Supplemental Materials. Matrix Proteases Contribute to Progression of Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Mice and Humans
|
|
|
- Hillary Porter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Materials Matrix Proteases Contribute to Progression of Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Mice and Humans Madhusudhan Budatha, Shayzreen Roshanravan, Qian Zheng, Cecilia Weislander, Shelby L. Chapman, Elaine C. Davis, Barry Starcher, R. Ann Word and Hiromi Yanagisawa 52
2 Figure S1. Generation of D56E knock-in mutant mice. (A) Knock-in strategy. The RGD in exon 4 of the Fbln5 gene is replaced with the short arm containing the RGE and a de novo EcoRI site. Exons 1 through 4 are numbered. WT allele, targeting vector and targeted alleles with or without a Neomycin cassette (Neo) are shown. Cre-mediated recombination removes Neo to generate a D56E allele (RGE). (B) Southern blot analysis with EcoRIdigested genomic DNA hybridizing with a 5 probe yields a 15-kb band for the WT, 11-kb for the Neo allele, and a 12-kb band for the RGE allele. (C) Genomic PCR detecting RGE alleles after Neo excision. WT and RGE alleles generate 900 bp and 930 bp bands, respectively. 53
3 Figure S2. Evaluation of elastic fiber formation in Fbln5RGE/RGE mice. (A) Hart s staining of elastic fibers in the aorta (Bars=40 µm), skin (Bars=20 µm), lungs (Bars=40 µm) and coronary arteries (Bars=40 µm) from Fbln5RGE/+ and Fbln5RGE/RGE mice. Arrows indicate elastic fibers. (B) Electron microscopic observation of the aorta. Representative images of transverse sections of the aorta from WT and Fbln5RGE/RGE mice at P5 (n=3 per genotype) and P90 (n=4 per genotype) are shown. Bars=5 µm. Both WT and mutants show normal elastic fibers. (C) Desmosine levels were measured in the aorta, lungs and skin of 2 month old Fbln5RGE/+ and Fbln5RGE/RGE mice. No statistical difference was observed between the genotypes. Means ± SEM. 54
4 Figure S3. Predominant upregulation of prommp-9 in vaginal tissues from Fbln5 mutant mice. Gelatin zymography with or without 2 mm 4-aminophenylmercuric acetate (APMA) distinguishes prommp-9 and MMP-9 activity. 55
5 Figure S4. Characterization of primary vaginal stromal cells. (A) Representative images of fibronectin immunostaining of the vagina from 4 week old WT, Fbln5-/and Fbln5RGE/RGE mice. Corresponding DAPI staining is shown. Fibronectin is strongly expressed in the stroma (s). ep; epithelium. (B) Representative immunostaining of passage 1 WT vaginal stromal cells with α-sm actin, vimentin, cytokeratin and CD68. Note that stromal cells are positive (> 99%) for mesenchymal markers (upper panel) but negative (<1%) for epithelial or activated macrophage markers. (C) RT-PCR analysis of various integrin transcripts levels in vaginal stromal cells. No difference was observed between WT, Fbln5-/- and Fbln5RGE/RGE cells. 56
6 Figure S5. Effects of β1 integrin blocking antibodies or control IgG on fibronectinmediated MMP-9 upregulation in primary vaginal stromal cells. WT, Fbln5 -/- and Fbln5 RGE/RGE stromal cells were incubated with fibronectin (50 µg/ml) in the presence of ß1 blocking antibodies (10 µg/ml, ß1ab), IgG control (10 µg/ml) or PBS. Arrows indicate MMP-9. Note that fibronectin-mediated MMP-9 upregulation was inhibited by ß1ab but not by IgG. 57
7 Figure S6. DKO vaginal tissues contain more collagen fibers compared to Fbln5 -/- mice. Representative images of picrosirius red staining on transverse sections of vaginal tissues from Fbln5 -/- (n=4) or DKO (n=6) mice. Bars=20 µm. 58
8 Table S1. Characterization of primary vaginal stromal cells. Table shows % of positive cells per total nuclei in corresponding genotype. Value is the mean ± SD. At least 200 nuclei were counted from 5 fields taken under 20x objective lens. The experiments were repeated 3 times. No statistically significant difference was observed between genotypes. 59
9 Table S2. Absence of Mmp9 alters the frequency of POP in nulliparous Fbln5 -/- mice. The frequency of prolapse Stage 2 was determined as a function of age in all genotypes.*p<0.05 compared with Fbln5 -/- ;Mmp9 -/- or Fbln5 -/- ;Mmp9 +/-. 60
10 Table S3. Demographics of human subjects from whom samples were used for qpcr. Tissues were obtained from the apex of the anterior vaginal wall. Women with prolapse had descent of the anterior or central compartments as outlined in Materials and Methods. Age represents mean ± SEM. Parity represents median [range]. *p 0.01 compared with other groups. **p < 0.01 compared with premenopausal prolapse. 61
11 Table S4. Demographics of human subjects from whom samples were used for gelatin zymography. Tissues were obtained from the apex of the anterior vaginal wall. Women with prolapse had descent of the anterior or central compartments as outlined in Materials and Methods. Age represents mean ± SEM. Parity represent median [range]. *P 0.01 compared with premenopausal controls, premenopausal prolapse, and postmenopausal controls. 62
12 Table S5. PCR primer sequences Mouse Gene Forward primer 5ʼ-3ʼ Reverse primer 5ʼ-3ʼ Itga2 gcatggcattggtgactatccac gcagcaaagggtggtgttggaa Itga3 tgagaaccagcatccctaccatc tgcctcttagcttcatacagggc Itga5 accagccatttagccttcagtgtg tgaagaagccgagcttgtagagga Itga6 tcaccgctgctgctcagaatatca aatgctgtcatcgtacctagagcg Itga9 actgcaaccttagtgctcttccga caccagcaaactgatggcgatgat Itgav agccagacccgttgtcactgtaaa atggagaaacagtgctcgtcggat Itgb1 tgtggacagtgtgtgtgtaggaag gtctcacaagttggcccttgaaac Itgb4 agaatctgcgagaatcccagccat ttcaccaggtgctcagtgtcatca Itgb5 actgtggagaatgcaaatgccacg tttggaacttggcaaactctcggc Mmp2 ggactatgaccgggataagaaatatg gggcaccttctgaatttcca Mmp9 agaccaagggtacagcctgttc gcacgctggaatgatctaagc Timp1 catggaaagcctctgtggatatg aggcggcccgtgatg Timp2 ggtggattccgggaatgac tttgaacatctttatctgcttgatctc Actb acagtccgcctagaagcact tccgatgccctgaggctctt B2m ccgagcccaagaccgtcta aactggatttgtaattaagcaggttca Gapdh agtatgactccactcacggcaa tctcgctcctggaagatggt Human Gene Forward primer 5ʼ-3ʼ Reverse primer 5ʼ-3ʼ MMP2 ttgatggcatcgctcagatc tgtcacgtggcgtcacagt MMP9 gaactttgacagcgacaagaagtg gccgccacgaggaaca 63
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information MicroRNA-212/132 family is required for epithelial stromal interactions necessary for mouse mammary gland development Ahmet Ucar, Vida Vafaizadeh, Hubertus Jarry, Jan Fiedler,
Supplementary Information MicroRNA-212/132 family is required for epithelial stromal interactions necessary for mouse mammary gland development Ahmet Ucar, Vida Vafaizadeh, Hubertus Jarry, Jan Fiedler,
Figure S1. Figure S2. Figure S3 HB Anti-FSP27 (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab. Anti-GST-FSP27(45-127) Ab.
 / 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
/ 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
DRG Pituitary Cerebral Cortex
 Liver Spinal cord Pons Atg5 -/- Atg5 +/+ DRG Pituitary Cerebral Cortex WT KO Supplementary Figure S1 Ubiquitin-positive IBs accumulate in Atg5 -/- tissues. Atg5 -/- neonatal tissues were fixed and decalcified.
Liver Spinal cord Pons Atg5 -/- Atg5 +/+ DRG Pituitary Cerebral Cortex WT KO Supplementary Figure S1 Ubiquitin-positive IBs accumulate in Atg5 -/- tissues. Atg5 -/- neonatal tissues were fixed and decalcified.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of inducible BICD2 knock-out mice. A) The mouse BICD2 locus and gene targeting constructs. To generate an inducible Bicd2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of inducible BICD2 knock-out mice. A) The mouse BICD2 locus and gene targeting constructs. To generate an inducible Bicd2
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of B2M -/- ESCs. Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.3860
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of B2M -/- ESCs. (a) Maps of the B2M alleles in cells with the indicated B2M genotypes. Probes and restriction enzymes used in Southern blots are indicated (H, Hind III;
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of B2M -/- ESCs. (a) Maps of the B2M alleles in cells with the indicated B2M genotypes. Probes and restriction enzymes used in Southern blots are indicated (H, Hind III;
bronchial epithelial cells (I). Bronchi are outlined with dashed line. Scale bars = 25 µm, if not
 Supplemental Figure S1: ronchial epithelial cell polarity and integrity is maintained in bronchi. (A-E) Staining for selected markers of bronchial cell differentiation and intracellular compartments is
Supplemental Figure S1: ronchial epithelial cell polarity and integrity is maintained in bronchi. (A-E) Staining for selected markers of bronchial cell differentiation and intracellular compartments is
Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured
 Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured in 90-Pa 3D fibrin gels for 5 days in the presence
Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured in 90-Pa 3D fibrin gels for 5 days in the presence
Revised: RG-RV2 by Fukuhara et al.
 Supplemental Figure 1 The generation of Spns2 conditional knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the wild type Spns2 locus (Spns2 + ), the targeted allele, the floxed allele (Spns2 f ) and the
Supplemental Figure 1 The generation of Spns2 conditional knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the wild type Spns2 locus (Spns2 + ), the targeted allele, the floxed allele (Spns2 f ) and the
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Generation of TSPOΔ/Δ murine embryonic fibroblasts Embryos were harvested from 13.5-day pregnant TSPOfl/fl mice. After dissection to eviscerate and remove the
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Generation of TSPOΔ/Δ murine embryonic fibroblasts Embryos were harvested from 13.5-day pregnant TSPOfl/fl mice. After dissection to eviscerate and remove the
Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
monoclonal antibody. (a) The specificity of the anti-rhbdd1 monoclonal antibody was examined in
 Supplementary information Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1 Determination of the s pecificity of in-house anti-rhbdd1 mouse monoclonal antibody. (a) The specificity of the anti-rhbdd1 monoclonal
Supplementary information Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1 Determination of the s pecificity of in-house anti-rhbdd1 mouse monoclonal antibody. (a) The specificity of the anti-rhbdd1 monoclonal
Table S1. Primers used in the study
 Table S1. Primers used in the study Primer name Application Sequence I1F16 Genotyping GGCAAGTGAGTGAGTGCCTA I1R11 Genotyping CCCACTCGTATTGACGCTCT V19 Genotyping GGGTCTCAAAGTCAGGGTCA D18Mit184-F Genotyping
Table S1. Primers used in the study Primer name Application Sequence I1F16 Genotyping GGCAAGTGAGTGAGTGCCTA I1R11 Genotyping CCCACTCGTATTGACGCTCT V19 Genotyping GGGTCTCAAAGTCAGGGTCA D18Mit184-F Genotyping
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS. -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells. - Two methods to produce transgenic animals:
 TRANSGENIC ANIMALS -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection - random insertion 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated gene
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection - random insertion 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated gene
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Cell Selective Cardiovascular Biology of Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthase- Chen, et al Cell specific role of mpges- Lihong Chen,,*, MD, PhD; Guangrui Yang,,*, MD, PhD; Xiufeng
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Cell Selective Cardiovascular Biology of Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthase- Chen, et al Cell specific role of mpges- Lihong Chen,,*, MD, PhD; Guangrui Yang,,*, MD, PhD; Xiufeng
The RRPA knock-in allele was generated by homologous recombination in TC1 ES cells.
 Supplemental Materials Materials & Methods Generation of RRPA and RAPA Knock-in Mice The RRPA knock-in allele was generated by homologous recombination in TC1 ES cells. Targeted ES clones in which the
Supplemental Materials Materials & Methods Generation of RRPA and RAPA Knock-in Mice The RRPA knock-in allele was generated by homologous recombination in TC1 ES cells. Targeted ES clones in which the
Accelerating skin wound healing by M-CSF through generating SSEA-1 and -3 stem cells. in the injured sites
 Accelerating skin wound healing by M-CSF through generating SSEA-1 and -3 stem cells in the injured sites Yunyuan Li, Reza Baradar Jalili, Aziz Ghahary Department of Surgery, University of British Columbia,
Accelerating skin wound healing by M-CSF through generating SSEA-1 and -3 stem cells in the injured sites Yunyuan Li, Reza Baradar Jalili, Aziz Ghahary Department of Surgery, University of British Columbia,
A Low salt diet. C Low salt diet + mf4-31c1 3. D High salt diet + mf4-31c1 3. B High salt diet
 A Low salt diet GV [AU]:. [mmhg]: 0..... 09 9 7 B High salt diet GV [AU]:. [mmhg]: 7 8...0. 7.8 8.. 0 8 7 C Low salt diet + mf-c GV [AU]:. [mmhg]:.0.9 8.7.7. 7 8 0 D High salt diet + mf-c E Lymph capillary
A Low salt diet GV [AU]:. [mmhg]: 0..... 09 9 7 B High salt diet GV [AU]:. [mmhg]: 7 8...0. 7.8 8.. 0 8 7 C Low salt diet + mf-c GV [AU]:. [mmhg]:.0.9 8.7.7. 7 8 0 D High salt diet + mf-c E Lymph capillary
 Figure S1. Generation of HspA4 -/- mice. (A) Structures of the wild-type (Wt) HspA4 -/- allele, targeting vector and targeted allele are shown together with the relevant restriction sites. The filled rectangles
Figure S1. Generation of HspA4 -/- mice. (A) Structures of the wild-type (Wt) HspA4 -/- allele, targeting vector and targeted allele are shown together with the relevant restriction sites. The filled rectangles
Gene Sequence Annealing Temperature. Actin 5 : 5 -CATCACTATTGGCAACGAGC-3 60 C 3 : 5 -ACGCAGCTCAGTAACAGTCC-3 PCR product: 410 bp
 Supporting Materials and Methods RT-PCR RT-PCR was performed as described in ref. 1 using the following oligonucleotides and PCR conditions: 2 min at 95 C, (20 s at 95 C, 20 s at the annealing temp, and
Supporting Materials and Methods RT-PCR RT-PCR was performed as described in ref. 1 using the following oligonucleotides and PCR conditions: 2 min at 95 C, (20 s at 95 C, 20 s at the annealing temp, and
Control + SDS + 2BME. Control + SDS. Control
 Supplementary Figure 1 2BME:2-mercaptoethanol Control Control + SDS Control + SDS + 2BME Control Control + SDS Control + SDS + 2BME Control Control + SDS Control + SDS + 2BME Ephrin-B2 Oligomers Ephrin-B2
Supplementary Figure 1 2BME:2-mercaptoethanol Control Control + SDS Control + SDS + 2BME Control Control + SDS Control + SDS + 2BME Control Control + SDS Control + SDS + 2BME Ephrin-B2 Oligomers Ephrin-B2
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Reverse transcribed Quantitative PCR. Total RNA was isolated from bone marrow derived macrophages using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), DNase-treated (Promega RQ1), and reverse transcribed
Supplementary Methods Reverse transcribed Quantitative PCR. Total RNA was isolated from bone marrow derived macrophages using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), DNase-treated (Promega RQ1), and reverse transcribed
amplify the conditional allele (2-lox) and recombined allele (1-lox) following tamoxifen
 Supplementary data Supplementary Table 1. Real-time PCR primer sequences Supplementary Fig. 1. (A) Genomic map of the Vhl (2-lox) conditional allele. Numbered boxes represent exon 1, which is targeted
Supplementary data Supplementary Table 1. Real-time PCR primer sequences Supplementary Fig. 1. (A) Genomic map of the Vhl (2-lox) conditional allele. Numbered boxes represent exon 1, which is targeted
- 1 - Supplemental Data
 - 1-1 Supplemental Data 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Supplemental Figure S1. Differential expression of AtPIP Genes in DC3000-inoculated plants. Gene expression in leaves was analyzed by real-time RT-PCR and expression
- 1-1 Supplemental Data 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Supplemental Figure S1. Differential expression of AtPIP Genes in DC3000-inoculated plants. Gene expression in leaves was analyzed by real-time RT-PCR and expression
WT Day 90 after injections
 Supplementary Figure 1 a Day 1 after injections Day 9 after injections Klf5 +/- Day 1 after injections Klf5 +/- Day 9 after injections BLM PBS b Day 1 after injections Dermal thickness (μm) 3 1 Day 9 after
Supplementary Figure 1 a Day 1 after injections Day 9 after injections Klf5 +/- Day 1 after injections Klf5 +/- Day 9 after injections BLM PBS b Day 1 after injections Dermal thickness (μm) 3 1 Day 9 after
Pei et al. Supplementary Figure S1
 Pei et al. Supplementary Figure S1 C H-CUL9: + + + + + Myc-ROC1: - - + + + U2OS/pcDN3 U2OS/H-CUL9 U2OS/ + H-CUL9 IP: -H -myc input -H -myc 1 2 3 4 5 H-CUL9 Myc-ROC1 -H -H -H -H H-CUL9: wt RR myc-roc1:
Pei et al. Supplementary Figure S1 C H-CUL9: + + + + + Myc-ROC1: - - + + + U2OS/pcDN3 U2OS/H-CUL9 U2OS/ + H-CUL9 IP: -H -myc input -H -myc 1 2 3 4 5 H-CUL9 Myc-ROC1 -H -H -H -H H-CUL9: wt RR myc-roc1:
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS. transient. stable. - Two methods to produce transgenic animals:
 Only for teaching purposes - not for reproduction or sale CELL TRANSFECTION transient stable TRANSGENIC ANIMALS - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated
Only for teaching purposes - not for reproduction or sale CELL TRANSFECTION transient stable TRANSGENIC ANIMALS - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated
Supplementary Figure S1: (A) Schematic representation of the Jarid2 Flox/Flox
 Supplementary Figure S1: (A) Schematic representation of the Flox/Flox locus and the strategy used to visualize the wt and the Flox/Flox mrna by PCR from cdna. An example of the genotyping strategy is
Supplementary Figure S1: (A) Schematic representation of the Flox/Flox locus and the strategy used to visualize the wt and the Flox/Flox mrna by PCR from cdna. An example of the genotyping strategy is
Ma, et al. Supplemental Data
 Ma, et al Supplemental Data Title: Calpain mediates pulmonary vascular remodeling in rodent models of pulmonary hypertension and its inhibition attenuates pathologic features of disease Authors: Wanli
Ma, et al Supplemental Data Title: Calpain mediates pulmonary vascular remodeling in rodent models of pulmonary hypertension and its inhibition attenuates pathologic features of disease Authors: Wanli
Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified
 Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified by primers used for mrna expression analysis. Gray
Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified by primers used for mrna expression analysis. Gray
Supplementary Table 1. PCR amplification conditions for each primer pair. Primer sequence
 - 1 - Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1. PCR amplification conditions for each primer pair Primer sequence FN1 S - CAAAGCAAGCCCGGTTGT AS - CGCTCCCACTGTTGATTTATCTG ITGα2 S - TTAGGTTACTCTGTGGCTGCAATT
- 1 - Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1. PCR amplification conditions for each primer pair Primer sequence FN1 S - CAAAGCAAGCCCGGTTGT AS - CGCTCCCACTGTTGATTTATCTG ITGα2 S - TTAGGTTACTCTGTGGCTGCAATT
Fig. S1. eif6 expression in HEK293 transfected with shrna against eif6 or pcmv-eif6 vector.
 Fig. S1. eif6 expression in HEK293 transfected with shrna against eif6 or pcmv-eif6 vector. (a) Western blotting analysis and (b) qpcr analysis of eif6 expression in HEK293 T cells transfected with either
Fig. S1. eif6 expression in HEK293 transfected with shrna against eif6 or pcmv-eif6 vector. (a) Western blotting analysis and (b) qpcr analysis of eif6 expression in HEK293 T cells transfected with either
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.4166
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Supplemental Figure 1 (Figure S1), related to Figure 1 Figure S1 provides evidence to demonstrate Nfatc1Cre is a mouse line that directed gene
 Developmental Cell, Volume 25 Supplemental Information Brg1 Governs a Positive Feedback Circuit in the Hair Follicle for Tissue Regeneration and Repair Yiqin Xiong, Wei Li, Ching Shang, Richard M. Chen,
Developmental Cell, Volume 25 Supplemental Information Brg1 Governs a Positive Feedback Circuit in the Hair Follicle for Tissue Regeneration and Repair Yiqin Xiong, Wei Li, Ching Shang, Richard M. Chen,
Myofibroblasts in kidney fibrosis. LeBleu et al.
 Origin and Function of Myofibroblasts in Kidney Fibrosis Valerie S. LeBleu, Gangadhar Taduri, Joyce O Connell, Yingqi Teng, Vesselina G. Cooke, Craig Woda, Hikaru Sugimoto and Raghu Kalluri Supplementary
Origin and Function of Myofibroblasts in Kidney Fibrosis Valerie S. LeBleu, Gangadhar Taduri, Joyce O Connell, Yingqi Teng, Vesselina G. Cooke, Craig Woda, Hikaru Sugimoto and Raghu Kalluri Supplementary
At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Supplementary Table-1: List of genes that were identically matched between the ST2 and
 Supplementary data Supplementary Table-1: List of genes that were identically matched between the ST2 and ST3. Supplementary Table-2: List of genes that were differentially expressed in GD2 + cells compared
Supplementary data Supplementary Table-1: List of genes that were identically matched between the ST2 and ST3. Supplementary Table-2: List of genes that were differentially expressed in GD2 + cells compared
Supplementary Figure 1. Isolation of GFPHigh cells.
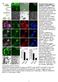 Supplementary Figure 1. Isolation of GFP High cells. (A) Schematic diagram of cell isolation based on Wnt signaling activity. Colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines were stably transduced with lentivirus encoding
Supplementary Figure 1. Isolation of GFP High cells. (A) Schematic diagram of cell isolation based on Wnt signaling activity. Colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines were stably transduced with lentivirus encoding
CFTR-null wt CFTR-null 1.0. Probe: Neo R. Figure S1
 A. B. 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Probe: Neo R CFTR-null wt CFTR-null Figure S1 A. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 10kb 8kb CFTR-null wt B. Probe: CFTR
A. B. 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Probe: Neo R CFTR-null wt CFTR-null Figure S1 A. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 10kb 8kb CFTR-null wt B. Probe: CFTR
Supplementary information for: Ten-Eleven Translocation-2 (Tet2) Is Involved in Myogenic Differentiation of Skeletal Myoblast Cells in
 Supplementary information for: Ten-Eleven Translocation-2 (Tet2) Is Involved in Myogenic Differentiation of Skeletal Myoblast Cells in Vitro Xia Zhong*, Qian-Qian Wang*, Jian-Wei Li, Yu-Mei Zhang, Xiao-Rong
Supplementary information for: Ten-Eleven Translocation-2 (Tet2) Is Involved in Myogenic Differentiation of Skeletal Myoblast Cells in Vitro Xia Zhong*, Qian-Qian Wang*, Jian-Wei Li, Yu-Mei Zhang, Xiao-Rong
Supplementary Information (Ha, et. al) Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. S1
 Supplementary Information (Ha, et. al) Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. S1 a His-ORMDL3 ~ 17 His-ORMDL3 GST-ORMDL3 - + - + IPTG GST-ORMDL3 ~ b Integrated Density (ORMDL3/ -actin) 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1
Supplementary Information (Ha, et. al) Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. S1 a His-ORMDL3 ~ 17 His-ORMDL3 GST-ORMDL3 - + - + IPTG GST-ORMDL3 ~ b Integrated Density (ORMDL3/ -actin) 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1
(a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of Diaph3 ko mice. (a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for different regions of Diaph3 mrna from WT, heterozygote
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of Diaph3 ko mice. (a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for different regions of Diaph3 mrna from WT, heterozygote
Supplementary Data. Flvcr1a TCTAAGGCCCAGTAGGACCC GGCCTCAACTGCCTGGGAGC AGAGGGCAACCTCGGTGTCC
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Materials and Methods Measurement of reactive oxygen species accumulation in fresh intestinal rings Accumulation of reactive oxygen species in fresh intestinal rings was
Supplementary Data Supplementary Materials and Methods Measurement of reactive oxygen species accumulation in fresh intestinal rings Accumulation of reactive oxygen species in fresh intestinal rings was
Multiple layers of B cell memory with different effector functions. Ismail Dogan, Barbara Bertocci, Valérie Vilmont, Frédéric Delbos,
 Multiple layers of B cell memory with different effector functions Ismail Dogan, Barbara Bertocci, Valérie Vilmont, Frédéric Delbos, Jérome Mégret, Sébastien Storck, Claude-Agnès Reynaud & Jean-Claude
Multiple layers of B cell memory with different effector functions Ismail Dogan, Barbara Bertocci, Valérie Vilmont, Frédéric Delbos, Jérome Mégret, Sébastien Storck, Claude-Agnès Reynaud & Jean-Claude
PIE1 ARP6 SWC6 KU70 ARP6 PIE1. HSA SNF2_N HELICc SANT. pie1-3 A1,A2 K1,K2 K1,K3 K3,LB2 A3, A4 A3,LB1 A1,A2 K1,K2 K1,K3. swc6-1 A3,A4.
 A B N-terminal SWC2 H2A.Z SWC6 ARP6 PIE1 HSA SNF2_N HELICc SANT C pie1-3 D PIE1 ARP6 5 Kb A1 200 bp A3 A2 LB1 arp6-3 A4 E A1,A2 A3, A4 A3,LB1 K1,K2 K1,K3 K3,LB2 SWC6 swc6-1 A1,A2 A3,A4 K1,K2 K1,K3 100
A B N-terminal SWC2 H2A.Z SWC6 ARP6 PIE1 HSA SNF2_N HELICc SANT C pie1-3 D PIE1 ARP6 5 Kb A1 200 bp A3 A2 LB1 arp6-3 A4 E A1,A2 A3, A4 A3,LB1 K1,K2 K1,K3 K3,LB2 SWC6 swc6-1 A1,A2 A3,A4 K1,K2 K1,K3 100
Supplementary Figure Legends
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 gene targeting strategy for disruption of chicken gene, related to Figure 1 (f)-(i). (a) The locus and the targeting constructs showing HpaI restriction sites. The
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 gene targeting strategy for disruption of chicken gene, related to Figure 1 (f)-(i). (a) The locus and the targeting constructs showing HpaI restriction sites. The
a KYSE270-CON KYSE270-Id1
 a KYSE27-CON KYSE27- shcon shcon sh b Human Mouse CD31 Relative MVD 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1.5 *** *** c KYSE15 KYSE27 sirna (nm) 5 1 Id2 Id2 sirna 5 1 sirna (nm) 5 1 Id2 sirna 5 1 Id2 [h] (pg per ml) d 3 2 1
a KYSE27-CON KYSE27- shcon shcon sh b Human Mouse CD31 Relative MVD 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1.5 *** *** c KYSE15 KYSE27 sirna (nm) 5 1 Id2 Id2 sirna 5 1 sirna (nm) 5 1 Id2 sirna 5 1 Id2 [h] (pg per ml) d 3 2 1
Aspergillus fumigatus CalA binds to integrin α 5 β 1 and mediates host cell invasion
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION ARTICLE NUMBER: 16211 DOI: 10.1038/NMICROBIOL.2016.211 Aspergillus fumigatus CalA binds to integrin α 5 β 1 and mediates host
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION ARTICLE NUMBER: 16211 DOI: 10.1038/NMICROBIOL.2016.211 Aspergillus fumigatus CalA binds to integrin α 5 β 1 and mediates host
Anti-ERK1/2, anti-p-erk1/2, anti-p38 anti-p-msk1 (Thr581) and anti-p-msk2
 Supplementary methods Antibodies Anti-ERK1/2, anti-p-erk1/2, anti-p38 anti-p-msk1 (Thr581) and anti-p-msk2 polyclonal were from Cell Signalling and the anti-p-histone H3(Ser1) antibody was from Upstate.
Supplementary methods Antibodies Anti-ERK1/2, anti-p-erk1/2, anti-p38 anti-p-msk1 (Thr581) and anti-p-msk2 polyclonal were from Cell Signalling and the anti-p-histone H3(Ser1) antibody was from Upstate.
Figure S1. Verification of ihog Mutation by Protein Immunoblotting Figure S2. Verification of ihog and boi
 Figure S1. Verification of ihog Mutation by Protein Immunoblotting Extracts from S2R+ cells, embryos, and adults were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with anti-ihog antibody. The Ihog
Figure S1. Verification of ihog Mutation by Protein Immunoblotting Extracts from S2R+ cells, embryos, and adults were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with anti-ihog antibody. The Ihog
Cell proliferation was measured with Cell Counting Kit-8 (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan).
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Supplemental Materials and Methods Cell proliferation assay Cell proliferation was measured with Cell Counting Kit-8 (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan). GCs were plated at 96-well
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Supplemental Materials and Methods Cell proliferation assay Cell proliferation was measured with Cell Counting Kit-8 (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan). GCs were plated at 96-well
administration of tamoxifen. Bars show mean ± s.e.m (n=10-11). P-value was determined by
 Supplementary Figure 1. Chimerism of CD45.2 + GFP + cells at 1 month post transplantation No significant changes were detected in chimerism of CD45.2 + GFP + cells between recipient mice repopulated with
Supplementary Figure 1. Chimerism of CD45.2 + GFP + cells at 1 month post transplantation No significant changes were detected in chimerism of CD45.2 + GFP + cells between recipient mice repopulated with
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTRY INFORMTION DOI:.38/ncb Kdmb locus kb Long isoform Short isoform Long isoform Jmj XX PHD F-box LRR Short isoform XX PHD F-box LRR Target Vector 3xFlag Left H Neo Right H TK LoxP LoxP Kdmb Locus
SUPPLEMENTRY INFORMTION DOI:.38/ncb Kdmb locus kb Long isoform Short isoform Long isoform Jmj XX PHD F-box LRR Short isoform XX PHD F-box LRR Target Vector 3xFlag Left H Neo Right H TK LoxP LoxP Kdmb Locus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.2548
 Supplementary Table 1: Genotypes of offspring and embryos from matings of Pmm2 WT/F118L mice with Pmm2 WT/R137H mice total events Pmm2 WT/WT Pmm2 WT/R137H Pmm2 WT/F118L Pmm2 R137H/F118L offspring 117 (100%)
Supplementary Table 1: Genotypes of offspring and embryos from matings of Pmm2 WT/F118L mice with Pmm2 WT/R137H mice total events Pmm2 WT/WT Pmm2 WT/R137H Pmm2 WT/F118L Pmm2 R137H/F118L offspring 117 (100%)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Integrin alpha 11 in regulation of myofibroblasts phenotype: Implication for fibrotic diseases
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Integrin alpha 11 in regulation of myofibroblasts phenotype: Implication for fibrotic diseases Ruchi Bansal 1, Shigeki Nakagawa 2, Saleh Yazdani 1, Joop van Baarlen 3, Anu Venkatesh
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Integrin alpha 11 in regulation of myofibroblasts phenotype: Implication for fibrotic diseases Ruchi Bansal 1, Shigeki Nakagawa 2, Saleh Yazdani 1, Joop van Baarlen 3, Anu Venkatesh
Figure S1. Schematic of myeloid lineage reporter mouse model used in this study.
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Schematic of myeloid lineage reporter mouse model used in this study. (A) The Lyzs-Cre mouse was crossed with Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(eyfp)cos/ J mice to label cells expressing
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Schematic of myeloid lineage reporter mouse model used in this study. (A) The Lyzs-Cre mouse was crossed with Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(eyfp)cos/ J mice to label cells expressing
Isolation, culture, and transfection of primary mammary epithelial organoids
 Supplementary Experimental Procedures Isolation, culture, and transfection of primary mammary epithelial organoids Primary mammary epithelial organoids were prepared from 8-week-old CD1 mice (Charles River)
Supplementary Experimental Procedures Isolation, culture, and transfection of primary mammary epithelial organoids Primary mammary epithelial organoids were prepared from 8-week-old CD1 mice (Charles River)
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Song et al. 10.1073/pnas.1218131110 SI Materials and Methods In Vivo Dislodgment Assays. In vivo dislodgement experiments were performed as previously described (1) using function
Supporting Information Song et al. 10.1073/pnas.1218131110 SI Materials and Methods In Vivo Dislodgment Assays. In vivo dislodgement experiments were performed as previously described (1) using function
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of the expression levels of E-cadherin
 Supplementary Information 1 Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of the expression levels of E-cadherin and ribosomal protein L19 (RPL19) mrna in cleft and bud epithelial cells of embryonic salivary
Supplementary Information 1 Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of the expression levels of E-cadherin and ribosomal protein L19 (RPL19) mrna in cleft and bud epithelial cells of embryonic salivary
immunofluorescence. Name of antibodies Manufacturer Catalog Number Rabbit anti-pdyn Rabbit anti-kor-1
 Supplemental Tables Table S1. List of primary antibodies used for immunohistochemistry, FACS, and immunofluorescence. Name of antibodies Manufacturer Catalog Number Rabbit anti-pdyn Bioss USA bs-13041r
Supplemental Tables Table S1. List of primary antibodies used for immunohistochemistry, FACS, and immunofluorescence. Name of antibodies Manufacturer Catalog Number Rabbit anti-pdyn Bioss USA bs-13041r
Supplementary Figure and Table Legends
 1 Supplementary Figure and Table Legends Figure S1: Whole-animal metabolic analysis. 12 week old WT and Dvl1 / were singly housed in CLAMS cages (Comprehensive Laboratory Animals Monitoring System) for
1 Supplementary Figure and Table Legends Figure S1: Whole-animal metabolic analysis. 12 week old WT and Dvl1 / were singly housed in CLAMS cages (Comprehensive Laboratory Animals Monitoring System) for
Supplementary Figure 1. ERK signaling is not activated at early hypertension. a, Western blot analysis for the level of phospho-erk (perk) and total
 Supplementary Figure 1. ERK signaling is not activated at early hypertension. a, Western blot analysis for the level of phospho-erk (perk) and total ERK in the aortic tissue from the saline- or AngII-infused
Supplementary Figure 1. ERK signaling is not activated at early hypertension. a, Western blot analysis for the level of phospho-erk (perk) and total ERK in the aortic tissue from the saline- or AngII-infused
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Taylor et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201403021/dc1 Figure S1. Representative images of Cav 1a -YFP mutants with and without LMB treatment.
Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Taylor et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201403021/dc1 Figure S1. Representative images of Cav 1a -YFP mutants with and without LMB treatment.
Supplementary Table, Figures and Videos
 Supplementary Table, Figures and Videos Table S1. Oligonucleotides used for different approaches. (A) RT-qPCR study. (B) qpcr study after ChIP assay. (C) Probes used for EMSA. Figure S1. Notch activation
Supplementary Table, Figures and Videos Table S1. Oligonucleotides used for different approaches. (A) RT-qPCR study. (B) qpcr study after ChIP assay. (C) Probes used for EMSA. Figure S1. Notch activation
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of migg1-yf mice. (A) Targeting strategy. Upper panel: schematic organization of the murine ɣ1 immunoglobulin
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of migg1-yf mice. (A) Targeting strategy. Upper panel: schematic organization of the murine ɣ1 immunoglobulin locus. The EcoRI restriction site between exons M1 and M2
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of migg1-yf mice. (A) Targeting strategy. Upper panel: schematic organization of the murine ɣ1 immunoglobulin locus. The EcoRI restriction site between exons M1 and M2
Summary MicroRNAs (mirnas) are genomically encoded small RNAs used by organisms to regulate the expression of proteins generated from messenger RNA
 Summary MicroRNAs (mirnas) are genomically encoded small RNAs used by organisms to regulate the expression of proteins generated from messenger RNA transcripts. The in vivo requirement of specific mirnas
Summary MicroRNAs (mirnas) are genomically encoded small RNAs used by organisms to regulate the expression of proteins generated from messenger RNA transcripts. The in vivo requirement of specific mirnas
Supplemental data. Zhao et al. (2009). The Wuschel-related homeobox gene WOX11 is required to activate shoot-borne crown root development in rice.
 Supplemental data. Zhao et al. (2009). The Wuschel-related homeobox gene WOX11 is required to activate shoot-borne crown root development in rice. A B Supplemental Figure 1. Expression of WOX11p-GUS WOX11-GFP
Supplemental data. Zhao et al. (2009). The Wuschel-related homeobox gene WOX11 is required to activate shoot-borne crown root development in rice. A B Supplemental Figure 1. Expression of WOX11p-GUS WOX11-GFP
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of hipscs derived from primary human fibroblasts. a,b. Morphology of hipscs. hipscs exhibit hesc-like
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of hipscs derived from primary human fibroblasts. a,b. Morphology of hipscs. hipscs exhibit hesc-like morphology in co-culture with mouse embryonic feeder fibroblasts
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of hipscs derived from primary human fibroblasts. a,b. Morphology of hipscs. hipscs exhibit hesc-like morphology in co-culture with mouse embryonic feeder fibroblasts
Supplemental Information. Role of phosphatase of regenerating liver 1 (PRL1) in spermatogenesis
 Supplemental Information Role of phosphatase of regenerating liver 1 (PRL1) in spermatogenesis Yunpeng Bai ;, Lujuan Zhang #, Hongming Zhou #, Yuanshu Dong #, Qi Zeng, Weinian Shou, and Zhong-Yin Zhang
Supplemental Information Role of phosphatase of regenerating liver 1 (PRL1) in spermatogenesis Yunpeng Bai ;, Lujuan Zhang #, Hongming Zhou #, Yuanshu Dong #, Qi Zeng, Weinian Shou, and Zhong-Yin Zhang
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
GENETICS EXAM 3 FALL a) is a technique that allows you to separate nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) by size.
 Student Name: All questions are worth 5 pts. each. GENETICS EXAM 3 FALL 2004 1. a) is a technique that allows you to separate nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) by size. b) Name one of the materials (of the two
Student Name: All questions are worth 5 pts. each. GENETICS EXAM 3 FALL 2004 1. a) is a technique that allows you to separate nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) by size. b) Name one of the materials (of the two
Supplementary Figure 1. Reconstitution of human-acquired lymphoid system in
 Supplementary Figure 1. Reconstitution of human-acquired lymphoid system in mouse NOD/SCID/Jak3 null mice were transplanted with human CD34 + hematopoietic stem cells. (Top) Four weeks after the transplantation
Supplementary Figure 1. Reconstitution of human-acquired lymphoid system in mouse NOD/SCID/Jak3 null mice were transplanted with human CD34 + hematopoietic stem cells. (Top) Four weeks after the transplantation
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. ZBTB20 expression in the developing DRG. ZBTB20 expression in the developing DRG was detected by immunohistochemistry using anti-zbtb20 antibody 9A10 on
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. ZBTB20 expression in the developing DRG. ZBTB20 expression in the developing DRG was detected by immunohistochemistry using anti-zbtb20 antibody 9A10 on
Ramp1 EPD0843_4_B11. EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping
 EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping Introduction The majority of animals produced from the EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD ES cell resource contain the Knockout-First-Reporter Tagged Insertion allele. As well as
EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping Introduction The majority of animals produced from the EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD ES cell resource contain the Knockout-First-Reporter Tagged Insertion allele. As well as
Usp14 EPD0582_2_G09. EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping
 EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping Introduction The majority of animals produced from the EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD ES cell resource contain the Knockout-First-Reporter Tagged Insertion allele. As well as
EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD Knockout-First Genotyping Introduction The majority of animals produced from the EUCOMM/KOMP-CSD ES cell resource contain the Knockout-First-Reporter Tagged Insertion allele. As well as
0.9 5 H M L E R -C tr l in T w is t1 C M
 a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. 2.5 C elltiter-g lo A ssay 1.1 5 M T S a s s a y Lum inescence (A.U.) 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 n s H M L E R -C tr l in C tr l C M H M L E R -C tr l in S n a il1 C M A bsorbance (@ 490nm
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. 2.5 C elltiter-g lo A ssay 1.1 5 M T S a s s a y Lum inescence (A.U.) 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 n s H M L E R -C tr l in C tr l C M H M L E R -C tr l in S n a il1 C M A bsorbance (@ 490nm
Regulation of axonal and dendritic growth by the extracellular calcium-sensing
 Regulation of axonal and dendritic growth by the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR). Thomas N. Vizard, Gerard W. O Keeffe, Humberto Gutierrez, Claudine H. Kos, Daniela Riccardi, Alun M. Davies
Regulation of axonal and dendritic growth by the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR). Thomas N. Vizard, Gerard W. O Keeffe, Humberto Gutierrez, Claudine H. Kos, Daniela Riccardi, Alun M. Davies
somatic transition to was evident into airways in the
 Supplementary Fig. 1. A. Activation of an oncogenic K-Ras allele by recombination in somatic cells leads to spontaneous lung cancer in LA1 mice (ref. 20). In this mouse model, subpleural precancerous adenomas
Supplementary Fig. 1. A. Activation of an oncogenic K-Ras allele by recombination in somatic cells leads to spontaneous lung cancer in LA1 mice (ref. 20). In this mouse model, subpleural precancerous adenomas
Table S1. Oligonucleotide primer sequences
 Table S1. Oligonucleotide primer sequences Primer Name DNA Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Description CD19c CD19d Cre7 Sfpi1lox1 Sfpi1lox2 Sfpi1lox3 5 -AACCAGTCAACACCCTTCC-3 5 -CCAGACTAGATACAGACCAG-3 5 -TCAGCTACACCAGAGACGG-3
Table S1. Oligonucleotide primer sequences Primer Name DNA Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Description CD19c CD19d Cre7 Sfpi1lox1 Sfpi1lox2 Sfpi1lox3 5 -AACCAGTCAACACCCTTCC-3 5 -CCAGACTAGATACAGACCAG-3 5 -TCAGCTACACCAGAGACGG-3
Lacombe et al. Supplemental material ms INS-BR-TR-2
 Supplemental Figure 1: Rabbit α-gla antibodies specifically recognize carboxylated VKD proteins. (A) HEK293 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding GGCX-FLAG, PT- FLAG or tagged proline rich Gla
Supplemental Figure 1: Rabbit α-gla antibodies specifically recognize carboxylated VKD proteins. (A) HEK293 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding GGCX-FLAG, PT- FLAG or tagged proline rich Gla
Supplemental Data. Sethi et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. MYC2 Binds to the E-box but not the E1-box of the MPK6 Promoter. (A) E1-box and E-box (wild type) containing MPK6 promoter fragment. The region shown in red denotes
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. MYC2 Binds to the E-box but not the E1-box of the MPK6 Promoter. (A) E1-box and E-box (wild type) containing MPK6 promoter fragment. The region shown in red denotes
Generation of App knock-in mice reveals deletion mutations protective against Alzheimer s. disease-like pathology. Nagata et al.
 Generation of App knock-in mice reveals deletion mutations protective against Alzheimer s disease-like pathology Nagata et al. Supplementary Fig 1. Previous App knock-in model did not show Aβ accumulation
Generation of App knock-in mice reveals deletion mutations protective against Alzheimer s disease-like pathology Nagata et al. Supplementary Fig 1. Previous App knock-in model did not show Aβ accumulation
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Ricke et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201205115/dc1 Figure S1. Kinetochore localization of mitotic regulators in wild-type
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Ricke et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201205115/dc1 Figure S1. Kinetochore localization of mitotic regulators in wild-type
SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector
 SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector Richard J. Wall 1,#, Magali Roques 1,+, Nicholas J. Katris
SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector Richard J. Wall 1,#, Magali Roques 1,+, Nicholas J. Katris
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic and results of screening the combinatorial antibody library for Sox2 replacement activity. A single batch of MEFs were plated and transduced with doxycycline inducible
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic and results of screening the combinatorial antibody library for Sox2 replacement activity. A single batch of MEFs were plated and transduced with doxycycline inducible
PE11, a PE/PPE family protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is involved in cell wall remodeling and virulence
 PE11, a PE/PPE family protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is involved in cell wall remodeling and virulence Parul Singh 1,2, Rameshwaram Nagender Rao 1, Jala Ram Chandra Reddy 3, R.B.N. Prasad 3, Sandeep
PE11, a PE/PPE family protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is involved in cell wall remodeling and virulence Parul Singh 1,2, Rameshwaram Nagender Rao 1, Jala Ram Chandra Reddy 3, R.B.N. Prasad 3, Sandeep
Supplementary Table 1. Sequences for BTG2 and BRCA1 sirnas.
 Supplementary Table 1. Sequences for BTG2 and BRCA1 sirnas. Target Gene Non-target / Control BTG2 BRCA1 NFE2L2 Target Sequence ON-TARGET plus Non-targeting sirna # 1 (Cat# D-001810-01-05) sirna1: GAACCGACAUGCUCCCGGA
Supplementary Table 1. Sequences for BTG2 and BRCA1 sirnas. Target Gene Non-target / Control BTG2 BRCA1 NFE2L2 Target Sequence ON-TARGET plus Non-targeting sirna # 1 (Cat# D-001810-01-05) sirna1: GAACCGACAUGCUCCCGGA
Supporting Online Material. 3. Analysis of in vivo TLR4-mediated response in TRIF-deficient mice
 Supporting Online Material 1. Materials and Methods 2. Generation of TRIF-deficient mice 3. Analysis of in vivo TLR4-mediated response in TRIF-deficient mice 4. Measurement of LPS-induced IRAK-1 kinase
Supporting Online Material 1. Materials and Methods 2. Generation of TRIF-deficient mice 3. Analysis of in vivo TLR4-mediated response in TRIF-deficient mice 4. Measurement of LPS-induced IRAK-1 kinase
indicated numbers of pups at day of life (DOL) 10, or embryonic day (ED) B. Male mice of
 SUPPLEMENTRY FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1. USP44 loss leads to chromosome missegregation.. Genotypes obtained from the indicated numbers of pups at day of life (DOL) 10, or embryonic day (ED) 13.5.. Male mice
SUPPLEMENTRY FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1. USP44 loss leads to chromosome missegregation.. Genotypes obtained from the indicated numbers of pups at day of life (DOL) 10, or embryonic day (ED) 13.5.. Male mice
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Ex2 promotor region Cre IRES cherry pa Ex4 Ex5 Ex1 untranslated Ex3 Ex5 untranslated EYFP pa Rosa26 STOP loxp loxp Cre recombinase EYFP pa Rosa26 loxp 1 kb Interleukin-9 fate reporter
Supplementary Figure 1 Ex2 promotor region Cre IRES cherry pa Ex4 Ex5 Ex1 untranslated Ex3 Ex5 untranslated EYFP pa Rosa26 STOP loxp loxp Cre recombinase EYFP pa Rosa26 loxp 1 kb Interleukin-9 fate reporter
Experimental genetics - 2 Partha Roy
 Partha Roy Experimental genetics - 2 Making genetically altered animal 1) Gene knock-out k from: a) the entire animal b) selected cell-type/ tissue c) selected cell-type/tissue at certain time 2) Transgenic
Partha Roy Experimental genetics - 2 Making genetically altered animal 1) Gene knock-out k from: a) the entire animal b) selected cell-type/ tissue c) selected cell-type/tissue at certain time 2) Transgenic
Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy
 Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy HL-6 and cells were cultured and cytospun onto glass slides. The cells were double immunofluorescence stained for Mt NPM1 and fibrillarin (nucleolar marker). Briefly,
Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy HL-6 and cells were cultured and cytospun onto glass slides. The cells were double immunofluorescence stained for Mt NPM1 and fibrillarin (nucleolar marker). Briefly,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assays of hepatocyte-like cells induced from H1 hescs (a) P450 and AAT staining, PAS staining, LDL uptake assay, and ICG uptake and release assay
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assays of hepatocyte-like cells induced from H1 hescs (a) P450 and AAT staining, PAS staining, LDL uptake assay, and ICG uptake and release assay
Hyper sensitive protein detection by Tandem-HTRF reveals Cyclin D1
 Hyper sensitive protein detection by Tandem-HTRF reveals Cyclin D1 dynamics in adult mouse Alexandre Zampieri, Julien Champagne, Baptiste Auzemery, Ivanna Fuentes, Benjamin Maurel and Frédéric Bienvenu
Hyper sensitive protein detection by Tandem-HTRF reveals Cyclin D1 dynamics in adult mouse Alexandre Zampieri, Julien Champagne, Baptiste Auzemery, Ivanna Fuentes, Benjamin Maurel and Frédéric Bienvenu
Supplementary information Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase
 Supplementary information Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase 2 by nicotine instigates formation of abdominal aortic aneurysms in mice in vivo Shuangxi Wang 1,2,5, Cheng Zhang 1,2,5, Miao Zhang
Supplementary information Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase 2 by nicotine instigates formation of abdominal aortic aneurysms in mice in vivo Shuangxi Wang 1,2,5, Cheng Zhang 1,2,5, Miao Zhang
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 Supplemental figure 1. Generation of gene targeted mice expressing an anti-id BCR. (A,B) Generation of the VDJ aid H KI mouse. (A) Targeting Construct. Top: Targeting construct for
Supplemental Figure 1 Supplemental figure 1. Generation of gene targeted mice expressing an anti-id BCR. (A,B) Generation of the VDJ aid H KI mouse. (A) Targeting Construct. Top: Targeting construct for
MLN8237 induces proliferation arrest, expression of differentiation markers and
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1 827 induces proliferation arrest, expression of differentiation markers and polyploidization of a human erythroleukemia cell line with the activating
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1 827 induces proliferation arrest, expression of differentiation markers and polyploidization of a human erythroleukemia cell line with the activating
We designed the targeting vector in such a way that the first exon was flanked by two LoxP sites and
 Mice We designed the targeting vector in such a way that the first exon was flanked by two LoxP sites and an Frt flanked neo cassette (Fig. S1A). Targeted BA1 (C57BL/6 129/SvEv) hybrid embryonic stem cells
Mice We designed the targeting vector in such a way that the first exon was flanked by two LoxP sites and an Frt flanked neo cassette (Fig. S1A). Targeted BA1 (C57BL/6 129/SvEv) hybrid embryonic stem cells
Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of STOML3-modulating molecules on other stomatin-domain proteins
 Supplementary Figure 1 Effects of STOML3-modulating molecules on other stomatin-domain proteins (a) BiFC signal development observed when cells were transfected with stomatin VC/-VN, STOML1-VC/- VN, STOML2-VC/-VN,
Supplementary Figure 1 Effects of STOML3-modulating molecules on other stomatin-domain proteins (a) BiFC signal development observed when cells were transfected with stomatin VC/-VN, STOML1-VC/- VN, STOML2-VC/-VN,
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 UTX/KDM6A demethylase activity is required for satellite cell-mediated muscle regeneration Hervé Faralli 1,2, Chaochen Wang 3, Kiran Nakka 1,2, Soji Sebastian 1,, Aissa Benyoucef 1,2, Lenan Zhuang 3, Alphonse
UTX/KDM6A demethylase activity is required for satellite cell-mediated muscle regeneration Hervé Faralli 1,2, Chaochen Wang 3, Kiran Nakka 1,2, Soji Sebastian 1,, Aissa Benyoucef 1,2, Lenan Zhuang 3, Alphonse
