Comparative Genomic Hybridization
|
|
|
- Edwin Stanley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Comparative Genomic Hybridization Srikesh G. Arunajadai Division of Biostatistics University of California Berkeley PH 296 Presentation Fall 2002 December 9 th 2002
2 OUTLINE CGH Introduction Methodology, Analysis and Interpretation Application 1 - BT474 Application 2 - Bladder Tumors
3 Comparative Genomic Hybridization Comparative genomic hybridization allows a comprehensive analysis of multiple DNA gains and losses in entire genomes within a single experiment Genomic DNA from the tissue to be investigated, and normal reference DNA are differentially labeled and simultaneously hybridized in situ to normal metaphase chromosomes By comparing the fluorescence intensities of test and control DNA, changes in signal intensities caused by imbalances of the test DNA can be identified Previous methods are highly focused, they target one specific gene or chromosome region at a time and leave the majority of the genome unexamined.
4 Basic Assumption Ratio of the binding intensities of test and control DNA is proportional to the ratio of the concentrations of sequences in the two samples.
5 A Very Important Application Measurement of alterations in DNA copy number which are involved in developmental abnormalities and cancer Down Syndrome Extra copy of DNA sequences from a portion of chromosome 21 Cancer Changes in copy number are associated with changes in the gene expression that occur in tumor development. Loss of DNA sequences contributes to the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes,while amplifications may activate oncogenes.
6 CGH The regions of DNA that are altered in copy number are typically much larger than the important genes that are being affected, so there will be contiguous regions of the genome with constant copy number, with an abrupt step to different level at the edge of an aberration. E.g..-If a portion of a chromosome is lost in the cell population we would expect a CH of this genomic DNA with Normal Genomic DNA to produce ratios that were constant for all array elements not in the deletion and half the value for elements mapping in the deletion.
7 Fundamental Measurement Limits Ratio measurements are accurate Insensitive to production Variability Compensate for the many physical-chemical aspects of the measurement process that may vary among hybridizations. Reassociation of double stranded labeled molecules in hybridization solution Non-Specific Binding of the labeled molecules to array surfaces and cover slip Diffusion limits on the ability of the labeled molecules to find their complimentary targets The proportion of binding sites in a spot that are hybridized. IF THE LABELS DO NOT DIFFERENTIALLY AFFECT ANY OF THESE PROCESSES THEN IN PRINICIPLE THE RATIOS ARE ACCURATELY PRESERVED
8 Factors Affecting Ratio Measurements Non-Specific Binding of labeled molecules to array spots Differential non-specific binding to array spots and substrate surface which make determination of proper amount of Background Correction problematic Signals from repetitive sequences Problems with labeling the DNA Defects in the detection system
9 Normalization Perform a series of Normal Vs.Normal hybridizations to define the set of clones having consistently good hybridization quality and constant intensity ratios.
10 Array Production Signal Intensity that is generated on an array spot is a function of Density of hybridizable DNA that is bound to the Spot Ability of the labeled molecules to get to the spots that contain the complimentary sequences Conditions of hybridization environment Array used is made from ligation-mediated PCR products BAC clones.
11 Hybridization Non-specific binding to the substrate is blocked by a short pre-hybridization with unlabeled salmon or herring DNA in hybridization buffer. A slow rocking motion of 1-2 cycles per minute is provided to assist diffusion Slides washed after hybridization and typically mounted in glycerol containing the DNA stain DAPI Imaged in CCD Imaging System
12 Analysis and Interpretation Ratio of the total fluorescence intensities of a spot is used as a measure of elative abundances of the nucleic acid sequences in the specimen. Presence of copy number changes in the specimen can be detected even without mapping the data according to position in the Genome.
13 Scatter Plot Test Intensity Single Copy Deletion Reference Intensity
14 DNA Copy Number Profiles Averaging the ratios of the triplicate spots for each clone Normalizing them to the median of the log 2 Ratios of the triplicate averages Plotting them according to their positions in the Genome Thus single copy changes, which ideally would result in a ratio of 0.5 for a deletion and 1.5 for a gain of a single chromosome, can be detected with very high precision
15 Ratios Depart from Ideal Value Imperfect background corrections Non-specific binding of labeled molecules to the array spots Repetitive sequence content of the genome Suppress the signal from the repetitive sequences by the inclusion of large amounts of unlabeled repetitive sequences in the hybridization. These reassociate with the labeled repetitive sequences and thus reduce their ability to contribute to the signal.
16 Relationship of measured ratio of DNA Within one hybridization, the relationship of ratio and copy number is basically linear, except that the slope is slightly lower than ideal. All autosomal clones behave with about the same slope because the ratio variation among clones at the same copy number is the same, independent of copy number to copy number
17 Ligation Mediated PCR Preparation and spotting of BAC DNA is problematic BACs are single copy vectors The yield of DNA from BAC cultures is low compared to that from plasmid-bearing cultures Spotting high molecular weight DNA at sufficient concentration to obtain good ratio of signal to noise in the hybridization may be difficult. Previous methods resulted in highly variable ratios,so that detecting single copy changes required averaging over several adjacent clones. Ligation Mediated PCR provide reliable data from single clones.
18 Application 1 (Pollack et.al.) Genome-wide analysis of DNA copy-number changes using cdna microarrays Published array CGH methods have relied on large genomic clone (for example BAC) array targets and have covered only a small fraction of the human genome. cdnas representing over30,000 radiation-hybrid (RH) mapped human genes provide an alternative and readily available genomic resource for mapping DNA copy-number changes. Analysis of DNA copy-number variation using cdna microarrays would require a sensitivity of detection an order of magnitude greater than has been routinely reported
19 Feasibility of cdna based CGH analyzing genomic DNAs from tumour cell lines with known gene amplifications or deletions. BT474 is a human breast cancer cell line in which ERBB2 is amplified. Genomic DNA BT474 Cy5 Normal Female genomic DNA Cy3 The average red/green fluorescence ratio of 4 independent cdna elements representing ERBB2 on the array was 8.5 closely approximating (but slightly underestimating) the 10 15:1 ratio determined by Southern-blot analysis
20 Comparing two Samples of Normal Female Genomic DNA the red/green fluorescence ratios measured for both autosomal and X- chromosomal genes were tightly distributed around a mean value of 1. In contrast, when we compared genomic DNA
21 Comparing with 45,XO (Turner Syndrome) from a 45, XO (Turner syndrome) cell line (red) with normal female (46, XX) genomic DNA (green), the distribution of fluorescence ratios for X- chromosomal genes was shifted leftward (mean 0.72) reflecting the singlecopy loss of X- chromosomal genes in the XO sample. Expected Value of mean = 1
22 Comparing with 47,XXX; 48,XXXX; 49,XXXXX distributions of fluorescence ratios for X- chromosomal genes shifted rightward (means 1.31, 1.58 and 1.84, respectively reflecting X-chromosomal DNA copy-number gain. Expected Value of mean =1
23 Relation between Fluorescence Ratios and DNA Copy number The mean fluorescence ratios for X- chromosomal genes obtained in the different experiments fitted tightly to a line with a regression correlation of 0.99, demonstrating that fluorescence ratios were linearly proportional to DNA copy number in this range of low-level gene amplification or singlecopy deletion (in the case of XO versus XX).
24 Plot of Fluorescence ratios for each RH-mapped element on the array according to their RH map location on the genome
25 Enlarged View of Chromosome 17 and reproducibility
26 Application 2 ( Veltman et.al) Array based CGH for high resolution mapping of copy number changes in different stages of bladder carcinogenesis in 41 primary human tumors. Two arrays were used in this study. The first (Array1) consisted of 1777 clones covering the human genome at roughly a 1.5 Mb resolution. The second array (Array2) consisted of 380 clones specifically selected to contain important tumor suppressor and oncogene loci
27 Method Each tumor sample was hybridized to both arrays Sixteen bit fluorescence intensity images were obtained using a CCD camera coupled to a 1X magnification optical system. DNA spots were automatically segmented, local background was subtracted and the total intensity and the intensity ratio of the two dyes for each spot were calculated. Spots composed of less than 9 pixels, showing bad correlations of the two fluorescent dyes, or showing auto fluorescent particles over the target were discarded.
28 Data Analysis A series of 8 normal vs. normal hybridizations was used to define the set of clones having consistently good hybridization quality For each analysis, clones were excluded for which none or only one spot remained after the Genepix analysis. For all analyses, the 5% of clones with the most extreme average test over reference ratio deviations from 1.0, and the 1% of clones with the largest standard deviation in this set of normal controls was excluded. This procedure resulted in the exclusion of 174 clones. In addition, all X-chromosome clones were excluded from data analysis The final set, on which all analyses were performed, contained 1747 clones
29 Data Analysis Log2 intensity ratios obtained for each array for each case were individually centered by subtracting the median of log2 intensity ratios for that case over all clones that met the quality control parameters described above. Data on the two arrays was then merged into one dataset using the genomic mapping information from all clones. There were 19 clones in common on the two arrays. A matched-pair t-test on each of the 19 revealed no clones to show significantly different ratios at the 5% level.
30 Statistical Analysis Whether there were associations between copy number alterations and tumor stage or grade; Whether gene pairs exhibited significant correlations; and Whether gene pairs exhibited complementary or concordant behavior based on a categorical analysis.
31 Association Analysis The association analyses consisted of statistical correlation with permutationbased assessment of significance, visualization by hierarchical clustering, and automatic pattern classification with cross-validation to assess predictive power.
32 Quality of CGH Arrays thresholds of 0.2 and 0.2 (log2ratio) for calculating the frequencies of genomic copy number gains and losses, respectively, in the bladder tumor cases. Less than 10 out of the 1745 clones included in the final dataset crossed these thresholds for this control
33 Genomic Profiles From Bladder Cancers
34 Genome Wide Frequency of Copy Number Alterations
35 Gene Correlation Matrix 24 clones containing known bladder cancer oncogenes 22 non-overlapping clones that were most frequently aberrant The values of clones spanning the same gene were averaged. Permutation analysis was performed to establish the appropriate significance threshold for the correlation coefficient, significant correlations are highlighted by yellow squares. The color scale reaches full saturation in green for significant positive correlations (copy number gain in one clone combined with copy number gain in the other clone or copy number loss in one clone combined with copy number loss in the other clone) and full saturation in red for significant negative correlations (copy number gain in one clone combined with copy number loss in the other clone).
36 Reference Genome Wide Analysis of DNA Copy Number changes using cdna Microarrays Pollack et.al.,nature Genetics, Sept 1999 Assembly of Microarrays for Genome wide measurement of DNA copy number.snijders et.al. Technical Approaches for Efficient, High Precision Nucleic Acid Analysis using DNA,Microarrays Array-Based comparative genomic Hybridization for genome-wide screening of DNA copy number in bladder Tumors,Veltman et.al
37 Thanks Dr. Sandrine Dudoit, UCB Dr.Jane Fridlyand, UCSF
Quality Measures for CytoChip Microarrays
 Quality Measures for CytoChip Microarrays How to evaluate CytoChip Oligo data quality in BlueFuse Multi software. Data quality is one of the most important aspects of any microarray experiment. This technical
Quality Measures for CytoChip Microarrays How to evaluate CytoChip Oligo data quality in BlueFuse Multi software. Data quality is one of the most important aspects of any microarray experiment. This technical
3.1.4 DNA Microarray Technology
 3.1.4 DNA Microarray Technology Scientists have discovered that one of the differences between healthy and cancer is which genes are turned on in each. Scientists can compare the gene expression patterns
3.1.4 DNA Microarray Technology Scientists have discovered that one of the differences between healthy and cancer is which genes are turned on in each. Scientists can compare the gene expression patterns
Introduction to Microarray Analysis
 Introduction to Microarray Analysis Methods Course: Gene Expression Data Analysis -Day One Rainer Spang Microarrays Highly parallel measurement devices for gene expression levels 1. How does the microarray
Introduction to Microarray Analysis Methods Course: Gene Expression Data Analysis -Day One Rainer Spang Microarrays Highly parallel measurement devices for gene expression levels 1. How does the microarray
Methods of Biomaterials Testing Lesson 3-5. Biochemical Methods - Molecular Biology -
 Methods of Biomaterials Testing Lesson 3-5 Biochemical Methods - Molecular Biology - Chromosomes in the Cell Nucleus DNA in the Chromosome Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) DNA has double-helix structure The
Methods of Biomaterials Testing Lesson 3-5 Biochemical Methods - Molecular Biology - Chromosomes in the Cell Nucleus DNA in the Chromosome Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) DNA has double-helix structure The
Gene Expression Technology
 Gene Expression Technology Bing Zhang Department of Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University bing.zhang@vanderbilt.edu Gene expression Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene
Gene Expression Technology Bing Zhang Department of Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University bing.zhang@vanderbilt.edu Gene expression Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene
Technical Review. Real time PCR
 Technical Review Real time PCR Normal PCR: Analyze with agarose gel Normal PCR vs Real time PCR Real-time PCR, also known as quantitative PCR (qpcr) or kinetic PCR Key feature: Used to amplify and simultaneously
Technical Review Real time PCR Normal PCR: Analyze with agarose gel Normal PCR vs Real time PCR Real-time PCR, also known as quantitative PCR (qpcr) or kinetic PCR Key feature: Used to amplify and simultaneously
Fluorescent in-situ Hybridization
 Fluorescent in-situ Hybridization Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 Definition In situ hybridization is the method of localizing/ detecting specific nucleotide sequences in morphologically preserved
Fluorescent in-situ Hybridization Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 Definition In situ hybridization is the method of localizing/ detecting specific nucleotide sequences in morphologically preserved
Lecture #1. Introduction to microarray technology
 Lecture #1 Introduction to microarray technology Outline General purpose Microarray assay concept Basic microarray experimental process cdna/two channel arrays Oligonucleotide arrays Exon arrays Comparing
Lecture #1 Introduction to microarray technology Outline General purpose Microarray assay concept Basic microarray experimental process cdna/two channel arrays Oligonucleotide arrays Exon arrays Comparing
Please purchase PDFcamp Printer on to remove this watermark. DNA microarray
 DNA microarray Example of an approximately 40,000 probe spotted oligo microarray with enlarged inset to show detail. A DNA microarray is a multiplex technology used in molecular biology. It consists of
DNA microarray Example of an approximately 40,000 probe spotted oligo microarray with enlarged inset to show detail. A DNA microarray is a multiplex technology used in molecular biology. It consists of
Roche Molecular Biochemicals Technical Note No. LC 10/2000
 Roche Molecular Biochemicals Technical Note No. LC 10/2000 LightCycler Overview of LightCycler Quantification Methods 1. General Introduction Introduction Content Definitions This Technical Note will introduce
Roche Molecular Biochemicals Technical Note No. LC 10/2000 LightCycler Overview of LightCycler Quantification Methods 1. General Introduction Introduction Content Definitions This Technical Note will introduce
DNA Arrays Affymetrix GeneChip System
 DNA Arrays Affymetrix GeneChip System chip scanner Affymetrix Inc. hybridization Affymetrix Inc. data analysis Affymetrix Inc. mrna 5' 3' TGTGATGGTGGGAATTGGGTCAGAAGGACTGTGGGCGCTGCC... GGAATTGGGTCAGAAGGACTGTGGC
DNA Arrays Affymetrix GeneChip System chip scanner Affymetrix Inc. hybridization Affymetrix Inc. data analysis Affymetrix Inc. mrna 5' 3' TGTGATGGTGGGAATTGGGTCAGAAGGACTGTGGGCGCTGCC... GGAATTGGGTCAGAAGGACTGTGGC
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids
 Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Recent technology allow production of microarrays composed of 70-mers (essentially a hybrid of the two techniques)
 Microarrays and Transcript Profiling Gene expression patterns are traditionally studied using Northern blots (DNA-RNA hybridization assays). This approach involves separation of total or polya + RNA on
Microarrays and Transcript Profiling Gene expression patterns are traditionally studied using Northern blots (DNA-RNA hybridization assays). This approach involves separation of total or polya + RNA on
Quantitative Real time PCR. Only for teaching purposes - not for reproduction or sale
 Quantitative Real time PCR PCR reaction conventional versus real time PCR real time PCR principles threshold cycle C T efficiency relative quantification reference genes primers detection chemistry GLP
Quantitative Real time PCR PCR reaction conventional versus real time PCR real time PCR principles threshold cycle C T efficiency relative quantification reference genes primers detection chemistry GLP
Class Information. Introduction to Genome Biology and Microarray Technology. Biostatistics Rafael A. Irizarry. Lecture 1
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons ttribution-noncommercial-sharelike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons ttribution-noncommercial-sharelike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
High-Resolution Oligonucleotide- Based acgh Analysis of Single Cells in Under 24 Hours
 High-Resolution Oligonucleotide- Based acgh Analysis of Single Cells in Under 24 Hours Application Note Authors Paula Costa and Anniek De Witte Agilent Technologies, Inc. Santa Clara, CA USA Abstract As
High-Resolution Oligonucleotide- Based acgh Analysis of Single Cells in Under 24 Hours Application Note Authors Paula Costa and Anniek De Witte Agilent Technologies, Inc. Santa Clara, CA USA Abstract As
Introduction to Bioinformatics. Fabian Hoti 6.10.
 Introduction to Bioinformatics Fabian Hoti 6.10. Analysis of Microarray Data Introduction Different types of microarrays Experiment Design Data Normalization Feature selection/extraction Clustering Introduction
Introduction to Bioinformatics Fabian Hoti 6.10. Analysis of Microarray Data Introduction Different types of microarrays Experiment Design Data Normalization Feature selection/extraction Clustering Introduction
4.1. Genetics as a Tool in Anthropology
 4.1. Genetics as a Tool in Anthropology Each biological system and every human being is defined by its genetic material. The genetic material is stored in the cells of the body, mainly in the nucleus of
4.1. Genetics as a Tool in Anthropology Each biological system and every human being is defined by its genetic material. The genetic material is stored in the cells of the body, mainly in the nucleus of
Background Correction and Normalization. Lecture 3 Computational and Statistical Aspects of Microarray Analysis June 21, 2005 Bressanone, Italy
 Background Correction and Normalization Lecture 3 Computational and Statistical Aspects of Microarray Analysis June 21, 2005 Bressanone, Italy Feature Level Data Outline Affymetrix GeneChip arrays Two
Background Correction and Normalization Lecture 3 Computational and Statistical Aspects of Microarray Analysis June 21, 2005 Bressanone, Italy Feature Level Data Outline Affymetrix GeneChip arrays Two
PV92 PCR Bio Informatics
 Purpose of PCR Chromosome 16 PV92 PV92 PCR Bio Informatics Alu insert, PV92 locus, chromosome 16 Introduce the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique Apply PCR to population genetics Directly measure
Purpose of PCR Chromosome 16 PV92 PV92 PCR Bio Informatics Alu insert, PV92 locus, chromosome 16 Introduce the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique Apply PCR to population genetics Directly measure
Chapter 20: Biotechnology
 Name Period The AP Biology exam has reached into this chapter for essay questions on a regular basis over the past 15 years. Student responses show that biotechnology is a difficult topic. This chapter
Name Period The AP Biology exam has reached into this chapter for essay questions on a regular basis over the past 15 years. Student responses show that biotechnology is a difficult topic. This chapter
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 3. Questions & Answers
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 3 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 3.1 Which of the following statements, if any, is false? a) Amplifying DNA means making many identical
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 3 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 3.1 Which of the following statements, if any, is false? a) Amplifying DNA means making many identical
Introduction to BioMEMS & Medical Microdevices DNA Microarrays and Lab-on-a-Chip Methods
 Introduction to BioMEMS & Medical Microdevices DNA Microarrays and Lab-on-a-Chip Methods Companion lecture to the textbook: Fundamentals of BioMEMS and Medical Microdevices, by Prof., http://saliterman.umn.edu/
Introduction to BioMEMS & Medical Microdevices DNA Microarrays and Lab-on-a-Chip Methods Companion lecture to the textbook: Fundamentals of BioMEMS and Medical Microdevices, by Prof., http://saliterman.umn.edu/
BENG 183 Trey Ideker. Genome Assembly and Physical Mapping
 BENG 183 Trey Ideker Genome Assembly and Physical Mapping Reasons for sequencing Complete genome sequencing!!! Resequencing (Confirmatory) E.g., short regions containing single nucleotide polymorphisms
BENG 183 Trey Ideker Genome Assembly and Physical Mapping Reasons for sequencing Complete genome sequencing!!! Resequencing (Confirmatory) E.g., short regions containing single nucleotide polymorphisms
Genetics Lecture 21 Recombinant DNA
 Genetics Lecture 21 Recombinant DNA Recombinant DNA In 1971, a paper published by Kathleen Danna and Daniel Nathans marked the beginning of the recombinant DNA era. The paper described the isolation of
Genetics Lecture 21 Recombinant DNA Recombinant DNA In 1971, a paper published by Kathleen Danna and Daniel Nathans marked the beginning of the recombinant DNA era. The paper described the isolation of
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
Quantitative Real Time PCR USING SYBR GREEN
 Quantitative Real Time PCR USING SYBR GREEN SYBR Green SYBR Green is a cyanine dye that binds to double stranded DNA. When it is bound to D.S. DNA it has a much greater fluorescence than when bound to
Quantitative Real Time PCR USING SYBR GREEN SYBR Green SYBR Green is a cyanine dye that binds to double stranded DNA. When it is bound to D.S. DNA it has a much greater fluorescence than when bound to
SIMS2003. Instructors:Rus Yukhananov, Alex Loguinov BWH, Harvard Medical School. Introduction to Microarray Technology.
 SIMS2003 Instructors:Rus Yukhananov, Alex Loguinov BWH, Harvard Medical School Introduction to Microarray Technology. Lecture 1 I. EXPERIMENTAL DETAILS II. ARRAY CONSTRUCTION III. IMAGE ANALYSIS Lecture
SIMS2003 Instructors:Rus Yukhananov, Alex Loguinov BWH, Harvard Medical School Introduction to Microarray Technology. Lecture 1 I. EXPERIMENTAL DETAILS II. ARRAY CONSTRUCTION III. IMAGE ANALYSIS Lecture
EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics
 EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics Lecture 14: Microarray Some slides were adapted from Dr. Luke Huan (University of Kansas), Dr. Shaojie Zhang (University of Central Florida), and Dr. Dong Xu and
EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics Lecture 14: Microarray Some slides were adapted from Dr. Luke Huan (University of Kansas), Dr. Shaojie Zhang (University of Central Florida), and Dr. Dong Xu and
DNA Microarrays and Computational Analysis of DNA Microarray. Data in Cancer Research
 DNA Microarrays and Computational Analysis of DNA Microarray Data in Cancer Research Mario Medvedovic, Jonathan Wiest Abstract 1. Introduction 2. Applications of microarrays 3. Analysis of gene expression
DNA Microarrays and Computational Analysis of DNA Microarray Data in Cancer Research Mario Medvedovic, Jonathan Wiest Abstract 1. Introduction 2. Applications of microarrays 3. Analysis of gene expression
IQFISH on Dako Omnis. Panel for Lung Cancer. Dako FAST RESULTS. ALK, ROS1, RET and MET IQFISH. Dako Omnis. Agilent Pathology Solutions
 PRODUCT INFORMATION Dako Omnis ALK, ROS1, RET and MET IQFISH Dako Agilent Pathology Solutions IQFISH on Dako Omnis Panel for Lung Cancer FAST RESULTS Fast, high-quality FISH Integrated into your IHC workflow
PRODUCT INFORMATION Dako Omnis ALK, ROS1, RET and MET IQFISH Dako Agilent Pathology Solutions IQFISH on Dako Omnis Panel for Lung Cancer FAST RESULTS Fast, high-quality FISH Integrated into your IHC workflow
Microarrays: since we use probes we obviously must know the sequences we are looking at!
 These background are needed: 1. - Basic Molecular Biology & Genetics DNA replication Transcription Post-transcriptional RNA processing Translation Post-translational protein modification Gene expression
These background are needed: 1. - Basic Molecular Biology & Genetics DNA replication Transcription Post-transcriptional RNA processing Translation Post-translational protein modification Gene expression
An Introduction to printing spotted microarrays
 http://www.flychip.org.uk/printingintroduction.php An Introduction to printing spotted microarrays Overview Microarrays are typically produced by transferring gene or transcript specific PCR amplified
http://www.flychip.org.uk/printingintroduction.php An Introduction to printing spotted microarrays Overview Microarrays are typically produced by transferring gene or transcript specific PCR amplified
DNA Microarray Data Oligonucleotide Arrays
 DNA Microarray Data Oligonucleotide Arrays Sandrine Dudoit, Robert Gentleman, Rafael Irizarry, and Yee Hwa Yang Bioconductor Short Course 2003 Copyright 2002, all rights reserved Biological question Experimental
DNA Microarray Data Oligonucleotide Arrays Sandrine Dudoit, Robert Gentleman, Rafael Irizarry, and Yee Hwa Yang Bioconductor Short Course 2003 Copyright 2002, all rights reserved Biological question Experimental
2. Outline the levels of DNA packing in the eukaryotic nucleus below next to the diagram provided.
 AP Biology Reading Packet 6- Molecular Genetics Part 2 Name Chapter 19: Eukaryotic Genomes 1. Define the following terms: a. Euchromatin b. Heterochromatin c. Nucleosome 2. Outline the levels of DNA packing
AP Biology Reading Packet 6- Molecular Genetics Part 2 Name Chapter 19: Eukaryotic Genomes 1. Define the following terms: a. Euchromatin b. Heterochromatin c. Nucleosome 2. Outline the levels of DNA packing
LATE-PCR. Linear-After-The-Exponential
 LATE-PCR Linear-After-The-Exponential A Patented Invention of the Laboratory of Human Genetics and Reproductive Biology Lab. Director: Lawrence J. Wangh, Ph.D. Department of Biology, Brandeis University,
LATE-PCR Linear-After-The-Exponential A Patented Invention of the Laboratory of Human Genetics and Reproductive Biology Lab. Director: Lawrence J. Wangh, Ph.D. Department of Biology, Brandeis University,
1. A brief overview of sequencing biochemistry
 Supplementary reading materials on Genome sequencing (optional) The materials are from Mark Blaxter s lecture notes on Sequencing strategies and Primary Analysis 1. A brief overview of sequencing biochemistry
Supplementary reading materials on Genome sequencing (optional) The materials are from Mark Blaxter s lecture notes on Sequencing strategies and Primary Analysis 1. A brief overview of sequencing biochemistry
Philippe Hupé 1,2. The R User Conference 2009 Rennes
 A suite of R packages for the analysis of DNA copy number microarray experiments Application in cancerology Philippe Hupé 1,2 1 UMR144 Institut Curie, CNRS 2 U900 Institut Curie, INSERM, Mines Paris Tech
A suite of R packages for the analysis of DNA copy number microarray experiments Application in cancerology Philippe Hupé 1,2 1 UMR144 Institut Curie, CNRS 2 U900 Institut Curie, INSERM, Mines Paris Tech
6. GENE EXPRESSION ANALYSIS MICROARRAYS
 6. GENE EXPRESSION ANALYSIS MICROARRAYS BIOINFORMATICS COURSE MTAT.03.239 16.10.2013 GENE EXPRESSION ANALYSIS MICROARRAYS Slides adapted from Konstantin Tretyakov s 2011/2012 and Priit Adlers 2010/2011
6. GENE EXPRESSION ANALYSIS MICROARRAYS BIOINFORMATICS COURSE MTAT.03.239 16.10.2013 GENE EXPRESSION ANALYSIS MICROARRAYS Slides adapted from Konstantin Tretyakov s 2011/2012 and Priit Adlers 2010/2011
Introduction to Bioinformatics and Gene Expression Technologies
 Introduction to Bioinformatics and Gene Expression Technologies Utah State University Fall 2017 Statistical Bioinformatics (Biomedical Big Data) Notes 1 1 Vocabulary Gene: hereditary DNA sequence at a
Introduction to Bioinformatics and Gene Expression Technologies Utah State University Fall 2017 Statistical Bioinformatics (Biomedical Big Data) Notes 1 1 Vocabulary Gene: hereditary DNA sequence at a
Detecting copy-neutral LOH in cancer using Agilent SurePrint G3 Cancer CGH+SNP Microarrays
 Detecting copy-neutral LOH in cancer using Agilent SurePrint G3 Cancer CGH+SNP Microarrays Application Note Authors Paula Costa Anniek De Witte Jayati Ghosh Agilent Technologies, Inc. Santa Clara, CA USA
Detecting copy-neutral LOH in cancer using Agilent SurePrint G3 Cancer CGH+SNP Microarrays Application Note Authors Paula Costa Anniek De Witte Jayati Ghosh Agilent Technologies, Inc. Santa Clara, CA USA
Complementary Technologies for Precision Genetic Analysis
 Complementary NGS, CGH and Workflow Featured Publication Zhu, J. et al. Duplication of C7orf58, WNT16 and FAM3C in an obese female with a t(7;22)(q32.1;q11.2) chromosomal translocation and clinical features
Complementary NGS, CGH and Workflow Featured Publication Zhu, J. et al. Duplication of C7orf58, WNT16 and FAM3C in an obese female with a t(7;22)(q32.1;q11.2) chromosomal translocation and clinical features
Additional Practice Problems for Reading Period
 BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Reading Period Additional Practice Problems for Reading Period Question 1. In patients with a particular type of leukemia, their leukemic B lymphocytes display a translocation
BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Reading Period Additional Practice Problems for Reading Period Question 1. In patients with a particular type of leukemia, their leukemic B lymphocytes display a translocation
FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO VARIABILITY IN DNA MICROARRAY RESULTS: THE ABRF MICROARRAY RESEARCH GROUP 2002 STUDY
 FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO VARIABILITY IN DNA MICROARRAY RESULTS: THE ABRF MICROARRAY RESEARCH GROUP 2002 STUDY K. L. Knudtson 1, C. Griffin 2, A. I. Brooks 3, D. A. Iacobas 4, K. Johnson 5, G. Khitrov 6,
FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO VARIABILITY IN DNA MICROARRAY RESULTS: THE ABRF MICROARRAY RESEARCH GROUP 2002 STUDY K. L. Knudtson 1, C. Griffin 2, A. I. Brooks 3, D. A. Iacobas 4, K. Johnson 5, G. Khitrov 6,
Fatchiyah
 Fatchiyah Email: fatchiya@yahoo.co.id RNAs: mrna trna rrna RNAi DNAs: Protein: genome DNA cdna mikro-makro mono-poly single-multi Analysis: Identification human and animal disease Finger printing Sexing
Fatchiyah Email: fatchiya@yahoo.co.id RNAs: mrna trna rrna RNAi DNAs: Protein: genome DNA cdna mikro-makro mono-poly single-multi Analysis: Identification human and animal disease Finger printing Sexing
Outline. Array platform considerations: Comparison between the technologies available in microarrays
 Microarray overview Outline Array platform considerations: Comparison between the technologies available in microarrays Differences in array fabrication Differences in array organization Applications of
Microarray overview Outline Array platform considerations: Comparison between the technologies available in microarrays Differences in array fabrication Differences in array organization Applications of
Recombinant DNA Technology. The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology. yeast. Biotechnology. Recombinant DNA technology.
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 8 Recombinant DNA Technology The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology Biotechnology?
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 8 Recombinant DNA Technology The Role of Recombinant DNA Technology in Biotechnology Biotechnology?
Masayoshi Honda, Jeehae Park, Robert A. Pugh, Taekjip Ha, and Maria Spies
 Molecular Cell, Volume 35 Supplemental Data Single-Molecule Analysis Reveals Differential Effect of ssdna-binding Proteins on DNA Translocation by XPD Helicase Masayoshi Honda, Jeehae Park, Robert A. Pugh,
Molecular Cell, Volume 35 Supplemental Data Single-Molecule Analysis Reveals Differential Effect of ssdna-binding Proteins on DNA Translocation by XPD Helicase Masayoshi Honda, Jeehae Park, Robert A. Pugh,
Biology 201 (Genetics) Exam #3 120 points 20 November Read the question carefully before answering. Think before you write.
 Name KEY Section Biology 201 (Genetics) Exam #3 120 points 20 November 2006 Read the question carefully before answering. Think before you write. You will have up to 50 minutes to take this exam. After
Name KEY Section Biology 201 (Genetics) Exam #3 120 points 20 November 2006 Read the question carefully before answering. Think before you write. You will have up to 50 minutes to take this exam. After
Introduction to gene expression microarray data analysis
 Introduction to gene expression microarray data analysis Outline Brief introduction: Technology and data. Statistical challenges in data analysis. Preprocessing data normalization and transformation. Useful
Introduction to gene expression microarray data analysis Outline Brief introduction: Technology and data. Statistical challenges in data analysis. Preprocessing data normalization and transformation. Useful
Gene Regulation Solutions. Microarrays and Next-Generation Sequencing
 Gene Regulation Solutions Microarrays and Next-Generation Sequencing Gene Regulation Solutions The Microarrays Advantage Microarrays Lead the Industry in: Comprehensive Content SurePrint G3 Human Gene
Gene Regulation Solutions Microarrays and Next-Generation Sequencing Gene Regulation Solutions The Microarrays Advantage Microarrays Lead the Industry in: Comprehensive Content SurePrint G3 Human Gene
Soybean Microarrays. An Introduction. By Steve Clough. November Common Microarray platforms
 Soybean Microarrays Microarray construction An Introduction By Steve Clough November 2005 Common Microarray platforms cdna: spotted collection of PCR products from different cdna clones, each representing
Soybean Microarrays Microarray construction An Introduction By Steve Clough November 2005 Common Microarray platforms cdna: spotted collection of PCR products from different cdna clones, each representing
Biotechnology. Chapter 20. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 20 Biotechnology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Chapter 20 Biotechnology PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Predicting Microarray Signals by Physical Modeling. Josh Deutsch. University of California. Santa Cruz
 Predicting Microarray Signals by Physical Modeling Josh Deutsch University of California Santa Cruz Predicting Microarray Signals by Physical Modeling p.1/39 Collaborators Shoudan Liang NASA Ames Onuttom
Predicting Microarray Signals by Physical Modeling Josh Deutsch University of California Santa Cruz Predicting Microarray Signals by Physical Modeling p.1/39 Collaborators Shoudan Liang NASA Ames Onuttom
Enhancers mutations that make the original mutant phenotype more extreme. Suppressors mutations that make the original mutant phenotype less extreme
 Interactomics and Proteomics 1. Interactomics The field of interactomics is concerned with interactions between genes or proteins. They can be genetic interactions, in which two genes are involved in the
Interactomics and Proteomics 1. Interactomics The field of interactomics is concerned with interactions between genes or proteins. They can be genetic interactions, in which two genes are involved in the
Reviewed: Hamilton. Contents; Overview. 2.0 Methods 3.0 Notes 4.0 Acknowledgements & References
 Microarray Core UCSF Comprehensive Cancer Center Standard Operating Procedure Title: Array CGH Hybridization Protocol HumArray 3.2 SOP No.: MC023QA Version: 5 Date: 5-12-06 Page No.: 1 of 5 Authors: Albertson,
Microarray Core UCSF Comprehensive Cancer Center Standard Operating Procedure Title: Array CGH Hybridization Protocol HumArray 3.2 SOP No.: MC023QA Version: 5 Date: 5-12-06 Page No.: 1 of 5 Authors: Albertson,
Introduction to Microarray Data Analysis and Gene Networks. Alvis Brazma European Bioinformatics Institute
 Introduction to Microarray Data Analysis and Gene Networks Alvis Brazma European Bioinformatics Institute A brief outline of this course What is gene expression, why it s important Microarrays and how
Introduction to Microarray Data Analysis and Gene Networks Alvis Brazma European Bioinformatics Institute A brief outline of this course What is gene expression, why it s important Microarrays and how
7 Gene Isolation and Analysis of Multiple
 Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Corinne A. Michels Copyright q 2002 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBNs: 0-471-89921-6 (Hardback); 0-470-84662-3 (Electronic) 7 Gene Isolation and Analysis of Multiple
Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Corinne A. Michels Copyright q 2002 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBNs: 0-471-89921-6 (Hardback); 0-470-84662-3 (Electronic) 7 Gene Isolation and Analysis of Multiple
Biotechnology and Genomics in Public Health. Sharon S. Krag, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Relative Fluorescent Quantitation on Capillary Electrophoresis Systems:
 Application Note Relative Fluorescent Quantitation on the 3130 Series Systems Relative Fluorescent Quantitation on Capillary Electrophoresis Systems: Screening for Loss of Heterozygosity in Tumor Samples
Application Note Relative Fluorescent Quantitation on the 3130 Series Systems Relative Fluorescent Quantitation on Capillary Electrophoresis Systems: Screening for Loss of Heterozygosity in Tumor Samples
REAL TIME PCR USING SYBR GREEN
 REAL TIME PCR USING SYBR GREEN 1 THE PROBLEM NEED TO QUANTITATE DIFFERENCES IN mrna EXPRESSION SMALL AMOUNTS OF mrna LASER CAPTURE SMALL AMOUNTS OF TISSUE PRIMARY CELLS PRECIOUS REAGENTS 2 THE PROBLEM
REAL TIME PCR USING SYBR GREEN 1 THE PROBLEM NEED TO QUANTITATE DIFFERENCES IN mrna EXPRESSION SMALL AMOUNTS OF mrna LASER CAPTURE SMALL AMOUNTS OF TISSUE PRIMARY CELLS PRECIOUS REAGENTS 2 THE PROBLEM
Introduction to Bioinformatics and Gene Expression Technology
 Vocabulary Introduction to Bioinformatics and Gene Expression Technology Utah State University Spring 2014 STAT 5570: Statistical Bioinformatics Notes 1.1 Gene: Genetics: Genome: Genomics: hereditary DNA
Vocabulary Introduction to Bioinformatics and Gene Expression Technology Utah State University Spring 2014 STAT 5570: Statistical Bioinformatics Notes 1.1 Gene: Genetics: Genome: Genomics: hereditary DNA
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Retention of RNA with LabelX.
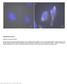 Supplementary Figure 1 Retention of RNA with LabelX. (a) Epi-fluorescence image of single molecule FISH (smfish) against GAPDH on HeLa cells expanded without LabelX treatment. (b) Epi-fluorescence image
Supplementary Figure 1 Retention of RNA with LabelX. (a) Epi-fluorescence image of single molecule FISH (smfish) against GAPDH on HeLa cells expanded without LabelX treatment. (b) Epi-fluorescence image
DNA Microarray Technology
 CHAPTER 1 DNA Microarray Technology All living organisms are composed of cells. As a functional unit, each cell can make copies of itself, and this process depends on a proper replication of the genetic
CHAPTER 1 DNA Microarray Technology All living organisms are composed of cells. As a functional unit, each cell can make copies of itself, and this process depends on a proper replication of the genetic
Applications and Uses. (adapted from Roche RealTime PCR Application Manual)
 What Can You Do With qpcr? Applications and Uses (adapted from Roche RealTime PCR Application Manual) What is qpcr? Real time PCR also known as quantitative PCR (qpcr) measures PCR amplification as it
What Can You Do With qpcr? Applications and Uses (adapted from Roche RealTime PCR Application Manual) What is qpcr? Real time PCR also known as quantitative PCR (qpcr) measures PCR amplification as it
Bioinformatics and Genomics: A New SP Frontier?
 Bioinformatics and Genomics: A New SP Frontier? A. O. Hero University of Michigan - Ann Arbor http://www.eecs.umich.edu/ hero Collaborators: G. Fleury, ESE - Paris S. Yoshida, A. Swaroop UM - Ann Arbor
Bioinformatics and Genomics: A New SP Frontier? A. O. Hero University of Michigan - Ann Arbor http://www.eecs.umich.edu/ hero Collaborators: G. Fleury, ESE - Paris S. Yoshida, A. Swaroop UM - Ann Arbor
Molecular Biology: DNA sequencing
 Molecular Biology: DNA sequencing Author: Prof Marinda Oosthuizen Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. SEQUENCING OF LARGE TEMPLATES As we have seen, we can obtain up to 800 nucleotides
Molecular Biology: DNA sequencing Author: Prof Marinda Oosthuizen Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution license. SEQUENCING OF LARGE TEMPLATES As we have seen, we can obtain up to 800 nucleotides
Functional Genomics Research Stream. Research Meetings: November 2 & 3, 2009 Next Generation Sequencing
 Functional Genomics Research Stream Research Meetings: November 2 & 3, 2009 Next Generation Sequencing Current Issues Research Meetings: Meet with me this Thursday or Friday. (bring laboratory notebook
Functional Genomics Research Stream Research Meetings: November 2 & 3, 2009 Next Generation Sequencing Current Issues Research Meetings: Meet with me this Thursday or Friday. (bring laboratory notebook
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
Computational Biology I LSM5191
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 Lecture 5 Notes: Genetic manipulation & Molecular Biology techniques Broad Overview of: Enzymatic tools in Molecular Biology Gel electrophoresis Restriction mapping DNA
Computational Biology I LSM5191 Lecture 5 Notes: Genetic manipulation & Molecular Biology techniques Broad Overview of: Enzymatic tools in Molecular Biology Gel electrophoresis Restriction mapping DNA
Bio Rad PCR Song Lyrics
 Bio Rad PCR Song Lyrics There was a time when to amplify DNA, You had to grow tons and tons of tiny cells. (Oooh) Then along came a guy named Dr. Kary Mullis, Said you can amplify in vitro just as well.
Bio Rad PCR Song Lyrics There was a time when to amplify DNA, You had to grow tons and tons of tiny cells. (Oooh) Then along came a guy named Dr. Kary Mullis, Said you can amplify in vitro just as well.
Quality Control Assessment in Genotyping Console
 Quality Control Assessment in Genotyping Console Introduction Prior to the release of Genotyping Console (GTC) 2.1, quality control (QC) assessment of the SNP Array 6.0 assay was performed using the Dynamic
Quality Control Assessment in Genotyping Console Introduction Prior to the release of Genotyping Console (GTC) 2.1, quality control (QC) assessment of the SNP Array 6.0 assay was performed using the Dynamic
Intracellular receptors specify complex patterns of gene expression that are cell and gene
 SUPPLEMENTAL RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Some HPr-1AR ARE-containing Genes Are Unresponsive to Androgen Intracellular receptors specify complex patterns of gene expression that are cell and gene specific. For
SUPPLEMENTAL RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Some HPr-1AR ARE-containing Genes Are Unresponsive to Androgen Intracellular receptors specify complex patterns of gene expression that are cell and gene specific. For
Molecular Genetics Techniques. BIT 220 Chapter 20
 Molecular Genetics Techniques BIT 220 Chapter 20 What is Cloning? Recombinant DNA technologies 1. Producing Recombinant DNA molecule Incorporate gene of interest into plasmid (cloning vector) 2. Recombinant
Molecular Genetics Techniques BIT 220 Chapter 20 What is Cloning? Recombinant DNA technologies 1. Producing Recombinant DNA molecule Incorporate gene of interest into plasmid (cloning vector) 2. Recombinant
Typical probes. Slides per pack Aminosilane. Long oligo- Slide AStar None D surface. nucleotides
 Aminosilane coating Nexterion Slide A+ and Slide AStar Overview Type of coating Immobilization method Typical probes Ordering information Nexterion product Barcode option Item number Slides per pack Aminosilane
Aminosilane coating Nexterion Slide A+ and Slide AStar Overview Type of coating Immobilization method Typical probes Ordering information Nexterion product Barcode option Item number Slides per pack Aminosilane
American Society of Cytopathology Core Curriculum in Molecular Biology
 American Society of Cytopathology Core Curriculum in Molecular Biology American Society of Cytopathology Core Curriculum in Molecular Biology Chapter 3 Molecular Techniques Separation and Detection, Part
American Society of Cytopathology Core Curriculum in Molecular Biology American Society of Cytopathology Core Curriculum in Molecular Biology Chapter 3 Molecular Techniques Separation and Detection, Part
Data Analysis on the ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System: Setting Baselines and Thresholds. Overview. Data Analysis Tutorial
 Data Analysis on the ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System: Setting Baselines and Thresholds Overview In order for accuracy and precision to be optimal, the assay must be properly evaluated and a few
Data Analysis on the ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System: Setting Baselines and Thresholds Overview In order for accuracy and precision to be optimal, the assay must be properly evaluated and a few
Exam 2 3/19/07 P. Sengupta BISC 4A
 Exam 2 3/19/07 P. Sengupta BISC 4A TOTAL of 6 questions. 100 points. QUESTION 1. Circle the correct answer - 4 points each total of 40 points. 1. During fertilization, a single sperm binds to receptors
Exam 2 3/19/07 P. Sengupta BISC 4A TOTAL of 6 questions. 100 points. QUESTION 1. Circle the correct answer - 4 points each total of 40 points. 1. During fertilization, a single sperm binds to receptors
Introduction to Molecular Biology
 Introduction to Molecular Biology Bioinformatics: Issues and Algorithms CSE 308-408 Fall 2007 Lecture 2-1- Important points to remember We will study: Problems from bioinformatics. Algorithms used to solve
Introduction to Molecular Biology Bioinformatics: Issues and Algorithms CSE 308-408 Fall 2007 Lecture 2-1- Important points to remember We will study: Problems from bioinformatics. Algorithms used to solve
qpcr Quantitative PCR or Real-time PCR Gives a measurement of PCR product at end of each cycle real time
 qpcr qpcr Quantitative PCR or Real-time PCR Gives a measurement of PCR product at end of each cycle real time Differs from endpoint PCR gel on last cycle Used to determines relative amount of template
qpcr qpcr Quantitative PCR or Real-time PCR Gives a measurement of PCR product at end of each cycle real time Differs from endpoint PCR gel on last cycle Used to determines relative amount of template
Development and application of CGHPRO, a novel software package for retrieving, handling and analysing array CGH data
 Aus dem Max Planck Institut für molekulare Genetik DISSERTATION Development and application of CGHPRO, a novel software package for retrieving, handling and analysing array CGH data Zur Erlangung des akademischen
Aus dem Max Planck Institut für molekulare Genetik DISSERTATION Development and application of CGHPRO, a novel software package for retrieving, handling and analysing array CGH data Zur Erlangung des akademischen
Feature Selection of Gene Expression Data for Cancer Classification: A Review
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 50 (2015 ) 52 57 2nd International Symposium on Big Data and Cloud Computing (ISBCC 15) Feature Selection of Gene Expression
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 50 (2015 ) 52 57 2nd International Symposium on Big Data and Cloud Computing (ISBCC 15) Feature Selection of Gene Expression
Rapid Learning Center Presents. Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours
 Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours 1/35 *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours 1/35 *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not
DNA Microarrays Introduction Part 2. Todd Lowe BME/BIO 210 April 11, 2007
 DNA Microarrays Introduction Part 2 Todd Lowe BME/BIO 210 April 11, 2007 Reading Assigned For Friday, please read two papers and be prepared to discuss in detail: Comprehensive Identification of Cell Cycle-related
DNA Microarrays Introduction Part 2 Todd Lowe BME/BIO 210 April 11, 2007 Reading Assigned For Friday, please read two papers and be prepared to discuss in detail: Comprehensive Identification of Cell Cycle-related
Module1TheBasicsofRealTimePCR Monday, March 19, 2007
 Objectives Slide notes: Page 1 of 41 Module 1: The Basics Of Real Time PCR Slide notes: Module 1: The Basics of real time PCR Page 2 of 41 Polymerase Chain Reaction Slide notes: Here is a review of PCR,
Objectives Slide notes: Page 1 of 41 Module 1: The Basics Of Real Time PCR Slide notes: Module 1: The Basics of real time PCR Page 2 of 41 Polymerase Chain Reaction Slide notes: Here is a review of PCR,
in-situ PCR Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 in-situ PCR Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 in situ Hybridization - Definition in situ PCR is a method in which the polymerase chain reaction actually takes place in the cell on a slide, and the product
in-situ PCR Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 in situ Hybridization - Definition in situ PCR is a method in which the polymerase chain reaction actually takes place in the cell on a slide, and the product
Bioinformatics III Structural Bioinformatics and Genome Analysis. PART II: Genome Analysis. Chapter 7. DNA Microarrays
 Bioinformatics III Structural Bioinformatics and Genome Analysis PART II: Genome Analysis Chapter 7. DNA Microarrays 7.1 Motivation 7.2 DNA Microarray History and current states 7.3 DNA Microarray Techniques
Bioinformatics III Structural Bioinformatics and Genome Analysis PART II: Genome Analysis Chapter 7. DNA Microarrays 7.1 Motivation 7.2 DNA Microarray History and current states 7.3 DNA Microarray Techniques
Humboldt Universität zu Berlin. Grundlagen der Bioinformatik SS Microarrays. Lecture
 Humboldt Universität zu Berlin Microarrays Grundlagen der Bioinformatik SS 2017 Lecture 6 09.06.2017 Agenda 1.mRNA: Genomic background 2.Overview: Microarray 3.Data-analysis: Quality control & normalization
Humboldt Universität zu Berlin Microarrays Grundlagen der Bioinformatik SS 2017 Lecture 6 09.06.2017 Agenda 1.mRNA: Genomic background 2.Overview: Microarray 3.Data-analysis: Quality control & normalization
Introducing a new generation of affordable choices from the leader in real-time PCR. Applied Biosystems 7500 Fast Real-Time PCR System
 7300/7500 Real-Time PCR Systems Introducing a new generation of affordable choices from the leader in real-time PCR. Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR System Applied Biosystems 7500 Fast Real-Time
7300/7500 Real-Time PCR Systems Introducing a new generation of affordable choices from the leader in real-time PCR. Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR System Applied Biosystems 7500 Fast Real-Time
Serial Analysis of Gene Expression
 Serial Analysis of Gene Expression Cloning of Tissue-Specific Genes Using SAGE and a Novel Computational Substraction Approach. Genomic (2001) Hung-Jui Shih Outline of Presentation SAGE EST Article TPE
Serial Analysis of Gene Expression Cloning of Tissue-Specific Genes Using SAGE and a Novel Computational Substraction Approach. Genomic (2001) Hung-Jui Shih Outline of Presentation SAGE EST Article TPE
New Stringent Two-Color Gene Expression Workflow Enables More Accurate and Reproducible Microarray Data
 Application Note GENOMICS INFORMATICS PROTEOMICS METABOLOMICS A T C T GATCCTTC T G AAC GGAAC T AATTTC AA G AATCTGATCCTTG AACTACCTTCCAAGGTG New Stringent Two-Color Gene Expression Workflow Enables More
Application Note GENOMICS INFORMATICS PROTEOMICS METABOLOMICS A T C T GATCCTTC T G AAC GGAAC T AATTTC AA G AATCTGATCCTTG AACTACCTTCCAAGGTG New Stringent Two-Color Gene Expression Workflow Enables More
Probe-Level Data Normalisation: RMA and GC-RMA Sam Robson Images courtesy of Neil Ward, European Application Engineer, Agilent Technologies.
 Probe-Level Data Normalisation: RMA and GC-RMA Sam Robson Images courtesy of Neil Ward, European Application Engineer, Agilent Technologies. References Summaries of Affymetrix Genechip Probe Level Data,
Probe-Level Data Normalisation: RMA and GC-RMA Sam Robson Images courtesy of Neil Ward, European Application Engineer, Agilent Technologies. References Summaries of Affymetrix Genechip Probe Level Data,
Fusion Gene Analysis. ncounter Elements. Molecules That Count WHITE PAPER. v1.0 OCTOBER 2014 NanoString Technologies, Inc.
 Fusion Gene Analysis NanoString Technologies, Inc. Fusion Gene Analysis ncounter Elements v1.0 OCTOBER 2014 NanoString Technologies, Inc., Seattle WA 98109 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. Not for use in diagnostic
Fusion Gene Analysis NanoString Technologies, Inc. Fusion Gene Analysis ncounter Elements v1.0 OCTOBER 2014 NanoString Technologies, Inc., Seattle WA 98109 FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. Not for use in diagnostic
Introduction to Basic Human Genetics. Professor Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Switzerland
 Introduction to Basic Human Genetics Professor Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Switzerland Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva
Introduction to Basic Human Genetics Professor Hanan Hamamy Department of Genetic Medicine and Development Geneva University Switzerland Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva
Chapter 10 Analytical Biotechnology and the Human Genome
 Chapter 10 Analytical Biotechnology and the Human Genome Chapter Outline Enzyme tests and biosensors DNA-based tests DNA analysis technologies Human genome and genome-based analytical methods 1 Enzyme-based
Chapter 10 Analytical Biotechnology and the Human Genome Chapter Outline Enzyme tests and biosensors DNA-based tests DNA analysis technologies Human genome and genome-based analytical methods 1 Enzyme-based
Lecture 20: Drosophila melanogaster
 Lecture 20: Drosophila melanogaster Model organisms Polytene chromosome Life cycle P elements and transformation Embryogenesis Read textbook: 732-744; Fig. 20.4; 20.10; 20.15-26 www.mhhe.com/hartwell3
Lecture 20: Drosophila melanogaster Model organisms Polytene chromosome Life cycle P elements and transformation Embryogenesis Read textbook: 732-744; Fig. 20.4; 20.10; 20.15-26 www.mhhe.com/hartwell3
Mate-pair library data improves genome assembly
 De Novo Sequencing on the Ion Torrent PGM APPLICATION NOTE Mate-pair library data improves genome assembly Highly accurate PGM data allows for de Novo Sequencing and Assembly For a draft assembly, generate
De Novo Sequencing on the Ion Torrent PGM APPLICATION NOTE Mate-pair library data improves genome assembly Highly accurate PGM data allows for de Novo Sequencing and Assembly For a draft assembly, generate
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Workflow for multimodal analysis using sc-gem on a programmable microfluidic device (Fluidigm). 1) Cells are captured and lysed, 2) RNA from lysed single cell is reverse-transcribed
Supplementary Figure 1 Workflow for multimodal analysis using sc-gem on a programmable microfluidic device (Fluidigm). 1) Cells are captured and lysed, 2) RNA from lysed single cell is reverse-transcribed
Using Low Input of Poly (A) + RNA and Total RNA for Oligonucleotide Microarrays Application
 Using Low Input of Poly (A) + RNA and Total RNA for Oligonucleotide Microarrays Application Gene Expression Author Michelle M. Chen Agilent Technologies, Inc. 3500 Deer Creek Road, MS 25U-7 Palo Alto,
Using Low Input of Poly (A) + RNA and Total RNA for Oligonucleotide Microarrays Application Gene Expression Author Michelle M. Chen Agilent Technologies, Inc. 3500 Deer Creek Road, MS 25U-7 Palo Alto,
