Nitrate Dynamics at ALOHA and K2. Karen Casciotti Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Department of Marine Chemistry and Geochemistry
|
|
|
- Roland Chapman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nitrate Dynamics at ALOHA and K2 Karen Casciotti Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Department of Marine Chemistry and Geochemistry
2 VERTIGO 24 Experiments Nitrate isotopic profiles Coupled δ 15 N and δ 18 O analysis Rates of microbial activity Nitrification Rates Whole water samples and MULVFS particles Microbial community analysis: freeliving vs. particle attached Nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria Suspended particles (MULVFS) Sinking particles (CLAP traps Hg vs. Formalin preservation) Handpicked squiggles, tufts, and puffs
3 VERTIGO 25 Experiments Nitrate isotopic profiles Coupled δ 15 N and δ 18 O analysis Microbial community analysis: Nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria Freeliving vs. particle attached
4 Eppley and Peterson, 1979: Export Production and the Biological Pump N 2 fixation CO 2 Atmospheric deposition New Production NO 3 NH 4 CO 2 CO 2 Phytoplankton Zooplankton Regenerated Production NH 4 DON, DOC CO 2 Bacteria Euphotic zone Export Aphotic zone Dead organic production matter
5 Map of Surface Nitrate Subarctic Front
6 Comparison of Basic Chemical and Physical Parameters T S σ θ O 2 Si NO 3 ALOHA = Blue K2 = Red
7 What we can learn from NO 3 isotopes? Supply of N to the surface N cycling/turnover N export and remineralization
8 Rayleigh Fractionation δ 15 NO 3 15 δ15 NO 3 1 δ 15 NPN inst ε 5 ε ε δ 15 NPN accum f = [NO 3 ]/[NO3initial substrate]
9 N and O isotopic fractionation during N cycling Nitrogen fixation NH 4 Nitrification O 2, H 2 O N 2 N org Assimilation NO 3 N org H 2 O Denitrification N 2 H 2 O δ 18 ONO 3 NO 3 N 2 fix. Assimilation Deep Denitrification Nitrification δ 15 NNO 3
10 Nitrate Isotopic Profiles 1 profiles from ALOHA 6 profiles from K2 Analyzed for δ 15 N and δ 18 O using denitrifier method Allows isotopic analysis of previously inaccessible pools of NO 3
11 The denitrifier method Pseudomonas aureofaciens or Pseudomonas chlororaphis Inject NO 3 or NO 2 sample NO 3 NO 2 NO N 2 O N 2 Denitrification takes place N 2 O (g) Analyze N 2 O isotopes Sigman et al., 21. Analytical Chemistry: 15 NNO 3 Casciotti et al., 22. Analytical Chemistry: 18 ONO 3
12 K2: T, S, NO 3, and PO 4 Depth (m) Sigma Theta Temperature (¼C) Salinity (PSU) Depth (m) Nitrate, cast 24 Nitrate, cast 73 Nitrate, cast 27 Nitrate, cast 5 Nitrate, cast 72 Phoshpate, cast 24 Phosphate, cast Phosphate (µm) 4 Nitrate (µm)
13 δ 15 N and δ 18 ONO 3 at K2 2 4 δ 18 ONO δ 15 NNO Depth (m) 15 Depth (m)
14 Nitrate consumption and mixing 12 δ 15 NNO 3 Cast 24 δ 15 NNO 3 Cast 73 1 δ 15 NNO 3 Cast 27 δ 15 NNO 3 Cast 5 δ 15 NNO 3 Cast 72 and δ 15 NNO δ 15 NNO 3 Closed system model δ 15 NNO 3 δ 18 ONO δ 18 ONO 3 Cast 24 δ 18 ONO 3 Cast 73 δ 18 ONO 3 Cast 27 δ 18 ONO 3 Cast 5 δ 18 ONO 3 Cast 72 δ 18 ONO 3 δ 18 ONO 3 Closed system model ln [NO 3 ]
15 Isotope mixing Fractionation alone Fractionation and mixing δ 15 NO 3 ε δ 15 NO 3 ε ln[no 3 ] ln[no 3 ]
16 Nitrate consumption and mixing and δ 15 NNO 3 δ 18 ONO Upper 5 m T min Below 2 m δ 15 NNO 3 Cast 24 δ 15 NNO 3 Cast 73 δ 15 NNO 3 Cast 27 δ 15 NNO 3 Cast 5 δ 15 NNO 3 Cast 72 δ 15 NNO 3 Closed system model δ 18 ONO 3 Cast 24 δ 18 ONO 3 Cast 73 δ 18 ONO 3 Cast 27 δ 18 ONO 3 Cast 5 δ 18 ONO 3 Cast 72 δ 18 ONO 3 Closed system model ln [NO 3 ] δ 15 NNO 3 δ 18 ONO 3
17 δ 15 N vs. δ 18 O 12 1 δ 18 ONO δ 15 N vs. δ 18 O, slope =1.11 ± δ 15 NNO
18 Fluxes of N at Station K2 Export Less Efficient Remineralization? 15 m trap 3 m trap PN Flux, δ 15 N Remineralization flux PN Flux, δ 15 N Remineralization flux 5 m trap PN Flux, δ 15 N
19 ALOHA T, S, NO 3, and PO 4 Temperature (C) Nitrate (µm) Depth (m) Depth (m) Sigma Theta (kg m 3 ) Salinity (PSU) Phosphate (µm)
20 δ 15 N and δ 18 ONO 3 at ALOHA 1 2 δ 18 ONO δ 15 NNO Depth (m) 15 Depth (m)
21 ALOHA ln[no 3 ] vs. δ 12 δ 18 ONO 3 δ 15 NNO 3 1 and δ 15 NNO 3 δ 18 ONO ln [NO 3 ] 3. 4.
22 ALOHA δ 15 N vs. δ 18 O
23 Interpretation 12 A. B. δ 18 ONO Surface Deep δ 18 ONO 3 N 2 fix. Assimilation Denitrification Thermocline Nitrification 4 8 δ 15 NNO 3 12 δ 15 NNO 3
24 N cycling at ALOHA N 2 fixation Export δ 15 NPN ~ 1.5 in summer 7 Efficient Remineralization 15 m trap 3 m trap PN Flux PN Flux Remineralization flux Remineralization flux PN Flux 5 m trap
25
26 North Pacific Nitrate Section K2 ALOHA Subtropical Subpolar
27 Nitrification Rate Profiles On Board Collect water samples from niskin or resuspended particles from MULVFS Aliquot in replicate 25 ml polycarbonate bottles Spike with 15 NNO 3 (5 ) Subsample over 5 days, freeze samples On Shore Analyze nitrate concentration, δ 15 N, δ 18 O Calculate nitrate production by isotope dilution
28 Microbial Community Analysis N 2 O NO DNA extracted from MULFVS and trap samples, as well as handpicked plankton Ammoniaoxidizing bacterium N 2 O NOR NH 4 O 2 AMO HAO H NH 2 OH 2 O H 2 O NO NIR NO 2 PCR products obtained for amoa, haoa, and norb from a handful of samples.
29 Microbial community investigations Sample Description amoa haoa norb 4_1 MULVFS surface 3_2 MULVFS ~15 m 3_4 MULVFS ~3 m 4_5 MULVFS ~5 m 3_6 blank 21C NBST 15 m Hg 211C NBST 15 m Formalin 231C NBST 3 m Hg 232C NBST 3 m Formalin 252C NBST 5 m Hg 253C NBST 5 m Formalin 265C blank clap trap Squiggles Handpicked nd Tufts Handpicked nd Puffs Handpicked nd
30 North Pacific Surface Currents
31 Further context Vertigo ALOHA,K2 d15nno ALOHA26 ALOHA29 K2 K2 K2 KM45 KM45 2 PAPA DannyETNP 25 peru
Nitrogen Cycling in the Sea
 Nitrogen Cycling in the Sea NH 4 + N0 2 N0 2 NH 4 + Outline Nitrogen species in marine watersdistributions and concentrations New, regenerated, and export production The processes: Assimilation, N 2 fixation,
Nitrogen Cycling in the Sea NH 4 + N0 2 N0 2 NH 4 + Outline Nitrogen species in marine watersdistributions and concentrations New, regenerated, and export production The processes: Assimilation, N 2 fixation,
Nitrogen Cycling in the Sea
 Nitrogen Cycling in the Sea Matt Church (MSB 612 / 9568779/ mjchurch@hawaii.edu) Marine Microplankton Ecology / OCN 626 NH 4 N0 2 N0 2 NH 4 Outline Nitrogen species in marine watersdistributions and concentrations
Nitrogen Cycling in the Sea Matt Church (MSB 612 / 9568779/ mjchurch@hawaii.edu) Marine Microplankton Ecology / OCN 626 NH 4 N0 2 N0 2 NH 4 Outline Nitrogen species in marine watersdistributions and concentrations
11/9/2010. Stoichiometry of POM and DOM. DOC cycling via DO 14 C Williams, Oeschger, and Kinney; Nature v224 (1969)
 DOC cycling via DO 1 C Williams, Oeschger, and Kinney; Nature v22 (1969) UV photooxidation Radiocarbon in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans Peter M. Williams and Ellen Druffel; Nature 1987, JGR 1992 DIC
DOC cycling via DO 1 C Williams, Oeschger, and Kinney; Nature v22 (1969) UV photooxidation Radiocarbon in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans Peter M. Williams and Ellen Druffel; Nature 1987, JGR 1992 DIC
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1745 Isotopic ratios of nitrite as source and age tracers for oceanic nitrite Carolyn Buchwald 1 and Karen L. Casciotti 2 1 Massachusetts Institute of Technology/
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1745 Isotopic ratios of nitrite as source and age tracers for oceanic nitrite Carolyn Buchwald 1 and Karen L. Casciotti 2 1 Massachusetts Institute of Technology/
A functional gene approach to studying nitrogen cycling in the sea. Matthew Church (MSB 612 / March 20, 2007
 A functional gene approach to studying nitrogen cycling in the sea Matthew Church (MSB 612 / 6-8779 mjchurch@hawaii.edu) March 20, 2007 Overview Climate change, carbon cycling, and ocean biology Distributions
A functional gene approach to studying nitrogen cycling in the sea Matthew Church (MSB 612 / 6-8779 mjchurch@hawaii.edu) March 20, 2007 Overview Climate change, carbon cycling, and ocean biology Distributions
Tracking the fate of carbon in the ocean using thorium-234
 Tracking the fate of carbon in the ocean using thorium-234 Ken Buesseler Dept. of Marine Chemistry and Geochemistry Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Outline 1. Background- the biological pump & why
Tracking the fate of carbon in the ocean using thorium-234 Ken Buesseler Dept. of Marine Chemistry and Geochemistry Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Outline 1. Background- the biological pump & why
Phytoplankton and bacterial biomass, production and growth in various ocean ecosystems
 Phytoplankton and bacterial biomass, production and growth in various ocean ecosystems Location Bact. Biomass (mg C m -2 ) Phyto. Biomass (mg C m -2 ) BactB: PhytoB BactP (mg C m -2 d -1 ) 1 o Pro (mg
Phytoplankton and bacterial biomass, production and growth in various ocean ecosystems Location Bact. Biomass (mg C m -2 ) Phyto. Biomass (mg C m -2 ) BactB: PhytoB BactP (mg C m -2 d -1 ) 1 o Pro (mg
Oceanic CO 2 system - Significance
 OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (10.25.18) (10.30.18) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) (11.27.18) Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling - Part 2 Lecture Outline 1. The Oceanic Carbon System 2. Nutrient Cycling in
OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (10.25.18) (10.30.18) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) (11.27.18) Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling - Part 2 Lecture Outline 1. The Oceanic Carbon System 2. Nutrient Cycling in
SUNLIGHT & OCEAN ZONATION
 PLANKTON, PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY, AND BIOGEOCHEMISTRY EPSS 15 Fall 2017 LAB #7 SUNLIGHT & OCEAN ZONATION Sunlight is critical to the distribution of oceanic life The base of the food chain (phytoplankton)
PLANKTON, PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY, AND BIOGEOCHEMISTRY EPSS 15 Fall 2017 LAB #7 SUNLIGHT & OCEAN ZONATION Sunlight is critical to the distribution of oceanic life The base of the food chain (phytoplankton)
Determining the f ratio 11/16/2010. Incubate seawater in the presence of trace 15
 Plankton production is supported by 2 types of nitrogen: 1) new production supported by external sources of N (e.g. NO 3 and N 2 ), 2) recycled or regenerated production, sustained by recycling of N. Assumptions:
Plankton production is supported by 2 types of nitrogen: 1) new production supported by external sources of N (e.g. NO 3 and N 2 ), 2) recycled or regenerated production, sustained by recycling of N. Assumptions:
PROPOSAL FOR AN INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH CRUISE IN THE ARABIAN SEA (19 September 23 October 2007) Bess Ward Princeton University 3 May 2007
 PROPOSAL FOR AN INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH CRUISE IN THE ARABIAN SEA (19 September 23 October 2007) Bess Ward Princeton University 3 May 2007 1. Background The Arabian Sea is a unique oceanographic province,
PROPOSAL FOR AN INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH CRUISE IN THE ARABIAN SEA (19 September 23 October 2007) Bess Ward Princeton University 3 May 2007 1. Background The Arabian Sea is a unique oceanographic province,
Meredith Howard Karen McLaughlin Nikolay Nezlin
 Meredith Howard Karen McLaughlin Nikolay Nezlin SCCWRP Objectives For Diversion Determine the fate of effluent nitrogen How quickly is effluent nitrogen consumed or transformed? Is effluent nitrogen being
Meredith Howard Karen McLaughlin Nikolay Nezlin SCCWRP Objectives For Diversion Determine the fate of effluent nitrogen How quickly is effluent nitrogen consumed or transformed? Is effluent nitrogen being
Marine Microbial Processes
 Marine Microbial Processes Outline size-structured food webs brief history of the development of our current understanding of microbially dominated food webs carbon cycling in marine food webs evolving
Marine Microbial Processes Outline size-structured food webs brief history of the development of our current understanding of microbially dominated food webs carbon cycling in marine food webs evolving
Nutrients, biology and elemental stoichiometry
 Nutrients, biology and elemental stoichiometry Subtropics and tropics: oligotrophic = low nutrient, low biomass. Equatorial upwelling regions: Elevated nutrients (1 10 MNO 3 ) and biomass (relative to
Nutrients, biology and elemental stoichiometry Subtropics and tropics: oligotrophic = low nutrient, low biomass. Equatorial upwelling regions: Elevated nutrients (1 10 MNO 3 ) and biomass (relative to
Global Biogeochemical Cycles. Supporting Information for
 Global Biogeochemical Cycles Supporting Information for The annual cycle of gross primary production, net community production and export efficiency across the North Pacific Ocean Hilary I. Palevsky 1a,
Global Biogeochemical Cycles Supporting Information for The annual cycle of gross primary production, net community production and export efficiency across the North Pacific Ocean Hilary I. Palevsky 1a,
Denitrification 2/11/2011. Energy to be gained in oxidation. Oxidized N. Reduced N
 Oxidized N Energy to be gained in oxidation Reduced N (Sarmiento & Gruber, 2006) Denitrification The reduction of NO 3 and NO 2 to N 2 during heterotrophic respiration of organic matter. Occurs predominately
Oxidized N Energy to be gained in oxidation Reduced N (Sarmiento & Gruber, 2006) Denitrification The reduction of NO 3 and NO 2 to N 2 during heterotrophic respiration of organic matter. Occurs predominately
Nitrogen Isotopes.
 Nitrogen Isotopes http://wordsinmocean.files.wordpress.com/2012/02/n-cycle.png Stable Isotope Notation Isotope data reported in standard or notation: Nitrogen 15 N 15 15 N/ N/ 14 14 N N sample AIR 1 1000
Nitrogen Isotopes http://wordsinmocean.files.wordpress.com/2012/02/n-cycle.png Stable Isotope Notation Isotope data reported in standard or notation: Nitrogen 15 N 15 15 N/ N/ 14 14 N N sample AIR 1 1000
The Carbon cycle. Atmosphere, terrestrial biosphere and ocean are constantly exchanging carbon
 The Carbon cycle Atmosphere, terrestrial biosphere and ocean are constantly exchanging carbon The oceans store much more carbon than the atmosphere and the terrestrial biosphere The oceans essentially
The Carbon cycle Atmosphere, terrestrial biosphere and ocean are constantly exchanging carbon The oceans store much more carbon than the atmosphere and the terrestrial biosphere The oceans essentially
Nitrogen and phosphorus cycling in the ocean
 Nitrogen and phosphorus cycling in the ocean Deborah A. Bronk Department of Physical Sciences Outline: 1. The Redfield ratio 2. Liebig s Law of the Minimum 3. The nitrogen cycle 4. The phosphorus cycle
Nitrogen and phosphorus cycling in the ocean Deborah A. Bronk Department of Physical Sciences Outline: 1. The Redfield ratio 2. Liebig s Law of the Minimum 3. The nitrogen cycle 4. The phosphorus cycle
Nutrient-uptake kinetics and ecological/evolutionary selection
 Nutrient-uptake kinetics and ecological/evolutionary selection Specific Rate of Uptake (d -1 ) 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 Nutrient Uptake V max = 2.25 d -1 K = 2.0 µm s V max = 1.5 d -1 K = 0.5 µm s II I 0.0
Nutrient-uptake kinetics and ecological/evolutionary selection Specific Rate of Uptake (d -1 ) 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 Nutrient Uptake V max = 2.25 d -1 K = 2.0 µm s V max = 1.5 d -1 K = 0.5 µm s II I 0.0
Part 3. Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling
 OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (10.27.16) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) Part 3. Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling Lecture Outline 1. The Oceanic Carbon System 2. Nutrient Cycling in the Ocean 3. Other elements
OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (10.27.16) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) Part 3. Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling Lecture Outline 1. The Oceanic Carbon System 2. Nutrient Cycling in the Ocean 3. Other elements
Background Information: Exploring the Nitrogen Cycle
 1 Background Information: Exploring the Nitrogen Cycle Alexandria G. Hounshell Doctoral Student Department of Marine Sciences University of North CarolinaChapel Hill Email: alexgh@live.unc.edu Twitter:
1 Background Information: Exploring the Nitrogen Cycle Alexandria G. Hounshell Doctoral Student Department of Marine Sciences University of North CarolinaChapel Hill Email: alexgh@live.unc.edu Twitter:
The Global Nitrogen Cycle
 OCN 401 The Global Nitrogen Cycle (11.30.10) Fig. 12.2. Units are 10 12 g N/yr (Tg) Role of N in Biogeochemistry Bioavailability of N (and/or P) can limit NPP on land/oceans; controls size of biomass N
OCN 401 The Global Nitrogen Cycle (11.30.10) Fig. 12.2. Units are 10 12 g N/yr (Tg) Role of N in Biogeochemistry Bioavailability of N (and/or P) can limit NPP on land/oceans; controls size of biomass N
D. R. Clark et al. C9253
 Biogeosciences Discuss., 12, C9253 C9267, 2016 www.biogeosciences-discuss.net/12/c9253/2016/ Author(s) 2016. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License. Interactive comment
Biogeosciences Discuss., 12, C9253 C9267, 2016 www.biogeosciences-discuss.net/12/c9253/2016/ Author(s) 2016. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License. Interactive comment
Intro to Biogeochemical Modeling Ocean & Coupled
 Intro to Biogeochemical Modeling Ocean & Coupled Keith Lindsay, NCAR/CGD NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation Lecture Outline 1) Large Scale Ocean Biogeochemical Features 2) Techniques
Intro to Biogeochemical Modeling Ocean & Coupled Keith Lindsay, NCAR/CGD NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation Lecture Outline 1) Large Scale Ocean Biogeochemical Features 2) Techniques
Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake
 Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake Fig. 6.6 Recall: Current ocean is gaining Carbon.. OCEAN Reservoir size: 38000 Flux in: 90 Flux out: 88+0.2=88.2 90-88.2 = 1.8 Pg/yr OCEAN is gaining 1.8 Pg/yr Sum of the
Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake Fig. 6.6 Recall: Current ocean is gaining Carbon.. OCEAN Reservoir size: 38000 Flux in: 90 Flux out: 88+0.2=88.2 90-88.2 = 1.8 Pg/yr OCEAN is gaining 1.8 Pg/yr Sum of the
DOC and major carbon reservoirs and fluxes
 The Composition and cycling of Dissolved organic matter-i Review of DOC distribution Review of radiocarbon in DOC Sources of DOC Seasonal cycling of DOC above the permanent thermocline Composition of DOC
The Composition and cycling of Dissolved organic matter-i Review of DOC distribution Review of radiocarbon in DOC Sources of DOC Seasonal cycling of DOC above the permanent thermocline Composition of DOC
Biogeochemistry of Nitrogen Isotopes in Northern Indian Ocean
 Biogeochemistry of Nitrogen Isotopes in Northern Indian Ocean Thesis submitted to The Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, Vadodara, India For the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Geology By Sanjeev
Biogeochemistry of Nitrogen Isotopes in Northern Indian Ocean Thesis submitted to The Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, Vadodara, India For the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Geology By Sanjeev
Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Nutrients!
 Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Nutrients! Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Critical Depth Recycled Nutrients! Oxidized Nutrients! Detritus! Rest of Ocean Biological and Solubility Pumps New (Export) vs. Regenerated
Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Nutrients! Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Critical Depth Recycled Nutrients! Oxidized Nutrients! Detritus! Rest of Ocean Biological and Solubility Pumps New (Export) vs. Regenerated
Part 3. Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling
 OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (11.03.11) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) Part 3. Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling Lecture Outline 1. Models of Carbon in the Ocean 2. Nutrient Cycling in the Ocean Atmospheric-Ocean
OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (11.03.11) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) Part 3. Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling Lecture Outline 1. Models of Carbon in the Ocean 2. Nutrient Cycling in the Ocean Atmospheric-Ocean
5/2/13. Zooplankton! Phytoplankton! Nutrients!
 Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Nutrients! 1 Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Critical Depth Recycled Nutrients! Oxidized Nutrients! Detritus! Rest of Ocean Biological and Solubility Pumps 2 New (Export) vs. Regenerated
Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Nutrients! 1 Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Critical Depth Recycled Nutrients! Oxidized Nutrients! Detritus! Rest of Ocean Biological and Solubility Pumps 2 New (Export) vs. Regenerated
Food web structure in the continental shelf and slope waters of the Korean peninsula: Stable isotope approach and prospects for future research
 PICES XVII End-to-end food webs: Impacts of a changing ocean October 28 28 Food web structure in the continental shelf and slope waters of the Korean peninsula: Stable isotope approach and prospects for
PICES XVII End-to-end food webs: Impacts of a changing ocean October 28 28 Food web structure in the continental shelf and slope waters of the Korean peninsula: Stable isotope approach and prospects for
Aquatic respiration and ocean metabolism
 Aquatic respiration and ocean metabolism Remember what life is all about: Energy (ATP) Reducing power (NADPH) Nutrients (C, N, P, S, Fe, etc., etc.) Photosynthetic organisms use sunlight, H 2 O, and dissolved
Aquatic respiration and ocean metabolism Remember what life is all about: Energy (ATP) Reducing power (NADPH) Nutrients (C, N, P, S, Fe, etc., etc.) Photosynthetic organisms use sunlight, H 2 O, and dissolved
The Global Nitrogen Cycle, and Linkages Between C, N, and P Cycles
 OCN 401 The Global Nitrogen Cycle, and Linkages Between C, N, and P Cycles (12.1.11) The Contemporary N Cycle - Basic Facts - Reservoirs and Fluxes Global N and P Budgets - balance between N-fixation and
OCN 401 The Global Nitrogen Cycle, and Linkages Between C, N, and P Cycles (12.1.11) The Contemporary N Cycle - Basic Facts - Reservoirs and Fluxes Global N and P Budgets - balance between N-fixation and
CHEMICAL: NITROGEN AND PHOSPHORUS (read pp in Dodson)
 BIOE 155, Fall 010 BACKGROUND CHEMICAL: NITROGEN AND PHOSPHORUS (read pp39-50 in Dodson) Lakes are often classified according to trophic status, specifically how much energy or food is available for the
BIOE 155, Fall 010 BACKGROUND CHEMICAL: NITROGEN AND PHOSPHORUS (read pp39-50 in Dodson) Lakes are often classified according to trophic status, specifically how much energy or food is available for the
1. Energy to do work 2. Raw material to build/repair things (nutrients)
 1. Energy to do work 2. Raw material to build/repair things (nutrients) Living things are built from water Nutrients: carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen 3. Essential nutrients are cycled through environment
1. Energy to do work 2. Raw material to build/repair things (nutrients) Living things are built from water Nutrients: carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen 3. Essential nutrients are cycled through environment
Scenarios of the Baltic Sea ecosystem calculated with a regional climate model
 Scenarios of the Baltic Sea ecosystem calculated with a regional climate model Markus Meier*/**, Kari Eilola* and Elin Almroth* *Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute, Norrköping and **Stockholm
Scenarios of the Baltic Sea ecosystem calculated with a regional climate model Markus Meier*/**, Kari Eilola* and Elin Almroth* *Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute, Norrköping and **Stockholm
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems
 2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems CARBON CYCLE A. Carbon Facts: Carbon is found in all living matter. Places that carbon is found are called stores or sinks Short-term Stores Long-term Stores - living
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems CARBON CYCLE A. Carbon Facts: Carbon is found in all living matter. Places that carbon is found are called stores or sinks Short-term Stores Long-term Stores - living
OPTION C.6 NITROGEN & PHOSPHORUS CYCLES
 OPTION C.6 NITROGEN & PHOSPHORUS CYCLES C.6 A Cycle INTRO https://www.thewastewaterblog.com/single-post/2017/04/29/-cycle-and-other-graphics IB BIO C.6 3 The nitrogen cycle describes the movement of nitrogen
OPTION C.6 NITROGEN & PHOSPHORUS CYCLES C.6 A Cycle INTRO https://www.thewastewaterblog.com/single-post/2017/04/29/-cycle-and-other-graphics IB BIO C.6 3 The nitrogen cycle describes the movement of nitrogen
The Hawaii Ocean Time-series (HOT): Highlights and perspectives from two decades of ocean observations
 The Hawaii Ocean Time-series (HOT): Highlights and perspectives from two decades of ocean observations MATTHEW CHURCH UNIVERSITY OF HAWAII OCB SCOPING WORKSHOP SEPTEMBER 2010 A Dedicated HOT Team NSF What
The Hawaii Ocean Time-series (HOT): Highlights and perspectives from two decades of ocean observations MATTHEW CHURCH UNIVERSITY OF HAWAII OCB SCOPING WORKSHOP SEPTEMBER 2010 A Dedicated HOT Team NSF What
Equatorial Pacific HNLC region
 Equatorial Pacific HNLC region Another region with high nitrogen left over after the growing season Iron and grazing constraints on primary production in the central equatorial Pacific: An EqPac synthesis
Equatorial Pacific HNLC region Another region with high nitrogen left over after the growing season Iron and grazing constraints on primary production in the central equatorial Pacific: An EqPac synthesis
MOLECULAR ASPECTS OF NITROUS OXIDE EMISSIONS
 MOLECULAR ASPECTS OF NITROUS OXIDE EMISSIONS Eulogio J. Bedmar Department of Soil Microbiology and Symbiotic Systems Estación Experimental del Zaidín CSIC, Granada Red Sirena Madrid, 2021 de enero de 2016
MOLECULAR ASPECTS OF NITROUS OXIDE EMISSIONS Eulogio J. Bedmar Department of Soil Microbiology and Symbiotic Systems Estación Experimental del Zaidín CSIC, Granada Red Sirena Madrid, 2021 de enero de 2016
Phytoplankton and Upper Ocean Biogeochemical Cycles Along Line P
 Phytoplankton and Upper Ocean Biogeochemical Cycles Along Line P Angelica Peña Institute of Ocean Sciences, Fisheries & Oceans Canada. Contribution: Diana Varela, Department of Biology & School of Earth
Phytoplankton and Upper Ocean Biogeochemical Cycles Along Line P Angelica Peña Institute of Ocean Sciences, Fisheries & Oceans Canada. Contribution: Diana Varela, Department of Biology & School of Earth
WHY DO WE NEED NITROGEN?? Nitrogen is needed to make up DNA and protein!
 Nitrogen Cycle 2.2 WHY DO WE NEED NITROGEN?? Nitrogen is needed to make up DNA and protein! In animals, proteins are vital for muscle function. In plants, nitrogen is important for growth. NITROGEN Nitrogen
Nitrogen Cycle 2.2 WHY DO WE NEED NITROGEN?? Nitrogen is needed to make up DNA and protein! In animals, proteins are vital for muscle function. In plants, nitrogen is important for growth. NITROGEN Nitrogen
Benthic Nutrient Cycling in Boston Harbor and Massachusetts Bay
 Benthic Nutrient Cycling in Boston Harbor and Massachusetts Bay Anne Giblin, Charles Hopkinson & Jane Tucker The Ecosystems Center, Marine Biological Laboratory Woods Hole, MA 2543 September 22, 1999 Boston
Benthic Nutrient Cycling in Boston Harbor and Massachusetts Bay Anne Giblin, Charles Hopkinson & Jane Tucker The Ecosystems Center, Marine Biological Laboratory Woods Hole, MA 2543 September 22, 1999 Boston
Reduced Nitrogen in Coastal Waters. Maren Voss Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde, Germany
 Reduced Nitrogen in Coastal Waters Maren Voss Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde, Germany Topics of this talk N-cycling of coastal zones and human impact Eutrophication in the Baltic
Reduced Nitrogen in Coastal Waters Maren Voss Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde, Germany Topics of this talk N-cycling of coastal zones and human impact Eutrophication in the Baltic
Sources, transformations and sinks of nitrogen in watersheds with multiple anthropogenic pressures
 Sources, transformations and sinks of nitrogen in watersheds with multiple anthropogenic pressures Bartoli, M. Department of Life Sciences, University of Parma, Italy marco.bartoli@unipr.it Roma, 2324/01/2014
Sources, transformations and sinks of nitrogen in watersheds with multiple anthropogenic pressures Bartoli, M. Department of Life Sciences, University of Parma, Italy marco.bartoli@unipr.it Roma, 2324/01/2014
Lakes: Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling. Lecture Outline
 OCN 401-Biogeochemical Systems (10.06.16) Lakes: Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 8 Lecture Outline 1. Seasonal cycle of lake stratification Temperature / density relationship
OCN 401-Biogeochemical Systems (10.06.16) Lakes: Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 8 Lecture Outline 1. Seasonal cycle of lake stratification Temperature / density relationship
Global Biogeochemical cycles and Ocean Productivity
 Global Biogeochemical cycles and Ocean Productivity Biological Oceanography Recall: goal is not to understand the biology of one particular organism (or group), but to understand organisms fit into the
Global Biogeochemical cycles and Ocean Productivity Biological Oceanography Recall: goal is not to understand the biology of one particular organism (or group), but to understand organisms fit into the
See the Appendix for additional information about the priority guidelines.
 US GEOTRACES Guidelines for participating in the Peru-Tahiti section 28 November 2011 PURPOSE This document was prepared by the US GEOTRACES Scientific Steering Committee (SSC) to serve as a resource for
US GEOTRACES Guidelines for participating in the Peru-Tahiti section 28 November 2011 PURPOSE This document was prepared by the US GEOTRACES Scientific Steering Committee (SSC) to serve as a resource for
The Carbon Cycle. Goal Use this page to review the carbon cycle. CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-19 DATE: NAME: CLASS:
 CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-19 The Carbon Cycle Goal Use this page to review the carbon cycle. CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-20 The Carbon Cycle Concept Map Goal Use this page to make a concept map about the carbon cycle. What
CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-19 The Carbon Cycle Goal Use this page to review the carbon cycle. CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-20 The Carbon Cycle Concept Map Goal Use this page to make a concept map about the carbon cycle. What
Lakes: Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling
 OCN 401-Biogeochemical Systems (9.28.17) Lakes: Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 8 Lecture Outline 1. Seasonal cycle of lake stratification Temperature / density relationship
OCN 401-Biogeochemical Systems (9.28.17) Lakes: Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 8 Lecture Outline 1. Seasonal cycle of lake stratification Temperature / density relationship
Answer THREE questions, at least ONE question from EACH section.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Environmental Sciences Main Series Undergraduate Examination 2012-2013 CHEMICAL OCEANOGRAPHY ENV-2A45 Time allowed: 2 hours. Answer THREE questions, at least ONE question
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Environmental Sciences Main Series Undergraduate Examination 2012-2013 CHEMICAL OCEANOGRAPHY ENV-2A45 Time allowed: 2 hours. Answer THREE questions, at least ONE question
Patterns of Productivity
 Patterns of Productivity Limitation by Light and Nutrients OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of biomass by autotrophs Secondary Production - the production of biomass by heterotrophs
Patterns of Productivity Limitation by Light and Nutrients OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of biomass by autotrophs Secondary Production - the production of biomass by heterotrophs
Where does primary production go? Export Bacteria Grazing Dissolved organic matter
 Where does primary production go? Export Bacteria Grazing Dissolved organic matter The Microbial Loop Classic Food web Phytoplankton Inorganic Nutrients A simplified depiction of the microbial loop Heterotrophic
Where does primary production go? Export Bacteria Grazing Dissolved organic matter The Microbial Loop Classic Food web Phytoplankton Inorganic Nutrients A simplified depiction of the microbial loop Heterotrophic
The effects of salt marsh restoration on nutrient retention and nitrogen cycling
 The effects of salt marsh restoration on nutrient retention and nitrogen cycling Katherine Klammer Skidmore College 16 Advisor: Anne E. Giblin The Ecosystems Center at the Marine Biological Laboratory
The effects of salt marsh restoration on nutrient retention and nitrogen cycling Katherine Klammer Skidmore College 16 Advisor: Anne E. Giblin The Ecosystems Center at the Marine Biological Laboratory
Production and Life OCEA 101
 Production and Life OCEA 101 Overview Photosynthesis Primary production Phytoplankton biomass Controls on primary production and biomass Food webs Photosynthesis Photosynthesis requires: (i) sunlight (ii)
Production and Life OCEA 101 Overview Photosynthesis Primary production Phytoplankton biomass Controls on primary production and biomass Food webs Photosynthesis Photosynthesis requires: (i) sunlight (ii)
Working towards an ecosystem level understanding of how different oyster aquaculture practices alter nitrogen cycling.
 Working towards an ecosystem level understanding of how different oyster aquaculture practices alter nitrogen cycling. Daniel Rogers, Stonehill College Virginia Edgcomb and Vivian Mara, Woods Hole Oceanographic
Working towards an ecosystem level understanding of how different oyster aquaculture practices alter nitrogen cycling. Daniel Rogers, Stonehill College Virginia Edgcomb and Vivian Mara, Woods Hole Oceanographic
Interannual variations of nutrients and primary production over the southeastern Beirng Sea shelf during spring of 1997,1998,and 1999
 Interannual variations of nutrients and primary production over the southeastern Beirng Sea shelf during spring of 1997,1998,and 1999 TaeKeun Rho,Terry E. Whitledge, and John J. Goering Institute of Marine
Interannual variations of nutrients and primary production over the southeastern Beirng Sea shelf during spring of 1997,1998,and 1999 TaeKeun Rho,Terry E. Whitledge, and John J. Goering Institute of Marine
Patterns of Productivity
 Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of autotrophic biomass Secondary Production - the production of heterotrophic biomass Production vs Biomass Biomass
Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of autotrophic biomass Secondary Production - the production of heterotrophic biomass Production vs Biomass Biomass
observatory framework
 From marine terrestrial interactions to the warm blob : integrating land-oceanatmospheric research in a coastal observatory framework Brian Hunt, Jennifer Burt, Wiley Evans, William Floyd, Ian Giesbrecht,
From marine terrestrial interactions to the warm blob : integrating land-oceanatmospheric research in a coastal observatory framework Brian Hunt, Jennifer Burt, Wiley Evans, William Floyd, Ian Giesbrecht,
Nitrogen biogeochemistry. Lecture 1 Universidade do algarve
 Nitrogen biogeochemistry Lecture 1 Universidade do algarve Cycling of elements in the early stages of earth was slow, dependent on extreme conditions temperature, pressure, high energy radiations.. Purely
Nitrogen biogeochemistry Lecture 1 Universidade do algarve Cycling of elements in the early stages of earth was slow, dependent on extreme conditions temperature, pressure, high energy radiations.. Purely
WHY CARBON? The Carbon Cycle 1/17/2011. All living organisms utilize the same molecular building blocks. Carbon is the currency of life
 The Carbon Cycle WHY CARBON? Inventories: black text Fluxes: purple arrows Carbon dioxide (+4) AN = 6 (6P/6N) AW = 12.011 Oxidation: -4 to +4 Isotopes: 11 C, 12 C, 1 C, 14 C Methane (-4) Carbon is the
The Carbon Cycle WHY CARBON? Inventories: black text Fluxes: purple arrows Carbon dioxide (+4) AN = 6 (6P/6N) AW = 12.011 Oxidation: -4 to +4 Isotopes: 11 C, 12 C, 1 C, 14 C Methane (-4) Carbon is the
Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability. Matt Church Department of Oceanography MSB 612
 Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability Matt Church Department of Oceanography MSB 612 Sunlight CO 2 + 2H 2 O CH 2 O + O 2 + H 2 O + heat Gross Primary Production (GPP): The rate of organic
Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability Matt Church Department of Oceanography MSB 612 Sunlight CO 2 + 2H 2 O CH 2 O + O 2 + H 2 O + heat Gross Primary Production (GPP): The rate of organic
Examine annual or seasonal scale changes in
 Primary production approach 5: Estimate Net community production based on in situ variations in oxygen, nutrients, carbon, or biomass (often chlorophyll) Examine annual or seasonal scale changes in O 2,
Primary production approach 5: Estimate Net community production based on in situ variations in oxygen, nutrients, carbon, or biomass (often chlorophyll) Examine annual or seasonal scale changes in O 2,
Assessment and Modelling of Baltic Ecosystem Response (AMBER)
 Assessment and Modelling of Baltic Ecosystem Response (AMBER) Joachim W Dippner and the AMBER team AMBER Kick-off meeting 19. 1. 2009 Participants Leibniz-Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde,
Assessment and Modelling of Baltic Ecosystem Response (AMBER) Joachim W Dippner and the AMBER team AMBER Kick-off meeting 19. 1. 2009 Participants Leibniz-Institute for Baltic Sea Research Warnemünde,
CO 2. and the carbonate system II. Carbon isotopes as a tracer for circulation. The (solid) carbonate connection with. The ocean climate connection
 CO 2 and the carbonate system II Carbon isotopes as a tracer for circulation The (solid) carbonate connection with ocean acidity Climate The ocean climate connection The carbon cycle the carbon cycle involves
CO 2 and the carbonate system II Carbon isotopes as a tracer for circulation The (solid) carbonate connection with ocean acidity Climate The ocean climate connection The carbon cycle the carbon cycle involves
Microbial biomass in the sea: Methods, limitations, and distributions
 Microbial biomass in the sea: Methods, limitations, and distributions Matt Church (MSB 612 / 956-8779 / mjchurch@hawaii.edu) Marine Microplankton Ecology OCN 626 E. F. DeLong The tripartite goals of microbial
Microbial biomass in the sea: Methods, limitations, and distributions Matt Church (MSB 612 / 956-8779 / mjchurch@hawaii.edu) Marine Microplankton Ecology OCN 626 E. F. DeLong The tripartite goals of microbial
In situ methods to measure Primary Production and Net Community Production. What have we learned?
 In situ methods to measure Primary Production and Net Community Production What have we learned? Time Series Sites Time series sites provide: - test bed for new PP methods - evaluation of the annual carbon
In situ methods to measure Primary Production and Net Community Production What have we learned? Time Series Sites Time series sites provide: - test bed for new PP methods - evaluation of the annual carbon
What shapes the metabolic and phylogenetic structure of microbial communities in aquatic systems?
 What shapes the metabolic and phylogenetic structure of microbial communities in aquatic systems? What is a microbial food web and what is the ecological importance? Marine Microbial Food Web Dynamics
What shapes the metabolic and phylogenetic structure of microbial communities in aquatic systems? What is a microbial food web and what is the ecological importance? Marine Microbial Food Web Dynamics
External N inputs and internal N cycling traced by isotope ratios of nitrate, dissolved reduced nitrogen, and particulate nitrogen
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jg001214, 2010 External N inputs and internal N cycling traced by isotope ratios of nitrate, dissolved reduced nitrogen, and particulate nitrogen
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jg001214, 2010 External N inputs and internal N cycling traced by isotope ratios of nitrate, dissolved reduced nitrogen, and particulate nitrogen
Nutrients; Aerobic Carbon Production and Consumption
 Nutrients; Aerobic Carbon Production and Consumption OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 5 February 2013 Reading: Libes, Chapters 8-10 Outline 1. Overview - photosynthesis & respiration 2. Nutrients - chemical
Nutrients; Aerobic Carbon Production and Consumption OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 5 February 2013 Reading: Libes, Chapters 8-10 Outline 1. Overview - photosynthesis & respiration 2. Nutrients - chemical
Lakes, Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling
 OCN 401-Biogeochemical Systems Lecture #10 (9.22.11) Lakes, Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling (Schlesinger: Chapter 7) 1. Primary Production and Nutrient Cycling in Lakes Physical aspects and nomenclature
OCN 401-Biogeochemical Systems Lecture #10 (9.22.11) Lakes, Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling (Schlesinger: Chapter 7) 1. Primary Production and Nutrient Cycling in Lakes Physical aspects and nomenclature
25 years of Hawaii Ocean Time-series carbon flux determinations: Insights into productivity, export, and nutrient supply in the oligotrophic ocean
 25 years of Hawaii Ocean Time-series carbon flux determinations: Insights into productivity, export, and nutrient supply in the oligotrophic ocean MATTHEW CHURCH, ROBERT BIDIGARE, JOHN DORE, DAVID KARL,
25 years of Hawaii Ocean Time-series carbon flux determinations: Insights into productivity, export, and nutrient supply in the oligotrophic ocean MATTHEW CHURCH, ROBERT BIDIGARE, JOHN DORE, DAVID KARL,
MAR 650-Lecture 1: Influences of Light on Biological Production. Importance: In the ocean: 1) Photosynthesis and Primary Production
 MAR 650-Lecture 1: nfluences of Light on Biological Production 1) Photosynthesis and Primary Production photosynthesis CO 2 H 2 O Carbohydrate O 2 respiration mportance: Photosynthesis requires lights,
MAR 650-Lecture 1: nfluences of Light on Biological Production 1) Photosynthesis and Primary Production photosynthesis CO 2 H 2 O Carbohydrate O 2 respiration mportance: Photosynthesis requires lights,
SEASONAL NUTRIENT FLUXES IN THE OGEECHEE RIVER ESTUARY
 SEASONAL NUTRIENT FLUXES IN THE OGEECHEE RIVER ESTUARY William B. Savidge 1 and Katherine R. Doyle 1 AUTHORS: 1 Skidaway Institute of Oceanography, 10 Ocean Science Circle, Savannah, GA 31411 REFERENCE:
SEASONAL NUTRIENT FLUXES IN THE OGEECHEE RIVER ESTUARY William B. Savidge 1 and Katherine R. Doyle 1 AUTHORS: 1 Skidaway Institute of Oceanography, 10 Ocean Science Circle, Savannah, GA 31411 REFERENCE:
Eddie Fadeev
 Eddie Fadeev (efadeev@awi.de) HGF MPG Joint Research Group for Deep-Sea Ecology and Technology, Alfred-Wegener-Institute Helmholtz-Centre for Polar and Marine Research and Max-Planck-Institute for Marine
Eddie Fadeev (efadeev@awi.de) HGF MPG Joint Research Group for Deep-Sea Ecology and Technology, Alfred-Wegener-Institute Helmholtz-Centre for Polar and Marine Research and Max-Planck-Institute for Marine
Biological Oceanography
 Biological Oceanography What controls production in the sea? The BIG 2: 1) Light (energy) 2) Nutrients (matter) Secondarily 3) Temperature 4) Stratification (coupled to 2 & 3) 5) Grazing/predation The
Biological Oceanography What controls production in the sea? The BIG 2: 1) Light (energy) 2) Nutrients (matter) Secondarily 3) Temperature 4) Stratification (coupled to 2 & 3) 5) Grazing/predation The
Oceans OUTLINE. Reading: White, Chapter 15 Today Finish estuaries and particles, then: 1. The oceans: currents, stratification and chemistry
 Oceans OUTLINE Reading: White, Chapter 15 Today Finish estuaries and particles, then: 1. The oceans: currents, stratification and chemistry Next Time Salinity Exercise bring something to calculate with
Oceans OUTLINE Reading: White, Chapter 15 Today Finish estuaries and particles, then: 1. The oceans: currents, stratification and chemistry Next Time Salinity Exercise bring something to calculate with
The Oceanic Phosphorus Cycle and Ecological Stoichiometry
 Ocean 626: Marine Microplankton Ecology 2 October 2007 The Oceanic Phosphorus Cycle and Ecological Stoichiometry David M. Karl Department of Oceanography MSB 629, ph: x68964, e-mail: dkarl@hawaii.edu OUTLINE
Ocean 626: Marine Microplankton Ecology 2 October 2007 The Oceanic Phosphorus Cycle and Ecological Stoichiometry David M. Karl Department of Oceanography MSB 629, ph: x68964, e-mail: dkarl@hawaii.edu OUTLINE
CO 2 is the raw material used to build biomass (reduced to form organic matter)
 1. The oceanic carbon system (a) Significance (b) CO 2 speciation (c) Total CO 2 (d) Atmosphere-ocean CO 2 exchange (e) Global status of CO 2 2. Human perturbations of N and P cycling 3. Other elements:
1. The oceanic carbon system (a) Significance (b) CO 2 speciation (c) Total CO 2 (d) Atmosphere-ocean CO 2 exchange (e) Global status of CO 2 2. Human perturbations of N and P cycling 3. Other elements:
Subtropical Ocean Ecosystem. North Pacific Climate Variations
 Subtropical Ocean Ecosystem Structure Changes Forced by North Pacific Climate Variations Bob Bidigare Hawaii Institute tute of Marine Biology ogy University of Hawaii at Manoa Acknowledgements HOT Personnel
Subtropical Ocean Ecosystem Structure Changes Forced by North Pacific Climate Variations Bob Bidigare Hawaii Institute tute of Marine Biology ogy University of Hawaii at Manoa Acknowledgements HOT Personnel
Seasonal Anoxia over the Western Indian Continental Shelf
 Seasonal Anoxia over the Western Indian Continental Shelf S.W.A. Naqvi, Hema Naik, A.K. Pratihary, M. Gauns, Witty D Souza, Gayatree Narvenkar, D.A. Jayakumar, M.S. Shailaja & P.V. Narvekar National Institute
Seasonal Anoxia over the Western Indian Continental Shelf S.W.A. Naqvi, Hema Naik, A.K. Pratihary, M. Gauns, Witty D Souza, Gayatree Narvenkar, D.A. Jayakumar, M.S. Shailaja & P.V. Narvekar National Institute
LIMNOLOGY. Inland Water Ecosystems. JACOB KALFF McGill University. Prentice Hall. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
 LIMNOLOGY Inland Water Ecosystems JACOB KALFF McGill University Prentice Hall Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 Contents CHAPTER 1 Inland Waters and Their Catchments: An Introduction and
LIMNOLOGY Inland Water Ecosystems JACOB KALFF McGill University Prentice Hall Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 Contents CHAPTER 1 Inland Waters and Their Catchments: An Introduction and
Productivity and fisheries. Energy flow. Biological pyramids. Why study production processes?
 Productivity and fisheries Why study production processes? Fisheries strongly tied to spatial and temporal variation in primary productivity Better understanding of distribution of fishery resources Interpret
Productivity and fisheries Why study production processes? Fisheries strongly tied to spatial and temporal variation in primary productivity Better understanding of distribution of fishery resources Interpret
If your die reads: 3, 4 or 5 Nitrogen gas (N 2 ) is extracted from the air by humans.
 DICE CODES Instructions: These pages are for the Traveling Nitrogen activity, which was modified from Windows to the Universe. Print the following dice code pages. Cut each reservoir apart. Place dice
DICE CODES Instructions: These pages are for the Traveling Nitrogen activity, which was modified from Windows to the Universe. Print the following dice code pages. Cut each reservoir apart. Place dice
Oceanic Microbial Observatory Objectives
 Connecting Heterotrophic Microorganisms to the Ocean C cycle at the Sargasso Sea Microbial Observatory Craig Carlson Steve Bob Giovannoni Morris Dennis Steve Hansell Giovannoni Alexander Treusch Bob Morris
Connecting Heterotrophic Microorganisms to the Ocean C cycle at the Sargasso Sea Microbial Observatory Craig Carlson Steve Bob Giovannoni Morris Dennis Steve Hansell Giovannoni Alexander Treusch Bob Morris
Stable carbon isotopes of DIC and dissolved methane concentrations on the western Iberian Margin
 Stable carbon isotopes of DIC and dissolved methane concentrations on the western Iberian Margin G. Rehder and R.S. Keir GEOMAR D - 24148 Kiel, Germany Introduction The 13 C/ 12 C ratio of total CO 2 (δ
Stable carbon isotopes of DIC and dissolved methane concentrations on the western Iberian Margin G. Rehder and R.S. Keir GEOMAR D - 24148 Kiel, Germany Introduction The 13 C/ 12 C ratio of total CO 2 (δ
Nutrient Cycles. Why? Model 1 The Water Cycle. How are nutrients recycled through ecosystems?
 Why? Nutrient Cycles How are nutrients recycled through ecosystems? We have learned the importance of recycling our trash. It allows us to use something again for another purpose and prevents the loss
Why? Nutrient Cycles How are nutrients recycled through ecosystems? We have learned the importance of recycling our trash. It allows us to use something again for another purpose and prevents the loss
Increased N efficiency in pastoral systems: the urine-n cascade. Tim Clough
 Increased N efficiency in pastoral systems: the urine-n cascade Tim Clough BIOLOGY SOIL PHYSICS CHEMISTRY BIOLOGY SOIL PHYSICS TIME CHEMISTRY SOIL PHYSICS BIOLOGY Soil factors Plant factors Climate Management
Increased N efficiency in pastoral systems: the urine-n cascade Tim Clough BIOLOGY SOIL PHYSICS CHEMISTRY BIOLOGY SOIL PHYSICS TIME CHEMISTRY SOIL PHYSICS BIOLOGY Soil factors Plant factors Climate Management
Designing Single-Sludge Bionutrient Removal Systems
 Designing Single-Sludge Bionutrient Removal Systems Richard O. Mines, Jr., Ph.D., P.E. Environmental Engineering Mercer University 2001 World Water & Environmental Resources Conference Orlando, FL Activated
Designing Single-Sludge Bionutrient Removal Systems Richard O. Mines, Jr., Ph.D., P.E. Environmental Engineering Mercer University 2001 World Water & Environmental Resources Conference Orlando, FL Activated
1. Where are nutrients accumulated or stored for short or long periods?
 Use with textbook pages 68 87. Nutrient cycles Answer the questions below. Comprehension 1. Where are nutrients accumulated or stored for short or long periods? 2. Name a biotic process and an abiotic
Use with textbook pages 68 87. Nutrient cycles Answer the questions below. Comprehension 1. Where are nutrients accumulated or stored for short or long periods? 2. Name a biotic process and an abiotic
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems. Review How energy flows What is the difference between a food chain, food web, and food pyramid?
 2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Review How energy flows What is the difference between a food chain, food web, and food pyramid? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xhr1iebeops https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=alusi_6ol8m
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Review How energy flows What is the difference between a food chain, food web, and food pyramid? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xhr1iebeops https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=alusi_6ol8m
A sense of place N, W LNLC region two layered system. < 50m mixed layer ~125 m euphotic zone/nutricline. Station ALOHA (1988 onwards)
 STATION ALOHA 1. Introduction to the region 2. Types of blooms (enhanced biomass/growth emphasis on the mixed layer) 3. Drivers of variability 4. Beyond biomass towards productivity angelicque white, oregon
STATION ALOHA 1. Introduction to the region 2. Types of blooms (enhanced biomass/growth emphasis on the mixed layer) 3. Drivers of variability 4. Beyond biomass towards productivity angelicque white, oregon
Traveling Nitrogen DICE CODES AND RESERVOIR STATION SIGNS
 Traveling Nitrogen DICE CODES AND RESERVOIR STATION SIGNS Instructions: 1. Hang these dice codes signs at stations around the classroom. 2. Equip each station with dice and either, a rubber stamp and ink
Traveling Nitrogen DICE CODES AND RESERVOIR STATION SIGNS Instructions: 1. Hang these dice codes signs at stations around the classroom. 2. Equip each station with dice and either, a rubber stamp and ink
Biogeochemical Cycles
 Biogeochemical Cycles Biogeochemical Cycles refers to the cycling of materials between living things and the environment. Text Pages 50 51, 62 69 1 The Oxygen Cycle the movement of oxygen between the atmosphere
Biogeochemical Cycles Biogeochemical Cycles refers to the cycling of materials between living things and the environment. Text Pages 50 51, 62 69 1 The Oxygen Cycle the movement of oxygen between the atmosphere
Primary Production in the Ocean
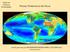 Primary Production in the Ocean A global composite of sea surface chlorophyll concentration Oligotrophic gyre (LNLC) Seasonal Phytoplankton blooms Coastal Upwelling High-nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC)
Primary Production in the Ocean A global composite of sea surface chlorophyll concentration Oligotrophic gyre (LNLC) Seasonal Phytoplankton blooms Coastal Upwelling High-nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC)
BC Science Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems
 BC Science 10 2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Notes Nutrients are chemicals required for growth and other life processes. Nutrients move through the biosphere in nutrient cycles (n.c), or exchanges.
BC Science 10 2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Notes Nutrients are chemicals required for growth and other life processes. Nutrients move through the biosphere in nutrient cycles (n.c), or exchanges.
COUPLED PHYSICAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL MODELS
 COUPLED PHYSICAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL MODELS Upwelling CONCEPTUAL MODEL OF EUTROPHICATION IN THE COASTAL OCEAN Nutrient/ Acid Deposition Local Emissions HABs! Phytoplankton Blooms Senesce and Settling Respiration:
COUPLED PHYSICAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL MODELS Upwelling CONCEPTUAL MODEL OF EUTROPHICATION IN THE COASTAL OCEAN Nutrient/ Acid Deposition Local Emissions HABs! Phytoplankton Blooms Senesce and Settling Respiration:
Deliverables Workpackage Process Studies. 1. Data Base. WP2: Measurements of the Baltic Sea CO 2 system and carbon inventories
 Deliverables Workpackage 2 1. Data Base 2. Process Studies D5 D6 D7 Seasonally resolved pco 2 fields for the entire Baltic Sea Seasonally resolved pco 2 fields for the entire Baltic Sea: Updates Improved
Deliverables Workpackage 2 1. Data Base 2. Process Studies D5 D6 D7 Seasonally resolved pco 2 fields for the entire Baltic Sea Seasonally resolved pco 2 fields for the entire Baltic Sea: Updates Improved
