martin Article Overview
PROGRESS IN PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY EFFECTS OF WATERSHED TOPOGRAPHY, SOILS, LAND USE, AND CLIMATE ON BASEFLOW HYDROLOGY IN HUMID REGIONS: A REVIEW KATIE PRICE 2011 Presented by: Jordan Martin Article Overview
DEFINITION OF TERMS AND ACRONYMS 31 TAC EFFECTIVE DECEMBER 8, 2016
 DEFINITION OF TERMS AND ACRONYMS 31 TAC 357.10 EFFECTIVE DECEMBER 8, 2016 The terms and acronyms used in this guidance document as defined in 31 TAC 357.10 have the following meanings: 1. Agricultural
DEFINITION OF TERMS AND ACRONYMS 31 TAC 357.10 EFFECTIVE DECEMBER 8, 2016 The terms and acronyms used in this guidance document as defined in 31 TAC 357.10 have the following meanings: 1. Agricultural
WATER MANAGEMENT PLAN FOR UNCONVENTIONAL GAS WELL DEVELOPMENT
 COMMONWEALTH OF PENNSYLVANIA Example Format DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION OFFICE OF OIL AND GAS MANAGEMENT WATER MANAGEMENT PLAN FOR UNCONVENTIONAL GAS WELL DEVELOPMENT APPLICANT AND PLAN COVERAGE
COMMONWEALTH OF PENNSYLVANIA Example Format DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION OFFICE OF OIL AND GAS MANAGEMENT WATER MANAGEMENT PLAN FOR UNCONVENTIONAL GAS WELL DEVELOPMENT APPLICANT AND PLAN COVERAGE
Numerical Groundwater Model for the Kaweah Delta Water Conservation District
 Numerical Groundwater Model for the Kaweah Delta Water Conservation District Nels Ruud and Peter Leffler Fugro West, Inc. Larry Dotson Kaweah Delta Water Conservation District Presentation Outline Background
Numerical Groundwater Model for the Kaweah Delta Water Conservation District Nels Ruud and Peter Leffler Fugro West, Inc. Larry Dotson Kaweah Delta Water Conservation District Presentation Outline Background
Wickes Manufacturing TCE Plume Site Mancelona, Michigan
 Wickes Manufacturing TCE Plume Site Mancelona, Michigan December 2017 What is TCE? Trichloroethylene (TCE) Common Industrial Solvent Known Human Carcinogen Federal and State Safe Drinking Water of 5 µg/l
Wickes Manufacturing TCE Plume Site Mancelona, Michigan December 2017 What is TCE? Trichloroethylene (TCE) Common Industrial Solvent Known Human Carcinogen Federal and State Safe Drinking Water of 5 µg/l
Workshop 1 Our Groundwater and Surfacewaters are Connected and We are What We Drink Hosted by: Lackawanna County Conservation District
 Workshop 1 Our Groundwater and Surfacewaters are Connected and We are What We Drink Hosted by: Lackawanna County Conservation District Sponsored by: Pocono Northeast RC&D Council Through the C-SAW C Program
Workshop 1 Our Groundwater and Surfacewaters are Connected and We are What We Drink Hosted by: Lackawanna County Conservation District Sponsored by: Pocono Northeast RC&D Council Through the C-SAW C Program
Safe Drinking Water Program. Public Water System Permitting
 Safe Drinking Water Program Public Water System Permitting NC Region DEP Regions in Susquehanna Basin PA Safe Drinking Water Program The Safe Drinking Water Program implements the 1984 Safe Drinking Water
Safe Drinking Water Program Public Water System Permitting NC Region DEP Regions in Susquehanna Basin PA Safe Drinking Water Program The Safe Drinking Water Program implements the 1984 Safe Drinking Water
15A NCAC 02C.0219 AQUIFER STORAGE AND RECOVERY WELLS (a) Aquifer Storage and Recovery Wells are used to inject potable water for the purposes of
 15A NCAC 02C.0219 AQUIFER STORAGE AND RECOVERY WELLS (a) Aquifer Storage and Recovery Wells are used to inject potable water for the purposes of subsurface storage and for later recovery of the injected
15A NCAC 02C.0219 AQUIFER STORAGE AND RECOVERY WELLS (a) Aquifer Storage and Recovery Wells are used to inject potable water for the purposes of subsurface storage and for later recovery of the injected
Effect of Conjunctive Use of Water for Paddy Field Irrigation on Groundwater Budget in an Alluvial Fan ABSTRACT
 1 Effect of Conjunctive Use of Water for Paddy Field Irrigation on Groundwater Budget in an Alluvial Fan Ali M. Elhassan (1), A. Goto (2), M. Mizutani (2) (1) New Mexico Interstate Stream Commission, P.
1 Effect of Conjunctive Use of Water for Paddy Field Irrigation on Groundwater Budget in an Alluvial Fan Ali M. Elhassan (1), A. Goto (2), M. Mizutani (2) (1) New Mexico Interstate Stream Commission, P.
IV. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS G. HYDROLOGY/WATER QUALITY
 IV. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS G. HYDROLOGY/WATER QUALITY ENVIRONMENTAL SETTING The project site is located in the Wilshire community of the City of Los Angeles and is bound by S. Wetherly Drive to
IV. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS G. HYDROLOGY/WATER QUALITY ENVIRONMENTAL SETTING The project site is located in the Wilshire community of the City of Los Angeles and is bound by S. Wetherly Drive to
Environmental Management Chapter ALABAMA DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT WATER DIVISION-WATER SUPPLY PROGRAM ADMINISTRATIVE CODE
 ALABAMA DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT WATER DIVISION-WATER SUPPLY PROGRAM ADMINISTRATIVE CODE CHAPTER 335-7-15 SOURCE WATER ASSESSMENT PROGRAM TABLE OF CONTENTS 335-7-15-.01 Applicability 335-7-15-.02
ALABAMA DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT WATER DIVISION-WATER SUPPLY PROGRAM ADMINISTRATIVE CODE CHAPTER 335-7-15 SOURCE WATER ASSESSMENT PROGRAM TABLE OF CONTENTS 335-7-15-.01 Applicability 335-7-15-.02
Environmental Information Worksheet
 Environmental Information Worksheet Water System Owner (Attach additional sheets if necessary) Needs and Alternatives Provide a brief narrative that describes: Current drinking water system needs. Project
Environmental Information Worksheet Water System Owner (Attach additional sheets if necessary) Needs and Alternatives Provide a brief narrative that describes: Current drinking water system needs. Project
Numerical Groundwater Flow Model Report. Caloosa Materials, LLC 3323 Gulf City Road Ruskin, Florida 33570
 Numerical Groundwater Flow Model Report Caloosa Materials, LLC 3323 Gulf City Road Ruskin, Florida 33570 GHD 2675 Winkler Ave Suite 180 Fort Myers, FL 33901 11138224 Report July 27, 2017 Table of Contents
Numerical Groundwater Flow Model Report Caloosa Materials, LLC 3323 Gulf City Road Ruskin, Florida 33570 GHD 2675 Winkler Ave Suite 180 Fort Myers, FL 33901 11138224 Report July 27, 2017 Table of Contents
Appendix B Stormwater Site Plan Submittal Requirements Checklist
 Stormwater Site Plan Submittal Requirements Checklist The Submittal Requirements Checklist is intended to aid the design engineer in preparing a Stormwater Site Plan. All items included in the following
Stormwater Site Plan Submittal Requirements Checklist The Submittal Requirements Checklist is intended to aid the design engineer in preparing a Stormwater Site Plan. All items included in the following
WASA Quiz Review. Chapter 2
 WASA Quiz Review Chapter 2 Question#1 What is surface runoff? part of the water cycle that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed into groundwater or evaporating Question #2 What are
WASA Quiz Review Chapter 2 Question#1 What is surface runoff? part of the water cycle that flows over land as surface water instead of being absorbed into groundwater or evaporating Question #2 What are
Performance and Analysis of Aquifer Slug Tests and Pumping Tests Policy
 Performance and Analysis of Aquifer Slug Tests and Pumping Tests Policy May 31, 2007 Table of Contents page Introduction... 2 (1) Purpose of policy...2 (2) Basis for technical approach...2 (3) The purpose
Performance and Analysis of Aquifer Slug Tests and Pumping Tests Policy May 31, 2007 Table of Contents page Introduction... 2 (1) Purpose of policy...2 (2) Basis for technical approach...2 (3) The purpose
Overview of Water Resources (Part 2): Groundwater in Sonoma Valley
 . Overview of Water Resources (Part 2): Groundwater in Sonoma Valley Marcus Trotta, PG, CHg Principal Hydrogeologist Sonoma County Water Agency Sonoma Valley Groundwater Sustainability Agency October 23,
. Overview of Water Resources (Part 2): Groundwater in Sonoma Valley Marcus Trotta, PG, CHg Principal Hydrogeologist Sonoma County Water Agency Sonoma Valley Groundwater Sustainability Agency October 23,
Science Olympiad. Mentor Invitational Hydrogeology ANSWER KEY. Name(s): School Name: Point Totals
 Science Olympiad Mentor Invitational Hydrogeology ANSWER KEY Team Number: Raw Score: Rank: Name(s): School Name: Point Totals Possible Part 1: Groundwater Concepts and Vocabulary 30 Part 2: The Hydrogeology
Science Olympiad Mentor Invitational Hydrogeology ANSWER KEY Team Number: Raw Score: Rank: Name(s): School Name: Point Totals Possible Part 1: Groundwater Concepts and Vocabulary 30 Part 2: The Hydrogeology
What is Hydrogeology?
 What is Hydrogeology? It is the comprehensive study of groundwater, its distribution and evolution through time and space, under regional geology. Geohydrology studies water behavior in geological environment,
What is Hydrogeology? It is the comprehensive study of groundwater, its distribution and evolution through time and space, under regional geology. Geohydrology studies water behavior in geological environment,
Water Resources on PEI: an overview and brief discussion of challenges
 Water Resources on PEI: an overview and brief discussion of challenges Components: Components and links Atmospheric water Surface water (including glacial water) Groundwater Links: Precipitation (atm(
Water Resources on PEI: an overview and brief discussion of challenges Components: Components and links Atmospheric water Surface water (including glacial water) Groundwater Links: Precipitation (atm(
