Supplementary Figure 1. Screening for monoclonal antibodies against GluA1 by immunoblotting.
|
|
|
- Angelina Lane
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
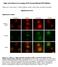
1 Supplementary Figure 1 Screening for monoclonal antibodies against GluA1 by immunoblotting. Hippocampal extract was subjected to western blotting with the hybridoma supernatants of candidate monoclonal antibodies against GluA1. Positive antibodies are labeled with an asterisk. First upper left lane was blotted with an anti- GluA1 monoclonal antibody (Millipore, C3T, raised against the GluA1 cytoplasmic tail: anti-glua1-ct). Second upper left lane was blotted with an anti-gfp monoclonal antibody (anti-gfp). To check the weak positive samples, we also examined Z9131 and Z9141 in staining shown in figure 1c. To test the negative samples, we also examined Z in figure 1c.
2 Supplementary Figure 2 Basic conditions of the CALI experiment with Z9139-eosin in vitro and effect of NASPM. a. Power and time dependence of light irradiation on the CALI effect with Z9139-eosin in vitro. Glutamate puff-induced responses were obtained in GluA1 expressing CHO cells with the indicated combinations of time and power for CALI. The data for 0 mw and 7.5 mw/cm 2, 1 min were the same as in Figure 2a. F(4,31)=5.618, *p<0.001, **p<0.05 and p=0.296 in 2.5mW/cm 2-1min vs 0mW (one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis with the Fisher s PLSD test). n=5, 7, 6, 8 and 8 cells for 0mW, 2.5mW-1min, 5mW-1min, 7.5mW-1min and 7.5mW-0.5min, respectively. b. A saturating concentration of NASPM reduced the synaptic AMPA receptor-mediated currents in hippocampal primary cultures ~50%. AMPA receptor-mediated synaptic currents after NASPM application at different concentrations; values are the ratio of the current after to before NASPM application. Note that the effect of a saturating concentration (20 M) of NASPM on synaptic AMPA receptor currents was examined in the experiment in Figure 3d. F(5,49)=9.805, *p<0.001, **p<0.01 and p=0.273 in 0.01 vs 0 M (one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc analysis with the Fisher s PLSD test). n=11, 7, 8, 11, 9 and 9 cells for 0 M, 0.01 M, 0.1 M, 0.5 M, 5 M and 20 M, respectively. n.s. indicates no significance.
3 Supplementary Figure 3 Endosomal trafficking is not affected by CALI with Z9139-eosin. Fluorescence images of Alexa488-transferrin before and after recycling for 30 min with or without CALI using Z9139- eosin. The relative fluorescence intensity was examined before and after recycling in the dendrites and cell body (n=30 regions of interest [ROIs]). ROIs were obtained from 3 independent experiments. Scale bar indicates 5 m. t(52.769)=1.002, p=0.321 (unpaired two-tailed t-test). n.s. indicates no significance.
4 Supplementary Figure 4 Basic properties of the IA task-related experiment. a. Expression of GluA1 cytoplasmic tail in the hippocampus prevents the acquisition of IA memory. Latency period for re-entering the dark box of IA-trained mice expressing GFP or GFP-ctail (cytoplasmic terminus of GluA1: a peptide that blocks synaptic GluA1 delivery) in the CA1 region of the dorsal hippocampus. The latency period for re-entering the dark box was significantly shorter in the GFP-ctail-expressing animals than in the GFP-expressing ones. *p<0.001 (Mann-Whitney U test). n=9 and 7 animals for GFP and c-tail, respectively. b. Membrane properties of the examined neurons (n=14 cells shown in Figure 4b) in slices with or without IA conditioning. t(26)=1.127, p =0.270 in Cm, t(26)=0.028, p =0.781 in Rm and t(26)=0.139, p =0.891 in Ra (unpaired two-tailed t-test). n.s. indicates no significance.
5 Supplementary Figure 5 Infusion of Z9139 into the hippocampus in vivo. a. (Left) Bright field image of a brain slice including the hippocampus obtained from an animal in which a cannula was implanted. (Right) Location of the cannula labeled with DiI. b. Distribution of injected Alexa546-labeled Z9139 in the hippocampus of mice in which a cannula was implanted. To visualize the Z9139 antibody, it was labeled with Alexa546. Z9139-Alexa546 was bilaterally injected at the same stereotaxic coordinates. After 7.5 hours (the same duration as in the in vivo CALI experiment), the mice were fixed by perfusion, and the brain was removed and sliced (100 m) on a microtome. The coordinates m are the distance from the anterior end of the hippocampus. The intensity of the Alexa-546 signal was plotted along the CA1 region (yellow dashed line) in the right panels. Scale bar indicates 200 m. The Z9139 antibody diffused approximately 400 m laterally and 200 m sagittally in the CA1 region. c. Quantitative analysis of the alexa546-labeled Z9139 diffusion using the slices at 1000 and 1100 m obtained from 4 animals. d. Location of whole-cell recordings after in vivo CALI. Right panel is an enlarged view of the red box in the left panel. Yellow box indicates the position of the light cannula, determined by the injury in the cortex. We performed whole-cell patch clamp experiments (Figures 4e, 5b) within the white box, which was 150 m bilaterally, from just under the cannula (asterisk) along the CA1 region. Scale bars are 1 mm (left panel) and 150 m (right panel).
6 Supplementary Figure 6 in vivo CALI with Z9139-eosin under different conditions. a. Power and time dependence of the laser irradiation on the in vivo CALI effect. Latency for re-entering the dark box after the IA task in Z9139-eosin-treated animals with CALI was measured under the indicated conditions. The data for 0 mw and 60 mw, 2 min were same as in Figure 4c. *p<0.005, p=0.188 in 60mW-1min and p=0.854 in 30mW-2min vs 0mW (Kraskal-Wails test by post hoc analysis with Dunne s test). n=6, 8, 6 and 10 animals for 0mW, 60mW-1min, 30mW-2min and 60mW-2min, respectively. n.s. indicates no significance. b. The in vivo CALI effect with Z9139-eosin was retained for 1 week. The latency period for re-entering the dark box of IA-trained mice 1 week after treatment with or without CALI by Z9139-eosin. *p<0.05 (Mann-Whitney U test). n=11 and 15 animals for CALI- and CALI+, respectively. c. In vivo CALI with Z9139-eosin induced fear memory erasure in 8-week-old ICR mice. Eight-week-old ICR mice were subjected to in vivo CALI with Z9139-eosin. The experimental conditions were same as those used for 4-week-old ICR mice, shown in Figure 4c. *p<0.005 in Z9139 and p=0.852 in anti-myc (Mann-Whitney U test). n=6, 8, 7 nad 8 animals for Myc CALI-, Myc CALI+, Z9139 CALI- and Z9139 CALI+, respectively. n.s. indicates no significance.
7 Supplementary Figure 7 In vivo CALI with Z9139-eosin did not induce acute damage in memory-erased animals. Acute effect of in vivo CALI with Z9139-eosin was examined by re-conditioning 30 min after in vivo CALI. We reconditioned the mice whose IA memory we had erased by in vivo CALI with Z9139-eosin (IA test 1 & re-cond.) and tested them by IA test 2. Latencies for re-entering the dark box after the IA task in Z9139-eosin-treated animals without or with (IA test 1) CALI and in mice subjected to re-conditioning after Z9139-CALI (IA test 2). n=5 (CALI-) and n=8 (IA test1 and test2) animals. Data were analyzed by Kraskal-Wails test by post hoc analysis with Dunne s test. *p<0.01 vs CALI- and p=0.352 in IA test2 vs CALI-. n.s. indicates no significance.
8 Supplementary Figure 8 Specificity of in vivo CALI with Z9139-eosin for GluA1 homomeric receptors. a. GluA1 homomers were not detectable in synapses before learning. Responses at the hippocampal CA3-CA1 synapses in the acute brain slices obtained from IA-trained or untrained animals with or without NASPM. Average AMPA/NMDA ratio with or without NASPM before and after learning. t(18)=2.662, *p<0.05 in 1hr after learning and t(14)=0.667, p=0.515 in before learning (unpaired two-tailed t-test). n=8, 8, 9 and 11 cells for before learning DW, before learning NASPM, after learning DW and after learning NASPM, respectively. b. In vivo CALI with Z9139-eosin did not inactivate the GluA1 homomer-unrelated AMPA response. Responses at hippocampal CA3-CA1 synapses in the acute brain slices obtained from IA-untrained animals with or without in vivo CALI. Average AMPA/NMDA ratio with or without in vivo CALI. t(12)=0.388, p=0.705 (unpaired two-tailed t-test). n=8 cells, respectively. In Supplementary Figure 8a, the results of DW(before learning), NASPM(before learning), DW(after learning) and NASPM(after learning) were obtained from 6, 3, 5 and 3 animals, respectively. In Supplementary Figure 8b, the results of CALI- and CALI+ were obtained from 4 animals, respectively. n.s. indicates no significance.
9 Supplementary Figure 9 Re-learning of the IA task increased the synaptic delivery of homomeric GluA1. Synaptic responses at the hippocampal CA3-CA1 synapses in acute brain slices obtained from animals with or without reconditioning 0.5 h or 24 h after in vivo CALI. Average rectification index at hippocampal CA3-CA1 synapses with or without re-conditioning after in vivo CALI. t(14)=2.650, *p<0.05 in 24hr and t(15)=1.427, p=0.174 in 0.5hr (unpaired twotailed t-test). n=8, 9, 7 and 9 cells for 0.5hr re-cond-, 0.5hr re-cond+, 24hr re-cond- and 24hr re-cond+, respectively. The results of 0.5hr(re-cond-), 0.5hr(re-cond+), 24hr(re-cond-) and 24hr(re-cond+) were obtained from 3, 4, 4 and 3 animals, respectively. n.s. indicates no significance.
10 Supplementary Figure 10 Spatial specificity of in vivo CALI with Z9139-eosin. a. Expression of GluA1 cytoplasmic tail in the auditory cortex did not prevent the acquisition of IA memory. Latency period for re-entering the dark box of IA-trained mice expressing GFP or GFP-ctail in the auditory cortex. p= n=5 and 6 animals for GFP and c-tail, respectively. b. In vivo CALI with Z9139-eosin did not erase hippocampus-dependent IA fear memory. Latency period for re-entering the dark box of IA-trained mice with or without in vivo CALI. p= n=9 and 11 animals for CALI- and CALI+, respectively. Data were analyzed by Mann-Whitney U test. n.s. indicates no significance.
11 Supplementary Figure 11 Full-length of western blot by Z9139, anti-glua2, anti-glua3 and anti-actin antibody Full length immunoblots shown in Figure 1e. In GluA3 blots, asterisk indicates three lanes which was used in Figure 1e.
12 Supplementary Figure 12 Full-length of western blot by anti-arc and anti-gapdh antibodies. Full length immunoblots shown in Figure 4g. In GAPDH blots, asterisk indicates two lanes which was used in Figure 4g.
Stargazin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through adaptor protein. complexes during long term depression
 Supplementary Information Stargazin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through adaptor protein complexes during long term depression Shinji Matsuda, Wataru Kakegawa, Timotheus Budisantoso, Toshihiro Nomura,
Supplementary Information Stargazin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through adaptor protein complexes during long term depression Shinji Matsuda, Wataru Kakegawa, Timotheus Budisantoso, Toshihiro Nomura,
Supplemental figures (1-9) Gu et al. ADF/Cofilin-Mediated Actin Dynamics Regulate AMPA Receptor Trafficking during Synaptic Plasticity
 Supplemental figures (1-9) Gu et al. ADF/Cofilin-Mediated Actin Dynamics Regulate AMPA Receptor Trafficking during Synaptic Plasticity Supplemental figure 1. The quantification method to determine the
Supplemental figures (1-9) Gu et al. ADF/Cofilin-Mediated Actin Dynamics Regulate AMPA Receptor Trafficking during Synaptic Plasticity Supplemental figure 1. The quantification method to determine the
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 PCR-genotyping of the three mouse models used in this study and controls for behavioral experiments after semi-chronic Pten inhibition. a-c. DNA from App/Psen1 (a), Pten tg (b) and
Supplementary Figure 1 PCR-genotyping of the three mouse models used in this study and controls for behavioral experiments after semi-chronic Pten inhibition. a-c. DNA from App/Psen1 (a), Pten tg (b) and
Supplementary Figure 1. APP cleavage assay. HEK293 cells were transfected with various
 Supplementary Figure 1. APP cleavage assay. HEK293 cells were transfected with various GST-tagged N-terminal truncated APP fragments including GST-APP full-length (FL), APP (123-695), APP (189-695), or
Supplementary Figure 1. APP cleavage assay. HEK293 cells were transfected with various GST-tagged N-terminal truncated APP fragments including GST-APP full-length (FL), APP (123-695), APP (189-695), or
LiveReceptor AMPAR <Endogenous AMPAR Labeling Reagent>
 9-7 Hongo 2-Chome, Bunkyo-Ku Tokyo 113-0033, Japan LiveReceptor AMPAR Product Background Neurotransmitter receptors including glutamate receptors and GABA receptors
9-7 Hongo 2-Chome, Bunkyo-Ku Tokyo 113-0033, Japan LiveReceptor AMPAR Product Background Neurotransmitter receptors including glutamate receptors and GABA receptors
DCLK-immunopositive. Bars, 100 µm for B, 50 µm for C.
 Supplementary Figure S1. Characterization of rabbit polyclonal anti-dclk antibody. (A) Immunoblotting of COS7 cells transfected with DCLK1-GFP and DCLK2-GFP expression plasmids probed with anti-dclk antibody
Supplementary Figure S1. Characterization of rabbit polyclonal anti-dclk antibody. (A) Immunoblotting of COS7 cells transfected with DCLK1-GFP and DCLK2-GFP expression plasmids probed with anti-dclk antibody
Supplementary Figures and Legends.
 Supplementary Figures and Legends. Supplementary Figure 1: Impact of injury on Rb1 and PPARϒ expression. Following ipsilateral axotomy injury, adult DRG expression of Rb1 mrna declined (*p
Supplementary Figures and Legends. Supplementary Figure 1: Impact of injury on Rb1 and PPARϒ expression. Following ipsilateral axotomy injury, adult DRG expression of Rb1 mrna declined (*p
Acoustically targeted chemogenetics for the non-invasive control of neural circuits
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-018-0258-2 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Acoustically targeted chemogenetics for the non-invasive control of neural
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-018-0258-2 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Acoustically targeted chemogenetics for the non-invasive control of neural
Supplementary Figure 1. α-synuclein is truncated in PD and LBD brains. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.
 Supplementary Figure 1 α-synuclein is truncated in PD and LBD brains. (a) Specificity of anti-n103 antibody. Anti-N103 antibody was coated on an ELISA plate and different concentrations of full-length
Supplementary Figure 1 α-synuclein is truncated in PD and LBD brains. (a) Specificity of anti-n103 antibody. Anti-N103 antibody was coated on an ELISA plate and different concentrations of full-length
To examine the silencing effects of Celsr3 shrna, we co transfected 293T cells with expression
 Supplemental figures Supplemental Figure. 1. Silencing expression of Celsr3 by shrna. To examine the silencing effects of Celsr3 shrna, we co transfected 293T cells with expression plasmids for the shrna
Supplemental figures Supplemental Figure. 1. Silencing expression of Celsr3 by shrna. To examine the silencing effects of Celsr3 shrna, we co transfected 293T cells with expression plasmids for the shrna
Supplementary Figure 1. Serial deletion mutants of BLITz.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Serial deletion mutants of BLITz. (a) Design of TEVseq insertion into J -helix. C-terminal end of J -helix was serially deleted and replaced by TEVseq. TEV cleavage site is labeled
Supplementary Figure 1 Serial deletion mutants of BLITz. (a) Design of TEVseq insertion into J -helix. C-terminal end of J -helix was serially deleted and replaced by TEVseq. TEV cleavage site is labeled
Supplementary Figures and supplementary figure legends
 Supplementary Figures and supplementary figure legends Figure S1. Effect of different percentage of FGF signaling knockdown on TGF signaling and EndMT marker gene expression. HUVECs were subjected to different
Supplementary Figures and supplementary figure legends Figure S1. Effect of different percentage of FGF signaling knockdown on TGF signaling and EndMT marker gene expression. HUVECs were subjected to different
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
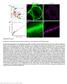 Supplementary Figure 1 Nanoscale localization precision and relative quantification of CB 1 receptors by 3D-STORM imaging (a) Schematic representation of the experimental paradigm for combined confocal/storm
Supplementary Figure 1 Nanoscale localization precision and relative quantification of CB 1 receptors by 3D-STORM imaging (a) Schematic representation of the experimental paradigm for combined confocal/storm
Figure S1 is related to Figure 1B, showing more details of outer segment of
 Supplemental Information Supplementary Figure legends and Figures Figure S1. Electron microscopic images in Sema4A +/+ and Sema4A / retinas Figure S1 is related to Figure 1B, showing more details of outer
Supplemental Information Supplementary Figure legends and Figures Figure S1. Electron microscopic images in Sema4A +/+ and Sema4A / retinas Figure S1 is related to Figure 1B, showing more details of outer
Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of sirna in PC3 and H1299 cells PC3 (a) and H1299 (b) cells were transfected with sirna oligonucleotides
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of sirna in PC3 and H1299 cells PC3 (a) and H1299 (b) cells were transfected with sirna oligonucleotides targeting RCP (SMARTPool (RCP) or two individual oligos (RCP#1
Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of sirna in PC3 and H1299 cells PC3 (a) and H1299 (b) cells were transfected with sirna oligonucleotides targeting RCP (SMARTPool (RCP) or two individual oligos (RCP#1
Supplementary Figure 1. Drawing of spinal cord open-book preparations and DiI tracing. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.3893
 Supplementary Figure 1 Drawing of spinal cord open-book preparations and DiI tracing. Supplementary Figure 2 In ovo electroporation of dominant-negative PlexinA1 in commissural neurons induces midline
Supplementary Figure 1 Drawing of spinal cord open-book preparations and DiI tracing. Supplementary Figure 2 In ovo electroporation of dominant-negative PlexinA1 in commissural neurons induces midline
Supplementary Figure 1. Antigens generated for mab development (a) K9M1P1-mIgG and hgh-k9m1p1 antigen (~37 kda) expression verified by western blot
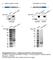 Supplementary Figure 1. Antigens generated for mab development (a) K9M1P1-mIgG and hgh-k9m1p1 antigen (~37 kda) expression verified by western blot (vector: ~25 kda). (b) Silver staining was used to assess
Supplementary Figure 1. Antigens generated for mab development (a) K9M1P1-mIgG and hgh-k9m1p1 antigen (~37 kda) expression verified by western blot (vector: ~25 kda). (b) Silver staining was used to assess
Cleavage of tau by asparagine endopeptidase mediates the neurofibrillary pathology in
 Supplementary information Cleavage of tau by asparagine endopeptidase mediates the neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer s disease Zhentao Zhang, Mingke Song, Xia Liu, Seong Su Kang, Il-Sun Kwon, Duc
Supplementary information Cleavage of tau by asparagine endopeptidase mediates the neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer s disease Zhentao Zhang, Mingke Song, Xia Liu, Seong Su Kang, Il-Sun Kwon, Duc
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure S1. Generation of a synaptobrevin2-mrfp knock-in mouse. (a) Targeting strategy of Syb2-mRFP knock-in mouse leaving the synaptobrevin2 gene locus intact except
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure S1. Generation of a synaptobrevin2-mrfp knock-in mouse. (a) Targeting strategy of Syb2-mRFP knock-in mouse leaving the synaptobrevin2 gene locus intact except
Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss Yunjong Lee, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Joo-Ho Shin, Yun-Il Lee, Han Seok Ko, Debbie Swing,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss Yunjong Lee, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Joo-Ho Shin, Yun-Il Lee, Han Seok Ko, Debbie Swing,
Supplementary Figure 1 Collision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of peptides from PPK1, PPK2, PPK3 and PPK4 respectively.
 Supplementary Figure 1 lision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of peptides from PPK1, PPK, PPK3 and PPK respectively. % of nuclei with signal / field a 5 c ppif3:gus pppk1:gus 0 35 30 5 0 15 10
Supplementary Figure 1 lision-induced dissociation (CID) mass spectra of peptides from PPK1, PPK, PPK3 and PPK respectively. % of nuclei with signal / field a 5 c ppif3:gus pppk1:gus 0 35 30 5 0 15 10
Supplementary Figure 1. Pathologically phosphorylated Tau is localized to the presynaptic terminals of Alzheimer s disease (AD) patient brains.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Pathologically phosphorylated Tau is localized to the presynaptic terminals of Alzheimer s disease (AD) patient brains. Ultrathin (70 nm) sections of healthy control or AD patient
Supplementary Figure 1. Pathologically phosphorylated Tau is localized to the presynaptic terminals of Alzheimer s disease (AD) patient brains. Ultrathin (70 nm) sections of healthy control or AD patient
Class 7: Methods in Research By: Ray
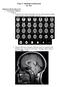 Class 7: Methods in Research By: Ray Method in Brain Research 1. Non-Invasive (Human) o Imaging Computerized (Axial) Tomography (X-rays). Static pictures and high spatial resolution. Horizontal plane only.
Class 7: Methods in Research By: Ray Method in Brain Research 1. Non-Invasive (Human) o Imaging Computerized (Axial) Tomography (X-rays). Static pictures and high spatial resolution. Horizontal plane only.
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Rainero et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201109112/dc1 Figure S1. The expression of DGK- is reduced upon transfection
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Rainero et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201109112/dc1 Figure S1. The expression of DGK- is reduced upon transfection
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Moutin et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110101/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Tagged Homer1a and Homer are functional and display different
Supplemental material Moutin et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110101/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Tagged Homer1a and Homer are functional and display different
DRG Pituitary Cerebral Cortex
 Liver Spinal cord Pons Atg5 -/- Atg5 +/+ DRG Pituitary Cerebral Cortex WT KO Supplementary Figure S1 Ubiquitin-positive IBs accumulate in Atg5 -/- tissues. Atg5 -/- neonatal tissues were fixed and decalcified.
Liver Spinal cord Pons Atg5 -/- Atg5 +/+ DRG Pituitary Cerebral Cortex WT KO Supplementary Figure S1 Ubiquitin-positive IBs accumulate in Atg5 -/- tissues. Atg5 -/- neonatal tissues were fixed and decalcified.
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Over-expression of CD300f in NIH3T3 cells enhances their capacity to phagocytize AC. (a) NIH3T3 cells were stably transduced by EV, CD300f WT or CD300f
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Over-expression of CD300f in NIH3T3 cells enhances their capacity to phagocytize AC. (a) NIH3T3 cells were stably transduced by EV, CD300f WT or CD300f
Supplementary Information Cyclin Y inhibits plasticity-induced AMPA receptor exocytosis and LTP
 Supplementary Information Cyclin Y inhibits plasticity-induced AMPA receptor exocytosis and LTP Eunsil Cho, Dong-Hyun Kim, Young-Na Hur, Daniel J. Whitcomb, Philip Regan, Jung-Hwa Hong, Hanna Kim, Young
Supplementary Information Cyclin Y inhibits plasticity-induced AMPA receptor exocytosis and LTP Eunsil Cho, Dong-Hyun Kim, Young-Na Hur, Daniel J. Whitcomb, Philip Regan, Jung-Hwa Hong, Hanna Kim, Young
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. ZBTB20 expression in the developing DRG. ZBTB20 expression in the developing DRG was detected by immunohistochemistry using anti-zbtb20 antibody 9A10 on
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. ZBTB20 expression in the developing DRG. ZBTB20 expression in the developing DRG was detected by immunohistochemistry using anti-zbtb20 antibody 9A10 on
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1
 SUPPLEMENTRY FIGURE 1 C D E F G * Supplementary Fig. 1: Platelets from Pik3c2b mice exhibit normal function. () Expression of platelet-specific glycoproteins on the surface of platelets in whole blood
SUPPLEMENTRY FIGURE 1 C D E F G * Supplementary Fig. 1: Platelets from Pik3c2b mice exhibit normal function. () Expression of platelet-specific glycoproteins on the surface of platelets in whole blood
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 PDE4 phosphorylation state-specific antibody generation, distribution of PDE4 in brain, and cgmp levels in striatal slices. (a) Identification of the dependent phosphorylation site
Supplementary Figure 1 PDE4 phosphorylation state-specific antibody generation, distribution of PDE4 in brain, and cgmp levels in striatal slices. (a) Identification of the dependent phosphorylation site
Genetically targeted all-optical electrophysiology with a transgenic Credependent
 Genetically targeted all-optical electrophysiology with a transgenic Credependent Optopatch mouse Short title: Transgenic Optopatch mouse Shan Lou 1, Yoav Adam 1, Eli N. Weinstein 1,4, Erika Williams 2,
Genetically targeted all-optical electrophysiology with a transgenic Credependent Optopatch mouse Short title: Transgenic Optopatch mouse Shan Lou 1, Yoav Adam 1, Eli N. Weinstein 1,4, Erika Williams 2,
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Supplementary Figure 1 (a) EM image of the pyramidal layer of wt mice. CA3 pyramidal neurons were selected according to their typical alignment, size and shape for subsequent
Supplementary information Supplementary Figure 1 (a) EM image of the pyramidal layer of wt mice. CA3 pyramidal neurons were selected according to their typical alignment, size and shape for subsequent
Regulation of Acetylcholine Receptor Clustering by ADF/Cofilin- Directed Vesicular Trafficking
 Regulation of Acetylcholine Receptor Clustering by ADF/Cofilin- Directed Vesicular Trafficking Chi Wai Lee, Jianzhong Han, James R. Bamburg, Liang Han, Rachel Lynn, and James Q. Zheng Supplementary Figures
Regulation of Acetylcholine Receptor Clustering by ADF/Cofilin- Directed Vesicular Trafficking Chi Wai Lee, Jianzhong Han, James R. Bamburg, Liang Han, Rachel Lynn, and James Q. Zheng Supplementary Figures
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Selective control of inhibitory synapse development by Slitrk3-PTPδ trans-synaptic interaction Hideto Takahashi 1, Kei-ichi Katayama 2, Kazuhiro Sohya 3,4, Hiroyuki Miyamoto 4,5,
Supplementary Information Selective control of inhibitory synapse development by Slitrk3-PTPδ trans-synaptic interaction Hideto Takahashi 1, Kei-ichi Katayama 2, Kazuhiro Sohya 3,4, Hiroyuki Miyamoto 4,5,
Figure S1. USP-46 is expressed in several tissues including the nervous system
 Supplemental Figure legends Figure S1. USP-46 is expressed in several tissues including the nervous system Transgenic animals expressing a transcriptional reporter (P::GFP) were imaged using epifluorescence
Supplemental Figure legends Figure S1. USP-46 is expressed in several tissues including the nervous system Transgenic animals expressing a transcriptional reporter (P::GFP) were imaged using epifluorescence
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of RNF8, HERC2 and NEURL4 in the cerebellum and knockdown of RNF8 by RNAi (a) Lysates of the cerebellum from rat
 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of RNF8, HERC2 and NEURL4 in the cerebellum and knockdown of RNF8 by RNAi (a) Lysates of the cerebellum from rat pups at P6, P14, P22, P30 and adult (A) rats were subjected
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of RNF8, HERC2 and NEURL4 in the cerebellum and knockdown of RNF8 by RNAi (a) Lysates of the cerebellum from rat pups at P6, P14, P22, P30 and adult (A) rats were subjected
Serine phosphorylation of ephrinb2 regulates trafficking of synaptic
 Serine phosphorylation of ephrinb2 regulates trafficking of synaptic AMPA receptors Clara L. Essmann, Elsa Martinez, Julia C. Geiger, Manuel Zimmer, Matthias H. Traut, Valentin Stein, Rüdiger Klein and
Serine phosphorylation of ephrinb2 regulates trafficking of synaptic AMPA receptors Clara L. Essmann, Elsa Martinez, Julia C. Geiger, Manuel Zimmer, Matthias H. Traut, Valentin Stein, Rüdiger Klein and
Regulation of axonal and dendritic growth by the extracellular calcium-sensing
 Regulation of axonal and dendritic growth by the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR). Thomas N. Vizard, Gerard W. O Keeffe, Humberto Gutierrez, Claudine H. Kos, Daniela Riccardi, Alun M. Davies
Regulation of axonal and dendritic growth by the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR). Thomas N. Vizard, Gerard W. O Keeffe, Humberto Gutierrez, Claudine H. Kos, Daniela Riccardi, Alun M. Davies
Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia-1 (DISC1) regulates spines of the glutamate synapse via Rac1
 Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia-1 () regulates spines of the glutamate synapse via Rac1 By Akiko Hayashi-Takagi, Manabu Takaki, Nick Graziane, Saurav Seshadri, Hannah Murdoch, Allan J Dunlop, Yuichi Makino,
Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia-1 () regulates spines of the glutamate synapse via Rac1 By Akiko Hayashi-Takagi, Manabu Takaki, Nick Graziane, Saurav Seshadri, Hannah Murdoch, Allan J Dunlop, Yuichi Makino,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Legends for Supplementary Tables. Supplementary Table 1. An excel file containing primary screen data. Worksheet 1, Normalized quantification data from a duplicated screen: valid
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Legends for Supplementary Tables. Supplementary Table 1. An excel file containing primary screen data. Worksheet 1, Normalized quantification data from a duplicated screen: valid
Supplementary Figure1: ClustalW comparison between Tll, Dsf and NR2E1.
 P-Box Dsf -----------------MG-TAG--DRLLD-IPCKVCGDRSSGKHYGIYSCDGCSGFFKR 39 NR2E1 -----------------MSKPAGSTSRILD-IPCKVCGDRSSGKHYGVYACDGCSGFFKR 42 Tll MQSSEGSPDMMDQKYNSVRLSPAASSRILYHVPCKVCRDHSSGKHYGIYACDGCAGFFKR
P-Box Dsf -----------------MG-TAG--DRLLD-IPCKVCGDRSSGKHYGIYSCDGCSGFFKR 39 NR2E1 -----------------MSKPAGSTSRILD-IPCKVCGDRSSGKHYGVYACDGCSGFFKR 42 Tll MQSSEGSPDMMDQKYNSVRLSPAASSRILYHVPCKVCRDHSSGKHYGIYACDGCAGFFKR
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of B2M -/- ESCs. Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.3860
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of B2M -/- ESCs. (a) Maps of the B2M alleles in cells with the indicated B2M genotypes. Probes and restriction enzymes used in Southern blots are indicated (H, Hind III;
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of B2M -/- ESCs. (a) Maps of the B2M alleles in cells with the indicated B2M genotypes. Probes and restriction enzymes used in Southern blots are indicated (H, Hind III;
Supplementary Figure 1. ERK signaling is not activated at early hypertension. a, Western blot analysis for the level of phospho-erk (perk) and total
 Supplementary Figure 1. ERK signaling is not activated at early hypertension. a, Western blot analysis for the level of phospho-erk (perk) and total ERK in the aortic tissue from the saline- or AngII-infused
Supplementary Figure 1. ERK signaling is not activated at early hypertension. a, Western blot analysis for the level of phospho-erk (perk) and total ERK in the aortic tissue from the saline- or AngII-infused
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information of Laser Immunotherapy in Combination with Perdurable PD-1 Blocking for Treatment of Metastatic Tumor Lihua Luo, Chunqi Zhu, Hang Yin, Mengshi Jiang, Junlei Zhang, Bing Qin, Zhenyu
Supporting Information of Laser Immunotherapy in Combination with Perdurable PD-1 Blocking for Treatment of Metastatic Tumor Lihua Luo, Chunqi Zhu, Hang Yin, Mengshi Jiang, Junlei Zhang, Bing Qin, Zhenyu
Supplementary Figure 1. The integrity of myelin sheaths is not affected in MAP6 KO mice
 Supplementary Figure 1. The integrityy of myelin sheaths is i not affected in MAP6 KO mice (A) Representativee ultrastructural imagess of cross-sectioned axons within the corpus callosum from WT and KO
Supplementary Figure 1. The integrityy of myelin sheaths is i not affected in MAP6 KO mice (A) Representativee ultrastructural imagess of cross-sectioned axons within the corpus callosum from WT and KO
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. VEH NI Supplementary Figure 1. Cannula tip placement in mice infused with vehicle (VEH) or anisomycin (NI). Cannula tip placement in mice infused with VEH (open circles) or NI (solid
Supplementary Figure 1. VEH NI Supplementary Figure 1. Cannula tip placement in mice infused with vehicle (VEH) or anisomycin (NI). Cannula tip placement in mice infused with VEH (open circles) or NI (solid
Methanol fixation allows better visualization of Kal7. To compare methods for
 Supplementary Data Methanol fixation allows better visualization of Kal7. To compare methods for visualizing Kal7 in dendrites, mature cultures of dissociated hippocampal neurons (DIV21) were fixed with
Supplementary Data Methanol fixation allows better visualization of Kal7. To compare methods for visualizing Kal7 in dendrites, mature cultures of dissociated hippocampal neurons (DIV21) were fixed with
CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration
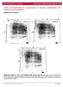 /, Supplementary Advance Publications Materials 2016 CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1: In ECs CD93 silencing
/, Supplementary Advance Publications Materials 2016 CD93 and dystroglycan cooperation in human endothelial cell adhesion and migration Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1: In ECs CD93 silencing
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of EVs (a) Phase-contrast electron microscopy was used to visualize resuspended EV pellets.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of EVs (a) Phase-contrast electron microscopy was used to visualize resuspended EV pellets. Scale bar represent 100 nm. The sizes of EVs from MDA-MB-231-D3H1 (D3H1),
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of EVs (a) Phase-contrast electron microscopy was used to visualize resuspended EV pellets. Scale bar represent 100 nm. The sizes of EVs from MDA-MB-231-D3H1 (D3H1),
Control of cortex development by ULK4, a rare risk gene for mental disorders including schizophrenia
 Control of cortex development by ULK4, a rare risk gene for mental disorders including schizophrenia Bing Lang, Lei Zhang, Guanyu Jiang, Ling Hu, Wei Lan, Lei Zhao, Irene Hunter, Michal Pruski, Ning-Ning
Control of cortex development by ULK4, a rare risk gene for mental disorders including schizophrenia Bing Lang, Lei Zhang, Guanyu Jiang, Ling Hu, Wei Lan, Lei Zhao, Irene Hunter, Michal Pruski, Ning-Ning
Figure legends for supplement
 Figure legends for supplement Supplemental Figure 1 Characterization of purified and recombinant proteins Relevant fractions related the final stage of the purification protocol(bingham et al., 1998; Toba
Figure legends for supplement Supplemental Figure 1 Characterization of purified and recombinant proteins Relevant fractions related the final stage of the purification protocol(bingham et al., 1998; Toba
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of inducible BICD2 knock-out mice. A) The mouse BICD2 locus and gene targeting constructs. To generate an inducible Bicd2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of inducible BICD2 knock-out mice. A) The mouse BICD2 locus and gene targeting constructs. To generate an inducible Bicd2
In vitro EGFP-CALI comprehensive analysis. Liang CAI. David Humphrey. Jessica Wilson. Ken Jacobson. Dept. of Cell and Developmental Biology
 In vitro EGFP-CALI comprehensive analysis Liang CAI David Humphrey Jessica Wilson Ken Jacobson Dept. of Cell and Developmental Biology 1/15 Liang s Rotation in Ken s Lab, Sep-Nov, 2003 1. CALI background
In vitro EGFP-CALI comprehensive analysis Liang CAI David Humphrey Jessica Wilson Ken Jacobson Dept. of Cell and Developmental Biology 1/15 Liang s Rotation in Ken s Lab, Sep-Nov, 2003 1. CALI background
Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of STOML3-modulating molecules on other stomatin-domain proteins
 Supplementary Figure 1 Effects of STOML3-modulating molecules on other stomatin-domain proteins (a) BiFC signal development observed when cells were transfected with stomatin VC/-VN, STOML1-VC/- VN, STOML2-VC/-VN,
Supplementary Figure 1 Effects of STOML3-modulating molecules on other stomatin-domain proteins (a) BiFC signal development observed when cells were transfected with stomatin VC/-VN, STOML1-VC/- VN, STOML2-VC/-VN,
0.9 5 H M L E R -C tr l in T w is t1 C M
 a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. 2.5 C elltiter-g lo A ssay 1.1 5 M T S a s s a y Lum inescence (A.U.) 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 n s H M L E R -C tr l in C tr l C M H M L E R -C tr l in S n a il1 C M A bsorbance (@ 490nm
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. 2.5 C elltiter-g lo A ssay 1.1 5 M T S a s s a y Lum inescence (A.U.) 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 n s H M L E R -C tr l in C tr l C M H M L E R -C tr l in S n a il1 C M A bsorbance (@ 490nm
Supplementary Information attached to:
 Supplementary Information attached to: "Involvement of TrkB- and p75 NTR -signaling pathways in two contrasting forms of long-lasting synaptic plasticity" by Sakuragi, S., Tominaga-Yoshino, K. & Ogura,
Supplementary Information attached to: "Involvement of TrkB- and p75 NTR -signaling pathways in two contrasting forms of long-lasting synaptic plasticity" by Sakuragi, S., Tominaga-Yoshino, K. & Ogura,
Single cell resolution in vivo imaging of DNA damage following PARP inhibition. Supplementary Data
 Single cell resolution in vivo imaging of DNA damage following PARP inhibition Katherine S. Yang, Rainer H. Kohler, Matthieu Landon, Randy Giedt, and Ralph Weissleder Supplementary Data Supplementary Figures
Single cell resolution in vivo imaging of DNA damage following PARP inhibition Katherine S. Yang, Rainer H. Kohler, Matthieu Landon, Randy Giedt, and Ralph Weissleder Supplementary Data Supplementary Figures
(B) Comparable expression of major integrin subunits and glycoproteins on the surface of resting WT and Lnk -/- platelets.
 Supplemental Figure S1. Characteristics of Lnk -/- platelets. (A) Electron micrographs of resting platelets showing the normal intracellular structure of Lnk -/ platelets. Samples were fixed with 4% PFA
Supplemental Figure S1. Characteristics of Lnk -/- platelets. (A) Electron micrographs of resting platelets showing the normal intracellular structure of Lnk -/ platelets. Samples were fixed with 4% PFA
Supplementary Figure 1 Phosphorylated tau accumulates in Nrf2 (-/-) mice. Hippocampal tissues obtained from Nrf2 (-/-) (10 months old, 4 male; 2
 Supplementary Figure 1 Phosphorylated tau accumulates in Nrf2 (-/-) mice. Hippocampal tissues obtained from Nrf2 (-/-) (10 months old, 4 male; 2 female) or wild-type (5 months old, 1 male; 11 months old,
Supplementary Figure 1 Phosphorylated tau accumulates in Nrf2 (-/-) mice. Hippocampal tissues obtained from Nrf2 (-/-) (10 months old, 4 male; 2 female) or wild-type (5 months old, 1 male; 11 months old,
Supplementary Information. Real-time imaging of oxidative and nitrosative stress in the liver of live animals for drug-toxicity testing
 Supplementary Information Real-time imaging of oxidative and nitrosative stress in the liver of live animals for drug-toxicity testing Adam J. Shuhendler 1*, Kanyi Pu 1*, Lina Cui 1, Jack P. Uetrecht &
Supplementary Information Real-time imaging of oxidative and nitrosative stress in the liver of live animals for drug-toxicity testing Adam J. Shuhendler 1*, Kanyi Pu 1*, Lina Cui 1, Jack P. Uetrecht &
Expanded View Figures
 EMO Molecular Medicine nolactone inhibits NRG1-ER4 signaling Michael Wehr et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV1. co-culture assay based on the split TEV technique to monitor NRG1-ER4 signaling activity.
EMO Molecular Medicine nolactone inhibits NRG1-ER4 signaling Michael Wehr et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV1. co-culture assay based on the split TEV technique to monitor NRG1-ER4 signaling activity.
Farnesoid X Receptor and its ligands inhibit the function of platelets
 Farnesoid X Receptor and its ligands inhibit the function of platelets Article Accepted Version Figures and Legends Moraes, L. A., Unsworth, A. J., Vaiyapuri, S., Ali, M. S., Sasikumar, P., Sage, T., Flora,
Farnesoid X Receptor and its ligands inhibit the function of platelets Article Accepted Version Figures and Legends Moraes, L. A., Unsworth, A. J., Vaiyapuri, S., Ali, M. S., Sasikumar, P., Sage, T., Flora,
Supplementary Figure 1. The Hsp70 acetylation level is related to the co-chaperone binding of Hsp70 under various stress conditions.
 Supplementary Figure 1. The Hsp70 acetylation level is related to the co-chaperone binding of Hsp70 under various stress conditions. 1 (a) Etoposide treatment gradually changes acetylation level and co-chaperone
Supplementary Figure 1. The Hsp70 acetylation level is related to the co-chaperone binding of Hsp70 under various stress conditions. 1 (a) Etoposide treatment gradually changes acetylation level and co-chaperone
Regulation of hepcidin expression by inflammation-induced activin B
 Regulation of hepcidin expression by inflammation-induced activin B Yohei Kanamori, Makoto Sugiyama, Osamu Hashimoto, Masaru Murakami, Tohru Matsui and Masayuki Funaba Supplemental methods Liver cell separation
Regulation of hepcidin expression by inflammation-induced activin B Yohei Kanamori, Makoto Sugiyama, Osamu Hashimoto, Masaru Murakami, Tohru Matsui and Masayuki Funaba Supplemental methods Liver cell separation
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Design and sequence of system 1 for targeted demethylation.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Design and sequence of system 1 for targeted demethylation. (a) Design of system 1 for targeted demethylation. TET1CD was fused to a catalytic inactive Cas9 nuclease (dcas9) and
Supplementary Figure 1 Design and sequence of system 1 for targeted demethylation. (a) Design of system 1 for targeted demethylation. TET1CD was fused to a catalytic inactive Cas9 nuclease (dcas9) and
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Liu NNA52890T Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 4 # Supplementary Figures: 3 # Supplementary Tables: 1 # Supplementary
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Liu NNA52890T Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 4 # Supplementary Figures: 3 # Supplementary Tables: 1 # Supplementary
Supplementary Fig. 1 related to Fig. 1 Clinical relevance of lncrna candidate
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Fig. 1 related to Fig. 1 Clinical relevance of lncrna candidate BC041951 in gastric cancer. (A) The flow chart for selected candidate lncrnas in 660 up-regulated
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Fig. 1 related to Fig. 1 Clinical relevance of lncrna candidate BC041951 in gastric cancer. (A) The flow chart for selected candidate lncrnas in 660 up-regulated
Supplementary Fig. 1
 a FL (1-2266) NL (1-1190) CL (1191-2266) HA-ICE1: - HA-ICE1: - - - FLAG-ICE2: + + + + FLAG-ELL: + + + + + + IP: anti-ha FLAG-ICE2 HA-ICE1-FL HA-ICE1-NL HA-ICE1-CL FLAG-ICE2 b IP: anti-ha FL (1-2266) NL
a FL (1-2266) NL (1-1190) CL (1191-2266) HA-ICE1: - HA-ICE1: - - - FLAG-ICE2: + + + + FLAG-ELL: + + + + + + IP: anti-ha FLAG-ICE2 HA-ICE1-FL HA-ICE1-NL HA-ICE1-CL FLAG-ICE2 b IP: anti-ha FL (1-2266) NL
Supplementary Fig.1 Luton
 Supplementary Fig.1 Luton a 175 Brain Thymus Spleen Small Intestine Kidney Testis HeLa b 250 Lung Kidney MDCK c EFA6B si Control si Mismatch #637 #1564 #1770 83 62 47.5 175 IB: anti-efa6b #B1 130 66 Lysates
Supplementary Fig.1 Luton a 175 Brain Thymus Spleen Small Intestine Kidney Testis HeLa b 250 Lung Kidney MDCK c EFA6B si Control si Mismatch #637 #1564 #1770 83 62 47.5 175 IB: anti-efa6b #B1 130 66 Lysates
Post-expansion antibody delivery, after epitope-preserving homogenization.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Post-expansion antibody delivery, after epitope-preserving homogenization. (a, b) Wide-field fluorescence images of Thy1-YFP-expressing mouse brain hemisphere slice before expansion
Supplementary Figure 1 Post-expansion antibody delivery, after epitope-preserving homogenization. (a, b) Wide-field fluorescence images of Thy1-YFP-expressing mouse brain hemisphere slice before expansion
(A) Schematic illustration of sciatic nerve ligation. P, proximal; D, distal to the ligation site.
 SUPPLEMENTRY INFORMTION SUPPLEMENTL FIGURES Figure S1. () Schematic illustration of sciatic nerve ligation. P, proximal; D, distal to the ligation site. () Western blot of ligated and unligated sciatic
SUPPLEMENTRY INFORMTION SUPPLEMENTL FIGURES Figure S1. () Schematic illustration of sciatic nerve ligation. P, proximal; D, distal to the ligation site. () Western blot of ligated and unligated sciatic
Expanded View Figures
 Vasco Meneghini et al Effective lentiviral GT in NHP brains EMO Molecular Medicine Expanded View Figures Figure EV1. VN and GFP distribution in LV.GFPinjected NHPs. Vector copy number (VN) cartography
Vasco Meneghini et al Effective lentiviral GT in NHP brains EMO Molecular Medicine Expanded View Figures Figure EV1. VN and GFP distribution in LV.GFPinjected NHPs. Vector copy number (VN) cartography
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3363 Supplementary Figure 1 Several WNTs bind to the extracellular domains of PKD1. (a) HEK293T cells were co-transfected with indicated plasmids. Flag-tagged proteins were immunoprecipiated
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3363 Supplementary Figure 1 Several WNTs bind to the extracellular domains of PKD1. (a) HEK293T cells were co-transfected with indicated plasmids. Flag-tagged proteins were immunoprecipiated
Expanded View Figures
 MO reports Phenotype of 1T human tau transgenic mice Sumihiro Maeda et al xpanded View igures Western lotting LIS HT7/GPH 3 1 HT7/ctin 3 1 HT7-77G7P htau Level (ng/mg) 1 1 htau-wt (L1) htau-1t (L3) htau
MO reports Phenotype of 1T human tau transgenic mice Sumihiro Maeda et al xpanded View igures Western lotting LIS HT7/GPH 3 1 HT7/ctin 3 1 HT7-77G7P htau Level (ng/mg) 1 1 htau-wt (L1) htau-1t (L3) htau
Supplemental Figure 1 Human REEP family of proteins can be divided into two distinct subfamilies. Residues (single letter amino acid code) identical
 Supplemental Figure Human REEP family of proteins can be divided into two distinct subfamilies. Residues (single letter amino acid code) identical in all six REEPs are highlighted in green. Additional
Supplemental Figure Human REEP family of proteins can be divided into two distinct subfamilies. Residues (single letter amino acid code) identical in all six REEPs are highlighted in green. Additional
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Integrative Biology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Table S1. Definition of quantitative cellular features
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Integrative Biology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Table S1. Definition of quantitative cellular features
supplementary information
 Figure S1 Distribution of heterokaryons in vermis and hemispheres of the cerebellum. Schematic dorsal view of an adult cerebellum with the vermis in the middle (red) flanked by the two hemispheres (grey).
Figure S1 Distribution of heterokaryons in vermis and hemispheres of the cerebellum. Schematic dorsal view of an adult cerebellum with the vermis in the middle (red) flanked by the two hemispheres (grey).
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Leonard Petrucelli NNA52530C Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main s: 8 # Supplementary s: 10 # Supplementary Tables: 3 #
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Leonard Petrucelli NNA52530C Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main s: 8 # Supplementary s: 10 # Supplementary Tables: 3 #
Cancer cells that survive radiation therapy acquire HIF-1 activity and translocate toward tumor blood vessels Supplementary Information
 Cancer cells that survive radiation therapy acquire HIF-1 activity and translocate toward tumor blood vessels Supplementary Information 1. Supplementary Figure S1-S10: Pages 2-11 2. Supplementary References:
Cancer cells that survive radiation therapy acquire HIF-1 activity and translocate toward tumor blood vessels Supplementary Information 1. Supplementary Figure S1-S10: Pages 2-11 2. Supplementary References:
Supplemental Methods. Animals
 Supplemental Methods Animals Ten to eleven weeks old male C57BL/6 (B6), ob/ob and db/db mice were obtained from Japan SLC (Hamamatsu, Japan). Mice were fed a standard chow diet (Samyang, Seoul, Korea)
Supplemental Methods Animals Ten to eleven weeks old male C57BL/6 (B6), ob/ob and db/db mice were obtained from Japan SLC (Hamamatsu, Japan). Mice were fed a standard chow diet (Samyang, Seoul, Korea)
Assembly of synapses by neuronal adhesion molecules: single molecule studies
 Assembly of synapses by neuronal adhesion molecules: single molecule studies Olivier Thoumine Interdisciplinary Institute of Neurosciences CNRS - University of Bordeaux Connectivity in the brain 300 nm
Assembly of synapses by neuronal adhesion molecules: single molecule studies Olivier Thoumine Interdisciplinary Institute of Neurosciences CNRS - University of Bordeaux Connectivity in the brain 300 nm
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4356
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1: Characterization of IVT mrna encoding highly active bsab. (a) IVT mrna quality and purity analysis on an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer. Full-length mrna peaks are
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1: Characterization of IVT mrna encoding highly active bsab. (a) IVT mrna quality and purity analysis on an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer. Full-length mrna peaks are
Supporting Figure 1: Meis2 and Pax6 transcripts in the adult murine brain detected by in situ
 DEVELOP2013097295_supplementary figures Supporting Figure 1: Meis2 and Pax6 transcripts in the adult murine brain detected by in situ hybridization on vibratome sections. (A) Meis2-specific transcripts
DEVELOP2013097295_supplementary figures Supporting Figure 1: Meis2 and Pax6 transcripts in the adult murine brain detected by in situ hybridization on vibratome sections. (A) Meis2-specific transcripts
Gene Sequence Fragment size ΔEGFR F 5' GGGCTCTGGAGGAAAAGAAAG GT 3' 116 bp R 5' CTTCTTACACTTGCGGACGC 3'
 Supplementary Table 1: Real-time PCR primer sequences for ΔEGFR, wtegfr, IL-6, LIF and GAPDH. Gene Sequence Fragment size ΔEGFR F 5' GGGCTCTGGAGGAAAAGAAAG GT 3' 116 bp R 5' CTTCTTACACTTGCGGACGC 3' wtegfr
Supplementary Table 1: Real-time PCR primer sequences for ΔEGFR, wtegfr, IL-6, LIF and GAPDH. Gene Sequence Fragment size ΔEGFR F 5' GGGCTCTGGAGGAAAAGAAAG GT 3' 116 bp R 5' CTTCTTACACTTGCGGACGC 3' wtegfr
Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of LRRK1 bind to Grb2.
 Myc- HA-Grb2 Mr(K) 105 IP HA 75 25 105 1-1163 1-595 - + - + - + 1164-1989 Blot Myc HA total lysate 75 25 Myc HA Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of bind to Grb2. COS7 cells were cotransfected
Myc- HA-Grb2 Mr(K) 105 IP HA 75 25 105 1-1163 1-595 - + - + - + 1164-1989 Blot Myc HA total lysate 75 25 Myc HA Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of bind to Grb2. COS7 cells were cotransfected
In vivo recording, forepaw denervation, and isolation of slices: Methods for mapping the forepaw/lower jaw border in anesthetized adult rat primary
 Supplementary Methods In vivo recording, forepaw denervation, and isolation of slices: Methods for mapping the forepaw/lower jaw border in anesthetized adult rat primary somatosensory cortex (S1), forepaw
Supplementary Methods In vivo recording, forepaw denervation, and isolation of slices: Methods for mapping the forepaw/lower jaw border in anesthetized adult rat primary somatosensory cortex (S1), forepaw
Improved Immunoblot by Brief Application of Low Dose Paraformaldehyde
 ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / /cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2013 12 29 12 1187 ~ 1193 1 1 2 * 1 310012 2 310053 protein immunoblot Western blot 0 4% 0
ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / /cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2013 12 29 12 1187 ~ 1193 1 1 2 * 1 310012 2 310053 protein immunoblot Western blot 0 4% 0
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic and results of screening the combinatorial antibody library for Sox2 replacement activity. A single batch of MEFs were plated and transduced with doxycycline inducible
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic and results of screening the combinatorial antibody library for Sox2 replacement activity. A single batch of MEFs were plated and transduced with doxycycline inducible
Direct Imaging of APP Proteolysis in Living Cells
 Direct Imaging of APP Proteolysis in Living Cells Niccoló Parenti, Ambra Del Grosso, Claudia Antoni, Marco Cecchini, Renato Corradetti, Francesco S. Pavone, Martino Calamai Supplementary Information Supplementary
Direct Imaging of APP Proteolysis in Living Cells Niccoló Parenti, Ambra Del Grosso, Claudia Antoni, Marco Cecchini, Renato Corradetti, Francesco S. Pavone, Martino Calamai Supplementary Information Supplementary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2743 Figure S1 stabilizes cellular protein level, post-transcriptionally. (a, b) and DDR1 were RNAi-depleted from HEK.293.-CBG cells. Western blots with indicated antibodies (a). RT-PCRs
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2743 Figure S1 stabilizes cellular protein level, post-transcriptionally. (a, b) and DDR1 were RNAi-depleted from HEK.293.-CBG cells. Western blots with indicated antibodies (a). RT-PCRs
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4169
 Supplementary Fig.1. EC-specific deletion of Ccm3 by Cdh5-CreERT2. a. mt/mg reporter mice were bred with Cdh5CreERT2 deleter mice followed by tamoxifen feeding from P1 to P3. mg expression was specifically
Supplementary Fig.1. EC-specific deletion of Ccm3 by Cdh5-CreERT2. a. mt/mg reporter mice were bred with Cdh5CreERT2 deleter mice followed by tamoxifen feeding from P1 to P3. mg expression was specifically
Regulation of Synaptic Structure and Function by FMRP- Associated MicroRNAs mir-125b and mir-132
 Neuron, Volume 65 Regulation of Synaptic Structure and Function by FMRP- Associated MicroRNAs mir-125b and mir-132 Dieter Edbauer, Joel R. Neilson, Kelly A. Foster, Chi-Fong Wang, Daniel P. Seeburg, Matthew
Neuron, Volume 65 Regulation of Synaptic Structure and Function by FMRP- Associated MicroRNAs mir-125b and mir-132 Dieter Edbauer, Joel R. Neilson, Kelly A. Foster, Chi-Fong Wang, Daniel P. Seeburg, Matthew
Sélection Internationale Ens Ulm 2012, Cell Biology
 Sélection Internationale Ens Ulm 2012, Cell Biology Please read the whole subject before starting. Questions 1-8 and 12-14 are general biology questions. In questions 9, 10, 11 and15, we ask you to interpret
Sélection Internationale Ens Ulm 2012, Cell Biology Please read the whole subject before starting. Questions 1-8 and 12-14 are general biology questions. In questions 9, 10, 11 and15, we ask you to interpret
A 3D human triculture system modeling neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer s disease
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0175-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. A 3D human triculture system modeling neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0175-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. A 3D human triculture system modeling neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation
Intestinal Epithelial Cell-Specific Deletion of PLD2 Alleviates DSS-Induced Colitis by. Regulating Occludin
 Intestinal Epithelial Cell-Specific Deletion of PLD2 Alleviates DSS-Induced Colitis by Regulating Occludin Chaithanya Chelakkot 1,ǂ, Jaewang Ghim 2,3,ǂ, Nirmal Rajasekaran 4, Jong-Sun Choi 5, Jung-Hwan
Intestinal Epithelial Cell-Specific Deletion of PLD2 Alleviates DSS-Induced Colitis by Regulating Occludin Chaithanya Chelakkot 1,ǂ, Jaewang Ghim 2,3,ǂ, Nirmal Rajasekaran 4, Jong-Sun Choi 5, Jung-Hwan
VERIFY Tagged Antigen. Validation Data
 VERIFY Tagged Antigen Validation Data Antibody Validation Figure 1. Over-expression cell lysate for human STAT3 (NM_139276) was used to test 3 commercial antibodies. Antibody A shows strong antigen binding.
VERIFY Tagged Antigen Validation Data Antibody Validation Figure 1. Over-expression cell lysate for human STAT3 (NM_139276) was used to test 3 commercial antibodies. Antibody A shows strong antigen binding.
by Neurobasal medium (supplemented with B27, 0.5mM glutamine, and 100 U/mL
 Supplementary Materials and methods Neuronal cultures and transfection The hippocampus was dissected from E8 rat embryos, dissociated, and neurons plated onto glass coverslips coated with poly-ornithine
Supplementary Materials and methods Neuronal cultures and transfection The hippocampus was dissected from E8 rat embryos, dissociated, and neurons plated onto glass coverslips coated with poly-ornithine
Grb2-Mediated Alteration in the Trafficking of AβPP: Insights from Grb2-AICD Interaction
 Journal of Alzheimer s Disease 20 (2010) 1 9 1 IOS Press Supplementary Material Grb2-Mediated Alteration in the Trafficking of AβPP: Insights from Grb2-AICD Interaction Mithu Raychaudhuri and Debashis
Journal of Alzheimer s Disease 20 (2010) 1 9 1 IOS Press Supplementary Material Grb2-Mediated Alteration in the Trafficking of AβPP: Insights from Grb2-AICD Interaction Mithu Raychaudhuri and Debashis
