Titanium and titanium alloys. Josef Stráský
|
|
|
- Annabella Austin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Titanium and titanium alloys Josef Stráský
2 Lecture 2: Fundamentals of Ti alloys Polymorphism Alpha phase Beta phase Pure titanium Titanium alloys alloys alloys alloys Phase transformation β α phase Hardening mechanisms in Ti Hardening of α+β alloys Hardening of metastable β alloys
3 Polymorphism Pure titanium is polymorphic it exists in more crystallographic structures (phases) Similarly to iron Above 882 C the titanium is body-centered cubic material (bcc) phase Upon cooling below 882 C (so-called transus temperature) phase martensitically transforms to hexagonal closepacked structure - phase
4 Stable phases pure titanium phase stable above 882 C ( transus temperature) Under room temperature, only phase is stable Hexagonal close-packed lattice (hcp) Phase Body-centered cubic lattice (bcc) Phase 6 atoms / m 3 = 56,6 2 atoms / m 3 = 54,6 This difference allows dilatometry studies.
5 HCP hexagonal closed packed phase Plane - (hkl) Set of planes - {hkl} Direction - [UVW] Set of directions <UVW> c/a(ti) = < (optimal) c/a(cd) = c/a(zn) = c/a(mg) = c/a(co) = c/a(zr) = Slip systems: Principal: Prismatic { } < > Secondary: Basal { } < > Other: Pyramidal { } < > and { } < >
6 HCP hexagonal closed packed Slip systems Principal: Prismatic { } < > Secondary: Basal { } < > Other: Pyramidal { } < > and { } < >
7 The effect of alloying elements on phase composition Neutral - stabilizing - stabilizing (izomorphous) Alloying elements affect the beta-transus temperature stabilizing elements increase beta-transus temperature stabilizing elements increase beta-transus temperature Isomorphous completely soluble in solid solution Eutectoid intermetallic particles are created - stabilizing (eutectoid)
8 The effect of alloying elements on phase composition Neutral - stabilizing - stabilizing (isomophous) Neutral elements Zr, Sn - stabilizing elements Al, O, N, C - stabilizing (eutectoid) - stabilizing elements isomorphous Mo, V, Ta, Nb - stabilizing elements eutectoid Fe, Mn, Cr, Co, Ni, Cu, H
9 Titanium alloys Pure Ti at room temperature only phase Low-content of -stabilizing elements (and/or outweighted by -stabilizing elements) only phase is stable at RT so-called alloys Increased content of -stabilizing elements phase becomes stable at room-temperature alloys
10 Titanium alloys Further increased content of -stabilizing elements The temperature martenzite start of phase transition is decreased below room temperature Phase Metastable -alloys is not formed during quenching During annealing below -transus temperature, the phase is created until the balance composition is achieved
11 Titanium alloys Even more increased content of -stabilizing elements Beta transus temperature can be decreased below RT Afer cooling to room temperature, phase remain stable Stable -alloys
12 Molybdenum equivalence one of the most important stabilizing elements Comparison of stabilizing effect of different elements so-called molybdenum equivalence [Mo] eq = [Mo] + 0,67 [V] + 0,44 [W] + 0,28 [Nb] + 0,22 [Ta] + + 2,9 [Fe] + 1,6 [Cr] + 1,25 [Ni] + 1,7 [Mn] + 1,7 [Co] - 1,0 [Al] i.e. Vanadium content must be 1.5 times higher then Molybdenum to achieve the same effect on stability of beta phase i.e. Iron is three times stronger beta stabilizer than Mo a 4x than V Molybdenum equivalence is only empirical rule based on analysis of binary alloys Molybdenum equivalence cannot be used quantitatively to compute beta transus temperature or equilibrium phase composition Especially in the case of ternary and more complicated alloys
13 Aluminium equivalence Less used analogy of molybdenum equivalence for - stabilizers Al one of the most important stabilizing elements [Al] eq = [Al] + 0,33 [Sn] + 0,17 [Zr] + 10 [O + C +2N] In the case that Al equivalence is higher than approx 9% (some sources say 5%), then Ti 3 X intermetalic particles are formed The effect of Zr remains unknown and depends strongly on the content of other alloying elements
14 Phase transformation Occurs below -transus temperature In pure Ti, -alloys and alloys martensitic transformation But not until equilibrium phase composition Followed by growth of particles (lamellae) In metastable alloys Precipitation of particles Homogeneous precipitation Heterogeneous precipitation Grain boundaries Particles of other phases Chemical inhomogeneities
15 Phase transformations in metastable 1. Phase separation: lean + rich také + Occurs in strongly stabilized -alloys alloys -stabilization elements form clusters via spinodal decomposition rich regions 2. Formation of phase Less stabilized -alloys Formation of particles Small coherent particles, size: 1-20 nm 3. Precipitation of phase from phase Small phase particles serve as precursors of phase precipitation precipitates of phase are tiny and homogeneously distrbiuted significant strengthening
16 -phase Hexagonal (but not hcp) phase Nanometer sized particles Created after quenching ( - athermal) Grow during ageing Transmission electron microscopy Devaraj et al., Acta Mat 2012 Ti-9Mo a,b) quenched from ; c)-e) 475 C/30 mins; f)-h) C/48 h
17 phase transformations Volume fraction of phases in Ti-LCB alloy studied by X-ray diffraction transforms to with increasing ageing temperature and ageing time (isothermal annealing) Ageing at 400 C Ageing at 450 C Smilauerova et al., unpublished research
18 phase transformations Identified by in-situ methods Differential scanning calorimetry Measurements of electrical resistivity transformations identified during heating 5 C/min I. Dissolution of athermal phase, reversible diffusionless process II. Stabilization and growth of isothermal phase diffuse prodcess III. Dissolution of phase IV. Precipitation of phase V. Dissolution of phase VI. Above -transus temperature phase
19 observed by 3D atom probe Observation is based on chemical differences Deveraj et al., Scripta Mat 61 (2009)
20 Hardening of Titanium 1. Inerstitial oxygen atoms If oxygen content in pure Ti is increased from 0.18 to 0.4 wt. % the strength is increased from 180 MPa to 480 MPa (!) Typical oxygen content in commercial Ti alloys is hm. % Higher oxygen content often causes embrittelment Positions of oxygen atoms are correlated to vacancies positron annihilation spectroscopy study 2. Solid solution strengthening -stabilizing substitutional elements (Al, Sn) strengthen phase (Ti-5Al-2.5Sn 800 MPa) Some fully soluble -stabilizing elements strengthen phase (Mo, Fe, Ta), others have negligible effect (Nb) Size of the atoms and electron structure is decisive for this effect Some atoms serve as obstacles for dislocation motion
21 Hardening of Titanium 3. Intermetallic particles (precipitation hardening) Eg. Aluminides nitrides, carbides, silicide and many others Size of the particles and their distribution are crucial for the strengthening effect (Orowan strengthening) 4. Dislocation density and grain refinement Forming/working (e.g. extrusion, forging, etc.) can increase dislocation density and cause grain refinement Dislocations cause obstacles to movement of other dislocations causing increase strength Grain and sub-grain boundaries may also act as dislocation obstacles Working must be done at sufficiently low temperatures to suppress extensive grain growth and dislocation annihilation
22 Hardening of alloys Sufficient content of Al (or Sn) leads to formation of Ti 3 Al particles (when content of Al is above 9 wt. %) Solvus of Ti 3 Al particles is approx. 550 C, final annealing temperature must be below this temperature Ti 3 Al particles are hexagonal and coherent and block the dislocation movement causing precipitation hardening In alloys occurs separation of elements during annealing - stabilizers diffuse to -phase, whereas stabilizers diffuse to -phase Intermetallic particles (Ti 3 Al) can be created in -phase due to sufficient amount of -stabilizer despite overall (average) chemical composition does not allow such precipitation Phase boundaries serve as dislocation motion obstacles The smaller are morphological features of respective phases, the bigger is strengthening effect
23 Hardening of metastable alloys Interstitial, solid solution and dislocation density strengthening Precipitation hardening/phase boundary hardening caused by phase transformation of -matrix Phase separation lean + rich Formation of phase particles Precipitation of phase particles
24 Lecture 2: Conclusion Titanium is polymorphous material two stable phases -phase hexagonal close-packed (hcp) -phase body-centered cubic (bcc) Below -transus temperature - phase is formed Pure Ti at room temperature only -phase alloys At room temperature mix of phases + phase formation cannot be suppressed Metastable -alloys After quenching - only -phase Upon annealing phase is formed transformation Martensitic followed by growth ( alloys) Precipitation followed by growth ( alloys) phase Nano-sized particles, precursor for -phase particles precipitation Hardening of Ti and Ti alloys Pure ti is hardenend mainly by oxygen content Alloys are hardened by solid solution strengthening, intermetalic particles and particles of other phases
25 Titanium and titanium alloys Josef Stráský Thank you! Project FRVŠ 559/2013 is gratefully acknowledged for providing financial support.
Titanium and titanium alloys. Josef Stráský
 Titanium and titanium alloys Josef Stráský Lecture 3: Technological aspects of Ti alloys Pure Ti metallurgy, properties and applications α+β alloys microstructures, metallurgy, heat treatment Ti-6Al-4V
Titanium and titanium alloys Josef Stráský Lecture 3: Technological aspects of Ti alloys Pure Ti metallurgy, properties and applications α+β alloys microstructures, metallurgy, heat treatment Ti-6Al-4V
IMAGING OF MICROSTRUCTURAL FEATURES AND LOCAL STIFFNESS OF Α- AND Β-PHASES IN THE TITANIUM ALLOY TI- 6AL-4V BY ATOMIC FORCE ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY
 IMAGING OF MICROSTRUCTURAL FEATURES AND LOCAL STIFFNESS OF Α- AND Β-PHASES IN THE TITANIUM ALLOY TI- 6AL-4V BY ATOMIC FORCE ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY Jonas O. RABE, Ute RABE, Sigrun HIRSEKORN Fraunhofer Institute
IMAGING OF MICROSTRUCTURAL FEATURES AND LOCAL STIFFNESS OF Α- AND Β-PHASES IN THE TITANIUM ALLOY TI- 6AL-4V BY ATOMIC FORCE ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY Jonas O. RABE, Ute RABE, Sigrun HIRSEKORN Fraunhofer Institute
MICROSTRUCTURE CHARACTERIZATION AND IMAGING IN TITANIUM ALLOYS BY ATOMIC FORCE ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY
 MICROSTRUCTURE CHARACTERIZATION AND IMAGING IN TITANIUM ALLOYS BY ATOMIC FORCE ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY Sigrun HIRSEKORN, Jonas RABE, Ute RABE, FRAUNHOFER IZFP, Campus E3 1, 66123 Saarbrücken, Germany INTRODUCTION
MICROSTRUCTURE CHARACTERIZATION AND IMAGING IN TITANIUM ALLOYS BY ATOMIC FORCE ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY Sigrun HIRSEKORN, Jonas RABE, Ute RABE, FRAUNHOFER IZFP, Campus E3 1, 66123 Saarbrücken, Germany INTRODUCTION
Lecture 12: High Temperature Alloys
 Part IB Materials Science & Metallurgy H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Course A, Metals and Alloys Lecture 12: High Temperature Alloys Metallic materials capable of operating at ever increasing temperatures are
Part IB Materials Science & Metallurgy H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Course A, Metals and Alloys Lecture 12: High Temperature Alloys Metallic materials capable of operating at ever increasing temperatures are
Module-6. Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms
 Module-6 Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms Contents 1) Dislocations & Plastic deformation and Mechanisms of plastic deformation in metals 2) Strengthening mechanisms in metals 3) Recovery, Recrystallization
Module-6 Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms Contents 1) Dislocations & Plastic deformation and Mechanisms of plastic deformation in metals 2) Strengthening mechanisms in metals 3) Recovery, Recrystallization
THE REGULARITIES OF PHASE AND STRUCTURAL TRANSFORMATION IN BINARY TITANIUM ALLOYS WITH METALS OF IV VIII GROUPS OF THE PERIODIC TABLE
 DOI: 10.2478/v10077-008-0004-7 A.V. Dobromyslov Institute of Metal Physics, Ural Branch of Russian Academy of Sciences, Еkaterinburg, Russia THE REGULARITIES OF PHASE AND STRUCTURAL TRANSFORMATION IN BINARY
DOI: 10.2478/v10077-008-0004-7 A.V. Dobromyslov Institute of Metal Physics, Ural Branch of Russian Academy of Sciences, Еkaterinburg, Russia THE REGULARITIES OF PHASE AND STRUCTURAL TRANSFORMATION IN BINARY
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name METALLURGY AND MATERIAL SCIENCE Course Code AME005 Class III Semester
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name METALLURGY AND MATERIAL SCIENCE Course Code AME005 Class III Semester
Phase Transformations in Metals Tuesday, December 24, 2013 Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE 1
 Ferrite - BCC Martensite - BCT Fe 3 C (cementite)- orthorhombic Austenite - FCC Chapter 10 Phase Transformations in Metals Tuesday, December 24, 2013 Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE 1 Why do we study
Ferrite - BCC Martensite - BCT Fe 3 C (cementite)- orthorhombic Austenite - FCC Chapter 10 Phase Transformations in Metals Tuesday, December 24, 2013 Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE 1 Why do we study
Titanium and titanium alloys. Josef Stráský
 Titanium and titanium alloys Josef Stráský Lecture 4: Production technologies, experimental investigation, modern problems Technology Casting, forming Experimental methods Metalography Scanning and transmission
Titanium and titanium alloys Josef Stráský Lecture 4: Production technologies, experimental investigation, modern problems Technology Casting, forming Experimental methods Metalography Scanning and transmission
Chapter 2 Metallurgy and Microstructure
 Chapter 2 Metallurgy and Microstructure 2.1 The General Metallurgy of Titanium Alloys Unalloyed titanium has two allotropic forms. The low temperature form, a, exists as an hexagonal-close-packed (hcp)
Chapter 2 Metallurgy and Microstructure 2.1 The General Metallurgy of Titanium Alloys Unalloyed titanium has two allotropic forms. The low temperature form, a, exists as an hexagonal-close-packed (hcp)
of Metal Alloys This is just an extension of the previous chapter Hardenability of Steels: The Jominy Test
 Chapter 11 Applications and Processing of Metal Alloys This is just an extension of the previous chapter Hardenability of Steels: The Jominy Test As usual, everything is standardized! After the Jominy
Chapter 11 Applications and Processing of Metal Alloys This is just an extension of the previous chapter Hardenability of Steels: The Jominy Test As usual, everything is standardized! After the Jominy
Chapter 9 Phase Diagrams. Dr. Feras Fraige
 Chapter 9 Phase Diagrams Dr. Feras Fraige Chapter Outline Definitions and basic concepts Phases and microstructure Binary isomorphous systems (complete solid solubility) Binary eutectic systems (limited
Chapter 9 Phase Diagrams Dr. Feras Fraige Chapter Outline Definitions and basic concepts Phases and microstructure Binary isomorphous systems (complete solid solubility) Binary eutectic systems (limited
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School. Department of Materials Science and Engineering
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Materials Science and Engineering PHASE TRANSFORMATIONS DURING CONTINUOUS HEATING AND COOLING IN A TI-AL-RU ALLOY A Dissertation in Materials
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Materials Science and Engineering PHASE TRANSFORMATIONS DURING CONTINUOUS HEATING AND COOLING IN A TI-AL-RU ALLOY A Dissertation in Materials
MT 348 Outline No MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
 MT 348 Outline No. 1 2009 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES I. Introduction A. Stresses and Strains, Normal and Shear Loading B. Elastic Behavior II. Stresses and Metal Failure A. ʺPrincipal Stressʺ Concept B. Plastic
MT 348 Outline No. 1 2009 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES I. Introduction A. Stresses and Strains, Normal and Shear Loading B. Elastic Behavior II. Stresses and Metal Failure A. ʺPrincipal Stressʺ Concept B. Plastic
Recrystallisation in a rapidly annealed low cost β- titanium alloy
 University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 2012 Recrystallisation in a rapidly annealed low cost β- titanium alloy Quoc
University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 2012 Recrystallisation in a rapidly annealed low cost β- titanium alloy Quoc
Physical Metallurgy Friday, January 28, 2011; 8:30 12:00 h
 Physical Metallurgy Friday, January 28, 2011; 8:30 12:00 h Always motivate your answers All sub-questions have equal weight in the assessment Question 1 Precipitation-hardening aluminium alloys are, after
Physical Metallurgy Friday, January 28, 2011; 8:30 12:00 h Always motivate your answers All sub-questions have equal weight in the assessment Question 1 Precipitation-hardening aluminium alloys are, after
Tutorial 2 : Crystalline Solid, Solidification, Crystal Defect and Diffusion
 Tutorial 1 : Introduction and Atomic Bonding 1. Explain the difference between ionic and metallic bonding between atoms in engineering materials. 2. Show that the atomic packing factor for Face Centred
Tutorial 1 : Introduction and Atomic Bonding 1. Explain the difference between ionic and metallic bonding between atoms in engineering materials. 2. Show that the atomic packing factor for Face Centred
ME 254 MATERIALS ENGINEERING 1 st Semester 1431/ rd Mid-Term Exam (1 hr)
 1 st Semester 1431/1432 3 rd Mid-Term Exam (1 hr) Question 1 a) Answer the following: 1. Do all metals have the same slip system? Why or why not? 2. For each of edge, screw and mixed dislocations, cite
1 st Semester 1431/1432 3 rd Mid-Term Exam (1 hr) Question 1 a) Answer the following: 1. Do all metals have the same slip system? Why or why not? 2. For each of edge, screw and mixed dislocations, cite
Metallic Materials-Phase Diagrams
 Engineering Alloys Metals and alloys have many useful engineering properties and so have wide spread application in engineering designs. Iron and its alloys (principally steel) account for about 90 percent
Engineering Alloys Metals and alloys have many useful engineering properties and so have wide spread application in engineering designs. Iron and its alloys (principally steel) account for about 90 percent
Thermodynamic Modelling of High Strength, High Toughness Ti Alloys
 Thermodynamic Modelling of High Strength, High Toughness Ti Alloys By Hang Wang School of Metallurgy and Materials University of Birmingham A thesis submitted to: The University of Birmingham. for the
Thermodynamic Modelling of High Strength, High Toughness Ti Alloys By Hang Wang School of Metallurgy and Materials University of Birmingham A thesis submitted to: The University of Birmingham. for the
Fundamentals of. Steel Product. Graduate Institute of Ferrous Metallurgy
 Fundamentals of Steel Product Physical Metallurgy B.C. De Cooman Graduate Institute of Ferrous Metallurgy Pohang University of Science and Technology, South Korea J.G Speer Advanced Steel Products and
Fundamentals of Steel Product Physical Metallurgy B.C. De Cooman Graduate Institute of Ferrous Metallurgy Pohang University of Science and Technology, South Korea J.G Speer Advanced Steel Products and
In their simplest form, steels are alloys of Iron (Fe) and Carbon (C).
 Iron-Carbon Phase Diagram Its defined as:- A map of the temperature at which different phase changes occur on very slow heating and cooling in relation to Carbon content. is Isothermal and continuous cooling
Iron-Carbon Phase Diagram Its defined as:- A map of the temperature at which different phase changes occur on very slow heating and cooling in relation to Carbon content. is Isothermal and continuous cooling
Phase Transformation in Materials
 2015 Fall Phase Transformation in Materials 09. 02. 2015 Eun Soo Park Office: 33-313 Telephone: 880-7221 Email: espark@snu.ac.kr Office hours: by an appointment 1 Introduction Web lecture assistance: http://etl.snu.ac.kr
2015 Fall Phase Transformation in Materials 09. 02. 2015 Eun Soo Park Office: 33-313 Telephone: 880-7221 Email: espark@snu.ac.kr Office hours: by an appointment 1 Introduction Web lecture assistance: http://etl.snu.ac.kr
Strengthening Mechanisms
 Strengthening Mechanisms The ability of a metal/ alloy to plastically deform depends on the ability of dislocations to move. Strengthening techniques rely on restricting dislocation motion to render a
Strengthening Mechanisms The ability of a metal/ alloy to plastically deform depends on the ability of dislocations to move. Strengthening techniques rely on restricting dislocation motion to render a
Each carbon atom causes a tetragonal distortion since the principal
 Ferrous alloys Fig. 1: Iron-carbon equilibrium phase diagram martensite start temperature or M S. The fraction of martensite increases with the undercooling below M S. The martensite in steels is supersaturated
Ferrous alloys Fig. 1: Iron-carbon equilibrium phase diagram martensite start temperature or M S. The fraction of martensite increases with the undercooling below M S. The martensite in steels is supersaturated
Isothermal Aging Behavior of Beta Titanium Manganese Alloys
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 5, No. 12 (29) pp. 2737 to 2743 Special Issue on Low Cost Reduction Processes, Roles of Low Cost Elements and Interstitial Elements, and Microstructural Control for Generalization
Materials Transactions, Vol. 5, No. 12 (29) pp. 2737 to 2743 Special Issue on Low Cost Reduction Processes, Roles of Low Cost Elements and Interstitial Elements, and Microstructural Control for Generalization
MSE307 Engineering Alloys L5: Phase Metallurgy of Titanium Alloys
 MSE307 Engineering Alloys 2014-15 L5: Phase Metallurgy of Titanium Alloys D. Dye a a Rm G03b, Department of Materials, Imperial College London, London SW7 2AZ, UK. david.dye@imperial.ac.uk We turn now
MSE307 Engineering Alloys 2014-15 L5: Phase Metallurgy of Titanium Alloys D. Dye a a Rm G03b, Department of Materials, Imperial College London, London SW7 2AZ, UK. david.dye@imperial.ac.uk We turn now
Effects in Ductile Iron
 Summary of Element Effects in Ductile Iron Rick Gundlach Element Materials Technology Wixom Insert Company Logo Here DIS Annual Meeting, June 7, 2012 Muskegon, Michigan Types of Alloying Elements Substitutional
Summary of Element Effects in Ductile Iron Rick Gundlach Element Materials Technology Wixom Insert Company Logo Here DIS Annual Meeting, June 7, 2012 Muskegon, Michigan Types of Alloying Elements Substitutional
PHASE DIAGRAMS. IE-114 Materials Science and General Chemistry Lecture-10
 PHASE DIAGRAMS IE-114 Materials Science and General Chemistry Lecture-10 Importance of Phase Diagrams There is a strong correlation between microstructure and mechanical properties. Phase diagrams provides
PHASE DIAGRAMS IE-114 Materials Science and General Chemistry Lecture-10 Importance of Phase Diagrams There is a strong correlation between microstructure and mechanical properties. Phase diagrams provides
(12) 1. Just one True and False question and a couple of multiple choice calculations, circle one answer for each problem, no partial credit.
 (1) 1. Just one True and False question and a couple of multiple choice calculations, circle one answer for each problem, no partial credit. The next page is left blank for your use, but no partial will
(1) 1. Just one True and False question and a couple of multiple choice calculations, circle one answer for each problem, no partial credit. The next page is left blank for your use, but no partial will
Question Grade Maximum Grade Total 100
 The Islamic University of Gaza Industrial Engineering Department Engineering Materials, EIND 3301 Final Exam Instructor: Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, P.E. Exam date: 31/12/2013 Final Exam (Open Book) Fall 2013
The Islamic University of Gaza Industrial Engineering Department Engineering Materials, EIND 3301 Final Exam Instructor: Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, P.E. Exam date: 31/12/2013 Final Exam (Open Book) Fall 2013
Diffusional Transformations in Solids
 Diffusional Transformations in Solids The majority of phase transformations that occur in the solid state take place by thermally activated atomic movements. The transformations that will be dealt with
Diffusional Transformations in Solids The majority of phase transformations that occur in the solid state take place by thermally activated atomic movements. The transformations that will be dealt with
Introduction to Materials Science
 EPMA Powder Metallurgy Summer School 27 June 1 July 2016 Valencia, Spain Introduction to Materials Science Prof. Alberto Molinari University of Trento, Italy Some of the figures used in this presentation
EPMA Powder Metallurgy Summer School 27 June 1 July 2016 Valencia, Spain Introduction to Materials Science Prof. Alberto Molinari University of Trento, Italy Some of the figures used in this presentation
Chapter 9 Heat treatment (This chapter covers selective sections in Callister Chap. 9, 10 &11)
 Chapter 9 Heat treatment (This chapter covers selective sections in Callister Chap. 9, 10 &11) Study theme outcomes: After studying this chapter, students should or should be able to: - know and understand
Chapter 9 Heat treatment (This chapter covers selective sections in Callister Chap. 9, 10 &11) Study theme outcomes: After studying this chapter, students should or should be able to: - know and understand
Microstructural effects of phase transformations Marek Faryna
 Microstructural effects of phase transformations Marek Faryna Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Science m.faryna@imim.pl 012 2952828 mobile 697 225 186 Outline Transformation in solids Formal theories
Microstructural effects of phase transformations Marek Faryna Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Science m.faryna@imim.pl 012 2952828 mobile 697 225 186 Outline Transformation in solids Formal theories
4.0 Alloying Elements and Microstructural Phases
 4.0 Alloying Elements and Microstructural Phases There is a direct link between microstructure and properties and if the microstructure is altered by heat treatment, fabrication or composition then the
4.0 Alloying Elements and Microstructural Phases There is a direct link between microstructure and properties and if the microstructure is altered by heat treatment, fabrication or composition then the
PHASE DIAGRAMS UNDERSTANDING BASICS THE. Edited. F.C. Campbell. Materials Park, Ohio The Materials Information Society.
 PHASE DIAGRAMS UNDERSTANDING THE BASICS Edited by F.C. Campbell The Materials Information Society ASM International Materials Park, Ohio 44073-0002 www.asm i nternational.org Phase Diagrams Understanding
PHASE DIAGRAMS UNDERSTANDING THE BASICS Edited by F.C. Campbell The Materials Information Society ASM International Materials Park, Ohio 44073-0002 www.asm i nternational.org Phase Diagrams Understanding
Strengthening Mechanisms. Today s Topics
 MME 131: Lecture 17 Strengthening Mechanisms Prof. A.K.M.B. Rashid Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Today s Topics Strengthening strategies: Grain strengthening Solid solution strengthening Work hardening
MME 131: Lecture 17 Strengthening Mechanisms Prof. A.K.M.B. Rashid Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Today s Topics Strengthening strategies: Grain strengthening Solid solution strengthening Work hardening
Phase Transformations Workshop David Laughlin
 Phase Transformations Workshop David Laughlin Materials Science and Engineering Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 Outline What is a Phase? Heterogeneous / Homogeneous Transformations Nucleation
Phase Transformations Workshop David Laughlin Materials Science and Engineering Carnegie Mellon University Pittsburgh, PA 15213 Outline What is a Phase? Heterogeneous / Homogeneous Transformations Nucleation
CHAPTER 9: PHASE DIAGRAMS
 CHAPTER 9: PHASE DIAGRAMS ISSUES TO ADDRESS... When we combine two elements... what equilibrium state do we get? In particular, if we specify... --a composition (e.g., wt%cu - wt%ni), and --a temperature
CHAPTER 9: PHASE DIAGRAMS ISSUES TO ADDRESS... When we combine two elements... what equilibrium state do we get? In particular, if we specify... --a composition (e.g., wt%cu - wt%ni), and --a temperature
Fe-Fe 3 C phase diagram is given on the last page of the exam. Multiple choices (2.5 points each):
 Materials Science and Engineering Department MSE 200, Exam #3 ID number First letter of your last name: Name: No notes, books, or information stored in calculator memories may be used. Cheating will be
Materials Science and Engineering Department MSE 200, Exam #3 ID number First letter of your last name: Name: No notes, books, or information stored in calculator memories may be used. Cheating will be
Precipitation Hardening. Outline. Precipitation Hardening. Precipitation Hardening
 Outline Dispersion Strengthening Mechanical Properties of Steel Effect of Pearlite Particles impede dislocations. Things that slow down/hinder/impede dislocation movement will increase, y and TS And also
Outline Dispersion Strengthening Mechanical Properties of Steel Effect of Pearlite Particles impede dislocations. Things that slow down/hinder/impede dislocation movement will increase, y and TS And also
Single vs Polycrystals
 WEEK FIVE This week, we will Learn theoretical strength of single crystals Learn metallic crystal structures Learn critical resolved shear stress Slip by dislocation movement Single vs Polycrystals Polycrystals
WEEK FIVE This week, we will Learn theoretical strength of single crystals Learn metallic crystal structures Learn critical resolved shear stress Slip by dislocation movement Single vs Polycrystals Polycrystals
ENGR 151: Materials of Engineering LECTURE #15: PHASE DIAGRAMS
 ENGR 151: Materials of Engineering LECTURE #15: PHASE DIAGRAMS TENSILE TESTING VIDEO https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-qukvzo2jse PROPERTIES OF ISOMORPHOUS ALLOYS Solid solution strengthening For Ni-Cu
ENGR 151: Materials of Engineering LECTURE #15: PHASE DIAGRAMS TENSILE TESTING VIDEO https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-qukvzo2jse PROPERTIES OF ISOMORPHOUS ALLOYS Solid solution strengthening For Ni-Cu
Effect of titanium additions to low carbon, low manganese steels on sulphide precipitation
 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections University of Wollongong Thesis Collection University of Wollongong Year 2008 Effect of titanium additions to low carbon, low manganese steels on sulphide precipitation
University of Wollongong Thesis Collections University of Wollongong Thesis Collection University of Wollongong Year 2008 Effect of titanium additions to low carbon, low manganese steels on sulphide precipitation
ASTM Conference, May , Hilton Head Island, SC
 ASTM Conference, May 17 2016, Hilton Head Island, SC Understanding Irradiation Growth through Atomistic Simulations: Defect Diffusion and Clustering in Alpha-Zirconium and the Influence of Alloying Elements
ASTM Conference, May 17 2016, Hilton Head Island, SC Understanding Irradiation Growth through Atomistic Simulations: Defect Diffusion and Clustering in Alpha-Zirconium and the Influence of Alloying Elements
Phase Diagrams, Solid Solutions, Phase Strengthening, Phase Transformations
 Phase Diagrams, Solid Solutions, Phase Strengthening, Phase Transformations Components and Phases Components: The elements or compounds that are mixed initially (Al and Cu). Phases: A phase is a homogenous,
Phase Diagrams, Solid Solutions, Phase Strengthening, Phase Transformations Components and Phases Components: The elements or compounds that are mixed initially (Al and Cu). Phases: A phase is a homogenous,
Equilibria in Materials
 2009 fall Advanced Physical Metallurgy Phase Equilibria in Materials 09.01.2009 Eun Soo Park Office: 33-316 Telephone: 880-7221 Email: espark@snu.ac.kr Office hours: by an appointment 1 Text: A. PRINCE,
2009 fall Advanced Physical Metallurgy Phase Equilibria in Materials 09.01.2009 Eun Soo Park Office: 33-316 Telephone: 880-7221 Email: espark@snu.ac.kr Office hours: by an appointment 1 Text: A. PRINCE,
Continuous Cooling Diagrams
 Continuous Cooling Diagrams Isothermal transformation (TTT) diagrams are obtained by rapidly quenching to a given temperature and then measuring the volume fraction of the various constituents that form
Continuous Cooling Diagrams Isothermal transformation (TTT) diagrams are obtained by rapidly quenching to a given temperature and then measuring the volume fraction of the various constituents that form
Chapter 8 Strain Hardening and Annealing
 Chapter 8 Strain Hardening and Annealing This is a further application of our knowledge of plastic deformation and is an introduction to heat treatment. Part of this lecture is covered by Chapter 4 of
Chapter 8 Strain Hardening and Annealing This is a further application of our knowledge of plastic deformation and is an introduction to heat treatment. Part of this lecture is covered by Chapter 4 of
Chapter 7: Dislocations and strengthening mechanisms. Strengthening by grain size reduction
 Chapter 7: Dislocations and strengthening mechanisms Mechanisms of strengthening in metals Strengthening by grain size reduction Solid-solution strengthening Strain hardening Recovery, recrystallization,
Chapter 7: Dislocations and strengthening mechanisms Mechanisms of strengthening in metals Strengthening by grain size reduction Solid-solution strengthening Strain hardening Recovery, recrystallization,
Designing martensitic steels: structure & properties Enrique Galindo-Nava and Pedro Rivera
 Designing martensitic steels: structure & properties Enrique Galindo-Nava and Pedro Rivera Feng Qian, Mark Rainforth (Sheffield); Wenwen Song (Aachen) 1 Outline Aim: Understand the factors controlling
Designing martensitic steels: structure & properties Enrique Galindo-Nava and Pedro Rivera Feng Qian, Mark Rainforth (Sheffield); Wenwen Song (Aachen) 1 Outline Aim: Understand the factors controlling
Recrystallization textures in metals and alloys
 Recrystallization textures in metals and alloys Uniaxial deformation Aluminium wire F.C.C. Metals and alloys FCC wires retain deformation texture ([111]+[100]) upon recrystallisation Composition / Purity
Recrystallization textures in metals and alloys Uniaxial deformation Aluminium wire F.C.C. Metals and alloys FCC wires retain deformation texture ([111]+[100]) upon recrystallisation Composition / Purity
J = D C A C B x A x B + D C A C. = x A kg /m 2
 1. (a) Compare interstitial and vacancy atomic mechanisms for diffusion. (b) Cite two reasons why interstitial diffusion is normally more rapid than vacancy diffusion. (a) With vacancy diffusion, atomic
1. (a) Compare interstitial and vacancy atomic mechanisms for diffusion. (b) Cite two reasons why interstitial diffusion is normally more rapid than vacancy diffusion. (a) With vacancy diffusion, atomic
Phase Transformation in Materials
 2016 Fall Phase Transformation in Materials 09. 05. 2016 Eun Soo Park Office: 33-313 Telephone: 880-7221 Email: espark@snu.ac.kr Office hours: by an appointment 1 Introduction Web lecture assistance: http://etl.snu.ac.kr
2016 Fall Phase Transformation in Materials 09. 05. 2016 Eun Soo Park Office: 33-313 Telephone: 880-7221 Email: espark@snu.ac.kr Office hours: by an appointment 1 Introduction Web lecture assistance: http://etl.snu.ac.kr
Cu/Ag Eutectic System
 Eutectic Systems The simplest kind of system with two solid phases is called a eutectic system. A eutectic system contains two solid phases at low temperature. These phases may have different crystal structures,
Eutectic Systems The simplest kind of system with two solid phases is called a eutectic system. A eutectic system contains two solid phases at low temperature. These phases may have different crystal structures,
Binary Phase Diagrams - II
 Binary Phase Diagrams - II Note the alternating one phase / two phase pattern at any given temperature Binary Phase Diagrams - Cu-Al Can you spot the eutectoids? The peritectic points? How many eutectic
Binary Phase Diagrams - II Note the alternating one phase / two phase pattern at any given temperature Binary Phase Diagrams - Cu-Al Can you spot the eutectoids? The peritectic points? How many eutectic
CompuTherm LLC Thermodynamic Databases. PanTitanium. Thermodynamic Database for Titanium-Based Alloys. Al B C. Ni Nb N. Copyright CompuTherm LLC
 PanTitanium Thermodynamic Database for Titanium-Based Alloys V Zr Al B C Ta Cr Sn Si Ti Cu Fe O H Ni Nb N Mo Mn Copyright CompuTherm LLC 1 Components A total of 19 components are included in the database
PanTitanium Thermodynamic Database for Titanium-Based Alloys V Zr Al B C Ta Cr Sn Si Ti Cu Fe O H Ni Nb N Mo Mn Copyright CompuTherm LLC 1 Components A total of 19 components are included in the database
Direct observation of niobium segregation to dislocations in steel
 Charles Hatchett Award 2017 of the Institute of Materials, Minerals and Mining (IOM3) 1 Direct observation of niobium segregation to dislocations in steel J. Takahashi, K. Kawakami, J. Hamada *, K. Kimura
Charles Hatchett Award 2017 of the Institute of Materials, Minerals and Mining (IOM3) 1 Direct observation of niobium segregation to dislocations in steel J. Takahashi, K. Kawakami, J. Hamada *, K. Kimura
A STUDY OF MECHANISMS TO ENGINEER FINE SCALE ALPHA PHASE PRECIPITATION IN BETA TITANIUM ALLOY, BETA 21S. Amit Kishan Behera
 A STUDY OF MECHANISMS TO ENGINEER FINE SCALE ALPHA PHASE PRECIPITATION IN BETA TITANIUM ALLOY, BETA 21S Amit Kishan Behera Thesis Prepared for the Degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH TEXAS
A STUDY OF MECHANISMS TO ENGINEER FINE SCALE ALPHA PHASE PRECIPITATION IN BETA TITANIUM ALLOY, BETA 21S Amit Kishan Behera Thesis Prepared for the Degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH TEXAS
Titanium alloys: modelling of microstructure, properties and applications
 Titanium alloys: modelling of microstructure, properties and applications Wei Sha and Savko Malinov @ CRC Press Boca Raton Boston New York Washington, DC WOODHEAD PUBLISHING LIMITED Oxford Cambridge New
Titanium alloys: modelling of microstructure, properties and applications Wei Sha and Savko Malinov @ CRC Press Boca Raton Boston New York Washington, DC WOODHEAD PUBLISHING LIMITED Oxford Cambridge New
Metals I. Anne Mertens
 "MECA0139-1: Techniques "MECA0462-2 additives : et Materials 3D printing", Selection", ULg, 19/09/2017 25/10/2016 Metals I Anne Mertens Introduction Outline Metallic materials Materials Selection: case
"MECA0139-1: Techniques "MECA0462-2 additives : et Materials 3D printing", Selection", ULg, 19/09/2017 25/10/2016 Metals I Anne Mertens Introduction Outline Metallic materials Materials Selection: case
Phase Diagrams of Pure Substances Predicts the stable phase as a function of P total and T. Example: water can exist in solid, liquid and vapor
 PHASE DIAGRAMS Phase a chemically and structurally homogenous region of a material. Region of uniform physical and chemical characteristics. Phase boundaries separate two distinct phases. A single phase
PHASE DIAGRAMS Phase a chemically and structurally homogenous region of a material. Region of uniform physical and chemical characteristics. Phase boundaries separate two distinct phases. A single phase
In-situ Electron Microscopy Mechanical Testing for Steels
 Technical Report UDC 621. 385. 2 : 620. 17 : 669. 14 In-situ Electron Microscopy Mechanical Testing for Steels Shunsuke TANIGUCHI* Gerhard DEHM Abstract This paper outlines the techniques of in-situ electron
Technical Report UDC 621. 385. 2 : 620. 17 : 669. 14 In-situ Electron Microscopy Mechanical Testing for Steels Shunsuke TANIGUCHI* Gerhard DEHM Abstract This paper outlines the techniques of in-situ electron
Metallurgy in Production
 In the Name of Allah University of Hormozgan Metallurgy in Production First semester 95-96 Mohammad Ali Mirzai 1 Chapter 6 : the iron carbon phase diagram 2 The Iron-Carbon Alloy Classification 3 The Iron-Carbon
In the Name of Allah University of Hormozgan Metallurgy in Production First semester 95-96 Mohammad Ali Mirzai 1 Chapter 6 : the iron carbon phase diagram 2 The Iron-Carbon Alloy Classification 3 The Iron-Carbon
MTLS 4L04 Steel Section. Lecture 6
 MTLS 4L04 Steel Section Lecture 6 Tempering of Martensite To get around the problem of the brittleness of the Martensite, Martensite is heat treated at elevated temperatures (200-700 C) to precipitate
MTLS 4L04 Steel Section Lecture 6 Tempering of Martensite To get around the problem of the brittleness of the Martensite, Martensite is heat treated at elevated temperatures (200-700 C) to precipitate
Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction
 Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction Callister, William D. ISBN-13: 9780470419977 Table of Contents List of Symbols. 1 Introduction. 1.1 Historical Perspective. 1.2 Materials Science and
Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction Callister, William D. ISBN-13: 9780470419977 Table of Contents List of Symbols. 1 Introduction. 1.1 Historical Perspective. 1.2 Materials Science and
Schematic representation of the development of microstructure. during the equilibrium solidification of a 35 wt% Ni-65 wt% Cu alloy
 Schematic representation of the development of microstructure during the equilibrium solidification of a 35 wt% Ni-65 wt% Cu alloy At 1300 ºC (point a) the alloy is in the liquid condition This continues
Schematic representation of the development of microstructure during the equilibrium solidification of a 35 wt% Ni-65 wt% Cu alloy At 1300 ºC (point a) the alloy is in the liquid condition This continues
Equilibrium phase diagram of metallic alloy
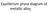 Equilibrium phase diagram of metallic alloy Motivation New structure, concentration (mixing level) (at what temperature? for how long? ) Phase Diagrams - Introduction. Many materials systems can exist
Equilibrium phase diagram of metallic alloy Motivation New structure, concentration (mixing level) (at what temperature? for how long? ) Phase Diagrams - Introduction. Many materials systems can exist
Mechanisms for Boron Effect on Microstructure and Creep Strength of Ferritic Power Plant Steels
 Mechanisms for Boron Effect on Microstructure and Creep Strength of Ferritic Power Plant Steels - Boron Metallurgy of Ferritic Power Plant Steels - Fujio Abe, M Tabuchi and S Tsukamoto National Institute
Mechanisms for Boron Effect on Microstructure and Creep Strength of Ferritic Power Plant Steels - Boron Metallurgy of Ferritic Power Plant Steels - Fujio Abe, M Tabuchi and S Tsukamoto National Institute
Not measured by atom-probe tomography: Pair correlation functions Inter-precipitate distance distributions (IDDs)
 Additional measurements possible using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) Not measured by atom-probe tomography: Pair correlation functions Inter-precipitate distance distributions (IDDs) Also measurable
Additional measurements possible using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) Not measured by atom-probe tomography: Pair correlation functions Inter-precipitate distance distributions (IDDs) Also measurable
MICROSTRUCTURAL STUDIES OF HEAT-TREATED Zr-2.5Nb ALLOY FOR PRESSURE TUBE APPLICATIONS. N. Saibaba Nuclear Fuel Complex, Hyderabad, INDIA
 MICROSTRUCTURAL STUDIES OF HEAT-TREATED Zr-2.5Nb ALLOY FOR PRESSURE TUBE APPLICATIONS N. Saibaba Nuclear Fuel Complex, Hyderabad, INDIA OUTLINE Introduction Objective Background Optimization of Quenching
MICROSTRUCTURAL STUDIES OF HEAT-TREATED Zr-2.5Nb ALLOY FOR PRESSURE TUBE APPLICATIONS N. Saibaba Nuclear Fuel Complex, Hyderabad, INDIA OUTLINE Introduction Objective Background Optimization of Quenching
Heat Treating Basics-Steels
 Heat Treating Basics-Steels Semih Genculu, P.E. Steel is the most important engineering material as it combines strength, ease of fabrication, and a wide range of properties along with relatively low cost.
Heat Treating Basics-Steels Semih Genculu, P.E. Steel is the most important engineering material as it combines strength, ease of fabrication, and a wide range of properties along with relatively low cost.
Engineering Materials
 Engineering Materials Heat Treatments of Ferrous Alloys Annealing Processes The term annealing refers to a heat treatment in which a material is exposed to an elevated temperature for an extended time
Engineering Materials Heat Treatments of Ferrous Alloys Annealing Processes The term annealing refers to a heat treatment in which a material is exposed to an elevated temperature for an extended time
Mohammad Anwar Karim Id :
 Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering ME 8109 Casting and Solidification of Materials EFFECTS OF RAPID SOLIDIFICATION ON MICROSTRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF AL, MG & TI ALLOYS Winter 2012 Presented
Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering ME 8109 Casting and Solidification of Materials EFFECTS OF RAPID SOLIDIFICATION ON MICROSTRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF AL, MG & TI ALLOYS Winter 2012 Presented
Objective To study the time and temperature variations in the hardness of Al-4% Cu alloy on isothermal aging.
 EXPERIMENT 8 PRECIPITATION HARDENING IN 2024 ALUMINUM Objective To study the time and temperature variations in the hardness of Al-4% Cu alloy on isothermal aging. Introduction Materials can be hardened
EXPERIMENT 8 PRECIPITATION HARDENING IN 2024 ALUMINUM Objective To study the time and temperature variations in the hardness of Al-4% Cu alloy on isothermal aging. Introduction Materials can be hardened
Materials Engineering. Phase transformation Phase diagrams
 Materials Engineering Phase transformation Phase diagrams Phase Transformation Why is it important for us? o Temperature, chemical composition and pressure can change the properties of materials o Understanding
Materials Engineering Phase transformation Phase diagrams Phase Transformation Why is it important for us? o Temperature, chemical composition and pressure can change the properties of materials o Understanding
Chapter 1. Iron-Carbon AlloysⅠ. /MS371/ Structure and Properties of Engineering Alloys
 Chapter 1 Iron-Carbon AlloysⅠ Iron pure iron : to be obtained through zone refining adding a small amount of C, Mn, P, S 증가 pure iron 의 allotropic forms Allotropic forms Crystallographic form Unit cube
Chapter 1 Iron-Carbon AlloysⅠ Iron pure iron : to be obtained through zone refining adding a small amount of C, Mn, P, S 증가 pure iron 의 allotropic forms Allotropic forms Crystallographic form Unit cube
From sand to silicon wafer
 From sand to silicon wafer 25% of Earth surface is silicon Metallurgical grade silicon (MGS) Electronic grade silicon (EGS) Polycrystalline silicon (polysilicon) Single crystal Czochralski drawing Single
From sand to silicon wafer 25% of Earth surface is silicon Metallurgical grade silicon (MGS) Electronic grade silicon (EGS) Polycrystalline silicon (polysilicon) Single crystal Czochralski drawing Single
Oxidation of Chromium
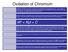 Oxidation of Chromium Oxidation of chromium is very simple as it usually forms a single oxide Cr 2 O 3, It is a p-type of oxide with Cr 3+ ions diffusing outward. Since the defect concentration is so low
Oxidation of Chromium Oxidation of chromium is very simple as it usually forms a single oxide Cr 2 O 3, It is a p-type of oxide with Cr 3+ ions diffusing outward. Since the defect concentration is so low
Part IV. Solid-solid transformations I
 Part IV : Solid-Solid Phase Transformations I Module 1 : Precipitation Part IV. Solid-solid transformations I In this part, we discuss a few of the important solid-solid transformations, namely, precipitation,
Part IV : Solid-Solid Phase Transformations I Module 1 : Precipitation Part IV. Solid-solid transformations I In this part, we discuss a few of the important solid-solid transformations, namely, precipitation,
3.40 Sketch within a cubic unit cell the following planes: (a) (01 1 ) (b) (112 ) (c) (102 ) (d) (13 1) Solution
 3.40 Sketch within a cubic unit cell the following planes: (a) (01 1 ) (b) (11 ) (c) (10 ) (d) (13 1) The planes called for are plotted in the cubic unit cells shown below. 3.41 Determine the Miller indices
3.40 Sketch within a cubic unit cell the following planes: (a) (01 1 ) (b) (11 ) (c) (10 ) (d) (13 1) The planes called for are plotted in the cubic unit cells shown below. 3.41 Determine the Miller indices
High strength low alloy (HSLA).
 7 Alloy Steels High strength low alloy (HSLA). a type of steel alloy that provides many benefits over regular steel alloys contain a very small percentage of carbon (less than one-tenth of a percent) and
7 Alloy Steels High strength low alloy (HSLA). a type of steel alloy that provides many benefits over regular steel alloys contain a very small percentage of carbon (less than one-tenth of a percent) and
1. Use the Ellingham Diagram (reproduced here as Figure 0.1) to answer the following.
 315 Problems 1. Use the Ellingham Diagram (reproduced here as Figure 0.1) to answer the following. (a) Find the temperature and partial pressure of O 2 where Ni(s), Ni(l), and NiO(s) are in equilibrium.
315 Problems 1. Use the Ellingham Diagram (reproduced here as Figure 0.1) to answer the following. (a) Find the temperature and partial pressure of O 2 where Ni(s), Ni(l), and NiO(s) are in equilibrium.
Incorporation of Titanium, Tantalum, and Vanadium Into the Hexagonal WC Lattice. A. Pasquazzi*, W.D. Schubert*, E. Halwax*, G.
 18 th Plansee Seminar HM 108/1 Incorporation of Titanium, Tantalum, and Vanadium Into the Hexagonal WC Lattice A. Pasquazzi*, W.D. Schubert*, E. Halwax*, G. Kremser** * Vienna University of Technology,
18 th Plansee Seminar HM 108/1 Incorporation of Titanium, Tantalum, and Vanadium Into the Hexagonal WC Lattice A. Pasquazzi*, W.D. Schubert*, E. Halwax*, G. Kremser** * Vienna University of Technology,
Lecture # 11 References:
 Lecture # 11 - Line defects (1-D) / Dislocations - Planer defects (2D) - Volume Defects - Burgers vector - Slip - Slip Systems in FCC crystals - Slip systems in HCP - Slip systems in BCC Dr.Haydar Al-Ethari
Lecture # 11 - Line defects (1-D) / Dislocations - Planer defects (2D) - Volume Defects - Burgers vector - Slip - Slip Systems in FCC crystals - Slip systems in HCP - Slip systems in BCC Dr.Haydar Al-Ethari
Heat Treatment of Steels : Metallurgical Principle
 Heat Treatment of Steels : Metallurgical Principle Outlines: Fe ad Fe-Fe 3 C system Phases and Microstructure Fe-Fe 3 C Phase Diaram General Physical and Mechanical Properties of each Microstructure Usanee
Heat Treatment of Steels : Metallurgical Principle Outlines: Fe ad Fe-Fe 3 C system Phases and Microstructure Fe-Fe 3 C Phase Diaram General Physical and Mechanical Properties of each Microstructure Usanee
Part IV : Solid-Solid Phase Transformations I Module 2 : Cellular precipitation
 Part IV : Solid-Solid Phase Transformations I Module 2 : Cellular precipitation 2. Cellular precipitation 2.1 Motivation Consider the microstructure (schematic) shown in Fig. 18. This is a typical microstructure
Part IV : Solid-Solid Phase Transformations I Module 2 : Cellular precipitation 2. Cellular precipitation 2.1 Motivation Consider the microstructure (schematic) shown in Fig. 18. This is a typical microstructure
Engineering materials
 1 Engineering materials Lecture 6 Metal and Alloys Phase Diagrams 2 Metals and alloys Some metals may have more than one crystal structure, a phenomenon known as polymorphism ( 同質異性 ), when found in elemental
1 Engineering materials Lecture 6 Metal and Alloys Phase Diagrams 2 Metals and alloys Some metals may have more than one crystal structure, a phenomenon known as polymorphism ( 同質異性 ), when found in elemental
Chapter 11 Part 2. Metals and Alloys
 Chapter 11 Part 2 Metals and Alloys Nomenclature of Steels Historically, many methods for identifying alloys by their composition have been developed The commonly used schemes in this country are those
Chapter 11 Part 2 Metals and Alloys Nomenclature of Steels Historically, many methods for identifying alloys by their composition have been developed The commonly used schemes in this country are those
Hypoeutectoid Carbon Steels. Hypereutectoid Carbon Steels
 Hypoeutectoid Carbon Steels Another example: Amount of carbon? 1035 Steel: white regions are proeutectoid ferrite grains By the end of this lecture you should be able to predict the amount of carbon in
Hypoeutectoid Carbon Steels Another example: Amount of carbon? 1035 Steel: white regions are proeutectoid ferrite grains By the end of this lecture you should be able to predict the amount of carbon in
THE EFFECT OF MICROSTRUCTURE ON MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SINGLE CRYSTAL CMSX-4 SUPERALLOY
 THE EFFECT OF MICROSTRUCTURE ON MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SINGLE CRYSTAL CMSX-4 SUPERALLOY Juraj LAPIN a, Tatiana PELACHOVÁ a, Oto BAJANA a a Institute of Materials and Machine Mechanics, Slovak Academy
THE EFFECT OF MICROSTRUCTURE ON MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SINGLE CRYSTAL CMSX-4 SUPERALLOY Juraj LAPIN a, Tatiana PELACHOVÁ a, Oto BAJANA a a Institute of Materials and Machine Mechanics, Slovak Academy
Design of 10%Cr Martensitic Steels for Improved Creep Resistance in Power Plant Applications
 Design of 10%Cr Martensitic Steels for Improved Creep Resistance in Power Plant Applications U.A. Sachadel, P.F. Morris, P.D. Clarke Tata Steel Europe 8th International Charles Parsons Turbine Conference
Design of 10%Cr Martensitic Steels for Improved Creep Resistance in Power Plant Applications U.A. Sachadel, P.F. Morris, P.D. Clarke Tata Steel Europe 8th International Charles Parsons Turbine Conference
Problems. 104 CHAPTER 3 Atomic and Ionic Arrangements
 104 CHAPTER 3 Atomic and Ionic Arrangements Repeat distance The distance from one lattice point to the adjacent lattice point along a direction. Short-range order The regular and predictable arrangement
104 CHAPTER 3 Atomic and Ionic Arrangements Repeat distance The distance from one lattice point to the adjacent lattice point along a direction. Short-range order The regular and predictable arrangement
REINFORCING AGE HARDENABLE Al-Cr MATRIX ALLOY IN-SITU AND BY SiC/AI203 PARTICULATES
 122 REINFORCING AGE HARDENABLE Al-Cr MATRIX ALLOY IN-SITU AND BY SiC/AI203 PARTICULATES S.DATTA, P.DEB, N.R.BANDYOPADHYAY AND M.K.BANERJEE Department of Metallurgy, B.E. College (D. U.), Howrah-711103.
122 REINFORCING AGE HARDENABLE Al-Cr MATRIX ALLOY IN-SITU AND BY SiC/AI203 PARTICULATES S.DATTA, P.DEB, N.R.BANDYOPADHYAY AND M.K.BANERJEE Department of Metallurgy, B.E. College (D. U.), Howrah-711103.
14ME406/ME 226. Material science &Metallurgy. Hall Ticket Number: Fourth Semester. II/IV B.Tech (Regular/Supplementary) DEGREE EXAMINATION
 Hall Ticket Number: 14ME406/ME 226 April, 2017 Fourth Semester Time: Three Hours Answer Question No.1 compulsorily. Answer ONE question from each unit. II/IV B.Tech (Regular/Supplementary) DEGREE EXAMINATION
Hall Ticket Number: 14ME406/ME 226 April, 2017 Fourth Semester Time: Three Hours Answer Question No.1 compulsorily. Answer ONE question from each unit. II/IV B.Tech (Regular/Supplementary) DEGREE EXAMINATION
Characterization of Nano-Scale Fine Precipitates in Al-Mg-Si Alloys for Automotive Applications
 UDC 669. 715 721 782 : 629. 11. 011. 5 Characterization of Nano-Scale Fine Precipitates in Al-Mg-Si Alloys for Automotive Applications Makoto SAGA* 1 Naoki MARUYAMA* 1 Abstract Bake-hadenable Al-Mg-Si
UDC 669. 715 721 782 : 629. 11. 011. 5 Characterization of Nano-Scale Fine Precipitates in Al-Mg-Si Alloys for Automotive Applications Makoto SAGA* 1 Naoki MARUYAMA* 1 Abstract Bake-hadenable Al-Mg-Si
Formability and Crystallographic Texture in Novel Magnesium Alloys
 Formability and Crystallographic Texture in Novel Magnesium Alloys Carlos Soto, Dr. Pnina Ari-Gur, Andreas, Quojo Quainoo, Dr. Betsy Aller, Dr. Andrew Kline Western Michigan University Abstract By looking
Formability and Crystallographic Texture in Novel Magnesium Alloys Carlos Soto, Dr. Pnina Ari-Gur, Andreas, Quojo Quainoo, Dr. Betsy Aller, Dr. Andrew Kline Western Michigan University Abstract By looking
Alloys & Their Phase Diagrams. مرجع علمى مهندسى مواد
 Alloys & Their Phase Diagrams Objectives of the class Gibbs phase rule Introduction to phase diagram Practice phase diagram Lever rule Important Observation: One question in the midterm Gibbs phase rule
Alloys & Their Phase Diagrams Objectives of the class Gibbs phase rule Introduction to phase diagram Practice phase diagram Lever rule Important Observation: One question in the midterm Gibbs phase rule
Free Electron Model What kind of interactions hold metal atoms together? How does this explain high electrical and thermal conductivity?
 Electrical Good conductors of heat & electricity Create semiconductors Oxides are basic ionic solids Aqueous cations (positive charge, Lewis acids) Reactivity increases downwards in family Mechanical Lustrous
Electrical Good conductors of heat & electricity Create semiconductors Oxides are basic ionic solids Aqueous cations (positive charge, Lewis acids) Reactivity increases downwards in family Mechanical Lustrous
