Supplementary data. Transmission blocking compound prevents malaria infection of mosquitoes.
|
|
|
- Dustin Allison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary data Transmission blocking compound prevents malaria infection of mosquitoes. Kayode K. Ojo 1, Claudia Pfander 2, Natascha R. Mueller 1, Charlotte Burstroem 2, Eric T. Larson 3, Cassie M. Bryan 3, Anna M.W. Fox 1, Molly C. Reid 1, Steven M. Johnson 4, Ryan C. Murphy 4, Mark Kennedy 5, Henning Mann 5, David J. Leibly 3, Stephen N. Hewitt 3, Christophe L.M.J. Verlinde 3, Stefan Kappe 5, Ethan A. Merritt 3, Dustin J. Maly 4, Oliver Billker 2, & Wesley C. Van Voorhis 1 1 Division of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington, USA. 2 The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, Hinxton, Cambridge CB10 1SA, UK. 3 Department of Biochemistry, 4 Department of Chemistry, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington, USA. 5 Seattle Biomedical Research Institute, Seattle, Washington, USA. Correspondence should be addressed to: Wesley C. Van Voorhis; Division of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Box University of Washington, 1959 NE Pacific Ave. Phone (206) ; Fax (206) wesley@uw.edu
2 Supplementary Table 1 Supplementary Table 1: Inhibition by BKIs (structures demonstrated) of exflagellation, wt rpfcdpk4, Toxoplasma gondii CDPK1, Cryptosporidium parvum CDPK1, S147M rpfcdpk4, human Src & Abl kinases, and mammalian cell proliferation. Compound Structure P. falciparum Exflagellation inhibition EC 50 (µm) Wild type PfCDPK4 IC 50 (µm) P. falciparum NF54 asexual growth inhibition EC 50 (µm) Wild type PfCDPK1 IC 50 (µm) Wild type TgCDPK1 IC 50 (µm) Wild type CpCDPK1 IC 50 (µm) S147M PfCDPK4 IC 50 (µm) Src IC 50 (µm) Abl IC 50 (µm) Mammalian fibroblasts EC 50 (µm) BKI >3 >20 >50 > > > >15 Rm >3 >20 >20 > >3 ND ND > >3 >3 > >3 ND ND ND NA-PP2 > > > >15
3 A Supplementary Figure 1. B C D wild type Not comple- mented cdpk4 - + Pbcpdk4-2myc + Pfcpdk4-2myc
4 Supplementary Figure 1. Generation and characterization of a P. berghei line expressing myc epitope tagged PfCDPK4. (A) Schematic illustrating the replacement of Pbcdpk4 with the Tgdhfr/ts selection marker and the subsequent complementation of the mutant by insertion of cdpk4 cdna sequences from either P. berghei or P. falciparum. (B) Southern hybridization of HindIII restricted genomic DNA probed with a 720 bp HpaI-NheI fragment from the cdpk4 upstream intergenic region (as indicated in panel A) identifies a 5.1 kb fragment in wild type and a 0.8 kb fragment in cdpk4 mutant lines as predicted. Complementation duplicates part of the upstream intergenic region and leads to the appearance of an additional band of 7.5 kb (P. berghei) or 7.7 kb (P. falciparum), as expected. (C) Western blot analysis showing expression of myc-tagged protein of the expected mobility in PfCDPK4 complemented parasites. In each lane 1.4x10 7 blood stage parasites (asexual and gametocytes) were loaded. (D) Effect of complementation on exflagellation and progression to the ookinete stage. Supplementary Figure 2. Supplementary Figure 2. BKI-1 blocks exflagellation of P. berghei WT and that expressing PbCDPK4 and PfCDPK4. Exflagellation inducing medium containing different concentrations of BKI-1 or vehicle was mixed with gametocytes from wild type or cdpk4 complemented mutants in vitro. Exflagellation centers in 10 microscopic fields are expressed as a percentage of a solvent control. Error bars show standard deviations of triplicate measurements from 2 infected mice per parasite strain.
5 Supplementary Figure 3 PvCDPK4 PkCDPK4 PbCDPK4 PfalCDPK4 QNSNVVFNEQYKGIKILGKGSFGEVILSRDKHTGHEYAIKVISKKHVKRKTDKQSLLREV QNSNVVFNEQYKGIKILGKGSFGEVILSRDKHTGHEYAIKVISKKHVKRKTDKQSLLREV QNSNVVFNEQYKGIKILGKGSFGEVILSKDKHTGHEYAIKVISKKHVKRKTDKQSLLREV QNSNVVFNEQYKGIKILGKGSFGEVILSRDKHTGHEYAIKVISKKHVKRKTDKESLLREV PvCDPK4 PkCDPK4 PbCDPK4 PfalCDPK4 PvCDPK4 PkCDPK4 PbCDPK4 PfalCDPK4 ELLKMLDHINIMKLYEFFEDNNYYYLVSDVYSGGELFDEIISRKRFYEVDAARIIKQVLS ELLKMLDHINIMKLYEFFEDNNYYYLVSDVYSGGELFDEIISRKRFYEVDAARIIKQVLS ELLKMLDHINIMKLYEFFEDNNYYYLVSDVYSGGELFDEIISRKRFYEVDAARIIKQVLS ELLKMLDHINIMKLYEFFEDNNYYYLVSDVYTGGELFDEIISRKRFYEIDAARIIKQILS GITYMHKNNVVHRDLKPENILLETKNKEDMIIKIIDFGLSTHFEYSKKMKDKIGTAYYIA GITYMHKNNVVHRDLKPENILLETKNKEDMIIKIIDFGLSTHFEYSKKMKDKIGTAYYIA GITYMHKNNVVHRDLKPENILLETKNKEDMIIKIIDFGLSTHFEYSKKMKDKIGTAYYIA GITYMHKNNVVHRDLKPENILLETKNKEDMIIKIIDFGLSTHFEYSKKMKDKIGTAYYIA Supplementary Figure 3. Sequence alignment of CDPK4 kinase domain active site in Plasmodium spp of public health importance: Residues that contribute to inhibitor binding in the active sites of CDPK4 homologs are boxed. Gatekeeper residues are shaded yellow. The only residue that differs between the four homologs is shown in green. This residue does not appear to contribute to differential inhibitor sensitivity because P. berghei and P. falciparum exflagellation are both potently inhibited by BKI-1 (Supplementary Figure 2). Supplementary Figure 4
6 BKI-1 plasma levels after a single oral 50 mg/kg dose. Mean concentration of BKI-1 blood levels from three mice (error bars are standard deviation of the mean) dosed with 50 mg/kg show oral exposure. Blood levels of about 5-fold less were seen when mice were given an oral 10mg/kg dose (data not shown). Supplementary Methods Expression, purification and enzyme activity assays. Recombinant PfCDPK1 and PfCDPK4 proteins expressed in E. coli (Rosetta Oxford strain) were purified as earlier described (1). A luminescence assay that measures the depletion of ATP in the presence of the peptide substrate, Syntide 2 (PLARTLSVAGLPGKK) (1,2), was used to determine the catalytic activity of these enzymes. Assays were performed with 10 µm ATP, 40 µm Syntide-2, and 6.6 nm or 208 nm of PfCDPK1 and PfCDPK4, respectively, in 20 mm HEPES (ph 7.5), 0.1% BSA (w/v), 10 mm MgCl 2, 1 mm EGTA, with or without 2 mm CaCl 2. The BKI compound library (2) was tested at serial concentrations between 3 µm and 1nM. Binding mode modeling. The kinase domain of PfCDPK4 was modeled by the I-TASSER server (3) using structures of TgCDPK1 available in the Protein Data Bank as a template. Subsequent docking of BKI-1 into the active site of this model was carried out using QXP/FLO (4) (version +0602). BKI-1 was initially placed in the active site of PfCDPK4 by SSM superposition (5) of an in-house TgCDPK1:BKI-1 co-crystal structure (PDB3sx9). The binding pocket was defined as all residues within 10 Å of the roughly placed inhibitor. Protein atoms were fixed with the exception of sidechain atoms that project into the binding pocket. The two H-bonds between the pyrazolopyrimidine inhibitor scaffold and the hinge region of the kinase, which are conserved in most ATP/ATP-homolog:kinase complexes, were restrained. The interaction between the R2-piperidine nitrogen and Glu154 sidechain was also restrained because
7 we see this interaction in >15 co-crystal structures of TgCDPK1/CpCDPK1 with BKIs containing the methylpiperidine R2-substituent (2). Docking of BKI-1 was subsequently carried out using 1100 cycles of Metropolis Monte Carlo conformational searching followed by energy minimization. The 25 lowest energy binding modes were visually inspected and conformations 1 and 3 were selected as favorable representatives shown in Figure 1. Conformation 2 was excluded because the methyl-group was axial to the piperidine of the methylpiperidine R2- substituent. P. berghei maintenance and genetic modification. The P. berghei ANKA wild type clone 2.34 and the transgenic lines derived from it were maintained in Theiler's Original (TO) or Swiss Webster outbred mice and infections monitored on Giemsa-stained blood films. The cdpk4- mutant clone and its complementation with P. berghei cdpk4 were described previously (6). A transfection vector for complementing the cdpk4- mutant with Pfcdpk4 was generated by replacing the P. berghei sequence in plasmid p150 with a Pfcdpk4 sequence amplified by PCR from P. falciparum 3D7 gametocyte cdna as an NheI-ApaI restriction fragment, placing it in frame with a carboxy terminal 2x myc epitope tag, a 3 UTR and terminator derived from the P. berghei dhfr/ts gene. Following verification of the Pfcdpk4 sequence, the plasmid was linearized in a unique HpaI site within the cdpk4 5 intergenic region and transfected into P. berghei cdpk4- using established protocols (7). Homologous insertion of the complementation vector into the upstream intergenic region of the cdpk4 mutant placed Pfcdpk4 under the control of the endogenous P. berghei promoter (Supplementary Figure 1A). Transgenic clones were genotyped by diagnostic PCR followed by Southern blot analysis (Supplementary Figure 1B).
8 Phenotypic analysis of P. berghei gametocytes expressing PfCDPK4-2x-myc and sensitivity to BKI-1. Expression of CDPK4-2x-myc proteins was verified by western blot analysis of mixed asexual parasite and gametocytes purified from peripheral blood of infected mice by ammonium chloride lysis. Parasites were suspended and lysed in SDS loading buffer containing 0.1 M DTT. Protein blots were probed with anti-myc mouse monoclonal antibody 9E10 (Sigma) at 1:2000 dilution. To assess the effect of complementation, exflagellation was quantified 3 to 4 days post infection by adding 4 µl of blood from a superficial tail vein to 150 µl exflagellation medium (RPMI1640 containing 25 mm HEPES (Sigma), 10% FCS, 100 µm xanthurenic acid, ph 7.5). Between 15 and 18 minutes after activation the number of exflagellating microgametocytes was counted in a haemocytometer and the red blood cell (RBC) count determined. The percentage of RBCs containing microgametocytes was assessed on Giemsa-stained blood smears and the number of exflagellations per 100 microgametocytes was then calculated. Ookinetes formation was analysed in vitro largely as described (8). The conversion rate was determined as the number of banana shaped ookinetes as a percentage of the total number of P28 expressing cells. For the experiments monitoring exflagellation after compound administration, mice bearing P. berghei gametocytes expressing PfCDPK4-2x-myc were treated with 50 mg/kg i.p. of BKI-1 or NA-PP2 or vehicle (90% saline 7% EtOH 3% DMSO), bled at the time points noted in Figure 2, exflagellation events determined as above, and compound concentration in the blood determined by quantitative liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. P. berghei transmission experiments. Mice were injected i.p. with drug or vehicle 3 days after an infection had been initiated with ~106 P. berghei ANKA parasites constitutively expressing GFP (9). After 30 minutes; treated mice were anaesthetized by i.p. injection of a mixture of
9 ketamine (Ketalar, 80 mg/kg) and xylazine (Rompun, 8 mg/kg) and exposed to 25 female A. stephensi mosquitoes. After 5 days midguts were dissected and imaged using a fluorescence microscope and oocysts quantified. P. falciparum transmission experiments. P. falciparum strain NF54 parasites were cultured in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 50 µm hypoxanthine and 10% A+ human serum. Cultures were started at 0.5% and grown for 16 days with daily media changes. Beginning on day 14 exflagellation was monitored. On Day 16, all cultures were pooled and divided into flasks to which BKI-1 was added for 30 minutes at 50 nm, 100 nm, 300nM, 1 µm and 3 µm with one flask as a vehicle-only control and NA-PP2 flasks with 50 nm, 300 nm, and 3 µm. A wet mount was taken to check exflagellation and monitored beginning at 10 minutes and observed until 25 minutes had elapsed. Each flask of culture was fed to approximately day old A. stephensi mosquitoes for 20 minutes. Ten days post feed ~50 mosquitoes from each cage was checked for midgut oocyst infection. On day 14 remaining mosquitoes in each cage were dissected and pooled to check for salivary gland sporozoites. Reference List 1. Ojo KK, et al. Toxoplasma gondii calcium-dependent protein kinase 1 is a target for selective kinase inhibitors. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010;17(5): Murphy RC, et al. Discovery of Potent and Selective Inhibitors of Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinase 1 (CDPK1) from C. parvum and T. gondii. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2010;1(7): Roy A, Kucukural A, Zhang Y. I-TASSER: a unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat Protoc. 2010;5(4): McMartin C, Bohacek RS. QXP: powerful, rapid computer algorithms for structure-based drug design. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 1997;11(4):
10 5. Krissinel E, Henrick K. Secondary-structure matching (SSM), a new tool for fast protein structure alignment in three dimensions. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2004;60(Pt 12 Pt 1): Billker O, et al. Calcium and a calcium-dependent protein kinase regulate gamete formation and mosquito transmission in a malaria parasite. Cell. 2004;117(4): Janse CJ, Franke-Fayard B, Waters AP,. Selection by flow-sorting of genetically transformed, GFP-expressing blood stages of the rodent malaria parasite, Plasmodium berghei. Nat.Protoc. 2006;1: Moon RW, et al. A cyclic GMP signalling module that regulates gliding motility in a malaria parasite. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5(9):e Eichner M, Diebner HH, Molineaux L, Collins WE, Jeffery GM, Dietz K. Genesis, sequestration and survival of Plasmodium falciparum gametocytes: parameter estimates from fitting a model to malaria therapy data. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2001;95:
SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector
 SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector Richard J. Wall 1,#, Magali Roques 1,+, Nicholas J. Katris
SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector Richard J. Wall 1,#, Magali Roques 1,+, Nicholas J. Katris
University of Dundee. Published in: Scientific Reports. DOI: /srep Publication date: 2016
 University of Dundee SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector Wall, Richard J.; Roques, Magali; Katris,
University of Dundee SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector Wall, Richard J.; Roques, Magali; Katris,
Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Attenuated Plasmodium yoelii Lacking Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase Confer Protective. Immunity. LM Ting, M Gissot, A Coppi, P Sinnis, K Kim
 Attenuated Plasmodium yoelii Lacking Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase Confer Protective Immunity LM Ting, M Gissot, A Coppi, P Sinnis, K Kim Supplementary Figures 1 * Py MD-EEQRHIKLSKKHATPVVLVVGDPGRVD-KIKVLCDSYVDLACNREYKSVECHYKGQK
Attenuated Plasmodium yoelii Lacking Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase Confer Protective Immunity LM Ting, M Gissot, A Coppi, P Sinnis, K Kim Supplementary Figures 1 * Py MD-EEQRHIKLSKKHATPVVLVVGDPGRVD-KIKVLCDSYVDLACNREYKSVECHYKGQK
Paul Bowyer. (Baker Lab, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine)
 Evaluation of selective inhibitors of the malarial cyclic GMP dependent protein kinase (PKG) Paul Bowyer (Baker Lab, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine) Talk summary An overview of the P. falciparum
Evaluation of selective inhibitors of the malarial cyclic GMP dependent protein kinase (PKG) Paul Bowyer (Baker Lab, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine) Talk summary An overview of the P. falciparum
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In format provided by Orchard et al. (SEPTEMBER 2011) Supplementary information S1 Sample MIABE file exemplifying data extracted from PMID: 20568778 Responsible Person or Role Contact Person Bryan K. S.
In format provided by Orchard et al. (SEPTEMBER 2011) Supplementary information S1 Sample MIABE file exemplifying data extracted from PMID: 20568778 Responsible Person or Role Contact Person Bryan K. S.
Comparative assessment of vaccine vectors encoding ten. malaria antigens identifies two protective liver-stage
 Supplementary Information Comparative assessment of vaccine vectors encoding ten malaria antigens identifies two protective liver-stage candidates Rhea J. Longley 1,,,*, Ahmed M. Salman 1,2,, Matthew G.
Supplementary Information Comparative assessment of vaccine vectors encoding ten malaria antigens identifies two protective liver-stage candidates Rhea J. Longley 1,,,*, Ahmed M. Salman 1,2,, Matthew G.
Beyond Viagra: Novel use of Nus-A fusion and Gateway cloning technology in the heterologous expression of Plasmodium falciparum phosphodiesterases
 Beyond Viagra: Novel use of Nus-A fusion and Gateway cloning technology in the heterologous expression of Plasmodium falciparum phosphodiesterases Daniel T Leung, MD; Paul S Pottinger, MD; Wesley C Van
Beyond Viagra: Novel use of Nus-A fusion and Gateway cloning technology in the heterologous expression of Plasmodium falciparum phosphodiesterases Daniel T Leung, MD; Paul S Pottinger, MD; Wesley C Van
Supplemental Figure 1 HDA18 has an HDAC domain and therefore has concentration dependent and TSA inhibited histone deacetylase activity.
 Supplemental Figure 1 HDA18 has an HDAC domain and therefore has concentration dependent and TSA inhibited histone deacetylase activity. (A) Amino acid alignment of HDA5, HDA15 and HDA18. The blue line
Supplemental Figure 1 HDA18 has an HDAC domain and therefore has concentration dependent and TSA inhibited histone deacetylase activity. (A) Amino acid alignment of HDA5, HDA15 and HDA18. The blue line
At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
7.012 Problem Set 5. Question 1
 Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 5 Question 1 While studying the problem of infertility, you attempt to isolate a hypothetical rabbit gene that accounts for the prolific reproduction of rabbits. After much
Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 5 Question 1 While studying the problem of infertility, you attempt to isolate a hypothetical rabbit gene that accounts for the prolific reproduction of rabbits. After much
pt7ht vector and over-expressed in E. coli as inclusion bodies. Cells were lysed in 6 M
 Supplementary Methods MIG6 production, purification, inhibition, and kinase assays MIG6 segment 1 (30mer, residues 334 364) peptide was synthesized using standard solid-phase peptide synthesis as described
Supplementary Methods MIG6 production, purification, inhibition, and kinase assays MIG6 segment 1 (30mer, residues 334 364) peptide was synthesized using standard solid-phase peptide synthesis as described
Supplementary data. sienigma. F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM. a-p53
 Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS. Figure S1: Homology alignment of DDR2 amino acid sequence. Shown are
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1: Homology alignment of DDR2 amino acid sequence. Shown are the amino acid sequences of human DDR2, mouse DDR2 and the closest homologs in zebrafish and C. Elegans.
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1: Homology alignment of DDR2 amino acid sequence. Shown are the amino acid sequences of human DDR2, mouse DDR2 and the closest homologs in zebrafish and C. Elegans.
Cancer cells that survive radiation therapy acquire HIF-1 activity and translocate toward tumor blood vessels Supplementary Information
 Cancer cells that survive radiation therapy acquire HIF-1 activity and translocate toward tumor blood vessels Supplementary Information 1. Supplementary Figure S1-S10: Pages 2-11 2. Supplementary References:
Cancer cells that survive radiation therapy acquire HIF-1 activity and translocate toward tumor blood vessels Supplementary Information 1. Supplementary Figure S1-S10: Pages 2-11 2. Supplementary References:
Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic structure of TRAIP and RAP80. The prey line below TRAIP indicates bait and the two lines above RAP80 highlight the
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic structure of TRAIP and RAP80. The prey line below TRAIP indicates bait and the two lines above RAP80 highlight the prey clones identified in the yeast two hybrid screen.
Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic structure of TRAIP and RAP80. The prey line below TRAIP indicates bait and the two lines above RAP80 highlight the prey clones identified in the yeast two hybrid screen.
Revised: RG-RV2 by Fukuhara et al.
 Supplemental Figure 1 The generation of Spns2 conditional knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the wild type Spns2 locus (Spns2 + ), the targeted allele, the floxed allele (Spns2 f ) and the
Supplemental Figure 1 The generation of Spns2 conditional knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the wild type Spns2 locus (Spns2 + ), the targeted allele, the floxed allele (Spns2 f ) and the
Hossain_Supplemental Figure 1
 Hossain_Supplemental Figure 1 GFP-PACT GFP-PACT Motif I GFP-PACT Motif II A. MG132 (1µM) GFP Tubulin GFP-PACT Pericentrin GFP-PACT GFP-PACT Pericentrin Fig. S1. Expression and localization of Orc1 PACT
Hossain_Supplemental Figure 1 GFP-PACT GFP-PACT Motif I GFP-PACT Motif II A. MG132 (1µM) GFP Tubulin GFP-PACT Pericentrin GFP-PACT GFP-PACT Pericentrin Fig. S1. Expression and localization of Orc1 PACT
The Plasmodium palmitoyl-s-acyl-transferase DHHC2 is essential for ookinete morphogenesis and malaria transmission
 The Plasmodium palmitoyl-s-acyl-transferase DHHC2 is essential for ookinete morphogenesis and malaria transmission Jorge M. Santos, Jessica Kehrer, Blandine Franke-Fayard, Friedrich Frischknecht, Chris
The Plasmodium palmitoyl-s-acyl-transferase DHHC2 is essential for ookinete morphogenesis and malaria transmission Jorge M. Santos, Jessica Kehrer, Blandine Franke-Fayard, Friedrich Frischknecht, Chris
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.2548
 Supplementary Table 1: Genotypes of offspring and embryos from matings of Pmm2 WT/F118L mice with Pmm2 WT/R137H mice total events Pmm2 WT/WT Pmm2 WT/R137H Pmm2 WT/F118L Pmm2 R137H/F118L offspring 117 (100%)
Supplementary Table 1: Genotypes of offspring and embryos from matings of Pmm2 WT/F118L mice with Pmm2 WT/R137H mice total events Pmm2 WT/WT Pmm2 WT/R137H Pmm2 WT/F118L Pmm2 R137H/F118L offspring 117 (100%)
fibrils, however, oligomeric structures and amorphous protein aggregates were
 Supplementary Figure 1: Effect of equimolar EGCG on αs and Aβ aggregate formation. A D B E αs C F Figure S1: (A-C) Analysis of EGCG treated αs (1 µm) aggregation reactions by EM. A 1:1 molar ratio of EGCG
Supplementary Figure 1: Effect of equimolar EGCG on αs and Aβ aggregate formation. A D B E αs C F Figure S1: (A-C) Analysis of EGCG treated αs (1 µm) aggregation reactions by EM. A 1:1 molar ratio of EGCG
Enzyme that uses RNA as a template to synthesize a complementary DNA
 Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Comparison of two or more protein or DNA sequence to ascertain similarities in sequences. If two genes have
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Comparison of two or more protein or DNA sequence to ascertain similarities in sequences. If two genes have
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS. -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells. - Two methods to produce transgenic animals:
 TRANSGENIC ANIMALS -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection - random insertion 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated gene
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection - random insertion 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated gene
Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than. SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with
 Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with concentration of 800nM) were incubated with 1mM dgtp for the indicated
Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with concentration of 800nM) were incubated with 1mM dgtp for the indicated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 1 Supplementary Figure S1. Proportion of HEK293T transfectants showing fluorescent foci after heat sho Blinded slides were counted for the appearance of fluorescent foci of tagrfp-t
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 1 Supplementary Figure S1. Proportion of HEK293T transfectants showing fluorescent foci after heat sho Blinded slides were counted for the appearance of fluorescent foci of tagrfp-t
Genetic Approaches for Malaria Control. Marcelo Jacobs-Lorena, PhD
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Figure S1, related to Figure 1. Characterization of biosensor behavior in vivo.
 Developmental Cell, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Separase Biosensor Reveals that Cohesin Cleavage Timing Depends on Phosphatase PP2A Cdc55 Regulation Gilad Yaakov, Kurt Thorn, and David O. Morgan
Developmental Cell, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Separase Biosensor Reveals that Cohesin Cleavage Timing Depends on Phosphatase PP2A Cdc55 Regulation Gilad Yaakov, Kurt Thorn, and David O. Morgan
Chapter 20 Recombinant DNA Technology. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 20 Recombinant DNA Technology Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 20.1 Recombinant DNA Technology Began with Two Key Tools: Restriction Enzymes and DNA Cloning Vectors Recombinant DNA refers
Chapter 20 Recombinant DNA Technology Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 20.1 Recombinant DNA Technology Began with Two Key Tools: Restriction Enzymes and DNA Cloning Vectors Recombinant DNA refers
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06147 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 The genomic and domain structure of Dscam. The Dscam gene comprises 24 exons, encoding a signal peptide (SP), 10 IgSF domains, 6 fibronectin
doi: 10.1038/nature06147 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 The genomic and domain structure of Dscam. The Dscam gene comprises 24 exons, encoding a signal peptide (SP), 10 IgSF domains, 6 fibronectin
The Biotechnology Toolbox
 Chapter 15 The Biotechnology Toolbox Cutting and Pasting DNA Cutting DNA Restriction endonuclease or restriction enzymes Cellular protection mechanism for infected foreign DNA Recognition and cutting specific
Chapter 15 The Biotechnology Toolbox Cutting and Pasting DNA Cutting DNA Restriction endonuclease or restriction enzymes Cellular protection mechanism for infected foreign DNA Recognition and cutting specific
Single cell imaging of Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase using an irreversible inhibitor
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Single cell imaging of Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase using an irreversible inhibitor Anna Turetsky 1,a, Eunha Kim 1,a, Rainer H. Kohler 1, Miles A. Miller 1, Ralph Weissleder 1,2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Single cell imaging of Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase using an irreversible inhibitor Anna Turetsky 1,a, Eunha Kim 1,a, Rainer H. Kohler 1, Miles A. Miller 1, Ralph Weissleder 1,2,
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or
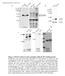 Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
Supplementary Figure 1 Collision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of peptides from PPK1, PPK2, PPK3 and PPK4 respectively.
 Supplementary Figure 1 lision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of peptides from PPK1, PPK, PPK3 and PPK respectively. % of nuclei with signal / field a 5 c ppif3:gus pppk1:gus 0 35 30 5 0 15 10
Supplementary Figure 1 lision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of peptides from PPK1, PPK, PPK3 and PPK respectively. % of nuclei with signal / field a 5 c ppif3:gus pppk1:gus 0 35 30 5 0 15 10
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 (Supplementary Methods and Materials) GST pull-down assay GST-fusion proteins Fe65 365-533, and Fe65 538-700 were expressed in BL21 bacterial cells and purified with glutathione-agarose beads (Sigma).
(Supplementary Methods and Materials) GST pull-down assay GST-fusion proteins Fe65 365-533, and Fe65 538-700 were expressed in BL21 bacterial cells and purified with glutathione-agarose beads (Sigma).
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Reverse transcribed Quantitative PCR. Total RNA was isolated from bone marrow derived macrophages using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), DNase-treated (Promega RQ1), and reverse transcribed
Supplementary Methods Reverse transcribed Quantitative PCR. Total RNA was isolated from bone marrow derived macrophages using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), DNase-treated (Promega RQ1), and reverse transcribed
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Part I: Definitions. Homology: Reverse transcriptase. Allostery: cdna library
 Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Reverse transcriptase Allostery: cdna library Transformation Part II Short Answer 1. Describe the reasons for
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Reverse transcriptase Allostery: cdna library Transformation Part II Short Answer 1. Describe the reasons for
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1: Suv39h1, but not Suv39h2, promotes HP1α sumoylation in vivo. In vivo HP1α sumoylation assay. Top: experimental scheme. Middle: we
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1: Suv39h1, but not Suv39h2, promotes HP1α sumoylation in vivo. In vivo HP1α sumoylation assay. Top: experimental scheme. Middle: we
Supplementary information to accompany: A novel role for the DNA repair gene Rad51 in Netrin-1 signalling
 Supplementary information to accompany: A novel role for the DNA repair gene Rad51 in Netrin-1 signalling Glendining KA 1, Markie D 2, Gardner RJM 4, Franz EA 3, Robertson SP 4, Jasoni CL 1 Supplementary
Supplementary information to accompany: A novel role for the DNA repair gene Rad51 in Netrin-1 signalling Glendining KA 1, Markie D 2, Gardner RJM 4, Franz EA 3, Robertson SP 4, Jasoni CL 1 Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1 (A), (B), and (C) Docking of a physiologic ligand of integrin αvβ3, the tenth type III RGD domain of wild-type fibronectin
 Supplementary Figure 1 (A), (B), and (C) Docking of a physiologic ligand of integrin αvβ3, the tenth type III RGD domain of wild-type fibronectin (A), D1-CD2 (B), and the D1-CD2 variant 3 (C) to Adomain
Supplementary Figure 1 (A), (B), and (C) Docking of a physiologic ligand of integrin αvβ3, the tenth type III RGD domain of wild-type fibronectin (A), D1-CD2 (B), and the D1-CD2 variant 3 (C) to Adomain
Chapter 6 - Molecular Genetic Techniques
 Chapter 6 - Molecular Genetic Techniques Two objects of molecular & genetic technologies For analysis For generation Molecular genetic technologies! For analysis DNA gel electrophoresis Southern blotting
Chapter 6 - Molecular Genetic Techniques Two objects of molecular & genetic technologies For analysis For generation Molecular genetic technologies! For analysis DNA gel electrophoresis Southern blotting
Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified
 Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified by primers used for mrna expression analysis. Gray
Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified by primers used for mrna expression analysis. Gray
Attenuation of synaptic toxicity and MARK4/PAR1-mediated Tau phosphorylation by
 Supplementary Methods and Figures Attenuation of synaptic toxicity and MARK4/PAR1-mediated Tau phosphorylation by methylene blue for Alzheimer s disease treatment Wenchao Sun 1, Seongsoo Lee 1,2, Xiaoran
Supplementary Methods and Figures Attenuation of synaptic toxicity and MARK4/PAR1-mediated Tau phosphorylation by methylene blue for Alzheimer s disease treatment Wenchao Sun 1, Seongsoo Lee 1,2, Xiaoran
LINGO-1, A TRANSMEMBRANE SIGNALING PROTEIN, INHIBITS OLIGODENDROCYTE DIFFERENTIATION AND MYELINATION THROUGH INTERCELLULAR SELF- INTERACTIONS.
 Supplemental Data: LINGO-1, A TRANSMEMBRANE SIGNALING PROTEIN, INHIBITS OLIGODENDROCYTE DIFFERENTIATION AND MYELINATION THROUGH INTERCELLULAR SELF- INTERACTIONS. Scott Jepson, Bryan Vought, Christian H.
Supplemental Data: LINGO-1, A TRANSMEMBRANE SIGNALING PROTEIN, INHIBITS OLIGODENDROCYTE DIFFERENTIATION AND MYELINATION THROUGH INTERCELLULAR SELF- INTERACTIONS. Scott Jepson, Bryan Vought, Christian H.
Develop Better Assays for Every Human Protein
 Develop Better Assays for Every Human Protein OriGene overview Application of transfected over-expression lysates Application of purified recombinant human proteins About OriGene Started in1996 with the
Develop Better Assays for Every Human Protein OriGene overview Application of transfected over-expression lysates Application of purified recombinant human proteins About OriGene Started in1996 with the
ATPlite Assay Performance in Human Primary Cells
 A P P L I C AT I O N N O T E Cell Viability Assays Author: Verena Brucklacher-Waldert Crescendo Biologics Cambridge, UK Assay Performance in Human Primary Cells Introduction In vitro assays using primary
A P P L I C AT I O N N O T E Cell Viability Assays Author: Verena Brucklacher-Waldert Crescendo Biologics Cambridge, UK Assay Performance in Human Primary Cells Introduction In vitro assays using primary
Figure legends for supplement
 Figure legends for supplement Supplemental Figure 1 Characterization of purified and recombinant proteins Relevant fractions related the final stage of the purification protocol(bingham et al., 1998; Toba
Figure legends for supplement Supplemental Figure 1 Characterization of purified and recombinant proteins Relevant fractions related the final stage of the purification protocol(bingham et al., 1998; Toba
Supplemental Data. Li et al. (2015). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1: Characterization of asr3 T-DNA knockout lines and complementation transgenic lines. (A) The scheme of At2G33550 (ASR3) with gray boxes indicating exons and dash
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1: Characterization of asr3 T-DNA knockout lines and complementation transgenic lines. (A) The scheme of At2G33550 (ASR3) with gray boxes indicating exons and dash
Supplementary Figure 1. α-synuclein is truncated in PD and LBD brains. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.
 Supplementary Figure 1 α-synuclein is truncated in PD and LBD brains. (a) Specificity of anti-n103 antibody. Anti-N103 antibody was coated on an ELISA plate and different concentrations of full-length
Supplementary Figure 1 α-synuclein is truncated in PD and LBD brains. (a) Specificity of anti-n103 antibody. Anti-N103 antibody was coated on an ELISA plate and different concentrations of full-length
FIG S1: Calibration curves of standards for HPLC detection of Dopachrome (Dopac), Dopamine (DA) and Homovanillic acid (HVA), showing area of peak vs
 FIG S1: Calibration curves of standards for HPLC detection of Dopachrome (Dopac), Dopamine (DA) and Homovanillic acid (HVA), showing area of peak vs amount of standard analysed. Each point represents the
FIG S1: Calibration curves of standards for HPLC detection of Dopachrome (Dopac), Dopamine (DA) and Homovanillic acid (HVA), showing area of peak vs amount of standard analysed. Each point represents the
Deep sequencing reveals global patterns of mrna recruitment
 Supplementary information for: Deep sequencing reveals global patterns of mrna recruitment during translation initiation Rong Gao 1#*, Kai Yu 1#, Ju-Kui Nie 1,Teng-Fei Lian 1, Jian-Shi Jin 1, Anders Liljas
Supplementary information for: Deep sequencing reveals global patterns of mrna recruitment during translation initiation Rong Gao 1#*, Kai Yu 1#, Ju-Kui Nie 1,Teng-Fei Lian 1, Jian-Shi Jin 1, Anders Liljas
Supplemental Data. Hu et al. Plant Cell (2017) /tpc
 1 2 3 4 Supplemental Figure 1. DNA gel blot analysis of homozygous transgenic plants. (Supports Figure 1.) 5 6 7 8 Rice genomic DNA was digested with the restriction enzymes EcoRⅠ and BamHⅠ. Lanes in the
1 2 3 4 Supplemental Figure 1. DNA gel blot analysis of homozygous transgenic plants. (Supports Figure 1.) 5 6 7 8 Rice genomic DNA was digested with the restriction enzymes EcoRⅠ and BamHⅠ. Lanes in the
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Drugs Modulate Interactions Between the First Nucleotide-Binding Domain and the Fourth Cytoplasmic Loop of Human P-glycoprotein Tip W. Loo and David M. Clarke Department of Medicine
Supporting Information Drugs Modulate Interactions Between the First Nucleotide-Binding Domain and the Fourth Cytoplasmic Loop of Human P-glycoprotein Tip W. Loo and David M. Clarke Department of Medicine
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Design and Characterization of Bivalent BET Inhibitors
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Design and Characterization of Bivalent BET Inhibitors Minoru Tanaka 1,2,#, Justin M. Roberts 1,#, Hyuk-Soo Seo 3, Amanda Souza 1, Joshiawa Paulk 1, Thomas G. Scott 1, Stephen
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Design and Characterization of Bivalent BET Inhibitors Minoru Tanaka 1,2,#, Justin M. Roberts 1,#, Hyuk-Soo Seo 3, Amanda Souza 1, Joshiawa Paulk 1, Thomas G. Scott 1, Stephen
2054, Chap. 14, page 1
 2054, Chap. 14, page 1 I. Recombinant DNA technology (Chapter 14) A. recombinant DNA technology = collection of methods used to perform genetic engineering 1. genetic engineering = deliberate modification
2054, Chap. 14, page 1 I. Recombinant DNA technology (Chapter 14) A. recombinant DNA technology = collection of methods used to perform genetic engineering 1. genetic engineering = deliberate modification
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3494
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
Fig. S1. Effect of p120-catenin overexpression on the interaction of SCUBE2 with E-cadherin. The expression plasmid encoding FLAG.
 Fig. S1. Effect of p120-catenin overexpression on the interaction of SCUBE2 with E-cadherin. The expression plasmid encoding FLAG.SCUBE2, E-cadherin.Myc, or HA.p120-catenin was transfected in a combination
Fig. S1. Effect of p120-catenin overexpression on the interaction of SCUBE2 with E-cadherin. The expression plasmid encoding FLAG.SCUBE2, E-cadherin.Myc, or HA.p120-catenin was transfected in a combination
Figure S1. Figure S2. Figure S3 HB Anti-FSP27 (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab. Anti-GST-FSP27(45-127) Ab.
 / 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
/ 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
Supplementary Figure 1. Immunoprecipitation of synthetic SUMOm-remnant peptides using UMO monoclonal antibody. (a) LC-MS analyses of tryptic
 Supplementary Figure 1. Immunoprecipitation of synthetic SUMOm-remnant peptides using UMO 1-7-7 monoclonal antibody. (a) LC-MS analyses of tryptic digest from HEK293 cells spiked with 6 SUMOmremnant peptides
Supplementary Figure 1. Immunoprecipitation of synthetic SUMOm-remnant peptides using UMO 1-7-7 monoclonal antibody. (a) LC-MS analyses of tryptic digest from HEK293 cells spiked with 6 SUMOmremnant peptides
Freire et al. - Supplemental Material for Trypanosoma brucei translation-initiation factor homolog EIF4E6 is linked to posttranscriptional regulation
 Freire et al. - Supplemental Material for Trypanosoma brucei translation-initiation factor homolog EIF4E6 is linked to posttranscriptional regulation Table S1 Oligonucleotides used in this study Table
Freire et al. - Supplemental Material for Trypanosoma brucei translation-initiation factor homolog EIF4E6 is linked to posttranscriptional regulation Table S1 Oligonucleotides used in this study Table
Supplementary Figure S1 Purification of deubiquitinases HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated DUB-expressing plasmids.
 Supplementary Figure S1 Purification of deubiquitinases HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated DUB-expressing plasmids. The cells were harvested 72 h after transfection. FLAG-tagged deubiquitinases
Supplementary Figure S1 Purification of deubiquitinases HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated DUB-expressing plasmids. The cells were harvested 72 h after transfection. FLAG-tagged deubiquitinases
Motivation From Protein to Gene
 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 2003-4 Topic B Recombinant DNA -principles and tools Construct a library - what for, how Major techniques +principles Bioinformatics - in brief Chapter 7 (MCB) 1 Motivation From Protein
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 2003-4 Topic B Recombinant DNA -principles and tools Construct a library - what for, how Major techniques +principles Bioinformatics - in brief Chapter 7 (MCB) 1 Motivation From Protein
5.36 Biochemistry Laboratory Spring 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.36 Biochemistry Laboratory Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Laboratory Manual for URIECA
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.36 Biochemistry Laboratory Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Laboratory Manual for URIECA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09937 a Name Position Primersets 1a 1b 2 3 4 b2 Phenotype Genotype b Primerset 1a D T C R I E 10000 8000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 800 Donor (D)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09937 a Name Position Primersets 1a 1b 2 3 4 b2 Phenotype Genotype b Primerset 1a D T C R I E 10000 8000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 800 Donor (D)
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic and results of screening the combinatorial antibody library for Sox2 replacement activity. A single batch of MEFs were plated and transduced with doxycycline inducible
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic and results of screening the combinatorial antibody library for Sox2 replacement activity. A single batch of MEFs were plated and transduced with doxycycline inducible
b alternative classical none
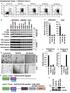 Supplementary Figure. 1: Related to Figure.1 a d e b alternative classical none NIK P-IkBa Total IkBa Tubulin P52 (Lighter) P52 (Darker) RelB (Lighter) RelB (Darker) HDAC1 Control-Sh RelB-Sh NF-kB2-Sh
Supplementary Figure. 1: Related to Figure.1 a d e b alternative classical none NIK P-IkBa Total IkBa Tubulin P52 (Lighter) P52 (Darker) RelB (Lighter) RelB (Darker) HDAC1 Control-Sh RelB-Sh NF-kB2-Sh
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS. transient. stable. - Two methods to produce transgenic animals:
 Only for teaching purposes - not for reproduction or sale CELL TRANSFECTION transient stable TRANSGENIC ANIMALS - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated
Only for teaching purposes - not for reproduction or sale CELL TRANSFECTION transient stable TRANSGENIC ANIMALS - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated
CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration
 /, Supplementary Advance Publications Materials 2016 CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1: In ECs CD93 silencing
/, Supplementary Advance Publications Materials 2016 CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1: In ECs CD93 silencing
Supplementary Fig. 1 Proteomic analysis of ATR-interacting proteins. ATR, ARID1A and
 Supplementary Figure Legend: Supplementary Fig. 1 Proteomic analysis of ATR-interacting proteins. ATR, ARID1A and ATRIP protein peptides identified from our mass spectrum analysis were shown. Supplementary
Supplementary Figure Legend: Supplementary Fig. 1 Proteomic analysis of ATR-interacting proteins. ATR, ARID1A and ATRIP protein peptides identified from our mass spectrum analysis were shown. Supplementary
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2116 Figure S1 CDK phosphorylation of EZH2 in cells. (a) Comparison of candidate CDK phosphorylation sites on EZH2 with known CDK substrates by multiple sequence alignments. (b) CDK1 and
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2116 Figure S1 CDK phosphorylation of EZH2 in cells. (a) Comparison of candidate CDK phosphorylation sites on EZH2 with known CDK substrates by multiple sequence alignments. (b) CDK1 and
A RRM1 H2AX DAPI. RRM1 H2AX DAPI Merge. Cont. sirna RRM1
 A H2AX DAPI H2AX DAPI Merge Cont sirna Figure S1: Accumulation of RRM1 at DNA damage sites (A) HeLa cells were subjected to in situ detergent extraction without IR irradiation, and immunostained with the
A H2AX DAPI H2AX DAPI Merge Cont sirna Figure S1: Accumulation of RRM1 at DNA damage sites (A) HeLa cells were subjected to in situ detergent extraction without IR irradiation, and immunostained with the
3 -end. Sau3A. 3 -end TAA TAA. ~9.1kb SalI TAA. ~12.6kb. HindШ ATG 5,860bp TAA. ~12.7kb
 Supplemental Data. Chen et al. (2008). Badh2, encoding betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase, inhibits the biosynthesis of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline, a major component in rice fragrance. A pcam-cah/cah Sau3A Promoter
Supplemental Data. Chen et al. (2008). Badh2, encoding betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase, inhibits the biosynthesis of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline, a major component in rice fragrance. A pcam-cah/cah Sau3A Promoter
Cell lines and cell culture. GM08505 is an SV40-transformed skin fibroblast cell line
 Materials and Methods Cell lines and cell culture. GM08505 is an SV40-transformed skin fibroblast cell line derived from a BS patient and contains the BLM Ash founder mutation identified in patients of
Materials and Methods Cell lines and cell culture. GM08505 is an SV40-transformed skin fibroblast cell line derived from a BS patient and contains the BLM Ash founder mutation identified in patients of
Design. Construction. Characterization
 Design Construction Characterization DNA mrna (messenger) A C C transcription translation C A C protein His A T G C T A C G Plasmids replicon copy number incompatibility selection marker origin of replication
Design Construction Characterization DNA mrna (messenger) A C C transcription translation C A C protein His A T G C T A C G Plasmids replicon copy number incompatibility selection marker origin of replication
Z -LYTE KINASE ASSAY KIT TYR 3 PEPTIDE PROTOCOL
 Z -LYTE KINASE ASSAY KIT TYR 3 PEPTIDE PROTOCOL Cat. no. PV3192 O-062193-r1 US 0405 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 2 2.0 ASSAY THEORY... 2 3.0 Z9-LYTE KINASE ASSAY KIT TYR 3 PEPTIDE MATERIALS PROVIDED...
Z -LYTE KINASE ASSAY KIT TYR 3 PEPTIDE PROTOCOL Cat. no. PV3192 O-062193-r1 US 0405 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 2 2.0 ASSAY THEORY... 2 3.0 Z9-LYTE KINASE ASSAY KIT TYR 3 PEPTIDE MATERIALS PROVIDED...
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Secondary mutations as a mechanism of cisplatin resistance in BRCA2-mutated cancers Wataru Sakai, Elizabeth M. Swisher, Beth Y. Karlan, Mukesh K. Agarwal, Jake Higgins, Cynthia Friedman, Emily Villegas,
Secondary mutations as a mechanism of cisplatin resistance in BRCA2-mutated cancers Wataru Sakai, Elizabeth M. Swisher, Beth Y. Karlan, Mukesh K. Agarwal, Jake Higgins, Cynthia Friedman, Emily Villegas,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Kilian et al. 10.1073/pnas.1105861108 SI Materials and Methods Determination of the Electric Field Strength Required for Successful Electroporation. The transformation construct
Supporting Information Kilian et al. 10.1073/pnas.1105861108 SI Materials and Methods Determination of the Electric Field Strength Required for Successful Electroporation. The transformation construct
Supplementary Figure 1. TSA (10 nmol/l), non-class-selective HDAC inhibitor, potentiates
 Supplementary Figure 1. TSA (10 nmol/l), non-class-selective HDAC inhibitor, potentiates vascular calcification (VC). (a) Von Kossa staining shows that TSA potentiated the Pi-induced VC. Scale bar, 100
Supplementary Figure 1. TSA (10 nmol/l), non-class-selective HDAC inhibitor, potentiates vascular calcification (VC). (a) Von Kossa staining shows that TSA potentiated the Pi-induced VC. Scale bar, 100
Lecture 25 (11/15/17)
 Lecture 25 (11/15/17) Reading: Ch9; 328-332 Ch25; 990-995, 1005-1012 Problems: Ch9 (study-guide: applying); 1,2 Ch9 (study-guide: facts); 7,8 Ch25 (text); 1-3,5-7,9,10,13-15 Ch25 (study-guide: applying);
Lecture 25 (11/15/17) Reading: Ch9; 328-332 Ch25; 990-995, 1005-1012 Problems: Ch9 (study-guide: applying); 1,2 Ch9 (study-guide: facts); 7,8 Ch25 (text); 1-3,5-7,9,10,13-15 Ch25 (study-guide: applying);
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1137999/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Disrupting the Pairing Between let-7 and Enhances Oncogenic Transformation Christine Mayr, Michael T. Hemann, David P. Bartel*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1137999/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Disrupting the Pairing Between let-7 and Enhances Oncogenic Transformation Christine Mayr, Michael T. Hemann, David P. Bartel*
Figure S1. Sequence alignments of ATRIP and ATR TopBP1 interacting regions.
 A H. sapiens 204 TKLQTS--ERANKLAAPSVSH VSPRKNPSVVIKPEACS-PQFGKTSFPTKESFSANMS LP 259 B. taurus 201 TKLQSS--ERANKLAVPTVSH VSPRKSPSVVIKPEACS-PQFGKPSFPTKESFSANKS LP 257 M. musculus 204 TKSQSN--GRTNKPAAPSVSH
A H. sapiens 204 TKLQTS--ERANKLAAPSVSH VSPRKNPSVVIKPEACS-PQFGKTSFPTKESFSANMS LP 259 B. taurus 201 TKLQSS--ERANKLAVPTVSH VSPRKSPSVVIKPEACS-PQFGKPSFPTKESFSANKS LP 257 M. musculus 204 TKSQSN--GRTNKPAAPSVSH
Single cell resolution in vivo imaging of DNA damage following PARP inhibition. Supplementary Data
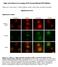 Single cell resolution in vivo imaging of DNA damage following PARP inhibition Katherine S. Yang, Rainer H. Kohler, Matthieu Landon, Randy Giedt, and Ralph Weissleder Supplementary Data Supplementary Figures
Single cell resolution in vivo imaging of DNA damage following PARP inhibition Katherine S. Yang, Rainer H. Kohler, Matthieu Landon, Randy Giedt, and Ralph Weissleder Supplementary Data Supplementary Figures
Supplemental Data. Sethi et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. MYC2 Binds to the E-box but not the E1-box of the MPK6 Promoter. (A) E1-box and E-box (wild type) containing MPK6 promoter fragment. The region shown in red denotes
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. MYC2 Binds to the E-box but not the E1-box of the MPK6 Promoter. (A) E1-box and E-box (wild type) containing MPK6 promoter fragment. The region shown in red denotes
Supplementary Fig. 1
 a FL (1-2266) NL (1-1190) CL (1191-2266) HA-ICE1: - HA-ICE1: - - - FLAG-ICE2: + + + + FLAG-ELL: + + + + + + IP: anti-ha FLAG-ICE2 HA-ICE1-FL HA-ICE1-NL HA-ICE1-CL FLAG-ICE2 b IP: anti-ha FL (1-2266) NL
a FL (1-2266) NL (1-1190) CL (1191-2266) HA-ICE1: - HA-ICE1: - - - FLAG-ICE2: + + + + FLAG-ELL: + + + + + + IP: anti-ha FLAG-ICE2 HA-ICE1-FL HA-ICE1-NL HA-ICE1-CL FLAG-ICE2 b IP: anti-ha FL (1-2266) NL
Bootcamp: Molecular Biology Techniques and Interpretation
 Bootcamp: Molecular Biology Techniques and Interpretation Bi8 Winter 2016 Today s outline Detecting and quantifying nucleic acids and proteins: Basic nucleic acid properties Hybridization PCR and Designing
Bootcamp: Molecular Biology Techniques and Interpretation Bi8 Winter 2016 Today s outline Detecting and quantifying nucleic acids and proteins: Basic nucleic acid properties Hybridization PCR and Designing
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Small molecule activation of the TRAIL receptor DR5 in human cancer cells
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Small molecule activation of the TRAIL receptor DR5 in human cancer cells Gelin Wang 1*, Xiaoming Wang 2, Hong Yu 1, Shuguang Wei 1, Noelle Williams 1, Daniel L. Holmes 1, Randal
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Small molecule activation of the TRAIL receptor DR5 in human cancer cells Gelin Wang 1*, Xiaoming Wang 2, Hong Yu 1, Shuguang Wei 1, Noelle Williams 1, Daniel L. Holmes 1, Randal
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Tal et al. 10.1073/pnas.0807694106 SI Materials and Methods VSV Infection and Quantification. Infection was carried out by seeding 5 10 5 MEF cells per well in a 6-well plate and
Supporting Information Tal et al. 10.1073/pnas.0807694106 SI Materials and Methods VSV Infection and Quantification. Infection was carried out by seeding 5 10 5 MEF cells per well in a 6-well plate and
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Han et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201311007/dc1 Figure S1. SIVA1 interacts with PCNA. (A) HEK293T cells were transiently
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Han et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201311007/dc1 Figure S1. SIVA1 interacts with PCNA. (A) HEK293T cells were transiently
Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg
![Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg](/thumbs/84/90687567.jpg) Supplementary information Supplementary methods PCNA antibody and immunodepletion Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg extracts, one volume of protein
Supplementary information Supplementary methods PCNA antibody and immunodepletion Antibodies against PCNA were previously described [1]. To deplete PCNA from Xenopus egg extracts, one volume of protein
Supplementary Information: Materials and Methods. GST and GST-p53 were purified according to standard protocol after
 Supplementary Information: Materials and Methods Recombinant protein expression and in vitro kinase assay. GST and GST-p53 were purified according to standard protocol after induction with.5mm IPTG for
Supplementary Information: Materials and Methods Recombinant protein expression and in vitro kinase assay. GST and GST-p53 were purified according to standard protocol after induction with.5mm IPTG for
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information The E3 ligase RNF8 regulates KU80 removal and NHEJ repair Lin Feng 1, Junjie Chen 1 1 Department of Experimental Radiation Oncology, The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer
Supplementary information The E3 ligase RNF8 regulates KU80 removal and NHEJ repair Lin Feng 1, Junjie Chen 1 1 Department of Experimental Radiation Oncology, The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES A B Flag-ALDH1A1 IP: α-ac HEK293T WT 91R 128R 252Q 367R 41/ 419R 435R 495R 412R C Flag-ALDH1A1 NAM IP: HEK293T + + - + D NAM - + + E Relative ALDH1A1 activity 1..8.6.4.2
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES A B Flag-ALDH1A1 IP: α-ac HEK293T WT 91R 128R 252Q 367R 41/ 419R 435R 495R 412R C Flag-ALDH1A1 NAM IP: HEK293T + + - + D NAM - + + E Relative ALDH1A1 activity 1..8.6.4.2
SCREENING AND PRESERVATION OF DNA LIBRARIES
 MODULE 4 LECTURE 5 SCREENING AND PRESERVATION OF DNA LIBRARIES 4-5.1. Introduction Library screening is the process of identification of the clones carrying the gene of interest. Screening relies on a
MODULE 4 LECTURE 5 SCREENING AND PRESERVATION OF DNA LIBRARIES 4-5.1. Introduction Library screening is the process of identification of the clones carrying the gene of interest. Screening relies on a
Combinatorial Evolution of Enzymes and Synthetic pathways Using
 Supplementary data Combinatorial Evolution of Enzymes and Synthetic pathways Using One-Step PCR Peng Jin,, Zhen Kang,,, *, Junli Zhang,, Linpei Zhang,, Guocheng Du,, and Jian Chen, The Key Laboratory of
Supplementary data Combinatorial Evolution of Enzymes and Synthetic pathways Using One-Step PCR Peng Jin,, Zhen Kang,,, *, Junli Zhang,, Linpei Zhang,, Guocheng Du,, and Jian Chen, The Key Laboratory of
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Super-resolution imaging of fluorescently labeled, endogenous RNA Polymerase II in living cells with CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing Won-Ki Cho 1, Namrata Jayanth 1, Susan Mullen
Supplementary Information Super-resolution imaging of fluorescently labeled, endogenous RNA Polymerase II in living cells with CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing Won-Ki Cho 1, Namrata Jayanth 1, Susan Mullen
Data Sheet CD137/NF-κB Reporter - HEK293 Recombinant Cell Line Catalog # 79289
 Data Sheet CD137/NF-κB Reporter - HEK293 Recombinant Cell Line Catalog # 79289 Background Human CD137 (4-1BB; TNFRS9) is an inducible co-stimulatory molecule that activates T cells. CD137:CD137L-mediated
Data Sheet CD137/NF-κB Reporter - HEK293 Recombinant Cell Line Catalog # 79289 Background Human CD137 (4-1BB; TNFRS9) is an inducible co-stimulatory molecule that activates T cells. CD137:CD137L-mediated
Adenoviral Expression Systems. Lentivirus is not the only choice for gene delivery. Adeno-X
 Adenoviral Expression Systems Lentivirus is not the only choice for gene delivery 3 Adeno-X Why choose adenoviral gene delivery? Table I: Adenoviral vs. Lentiviral Gene Delivery Lentivirus Adenovirus Infects
Adenoviral Expression Systems Lentivirus is not the only choice for gene delivery 3 Adeno-X Why choose adenoviral gene delivery? Table I: Adenoviral vs. Lentiviral Gene Delivery Lentivirus Adenovirus Infects
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Biagini et al. 10.1073/pnas.1205651109 SI Materials and Methods Generation of CK-2 68 Resistant Plasmodium falciparum and Sequencing of the Plasmodium falciparum NDH2 Gene. Plasmodium
Supporting Information Biagini et al. 10.1073/pnas.1205651109 SI Materials and Methods Generation of CK-2 68 Resistant Plasmodium falciparum and Sequencing of the Plasmodium falciparum NDH2 Gene. Plasmodium
Data Sheet GITR / NF-ĸB-Luciferase Reporter (Luc) - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60546
 Data Sheet GITR / NF-ĸB-Luciferase Reporter (Luc) - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60546 Description This cell line expresses a surface human GITR (glucocorticoid-induced TNFR family related gene; TNFRSF18;
Data Sheet GITR / NF-ĸB-Luciferase Reporter (Luc) - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60546 Description This cell line expresses a surface human GITR (glucocorticoid-induced TNFR family related gene; TNFRSF18;
GENETICS EXAM 3 FALL a) is a technique that allows you to separate nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) by size.
 Student Name: All questions are worth 5 pts. each. GENETICS EXAM 3 FALL 2004 1. a) is a technique that allows you to separate nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) by size. b) Name one of the materials (of the two
Student Name: All questions are worth 5 pts. each. GENETICS EXAM 3 FALL 2004 1. a) is a technique that allows you to separate nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) by size. b) Name one of the materials (of the two
