FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions) about custom DNA Synthesis
|
|
|
- Kathleen Oliver
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions) about custom DNA Synthesis 1. What is scale of synthesis? Scale of synthesis refers to the amount of starting CPG (controlled-pore glass) support-bound monomer used to initiate the DNA synthesis, not the amount of final material synthesized. As an example, a 20 mer synthesized at a 200 nanomole scale of synthesis will produce approximately 80 nanomoles. The losses occur during synthesis, post-synthetic processing, transfer of material, and quality control. 2. Do I need to have my oligo purified? It depends on whether or not modifications are requested and what the application will be. Failure sequences may be generated both during the synthesis and post-synthesis processing. We recommend that all modifications be purified either by cartridge or HPLC. For recommended purity and scale (based upon application), please see Table I. Table I Recommended Scales of Synthesis and Purification Application Scale of Synthesis Purification For Non-modified Oligos DNA sequencing 50 or 200 umol OPC OR PAGE PCR (general mplification) 50 or 200 umol OPC PCR (diagnosticapplication) 200 umol OPC OR PAGE Subcloning, site-directed mutageneses or cdna synthesis 200 umol OPC\PAGE\HPLC Gene Construction <80mer 200 umol PAGE >80mer 1.0 umol PAGE Antisense 1.0 um or more PAGE\HPLC For Modified Oligos Modified bases and chemical linkers 200 umol PAGE\HPLC Reporter groups (biotin, DIG or fluorescent dyes) 200 umol PAGE\HPLC 3. How much do I get or what scale of synthesis should I order? Refer to the Table II
2 Table II Scale of Synthesis, Purification and Yields Scale of synthesis Purification Yield 50 nanomole Desalt Reverse phase cartridge Reverse phase HPLC Anion-exchange HPLC 150 ug: actual yield is sequence and length dependent Average yield: ug Average yield: ug Average yield: ug 200 nanomole Desalt Average yield: 600 ug Reverse phase cartridge Average yield: 300 ug Reverse phase HPLC Average yield: 300 ug Anion-exchange HPLC Average yield: 300 ug PAGE: less than 40mer Average yield: ug Greater than 40mer Average yield: 10 ug 1 umole Desalt Average yield: 2 mg Reverse phase cartridge Average yield: 1 mg Reverse phase HPLC Average yield: 1 mg Anion-exchange HPLC Average yield: 1 mg 4. What do I re-suspend my oligo in and what concentration should I make it? Purified water, PBS or any biological buffers are acceptable as diluents. The recommended diluent volume is 100 ul - 1 ml, the concentration depending on the application to be used and the yield of the resulting product. Standard concentration for PCR primers is 0.1 mm. 5. How do I determine my concentration? Concentration is determined by measuring the OD260 of the diluted oligo. Prepare a dilution of the resuspended oligo and measure the OD260. Determine the concentration as follows: (?g or pmoles/ OD260 ) X dilution factor = final concentration / ml. 6. How stable is my oligo once I have resuspended it? If sterile diluent is used to resuspend the oligo, it will be stable at 4 for about a month. If stored frozen
3 at -20 or -70, it will remain stable for 2-3 months. Repeated freeze-thaw should be avoided, as it will denature the oligo. Avoid the use of distilled water, since solution ph may be as low as Does my oligo have a phosphate on the 5' end? Unless requested, oligos are synthesized without either 3 or 5 phosphate. The 5 phosphate modification is available, normally as an additional charge. 8. My annealed oligos will not ligate. What is the problem? Ligation reactions require a 5 phosphate. If your oligos do not contain a 5 phosphate, ligation will not occur. The problem can be addressed without ordering an additional oligo pair: phosphorylate your oligos enzymatically with kinase before use in ligation reactions. 9. How do you calculate the molecular weight of my oligo? The molecular weights for oligos is the sum of the component molecular weights of all bases, with mixed bases contributing proportionately. The component molecular weights of the bases vary as to their salt form. Many times desalted oligos are ammonium salts, while cartridge, HPLC and PAGE purified oligos are sodium salts. The molecular weights used in the calculations are listed in the following Table III. Table III Molecular Weight Calculations Molecular Weights of the Bases Sodium Salt Ammonium Salt DNA Thioate DNA WA WC WG WT WCORR Molecular Weight Calculation: (PA * WA) + (PC * WC) + (PG * WG) + (PT * WT) +(Pmod * Wmod) - WCORR Where PA is the number of As and WA is the component weight of A and Pmod is the number of Modifications, and Wmod is the component weight of the added modification. Please refer to Table IV for the molecular weights of common modifications. Table IV
4 Molecular Weights of Common Modifications Modification Molecular Weight Modification Molecular Weight 5 -Biotin TAMARA (6 FAM) Dabsyl HEX Fluorescein-dT TET (6 FAM) Cy Amino Modifier C Cy Amino Modifier C Dabcyl Thiol Modifier C What is coupling efficiency? Coupling efficiency is a measure of the DNA synthesizer s ability to couple each new monomer to the growing chain. If all the monomers coupled completely to the growing chain, the coupling efficiency would be 100%. If 1% of the growing monomer chain fails to react, then the coupling efficiency of that step is only 99%. The coupling efficiency for the complete synthesis of the oligo is usually determined from the yields of full-length sequence after the first and last cycle. Coupling efficiencies greater than 99.0% are essential for good oligo product with minimum purification. 12. How is the coupling efficiency determined? Following the first coupling step, the amount of Trityl released during deblocking is directly proportional to the amount of full-length oligo made in the previous cycle. When the Trityl is cleaved during the deblocking step, the resulting Trityl cation is orange in color. The intensity of this color can be measure by UV spectrophometry. By comparing the intensities of the Trityl produced after the first and last coupling, one can calculate the average successful base coupling per cycle and hence the coupling efficiencies. 13. I sequenced a clone I prepared with your primer and the sequence for the primer region was different from the one I ordered. Why? There are number of possible explanations for apparent errors in the sequence of the oligonucleotide used in cloning experiments. There could have been human error during the ordering and synthesis of the oligonucleotides. Human error can be easily checked by looking at the sequence on the specification sheet that accompanies each oligo. Below is a list of problems associated with using the beta-cyanoethyl phosphoramidite chemistry that give the impression that a synthesis error had been introduced. 1. The G base may have been converted to the enol tautomer, 2,6 diaminopurine, which is recognized as A by DNA polymerase. Thus, clones generated from an oligo with this modified base will appear as a G to A transition.
5 2. The chemical process of synthesis may cause depurination. Depurinated oligos are usually degraded at the deprotection stage, but it is possible for a small percentage to remain. Clones containing an inserted oligo that was depurinated will appear as having an A or G deletion. Oligos that are purine rich have an increased risk of having these artifacts. 3. Usually failed sequences that do not couple to the next incoming base are capped to prevent further synthesis. Unfortunately, sequence failure that are not capped are still capable of further synthesis and will appear as deletions in cloning experiments. These events are usually rare and the effects can be overcome by screening additional clones for those that were created with an oligo with the correct sequence. 4. During the base addition step, a small percentage of the incoming bases may couple with each other prior to coupling with the growing oligo chain. Clones generated using these oligos will appear as an insertion. Again, this event is rare and the effects can be overcome by screening additional clones for those that were created with an oligo with the correct sequence. It is therefore highly recommended that HPLC or PAGE purified oligos be used for cloning experiments and that more than 1 clone should be collected and screened. 14. Why are some modified oligos so expensive in relation to the cost of the modifying reagent? The limited reagent stability (most <48 hours) and lower coupling efficiencies of the reagent requires that excess modifying reagent be used to insure adequate quantities of full length product is made. As a result, higher cost incurred in synthesis. 15. Why are the yields lower for modified bases? Many of the modified amidites are unstable and do not couple as efficiently as the unmodified bases (even though longer coupling procedures may be used), thus failure sequences are more abundant than in normal synthesis. Consequently, all modified oligos should be purified either by cartridge or HPLC to remove the more abundant failure sequences. Yields are reduced as a result of purification.. The end product, although with a lower yield, is much more pure. 16. Why isn't the yield for 1?m scale syntheses five times greater than 0.2 um ol scale syntheses? For 0.2 umol scale, the monomer coupling is done at a fold excess. To do so for larger scale syntheses (such as 1.0 umol scale) would be cost-prohibitive. Large-scale syntheses are done at 10-fold mole excess of amidites. However, to increase the yields for these larger scale syntheses, the coupling times are extended to increase coupling efficiencies. 17. What is the longest length an oligo can be synthesized? The real answers lies in the limit of resolution of the purification method and the coupling efficiency of the DNA synthesizer. It is not unusal to synthesize oligo in excess of 150 bases and to obtain sufficient
6 quantities by PAGE purification to do successful gene construction. It should be remembered that the longer the oligo, the greater the chance of accumulated sequence errors. 18.What is the best way to calculate the Tm of my oligo? We use an algorithm to calculate the Tm, rather than the CG ratio as is gives a more accurate result. The values will be given on the oligo data sheet. The Tm can be calculated online at:- ( Biocolors used a similar method to these ) You could also use the equation: Tm = * (%C + G) / #bases) not as accurate but it gives a good idea. 19. Codes for the mixed bases K=G+T M=A+C R=A+G S=C+G W=A+T Y=C+T B=C+G+T D=A+G+T H=A+C+T V=A+C+G N=A+C+G+T 20. Standard Oligo Structure
7 21. Modified Oligo Structure 5 -Biotinylated Oligonucleotide Biotinylated oligonucleotides are used for a number of applications, which include colorimetric detection of DNA and solid phase capture by Streptavidin coated magnetic beads for use in restriction mapping, genomic walking and differential display. 5 -Fluorescein Labeled Oligonucleotide Cy3, Cy5 and TAMRA are also available as labeling dyes for oligonucleotides. Fluorescent dye-labeled oligonucleotides have been widely used in automated DNA sequencing, quantitative PCR, and in situ hybridization reactions.
8 5 -Phosphorylated Oligonucleotide 5 -Phosphorylated oligonucleotides are commonly used in site directed mutagenesis and linker insertion. Phosphorothioation (S-Oligo) The modified backbone of an S-Oligo is resistant to the degradation by most endo- and exonucleases. This property allows increased intracellular effectiveness of antisense oligonucleotides. The replacement of the inter-nucleotide phosphate groups with phosphorothioate groups (substituting one of the oxygen atoms of phosphate group with a sulfur atom) can be made in the entire of partial sequences of oligo depending on the customers needs. 5 -Amino Modified Oligonucleotide 3 -Amino Modified Oligonucleotide The presence of a primary aliphatic amine group at the terminus of an oligonucleotide allows the post?synthesis attachment of a number of amine reactive molecules. The amino modified oligonucleotides can also be used for the immobilization of the desired oligonucleotide on the matrix to
9 make the oligonucleotide-based microarray. 22. Can you do mixed bases? Yes. There is no charge for any equal molar mixed bases except for the 3' end bases. We can also do "poisoned" bases for an extra charge. 23.Can you do other bases besides A, C, T and G? If the amidite or NHS-ester of the base of choice is commercially available, we can incorporate it into an oligo. 24. TaqMan Probe &Primer Design guidelines Probe Design Guidelines The melting temperature (Tm) of the probe should be Keep G-C contents in the 30-80% range. Avoid runs of an identical nucleotide. This is true especially for G, where runs of four or more Gs should be avoided. Do not put Gs on the 5 end. Select the strand that gives the probe more Cs than Gs. Primer express does not automatically screen for this feature. It needs to be done manually. If the TaqMan probe is designed for allelic discrimination, the position of the polymorphic site (mismatch) should be approximately in the middle third of the sequence. The principle of taqman
10 Primer Design Guidelines Design primers as close to probe as possible Keep G-C contents in the 30-80% range. Avoid runs of an identical nucleotide. This is true especially for G, where runs of four or more Gs should be avoided. The melting temperature (Tm) of the primer should be The total number of Gs and Cs in the last five nucleotides at the 3?end of the primer should not exceed two. The software does this automatically if the option is selected. Primers should scan exon-exon junction. Contaminating genomic DNA will not be amplified by these primers. Use primers that contain da nucleotides near the 3 ends so that any primer-dimer generated is efficiently degraded by AmpErase UNG. If primers cannot be selected with da nucleotides near the ends, the use of primers with 3 terminal du nucleotide should be considered. Of course,you can visit the websites of real time PCR primer design. Also you can download the soft from the next websits to design it. If you want to get more information,please visit the next websites Introduction to Molecular Beacons Molecular beacons are single-stranded oligonucleotide hybridization probes that form a stem-and-loop structure. The loop contains a probe sequence that is complementary to a target sequence, and the stem is formed by the annealing of complementary arm sequences that are located on either side of the probe sequence. A fluorophore is covalently linked to the end of one arm and a quencher is covalently linked to the end of the other arm. Molecular beacons do not fluoresce when they are free in solution. However, when they hybridize to a nucleic acid strand containing a target sequence they undergo a conformational change that enables them to fluoresce brightly. In the absence of targets, the probe is dark, because the stem places the fluorophore so close to the nonfluorescent quencher that they transiently share electrons, eliminating the ability of the fluorophore to fluoresce. When the probe encounters a target molecule, it forms a probe-target hybrid that is longer and more stable than the stem hybrid. The
11 rigidity and length of the probe-target hybrid precludes the simultaneous existence of the stem hybrid. Consequently, the molecular beacon undergoes a spontaneous conformational reorganization that forces the stem hybrid to dissociate and the fluorophore and the quencher to move away from each other, restoring fluorescence. If you want to get more information about it,please visit the next website Can you help us to design primers? Yes.of course,you can visit the next websites to design it online Fluorescein Labeled Name Name Absorbwavelenth Emissionwavelenth colors 6-FAM 6-carboxy-fluorescein 494nm 518nm Green TET 5-tetrachloro-fluorescein 521nm 538nm Orange HEX 5-hexachloro-fluorescein 535nm 553nm Pink TAMRA tetramethyl-6-carboxyrhodamine 560nm 582nm Rose ROX 6-carboxy-x-rhodamine 587nm 607nm Red Cy3 Indodicarbocyanine 552nm 570nm Red Cy5 Indodicarbocyanine 643nm 667nm Violet 28. How do I make double-stranded DNA?
12 It is sometimes necessary to make double-stranded DNA from single-stranded oligos. While the annealing procedure is very simple, attention to a few details can greatly reduce the presence of undesired single stranded material. Method: 1. Dissolve oligos in STE Buffer (10 mm Tris ph 8.0, 50 mm NaCl, 1 mm EDTA). The presence of some salt is necessary for the oligos to hybridize. Dissolve each oligo at high concentration (1-10 OD 260 units / 100 ul). 2. Mix two stands together in equal molar amounts. If you do not there will always be single stranded material left over. 3. Heat to 94 o C and gradually cool. For many oligos this can be as simple as transferring to the bench-top at room temperature. For sequences with significant hairpin potential, a more gradual cooling/annealing step is beneficial; this is easily done by placing the oligos in a water bath or temp block and "unplugging the machine". 4. The resulting product will be in stable, double-stranded form and can be stored at 4 o C or frozen. Things to consider: If the product will be used in a ligation reaction, the addition of 5' -phosphate may be needed. This can be done at the time of oligo synthesis (chemical phosphorylation) or at any time thereafter using PNK (enzymatic phosphorylation). If the oligos are relatively long or to be used in cloning, starting with PAGE purified oligos is recommended. 29. How are oligonucleotides synthesized? Oligonucleotides are produced using an automated DNA synthesizer that adds a base in the 3 to 5 direction. The addition of each base is termed a cycle. There are 4 basic steps to a cycle. 1. A new base is added to the 5 end of the growing chain. Approximately 99% of the available sites will react. 2. The sites that did not react are chemically capped. These capped bases will no longer be used in the synthesis and result in failed sequences. 3. The new base-to-base bond is stabilized by oxidation. 4. The 5 base has its protecting groups removed and is now ready to bond with the next added base when the first step is repeated. When the oligonucleotide synthesis has completed the oligo is cleaved form its solid support, which was used to hold it in place during synthesis. Protecting groups are then removed using concentrated ammonium hydroxide. While the oligo is ready for use in some application at this point, the commercial oligo vendors used by the DNA Facility will also remove the reaction salts (a process called Desalting ). Desalting will not remove the failed sequences.
13 30.Other data which we have been often asked for: ( although if you don't know this you should be ashamed of yourself ) 1 millimole = 1000 micromoles 1 micromole = 1000 nanomoles 1 nanomole = 1000 picomoles to convert moles to grams:- multiply by the molecular weight to convert grams to moles:- divide by the molecular weight
What is a microarray
 DNA Microarrays What is a microarray A surface on which sequences from thousands of different genes are covalently attached to fixed locations (probes). Glass slides Silicon chips Utilize the selective
DNA Microarrays What is a microarray A surface on which sequences from thousands of different genes are covalently attached to fixed locations (probes). Glass slides Silicon chips Utilize the selective
Product Specifications & Manual
 Product Specifications & Manual Custom Oligo Synthesis, antisense oligos, RNA oligos, chimeric oligos, Fluorescent dye labeled oligos, Molecular Beacons, sirna, phosphonates Affinity Ligands, 2-5 linked
Product Specifications & Manual Custom Oligo Synthesis, antisense oligos, RNA oligos, chimeric oligos, Fluorescent dye labeled oligos, Molecular Beacons, sirna, phosphonates Affinity Ligands, 2-5 linked
Recombinant DNA Technology
 History of recombinant DNA technology Recombinant DNA Technology (DNA cloning) Majid Mojarrad Recombinant DNA technology is one of the recent advances in biotechnology, which was developed by two scientists
History of recombinant DNA technology Recombinant DNA Technology (DNA cloning) Majid Mojarrad Recombinant DNA technology is one of the recent advances in biotechnology, which was developed by two scientists
Streptavidin Particles Technical Information
 Streptavidin Particles Technical Information Streptavidin Streptavidin is a protein (MW of approx. 66,000) made up of four identical subunits, each containing a high affinity binding site for biotin (KD
Streptavidin Particles Technical Information Streptavidin Streptavidin is a protein (MW of approx. 66,000) made up of four identical subunits, each containing a high affinity binding site for biotin (KD
Chemical Structure. User Bulletin: ABI 392/4 Nucleic Acid Synthesizers. Subject: Biotin Labeling of Oligonucleotides on a DNA/RNA Synthesizer
 Technical Resources FAQs Error Codes Request Forms Doc. Library Software Library Fax on Demand Course Listing Contact Information Part Numbers Our Teams User Bulletin - Number 70 Models 38X/39X Biotin
Technical Resources FAQs Error Codes Request Forms Doc. Library Software Library Fax on Demand Course Listing Contact Information Part Numbers Our Teams User Bulletin - Number 70 Models 38X/39X Biotin
Polymerase Chain Reaction PCR
 1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 1. To understand principle of 2. Types 3. Applications 2. Lay Out 3 Types of Qualitative
1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 1. To understand principle of 2. Types 3. Applications 2. Lay Out 3 Types of Qualitative
DNA Oligos - Single Tube Format
 Hysel India PL 2017-18 DNA Oligos - Single Tube Format zurück Standard Small Scale Synthesis - price/base in Rs 100% Rabatt Scale [µmol] Standard Yield (OD 260 ) OPC Purified Yield (OD 260 ) HPLC Purified
Hysel India PL 2017-18 DNA Oligos - Single Tube Format zurück Standard Small Scale Synthesis - price/base in Rs 100% Rabatt Scale [µmol] Standard Yield (OD 260 ) OPC Purified Yield (OD 260 ) HPLC Purified
DNA Hybridization and Detection
 Chapter 6 DNA Hybridization and Detection Fluorescence Polarization Detection of DNA Hybridization........................................................ 6-2 Introduction.............................................................................................................
Chapter 6 DNA Hybridization and Detection Fluorescence Polarization Detection of DNA Hybridization........................................................ 6-2 Introduction.............................................................................................................
Designing Real-Time Assays on the SmartCycler II System
 Designing eal-time Assays on the SmartCycler II System Cepheid Technical Support Overview This document provides general guidelines for the design of real-time experiments on the Cepheid SmartCycler II
Designing eal-time Assays on the SmartCycler II System Cepheid Technical Support Overview This document provides general guidelines for the design of real-time experiments on the Cepheid SmartCycler II
LIGHTCYCLER EXPERIMENTAL
 LIGHTCYCLER EXPERIMENTAL D E S I G N CONTENTS PART 1 INTRODUCTION...4 1.1 Introduction to fluorescence applications for the LightCycler. 4 1.2 Fluorescence techniques for the LightCycler 5 1.2.1 Double
LIGHTCYCLER EXPERIMENTAL D E S I G N CONTENTS PART 1 INTRODUCTION...4 1.1 Introduction to fluorescence applications for the LightCycler. 4 1.2 Fluorescence techniques for the LightCycler 5 1.2.1 Double
Solid Phase cdna Synthesis Kit
 #6123 v.02.09 Table of Contents I. Description... 2 II. Kit components... 2 III. Storage... 2 IV. Principle... 3 V. Protocol V-1. Preparation of immobilized mrna... 4 Protocol A: Starting from Tissue or
#6123 v.02.09 Table of Contents I. Description... 2 II. Kit components... 2 III. Storage... 2 IV. Principle... 3 V. Protocol V-1. Preparation of immobilized mrna... 4 Protocol A: Starting from Tissue or
Molecular Applications:
 Theory & Method Booklet 1 Molecular Applications: Oligonucleotides, PCR & RT-PCR Vol.1 Molecular Applications: Oligonucleotides, PCR & RT-PCR Table of Contents Introduction....................................................2
Theory & Method Booklet 1 Molecular Applications: Oligonucleotides, PCR & RT-PCR Vol.1 Molecular Applications: Oligonucleotides, PCR & RT-PCR Table of Contents Introduction....................................................2
Amino-allyl Dye Coupling Protocol
 Amino-allyl Dye Coupling Protocol Joseph DeRisi, June 2001 Typically, fluorescently labeled cdna is generated by incorporation of dyeconjugated nucleotide analogs during the reverse transcription process.
Amino-allyl Dye Coupling Protocol Joseph DeRisi, June 2001 Typically, fluorescently labeled cdna is generated by incorporation of dyeconjugated nucleotide analogs during the reverse transcription process.
DNA Microarray Technology
 2 DNA Microarray Technology 2.1 Overview DNA microarrays are assays for quantifying the types and amounts of mrna transcripts present in a collection of cells. The number of mrna molecules derived from
2 DNA Microarray Technology 2.1 Overview DNA microarrays are assays for quantifying the types and amounts of mrna transcripts present in a collection of cells. The number of mrna molecules derived from
BENG 183 Trey Ideker (the details )
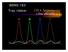 BENG 183 Trey Ideker (the details ) (1) Devils in the details: Sequencing topics to be covered in today s lecture DNA preparation prior to sequencing Amplification: vectors or cycle sequencing PAGE and
BENG 183 Trey Ideker (the details ) (1) Devils in the details: Sequencing topics to be covered in today s lecture DNA preparation prior to sequencing Amplification: vectors or cycle sequencing PAGE and
Gene Expression Technology
 Gene Expression Technology Bing Zhang Department of Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University bing.zhang@vanderbilt.edu Gene expression Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene
Gene Expression Technology Bing Zhang Department of Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University bing.zhang@vanderbilt.edu Gene expression Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene
Module1TheBasicsofRealTimePCR Monday, March 19, 2007
 Objectives Slide notes: Page 1 of 41 Module 1: The Basics Of Real Time PCR Slide notes: Module 1: The Basics of real time PCR Page 2 of 41 Polymerase Chain Reaction Slide notes: Here is a review of PCR,
Objectives Slide notes: Page 1 of 41 Module 1: The Basics Of Real Time PCR Slide notes: Module 1: The Basics of real time PCR Page 2 of 41 Polymerase Chain Reaction Slide notes: Here is a review of PCR,
Polymerase Chain Reaction: Application and Practical Primer Probe Design qrt-pcr
 Polymerase Chain Reaction: Application and Practical Primer Probe Design qrt-pcr review Enzyme based DNA amplification Thermal Polymerarase derived from a thermophylic bacterium DNA dependant DNA polymerase
Polymerase Chain Reaction: Application and Practical Primer Probe Design qrt-pcr review Enzyme based DNA amplification Thermal Polymerarase derived from a thermophylic bacterium DNA dependant DNA polymerase
Custom Oligonucleotide:
 Custom Oligonucleotide: Products & Services The Modified Nucleic Acid Experts Custom Oligonucleotide Synthesis Partnering to Help Advance Innovation For over 20 years, TriLink has been an industry leader
Custom Oligonucleotide: Products & Services The Modified Nucleic Acid Experts Custom Oligonucleotide Synthesis Partnering to Help Advance Innovation For over 20 years, TriLink has been an industry leader
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 3. Questions & Answers
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 3 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 3.1 Which of the following statements, if any, is false? a) Amplifying DNA means making many identical
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 3 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 3.1 Which of the following statements, if any, is false? a) Amplifying DNA means making many identical
A Recommended Procedure for Real-Time Quantitative TaqMan PCR for Roundup Ready Canola RT73 Monsanto Biotechnology Regulatory Sciences
 Page 1 of 7 Overview Purpose & Scope This procedure describes an event-specific real-time TaqMan PCR method for determination of the relative content of Roundup Ready canola RT73 (hereafter referred to
Page 1 of 7 Overview Purpose & Scope This procedure describes an event-specific real-time TaqMan PCR method for determination of the relative content of Roundup Ready canola RT73 (hereafter referred to
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Efficient RNA synthesis by in vitro transcription of a triazole-modified DNA template Afaf H. El-Sagheer a,b and Tom Brown a a School of Chemistry, University of Southampton, Highfield,
Supporting Information Efficient RNA synthesis by in vitro transcription of a triazole-modified DNA template Afaf H. El-Sagheer a,b and Tom Brown a a School of Chemistry, University of Southampton, Highfield,
Custom Oligonucleotide Synthesis & Products. The Modified Nucleic Acid Experts
 Custom Oligonucleotide Synthesis & Products The Modified Nucleic Acid Experts For over 20 years, TriLink has been an industry leader synthesizing oligonucleotides for research, diagnostics, OEM, & therapeutics.
Custom Oligonucleotide Synthesis & Products The Modified Nucleic Acid Experts For over 20 years, TriLink has been an industry leader synthesizing oligonucleotides for research, diagnostics, OEM, & therapeutics.
Price List. Primers and Oligonucleotides. DNA and RNA Oligos. Content
 Content Content... 1 Unmodified DNA Oligonucleotides... 2 Modified DNA Oligonucleotides - 5' Fluorescent Labels... 2 Modified DNA Oligonucleotides - 5' Non-Fluorescent Labels... 3 Modified DNA Oligonucleotides
Content Content... 1 Unmodified DNA Oligonucleotides... 2 Modified DNA Oligonucleotides - 5' Fluorescent Labels... 2 Modified DNA Oligonucleotides - 5' Non-Fluorescent Labels... 3 Modified DNA Oligonucleotides
INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES. Products & Services
 INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES THE CUSTOM BIOLOGY COMPANY Products & Services CUSTOM DNA & RNA Custom DNA Synthesis Synthesis Scale Length (Tubes) (Plates) 25 nmole 15-60 bases.09/base.08/base 100 nmole 10-90
INTEGRATED DNA TECHNOLOGIES THE CUSTOM BIOLOGY COMPANY Products & Services CUSTOM DNA & RNA Custom DNA Synthesis Synthesis Scale Length (Tubes) (Plates) 25 nmole 15-60 bases.09/base.08/base 100 nmole 10-90
Real Time PCR. Advanced Biotechnology Lab I Florida Atlantic University April 2, 2008
 Real Time PCR Advanced Biotechnology Lab I Florida Atlantic University April 2, 2008 Introduction We wish to compare the expression levels of our gene under study (Drosophila MsrA) for two different treatment
Real Time PCR Advanced Biotechnology Lab I Florida Atlantic University April 2, 2008 Introduction We wish to compare the expression levels of our gene under study (Drosophila MsrA) for two different treatment
Custom Oligonucleotide Synthesis
 Custom Oligonucleotide Synthesis Custom Oligo Synthesis, antisense oligos, RNA oligos, chimeric oligos, Fluorescent dye labeled oligos, Molecular Beacons, sirna, phosphonates Affinity Ligands, 2-5 linked
Custom Oligonucleotide Synthesis Custom Oligo Synthesis, antisense oligos, RNA oligos, chimeric oligos, Fluorescent dye labeled oligos, Molecular Beacons, sirna, phosphonates Affinity Ligands, 2-5 linked
DNA/RNA Oligonucleotide Services General Price List; valid from
 Optimised Application Oligos All our application oligos are optimised and scientifically proven to show highly consistent results in respective application Online synthesis reports, data sheets and quality
Optimised Application Oligos All our application oligos are optimised and scientifically proven to show highly consistent results in respective application Online synthesis reports, data sheets and quality
Agilent s Mx3000P and Mx3005P
 Agilent s Mx3000P and Mx3005P Realtime PCR just got better Dr. Ivan Bendezu Genomics Agent Andalucia Real-time PCR Chemistries SYBR Green SYBR Green: Dye attaches to the minor groove of double-stranded
Agilent s Mx3000P and Mx3005P Realtime PCR just got better Dr. Ivan Bendezu Genomics Agent Andalucia Real-time PCR Chemistries SYBR Green SYBR Green: Dye attaches to the minor groove of double-stranded
DNA/RNA Oligonucleotide Services Price List UK; valid from
 Optimised Application Oligos All our application oligos are optimised and scientifically proven to show highly consistent results in respective application Online synthesis reports, data sheets and quality
Optimised Application Oligos All our application oligos are optimised and scientifically proven to show highly consistent results in respective application Online synthesis reports, data sheets and quality
Factors affecting PCR
 Lec. 11 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Factors affecting PCR The sequences of the primers are critical to the success of the experiment, as are the precise temperatures used in the heating and cooling stages of the
Lec. 11 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Factors affecting PCR The sequences of the primers are critical to the success of the experiment, as are the precise temperatures used in the heating and cooling stages of the
DNA/RNA Oligonucleotide Services Price List Sweden; valid from
 Optimised Application Oligos All our application oligos are optimised and scientifically proven to show highly consistent results in respective application Online synthesis reports, data sheets and quality
Optimised Application Oligos All our application oligos are optimised and scientifically proven to show highly consistent results in respective application Online synthesis reports, data sheets and quality
Product Specifications & Manual
 Product Specifications & Manual Custom Oligo Synthesis, antisense oligos, RNA oligos, chimeric oligos, Fluorescent dye labeled oligos, Molecular Beacons, sirna, phosphonates Affinity Ligands, 2-5 linked
Product Specifications & Manual Custom Oligo Synthesis, antisense oligos, RNA oligos, chimeric oligos, Fluorescent dye labeled oligos, Molecular Beacons, sirna, phosphonates Affinity Ligands, 2-5 linked
Applied Biosystems Real-Time PCR Rapid Assay Development Guidelines
 Applied Biosystems Real-Time PCR Rapid Assay Development Guidelines Description This tutorial will discuss recommended guidelines for designing and running real-time PCR quantification and SNP Genotyping
Applied Biosystems Real-Time PCR Rapid Assay Development Guidelines Description This tutorial will discuss recommended guidelines for designing and running real-time PCR quantification and SNP Genotyping
A revolution in PCR analysis!
 A revolution in PCR analysis! Fast, convenient qualitative and quantitative PCR analysis Detect amplicon in seconds Generate accurate quantitative gene expression data Eliminate post-pcr processing Minimize
A revolution in PCR analysis! Fast, convenient qualitative and quantitative PCR analysis Detect amplicon in seconds Generate accurate quantitative gene expression data Eliminate post-pcr processing Minimize
AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 647 Protein Labeling Kit
 AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 647 Protein Labeling Kit Catalog # 72049 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate HiLyte Fluor 647 SE to proteins (e.g., IgG). It provides ample materials
AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 647 Protein Labeling Kit Catalog # 72049 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate HiLyte Fluor 647 SE to proteins (e.g., IgG). It provides ample materials
Molecular Genetics II - Genetic Engineering Course (Supplementary notes)
 1 von 12 21.02.2015 15:13 Molecular Genetics II - Genetic Engineering Course (Supplementary notes) Figures showing examples of cdna synthesis (currently 11 figures) cdna is a DNA copy synthesized from
1 von 12 21.02.2015 15:13 Molecular Genetics II - Genetic Engineering Course (Supplementary notes) Figures showing examples of cdna synthesis (currently 11 figures) cdna is a DNA copy synthesized from
P HENIX. PHENIX PCR Enzyme Guide Tools For Life Science Discovery RESEARCH PRODUCTS
 PHENIX PCR Enzyme Guide PHENIX offers a broad line of premium quality PCR Enzymes. This PCR Enzyme Guide will help simplify your polymerase selection process. Each DNA Polymerase has different characteristics
PHENIX PCR Enzyme Guide PHENIX offers a broad line of premium quality PCR Enzymes. This PCR Enzyme Guide will help simplify your polymerase selection process. Each DNA Polymerase has different characteristics
Technical Review. Real time PCR
 Technical Review Real time PCR Normal PCR: Analyze with agarose gel Normal PCR vs Real time PCR Real-time PCR, also known as quantitative PCR (qpcr) or kinetic PCR Key feature: Used to amplify and simultaneously
Technical Review Real time PCR Normal PCR: Analyze with agarose gel Normal PCR vs Real time PCR Real-time PCR, also known as quantitative PCR (qpcr) or kinetic PCR Key feature: Used to amplify and simultaneously
DNA/RNA Oligonucleotide Services Price List UK; valid from
 Optimised Application Oligos All our application oligos are optimised and scientifically proven to show highly consistent results in respective application Online synthesis reports, data sheets and quality
Optimised Application Oligos All our application oligos are optimised and scientifically proven to show highly consistent results in respective application Online synthesis reports, data sheets and quality
Roche Molecular Biochemicals Technical Note No. LC 12/2000
 Roche Molecular Biochemicals Technical Note No. LC 12/2000 LightCycler Absolute Quantification with External Standards and an Internal Control 1. General Introduction Purpose of this Note Overview of Method
Roche Molecular Biochemicals Technical Note No. LC 12/2000 LightCycler Absolute Quantification with External Standards and an Internal Control 1. General Introduction Purpose of this Note Overview of Method
2. Pyrosequencing Assay Design
 2. Pyrosequencing Assay Design 2.1 Guidelines for PCR set-up and primer design 2.1.1 PCR primer design Design of PCR primers follows standard rules, i.e. calculated Tm of 62-65 C, primer length of about
2. Pyrosequencing Assay Design 2.1 Guidelines for PCR set-up and primer design 2.1.1 PCR primer design Design of PCR primers follows standard rules, i.e. calculated Tm of 62-65 C, primer length of about
Custom Oligonucleotide Synthesis
 Custom ligonucleotide Synthesis You Design. We Synthesize. Signature TriLink Quality With our expertise and extensive selection of dyes, quenchers, modified bases, linkers, spacers and conjugates, your
Custom ligonucleotide Synthesis You Design. We Synthesize. Signature TriLink Quality With our expertise and extensive selection of dyes, quenchers, modified bases, linkers, spacers and conjugates, your
Custom DNA Oligonucleotides. accelerate > primers
 Custom DNA Oligonucleotides accelerate > primers Custom DNA Oligonucleotides accelerate > primers Highest quality oligos with rigorous quality control Industry-leading pricing Reliable delivery times
Custom DNA Oligonucleotides accelerate > primers Custom DNA Oligonucleotides accelerate > primers Highest quality oligos with rigorous quality control Industry-leading pricing Reliable delivery times
Recitation CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies
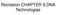 Recitation CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies DNA Cloning: General Scheme A cloning vector and eukaryotic chromosomes are separately cleaved with the same restriction endonuclease. (A single chromosome is shown
Recitation CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies DNA Cloning: General Scheme A cloning vector and eukaryotic chromosomes are separately cleaved with the same restriction endonuclease. (A single chromosome is shown
DNA/RNA Oligonucleotide Services Price List Denmark; valid from
 Optimised Application Oligos All our application oligos are optimised and scientifically proven to show highly consistent results in respective application Online synthesis reports, data sheets and quality
Optimised Application Oligos All our application oligos are optimised and scientifically proven to show highly consistent results in respective application Online synthesis reports, data sheets and quality
Please purchase PDFcamp Printer on to remove this watermark. DNA microarray
 DNA microarray Example of an approximately 40,000 probe spotted oligo microarray with enlarged inset to show detail. A DNA microarray is a multiplex technology used in molecular biology. It consists of
DNA microarray Example of an approximately 40,000 probe spotted oligo microarray with enlarged inset to show detail. A DNA microarray is a multiplex technology used in molecular biology. It consists of
Frequently Asked Questions
 Frequently Asked Questions VeriQuest qpcr Master Mixes VeriQuest Probe qpcr Master Mix 1. What is the VeriQuest Probe qpcr Master Mix? VeriQuest Probe qpcr Master Mix is a ready-to-use mix for real-time
Frequently Asked Questions VeriQuest qpcr Master Mixes VeriQuest Probe qpcr Master Mix 1. What is the VeriQuest Probe qpcr Master Mix? VeriQuest Probe qpcr Master Mix is a ready-to-use mix for real-time
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit
 HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
Fluorous Affinity Purification of Oligonucleotides
 Fluorous Affinity Purification of Oligonucleotides A higher affinity alternative to RP cartridge purification. One-pass loading without ammonia removal. High recoveries (typically 70-100%). High selectivity
Fluorous Affinity Purification of Oligonucleotides A higher affinity alternative to RP cartridge purification. One-pass loading without ammonia removal. High recoveries (typically 70-100%). High selectivity
Genotyping Manual. KASP version 4.0. P Robinson Dr J Holme
 Genotyping Manual 0 g KASP version 4.0 SNP Genotyping Manual P Robinson Dr J Holme 26 th May 2011 Contents KASP version 4.0 SNP Genotyping Manual Introduction Improvements of KASP version 4.0 Principal
Genotyping Manual 0 g KASP version 4.0 SNP Genotyping Manual P Robinson Dr J Holme 26 th May 2011 Contents KASP version 4.0 SNP Genotyping Manual Introduction Improvements of KASP version 4.0 Principal
Sensitive Detection of Small Molecules by Competitive Immunomagnetic-Proximity Ligation Assay
 Sensitive Detection of Small Molecules by Competitive Immunomagnetic-Proximity Ligation Assay Shuyan Cheng a, Feng Shi a, Xuecheng Jiang a, Luming Wang a, Weiqing Chen b, Chenggang Zhu a * a College of
Sensitive Detection of Small Molecules by Competitive Immunomagnetic-Proximity Ligation Assay Shuyan Cheng a, Feng Shi a, Xuecheng Jiang a, Luming Wang a, Weiqing Chen b, Chenggang Zhu a * a College of
Optimizing a Conventional Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Primer Design
 Optimizing a Conventional Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Primer Design The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a powerful technique used for the amplification of a specific segment of a nucleic acid
Optimizing a Conventional Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Primer Design The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is a powerful technique used for the amplification of a specific segment of a nucleic acid
2 march 06 Seminar on RT-PCR. About Real-time PCR. Aurélie OLIVIER Université Catholique de Louvain Unité de pharmacologie cellulaire et moléculaire
 2 march 06 Seminar on RT-PCR About Real-time PCR Aurélie OLIVIER Université Catholique de Louvain Unité de pharmacologie cellulaire et moléculaire Target DNA PCR Applications: Gene Plasmide, phage Diagnostic
2 march 06 Seminar on RT-PCR About Real-time PCR Aurélie OLIVIER Université Catholique de Louvain Unité de pharmacologie cellulaire et moléculaire Target DNA PCR Applications: Gene Plasmide, phage Diagnostic
AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 555 Protein Labeling Kit
 AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 555 Protein Labeling Kit Revision number: 1.3 Last updated: April 2018 Catalog # AS-72045 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate HiLyte Fluor 555 SE to
AnaTag HiLyte Fluor 555 Protein Labeling Kit Revision number: 1.3 Last updated: April 2018 Catalog # AS-72045 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate HiLyte Fluor 555 SE to
Boost Your Real-Time Results
 Boost Your Real-Time Results Refresh your knowledge of the fundamentals of real-time PCR Sample & Assay Technologies 1 Introduction Real-time PCR and RT-PCR are highly sensitive techniques that enable
Boost Your Real-Time Results Refresh your knowledge of the fundamentals of real-time PCR Sample & Assay Technologies 1 Introduction Real-time PCR and RT-PCR are highly sensitive techniques that enable
Quantitation of mrna Using Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-PCR)
 Quantitation of mrna Using Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-PCR) Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR Versus RT-PCR In Real-Time RT- PCR, DNA amplification monitored at each cycle but RT-PCR measures the
Quantitation of mrna Using Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-PCR) Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR Versus RT-PCR In Real-Time RT- PCR, DNA amplification monitored at each cycle but RT-PCR measures the
Premix Ex Taq (Probe qpcr)
 For Research Use Premix Ex Taq (Probe qpcr) Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Principle... 4 III. Components... 5 IV. Materials Required but not Provided... 5 V. Storage... 5 VI.
For Research Use Premix Ex Taq (Probe qpcr) Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Principle... 4 III. Components... 5 IV. Materials Required but not Provided... 5 V. Storage... 5 VI.
Basics of Recombinant DNA Technology Biochemistry 302. March 5, 2004 Bob Kelm
 Basics of Recombinant DNA Technology Biochemistry 302 March 5, 2004 Bob Kelm Applications of recombinant DNA technology Mapping and identifying genes (DNA cloning) Propagating genes (DNA subcloning) Modifying
Basics of Recombinant DNA Technology Biochemistry 302 March 5, 2004 Bob Kelm Applications of recombinant DNA technology Mapping and identifying genes (DNA cloning) Propagating genes (DNA subcloning) Modifying
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids
 Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
AnaTag 5-FAM Protein Labeling Kit
 AnaTag 5-FAM Protein Labeling Kit Catalog # 72053 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate 5-FAM SE (5-carboxyfluorescein) to proteins (e.g., IgG). It provides ample materials
AnaTag 5-FAM Protein Labeling Kit Catalog # 72053 Kit Size 3 Conjugation Reactions This kit is optimized to conjugate 5-FAM SE (5-carboxyfluorescein) to proteins (e.g., IgG). It provides ample materials
USB HotStart-IT. for increased specificity and consistent results. PCR, qpcr and qrt-pcr
 USB HotStart-IT for increased specificity and consistent results PCR, qpcr and qrt-pcr USB PCR Reagents Choose USB HotStart-IT products for increased specificity and consistent results. Long and Accurate
USB HotStart-IT for increased specificity and consistent results PCR, qpcr and qrt-pcr USB PCR Reagents Choose USB HotStart-IT products for increased specificity and consistent results. Long and Accurate
Agilent PL-SAX Anion-Exchange Media for Nucleotide and Oligonucleotide Analysis
 Agilent PL-SAX Anion-Exchange Media for Nucleotide and Oligonucleotide Analysis Technical Overview Introduction The physical stability of Agilent PL-SAX ensures rapid equilibration between separations,
Agilent PL-SAX Anion-Exchange Media for Nucleotide and Oligonucleotide Analysis Technical Overview Introduction The physical stability of Agilent PL-SAX ensures rapid equilibration between separations,
Molecular Genetics Techniques. BIT 220 Chapter 20
 Molecular Genetics Techniques BIT 220 Chapter 20 What is Cloning? Recombinant DNA technologies 1. Producing Recombinant DNA molecule Incorporate gene of interest into plasmid (cloning vector) 2. Recombinant
Molecular Genetics Techniques BIT 220 Chapter 20 What is Cloning? Recombinant DNA technologies 1. Producing Recombinant DNA molecule Incorporate gene of interest into plasmid (cloning vector) 2. Recombinant
Imaging of RNA in Bacteria with Self-ligating Quenched Probes
 Imaging of RNA in Bacteria with Self-ligating Quenched Probes Shinsuke Sando and Eric T. Kool* Department of Chemistry, Stanford University, Stanford CA 94305-5080 CONTENTS: 3 -Phosphorothioate oligonucleotides.
Imaging of RNA in Bacteria with Self-ligating Quenched Probes Shinsuke Sando and Eric T. Kool* Department of Chemistry, Stanford University, Stanford CA 94305-5080 CONTENTS: 3 -Phosphorothioate oligonucleotides.
7/24/2012. DNA Probes. Hybridization and Probes. CLS 420 Immunology & Molecular Diagnostics. Target Sequences. Target Sequences. Nucleic Acid Probes
 Hybridization and Probes CLS 420 Immunology & Molecular Diagnostics Molecular Diagnostics Techniques: Hybridization and Probes Nucleic acid probes: A short, known sequence of DNA or RNA Used to detect
Hybridization and Probes CLS 420 Immunology & Molecular Diagnostics Molecular Diagnostics Techniques: Hybridization and Probes Nucleic acid probes: A short, known sequence of DNA or RNA Used to detect
PCR. CSIBD Molecular Genetics Course July 12, 2011 Michael Choi, M.D.
 PCR CSIBD Molecular Genetics Course July 12, 2011 Michael Choi, M.D. General Outline of the Lecture I. Background II. Basic Principles III. Detection and Analysis of PCR Products IV. Common Applications
PCR CSIBD Molecular Genetics Course July 12, 2011 Michael Choi, M.D. General Outline of the Lecture I. Background II. Basic Principles III. Detection and Analysis of PCR Products IV. Common Applications
Computational Biology I LSM5191
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 Lecture 5 Notes: Genetic manipulation & Molecular Biology techniques Broad Overview of: Enzymatic tools in Molecular Biology Gel electrophoresis Restriction mapping DNA
Computational Biology I LSM5191 Lecture 5 Notes: Genetic manipulation & Molecular Biology techniques Broad Overview of: Enzymatic tools in Molecular Biology Gel electrophoresis Restriction mapping DNA
3 Designing Primers for Site-Directed Mutagenesis
 3 Designing Primers for Site-Directed Mutagenesis 3.1 Learning Objectives During the next two labs you will learn the basics of site-directed mutagenesis: you will design primers for the mutants you designed
3 Designing Primers for Site-Directed Mutagenesis 3.1 Learning Objectives During the next two labs you will learn the basics of site-directed mutagenesis: you will design primers for the mutants you designed
Only for teaching purposes - not for reproduction or sale
 PCR reaction conventional versus real time PCR real time PCR principles threshold cycle C T efficiency relative quantification reference genes primers detection chemistry GLP in real time PCR Relative
PCR reaction conventional versus real time PCR real time PCR principles threshold cycle C T efficiency relative quantification reference genes primers detection chemistry GLP in real time PCR Relative
THUNDERBIRD SYBR qpcr Mix
 Instruction manual THUNDERBIRD SYBR qpcr Mix 1304 A4251K THUNDERBIRD SYBR qpcr Mix QPS-201T 1 ml x 1 QPS-201 1.67 ml x 3 Contents [1] Introduction [2] Components [3] Primer design [4] Template DNA [5]
Instruction manual THUNDERBIRD SYBR qpcr Mix 1304 A4251K THUNDERBIRD SYBR qpcr Mix QPS-201T 1 ml x 1 QPS-201 1.67 ml x 3 Contents [1] Introduction [2] Components [3] Primer design [4] Template DNA [5]
Sanger Sequencing: Troubleshooting Guide
 If you need help analysing your Sanger sequencing output, this guide can help. CONTENTS 1 Introduction... 2 2 Sequence Data Evaluation... 2 3 Troubleshooting... 4 3.1 Reviewing the Sequence... 4 3.1.1
If you need help analysing your Sanger sequencing output, this guide can help. CONTENTS 1 Introduction... 2 2 Sequence Data Evaluation... 2 3 Troubleshooting... 4 3.1 Reviewing the Sequence... 4 3.1.1
Multiplex detection of single-nucleotide variations using molecular beacons
 Genetic Analysis: Biomolecular Engineering 14 (1999) 151 156 Multiplex detection of single-nucleotide variations using molecular beacons Salvatore A.E. Marras *, Fred Russell Kramer, Sanjay Tyagi Department
Genetic Analysis: Biomolecular Engineering 14 (1999) 151 156 Multiplex detection of single-nucleotide variations using molecular beacons Salvatore A.E. Marras *, Fred Russell Kramer, Sanjay Tyagi Department
mrnadembeads Purification Mini Kit (cat #06011) Instruction manual for mrna purification
 mrnadembeads Purification Mini Kit (cat #06011) Instruction manual for mrna purification Ademtech * Bioparc BioGalien 27 Allée Charles Darwin * 33600 Pessac France Tel : + 33 (0) 57 02 02 01, Fax : + 33
mrnadembeads Purification Mini Kit (cat #06011) Instruction manual for mrna purification Ademtech * Bioparc BioGalien 27 Allée Charles Darwin * 33600 Pessac France Tel : + 33 (0) 57 02 02 01, Fax : + 33
EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT CHEMICAL STRATEGIES FOR CONJUGATION OF OLIGONUCLEOTIDES TO PEPTIDES
 Nucleosides, Nucleotides, and Nucleic Acids, 26:1353 1357, 2007 Copyright C Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 1525-7770 print / 1532-2335 online DOI: 10.1080/15257770701533909 EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT CHEMICAL
Nucleosides, Nucleotides, and Nucleic Acids, 26:1353 1357, 2007 Copyright C Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 1525-7770 print / 1532-2335 online DOI: 10.1080/15257770701533909 EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT CHEMICAL
ZR-96 Genomic DNA Clean & Concentrator -5 Catalog Nos. D4066 & D4067
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZR-96 Genomic DNA Clean & Concentrator -5 Catalog Nos. D4066 & D4067 Highlights 96-well plate recovery of large-sized DNA (e.g., genomic, mitochondrial, plasmid (BAC/PAC), viral, phage,
INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZR-96 Genomic DNA Clean & Concentrator -5 Catalog Nos. D4066 & D4067 Highlights 96-well plate recovery of large-sized DNA (e.g., genomic, mitochondrial, plasmid (BAC/PAC), viral, phage,
Bootcamp: Molecular Biology Techniques and Interpretation
 Bootcamp: Molecular Biology Techniques and Interpretation Bi8 Winter 2016 Today s outline Detecting and quantifying nucleic acids and proteins: Basic nucleic acid properties Hybridization PCR and Designing
Bootcamp: Molecular Biology Techniques and Interpretation Bi8 Winter 2016 Today s outline Detecting and quantifying nucleic acids and proteins: Basic nucleic acid properties Hybridization PCR and Designing
One Step SYBR PrimeScript RT-PCR Kit II (Perfect Real Time)
 Cat. # RR086A For Research Use One Step SYBR PrimeScript RT-PCR Kit II Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description...3 II. III. IV. Principle...3 Components...5 Storage...6 V. Features...6 VI. VII.
Cat. # RR086A For Research Use One Step SYBR PrimeScript RT-PCR Kit II Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description...3 II. III. IV. Principle...3 Components...5 Storage...6 V. Features...6 VI. VII.
LightCycler Red 640-N-hydroxysuccinimide ester
 For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. R LightCycler Red 640-N-hydroxysuccinimide ester For labeling a minimum of 5 50 nmol oligonucleotides Content version: September 2016
For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. R LightCycler Red 640-N-hydroxysuccinimide ester For labeling a minimum of 5 50 nmol oligonucleotides Content version: September 2016
DNAPac PA200 and PA200 RS Columns Solutions for Nucleic Acid Analysis
 CHMATGAPHY DAPac PA and PA S Columns Solutions for ucleic Acid Analysis Product Specifications Thermo Scientific DAPac PA HPLC and DAPac PA S (apid Separation) UHPLC columns for high-resolution separations
CHMATGAPHY DAPac PA and PA S Columns Solutions for ucleic Acid Analysis Product Specifications Thermo Scientific DAPac PA HPLC and DAPac PA S (apid Separation) UHPLC columns for high-resolution separations
QUICK-Clone TM User Manual. cdna
 QUICK-Clone TM User Manual cdna PT1150-1 (PR752268) Published 25 May 2007 Table of Contents I. Introduction 3 II. Applications Discussion 4 A. Primer Design 4 B. Setting up the PCR Reaction 4 C. Example
QUICK-Clone TM User Manual cdna PT1150-1 (PR752268) Published 25 May 2007 Table of Contents I. Introduction 3 II. Applications Discussion 4 A. Primer Design 4 B. Setting up the PCR Reaction 4 C. Example
NZYGene Synthesis kit
 Kit components Component Concentration Amount NZYGene Synthesis kit Catalogue number: MB33901, 10 reactions GS DNA Polymerase 1U/ μl 30 μl Reaction Buffer for GS DNA Polymerase 10 150 μl dntp mix 2 mm
Kit components Component Concentration Amount NZYGene Synthesis kit Catalogue number: MB33901, 10 reactions GS DNA Polymerase 1U/ μl 30 μl Reaction Buffer for GS DNA Polymerase 10 150 μl dntp mix 2 mm
Exam 2 Key - Spring 2008 A#: Please see us if you have any questions!
 Page 1 of 5 Exam 2 Key - Spring 2008 A#: Please see us if you have any questions! 1. A mutation in which parts of two nonhomologous chromosomes change places is called a(n) A. translocation. B. transition.
Page 1 of 5 Exam 2 Key - Spring 2008 A#: Please see us if you have any questions! 1. A mutation in which parts of two nonhomologous chromosomes change places is called a(n) A. translocation. B. transition.
Fundamentals of Real Time PCR
 Fundamentals of Real Time PCR Mohamed Abdel Fattah Senior Technical Specialist Scientific Support - Molecular Biology Dept. AnalysisAB Co. Mobile: 012 27 906 74 E-mail: analysis@analysis-ab.com What is
Fundamentals of Real Time PCR Mohamed Abdel Fattah Senior Technical Specialist Scientific Support - Molecular Biology Dept. AnalysisAB Co. Mobile: 012 27 906 74 E-mail: analysis@analysis-ab.com What is
ZR-96 Oligo Clean & Concentrator Catalog Nos. D4062 & D4063
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZR-96 Oligo Clean & Concentrator Catalog Nos. D4062 & D4063 Highlights Quick, high-throughput (96-well) recovery of ultra-pure DNA and RNA oligonucleotides. Complete removal of dyes,
INSTRUCTION MANUAL ZR-96 Oligo Clean & Concentrator Catalog Nos. D4062 & D4063 Highlights Quick, high-throughput (96-well) recovery of ultra-pure DNA and RNA oligonucleotides. Complete removal of dyes,
HumqPCR-realtime JEV. Japanese encephalitisvirus - Real Time. Instrument Compatibility in: 50 / 100 /150 tests (Ready to use kit)
 Japanese encephalitisvirus - Real Time 50 / 100 /150 tests (Ready to use kit) Real Time Kit is a screening assay for the detection of Japanese encephalitisvirus. Principles of the test: The Japanese encephalitisvirus
Japanese encephalitisvirus - Real Time 50 / 100 /150 tests (Ready to use kit) Real Time Kit is a screening assay for the detection of Japanese encephalitisvirus. Principles of the test: The Japanese encephalitisvirus
Solid Phase cdna Synthesis Kit
 Table of Contents I. Description... 2 II. Kit components... 2 III. Storage... 2 IV. Principle... 3 V. Protocol V-1. Preparation of immobilized mrna... 4 Protocol A: Starting from Tissue or Cells... 4 Protocol
Table of Contents I. Description... 2 II. Kit components... 2 III. Storage... 2 IV. Principle... 3 V. Protocol V-1. Preparation of immobilized mrna... 4 Protocol A: Starting from Tissue or Cells... 4 Protocol
Primer Design Ameer Effat M. Elfarash
 Primer Design Ameer Effat M. Elfarash Dept. of Genetics Fac. of Agriculture, Assiut Univ. amir_effat@yahoo.com PCR Cycle Each cycle (Round) of PCR contains 3 steps: 1- Denaturation 2- Primer annealing
Primer Design Ameer Effat M. Elfarash Dept. of Genetics Fac. of Agriculture, Assiut Univ. amir_effat@yahoo.com PCR Cycle Each cycle (Round) of PCR contains 3 steps: 1- Denaturation 2- Primer annealing
Bauer Core Standard Protocol Title: Guidelines for Designing Real Time PCR Experiments Pages: 5 Revision: 1.1 Date: 4/15/04
 Bauer Core Standard Protocol Title: Guidelines for Designing Real Time PCR Experiments Pages: 5 Revision: 1.1 Date: 4/15/04 Author(s): Claire Reardon Reviewers: Christian Daly Contact: claire@cgr.harvard.edu
Bauer Core Standard Protocol Title: Guidelines for Designing Real Time PCR Experiments Pages: 5 Revision: 1.1 Date: 4/15/04 Author(s): Claire Reardon Reviewers: Christian Daly Contact: claire@cgr.harvard.edu
Real-Time PCR. lyophilisates
 Real-Time PCR dye- and probe-based mixes single to multiplex dual labeled probes qpcr lyophilisates qpcr FastMixes ACCCACGAAAGGGAA ATAAGC AACO TTCAGGGAAGAA CTAUAACTGCCAC ACCCACGAAAGGGAA ATAAGC AACO TTCAGGGAAGAA
Real-Time PCR dye- and probe-based mixes single to multiplex dual labeled probes qpcr lyophilisates qpcr FastMixes ACCCACGAAAGGGAA ATAAGC AACO TTCAGGGAAGAA CTAUAACTGCCAC ACCCACGAAAGGGAA ATAAGC AACO TTCAGGGAAGAA
Genomic DNA Clean & Concentrator -25 Catalog Nos. D4064 & D4065
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Genomic DNA Clean & Concentrator -25 Catalog Nos. D4064 & D4065 Highlights Quick (5 minute) spin column recovery of large-sized DNA (e.g., genomic, mitochondrial, plasmid (BAC/PAC),
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Genomic DNA Clean & Concentrator -25 Catalog Nos. D4064 & D4065 Highlights Quick (5 minute) spin column recovery of large-sized DNA (e.g., genomic, mitochondrial, plasmid (BAC/PAC),
Rotor-Gene Multiplex Handbook
 Second Edition July 2011 Rotor-Gene Multiplex Handbook Rotor-Gene Multiplex PCR Kit Rotor-Gene Multiplex RT-PCR Kit For fast multiplex real-time PCR, two-step RT-PCR, and one-step RT-PCR using sequence-specific
Second Edition July 2011 Rotor-Gene Multiplex Handbook Rotor-Gene Multiplex PCR Kit Rotor-Gene Multiplex RT-PCR Kit For fast multiplex real-time PCR, two-step RT-PCR, and one-step RT-PCR using sequence-specific
REAL-TIME AMPLIFICATION ON THE ROTOR-GENE
 REAL-TIME AMPLIFICATION ON THE ROTOR-GENE Overview of the chemistries and optimizations 1 Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 4 1.1 Real-Time Detection of Amplification Products... 4 2 Real-Time Chemistries...
REAL-TIME AMPLIFICATION ON THE ROTOR-GENE Overview of the chemistries and optimizations 1 Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 4 1.1 Real-Time Detection of Amplification Products... 4 2 Real-Time Chemistries...
Detecting Rare Genomic Copies or Events
 Detecting Rare Genomic Copies or Events Integrated DNA Technologies Nick Downey, PhD Common Diagnostics Challenges Detecting targets early with accuracy Detecting different strains (e.g., antibiotic resistance)
Detecting Rare Genomic Copies or Events Integrated DNA Technologies Nick Downey, PhD Common Diagnostics Challenges Detecting targets early with accuracy Detecting different strains (e.g., antibiotic resistance)
Table of Contents. I. Kit Components...2. Storage...2. Principle...2. IV. Precautions for operation...3. V. Protocol : reverse transcription...
 Table of Contents I. Kit Components...2 II. III. Storage...2 Principle...2 IV. Precautions for operation...3 V. Protocol : reverse transcription...3 VI. Protocol : Real-time PCR...5 VII. Appendix...7 VIII.
Table of Contents I. Kit Components...2 II. III. Storage...2 Principle...2 IV. Precautions for operation...3 V. Protocol : reverse transcription...3 VI. Protocol : Real-time PCR...5 VII. Appendix...7 VIII.
The Agilent Total RNA Isolation Kit
 Better RNA purity. Better data. Without DNase treatment. The Agilent Total RNA Isolation Kit Now you can isolate highly purified, intact RNA without DNase treatment Introducing the Agilent Total RNA Isolation
Better RNA purity. Better data. Without DNase treatment. The Agilent Total RNA Isolation Kit Now you can isolate highly purified, intact RNA without DNase treatment Introducing the Agilent Total RNA Isolation
Optimizing Multiplex qpcr for Detecting Infectious Diseases
 Optimizing Multiplex qpcr for Detecting Infectious Diseases Aurita Menezes Ph.D, qpcr Product Manager Integrated DNA Technologies Agenda Establishing robust multiplex assays In the context of Gene expression
Optimizing Multiplex qpcr for Detecting Infectious Diseases Aurita Menezes Ph.D, qpcr Product Manager Integrated DNA Technologies Agenda Establishing robust multiplex assays In the context of Gene expression
DNA and RNA are both composed of nucleotides. A nucleotide contains a base, a sugar and one to three phosphate groups. DNA is made up of the bases
 1 DNA and RNA are both composed of nucleotides. A nucleotide contains a base, a sugar and one to three phosphate groups. DNA is made up of the bases Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine whereas in RNA
1 DNA and RNA are both composed of nucleotides. A nucleotide contains a base, a sugar and one to three phosphate groups. DNA is made up of the bases Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine whereas in RNA
HiPer Real-Time PCR Teaching Kit
 HiPer Real-Time PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM032 Number of experiments that can be performed: 10 Duration of Experiment Protocol: 1.5 hours Storage Instructions: The kit is stable for 12 months from
HiPer Real-Time PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM032 Number of experiments that can be performed: 10 Duration of Experiment Protocol: 1.5 hours Storage Instructions: The kit is stable for 12 months from
For Research Use Only Ver
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Oligo Clean & Concentrator Catalog Nos. D4060 & D4061 Highlights Quick (2 minute) recovery of ultra-pure DNA and RNA oligonucleotides. Complete removal of dyes, salts, enzymes, nucleotides,
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Oligo Clean & Concentrator Catalog Nos. D4060 & D4061 Highlights Quick (2 minute) recovery of ultra-pure DNA and RNA oligonucleotides. Complete removal of dyes, salts, enzymes, nucleotides,
