Scientific Background Synechococcus pigment types
|
|
|
- Brandon Barker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Scientific Background Synechococcus pigment types Oligotrophic Mesotrophic Coastal 0 m Nutrients 50 m 100 m 150 m
2 Scientific Background Synechococcus Genomes BL107 CA RS9917 Clade I Clade II Clade III Clade IV Clade VIII Clade IX Clade V Clade VI Clade VII Clade X HL H L L LL Core genome Main Title Genus- / cladespecific genes RS9917 WH7805 MED4 Strain-specific genes MED4 SS120 MIT9313 WH7803 WH7805 CC9902 CC9605 CC9311 WH8102 RS9917 RS9916 RCC307 WH5701
3 BOUM Cruise Main Objectives 1) Study the physiological response of Prochlorococcus cells to various environmental factors and its consequences on the distribution of these organisms 2) Determine the impact of Synechococcus pigmentation on the distribution of this organism 3) Identify the set of genes that allow specific lineages to occupy distinct niches in the water column 4) Correlate these informations to better understand the community structure of these organisms and the relationship with their phylogeny.
4 BOUM Cruise PE PEII 2 cg ec ee pespetper aplacp unk5 cp mped cpunk6 mpee unk1unk3 c cc unk4 2 FISH Cultures BL107 CC9605 WH8102 RS9916 WH /100/100 WH /88/66 CC9311 Diversity Diversity markers (DNA) PC U pe m BA pe pe mpeym m ev p unk10 m ba bb cb ca pe pe rp rprpct unk12 rpcs A B ey ez cp pe pe cp unk11 c c ba bb cb A rpcspe pe rp rpcrpct rpce rpcf unk12 ev p unk10 m ey cp unk11 ez ee ea eb cp mp cp cp PEIIsubunit PEIsubunit 2 PCsubunit ev ba bb cb ca p cg ec ee pes etper rpcspe pe rp rprpce c cp c unk10 m unk12 rpcf unk1cpct PEassociatedlinker unk4 cp unk5 cp cped cpunk6 PCassociatedlinker WH780 Rod-corelinker Z A B PEgeneregulation ey e e e 5 unk2 cp unk11 cp cp cp Phycobilin lyase (or homolog) Bilin synthesis Phosphatase cpcs cpcg1 unk1 cpct cpcg2cpcc cpcd cpcb cpca cpcccpcb cpca cpce cpcf Conservedhypothetical RS9917 Hypothetical unk9 unk8+7 WH5701 unk2 ITS2 ITS1 16S PE ba bb cb ca rpcspe pe rp rp rpct unk12 WH7803 unk2 Pigment markers ITS BA C pe pe pe ee pes pet er RS9916 mpezmpefmpee unk1unk3unk4aplacpcgunk5 cpec mped cpunk6 c c cp mpey m m m RCC307 BL107 CC9902 CC9311 unk2 unk7 unk8 unk9 2 cg ec ee pespetper c cc unk1unk4 apla cp unk5cp mped cpunk6 unk10 ez ey ea eb cp cp unk11 cp cp unk9 unk7 unk8 unk2 CC9902 PEI BA C U pe pe pe pe mpey m m m m ce rp cf WH8102 CC9605 rp Methodology 5S 23S RS9917 WH5701 RCC307 Gloeobacter P hos phate Molybdate 1533, ? Cation trans porterdi-,tri-dic arboxylate 0097 A T P as e , 1577 Gly cine 0095 Xy lulose -5-P Alanine Leucine Valine 1362, 0766 D -Sedoheptulose -7-P 0890? Chlorophy llidea2 5-Phosphoribosy l diphosphate Histidine Purines, Py rimidines Ribof lav in, FAD, Folate cis-aconitate Nicotinamide N icotinam ide mononucleotide m ononucleotide Malate 1620 Fe ? Fe2+ or Mn2+ NRAMP-type 1203 TCA Cycle Cobalamine C obalam ine Fumarate NAD N AD Succinate Zn2+ or Mn Chl b Chl Cycle Chlide b Citrate Oxaloacetate Pcb PsaJF Flvd PsaE PsaC PsaB FeS PsaD PsaA Isocitrate 1752 Oxalosuccinate Protopor phy rin IX ATP Synthase NADH N AD H d eh yd ro g en ase dehydrogenase D1 D2 Cyt b Cyt C yt b6/f Pcb Cyt b559 D1 D2 Mg-Protoporphy rin IX PS I Cyt f SIV F es Cytb6 FNR PQ/PQH2 Mg-2,4-div iny l phaeoporphy rin a5monomethy lester Mg-Protoporphy rin IX monomethy lester Plas to Plasto cyanin c yanin PsaLIKM Heme 1866 H+ Cytochrome C yto ch ro me o xid ase oxidase Chl a Ribose-5-P DV-Protochlorophy llide L-Aspartate Oligopeptides Py ruv ate Acety l-coa Spermidine/Putrescine 0881 K+ Kef-type 1227 Chl b CO Na+/bicarbonate, Na+/bic arbonate, SbtA 0241 Glucose-6-P D-Erythrose-4-P 0855, 0856 D-Sedoheptulose-1,7-PP D -Sedoheptulose-1,7-PP 1770 Asparagine Threonine Methionine Leucine Isoleucine SO , 0804 Polar amino acids Calvin Cycle D-Ribulose Phosphoenolpy ruv ate-5-p PAPS 0190 APS , D-Ribulose-1,5-PP 2-P-Gly cerate ATP ADP O-acety lserine Dihy droxy acetone-p F Fructoseructose1,6-PP , 0856 Fructose-6-P F ructose-6-p P-Gly cerate CO2 Serine 0143 SO 3 2- Try ptophane Ty rosine Pheny lalanine 0505,1157, Cy steine H 2S D eoxy -D -ribose 2-Deoxy -D-ribose-5-P Gly ceral1,3-pp-gly ceratedehy de-3-p Cobalt 0389,10 26? F es CP43 Real time PCR PsbO CP47 CP47 PsbO PS II dimer d imer CP43 P cb 2 Oxoglutarate 1668 Arginine Proline L-Glutamate Na+/galac tos idena+/alanine Na+/galactoside 1625 Na+/proline 0784 Na+/glutamate L-Glutamine NH Cl Na+/H+ K+/H Ca2+/Na+ Genomics Cell sorting Whole genome amplification 454 sequencing Physiology Physiological markers (RNA) UV stress (reca) Cell cycle (ftsz) Phosphate limitation Temperature Oxygen evolution PAM fluorimetry
5 BOUM Cruise Sampling 24 stations Short Stations QPCR DNA (6 depths, 2L/depth) FISH (6 depths, 150 ml/depth) 6 stations Cultures (2 depths, 500 ml/depth) 3 stations Env Genomic (1 depths, 3 L/depth) 2 stations (B, C) Long Stations Env Genomic (1 depths, 3 L/depth) Cycle experiments (A, A, B, C, 72 h) 3 CTD/day QPCR DNA (6 depths, 2L/depth) QPCR RNA (6 depths, 12L/depth) Flow cytometry (12 depth, 5 ml/depth) Surface QPCR DNA (2L every 2-3 h) QPCR RNA (12 L every 2-3 h) Flow cytometry (12 depth, 5 ml/depth)
6
7 Aménagements intérieurs : revêtement de sol Plaques quadrillées en plastique, épaisses et amovibles
8 Objectif/Methodology BOUM Cruise Physiological status of Prochlorococcus Prochlorococcus Genome Comparison Stress Experiments (Light, nutrient, temp, etc) Microarray Real time PCR Identification of potentiel markers and optimisation Elaboration of sequence data base Design of specific primers Check for specificity QPCR Optimisation Application to natural samples
9 Methodology Synechococcus Functional diversity Physiological status Pigment type/its Genomic UV stress (reca) Cell cycle (ftsz) Phosphate limitation Temperature Oxygen evolution Real time PCR Design specific primers Optimisation of RT-PCR conditions Flow cytometry cell sorting Whole genome amplification 454 Sequencing Additional sample Culture FISH PAM sepctrofluorimetry Synechococcus Functionnal Diversity
10 Objectives for the BOUM Cruise Effets des facteurs environnementaux Understand repartition en clades des syn Parametres influencant la repartition des differents clades L effet de la pigmentation sur la repartition de ces organismes 1: Study the physiological status of Prochlorococcus cell using molecular markers: UV stress (reca) Cell cycle (ftsz) Phosphate Limitation Temperature Oxygen evolution 2: Study the Functional Diversity of Marine Synechococcus using : Pigment content ITS Genomic approach
11 Thématique 3: Diversité fonctionnelle des cyanobactéries marines et acclimatation aux facteurs environnementaux Simulation des conditions environnementales IN flux set up Fresh culture medium Peristaltic pump Rapid clip Filtration cartwridge 0.2 µm UVA, UVB Automatic sampling (Cell cycle, growth rate) Waste Culture Manual sampling (ARN)
MODEL 1. provides additional information about the performance of the CeSS algorithm.
 MODEL 1 Sections 1 to 4 describe Model 1, a metabolic model of E. coli s Central Carbon Metabolism. Section 5 provides additional information about the performance of the CeSS algorithm. 1 Model structure:
MODEL 1 Sections 1 to 4 describe Model 1, a metabolic model of E. coli s Central Carbon Metabolism. Section 5 provides additional information about the performance of the CeSS algorithm. 1 Model structure:
What is necessary for life?
 Life What is necessary for life? Most life familiar to us: Eukaryotes FREE LIVING Or Parasites First appeared ~ 1.5-2 10 9 years ago Requirements: DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, complex structure,
Life What is necessary for life? Most life familiar to us: Eukaryotes FREE LIVING Or Parasites First appeared ~ 1.5-2 10 9 years ago Requirements: DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, complex structure,
What is necessary for life?
 Life What is necessary for life? Most life familiar to us: Eukaryotes FREE LIVING Or Parasites First appeared ~ 1.5-2 10 9 years ago Requirements: DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, complex structure,
Life What is necessary for life? Most life familiar to us: Eukaryotes FREE LIVING Or Parasites First appeared ~ 1.5-2 10 9 years ago Requirements: DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, complex structure,
11 questions for a total of 120 points
 Your Name: BYS 201, Final Exam, May 3, 2010 11 questions for a total of 120 points 1. 25 points Take a close look at these tables of amino acids. Some of them are hydrophilic, some hydrophobic, some positive
Your Name: BYS 201, Final Exam, May 3, 2010 11 questions for a total of 120 points 1. 25 points Take a close look at these tables of amino acids. Some of them are hydrophilic, some hydrophobic, some positive
Basic concepts of molecular biology
 Basic concepts of molecular biology Gabriella Trucco Email: gabriella.trucco@unimi.it Life The main actors in the chemistry of life are molecules called proteins nucleic acids Proteins: many different
Basic concepts of molecular biology Gabriella Trucco Email: gabriella.trucco@unimi.it Life The main actors in the chemistry of life are molecules called proteins nucleic acids Proteins: many different
Name. Student ID. Midterm 2, Biology 2020, Kropf 2004
 Midterm 2, Biology 2020, Kropf 2004 1 1. RNA vs DNA (5 pts) The table below compares DNA and RNA. Fill in the open boxes, being complete and specific Compare: DNA RNA Pyrimidines C,T C,U Purines 3-D structure
Midterm 2, Biology 2020, Kropf 2004 1 1. RNA vs DNA (5 pts) The table below compares DNA and RNA. Fill in the open boxes, being complete and specific Compare: DNA RNA Pyrimidines C,T C,U Purines 3-D structure
Algorithms in Bioinformatics ONE Transcription Translation
 Algorithms in Bioinformatics ONE Transcription Translation Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University sami.khuri@sjsu.edu Biology Review DNA RNA Proteins Central Dogma Transcription
Algorithms in Bioinformatics ONE Transcription Translation Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University sami.khuri@sjsu.edu Biology Review DNA RNA Proteins Central Dogma Transcription
Biochemistry and Cell Biology
 Biochemistry and Cell Biology Monomersare simple molecules that can be linked into chains. (Nucleotides, Amino acids, monosaccharides) Polymersare the long chains of monomers. (DNA, RNA, Cellulose, Protein,
Biochemistry and Cell Biology Monomersare simple molecules that can be linked into chains. (Nucleotides, Amino acids, monosaccharides) Polymersare the long chains of monomers. (DNA, RNA, Cellulose, Protein,
 Problem: The GC base pairs are more stable than AT base pairs. Why? 5. Triple-stranded DNA was first observed in 1957. Scientists later discovered that the formation of triplestranded DNA involves a type
Problem: The GC base pairs are more stable than AT base pairs. Why? 5. Triple-stranded DNA was first observed in 1957. Scientists later discovered that the formation of triplestranded DNA involves a type
EE550 Computational Biology
 EE550 Computational Biology Week 1 Course Notes Instructor: Bilge Karaçalı, PhD Syllabus Schedule : Thursday 13:30, 14:30, 15:30 Text : Paul G. Higgs, Teresa K. Attwood, Bioinformatics and Molecular Evolution,
EE550 Computational Biology Week 1 Course Notes Instructor: Bilge Karaçalı, PhD Syllabus Schedule : Thursday 13:30, 14:30, 15:30 Text : Paul G. Higgs, Teresa K. Attwood, Bioinformatics and Molecular Evolution,
The Transition to Life!
 The Transition to Life The Transition to Life Chemical Evolution Biological Evolution? Interacting Chemical Reproduction of Organisms Natural Selection Based on Simplest Life Now: Need: 1. Nucleic Acids
The Transition to Life The Transition to Life Chemical Evolution Biological Evolution? Interacting Chemical Reproduction of Organisms Natural Selection Based on Simplest Life Now: Need: 1. Nucleic Acids
36. The double bonds in naturally-occuring fatty acids are usually isomers. A. cis B. trans C. both cis and trans D. D- E. L-
 36. The double bonds in naturally-occuring fatty acids are usually isomers. A. cis B. trans C. both cis and trans D. D- E. L- 37. The essential fatty acids are A. palmitic acid B. linoleic acid C. linolenic
36. The double bonds in naturally-occuring fatty acids are usually isomers. A. cis B. trans C. both cis and trans D. D- E. L- 37. The essential fatty acids are A. palmitic acid B. linoleic acid C. linolenic
Basic concepts of molecular biology
 Basic concepts of molecular biology Gabriella Trucco Email: gabriella.trucco@unimi.it What is life made of? 1665: Robert Hooke discovered that organisms are composed of individual compartments called cells
Basic concepts of molecular biology Gabriella Trucco Email: gabriella.trucco@unimi.it What is life made of? 1665: Robert Hooke discovered that organisms are composed of individual compartments called cells
Targeted metabolic profiling of the Tg197 mouse model reveals itaconic acid as a marker of Rheumatoid Arthritis.
 Targeted metabolic profiling of the Tg197 mouse model reveals itaconic acid as a marker of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Filippos Michopoulos 1,2,, Niki Karagianni 3, Nichola Whalley 1, Mike Firth 8, Christoforos
Targeted metabolic profiling of the Tg197 mouse model reveals itaconic acid as a marker of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Filippos Michopoulos 1,2,, Niki Karagianni 3, Nichola Whalley 1, Mike Firth 8, Christoforos
DNA.notebook March 08, DNA Overview
 DNA Overview Deoxyribonucleic Acid, or DNA, must be able to do 2 things: 1) give instructions for building and maintaining cells. 2) be copied each time a cell divides. DNA is made of subunits called nucleotides
DNA Overview Deoxyribonucleic Acid, or DNA, must be able to do 2 things: 1) give instructions for building and maintaining cells. 2) be copied each time a cell divides. DNA is made of subunits called nucleotides
BIOLOGY. Monday 14 Mar 2016
 BIOLOGY Monday 14 Mar 2016 Entry Task List the terms that were mentioned last week in the video. Translation, Transcription, Messenger RNA (mrna), codon, Ribosomal RNA (rrna), Polypeptide, etc. Agenda
BIOLOGY Monday 14 Mar 2016 Entry Task List the terms that were mentioned last week in the video. Translation, Transcription, Messenger RNA (mrna), codon, Ribosomal RNA (rrna), Polypeptide, etc. Agenda
From mechanism to medicne
 From mechanism to medicne a look at proteins and drug design Chem 342 δ δ δ+ M 2009 δ+ δ+ δ M Drug Design - an Iterative Approach @ DSU Structural Analysis of Receptor Structural Analysis of Ligand-Receptor
From mechanism to medicne a look at proteins and drug design Chem 342 δ δ δ+ M 2009 δ+ δ+ δ M Drug Design - an Iterative Approach @ DSU Structural Analysis of Receptor Structural Analysis of Ligand-Receptor
Bi Lecture 3 Loss-of-function (Ch. 4A) Monday, April 8, 13
 Bi190-2013 Lecture 3 Loss-of-function (Ch. 4A) Infer Gene activity from type of allele Loss-of-Function alleles are Gold Standard If organism deficient in gene A fails to accomplish process B, then gene
Bi190-2013 Lecture 3 Loss-of-function (Ch. 4A) Infer Gene activity from type of allele Loss-of-Function alleles are Gold Standard If organism deficient in gene A fails to accomplish process B, then gene
Photosynthetic production of biofuels from CO 2 by cyanobacteria using Algenol s Direct to Ethanol process Strain development aspects
 Photosynthetic production of biofuels from CO 2 by cyanobacteria using Algenol s Direct to Ethanol process Strain development aspects Paul Roessler - Oct 1, 2014 Algal Biomass Summit Algenol Overview Advanced
Photosynthetic production of biofuels from CO 2 by cyanobacteria using Algenol s Direct to Ethanol process Strain development aspects Paul Roessler - Oct 1, 2014 Algal Biomass Summit Algenol Overview Advanced
DNA is normally found in pairs, held together by hydrogen bonds between the bases
 Bioinformatics Biology Review The genetic code is stored in DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA molecules are chains of four nucleotide bases Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine, Adenine DNA is normally found in pairs,
Bioinformatics Biology Review The genetic code is stored in DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA molecules are chains of four nucleotide bases Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine, Adenine DNA is normally found in pairs,
Bioinformatics. ONE Introduction to Biology. Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Biology/CS 123A Fall 2012
 Bioinformatics ONE Introduction to Biology Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Biology/CS 123A Fall 2012 Biology Review DNA RNA Proteins Central Dogma Transcription Translation
Bioinformatics ONE Introduction to Biology Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Biology/CS 123A Fall 2012 Biology Review DNA RNA Proteins Central Dogma Transcription Translation
Using DNA sequence, distinguish species in the same genus from one another.
 Species Identification: Penguins 7. It s Not All Black and White! Name: Objective Using DNA sequence, distinguish species in the same genus from one another. Background In this activity, we will observe
Species Identification: Penguins 7. It s Not All Black and White! Name: Objective Using DNA sequence, distinguish species in the same genus from one another. Background In this activity, we will observe
SMIBIO Case Study in Germany - Green Biorefineries in the Bavarian region of Straubing-Bogen (a case study in progress)
 SMIBIO Case Study in Germany - Green Biorefineries in the Bavarian region of Straubing-Bogen (a case study in progress) SMIBIO Workshop Small-scale Biorefineries for Rural Development in Latin America
SMIBIO Case Study in Germany - Green Biorefineries in the Bavarian region of Straubing-Bogen (a case study in progress) SMIBIO Workshop Small-scale Biorefineries for Rural Development in Latin America
Microbiology 微生物学 Spring-Summer
 Microbiology 微生物学 2016 Spring-Summer Relevant Information and Resources Course slides can be found at http://mypage.zju.edu.cn/haichun 教学工作 Course-related questions will be answered through emails. Textbook:
Microbiology 微生物学 2016 Spring-Summer Relevant Information and Resources Course slides can be found at http://mypage.zju.edu.cn/haichun 教学工作 Course-related questions will be answered through emails. Textbook:
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
 Standardizing Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics Maria I Klapa Metabolic Engineering and Systems Biology Laboratory Institute of Chemical Engineering and High Temperature Chemical Processes,
Standardizing Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics Maria I Klapa Metabolic Engineering and Systems Biology Laboratory Institute of Chemical Engineering and High Temperature Chemical Processes,
Proteins: Wide range of func2ons. Polypep2des. Amino Acid Monomers
 Proteins: Wide range of func2ons Proteins coded in DNA account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein func9ons structural support storage transport cellular communica9ons movement defense
Proteins: Wide range of func2ons Proteins coded in DNA account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein func9ons structural support storage transport cellular communica9ons movement defense
ENZYMES AND METABOLIC PATHWAYS
 ENZYMES AND METABOLIC PATHWAYS This document is licensed under the Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 Italy license, available at http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/it/ 1. Enzymes build
ENZYMES AND METABOLIC PATHWAYS This document is licensed under the Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 2.5 Italy license, available at http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/it/ 1. Enzymes build
ORFs, unknown function GC (%) # of ORFs. Fen-75cm Fn (91) Nitrosopumilus maritimus
 Table S1 Comparison of genome properties for 10 distinct bins identified from two metagenomes. The mean coverage is calculated by dividing total read counts with read length. ORF, open reading frame. Nearest
Table S1 Comparison of genome properties for 10 distinct bins identified from two metagenomes. The mean coverage is calculated by dividing total read counts with read length. ORF, open reading frame. Nearest
The Transition to Life
 The Transition to Life The Transition to Life? Chemical Evolution Biological Interacting Chemicals Reproduction of Organisms Natural Selection Based on Simplest Life Now: Need: 1. Nucleic Acids Replicable
The Transition to Life The Transition to Life? Chemical Evolution Biological Interacting Chemicals Reproduction of Organisms Natural Selection Based on Simplest Life Now: Need: 1. Nucleic Acids Replicable
Unit 1. DNA and the Genome
 Unit 1 DNA and the Genome Gene Expression Key Area 3 Vocabulary 1: Transcription Translation Phenotype RNA (mrna, trna, rrna) Codon Anticodon Ribosome RNA polymerase RNA splicing Introns Extrons Gene Expression
Unit 1 DNA and the Genome Gene Expression Key Area 3 Vocabulary 1: Transcription Translation Phenotype RNA (mrna, trna, rrna) Codon Anticodon Ribosome RNA polymerase RNA splicing Introns Extrons Gene Expression
Nature Methods doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Screening for cancer stem cell marker(s)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Screening for cancer stem cell marker(s) (a) Flow cytometry analysis of CD133 at increasing times to analysis. Cells were trypsinized, stained, transferred to RPMI medium and then
Supplementary Figure 1 Screening for cancer stem cell marker(s) (a) Flow cytometry analysis of CD133 at increasing times to analysis. Cells were trypsinized, stained, transferred to RPMI medium and then
Chap 14 Amino Acids. I. Amino acids: Introduction
 Chap 14 Amino Acids Introduction Biotechnology has numerous applications: Medicine: the advent of genetic engineering has advanced the drug design to molecular levels. Molecular biology methods and genomics-based
Chap 14 Amino Acids Introduction Biotechnology has numerous applications: Medicine: the advent of genetic engineering has advanced the drug design to molecular levels. Molecular biology methods and genomics-based
6-Foot Mini Toober Activity
 Big Idea The interaction between the substrate and enzyme is highly specific. Even a slight change in shape of either the substrate or the enzyme may alter the efficient and selective ability of the enzyme
Big Idea The interaction between the substrate and enzyme is highly specific. Even a slight change in shape of either the substrate or the enzyme may alter the efficient and selective ability of the enzyme
Human Biology 175 Lecture Notes: Cells. Section 1 Introduction
 Human Biology 175 Lecture Notes: Cells Section 1 Introduction A) 1) All organisms are composed of at least one cell. a) Unicellular example: b) Multicellular example(s): 2) All cells are similar in their
Human Biology 175 Lecture Notes: Cells Section 1 Introduction A) 1) All organisms are composed of at least one cell. a) Unicellular example: b) Multicellular example(s): 2) All cells are similar in their
*AB221* Biology. Assessment Unit A2 2 assessing Biochemistry, Genetics and Evolutionary Trends [AB221] MONDAY 1 JUNE, AFTERNOON. TIME 2 hours.
![*AB221* Biology. Assessment Unit A2 2 assessing Biochemistry, Genetics and Evolutionary Trends [AB221] MONDAY 1 JUNE, AFTERNOON. TIME 2 hours. *AB221* Biology. Assessment Unit A2 2 assessing Biochemistry, Genetics and Evolutionary Trends [AB221] MONDAY 1 JUNE, AFTERNOON. TIME 2 hours.](/thumbs/80/80980435.jpg) Centre Number ADVANCED General Certificate of Education 2015 Biology Candidate Number Assessment Unit A2 2 assessing Biochemistry, Genetics and Evolutionary Trends [AB221] MONDAY 1 JUNE, AFTERNOON *AB221*
Centre Number ADVANCED General Certificate of Education 2015 Biology Candidate Number Assessment Unit A2 2 assessing Biochemistry, Genetics and Evolutionary Trends [AB221] MONDAY 1 JUNE, AFTERNOON *AB221*
Steroids. Steroids. Proteins: Wide range of func6ons. lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consis3ng of four fused rings
 Steroids Steroids lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consis3ng of four fused rings 3 six sided, and 1 five sided Cholesterol important steroid precursor component in animal cell membranes Although
Steroids Steroids lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consis3ng of four fused rings 3 six sided, and 1 five sided Cholesterol important steroid precursor component in animal cell membranes Although
1) Introduction. 2. Basic Concepts. A Brief Guide to Enzyme Nomenclature and Classification Keith Tipton and Andrew McDonald
 A Brief Guide to Enzyme Nomenclature and Classification Keith Tipton and Andrew McDonald 1) Introduction NC-IUBMB Enzyme List, or, to give it its full title, Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee
A Brief Guide to Enzyme Nomenclature and Classification Keith Tipton and Andrew McDonald 1) Introduction NC-IUBMB Enzyme List, or, to give it its full title, Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee
Molecular Biology. Biology Review ONE. Protein Factory. Genotype to Phenotype. From DNA to Protein. DNA à RNA à Protein. June 2016
 Molecular Biology ONE Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Biology Review DNA RNA Proteins Central Dogma Transcription Translation Genotype to Phenotype Protein Factory DNA
Molecular Biology ONE Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Biology Review DNA RNA Proteins Central Dogma Transcription Translation Genotype to Phenotype Protein Factory DNA
Protein Structure Analysis
 BINF 731 Protein Structure Analysis http://binf.gmu.edu/vaisman/binf731/ Secondary Structure: Computational Problems Secondary structure characterization Secondary structure assignment Secondary structure
BINF 731 Protein Structure Analysis http://binf.gmu.edu/vaisman/binf731/ Secondary Structure: Computational Problems Secondary structure characterization Secondary structure assignment Secondary structure
Create a model to simulate the process by which a protein is produced, and how a mutation can impact a protein s function.
 HASPI Medical Biology Lab 0 Purpose Create a model to simulate the process by which a protein is produced, and how a mutation can impact a protein s function. Background http://mssdbio.weebly.com/uploads/1//7/6/17618/970_orig.jpg
HASPI Medical Biology Lab 0 Purpose Create a model to simulate the process by which a protein is produced, and how a mutation can impact a protein s function. Background http://mssdbio.weebly.com/uploads/1//7/6/17618/970_orig.jpg
Connect the dots DNA to DISEASE
 Teachers Material Connect the dots DNA to DISEASE Developed by: M. Oltmann & A. James. California State Standards Cell Biology 1.d. Students know the central dogma of molecular biology outlines the flow
Teachers Material Connect the dots DNA to DISEASE Developed by: M. Oltmann & A. James. California State Standards Cell Biology 1.d. Students know the central dogma of molecular biology outlines the flow
NORWEGIAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF BIOTECHNOLOGY Professor Bjørn E. Christensen, Department of Biotechnology
 Page 1 NRWEGIAN UNIVERSITY F SCIENCE AND TECNLGY DEPARTMENT F BITECNLGY Professor Bjørn E. Christensen, Department of Biotechnology Contact during the exam: phone: 73593327, 92634016 EXAM TBT4135 BIPLYMERS
Page 1 NRWEGIAN UNIVERSITY F SCIENCE AND TECNLGY DEPARTMENT F BITECNLGY Professor Bjørn E. Christensen, Department of Biotechnology Contact during the exam: phone: 73593327, 92634016 EXAM TBT4135 BIPLYMERS
Materials Protein synthesis kit. This kit consists of 24 amino acids, 24 transfer RNAs, four messenger RNAs and one ribosome (see below).
 Protein Synthesis Instructions The purpose of today s lab is to: Understand how a cell manufactures proteins from amino acids, using information stored in the genetic code. Assemble models of four very
Protein Synthesis Instructions The purpose of today s lab is to: Understand how a cell manufactures proteins from amino acids, using information stored in the genetic code. Assemble models of four very
Granby Transcription and Translation Services plc
 ompany Resources ranby Transcription and Translation Services plc has invested heavily in the Protein Synthesis business. mongst the resources available to new recruits are: the latest cellphones which
ompany Resources ranby Transcription and Translation Services plc has invested heavily in the Protein Synthesis business. mongst the resources available to new recruits are: the latest cellphones which
BME205: Lecture 2 Bio systems. David Bernick
 BME205: Lecture 2 Bio systems David Bernick Bioinforma;cs Infer pa>erns from life biological sequences structures molecular pathways. Suggest hypotheses from inferred pa>erns Structure and Func;on Novel
BME205: Lecture 2 Bio systems David Bernick Bioinforma;cs Infer pa>erns from life biological sequences structures molecular pathways. Suggest hypotheses from inferred pa>erns Structure and Func;on Novel
Key Concept Translation converts an mrna message into a polypeptide, or protein.
 8.5 Translation VOBLRY translation codon stop codon start codon anticodon Key oncept Translation converts an mrn message into a polypeptide, or protein. MIN IDES mino acids are coded by mrn base sequences.
8.5 Translation VOBLRY translation codon stop codon start codon anticodon Key oncept Translation converts an mrn message into a polypeptide, or protein. MIN IDES mino acids are coded by mrn base sequences.
Constraint-Based Workshops
 Constraint-Based Workshops 10. Flux Coupling (again) & Metabolic Engineering February 28 th, 2008 Constraint-Based Methods Optimal Solutions 1. FBA 2. Flux Variability Flux Dependencies 1. Robustness 2.
Constraint-Based Workshops 10. Flux Coupling (again) & Metabolic Engineering February 28 th, 2008 Constraint-Based Methods Optimal Solutions 1. FBA 2. Flux Variability Flux Dependencies 1. Robustness 2.
Protein Synthesis. Application Based Questions
 Protein Synthesis Application Based Questions MRNA Triplet Codons Note: Logic behind the single letter abbreviations can be found at: http://www.biology.arizona.edu/biochemistry/problem_sets/aa/dayhoff.html
Protein Synthesis Application Based Questions MRNA Triplet Codons Note: Logic behind the single letter abbreviations can be found at: http://www.biology.arizona.edu/biochemistry/problem_sets/aa/dayhoff.html
Turning λ Cro into a
 Turning λ Cro into a 3 Transcriptional Activator Figure by MIT pencourseware. Fred Bushman and Mark Ptashne Cell (1988) 54:191-197 Presented by atalie Kuldell for 0.90 February 4th, 009 Small patch of
Turning λ Cro into a 3 Transcriptional Activator Figure by MIT pencourseware. Fred Bushman and Mark Ptashne Cell (1988) 54:191-197 Presented by atalie Kuldell for 0.90 February 4th, 009 Small patch of
Higher Human Biology. Unit 1: Human Cells
 Calderglen High School Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Homework Questions Contents Page Sub-Topic 1: Differentiation and stem cells 3-5 Sub-Topic 2: DNA and its replication 6-10 Sub-Topic 3: RNA,
Calderglen High School Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Homework Questions Contents Page Sub-Topic 1: Differentiation and stem cells 3-5 Sub-Topic 2: DNA and its replication 6-10 Sub-Topic 3: RNA,
Protein Structure and Function! Lecture 4: ph, pka and pi!
 Protein Structure and Function! Lecture 4: ph, pka and pi! Definition of ph and pk a! ph is a measure of the concentration of H +.! + ph = log 10[H ] For a weak acid,! HA #!!"! H + + A!, K a = [H + ][A!
Protein Structure and Function! Lecture 4: ph, pka and pi! Definition of ph and pk a! ph is a measure of the concentration of H +.! + ph = log 10[H ] For a weak acid,! HA #!!"! H + + A!, K a = [H + ][A!
BIOSTAT516 Statistical Methods in Genetic Epidemiology Autumn 2005 Handout1, prepared by Kathleen Kerr and Stephanie Monks
 Rationale of Genetic Studies Some goals of genetic studies include: to identify the genetic causes of phenotypic variation develop genetic tests o benefits to individuals and to society are still uncertain
Rationale of Genetic Studies Some goals of genetic studies include: to identify the genetic causes of phenotypic variation develop genetic tests o benefits to individuals and to society are still uncertain
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
 Review Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Protein synthesis requires two steps: transcription and translation. DNA contains codes Three bases in DNA code
Review Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Protein synthesis requires two steps: transcription and translation. DNA contains codes Three bases in DNA code
Your Name. Mean ± SD = 72.3 ± 17.6 Range = out of 112 points N = Points
 Introduction to Biochemistry Final Examination - Individual (Part I) Thursday, 24 May 2012 3:30 5:30 PM, 206 Brown Lab H. B. White Instructor Your Name Mean ± SD = 72.3 ± 17.6 Range = 23 99 out of 112
Introduction to Biochemistry Final Examination - Individual (Part I) Thursday, 24 May 2012 3:30 5:30 PM, 206 Brown Lab H. B. White Instructor Your Name Mean ± SD = 72.3 ± 17.6 Range = 23 99 out of 112
Chapter 12-3 RNA & Protein Synthesis Notes From DNA to Protein (DNA RNA Protein)
 Chapter 12-3 RNA & Protein Synthesis Notes From DNA to Protein (DNA RNA Protein) I. Review A. Cells copy their DNA (in S phase of Interphase)-Why? Prepare for Cell Division (Mitosis & Cytokinesis) Genes
Chapter 12-3 RNA & Protein Synthesis Notes From DNA to Protein (DNA RNA Protein) I. Review A. Cells copy their DNA (in S phase of Interphase)-Why? Prepare for Cell Division (Mitosis & Cytokinesis) Genes
Nucleic acid and protein Flow of genetic information
 Nucleic acid and protein Flow of genetic information References: Glick, BR and JJ Pasternak, 2003, Molecular Biotechnology: Principles and Applications of Recombinant DNA, ASM Press, Washington DC, pages.
Nucleic acid and protein Flow of genetic information References: Glick, BR and JJ Pasternak, 2003, Molecular Biotechnology: Principles and Applications of Recombinant DNA, ASM Press, Washington DC, pages.
Lecture 19A. DNA computing
 Lecture 19A. DNA computing What exactly is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)? DNA is the material that contains codes for the many physical characteristics of every living creature. Your cells use different
Lecture 19A. DNA computing What exactly is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)? DNA is the material that contains codes for the many physical characteristics of every living creature. Your cells use different
APPENDIX. Appendix. Table of Contents. Ethics Background. Creating Discussion Ground Rules. Amino Acid Abbreviations and Chemistry Resources
 Appendix Table of Contents A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A9 Ethics Background Creating Discussion Ground Rules Amino Acid Abbreviations and Chemistry Resources Codons and Amino Acid Chemistry Behind the Scenes with
Appendix Table of Contents A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A9 Ethics Background Creating Discussion Ground Rules Amino Acid Abbreviations and Chemistry Resources Codons and Amino Acid Chemistry Behind the Scenes with
The Nature of Life. Some properties of life. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 The Nature of Life Some properties of life opyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin ummings Life Displays rder opyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin ummings Life
The Nature of Life Some properties of life opyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin ummings Life Displays rder opyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin ummings Life
Student Guide. Level: basic. Bioinformatics: life in the computer
 Student Guide Level: basic Bioinformatics: life in the computer Developed by the Netherlands Bioinformatics Centre in cooperation with the Centre for Molecular and Biomolecular Informatics of the Radboud
Student Guide Level: basic Bioinformatics: life in the computer Developed by the Netherlands Bioinformatics Centre in cooperation with the Centre for Molecular and Biomolecular Informatics of the Radboud
A self- created drawing, collage, or computer generated picture of your creature.
 Protein Synthesis Project 40 pts Part I Due Date Part II Due Date Objectives: I can demonstrate how the genes in DNA are transcribed through RNA polymerase into mrna and translated by ribosomes, mrna,
Protein Synthesis Project 40 pts Part I Due Date Part II Due Date Objectives: I can demonstrate how the genes in DNA are transcribed through RNA polymerase into mrna and translated by ribosomes, mrna,
STRUCTURE, DYNAMICS AND INTERACTIONS OF PROTEINS BY NMR SPECTROSCOPY
 STRUCTURE, DYNAMICS AND INTERACTIONS OF PROTEINS BY NMR SPECTROSCOPY Constantin T. Craescu INSERM & Institut Curie - Recherche Orsay, France A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE Chemical composition
STRUCTURE, DYNAMICS AND INTERACTIONS OF PROTEINS BY NMR SPECTROSCOPY Constantin T. Craescu INSERM & Institut Curie - Recherche Orsay, France A SHORT INTRODUCTION TO PROTEIN STRUCTURE Chemical composition
2) Which functional group is least important in biochemistry? A) amine B) ester C) hydroxyl D) aromatic E) amide
 1) All of the following can be classified as biomolecules except A) lipids. B) proteins. C) carbohydrates. D) nucleic acids. E) All of the above are biomolecules. 2) Which functional group is least important
1) All of the following can be classified as biomolecules except A) lipids. B) proteins. C) carbohydrates. D) nucleic acids. E) All of the above are biomolecules. 2) Which functional group is least important
Central Dogma. 1. Human genetic material is represented in the diagram below.
 Central Dogma 1. Human genetic material is represented in the diagram below. 4. If 15% of a DNA sample is made up of thymine, T, what percentage of the sample is made up of cytosine, C? A) 15% B) 35% C)
Central Dogma 1. Human genetic material is represented in the diagram below. 4. If 15% of a DNA sample is made up of thymine, T, what percentage of the sample is made up of cytosine, C? A) 15% B) 35% C)
The study of protein secondary structure and stability at equilibrium ABSTRACT
 The study of protein secondary structure and stability at equilibrium Michelle Planicka Dept. of Physics, North Georgia College and State University, Dahlonega, GA REU, Dept. of Physics, University of
The study of protein secondary structure and stability at equilibrium Michelle Planicka Dept. of Physics, North Georgia College and State University, Dahlonega, GA REU, Dept. of Physics, University of
Microbiology 微生物学 Spring-Summer
 Microbiology 微生物学 2017 Spring-Summer Relevant Information and Resources Course slides can be found at http://mypage.zju.edu.cn/haichun 教学工作 Course-related questions will be answered through emails. Textbook:
Microbiology 微生物学 2017 Spring-Summer Relevant Information and Resources Course slides can be found at http://mypage.zju.edu.cn/haichun 教学工作 Course-related questions will be answered through emails. Textbook:
A Zero-Knowledge Based Introduction to Biology
 A Zero-Knowledge Based Introduction to Biology Konstantinos (Gus) Katsiapis 25 Sep 2009 Thanks to Cory McLean and George Asimenos Cells: Building Blocks of Life cell, membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondrion
A Zero-Knowledge Based Introduction to Biology Konstantinos (Gus) Katsiapis 25 Sep 2009 Thanks to Cory McLean and George Asimenos Cells: Building Blocks of Life cell, membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondrion
Fundamentals of Protein Structure
 Outline Fundamentals of Protein Structure Yu (Julie) Chen and Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University CS597A, Fall 2005 Protein structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Forces and factors Levels
Outline Fundamentals of Protein Structure Yu (Julie) Chen and Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University CS597A, Fall 2005 Protein structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Forces and factors Levels
THE GENETIC CODE Figure 1: The genetic code showing the codons and their respective amino acids
 THE GENETIC CODE As DNA is a genetic material, it carries genetic information from cell to cell and from generation to generation. There are only four bases in DNA and twenty amino acids in protein, so
THE GENETIC CODE As DNA is a genetic material, it carries genetic information from cell to cell and from generation to generation. There are only four bases in DNA and twenty amino acids in protein, so
From Gene to Protein via Transcription and Translation i
 How do genes influence our characteristics? From Gene to Protein via Transcription and Translation i A gene is a segment of DNA that provides the instructions for making a protein. Proteins have many different
How do genes influence our characteristics? From Gene to Protein via Transcription and Translation i A gene is a segment of DNA that provides the instructions for making a protein. Proteins have many different
UNIT I RNA AND TYPES R.KAVITHA,M.PHARM LECTURER DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICS SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY KATTANKULATUR
 UNIT I RNA AND TYPES R.KAVITHA,M.PHARM LECTURER DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICS SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY KATTANKULATUR RNA, as previously mentioned, is an acronym for ribonucleic acid. There are many forms
UNIT I RNA AND TYPES R.KAVITHA,M.PHARM LECTURER DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICS SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY KATTANKULATUR RNA, as previously mentioned, is an acronym for ribonucleic acid. There are many forms
2 nd Term Final. Revision Sheet. Students Name: Grade: 12-A/B. Subject: Chemistry. Teacher Signature. Page 1 of 10
 2 nd Term Final Revision Sheet Students Name: Grade: 12-A/B Subject: Chemistry Teacher Signature Page 1 of 10 Chapter-23, Lesson-1 I. MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. How does the number of hydrogen atoms in a carbohydrate
2 nd Term Final Revision Sheet Students Name: Grade: 12-A/B Subject: Chemistry Teacher Signature Page 1 of 10 Chapter-23, Lesson-1 I. MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. How does the number of hydrogen atoms in a carbohydrate
Nucleotide Metabolism
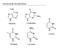 Nucleotide Metabolism Adenine Guanidine Uracil Thymine Cytosine Last Week Nucleotide Metabolism - Mostly, we think of nucleotides as being part of RNA/DNA, but now that we ve studied metabolism, we know
Nucleotide Metabolism Adenine Guanidine Uracil Thymine Cytosine Last Week Nucleotide Metabolism - Mostly, we think of nucleotides as being part of RNA/DNA, but now that we ve studied metabolism, we know
GENES and the NUCLEUS
 ENES and the NULEUS () DN the nucleus contains the set of that determines: (a) what each cell will become (muscle cell, nerve cell, eye cell, etc) (b) how each cell will (through the production of ) (c)
ENES and the NULEUS () DN the nucleus contains the set of that determines: (a) what each cell will become (muscle cell, nerve cell, eye cell, etc) (b) how each cell will (through the production of ) (c)
The implementation of laboratory investigations for diagnosing. pyruvate kinase deficiency at the Johannesburg Hospital
 The implementation of laboratory investigations for diagnosing pyruvate kinase deficiency at the Johannesburg Hospital Pierre Durand (Student no: 8604833/H) A report submitted to the Faculty of Health
The implementation of laboratory investigations for diagnosing pyruvate kinase deficiency at the Johannesburg Hospital Pierre Durand (Student no: 8604833/H) A report submitted to the Faculty of Health
Development of an Improved Avian Pneumovirus Vaccine Differentiable from Wild Virus
 Development of an Improved Avian Pneumovirus Vaccine Differentiable from Wild Virus AUTHORS Dr. Sagar Goyal, Principal Investigator Department of Veterinary Population Medicine, 1333 Gortner Ave., Saint
Development of an Improved Avian Pneumovirus Vaccine Differentiable from Wild Virus AUTHORS Dr. Sagar Goyal, Principal Investigator Department of Veterinary Population Medicine, 1333 Gortner Ave., Saint
Just one nucleotide! Exploring the effects of random single nucleotide mutations
 Dr. Beatriz Gonzalez In-Class Worksheet Name: Learning Objectives: Just one nucleotide! Exploring the effects of random single nucleotide mutations Given a coding DNA sequence, determine the mrna Based
Dr. Beatriz Gonzalez In-Class Worksheet Name: Learning Objectives: Just one nucleotide! Exploring the effects of random single nucleotide mutations Given a coding DNA sequence, determine the mrna Based
number Done by Corrected by Doctor
 number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala Nucleotide metabolism 1 P age In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala Nucleotide metabolism 1 P age In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
Basic modeling approaches for biological systems -II. Mahesh Bule
 Basic modeling approaches for biological systems -II Mahesh Bule Modeling Metabolism Metabolism is general term for two kind of reactions Catabolic reactions (breakdown of complex compounds to get energy
Basic modeling approaches for biological systems -II Mahesh Bule Modeling Metabolism Metabolism is general term for two kind of reactions Catabolic reactions (breakdown of complex compounds to get energy
Biosynthesis of nucleotides
 Biosynthesis of nucleotides De novo pathways De novo purine nucleotide synthesis Regulation of purine biosynthesis De novo pyrimidine nucleotides biosynthesis Salvage pathways Lesch-Nyhan syndrome Why
Biosynthesis of nucleotides De novo pathways De novo purine nucleotide synthesis Regulation of purine biosynthesis De novo pyrimidine nucleotides biosynthesis Salvage pathways Lesch-Nyhan syndrome Why
Verticillium wilt on flax: deciphering the tolerance mechanisms through -omics approaches. Sylvain LECOMTE phd student
 Verticillium wilt on flax: deciphering the tolerance mechanisms through -omics approaches Sylvain LECOMTE phd student FLAX: LINUM USITATISSIMUM An ancient crop grown since the beginning of civilization
Verticillium wilt on flax: deciphering the tolerance mechanisms through -omics approaches Sylvain LECOMTE phd student FLAX: LINUM USITATISSIMUM An ancient crop grown since the beginning of civilization
OMICS International Conferences
 About OMICS Group OMICS Group is an amalgamation of Open Access Publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of making the information
About OMICS Group OMICS Group is an amalgamation of Open Access Publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of making the information
Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA. Structure of DNA. Structure of DNA. Nucleotide. Nucleotides 5/13/2013
 Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA The Secret of Life DNA is the molecule responsible for controlling the activities of the cell It is the hereditary molecule DNA directs the production of protein In 1953, Watson
Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA The Secret of Life DNA is the molecule responsible for controlling the activities of the cell It is the hereditary molecule DNA directs the production of protein In 1953, Watson
From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation i
 How do genes influence our characteristics? From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation i A gene is a segment of DNA that provides the instructions for making a protein. Proteins have many different
How do genes influence our characteristics? From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation i A gene is a segment of DNA that provides the instructions for making a protein. Proteins have many different
Aipotu II: Biochemistry
 Aipotu II: Biochemistry Introduction: The Biological Phenomenon Under Study In this lab, you will continue to explore the biological mechanisms behind the expression of flower color in a hypothetical plant.
Aipotu II: Biochemistry Introduction: The Biological Phenomenon Under Study In this lab, you will continue to explore the biological mechanisms behind the expression of flower color in a hypothetical plant.
Chemistry 121 Winter 17
 Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
TaKaRa MiniBEST Viral RNA/DNA Extraction Kit Ver.5.0
 Cat. # 9766 For Research Use TaKaRa MiniBEST Viral RNA/DNA Extraction Kit Ver.5.0 Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage and shipping... 3 IV. Preparation
Cat. # 9766 For Research Use TaKaRa MiniBEST Viral RNA/DNA Extraction Kit Ver.5.0 Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage and shipping... 3 IV. Preparation
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables
 Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Complete mass isotopomer distribution
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tables Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Complete mass isotopomer distribution
Forensic Science: DNA Evidence Unit
 Day 2 : Cooperative Lesson Topic: Protein Synthesis Duration: 55 minutes Grade Level: 10 th Grade Forensic Science: DNA Evidence Unit Purpose: The purpose of this lesson is to review and build upon prior
Day 2 : Cooperative Lesson Topic: Protein Synthesis Duration: 55 minutes Grade Level: 10 th Grade Forensic Science: DNA Evidence Unit Purpose: The purpose of this lesson is to review and build upon prior
3. Use the codon chart to translate the mrna sequence into an amino acid sequence.
 Honors Biology 317 The Beads of Translation: Using Beads to translate DNA into a Polypeptide Bracelet Objectives: 1. Using plastic beads, construct a representation of "standard" sequence of amino acids
Honors Biology 317 The Beads of Translation: Using Beads to translate DNA into a Polypeptide Bracelet Objectives: 1. Using plastic beads, construct a representation of "standard" sequence of amino acids
IB HL Biology Test: Topics 1 and 3
 October 26, 2011 IB HL Biology Test: Topics 1 and 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What conditions must be met for the t-test to be applied?
October 26, 2011 IB HL Biology Test: Topics 1 and 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What conditions must be met for the t-test to be applied?
Photosynthetic Biofuels Issues and Prospects
 Photosynthetic Biofuels Issues and Prospects Tasios Melis University of California - Berkeley Monday, 30-Mar-2009 Solar Biofuels from Microorganisms Lorentz Center, Leiden 1 Photosynthetic Biofuels -----------------------------------
Photosynthetic Biofuels Issues and Prospects Tasios Melis University of California - Berkeley Monday, 30-Mar-2009 Solar Biofuels from Microorganisms Lorentz Center, Leiden 1 Photosynthetic Biofuels -----------------------------------
Proposing Biological Engineering Projects
 Proposing Biological Engineering Projects Linda L. Sutliff, BA, MA, MBA Lecturer, Writing across the Curriculum December 2009 With special thanks to work previously done by my colleague, Atissa Banuazizi
Proposing Biological Engineering Projects Linda L. Sutliff, BA, MA, MBA Lecturer, Writing across the Curriculum December 2009 With special thanks to work previously done by my colleague, Atissa Banuazizi
CS 4491/CS 7990 SPECIAL TOPICS IN BIOINFORMATICS
 1 CS 4491/CS 7990 SPECIAL TOPICS IN BIOINFORMATICS * Some contents are adapted from Dr. Jean Gao at UT Arlington Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University 2 Genetics The discovery of
1 CS 4491/CS 7990 SPECIAL TOPICS IN BIOINFORMATICS * Some contents are adapted from Dr. Jean Gao at UT Arlington Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University 2 Genetics The discovery of
Additional Case Study: Amino Acids and Evolution
 Student Worksheet Additional Case Study: Amino Acids and Evolution Objectives To use biochemical data to determine evolutionary relationships. To test the hypothesis that living things that are morphologically
Student Worksheet Additional Case Study: Amino Acids and Evolution Objectives To use biochemical data to determine evolutionary relationships. To test the hypothesis that living things that are morphologically
Structure formation and association of biomolecules. Prof. Dr. Martin Zacharias Lehrstuhl für Molekulardynamik (T38) Technische Universität München
 Structure formation and association of biomolecules Prof. Dr. Martin Zacharias Lehrstuhl für Molekulardynamik (T38) Technische Universität München Motivation Many biomolecules are chemically synthesized
Structure formation and association of biomolecules Prof. Dr. Martin Zacharias Lehrstuhl für Molekulardynamik (T38) Technische Universität München Motivation Many biomolecules are chemically synthesized
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Diala
 number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala 1 P a g e Nucleotide metabolism In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
number 34 Done by Abdulrahman Alhanbali Corrected by Mohammad Mahmoud Tarabeih Doctor Diala 1 P a g e Nucleotide metabolism In this lecture we will talk about nucleotides; their structures, the synthesis
Innovative Technology for Ribonucleic acid (RNA) Biobanking at Room Temperature
 Innovative Technology for Ribonucleic acid (RNA) Biobanking at Room Temperature Evry Genopole European Biopark fabre@imagene.fr www.imagene.fr Reliable room temperature preservation Easy opening of the
Innovative Technology for Ribonucleic acid (RNA) Biobanking at Room Temperature Evry Genopole European Biopark fabre@imagene.fr www.imagene.fr Reliable room temperature preservation Easy opening of the
MOLEBIO LAB #3: Electrophoretic Separation of Proteins
 MOLEBIO LAB #3: Electrophoretic Separation of Proteins Introduction: Proteins occupy a central position in the structure and function of all living organisms. Some proteins serve as structural components
MOLEBIO LAB #3: Electrophoretic Separation of Proteins Introduction: Proteins occupy a central position in the structure and function of all living organisms. Some proteins serve as structural components
