GCSE GEOGRAPHY KS4 Knowledge Book Case Studies and Examples
|
|
|
- Virgil Dalton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GCSE GEOGRAPHY KS4 Knowledge Book Case Studies and Examples Page 1
2 CASE STUDIES AND EXAMPLES Can be used for any question BUT are essential for 6 and 9 mark questions: Case Studies involve a large scale with multiple topics looked at in-depth Examples involve a smaller scale with a key focus PAPER 1: LIVING WITH THE PHYSICAL ENVIRONMENT 2 large case studies 8 smaller examples Section Examples Case Studies The challenge of natural Hazards Tectonic hazard-two contrasting countries: Iceland vs Nyiragongo (DRC) Tropical storm-effects and responses: Typhoon Hyain Recent extreme weather event in UK- causes impacts, management: Somerset Floods The living world Small scale UK ecosystem: Epping Forest Tropical rainforest-causes of deforestation, impacts and issues: Malaysia Cold environment: development opportunities and challenges Alaska or Svalbard Physical landscapes in the United Kingdom (two from rivers, coasts, glacial) Section of river valley - landforms of erosion and deposition River Tees Section of coastline - landforms of erosion and deposition Swanage Coastal management scheme: Lyme Regis or Holderness River flood management scheme: Banbury or River Nene Page 2
3 PAPER 2: CHALLENGES IN THE HUMAN ENVIRONMENT 3 large case studies 6 smaller examples Section Examples Case Studies Urban issues and challenges Rio urban planning: Favela Bairro Project, Rio Urban regeneration: Olympic Park, London Major city in a LIC or NEE -causes of growth, opportunities, challenges: social, economic, environmental: Rio Major city in the UK - importance, migration, opportunities, challenges: London The changing economic world Growth of tourism in one LIC or NEE: Jamaica One LIC or NEE-economic structure, TNCs, trade, aid, debt: Nigeria UK economic futures industrial Sustainability: Nissan Car plant Sunderland The challenge of resource management (one from food, water, energy) Large scale water transfer scheme: Lesotho Local scheme to increase water supply: Rajasthan, India Page 3
4 PAPER 1 Case Study Content - what do you have to do? Key thoughts/ideas Malaysia, Causes of deforestation 1. Assess the (size) of the threats how big is the tropical rainforests subsistence and commercial farming threat from humans? 2. Which are the biggest threats why logging 3. What are the problems with each cause how road building does it impact the environment? mineral extraction energy development settlement population Impacts of deforestation 1. Evaluate which is the most important why? economic 2. To what extent does the TRF provide both development economic opportunities and challenges soil erosion loss of biodiversity contribution to climate change Value of the tropical rainforest to people and environment 1. Assess the extent to which the TRF is more valuable to the people than the environment. Strategies used to manage the rainforest sustainably: 1. Evaluate the effectiveness of strategies used to manage the rainforest sustainably selective logging and replanting 2. To what extent are management strategies conservation and education successful in the TRF? ecotourism and international agreements about the use of tropical hardwoods debt reduction To what extent are TRF s at risk from human activities? Assess the importance of management strategies used to reduce the risk of environmental damage. Using Figure 8 and your own understanding, explain how deforestation can have economic impacts. Case Study Content - what do you have to do? Key thoughts/ideas Alaska or Development opportunities: 1. How significant are the opportunities? Svalbard mineral extraction 2. What is the potential damage they can cause? energy fishing tourism Challenges of developing cold environments: 1. How significant are the challenges? 2. How have humans overcome these extreme temperature challenges? inaccessibility 3. Are the challenges restricting development provision of building and infrastructure opportunities? Choose one of the following environments: Environments on the fringe of hot deserts OR Cold environments: To what extent is your chosen environment at risk from human activity? Choose one of the following environments: an area on the fringe of a hot desert or a cold environment. For your chosen environment, assess the importance of management strategies used to reduce the risk of environmental damage. Page 4
5 Iceland vs Nyiragongo (DRC) Primary and Secondary Effects 1. Which are more important? Why? 2. Which were more devastating? Immediate and long-term responses 1. Which were the most important why? How the responses vary between the two 2. Which were the most effective? 3. Were the responses effective/successful? Choose either an earthquake or a volcanic eruption. Assess the extent to which primary effects are more significant than secondary effects. Use Figure 5a or 5b and an example you have studied. Using a named example, evaluate the immediate and long-term responses to a tectonic event you have studied Using Figure 2 and your own knowledge, suggest why the effects of a tectonic hazard vary between areas of contrasting levels of wealth. Typhoon Hyain Primary and Secondary Effects 1. Which are more important? Why? 2. Which were more devastating? Immediate and long-term responses (including planning look at Hyain, USA and Bangladesh) secondary effects. 1. Which were the most important why? 2. Which were the most effective? 3. Were the responses effective/successful? For a tropical storm you have studied: Assess the extent to which primary effects are more significant than Using a named example, evaluate the immediate and long-term responses to a tropical storm you have studied Assess the extent to which prediction is the most important factor in reducing the effects of tropical storms Somerset Floods Causes 1. Physical factors were more important than human factors? 2. Which factors were the most important in causing the flood? 3. Assess the human/physical factors Social, economic and environmental impacts How management strategies can reduce risk 1. Which were the most important why? 2. Which were the most devastating? 3. Can you explain these fully? 4. Assess the impacts e.g. scales/size 1. How effective/successful? 2. Which were the most important 3. Can you explain how the strategies work? For an extreme weather event in the UK you have studied, evaluate its attempts to reduce future risk Explain the impacts of an extreme weather event in the UK you have studied Assess the causes of an extreme weather event in the UK you have studied Page 5
6 Epping Forest Concept of inter-relationships: 1. Assess impact of removing/damaging (deciduous producers producers forest) (could consumers 2. Exemplify inter-dependence (biomass, also use pond as decomposers nutrient cycling, vs leeching etc.) a small-scale food chain ecosystems) food web nutrient cycle Explain why the diagram shown in Figure 9 is an example of nature s recycling system. (can use TRF for this) Section of a coast: Swanage Identify a section of a coastline in the UK to identify its major landforms of erosion and deposition 1. Describe and explain every landform in sequential step by step detail using high level key terms Section of a River Valley: River Tess Describe and explain every landform in sequential step by step detail using high level key terms Rivers: Coasts: V-shaped valleys and inter-locking spurs Bays and headlands (concordant vs discordant) Waterfalls and gorges Wave cut-notches and wave-cut platforms Meanders and ox-bow lakes Caves, arches, stacks and stumps Floodplains and levees Beaches Estuary Sand dunes (entire sequence) Spits Bay Bars (and tombolo s) Coastal management: Lyme Regis or Holderness Understand reasons for management/why the scheme was required The management strategies employed The effects/outcomes and conflicts N/A 1. How effective was the strategy? Was it successful? 2. Why different groups of people had different views? Page 6
7 River flood management: Banbury or River Nene Understand reasons for management/why the scheme was required N/A The management strategies employed Social, economic and environmental issues 1. How effective was the strategy? Was it successful? 2. Why different groups of people had different views? PAPER 1: 9 MARK QUESTIONS FROM SAMS 1. Using a named example, evaluate the immediate and long-term responses to tropical storms. [9 marks] [+ 3 SPaG marks] 2. Choose one of the following environments: Environments on the fringe of hot deserts OR Cold environments: To what extent is your chosen environment at risk from human activity? [9 marks] 3. Choose either an earthquake or a volcanic eruption. Assess the extent to which primary effects are more significant than secondary effects. Use Figure 5a or 5b and an example you have studied. [9 marks] [+ 3 SPaG marks] 4. Assess the extent to which prediction is the most important factor in reducing the effects of tropical storms. [9 marks] [+ 3 SPaG marks] 5. Choose one of the following environments: an area on the fringe of a hot desert or a cold environment. For your chosen environment, assess the importance of management strategies used to reduce the risk of environmental damage. [9 marks] Page 7
8 PAPER 2 Case Study Content - what do you have to do? Key thoughts/ideas Rio De Janerio The location and importance of the city 1. Why is its location an advantage? regionally, nationally and internationally Causes of growth: natural increase and 1. Why is Rio so attractive vs rural areas? migration Urban growth has created opportunities: 1. How significant are the opportunities? Social access to services (health, education, water, energy) 2. Why do people want to access theses? 3. How will these improve people s quality of Economic how industrial areas can be a stimulus for economic development life? How urban growth has created challenges: 1. How significant are these challenges? Managing urban growth slums, squatter settlements 2. Are these challenges important? 3. How do these challenges affect people s Services - access to clean water, sanitation systems, energy, health and education quality of life? 4. Do the challenges outweigh the opportunities? Reducing unemployment and crime Managing environmental issues waste disposal, air and water pollution, traffic congestion Assess the challenges for city in an NEE you have studied To what extent has urban change created opportunities in a LIC/NEE city you have studied? For a city in an NEE/LIC you have studied, to what extent does it provide both opportunities and challenges? Favela Bairro How urban planning is improving the quality of life for the poor 1. What was involved? 2. How did it improve people s quality of life? 3. What were the successes and failures? 4. How effective was the urban planning scheme overall? Evaluate the effectiveness of an urban planning strategy in helping to improve the quality of life for the urban poor. Page 8
9 Case Study Content - what do you have to do? Key thoughts/ideas London The location and importance of the city in 1. Why is its location an advantage? the UK Impacts of national and international migration on the growth and character of the city 1. What are the major impacts positive and negative (area of origin and destination) Urban growth has created opportunities: Social and economic cultural mix, recreation/entertainment, employment, integrated transport system Environmental urban greening How urban growth has created challenges: Social and economic urban deprivation, inequalities in housing, education, health and employment Environmental dereliction, building on brownfield sites, waste disposal Impact of urban sprawl on the urban-rural fringe and the growth of commuter settlements Assess the challenges for a major UK city you have studied 1. How significant are the opportunities? 2. Why do people want to access theses? 3. How will these improve people s quality of life? 1. How significant are these challenges? 2. Are these challenges important? 3. How do these challenges affect people s quality of life? 4. Do the challenges outweigh the opportunities? To what extent has urban change created opportunities in a major UK city you have studied? For a major city in the UK you have studied, to what extent does it provide both opportunities and challenges? Evaluate the effectiveness of an urban transport scheme(s) you have studied Olympic Park, London Reasons why the regeneration was needed and the main features of the project 1. What was involved? 2. How did it improve people s quality of life? 3. Was it successful socially, economically and environmentally? 4. What were the successes and failures? 5. How effective was the regeneration project overall? Evaluate the success of a regeneration project in helping people improve their quality of life. Evaluate the success of a regeneration project in helping improve the local environment and economy Page 9
10 Case Study Content - what do you have to do? Key thoughts/ideas Nigeria The location and importance of the country 1. Why is its location an advantage? regionally and globally The wider political, social, cultural and environmental context within which the country is placed Changing industrial structure and the balance of the different sectors within the economy. How the manufacturing industry can stimulate economic development. The role of TNC s in relation to development and the advantages and disadvantages of TNC s to Nigeria The changing political relationships with the wider world International aid types of aid, impacts of aid on the receiving country The environmental impacts of economic development The effects of economic development on the quality of life for the population 1. What is the most important factor influencing the key challenges for Nigeria 1. Why is moving people from primary to secondary to tertiary sector so important for the people and the government? 2. How does manufacturing drive the multiplier effect: a. Wages increases and raised employment b. Taxes invested (education, health and infrastructure c. Nigeria becomes more attractive to further investment d. Increase spending causes more local shops to open which drives employment 1. Do the advantages outweigh the disadvantages? 2. Social, economic and environmental impacts (positive and negative) 1. How will the changing role facilitate growth? 1. Which types of aid are most successful? Why? 1. How big are the challenges and how big are the opportunities of economic development 2. Are the economic gains worth it? 1. Does everyone win? 2. Is Nigeria improving everyone s quality of life? Transnational corporations (TNCs) only bring advantages to the host country. Do you agree with this statement? Yes No Justify your decision. To what extent do the benefits of economic development outweigh the environmental impacts? Refer to a NEE/LIC you have studied Content - what do you have to do? Key thoughts/ideas Jamaica How tourism helps to reduce the development gap 1. Benefits and problems of tourism evaluate 2. Evaluate the idea it reduces gap Use an example of a city in a lower income country (LIC) or newly emerging economy (NEE). Evaluate the effectiveness of tourism in reducing the development gap. Use Figure 9 and your own knowledge. Page 10
11 Nissan Car Plant Content - what do you have to do? How modern industrial development can be more environmentally sustainable Key thoughts/ideas 1. Key features 2. Evaluate how environmentally successful is for the future issues and successes 3. Define environmentally sustainable Using Figure 8 to help you, explain how modern industrial developments can be made more environmentally sustainable. Lesotho Content - what do you have to do? Advantages and disadvantages of a largescale water transfer scheme Key thoughts/ideas 1. What was involved? 2. Social, economic and environmental advantages and disadvantages for both Lesotho and South Africa 3. Evaluate how successful it was Examine the advantages and disadvantages of a large scale water transfer scheme that you have studied. Rajasthan, India Content - what do you have to do? How a local scheme has increased sustainable water supplies Key thoughts/ideas 1. What was involved what strategies were used? 2. Social, economic and environmental advantages and disadvantages 3. Did it work? 4. Evaluate how successful it was Use an example from a LIC/NEE to explain how local strategies are being used to increase sustainable supplies of water. PAPER 2: 9 MARK QUESTIONS FROM SAMS 1. To what extent has urban change created opportunities in a UK city you have studied? 2. Suggest how one or more strategies might reduce regional differences in the UK. 3. Evaluate the effectiveness of an urban transport scheme(s) you have studied. 4. Transnational corporations (TNCs) only bring advantages to the host country. Do you agree with this statement? Yes No Justify your decision. 5. Evaluate the effectiveness of an urban planning strategy in helping to improve the quality of life for the urban poor. 6. Use an example of a city in a lower income country (LIC) or newly emerging economy (NEE). Evaluate the effectiveness of tourism in reducing the development gap. Use Figure 9 and your own knowledge. Page 11
PERSONALISED LEARNING CHECKLISTS
 Area of Study: Physical Landscapes in the UK I can describe the location of the major upland and lowland areas within the UK I can describe the location of the major river systems within the UK Area of
Area of Study: Physical Landscapes in the UK I can describe the location of the major upland and lowland areas within the UK I can describe the location of the major river systems within the UK Area of
LIST OF CASE STUDIES HOMEWORK TASK
 LIST OF CASE STUDIES HOMEWORK TASK Use your CGP revision guide in order to produce a fact file, mind map, poster or PowerPoint presentation to summarise all of the case studies and key content across all
LIST OF CASE STUDIES HOMEWORK TASK Use your CGP revision guide in order to produce a fact file, mind map, poster or PowerPoint presentation to summarise all of the case studies and key content across all
The information in this document will help you plan focused revision between now and your exams.
 Rickmansworth School Geography Department AQA GCSE Revision guide 2018 Dear student and parent/carer, The information in this document will help you plan focused revision between now and your exams. Ensure
Rickmansworth School Geography Department AQA GCSE Revision guide 2018 Dear student and parent/carer, The information in this document will help you plan focused revision between now and your exams. Ensure
The challenge of natural hazards
 Year 10 end of unit revision list The challenge of natural hazards Tectonic hazards Specification content Plate tectonics theory- what is this and what has it got to do with Alfred Wegner? To know where
Year 10 end of unit revision list The challenge of natural hazards Tectonic hazards Specification content Plate tectonics theory- what is this and what has it got to do with Alfred Wegner? To know where
Restless Earth. Unique landforms occur at plate margins Location and formation of fold mountains ocean trenches composite volcanoes shield volcanoes.
 Restless Earth The Earth s crust is unstable, especially at plate margins Distribution of plates Contrasts between continental and oceanic plates. Destructive, constructive and conservative plate margins.
Restless Earth The Earth s crust is unstable, especially at plate margins Distribution of plates Contrasts between continental and oceanic plates. Destructive, constructive and conservative plate margins.
Year 11 Revision Booklet
 Year 11 Revision Booklet Paper 2: Challenges in the human environment Urban issues and challenges Question 1 The changing economic world Question 2 The challenge of resource management Question 3 Water
Year 11 Revision Booklet Paper 2: Challenges in the human environment Urban issues and challenges Question 1 The changing economic world Question 2 The challenge of resource management Question 3 Water
Year 11 Revision Booklet
 Year 11 Revision Booklet Paper 2: Challenges in the human environment Urban issues and challenges Question 1 The changing economic world Question 2 The challenge of resource management Question 3 Energy
Year 11 Revision Booklet Paper 2: Challenges in the human environment Urban issues and challenges Question 1 The changing economic world Question 2 The challenge of resource management Question 3 Energy
Salendine Nook High school GCSE Geography. The fragile world physical systems and environmental issues
 Salendine Nook High school GCSE Geography The fragile world physical systems and environmental issues Ice, Rivers and the Sea Weather and climate Sustainable development of the environment Paper 1 2 hr
Salendine Nook High school GCSE Geography The fragile world physical systems and environmental issues Ice, Rivers and the Sea Weather and climate Sustainable development of the environment Paper 1 2 hr
Paper Reference. 1313/2F Edexcel GCSE Geography B Paper 2F. Foundation Tier. Monday 12 June 2006 Afternoon Time: 2 hours
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1313/2F Edexcel GCSE Geography B Paper 2F Foundation Tier Monday 12 June 2006 Afternoon Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1313/2F Edexcel GCSE Geography B Paper 2F Foundation Tier Monday 12 June 2006 Afternoon Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Nil Paper Reference
What is an ecosystem? Food chains show. Within a food chain there are various stages. Draw a mon-living / living organism: Primary producer
 What is an ecosystem? Within a food chain there are various stages. Draw a mon-living / living organism: Food chains show Decomposer Primary producer Primary consumer Secondary consumer Tertiary consumer
What is an ecosystem? Within a food chain there are various stages. Draw a mon-living / living organism: Food chains show Decomposer Primary producer Primary consumer Secondary consumer Tertiary consumer
AQA Geography practice paper answers
 Paper Section A: The challenge of natural hazards.. One mark for either: Sea temperatures decrease and then increase. Sea temperatures fluctuate quite considerably. Second mark for use of data shown on
Paper Section A: The challenge of natural hazards.. One mark for either: Sea temperatures decrease and then increase. Sea temperatures fluctuate quite considerably. Second mark for use of data shown on
Stewards Pooi Kei College TEACHING SCHEDULE ( ) Form: S3 Subject : Geography No. of periods per cycle: 4 Teacher: Mr. Ray Hon & Ms May Au
 Form: S3 Subject : Geography No. of periods per cycle: 4 Teacher: Mr. Ray Hon & Ms May Au Topic Cycle Geographical knowledge Class work/ Remarks/ Homework Adjustments 1 Part 2 Food problems- Trend of food
Form: S3 Subject : Geography No. of periods per cycle: 4 Teacher: Mr. Ray Hon & Ms May Au Topic Cycle Geographical knowledge Class work/ Remarks/ Homework Adjustments 1 Part 2 Food problems- Trend of food
GCSE Geography B. Mark Scheme for June Unit B563/01: Key Geographical Themes (Foundation Tier) General Certificate of Secondary Education
 GCSE Geography B Unit B563/01: Key Geographical Themes (Foundation Tier) General Certificate of Secondary Education Mark Scheme for June 2014 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge
GCSE Geography B Unit B563/01: Key Geographical Themes (Foundation Tier) General Certificate of Secondary Education Mark Scheme for June 2014 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level * 839 1 5 7 * GEOGRAPHY 17/13 Paper 1 May/June 1 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Ruler READ
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level * 839 1 5 7 * GEOGRAPHY 17/13 Paper 1 May/June 1 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Ruler READ
GCSE GEOGRAPHY KS4 CASE STUDY: TROPICAL RAINFORESTS (MALAYSIA) KNOWLEDGE BOOK
 GCSE GEOGRAPHY KS4 CASE STUDY: TROPICAL RAINFORESTS (MALAYSIA) KNOWLEDGE BOOK Page 1 TROPICAL RAINFOREST CASE STUDY: MALAYSIA AQA GCSE This is an important case study and you will have an assessment on
GCSE GEOGRAPHY KS4 CASE STUDY: TROPICAL RAINFORESTS (MALAYSIA) KNOWLEDGE BOOK Page 1 TROPICAL RAINFOREST CASE STUDY: MALAYSIA AQA GCSE This is an important case study and you will have an assessment on
Chapter 22: West Africa
 Chapter 22: West Africa Section 1 - Physical Geography of West Africa Landforms West Africa has a long coastline along the Atlantic Ocean, with the northern part of the subregion extending into the
Chapter 22: West Africa Section 1 - Physical Geography of West Africa Landforms West Africa has a long coastline along the Atlantic Ocean, with the northern part of the subregion extending into the
0680 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0680 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/12 Paper 1, maximum raw mark 60
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0680 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/12 Paper 1, maximum raw mark 60
A CASE STUDY COLLECTION
 GCSE GEOGRAPHY AQA A CASE STUDY COLLECTION Contents Paper 1: Living in the Physical Environment The Challenges of Natural Hazards 1. Haiti Earthquake (2011) Page 2 2. E15 Icelandic Eruption (2010) Page
GCSE GEOGRAPHY AQA A CASE STUDY COLLECTION Contents Paper 1: Living in the Physical Environment The Challenges of Natural Hazards 1. Haiti Earthquake (2011) Page 2 2. E15 Icelandic Eruption (2010) Page
Urban issues and challenges
 Urban issues and challenges Describe the distribution of the percentage of people living in urban settlements (3 Marks) Describe how the rural and urban populations have changed from 1950 to 2050 (3 Marks)
Urban issues and challenges Describe the distribution of the percentage of people living in urban settlements (3 Marks) Describe how the rural and urban populations have changed from 1950 to 2050 (3 Marks)
GCSE 4232/02 GEOGRAPHY (Specification A) HIGHER TIER UNIT 2 Options Geography
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 4232/02 GEOGRAPHY (Specification A) HIGHER TIER UNIT 2 Options Geography A.M. MONDAY, 18 June 2012 1 hour 15 minutes For s Use Only Theme 7 Section
Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number GCSE 4232/02 GEOGRAPHY (Specification A) HIGHER TIER UNIT 2 Options Geography A.M. MONDAY, 18 June 2012 1 hour 15 minutes For s Use Only Theme 7 Section
: ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE AND DISASTER MANAGEMENT COURSE CODE : 3001 COURSE CATEGORY : P PERIODS/ WEEK : 3 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 45 CREDIT : 3
 COURSE TITLE : ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE AND DISASTER MANAGEMENT COURSE CODE : 3001 COURSE CATEGORY : P PERIODS/ WEEK : 3 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 45 CREDIT : 3 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Renewable and
COURSE TITLE : ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE AND DISASTER MANAGEMENT COURSE CODE : 3001 COURSE CATEGORY : P PERIODS/ WEEK : 3 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 45 CREDIT : 3 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Renewable and
For the multiple-choice questions, completely fill in the circle alongside the appropriate answer.
 SPECIMEN ASSESSMENT MATERIAL A-level GEOGRAPHY Paper 1 Physical geography Specimen Question Paper Materials For this paper you must have: a pencil a rubber a ruler. You may use a calculator. Instructions
SPECIMEN ASSESSMENT MATERIAL A-level GEOGRAPHY Paper 1 Physical geography Specimen Question Paper Materials For this paper you must have: a pencil a rubber a ruler. You may use a calculator. Instructions
3rd Year Geography Higher Level
 3rd Year Geography Higher Level Rivers No part of this publication may be copied, reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without
3rd Year Geography Higher Level Rivers No part of this publication may be copied, reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without
1. Only about 25% of the annual precipitation actually ends up in the river. Where does the other 85% go?
 Earth Revealed #19: Running Water 1: Rivers, Erosion and Deposition Name 1. Only about 25% of the annual precipitation actually ends up in the river. Where does the other 85% go? 2. Describe how the following
Earth Revealed #19: Running Water 1: Rivers, Erosion and Deposition Name 1. Only about 25% of the annual precipitation actually ends up in the river. Where does the other 85% go? 2. Describe how the following
Subject specific vocabulary
 Subject specific vocabulary All terms stated in the specification can be used in the exam. Students should be familiar with, and gain some understanding of, these terms in relation to the topics that they
Subject specific vocabulary All terms stated in the specification can be used in the exam. Students should be familiar with, and gain some understanding of, these terms in relation to the topics that they
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6576910538* GEOGRAPHY 0460/11 Paper 1 May/June 2011 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates answer on the
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6576910538* GEOGRAPHY 0460/11 Paper 1 May/June 2011 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates answer on the
Ecosystems SOW. Environmentalist, scientist
 Key idea Distribution and characteristics of large scale ecosystems: Tropical, Temperate and boreal forests, tropical and temperate grasslands, deserts and tundra The role of climate and local factors
Key idea Distribution and characteristics of large scale ecosystems: Tropical, Temperate and boreal forests, tropical and temperate grasslands, deserts and tundra The role of climate and local factors
A Partnership for Saving West Africa s Coastal Assets
 A Partnership for Saving West Africa s Coastal Assets 2015 West Africa Coastal Areas Management Program (WACA) 1 Africa s development and climate agendas are inextricably linked: If unaddressed, climate
A Partnership for Saving West Africa s Coastal Assets 2015 West Africa Coastal Areas Management Program (WACA) 1 Africa s development and climate agendas are inextricably linked: If unaddressed, climate
UNIT I ENVIRONMENT, ECOSYSTEMS AND BIODIVERSITY
 PART A (2 MARKS) UNIT I ENVIRONMENT, ECOSYSTEMS AND BIODIVERSITY 1. Define Producers. 2. Name the four ecosystems. 3. What is Ecological succession? 4. What are food chain & food Webs? 5. What is the classification
PART A (2 MARKS) UNIT I ENVIRONMENT, ECOSYSTEMS AND BIODIVERSITY 1. Define Producers. 2. Name the four ecosystems. 3. What is Ecological succession? 4. What are food chain & food Webs? 5. What is the classification
The Living world. Tropical rainforests (core content) Revisio n undert aken. Cover ed in class?
 The Living world Using an example from the UK, I can explain the interrelationship within the natural system. I can define and give UK examples of producers consumers, decomposer, food chain, food web
The Living world Using an example from the UK, I can explain the interrelationship within the natural system. I can define and give UK examples of producers consumers, decomposer, food chain, food web
SDME Sustainable Decision Making Exam
 Geography Revision Booklet Mock Exams 2015 SDME Sustainable Decision Making Exam Wednesday 25 th November 2015 11:15am Worth 25% of your GCSE 90 minutes Based on a resource booklet about a controversial
Geography Revision Booklet Mock Exams 2015 SDME Sustainable Decision Making Exam Wednesday 25 th November 2015 11:15am Worth 25% of your GCSE 90 minutes Based on a resource booklet about a controversial
Rock/ soil type and altitude differences.
 How does climate affect an ecosystem? The Earth s climate depends on energy from the sun. It affects growing conditions for vegetation and affects the location and characteristics of large scale eco-systems.
How does climate affect an ecosystem? The Earth s climate depends on energy from the sun. It affects growing conditions for vegetation and affects the location and characteristics of large scale eco-systems.
Name and define the parts of a food chain.
 Define Ecosystem Name and define the parts of a food chain. Name and locate an example of a UK small ecosystem. Give examples of species that live in Epping Forest. Explain the impact the Great Storm of
Define Ecosystem Name and define the parts of a food chain. Name and locate an example of a UK small ecosystem. Give examples of species that live in Epping Forest. Explain the impact the Great Storm of
Unit III Nutrients & Biomes
 Unit III Nutrients & Biomes Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Based on CO 2 cycling from animals to plants during respiration and photosynthesis. Heavy deposits are stored in wetland soils, oceans, sedimentary
Unit III Nutrients & Biomes Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Based on CO 2 cycling from animals to plants during respiration and photosynthesis. Heavy deposits are stored in wetland soils, oceans, sedimentary
General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2010
 General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2010 Geography GEOG3 Unit 3 Contemporary Geographical Issues Monday 21 June 2010 1.30 pm to 4.00 pm For this paper you must have: an AQA
General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination June 2010 Geography GEOG3 Unit 3 Contemporary Geographical Issues Monday 21 June 2010 1.30 pm to 4.00 pm For this paper you must have: an AQA
Chapter 6. Aquatic Biodiversity. Chapter Overview Questions
 Chapter 6 Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter Overview Questions Ø What are the basic types of aquatic life zones and what factors influence the kinds of life they contain? Ø What are the major types of saltwater
Chapter 6 Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter Overview Questions Ø What are the basic types of aquatic life zones and what factors influence the kinds of life they contain? Ø What are the major types of saltwater
Session 2: Frameworks for Environmental Statistics and for the Development of Indicators
 Session 2: Frameworks for Environmental Statistics and for the Development of Indicators Reena Shah United Nations Statistics Division Workshop on Environment Statistics (Abuja, 19-23 May 2008) Frameworks
Session 2: Frameworks for Environmental Statistics and for the Development of Indicators Reena Shah United Nations Statistics Division Workshop on Environment Statistics (Abuja, 19-23 May 2008) Frameworks
Gas Guzzlers. Biological Pump
 Gas Guzzlers Biological Pump Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter 8 Coral Reefs Open Ocean Deep Sea Marine equivalent of tropical rain forests Habitats for one-fourth of all marine species Coral polyps, which
Gas Guzzlers Biological Pump Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter 8 Coral Reefs Open Ocean Deep Sea Marine equivalent of tropical rain forests Habitats for one-fourth of all marine species Coral polyps, which
The growth of people living in towns and cities. Caused by rural- urban migration in LEDCs. How land is used and modified by humans.
 The growth of people living in towns and cities. Caused by rural- urban migration in LEDCs How land is used and modified by humans. An area of green land which has not been previously built on. An area
The growth of people living in towns and cities. Caused by rural- urban migration in LEDCs How land is used and modified by humans. An area of green land which has not been previously built on. An area
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY 0460/01
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY 060/01 Paper 1 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Ruler May/June 2006 1 hour
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY 060/01 Paper 1 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Ruler May/June 2006 1 hour
Questions 3-6 refer to the diagram of surface currents in the oceans. 3. A current responsible for moving heat away from the equator.
 1. Long term differences in which two variables are the primary determinants of climate? (A) Temperature and cloud cover (B) Precipitation and temperature (C) Precipitation and soil type (D) Temperature
1. Long term differences in which two variables are the primary determinants of climate? (A) Temperature and cloud cover (B) Precipitation and temperature (C) Precipitation and soil type (D) Temperature
Chapter 10. Latin America Today
 Chapter 10 Latin America Today Chapter Objectives Discuss aspects of the Latin American economy and how geography affects transportation and communications. Explain how Latin America s forest resources
Chapter 10 Latin America Today Chapter Objectives Discuss aspects of the Latin American economy and how geography affects transportation and communications. Explain how Latin America s forest resources
Promoting PES in the Danube Basin
 Promoting PES in the Danube Basin Fostering PES projects in CEE and NIS Training Seminar, December 7-9 2006, Isle of Vilm Yanka Kazakova WWF Danube Carpathian Programme The Danube The most international
Promoting PES in the Danube Basin Fostering PES projects in CEE and NIS Training Seminar, December 7-9 2006, Isle of Vilm Yanka Kazakova WWF Danube Carpathian Programme The Danube The most international
Chapter 10 Land, Public and Private
 Chapter 10 Land, Public and Private Friedland and Relyea Environmental Science for AP, second edition 2015 W.H. Freeman and Company/BFW AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Chapter 10 Land, Public and Private Friedland and Relyea Environmental Science for AP, second edition 2015 W.H. Freeman and Company/BFW AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
PRIORITY AXIS 1: A well connected region
 PRIORITY AXIS 1: A well connected region Corresponds to Thematic objective 7- promoting sustainable transport and removing bottlenecks in key network infrastructures All data presented is published for
PRIORITY AXIS 1: A well connected region Corresponds to Thematic objective 7- promoting sustainable transport and removing bottlenecks in key network infrastructures All data presented is published for
STUDY GUIDE. Living in Southeast Asia. Chapter 31, Section 1. Terms to Know DRAWING FROM EXPERIENCE ORGANIZING YOUR THOUGHTS
 Chapter 31, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 759 765. Living in Southeast Asia Terms to Know paddy A flooded field in which rice is grown (page 760) sickle A long, sharp, curved knife (page 760) subsistence
Chapter 31, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 759 765. Living in Southeast Asia Terms to Know paddy A flooded field in which rice is grown (page 760) sickle A long, sharp, curved knife (page 760) subsistence
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education. GEOGRAPHY 0460/11 Paper 1 May/June 2013
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6523019788* GEOGRAPHY 0460/11 Paper 1 May/June 2013 Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6523019788* GEOGRAPHY 0460/11 Paper 1 May/June 2013 Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
Battle for the Biosphere
 Battle for the Biosphere Biome: A large community of plants and animals that occupies a distinct region e.g. the Tropical rainforest. Biosphere: The parts of the land, sea and atmosphere where organisms
Battle for the Biosphere Biome: A large community of plants and animals that occupies a distinct region e.g. the Tropical rainforest. Biosphere: The parts of the land, sea and atmosphere where organisms
GET CREATIVE FOR CLIMATE CHANGE
 INTRODUCE GET CREATIVE FOR CLIMATE CHANGE PARTICIPATE IN OUR CONTEST Learn more about climate change. Create a superhero with an earth-saving adventure! The world will vote on the top submissions at the
INTRODUCE GET CREATIVE FOR CLIMATE CHANGE PARTICIPATE IN OUR CONTEST Learn more about climate change. Create a superhero with an earth-saving adventure! The world will vote on the top submissions at the
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *0606218973* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 5014/11 Paper 1 October/November 2016 2 hours 15 minutes Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *0606218973* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 5014/11 Paper 1 October/November 2016 2 hours 15 minutes Candidates answer on the Question Paper. No
ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE: UNEP-Supported Options for Closing the Gap. Valerie Kapos UNEP-WCMC
 ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE: UNEP-Supported Options for Closing the Gap Valerie Kapos UNEP-WCMC The Adaptation Gap Goals... Finance - $70-100 Bn/year by 2050 Increasing adaptation effort Impact reduction
ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE: UNEP-Supported Options for Closing the Gap Valerie Kapos UNEP-WCMC The Adaptation Gap Goals... Finance - $70-100 Bn/year by 2050 Increasing adaptation effort Impact reduction
ICCG Think Tank Map: a worldwide observatory on climate think tanks Arctic, Energy Poverty and Health in the Second Volume of IPCC s AR 5
 ICCG Think Tank Map: a worldwide observatory on climate think tanks Arctic, Energy Poverty and Health in the Second Volume of IPCC s AR 5 Alice Favero, ICCG Arctic, Energy Poverty and Health Alice Favero
ICCG Think Tank Map: a worldwide observatory on climate think tanks Arctic, Energy Poverty and Health in the Second Volume of IPCC s AR 5 Alice Favero, ICCG Arctic, Energy Poverty and Health Alice Favero
Presented By. Samuel Muriithi KENYA FOREST SERVICE
 Presented By Samuel Muriithi smuriithi2000@yahoo.co.uk, skunyiha@kenyaforestservice.org KENYA FOREST SERVICE General information on Kenya and forest assets in Kenya The vision 2030 Relevance of forests
Presented By Samuel Muriithi smuriithi2000@yahoo.co.uk, skunyiha@kenyaforestservice.org KENYA FOREST SERVICE General information on Kenya and forest assets in Kenya The vision 2030 Relevance of forests
Unit 2 People and the Planet Topic 6 The Challenges of an Urban Worlds
 Unit 2 People and the Planet Topic 6 The Challenges of an Urban Worlds Global Urbanisation trends Urbanisation - the movement of people from rural areas to urban areas like towns and cities. Urbanisation
Unit 2 People and the Planet Topic 6 The Challenges of an Urban Worlds Global Urbanisation trends Urbanisation - the movement of people from rural areas to urban areas like towns and cities. Urbanisation
GRADE 3 Scientific Inquiry
 GRADE 3 Scientific Inquiry Standard 3-1: The student will demonstrate an understanding of scientific inquiry, including the processes, skills, and mathematical thinking necessary to conduct a simple scientific
GRADE 3 Scientific Inquiry Standard 3-1: The student will demonstrate an understanding of scientific inquiry, including the processes, skills, and mathematical thinking necessary to conduct a simple scientific
Climate Change and the Urban Poor in Khulna Presentation on the Existing Situation and Outlook
 Climate Change and the Urban Poor in Khulna Presentation on the Existing Situation and Outlook S.M. Mehedi Ahsan Urban Governance and Development Expert Good Urban Governance Program, GIZ Bangladesh Friday,
Climate Change and the Urban Poor in Khulna Presentation on the Existing Situation and Outlook S.M. Mehedi Ahsan Urban Governance and Development Expert Good Urban Governance Program, GIZ Bangladesh Friday,
SPECIMEN. Date Morning/Afternoon. GCSE (9 1) Geography A (Geographical Themes) J383/03 Geographical Skills Sample Question Paper
 GCSE (9 1) Geography A (Geographical Themes) J383/03 Geographical Skills Sample Question Paper Date Morning/Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes You must have: the Resource Booklet You may use: a
GCSE (9 1) Geography A (Geographical Themes) J383/03 Geographical Skills Sample Question Paper Date Morning/Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes You must have: the Resource Booklet You may use: a
United Nations Environment Programme
 UNITED NATIONS EP United Nations Environment Programme UNEP (DEPI)/RS.15/INF.2.RS Original: ENGLISH 15 th Global Meeting of the Regional Seas Conventions and Action Plans Montego Bay, Jamaica 30 th September
UNITED NATIONS EP United Nations Environment Programme UNEP (DEPI)/RS.15/INF.2.RS Original: ENGLISH 15 th Global Meeting of the Regional Seas Conventions and Action Plans Montego Bay, Jamaica 30 th September
WILDLIFE ECOLOGY AND CONSERVATION STUDY NOTES
 WILDLIFE ECOLOGY AND CONSERVATION STUDY NOTES 1.0 Introduction: General principles of ecosystems management 2.0 Objectives 3.0 Main content 3.1. Principles of sustainable management of the ecosystems 3.2
WILDLIFE ECOLOGY AND CONSERVATION STUDY NOTES 1.0 Introduction: General principles of ecosystems management 2.0 Objectives 3.0 Main content 3.1. Principles of sustainable management of the ecosystems 3.2
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer GCSE Geography (5GB1H) Paper 01 Dynamic Planet- Higher
 Scheme (Results) Summer 2013 GCSE Geography (5GB1H) Paper 01 Dynamic Planet- Higher Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning company.
Scheme (Results) Summer 2013 GCSE Geography (5GB1H) Paper 01 Dynamic Planet- Higher Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning company.
South Carolina Interactive Science 2017
 A Correlation of Interactive Science 2017 To the Academic Standards and Performance Indicators A Correlation of Academic Standards Table of Contents SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING PRACTICES... 3 PHYSICAL SCIENCE:
A Correlation of Interactive Science 2017 To the Academic Standards and Performance Indicators A Correlation of Academic Standards Table of Contents SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING PRACTICES... 3 PHYSICAL SCIENCE:
Colorado Basin. Colorado Scheme - Benefits / Problems
 Colorado Basin By the end of this section you should be able to : Describe and explain the benefits and problems of the Colorado scheme. Use a range of resources. Extract information from given resources.
Colorado Basin By the end of this section you should be able to : Describe and explain the benefits and problems of the Colorado scheme. Use a range of resources. Extract information from given resources.
Community Disaster Resilience
 Community Disaster Resilience Overview Disaster Management Cycle Community Disaster Resilience Hands on Approach for Increasing Community Disaster Resilience Addressing Weaknesses Planning for the Future
Community Disaster Resilience Overview Disaster Management Cycle Community Disaster Resilience Hands on Approach for Increasing Community Disaster Resilience Addressing Weaknesses Planning for the Future
Can we produce enough food for our growing population?
 Geography Curriculum 1718 Form 1 Book 1 Using Urban Space Wisely Unit 1.1 What are urban areas and rural areas? Unit 1.2 What are the major types of urban land use in Hong Kong? Unit 1.4 Why are some residential
Geography Curriculum 1718 Form 1 Book 1 Using Urban Space Wisely Unit 1.1 What are urban areas and rural areas? Unit 1.2 What are the major types of urban land use in Hong Kong? Unit 1.4 Why are some residential
Bellringer. What Lies Beneath? Natural Resources
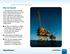 What Lies Beneath? Do deposits of oil or natural gas lie deep beneath this section of the ocean? The owners of these exploration rigs hope so. These rigs are used to drill small test wells in the ocean
What Lies Beneath? Do deposits of oil or natural gas lie deep beneath this section of the ocean? The owners of these exploration rigs hope so. These rigs are used to drill small test wells in the ocean
National Quali cations
 H 216 X733/76/11 National Quali cations Geography FRIDAY, 6 MAY 9: AM 11:15 AM Total marks 6 SECTION 1 PHYSICAL ENVIRONMENTS 15 marks Attempt ALL questions. SECTION 2 HUMAN ENVIRONMENTS 15 marks Attempt
H 216 X733/76/11 National Quali cations Geography FRIDAY, 6 MAY 9: AM 11:15 AM Total marks 6 SECTION 1 PHYSICAL ENVIRONMENTS 15 marks Attempt ALL questions. SECTION 2 HUMAN ENVIRONMENTS 15 marks Attempt
Climate Change & Small Island Developing States
 Climate Change & Small Island Developing States 49th Session of United Nations Statistical Commission 7 March 2018 Statistical Institute of Jamaica Contents What is climate change? Small island developing
Climate Change & Small Island Developing States 49th Session of United Nations Statistical Commission 7 March 2018 Statistical Institute of Jamaica Contents What is climate change? Small island developing
Economic Development Unit Case Studies
 Economic Development Unit Case Studies For this unit you will need to know 5 case studies. In the examination you will 1 case study to answer. Economic Development 1. An Aid project in an LEDC Farm Africa
Economic Development Unit Case Studies For this unit you will need to know 5 case studies. In the examination you will 1 case study to answer. Economic Development 1. An Aid project in an LEDC Farm Africa
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY 0460/01
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY 060/01 Paper 1 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Ruler May/June 2006 1 hour
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY 060/01 Paper 1 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Ruler May/June 2006 1 hour
Ecosystem consists of the organism which live in a particular area, the relationship between them, and their physical environment.
 Ecosystem consists of the organism which live in a particular area, the relationship between them, and their physical environment. An ecosystem can be terrestrial (on land) or aquatic (in water) An ecosystem
Ecosystem consists of the organism which live in a particular area, the relationship between them, and their physical environment. An ecosystem can be terrestrial (on land) or aquatic (in water) An ecosystem
IPCC 5 th Assessment Report : Coastal systems and lowlying
 IPCC 5 th Assessment Report : Coastal systems and lowlying areas University of Adelaide, Australia 20 November 2014 Poh Poh Wong Coordinating Lead Author wong3921@gmail.com IPCC Intergovernmental Panel
IPCC 5 th Assessment Report : Coastal systems and lowlying areas University of Adelaide, Australia 20 November 2014 Poh Poh Wong Coordinating Lead Author wong3921@gmail.com IPCC Intergovernmental Panel
K-5 Science Curriculum. Kindergarten
 K-5 Science Curriculum Kindergarten Investigating Properties Weather Animals Objects have observable properties such as color, size, shape and texture, which can be used for describing and sorting Weather
K-5 Science Curriculum Kindergarten Investigating Properties Weather Animals Objects have observable properties such as color, size, shape and texture, which can be used for describing and sorting Weather
Chapter 1 Lesson 4 Changes in Ecosystems
 Chapter 1 Lesson 4 Changes in Ecosystems PAGE 64 WORKBOOK PAGES 16-17 Look and Wonder: This stone building was once a magnificent temple built by kings. Today trees and plants grow out of the stone. What
Chapter 1 Lesson 4 Changes in Ecosystems PAGE 64 WORKBOOK PAGES 16-17 Look and Wonder: This stone building was once a magnificent temple built by kings. Today trees and plants grow out of the stone. What
The Social and Economic Importance of Canada s Privately Owned Forest Lands
 The Social and Economic Importance of Canada s Privately Owned Forest Lands Key Points n Private forests make up 6% of Canada s 402 million ha of forested land and 13% of the managed forest. n Private
The Social and Economic Importance of Canada s Privately Owned Forest Lands Key Points n Private forests make up 6% of Canada s 402 million ha of forested land and 13% of the managed forest. n Private
Master 5.1, Newspaper Articles. Special Edition December 14. Special Edition March 17
 Master 5.1, Newspaper Articles THE DAILY HERALD Special Edition December 14 Study Forecasts Future Food Shortage A new study published in the Journal of World Agriculture raises concerns that in the future
Master 5.1, Newspaper Articles THE DAILY HERALD Special Edition December 14 Study Forecasts Future Food Shortage A new study published in the Journal of World Agriculture raises concerns that in the future
9/23/2015 Question 1 Review Chapter 15 What biome do you live in? Biomes Answer 1 Question 2 Temperate Deciduous Forest Name the 6 Major biomes.
 Review Chapter 15 Biomes Question 1 What biome do you live in? Answer 1 Question 2 Temperate Deciduous Forest Name the 6 Major biomes. 1 Answer 2 Question 3 Fill in Tropical Rainforest Desert Temperate
Review Chapter 15 Biomes Question 1 What biome do you live in? Answer 1 Question 2 Temperate Deciduous Forest Name the 6 Major biomes. 1 Answer 2 Question 3 Fill in Tropical Rainforest Desert Temperate
Property Rights and Collective Action for Pro-Poor Watershed Management
 Property Rights and Collective Action for Pro-Poor Watershed Management Watersheds are simultaneously managed at various social and spatial scales, from microcatchments to transnational river systems and
Property Rights and Collective Action for Pro-Poor Watershed Management Watersheds are simultaneously managed at various social and spatial scales, from microcatchments to transnational river systems and
NATIONAL GEOGRAPHIC EDUCATOR S GUIDE
 NATIONAL GEOGRAPHIC EDUCATOR S GUIDE NEXT GENERATION SCIENCE ALIGNMENTS 1145 17th ST NW Washington, DC Visit us at www.ngchildrensbooks.org Follow us on NGKidsBks E TREME WEATHER Instructional Note The
NATIONAL GEOGRAPHIC EDUCATOR S GUIDE NEXT GENERATION SCIENCE ALIGNMENTS 1145 17th ST NW Washington, DC Visit us at www.ngchildrensbooks.org Follow us on NGKidsBks E TREME WEATHER Instructional Note The
General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination January 2012
 General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination January 2012 Geography GEOG3 Unit 3 Contemporary Geographical Issues Monday 30 January 2012 1.30 pm to 4.00 pm For this paper you must have:
General Certificate of Education Advanced Level Examination January 2012 Geography GEOG3 Unit 3 Contemporary Geographical Issues Monday 30 January 2012 1.30 pm to 4.00 pm For this paper you must have:
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY 0460/01
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY 0460/01 Paper 1 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper October/November 2004 1
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY 0460/01 Paper 1 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper October/November 2004 1
An introduction to incentives for forest-water ecosystem services. Thomas Enters, UNEP
 An introduction to incentives for forest-water ecosystem services Thomas Enters, UNEP Forest-water ecosystem services What do we know? There is a solid body of scientific information, developed over past
An introduction to incentives for forest-water ecosystem services Thomas Enters, UNEP Forest-water ecosystem services What do we know? There is a solid body of scientific information, developed over past
AP Biology Preliminary Information and Summer Assignment
 AP Biology Preliminary Information and Summer Assignment Requirements: AP Biology is a college level course that covers the same information as an introductory Biology course for Biology majors. It is
AP Biology Preliminary Information and Summer Assignment Requirements: AP Biology is a college level course that covers the same information as an introductory Biology course for Biology majors. It is
Environmental science: An interdisciplinary area of study that includes both applied and theoretical aspects of human impact on the world.
 Chapter 1: Environmental Interrelationships THE NATURE OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE Environmental science: An interdisciplinary area of study that includes both applied and theoretical aspects of human impact
Chapter 1: Environmental Interrelationships THE NATURE OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE Environmental science: An interdisciplinary area of study that includes both applied and theoretical aspects of human impact
National Revision- Global Issues- Climate Change
 National Revision- Global Issues- Climate Change Our planet is encased in a blanket of gases, held in place by the force of gravity. This mixture gives us our life and makes our planet unique and distinctive.
National Revision- Global Issues- Climate Change Our planet is encased in a blanket of gases, held in place by the force of gravity. This mixture gives us our life and makes our planet unique and distinctive.
CLIMATE GRAPHS AND INTERPRETING CLIMATE GRAPHS
 Y10 REVISION MATERIAL ECOSYSTEMS AND URBAN FIELDWORK CLIMATE GRAPHS AND INTERPRETING CLIMATE GRAPHS Climate graphs are a combination of a bar graph and a line graph. Temperature is shown on a line graph,
Y10 REVISION MATERIAL ECOSYSTEMS AND URBAN FIELDWORK CLIMATE GRAPHS AND INTERPRETING CLIMATE GRAPHS Climate graphs are a combination of a bar graph and a line graph. Temperature is shown on a line graph,
Sorting the Wood from the Trees
 Sorting the Wood from the Trees A GAME for 2, 3 or 4 players. How to Play: Pick up the set of situation cards and give them a good shuffle. Place the cards face down and take turns to pick one. Read out
Sorting the Wood from the Trees A GAME for 2, 3 or 4 players. How to Play: Pick up the set of situation cards and give them a good shuffle. Place the cards face down and take turns to pick one. Read out
Environmental Science Exam 5 Biomes Conserve Paper Don t Write on This Test!
 Environmental Science Exam 5 Biomes Conserve Paper Don t Write on This Test! 1. What are the two most significant abiotic factors that influence what type of biome is found in a geographic area? a. Wind
Environmental Science Exam 5 Biomes Conserve Paper Don t Write on This Test! 1. What are the two most significant abiotic factors that influence what type of biome is found in a geographic area? a. Wind
Professor and Director. University of Dar Es Salaam,
 Climate Change Impacts, Vulnerability and Adaptation in the Southern African Region Pius Z. Yanda Professor and Director Institute of Resource Assessment University of Dar Es Salaam, Tanzania Presentation
Climate Change Impacts, Vulnerability and Adaptation in the Southern African Region Pius Z. Yanda Professor and Director Institute of Resource Assessment University of Dar Es Salaam, Tanzania Presentation
What is Ecology? Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
 ECOLOGY What is Ecology? The scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings Factors involved in ecology Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
ECOLOGY What is Ecology? The scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings Factors involved in ecology Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
Effectively Managing Mangroves in a Changing World
 Effectively Managing Mangroves in a Changing World Dr. Zafar Adeel Director, UNU-INWEH 175 Longwood Road South, Hamilton, Canada Zafar.Adeel@unu.edu Worldwide Challenges for Coastal Areas s the world population
Effectively Managing Mangroves in a Changing World Dr. Zafar Adeel Director, UNU-INWEH 175 Longwood Road South, Hamilton, Canada Zafar.Adeel@unu.edu Worldwide Challenges for Coastal Areas s the world population
Integrated Coastal Zone Management Project Republic of India
 Integrated Coastal Zone Management Project Republic of India Restoration and conservation of mangroves, coral reefs transplantation along the coastline of Gujarat and Orissa regions Abstract The ICZM project
Integrated Coastal Zone Management Project Republic of India Restoration and conservation of mangroves, coral reefs transplantation along the coastline of Gujarat and Orissa regions Abstract The ICZM project
Chapter 13 of Agenda 21
 Chapter 13 of Agenda 21 What is Agenda 21? Agenda 21 is the global plan of action that was adopted at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil,
Chapter 13 of Agenda 21 What is Agenda 21? Agenda 21 is the global plan of action that was adopted at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED) held in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil,
BIOMES. Living World
 BIOMES Living World Biomes Biomes are large regions of the world with distinctive climate, wildlife and vegetation. They are divided by terrestrial (land) or aquatic biomes. Terrestrial Biomes Terrestrial
BIOMES Living World Biomes Biomes are large regions of the world with distinctive climate, wildlife and vegetation. They are divided by terrestrial (land) or aquatic biomes. Terrestrial Biomes Terrestrial
Ecology Unit Guide Answers Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 24- Intro and Review Lab Safety
 Ecology Unit Guide Answers Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 24- Intro and Review Lab Safety 31- Part 4 Environmental Change 25- Unit Guide, Vocab and Choose & Research Country 1- Part 5 Natural
Ecology Unit Guide Answers Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 24- Intro and Review Lab Safety 31- Part 4 Environmental Change 25- Unit Guide, Vocab and Choose & Research Country 1- Part 5 Natural
Grade 7 Practice Test for State Geography CRT 2007
 Grade 7 Practice Test for State Geography CRT 2007 PASS 1.2 Sample Test Items: Depth of Knowledge: 2 Correct Answer: C Compared to the rest of Australia, the climate of Tasmania is A warmer. B drier. C
Grade 7 Practice Test for State Geography CRT 2007 PASS 1.2 Sample Test Items: Depth of Knowledge: 2 Correct Answer: C Compared to the rest of Australia, the climate of Tasmania is A warmer. B drier. C
Agriculture and the Environment IX, Valuing Ecosystems: Policy, Economic and Management Interactions (2012)
 DELIVERING ECOSYSTEM SERVICES IN NATIONAL TRUST LANDSCAPES: DEVELOPING A LAND CAPABILITY PROCESS KA Hearn 1 and TRE Thompson 2 1 National Trust, Heelis, Kemble Drive, Swindon, Wilts, SN2 2NA, UK, E-mail:
DELIVERING ECOSYSTEM SERVICES IN NATIONAL TRUST LANDSCAPES: DEVELOPING A LAND CAPABILITY PROCESS KA Hearn 1 and TRE Thompson 2 1 National Trust, Heelis, Kemble Drive, Swindon, Wilts, SN2 2NA, UK, E-mail:
AP Environmental Science
 AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
2018 MOCK COMPONENT 3 MARK SCHEME. Instructions for examiners of GCSE Geography when applying the marking scheme
 2018 MOCK COMPONENT 3 MARK SCHEME Instructions for examiners of GCSE Geography when applying the marking scheme 1 Positive marking It should be remembered that learners are writing under examination conditions
2018 MOCK COMPONENT 3 MARK SCHEME Instructions for examiners of GCSE Geography when applying the marking scheme 1 Positive marking It should be remembered that learners are writing under examination conditions
5 NATURAL HAZARDS. Contents. 5.1 Introduction Flooding Land Instability Coastal Hazards Fire. 5.1.
 5 NATURAL HAZARDS Contents 5.1 Introduction 5.1.1 Flooding 5.1.2 Land Instability 5.1.3 Coastal Hazards 5.1.4 Fire 5.1.5 Climate Change 5.2 Resource Management Issues 5.3 Objectives 5.4 Policies 5.5 Strategy
5 NATURAL HAZARDS Contents 5.1 Introduction 5.1.1 Flooding 5.1.2 Land Instability 5.1.3 Coastal Hazards 5.1.4 Fire 5.1.5 Climate Change 5.2 Resource Management Issues 5.3 Objectives 5.4 Policies 5.5 Strategy
