Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology
|
|
|
- Caroline Williams
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology
2
3 F. Stuart Chapin, III Pamela A. Matson Peter M.Vitousek Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology Second Edition Illustrated by Melissa C. Chapin
4 F. Stuart Chapin, III University of Alaska Fairbanks Institute of Arctic Biology Department of Biology & Wildlife Fairbanks, AK, USA Pamela A. Matson School of Earth Sciences Stanford University Stanford, CA, USA Peter M. Vitousek Department of Biological Sciences Stanford University Stanford, CA, USA ISBN e-isbn DOI / Springer New York Dordrecht Heidelberg London Library of Congress Control Number: Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2011 All rights reserved. This work may not be translated or copied in whole or in part without the written permission of the publisher (Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, 233 Spring Street, New York, NY 10013, USA), except for brief excerpts in connection with reviews or scholarly analysis. Use in connection with any form of information storage and retrieval, electronic adaptation, computer software, or by similar or dissimilar methodology now known or hereafter developed is forbidden. The use in this publication of trade names, trademarks, service marks, and similar terms, even if they are not identified as such, is not to be taken as an expression of opinion as to whether or not they are subject to proprietary rights. Cover illustrations: Temperate forest in the eastern U.S. (North Carolina), showing a complex multi-layered canopy with sunflecks common in all canopy layers. Cover Photograph courtesy of Norm Christensen Printed on acid-free paper Springer is part of Springer Science+Business Media (
5 Preface Human activities are affecting the global environment in many ways, with numerous direct and indirect effects on ecosystems. The climate and atmospheric composition of Earth are changing rapidly. Humans have directly modified half of the ice-free terrestrial surface and use 40% of terrestrial production. Our actions are causing the sixth major extinction event in the history of life on Earth and radically modify the interactions among forests, fields, streams, and oceans. This book is written to provide a conceptual basis for understanding terrestrial ecosystem processes and their sensitivity to environmental and biotic changes. We believe that an understanding of ecosystem dynamics must underlie our analysis of both the consequences and the mitigation of human-induced changes. This book is intended to introduce the science of terrestrial ecosystem ecology to advanced undergraduate students, beginning graduate students, and practicing scientists from a wide array of disciplines. We define terrestrial ecosystem ecology to include freshwater ecosystems and their terrestrial matrix. We also include a description of marine ecosystems to provide a broader context for understanding terrestrial ecosystems and as a basis for Earth-System analysis. We provide access to some of the rapidly expanding literature in the many disciplines that contribute to ecosystem understanding. This second edition incorporates new material that accounts for both the substantial scientific advances in ecosystem ecology during the past decade, as well as the evolution of our own understanding. The first section of this book provides the context for understanding ecosystem ecology. We introduce the science of ecosystem ecology and place it in the context of other components of the Earth System the atmosphere, ocean, climate and geological systems. We show how these components affect ecosystem processes and contribute to the global variation in terrestrial ecosystem structure and processes. In the second section of the book we consider the mechanisms by which terrestrial ecosystems function and focus on the flow of water and energy and the cycling of carbon and nutrients. We then consider the important role of organisms in ecosystem processes through trophic interactions (feeding relationships), environmental effects, and disturbance. The third section of the book addresses temporal and spatial patterns in ecosystem processes. We finish by considering the integrated effects of these processes at the global scale and their consequences for sustainable use by human societies. Powerpoint lecture notes that include the illustrations in v
6 vi Preface this book are available on the web ( as supplementary material. Many people have contributed to the development of this book. We particularly thank our families, whose patience has made the book possible, our students from whom we have learned many of the important ideas that are presented, and Hal Mooney who was a co-author of the first edition. In addition, we thank the following individuals for their constructively critical review of chapters in this book: Richard Bardgett, Dan Binkley, Dave Bowling, Pep Canadell, Mimi Chapin, Doug Cost, Joe Craine, Wolfgang Cramer, Eric Davidson, Sandra Díaz, Jim Elser, Eugenie Euskirchen, Valerie Eviner, Noah Fierer, Jacques Finlay, Doug Frank, Mark Harmon, Sarah Hobbie, Dave Hooper, Bob Howarth, Ivan Janssens, Julia Jones, Bill Lauenroth, Joe McFadden, Dave McGuire, Sam McNaughton, Russ Monson, Deb Peters, Mary Power, Steve Running, Josh Schimel, Ted Schuur, Tim Seastedt, Mark Serreze, Phil Sollins, Bob Sterner, Kevin Trenberth, Dave Turner, Monica Turner, Diana Wall, John Walsh. We also thank Julio Betancourt, Scott Chambers, Norm Christensen, Greg Cortopassi, Steve Davis, Sandra Díaz, Jack Dykinga, Jim Elser, Jim Estes, Peter Franks, Mark Harmon, Al Levno, Mike Kenner, Alan Knapp, Aaryn Olsson, Roger Ruess, Dave Schindler, and David Tongway for the use of their photographs. We particularly thank Joe Craine and Dana Nossov for their constructive comments on the entire book. Fairbanks, AK, USA Stanford, CA, USA Stanford, CA, USA F. Stuart Chapin, III Pamela A. Matson Peter M. Vitousek
7 Contents Part I Context 1 The Ecosystem Concept... 3 Introduction... 3 A Focal Issue... 3 Overview of Ecosystem Ecology... 4 History of Ecosystem Ecology... 8 Ecosystem Structure and Functioning Ecosystem Processes Ecosystem Structure and Constraints Controls over Ecosystem Processes Human-Induced Ecosystem Change Human Impacts on Ecosystems Resilience and Threshold Changes Degradation in Ecosystem Services Summary Review Questions Additional Reading Earth s Climate System Introduction A Focal Issue Earth s Energy Budget The Atmospheric System Atmospheric Composition and Chemistry Atmospheric Structure Atmospheric Circulation The Ocean Ocean Structure Ocean Circulation Landform Effects on Climate Vegetation Influences on Climate Temporal Variability in Climate Long-Term Changes Anthropogenic Climate Change Interannual Climate Variability vii
8 viii Contents Seasonal and Daily Variation Storms and Weather Relationship of Climate to Ecosystem Distribution and Structure Summary Review Questions Additional Reading Geology, Soils, and Sediments Introduction A Focal Issue Controls Over Soil Formation Parent Material Climate Topography Time Potential Biota Human Activities Controls Over Soil Loss Development of Soil Profiles Additions to Soils Soil Transformations Soil Transfers Losses from Soils Soil Horizons and Soil Classification Soil Properties and Ecosystem Functioning Soil Physical Properties Soil Chemical Properties Summary Review Questions Additional Reading Part II Mechanisms 4 Water and Energy Balance Introduction A Focal Issue Surface Energy Balance Radiation Budget Partitioning of Absorbed Radiation Overview of Ecosystem Water Budgets Water Inputs to Ecosystems Water Movements Within Ecosystems Water Movement from the Canopy to the Soil Water Storage and Movement in the Soil Water Movement from Soil to Roots Water Movement Through Plants
9 Contents ix Water Losses from Ecosystems Evaporation from Wet Canopies Evapotranspiration from Dry Canopies Changes in Storage Runoff Summary Review Questions Additional Reading Carbon Inputs to Ecosystems Introduction A Focal Issue Overview of Carbon Inputs to Ecosystems Biochemistry of Photosynthesis Pelagic Photosynthesis Light Limitation CO 2 Supply Nutrient Limitation Pelagic GPP Living on the Edge: Streams and Shorelines Terrestrial Photosynthesis Photosynthetic Structure of Terrestrial Ecosystems C 4 Photosynthesis Crassulacean Acid Metabolism CO 2 Limitation Light Limitation Nitrogen Limitation and Photosynthetic Capacity Water Limitation Temperature Effects Pollutants Terrestrial GPP Canopy Processes Leaf Area Length of the Photosynthetic Season Satellite-Based Estimates of GPP Summary Review Questions Additional Reading Plant Carbon Budgets Introduction A Focal Issue Plant Respiration What Is NPP? Marine NPP Lake NPP Stream and River NPP
10 x Contents Terrestrial NPP Physiological Controls Over NPP Environmental and Species Controls Over NPP Allocation Allocation of NPP Allocation Response to Multiple Resources Diurnal and Seasonal Cycles of Allocation Tissue Turnover Global Distribution of Biomass and NPP Biome Differences in Biomass Biome Differences in NPP Summary Review Questions Additional Reading Decomposition and Ecosystem Carbon Budgets Introduction A Focal Issue Overview of Decomposition and Ecosystem Carbon Balance Leaching of Litter Litter Fragmentation Chemical Alteration Fungi Bacteria and Archaea Soil Animals Temporal and Spatial Heterogeneity of Decomposition Temporal Pattern Vertical Distribution Factors Controlling Decomposition Litter Quality Rhizosphere Stimulation of Decomposition Microbial Community Composition and Enzymatic Capacity The Environment Soil Organic Matter Peat Accumulation and Trace Gas Emissions Heterotrophic Respiration Net Ecosystem Production (NEP) Net Ecosystem Carbon Balance Gaseous Carbon Fluxes Particulate Carbon Fluxes Dissolved Carbon Fluxes Stream Carbon Fluxes Stream Decomposition Stream Carbon Budgets Lake Carbon Fluxes Ocean Carbon Fluxes
11 Contents xi Carbon Exchange at the Global Scale Summary Review Questions Additional Reading Plant Nutrient Use Introduction A Focal Issue Overview Ocean Ecosystems Lake Ecosystems Rivers and Streams Terrestrial Ecosystems Nutrient Movement to the Root Diffusion Mass Flow Root Interception Nutrient Absorption Nutrient Supply Development of Root Length Mycorrhizae Nitrogen Fixation Root Absorption Properties Nutrient Use Nutrient Loss from Plants Senescence Leaching Loss from Plants Herbivory Other Avenues of Nutrient Loss from Plants Summary Review Questions Additional Reading Nutrient Cycling Introduction A Focal Point Overview of Nutrient Cycling Marine Nutrient Cycling Large-Scale Nutrient Cycles Estuaries Coastal Currents Lake Nutrient Cycling Stream Nutrient Cycling Nitrogen Inputs to Terrestrial Ecosystems Biological Nitrogen Fixation Nitrogen Deposition Internal Cycling of Nitrogen Overview of Mineralization Production and Fate of Dissolved Organic Nitrogen
12 xii Contents Production and Fate of Ammonium Production and Fate of Nitrate Temporal and Spatial Variability Pathways of Nitrogen Loss Gaseous Losses of Nitrogen Solution Losses Erosional Losses Other Element Cycles Phosphorus Sulfur Essential Cations Micronutrients and Nonessential Elements Nitrogen and Phosphorus Cycling in Agricultural Systems Summary Review Questions Additional Reading Trophic Dynamics Introduction A Focal Issue Overview of Trophic Dynamics Controls Over Energy Flow through Ecosystems Bottom-Up Controls Top-Down Controls Trophic Effects on Nutrient Cycling Ecological Efficiencies Trophic Efficiency and Energy Flow Consumption Efficiency Assimilation Efficiency Production Efficiency Food Chain Length Seasonal and Interannual Patterns Nutrient Transfers Detritus-Based Trophic Systems Integrated Food Webs Summary Review Questions Additional Reading Species Effects on Ecosystem Processes Introduction A Focal Issue Overview of Species Effects on Ecosystem Processes Effect Functional Types Species Effects on Biogeochemistry Species Effects on Biophysical Processes Species Effects on Trophic Interactions Species Effects on Disturbance Regime Response Functional Types
13 Contents xiii Integrating the Effects of Traits on Ecosystems Functional Matrix of Multiple Traits Linkages Between Response and Effect Traits Diversity as Insurance Species Interactions and Ecosystem Processes Summary Review Questions Additional Reading Part III Patterns 12 Temporal Dynamics Introduction A Focal Issue Ecosystem Resilience and Change Alternative Stable States Resilience and Thresholds Disturbance Conceptual Framework Impact of a Disturbance Event Recovery and Renewal after Disturbance Disturbance Regime Succession Ecosystem Structure and Composition Water and Energy Exchange Carbon Balance Nutrient Cycling Trophic Dynamics Temporal Scaling of Ecological Processes Summary Review Questions Additional Reading Landscape Heterogeneity and Ecosystem Dynamics Introduction A Focal Issue Concepts of Landscape Heterogeneity Causes of Spatial Heterogeneity Detection and Analysis of Spatial Heterogeneity State Factors and Interactive Controls Community Processes and Legacies Disturbance Interactions Among Sources of Heterogeneity Patch Interactions on the Landscape Topographic and Land Water Interactions Atmospheric Transfers Movement of Plants and Animals on the Landscape Disturbance Spread
14 xiv Contents Human Land-Use Change and Landscape Heterogeneity Extensification Intensification Extrapolation to Larger Scales Summary Review Questions Additional Reading Part IV Integration 14 Changes in the Earth System Introduction A Focal Issue Human Drivers of Change The Global Water Cycle Water Pools and Fluxes Anthropogenic Changes in the Water Cycle Consequences of Changes in the Water Cycle The Global Carbon Cycle Carbon Pools and Fluxes Changes in Atmospheric CO Marine Sinks for CO Terrestrial Sinks for CO CO 2 Effects on Climate The Global Methane Budget The Global Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen Pools and Fluxes Anthropogenic Changes in the Nitrogen Cycle The Global Phosphorus Cycle Phosphorus Pools and Fluxes Anthropogenic Changes in the Phosphorus Cycle The Global Sulfur Cycle Summary Review Questions Additional Reading Managing and Sustaining Ecosystems Introduction A Focal Issue Sustaining Social Ecological Systems Sustainability Ecological Dimensions of Sustainability Conceptual Framework for Ecosystem Management Sustaining Soil Resources Sustaining Biodiversity Sustaining Variability and Resilience Applying Ecosystem Principles to Management Forest Management Fisheries Management
15 Contents xv Ecosystem Renewal Management for Endangered Species Socioeconomic Contexts of Ecosystem Management Meeting Human Needs and Wants Managing Flows of Ecosystem Services Addressing Political Realities Innovation and Adaptive Management Sustainable Development: Social Ecological Transformation Summary Review Questions Additional Reading Abbreviations Glossary References Index
16
Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology
 E Stuart Chapin III Pamela A. Matson Harold A. Mooney Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology Illustrated by Melissa C. Chapin With 199 Illustrations Teehnische Un.fversitSt Darmstadt FACHBEREIGH 10
E Stuart Chapin III Pamela A. Matson Harold A. Mooney Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology Illustrated by Melissa C. Chapin With 199 Illustrations Teehnische Un.fversitSt Darmstadt FACHBEREIGH 10
Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology
 Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology Springer New York Berlin Heidelberg Barcelona Hong Kong London Milan Paris Singapore Tokyo F. Stuart Chapin III Pamela A. Matson Harold A. Mooney Principles
Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology Springer New York Berlin Heidelberg Barcelona Hong Kong London Milan Paris Singapore Tokyo F. Stuart Chapin III Pamela A. Matson Harold A. Mooney Principles
Guide 34. Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles. p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/
 Guide 34 Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/ Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists
Guide 34 Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/ Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists
ECOSYSTEMS. Follow along in chapter 54. *Means less important
 ECOSYSTEMS Follow along in chapter 54 *Means less important How do ecosystems function? What is an ecosystem? All living things in an area and their abiotic environment Ecosystem function can be easily
ECOSYSTEMS Follow along in chapter 54 *Means less important How do ecosystems function? What is an ecosystem? All living things in an area and their abiotic environment Ecosystem function can be easily
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Ecosystem Ecology Examines Interactions Between the Living and Non-Living World Ecosystem- A particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Ecosystem Ecology Examines Interactions Between the Living and Non-Living World Ecosystem- A particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology. Tuesday, September 19, 17
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
an ecosystem is a community of different species interacting with one another and with their nonliving environment of matter and energy
 1 Ecocsystems: Energy Flow and Materials Cycling 2 EVPP 111 Lecture Dr. Largen Spring 2004 Energy Flow and Matter Cycling Energy flow s through ecosystems ecosystems global energy budget physical laws
1 Ecocsystems: Energy Flow and Materials Cycling 2 EVPP 111 Lecture Dr. Largen Spring 2004 Energy Flow and Matter Cycling Energy flow s through ecosystems ecosystems global energy budget physical laws
Nutrients elements required for the development, maintenance, and reproduction of organisms.
 Nutrient Cycles Energy flows through ecosystems (one way trip). Unlike energy, however, nutrients (P, N, C, K, S ) cycle within ecosystems. Nutrients are important in controlling NPP in ecosystems. Bottom-up
Nutrient Cycles Energy flows through ecosystems (one way trip). Unlike energy, however, nutrients (P, N, C, K, S ) cycle within ecosystems. Nutrients are important in controlling NPP in ecosystems. Bottom-up
Ecology Ecosystem Characteristics. Ecosystem Characteristics, Nutrient Cycling and Energy Flow
 Ecology Ecosystem Characteristics Ecosystem Characteristics, Nutrient Cycling and Energy Flow Let us consider ecosystems We have looked at the biosphere, and the biomes within the biosphere, the populations
Ecology Ecosystem Characteristics Ecosystem Characteristics, Nutrient Cycling and Energy Flow Let us consider ecosystems We have looked at the biosphere, and the biomes within the biosphere, the populations
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology. Reading Questions
 APES Name 22 Module 7 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 17 Module 6 The Movement of Energy 18 Ecosystem Field Walk 19 Module 7 The 23 Module 8 Responses to Disturbances
APES Name 22 Module 7 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 17 Module 6 The Movement of Energy 18 Ecosystem Field Walk 19 Module 7 The 23 Module 8 Responses to Disturbances
Coastal studies in Long Term Ecological Research. Dan Reed Santa Barbara Coastal LTER
 Coastal studies in Long Term Ecological Research Dan Reed Santa Barbara Coastal LTER NSF s Long Term Ecological Research Program 24 sites representing a diverse array of biomes Major focus of research
Coastal studies in Long Term Ecological Research Dan Reed Santa Barbara Coastal LTER NSF s Long Term Ecological Research Program 24 sites representing a diverse array of biomes Major focus of research
Ecosystems: Nutrient Cycles
 Ecosystems: Nutrient Cycles Greeks, Native Peoples, Buddhism, Hinduism use(d) Earth, Air, Fire, and Water as the main elements of their faith/culture Cycling in Ecosystems the Hydrologic Cycle What are
Ecosystems: Nutrient Cycles Greeks, Native Peoples, Buddhism, Hinduism use(d) Earth, Air, Fire, and Water as the main elements of their faith/culture Cycling in Ecosystems the Hydrologic Cycle What are
Ecosystems and the Biosphere Outline
 Ecosystems and the Biosphere Outline Ecosystems Processes in an ecosystem Production, respiration, decomposition How energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem Biosphere Biogeochemical Cycles Gaia
Ecosystems and the Biosphere Outline Ecosystems Processes in an ecosystem Production, respiration, decomposition How energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem Biosphere Biogeochemical Cycles Gaia
1. Where are nutrients accumulated or stored for short or long periods?
 Use with textbook pages 68 87. Nutrient cycles Answer the questions below. Comprehension 1. Where are nutrients accumulated or stored for short or long periods? 2. Name a biotic process and an abiotic
Use with textbook pages 68 87. Nutrient cycles Answer the questions below. Comprehension 1. Where are nutrients accumulated or stored for short or long periods? 2. Name a biotic process and an abiotic
Exercises in Environmental Physics
 Exercises in Environmental Physics Valerio Faraoni Exercises in Environmental Physics Valerio Faraoni Physics Department Bishop s University Lennoxville, Quebec J1M 1Z7 Canada vfaraoni@cs-linux.ubishops.ca
Exercises in Environmental Physics Valerio Faraoni Exercises in Environmental Physics Valerio Faraoni Physics Department Bishop s University Lennoxville, Quebec J1M 1Z7 Canada vfaraoni@cs-linux.ubishops.ca
E E. International Series in Operations Research & Management Science. Series Editor: Fredrick S. Hillier Stanford University
 E E International Series in Operations Research & Management Science Series Editor: Fredrick S. Hillier Stanford University Special Editorial Consultant: Camille C. Price Stephen F. Austin State University
E E International Series in Operations Research & Management Science Series Editor: Fredrick S. Hillier Stanford University Special Editorial Consultant: Camille C. Price Stephen F. Austin State University
Chapter 19. Nutrient Cycling and Retention. Chapter Focus. The hydrological cycle. Global biogeochemical cycles. Nutrient cycling
 Chapter Focus Chapter 19 Nutrient Cycling and Retention Nutrient cycling Phosphorus Nitrogen Carbon Water, Sulfur Decomposition Biotic effect on nutrient distribution and cycling Disturbance Global biogeochemical
Chapter Focus Chapter 19 Nutrient Cycling and Retention Nutrient cycling Phosphorus Nitrogen Carbon Water, Sulfur Decomposition Biotic effect on nutrient distribution and cycling Disturbance Global biogeochemical
Forest Production Ecology
 Objectives Forest Production Ecology Overview of forest production ecology C cycling Primary productivity of trees and forest ecosystems ecologists and ecosystem managers are unlikely to achieve desired
Objectives Forest Production Ecology Overview of forest production ecology C cycling Primary productivity of trees and forest ecosystems ecologists and ecosystem managers are unlikely to achieve desired
Ecosystem element cycling
 Ecosystem element cycling Introduction An ecosystem consists of all the biological organisms and the physical environments they occupy together within a defined area [1]. The actual boundaries of an ecosystem
Ecosystem element cycling Introduction An ecosystem consists of all the biological organisms and the physical environments they occupy together within a defined area [1]. The actual boundaries of an ecosystem
Arctic ecosystems as key biomes in climate-carbon feedback. Hanna Lee Climate and Global Dynamics Division National Center for Atmospheric Research
 Arctic ecosystems as key biomes in climate-carbon feedback Hanna Lee Climate and Global Dynamics Division National Center for Atmospheric Research Outline Permafrost carbon Permafrost carbon-climate feedback
Arctic ecosystems as key biomes in climate-carbon feedback Hanna Lee Climate and Global Dynamics Division National Center for Atmospheric Research Outline Permafrost carbon Permafrost carbon-climate feedback
C Nutrient Cycling Begin Climate Discussion. Day 29 December 2, Take-Home Test Due Dec 11 5 pm No Final Exam
 NREM 301 Forest Ecology & Soils C Nutrient Cycling Begin Climate Discussion Day 29 December 2, 2008 Take-Home Test Due Dec 11 5 pm No Final Exam Our discussions for the semester have centered on Clipsrot
NREM 301 Forest Ecology & Soils C Nutrient Cycling Begin Climate Discussion Day 29 December 2, 2008 Take-Home Test Due Dec 11 5 pm No Final Exam Our discussions for the semester have centered on Clipsrot
Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs
 How Ecosystems Work Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs Autotrophs make their own food so they are called PRODUCERS Heterotrophs get their food from another source so they are called CONSUMERS Two Main forms of
How Ecosystems Work Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs Autotrophs make their own food so they are called PRODUCERS Heterotrophs get their food from another source so they are called CONSUMERS Two Main forms of
Unit 3: Ecology II Section 1: Environmental Systems and Nutrient Cycling
 Unit 3: Ecology II Section 1: Environmental Systems and Nutrient Cycling Systems in the Environment are not Independent of one Another Central Case Study: The Vanishing Oysters of the Chesapeake Bay Chesapeake
Unit 3: Ecology II Section 1: Environmental Systems and Nutrient Cycling Systems in the Environment are not Independent of one Another Central Case Study: The Vanishing Oysters of the Chesapeake Bay Chesapeake
Chapter 4. Ecosystems
 Chapter 4 Ecosystems Chapter 4 Section 1: What Is an Ecosystem Key Vocabulary Terms 7 Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Community A group of various species that live in the same habitat and interact with
Chapter 4 Ecosystems Chapter 4 Section 1: What Is an Ecosystem Key Vocabulary Terms 7 Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Community A group of various species that live in the same habitat and interact with
MONDAY, 27 FEBRUARY 2017
 MONDAY, 27 FEBRUARY 2017 Room 301 B 302 A/B 304 A/B 305 A/B 306 A 306 B 308 A/B 199 168 258 162 150 168 194 9:00-9:50 9:50 - MORNING PLENARY - Marcia McNutt - 9:00 to 9:50 Session# 71 96 12 9 34 58 65
MONDAY, 27 FEBRUARY 2017 Room 301 B 302 A/B 304 A/B 305 A/B 306 A 306 B 308 A/B 199 168 258 162 150 168 194 9:00-9:50 9:50 - MORNING PLENARY - Marcia McNutt - 9:00 to 9:50 Session# 71 96 12 9 34 58 65
Chapter 54. Ecosystems. PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition. Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 54 Ecosystems PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in a community,
Chapter 54 Ecosystems PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in a community,
Allegheny-Clarion Valley School District
 Allegheny-Clarion Valley School District Jr./Sr. High School Name of Course: Ecology Grade Level: 9-12 Persons Writing/Revising Curriculum: Joni Runyan Laura Jamison *** Created 2015-16 School Year Unit
Allegheny-Clarion Valley School District Jr./Sr. High School Name of Course: Ecology Grade Level: 9-12 Persons Writing/Revising Curriculum: Joni Runyan Laura Jamison *** Created 2015-16 School Year Unit
Ecosystems. Studying Organisms In Their Environment. Division Ave. High School AP Biology. organism. population. community. ecosystem.
 Ecosystems Studying Organisms In Their Environment organism population community ecosystem biosphere 1 Essential questions What limits the production in ecosystems? How do nutrients move in the ecosystem?
Ecosystems Studying Organisms In Their Environment organism population community ecosystem biosphere 1 Essential questions What limits the production in ecosystems? How do nutrients move in the ecosystem?
What does each part of the equation mean? q=cm T
 Assignment #10 Energy Pyramids LO: I can define trophic levels and explain the energy flow. I can apply those ideas to food webs EQ: Where does all the energy from the sun go? (4-5 sentences) LEVEL ZERO
Assignment #10 Energy Pyramids LO: I can define trophic levels and explain the energy flow. I can apply those ideas to food webs EQ: Where does all the energy from the sun go? (4-5 sentences) LEVEL ZERO
7.014 Lecture 20: Biogeochemical Cycles April 1, 2007
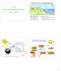 Global Nutrient Cycling - Biogeochemical Cycles 7.14 Lecture 2: Biogeochemical Cycles April 1, 27 Uptake Bioelements in Solution Weathering Precipitation Terrestrial Biomass Decomposition Volatile Elements
Global Nutrient Cycling - Biogeochemical Cycles 7.14 Lecture 2: Biogeochemical Cycles April 1, 27 Uptake Bioelements in Solution Weathering Precipitation Terrestrial Biomass Decomposition Volatile Elements
Human Biology. Chapter 23 Global Ecology and Human Interferences Lecture Outline. Sylvia S. Mader Michael Windelspecht
 Human Biology Sylvia S. Mader Michael Windelspecht Chapter 23 Global Ecology and Human Interferences Lecture Outline See separate FlexArt PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into
Human Biology Sylvia S. Mader Michael Windelspecht Chapter 23 Global Ecology and Human Interferences Lecture Outline See separate FlexArt PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into
Cycles of Ma,er. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 3.4 Cycles of Matter
 Lesson Overview Cycles of Ma,er Lesson Overview 3.4 Cycles of Matter THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these
Lesson Overview Cycles of Ma,er Lesson Overview 3.4 Cycles of Matter THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these
Lecture 1 Integrated water resources management and wetlands
 Wetlands and Poverty Reduction Project (WPRP) Training module on Wetlands and Water Resources Management Lecture 1 Integrated water resources management and wetlands 1 Water resources and use The hydrological
Wetlands and Poverty Reduction Project (WPRP) Training module on Wetlands and Water Resources Management Lecture 1 Integrated water resources management and wetlands 1 Water resources and use The hydrological
The Law of Conservation of Matter. Matter cannot be created nor destroyed Matter only changes form There is no away
 Review Items Ecosystem Structure The Law of Conservation of Matter Matter cannot be created nor destroyed Matter only changes form There is no away Laws Governing Energy Changes First Law of Thermodynamics
Review Items Ecosystem Structure The Law of Conservation of Matter Matter cannot be created nor destroyed Matter only changes form There is no away Laws Governing Energy Changes First Law of Thermodynamics
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: The RECYCLING of MATERIALS through living organisms and the physical environment.
 BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: The RECYCLING of MATERIALS through living organisms and the physical environment. BIOCHEMIST: Scientists who study how LIFE WORKS at a CHEMICAL level. The work of biochemists has
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: The RECYCLING of MATERIALS through living organisms and the physical environment. BIOCHEMIST: Scientists who study how LIFE WORKS at a CHEMICAL level. The work of biochemists has
Ecosystem goods and services Ecosystem goods and services
 Course goals 1) Have you develop a firm understanding of the concepts and mechanisms of ecosystem ecology; 2) Have you enhance your understanding of how human society is altering ecosystems, some of the
Course goals 1) Have you develop a firm understanding of the concepts and mechanisms of ecosystem ecology; 2) Have you enhance your understanding of how human society is altering ecosystems, some of the
Nutrient Cycling 1: The nitrogen cycle
 Nutrient Cycling 1: The nitrogen cycle I. Introduction A. Changes to the global N cycle (Ch. 15) 1. Global pools and fluxes 2. Changes 3. Consequences B. Overview of the ecosystem N cycle (Ch. 9) 1. Major
Nutrient Cycling 1: The nitrogen cycle I. Introduction A. Changes to the global N cycle (Ch. 15) 1. Global pools and fluxes 2. Changes 3. Consequences B. Overview of the ecosystem N cycle (Ch. 9) 1. Major
Dynamics of Ecosystems. Chapter 57
 Dynamics of Ecosystems Chapter 57 1 The Water Cycle Nutrient Cycles Trophic Levels Primary Productivity Outline The Energy in Food Chains Ecological Pyramids Interactions Among Trophic Levels Species Richness
Dynamics of Ecosystems Chapter 57 1 The Water Cycle Nutrient Cycles Trophic Levels Primary Productivity Outline The Energy in Food Chains Ecological Pyramids Interactions Among Trophic Levels Species Richness
Unit 2: Ecology. Chapters 2: Principles of Ecology
 Unit 2: Ecology Chapters 2: Principles of Ecology Ecology Probe: Answer the questions and turn it in! This is a standard aquarium with a population of fish. There is no filter in this aquarium and no one
Unit 2: Ecology Chapters 2: Principles of Ecology Ecology Probe: Answer the questions and turn it in! This is a standard aquarium with a population of fish. There is no filter in this aquarium and no one
Human perturbations to the global Nitrogen cycle
 Human perturbations to the global Nitrogen cycle Lecture for Biogeochemistry and Global Change Edzo Veldkamp The pace of human caused global change has increased in modern history, but none so rapidly
Human perturbations to the global Nitrogen cycle Lecture for Biogeochemistry and Global Change Edzo Veldkamp The pace of human caused global change has increased in modern history, but none so rapidly
Microbial biomass, ammonium, and nitrate levels in the soil across a northeastern hardwood/mixed conifer chronosequence Abstract Intro
 Molly Radosevich EEB 381 General Ecology Dr. Shannon Pelini Microbial biomass, ammonium, and nitrate levels in the soil across a northeastern hardwood/mixed conifer chronosequence Abstract Wildfire is
Molly Radosevich EEB 381 General Ecology Dr. Shannon Pelini Microbial biomass, ammonium, and nitrate levels in the soil across a northeastern hardwood/mixed conifer chronosequence Abstract Wildfire is
Niche and Habitat a species plays in a community. What it does all
 Ecosystem Dynamics What is ecology? Study of the interactions between parts of the environment Connections in nature Abiotic: soil comp. Biotic: and Abiotic and Biotic factors factors in the environment
Ecosystem Dynamics What is ecology? Study of the interactions between parts of the environment Connections in nature Abiotic: soil comp. Biotic: and Abiotic and Biotic factors factors in the environment
Net Ecosystem Carbon Exchange of Mangroves: Complexities in Developing Global Budgets
 Net Ecosystem Carbon Exchange of Mangroves: Complexities in Developing Global Budgets Robert R. Twilley Victor Rivera-Monroy Edward Castaneda Department of Oceanography and Coastal Science Louisiana State
Net Ecosystem Carbon Exchange of Mangroves: Complexities in Developing Global Budgets Robert R. Twilley Victor Rivera-Monroy Edward Castaneda Department of Oceanography and Coastal Science Louisiana State
Ecosystems & Energy Chapter 5
 Ecosystems & Energy Chapter 5 Energy Exchange in Ecosystems Cells Cells - minute compartments in a living organism which carry out processes of life Surrounded by lipid membrane controlling flow of materials
Ecosystems & Energy Chapter 5 Energy Exchange in Ecosystems Cells Cells - minute compartments in a living organism which carry out processes of life Surrounded by lipid membrane controlling flow of materials
Chapter 3 The Biosphere. Section Objectives:
 Chapter 3 The Biosphere Section Objectives: Distinguish between the biotic and abiotic factors in the environment. Compare the different levels of biological organization and living relationships important
Chapter 3 The Biosphere Section Objectives: Distinguish between the biotic and abiotic factors in the environment. Compare the different levels of biological organization and living relationships important
MILLER/SPOOLMAN 17 TH LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT. CHAPTER 3 Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work?
 MILLER/SPOOLMAN LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT 17 TH CHAPTER 3 Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work? Core Case Study: Tropical Rain Forests Are Disappearing Cover about 2% of the earth s land surface
MILLER/SPOOLMAN LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT 17 TH CHAPTER 3 Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work? Core Case Study: Tropical Rain Forests Are Disappearing Cover about 2% of the earth s land surface
EC FLUXES: BASIC CONCEPTS AND BACKGROUND. Timo Vesala (thanks to e.g. Samuli Launiainen and Ivan Mammarella)
 EC FLUXES: BASIC CONCEPTS AND BACKGROUND Timo Vesala (thanks to e.g. Samuli Launiainen and Ivan Mammarella) Scales of meteorological processes: Synoptic scale, ~ 1000 km (weather predictions, ~ day) Mesoscale,
EC FLUXES: BASIC CONCEPTS AND BACKGROUND Timo Vesala (thanks to e.g. Samuli Launiainen and Ivan Mammarella) Scales of meteorological processes: Synoptic scale, ~ 1000 km (weather predictions, ~ day) Mesoscale,
Streamside Management. How the area around your pond effects the water.
 Streamside Management Zones and Water Quality How the area around your pond effects the water. Stream(pond)side Management Zone A streamside management zone (SMZ) is a strip of land immediately adjacent
Streamside Management Zones and Water Quality How the area around your pond effects the water. Stream(pond)side Management Zone A streamside management zone (SMZ) is a strip of land immediately adjacent
Ecology: Part 2. Biology Mrs. Bradbury
 Ecology: Part 2 Biology Mrs. Bradbury Model 1: Food Chains Food Chain simple model showing the movement of matter and energy through ecosystems. Autotrophs Heterotrophs Decomposers Arrows show energy transfer
Ecology: Part 2 Biology Mrs. Bradbury Model 1: Food Chains Food Chain simple model showing the movement of matter and energy through ecosystems. Autotrophs Heterotrophs Decomposers Arrows show energy transfer
Ch. 5 - Nutrient Cycles and Soils
 Ch. 5 - Nutrient Cycles and Soils What are Nutrient (biogeochemical) Cycles? a process by which nutrients are recycled between living organisms and nonliving environment. The three general types of nutrient
Ch. 5 - Nutrient Cycles and Soils What are Nutrient (biogeochemical) Cycles? a process by which nutrients are recycled between living organisms and nonliving environment. The three general types of nutrient
Chapter 2. Table of Contents. Section 1 Organisms and Their Releationships. Section 2 Flow of Energy in an Ecosystem. Section 3 Cycling of Matter
 Ecosystems Table of Contents Section 1 Organisms and Their Releationships Section 2 Flow of Energy in an Ecosystem Section 3 Cycling of Matter Section 1 Organisms and Their Releationships Interactions
Ecosystems Table of Contents Section 1 Organisms and Their Releationships Section 2 Flow of Energy in an Ecosystem Section 3 Cycling of Matter Section 1 Organisms and Their Releationships Interactions
Soil Properties and Processes NRE EEB :00-11:00 Monday & Wednesday Fall Term 2004
 Soil Properties and Processes NRE 430 - EEB 489 10:00-11:00 Monday & Wednesday Fall Term 2004 Instructor: Dr. Donald R. Zak 2540 Dana Building Phone: 763-4991 Office Hours: M and W 9:00 to 10:00 pm; or
Soil Properties and Processes NRE 430 - EEB 489 10:00-11:00 Monday & Wednesday Fall Term 2004 Instructor: Dr. Donald R. Zak 2540 Dana Building Phone: 763-4991 Office Hours: M and W 9:00 to 10:00 pm; or
Transport & Transformation of chemicals in an ecosystem, involving numerous interrelated physical, chemical, & biological processes
 OPEN Wetland Ecology Lectures 14-15-16 Wetland Biogeochemistry What is biogeochemical cycling? Transport & Transformation of chemicals in an ecosystem, involving numerous interrelated physical, chemical,
OPEN Wetland Ecology Lectures 14-15-16 Wetland Biogeochemistry What is biogeochemical cycling? Transport & Transformation of chemicals in an ecosystem, involving numerous interrelated physical, chemical,
Palmer June /13/01
 7/3/ Day 4_Ecosystem Functions_intro + OM processes Ecosystem Function = Ecosystem or Ecological Processes Primary Production Whole Stream metabolism Organic matter processing (Decomposition and use of
7/3/ Day 4_Ecosystem Functions_intro + OM processes Ecosystem Function = Ecosystem or Ecological Processes Primary Production Whole Stream metabolism Organic matter processing (Decomposition and use of
Chapter 22: Energy in the Ecosystem
 Chapter 22: Energy in the Ecosystem What is ecology? Global human issues Physical limits Ecosystems Organisms Populations Species Interactions Communities Energy flows and nutrients cycle C, H 2 0, P,
Chapter 22: Energy in the Ecosystem What is ecology? Global human issues Physical limits Ecosystems Organisms Populations Species Interactions Communities Energy flows and nutrients cycle C, H 2 0, P,
Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake
 Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake Fig. 6.6 Recall: Current ocean is gaining Carbon.. OCEAN Reservoir size: 38000 Flux in: 90 Flux out: 88+0.2=88.2 90-88.2 = 1.8 Pg/yr OCEAN is gaining 1.8 Pg/yr Sum of the
Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake Fig. 6.6 Recall: Current ocean is gaining Carbon.. OCEAN Reservoir size: 38000 Flux in: 90 Flux out: 88+0.2=88.2 90-88.2 = 1.8 Pg/yr OCEAN is gaining 1.8 Pg/yr Sum of the
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from soils
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from soils
Crosswalk of Georgia Performance Standards & Georgia Standards of Excellence GSE Implementation in Environmental Science
 SEV1. Students will investigate the flow of energy and cycling of matter within an ecosystem and relate these phenomena to human society. a. Interpret biogeochemical cycles including hydrologic, nitrogen,
SEV1. Students will investigate the flow of energy and cycling of matter within an ecosystem and relate these phenomena to human society. a. Interpret biogeochemical cycles including hydrologic, nitrogen,
Ecology, the Environment, and Us
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 23 Ecology, the Environment, and Us Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 23 Ecology, the Environment, and Us Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
Ecological Studies. Analysis and Synthesis
 Ecological Studies Analysis and Synthesis Edited by W.D. Billings, Durham () F. Golley, Athens () O.L. Lange, Wiirzburg (FRG) J.S. Olson, Oak Ridge () H. Remmert, Marburg (FRG) Volume 72 Ecological Studies
Ecological Studies Analysis and Synthesis Edited by W.D. Billings, Durham () F. Golley, Athens () O.L. Lange, Wiirzburg (FRG) J.S. Olson, Oak Ridge () H. Remmert, Marburg (FRG) Volume 72 Ecological Studies
Environmental Principles & Concepts (EP&C)/COSA Correlation of 4 th - 7 th Grade CA Science Standards
 Environmental Principles & Concepts (EP&C)/COSA Correlation of 4 th - 7 th Grade CA Science Standards For ROSS Certifications at least nine of the 14 science standards are addressed during a 5-day program,
Environmental Principles & Concepts (EP&C)/COSA Correlation of 4 th - 7 th Grade CA Science Standards For ROSS Certifications at least nine of the 14 science standards are addressed during a 5-day program,
The Biosphere and Biogeochemical Cycles
 The Biosphere and Biogeochemical Cycles The Earth consists of 4 overlapping layers: Lithosphere Hydrosphere (and cryosphere) Atmosphere Biosphere The Biosphere The biosphere is the layer of life around
The Biosphere and Biogeochemical Cycles The Earth consists of 4 overlapping layers: Lithosphere Hydrosphere (and cryosphere) Atmosphere Biosphere The Biosphere The biosphere is the layer of life around
Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary. Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP)
 Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP) Introduction: A key theme of the ongoing DCERP program is monitoring
Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP) Introduction: A key theme of the ongoing DCERP program is monitoring
Biogeochemical Cycles Webquest
 Name: Date: Biogeochemical Cycles Webquest In this webquest you will search for information that will answer questions about the water, carbon/oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorous cycles using the listed websites.
Name: Date: Biogeochemical Cycles Webquest In this webquest you will search for information that will answer questions about the water, carbon/oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorous cycles using the listed websites.
The Nutrient Cycle. Atmospheric pool. Organic material. 5 Soil solution storage
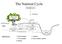 The Nutrient Cycle Atmospheric pool Precipitation Canopy, wood, and root Litter fall SOIL 2 Soil and rock minerals cations 1 2 3 Groundwater level Organic material 5 Soil solution storage 4 4 Channel BEDROCK
The Nutrient Cycle Atmospheric pool Precipitation Canopy, wood, and root Litter fall SOIL 2 Soil and rock minerals cations 1 2 3 Groundwater level Organic material 5 Soil solution storage 4 4 Channel BEDROCK
4) Ecosystem Feedbacks from Carbon and Water Cycle Changes
 4) Ecosystem Feedbacks from Carbon and Water Cycle Changes Summary: Climate change can affect terrestrial and marine ecosystems which in turn has impacts on both the water and carbon cycles and then feeds
4) Ecosystem Feedbacks from Carbon and Water Cycle Changes Summary: Climate change can affect terrestrial and marine ecosystems which in turn has impacts on both the water and carbon cycles and then feeds
 CHAPTER 14 ECOSYSTEM POINTS TO REMEMBER Startification : Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels in an ecosystem. Primary Production : Amount of biomas or organic matter produced
CHAPTER 14 ECOSYSTEM POINTS TO REMEMBER Startification : Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels in an ecosystem. Primary Production : Amount of biomas or organic matter produced
Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work?
 Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work? Chapter 3 Section 3-1 WHAT KEEPS US AND OTHER ORGANISMS ALIVE? Earth s life-support system has four major components The atmosphere is the thin membrane
Ecosystems: What Are They and How Do They Work? Chapter 3 Section 3-1 WHAT KEEPS US AND OTHER ORGANISMS ALIVE? Earth s life-support system has four major components The atmosphere is the thin membrane
Chapter 36: Population Growth
 Chapter 36: Population Growth Population: Population Concepts interbreeding group of same species Carrying Capacity: maximum population size an ecosystem can sustainably support Critical Number: minimum
Chapter 36: Population Growth Population: Population Concepts interbreeding group of same species Carrying Capacity: maximum population size an ecosystem can sustainably support Critical Number: minimum
Threats to Forest Ecosystem Health Activities together influence ecosystem structure & function
 Threats to Forest Ecosystem Health Activities together influence ecosystem structure & function introduced species poor management air pollution global warming habitat fragmentation American Chestnut From
Threats to Forest Ecosystem Health Activities together influence ecosystem structure & function introduced species poor management air pollution global warming habitat fragmentation American Chestnut From
CHAPTER. Evolution and Community Ecology
 CHAPTER 5 Evolution and Community Ecology Lesson 5.3 Ecological Communities https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gu2ezaisvqu The sun provides the energy for almost all of the ecological communities and species
CHAPTER 5 Evolution and Community Ecology Lesson 5.3 Ecological Communities https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gu2ezaisvqu The sun provides the energy for almost all of the ecological communities and species
AP Environmental Science
 AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
Soil Carbon Sequestration
 Soil Carbon Sequestration Rattan Lal Carbon Management and The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 USA 1 BIOSEQUESTRATION OF ATMOSPHERIC CO 2 Only 0.05% of the 3800 zettajoules (10 21 J) of solar
Soil Carbon Sequestration Rattan Lal Carbon Management and The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 USA 1 BIOSEQUESTRATION OF ATMOSPHERIC CO 2 Only 0.05% of the 3800 zettajoules (10 21 J) of solar
Chapter Two: Cycles of Matter (pages 32-65)
 Biology 20 Chapter 2.1_keyed Chapter Two: Cycles of Matter (pages 32-65) 2.1 The Role of Water in the Cycles of Matter (pages 34 40) Due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds, water has several unique
Biology 20 Chapter 2.1_keyed Chapter Two: Cycles of Matter (pages 32-65) 2.1 The Role of Water in the Cycles of Matter (pages 34 40) Due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds, water has several unique
Soil and Environmental Biochemistry and Microbial Ecology (ENR 6610) Course Syllabus Winter/Spring Semester 2016
 Soil and Environmental Biochemistry and Microbial Ecology (ENR 6610) Course Syllabus Winter/Spring Semester 2016 Instructor: Office Hours: Warren A. Dick The Ohio State University / The Ohio Agricultural
Soil and Environmental Biochemistry and Microbial Ecology (ENR 6610) Course Syllabus Winter/Spring Semester 2016 Instructor: Office Hours: Warren A. Dick The Ohio State University / The Ohio Agricultural
Ecosystems Section 1 What Is an Ecosystem? Objectives Distinguish Describe Sequence Interactions of Organisms and Their Environment Ecology Habitat
 Name Period Ecosystems Section 1 What Is an Ecosystem? Objectives Distinguish an ecosystem from a community. Describe the diversity of a representative ecosystem. Sequence the process of succession. Interactions
Name Period Ecosystems Section 1 What Is an Ecosystem? Objectives Distinguish an ecosystem from a community. Describe the diversity of a representative ecosystem. Sequence the process of succession. Interactions
Dynamic Regional Carbon Budget Based on Multi-Scale Data-Model Fusion
 Dynamic Regional Carbon Budget Based on Multi-Scale Data-Model Fusion Mingkui Cao, Jiyuan Liu, Guirui Yu Institute Of Geographic Science and Natural Resource Research Chinese Academy of Sciences Toward
Dynamic Regional Carbon Budget Based on Multi-Scale Data-Model Fusion Mingkui Cao, Jiyuan Liu, Guirui Yu Institute Of Geographic Science and Natural Resource Research Chinese Academy of Sciences Toward
How Ecosystems Work Section 1. Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1
 Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1 Life Depends on the Sun Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1 Life Depends on the Sun Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
Chapter 6. Aquatic Biodiversity. Chapter Overview Questions
 Chapter 6 Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter Overview Questions Ø What are the basic types of aquatic life zones and what factors influence the kinds of life they contain? Ø What are the major types of saltwater
Chapter 6 Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter Overview Questions Ø What are the basic types of aquatic life zones and what factors influence the kinds of life they contain? Ø What are the major types of saltwater
Ecology: Chapters Worksheet
 Ecology: Chapters 34 36 Worksheet Name: Chapter 34: The Biosphere Concept 34.1 The biosphere is the global ecosystem. (pp. 744 749) The scientific study of the interactions among organisms and between
Ecology: Chapters 34 36 Worksheet Name: Chapter 34: The Biosphere Concept 34.1 The biosphere is the global ecosystem. (pp. 744 749) The scientific study of the interactions among organisms and between
Biol 210 Environmental Biology Exam 1C Spring 2016
 Biol 210 Environmental Biology Exam 1C Spring 2016 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Abundant light and constant nutrient input make
Biol 210 Environmental Biology Exam 1C Spring 2016 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Abundant light and constant nutrient input make
Lakes, Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling
 OCN 401-Biogeochemical Systems Lecture #10 (9.22.11) Lakes, Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling (Schlesinger: Chapter 7) 1. Primary Production and Nutrient Cycling in Lakes Physical aspects and nomenclature
OCN 401-Biogeochemical Systems Lecture #10 (9.22.11) Lakes, Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling (Schlesinger: Chapter 7) 1. Primary Production and Nutrient Cycling in Lakes Physical aspects and nomenclature
How Ecosystems Work Section 1. Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1
 Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1 Life Depends on the Sun Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
Chapter 5 How Ecosystems Work Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems DAY 1 Life Depends on the Sun Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
Bio 112 Ecology: Final Study Guide
 Bio 112 Ecology: Final Study Guide Below is an outline of the topics and concepts covered on the final exam. This packet also includes a practice test, along with answers to questions 1-44. You may submit
Bio 112 Ecology: Final Study Guide Below is an outline of the topics and concepts covered on the final exam. This packet also includes a practice test, along with answers to questions 1-44. You may submit
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Ecosystem Ecology Examines Interactions Between the Living and Non-Living World Ecosystem- A particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Ecosystem Ecology Examines Interactions Between the Living and Non-Living World Ecosystem- A particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting
Principles of Food Sanitation. Fifth Edition
 Principles of Food Sanitation Fifth Edition Principles of Food Sanitation Fifth Edition Norman G. Marriott, PhD Extension Food Scientist and Professor Emeritus Department of Food Science and Technology
Principles of Food Sanitation Fifth Edition Principles of Food Sanitation Fifth Edition Norman G. Marriott, PhD Extension Food Scientist and Professor Emeritus Department of Food Science and Technology
IB Environmental Systems & Societies
 IB Environmental Systems & Societies YEAR 1 Syllabus Content: Topics and Assessment Statements Mr. Rees Topic 7: Environmental Value Systems 7.1.1 State what it is meant by an environmental value system.
IB Environmental Systems & Societies YEAR 1 Syllabus Content: Topics and Assessment Statements Mr. Rees Topic 7: Environmental Value Systems 7.1.1 State what it is meant by an environmental value system.
AIR POLLUTION AND ACID RAIN: The Biological Impact
 A DIRECTOR OF BIOCHEMISTRY, DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES, UNIVERSITY OF LANCASTER, UK AIR POLLUTION AND ACID RAIN: The Biological Impact Longman Scientific & Technical Copublished in the United States
A DIRECTOR OF BIOCHEMISTRY, DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES, UNIVERSITY OF LANCASTER, UK AIR POLLUTION AND ACID RAIN: The Biological Impact Longman Scientific & Technical Copublished in the United States
BSc Minors in English
 BSc Minors in English Wageningen University Overview BSc Minors for Exchange Students All minors presented on this information sheet are taught in English. For more information please surf to: www.wageningenuniversity.nl/minors
BSc Minors in English Wageningen University Overview BSc Minors for Exchange Students All minors presented on this information sheet are taught in English. For more information please surf to: www.wageningenuniversity.nl/minors
06/10/2015. Lecture 3: Ecological Pyramids and the Transfer of Energy in Ecosystems PYRAMID OF NUMBERS. Pyramid of Numbers. Pyramid of numbers cont.
 Lecture 3: Ecological Pyramids and the Transfer of Energy in Ecosystems ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS The trophic levels of an ecosystem can be arranged into in a pyramid and these are called the ecological pyramids
Lecture 3: Ecological Pyramids and the Transfer of Energy in Ecosystems ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS The trophic levels of an ecosystem can be arranged into in a pyramid and these are called the ecological pyramids
AP Lab 12--DISSOLVED OXYGEN & AQUATIC PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY (LabBench)
 Name AP Biology AP Lab 12--DISSOLVED OXYGEN & AQUATIC PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY (LabBench) Web address: http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench Click on Lab 12: Dissolved Oxygen & Aquatic Primary
Name AP Biology AP Lab 12--DISSOLVED OXYGEN & AQUATIC PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY (LabBench) Web address: http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench Click on Lab 12: Dissolved Oxygen & Aquatic Primary
The Cycling of Matter
 Section 2 Objectives Describe the short-term and long-term process of the carbon cycle. Identify one way that humans are affecting the carbon cycle. List the three stages of the nitrogen cycle. Describe
Section 2 Objectives Describe the short-term and long-term process of the carbon cycle. Identify one way that humans are affecting the carbon cycle. List the three stages of the nitrogen cycle. Describe
Water cycles through ecosystems.
 Water cycles through ecosystems. Water is stored on Earth s surface in lakes, rivers, and oceans. Water is found underground, filling the spaces between soil particles and cracks in rocks. Large amounts
Water cycles through ecosystems. Water is stored on Earth s surface in lakes, rivers, and oceans. Water is found underground, filling the spaces between soil particles and cracks in rocks. Large amounts
Carbon, Part 3, Net Ecosystem Production
 Carbon, Part 3, Net Ecosystem Production Carbon Balance of Ecosystems NEP,NPP, GPP Seasonal Dynamics of Ecosystem Carbon Fluxes Carbon Flux Partitioning Chain-saw and Shovel Ecology Dennis Baldocchi ESPM
Carbon, Part 3, Net Ecosystem Production Carbon Balance of Ecosystems NEP,NPP, GPP Seasonal Dynamics of Ecosystem Carbon Fluxes Carbon Flux Partitioning Chain-saw and Shovel Ecology Dennis Baldocchi ESPM
Introduction (Welcome!)
 Introduction (Welcome!) OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems LECTURES Lectures will generally be given using PowerPoint presentations. As a convenience to students, copies of the PowerPoint slides will be
Introduction (Welcome!) OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems LECTURES Lectures will generally be given using PowerPoint presentations. As a convenience to students, copies of the PowerPoint slides will be
Martin Heimann Max-Planck-Institute for Biogeochemistry, Jena, Germany
 Martin Heimann Max-Planck-Institute for Biogeochemistry, Jena, Germany martin.heimann@bgc-jena.mpg.de 1 Northern Eurasia: winter: enhanced warming in arctic, more precip summer: general warming in center,
Martin Heimann Max-Planck-Institute for Biogeochemistry, Jena, Germany martin.heimann@bgc-jena.mpg.de 1 Northern Eurasia: winter: enhanced warming in arctic, more precip summer: general warming in center,
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 20 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2016 Frank Sansone 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 20 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2016 Frank Sansone 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen
Integrated Science for Society and the Environment
 Integrated Science for Society and the Environment Scott Collins, Ali Whitmer, Barbara Benson, Dan Childers http://intranet.lternet.edu/planning/ A DECADE OF SYNTHESIS: GOALS OF THE LTER PLANNING PROCESS
Integrated Science for Society and the Environment Scott Collins, Ali Whitmer, Barbara Benson, Dan Childers http://intranet.lternet.edu/planning/ A DECADE OF SYNTHESIS: GOALS OF THE LTER PLANNING PROCESS
AP Environmental Science
 Name AP Environmental Science DISSOLVED OXYGEN & AQUATIC PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY (LabBench) Web address: http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench Click on Lab 12: Dissolved Oxygen & Aquatic
Name AP Environmental Science DISSOLVED OXYGEN & AQUATIC PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY (LabBench) Web address: http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench Click on Lab 12: Dissolved Oxygen & Aquatic
The Hydrological Cycle. Hydrological Cycle. Definition of Terms. Soils and Water, Spring Lecture 7, The Hydrological Cycle 1
 The Hydrological Cycle Water vapor helps warm up the earth Evaporation+Transpiration Chemical Spill Runoff To Oceans Water potential, atmosphere Hydrological Cycle Transpiration, T Atmospheric pool Interception
The Hydrological Cycle Water vapor helps warm up the earth Evaporation+Transpiration Chemical Spill Runoff To Oceans Water potential, atmosphere Hydrological Cycle Transpiration, T Atmospheric pool Interception
