Dear Teachers: Welcome to dynamic science
|
|
|
- Della Clarke
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Educator s Resource Guide Grades 6 8 Dear Teachers: Welcome to dynamic science activities inspired by the IMAX film. These materials, created by Scholastic Inc., IMAX Corporation, and Warner Bros. Pictures, can build student skills through engaging critical-thinking activities and hands-on experiments. You can also further students learning experience with a film field trip (see below), allowing students to experience face-to-face encounters with some of the underwater world s most mysterious and unusual creatures. We hope you enjoy! Worksheet Guide: For additional educational worksheets, visit SCHOLASTIC and associated logos are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of Scholastic Inc. All rights reserved. IMAX is a registered trademark of IMAX Corporation. Worksheet 1: Coral Crisis hone graph-reading skills as they learn how many of the world s coral reefs are at risk. Graph-reading skills Critical thinking Coral reefs Pollution Populations, resources, and environments Science and technology in society Lesson Ideas: Start a discussion about humancaused pollution. Ask students how pollution created on land can affect organisms that live in the ocean. book an IMAX Field Trip Worksheet 2: Creatures of the Deep learn the characteristics of the group of invertebrates called cephalopods. Reading comprehension Invertebrates Cephalopods Diversity and adaptations of organisms Form and function Lesson Ideas: Extend the lesson by having students research the most mysterious cephalopod: the giant squid. Find out why this creature is so hard for scientists to study. Worksheet 3: Oceans learn how carbon dioxide affects the oceans and calculate how daily activities release carbon dioxide. Math skills Fossil fuels Carbon dioxide Acids Coral reefs Properties and changes of properties in matter Understanding about science and technology Lesson Ideas: Extend the lesson by having students calculate their total carbon footprint at com. Have them track their footprint over time. Engage your students with an unforgettable learning experience. Each of the activities inside provides eye-opening extensions connected to viewing. IMAX films are ideal teaching tools that: Present new knowledge in a powerful, popular medium Inspire thoughtful and lively classroom discussion Motivate students for extended learning Worksheet 4: Hot Spot Field trips are economical and easily arranged. To book a field trip, contact your local IMAX theatre today! For locations near you, visit learn about the Coral Triangle the region of the world with the highest diversity of coral. Map-reading skills Geography Ecosystems Biodiversity Coral reefs Populations and ecosystems Structure of the earth system Lesson Ideas: Start a class discussion about biodiversity by having students compare the life seen around their school with that found in a rain forest. Why might it be important to protect areas with a lot of diversity of life? Worksheet 5: Food Web learn about the coral reef ecosystem. They will create a food web for organisms in the ecosystem. Diagram-reading skills Ecosystems Food webs Structure and function in living systems Regulation and behavior Lesson Ideas: Start a discussion about the interdependence of animals by thinking about the organisms they need in order to survive. For instance, they need plants and animals for food. They need trees to build homes. WORKSHEET ANSWERS: Worksheet 1: 1. 58%; 2. 42%; 3. Southeast Asia; 4. 25,000 square kilometers; 5. Yes, the Coral Triangle is in an area that is at high risk; 6. It should be protected because it has a high diversity of organisms and reefs in that area are at high risk. Worksheet 2: 1. They are carnivores, invertebrates, live in the ocean, and have arms called tentacles; 2. It has an outer shell; 3. The octopus has the largest brain relative to body size of all invertebrates; 4. By having them navigate mazes, complete memory tasks; 5. No one had ever seen a live giant squid until recently. Worksheet 3: Transportation ways to reduce: Ride your bike or walk instead of getting a ride in a car. Drive smaller cars. Electricity ways to reduce: Turn off lights when you leave a room. Watch less television. Turn off computers when not using them. Worksheet 4: 1. Southern; 2. Australia; 3. It causes water to warm and causes the water to become acidic; 4. Fish and sea turtles would die off; 5. Local people need the coral reefs for food and jobs. Worksheet 5: If plankton disappeared the whole food web could disappear.
2 Worksheet #1 CORAL Crisis More than 1 million plants and animals live in the world s coral reefs. Coral reefs protect coastlines from storm damage, and organisms that live in them have been used to develop drugs to treat diseases. Many of the world s coral reefs are at risk. The threats include destructive fishing practices and pollution. Global warming is also threatening reefs. Scientists have found that warming ocean waters are killing off many coral plants. Use the graphs to answer questions about the threats to coral reefs. Percentage of the world s reefs that are at risk of disappearing Total area of coral reefs that are at medium to high risk of disappearing High 27% Low 42% Area (square km) Photo copyright 2008 Warner Bros. Entertainment Inc. Photo: Richard Herrmann, Location: J Bay, Normandy Island, Milne Bay. Medium 31% 1. According to the pie chart, what percentage of the world s reefs are at high or medium risk of disappearing? 2. There are approximately 255,000 square kilometers of coral reefs in the world. Look at the pie chart. Roughly what area of coral reef is at low risk? 3. In which region of the world is the largest area of coral reef at risk? highlights some of the threats facing the coral reefs in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Write a paragraph describing some of these threats and the damage they inflict on coral reefs. Coral plants in the waters off Papua New Guinea provide an important habitat for fish and other organisms. Region 4. Approximately what area of coral reef in the Caribbean and the Indian Ocean is at risk? 5. The Coral Triangle in Southeast Asia holds the greatest diversity of coral in the world. Based on the bar graph, are the reefs in the Coral Triangle at risk? 6. Do you think the reefs in the Coral Triangle and other places should be protected? Why or why not?
3 Worksheet #2 CREATURES of the DEEP Meet the world s most unusual invertebrates, or creatures without a backbone. Cephalopods such as octopus and cuttlefish are ocean-dwelling creatures that have arms called tentacles, which surround the animal s mouth. Check out some cephalopods that inhabit the oceans in the Coral Triangle, a region off the coasts of Australia and Southeast Asia. Cuttlefish Octopus Cuttlefish have a long, flat shell inside The largest octopuses can grow up to 16 feet their body. They have eight short long or more. Each of the octopus s eight arms and two longer tentacles that arms has two rows of suckers. Octopuses are covered in suckers to grasp prey. have the largest brain relative to body size Cuttlefish can camouflage themselves of all invertebrates. Like all cephalopods, by changing color to match their octopuses are carnivores; they eat other surroundings. They also flash colors to animals. Many octopuses are also cannibals communicate with other cuttlefish. they sometimes eat other octopuses. 1. Describe four characteristics shared by all cephalopods. Nautilus The nautilus is the only living cephalopod with an outer shell. The nautilus lives in the final chamber of its coil-shaped shell. When threatened, a nautilus shuts its body in its shell with a leathery hood. The nautilus has more than 80 arms, which guide prey into its mouth. Photo copyright 2008 Warner Bros. Entertainment Inc. Photo: Jeff Wildermuth, Location: South Australia. 2. What characteristic distinguishes the nautilus from other cephalopods? 3. Scientists believe that cephalopods are some of the most intelligent creatures in the oceans. What characteristic described above might support that claim? 4. What are some ways in which you think scientists test an animal s intelligence? 5. One of the most mysterious cephalopods is the giant squid. Research the animal and then write a paragraph on a separate piece of paper explaining why so little is known about this creature. The oceans cuttlefish exhibit many unusual behaviors from amazing camouflage to extremely aggressive hunting. The flamboyant cuttlefish is one of the cephalopods seen in. Write a paragraph about this creature, including information about how it hunts and finds a mate.
4 Worksheet #3 Protecting the Oceans The rising level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is one of the biggest threats to the world s oceans. Millions of tons of carbon dioxide are released into the atmosphere every year from burning fossil fuels, such as oil and gas. Carbon dioxide causes the atmosphere to warm a process called global warming. This heats the world s oceans. Many sea organisms can t adapt to the changing temperatures and may die out. Carbon dioxide also dissolves into the oceans, causing the water to become acidic. The acidic water dissolves the shells many ocean creatures rely on to survive. Complete the questions in the two charts below to become aware of how some activities involving transportation and electricity contribute to the world s level of carbon dioxide. Then answer the questions that follow to come up with some ways that you can help to reduce these levels. Data sources: Transportation figures: GHG Protocol Initiative. Electricity figures: U.S. Department of Energy (average for the United States). Transportation Every time you take a car ride, the car releases carbon dioxide by burning gasoline. Use the chart below to see how much carbon dioxide is released when you ride in a car. 1. Estimate the number of miles you ride in a car per month: 2. Determine how much gasoline is used for the number of miles you ride in a month. Divide your total monthly miles by gas mileage. For a small- to medium-size car, divide your monthly total by 28 miles per gallon. For a large car, divide your monthly total by 21 miles per gallon. Write your answer below: 3. Multiply the number of gallons of gas used by 19.5 to estimate the number of pounds of carbon dioxide released per month: What are some ways you could reduce the amount of carbon dioxide you release using transportation? Electricity Every time you turn on a light or the television, fossil fuels are burned to create electricity. Use the chart below to see how much carbon dioxide is released when you use electricity. 1. Determine your total household use by studying your family s energy bill. Look at your electricity bill to see how many kilowatt-hours of electricity you use in one month: 2. Calculate the number of pounds of carbon dioxide released by multiplying the kilowatt-hours used by 1.34: What are some ways you and your family could reduce the amount of carbon dioxide you release each month from your electricity use? highlights some of the effects of carbon dioxide on the oceans. Create a poster that explains how daily activities such as driving a car and using electricity can affect ocean life. Include tips on how people can reduce their carbon dioxide contribution.
5 Worksheet #4 Hot Spot The Coral Triangle is an area of the oceans between Southeast Asia and the northern tip of Australia containing 53% of the world s coral reefs. Read below and study the map to discover more about this important ocean region. Then answer the questions that follow on a separate sheet of paper. The Coral Triangle More than 75 percent of the world s species of coral are found in the Coral Triangle. The region is home to more than 3,000 species of fish and acts as a breeding ground for many sea organisms. Photo copyright 2008 Warner Bros. Entertainment Inc. Photo: Richard Herrmann, Location: J Bay, Normandy Island, Milne Bay. Its beaches serve as nesting grounds for five of the world s seven species of sea turtles. The reefs in the Coral Triangle are being threatened by human activities. Destructive fishing methods, such as the use of explosives, can destroy reefs. More than 150 million people call the Coral Triangle home. Many of these people rely on the coral reefs for food and jobs. Rising levels of carbon dioxide are harming the coral. Carbon dioxide causes Earth s temperatures to rise, warming the oceans and harming some ocean life. highlights the heart of the Coral Triangle, where animals like the warty frogfish live. Write a description of this region for a scuba-diving guidebook. Your guidebook entry should include descriptions of the organisms a diver might see, and explain why this region is a unique place to dive. 1. In which hemisphere is most of the Coral Triangle located: Northern or Southern? 2. Which of the following countries do not border or are not within the Coral Triangle: Australia, Philippines, Indonesia, Malaysia? 3. How does an increasing amount of carbon dioxide in the air affect coral reefs in the Coral Triangle? 4. What do you think would happen to the populations of fish and animals like sea turtles if the reefs in the Coral Triangle disappeared? 5. Conservation organizations are working with people who live in the region to try to protect the Coral Triangle. Why might it be beneficial for local people to protect the reefs?
6 Worksheet #5 Food Web The reefs created by corals are the basis for a rich oceanic ecosystem. The corals are part of a complex food web, or interconnected system, in which animals eat other animals to survive. If one organism in a food web were to disappear, it could disrupt the entire system. To learn more, study the coral reef ecosystem in the illustration below, and then do the activity that follows. Coral Reef Ecosystem 3 6 Ecosystem Key: 1. Ocean currents bring a constant supply of drifting plankton into a coral reef Corals are made up of tiny animals called polyps. Polyps eat plankton Small fish like fairy basslets feed mainly on plankton floating in the ocean water. Photo copyright 2008 Warner Bros. Entertainment Inc. Photo: Michele Hall, Location: Crystal Bommie, near Komodo. On a separate piece of paper draw a food web of this coral reef ecosystem. Your food web should show how each organism in the ecosystem relates to the other organisms according to what they eat. Each organism should have arrows going from it to organisms that rely upon it for food. Question When you have completed your food web, answer the following: What would happen to your food web if plankton were to disappear? After watching, add three new creatures to the above diagram of the coral reef ecosystem. Then, research the diets of those creatures and add them to your food web. Anemonefish eat mostly plankton floating in the water. They hide from bigger fish in the stinging tentacles of sea anemone. 4. Lionfish hunt for small fish and crustaceans, mostly during the night. 5. Octopuses hunt the seafloor for crabs and fish. 6. Shark feed on larger fish and invertebrates, such as octopuses.
Dear Teachers: Welcome to dynamic science
 Educator s Resource Guide GRADES 6 8 Dear Teachers: Welcome to dynamic science activities inspired by the IMAX film. These materials, created by Scholastic Inc., IMAX Corporation, and Warner Bros. Pictures,
Educator s Resource Guide GRADES 6 8 Dear Teachers: Welcome to dynamic science activities inspired by the IMAX film. These materials, created by Scholastic Inc., IMAX Corporation, and Warner Bros. Pictures,
Worksheet 3: Hiding Out. Students will learn about the animal adaptation called camouflage.
 Educator s Resource Guide GRADES 3 5 Dear Teachers: Welcome to dynamic science activities and a classroom poster inspired by the IMAX fi l m. These materials, created by Scholastic Inc., IMAX Corporation,
Educator s Resource Guide GRADES 3 5 Dear Teachers: Welcome to dynamic science activities and a classroom poster inspired by the IMAX fi l m. These materials, created by Scholastic Inc., IMAX Corporation,
The Oceans Global Garbage
 The Oceans Global Garbage Lesson Overview: The world s oceans are intentionally used as a disposal ground. Students will learn how the oceans are polluted through a review of examples of pollution and
The Oceans Global Garbage Lesson Overview: The world s oceans are intentionally used as a disposal ground. Students will learn how the oceans are polluted through a review of examples of pollution and
Chapter Biodiversity
 Chapter 6 6.3 Biodiversity Key Questions: 1) Why is biodiversity important? 2) What are the most significant threats to biodiversity? 3) How do we preserve biodiversity? Types of Biodiversity Biological
Chapter 6 6.3 Biodiversity Key Questions: 1) Why is biodiversity important? 2) What are the most significant threats to biodiversity? 3) How do we preserve biodiversity? Types of Biodiversity Biological
Ecosystem Comparison
 4 th grade Lesson Plan Ecosystem Comparison Standards: 2.a. Students know plants are the primary source of matter and energy entering most food chains. 3.a. Students know ecosystems can be characterized
4 th grade Lesson Plan Ecosystem Comparison Standards: 2.a. Students know plants are the primary source of matter and energy entering most food chains. 3.a. Students know ecosystems can be characterized
Teacher s Answer Key
 Ocean on the edge Scavenger Hunt Teacher s Answer Key (STUDENT ANSWERS MAY VARY SLIGHTLY) Thank you for choosing the Aquarium of the Pacific as your field trip destination! We are excited to share the
Ocean on the edge Scavenger Hunt Teacher s Answer Key (STUDENT ANSWERS MAY VARY SLIGHTLY) Thank you for choosing the Aquarium of the Pacific as your field trip destination! We are excited to share the
Coral Reefs and Climate Change
 and Populations oral Reefs and limate hange 1 There are many different types of environments on the planet, and often many ecosystems within each environment. Ecosystems all contain a balance of abiotic
and Populations oral Reefs and limate hange 1 There are many different types of environments on the planet, and often many ecosystems within each environment. Ecosystems all contain a balance of abiotic
Student Exploration: Coral Reefs 1 Abiotic Factors
 Name: Date: Per. Student Exploration: Coral Reefs 1 Abiotic Factors Vocabulary: consumer, coral, coral bleaching, coral reef, filter feeder, food chain, food web, grazer, nutrients, ocean acidification,
Name: Date: Per. Student Exploration: Coral Reefs 1 Abiotic Factors Vocabulary: consumer, coral, coral bleaching, coral reef, filter feeder, food chain, food web, grazer, nutrients, ocean acidification,
Climate Change and Coral Bleaching
 Rising ocean temperatures may push coral reefs to their limits. Climate Change and Coral Bleaching http://www.nova.org.au/coral-bleaching Essentials! Corals are animals that live in a mutually beneficial
Rising ocean temperatures may push coral reefs to their limits. Climate Change and Coral Bleaching http://www.nova.org.au/coral-bleaching Essentials! Corals are animals that live in a mutually beneficial
Pre-lab Homework Lab 10: Global Warming Prior to lab, answer the following questions to help you become prepared for the lab.
 Lab Section: Name: Pre-lab Homework Prior to lab, answer the following questions to help you become prepared for the lab. 1. You will be calculating your carbon footprint as part of lab (an estimate of
Lab Section: Name: Pre-lab Homework Prior to lab, answer the following questions to help you become prepared for the lab. 1. You will be calculating your carbon footprint as part of lab (an estimate of
Coral Reefs- A Challenging Ecosystem for Human Societies* B. Salvat Originally published in Global Environmental Change, 1992, vol. 2, pp.
 Coral Reefs- A Challenging Ecosystem for Human Societies* B. Salvat Originally published in Global Environmental Change, 1992, vol. 2, pp. 12-18 18 Presented by: Amy Dewees & Melissa Parente What is coral?
Coral Reefs- A Challenging Ecosystem for Human Societies* B. Salvat Originally published in Global Environmental Change, 1992, vol. 2, pp. 12-18 18 Presented by: Amy Dewees & Melissa Parente What is coral?
STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems
 Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems TEK 8.11D: Recognize human dependence on ocean systems and explain how human activities such as runoff, artificial
Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems TEK 8.11D: Recognize human dependence on ocean systems and explain how human activities such as runoff, artificial
Write the words from the article into the definitions. The paragraph numbers are given to help you.
 environment: [noun] the natural world, including the land, water, air, plants and animals environmentally conscious: [adjective] being aware of the environment and our effect on it 1 QUIZ - HOW ENVIRONMENTALLY
environment: [noun] the natural world, including the land, water, air, plants and animals environmentally conscious: [adjective] being aware of the environment and our effect on it 1 QUIZ - HOW ENVIRONMENTALLY
Reefs at Risk. Nancy J. Geldermann 1225 Longmeadow Glenview, IL /
 Reefs at Risk Nancy J. Geldermann 1225 Longmeadow Glenview, IL 60025 847/724-8837 nancy@geldermann.com Overview: This lesson is designed to provide a visual demonstration of the interdependency within
Reefs at Risk Nancy J. Geldermann 1225 Longmeadow Glenview, IL 60025 847/724-8837 nancy@geldermann.com Overview: This lesson is designed to provide a visual demonstration of the interdependency within
GRADE 8: Life science 5. UNIT 8L.5 7 hours. Feeding relationships. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning. Expectations
 GRADE 8: Life science 5 Feeding relationships UNIT 8L.5 7 hours About this unit This unit is the fifth of six units on life science for Grade 8. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching
GRADE 8: Life science 5 Feeding relationships UNIT 8L.5 7 hours About this unit This unit is the fifth of six units on life science for Grade 8. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching
Section Objectives: Explain biodiversity and its importance. Relate various threats to the loss of biodiversity.
 Section Objectives: Explain biodiversity and its importance. Relate various threats to the loss of biodiversity. Biological Diversity Biodiversity refers to the variety of species in a specific area. The
Section Objectives: Explain biodiversity and its importance. Relate various threats to the loss of biodiversity. Biological Diversity Biodiversity refers to the variety of species in a specific area. The
Choose 3 of the cartoons and write down what message you think they are trying to give.
 Task 1: Choose 3 of the cartoons and write down what message you think they are trying to give. Why do you think these cartoons were created? Do you think they are persuasive and how? Task 2 Draw a table
Task 1: Choose 3 of the cartoons and write down what message you think they are trying to give. Why do you think these cartoons were created? Do you think they are persuasive and how? Task 2 Draw a table
Biodiversity and Conservation
 Chapter Test A CHAPTER 5 Biodiversity and Conservation Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the phrase or sentence that best answers each question. Part B: Matching 1.
Chapter Test A CHAPTER 5 Biodiversity and Conservation Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the phrase or sentence that best answers each question. Part B: Matching 1.
treasures in the form of rocks and minerals. They have never been touched by humans. half the globe. The freezing water contains valuable
 Miners want to explore ocean's deep floor for precious rocks and minerals Coral reefs grow in the waters of Tatawa Besar, Komodo, Indonesia, April 30, 2015. Rising demand for copper, cobalt, gold and rare-earth
Miners want to explore ocean's deep floor for precious rocks and minerals Coral reefs grow in the waters of Tatawa Besar, Komodo, Indonesia, April 30, 2015. Rising demand for copper, cobalt, gold and rare-earth
(Total 5 marks) Khalid Mazhar Qureshi Haider Nawab
 6. A river is polluted by some raw sewage. This causes changes in the number of microorganisms in the river. This in turn has an effect on the number of large fish in the river. Describe and explain these
6. A river is polluted by some raw sewage. This causes changes in the number of microorganisms in the river. This in turn has an effect on the number of large fish in the river. Describe and explain these
Chapter 6. Aquatic Biodiversity. Chapter Overview Questions
 Chapter 6 Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter Overview Questions Ø What are the basic types of aquatic life zones and what factors influence the kinds of life they contain? Ø What are the major types of saltwater
Chapter 6 Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter Overview Questions Ø What are the basic types of aquatic life zones and what factors influence the kinds of life they contain? Ø What are the major types of saltwater
NOAA: The Heat is ON! Climate Change and Coral Reef Ecosystems
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP NOAA: The Heat is ON! Climate Change and Coral Reef Ecosystems Coral Bleaching Dr. Mark Eakin Thursday, April 30, 2009 Coral Bleaching 101 Presented by Mark Eakin
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP NOAA: The Heat is ON! Climate Change and Coral Reef Ecosystems Coral Bleaching Dr. Mark Eakin Thursday, April 30, 2009 Coral Bleaching 101 Presented by Mark Eakin
HUMAN IMPACT on the BIOSPHERE part 4
 HUMAN IMPACT on the BIOSPHERE part 4 Charting a course for the Future http://www.claybennett.com/pages2/mistletoe.html ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS DEAD ZONES OZONE DEPLETION ACID RAIN GLOBAL WARMING WASTE http://www.acmecompany.com/stock_thumbnails/13808.greenhouse_effect_2.jpg
HUMAN IMPACT on the BIOSPHERE part 4 Charting a course for the Future http://www.claybennett.com/pages2/mistletoe.html ENVIRONMENTAL PROBLEMS DEAD ZONES OZONE DEPLETION ACID RAIN GLOBAL WARMING WASTE http://www.acmecompany.com/stock_thumbnails/13808.greenhouse_effect_2.jpg
Life in the Estuary Fourth and Fifth Grade Lesson Plan
 Life in the Estuary Fourth and Fifth Grade Lesson Plan For more information, please contact: Veronica Frehm Director of Education John D. MacArthur Beach State Park T: (561) 776-7449 Ext 104 Email: veronica@macarthurbeach.org
Life in the Estuary Fourth and Fifth Grade Lesson Plan For more information, please contact: Veronica Frehm Director of Education John D. MacArthur Beach State Park T: (561) 776-7449 Ext 104 Email: veronica@macarthurbeach.org
Chapter Introduction. Matter. Ecosystems. Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Abiotic Factors Cycles of Matter Chapter Wrap-Up Energy in Ecosystems How do living things and the nonliving parts of the environment interact? What do you
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Abiotic Factors Cycles of Matter Chapter Wrap-Up Energy in Ecosystems How do living things and the nonliving parts of the environment interact? What do you
What is the carbon cycle?
 What is the carbon cycle? By NASA Earth Observatory, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.29.17 Word Count 1,160 Carbon is both the foundation of all life on Earth and the source of the majority of energy consumed
What is the carbon cycle? By NASA Earth Observatory, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.29.17 Word Count 1,160 Carbon is both the foundation of all life on Earth and the source of the majority of energy consumed
Teaching Time: 1 hour and 15 minutes
 Lesson Summary Students will discuss human output of greenhouse gasses and then calculate the amount of CO2 that their family cars produce per gallon. Prior Knowledge & Skills Data interpreting skills
Lesson Summary Students will discuss human output of greenhouse gasses and then calculate the amount of CO2 that their family cars produce per gallon. Prior Knowledge & Skills Data interpreting skills
Level 3 Advanced. Earth in danger
 1 QUIZ - HOW ENVIRONMENTALLY CONSCIOUS ARE YOU? Circle your answers and then add up your points. The more points you have, the more environmentally conscious you are. How often do you... always sometimes
1 QUIZ - HOW ENVIRONMENTALLY CONSCIOUS ARE YOU? Circle your answers and then add up your points. The more points you have, the more environmentally conscious you are. How often do you... always sometimes
student ocean acidification Part 1: What Happens to ph? Introduction Activity Materials: Procedure:
 ocean acidification Part 1: What Happens to ph? Introduction ph (potential of Hydrogen) is the measure of the acidity or alkalinity (basicity) of a substance. It is measured on a scale of 1.0 to 14.0.
ocean acidification Part 1: What Happens to ph? Introduction ph (potential of Hydrogen) is the measure of the acidity or alkalinity (basicity) of a substance. It is measured on a scale of 1.0 to 14.0.
Chapter 6 Review. 3. A resource that cannot be replenished by natural processes is called a. common. b. renewable. c. nonrenewable. d. conserved.
 Name Hour Chapter 6 Review 1. Which of the following human activities was NOT important in transforming the biosphere? a. agriculture b. industry c. urban development d. aquaculture 2. Civilizations could
Name Hour Chapter 6 Review 1. Which of the following human activities was NOT important in transforming the biosphere? a. agriculture b. industry c. urban development d. aquaculture 2. Civilizations could
Global warming has become perhaps the most complicated issue facing world nowadays.
 Global warming has become perhaps the most complicated issue facing world nowadays. What is global warming? The Planet Is Heating Up and Fast The earth heats up (the temperature rises)=> It happens when
Global warming has become perhaps the most complicated issue facing world nowadays. What is global warming? The Planet Is Heating Up and Fast The earth heats up (the temperature rises)=> It happens when
An Interconnected Planet
 An Interconnected Planet Key Ideas How are humans and the environment connected? What is the difference between renewable and nonrenewable resources? How can the state of the environment affect a person
An Interconnected Planet Key Ideas How are humans and the environment connected? What is the difference between renewable and nonrenewable resources? How can the state of the environment affect a person
buried in the sediment; the carbon they contain sometimes change into fossil fuels; this process takes millions of years
 STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 8 - ANSWERS 1) THE CARBON CYCLE - Describe the transformations related to the circulation of carbon. DEFINITION: the carbon cycle is a set of processes by which the essential element
STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 8 - ANSWERS 1) THE CARBON CYCLE - Describe the transformations related to the circulation of carbon. DEFINITION: the carbon cycle is a set of processes by which the essential element
Freshwater ecosystems
 Aquatic Ecosystems Aquatic Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are determined by the water s salinity. Salinity - Amount of salt in the water. Freshwater ecosystems do not have any
Aquatic Ecosystems Aquatic Ecosystems The types of organisms in an aquatic ecosystem are determined by the water s salinity. Salinity - Amount of salt in the water. Freshwater ecosystems do not have any
Did You Know? Climate Change & Coral Activities. Background Information Climate Change. Theme. Objectives
 Climate Change & Coral Activities Theme The Ocean stabilizes our respective climates. Global warming threatens to alter this delicate balance. We still have time to change our energy consumption patters
Climate Change & Coral Activities Theme The Ocean stabilizes our respective climates. Global warming threatens to alter this delicate balance. We still have time to change our energy consumption patters
16 Global Climate Change
 CHAPTER 16 Global Climate Change Slide #1 Rising Seas May Flood the Maldive Islands Slide #2 Sea levels are rising worldwide. Scientists link this to global climate change. Global climate change threatens
CHAPTER 16 Global Climate Change Slide #1 Rising Seas May Flood the Maldive Islands Slide #2 Sea levels are rising worldwide. Scientists link this to global climate change. Global climate change threatens
1. All the interconnected feeding relationships in an ecosystem make up a food. a. Interaction b. Chain c. Network d. Web
 Ecology Unit Test DO NOT WRITE ON TEST!!! Take a deep breath, take your time, and make sure you understand exactly what the question is asking you. For true/false, fill in the correct bubble ( A for true
Ecology Unit Test DO NOT WRITE ON TEST!!! Take a deep breath, take your time, and make sure you understand exactly what the question is asking you. For true/false, fill in the correct bubble ( A for true
Draw disruptive, stabilizing, and directional selection on the board. Explain disruptive selection using an example. What effects speciation most?
 Draw disruptive, stabilizing, and directional selection on the board. disruptive selection using an Disruptive selection is when the average physical characteristic of a population is not beneficial. Example:
Draw disruptive, stabilizing, and directional selection on the board. disruptive selection using an Disruptive selection is when the average physical characteristic of a population is not beneficial. Example:
De Hoop Nature Reserve Western Cape, South Africa. Shell midden that is over 100,000 years old
 Humans & the Sea De Hoop Nature Reserve Western Cape, South Africa Shell midden that is over 100,000 years old Shell fish hooks of South Coastal Californians (3000 BC-AD 900) 7 billion Human Population
Humans & the Sea De Hoop Nature Reserve Western Cape, South Africa Shell midden that is over 100,000 years old Shell fish hooks of South Coastal Californians (3000 BC-AD 900) 7 billion Human Population
Chapter 38 Conservation Biology
 Chapter 38 Conservation Biology PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Brian
Chapter 38 Conservation Biology PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Brian
Matter and Energy in Ecosystems
 Content Vocabulary LESSON 3 Matter and Energy in Ecosystems Directions: Complete the triangles below. In the bottom left section, write a definition for the term; include the word transfer in at least
Content Vocabulary LESSON 3 Matter and Energy in Ecosystems Directions: Complete the triangles below. In the bottom left section, write a definition for the term; include the word transfer in at least
ABBOTT HALL OF CONSERVATION RESTORING EARTH EXHIBITION CLIMATE CHANGE GUIDE
 CHICAGO COMMUNITY CLIMATE ACTION TOOLKIT Find this and other climate action tools at climatechicago.fieldmuseum.org ABBOTT HALL OF CONSERVATION RESTORING EARTH EXHIBITION CLIMATE CHANGE GUIDE The Field
CHICAGO COMMUNITY CLIMATE ACTION TOOLKIT Find this and other climate action tools at climatechicago.fieldmuseum.org ABBOTT HALL OF CONSERVATION RESTORING EARTH EXHIBITION CLIMATE CHANGE GUIDE The Field
NOTE TO TEACHER: It is appropriate to introduce the mitochondria (where energy is made) as a major structure common to all cells.
 5-2.1 Recall the cell as the smallest unit of life and identify its major structures (including cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuole). Taxonomy level: 1.1 and 1.2-A Remember Factual Knowledge
5-2.1 Recall the cell as the smallest unit of life and identify its major structures (including cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuole). Taxonomy level: 1.1 and 1.2-A Remember Factual Knowledge
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change Objective 2.2.1 Infer how human activities (including population growth, pollution, global warming, burning of fossil fuels, habitat destruction, and introduction of non-native species)
Global Climate Change Objective 2.2.1 Infer how human activities (including population growth, pollution, global warming, burning of fossil fuels, habitat destruction, and introduction of non-native species)
GEOGRAPHY Grade 7 Term
 1 GEOGRAPHY Grade 7 Term 4 2016 Table of Contents Topic: Natural resources and conservation in South Africa Page Content 2 Natural resources 8 Management of resources 11 Water in South Africa 2 NATURAL
1 GEOGRAPHY Grade 7 Term 4 2016 Table of Contents Topic: Natural resources and conservation in South Africa Page Content 2 Natural resources 8 Management of resources 11 Water in South Africa 2 NATURAL
Chapter 16 Human Impact on Ecosystems DAY ONE
 Chapter 16 Human Impact on Ecosystems DAY ONE Earth s resources As the human population grows, the demand for resources increases. Our population continues to grow. Earth s carrying capacity is actually
Chapter 16 Human Impact on Ecosystems DAY ONE Earth s resources As the human population grows, the demand for resources increases. Our population continues to grow. Earth s carrying capacity is actually
Do now pg 85. In at least 2 sentences, explain the difference between climate change and global warming
 Do now pg 85 In at least 2 sentences, explain the difference between climate change and global warming What is happening Evidence of a Warming Earth Rising global surface temperatures Changes in precipitation
Do now pg 85 In at least 2 sentences, explain the difference between climate change and global warming What is happening Evidence of a Warming Earth Rising global surface temperatures Changes in precipitation
Exploring Sawfish Ideas for Science and Technology
 Exploring Sawfish Ideas for Science and Technology Activities linked to grade levels 5-10 Choose a problem associated with marine creatures and their life in the marine environment. Use a problem-solving
Exploring Sawfish Ideas for Science and Technology Activities linked to grade levels 5-10 Choose a problem associated with marine creatures and their life in the marine environment. Use a problem-solving
Core Case Study: Southern Sea Otters: Are They Back from the Brink of Extinction?
 Core Case Study: Southern Sea Otters: Are They Back from the Brink of Extinction? Habitat Hunted: early 1900s Partial recovery Why care about sea otters? Ethics Keystone species Tourism dollars Just last
Core Case Study: Southern Sea Otters: Are They Back from the Brink of Extinction? Habitat Hunted: early 1900s Partial recovery Why care about sea otters? Ethics Keystone species Tourism dollars Just last
6 th Grade Cards 1. Which of these is NOT a benefit of biodiversity? 6. Which animal listed below would complete this food chain?
 1. Which of these is NOT a benefit of biodiversity? A. medicine B. food C. gold D. oxygen 6. Which animal listed below would complete this food chain? A. fly B. lizard C. butterfly D. hummingbird 2. Which
1. Which of these is NOT a benefit of biodiversity? A. medicine B. food C. gold D. oxygen 6. Which animal listed below would complete this food chain? A. fly B. lizard C. butterfly D. hummingbird 2. Which
7 Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem NOW THAT YOU are familiar with producers and consumers,
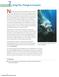 7 Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem NOW THAT YOU are familiar with producers and consumers, you are going to learn about how these organisms interact within an ecosystem. Picture a seal swimming in the
7 Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem NOW THAT YOU are familiar with producers and consumers, you are going to learn about how these organisms interact within an ecosystem. Picture a seal swimming in the
Bellringer. What Lies Beneath? Natural Resources
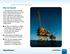 What Lies Beneath? Do deposits of oil or natural gas lie deep beneath this section of the ocean? The owners of these exploration rigs hope so. These rigs are used to drill small test wells in the ocean
What Lies Beneath? Do deposits of oil or natural gas lie deep beneath this section of the ocean? The owners of these exploration rigs hope so. These rigs are used to drill small test wells in the ocean
Kapolei Middle School Science Students Explore Plankton: Discover Intricate, Supportive Coral Reef with Scientists
 Kapolei Middle School Science Students Explore Plankton: Discover Intricate, Supportive Coral Reef with Scientists Continuing a collaboration spanning six years and involving more than one thousand students,
Kapolei Middle School Science Students Explore Plankton: Discover Intricate, Supportive Coral Reef with Scientists Continuing a collaboration spanning six years and involving more than one thousand students,
Ecosystems and Biomes
 Content Vocabulary LESSON 1 Ecosystems and Biomes Directions: Use the clues and the terms listed below to complete the puzzle. NOTE: There is no empty square in the puzzle between the words of two-word
Content Vocabulary LESSON 1 Ecosystems and Biomes Directions: Use the clues and the terms listed below to complete the puzzle. NOTE: There is no empty square in the puzzle between the words of two-word
Page 2. Draw one line from each energy source in List A to the statement about the energy source in List B. List A Energy source
 Q1.Three energy sources used to generate electricity are given in List A. Statements about the energy sources used to generate electricity are given in List B. Draw one line from each energy source in
Q1.Three energy sources used to generate electricity are given in List A. Statements about the energy sources used to generate electricity are given in List B. Draw one line from each energy source in
Illustrations/B.Harmon
 Illustrations/B.Harmon An underwater earthquake causes a tsunami to wash over a penguin nesting beach. reproduction Melting glaciers in Antarctica reduce the distance the female emperor penguin has to
Illustrations/B.Harmon An underwater earthquake causes a tsunami to wash over a penguin nesting beach. reproduction Melting glaciers in Antarctica reduce the distance the female emperor penguin has to
DRK-12 Carbon Assessment, Form B
 DRK-12 Carbon Assessment, Form B Fall, 2013 Please don t include this first sheet in student copies. This assessment is designed to elicit middle school or high school students accounts of carbon-transforming
DRK-12 Carbon Assessment, Form B Fall, 2013 Please don t include this first sheet in student copies. This assessment is designed to elicit middle school or high school students accounts of carbon-transforming
(a) The area of forest lost each year in Madagascar increased between 2009 and 2012.
 Q1.The graph below shows the area of forest lost in Madagascar from 2009 to 2012. (a) The area of forest lost each year in Madagascar increased between 2009 and 2012. Determine the total area of forest
Q1.The graph below shows the area of forest lost in Madagascar from 2009 to 2012. (a) The area of forest lost each year in Madagascar increased between 2009 and 2012. Determine the total area of forest
Ecology. - Air pollutants (Sulfur and Nitrogen) mix with water in the atmosphere - This rain destroys wildlife and habitats
 Ecology Study online at quizlet.com/_2dqy57 1. Acid Rain 7. Ozone Layer Depletion - Air pollutants (Sulfur and Nitrogen) mix with water in the atmosphere - This rain destroys wildlife and habitats 2. Exotic
Ecology Study online at quizlet.com/_2dqy57 1. Acid Rain 7. Ozone Layer Depletion - Air pollutants (Sulfur and Nitrogen) mix with water in the atmosphere - This rain destroys wildlife and habitats 2. Exotic
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0123456789* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/02 Paper 2 Management in context For Examination from
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0123456789* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/02 Paper 2 Management in context For Examination from
Marine Osteoporosis. Education. Grade Level. Activity Summary. Timeframe. Learning Objectives.
 Education Marine Osteoporosis Grade Level 5th - 8th Timeframe 2-45 minute lessons Observation time - 3 hours Experiment 1: Students will record observations every 30 minutes for 2-3 hours (but can complete
Education Marine Osteoporosis Grade Level 5th - 8th Timeframe 2-45 minute lessons Observation time - 3 hours Experiment 1: Students will record observations every 30 minutes for 2-3 hours (but can complete
5/12/15. We depend on environment for. Food Water Air Shelter Fuel, etc. Environmental science the study of the impact of humans on the environment
 List examples of chemical pollution from industry, agriculture, or everyday use. What are some possible effects that these pollutants can have on the environment? Doerfler Biology I How are humans and
List examples of chemical pollution from industry, agriculture, or everyday use. What are some possible effects that these pollutants can have on the environment? Doerfler Biology I How are humans and
AP ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE 2002 SCORING GUIDELINES
 Question 4 Total Score 10 Points (a) Describe what an El Niño is and clearly indicate where it occurs. What an El Niño is: (2 points) If the student takes the description of El Niño directly from the article,
Question 4 Total Score 10 Points (a) Describe what an El Niño is and clearly indicate where it occurs. What an El Niño is: (2 points) If the student takes the description of El Niño directly from the article,
Lesson 1b: The Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change
 Lesson 1b: The Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change SUBJECTS Earth Science Life Science Physical Science GRADE LEVELS 4 8 CA SCIENCE STANDARDS Grade 6: Heat (Thermal Energy) (Physical Sciences). 3. Heat
Lesson 1b: The Greenhouse Effect and Climate Change SUBJECTS Earth Science Life Science Physical Science GRADE LEVELS 4 8 CA SCIENCE STANDARDS Grade 6: Heat (Thermal Energy) (Physical Sciences). 3. Heat
1. Philippines Coastal & Marine Resources: An Introduction
 1. Philippines Coastal & Marine Resources: An Introduction Thousands of islands. With its thousands of. islands, the Philippines has one of the longest coastlines in the world estimated at 36,289 kilometers.
1. Philippines Coastal & Marine Resources: An Introduction Thousands of islands. With its thousands of. islands, the Philippines has one of the longest coastlines in the world estimated at 36,289 kilometers.
Let s Be Oral About Coral. much support has been placed on the preservation of polar bears, the fact that all animals are
 Let s Be Oral About Coral Allison Feng 1 Let s Be Oral About Coral When climate change is thought of in relation to animals, the archetypal image of a lone polar bear floating on a piece of melting ice
Let s Be Oral About Coral Allison Feng 1 Let s Be Oral About Coral When climate change is thought of in relation to animals, the archetypal image of a lone polar bear floating on a piece of melting ice
Changes in Biodiversity
 Changes in Biodiversity Hundreds of years ago, before North America was split up according to states and countries, native populations lived in the many varied areas of the continent. There were jungles,
Changes in Biodiversity Hundreds of years ago, before North America was split up according to states and countries, native populations lived in the many varied areas of the continent. There were jungles,
Please select the best answer from the choices provided
 4/23/13 10:53 M 1 The was a result of the 1992 Earth Summit. a. Kyoto Protocol b. International Tropical Timber greement c. onvention on Wetlands of International Importance d. United Nations Framework
4/23/13 10:53 M 1 The was a result of the 1992 Earth Summit. a. Kyoto Protocol b. International Tropical Timber greement c. onvention on Wetlands of International Importance d. United Nations Framework
Title: Wildlife Rescue. By Elizabeth Trowbridge. Theme: Oil spills can have a wide variety of effects on wildlife.
 Title: Wildlife Rescue By Elizabeth Trowbridge Theme: Oil spills can have a wide variety of effects on wildlife. Objectives: - Students will identify major habitats of southcoastal Alaska and their inhabitants.
Title: Wildlife Rescue By Elizabeth Trowbridge Theme: Oil spills can have a wide variety of effects on wildlife. Objectives: - Students will identify major habitats of southcoastal Alaska and their inhabitants.
Feedbacks of Ice and Clouds
 Activity DEVELOP For Educator 45 Minutes Grades 7-12+ Ages 12+ Feedbacks of Ice and Clouds How do ice and clouds cool the Earth? For the complete activity with media resources, visit: http://education.nationalgeographic.com/education/activity/feedbacks-ice-and-clouds/
Activity DEVELOP For Educator 45 Minutes Grades 7-12+ Ages 12+ Feedbacks of Ice and Clouds How do ice and clouds cool the Earth? For the complete activity with media resources, visit: http://education.nationalgeographic.com/education/activity/feedbacks-ice-and-clouds/
California Current Ecosystem Plankton Food Web
 TEACHER PAGES What role do plankton play in the food web? California Current Ecosystem Plankton Food Web and the Beth Simmons Education and Outreach Coordinator, CCE LTER, Scripps Institution of Oceanography,
TEACHER PAGES What role do plankton play in the food web? California Current Ecosystem Plankton Food Web and the Beth Simmons Education and Outreach Coordinator, CCE LTER, Scripps Institution of Oceanography,
THE CARBON CRISIS: IT S NOW OR NEVER TO SAVE CORAL REEFS
 MEDIA Q&As December 14, 2007 THE CARBON CRISIS: IT S NOW OR NEVER TO SAVE CORAL REEFS Q. The negative impact of climate change on coral reefs is not new. What does this paper tell us that we didn t already
MEDIA Q&As December 14, 2007 THE CARBON CRISIS: IT S NOW OR NEVER TO SAVE CORAL REEFS Q. The negative impact of climate change on coral reefs is not new. What does this paper tell us that we didn t already
Wake Acceleration Academy Earth & Environmental Science: Semester B Note Guide Unit 2: Earth s Changing Climate
 1 Wake Acceleration Academy Earth & Environmental Science: Semester B Note Guide Unit 2: Earth s Changing Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: The Mechanics of Change 1. What
1 Wake Acceleration Academy Earth & Environmental Science: Semester B Note Guide Unit 2: Earth s Changing Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: The Mechanics of Change 1. What
THE IMPO RTANCE O F SHARKS: YO U DO THE MATH!
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Activitydevelop THE IMPO RTANCE O F SHARKS: YO U DO THE MATH! What
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore Activitydevelop THE IMPO RTANCE O F SHARKS: YO U DO THE MATH! What
OUR OCEANS FACTSHEET. Ocean life
 The ocean makes our planet a wonderful place to live. It gives us more than half of the oxygen we breathe. It regulates the climate, absorbs a quarter of the carbon that we put into the atmosphere every
The ocean makes our planet a wonderful place to live. It gives us more than half of the oxygen we breathe. It regulates the climate, absorbs a quarter of the carbon that we put into the atmosphere every
Global warming, population growth, acid rain, eutrophication, CFCs/environmental toxins HUMAN IMPACTS
 Global warming, population growth, acid rain, eutrophication, CFCs/environmental toxins HUMAN IMPACTS GLOBAL WARMING GLOBAL WARMING Trapping of warm air close to the Earth s surface due to emission of
Global warming, population growth, acid rain, eutrophication, CFCs/environmental toxins HUMAN IMPACTS GLOBAL WARMING GLOBAL WARMING Trapping of warm air close to the Earth s surface due to emission of
What is the carbon cycle?
 What is the carbon cycle? By NASA Earth Observatory, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.29.17 Word Count 1,454 Carbon is both the foundation of all life on Earth and the source of the majority of energy consumed
What is the carbon cycle? By NASA Earth Observatory, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.29.17 Word Count 1,454 Carbon is both the foundation of all life on Earth and the source of the majority of energy consumed
AT HOME SCIENTIST! SHARKS
 SHARKS Sharks are amazing and often misunderstood creatures of the sea. Without them, the ocean food chain would be affected, and the balance of life in the ocean would be disrupted. Have you wondered
SHARKS Sharks are amazing and often misunderstood creatures of the sea. Without them, the ocean food chain would be affected, and the balance of life in the ocean would be disrupted. Have you wondered
Click the map to read about possible consequences of climate changes in different parts of the world. Africa
 How are people changing the climate? Read more Unit2: What will the future be like? In the Basics-section you will find links to the Read more-section. Follow those links if you want to explore an issue
How are people changing the climate? Read more Unit2: What will the future be like? In the Basics-section you will find links to the Read more-section. Follow those links if you want to explore an issue
AP Environmental Science
 AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
Science education. Precious Water
 Did you know? Precious Water South Africa has passed new legislation on its water usage. Approximately 12-14 million South Africans do not have access to safe drinking water and about 21 million South
Did you know? Precious Water South Africa has passed new legislation on its water usage. Approximately 12-14 million South Africans do not have access to safe drinking water and about 21 million South
Human Impacts Classwork. 2. What are the two ways we can measure how humans have changed the Earth?
 Human Impacts Classwork Name: 5 th Grade PSI 1. What impact do humans have on the Earth? 2. What are the two ways we can measure how humans have changed the Earth? 3. List 4 things humans depend on the
Human Impacts Classwork Name: 5 th Grade PSI 1. What impact do humans have on the Earth? 2. What are the two ways we can measure how humans have changed the Earth? 3. List 4 things humans depend on the
Welcome Back! The Final is Coming! 12/13/16
 Welcome Back! The Final is Coming! 12/13/16 1. The picture below depicts what level of organization? 2. What organelle assists plants with producing their own food? *Bonus: What are plants classified as
Welcome Back! The Final is Coming! 12/13/16 1. The picture below depicts what level of organization? 2. What organelle assists plants with producing their own food? *Bonus: What are plants classified as
1 An Interconnected Planet
 CHAPTER 6 1 An Interconnected Planet SECTION The Environment KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How are humans and the environment connected? What is the difference between
CHAPTER 6 1 An Interconnected Planet SECTION The Environment KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: How are humans and the environment connected? What is the difference between
5th Grade Ecosystems Resources. Books:
 5th Grade Ecosystems Resources Next Generation Science Standards: LS2.A: Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems The food of almost any kind of animal can be traced back to plants. Organisms are related
5th Grade Ecosystems Resources Next Generation Science Standards: LS2.A: Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems The food of almost any kind of animal can be traced back to plants. Organisms are related
APES Review Worksheet #1
 APES Review Worksheet #1 1. Name the following: NO NO 2 NO 2 NO 3 NO 2 N 2 O N 2 NH 3 + NH 4 HNO 3 NO x 2. In the box to the right, sketch a house and the surroundings of a house that is designed to make
APES Review Worksheet #1 1. Name the following: NO NO 2 NO 2 NO 3 NO 2 N 2 O N 2 NH 3 + NH 4 HNO 3 NO x 2. In the box to the right, sketch a house and the surroundings of a house that is designed to make
Human Impact on Ecosystems
 CHAPTER 16 Human Impact on Ecosystems GETTING READY TO LEARN Preview Key Concepts 16.1 Human Population Growth and Natural Resources As the human population grows, the demand for Earth s resources increases.
CHAPTER 16 Human Impact on Ecosystems GETTING READY TO LEARN Preview Key Concepts 16.1 Human Population Growth and Natural Resources As the human population grows, the demand for Earth s resources increases.
Norma s Story. Education Module - May Educational Module Prepared by Karen Hawley
 Norma s Story Education Module - May 2015 Educational Module Prepared by Karen Hawley Norma s Story 5 min 46 sec : Animated video Summary This animated short film is a stylistic and lively story of the
Norma s Story Education Module - May 2015 Educational Module Prepared by Karen Hawley Norma s Story 5 min 46 sec : Animated video Summary This animated short film is a stylistic and lively story of the
Bathypelagic Zone. By: Madeline Roberts, Amber Tanaka, Carsten Ronshaugen, Na?ale Mcdonald
 Bathypelagic Zone By: Madeline Roberts, Amber Tanaka, Carsten Ronshaugen, Na?ale Mcdonald Facts Pressure: The pressure in the midnight zone is said to be 800 Gmes the pressure of that at the surface. The
Bathypelagic Zone By: Madeline Roberts, Amber Tanaka, Carsten Ronshaugen, Na?ale Mcdonald Facts Pressure: The pressure in the midnight zone is said to be 800 Gmes the pressure of that at the surface. The
Monitoring Coral Reef Ecosystems with Quadrats
 Monitoring Coral Reef Ecosystems with Quadrats Background & Key Concepts Coral reefs grow at rates ranging from 1 cm to 100 cm per year. Over long periods of time, they can form huge structures, making
Monitoring Coral Reef Ecosystems with Quadrats Background & Key Concepts Coral reefs grow at rates ranging from 1 cm to 100 cm per year. Over long periods of time, they can form huge structures, making
Team name Ecology Science Olympiad Exam Middle School Level (Division B)
 Team name Ecology Science Olympiad Exam Middle School Level (Division B) You have 50 minutes to complete this test. You may use a non-programmable calculator on this exam. The number of points available
Team name Ecology Science Olympiad Exam Middle School Level (Division B) You have 50 minutes to complete this test. You may use a non-programmable calculator on this exam. The number of points available
Unit 2: Ecology. Chapters 2: Principles of Ecology
 Unit 2: Ecology Chapters 2: Principles of Ecology Ecology Probe: Answer the questions and turn it in! This is a standard aquarium with a population of fish. There is no filter in this aquarium and no one
Unit 2: Ecology Chapters 2: Principles of Ecology Ecology Probe: Answer the questions and turn it in! This is a standard aquarium with a population of fish. There is no filter in this aquarium and no one
Section 6.1: A Changing Landscape. Name: Block: Date:
 Section 6.1: A Changing Landscape Name: Block: Date: 1. Our daily activities impact the quality of Earth s natural resources:,, a. These activities are:,, 2. The Effect of Human Activity :Agriculture a.
Section 6.1: A Changing Landscape Name: Block: Date: 1. Our daily activities impact the quality of Earth s natural resources:,, a. These activities are:,, 2. The Effect of Human Activity :Agriculture a.
LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 20 & 21 FLASHCARDS
 LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 20 & 21 FLASHCARDS The base of the ocean s food chains is formed by A. blue whales. B. plankton. C. coral reefs. D. sargassums. The place where the ocean meets the land is the The
LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 20 & 21 FLASHCARDS The base of the ocean s food chains is formed by A. blue whales. B. plankton. C. coral reefs. D. sargassums. The place where the ocean meets the land is the The
Gas Guzzlers. Biological Pump
 Gas Guzzlers Biological Pump Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter 8 Coral Reefs Open Ocean Deep Sea Marine equivalent of tropical rain forests Habitats for one-fourth of all marine species Coral polyps, which
Gas Guzzlers Biological Pump Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter 8 Coral Reefs Open Ocean Deep Sea Marine equivalent of tropical rain forests Habitats for one-fourth of all marine species Coral polyps, which
Weather has always been a hot topic of conversation. We talk about whether it is hot or cold, windy or calm, snowy or dry. We listen to the radio to
 Weather has always been a hot topic of conversation. We talk about whether it is hot or cold, windy or calm, snowy or dry. We listen to the radio to figure out if the weather will be different tomorrow.
Weather has always been a hot topic of conversation. We talk about whether it is hot or cold, windy or calm, snowy or dry. We listen to the radio to figure out if the weather will be different tomorrow.
natural resources energy resources fossil fuels pollution environment deposition Acid Rain sulfur dioxide carbon dioxide nitrogen oxides
 Humans make use of many things found in nature. For example, we use trees to build our homes and cotton to make our clothes. Things that are not made by people, but instead occur naturally, are called
Humans make use of many things found in nature. For example, we use trees to build our homes and cotton to make our clothes. Things that are not made by people, but instead occur naturally, are called
