Testing Results for Lead-Free PWB s by the Massachusetts Lead-Free Electronics Research Consortium
|
|
|
- Sarah Craig
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Testing Results for Lead-Free PWB s by the Massachusetts Lead-Free Electronics Research Consortium Richard Anderson, andersor@tycoelectronics.com, M-A/COM Tyco Electronics, Lowell MA, Liz Harriman, harriman@turi.org, Massachusetts Toxics Use Reduction Institute (TURI). Donald Abbott, d-abbott1@ti.com, Texas Instruments, Attleboro, MA, Marie Kistler, kistlemd@apci.com, Air Products and Chemicals, Inc., David Pinsky, David_A_Pinsky@raytheon.com, Raytheon Company, Lexington, MA, Mark Quealy, mark.quealy@modicon.com; Schneider Electric; North Andover, MA,, Sammy Shina, (lead contact) sammy_shina@uml.edu, University of Massachusetts Lowell, Karen Walters, Kwaltersjobs@aol.com, Helena Pasquito Pasquith@typcoelectronics.com and George Wilkish, wilkishg@tycoelectronics.com; M-A/COM Tyco Electronics, Lowell MA Abstract The world-wide movement to phase out lead from electronic products presents many challenges for companies throughout the electronics supply chain. University of Massachusetts Lowell has brought together eight Massachusetts firms to collaborate on the manufacture and testing of lead-free printed wiring boards. The results of the first set of experiments showed that zero-defect soldering is achievable with lead-free materials. Test factors included: solder alloys (Sn/Ag/Cu, Sn/Ag, Sn/Bi), PWB surface finishes (OSP and ENIG), thermal profiles (soak and linear with various times above liquidus) and reflow environments (air and nitrogen). Following thermal cycling, the boards were visually inspected and the leads were pull tested. The results of pull testing indicated that there is no significant degradation of solder strength after 2000 hours of thermal cycling using the profile in Figure 1. In addition, all conditions examined in the lead free experiments exhibited better reliability (in the form of higher value lead pull strengths) than the leaded solder baseline A follow-on design of experiments stage was created and a second set of test PCBs with a wide variety of components and finishes were manufactured. The goal of this stage was to leverage new developments in the field and to further investigate conditions of various lead-free manufacturing processes. Three solder pastes based on the NEMI recommended Sn/Ag/Cu solder alloy were used with five commonly available surface finishes, and reflowed using either air or nitrogen. Visual inspection has been completed and reliability testing is underway. Reliability data will be available when completed. Introduction The world-wide movement to phase out lead from electronic products presents many challenges for companies throughout the electronics supply chain. Because lead is integral to the integrity and reliability of electronic products, it is necessary to make changes carefully, and with the full participation of all parts of the product supply chain. The University of Massachusetts Lowell and the Massachusetts Toxics Use Reduction
2 Institute have brought together several key companies in the Commonwealth to form a research consortium to investigate lead-free manufacturing. This paper provides some background on the drivers for lead-free electronics and the approach being taken in Massachusetts. The Massachusetts Lead-Free Research Consortium s testing program and results are then presented. The first phase of testing was completed in 2001 and the results are summarized. For the second phase of testing which is currently underway, the testing program and variable matrix will be described and visual test results discussed. Drivers for Change In January, 2003, The European Union published Directives 2002/96/EC on Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) and 2002/95/EC on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment (RoHS). These emerging directives have been the primary driver for global movement toward lead-free electronics. The RoHS prohibits products that contain lead to be sold in the EU after January, 2006, unless the use is specifically exempted. The second major influence has been the movement of electronics manufacturers, particularly Japanese companies, toward green products. JEIDA, the Japanese Electronics Industries Association, developed a lead-free roadmap in 1998, and many firms have set targets for elimination of lead in their products, and have selected lead-free products already on the market. In each case, suppliers must develop, test, and be able to ensure performance of lead-free components and assemblies for manufacturers of electronic products. The short timeframe for these changes requires a coordinated effort of all firms in the electronics supply chain, from manufacturers of basic materials and components, to assemblers and OEMs. In order to achieve the goal of an environmentally safer product life cycle, the supply chain also needs to include those that will close the materials loop the recyclers. The WEEE directive challenges electronics manufacturers to think in a fundamentally different way about their products and the materials they use, requiring both recycling at a product s end of life, and inclusion of recycled materials in new products. This, together with the required development of new materials that don t contain lead, cadmium, and other substances of concern, presents an opportunity for industry to design products that conserve resources and are safer for humans and the environment throughout their life cycle. Massachusetts Lead-Free Research Consortium The Massachusetts Toxics Use Reduction Act (TURA) program has a mission to assist companies in reducing or eliminating the use of toxic substances where possible, and in reducing the amount of toxic waste generated. TURA also has a goal to sustain, safeguard and promote the competitive advantage of Massachusetts businesses, large and small, while advancing innovation in toxic use reduction and management. These goals
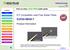
3 come together as we assist firms in meeting international materials restrictions on lead in electronic products. The Toxics Use Reduction Institute (TURI) at University of Massachusetts Lowell (UMass Lowell) provides training and information, and conducts research in innovative technologies in support of toxics use reduction. In 1999, as the movement toward leadfree emerged, TURI began supporting research at UMass Lowell to investigate the feasibility of alternative solders. As this work progressed under the leadership of Dr. Sammy Shina, it was clear that substituting such a basic material as tin-lead solder would require the collaboration of many parts of the supply chain. The Massachusetts Lead-Free Research Consortium was formed in 2000, consisting of at least one representative of each part of the supply chain. Members contribute time, materials, facilities, funding and expertise as they jointly develop and implement testing plans. Current consortium members are: M/A-COM/Tyco Electronics, Texas Instruments, Raytheon Company, Schneider Electric, BTU International, Air Products and Chemicals, Analog Devices, UMass Lowell and TURI. In addition to supporting the consortium, TURI periodically brings together firms from the electronics supply chain to exchange information, to communicate the latest technical and regulatory developments, and to report out on the consortium s research program (for summaries of workshops, presentations, and technical papers, see TURI s web site: Summary of First Round of Testing A preliminary round of testing compared 95.5Sn-3.8Ag-0.7Cu and 96.5Sn-3.5Ag with high, medium and low solids (residue) fluxes, ramp and soak versus linear ramp reflow profiles and a high versus low peak reflow oven temperature (250 vs. 230 C with 60 seconds above liquidus for the ramp and soak and 235 vs. 225 C with seconds above liquidus for the linear ramp profile). The Design of Experiments results showed that flux was the most critical factor for reducing visual defects with high solids content providing the most protection. The linear profile with the 235 C peak produced the fewest number of visual defects. Optimal results were obtained using these two conditions with the Sn-Ag-Cu solder alloy. It was also determined that the linear profile approach decreases the process window requiring tighter controls but used less energy and thus is more cost effective. The first round of testing examined the effects of different lead-free solders (95.5Sn- 3.8Ag-0.7Cu, 96.5Sn-3.5Ag, and 57Sn-43Bi) and their interactions with board surface finish (ENIG - Electroless Nickel-Immersion Gold and OSP Organic Solder Preservative), atmosphere (air versus nitrogen), reflow profile (ramp and soak versus linear ramp), and time above liquidus (TAL) of (60, seconds) on visual defects and on solder joint pull-test strength as reflowed and after thermal cycling. Thermal cycling used the profile shown in figure 1. 11
4 120 Ram p 10 C/m in Dwell tim e(20 m in.) Temperature in C Tim e in m inutes Figure 1. Thermal Profile for Reliability Testing of Lead free Soldering A tin-lead eutectic control set of PCBs was run on OSP and ENIG finished boards in both air and nitrogen to provide baseline data for comparison with lead free reliability results obtained from pull tests. Several of the combinations yielded visual defect free results. Table 1 shows these. Table 1. Conditions for Defect free and lead fee soldering materials and processes..paste S. Finish TAL Soak Nitrogen Sn/Ag/Cu ENIG 90sec No yes Sn/Ag/Cu ENIG 120sec Yes yes Sn/Ag ENIG 60sec Yes yes Sn/Ag ENIG 90sec No yes There were no solder joint failures throughout the entire 2000 thermal cycles test. Pull tests resulted in the following observations: Solder paste composition was the most significant factor with Sn-Ag-Cu yielding the highest strengths and Sn-Bi the lowest. OSP PWB finish yielded slightly higher pull strengths, perhaps due to gold-tin intermetallic formation. Slightly higher strengths were achieved with the linear ramp profile. Strength increased after thermal cycling, as indicated by conventional wisdom, due to changes in the inter-metallic composition of the copper migrating through the alloy towards the components.
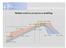
5 Figure 2 summarizes the pull test results with respect to the minimum pull strengths observed SnAgCu SnBi SnAg OSP Air ENIG OSP N Figure 2. Minimum Pull strengths (Newtons) versus factors showing before (solid line) and after cycling (dashed line). Experiment Matrix for Second Phase of Pb-free Testing. Experimental Design Matrix A designed experiment was developed with the following variables: 1. PWB Finishes Five Treatments Solder Mask Over Bare Copper with Hot Air Solder Leveling (SMOBC/HASL), Matte Finish Tin (Sn) Electroplate, Immersion Silver (Ag), Organic Solder Preservative (OSP), and Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG). 2. Reflow Atmospheres Two Treatments Air and Nitrogen. 3. Solder Pastes Three Treatments all with the same alloy composition 95.5Sn- 3.8 Ag-0.7Cu (NEMI recommended) from three different vendors, all incorporating no-clean fluxes. 4. Component Lead Finishes Four Treatments matte Sn plating, Tin/Silver/Copper, Nickel/Palladium/Gold, and Nickel/Gold. 5. Sn-Pb eutectic solder PWB using the solder treatments as control PWBs. The Design matrix is shown in Table 2. N Soak Linear Linear Pb OSP Pb ENIG
6 Table 2. 2 nd Phase Experimental Design Matrix Experimentation Matrix (Two (2) Circuit Boards per Trial) PWB PWB Finish Solder paste *Reflow Atmosphere Component Finish 1 SMOBC/HASL A Air Pb- free 2 SMOBC/HASL A Nitrogen Pb- free 3 SMOBC/HASL B Air Pb- free 4 SMOBC/HASL B Nitrogen Pb- free 5 SMOBC/HASL C Air Pb- free 6 SMOBC/HASL C Nitrogen Pb- free 7 SMOBC/HASL Standard Sn-Pb Air Sn-Pb Leads 8 OSP A Air Pb- free 9 OSP A Nitrogen Pb- free 10 OSP B Air Pb- free 11 OSP B Nitrogen Pb- free 12 OSP C Air Pb- free 13 OSP C Nitrogen Pb- free 14 OSP Standard Sn-Pb Air Sn-Pb Leads 15 ENIG A Air Pb- free 16 ENIG A Nitrogen Pb- free 17 ENIG B Air Pb- free 18 ENIG B Nitrogen Pb- free 19 ENIG C Air Pb- free 20 ENIG C Nitrogen Pb- free 21 ENIG Standard Sn-Pb Air Sn-Pb Leads 22 Matte Sn A Air Pb- free 23 Matte Sn A Nitrogen Pb- free 24 Matte Sn B Air Pb- free 25 Matte Sn B Nitrogen Pb- free 26 Matte Sn C Air Pb- free 27 Matte Sn C Nitrogen Pb- free 28 Matte Sn Standard Sn-Pb Air Sn-Pb Leads 29 Ag A Air Pb- free 30 Ag A Nitrogen Pb- free 31 Ag B Air Pb- free 32 Ag B Nitrogen Pb- free 33 Ag C Air Pb- free 34 Ag C Nitrogen Pb- free 35 Ag Standard Sn-Pb Air Sn-Pb Leads *Nitrogen was supplied by Air Products and Chemicals and contained 50 ppm Oxygen for these experiments. As seen, all test PWBs were run versus the standard 63Sn-37Pb eutectic, no-clean solder as a control. Package types included several SOICs, a FPQFP, an MLP, a BGA, a ceramic SOIC, and chip capacitors and resistors. The test PWB was laid out at M/A-COM taking into account daisy chain resistance test capabilities in some of the parts and fabricated by Sanmina-SCI with the five different finishes. Pastes were obtained from three vendors and a reflow profile was developed based on the manufacturers product data sheets. A reflow profile board was populated with parts and three K-probe thermocouples (TC) were attached to the surface. One TC was attached at the leading edge of the PWB, one at the lead attach area of a large QFP and one near the trailing edge. The thermocouples were connected to an industry standard data logger. The thermal readings were downloaded to the data collector software for comparison to the manufacturer recommended profiles. All three manufacturers recommended a 'ramp to spike' curve. Several runs were performed to ensure consistent performance. The reflow profile used for all three Pb-free solders is shown in Figure 3.
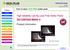
7 T ( C) t (sec) Figure 3. Reflow Profile for SMT Board Assembly Solder paste prints were made using a thick stainless steel laser cut, electropolished stencil. Ten percent aperture reductions were used on the fine pitch devices. PWBs were assembled at Schneider Electric on their assembly line consisting of an MPM AP-25 screen printer, Siemens S20 and F5 placement equipment and a BTU Pyramax 98N Reflow Oven with Air and Nitrogen capability supplied by BTU International for this experiment. The Schneider plant maintains a Relative Humidity (RH) level between 35-40%. After reflow, boards were packaged in ESD bags and taken to M/A-COM where two University of Massachusetts Lowell senior students visually inspected the solder joints based on training by a certified IPC inspector / trainer. Inspection criteria were established as follows: Total Defects, Cold Solder joints, Non-wetting, Solder Balls, Dewetting, Bridging, Pinholes, Shiny Appearance, Smooth Appearance, and Flux Residue. X-ray radiography of the BGA solder joints was also performed. Initial inspection data has been tabulated and statistically analyzed by University of Massachusetts Lowell and Air Products. To date Board Finish, Atmosphere, and paste (A, B, C) have been analyzed. Work is in progress on lead finish and component type. Results and Discussion to Date - Key Issues/Observations for Lead-Free Reliability Results - Assembly Process The major difficulties encountered in assembly were with stencil printing and placement system vision. In spite of using print parameters close to those in the application notes supplied for the three pastes, paste A had a tendency to adhere to the sides of the stencil openings. This resulted in scant prints on some of the fine pitch apertures. Paste B clogged the stencil necessitating cleaning after every four or five prints. Paste C performed as expected with little difficulty. All three pastes exhibited good tack or component holding qualities during and after placement. Vision problems were associated with the Sn-Pb version of the BGA. The difference in appearance (reflectivity) of the Sn-Pb spheres caused the vision system (programmed for the Pb-free
8 spheres) to reject many of the Sn-Pb BGAs. These had to be placed by hand which may affect some results. Visual Defects - Statistics Eight main categories of common defects were selected and all boards were inspected. Those defects observed were photographed and recorded into a spreadsheet. After statistical analysis the following significant effects were determined (all shown by the letter Y and a number indicating the rank starting with 1 being the most significant) are shown in Table 3 including interactions of various factors. Individual factor average defect analysis is shown in Tables 4 6 as well as an analysis of visual defect types. Table 3: Statistically Significant Effects Summary Main Effects 2 Factor Interactions 3 Factor Interaction Property Finish Paste Atmosphere Finish*Paste Finish*Atmosphere Paste*Atmosphere Finish*Paste*Atmosphere Total Defects Y - 3 Y - 2 Y - 1 N N Y N Cold Solder Joining Y - 3 Y - 2 Y - 1 N N Y N Nonwetting N Y - 2 Y - 1 N N N N Solder Balls Y N N N N N N Dewetting N N N N N N N Bridging Y N N N N N N Pin/Blow Holes* N N N N N N N Shiny** Y - 1 Y - 2 N N N N N Residue** N Y - 1 Y - 2 N N N N Smooth** N N N N N N N Table 4: Atmosphere Results Summary Atmosphere Property Air Nitrogen Total Defects Cold Solder Joining Nonwetting Solder Balls Dewetting Bridging Pin/Blow Holes* Shiny** Residue** Smooth** Nitrogen reflow atmosphere was shown to be significant in total defects, cold solder joints, non-wetting and residue generated. Table 5: Pb-Free Paste Results Summary Pb-Free Paste Property B A C Total Defects Cold Solder Joining Nonwetting Solder Balls Dewetting Bridging Pin/Blow Holes* Shiny** Residue** Smooth** A statistically significant Paste effect means that one or more of the pastes studied differ significantly from each other in terms of the type and / or number of defects generated. Significance is noted with bold numbers
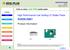
9 Table 6: Board Surface Finish Results Summary Finish Property ENIG Imm. AG Matte Sn OSP SMOBC/HASL Total Defects Cold Solder Joining Nonwetting Solder Balls Dewetting Bridging Pin/Blow Holes* Shiny** Residue** Smooth** A statistically significant Board Finish effect means that one or more of the surface finishes studied differ significantly from each other. Significance is noted with bold numbers Legend for all Tables * Pin/Blow Holes: No defects of this type were observed ** Qualitatively measured properties Statistically significant effects are bolded and in blue. As seen in Table 3, the two major defects observed were cold solder joints and nonwetting. All major variables impacted these two defects and a significant interaction effect between paste and atmosphere on cold solder joints was also observed. Solder ball defects were also impacted by board finish. Some variables also had a significant effect on the solder joint appearance with respect to shininess and flux residue. Since Pb-free solder is different in appearance, these were considered important for visual inspection criteria as well. Figure 3 shows the main visual defect phenomenon observed. This appears to be a function of flux, reflow atmosphere, and paste volume. The small volume of paste and flux resulted in the flux being spent prior to reaching the reflow temperature. These images are of a very fine pitch print with paste A that exhibited some problems with adherence of the paste to the side-walls of the stencil, especially in small apertures such as these. Figure 4 shows the same sample on a larger pitch part where the paste / flux volume did not dry out or become spent prior to reflow. Figure 3. Left: Paste A reflowed in Air Right: Paste A in Nitrogen - fine pitch print, Ni-Pd-Au lead SMOBC-HASL.
10 Figure 4. Paste A in Air, SOIC leads on the same board. Left: lead finish plated tin - Right: Ni-Pd-Au plated leads SMOBC-HASL Visual inspection, of course, does not tell the entire story. It is a good method of finding many defects but does not reveal weak solder joints, large internal voids, or many BGA solder joint defects. Moreover, the correlation between appearance and reliability has not been established for Pb-free solders, in the way that it has for Sn63 type solders. This correlation will be explored during the continuation of this study. HASL OSP ENIG Sn Ag A B C AIR Nitrogen Figure 5. Defect Density versus Independent Variables Based on Figure 5, ENIG, Paste B, and Nitrogen would be considered winners with Ag a close second for PCB finish. Within the confines of effect of these variables on visual defects / appearance issues this is correct. However, manufacturing cost issues were not addressed as part of the overall analysis. Nitrogen does cost more than using ambient Air so defect costs may have to be offset by Nitrogen costs. Electroless nickel used in ENIG has often been associated with black pad solderability defects (not an issue in this study) that may occur in some PWB assemblies. As noted above, paste B clogged the stencil requiring cleaning after every four or five prints and thus could have a large effect on throughput and other line costs. As shown in Figure 3 above, paste A clung to the aperture walls during printing resulting in scant prints on fine pitch pads. The flux tended to flow during reflow ramp and soak. Therefore, it was not able to prevent the paste spheres from re-oxidizing before reflow with an inappropriate volume of paste. The paste under the lead did wet and flow, as did areas with more paste volume. Perhaps an experiment to develop a better stencil print
11 would improve this result. The other alternative, Nitrogen, is more forgiving so this paste may be fine for larger pitch or when using Nitrogen for a reflow atmosphere. For Figure 5, paste C had more defects, mainly in Air, but also gave a good print nearly every board. Further experiments may improve performance for all pastes, C, B, and A. One must also consider that these pastes are not necessarily fully developed with good histories as Pb-free processing itself is still in its infancy. Total Defect Analysis Results Analysis provided by Tom Bzik of the Statistical Science Group and Air Products and Chemicals, Inc. Table 7 - Statistical Analysis Total Defects ANOVA for 0.35 Power Transformed Total Defect Data The GLM Procedure Dependent Variable: Total Defect Sum of Source DF Squares Mean Square F Value Pr > F Model <.0001 Error Corrected Total R-Square Coeff Var Root MSE TD Mean Source DF Type III SS Mean Square F Value Pr > F Board Finish Paste <.0001 Atmosphere <.0001 Finish*Paste Finish*Atmosphere Paste*Atmosphere <.0001 Finish*Paste*Atmosphere As seen above, the ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) is significant for the overall experiment and for the variables highlighted with probabilities Pr less then.05. Ryan-Einot-Gabriel-Welsch Multiple Range Test for Total Defects (Board Finish) Means with the same REGWQ Grouping letter (A, B) are not significantly different. REGWQ Groupings Mean N Finish A SMOBC/HASL B OSP B B Matte Sn B B Imm. AG B B ENIG
12 Interpretation: The PCB Finish level SMOBC/HASL significantly differs from all other finishes. No other finishes were found to be statistically different from one another at the 0.05 level. Ryan-Einot-Gabriel-Welsch Multiple Range Test for Total Defects (Paste) Means with the same REGWQ Grouping letter (A, B, ) are not significantly different. REGWQ Grouping Mean N Paste A A Pb-Free B C Pb-Free C B Pb-Free Interpretation: All Pastes were found to differ significantly from all other pastes. B Pb- Free performed best. Ryan-Einot-Gabriel-Welsch Multiple Range Test for Total Defects (Atmosphere) Means with the same REGWQ Grouping letter (A, B, ) are not significantly different. REGWQ Grouping Mean N Atmosphere A Air B Nitrogen Interpretation: Nitrogen preformed significantly better than Air. Ryan-Einot-Gabriel-Welsch Multiple Range Test for Total Defects (Paste x Atmosphere Interaction) Means with the same REGWQ Grouping letter (A, B) are not significantly different. REGWQ Grouping Mean N Paste x Atmosphere Interaction A A Pb-Free with Air B C Pb-Free with Air C B Pb-Free with Air C C B Pb-Free with Nitrogen C C A Pb-Free with Nitrogen C C C Pb-Free with Nitrogen Interpretation: The A Pb-Free, Air combination was significantly worse than all other combinations. The C Pb-Free, Air combination was significantly worse than all other remaining combinations. The bottom four combinations could not be told statistically apart from each other within the limitations of the current study.
13 Only in the case of solder paste B; it was shown that there is no significant difference between the use of Air or Nitrogen. However, as noted earlier this paste exhibited certain process issues relating to the cost of more frequently cleaning the stencil in the production process. Part of this effort is to develop inspection criteria for Pb-free solder joints. Two items inspected for were shiny appearance and flux residue. Like other effects these may bear on each other. Flux residue is often glossy and may cause a joint to look better than a dry joint. This may be further confused with Air versus Nitrogen, as a joint with residue may have less of a tendency to oxidize while cooling than an unprotected surface. There is considerable work to be done in terms of mechanical properties (lead pull, ball and chip shear), joint x-rays for voids and BGA flaws, and stress testing via thermal cycling (0 to 100 C) followed by more mechanical testing. Further analysis on lead finishes also is in progress and requires this data. Conclusions to Date We have shown the effects of atmosphere, paste selection, and surface finish on visual appearance defects. While Nitrogen and paste B yielded the fewest defects and SMOBC HASL was significantly worse as a surface finish, the assembly process was not optimized for any of the variable options. Further, throughput and cost can be significant issues that may override some of these results. Other data to be taken needs to be correlated with these findings to further clarify the effects of these variables on solder joint reliability and yield.. These data show it is possible to obtain visually acceptable solder joints using a variety of board finishes, lead finishes, paste formulations and Air/Nitrogen combinations. Visual inspection is often the only means of defect detection other than circuit testing, and the two often verify one another thus indicating a good Pbfree reflow process with high yield can be achieved. The TURI Lead-Free Consortium has demonstrated that Pb-Free SMT processing is feasible and can result in robust solder joints with a reasonable degree of experimentation on the process parameters, thus enabling Pb-free, environmentally responsible circuit assembly. There is considerable work to be done in terms of mechanical properties (lead pull, ball and chip shear), joint x-rays for voids and BGA flaws, and stress testing via thermal cycling (0 to 100 C) followed by more mechanical testing. Further analysis on lead finishes also is in progress and requires this data. The final report will present processing Considerations to ensure good reflow and assembly. Acknowledgements: The authors wish to acknowledge the following persons and organizations for their contributions to this effort: - Richard McCann and his company, Analog Devices of Wilmington, MA. For their contributions to the consortium and providing of Pb-free components. - John Pessia Tyco Electronics M/A-COM for laying out the test PWB and sharing his excellent knowledge in creating a diverse test vehicle for the Pb-free project.
14 - University of Massachusetts Lowell students Pat Retelle and Joey Pang for performing the visual tests under the guidance of Helena Pasquito. - Santos Alicea, Manufacturing Engineer, Dawn Gilbert and Tai Nguyen, Documentation and Programming, Schneider Electric for providing operational assistance to the consortium team. - BTU International of North Billerica, MA for providing the reflow oven and Rob DiMatteo and Fred DiMock for technical support and discussions. - Tom Bzik of the Statistical Science Group, Air Products and Chemicals, Inc., for statistical analysis and discussions. References and Consortium Publications 1. Lead Free Electronics Workshop, hosted by Lucent technologies, Merrimack Valley Works, North Andover. MA, Tuesday April 13, TURI continuing education conference, TUR in Massachusetts: the Next Generation on Tuesday April 25 th 2000, Session, C2, the Lead Free electronics, at the Best Western Royal Plaza and Trade Center, Marlborough, MA. 3. State of Massachusetts Legislative committee on education policy, UMASS President Bulger s Office, May 4 th, IMAPS New England, 27 th annual symposium and exhibition, May 2000, Holiday Inn Conference Center, Boxborough, MA, session F, Surface Mount Technology. 5. CEAM /TURI Colloquy on University Research in Sustainable Technologies Program (URST) at UMass Lowell, June nd Workshop on Lead-Free Electronics, Technical Issues and Challenges in the Transition To Lead-Free Technologies, Thursday, June 29, 2000, at BTU International North Billerica, Massachusetts 7. Consortium authors, Design Of Experiments For Lead Free Materials, Surface Finishes And Manufacturing Processes Of Printed Wiring Boards, published by the SMTA International Conference at Rosemount trade center, Chicago, IL, September Consortium authors, Design Of Experiments For Lead Free Materials, Surface Finishes And Manufacturing Processes Of Printed Wiring Boards, published by the Chinese Electronics Association Journal 9. Consortium authors, Selecting Material and Process Parameters for Lead Free SMT Soldering Using Design of Experiments Techniques, Apex Conference, January 2001, San Diego, CA, 10. Consortium authors, Reliability Testing Techniques For Lead Free Soldering Of SMT Technology, ETRONIX Conference, Anaheim, CA, March Process and Material Selection for zero defects and superior adhesion Lead Free SMT soldering, SMTA International Conference, Chicago, IL September Shina, S., Six Sigma for Electronics Design and Manufacturing, McGraw-Hill, NY, 2002.
Testing and Analysis of Surface Mounted Lead Free Soldering Materials and Processes
 Testing and Analysis of Surface Mounted Lead Free Soldering Materials and Processes 1 Abstract The Massachusetts Toxics Use Reduction Institute (TURI) has sponsored a consortium of Massachusetts based
Testing and Analysis of Surface Mounted Lead Free Soldering Materials and Processes 1 Abstract The Massachusetts Toxics Use Reduction Institute (TURI) has sponsored a consortium of Massachusetts based
A Comparative Analysis of Lead Free Materials and Processes Using Design of Experiments Techniques
 A Comparative Analysis of Lead Free Materials and Processes Using Design of Experiments Techniques Sammy Shina, Sammy_shina@uml.edu University of Massachusetts Lowell Liz Harriman, harriman@turi.org, Todd
A Comparative Analysis of Lead Free Materials and Processes Using Design of Experiments Techniques Sammy Shina, Sammy_shina@uml.edu University of Massachusetts Lowell Liz Harriman, harriman@turi.org, Todd
LEAD FREE ALLOY DEVELOPMENT
 LEAD FREE ALLOY DEVELOPMENT Karl F. Seelig, VP of Technology AIM Cranston, RI. USA. kseelig@aimsolder.com Abstract. When lead-free solders were first introduced to the electronics industry in the early
LEAD FREE ALLOY DEVELOPMENT Karl F. Seelig, VP of Technology AIM Cranston, RI. USA. kseelig@aimsolder.com Abstract. When lead-free solders were first introduced to the electronics industry in the early
A Successful Industry Collaboration Model to Achieve Toxics Use Reduction
 A Successful Industry Collaboration Model to Achieve Toxics Use Reduction Greg Morose Toxics Use Reduction Institute University of Massachusetts Lowell November 4, 2009 1 Lead in Electronics The printed
A Successful Industry Collaboration Model to Achieve Toxics Use Reduction Greg Morose Toxics Use Reduction Institute University of Massachusetts Lowell November 4, 2009 1 Lead in Electronics The printed
Welcome to SMTA Brazil Chapter Brook Sandy-Smith Dr. Ron Lasky Tim Jensen
 Welcome to SMTA Brazil Chapter 2013 Presented by Authors Ivan Castellanos Edward Briggs Brook Sandy-Smith Dr. Ron Lasky Tim Jensen Advantages / Concerns HP testing Mechanical properties New work Area ratio
Welcome to SMTA Brazil Chapter 2013 Presented by Authors Ivan Castellanos Edward Briggs Brook Sandy-Smith Dr. Ron Lasky Tim Jensen Advantages / Concerns HP testing Mechanical properties New work Area ratio
Optimizing Immersion Silver Chemistries For Copper
 Optimizing Immersion Silver Chemistries For Copper Ms Dagmara Charyk, Mr. Tom Tyson, Mr. Eric Stafstrom, Dr. Ron Morrissey, Technic Inc Cranston RI Abstract: Immersion silver chemistry has been promoted
Optimizing Immersion Silver Chemistries For Copper Ms Dagmara Charyk, Mr. Tom Tyson, Mr. Eric Stafstrom, Dr. Ron Morrissey, Technic Inc Cranston RI Abstract: Immersion silver chemistry has been promoted
Reliability of Lead-Free Solder Connections for Area-Array Packages
 Presented at IPC SMEMA Council APEX SM 2001 For additional information, please email marketing@amkor.com Reliability of Lead-Free Solder Connections for Area-Array Packages Ahmer Syed Amkor Technology,
Presented at IPC SMEMA Council APEX SM 2001 For additional information, please email marketing@amkor.com Reliability of Lead-Free Solder Connections for Area-Array Packages Ahmer Syed Amkor Technology,
Optimizing Immersion Silver Chemistries For Copper
 Optimizing Immersion Silver Chemistries For Copper Ms Dagmara Charyk, Mr. Tom Tyson, Mr. Eric Stafstrom, Dr. Ron Morrissey, Technic Inc Cranston RI Abstract: Immersion silver chemistry has been promoted
Optimizing Immersion Silver Chemistries For Copper Ms Dagmara Charyk, Mr. Tom Tyson, Mr. Eric Stafstrom, Dr. Ron Morrissey, Technic Inc Cranston RI Abstract: Immersion silver chemistry has been promoted
Lead Free Surface Mount Technology. Ian Wilding BSc Senior Applications Engineer Henkel Technologies
 Lead Free Surface Mount Technology Ian Wilding BSc Senior Applications Engineer Henkel Technologies Overview of the Presentation First contact: Impact on the production operator Packaging Labelling Impact
Lead Free Surface Mount Technology Ian Wilding BSc Senior Applications Engineer Henkel Technologies Overview of the Presentation First contact: Impact on the production operator Packaging Labelling Impact
Lead Free Solder for Flip Chip
 Lead Free Solder for Flip Chip Zhenwei Hou & R. Wayne Johnson Laboratory for Electronics Assembly & Packaging Auburn University 162 Broun Hall, ECE Dept. Auburn, AL 36489 USA 334-844-1880 johnson@eng.auburn.edu
Lead Free Solder for Flip Chip Zhenwei Hou & R. Wayne Johnson Laboratory for Electronics Assembly & Packaging Auburn University 162 Broun Hall, ECE Dept. Auburn, AL 36489 USA 334-844-1880 johnson@eng.auburn.edu
Becoming Lead Free. Automotive Electronics. Antonio Aires Soldering Technical Specialist Visteon Corporation - Palmela Plant
 Automotive Electronics Becoming Lead Free Antonio Aires Soldering Technical Specialist Visteon Corporation - Palmela Plant 1 Agenda 1. Leadfree Electronics Drivers 2. Requirements 3. Areas of Impact 4.
Automotive Electronics Becoming Lead Free Antonio Aires Soldering Technical Specialist Visteon Corporation - Palmela Plant 1 Agenda 1. Leadfree Electronics Drivers 2. Requirements 3. Areas of Impact 4.
ALPHA OM-5100 FINE PITCH SOLDER PASTE
 SM 797-7 ALPHA OM-5100 FINE PITCH SOLDER PASTE DESCRIPTION Cookson Electronics Assembly Material s ALPHA OM-5100, is a low residue, no-clean solder paste designed to maximize SMT line yields. The flux
SM 797-7 ALPHA OM-5100 FINE PITCH SOLDER PASTE DESCRIPTION Cookson Electronics Assembly Material s ALPHA OM-5100, is a low residue, no-clean solder paste designed to maximize SMT line yields. The flux
Minimizing Voiding. Cristian Tudor Applications Engineer Eastern Europe
 Minimizing Voiding Cristian Tudor Applications Engineer Eastern Europe ctudor@indium.com INDIUM CORPORATION 1 Indium Corporation s Business We develop, manufacture, market and support solders, electronics
Minimizing Voiding Cristian Tudor Applications Engineer Eastern Europe ctudor@indium.com INDIUM CORPORATION 1 Indium Corporation s Business We develop, manufacture, market and support solders, electronics
S3X58-M ICT Compatible Lead Free Solder Paste. Product Information. Koki no-clean LEAD FREE solder paste. Contents.
 Koki no-clean LEAD FREE solder paste www.ko-ki.co.jp #53002 Revised on Mar. 3, 2015 ICT Compatible Lead Free Solder Paste Product Information Conventional Product Picture of ICT Checker Probe The product
Koki no-clean LEAD FREE solder paste www.ko-ki.co.jp #53002 Revised on Mar. 3, 2015 ICT Compatible Lead Free Solder Paste Product Information Conventional Product Picture of ICT Checker Probe The product
Lead- free Alloys for Wave and SMT Assembly: Assembly with Two Alloys
 1 Lead- free Alloys for Wave and SMT Assembly: Assembly with Two Alloys Abstract Peter Biocca MBO Solder Inc. Allen, Texas 2002 Research on lead-free alternatives began over a decade ago. Starting primarily
1 Lead- free Alloys for Wave and SMT Assembly: Assembly with Two Alloys Abstract Peter Biocca MBO Solder Inc. Allen, Texas 2002 Research on lead-free alternatives began over a decade ago. Starting primarily
contaminated, or if the location of the assembly house is well above sea level.
 VAPOR PHASE REFLOW S EFFECT ON SOLDER PASTE RESIDUE SURFACE INSULATION RESISTANCE Karen Tellefsen. Mitch Holtzer, Corne Hoppenbrouwers Alpha Assembly Solutions South Plainfield, NJ, USA Roald Gontrum SmartTech
VAPOR PHASE REFLOW S EFFECT ON SOLDER PASTE RESIDUE SURFACE INSULATION RESISTANCE Karen Tellefsen. Mitch Holtzer, Corne Hoppenbrouwers Alpha Assembly Solutions South Plainfield, NJ, USA Roald Gontrum SmartTech
T E C H N I C A L B U L L E T I N
 T E C H N I C A L B U L L E T I N SM1193 ALPHA CVP-390 SAC305- HIGH PERFORMANCE LEAD-FREE ALLOY SOLDER PASTE FOR AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS DESCRIPTION CVP-390 SAC305 solder paste has been developed to provide
T E C H N I C A L B U L L E T I N SM1193 ALPHA CVP-390 SAC305- HIGH PERFORMANCE LEAD-FREE ALLOY SOLDER PASTE FOR AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS DESCRIPTION CVP-390 SAC305 solder paste has been developed to provide
Low-Silver BGA Assembly Phase II Reliability Assessment Fifth Report: Preliminary Thermal Cycling Results
 Low-Silver BGA Assembly Phase II Reliability Assessment Fifth Report: Preliminary Thermal Cycling Results Gregory Henshall 1 Michael Fehrenbach 2 Hewlett-Packard Co. 1 Palo Alto, CA USA 2 Houston, TX USA
Low-Silver BGA Assembly Phase II Reliability Assessment Fifth Report: Preliminary Thermal Cycling Results Gregory Henshall 1 Michael Fehrenbach 2 Hewlett-Packard Co. 1 Palo Alto, CA USA 2 Houston, TX USA
Reliability Assessment of No-clean and Water-soluble Solder Pastes Part II
 As originally published in the IPC APEX EXPO Conference Proceedings. Reliability Assessment of No-clean and Water-soluble Solder Pastes Part II Emmanuelle Guéné, Steven Teh INVENTEC Performance Chemicals
As originally published in the IPC APEX EXPO Conference Proceedings. Reliability Assessment of No-clean and Water-soluble Solder Pastes Part II Emmanuelle Guéné, Steven Teh INVENTEC Performance Chemicals
WS488 WATER SOLUBLE SOLDER PASTE
 WS488 WATER SOLUBLE SOLDER PASTE FEATURES Excellent Wetting Extended Cleaning Window Superior Slump Resistance 8 Hour+ Stencil Life Wash With Water Alone Low Foaming DESCRIPTION AIM s WS488 water soluble
WS488 WATER SOLUBLE SOLDER PASTE FEATURES Excellent Wetting Extended Cleaning Window Superior Slump Resistance 8 Hour+ Stencil Life Wash With Water Alone Low Foaming DESCRIPTION AIM s WS488 water soluble
Effect of Process Variations on Solder Joint Reliability for Nickel-based Surface Finishes
 Effect of Process Variations on Solder Joint Reliability for Nickel-based Surface Finishes Hugh Roberts Atotech USA Inc., Rock Hill, SC, USA Sven Lamprecht, Gustavo Ramos and Christian Sebald Atotech Deutschland
Effect of Process Variations on Solder Joint Reliability for Nickel-based Surface Finishes Hugh Roberts Atotech USA Inc., Rock Hill, SC, USA Sven Lamprecht, Gustavo Ramos and Christian Sebald Atotech Deutschland
PWB Dielectric Substrates for Lead-Free Electronics Manufacturing
 PWB Dielectric Substrates for Lead-Free Electronics Manufacturing Douglas Leys and Steven P. Schaefer* Park Electrochemical Corp. Anaheim, CA *Lake Success, NY Abstract In order to safely accommodate the
PWB Dielectric Substrates for Lead-Free Electronics Manufacturing Douglas Leys and Steven P. Schaefer* Park Electrochemical Corp. Anaheim, CA *Lake Success, NY Abstract In order to safely accommodate the
Composition/wt% Bal SA2 (SABI) Bal SA3 (SABI + Cu) Bal
 Improving Thermal Cycle and Mechanical Drop Impact Resistance of a Lead-free Tin-Silver-Bismuth-Indium Solder Alloy with Minor Doping of Copper Additive Takehiro Wada 1, Seiji Tsuchiya 1, Shantanu Joshi
Improving Thermal Cycle and Mechanical Drop Impact Resistance of a Lead-free Tin-Silver-Bismuth-Indium Solder Alloy with Minor Doping of Copper Additive Takehiro Wada 1, Seiji Tsuchiya 1, Shantanu Joshi
MARCH National Physical Laboratory Hampton Road Teddington Middlesex United Kingdom TW11 0LW
 NPL REPORT DEPC-MPR 044 Measuring the Impact of Land Size and Solder Joint Volume on Lead-free Solder Joint Reliability M Wickham, L Zou, M Dusek and C P Hunt NOT RESTRICTED MARCH 2006 National Physical
NPL REPORT DEPC-MPR 044 Measuring the Impact of Land Size and Solder Joint Volume on Lead-free Solder Joint Reliability M Wickham, L Zou, M Dusek and C P Hunt NOT RESTRICTED MARCH 2006 National Physical
Henkel Pb-Free Soldering Technology
 Transitioning to a Pb-free Process Dr. Brian J. Toleno Americas Application Engineering Team Leader brian.toleno@us.henkel.com Henkel Technologies Marketplace - Alloy Selection Japan still a range of materials
Transitioning to a Pb-free Process Dr. Brian J. Toleno Americas Application Engineering Team Leader brian.toleno@us.henkel.com Henkel Technologies Marketplace - Alloy Selection Japan still a range of materials
High-Reliability Lead-Free Solder Paste M705-GRN360-K-V. Senju Metal Industry Co.,Ltd. Senju Manufacturing (Europe) Ltd.
 Senju Metal Industry Co., Ltd. High-Reliability Lead-Free Solder Paste Manufacturer Senju Metal Industry Co.,Ltd. 23 Senju Hashido-cho, Adachi-Ku, Tokyo, Japan Phone: +81-33888-5156 Fax: +81-33870-3032
Senju Metal Industry Co., Ltd. High-Reliability Lead-Free Solder Paste Manufacturer Senju Metal Industry Co.,Ltd. 23 Senju Hashido-cho, Adachi-Ku, Tokyo, Japan Phone: +81-33888-5156 Fax: +81-33870-3032
Pa c ka ge s P G-H BS O F-4 a n d P G-H B 1 S O F-4
 Overmolded Packages PG-HBSOF-4 and PG-HB1SOF-4 Pa c ka ge s P G-H BS O F-4 a n d P G-H B 1 S O F-4 Application Note About this document Scope and purpose An Application Note providing guidelines for testing
Overmolded Packages PG-HBSOF-4 and PG-HB1SOF-4 Pa c ka ge s P G-H BS O F-4 a n d P G-H B 1 S O F-4 Application Note About this document Scope and purpose An Application Note providing guidelines for testing
Evaluation of Pb-free BGA Solder Joint Reliability on Ni-based Surface Finishes using Alternative Shear and Pull Metrologies
 Evaluation of Pb-free BGA Solder Joint Reliability on Ni-based Surface Finishes using Alternative Shear and Pull Metrologies Kuldip Johal and Hugh Roberts Atotech USA Inc., Rock Hill, SC Sven Lamprecht,
Evaluation of Pb-free BGA Solder Joint Reliability on Ni-based Surface Finishes using Alternative Shear and Pull Metrologies Kuldip Johal and Hugh Roberts Atotech USA Inc., Rock Hill, SC Sven Lamprecht,
Hi-performance S3X58-M406
 www.ko-ki.co.jp Ver. 42004.5 Prepared on Mar. 7, 2005 Koki no-clean LEAD FREE solder paste Hi-performance Product information 0.4mm pitch 0.3mm diameter This Product Information contains product performance
www.ko-ki.co.jp Ver. 42004.5 Prepared on Mar. 7, 2005 Koki no-clean LEAD FREE solder paste Hi-performance Product information 0.4mm pitch 0.3mm diameter This Product Information contains product performance
INTERFLUX ELECTRONICS NV
 Reflow soldering temperature profiling Min : 30sec Max : 120sec Max : +4 C/sec Max : 250 C Min : 230 C Min: +0,5 C/sec Min : +1 C/sec Max : +3 C/sec Max : +1 C/sec Max : -6 C/sec Min : -2 C/sec Min : +1
Reflow soldering temperature profiling Min : 30sec Max : 120sec Max : +4 C/sec Max : 250 C Min : 230 C Min: +0,5 C/sec Min : +1 C/sec Max : +3 C/sec Max : +1 C/sec Max : -6 C/sec Min : -2 C/sec Min : +1
The No Lead manufacturing Initiative
 The No Lead manufacturing Initiative Dr. Srinivas T. Rao UCLA Workshop on Lead-free Solder for Electronic, Optical, and MEMs Packaging and Manufacturing September 5 th 2002 Address Mfg. Needs of OEMs and
The No Lead manufacturing Initiative Dr. Srinivas T. Rao UCLA Workshop on Lead-free Solder for Electronic, Optical, and MEMs Packaging and Manufacturing September 5 th 2002 Address Mfg. Needs of OEMs and
Koki no-clean LEAD FREE solder paste. High-reliability Low Ag Lead Free Solder Paste
 www.ko-ki.co.jp #514- Revised on Feb.4, 214 Koki no-clean LEAD FREE solder paste High-reliability Low Ag Lead Free Solder Paste S1XBIG58-M5-4 Product information S1XBIG SAC35 After -4/125ºC, 1 cycles This
www.ko-ki.co.jp #514- Revised on Feb.4, 214 Koki no-clean LEAD FREE solder paste High-reliability Low Ag Lead Free Solder Paste S1XBIG58-M5-4 Product information S1XBIG SAC35 After -4/125ºC, 1 cycles This
S3X58-G801. High Performance Low Voiding LF Solder Paste. Product Information. Koki no-clean LEAD FREE solder paste.
 www.ko-ki.co.jp #55001-3 First issue: Jan.13, 2017 Revised: Jun. 28, 2017 Koki no-clean LEAD FREE solder paste High Performance Low Voiding LF Solder Paste S3X58-G801 Product Information 0603R 0603R Disclaimer
www.ko-ki.co.jp #55001-3 First issue: Jan.13, 2017 Revised: Jun. 28, 2017 Koki no-clean LEAD FREE solder paste High Performance Low Voiding LF Solder Paste S3X58-G801 Product Information 0603R 0603R Disclaimer
Freescale Semiconductor Tape Ball Grid Array (TBGA) Overview
 Freescale Semiconductor Tape Ball Grid Array (TBGA) Overview Revision 0 2006 Freescale and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the
Freescale Semiconductor Tape Ball Grid Array (TBGA) Overview Revision 0 2006 Freescale and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the
Lead-Free Connectors - An Overview
 Lead-Free Connectors - An Overview Pete Elmgren Molex Inc. 15 August 2003 Introduction For more than 50 years, lead-bearing solders have been used almost exclusively throughout the electronics industry
Lead-Free Connectors - An Overview Pete Elmgren Molex Inc. 15 August 2003 Introduction For more than 50 years, lead-bearing solders have been used almost exclusively throughout the electronics industry
IMPACT OF MICROVIA-IN-PAD DESIGN ON VOID FORMATION
 IMPACT OF MICROVIA-IN-PAD DESIGN ON VOID FORMATION Frank Grano, Felix Bruno Huntsville, AL Dana Korf, Eamon O Keeffe San Jose, CA Cheryl Kelley Salem, NH Joint Paper by Sanmina-SCI Corporation EMS, GTS
IMPACT OF MICROVIA-IN-PAD DESIGN ON VOID FORMATION Frank Grano, Felix Bruno Huntsville, AL Dana Korf, Eamon O Keeffe San Jose, CA Cheryl Kelley Salem, NH Joint Paper by Sanmina-SCI Corporation EMS, GTS
Acceptance Testing Of Low-Ag Reflow Solder Alloys
 Acceptance Testing Of Low-Ag Reflow Solder Alloys Kris Troxel 1, Aileen Allen 2, Elizabeth Elias Benedetto 3, Rahul Joshi 3 Hewlett-Packard Company 1 Boise, ID, USA 2 Palo Alto, CA, USA 3 Houston, TX,
Acceptance Testing Of Low-Ag Reflow Solder Alloys Kris Troxel 1, Aileen Allen 2, Elizabeth Elias Benedetto 3, Rahul Joshi 3 Hewlett-Packard Company 1 Boise, ID, USA 2 Palo Alto, CA, USA 3 Houston, TX,
A STUDY OF THE ENEPIG IMC FOR EUTECTIC AND LF SOLDERS
 A STUDY OF THE ENEPIG IMC FOR EUTECTIC AND LF SOLDERS G.Milad, D.Gudeczauskas, G.Obrien, A.Gruenwald Uyemura International Corporation Southington, CT ABSTRACT: The solder joint formed on an ENEPIG surface
A STUDY OF THE ENEPIG IMC FOR EUTECTIC AND LF SOLDERS G.Milad, D.Gudeczauskas, G.Obrien, A.Gruenwald Uyemura International Corporation Southington, CT ABSTRACT: The solder joint formed on an ENEPIG surface
Latest solder paste developments: Low Silver Alloys
 Latest solder paste developments: Low Silver Alloys Scanditron Technology Day, 11/09/2014 Petr Bettinec, AIM Solder AIM Introduction AIM is a subsidiary of American Iron & Metal Founded in 1936 in Montreal,
Latest solder paste developments: Low Silver Alloys Scanditron Technology Day, 11/09/2014 Petr Bettinec, AIM Solder AIM Introduction AIM is a subsidiary of American Iron & Metal Founded in 1936 in Montreal,
An Overview of IPC Plating Specification Completions, Revisions and Future Plans
 An Overview of IPC Plating Specification Completions, Revisions and Future Plans George Milad Uyemura International Corporation IMAPS New England Section 42nd Annual Symposium Technical Sessions May 5,
An Overview of IPC Plating Specification Completions, Revisions and Future Plans George Milad Uyemura International Corporation IMAPS New England Section 42nd Annual Symposium Technical Sessions May 5,
A Supplier s Perspective on the Development of Lead-free Soldering Materials
 A Supplier s Perspective on the Development of Lead-free Soldering Materials Keith Howell Nihon Superior Silicon Valley Chapter 13 November 2012 Agenda Solder Paste Flux Development Voiding Head-in-pillow
A Supplier s Perspective on the Development of Lead-free Soldering Materials Keith Howell Nihon Superior Silicon Valley Chapter 13 November 2012 Agenda Solder Paste Flux Development Voiding Head-in-pillow
STUDY OF IMMERSION GOLD PROCESSES THAT MAY BE USED FOR BOTH ENIG AND ENEPIG
 As originally published in the SMTA Proceedings STUDY OF IMMERSION GOLD PROCESSES THAT MAY BE USED FOR BOTH ENIG AND ENEPIG Don Gudeczauskas, Albin Gruenwald and George Milad UIC Technical Center Southington,
As originally published in the SMTA Proceedings STUDY OF IMMERSION GOLD PROCESSES THAT MAY BE USED FOR BOTH ENIG AND ENEPIG Don Gudeczauskas, Albin Gruenwald and George Milad UIC Technical Center Southington,
DSP 825HF X-TREME ACTIVITY HALOGEN FREE LEAD FREE NO CLEAN SOLDER PASTE
 SN/AG/CU. 863 Rev.A TECHNICAL DATA SHEET TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS SN/AG/CU. 863 Rev DSP 825HF X-TREME ACTIVITY HALOGEN FREE LEAD FREE NO CLEAN SOLDER PASTE CORPORATE HEADQUARTERS USA: 315 Fairbank St.
SN/AG/CU. 863 Rev.A TECHNICAL DATA SHEET TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS SN/AG/CU. 863 Rev DSP 825HF X-TREME ACTIVITY HALOGEN FREE LEAD FREE NO CLEAN SOLDER PASTE CORPORATE HEADQUARTERS USA: 315 Fairbank St.
Lead-Free HASL: Balancing Benefits and Risks for IBM Server and Storage Hardware
 Lead-Free HASL: Balancing Benefits and Risks for IBM Server and Storage Hardware November 19, 2009 M.Kelly, P.Eng, MBA Senior Engineer, ECAT Interconnect Technology Lead-Free Server Development Core Team
Lead-Free HASL: Balancing Benefits and Risks for IBM Server and Storage Hardware November 19, 2009 M.Kelly, P.Eng, MBA Senior Engineer, ECAT Interconnect Technology Lead-Free Server Development Core Team
High-Reliability Halogen Free Low Silver Lead-Free Solder Paste M40-LS720HF
 Senju Metal Industry Co., Ltd. High-Reliability Halogen Free Low Silver Lead-Free Solder Paste -LS720HF Manufacturer Senju Metal Industry Co.,Ltd. 23 Senju Hashido-cho, Adachi-Ku, Tokyo, Japan Phone: +81-33888-5156
Senju Metal Industry Co., Ltd. High-Reliability Halogen Free Low Silver Lead-Free Solder Paste -LS720HF Manufacturer Senju Metal Industry Co.,Ltd. 23 Senju Hashido-cho, Adachi-Ku, Tokyo, Japan Phone: +81-33888-5156
SOLDER PASTE EVALUATION TECHNIQUES TO SIMPLIFY THE TRANSITION TO PB-FREE
 SOLDER PASTE EVALUATION TECHNIQUES TO SIMPLIFY THE TRANSITION TO PB-FREE Timothy Jensen Indium Corporation of America Utica, NY, USA tjensen@indium.com INTRODUCTION As the July 1, 2006 Pb-free deadline
SOLDER PASTE EVALUATION TECHNIQUES TO SIMPLIFY THE TRANSITION TO PB-FREE Timothy Jensen Indium Corporation of America Utica, NY, USA tjensen@indium.com INTRODUCTION As the July 1, 2006 Pb-free deadline
S3X48-M500C-5. Powerful Wetting Lead Free Solder Paste. Product information. Koki no-clean LEAD FREE solder paste. Contents.
 Koki no-clean LEAD FREE solder paste www.ko-ki.co.jp #50011E-0 Revised on JAN.22, 2013 Powerful Wetting Lead Free Solder Paste Product information This Product Information contains product performance
Koki no-clean LEAD FREE solder paste www.ko-ki.co.jp #50011E-0 Revised on JAN.22, 2013 Powerful Wetting Lead Free Solder Paste Product information This Product Information contains product performance
PRODUCTION TESTING OF Ni-MODIFIED SnCu SOLDER PASTE
 Originally published in the Proceedings of SMTA International, Ft. Worth, TX, October, 2013 PRODUCTION TESTING OF Ni-MODIFIED SnCu SOLDER PASTE Karl Seelig, Timothy O Neill, Kevin Pigeon & Mehran Maaleckian
Originally published in the Proceedings of SMTA International, Ft. Worth, TX, October, 2013 PRODUCTION TESTING OF Ni-MODIFIED SnCu SOLDER PASTE Karl Seelig, Timothy O Neill, Kevin Pigeon & Mehran Maaleckian
Lead-Free Solder Bump Technologies for Flip-Chip Packaging Applications
 Lead-Free Solder Bump Technologies for Flip-Chip Packaging Applications Zaheed S. Karim 1 and Jim Martin 2 1 Advanced Interconnect Technology Ltd. 1901 Sunley Centre, 9 Wing Yin Street, Tsuen Wan, Hong
Lead-Free Solder Bump Technologies for Flip-Chip Packaging Applications Zaheed S. Karim 1 and Jim Martin 2 1 Advanced Interconnect Technology Ltd. 1901 Sunley Centre, 9 Wing Yin Street, Tsuen Wan, Hong
Question: Are RO4000 materials compatible with lead-free processes? Answer:
 Question: Are RO4 materials compatible with lead-free processes? Answer: RO4 cores and prepregs are among the most temperature stable products available. They easily meet or exceed all expectations for
Question: Are RO4 materials compatible with lead-free processes? Answer: RO4 cores and prepregs are among the most temperature stable products available. They easily meet or exceed all expectations for
A Proposed Mechanism and Remedy for Ball-in-Socket and Foot-in-Mud Soldering Defects on Ball Grid Array and Quad Flat Pack Components
 A Proposed Mechanism and Remedy for Ball-in-Socket and Foot-in-Mud Soldering Defects on Ball Grid Array and Quad Flat Pack Components Brian Smith Kester Des Plaines, IL Abstract A common source of defects
A Proposed Mechanism and Remedy for Ball-in-Socket and Foot-in-Mud Soldering Defects on Ball Grid Array and Quad Flat Pack Components Brian Smith Kester Des Plaines, IL Abstract A common source of defects
EFFECT OF Ag COMPOSITION, DWELL TIME AND COOLING RATE ON THE RELIABILITY OF Sn-Ag-Cu SOLDER JOINTS. Mulugeta Abtew
 EFFECT OF Ag COMPOSITION, DWELL TIME AND COOLING RATE ON THE RELIABILITY OF Sn-Ag-Cu SOLDER JOINTS Mulugeta Abtew Typical PCB Assembly Process PCB Loading Solder Paste Application Solder Paste Inspection
EFFECT OF Ag COMPOSITION, DWELL TIME AND COOLING RATE ON THE RELIABILITY OF Sn-Ag-Cu SOLDER JOINTS Mulugeta Abtew Typical PCB Assembly Process PCB Loading Solder Paste Application Solder Paste Inspection
POWERFUL PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD MANUFACTURING SOLUTIONS
 POWERFUL PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD MANUFACTURING SOLUTIONS Leading the PCB Industry in Quality & Innovation for over 25 Years Advanced Circuits, Inc. www.4pcb.com ABOUT ADVANCED CIRCUITS Founded in 1989 Third
POWERFUL PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD MANUFACTURING SOLUTIONS Leading the PCB Industry in Quality & Innovation for over 25 Years Advanced Circuits, Inc. www.4pcb.com ABOUT ADVANCED CIRCUITS Founded in 1989 Third
SN100C Technical Guide
 SN100C Technical Guide INTRODUCTION SN100C is a lead-free tin/copper//germanium alloy. It has been in use since about the year 2000. Since then SN100C has become a world leading alloy in wave and selective
SN100C Technical Guide INTRODUCTION SN100C is a lead-free tin/copper//germanium alloy. It has been in use since about the year 2000. Since then SN100C has become a world leading alloy in wave and selective
Active Projects and Research Review
 Active Projects and Research Review Denis Barbini, Ph.D., Vitronics Soltec Productronica Munich, Germany November 17, 2005 1 Overview 2 Pb-Free BGAs in SnPb Process Study Chair: Robert Kinyanjui, Sanmina-SCI
Active Projects and Research Review Denis Barbini, Ph.D., Vitronics Soltec Productronica Munich, Germany November 17, 2005 1 Overview 2 Pb-Free BGAs in SnPb Process Study Chair: Robert Kinyanjui, Sanmina-SCI
room and cold readouts were performed every 250 cycles. Failure data and Weibull plots were generated. Typically, the test vehicles were subjected to
 SOLDER JOINT RELIABILITY ASSESMENT OF Sn-Ag-Cu BGA COMPONENTS ATTACHED WITH EUTECTIC Pb-Sn SOLDER Fay Hua 1, Raiyo Aspandiar 2, Cameron Anderson 3, Greg Clemons 3, Chee-key Chung 4, Mustapha Faizul 4 Intel
SOLDER JOINT RELIABILITY ASSESMENT OF Sn-Ag-Cu BGA COMPONENTS ATTACHED WITH EUTECTIC Pb-Sn SOLDER Fay Hua 1, Raiyo Aspandiar 2, Cameron Anderson 3, Greg Clemons 3, Chee-key Chung 4, Mustapha Faizul 4 Intel
DSP 863 (Sn42/Bi58) LEAD FREE HALOGEN FREE NO CLEAN SOLDER PASTE
 SN/AG/CU. 862 Rev.A TECHNICAL DATA SHEET TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS SN/AG/CU. 862 Rev DSP 863 (Sn42/Bi58) LEAD FREE HALOGEN FREE NO CLEAN SOLDER PASTE CORPORATE HEADQUARTERS USA: 315 Fairbank St. Addison,
SN/AG/CU. 862 Rev.A TECHNICAL DATA SHEET TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS SN/AG/CU. 862 Rev DSP 863 (Sn42/Bi58) LEAD FREE HALOGEN FREE NO CLEAN SOLDER PASTE CORPORATE HEADQUARTERS USA: 315 Fairbank St. Addison,
ATS Document Cover Page
 221-008 Item Rev Status: RELEASED printed 9/20/2017 2:27:42 PM by Les Deenin ATS: OPERATIN PROCEDURE ATS Document Cover Page Responsible Department: Supply Chain This copy is uncontrolled unless otherwise
221-008 Item Rev Status: RELEASED printed 9/20/2017 2:27:42 PM by Les Deenin ATS: OPERATIN PROCEDURE ATS Document Cover Page Responsible Department: Supply Chain This copy is uncontrolled unless otherwise
Effects of Flux and Reflow Parameters on Lead-Free Flip Chip Assembly. Sandeep Tonapi 1 Doctoral Candidate
 Effects of Flux and Reflow Parameters on Lead-Free Flip Chip Assembly Sandeep Tonapi 1 Doctoral Candidate Peter Borgesen, Ph.D. 2 Manager, Area Array Consortium K. Srihari, Ph.D. 1 Professor, Department
Effects of Flux and Reflow Parameters on Lead-Free Flip Chip Assembly Sandeep Tonapi 1 Doctoral Candidate Peter Borgesen, Ph.D. 2 Manager, Area Array Consortium K. Srihari, Ph.D. 1 Professor, Department
ALPHA OM-325 Solder Paste product guide
 the product: a superior lead-free solder paste that simplifies the transition to µ-fine feature printing. ALPHA OM-325 Solder Paste product guide µ-fine Feature Solder Paste 1 Welcome to the Solder Paste
the product: a superior lead-free solder paste that simplifies the transition to µ-fine feature printing. ALPHA OM-325 Solder Paste product guide µ-fine Feature Solder Paste 1 Welcome to the Solder Paste
Editorial Manager(tm) for Microsystem Technologies Manuscript Draft
 Editorial Manager(tm) for Microsystem Technologies Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: Title: Electrical and Reliability Properties of Isotropic Conductive Adhesives on Immersion Silver Printed-Circuit
Editorial Manager(tm) for Microsystem Technologies Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: Title: Electrical and Reliability Properties of Isotropic Conductive Adhesives on Immersion Silver Printed-Circuit
Pb-free Challenges for High Complexity Products. inemi Jan 16 th 2008
 Pb-free Challenges for High Complexity Products inemi Jan 16 th 2008 All Rights Reserved Alcatel-Lucent 2007 Agenda RoHS 101 Typical complex of telecom products (different from consumable) Pb-free Concerns
Pb-free Challenges for High Complexity Products inemi Jan 16 th 2008 All Rights Reserved Alcatel-Lucent 2007 Agenda RoHS 101 Typical complex of telecom products (different from consumable) Pb-free Concerns
Sample Preparation for Mitigating Tin Whiskers in alternative Lead-Free Alloys
 As originally published in the IPC APEX EXPO Conference Proceedings. Sample Preparation for Mitigating Tin Whiskers in alternative Lead-Free Alloys Mehran Maalekian Karl Seelig, V.P. Technology Timothy
As originally published in the IPC APEX EXPO Conference Proceedings. Sample Preparation for Mitigating Tin Whiskers in alternative Lead-Free Alloys Mehran Maalekian Karl Seelig, V.P. Technology Timothy
Material Selection and Parameter Optimization for Reliable TMV Pop Assembly
 Selection and Parameter Optimization for Reliable TMV Pop Assembly Brian Roggeman, David Vicari Universal Instruments Corp. Binghamton, NY, USA Roggeman@uic.com Martin Anselm, Ph.D. - S09_02.doc Lee Smith,
Selection and Parameter Optimization for Reliable TMV Pop Assembly Brian Roggeman, David Vicari Universal Instruments Corp. Binghamton, NY, USA Roggeman@uic.com Martin Anselm, Ph.D. - S09_02.doc Lee Smith,
Robust Optimization of a Lead Free SMT Process
 Presented at IPC SMEMA Council APEX 2003 www.goapex.org Robust Optimization of a Lead Free SMT Process Craig Jensen, Fred Kuhlman and Mike Pepples Delphi Delco Electronics Kokomo, Indiana Abstract This
Presented at IPC SMEMA Council APEX 2003 www.goapex.org Robust Optimization of a Lead Free SMT Process Craig Jensen, Fred Kuhlman and Mike Pepples Delphi Delco Electronics Kokomo, Indiana Abstract This
INTRODUCTION OF A NEW PCB SURFACE FINISH FOR THE ELECTRONICS INDUSTRY
 INTRODUCTION OF A NEW PCB SURFACE FINISH FOR THE ELECTRONICS INDUSTRY Frank Ferdinandi Semblant Technologies Melbourne, United Kingdom ABSTRACT A new PCB surface finish has been developed that offers outstanding
INTRODUCTION OF A NEW PCB SURFACE FINISH FOR THE ELECTRONICS INDUSTRY Frank Ferdinandi Semblant Technologies Melbourne, United Kingdom ABSTRACT A new PCB surface finish has been developed that offers outstanding
THE EFFECTS OF PLATING MATERIALS, BOND PAD SIZE AND BOND PAD GEOMETRY ON SOLDER BALL SHEAR STRENGTH
 THE EFFECTS OF PLATING MATERIALS, BOND PAD SIZE AND BOND PAD GEOMETRY ON SOLDER BALL SHEAR STRENGTH Keith Rogers and Craig Hillman CALCE Electronic Products and Systems Center University of Maryland College
THE EFFECTS OF PLATING MATERIALS, BOND PAD SIZE AND BOND PAD GEOMETRY ON SOLDER BALL SHEAR STRENGTH Keith Rogers and Craig Hillman CALCE Electronic Products and Systems Center University of Maryland College
DSP 230 (Sn96.5/Ag3.5) LEAD FREE R.M.A. SOLDER PASTE
 SN/AG/CU. 862 Rev.A TECHNICAL DATA SHEET TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS SN/AG/CU. 862 Rev DSP 230 (Sn96.5/Ag3.5) LEAD FREE R.M.A. SOLDER PASTE CORPORATE HEADQUARTERS USA: 315 Fairbank St. Addison, IL 630-628-8083
SN/AG/CU. 862 Rev.A TECHNICAL DATA SHEET TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS SN/AG/CU. 862 Rev DSP 230 (Sn96.5/Ag3.5) LEAD FREE R.M.A. SOLDER PASTE CORPORATE HEADQUARTERS USA: 315 Fairbank St. Addison, IL 630-628-8083
Assembly and Rework of Lead Free Package on Package Technology By: Raymond G. Clark and Joseph D. Poole TT Electronics - IMS Perry, Ohio
 Assembly and Rework of Lead Free Package on Package Technology By: Raymond G. Clark and Joseph D. Poole TT Electronics - IMS Perry, Ohio Abstract: Miniaturization continues to be a driving force in both
Assembly and Rework of Lead Free Package on Package Technology By: Raymond G. Clark and Joseph D. Poole TT Electronics - IMS Perry, Ohio Abstract: Miniaturization continues to be a driving force in both
ALPHA SACX Plus Product Guide
 the product: Delivering the confidence you need to move to a lower silver alloy without sacrificing soldering performance or reliability ALPHA SACX Plus 0807 Product Guide the accuracy of this data. Liability
the product: Delivering the confidence you need to move to a lower silver alloy without sacrificing soldering performance or reliability ALPHA SACX Plus 0807 Product Guide the accuracy of this data. Liability
Addressing the Challenge of Head-In-Pillow Defects in Electronics Assembly
 Addressing the Challenge of Head-In-Pillow Defects in Electronics Assembly Mario Scalzo Senior Technical Support Engineer CSMTPE, Six-Sigma Black Belt ABSTRACT: The head-in-pillow defect has become a relatively
Addressing the Challenge of Head-In-Pillow Defects in Electronics Assembly Mario Scalzo Senior Technical Support Engineer CSMTPE, Six-Sigma Black Belt ABSTRACT: The head-in-pillow defect has become a relatively
Composition/wt% Bal SA2 (SABI) Bal SA3 (SABI + Cu) Bal
 Improving Thermal Cycle and Mechanical Drop Impact Resistance of a Lead-free Tin-Silver-Bismuth-Indium Solder Alloy with Minor Doping of Copper Additive Takehiro Wada 1, Seiji Tsuchiya 1, Shantanu Joshi
Improving Thermal Cycle and Mechanical Drop Impact Resistance of a Lead-free Tin-Silver-Bismuth-Indium Solder Alloy with Minor Doping of Copper Additive Takehiro Wada 1, Seiji Tsuchiya 1, Shantanu Joshi
Solder Alloy Evolution and Development
 Solder Alloy Evolution and Development SMTA Boston November 4, 2018 Presented by Timothy O Neill, Technical Marketing Manager, AIM A Brief Review of Electronic Solders 1960 s to 2006 Tin/Lead (Sn/Pb) Solder
Solder Alloy Evolution and Development SMTA Boston November 4, 2018 Presented by Timothy O Neill, Technical Marketing Manager, AIM A Brief Review of Electronic Solders 1960 s to 2006 Tin/Lead (Sn/Pb) Solder
IPC -7095C Design and Assembly Process Implementation For BGAs
 IPC -7095C Design and Assembly Process Implementation For BGAs 1 Overview With the introduction of BGA components, things had to change: New design New assembly process New repair process New inspection
IPC -7095C Design and Assembly Process Implementation For BGAs 1 Overview With the introduction of BGA components, things had to change: New design New assembly process New repair process New inspection
ALPHA WS-820 Water Soluble Lead-Free Solder Paste DESCRIPTION
 ALPHA WS-820 Water Soluble Lead-Free Solder Paste DESCRIPTION ALPHA WS-820 is the newest Alpha brand lead free, halide free solder paste offering the ideal combination of printability and reflow profile
ALPHA WS-820 Water Soluble Lead-Free Solder Paste DESCRIPTION ALPHA WS-820 is the newest Alpha brand lead free, halide free solder paste offering the ideal combination of printability and reflow profile
DSP 875 (Sn/Ag/Cu) LEAD FREE NO CLEAN SOLDER PASTE
 SN/AG/CU. 862 Rev.A TECHNICAL DATA SHEET TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS SN/AG/CU. 862 Rev DSP 875 (Sn/Ag/Cu) LEAD FREE NO CLEAN SOLDER PASTE CORPORATE HEADQUARTERS USA: 315 Fairbank St. Addison, IL 60101 630-628-8083
SN/AG/CU. 862 Rev.A TECHNICAL DATA SHEET TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS SN/AG/CU. 862 Rev DSP 875 (Sn/Ag/Cu) LEAD FREE NO CLEAN SOLDER PASTE CORPORATE HEADQUARTERS USA: 315 Fairbank St. Addison, IL 60101 630-628-8083
IMC Layers Formed with Various Combinations of Solders and Surface Finishes and Their Effect on Solder Joint Reliability
 IMC Layers Formed with Various Combinations of Solders and Surface Finishes and Their Effect on Solder Joint Reliability Per-Erik Tegehall, Swerea IVF 4 th Electronic Materials and Assembly Processes for
IMC Layers Formed with Various Combinations of Solders and Surface Finishes and Their Effect on Solder Joint Reliability Per-Erik Tegehall, Swerea IVF 4 th Electronic Materials and Assembly Processes for
Effects of Solder Reflow Conditions on the Assembly of Electronics Packaging and Printed Circuit Boards
 Effects of Solder Reflow Conditions on the Assembly of Electronics Packaging and Printed Circuit Boards Gregory K. Arslanian, Minfa Lin, Amy Wressell, Tom Mebrahtu, Victor Wang Air Products and Chemicals
Effects of Solder Reflow Conditions on the Assembly of Electronics Packaging and Printed Circuit Boards Gregory K. Arslanian, Minfa Lin, Amy Wressell, Tom Mebrahtu, Victor Wang Air Products and Chemicals
Qualification of Thin Form Factor PWBs for Handset Assembly
 Qualification of Thin Form Factor PWBs for Handset Assembly Mumtaz Y. Bora Kyocera Wireless Corporation San Diego, Ca. 92121 mbora@kyocera-wreless.com Abstract: The handheld wireless product market place
Qualification of Thin Form Factor PWBs for Handset Assembly Mumtaz Y. Bora Kyocera Wireless Corporation San Diego, Ca. 92121 mbora@kyocera-wreless.com Abstract: The handheld wireless product market place
Welcome to the Real World of Lead Free Soldering
 Welcome to the Real World of Lead Free Soldering Metallic Resources, Inc. Howard Stevens Nimal Liyanage,, Ph.D Objective: to Provide Education Regarding the Effects of Various Lead Free Soldering Alloys
Welcome to the Real World of Lead Free Soldering Metallic Resources, Inc. Howard Stevens Nimal Liyanage,, Ph.D Objective: to Provide Education Regarding the Effects of Various Lead Free Soldering Alloys
High-reliability Low-Ag Alloy
 http://www.ko-ki.co.jp #47002E 2009.8.18 Koki no-clean LEAD FREE solder paste High-reliability Low-Ag Alloy PAT. pend Product information Sn0.3Ag0.7Cu S01X7C- alloy After -40+125ºC 1500cycle This Product
http://www.ko-ki.co.jp #47002E 2009.8.18 Koki no-clean LEAD FREE solder paste High-reliability Low-Ag Alloy PAT. pend Product information Sn0.3Ag0.7Cu S01X7C- alloy After -40+125ºC 1500cycle This Product
DSP 798LF (Sn/Ag/Cu) LEAD FREE WATER SOLUBLE SOLDER PASTE
 LF217. 798LF Rev.A TECHNICAL DATA SHEET TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS LF217. 798LF Rev DSP 798LF (Sn/Ag/Cu) LEAD FREE WATER SOLUBLE SOLDER PASTE CORPORATE HEADQUARTERS USA: 315 Fairbank St. Addison, IL 60101
LF217. 798LF Rev.A TECHNICAL DATA SHEET TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS LF217. 798LF Rev DSP 798LF (Sn/Ag/Cu) LEAD FREE WATER SOLUBLE SOLDER PASTE CORPORATE HEADQUARTERS USA: 315 Fairbank St. Addison, IL 60101
XTSC SiCap 400µm - NiAu finishing - Assembly by soldering
 General description This document describes the attachment techniques recommended by Murata* for their XTSC silicon capacitors on the customer substrates. This document is non-exhaustive. Customers with
General description This document describes the attachment techniques recommended by Murata* for their XTSC silicon capacitors on the customer substrates. This document is non-exhaustive. Customers with
Development of a Lead-Free Alloy for High-Reliability, High-Temperature Applications
 Development of a Lead-Free Alloy for High-Reliability, High-Temperature Applications Hector Steen, Ph.D. 1 and Brian Toleno, Ph.D. 2 Henkel Corporation 1 Irvine, CA, USA 2 Hemel Hempstead, UK brian.toleno@us.henkel.com
Development of a Lead-Free Alloy for High-Reliability, High-Temperature Applications Hector Steen, Ph.D. 1 and Brian Toleno, Ph.D. 2 Henkel Corporation 1 Irvine, CA, USA 2 Hemel Hempstead, UK brian.toleno@us.henkel.com
Discrete Capacitor & Resistor Issues. Anthony Primavera Boston Scientific CRM 11/13/06
 Discrete Capacitor & Resistor Issues Anthony Primavera Boston Scientific CRM 11/13/06 Goal: Drive the Industry towards common test methods and best practices in manufacturing to reduce and or eliminate
Discrete Capacitor & Resistor Issues Anthony Primavera Boston Scientific CRM 11/13/06 Goal: Drive the Industry towards common test methods and best practices in manufacturing to reduce and or eliminate
LOW-SILVER BGA ASSEMBLY PHASE I REFLOW CONSIDERATIONS AND JOINT HOMOGENEITY SECOND REPORT: SAC105 SPHERES WITH TIN-LEAD PASTE
 LOW-SILVER BGA ASSEMBLY PHASE I REFLOW CONSIDERATIONS AND JOINT HOMOGENEITY SECOND REPORT: SAC105 SPHERES WITH TIN-LEAD PASTE Chrys Shea Ranjit Pandher Cookson Electronics South Plainfield, NJ, USA Ken
LOW-SILVER BGA ASSEMBLY PHASE I REFLOW CONSIDERATIONS AND JOINT HOMOGENEITY SECOND REPORT: SAC105 SPHERES WITH TIN-LEAD PASTE Chrys Shea Ranjit Pandher Cookson Electronics South Plainfield, NJ, USA Ken
Electroless Nickel / Electroless Palladium / Immersion Gold Process For Multi-Purpose Assembly Technology
 ckel / Palladium / Gold Process For Multi-Purpose Assembly Technology Kuldip Johal and Hugh Roberts, Atotech USA Inc. Sven Lamprecht, Atotech Deutschland GmbH ABSTRACT As the second part to a paper presented
ckel / Palladium / Gold Process For Multi-Purpose Assembly Technology Kuldip Johal and Hugh Roberts, Atotech USA Inc. Sven Lamprecht, Atotech Deutschland GmbH ABSTRACT As the second part to a paper presented
OM-5300 Product Guide
 OM-5300 Product Guide The information contained herein is based on data considered accurate and complete and is offered at no charge and without any other consideration provided by the recipient. No warranty,
OM-5300 Product Guide The information contained herein is based on data considered accurate and complete and is offered at no charge and without any other consideration provided by the recipient. No warranty,
Manufacturability and Reliability Impacts of Alternate Pb-Free BGA Ball Alloys. June 2007
 Manufacturability and Reliability Impacts of Alternate Pb-Free BGA Ball Alloys Greg Henshall Michael Roesch Kris Troxel Helen Holder Jian Miremadi HP Global Engineering Services The information contained
Manufacturability and Reliability Impacts of Alternate Pb-Free BGA Ball Alloys Greg Henshall Michael Roesch Kris Troxel Helen Holder Jian Miremadi HP Global Engineering Services The information contained
Murata Silicon Capacitors - XTSC 400µm NiAu finishing Assembly by Soldering High temperature silicon capacitor. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents...1 Introduction...2 Handling precautions and storage...2 Pad opening...3 Process Flow...5 Solder print material and stencil printing recommendations...6 Pick and Place...7
Table of Contents Table of Contents...1 Introduction...2 Handling precautions and storage...2 Pad opening...3 Process Flow...5 Solder print material and stencil printing recommendations...6 Pick and Place...7
Additional Information, DS6, March Recommendations for Printed Circuit Board Assembly of Infineon P(G)-VQFN Packages
 Additional Information, DS6, March 2008 Recommendations for Printed Circuit Board Assembly of Infineon P(G)-VQFN Packages Edition 2008-03 Published by Infineon Technologies AG 81726 München, Germany 2008
Additional Information, DS6, March 2008 Recommendations for Printed Circuit Board Assembly of Infineon P(G)-VQFN Packages Edition 2008-03 Published by Infineon Technologies AG 81726 München, Germany 2008
ELEC 6740 Electronics Manufacturing Chapter 5: Surface Mount Design Considerations
 ELEC 6740 Electronics Manufacturing Chapter 5: Surface Mount Design Considerations R. Wayne Johnson Alumni Professor 334-844 844-1880 johnson@eng.auburn. @eng.auburn.eduedu Outline System Design Issues
ELEC 6740 Electronics Manufacturing Chapter 5: Surface Mount Design Considerations R. Wayne Johnson Alumni Professor 334-844 844-1880 johnson@eng.auburn. @eng.auburn.eduedu Outline System Design Issues
ELEC 6740 Electronics Manufacturing Chapter 5: Surface Mount Design Considerations
 ELEC 6740 Electronics Manufacturing Chapter 5: Surface Mount Design Considerations R. Wayne Johnson Alumni Professor 334-844-1880 johnson@eng.auburn. @eng.auburn.eduedu Outline System Design Issues Package
ELEC 6740 Electronics Manufacturing Chapter 5: Surface Mount Design Considerations R. Wayne Johnson Alumni Professor 334-844-1880 johnson@eng.auburn. @eng.auburn.eduedu Outline System Design Issues Package
Sn623-5T-E SOLDER PASTE
 Sn623-5T-E SOLDER PASTE INTRODUCTION Singapore Asahi s solder paste Sn623-5T-E is a silver bearing paste to prevent silver migration and brittleness. It is formulated for fine pitch applications up to
Sn623-5T-E SOLDER PASTE INTRODUCTION Singapore Asahi s solder paste Sn623-5T-E is a silver bearing paste to prevent silver migration and brittleness. It is formulated for fine pitch applications up to
Mitigation of Pure Tin Risk by Tin-Lead SMT Reflow
 Mitigation of Pure Tin Risk by Tin-Lead SMT Reflow Results of an Industry Round-Robin David Pinsky - Raytheon Integrated Defense Systems Tom Hester - Raytheon Space and Airborne Systems Dr. Anduin Touw
Mitigation of Pure Tin Risk by Tin-Lead SMT Reflow Results of an Industry Round-Robin David Pinsky - Raytheon Integrated Defense Systems Tom Hester - Raytheon Space and Airborne Systems Dr. Anduin Touw
Lead-free soldering materials, some considerations. Presented at FHI conference, Gorinchem November 2005
 Lead-free soldering materials, some considerations Presented at FHI conference, Gorinchem November 2005 Outline Present situation in Europe towards RoHS Industry status Lead-free soldering materials Getting
Lead-free soldering materials, some considerations Presented at FHI conference, Gorinchem November 2005 Outline Present situation in Europe towards RoHS Industry status Lead-free soldering materials Getting
NPL REPORT MAT 6. Preliminary Measurements for Thermoplastic Electronics: Developing a Stress Screening Test. M WICKHAM, L ZOU and C HUNT
 NPL REPORT MAT 6 Preliminary Measurements for Thermoplastic Electronics: Developing a Stress Screening Test M WICKHAM, L ZOU and C HUNT NOT RESTRICTED NOVEMBER 7 Preliminary Measurements for Thermoplastic
NPL REPORT MAT 6 Preliminary Measurements for Thermoplastic Electronics: Developing a Stress Screening Test M WICKHAM, L ZOU and C HUNT NOT RESTRICTED NOVEMBER 7 Preliminary Measurements for Thermoplastic
Palladium as diffusion barrier - a way to a multifunctional printed circuit board finish
 Palladium as diffusion barrier - a way to a multifunctional printed circuit board finish Dr. Norbert Sitte, Schwaebisch Gmuend, Umicore Galvanotechnik GmbH 1. Introduction Due to the continuing miniaturization
Palladium as diffusion barrier - a way to a multifunctional printed circuit board finish Dr. Norbert Sitte, Schwaebisch Gmuend, Umicore Galvanotechnik GmbH 1. Introduction Due to the continuing miniaturization
WF6317. A superactive low-volatile/high heat-resistant water-soluble flux for ball soldering
 WF637 A superactive low-volatile/high heat-resistant water-soluble flux for ball soldering Low viscosity and high tacking power stabilize ball holding force and ensures excellent solder wettability Easy
WF637 A superactive low-volatile/high heat-resistant water-soluble flux for ball soldering Low viscosity and high tacking power stabilize ball holding force and ensures excellent solder wettability Easy
ALPHA EF-8300 product guide
 the product: A higher activity flux that delivers excellent solderability and doesn t compromise on and electrical reliability. ALPHA product guide ALPHA wave solder flux Welcome to the ALPHA Product Guide
the product: A higher activity flux that delivers excellent solderability and doesn t compromise on and electrical reliability. ALPHA product guide ALPHA wave solder flux Welcome to the ALPHA Product Guide
