Jeffrey Polovina 1, John Dunne 2, Phoebe Woodworth 1, and Evan Howell 1 Julia Blanchard 3
|
|
|
- Morris Cameron
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Projected expansion of the subtropical biome and contraction of the temperate and equatorial upwelling biomes in the North Pacific under global warming Jeffrey Polovina 1, John Dunne 2, Phoebe Woodworth 1, and Evan Howell 1 Julia Blanchard 3 1. NOAA, Pacific Islands Fisheries Science Center, Honolulu, HI 2. NOAA, Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, Princeton, NJ 3. Imperial College, London, UK
2 NOAA GFDL Earth System Model 2.1 (ESM2.1) Coupled climate and biogeochemical model Global coupled climate model CM2.1 Atmosphere, ocean, land, sea ice Tracers of Phytoplankton with Allometric Zooplankton (TOPAZ) Major nutrients and four phytoplankton classes Horizontal resolution in ocean: 1 x 1 north of 30 N, with latitudinal resolution increasing to 0.33 at equator Vertical resolution: Ocean: 50 levels, with 22 10m levels in the upper 220m Atmosphere: 24 levels We Used Monthly N Pacific output from
3 Tracers Of Phytoplankton with Allometric Zooplankton (TOPAZ) simulates the mechanisms that control the ocean carbon cycle Biogeochemistry Phytoplankton ecology DOM cycling Particle sinking Atm. Deposition Gas exchange River Input Recycled nutrients N 2 fixer Small phyto. Protist Filter feeder Removal Sediment Input Scavenging New nutrients Large phyto. DOM Detritus Carbon Oxygen Nitrogen Phosphorus Iron Alkalinity Silicon Lithogenic CaCO 3 Dunne et al (2005, 2007)
4 Validation of ESM2.1 with TOPAZ log(seawifs satellite Chlorophyll) log(model Chlorophyll) In historical simulation TOPAZ reproduces SeaWiFS chlorophyll spatial and temporal variability and captures much of the temporal variation in the 50-yr Continuous Plankton Recorder (Henson et al. 2009a, Henson et al. 2009b). However in the North Pacific while the Transition Zone is reproduced, its shape is not as zonal as it should be.
5 CO 2 Forcing Trajectory (Scenario A2)
6 Biomes Longhurst (1995) based on physical forcing defined 4 Biomes: (Polar, Westerlies, Tradewind,Coastal boundary ) further refined to 10 per ocean basin. Hardman-Mountford et al. (2008) defined 6 based on SeaWiFS surface Chl levels- very high to very low. Dynamic biomes and climate model - Sarmiento et al. (2004) biomes based on physical forcing (marginal sea ice, subpolar, subtropical seasonal, subtropical permanent, low-latitude upwelling).
7 20-Year Mean Phytoplankton Biomass ( ) Small Phytoplankton Large Phytoplankton Total Phytoplankton
8 Total Phytoplankton Model-derived Biome Boundaries Overlaid on SeaWiFS Climatology Biome definitions 1. Subtropical: area with phytoplankton not exceeding 1.35 gc/m 2 2. Temperate: Area north of 20 o N lat with phytoplankton exceeding 1.35 gc/m 2 3. Equatorial Upwelling: Area south of 20 o N lat with phytoplankton exceeding 1.35 gc/m2
9 Annual Mean Biome Area over the 21 st Century Temperate Subtropical Equatorial Upwelling Temperate: Area decreases 34%/100 yr Subtropical: Area increases 29.5%/100yr Equatorial Upwelling Area decreases 27.7%/100yr
10 Biome Boundaries at beginning and end of the 21 st Century Boundary box: N, 175 E W
11 Time series of Nitrate, Primary Production, Phytoplankton biomass, and proportion of large Phytoplankton in the boundary box: N, 175 E W,
12 Year Median Monthly Primary Productivity in the Boundary box at beginning and end of the 21 st Century
13 Summary table of percent change over 100 years of physical and biological variables for each biome and total North Pacific, Temp ST EU North Pacific Area Mean PP Total PP Phytoplankton Biomass Density % Large SST
14 Results from other model studies large scale weakening (Vecchi et al., 2006) and poleward shift (Yin, 2005) in northern hemisphere westerlies NP basin-scale decreases in the magnitude of vertical velocities in both temperate and subtropical biomes (Rykaczewski and Dunne, accepted). Reduced nutrient input to euphotic zone in low and mid-latitudes in response to increased stratification seen in multi-model study (Steinacher et al. 2010)
15 Size-based model Assumes size-based predation, and sizespecific growth and mortality are functions of food availability and SST Input: monthly plankton size spectrum and SST Output: monthly population size spectrum Jennings et al. 2008, Proc. R. Soc. B; Blanchard et al J Anim Ecol; Blanchard et al Theor. Ecol.
16 Summary table of percent change over 100 years of physical and biological variables for each biome and total North Pacific, Temp ST EU North Pacific Area Mean PP Total PP Phytoplankton Biomass % Large SST Pelagic Biomass >2kg
17 Current Forecast Weakening mid-latitude westerlies, increased vertical statification, reduced deep nutrients into euphotic zone in subtropical and temperate biomes, increased warming and deep nutrients to Calif Current and EU. North Pacific as a whole: 4% decline in primary productivity 13% decline in phytoplankton biomass 27% decline in the fraction of large phytoplankton 28% decline in fish biomass Subtropical habitat grows in area by 30% while temperate and EU shrink by 34% and 28%, respectively * 39% decline in fish biomass in Temperate Biome * 18% increase in fish biomass ST Biome * 29% decline in fish biomass EU Biome
18 Challenges in understanding and forecasting change Basin-wide ecosystem monitoring to evaluate the climate change forecast/models Improving our ability to forecast impacts to top trophic levels. Any hope to forecast species specific changes? Incorporate error and multimodel ensembles Managing fisheries with slow average 0.4% decline/yr
Using dynamic biomes and a climate model to describe the responses of the North Pacific to climate change over the 21 st Century
 Using dynamic biomes and a climate model to describe the responses of the North Pacific to climate change over the 21 st Century Jeffrey Polovina 1, John Dunne 2, Phoebe Woodworth 1, and Evan Howell 1
Using dynamic biomes and a climate model to describe the responses of the North Pacific to climate change over the 21 st Century Jeffrey Polovina 1, John Dunne 2, Phoebe Woodworth 1, and Evan Howell 1
Using climate model output to project climate change impacts over the 21 st Century in the North Pacific Subtropical Ecosystem
 Using climate model output to project climate change impacts over the 21 st Century in the North Pacific Subtropical Ecosystem Jeffrey Polovina and Phoebe Woodworth-Jefcoats Pacific Islands Fisheries Science
Using climate model output to project climate change impacts over the 21 st Century in the North Pacific Subtropical Ecosystem Jeffrey Polovina and Phoebe Woodworth-Jefcoats Pacific Islands Fisheries Science
Multicentury Climate Warming Impacts on Ocean Biogeochemistry
 Multicentury Climate Warming Impacts on Ocean Biogeochemistry Prof. J. Keith Moore University of California, Irvine Collaborators: Weiwei Fu, Francois Primeau, Greg Britten, Keith Lindsay, Matthew Long,
Multicentury Climate Warming Impacts on Ocean Biogeochemistry Prof. J. Keith Moore University of California, Irvine Collaborators: Weiwei Fu, Francois Primeau, Greg Britten, Keith Lindsay, Matthew Long,
Ocean s least productive waters are expanding
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L03618, doi:10.1029/2007gl031745, 2008 Ocean s least productive waters are expanding Jeffrey J. Polovina, 1 Evan A. Howell, 1 and Melanie
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L03618, doi:10.1029/2007gl031745, 2008 Ocean s least productive waters are expanding Jeffrey J. Polovina, 1 Evan A. Howell, 1 and Melanie
Climate Change and Trophic Mismatches between Plankton Blooms and Fish Phenology
 Climate Change and Trophic Mismatches between Plankton Blooms and Fish Phenology Rebecca G. Asch (Princeton) Co-authors: Charles A. Stock (NOAA GFDL) Jorge L. Sarmiento (Princeton) July 28, 2016 Phenology
Climate Change and Trophic Mismatches between Plankton Blooms and Fish Phenology Rebecca G. Asch (Princeton) Co-authors: Charles A. Stock (NOAA GFDL) Jorge L. Sarmiento (Princeton) July 28, 2016 Phenology
Satellite data show that phytoplankton biomass and growth generally decline as the
 Oceanography Plankton in a warmer world Scott C. Doney Satellite data show that phytoplankton biomass and growth generally decline as the oceans surface waters warm up. Is this trend, seen over the past
Oceanography Plankton in a warmer world Scott C. Doney Satellite data show that phytoplankton biomass and growth generally decline as the oceans surface waters warm up. Is this trend, seen over the past
RESPONSE OF PHYTOPLANKTON AND OCEAN BIOGEOCHEMISTRY IN A WARMING WORLD
 RESPONSE OF PHYTOPLANKTON AND OCEAN BIOGEOCHEMISTRY IN A WARMING WORLD Jeffery Scott, Michael Follows Massachusetts Institute of Technology Program in Atmospheres, Oceans and Climate INTRODUCTION: Marine
RESPONSE OF PHYTOPLANKTON AND OCEAN BIOGEOCHEMISTRY IN A WARMING WORLD Jeffery Scott, Michael Follows Massachusetts Institute of Technology Program in Atmospheres, Oceans and Climate INTRODUCTION: Marine
Biological Oceanography
 Biological Oceanography What controls production in the sea? The BIG 2: 1) Light (energy) 2) Nutrients (matter) Secondarily 3) Temperature 4) Stratification (coupled to 2 & 3) 5) Grazing/predation The
Biological Oceanography What controls production in the sea? The BIG 2: 1) Light (energy) 2) Nutrients (matter) Secondarily 3) Temperature 4) Stratification (coupled to 2 & 3) 5) Grazing/predation The
the future? From the Seattle Post-Intelligencer, October 20, 2005 Assessing the potential impacts of global warming Courtesy of Nate Mantua
 the future? From the Seattle Post-Intelligencer, October 20, 2005 Assessing the potential impacts of global warming Courtesy of Nate Mantua Climate Change: Assessing its Implications for Marine Ecosystems
the future? From the Seattle Post-Intelligencer, October 20, 2005 Assessing the potential impacts of global warming Courtesy of Nate Mantua Climate Change: Assessing its Implications for Marine Ecosystems
Responses of Eastern Boundary Current Ecosystems to Anthropogenic Climate Change
 Responses of Eastern Boundary Current Ecosystems to Anthropogenic Climate Change 1900 2100 Ryan R. Rykaczewski University of South Carolina ryk @ sc.edu We are united by an interest in understanding ecosystem
Responses of Eastern Boundary Current Ecosystems to Anthropogenic Climate Change 1900 2100 Ryan R. Rykaczewski University of South Carolina ryk @ sc.edu We are united by an interest in understanding ecosystem
Contrasting physical-biological interactions in the central gyres and ocean margins
 Contrasting physical-biological interactions in the central gyres and ocean margins Anand Gnanadesikan NOAA/Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Lab AOSC Seminar University of Maryland Nov. 11, 2010 Key points Well
Contrasting physical-biological interactions in the central gyres and ocean margins Anand Gnanadesikan NOAA/Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Lab AOSC Seminar University of Maryland Nov. 11, 2010 Key points Well
21 st Century Climate Change Impacts on Marine Fisheries
 21 st Century Climate Change Impacts on Marine Fisheries Anne B. Hollowed, NOAA, NMFS, Alaska Fisheries Science Center, Seattle, WA USA International Workshop on Climate and Oceanic Fisheries, Rarotonga,
21 st Century Climate Change Impacts on Marine Fisheries Anne B. Hollowed, NOAA, NMFS, Alaska Fisheries Science Center, Seattle, WA USA International Workshop on Climate and Oceanic Fisheries, Rarotonga,
Predicting and adapting to biome-scale marine resource changes in the North Pacific
 Predicting and adapting to biome-scale marine resource changes in the North Pacific PICES International Symposium Understanding Changes in Transitional Areas of the Pacific April 25, 2018 Presented by:
Predicting and adapting to biome-scale marine resource changes in the North Pacific PICES International Symposium Understanding Changes in Transitional Areas of the Pacific April 25, 2018 Presented by:
Phytoplankton and bacterial biomass, production and growth in various ocean ecosystems
 Phytoplankton and bacterial biomass, production and growth in various ocean ecosystems Location Bact. Biomass (mg C m -2 ) Phyto. Biomass (mg C m -2 ) BactB: PhytoB BactP (mg C m -2 d -1 ) 1 o Pro (mg
Phytoplankton and bacterial biomass, production and growth in various ocean ecosystems Location Bact. Biomass (mg C m -2 ) Phyto. Biomass (mg C m -2 ) BactB: PhytoB BactP (mg C m -2 d -1 ) 1 o Pro (mg
Physical / Chemical Drivers of the Ocean in a High CO 2 World
 Physical / Chemical Drivers of the Ocean in a High CO 2 World Laurent Bopp IPSL / LSCE, Gif s/ Yvette, France Introduction Climate Atmosphere Biosphere Soils Food Web / Fisheries Atmospheric Components
Physical / Chemical Drivers of the Ocean in a High CO 2 World Laurent Bopp IPSL / LSCE, Gif s/ Yvette, France Introduction Climate Atmosphere Biosphere Soils Food Web / Fisheries Atmospheric Components
MODELING NUTRIENT LOADING AND EUTROPHICATION RESPONSE TO SUPPORT THE ELKHORN SLOUGH NUTRIENT TOTAL MAXIMUM DAILY LOAD
 MODELING NUTRIENT LOADING AND EUTROPHICATION RESPONSE TO SUPPORT THE ELKHORN SLOUGH NUTRIENT TOTAL MAXIMUM DAILY LOAD Martha Sutula Southern California Coastal Water Research Project Workshop on The Science
MODELING NUTRIENT LOADING AND EUTROPHICATION RESPONSE TO SUPPORT THE ELKHORN SLOUGH NUTRIENT TOTAL MAXIMUM DAILY LOAD Martha Sutula Southern California Coastal Water Research Project Workshop on The Science
Continued from Lecture 20a
 IV. Primary Production (p.p.) Continued from Lecture 20a C. Biomass & Productivity 1. Biomass = mass of organic matter (in grams) a. Gross primary production = total amount of organic material synthesized
IV. Primary Production (p.p.) Continued from Lecture 20a C. Biomass & Productivity 1. Biomass = mass of organic matter (in grams) a. Gross primary production = total amount of organic material synthesized
Production and Life OCEA 101
 Production and Life OCEA 101 Overview Photosynthesis Primary production Phytoplankton biomass Controls on primary production and biomass Food webs Photosynthesis Photosynthesis requires: (i) sunlight (ii)
Production and Life OCEA 101 Overview Photosynthesis Primary production Phytoplankton biomass Controls on primary production and biomass Food webs Photosynthesis Photosynthesis requires: (i) sunlight (ii)
Study on the Diagnostics and Projection of Ecosystem Change Associated with Global Change
 Study on the Diagnostics and Projection of Ecosystem Change Associated with Global Change Project Representative Eitaro Wada Frontier Research Center for Global Change, Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science
Study on the Diagnostics and Projection of Ecosystem Change Associated with Global Change Project Representative Eitaro Wada Frontier Research Center for Global Change, Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science
Productivity and fisheries. Energy flow. Biological pyramids. Why study production processes?
 Productivity and fisheries Why study production processes? Fisheries strongly tied to spatial and temporal variation in primary productivity Better understanding of distribution of fishery resources Interpret
Productivity and fisheries Why study production processes? Fisheries strongly tied to spatial and temporal variation in primary productivity Better understanding of distribution of fishery resources Interpret
Earth System Modeling at GFDL:
 Earth System Modeling at GFDL: Goals, strategies and early results for the carbon system John Dunne In coordination with researchers at GFDL and PU Background The CO 2 Climate Forcing Question CCSP Strategic
Earth System Modeling at GFDL: Goals, strategies and early results for the carbon system John Dunne In coordination with researchers at GFDL and PU Background The CO 2 Climate Forcing Question CCSP Strategic
Arctic Ocean primary productivity and climate change
 Arctic Ocean primary productivity and climate change Patricia Matrai Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences with help from many colleagues! Arctic sea ice loss Snow cover loss Ice melt and surface warming
Arctic Ocean primary productivity and climate change Patricia Matrai Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences with help from many colleagues! Arctic sea ice loss Snow cover loss Ice melt and surface warming
Phytoplankton and Upper Ocean Biogeochemical Cycles Along Line P
 Phytoplankton and Upper Ocean Biogeochemical Cycles Along Line P Angelica Peña Institute of Ocean Sciences, Fisheries & Oceans Canada. Contribution: Diana Varela, Department of Biology & School of Earth
Phytoplankton and Upper Ocean Biogeochemical Cycles Along Line P Angelica Peña Institute of Ocean Sciences, Fisheries & Oceans Canada. Contribution: Diana Varela, Department of Biology & School of Earth
MONDAY, 27 FEBRUARY 2017
 MONDAY, 27 FEBRUARY 2017 Room 301 B 302 A/B 304 A/B 305 A/B 306 A 306 B 308 A/B 199 168 258 162 150 168 194 9:00-9:50 9:50 - MORNING PLENARY - Marcia McNutt - 9:00 to 9:50 Session# 71 96 12 9 34 58 65
MONDAY, 27 FEBRUARY 2017 Room 301 B 302 A/B 304 A/B 305 A/B 306 A 306 B 308 A/B 199 168 258 162 150 168 194 9:00-9:50 9:50 - MORNING PLENARY - Marcia McNutt - 9:00 to 9:50 Session# 71 96 12 9 34 58 65
Patterns of Productivity
 Patterns of Productivity Limitation by Light and Nutrients OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of biomass by autotrophs Secondary Production - the production of biomass by heterotrophs
Patterns of Productivity Limitation by Light and Nutrients OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of biomass by autotrophs Secondary Production - the production of biomass by heterotrophs
Modelling of higher trophic levels with an large ecosystem model: -state of the art -limitations -perspectives. Piet Ruardij
 Modelling of higher trophic levels with an large ecosystem model: -state of the art -limitations -perspectives Piet Ruardij 1 Modelling the North Sea: Actual situation: 8+1 coupled hydrodynamical-ecosystems
Modelling of higher trophic levels with an large ecosystem model: -state of the art -limitations -perspectives Piet Ruardij 1 Modelling the North Sea: Actual situation: 8+1 coupled hydrodynamical-ecosystems
Global Warming leads to Underwater Deserts. SUHAS.E.P I Year.Dept of Mechanical engineering RVCE
 Global Warming leads to Underwater Deserts SUHAS.E.P I Year.Dept of Mechanical engineering RVCE Introduction Oxygen-poor waters occupy large volumes of the intermediate-depth eastern tropical oceans. Oxygen-poor
Global Warming leads to Underwater Deserts SUHAS.E.P I Year.Dept of Mechanical engineering RVCE Introduction Oxygen-poor waters occupy large volumes of the intermediate-depth eastern tropical oceans. Oxygen-poor
Nitrogen Cycling in the Sea
 Nitrogen Cycling in the Sea Matt Church (MSB 612 / 9568779/ mjchurch@hawaii.edu) Marine Microplankton Ecology / OCN 626 NH 4 N0 2 N0 2 NH 4 Outline Nitrogen species in marine watersdistributions and concentrations
Nitrogen Cycling in the Sea Matt Church (MSB 612 / 9568779/ mjchurch@hawaii.edu) Marine Microplankton Ecology / OCN 626 NH 4 N0 2 N0 2 NH 4 Outline Nitrogen species in marine watersdistributions and concentrations
Detection and projection of climate change impacts on marine fisheries
 Detection and projection of climate change impacts on marine fisheries William W.L. Cheung w.cheung@fisheries.ubc.ca Changing Ocean Research Unit & Nippon Foundation- Nereus Program, The University i of
Detection and projection of climate change impacts on marine fisheries William W.L. Cheung w.cheung@fisheries.ubc.ca Changing Ocean Research Unit & Nippon Foundation- Nereus Program, The University i of
Climate and current anthropogenic impacts on marine fisheries
 Art: Glynn Gorick Climate and current anthropogenic impacts on marine fisheries Keith Brander - DTU Aqua Structure of the talk History of human impacts on marine fisheries Signs of improvement Ecosystem
Art: Glynn Gorick Climate and current anthropogenic impacts on marine fisheries Keith Brander - DTU Aqua Structure of the talk History of human impacts on marine fisheries Signs of improvement Ecosystem
Oceanic CO 2 system - Significance
 OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (10.25.18) (10.30.18) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) (11.27.18) Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling - Part 2 Lecture Outline 1. The Oceanic Carbon System 2. Nutrient Cycling in
OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (10.25.18) (10.30.18) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) (11.27.18) Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling - Part 2 Lecture Outline 1. The Oceanic Carbon System 2. Nutrient Cycling in
Detection of anthropogenic climate change in satellite records of ocean chlorophyll and productivity
 Author(s) 2010. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Biogeosciences Detection of anthropogenic climate change in satellite records of ocean chlorophyll and productivity
Author(s) 2010. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Biogeosciences Detection of anthropogenic climate change in satellite records of ocean chlorophyll and productivity
An Increase in the seasonal cycle of air-sea CO 2 fluxes over the 21st Century in IPCC Scenario Runs
 An Increase in the seasonal cycle of air-sea CO 2 fluxes over the 21st Century in IPCC Scenario Runs Keith Rodgers (Princeton) Laurent Bopp (LSCE) Olivier Aumont (IRD) Daniele Iudicone (Naples) Jorge Sarmiento
An Increase in the seasonal cycle of air-sea CO 2 fluxes over the 21st Century in IPCC Scenario Runs Keith Rodgers (Princeton) Laurent Bopp (LSCE) Olivier Aumont (IRD) Daniele Iudicone (Naples) Jorge Sarmiento
Scenarios of the Baltic Sea ecosystem calculated with a regional climate model
 Scenarios of the Baltic Sea ecosystem calculated with a regional climate model Markus Meier*/**, Kari Eilola* and Elin Almroth* *Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute, Norrköping and **Stockholm
Scenarios of the Baltic Sea ecosystem calculated with a regional climate model Markus Meier*/**, Kari Eilola* and Elin Almroth* *Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute, Norrköping and **Stockholm
How will biogeochemical processes in the ocean respond to surface warming? Anja Engel Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research (AWI)
 How will biogeochemical processes in the ocean respond to surface warming? Anja Engel Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research (AWI) The Naked Earth The Discovery of Global Warming Air traps
How will biogeochemical processes in the ocean respond to surface warming? Anja Engel Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research (AWI) The Naked Earth The Discovery of Global Warming Air traps
Seasonal Anoxia over the Western Indian Continental Shelf
 Seasonal Anoxia over the Western Indian Continental Shelf S.W.A. Naqvi, Hema Naik, A.K. Pratihary, M. Gauns, Witty D Souza, Gayatree Narvenkar, D.A. Jayakumar, M.S. Shailaja & P.V. Narvekar National Institute
Seasonal Anoxia over the Western Indian Continental Shelf S.W.A. Naqvi, Hema Naik, A.K. Pratihary, M. Gauns, Witty D Souza, Gayatree Narvenkar, D.A. Jayakumar, M.S. Shailaja & P.V. Narvekar National Institute
Intro to Biogeochemical Modeling Ocean & Coupled
 Intro to Biogeochemical Modeling Ocean & Coupled Keith Lindsay, NCAR/CGD NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation Lecture Outline 1) Large Scale Ocean Biogeochemical Features 2) Techniques
Intro to Biogeochemical Modeling Ocean & Coupled Keith Lindsay, NCAR/CGD NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation Lecture Outline 1) Large Scale Ocean Biogeochemical Features 2) Techniques
Patterns of Productivity
 Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of autotrophic biomass Secondary Production - the production of heterotrophic biomass Production vs Biomass Biomass
Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of autotrophic biomass Secondary Production - the production of heterotrophic biomass Production vs Biomass Biomass
4/28/2013. Transmission of Light in Seawater. Color in the Ocean Color of ocean ranges from deep blue to yellow-green Factors Turbidity from runoff
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer Chapter summary in haiku form Primary produce Sunlight and phytoplankton Ocean is garden Chapter Overview Productivity
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer Chapter summary in haiku form Primary produce Sunlight and phytoplankton Ocean is garden Chapter Overview Productivity
Modelling sea ice biogeochemistry: key findings from 1-D sensitivity experiments and plans for 3-D study
 Modelling sea ice biogeochemistry: key findings from 1-D sensitivity experiments and plans for 3-D study Hakase Hayashida1, Eric Mortenson1, Nadja Steiner2,3, Adam Monahan1 1 School of Earth and Ocean
Modelling sea ice biogeochemistry: key findings from 1-D sensitivity experiments and plans for 3-D study Hakase Hayashida1, Eric Mortenson1, Nadja Steiner2,3, Adam Monahan1 1 School of Earth and Ocean
Denitrification 2/11/2011. Energy to be gained in oxidation. Oxidized N. Reduced N
 Oxidized N Energy to be gained in oxidation Reduced N (Sarmiento & Gruber, 2006) Denitrification The reduction of NO 3 and NO 2 to N 2 during heterotrophic respiration of organic matter. Occurs predominately
Oxidized N Energy to be gained in oxidation Reduced N (Sarmiento & Gruber, 2006) Denitrification The reduction of NO 3 and NO 2 to N 2 during heterotrophic respiration of organic matter. Occurs predominately
Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Ling TONG Qisheng TANG
 Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Ling TONG Qisheng TANG Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, CAFS Both environmental and human factors affect the bioproducts in
Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Ling TONG Qisheng TANG Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, CAFS Both environmental and human factors affect the bioproducts in
Primary Production in the Ocean
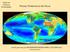 Primary Production in the Ocean A global composite of sea surface chlorophyll concentration Oligotrophic gyre (LNLC) Seasonal Phytoplankton blooms Coastal Upwelling High-nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC)
Primary Production in the Ocean A global composite of sea surface chlorophyll concentration Oligotrophic gyre (LNLC) Seasonal Phytoplankton blooms Coastal Upwelling High-nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC)
Chemical and biological effects on mesopelagic organisms and communities in a high-co 2 world
 Chemical and biological effects on mesopelagic organisms and communities in a high-co 2 world Louis Legendre Villefranche Oceanography Laboratory, France Richard B. Rivkin Memorial University of Newfoundland,
Chemical and biological effects on mesopelagic organisms and communities in a high-co 2 world Louis Legendre Villefranche Oceanography Laboratory, France Richard B. Rivkin Memorial University of Newfoundland,
Primary Production in the Ocean
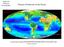 Primary Production in the Ocean A global composite of sea surface chlorophyll concentration Oligotrophic gyre (LNLC) Seasonal Phytoplankton blooms Coastal Upwelling High-nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC)
Primary Production in the Ocean A global composite of sea surface chlorophyll concentration Oligotrophic gyre (LNLC) Seasonal Phytoplankton blooms Coastal Upwelling High-nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC)
OCEANOGRAPHY Chapter 13
 OCEANOGRAPHY Chapter 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer part 3: Regional Productivity Energy and Nutrients in Marine Ecosystems, Fisheries Notes from the textbook, integrated with original
OCEANOGRAPHY Chapter 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer part 3: Regional Productivity Energy and Nutrients in Marine Ecosystems, Fisheries Notes from the textbook, integrated with original
Marine Microbial Processes
 Marine Microbial Processes Outline size-structured food webs brief history of the development of our current understanding of microbially dominated food webs carbon cycling in marine food webs evolving
Marine Microbial Processes Outline size-structured food webs brief history of the development of our current understanding of microbially dominated food webs carbon cycling in marine food webs evolving
Monitoring and modeling of phytoplankton and marine primary production. Nansen Environmental and Remote Sensing Center, Bergen, Norway
 Monitoring and modeling of phytoplankton and marine primary production Lasse H. Pettersson, Annette Samuelsen and Anton Korosov lasse.pettersson@nersc.no Nansen Environmental and Remote Sensing Center,
Monitoring and modeling of phytoplankton and marine primary production Lasse H. Pettersson, Annette Samuelsen and Anton Korosov lasse.pettersson@nersc.no Nansen Environmental and Remote Sensing Center,
Ecosystem Status Assessment in Korea
 Ecosystem Status Assessment in Korea Sinjae Yoo Indicators of Status and Change within North Pacific Marine Ecosystems: A FUTURE Workshop Honolulu, 2011.04.26-28 Purpose To introduce monitoring and assessment
Ecosystem Status Assessment in Korea Sinjae Yoo Indicators of Status and Change within North Pacific Marine Ecosystems: A FUTURE Workshop Honolulu, 2011.04.26-28 Purpose To introduce monitoring and assessment
Global Biogeochemical cycles and Ocean Productivity
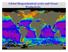 Global Biogeochemical cycles and Ocean Productivity Biological Oceanography Recall: goal is not to understand the biology of one particular organism (or group), but to understand organisms fit into the
Global Biogeochemical cycles and Ocean Productivity Biological Oceanography Recall: goal is not to understand the biology of one particular organism (or group), but to understand organisms fit into the
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL: Spatial and temporal variability in nutrients and carbon uptake during 2004 and 2005 in the eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean
 Manuscript prepared for Biogeosciences Discuss. with version 3.5 of the LATEX class copernicus discussions.cls. Date: August SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL: Spatial and temporal variability in nutrients and carbon
Manuscript prepared for Biogeosciences Discuss. with version 3.5 of the LATEX class copernicus discussions.cls. Date: August SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL: Spatial and temporal variability in nutrients and carbon
Includes the coastal zone and the pelagic zone, the realm of the oceanographer. I. Ocean Circulation
 Includes the coastal zone and the pelagic zone, the realm of the oceanographer I. Ocean Circulation II. Water Column Production A. Coastal Oceans B. Open Oceans E. Micronutrients F. Harmful Algal Blooms
Includes the coastal zone and the pelagic zone, the realm of the oceanographer I. Ocean Circulation II. Water Column Production A. Coastal Oceans B. Open Oceans E. Micronutrients F. Harmful Algal Blooms
The Global Carbon Cycle
 The Global Carbon Cycle Laurent Bopp LSCE, Paris Introduction CO2 is an important greenhouse gas Contribution to Natural Greenhouse Effect Contribution to Anthropogenic Effect 1 From NASA Website 2 Introduction
The Global Carbon Cycle Laurent Bopp LSCE, Paris Introduction CO2 is an important greenhouse gas Contribution to Natural Greenhouse Effect Contribution to Anthropogenic Effect 1 From NASA Website 2 Introduction
Determining the f ratio 11/16/2010. Incubate seawater in the presence of trace 15
 Plankton production is supported by 2 types of nitrogen: 1) new production supported by external sources of N (e.g. NO 3 and N 2 ), 2) recycled or regenerated production, sustained by recycling of N. Assumptions:
Plankton production is supported by 2 types of nitrogen: 1) new production supported by external sources of N (e.g. NO 3 and N 2 ), 2) recycled or regenerated production, sustained by recycling of N. Assumptions:
SALMON AS INTEGRATIVE SAMPLERS
 SALMON AS INTEGRATIVE SAMPLERS OF HIGH SEAS FOOD WEBS POSTER: INTEGRATING STABLE ISOTOPE ANALYSES OF ZOOPLANKTON & RETURNING ADULT SALMON TISSUES TO INFORM HIGH SEAS NORTH PACIFIC FOOD WEB DYNAMICS Brian
SALMON AS INTEGRATIVE SAMPLERS OF HIGH SEAS FOOD WEBS POSTER: INTEGRATING STABLE ISOTOPE ANALYSES OF ZOOPLANKTON & RETURNING ADULT SALMON TISSUES TO INFORM HIGH SEAS NORTH PACIFIC FOOD WEB DYNAMICS Brian
GLOBAL WARMING LEADS TO UNDERWATER DESERTS" AND COASTAL DEAD ZONES
 GLOBAL WARMING LEADS TO UNDERWATER DESERTS" AND COASTAL DEAD ZONES Suhas E.P RVCE (VTU) No. 4/1 Golden Residency, Rmv 2 stage, Sanjaynagar, Bangalore SYNOPSIS Oxygen-poor waters occupy large volumes of
GLOBAL WARMING LEADS TO UNDERWATER DESERTS" AND COASTAL DEAD ZONES Suhas E.P RVCE (VTU) No. 4/1 Golden Residency, Rmv 2 stage, Sanjaynagar, Bangalore SYNOPSIS Oxygen-poor waters occupy large volumes of
Patterns of Productivity
 Phytoplankton Zooplankton Nutrients Patterns of Productivity There is a large Spring Bloom in the North Atlantic (temperate latitudes remember the Gulf Stream!) What is a bloom? Analogy to terrestrial
Phytoplankton Zooplankton Nutrients Patterns of Productivity There is a large Spring Bloom in the North Atlantic (temperate latitudes remember the Gulf Stream!) What is a bloom? Analogy to terrestrial
Food web structure in the continental shelf and slope waters of the Korean peninsula: Stable isotope approach and prospects for future research
 PICES XVII End-to-end food webs: Impacts of a changing ocean October 28 28 Food web structure in the continental shelf and slope waters of the Korean peninsula: Stable isotope approach and prospects for
PICES XVII End-to-end food webs: Impacts of a changing ocean October 28 28 Food web structure in the continental shelf and slope waters of the Korean peninsula: Stable isotope approach and prospects for
Developments in the ecological box modelling of the Curonian Lagoon
 Developments in the ecological box modelling of the Curonian Lagoon /9/9, Klaipeda Dr. Ali Ertürk Istanbul Technical University Department of Environmental Engineering INTRODUCTION 1 What is ESTAS? EcoSystem
Developments in the ecological box modelling of the Curonian Lagoon /9/9, Klaipeda Dr. Ali Ertürk Istanbul Technical University Department of Environmental Engineering INTRODUCTION 1 What is ESTAS? EcoSystem
(Brief) History of Life
 Oldest fossils are 3.5 Ga Cyanobacteria (?) from the Australian Warraroona Group (ancient marine sediments) Bacteria represent the only life on Earth from 3.5 to ~1.5 Ga - and possibly longer Hard to kill
Oldest fossils are 3.5 Ga Cyanobacteria (?) from the Australian Warraroona Group (ancient marine sediments) Bacteria represent the only life on Earth from 3.5 to ~1.5 Ga - and possibly longer Hard to kill
Production vs Biomass
 Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 5 Production vs Biomass Biomass = amount of carbon per unit area (= standing stock * C/cell) Units (e.g.): g C m -2 Primary Production = amount of carbon
Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 5 Production vs Biomass Biomass = amount of carbon per unit area (= standing stock * C/cell) Units (e.g.): g C m -2 Primary Production = amount of carbon
Equatorial Pacific HNLC region
 Equatorial Pacific HNLC region Another region with high nitrogen left over after the growing season Iron and grazing constraints on primary production in the central equatorial Pacific: An EqPac synthesis
Equatorial Pacific HNLC region Another region with high nitrogen left over after the growing season Iron and grazing constraints on primary production in the central equatorial Pacific: An EqPac synthesis
Younjoo Lee and Walter Boynton. Horn Point Laboratory and Chesapeake Biological Laboratory University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science
 Younjoo Lee and Walter Boynton Horn Point Laboratory and Chesapeake Biological Laboratory University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science 1 Data and Method Summer Hypoxia Dissolve Oxygen Patterns
Younjoo Lee and Walter Boynton Horn Point Laboratory and Chesapeake Biological Laboratory University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science 1 Data and Method Summer Hypoxia Dissolve Oxygen Patterns
What ocean biogeochemical models can tell us about bottom-up control of ecosystem variability
 ICES Journal of Marine Science (2011), 68(6), 1030 1044. doi:10.1093/icesjms/fsr068 What ocean biogeochemical models can tell us about bottom-up control of ecosystem variability A. Gnanadesikan*, J. P.
ICES Journal of Marine Science (2011), 68(6), 1030 1044. doi:10.1093/icesjms/fsr068 What ocean biogeochemical models can tell us about bottom-up control of ecosystem variability A. Gnanadesikan*, J. P.
Trace Metal Iron (Fe), an important element to measure at sea. Dr. Thato Nicholas Mtshali
 Trace Metal Iron (Fe), an important element to measure at sea Dr. Thato Nicholas Mtshali Southern Atlantic Ocean and Antarctic Seminar (Cape Town): 5 December 2017 A CSIR-led multidisciplinary and multi-institutional
Trace Metal Iron (Fe), an important element to measure at sea Dr. Thato Nicholas Mtshali Southern Atlantic Ocean and Antarctic Seminar (Cape Town): 5 December 2017 A CSIR-led multidisciplinary and multi-institutional
Instructions: Answer the questions 1-8 to set up basic rules for how lateral current direction controls vertical motion of seawater.
 Activity 1.1. Vertical Ocean Circulation NAME Reading: Ocean circulation is an important aspect of ocean health because it controls redistribution of both heat and nutrients. Humans indirectly affect ocean
Activity 1.1. Vertical Ocean Circulation NAME Reading: Ocean circulation is an important aspect of ocean health because it controls redistribution of both heat and nutrients. Humans indirectly affect ocean
Answer THREE questions, at least ONE question from EACH section.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Environmental Sciences Main Series Undergraduate Examination 2012-2013 CHEMICAL OCEANOGRAPHY ENV-2A45 Time allowed: 2 hours. Answer THREE questions, at least ONE question
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Environmental Sciences Main Series Undergraduate Examination 2012-2013 CHEMICAL OCEANOGRAPHY ENV-2A45 Time allowed: 2 hours. Answer THREE questions, at least ONE question
Supplementary Note 1 Trend in ecosystem drivers For the business-as-usual scenario, the annual maximum in SST increases by 0.31 C per decade (global
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 Supplementary Note 1 Trend in ecosystem drivers For the business-as-usual scenario, the annual maximum in SST
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 Supplementary Note 1 Trend in ecosystem drivers For the business-as-usual scenario, the annual maximum in SST
SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL VARIATIONS IN SURFACE ZOOPLANKTON BIOMASS DISTRIBUTION IN THE GULF OF AQABA, RED SEA
 SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL VARIATIONS IN SURFACE ZOOPLANKTON BIOMASS DISTRIBUTION IN THE GULF OF AQABA, RED SEA Tariq Al-Najjar Marine Science Station, P.O. Box 195, Aqaba, Jordan tnajjar65@hotmail.com (Received
SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL VARIATIONS IN SURFACE ZOOPLANKTON BIOMASS DISTRIBUTION IN THE GULF OF AQABA, RED SEA Tariq Al-Najjar Marine Science Station, P.O. Box 195, Aqaba, Jordan tnajjar65@hotmail.com (Received
MARINE SYSTEMS Lecture Dan Cogalniceanu Course content Overview of marine systems
 Department of Environmental Sciences and Policy MARINE SYSTEMS Lecture 1 2009 Dan Cogalniceanu Course content 1. Overview of marine systems 2. Goods and services provided 3. Human impact on marine systems
Department of Environmental Sciences and Policy MARINE SYSTEMS Lecture 1 2009 Dan Cogalniceanu Course content 1. Overview of marine systems 2. Goods and services provided 3. Human impact on marine systems
SUNLIGHT & OCEAN ZONATION
 PLANKTON, PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY, AND BIOGEOCHEMISTRY EPSS 15 Fall 2017 LAB #7 SUNLIGHT & OCEAN ZONATION Sunlight is critical to the distribution of oceanic life The base of the food chain (phytoplankton)
PLANKTON, PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY, AND BIOGEOCHEMISTRY EPSS 15 Fall 2017 LAB #7 SUNLIGHT & OCEAN ZONATION Sunlight is critical to the distribution of oceanic life The base of the food chain (phytoplankton)
Changes in Arctic Ocean Primary Production from Kevin R. Arrigo G. L. van Dijken
 Changes in Arctic Ocean Primary Production from 1998-2008 Kevin R. Arrigo G. L. van Dijken Department of Environmental Earth System Science Stanford University Background Circulation influenced by both
Changes in Arctic Ocean Primary Production from 1998-2008 Kevin R. Arrigo G. L. van Dijken Department of Environmental Earth System Science Stanford University Background Circulation influenced by both
Present and future ocean-atmosphere CO 2 fluxes, and EO measurement needs
 Present and future ocean-atmosphere CO 2 fluxes, and EO measurement needs Andy Watson, Ute Schuster, Jamie Shutler, Ian Ashton College of Life and Environmental Science, University of Exeter Parvadha Suntharalingam,
Present and future ocean-atmosphere CO 2 fluxes, and EO measurement needs Andy Watson, Ute Schuster, Jamie Shutler, Ian Ashton College of Life and Environmental Science, University of Exeter Parvadha Suntharalingam,
Subtropical Ocean Ecosystem. North Pacific Climate Variations
 Subtropical Ocean Ecosystem Structure Changes Forced by North Pacific Climate Variations Bob Bidigare Hawaii Institute tute of Marine Biology ogy University of Hawaii at Manoa Acknowledgements HOT Personnel
Subtropical Ocean Ecosystem Structure Changes Forced by North Pacific Climate Variations Bob Bidigare Hawaii Institute tute of Marine Biology ogy University of Hawaii at Manoa Acknowledgements HOT Personnel
The 20 th century carbon budget simulated with CCCma first generation earth system model (CanESM1)
 1/21 The 2 th century carbon budget simulated with CCCma first generation earth system model (CanESM1) Vivek K Arora, George J Boer, Charles L Curry, James R Christian, Kos Zahariev, Kenneth L Denman,
1/21 The 2 th century carbon budget simulated with CCCma first generation earth system model (CanESM1) Vivek K Arora, George J Boer, Charles L Curry, James R Christian, Kos Zahariev, Kenneth L Denman,
GEOSCIENCE 001 OCEANOGRAPHY LAB
 Names: Lab Section: each group of 2 turns in one lab GEOSCIENCE 001 OCEANOGRAPHY LAB This is a computer-based lab exercise in which we will use an incredible computer resource to visually explore a huge
Names: Lab Section: each group of 2 turns in one lab GEOSCIENCE 001 OCEANOGRAPHY LAB This is a computer-based lab exercise in which we will use an incredible computer resource to visually explore a huge
Nitrogen Cycling in the Sea
 Nitrogen Cycling in the Sea NH 4 + N0 2 N0 2 NH 4 + Outline Nitrogen species in marine watersdistributions and concentrations New, regenerated, and export production The processes: Assimilation, N 2 fixation,
Nitrogen Cycling in the Sea NH 4 + N0 2 N0 2 NH 4 + Outline Nitrogen species in marine watersdistributions and concentrations New, regenerated, and export production The processes: Assimilation, N 2 fixation,
Global CO 2 and Climate Change
 Global CO 2 and Climate Change A deeper look at the carbon dioxide cycle, greenhouse gases, and oceanic processes over the last 200 years OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 17 April 2018 Reading: Libes, Chapter
Global CO 2 and Climate Change A deeper look at the carbon dioxide cycle, greenhouse gases, and oceanic processes over the last 200 years OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 17 April 2018 Reading: Libes, Chapter
The Global Carbon Cycle
 The Global Carbon Cycle In a nutshell We are mining fossil CO 2 and titrating into the oceans, (buffered by acid-base chemistry) Much of the fossil CO 2 will remain in the atmosphere for thousands of years
The Global Carbon Cycle In a nutshell We are mining fossil CO 2 and titrating into the oceans, (buffered by acid-base chemistry) Much of the fossil CO 2 will remain in the atmosphere for thousands of years
Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability
 Why should we care about productivity? Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability Photosynthetic activity in oceans created current O 2 -rich atmosphere Plankton form ocean sediments & fossil
Why should we care about productivity? Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability Photosynthetic activity in oceans created current O 2 -rich atmosphere Plankton form ocean sediments & fossil
Climate Change & Ocean Acidification
 Climate Change & Ocean Acidification Scott Doney Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Thus human beings are now carrying out a large scale geophysical experiment Revelle and Suess, Tellus, 1957 Ice core
Climate Change & Ocean Acidification Scott Doney Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Thus human beings are now carrying out a large scale geophysical experiment Revelle and Suess, Tellus, 1957 Ice core
U.S. ECoS. U.S. Eastern Continental Shelf Carbon Budget: Modeling, Data Assimilation, and Analysis
 U.S. ECoS U.S. Eastern Continental Shelf Carbon Budget: Modeling, Data Assimilation, and Analysis A project of the NASA Earth System Enterprise Interdisciplinary Science Program E. Hofmann, M. Friedrichs,
U.S. ECoS U.S. Eastern Continental Shelf Carbon Budget: Modeling, Data Assimilation, and Analysis A project of the NASA Earth System Enterprise Interdisciplinary Science Program E. Hofmann, M. Friedrichs,
Environmental studies for the assessment of myctophid resources in the Arabian Sea
 Environmental studies for the assessment of myctophid resources in the Arabian Sea Submitted to Centre for Marine Living Resources and Ecology (CMLRE) Ministry of Earth Sciences Government of India Kochi
Environmental studies for the assessment of myctophid resources in the Arabian Sea Submitted to Centre for Marine Living Resources and Ecology (CMLRE) Ministry of Earth Sciences Government of India Kochi
Progress in Oceanography
 Progress in Oceanography 86 (2010) 302 315 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Progress in Oceanography journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pocean Preliminary forecasts of Pacific bigeye tuna
Progress in Oceanography 86 (2010) 302 315 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Progress in Oceanography journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/pocean Preliminary forecasts of Pacific bigeye tuna
11/9/2010. Stoichiometry of POM and DOM. DOC cycling via DO 14 C Williams, Oeschger, and Kinney; Nature v224 (1969)
 DOC cycling via DO 1 C Williams, Oeschger, and Kinney; Nature v22 (1969) UV photooxidation Radiocarbon in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans Peter M. Williams and Ellen Druffel; Nature 1987, JGR 1992 DIC
DOC cycling via DO 1 C Williams, Oeschger, and Kinney; Nature v22 (1969) UV photooxidation Radiocarbon in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans Peter M. Williams and Ellen Druffel; Nature 1987, JGR 1992 DIC
Southern Ocean food web research &
 Southern Ocean food web research & Southern Ocean Sentinel Andrew Constable Antarctic Climate & Ecosystems Cooperative Research Centre & Australian Antarctic Division Thanks to many involved in ACE, AAD,
Southern Ocean food web research & Southern Ocean Sentinel Andrew Constable Antarctic Climate & Ecosystems Cooperative Research Centre & Australian Antarctic Division Thanks to many involved in ACE, AAD,
LIMNOLOGY. Inland Water Ecosystems. JACOB KALFF McGill University. Prentice Hall. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458
 LIMNOLOGY Inland Water Ecosystems JACOB KALFF McGill University Prentice Hall Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 Contents CHAPTER 1 Inland Waters and Their Catchments: An Introduction and
LIMNOLOGY Inland Water Ecosystems JACOB KALFF McGill University Prentice Hall Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 Contents CHAPTER 1 Inland Waters and Their Catchments: An Introduction and
Life in Water. Chapter 3
 Life in Water Chapter 3 Outline Hydrologic Cycle Oceans Shallow Marine Waters Marine Shores Estuaries, Salt Marshes, and Mangrove Forests Rivers and Streams Lakes 2 The Hydrologic Cycle Over 71% of the
Life in Water Chapter 3 Outline Hydrologic Cycle Oceans Shallow Marine Waters Marine Shores Estuaries, Salt Marshes, and Mangrove Forests Rivers and Streams Lakes 2 The Hydrologic Cycle Over 71% of the
HELCOM Baltic Sea Action Plan in a warmer world
 HELCOM Baltic Sea Action Plan in a warmer world H.E. Markus Meier 1,2 1 Research Department, Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute 2 Department of Meteorology, Stockholm University E-mail:
HELCOM Baltic Sea Action Plan in a warmer world H.E. Markus Meier 1,2 1 Research Department, Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute 2 Department of Meteorology, Stockholm University E-mail:
Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary. Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP)
 Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP) Introduction: A key theme of the ongoing DCERP program is monitoring
Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP) Introduction: A key theme of the ongoing DCERP program is monitoring
Modeling climate change effects on Delta phytoplankton in CASCaDE II
 Modeling climate change effects on Delta phytoplankton in CASCaDE II Lisa Lucas, USGS Wim Kimmerer, SF State Univ. Hans Los, Deltares Image Courtesy Mick van der Wegen 1. Why do we care? 2. What do phytoplankton
Modeling climate change effects on Delta phytoplankton in CASCaDE II Lisa Lucas, USGS Wim Kimmerer, SF State Univ. Hans Los, Deltares Image Courtesy Mick van der Wegen 1. Why do we care? 2. What do phytoplankton
Chapter 55: Ecosystems
 Ch. 55 Warm-Up 1. Draw an energy pyramid and label the following trophic levels: Primary producer Primary consumer Secondary consumer Tertiary consumer 2. What is an example of an organism at each level
Ch. 55 Warm-Up 1. Draw an energy pyramid and label the following trophic levels: Primary producer Primary consumer Secondary consumer Tertiary consumer 2. What is an example of an organism at each level
Announcements. What are the effects of anthropogenic CO 2 on the ocean? 12/7/2017. UN Commitment to plastics in the ocean
 Announcements UN Commitment to plastics in the ocean http://www.bbc.com/news/scienceenvironment-42239895 Today: Quiz on paper by Lee et al. 2009 Climate change and OA Review for final exam (Tuesday 8 AM)
Announcements UN Commitment to plastics in the ocean http://www.bbc.com/news/scienceenvironment-42239895 Today: Quiz on paper by Lee et al. 2009 Climate change and OA Review for final exam (Tuesday 8 AM)
Integrated End-to-End and Fisheries Bio-Economic Modeling for Evaluating Ecosystem-Wide Effects of Human Pressures in the Baltic Sea
 Integrated End-to-End and Fisheries Bio-Economic Modeling for Evaluating Ecosystem-Wide Effects of Human Pressures in the Baltic Sea J. Rasmus Nielsen, Artur Palacz, Sieme Bossier, Francois Bastardie,
Integrated End-to-End and Fisheries Bio-Economic Modeling for Evaluating Ecosystem-Wide Effects of Human Pressures in the Baltic Sea J. Rasmus Nielsen, Artur Palacz, Sieme Bossier, Francois Bastardie,
Highlights of CO 2 Science Jorge Sarmiento
 Highlights of CO 2 Science Jorge Sarmiento I. Carbon budget update for 2000-2006 Sources: (1) Emissions from fossil fuel burning & cement production have surged (2) Estimates of land use change source
Highlights of CO 2 Science Jorge Sarmiento I. Carbon budget update for 2000-2006 Sources: (1) Emissions from fossil fuel burning & cement production have surged (2) Estimates of land use change source
Climate Change and Phenology in Narragansett Bay Phytoplankton. Introduction
 Sarah Blackstock OCG561: Biological Oceanography Susanne Menden-Deuer Research Project 3 December 2013 Climate Change and Phenology in Narragansett Bay Phytoplankton Introduction As time-series on plankton
Sarah Blackstock OCG561: Biological Oceanography Susanne Menden-Deuer Research Project 3 December 2013 Climate Change and Phenology in Narragansett Bay Phytoplankton Introduction As time-series on plankton
Biogeochemical Cycles
 Biogeochemical Cycles N/P O 2 3 1 2 CO 2 4 1) Biological cycling 2) Gas exchange 3) Global sources/sinks 4) Chemical reactions and circulation, of course. WF: Chap. 5: Biological Fundamentals 6: Carbonate
Biogeochemical Cycles N/P O 2 3 1 2 CO 2 4 1) Biological cycling 2) Gas exchange 3) Global sources/sinks 4) Chemical reactions and circulation, of course. WF: Chap. 5: Biological Fundamentals 6: Carbonate
Chapter VI. Primary and Secondary Production rate in the Arabian Sea. Using Remote Sensing. 6.1 Introduction Results and Discussion
 Primary and Secondary Production rate in the Arabian Sea Using Remote Sensing 6.1 Introduction 6.2. Results and Discussion 6.2.1 Primary production 6.2.2 Secondary production CHAPTER VI Primary and Secondary
Primary and Secondary Production rate in the Arabian Sea Using Remote Sensing 6.1 Introduction 6.2. Results and Discussion 6.2.1 Primary production 6.2.2 Secondary production CHAPTER VI Primary and Secondary
increase in mean winter air temperature since 1950 (Ducklow et al, 2007). The ocean
 Exploring the relationship between Chlorophyll a, Dissolved Inorganic Carbon, and Dissolved Oxygen in the Western Antarctic Peninsula Ecosystem. Katie Coupland December 3, 2013 Since the start of the industrial
Exploring the relationship between Chlorophyll a, Dissolved Inorganic Carbon, and Dissolved Oxygen in the Western Antarctic Peninsula Ecosystem. Katie Coupland December 3, 2013 Since the start of the industrial
Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Nutrients!
 Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Nutrients! Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Critical Depth Recycled Nutrients! Oxidized Nutrients! Detritus! Rest of Ocean Biological and Solubility Pumps New (Export) vs. Regenerated
Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Nutrients! Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Critical Depth Recycled Nutrients! Oxidized Nutrients! Detritus! Rest of Ocean Biological and Solubility Pumps New (Export) vs. Regenerated
