Signal transducers and activators of transcription, STAT,
|
|
|
- Samuel Bell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE JOURNAL OF IMMUNOLOGY CUTTING EDGE Cutting Edge: Selective Tyrosine Dephosphorylation of Interferon-Activated Nuclear STAT5 by the VHR Phosphatase 1 Richard Hoyt, 2 * Wei Zhu, 2 * Fabio Cerignoli, 2 Andres Alonso, Tomas Mustelin, and Michael David 3 * Cytokine-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of the transcription factor STAT5 is required for its transcriptional activity. In this article we show that the small dual-specificity phosphatase VHR selectively dephosphorylates IFN- - and -activated, tyrosine-phosphorylated STAT5, leadingtothesubsequentinhibitionofstat5function.phosphorylation of VHR at Tyr 138 was required for its phosphatase activity toward STAT5. In addition, the Src homology 2 domain of STAT5 was required for the effective dephosphorylation of STAT5 by VHR. The tyrosine kinase Tyk2, which mediates the phosphorylation of STAT5, was also responsible for the phosphorylation of VHR at Tyr 138. The Journal of Immunology, 2007, 179: Signal transducers and activators of transcription, STAT, are a family of latent cytoplasmic transcription factors that are activated by many cytokines and growth factors (1). Upon ligand stimulation the receptor-associated Janus kinases selectively tyrosine phosphorylate STATs, which then dissociate from the receptor, dimerize, translocate to the nucleus, and bind to their respective enhancer elements (2). Activation of the Jak/STAT pathway is rapid and transient, with activated STAT molecules evident in the nucleus within minutes of cytokine stimulation but disappearing within a few hours (3). Several different levels at which negative regulation can be exerted over the Jak/STAT pathway have been demonstrated, including down-regulation of the receptor/ligand complex, induction of suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS), and dephosphorylation by nuclear tyrosine phosphatases (4). T cell protein tyrosine phosphatase (TcPTP) 4 was demonstrated to be the nuclear tyrosine phosphatase for STAT1 (5). Similar to STAT1, STAT5 undergoes a rapid activation and deactivation cycle upon cytokine stimulation. The transient kinetics of STAT5 tyrosine phosphorylation following cytokine stimulation strongly suggest that tyrosine dephosphorylation is a critical mechanism in the down-regulation of STAT5 activity (6). SHP-2 and protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) 1B (PTP1B) have been reported to be involved in the cytosolic tyrosine dephosphorylation of STAT5 (7, 8). Aoki and Matusa (9) suggested that the nuclear tyrosine phosphatase TcPTP was catalytically competent with respect to the dephosphorylation of STAT5. However, studies in TcPTP / murine embryonic fibroblasts revealed that TcPTP-deficiency was of no consequence to STAT5 tyrosine dephosphorylation (5). Thus, the identity of the nuclear tyrosine phosphatase inactivating STAT5 remained elusive. Materials and Methods Cell culture HEK293T, 2fTGH, HeLa, U1A, and U4A cells were maintained in DMEM with penicillin, streptomycin, and 10% FBS. Reagents IFN was a gift from Biogen Idec. Staurosporine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Abs used were against FLAG (Sigma-Aldrich), hemagglutinin (HA) or MYC (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), phospho-stat1(tyr 701 ) (New England Biolabs), phospho-stat5(tyr 694 /Tyr 699 ) (Upstate Biotechnology), phospho-tyr (Upstate Biotechnology), or phospho-stat5(ser 726 ) (Upstate Biotechnology). Cell extracts Nuclear extracts were prepared by Dounce homogenizing cells in buffer A (20 mm HEPES (ph 7.9), 10 mm KCl, 1 mm MgCl 2, 10% glycerol, and 0.1% Nonidet P-40) and the sedimentation of nuclei at 1000 rpm for 5 min. The supernatant was removed and collected as cytoplasmic extract, and nuclei were extracted with buffer A containing 300 mm NaCl to obtain nuclear extracts. To generate whole cell lysates, cells were lysed on the plates with buffer containing 20 mm HEPES (ph 7.4), 1% TX-100, 100 mm NaCl, 50 mm NaF, 10 mm -glycerophosphate, 1 mm sodium vanadate, and 1 mm PMSF. Lysates were centrifuged at 13,000 g for 5 min, and protein concentration was determined by the Lowry method (Bio-Rad protein assay). Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting Cell lysates were incubated with isotype control or protein-specific Abs and protein G-Sepharose overnight at 4 C. After SDS-PAGE and transfer onto *Division of Biological Sciences and University of California Cancer Center, University of California La Jolla, CA and The Burnham Institute, La Jolla, CA Received for publication June 21, Accepted for publication July 23, The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. This article must therefore be hereby marked advertisement in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact. 1 This work was supported in part by National Institutes of Health Grant R01 CA80105 (to M. D.). 2 R.H., W.Z, and F. C. contributed equally to this work. 3 Address correspondence and reprint requests to Dr. Michael David, University of California Department of Biology, Bonner Hall 3138, 9500 Gilman Drive, La Jolla, CA address: midavid@ucsd.edu 4 Abbreviations used in this paper: TcPTP, T cell protein tyrosine phosphatase; HA, hemagglutinin; PTP, protein tyrosine phosphatase; SH2, Src homology 2; Tyk2, tyrosine kinase 2; WT, wild type. Copyright 2007 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc /07/$2.00
2 The Journal of Immunology PVDF membrane, proteins were detected with the indicated primary Abs, HRP-conjugated secondary Abs and ECL. Results and Discussion To identify the nuclear tyrosine phosphatase responsible for STAT5 dephosphorylation, we screened HA-tagged tyrosine phosphatases with known or potential nuclear localization for their ability to dephosphorylate STAT5. In pulse-chase studies, most of the tyrosine phosphatases failed to affect the kinetics of STAT5 dephosphorylation (Fig. 1A, and data not shown). Indeed, the small dual-specificity phosphatase VHR was the only enzyme capable of altering the extent of IFN -induced STAT5 tyrosine phosphorylation in its wild-type (WT) or catalytically inactive forms (Fig. 1B). VHX, another member of the VH1 group of dual-specificity phosphatases, displayed no negative regulatory effects on STAT5 tyrosine phosphorylation, suggesting a high degree of specificity of these enzymes (Fig. 1C). Similar expression of all phosphatases was verified by anti-ha Western blotting (not shown). To test whether VHR bears a similar selectivity toward STAT5 as a TcPTP for STAT1, we examined the effects of VHR on STAT1 tyrosine dephosphorylation. In contrast to TcPTP, VHR appears to be unable to facilitate tyrosine dephosphorylation of STAT1 (Fig. 2A) or other STAT proteins (not shown). When both STAT1 and STAT5 were coexpressed in the presence or absence of VHR, only STAT5 displayed significantly altered tyrosine phosphorylation (Fig. 2B). We next wanted to exclude the possibility that VHR might affect STAT5 tyrosine phosphorylation indirectly via tyrosine dephosphorylation and inactivation of the upstream activators Jak1 and tyrosine kinase 2 (Tyk2). Substantiating our hypothesis, VHR did not affect phosphorylation of IFN - and -activated Jak1 (Fig. 2C) or Tyk2 (not shown). Similarly, phosphorylation of STAT5 on Ser 726, known to be required for the optimal transcriptional activity of STAT5, was not affected by VHR (not shown). Lastly, nuclear colocalization of VHR and pstat5 was confirmed by immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy (not shown), supporting the notion that VHR acts directly on the nuclear STAT5 rather than targeting upstream activators To verify that STAT5 is an authentic substrate for endogenous VHR, we used cells derived from animals with a targeted disruption of the VHR gene (F. Cerignoli, A. Alonso, and T. Mustelin, manuscript in preparation). Pulse-chase experiments on WT and VHR / splenic B cells revealed increased levels of STAT5 tyrosine phosphorylation upon IFN stimulation in VHR / cells (Fig. 2D, upper panels). Intriguingly, the difference was only evident when IFN was used for stimulation of cells, whereas no difference in STAT5 phosphorylation could be detected after IL-4 administration (Fig. 2D, lower panels). It is interesting to note that the loss of VHR again mainly affected the magnitude of STAT5 tyrosine phosphorylation, whereas the kinetics remained essentially unchanged. This speaks against a negative feedback regulation of VHR but is compatible with the activation of VHR by upstream signaling events. VHR belongs to the group of dual-specific phosphatases that inactivate the MAPKs ERK2 and JNK by dephosphorylating the phospho-thr and phospho-tyr residues in their respective activation loops (10 12). VHR, a predominantly nuclear enzyme, is phosphorylated at Tyr 138 by ZAP70 upon TCR stimulation (13). Expression of VHR in ZAP70-deficient cells or expression of a VHR Y138F mutant causes no inhibition of the ERK1/2 pathway, indicating that Tyr 138 phosphorylation is crucial for VHR to exert control over the MAPKs (13). To test whether phosphorylation of VHR at Tyr 138 also plays a role in its phosphatase activity toward STAT5, we examined the dynamics of STAT5 tyrosine dephosphorylation in the presence of ectopically expressed VHR(Y3 F). Like VHR(C3 S), VHR(Y3 F) acted in a fashion consistent with the function of a dominant negative mutant (Fig. 3A). In contrast to the other Jak kinase family members, Tyk2 shares a significant degree of homology with Syk/ZAP70 in the kinase domain (Ref. 14 and our unpublished observations). As ZAP70 was previously identified as a tyrosine kinase for VHR, it was conceivable that Tyk2 could act in a similar function. To test this hypothesis, we examined whether the Janus kinase family members Jak1, Jak2, Jak3, FIGURE 1. Identification of VHR as a STAT5 tyrosine phosphatase. A, 293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding Myc-STAT5A and either empty vector or the respective WT or catalytically inactive phosphatases as indicated. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were left untreated (control (Ctl)) or stimulated with IFN (1000 U/ml) for 60 min before the addition of staurosporine (STSP) at 500 nm, and incubation was continued for the indicated time periods. Tyrosine phosphorylation of immunoprecipitated Myc-STAT5A was analyzed by using anti-phospho-stat5 (upper panel) and anti- Myc Abs (lower panel). B and C, Same as in A, except that cells were transfected with Myc-STAT5 and empty vector or HA-tagged VHR or VHX. wb, Western blotting; LMPTP, low m.w. PTP, HePTP, hemopoietic PTP.
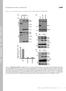
3 3404 CUTTING EDGE: STAT5 DEPHOSPHORYLATION BY VHR FIGURE 2. VHR selectively tyrosine dephosphorylates STAT5. A, Same as in Fig. 1A, except that FLAG-STAT1 was used instead of Myc- STAT5A. Immunoprecipitated FLAG-STAT1 was analyzed for its tyrosine phosphorylation using phospho-stat1 Abs (upper panel). B, Same as in A, except that cells were transfected with both FLAG-STAT1 and Myc-STAT5A in addition to either empty vector or WT or C3S mutant VHR. Nuclear extracts were divided and subjected to immunoprecipitation using either anti- FLAG or anti-myc Abs. Anti-FLAG and anti- Myc immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blotting (wb) using anti-phospho- STAT1 (lanes 1 12) and anti-phospho-stat5 Abs (lanes 13 24), respectively. C, Cells were transiently transfected with the indicated VHR plasmids and HA-tagged Jak1 constructs. Extracts were prepared after 48 h and subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-ha Abs. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed for phosphorylation using 4G10 anti-phosphotyrosine Abs. D, Splenic B cells were isolated from WT and VHR / mice and stimulated with IFN (1000 U/ml; upper panels) or IL-4 (lower panels) for 30 min before the addition of staurosporine (STSP; 500 nm), and incubation was continued for the indicated time periods. Tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT5 was analyzed by using anti-phospho-stat5 Abs (bar graphs represent average SD of pstat5 normalized to total STAT5; n 3). and Tyk2 could tyrosine phosphorylate VHR. Because VHR is known to auto-dephosphorylate, we also included the catalytically inactive phosphatase in these experiments. As shown in Fig. 3B, Tyk2 and Jak1 were as efficient as ZAP70 in tyrosine phosphorylating VHR, whereas Jak2 and Jak3 displayed no activity toward the phosphatase. The Tyk2-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of VHR was prevented by the additional mutation of Tyr 138 in VHR. Furthermore, tyrosine phosphorylation of VHR required the kinase activity of Tyk2, because a kinase-dead mutant of Tyk2 failed to phosphorylate VHR. It is interesting to note that tyrosine phosphorylation was detected only in the catalytically inactive VHR but not in the WT phosphatase when coexpressed with the different kinases (Fig. 3B). However, tyrosine phosphorylation of WT VHR, but not of VHR(Y138F), was restored when the experiment was performed in the presence of the tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor orthovanadate (not shown), suggesting auto-dephosphorylation or trans-dephosphorylation of WT VHR. It was surprising to find that Jak1 also induced VHR tyrosine phosphorylation, as the kinase bears little resemblance to Syk/ZAP70. Because 293T cells express endogenous Tyk2, we reasoned that Jak1 might drive Tyk2 activation through transphosphorylation. To test the hypothesis that phosphorylation of VHR by Jak1 may actually be mediated by Tyk2, we examined the ability of Jak1 to tyrosine phosphorylate VHR in the Tyk2-deficient U1A cell line (15). ZAP70 and Tyk2 still retained their ability to phosphorylate VHR (Fig. 3C) in U1A cells. In contrast, Jak1 could phosphorylate VHR only in the parental 2fTGH cell line but not in U1A cells despite the presence of overexpressed Jak1. When Jak1-deficient UA4 cells were used for the experiment (16), Tyk2-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of VHR occurred just as readily as in WT 2fTGH cells (Fig. 3D), indicating that Jak1 was not required for the phosphorylation of VHR by Tyk2. This finding can also explain the fact that altered STAT5 phosphorylation in VHR / B cells was only observed after IFN but not after IL-4 stimulation, as only IFN is known to activate Tyk2. Tyrosine phosphorylation of VHR does not effect its catalytic activity in vitro (13) and is therefore likely to exert a regulatory role by mediating protein-protein interactions. Thus, we hypothesized that if tyrosine-phosphorylated VHR can act as a binding partner for the STAT5 Src homology 2 (SH2) domain, it may act on the STAT5 dimer and displace one tyrosinephosphorylated STAT5 molecule from the SH2 domain of the other and subsequently dephosphorylate STAT5 on Tyr 694.
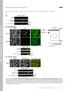
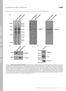
4 The Journal of Immunology 3405 FIGURE 3. Requirement for VHR-Tyr138 phosphorylation as a STAT5 phosphatase. A, 293T cells were transiently transfected with FLAG-STAT1 or Myc- STAT5A and either empty vector or WT VHR, VHR(C3S), or VHR(Y3F). A pulse-chase experiment was performed as described in Fig. 1A. Tyrosine phosphorylation and efficiency of immunoprecipitation of FLAG-STAT1 and Myc-STAT5A were analyzed using the indicated Abs. B, Cells were transfected with the indicated HA-tagged VHR and kinase constructs and phosphorylation of immunoprecipitated VHR was determined by anti-phosphotyrosine (py) Western blotting (wb). C, 2fTGH cells and their Tyk2-deficient counterparts (U1) were transfected with HA-VHR(C3S) and the indicated tyrosine kinase. Anti-HA immunoprecipitated VHR was analyzed for its tyrosine phosphorylation (upper panel). D, Same as C, except that Jak1-deficient U4 cells were used for transfection. E, Myc- STAT5A or STAT5A(R3K) were cotransfected with Tyk2 and HA-VHR as indicated. Phosphorylation of immunoprecipitated (Ip) STAT5 was determined by anti-phospho-stat5 (pstat5) immunoblotting. IgLC, Ig light chain; STSP, staurosporine; WCL, whole cell lysate. Indeed, we found that tyrosine dephosphorylation of STAT5 by VHR required the SH2 domain of STAT5, because STAT5(R3 K) harboring a defective SH2 domain was significantly less susceptible to dephosphorylation by VHR (Fig. 3E). Lastly, we assessed the effects of VHR on the transcriptional induction of the -casein gene promoter, a well known target of activated STAT5 (Fig. 4). STAT5 tyrosine phosphorylation and the luciferase reporter were fully induced by coexpression of STAT5 and Tyk2. VHR coexpression severely reduced Tyk2-induced, STAT5-mediated transcriptional activity to levels close to baseline values. The STAT5-mediated transcriptional induction appeared to be at maximum levels in this system, as the presence of the dominant-negative VHR(C3 S) or VHR(Y3 F) mutants did not further increase the reporter activity. Tyrosine dephosphorylation of activated STATs is an important component of the negative regulation of cytokine signaling. STAT5 is the first transcription factor reported, in this study, to be a substrate for the small dual-specificity phosphatase VHR. It is of interest to note that Tyk2 plays dual roles by directing the tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of STAT5 as well as VHR, the negative regulator of STAT5. The direct coupling of Tyk2 to VHR activation offers a mechanism by which the Jak/STAT signaling pathway ties its own down-regulation intimately and mechanistically to the initial stimulus. Disclosures The authors have no financial conflict of interest. FIGURE 4. Inhibition of STAT5-mediated transcription by VHR. 293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids and the STAT5-responsive -casein-luciferase. CMV-driven -galactosidase was included to normalize for transfection efficiency. Cells were lysed 48 h after transfection, and lysates were analyzed for luciferase and -galactosidase activity. Average results of four independent experiments are shown. CS, C3S; YF, Y3F. References 1. Larner, A. C., M. David, G. M. Feldman, K. Igarashi, R. H. Hackett, D. A. S. Webb, S. M. Sweitzer, E. F. Petricoin III, and D. S. Finbloom Tyrosine phosphorylation of DNA binding proteins by multiple cytokines. Science 261: Schindler, C., and J. E. Darnell, Jr Transcriptional responses to polypeptide ligands: the JAK-STAT pathway. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 64: David, M., P. M. Grimley, D. S. Finbloom, and A. C. Larner A nuclear tyrosine phosphatase downregulates interferon-induced gene expression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13: Hilton, D. J Negative regulators of cytokine signal transduction. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 55: ten Hoeve, J., M. de Jesus Ibarra-Sanchez, Y. Fu, W. Zhu, M. Tremblay, M. David, and K. Shuai Identification of a nuclear Stat1 protein tyrosine phosphatase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22:
5 3406 CUTTING EDGE: STAT5 DEPHOSPHORYLATION BY VHR 6. Yu, C. L., and S. J. Burakoff Involvement of proteasomes in regulating Jak- STAT pathways upon interleukin-2 stimulation. J. Biol. Chem. 272: Yu, C. L., Y. J. Jin, and S. J. Burakoff Cytosolic tyrosine dephosphorylation of STAT5. Potential role of SHP-2 in STAT5 regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 275: Aoki, N., and T. Matsuda A cytosolic protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTP1B specifically dephosphorylates and deactivates prolactin-activated STAT5a and STAT5b. J. Biol. Chem. 275: Aoki, N., and T. Matsuda A nuclear protein tyrosine phosphatase TC-PTP is a potential negative regulator of the PRL-mediated signaling pathway: dephosphorylation and deactivation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5a and 5b by TC-PTP in nucleus. Mol. Endocrinol. 16: Alonso, A., M. Saxena, S. Williams, and T. Mustelin Inhibitory role for dual specificity phosphatase VHR in T cell antigen receptor and CD28-induced Erk and Jnk activation. J. Biol. Chem. 276: Schumacher, M. A., J. L. Todd, A. E. Rice, K. G. Tanner, and J. M. Denu Structural basis for the recognition of a bisphosphorylated MAP kinase peptide by human VHR protein Phosphatase. Biochemistry 41: Todd, J. L., K. G. Tanner, and J. M. Denu Extracellular regulated kinases (ERK) 1 and ERK2 are authentic substrates for the dual-specificity protein-tyrosine phosphatase VHR. A novel role in down-regulating the ERK pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 274: Alonso, A., S. Rahmouni, S. Williams, M. van Stipdonk, L. Jaroszewski, A. Godzik, R. T. Abraham, S. P. Schoenberger, and T. Mustelin Tyrosine phosphorylation of VHR phosphatase by ZAP-70. Nat Immunol 4: Su, L., and M. David Distinct mechanisms of STAT phosphorylation via the interferon- / receptor. Selective inhibition of STAT3 and STAT5 by piceatannol. J. Biol. Chem. 275: Velazquez, L., M. Fellous, G. R. Stark, and S. Pellegrini A protein tyrosine kinase in the interferon / signaling pathway. Cell 70: Muller, M., J. Briscoe, C. Laxton, D. Guschin, A. Ziemiecki, O. Silvennoinen, A. G. Harpur, G. Barbieri, B. A. Withuhn, C. Schindler, et al The protein tyrosine kinase JAK1 complements defects in the interferon- / and - signal transduction. Nature 366:
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/9/eaat5401/dc1 Supplementary Materials for GLK-IKKβ signaling induces dimerization and translocation of the AhR-RORγt complex in IL-17A induction and autoimmune
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/9/eaat5401/dc1 Supplementary Materials for GLK-IKKβ signaling induces dimerization and translocation of the AhR-RORγt complex in IL-17A induction and autoimmune
Sarker et al. Supplementary Material. Subcellular Fractionation
 Supplementary Material Subcellular Fractionation Transfected 293T cells were harvested with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and centrifuged at 2000 rpm (500g) for 3 min. The pellet was washed, re-centrifuged
Supplementary Material Subcellular Fractionation Transfected 293T cells were harvested with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and centrifuged at 2000 rpm (500g) for 3 min. The pellet was washed, re-centrifuged
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or
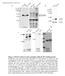 Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Han et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201311007/dc1 Figure S1. SIVA1 interacts with PCNA. (A) HEK293T cells were transiently
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Han et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201311007/dc1 Figure S1. SIVA1 interacts with PCNA. (A) HEK293T cells were transiently
The MAP Kinase Family
 The MAP Kinase Family Extracellular stimuli Classical MAP kinases Atypical MAP kinases MAPKKK MLK1/2/3/7; LZK RAF-1/A/B TAK1; TPL2 c-mos MEKK1-4; DLK ASK1/2; MLTK TAO1/2 ASK1 TAK1 MEKK1-4 MEKK2/3 TPL2???
The MAP Kinase Family Extracellular stimuli Classical MAP kinases Atypical MAP kinases MAPKKK MLK1/2/3/7; LZK RAF-1/A/B TAK1; TPL2 c-mos MEKK1-4; DLK ASK1/2; MLTK TAO1/2 ASK1 TAK1 MEKK1-4 MEKK2/3 TPL2???
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Table of Content: Supplementary Results... 2 Supplementary Figure S1: Experimental validation of AP-MS results by coimmunprecipitation Western blot analysis.... 3 Supplementary
Supplementary information Table of Content: Supplementary Results... 2 Supplementary Figure S1: Experimental validation of AP-MS results by coimmunprecipitation Western blot analysis.... 3 Supplementary
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Over-expression of CD300f in NIH3T3 cells enhances their capacity to phagocytize AC. (a) NIH3T3 cells were stably transduced by EV, CD300f WT or CD300f
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Over-expression of CD300f in NIH3T3 cells enhances their capacity to phagocytize AC. (a) NIH3T3 cells were stably transduced by EV, CD300f WT or CD300f
Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic structure of TRAIP and RAP80. The prey line below TRAIP indicates bait and the two lines above RAP80 highlight the
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic structure of TRAIP and RAP80. The prey line below TRAIP indicates bait and the two lines above RAP80 highlight the prey clones identified in the yeast two hybrid screen.
Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic structure of TRAIP and RAP80. The prey line below TRAIP indicates bait and the two lines above RAP80 highlight the prey clones identified in the yeast two hybrid screen.
Post-translational modification
 Protein expression Western blotting, is a widely used and accepted technique to detect levels of protein expression in a cell or tissue extract. This technique measures protein levels in a biological sample
Protein expression Western blotting, is a widely used and accepted technique to detect levels of protein expression in a cell or tissue extract. This technique measures protein levels in a biological sample
Beta Interferon and Oncostatin M Activate Raf-1 and Mitogen- Activated Protein Kinase through a JAK1-Dependent Pathway
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, July 1997, p. 3833 3840 Vol. 17, No. 7 0270-7306/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Beta Interferon and Oncostatin M Activate Raf-1 and Mitogen-
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, July 1997, p. 3833 3840 Vol. 17, No. 7 0270-7306/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Beta Interferon and Oncostatin M Activate Raf-1 and Mitogen-
Supplementary Fig. 1 Kinetics of appearence of the faster migrating form of Bcl-10.
 α-cd3 + α-cd28: Time (min): + + + + + + + + + 0 5 15 30 60 120 180 240 300 360 360 n.s. Supplementary Fig. 1 Kinetics of appearence of the faster migrating form of. Immunoblot of lysates from Jurkat cells
α-cd3 + α-cd28: Time (min): + + + + + + + + + 0 5 15 30 60 120 180 240 300 360 360 n.s. Supplementary Fig. 1 Kinetics of appearence of the faster migrating form of. Immunoblot of lysates from Jurkat cells
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table.
 Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Nakajima and Tanoue, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201104118/dc1 Figure S1. DLD-1 cells exhibit the characteristic morphology
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Nakajima and Tanoue, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201104118/dc1 Figure S1. DLD-1 cells exhibit the characteristic morphology
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. MLK1-4 phosphorylate MEK in the presence of RAF inhibitors. (a) H157 cells were transiently transfected with Flag- or HA-tagged MLK1-4
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. MLK1-4 phosphorylate MEK in the presence of RAF inhibitors. (a) H157 cells were transiently transfected with Flag- or HA-tagged MLK1-4
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Thompson et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200909067/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Modification-specific antibodies do not detect unmodified
Supplemental material Thompson et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200909067/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Modification-specific antibodies do not detect unmodified
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information LYP inhibits T cell activation when dissociated from CSK Torkel Vang 1,3, Wallace H. Liu 1,9, Laurence Delacroix 4,9, Shuangding Wu 1, Stefan Vasile 2, Russell Dahl 2, Li Yang
Supplementary Information LYP inhibits T cell activation when dissociated from CSK Torkel Vang 1,3, Wallace H. Liu 1,9, Laurence Delacroix 4,9, Shuangding Wu 1, Stefan Vasile 2, Russell Dahl 2, Li Yang
Supplemental Table 1: Sequences of real time PCR primers. Primers were intronspanning
 Symbol Accession Number Sense-primer (5-3 ) Antisense-primer (5-3 ) T a C ACTB NM_001101.3 CCAGAGGCGTACAGGGATAG CCAACCGCGAGAAGATGA 57 HSD3B2 NM_000198.3 CTTGGACAAGGCCTTCAGAC TCAAGTACAGTCAGCTTGGTCCT 60
Symbol Accession Number Sense-primer (5-3 ) Antisense-primer (5-3 ) T a C ACTB NM_001101.3 CCAGAGGCGTACAGGGATAG CCAACCGCGAGAAGATGA 57 HSD3B2 NM_000198.3 CTTGGACAAGGCCTTCAGAC TCAAGTACAGTCAGCTTGGTCCT 60
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods sirna sequences used in this study The sequences of Stealth Select RNAi for ALK and FLOT-1 were as follows: ALK sense no.1 (ALK): 5 -AAUACUGACAGCCACAGGCAAUGUC-3 ; ALK
Supplementary Materials and Methods sirna sequences used in this study The sequences of Stealth Select RNAi for ALK and FLOT-1 were as follows: ALK sense no.1 (ALK): 5 -AAUACUGACAGCCACAGGCAAUGUC-3 ; ALK
JCB. Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY. Kimura et al.,
 Supplemental material JCB Kimura et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201503023/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. TRIMs regulate IFN-γ induced autophagy. (A and B) HC image analysis
Supplemental material JCB Kimura et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201503023/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. TRIMs regulate IFN-γ induced autophagy. (A and B) HC image analysis
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information The E3 ligase RNF8 regulates KU80 removal and NHEJ repair Lin Feng 1, Junjie Chen 1 1 Department of Experimental Radiation Oncology, The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer
Supplementary information The E3 ligase RNF8 regulates KU80 removal and NHEJ repair Lin Feng 1, Junjie Chen 1 1 Department of Experimental Radiation Oncology, The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer
Species predicted to react based on 100% sequence homology: Chicken, Bovine, Dog.
 1 of 5 11/1/2013 10:25 PM Product Pathways - Jak/Stat Pathway Phospho-Stat3 (Tyr705) Antibody #9131 Have you tried your application using our XP monoclonal antibodies? Try products: 9145 PhosphoSitePlus
1 of 5 11/1/2013 10:25 PM Product Pathways - Jak/Stat Pathway Phospho-Stat3 (Tyr705) Antibody #9131 Have you tried your application using our XP monoclonal antibodies? Try products: 9145 PhosphoSitePlus
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Bays et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201309092/dc1 Figure S1. Specificity of the phospho-y822 antibody. (A) Total cell
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Bays et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201309092/dc1 Figure S1. Specificity of the phospho-y822 antibody. (A) Total cell
SHP-2 Is a Dual-specificity Phosphatase Involved in Stat1 Dephosphorylation at Both Tyrosine and Serine Residues in Nuclei*
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 277, No. 49, Issue of December 6, pp. 47572 47580, 2002 2002 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. SHP-2 Is a Dual-specificity
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 277, No. 49, Issue of December 6, pp. 47572 47580, 2002 2002 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. SHP-2 Is a Dual-specificity
NOVEMBER 11, 2005 VOLUME 280 NUMBER 45 JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 37471
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 280, NO. 45, pp. 37471 37480, November 11, 2005 2005 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in the U.S.A. Role of the Cytokine-induced
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 280, NO. 45, pp. 37471 37480, November 11, 2005 2005 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in the U.S.A. Role of the Cytokine-induced
Supplementary Figure 1. GST pull-down analysis of the interaction of GST-cIAP1 (A, B), GSTcIAP1
 Legends Supplementary Figure 1. GST pull-down analysis of the interaction of GST- (A, B), GST mutants (B) or GST- (C) with indicated proteins. A, B, Cell lysate from untransfected HeLa cells were loaded
Legends Supplementary Figure 1. GST pull-down analysis of the interaction of GST- (A, B), GST mutants (B) or GST- (C) with indicated proteins. A, B, Cell lysate from untransfected HeLa cells were loaded
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb1864 Figure S1 Apak specifically inhibits p53 transcriptional activity. Transcription activity of p53 was measured in U2OS (p53 wild-type) and H1299 (p53 deficient) cells which were transfected
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1864 Figure S1 Apak specifically inhibits p53 transcriptional activity. Transcription activity of p53 was measured in U2OS (p53 wild-type) and H1299 (p53 deficient) cells which were transfected
Gα 13 Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Gα 13 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 80401 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 Table of Content Product
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Gα 13 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 80401 20 assays NewEast Biosciences 1 Table of Content Product
Checkpoint Kinase Activity Immunoblot Kit
 Product Manual Checkpoint Kinase Activity Immunoblot Kit Catalog Number STA- 413 20 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cdc25C is a protein phosphatase responsible
Product Manual Checkpoint Kinase Activity Immunoblot Kit Catalog Number STA- 413 20 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cdc25C is a protein phosphatase responsible
HONGKYUN KIM AND HEINZ BAUMANN* Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology, Roswell Park Cancer Institute, Buffalo, New York 14263
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Aug. 1999, p. 5326 5338 Vol. 19, No. 8 0270-7306/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Dual Signaling Role of the Protein Tyrosine
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Aug. 1999, p. 5326 5338 Vol. 19, No. 8 0270-7306/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Dual Signaling Role of the Protein Tyrosine
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Peroxiredoxin-2 and STAT3 form a redox relay for H 2 O 2 signaling Mirko C. Sobotta 1, Willy Liou 1, Sarah Stöcker 1, Deepti Talwar 1, Michael Oehler 1, Thomas Ruppert 2, Annette
Supplementary Information Peroxiredoxin-2 and STAT3 form a redox relay for H 2 O 2 signaling Mirko C. Sobotta 1, Willy Liou 1, Sarah Stöcker 1, Deepti Talwar 1, Michael Oehler 1, Thomas Ruppert 2, Annette
The Transfection Collection TCF/LEF Transient Pack Wnt / -catenin Signaling Pathway Catalog #: 79273
 Data Sheet The Transfection Collection TCF/LEF Transient Pack Wnt / -catenin Signaling Pathway Catalog #: 79273 Background The Wnt / -catenin signaling pathway controls a large and diverse set of cell
Data Sheet The Transfection Collection TCF/LEF Transient Pack Wnt / -catenin Signaling Pathway Catalog #: 79273 Background The Wnt / -catenin signaling pathway controls a large and diverse set of cell
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/429/ra54/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Dephosphorylation of the adaptor LAT and phospholipase C by SHP-1 inhibits natural killer cell cytotoxicity Omri Matalon,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/429/ra54/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Dephosphorylation of the adaptor LAT and phospholipase C by SHP-1 inhibits natural killer cell cytotoxicity Omri Matalon,
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Fig. 1. Kinetics of,,, AKT and ERK activation in BMMCs following SCF stimulation. Starved BMMCs were stimulated with 250ng/mL of SCF for the indicated time. Soluble Cell Lysates (SCLs) were
Supplemental Fig. 1. Kinetics of,,, AKT and ERK activation in BMMCs following SCF stimulation. Starved BMMCs were stimulated with 250ng/mL of SCF for the indicated time. Soluble Cell Lysates (SCLs) were
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature09732 Supplementary Figure 1: Depletion of Fbw7 results in elevated Mcl-1 abundance. a, Total thymocytes from 8-wk-old Lck-Cre/Fbw7 +/fl (Control) or Lck-Cre/Fbw7 fl/fl (Fbw7 KO) mice
doi:10.1038/nature09732 Supplementary Figure 1: Depletion of Fbw7 results in elevated Mcl-1 abundance. a, Total thymocytes from 8-wk-old Lck-Cre/Fbw7 +/fl (Control) or Lck-Cre/Fbw7 fl/fl (Fbw7 KO) mice
Data Sheet. TCF/LEF Reporter Kit Wnt / -catenin signaling pathway Catalog #: 60500
 Data Sheet TCF/LEF Reporter Kit Wnt / -catenin signaling pathway Catalog #: 60500 Background The Wnt / -catenin signaling pathway controls a large and diverse set of cell fate decisions in embryonic development,
Data Sheet TCF/LEF Reporter Kit Wnt / -catenin signaling pathway Catalog #: 60500 Background The Wnt / -catenin signaling pathway controls a large and diverse set of cell fate decisions in embryonic development,
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/5/233/ra50/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Is Essential for Toll-Like Receptor 3 Signaling Michifumi Yamashita, Saurabh Chattopadhyay,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/5/233/ra50/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Is Essential for Toll-Like Receptor 3 Signaling Michifumi Yamashita, Saurabh Chattopadhyay,
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.1583
 Acetylation by GCN5 regulates CDC6 phosphorylation in the S-phase of the cell cycle Roberta Paolinelli 1,2, Ramiro Mendoza-Maldonado 2, Anna Cereseto 1 and Mauro Giacca 2 1 Molecular Biology Laboratory,
Acetylation by GCN5 regulates CDC6 phosphorylation in the S-phase of the cell cycle Roberta Paolinelli 1,2, Ramiro Mendoza-Maldonado 2, Anna Cereseto 1 and Mauro Giacca 2 1 Molecular Biology Laboratory,
Recruitment of Grb2 to surface IgG and IgE provides antigen receptor-intrinsic costimulation to class-switched B cells
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Recruitment of Grb2 to surface IgG and IgE provides antigen receptor-intrinsic costimulation to class-switched B cells Niklas Engels, Lars Morten König, Christina Heemann, Johannes
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Recruitment of Grb2 to surface IgG and IgE provides antigen receptor-intrinsic costimulation to class-switched B cells Niklas Engels, Lars Morten König, Christina Heemann, Johannes
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 The Supplementary Information (SI) Methods Cell culture and transfections H1299, U2OS, 293, HeLa cells were maintained in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. H1299 and 293 cells were
The Supplementary Information (SI) Methods Cell culture and transfections H1299, U2OS, 293, HeLa cells were maintained in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. H1299 and 293 cells were
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Dynamic Phosphorylation of HP1 Regulates Mitotic Progression in Human Cells Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NDR1 interacts with HP1. (a) Immunoprecipitation using
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Dynamic Phosphorylation of HP1 Regulates Mitotic Progression in Human Cells Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NDR1 interacts with HP1. (a) Immunoprecipitation using
Regulation of hepcidin expression by inflammation-induced activin B
 Regulation of hepcidin expression by inflammation-induced activin B Yohei Kanamori, Makoto Sugiyama, Osamu Hashimoto, Masaru Murakami, Tohru Matsui and Masayuki Funaba Supplemental methods Liver cell separation
Regulation of hepcidin expression by inflammation-induced activin B Yohei Kanamori, Makoto Sugiyama, Osamu Hashimoto, Masaru Murakami, Tohru Matsui and Masayuki Funaba Supplemental methods Liver cell separation
Supplementary Figure 1. Intracellular distribution of the EPE peptide. HeLa cells were serum-starved (16 h, 0.1%), and treated with EPE peptide,
 Supplementary Figure 1. Intracellular distribution of the EPE peptide. HeLa cells were serum-starved (16 h, 0.1%), and treated with EPE peptide, conjugated with either TAT or Myristic acid and biotin for
Supplementary Figure 1. Intracellular distribution of the EPE peptide. HeLa cells were serum-starved (16 h, 0.1%), and treated with EPE peptide, conjugated with either TAT or Myristic acid and biotin for
Figure S1 (related to Fig. 1): The prototypical mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis is involved in cell-death of v-src-transformed cells.
 Figure S1 (related to Fig. 1): The prototypical mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis is involved in cell-death of v-src-transformed cells. (A) Non-transformed (Control cells) and v-srctransformed 3T3 cells
Figure S1 (related to Fig. 1): The prototypical mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis is involved in cell-death of v-src-transformed cells. (A) Non-transformed (Control cells) and v-srctransformed 3T3 cells
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. Color. Fig.1. Cell-Based protein phosphorylation procedure
 Cell-Based ELISA Sampler Kit for detecting phospho-erk1/2 (pthr 202 /ptyr 204 ), phospho-jnk (pthr 183 /ptyr 185 ), and phospho-p38 MAPK (pthr 180 /ptyr 182 ) in cultured cell lines adequate for 192 assays
Cell-Based ELISA Sampler Kit for detecting phospho-erk1/2 (pthr 202 /ptyr 204 ), phospho-jnk (pthr 183 /ptyr 185 ), and phospho-p38 MAPK (pthr 180 /ptyr 182 ) in cultured cell lines adequate for 192 assays
Please read manual carefully before starting experiment
 RayBio Cell-Based Human/Mouse/Rat ERK1/2, JNK, p38 MAPK Phosphorylation ELISA Sampler Kit For the semi-quantitative detection of phosphorylated human, mouse, or rat ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204), JNK (Thr183/Tyr185),
RayBio Cell-Based Human/Mouse/Rat ERK1/2, JNK, p38 MAPK Phosphorylation ELISA Sampler Kit For the semi-quantitative detection of phosphorylated human, mouse, or rat ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204), JNK (Thr183/Tyr185),
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #2 March 20, 2003
 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #2 March 20, 2003 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #2 March 20, 2003 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books, a calculator, and notes but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write
The microtubule-associated tau protein has intrinsic acetyltransferase activity. Todd J. Cohen, Dave Friedmann, Andrew W. Hwang, Ronen Marmorstein and
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION: The microtubule-associated tau protein has intrinsic acetyltransferase activity Todd J. Cohen, Dave Friedmann, Andrew W. Hwang, Ronen Marmorstein and Virginia M.Y. Lee Cohen
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION: The microtubule-associated tau protein has intrinsic acetyltransferase activity Todd J. Cohen, Dave Friedmann, Andrew W. Hwang, Ronen Marmorstein and Virginia M.Y. Lee Cohen
7.06 Problem Set #3, 2006
 7.06 Problem Set #3, 2006 1. You are studying the EGF/Ras/MAPK pathway in cultured cells. When the pathway is activated, cells are signaled to proliferate. You generate various mutants described below.
7.06 Problem Set #3, 2006 1. You are studying the EGF/Ras/MAPK pathway in cultured cells. When the pathway is activated, cells are signaled to proliferate. You generate various mutants described below.
Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of LRRK1 bind to Grb2.
 Myc- HA-Grb2 Mr(K) 105 IP HA 75 25 105 1-1163 1-595 - + - + - + 1164-1989 Blot Myc HA total lysate 75 25 Myc HA Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of bind to Grb2. COS7 cells were cotransfected
Myc- HA-Grb2 Mr(K) 105 IP HA 75 25 105 1-1163 1-595 - + - + - + 1164-1989 Blot Myc HA total lysate 75 25 Myc HA Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of bind to Grb2. COS7 cells were cotransfected
Abrogation of Interleukin-3 Dependence of Myeloid Cells by the v-src Oncogene Requires SH2 and SH3 Domains Which Specify Activation of STATs
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, June 1997, p. 3295 3304 Vol. 17, No. 6 0270-7306/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Abrogation of Interleukin-3 Dependence of Myeloid Cells by
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, June 1997, p. 3295 3304 Vol. 17, No. 6 0270-7306/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Abrogation of Interleukin-3 Dependence of Myeloid Cells by
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/304/ra104/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Lysine Methylation Promotes VEGFR-2 Activation and Angiogenesis Edward J. Hartsough, Rosana D. Meyer, Vipul Chitalia,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/304/ra104/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Lysine Methylation Promotes VEGFR-2 Activation and Angiogenesis Edward J. Hartsough, Rosana D. Meyer, Vipul Chitalia,
Supplementary Information for Structural and Mechanistic Insights into Cooperative Assembly of Dimeric Notch Transcription Complexes
 Supplementary Information for Structural and Mechanistic Insights into Cooperative Assembly of Dimeric Notch Transcription Complexes Kelly L. Arnett 1,2, Matthew Hass 3, Debbie G. McArthur 1,2, Ma. Xenia
Supplementary Information for Structural and Mechanistic Insights into Cooperative Assembly of Dimeric Notch Transcription Complexes Kelly L. Arnett 1,2, Matthew Hass 3, Debbie G. McArthur 1,2, Ma. Xenia
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Zranb1 gene targeting.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Zranb1 gene targeting. (a) Schematic picture of Zranb1 gene targeting using an FRT-LoxP vector, showing the first 6 exons of Zranb1 gene (exons 7-9 are not shown). Targeted mice
Supplementary Figure 1 Zranb1 gene targeting. (a) Schematic picture of Zranb1 gene targeting using an FRT-LoxP vector, showing the first 6 exons of Zranb1 gene (exons 7-9 are not shown). Targeted mice
Protocol for induction of expression and cell lysate production
 Protocol for induction of expression and cell lysate production AV-04 Doxycyclin induction and cell lysate 1.0 Introduction / Description This method is intended for the treatment of the previously transfected
Protocol for induction of expression and cell lysate production AV-04 Doxycyclin induction and cell lysate 1.0 Introduction / Description This method is intended for the treatment of the previously transfected
Supplementary data. sienigma. F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM. a-p53
 Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
TRIM31 is recruited to mitochondria after infection with SeV.
 Supplementary Figure 1 TRIM31 is recruited to mitochondria after infection with SeV. (a) Confocal microscopy of TRIM31-GFP transfected into HEK293T cells for 24 h followed with SeV infection for 6 h. MitoTracker
Supplementary Figure 1 TRIM31 is recruited to mitochondria after infection with SeV. (a) Confocal microscopy of TRIM31-GFP transfected into HEK293T cells for 24 h followed with SeV infection for 6 h. MitoTracker
High-throughput Screening Assay Development for Small Molecule Inhibitor(s) of PIAS1
 High-throughput Screening Assay evelopment for Small Molecule Inhibitor(s) of PIAS1 Vipul Madahar, Vicente Nunez, Yang Song, and Jiayu Liao epartment of Bioengineering, University of California Riverside,
High-throughput Screening Assay evelopment for Small Molecule Inhibitor(s) of PIAS1 Vipul Madahar, Vicente Nunez, Yang Song, and Jiayu Liao epartment of Bioengineering, University of California Riverside,
Spironolactone ameliorates PIT1-dependent vascular osteoinduction in klotho-hypomorphic mice
 Spironolactone ameliorates PIT1-dependent vascular osteoinduction in klotho-hypomorphic mice Supplementary Material Supplementary Methods Materials Spironolactone, aldosterone and β-glycerophosphate were
Spironolactone ameliorates PIT1-dependent vascular osteoinduction in klotho-hypomorphic mice Supplementary Material Supplementary Methods Materials Spironolactone, aldosterone and β-glycerophosphate were
FIGURE LEGENDS, ONLINE SUPPLEMENT
 Online Supplement: Sierra O and Towler DA: Runx2 Transactivation Mediated by MINT, the Msx2- Interacting Nuclear Target, Requires Homeodomain Interacting Protein Kinase 3 ME-10-0029_v2 FIGURE LEGENDS,
Online Supplement: Sierra O and Towler DA: Runx2 Transactivation Mediated by MINT, the Msx2- Interacting Nuclear Target, Requires Homeodomain Interacting Protein Kinase 3 ME-10-0029_v2 FIGURE LEGENDS,
Gα i Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Gα i Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number 80301 20 assays NewEast Biosciences, Inc 1 Table of Content Product
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Gα i Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number 80301 20 assays NewEast Biosciences, Inc 1 Table of Content Product
STAT5b, a Mediator of Synergism between c-src and the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor*
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 278, No. 3, Issue of January 17, pp. 1671 1679, 2003 2003 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. STAT5b, a Mediator
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 278, No. 3, Issue of January 17, pp. 1671 1679, 2003 2003 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. STAT5b, a Mediator
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2116 Figure S1 CDK phosphorylation of EZH2 in cells. (a) Comparison of candidate CDK phosphorylation sites on EZH2 with known CDK substrates by multiple sequence alignments. (b) CDK1 and
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2116 Figure S1 CDK phosphorylation of EZH2 in cells. (a) Comparison of candidate CDK phosphorylation sites on EZH2 with known CDK substrates by multiple sequence alignments. (b) CDK1 and
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Intrinsic protein-protein interaction mediated and chaperonin assisted sequential assembly of a stable Bardet Biedl syndome protein complex, the BBSome * Qihong Zhang 1#, Dahai
Supplemental Information Intrinsic protein-protein interaction mediated and chaperonin assisted sequential assembly of a stable Bardet Biedl syndome protein complex, the BBSome * Qihong Zhang 1#, Dahai
Supplemental Materials and Methods
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assay Cells were lysed with NETN buffer (20 mm Tris-HCl, ph 8.0, 0 mm NaCl, 1 mm EDT, 0.5% Nonidet P-40) containing 50 mm β-glycerophosphate,
Supplemental Materials and Methods Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assay Cells were lysed with NETN buffer (20 mm Tris-HCl, ph 8.0, 0 mm NaCl, 1 mm EDT, 0.5% Nonidet P-40) containing 50 mm β-glycerophosphate,
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. MEK Activity Assay Kit. Product Code CS0490 Storage Temperature 20 C
 MEK Activity Assay Kit Product Code CS0490 Storage Temperature 20 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description The MAP kinase kinases (MAPKK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, also termed MEK) are a
MEK Activity Assay Kit Product Code CS0490 Storage Temperature 20 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description The MAP kinase kinases (MAPKK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase, also termed MEK) are a
96-well Checkpoint Kinase Activity Assay Kit
 Product Manual 96-well Checkpoint Kinase Activity Assay Kit Catalog Number STA-414 STA-414-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cdc25C is a
Product Manual 96-well Checkpoint Kinase Activity Assay Kit Catalog Number STA-414 STA-414-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cdc25C is a
ASPP1 Fw GGTTGGGAATCCACGTGTTG ASPP1 Rv GCCATATCTTGGAGCTCTGAGAG
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids: the following plasmids were used in the supplementary data: pwzl-myc- Lats2 (Aylon et al, 2006), pretrosuper-vector and pretrosuper-shp53 (generous gift of
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids: the following plasmids were used in the supplementary data: pwzl-myc- Lats2 (Aylon et al, 2006), pretrosuper-vector and pretrosuper-shp53 (generous gift of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 (Supplementary Methods and Materials) GST pull-down assay GST-fusion proteins Fe65 365-533, and Fe65 538-700 were expressed in BL21 bacterial cells and purified with glutathione-agarose beads (Sigma).
(Supplementary Methods and Materials) GST pull-down assay GST-fusion proteins Fe65 365-533, and Fe65 538-700 were expressed in BL21 bacterial cells and purified with glutathione-agarose beads (Sigma).
14_integrins_EGFR
 α1 Integrin α1 -/- fibroblasts from integrin α1 knockout animals Figure S1. Serum-starved fibroblasts from α -/- 1 and +/+ mice were stimulated with 10% FBS for 30 min. (FBS) or plated on collagen I (CI)
α1 Integrin α1 -/- fibroblasts from integrin α1 knockout animals Figure S1. Serum-starved fibroblasts from α -/- 1 and +/+ mice were stimulated with 10% FBS for 30 min. (FBS) or plated on collagen I (CI)
MAP Kinase (ERK1/2) Activity Assay Kit
 MAP Kinase (ERK/2) Activity Assay Kit For 96 tests Cat. No. SGT45 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures USA & Canada Phone: +(800) 437-7500 Fax: + (909) 676-9209 Europe +44 (0) 23
MAP Kinase (ERK/2) Activity Assay Kit For 96 tests Cat. No. SGT45 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures USA & Canada Phone: +(800) 437-7500 Fax: + (909) 676-9209 Europe +44 (0) 23
MEK1/2 (MAPK Kinase) Activity Assay Kit
 MEK1/2 (MAPK Kinase) Activity Assay Kit For 96 tests Cat. No. SGT440 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures USA & Canada Phone: +1(800) 437-7500 Fax: +1 (951) 676-9209 Europe +44 (0)
MEK1/2 (MAPK Kinase) Activity Assay Kit For 96 tests Cat. No. SGT440 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures USA & Canada Phone: +1(800) 437-7500 Fax: +1 (951) 676-9209 Europe +44 (0)
Universal Tyrosine Phosphatase Assay Kit
 #MK411 v.02.04 Table of contents 1. Description... 2 2. Principle... 2 3. Features... 2 4. Kit components... 2 5. Reagents and instruments not supplied in this kit... 3 6. Storage... 3 7. Assay characteristics...
#MK411 v.02.04 Table of contents 1. Description... 2 2. Principle... 2 3. Features... 2 4. Kit components... 2 5. Reagents and instruments not supplied in this kit... 3 6. Storage... 3 7. Assay characteristics...
Analysing protein protein interactions using a GST-fusion protein to pull down the interacting target from the cell lysate Hong Wang and Xin Zeng
 Analysing protein protein interactions using a GST-fusion protein to pull down the interacting target from the cell lysate Hong Wang and Xin Zeng Department of Molecular Genetics, Biochemistry and Microbiology,
Analysing protein protein interactions using a GST-fusion protein to pull down the interacting target from the cell lysate Hong Wang and Xin Zeng Department of Molecular Genetics, Biochemistry and Microbiology,
INVESTIGATING DYNAMICS OF THE STAT3 AND C/EBPβ PATHWAYS UPON STIMULATION BY INFLAMMATORY CYTOKINES
 INVESTIGATING DYNAMICS OF THE STAT3 AND C/EBPβ PATHWAYS UPON STIMULATION BY INFLAMMATORY CYTOKINES A Senior Scholars Thesis by PENG CHENG Submitted to the Office of Undergraduate Research Texas A&M University
INVESTIGATING DYNAMICS OF THE STAT3 AND C/EBPβ PATHWAYS UPON STIMULATION BY INFLAMMATORY CYTOKINES A Senior Scholars Thesis by PENG CHENG Submitted to the Office of Undergraduate Research Texas A&M University
Supplemental Online Material. The mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line #10 derived from β-arrestin1 -/- -β-arrestin2 -/-
 #1074683s 1 Supplemental Online Material Materials and Methods Cell lines and tissue culture The mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line #10 derived from β-arrestin1 -/- -β-arrestin2 -/- knock-out animals
#1074683s 1 Supplemental Online Material Materials and Methods Cell lines and tissue culture The mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line #10 derived from β-arrestin1 -/- -β-arrestin2 -/- knock-out animals
Cdc42 Activation Assay Kit
 A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Cdc42 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 80701 20 assays 1 Table of Content Product Description 3 Assay
A helping hand for your research Product Manual Configuration-specific Monoclonal Antibody Based Cdc42 Activation Assay Kit Catalog Number: 80701 20 assays 1 Table of Content Product Description 3 Assay
Supplementary Figure 1. α-synuclein is truncated in PD and LBD brains. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.
 Supplementary Figure 1 α-synuclein is truncated in PD and LBD brains. (a) Specificity of anti-n103 antibody. Anti-N103 antibody was coated on an ELISA plate and different concentrations of full-length
Supplementary Figure 1 α-synuclein is truncated in PD and LBD brains. (a) Specificity of anti-n103 antibody. Anti-N103 antibody was coated on an ELISA plate and different concentrations of full-length
CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration
 /, Supplementary Advance Publications Materials 2016 CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1: In ECs CD93 silencing
/, Supplementary Advance Publications Materials 2016 CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1: In ECs CD93 silencing
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. JNK 1&2 Activity Assay Kit. Product Number CS0380 Storage Temperature 20 C
 JNK 1&2 Activity Assay Kit Product Number CS0380 Storage Temperature 20 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description The c-jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs), also known as stress activated protein kinases (SAPKs),
JNK 1&2 Activity Assay Kit Product Number CS0380 Storage Temperature 20 C TECHNICAL BULLETIN Product Description The c-jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs), also known as stress activated protein kinases (SAPKs),
Development of an AlphaLISA MEK1 Kinase Assay Using Full-Length ERK2 Substrate
 TECHNICAL NOTE Development of an AlphaLISA MEK1 Kinase Assay Using Full-Length ERK2 Substrate AlphaLISA Technology Author: Jeanine Hinterneder, PhD PerkinElmer, Inc. Hopkinton, MA Introduction The mitogen-activated
TECHNICAL NOTE Development of an AlphaLISA MEK1 Kinase Assay Using Full-Length ERK2 Substrate AlphaLISA Technology Author: Jeanine Hinterneder, PhD PerkinElmer, Inc. Hopkinton, MA Introduction The mitogen-activated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
Toll Receptor-Mediated Hippo Signaling Controls Innate Immunity in Drosophila
 Cell Supplemental Information Toll Receptor-Mediated Hippo Signaling Controls Innate Immunity in Drosophila Bo Liu, Yonggang Zheng, Feng Yin, Jianzhong Yu, Neal Silverman, and Duojia Pan Supplemental Experimental
Cell Supplemental Information Toll Receptor-Mediated Hippo Signaling Controls Innate Immunity in Drosophila Bo Liu, Yonggang Zheng, Feng Yin, Jianzhong Yu, Neal Silverman, and Duojia Pan Supplemental Experimental
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Supplementary Methods Cell synchronization. For synchronized cell growth, thymidine was added to 30% confluent U2OS cells to a final concentration of 2.5mM. Cells were incubated
Supplementary Material Supplementary Methods Cell synchronization. For synchronized cell growth, thymidine was added to 30% confluent U2OS cells to a final concentration of 2.5mM. Cells were incubated
used at a final concentration of 5 ng/ml. Rabbit anti-bim and mouse anti-mkp2 antibodies were
 1 Supplemental Methods Reagents and chemicals: TGFβ was a generous gift from Genzyme Inc. (Cambridge, MA) and was used at a final concentration of 5 ng/ml. Rabbit anti-bim and mouse anti-mkp2 antibodies
1 Supplemental Methods Reagents and chemicals: TGFβ was a generous gift from Genzyme Inc. (Cambridge, MA) and was used at a final concentration of 5 ng/ml. Rabbit anti-bim and mouse anti-mkp2 antibodies
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure 1. PKM2 interacts with MLC2 in cytokinesis. a, U87, U87/EGFRvIII, and HeLa cells in cytokinesis were immunostained with DAPI and an anti-pkm2 antibody. Thirty
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure 1. PKM2 interacts with MLC2 in cytokinesis. a, U87, U87/EGFRvIII, and HeLa cells in cytokinesis were immunostained with DAPI and an anti-pkm2 antibody. Thirty
Molecular Characterization of Specific Interactions between SHP-2 Phosphatase and JAK Tyrosine Kinases*
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 272, No. 2, Issue of January 10, pp. 1032 1037, 1997 1997 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Molecular Characterization
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 272, No. 2, Issue of January 10, pp. 1032 1037, 1997 1997 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Molecular Characterization
LINGO-1, A TRANSMEMBRANE SIGNALING PROTEIN, INHIBITS OLIGODENDROCYTE DIFFERENTIATION AND MYELINATION THROUGH INTERCELLULAR SELF- INTERACTIONS.
 Supplemental Data: LINGO-1, A TRANSMEMBRANE SIGNALING PROTEIN, INHIBITS OLIGODENDROCYTE DIFFERENTIATION AND MYELINATION THROUGH INTERCELLULAR SELF- INTERACTIONS. Scott Jepson, Bryan Vought, Christian H.
Supplemental Data: LINGO-1, A TRANSMEMBRANE SIGNALING PROTEIN, INHIBITS OLIGODENDROCYTE DIFFERENTIATION AND MYELINATION THROUGH INTERCELLULAR SELF- INTERACTIONS. Scott Jepson, Bryan Vought, Christian H.
Flag-Rac Vector V12 V12 N17 C40. Vector C40 pakt (T308) Akt1. Myc-DN-PAK1 (N-SP)
 a b FlagRac FlagRac V2 V2 N7 C4 V2 V2 N7 C4 p (T38) p (S99, S24) p Flag (Rac) NIH 3T3 COS c +Serum p (T38) MycDN (NSP) Mycp27 3 6 2 3 6 2 3 6 2 min p Myc ( or p27) Figure S (a) Effects of Rac mutants on
a b FlagRac FlagRac V2 V2 N7 C4 V2 V2 N7 C4 p (T38) p (S99, S24) p Flag (Rac) NIH 3T3 COS c +Serum p (T38) MycDN (NSP) Mycp27 3 6 2 3 6 2 3 6 2 min p Myc ( or p27) Figure S (a) Effects of Rac mutants on
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Su et al. 10.1073/pnas.1211604110 SI Materials and Methods Cell Culture and Plasmids. Tera-1 and Tera-2 cells (ATCC: HTB- 105/106) were maintained in McCoy s 5A medium with 15% FBS
Supporting Information Su et al. 10.1073/pnas.1211604110 SI Materials and Methods Cell Culture and Plasmids. Tera-1 and Tera-2 cells (ATCC: HTB- 105/106) were maintained in McCoy s 5A medium with 15% FBS
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies and sirna The antibodies against BAF170, BAF155, BAF60a, BAF57 and BAF53 were purchased from Santa Cruz (TX), and the antibodies
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies and sirna The antibodies against BAF170, BAF155, BAF60a, BAF57 and BAF53 were purchased from Santa Cruz (TX), and the antibodies
The retroviral vectors encoding WT human SIRT1 or a mutant of SIRT in which a
 Supporting online material Constructs The retroviral vectors encoding WT human SIRT1 or a mutant of SIRT in which a critical histidine in the deacetylase domain of SIRT1 has been replaced by a tyrosine
Supporting online material Constructs The retroviral vectors encoding WT human SIRT1 or a mutant of SIRT in which a critical histidine in the deacetylase domain of SIRT1 has been replaced by a tyrosine
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3363 Supplementary Figure 1 Several WNTs bind to the extracellular domains of PKD1. (a) HEK293T cells were co-transfected with indicated plasmids. Flag-tagged proteins were immunoprecipiated
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3363 Supplementary Figure 1 Several WNTs bind to the extracellular domains of PKD1. (a) HEK293T cells were co-transfected with indicated plasmids. Flag-tagged proteins were immunoprecipiated
Data Sheet. Application Monitor glucocorticoid signaling pathway activity. Screen activators or inhibitors of the glucocorticoid signaling pathway.
 Data Sheet GAL4 Reporter Kit (Glucocorticoid Receptor Pathway) Catalog #: w70533 Background The glucocorticoid signaling pathway plays an important role in development, fluid homeostasis, cognition, immune
Data Sheet GAL4 Reporter Kit (Glucocorticoid Receptor Pathway) Catalog #: w70533 Background The glucocorticoid signaling pathway plays an important role in development, fluid homeostasis, cognition, immune
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.3554
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: Generation, purification and characterization of recombinant mouse IL-35 (ril-35). High-Five insect cells expressing high levels of the bicistronic
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1: Generation, purification and characterization of recombinant mouse IL-35 (ril-35). High-Five insect cells expressing high levels of the bicistronic
Please read manual carefully before starting experiment
 RayBio Cell Based Human STAT5 (Tyr694) Phosphorylation ELISA Kit For the semi quantitative detection of phosphorylated human STAT5 (Tyr694) and total STAT5 in adherent whole cell lines. User Manual (Revised
RayBio Cell Based Human STAT5 (Tyr694) Phosphorylation ELISA Kit For the semi quantitative detection of phosphorylated human STAT5 (Tyr694) and total STAT5 in adherent whole cell lines. User Manual (Revised
Data Supplement Plasmin Triggers Cytokine Induction in Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages
 Data Supplement Plasmin Triggers Cytokine Induction in Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages Qun Li, Yves Laumonnier, Tatiana Syrovets, and Thomas Simmet Methods Antibodies and Reagents Antibodies for immunoblotting:
Data Supplement Plasmin Triggers Cytokine Induction in Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages Qun Li, Yves Laumonnier, Tatiana Syrovets, and Thomas Simmet Methods Antibodies and Reagents Antibodies for immunoblotting:
transcription and the promoter occupancy of Smad proteins. (A) HepG2 cells were co-transfected with the wwp-luc reporter, and FLAG-tagged FHL1,
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1 FHL-mediated TGFβ-responsive reporter transcription and the promoter occupancy of Smad proteins. (A) HepG2 cells were co-transfected
Supplementary Data Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1 FHL-mediated TGFβ-responsive reporter transcription and the promoter occupancy of Smad proteins. (A) HepG2 cells were co-transfected
I B Kinase (IKK ) Regulation of IKK Kinase Activity
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, May 2000, p. 3655 3666 Vol. 20, No. 10 0270-7306/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. I B Kinase (IKK ) Regulation of IKK
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, May 2000, p. 3655 3666 Vol. 20, No. 10 0270-7306/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. I B Kinase (IKK ) Regulation of IKK
/08/$15.00/0 Molecular Endocrinology 22(10): Copyright 2008 by The Endocrine Society doi: /me
 0888-8809/08/$15.00/0 Molecular Endocrinology 22(10):2307 2321 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2008 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/me.2008-0055 Prolactin and ErbB4/HER4 Signaling Interact via Janus
0888-8809/08/$15.00/0 Molecular Endocrinology 22(10):2307 2321 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2008 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/me.2008-0055 Prolactin and ErbB4/HER4 Signaling Interact via Janus
Rabbit (polyclonal) Anti-IRS-1 [ps 616 ] Phosphospecific Antibody, Unconjugated
![Rabbit (polyclonal) Anti-IRS-1 [ps 616 ] Phosphospecific Antibody, Unconjugated Rabbit (polyclonal) Anti-IRS-1 [ps 616 ] Phosphospecific Antibody, Unconjugated](/thumbs/82/85710283.jpg) Rabbit (polyclonal) Anti-IRS-1 [ps 616 ] Phosphospecific Antibody, Unconjugated PRODUCT ANALYSIS SHEET Catalog Number: Lot Number: Volume: 44-550G (10 mini-blot size) See product label 100 μl Form of Antibody:
Rabbit (polyclonal) Anti-IRS-1 [ps 616 ] Phosphospecific Antibody, Unconjugated PRODUCT ANALYSIS SHEET Catalog Number: Lot Number: Volume: 44-550G (10 mini-blot size) See product label 100 μl Form of Antibody:
