High Speed Rail Distribution Study
|
|
|
- Brice Pitts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. Report No. SWUTC/16/ Title and Subtitle High Speed Rail Distribution Study Technical Report Documentation Page 2. Government Accession No. 3. Recipient's Catalog No. 5. Report Date August Performing Organization Code 7. Author(s) Carol Abel Lewis, Ph.D., Latissha Clark, Grace Asanaenyi, Wu Ying 8. Performing Organization Report No. Report Performing Organization Name and Address Center for Transportation Training and Research Texas Southern University 3100 Cleburne Houston, Texas Sponsoring Agency Name and Address Southwest Region University Transportation Center Texas A&M Transportation Institute Texas A&M University System College Station, Texas Work Unit No. (TRAIS) 11. Contract or Grant No. DTRT12-G-UTC Type of Report and Period Covered 14. Sponsoring Agency Code 15. Supplementary Notes Supported by a grant from the U.S. Department of Transportation, University Transportation Centers Program. 16. Abstract The Texas Central Partners are in the process of developing a high speed rail line connecting Houston and Dallas, Texas. Ultimately, plans are for 8 car trains that accommodate 200 people per vehicle scheduled every 30 minutes. In addition, Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT) and officials in Austin, Houston and San Antonio are investigating intercity (interregional) rail to provide frequent rail service linking those cities. After arriving, passengers will need disbursement throughout the cities from the rail terminal station. The menu of options includes passenger pick-up (private by a friend or relative or purchased through a provider), taxi/limousine, rental car or public transportation. This research investigates the distribution patterns of northeastern cities with a history of intercity ground transportation as well as distribution patterns from a Houston area airport to assess the potential modal choices of passengers disembarking from intercity rail systems in Texas. In addition, a gravity formula is applied to several employment/activity locations to anticipate patrons distribution choices. The research focuses on the proposed location for the high speed rail terminal. 17. Key Words First Mile, Last Mile, Transit Connectivity 19. Security Classif.(of this report) Unclassified Form DOT F (8-72) 20. Security Classif.(of this page) Unclassified 18. Distribution Statement: No restrictions. This document is available to the public through NTIS: National Technical Information Service 5285 Port Royal Road Springfield, Virginia No. of Pages Price Reproduction of completed page authorized
2 High Speed Rail Distribution Study by Carol Abel Lewis, Ph.D., Latissha Clark Graduate Students Grace Asanaenyi and Wu Ying SWUTC Project: Study Title: Intercity and High Speed Rail Passenger Distribution Performed in cooperation with the Southwest Region University Transportation Center with Houston Galveston Area Council Uptown Houston Association Central Houston Improvement District Texas Southern University Houston, Texas August 2016
3 DISCLAIMER The contents of this report reflect the views of the authors who are responsible for the facts and the accuracy of the information presented herein. This document is disseminated under the sponsorship of the U.S. Department of Transportation, University Transportation Centers Program, in the interest of information exchange. The U.S. Government assumes no liability for the contents or use thereof. Notice Mention of trade names or commercial products does not constitute endorsement of recommendation for use. Trade and manufacturers names appear herein solely because they are considered essential to the object of this report. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors recognize that support for this research was provided by a grant from the US Department of Transportation, University Transportation Centers Program to the Southwest Region University Transportation Center. Also, the authors appreciate the financial contributions of the Houston Galveston Area Council, Uptown Houston Association and Central Houston Improvement District to complete this work. The following individuals served on the advisory committee and provided comments and direction for this research. Their time and professional commitment are appreciated. Thomas Graham Bob Ethington Katrina Bayer Maureen Crocker Vijay Mahal Ujari Mohite Lauren Barash Houston Galveston Area Council Uptown Houston Association Central Houston Improvement District Gulf Coast Rail District HDR Metropolitan Transit Authority of Harris County The Wave (Houston s Jitney Shuttle Service) iii
4 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The Texas Central Partners (TC) are in the process of developing a high speed rail line connecting Houston and Dallas, Texas. Ultimately, plans are for 8 car trains that accommodate 200 people per vehicle scheduled every 30 minutes during rush hours and less frequently during mid-day. In addition, Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT) and officials in Austin, Houston and San Antonio are investigating intercity rail, also called interregional rail, to provide frequent rail service linking those cities. After arriving, passengers will need disbursement throughout the cities from the rail terminal station. The menu of options includes passenger pick-up (personal by a friend or relative or purchased from a provider), taxi/limousine, rental car or public transportation. Rail corridors, notably along the east coast have served intercity commuters for decades, key among them, the Boston, New York to Washington, DC corridor served by Amtrak. Lessons may be learned from these cities and also from intercity commuting corridors between cities in California in terms of efficiently connecting rail commuters to ground transportation. Previous US DOT studies showed five states with other modes meeting intercity rail systems at some stations and five additional states, where intercity rail connections may be made with other modes at all stations. Critical to the Houston area success of the rail linking Dallas and Houston is the connections from the terminal station, currently proposed for roughly the intersection of IH- 10/Old Katy Road. The methodology to assess the distribution began with investigation of the distribution patterns of northeastern cities with a history of intercity ground transportation as well as distribution patterns from a Houston area airport to anticipate mode split of passengers disembarking from intercity rail systems in Texas. Also, a gravity based equation was employed to show the relative attraction of several employment centers. First Mile/Last mile is a term used in transportation to describe the movement of people and goods from a terminal or station location to the ultimate intended destination. In this paper, purchased personal transportation is termed Transportation Network Companies (TNC) and refers to scheduled pick up with the reservation made via a mobile application or website (eg., Uber, Lyft, Via). Findings from this work are designed to assist in guiding area officials in assessing physical needs, such as vehicle bays, rental facilities, passenger pick-up areas to meet the anticipated disbursement of TC passengers. While there are no direct comparisons from other US cities with intercity rail or the Houston airports, the work allows several general thoughts. Transit users will likely be destined to Uptown and Downtown, particularly so as those connections are anticipated to be improved with the implementation of high speed rail. In fact, the transit travel time in future years may be better than personal vehicle travel time to these two locations. High speed rail patrons destined to other activity centers may choose transit, but are less likely to do so than those destined to Uptown and Downtown. High speed rail patrons destined to non-activity centers are most likely to use TNCs, other personal vehicle modes, or rental car. Taxi will likely be a prominent choice and should be well-accommodated It is important to ensure covered, protected amenities for all connections. Bicycle accommodations should be provided. iv
5 TABLE OF CONTENTS Page 1. BACKGROUND THE HIGH SPEED RAIL LINE...2 Description...2 Connectivity METHODOLOGY...5 Survey Gathering...5 Gravity Model FINDINGS...7 Survey Findings...7 Airport Select Modal Egress...7 Gravity Equation SUMMARY OF FINDINGS...10 REFERENCES...11 APPENDIX...12 v
6 LIST OF TABLES Page Table 1: Explanation of Variables...6 Table 2: Taxi, TNC and Limousine Usage from Houston Airports...8 Table 3: Summary of Gravity Index, Transit Travel Time and Distribution Options...9 LIST OF FIGURES Page Figure 1: Image of HSR Vehicle...2 Figure 2: HSR Route Options...2 Figure 3: Percent of Mega Commuters Rapino and Fields (2013)...3 Figure 4: Box A: Connectivity on the Coasts...3 Figure 5: Proposed terminal location near IH10 and Old Katy Road...4 vi
7 1. BACKGROUND The Texas Central Partners (TC) are in the process of developing a high speed rail line connecting Houston and Dallas, Texas. Ultimately, plans are for 8 car trains that accommodate 200 people per vehicle scheduled every 30 minutes during rush hours and less frequently during mid-day. In addition, Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT) and officials in Austin, Houston and San Antonio are investigating intercity rail, also called interregional rail, to provide frequent rail service linking those cities. After arriving, passengers will need disbursement throughout the cities from the rail terminal station. The menu of options includes passenger pick-up, taxi/limousine, rental car or public transportation. This research investigates the distribution patterns of northeastern cities with a history of intercity ground transportation as well as distribution patterns from a Houston area airport to anticipate mode split of passengers disembarking from intercity rail systems in Texas. Lastly, a gravity based equation is employed to show the relative attraction of several employment centers from the TC preferred terminus near the intersection of IH 610 and US 290. Findings from this from this work are designed to: Assist in guiding area officials in beginning to assess physical needs, such as vehicle bays, rental facilities, passenger pick-up areas to meet the anticipated disbursement of TC passengers Provide information for public and private transportation entities to anticipate how they might prepare for interregional rail and interconnectivity with their operation. Because there is no existing frequent interregional rail service in Texas, knowledge about expectations on this subject is lacking. Important to the ultimate demand is the quality and location of the intermodal terminal and intermodal connections. A 2007 nationwide study by Goldberg shows that bus is the most frequent vehicle for connecting intermodal services in the northeast corridor and bus must be viewed as a vital component. The Goldberg study found that a number of Amtrak rail stations are served by Amtrak Thruway, the company s intercity bus feeder network. Also important is that travel transfers across modes must be timely and convenient. Patrons must feel safe and the connecting walk must be pleasant and interesting. Connectivity criteria are established by US Bureau of Transportation Statistics and will be delineated as part of this study (Goldberg, 2009). Clearly, the public transportation and land patterns in Texas cities are unlike those in the nation s northeast corridor. Therefore, studying disbursements from inner city airports such as Hobby and Love Field could contribute to gaining insight about passenger distribution from high speed rail. 1
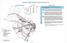
8 2. THE HIGH SPEED RAIL LINE Description The cities of Houston, Dallas, Austin and San Antonio form the core of the Texas megaregion termed the Texas Triangle. Connections between the megaregion cities in Texas are important for economic vitality. Transportation linkages must be for freight and passengers. Passenger rail connecting the cities is beginning through an approximately 240 mile high speed rail line proposed between Houston and Dallas by Texas Central Partners (TC) (Figures 1 and 2). Figure 1: Image of HSR Vehicle Figure 2: HSR Route Options - maps One phenomenon of the past several decades is a change in how Americans view their work trip. As residences and jobs moved further from the urban core, commute trip lengths increased showing that people are willing to live great distances from their jobs. The ultimate example of this acceptance is persons who commute between cities. Texas cities are shown on a national map of mega commuters, those traveling more than 90 minutes and 50 miles (Figure 3). While we cannot see the actual commute pairs underlying the graphic, Texas megaregions of Houston, Dallas metroplex, San Antonio and Austin are observable. Global Workplace Analytics analysis from the American Community Survey indicates that the number of people, who are not self-employed and work at home incresed103% since 2005, and roughly 50% of the population works at home at least part of a week. According to TC, approximately 50,000 people travel between Houston and Dallas/Fort Worth multiple times per week. 2
9 Figure 3: Percent of Mega Commuters Rapino and Fields (2013) Connectivity Rail corridors, notably along the east coast have served intercity commuters for decades, key among them, the Boston, New York to Washington, DC corridor served by Amtrak. Lessons may be learned from these cities and also from intercity commuting corridors between cities in California in terms of efficiently connecting rail commuters to ground transportation. A US DOT Rita Commissioned study (2007) showed five states with other modes meeting intercity rail systems at some stations and five additional states, where intercity rail connections may be made with other modes at all stations. The states are listed in Figure 4. The objective is for a smooth functioning trip end to the final desired destination, not just to the rail terminal. Figure 4: Box A: Connectivity on the Coasts and_issue_briefs/special_report/2007_09_18/html/box_a.html 3
10 Critical to success of the rail linking Dallas and Houston is the connections from the terminal station, currently proposed for roughly the intersection of IH-10/Old Katy Road (Figure 5). In transportation vernacular, this type of connection is known as first mile/last mile. First mile/last mile is a term used in transportation to describe the movement of people and goods from a terminal or station location to the ultimate intended destination. A number of modal choices are available for the connections transit, taxi/limousine, jitney, personal or purchased passenger pick-up, bicycle, and rental car. In this paper, purchased personal transportation is termed Transportation Network Companies (TNC) and refers to scheduled pick up with the reservation made via a mobile application or website (eg., Uber, Lyft, Via). The IH-10/Old Katy Road area is currently underdeveloped and houses a number of warehouses and low density commercial uses. There is also vacant property that will be attractive for higher density transit supportive land uses. Figure 5: Proposed terminal location near IH10 and Old Katy Road - maps 4
11 3. METHODOLOGY There are three components of the methodology: First a survey of cities with intercity rail was conducted. Secondly, a representative from Houston Hobby and Bush Intercontinental Airports sent information regarding several egress modes. The third component entailed implementation of a transportation gravity model. Additional detail for the survey gathering and gravity model follow. Survey Gathering The team solicited information from cities with intercity rail connections. Surveys were forwarded to 20 agencies (listed in the Appendix), followed by and telephone requests for response. Six agencies responded as shown. METROlink Southern California NM Rail Runner Santa Fe to Belen, NM VRE Virginia Railway Express MBTA Boston, MA Sounder Lakewood, Tacoma, Seattle Shoreline -- Connecticut Gravity Model Transportation professionals typically apply a number of sophisticated computer models to forecast travel movement and volume. These models work best when a number of basic variables are known, for instance, the potential audience for the travel, the trip purpose, family income and competitive travel time and cost (comparing personal vehicle to transit travel time). In this case, because the high speed rail is a new concept and is sometimes compared to the airlines, the traditional ground models may be problematic. Increasing the understanding of connecting ultimate origins and destinations to the terminal location near I10 and Old Katy Road led to a more historical approach. To gain a perspective of the potential for key locations in Houston to attract HSR riders, a gravity based model was calculated. The gravity model predicts movement of people by taking into account potential size of attractors, distance and time of travel. The relative strength of the linkage between two points is shown by the following formula modified from Erlander and Stewart (1990): In our study, variable definitions are shown in Table 1. 5
12 Table 1: Explanation of Variables P passengers/hour Trip production from HSR station j Destination Destination Zip Code T T j = A j *F j *K j Trip distribution index A F Employment density: Employment/Area Travel time peak and off peak Zone attraction factor Travel time factor K Median household income Social factor 6
13 4. FINDINGS Survey Findings In order to better understand egress from existing intercity rail systems, 20 agencies shown in the methodology section were forwarded survey instruments. Modes anticipated included transit, person vehicles, and rental options. Of the agencies queried, 6 respondents completed the survey. Responses are described according to transit connections, egress by individual private vehicles, pedestrian accommodation, and bicycle connections. Transit Connections (or shared ride egress): All 6 had connections to local bus systems. Three agencies had both light and rapid rail connections and one had rapid rail transit, as well. One agency s intercity rail connected with a commuter rail line. Of the agencies, one has 15 bus bays, 2 have 4 bays, 1 three bays and 1 with one bay. The survey asked whether special events resulted in ridership spikes or changes in required egress modes. Most indicated not, but one responded yes and additional buses were provided. Individual Vehicles Egress: Five respondents had taxi zones and space for personal vehicle pick-up, including TNCs. Of those, 2 have 4 spaces and 2 have 5 spaces. Respondents indicated that the allocation of space for these modes is adequate. Pedestrian Accommodations: Four of the six agencies answered questions about the pedestrian amenities. All indicated that the access to transit or personal vehicle pick-up was covered, lighted and easily walkable. The pathways were attached to the terminal structure requiring no exposure to the elements. Bicycle Connections: The six respondents had bicycle provisions at the terminal and 5 noted accommodations for bicycles on the trains. When asked whether bicycle accommodations were sufficient, one respondent indicated no. Airport Select Modal Egress: Table 2 shows the dominance of taxis and secondarily, TNCs (service by Uber at Houston airports), in the personal trip categories. Trips 1 and 2 for taxis and TNCs represent time allocations and add to the total. Limousines represented a small portion and Super Shuttle, while not in the table, reported 15 trips. Trip length is not provided, but both airports are distant from the central and employment areas of the city. The high speed rail patrons will likely be prone to taxi use. Taxi trips are more than double trips by TNCs. 7
14 Table 2: Taxi, TNC and Limousine Usage from Houston Airports Gravity Equation An important component of the project focused on relative attraction of the major activity center to the IH-10/Old Katy Road terminal location and the potential for HSR riders to take transit or another conveyance. Gravity model equation was used to assess the potential of select activity centers to attract riders by mode based on the peak and non-peak travel times, the employment numbers and household incomes of residents. The team prepared a trip distribution index reflecting the results of the gravity equation. The gravity model applies values reflecting peak and non-peak hour travel time; the attractiveness of the location called the zone attraction factor is the employment density, and the social factor is interpreted by the median household income. The lower the number on the Gravity Trip Distribution Index, the more competitive will be the transit option. Table 3 shows downtown and Uptown with similarly favorable index values. Westchase and the Energy Corridor follow, and the Woodlands has a large index, showing a long travel distance, low density and fairly high income. The table includes the time to take a transit vehicle to the named activity center. 8
15 Table 3: Summary of Gravity Index, Transit Travel Time and Distribution Options Employment Center Gravity Trip Distribution Index Transit Travel Time at 8:05 a.m. Weekday (minutes) Transit Competitive (+,0,-) Travel Options Downtown Transit, the Wave, TNC, Taxi, Rental Car Uptown Transit, the Wave, TNC, Taxi, Rental Car Westchase District Transit, TNC, Taxi, Rental Car Energy Corridor Transit, TNC, Taxi, Rental Car Woodlands Not Available -- TNC, Taxi Rental Car Key: Transit is likely (green, +), Transit is possible, but less likely than green (buff and 0), transit is unlikely (gray, --). Strong travel options are shown in bold black, and secondary option in gray. People exiting the high speed rail vehicles will be destined throughout the region. Their decision about the mode will depend on the travel time, parking space availability and cost and duration of stay. Five locations are identified to calculate the gravity distribution index. A transit choice increases if the travel time is competitive. When travel time is competitive, transit, taxi, the Wave and TNC are likely options. Decisions may vary if users are staying more than overnight; acquiring a car may be more likely if the trip duration is multiple days. Downtown and Uptown have competitive transit travel times based on today s METRO System. METRO transit system improvements to those two locations that provide exclusive transit options would improve transit speeds, and in some cases may be shorter than in a personal vehicle. The table shows that transit is most competitive for Downtown and Uptown, less likely for Westchase and the Energy Corridor, and unlikely for the Woodlands. Other vehicle options are most likely due to the distance from the terminal location. 9
16 5. SUMMARY OF FINDINGS This work examined the options for connectivity. Findings from this work are designed to assist in guiding area officials in beginning to assess physical needs, such as vehicle bays, rental facilities, passenger pick-up areas to meet the anticipated disbursement of TC passengers and provide information for public and private transportation entities to anticipate how they might prepare for interregional rail and interconnectivity with their operation. While there are no direct comparisons from other US cities with intercity rail or the Houston airports, the work allows several general thoughts. Transit users will likely be destined to Uptown and Downtown, particularly so as those connections are anticipated to be improved with the implementation of high speed rail. In fact, the transit travel time in future years may be better than personal vehicle travel time to these two locations. High speed rail patrons destined to other activity centers may choose transit, but are less likely to do so than those destined to Uptown and Downtown. High speed rail patrons destined to non-activity centers are most likely to use TNCs, other personal vehicle modes, or rental car. Taxi will likely be a prominent choice and should be well-accommodated. It is important to ensure covered, protected pedestrian amenities for all connections. Bicycle accommodations should be provided. As more information is known about the users of the high speed rail, additional research could more specifically examine the magnitude of distribution to the activity/employment centers and provide greater insight into bay location and sizing. 10
17 REFERENCES Erlander and N.F. Stewart, (1990). The Gravity Model In Transportation Analysis: Theory And Extensions. Global Workplace Analytics, (January 2016). Latest Telework Statistics, Retrieved June 6, Goldberg, Bruce (2011). Making Connections: Intermodal Links Available at 70 Percent of all Stations Served by Commuter Rail, RITA Bureau of Transportation Statistics, Special Report. Houston Hobby & Intercontinental Airport, Airport Ground Transport Trip Count forwarded by April 2016, from Jude Nwambuonwo. Rapino, Melanie A. and Fields, Allison K. (2013). Megacommuters in the U.S.; Defining the Long Commute using the American Community Survey. Work and Migration Statistics Branch, Economic, and Housing Statistics Division, US Census Bureau (Working Paper), Texas Central: Projects and Facts (retrieved June 20, 2016) from 11
18 APPENDIX ACE Stockton to San Jose, California UTA Utah Coaster San Diego, California TRE Ft. Worth, Texas METRA Northeastern Illinois NICTD Chicago, Michigan City, Illinois RTA Chicago area METROlink Southern California NM Rail Runner Santa Fe to Belen, NM Northstar Minneapolis to St. Paul, Minnesota Metro-North/Long Island RR SEPTA Southeastern Pennsylvania MARC Baltimore to Washington, DC VRE Virginia Railway Express MBTA Boston, MA NJ Transit New Jersey Transit Tri Rail Miami to Ft. Lauderdale, FL Caltrains San Francisco, Menlo Park to San Jose Sounder Lakewood, Tacoma, Seattle Shoreline -- Connecticut 12
GULF COAST RAIL DISTRICT VISION FOR REGIONAL RAIL
 GULF COAST RAIL DISTRICT VISION FOR REGIONAL RAIL OCTOBER 2014 Cover photographs courtesy of Top left - Mike Bates TABLE OF CONTENTS MISSION... 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 VISION STATEMENT... 1 BACKGROUND... 2
GULF COAST RAIL DISTRICT VISION FOR REGIONAL RAIL OCTOBER 2014 Cover photographs courtesy of Top left - Mike Bates TABLE OF CONTENTS MISSION... 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 VISION STATEMENT... 1 BACKGROUND... 2
Introduction... 1 Florida s Rail System... 1 Rail Freight... 3 Rail Passengers... 5 Conclusions... 9
 January 2011 Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Florida s Rail System... 1 Rail Freight... 3 Rail Passengers... 5 Conclusions... 9 Table of Figures and Tables Figure 1 Florida Rail System Map... 2 Figure
January 2011 Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Florida s Rail System... 1 Rail Freight... 3 Rail Passengers... 5 Conclusions... 9 Table of Figures and Tables Figure 1 Florida Rail System Map... 2 Figure
Assessment of Current Status, Plans, and Preliminary Alternatives for High Capacity Transportation in the I-5 Corridor
 CONNECTING THURSTON COUNTY AND THE CENTRAL PUGET SOUND Alternatives to Meet Transportation Needs in the I-5 Corridor Working Paper #1 June 2011 Assessment of Current Status, Plans, and Preliminary Alternatives
CONNECTING THURSTON COUNTY AND THE CENTRAL PUGET SOUND Alternatives to Meet Transportation Needs in the I-5 Corridor Working Paper #1 June 2011 Assessment of Current Status, Plans, and Preliminary Alternatives
American Public Transportation Association 1666 K Street, N.W. Suite 1100 Washington, DC (202)
 2010 PUBLIC TRANSPORTATION FACT BOOK APPENDIX A: HISTORICAL TABLES April 2010 American Public Transportation Association 1666 K Street, N.W. Suite 1100 Washington, DC 20006 (202) 496-4800 2010 Public Transportation
2010 PUBLIC TRANSPORTATION FACT BOOK APPENDIX A: HISTORICAL TABLES April 2010 American Public Transportation Association 1666 K Street, N.W. Suite 1100 Washington, DC 20006 (202) 496-4800 2010 Public Transportation
Northern Intermodal Transit Facility WHAT IS AN INTERMODAL TRANSIT FACILITY?
 WHAT IS AN INTERMODAL TRANSIT FACILITY? An intermodal transit facility gathers many modes of transportation together and is strategically located to increase destination alternatives. Intermodal facilities
WHAT IS AN INTERMODAL TRANSIT FACILITY? An intermodal transit facility gathers many modes of transportation together and is strategically located to increase destination alternatives. Intermodal facilities
APPENDIX B - GLOSSARY FEBRUARY 2017
 APPENDIX B - GLOSSARY FEBRUARY 2017 DENVERMOVES Transit Denver Moves: Transit - ii - APPENDIX B TRANSIT AND MOBILITY GLOSSARY Amenities, stop or station: Objects or facilities (such as a shelter, bench,
APPENDIX B - GLOSSARY FEBRUARY 2017 DENVERMOVES Transit Denver Moves: Transit - ii - APPENDIX B TRANSIT AND MOBILITY GLOSSARY Amenities, stop or station: Objects or facilities (such as a shelter, bench,
Year 24 Final Report. Determining Performance Measures to Evaluate the Effect of High Speed Rail on Communities Livability
 New England University Transportation Center 77 Massachusetts Avenue, E40-279 Cambridge, MA 02139 617.253.0753 utc.mit.edu Year 24 Final Report Grant Number: DTRT12-G-UTC01 Project Title: Determining Performance
New England University Transportation Center 77 Massachusetts Avenue, E40-279 Cambridge, MA 02139 617.253.0753 utc.mit.edu Year 24 Final Report Grant Number: DTRT12-G-UTC01 Project Title: Determining Performance
2004 FEASIBILITY STUDY UPDATE
 Austin-San Antonio Intermunicipal Commuter Rail District 2004 FEASIBILITY STUDY UPDATE December 2004 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY INTRODUCTION Almost 3 million people in Central Texas, living and working between
Austin-San Antonio Intermunicipal Commuter Rail District 2004 FEASIBILITY STUDY UPDATE December 2004 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY INTRODUCTION Almost 3 million people in Central Texas, living and working between
TRANSPORTATION FACTS. OUR CUSTOMERS: Travel Patterns
 OUR CUSTOMERS: Travel Patterns TRANSPORTATION FACTS The more than 6.5 million people in the Commonwealth have many reasons to travel and several ways to get to their destinations. A recent statewide survey
OUR CUSTOMERS: Travel Patterns TRANSPORTATION FACTS The more than 6.5 million people in the Commonwealth have many reasons to travel and several ways to get to their destinations. A recent statewide survey
Dogpatch-Central Waterfront Transit Demand Study Planning Study Key Takeaways
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The purpose of this memo is to assist the SFMTA Transit Division with its final recommendation for replacement service of the existing 22-Fillmore bus service. It is informed by Planning
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The purpose of this memo is to assist the SFMTA Transit Division with its final recommendation for replacement service of the existing 22-Fillmore bus service. It is informed by Planning
APPENDIX TRAVEL DEMAND MODELING OVERVIEW MAJOR FEATURES OF THE MODEL
 APPENDIX A TRAVEL DEMAND MODELING OVERVIEW The model set that the Central Transportation Planning Staff (CTPS), the Boston Region Metropolitan Planning Organization s (MPO) technical staff, uses for forecasting
APPENDIX A TRAVEL DEMAND MODELING OVERVIEW The model set that the Central Transportation Planning Staff (CTPS), the Boston Region Metropolitan Planning Organization s (MPO) technical staff, uses for forecasting
MARC Brunswick/Frederick Line Improvement Proposal
 MD State Highway Administration Project No. M00695172 IS 270 Innovative Congestion Management Project MARC Brunswick/Frederick Line Improvement Proposal Action Committee for Transit November 2016 MARC
MD State Highway Administration Project No. M00695172 IS 270 Innovative Congestion Management Project MARC Brunswick/Frederick Line Improvement Proposal Action Committee for Transit November 2016 MARC
Presentation To: HRTPO Passenger Rail Task Force
 Presentation To: HRTPO Passenger Rail Task Force HRTPO Norfolk-Richmond Passenger Rail Ridership and Revenue Forecasts Presentation By December 17, 2013 Transportation Economics & Management Systems, Inc.
Presentation To: HRTPO Passenger Rail Task Force HRTPO Norfolk-Richmond Passenger Rail Ridership and Revenue Forecasts Presentation By December 17, 2013 Transportation Economics & Management Systems, Inc.
WISCONSIN DOT PUTTING RESEARCH TO WORK
 Freight Model Improvement Project for ECWRPC Jessica Guo, Ph.D., Walt Raith, Qi Gong, and Jason Bittner University of Wisconsin-Madison WisDOT ID no. 0092-10-14 CFIRE ID no. 03-08 August 2011 Research
Freight Model Improvement Project for ECWRPC Jessica Guo, Ph.D., Walt Raith, Qi Gong, and Jason Bittner University of Wisconsin-Madison WisDOT ID no. 0092-10-14 CFIRE ID no. 03-08 August 2011 Research
Anaheim Resort Transportation
 Anaheim Resort Transportation Introduction The purpose of this paper is to describe, using quantitative measures of effectiveness to the extent feasible, the air quality and traffic congestion mitigation
Anaheim Resort Transportation Introduction The purpose of this paper is to describe, using quantitative measures of effectiveness to the extent feasible, the air quality and traffic congestion mitigation
Connectivity along Amtrak s NEC. Emmanuel S. Bruce Horowitz
 Connectivity along Amtrak s NEC Emmanuel S. Bruce Horowitz Creative Passenger Rail Transportation Economics Overview Overview of Amtrak s NEC Illustrated description of key intermodal connections at major
Connectivity along Amtrak s NEC Emmanuel S. Bruce Horowitz Creative Passenger Rail Transportation Economics Overview Overview of Amtrak s NEC Illustrated description of key intermodal connections at major
Intercity and Commuter Passenger Travel Element
 Intercity and Commuter Passenger Travel Element Intercity passenger services and facilities serve both long distance and commuter passengers traveling from one city to another. Typically, intercity passenger
Intercity and Commuter Passenger Travel Element Intercity passenger services and facilities serve both long distance and commuter passengers traveling from one city to another. Typically, intercity passenger
REGIONAL INTERMODAL RAIL TRANSIT SYSTEMS ENSURING OUR ECONOMIC AND TRANSPORTATION FUTURE
 REGIONAL INTERMODAL RAIL TRANSIT SYSTEMS ENSURING OUR ECONOMIC AND TRANSPORTATION FUTURE REGIONAL TRANSIT SYSTEMS Comprehensive transit system serving the mobility needs of an entire region Transit modes
REGIONAL INTERMODAL RAIL TRANSIT SYSTEMS ENSURING OUR ECONOMIC AND TRANSPORTATION FUTURE REGIONAL TRANSIT SYSTEMS Comprehensive transit system serving the mobility needs of an entire region Transit modes
General Population Survey Summary
 General Population Survey Summary A short online survey was used to get input from general population users of the Highway 169 corridor. The survey was promoted through a press release, email blast, social
General Population Survey Summary A short online survey was used to get input from general population users of the Highway 169 corridor. The survey was promoted through a press release, email blast, social
Appendix B2: Factors Affecting Transit Choice
 Appendix B2: Factors Affecting Transit Choice 1 TRANSIT MARKET The transit market comprises those trips which have the option of taking transit, that is, those trips for which the trip origin and trip
Appendix B2: Factors Affecting Transit Choice 1 TRANSIT MARKET The transit market comprises those trips which have the option of taking transit, that is, those trips for which the trip origin and trip
Long Bridge Project. Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) Revised Purpose and Need
 Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) Revised Purpose and Need June 23, 2017 1.0 What is the Proposed Action? The consists of potential improvements to the Long Bridge and related railroad infrastructure
Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) Revised Purpose and Need June 23, 2017 1.0 What is the Proposed Action? The consists of potential improvements to the Long Bridge and related railroad infrastructure
Database and Travel Demand Model
 Database and Travel Demand Model 7 The CMP legislation requires every CMA, in consultation with the regional transportation planning agency (the Metropolitan Transportation Commission (MTC) in the Bay
Database and Travel Demand Model 7 The CMP legislation requires every CMA, in consultation with the regional transportation planning agency (the Metropolitan Transportation Commission (MTC) in the Bay
Travel Demand Modeling At NCTCOG
 Travel Demand Modeling At NCTCOG Arash Mirzaei North Central Texas Council Of Governments For University of Texas at Arlington ITE Student Chapter March 9, 2005 Agenda Background DFW Regional Model Structure
Travel Demand Modeling At NCTCOG Arash Mirzaei North Central Texas Council Of Governments For University of Texas at Arlington ITE Student Chapter March 9, 2005 Agenda Background DFW Regional Model Structure
2010 Minnesota Comprehensive Statewide Freight and Passenger Rail Plan. Minnesota Department of Transportation
 2010 Minnesota Comprehensive Statewide Freight and Passenger Rail Plan Minnesota Department of Transportation ! First Statewide Comprehensive Rail Plan for MN! Commissioned by 2008 Legislature! Compliant
2010 Minnesota Comprehensive Statewide Freight and Passenger Rail Plan Minnesota Department of Transportation ! First Statewide Comprehensive Rail Plan for MN! Commissioned by 2008 Legislature! Compliant
REGIONAL INTERMODAL RAIL TRANSIT SYSTEMS ENSURING OUR ECONOMIC AND TRANSPORTATION FUTURE
 REGIONAL INTERMODAL RAIL TRANSIT SYSTEMS ENSURING OUR ECONOMIC AND TRANSPORTATION FUTURE REGIONAL TRANSIT SYSTEMS Comprehensive transit system serving the mobility needs of an entire region Transit modes
REGIONAL INTERMODAL RAIL TRANSIT SYSTEMS ENSURING OUR ECONOMIC AND TRANSPORTATION FUTURE REGIONAL TRANSIT SYSTEMS Comprehensive transit system serving the mobility needs of an entire region Transit modes
A National Survey of Commuter Rail Policy
 NURail Project No. # NURail2012-UKY-R02 A National Survey of Commuter Rail Policy By Timothy J. Brock Kentucky Transportation Center University of Kentucky TimothyBrock@MissouriState.edu and Reginald R.
NURail Project No. # NURail2012-UKY-R02 A National Survey of Commuter Rail Policy By Timothy J. Brock Kentucky Transportation Center University of Kentucky TimothyBrock@MissouriState.edu and Reginald R.
Minnesota Comprehensive Statewide Freight and Passenger Rail Plan
 Minnesota Comprehensive Statewide Freight and Passenger Rail Plan presented to Minnesota Rail Plan Open Houses presented by Cambridge Systematics, Inc. Kimley-Horn and Associates, Inc. TKDA, Inc. April-May,
Minnesota Comprehensive Statewide Freight and Passenger Rail Plan presented to Minnesota Rail Plan Open Houses presented by Cambridge Systematics, Inc. Kimley-Horn and Associates, Inc. TKDA, Inc. April-May,
Fairfax County Countywide Transit Network Study
 Fairfax County Countywide Transit Network Study Proposed High Quality Transit Network Concept Metropolitan Washington Council of Governments Travel Forecasting Subcommittee September 20, 2013 1 Presentation
Fairfax County Countywide Transit Network Study Proposed High Quality Transit Network Concept Metropolitan Washington Council of Governments Travel Forecasting Subcommittee September 20, 2013 1 Presentation
Transit Service Guidelines
 G R E AT E R VA N CO U V E R T R A N S P O RTAT I O N A U T H O R I T Y Transit Service Guidelines PUBLIC SUMMARY REPORT JUNE 2004 Greater Vancouver Transportation Authority TRANSIT SERVICE GUIDELINES
G R E AT E R VA N CO U V E R T R A N S P O RTAT I O N A U T H O R I T Y Transit Service Guidelines PUBLIC SUMMARY REPORT JUNE 2004 Greater Vancouver Transportation Authority TRANSIT SERVICE GUIDELINES
R T A T r i a n g l e M o b i l i t y R e p o r t
 RTA Tr i a n g l e M o b i l i t y R e p o r t 2 0 1 9 2 2 0 1 9 R T A T r i a n g l e R e g i o n a l M o b i l i t y R e p o r t WELCOME TO A GROWING COMMUNITY THAT WILL GROW ON YOU. The Triangle region
RTA Tr i a n g l e M o b i l i t y R e p o r t 2 0 1 9 2 2 0 1 9 R T A T r i a n g l e R e g i o n a l M o b i l i t y R e p o r t WELCOME TO A GROWING COMMUNITY THAT WILL GROW ON YOU. The Triangle region
Long Bridge Project. Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) Revised Purpose and Need
 Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) Revised Purpose and Need November 9, 2017 1.0 What is the Proposed Action? The consists of potential improvements to the Long Bridge and related railroad infrastructure
Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) Revised Purpose and Need November 9, 2017 1.0 What is the Proposed Action? The consists of potential improvements to the Long Bridge and related railroad infrastructure
Dallas City Council Transportation & Environment Committee. May 13, 2013
 Dallas City Council Transportation & Environment Committee May 13, 2013 Presentation Outline Technology Definitions Current RTC Policy Families of Alignment/Station Options RTC/NCTCOG Role in Statewide
Dallas City Council Transportation & Environment Committee May 13, 2013 Presentation Outline Technology Definitions Current RTC Policy Families of Alignment/Station Options RTC/NCTCOG Role in Statewide
CHAPTER 2.0: INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 2.0: INTRODUCTION 2.1 INTRODUCTION The Federal Transit Administration (FTA) and the Santa Clara Valley Transportation Authority (VTA) have prepared this Environmental Impact Statement/Environmental
CHAPTER 2.0: INTRODUCTION 2.1 INTRODUCTION The Federal Transit Administration (FTA) and the Santa Clara Valley Transportation Authority (VTA) have prepared this Environmental Impact Statement/Environmental
and Unmet Need: Methodology and Results
 2 Demand and Unmet Need: Methodology and Results Projecting unmet park-and-ride need is the key indicator for park-and-ride expansion. There is gross demand and net new demand (also known as unmet need)
2 Demand and Unmet Need: Methodology and Results Projecting unmet park-and-ride need is the key indicator for park-and-ride expansion. There is gross demand and net new demand (also known as unmet need)
CFIRE. Evaluation of Green House Gas Emissions Models. CFIRE November 2014
 Evaluation of Green House Gas Emissions Models CFIRE CFIRE 02-24 November 2014 National Center for Freight & Infrastructure Research & Education Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering College
Evaluation of Green House Gas Emissions Models CFIRE CFIRE 02-24 November 2014 National Center for Freight & Infrastructure Research & Education Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering College
Contents i Contents Page 1 A New Transportation Plan Community Involvement Goals and Objectives... 11
 Contents i Contents 1 A New Transportation Plan... 1 Why develop a new plan?... 1 What area does the LRTP focus on?... 2 Why is this LRTP important?... 3 Meeting Requirements for Transportation Planning...
Contents i Contents 1 A New Transportation Plan... 1 Why develop a new plan?... 1 What area does the LRTP focus on?... 2 Why is this LRTP important?... 3 Meeting Requirements for Transportation Planning...
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY REGIONAL TRANSPORTATION PLAN 2050
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY REGIONAL TRANSPORTATION PLAN 2050 Introduction Goals Policies, and Performance Measures Growth Forecast and Planned Land Use Development Key Recommendations i Executive Summary April
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY REGIONAL TRANSPORTATION PLAN 2050 Introduction Goals Policies, and Performance Measures Growth Forecast and Planned Land Use Development Key Recommendations i Executive Summary April
E2 D0 U 1 C 3 A E T D IUOCNA A T IL O S N E A R L I E S S E R I E S HUB/DBE/SBE R A I L
 2E 0D1U3CEAT D UI O CN ATAI LO NSAELR ISEESR I E S R AIL HUB/DBE/SBE RAIL IN TEXAS OVERVIEW Since its inception, the Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT) has focused on meeting the transportation
2E 0D1U3CEAT D UI O CN ATAI LO NSAELR ISEESR I E S R AIL HUB/DBE/SBE RAIL IN TEXAS OVERVIEW Since its inception, the Texas Department of Transportation (TxDOT) has focused on meeting the transportation
A Synthesis Report of Purpose and Need: Assessment of Event Egress for Houston s Reliant Stadium
 1. Report No. SWUTC/15/600451-00049-1 4. Title and Subtitle A Synthesis Report of Purpose and Need: Assessment of Event Egress for Houston s Reliant Stadium Technical Report Documentation Page 2. Government
1. Report No. SWUTC/15/600451-00049-1 4. Title and Subtitle A Synthesis Report of Purpose and Need: Assessment of Event Egress for Houston s Reliant Stadium Technical Report Documentation Page 2. Government
Airports in the Region Case Study
 DESTINATION LINDBERGH: COLLABORATION AND VISION TO MEET SAN DIEGO S MOBILITY NEEDS By Bob Leiter, FAICP, Keith Wilschetz, and Tait Galloway INTRODuCTION Destination Lindbergh was a year-long, comprehensive
DESTINATION LINDBERGH: COLLABORATION AND VISION TO MEET SAN DIEGO S MOBILITY NEEDS By Bob Leiter, FAICP, Keith Wilschetz, and Tait Galloway INTRODuCTION Destination Lindbergh was a year-long, comprehensive
PERSPECTIVES ON FRONT RANGE PASSENGER RAIL
 PERSPECTIVES ON FRONT RANGE PASSENGER RAIL Rocky Mountain Railroad Heritage Society Englewood, Colorado September 30, 2017 Jim Souby Colorado Rail Passenger Association www.colorail.org ABOUT COLORAIL
PERSPECTIVES ON FRONT RANGE PASSENGER RAIL Rocky Mountain Railroad Heritage Society Englewood, Colorado September 30, 2017 Jim Souby Colorado Rail Passenger Association www.colorail.org ABOUT COLORAIL
DART s Role in Transit - Oriented Development. Jack Wierzenski,, Director Economic Development & Planning Dallas Area Rapid Transit
 DART s Role in Transit - Oriented Development Jack Wierzenski,, Director Economic Development & Planning Dallas Area Rapid Transit The DART System Established in 1983 13 Member Cities Local Funding: $.01
DART s Role in Transit - Oriented Development Jack Wierzenski,, Director Economic Development & Planning Dallas Area Rapid Transit The DART System Established in 1983 13 Member Cities Local Funding: $.01
Infrastructure and Growth Leadership Advisory Group Ideas and Approaches Survey
 Infrastructure and Growth Leadership Advisory Group Ideas and Approaches Survey Maintain transportation system in state of good repair 1. Increase focus on maintenance of existing infrastructure in poor
Infrastructure and Growth Leadership Advisory Group Ideas and Approaches Survey Maintain transportation system in state of good repair 1. Increase focus on maintenance of existing infrastructure in poor
PUBLIC TRANSPORT ORGANIZATIONAL MODELS: A CRITICAL APPRAISAL AND PROSPECTS FOR FUTURE INDUSTRY RESTRUCTURING
 PUBLIC TRANSPORT ORGANIZATIONAL MODELS: A CRITICAL APPRAISAL AND PROSPECTS FOR FUTURE INDUSTRY RESTRUCTURING 1 Outline Organizational models US Implementation Industry structure Prospects for the future
PUBLIC TRANSPORT ORGANIZATIONAL MODELS: A CRITICAL APPRAISAL AND PROSPECTS FOR FUTURE INDUSTRY RESTRUCTURING 1 Outline Organizational models US Implementation Industry structure Prospects for the future
Mobility 2025 Update: The Metropolitan Transportation Plan
 Mobility 2025 Update: The Metropolitan Transportation Plan May, 2001 North Central Texas Council of Governments Transportation Department MOBILITY 2025 UPDATE FINANCIAL SUMMARY Metropolitan Transportation
Mobility 2025 Update: The Metropolitan Transportation Plan May, 2001 North Central Texas Council of Governments Transportation Department MOBILITY 2025 UPDATE FINANCIAL SUMMARY Metropolitan Transportation
11. Operating and Maintenance Costs
 11. Operating and Maintenance Costs This section provides an overview of the development and structure of operating and maintenance (O&M) cost-estimating models created for the modern streetcar and bus
11. Operating and Maintenance Costs This section provides an overview of the development and structure of operating and maintenance (O&M) cost-estimating models created for the modern streetcar and bus
SOUTHWEST LRT (METRO GREEN LINE EXTENSION)
 8 Evaluation of Alternatives This chapter evaluates the effectiveness of the No Build Alternative and the Southwest Light Rail Transit (LRT) Project (the Project) based on the information contained in
8 Evaluation of Alternatives This chapter evaluates the effectiveness of the No Build Alternative and the Southwest Light Rail Transit (LRT) Project (the Project) based on the information contained in
Northern Illinois Commuter Transportation Initiative (NICTI) Locally Preferred Alternative Briefing Paper
 Northern Illinois Commuter Transportation Initiative () Locally Preferred Alternative Briefing Paper 1. Background Winnebago and Boone Counties established a coalition in 2003 to explore commuter connections
Northern Illinois Commuter Transportation Initiative () Locally Preferred Alternative Briefing Paper 1. Background Winnebago and Boone Counties established a coalition in 2003 to explore commuter connections
BOSTON REGION METROPOLITAN PLANNING ORGANIZATION MEMORANDUM
 BOSTON REGION METROPOLITAN PLANNING ORGANIZATION State Transportation Building Ten Park Plaza, Suite 2150 Boston, MA 02116-3968 Tel. (617) 973-7100 Fax (617) 973-8855 TTY (617) 973-7089 www.bostonmpo.org
BOSTON REGION METROPOLITAN PLANNING ORGANIZATION State Transportation Building Ten Park Plaza, Suite 2150 Boston, MA 02116-3968 Tel. (617) 973-7100 Fax (617) 973-8855 TTY (617) 973-7089 www.bostonmpo.org
Technical Briefing Report
 Technical Briefing Report March 2007 CONGESTION MANAGEMENT PROCESS (CMP) The Congestion Management Process (CMP) seeks a management solution to a growing traffic problem by targeting resources to operational
Technical Briefing Report March 2007 CONGESTION MANAGEMENT PROCESS (CMP) The Congestion Management Process (CMP) seeks a management solution to a growing traffic problem by targeting resources to operational
Forecasting High-Speed Rail Ridership
 12 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1341 Forecasting High-Speed Rail Ridership DANIEL BRAND, THOMAS E. PARODY, PoH SER Hsu, AND KEVIN F. TIERNEY Advantages and disadvantages of various high-speed rail (HSR)
12 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1341 Forecasting High-Speed Rail Ridership DANIEL BRAND, THOMAS E. PARODY, PoH SER Hsu, AND KEVIN F. TIERNEY Advantages and disadvantages of various high-speed rail (HSR)
VIA Long Range Plan Glossary
 VIA Long Range Plan Glossary Accessibility. Accessibility is the ability to reach opportunities (economic, social, etc.) within a certain geographical area. Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Passed
VIA Long Range Plan Glossary Accessibility. Accessibility is the ability to reach opportunities (economic, social, etc.) within a certain geographical area. Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). Passed
South Sounder Capital Improvements Program
 Subarea South King/Pierce Primary Mode Commuter Rail Facility Type Infrastructure Improvement Length Date Last Modified July 1, 2016 PROJECT AREA AND REP RESENTATIVE ALIGNMENT SHORT PROJECT DESCRIPTION
Subarea South King/Pierce Primary Mode Commuter Rail Facility Type Infrastructure Improvement Length Date Last Modified July 1, 2016 PROJECT AREA AND REP RESENTATIVE ALIGNMENT SHORT PROJECT DESCRIPTION
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY ORGANIZATION OF REPORT
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Over the past year, the Dillon Consulting team conducted a comprehensive review of public transit in Guelph. The City of Guelph has for many years been a leader among Canadian municipalities
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Over the past year, the Dillon Consulting team conducted a comprehensive review of public transit in Guelph. The City of Guelph has for many years been a leader among Canadian municipalities
Creating a Transit Supply Index. Andrew Keller Regional Transportation Authority and University of Illinois at Chicago
 Creating a Transit Supply Index Andrew Keller Regional Transportation Authority and University of Illinois at Chicago Presented at Transport Chicago Conference June 1, 2012 Introduction This master's project
Creating a Transit Supply Index Andrew Keller Regional Transportation Authority and University of Illinois at Chicago Presented at Transport Chicago Conference June 1, 2012 Introduction This master's project
APPENDIX A - PLANS AND POLICY REVIEW FEBRUARY 2017
 APPENDIX A - PLANS AND POLICY REVIEW FEBRUARY 2017 DENVERMOVES Transit Denver Moves: Transit APPENDIX A PLANS AND POLICY REVIEW 2035 Metro Vision Regional Transportation Plan (MVRTP) (2011) 2040 Fiscally
APPENDIX A - PLANS AND POLICY REVIEW FEBRUARY 2017 DENVERMOVES Transit Denver Moves: Transit APPENDIX A PLANS AND POLICY REVIEW 2035 Metro Vision Regional Transportation Plan (MVRTP) (2011) 2040 Fiscally
Connecting the Nation's Capital Transportation System
 Connecting the Nation's Capital Transportation System 12th National Light Rail Conference November 2012 Greg Benz, Henry Kay Mike Madden, Monica Meade Overview New LRT systems can provide intermodal connectively
Connecting the Nation's Capital Transportation System 12th National Light Rail Conference November 2012 Greg Benz, Henry Kay Mike Madden, Monica Meade Overview New LRT systems can provide intermodal connectively
Sustainable Transportation & Land Use Integration Study
 Sustainable Transportation & Land Use Integration Study Stakeholders Group Meeting Two Includes additions made after meeting March 28, 2011 Hot Topics: Emerging themes, technologies, and techniques Outline
Sustainable Transportation & Land Use Integration Study Stakeholders Group Meeting Two Includes additions made after meeting March 28, 2011 Hot Topics: Emerging themes, technologies, and techniques Outline
CALIFORNIA URBAN INFILL TRIP GENERATION STUDY. Luke Schwartz Kimley-Horn and Associates
 CALIFORNIA URBAN INFILL TRIP GENERATION STUDY Luke Schwartz Kimley-Horn and Associates Overview What is the CA Urban Infill Trip Generation Study Why was this study undertaken? Research methodology Trip
CALIFORNIA URBAN INFILL TRIP GENERATION STUDY Luke Schwartz Kimley-Horn and Associates Overview What is the CA Urban Infill Trip Generation Study Why was this study undertaken? Research methodology Trip
SOUTHEAST FLORIDA REGIONAL COMPACT CLIMATE CHANGE. Sustainable Communities & Transportation Planning
 SOUTHEAST FLORIDA REGIONAL COMPACT CLIMATE CHANGE Draft Regional Climate Action Plan Sustainable Communities & Transportation Planning SP-1 Develop criteria in collaboration with municipal and county planning
SOUTHEAST FLORIDA REGIONAL COMPACT CLIMATE CHANGE Draft Regional Climate Action Plan Sustainable Communities & Transportation Planning SP-1 Develop criteria in collaboration with municipal and county planning
What is the Transportation Policy Plan (TPP)?
 Summary What is the Transportation Policy Plan (TPP)? The region s long range transportation plan Includes all modes of transportation: highways, transit, airports, freight, biking, pedestrians Meets the
Summary What is the Transportation Policy Plan (TPP)? The region s long range transportation plan Includes all modes of transportation: highways, transit, airports, freight, biking, pedestrians Meets the
SECTION 5. Existing Conditions TRANSPORTATION NETWORK TRANSPORTATION
 SECTION 5 TRANSPORTATION Transportation systems are vital for moving people and goods and serving existing businesses. They also play a major role in guiding the location and type of development. The following
SECTION 5 TRANSPORTATION Transportation systems are vital for moving people and goods and serving existing businesses. They also play a major role in guiding the location and type of development. The following
Transit, Intercity Bus, Taxi 8-1
 8-1 Introduction Public transit is a critical element of any transportation system. It both provides an alternative form of transportation to the traditional use of the automobile and provides mobility
8-1 Introduction Public transit is a critical element of any transportation system. It both provides an alternative form of transportation to the traditional use of the automobile and provides mobility
Chapter 4: Transportation and Land Use
 Chapter 4: Transportation and Land Use Transportation and land use together make possible the wide range of destination opportunities in the region. Transportation provides the connections, and, in turn,
Chapter 4: Transportation and Land Use Transportation and land use together make possible the wide range of destination opportunities in the region. Transportation provides the connections, and, in turn,
2040 Transportation Policy Plan Conversion to Performance Based Planning Basis. 25 th Annual CTS Transportation Research Conference May 21, 2014
 2040 Transportation Policy Plan Conversion to Performance Based Planning Basis 25 th Annual CTS Transportation Research Conference May 21, 2014 1 About the plan Long-range transportation plan for the Twin
2040 Transportation Policy Plan Conversion to Performance Based Planning Basis 25 th Annual CTS Transportation Research Conference May 21, 2014 1 About the plan Long-range transportation plan for the Twin
First-Mile/Last-Mile Solutions for Transit Access: A National Perspective on What Has and Hasn t Changed in 45 Years of Experience
 First-Mile/Last-Mile Solutions for Transit Access: A National Perspective on What Has and Hasn t Changed in 45 Years of Experience Roger Teal DemandTrans Solutions, Inc. April 29, 2017 roger.teal@demandtrans.com
First-Mile/Last-Mile Solutions for Transit Access: A National Perspective on What Has and Hasn t Changed in 45 Years of Experience Roger Teal DemandTrans Solutions, Inc. April 29, 2017 roger.teal@demandtrans.com
Massachusetts Rail Plan. September 16, 2010
 Massachusetts Rail Plan September 16, 2010 State Freight and Rail Plans State Rail Plan The plan describes state policy for freight and passenger rail transportation, including commuter rail Provides priorities
Massachusetts Rail Plan September 16, 2010 State Freight and Rail Plans State Rail Plan The plan describes state policy for freight and passenger rail transportation, including commuter rail Provides priorities
DRAFT ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT STATEMENT FOR HOUSTON DALLAS HIGH SPEED RAIL (TEXAS CENTRAL)
 DRAFT ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT STATEMENT FOR HOUSTON DALLAS HIGH SPEED RAIL (TEXAS CENTRAL) Background On June 25, 2014, the Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) issued a Notice of Intent to Prepare an Environmental
DRAFT ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT STATEMENT FOR HOUSTON DALLAS HIGH SPEED RAIL (TEXAS CENTRAL) Background On June 25, 2014, the Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) issued a Notice of Intent to Prepare an Environmental
NCRRP Developing Multi-state Institutions to Implement Intercity Passenger Rail Programs. Michael D. Meyer, Ph.D. Parsons Brinckerhoff
 NCRRP 07-02 Developing Multi-state Institutions to Implement Intercity Passenger Rail Programs Michael D. Meyer, Ph.D. Parsons Brinckerhoff Goal Create practical models for multi-state institutional arrangements
NCRRP 07-02 Developing Multi-state Institutions to Implement Intercity Passenger Rail Programs Michael D. Meyer, Ph.D. Parsons Brinckerhoff Goal Create practical models for multi-state institutional arrangements
12 Evaluation of Alternatives
 12 Evaluation of Alternatives This chapter evaluates the effectiveness of the No-Build Alternative and the proposed METRO Blue Line Light Rail Transit (BLRT) Extension project based on the information
12 Evaluation of Alternatives This chapter evaluates the effectiveness of the No-Build Alternative and the proposed METRO Blue Line Light Rail Transit (BLRT) Extension project based on the information
Rail Division 2012 Annual Summary
 Rail Division 2012 Annual Summary Overview The Rail Division oversees rail planning and inspection, highway rail crossings, management of stateowned lines (such as the South Orient Rail line (SORR) and
Rail Division 2012 Annual Summary Overview The Rail Division oversees rail planning and inspection, highway rail crossings, management of stateowned lines (such as the South Orient Rail line (SORR) and
Connecting Communities: A Passenger Rail Symposium The Lone Star Rail District. May 25, 2010 Ross Milloy
 Connecting Communities: A Passenger Rail Symposium The Lone Star Rail District. May 25, 2010 Ross Milloy The world is changing Population and trade are increasing at increasing rates The petroleum price
Connecting Communities: A Passenger Rail Symposium The Lone Star Rail District. May 25, 2010 Ross Milloy The world is changing Population and trade are increasing at increasing rates The petroleum price
INVESTMENT SCENARIOS CHAPTER Illustrative Investment Approaches Public Outreach 6-1
 CHAPTER 6 As detailed in Chapters 4 and 5, Texas multimodal transportation needs estimated at $21 billion annually (2014 constant dollars) illustrated in Exhibit 4-12 far outstrip the approximately $9.1
CHAPTER 6 As detailed in Chapters 4 and 5, Texas multimodal transportation needs estimated at $21 billion annually (2014 constant dollars) illustrated in Exhibit 4-12 far outstrip the approximately $9.1
15. Supplementary Notes Supported by a grant from the U.S. Department of Transportation, University Transportation Centers Program.
 1. Report No. SWUTC/12/476660-00050-1 4. Title and Subtitle Technical Report Documentation Page 2. Government Accession No 3. Recipient's Catalog No Reviewing, Analyzing and Updating Marketing Strategies
1. Report No. SWUTC/12/476660-00050-1 4. Title and Subtitle Technical Report Documentation Page 2. Government Accession No 3. Recipient's Catalog No Reviewing, Analyzing and Updating Marketing Strategies
2010 Minnesota Comprehensive Statewide Freight and Passenger Rail Plan
 2010 Minnesota Comprehensive Statewide Freight and Passenger Rail Plan Public Open House Meetings January 2010 presented by: Minnesota Department of Transportation Agenda Introductions State Rail Plan
2010 Minnesota Comprehensive Statewide Freight and Passenger Rail Plan Public Open House Meetings January 2010 presented by: Minnesota Department of Transportation Agenda Introductions State Rail Plan
INTERMODAL RAIL TRANSIT SYSTEMS ENSURING OUR ECONOMIC AND TRANSPORTATION FUTURE
 INTERMODAL RAIL TRANSIT SYSTEMS ENSURING OUR ECONOMIC AND TRANSPORTATION FUTURE INTERMODAL TRANSIT Seamless movement of passengers from one mode of transit to another through a central hub Transit modes
INTERMODAL RAIL TRANSIT SYSTEMS ENSURING OUR ECONOMIC AND TRANSPORTATION FUTURE INTERMODAL TRANSIT Seamless movement of passengers from one mode of transit to another through a central hub Transit modes
California State Rail Plan. Santa Cruz County Regional Transportation Commission November 2, 2017
 California State Rail Plan Santa Cruz County Regional Transportation Commission November 2, 2017 Page 2 Overview: Division of Rail & Mass Transportation Mass Transit Funding Programs Federal Transit Grants
California State Rail Plan Santa Cruz County Regional Transportation Commission November 2, 2017 Page 2 Overview: Division of Rail & Mass Transportation Mass Transit Funding Programs Federal Transit Grants
Chapter 3 Stakeholder Interviews and Summary of Needs
 Chapter 3 Stakeholder Interviews and Summary of Needs 42 CHAPTER 3 STAKEHOLDER INTERVIEWS AND SUMMARY OF NEEDS CHAPTER 3. STAKEHOLDER INTERVIEWS AND SUMMARY OF NEEDS An extensive stakeholder interview
Chapter 3 Stakeholder Interviews and Summary of Needs 42 CHAPTER 3 STAKEHOLDER INTERVIEWS AND SUMMARY OF NEEDS CHAPTER 3. STAKEHOLDER INTERVIEWS AND SUMMARY OF NEEDS An extensive stakeholder interview
Policy Research CENTER
 Connecting Demand Management and Economic Development Activities TRANSPORTATION Policy Research CENTER Recent research into employer-based demand management strategies highlighted the fact that most business
Connecting Demand Management and Economic Development Activities TRANSPORTATION Policy Research CENTER Recent research into employer-based demand management strategies highlighted the fact that most business
Highest Priority Performance Measures for the TPP
 Highest Priority Performance Measures for the TPP The following list of measures are the highest priority performance measures as identified by modal working groups. These groups consist of staff from
Highest Priority Performance Measures for the TPP The following list of measures are the highest priority performance measures as identified by modal working groups. These groups consist of staff from
Northern Virginia Region Draft Needs Summary
 Needs Map: Need A A DEMAND The ability of communities around transit stations (particularly the areas within 1-2 miles of the stations and other travel hubs) to attract skilled workers and grow businesses
Needs Map: Need A A DEMAND The ability of communities around transit stations (particularly the areas within 1-2 miles of the stations and other travel hubs) to attract skilled workers and grow businesses
Tier 1 Environmental Impact Statement for the Chicago, Illinois, to Detroit-Pontiac,
 This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 08/31/2012 and available online at http://federalregister.gov/a/2012-21587, and on FDsys.gov 4910-06-P DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION
This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 08/31/2012 and available online at http://federalregister.gov/a/2012-21587, and on FDsys.gov 4910-06-P DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION
Appendix C: Scenarios and Future Drivers Impacting Transportation
 Prepared for Washington County Prepared by David Evans and Associates, Inc. 2100 SW River Parkway Portland, Oregon 97201 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 2 2. SCENARIOS PLANNING OVERVIEW... 2 3. SCENARIOS
Prepared for Washington County Prepared by David Evans and Associates, Inc. 2100 SW River Parkway Portland, Oregon 97201 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 2 2. SCENARIOS PLANNING OVERVIEW... 2 3. SCENARIOS
TRANSIT SYSTEM SUMMARY REPORT
 Genesee County Shaping our Transportation Future Together 2035 Long Range Transportation Plan TRANSIT SYSTEM SUMMARY REPORT Introduction The Genesee County Transit Technical Report is one of 19 technical
Genesee County Shaping our Transportation Future Together 2035 Long Range Transportation Plan TRANSIT SYSTEM SUMMARY REPORT Introduction The Genesee County Transit Technical Report is one of 19 technical
1. Evaluation of route and service alternatives; 2. Tier 1 Environmental Impact Analysis; and 3. Service Development Plan.
 Rail Rail plays a significant role in transportation planning, especially when considering economic development, safety, freight, and intermodal connectivity. Jackson has two rail lines serving the area,
Rail Rail plays a significant role in transportation planning, especially when considering economic development, safety, freight, and intermodal connectivity. Jackson has two rail lines serving the area,
STATEWIDE ANALYSIS MODEL (SAM-V3) June 5, 2014 Janie Temple
 STATEWIDE ANALYSIS MODEL (SAM-V3) June 5, 2014 Janie Temple Introduction Brief SAM History Intro to SAM-V3 functionality Past and Current SAM projects Future additions to SAM Suggestions from model users
STATEWIDE ANALYSIS MODEL (SAM-V3) June 5, 2014 Janie Temple Introduction Brief SAM History Intro to SAM-V3 functionality Past and Current SAM projects Future additions to SAM Suggestions from model users
VDOT and DRPT MPO and PDC Winter Meeting Amy Inman Planning & Mobility Programs Administrator Virginia Department of Rail and Public Transportation
 VDOT and DRPT MPO and PDC Winter Meeting Amy Inman Planning & Mobility Programs Administrator Virginia Department of Rail and Public Transportation www.drpt.virginia.gov 1 DRPT Customers 54 Transit Systems
VDOT and DRPT MPO and PDC Winter Meeting Amy Inman Planning & Mobility Programs Administrator Virginia Department of Rail and Public Transportation www.drpt.virginia.gov 1 DRPT Customers 54 Transit Systems
Madison Metro Transit: Transfer Point Centers. Summary: Description:
 Madison Metro Transit: Transfer Point Centers Summary: It took nine years of planning, but on July 19, 1998, the Madison Metro Transit changed overnight into the timed transfer departure system. The Madison
Madison Metro Transit: Transfer Point Centers Summary: It took nine years of planning, but on July 19, 1998, the Madison Metro Transit changed overnight into the timed transfer departure system. The Madison
Los Angeles County Congestion Reduction Demonstration Project
 Los Angeles County Congestion Reduction Demonstration Project frequently asked questions update #1 /august 2008 Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority (Metro), California Department of
Los Angeles County Congestion Reduction Demonstration Project frequently asked questions update #1 /august 2008 Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority (Metro), California Department of
Q9N. Likelihood of using Xpress if it meant you were better informed about how to use the bus system
 Q9N. Likelihood of using Xpress if it meant you were better informed about how to use the bus system on a 5 point scale, where: 1.0 1.8 Very Unlikely 1.8 2.6 2.6 3.4 Neutral 3.4 4.2 4.2 5.0 Very Likely
Q9N. Likelihood of using Xpress if it meant you were better informed about how to use the bus system on a 5 point scale, where: 1.0 1.8 Very Unlikely 1.8 2.6 2.6 3.4 Neutral 3.4 4.2 4.2 5.0 Very Likely
SUPPLEMENTAL NOTICE OF PREPARATION OF AN ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT REPORT. ACEforward Notice of Additional Project Element Niles Junction Connections
 SUPPLEMENTAL NOTICE OF PREPARATION OF AN ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT REPORT DATE: May 9, 2016 FROM: TO: SUBJECT: San Joaquin Regional Rail Commission Agencies, Organizations, and Interested Parties ACEforward
SUPPLEMENTAL NOTICE OF PREPARATION OF AN ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT REPORT DATE: May 9, 2016 FROM: TO: SUBJECT: San Joaquin Regional Rail Commission Agencies, Organizations, and Interested Parties ACEforward
Comprehensive Operations Analysis (COA) to support development of the. Public Meetings. January 28, 29 and February 2, 2015
 Comprehensive Operations Analysis (COA) to support development of the Public Meetings January 28, 29 and February 2, 2015 1 Agenda Introductions DART Background and Services Phased Approach to 2040 Transit
Comprehensive Operations Analysis (COA) to support development of the Public Meetings January 28, 29 and February 2, 2015 1 Agenda Introductions DART Background and Services Phased Approach to 2040 Transit
Colorado Statewide Intercity and Regional Bus Network Plan Scope of Work October 5th, 2006
 Colorado Statewide Intercity and Regional Bus Network Plan Scope of Work October 5th, 2006 Study Purpose: The Colorado Department of Transportation (CDOT) is requesting proposals to conduct a study of
Colorado Statewide Intercity and Regional Bus Network Plan Scope of Work October 5th, 2006 Study Purpose: The Colorado Department of Transportation (CDOT) is requesting proposals to conduct a study of
This letter is intended for inclusion in the Public Record
 s2 Citizens for Appropriate Transportation 728 South Euclid Avenue Oak Park, Illinois 60304 www.citizensforappropriatetransportation.org This letter is intended for inclusion in the Public Record January
s2 Citizens for Appropriate Transportation 728 South Euclid Avenue Oak Park, Illinois 60304 www.citizensforappropriatetransportation.org This letter is intended for inclusion in the Public Record January
SCS Scenario Planning
 E SCS Scenario Planning Introduction As part of the 2035 MTP/SCS process, AMBAG developed a series of land use and transportation alternative scenarios for evaluation and testing to demonstrate how the
E SCS Scenario Planning Introduction As part of the 2035 MTP/SCS process, AMBAG developed a series of land use and transportation alternative scenarios for evaluation and testing to demonstrate how the
CHAPTER 9 TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL SUMMARY
 CHAPTER 9 TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL SUMMARY This chapter describes the OKI / MVRPC regional travel demand model, used to support traffic and transit forecasts for the NSTI study. This model is based on version
CHAPTER 9 TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL SUMMARY This chapter describes the OKI / MVRPC regional travel demand model, used to support traffic and transit forecasts for the NSTI study. This model is based on version
Travel Demand Forecasting User Guide
 Travel Demand Forecasting User Guide A Supplement to the Regional Transitway Guidelines Metropolitan Council February 2012 This document supplements the Project Development, Leadership, and Oversight discussion
Travel Demand Forecasting User Guide A Supplement to the Regional Transitway Guidelines Metropolitan Council February 2012 This document supplements the Project Development, Leadership, and Oversight discussion
Community Development Committee
 C Community Development Committee Meeting date: February 21, 2012 ADVISORY INFORMATION Date: February 14, 2012 Subject: Employment in the Twin Cities District(s), Member(s): All Policy/Legal Reference:
C Community Development Committee Meeting date: February 21, 2012 ADVISORY INFORMATION Date: February 14, 2012 Subject: Employment in the Twin Cities District(s), Member(s): All Policy/Legal Reference:
Project Planning Documentation
 Project Planning Documentation Overview of Project Project funding will be used to complete necessary preliminary engineering and NEPA for a new 250 mile high-speed core express service between Dallas-Fort
Project Planning Documentation Overview of Project Project funding will be used to complete necessary preliminary engineering and NEPA for a new 250 mile high-speed core express service between Dallas-Fort
JCDecaux N O R T H A M E R I C A
 JCDecaux N O R T H A M E R I C A Global Presence JCDecaux North America s parent, JCDecaux, is the No.1 Outdoor Advertising Company in the world reaching 300 million people every day across more than 50
JCDecaux N O R T H A M E R I C A Global Presence JCDecaux North America s parent, JCDecaux, is the No.1 Outdoor Advertising Company in the world reaching 300 million people every day across more than 50
