Interaction Rpb2 Clamp core
|
|
|
- Junior Sims
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SS_ SS_ SS_ -----aaa bbbbb----aaaa-----bbbbb bb BBBBBB-----AAA---BB aaaaa-bbbbb----aaaaa--bbbbb bbb Clamp core A Zipper Zn SS_ SS_ SS_ ----bbbb------bbbb------aaaaaaaaaaaa------bbbb aaaaaaaaaaaa BBBB----BBAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA----BBB bbbb------aaaaaaaaaaaaaa------bb-----aaaaaaaaa---aaaaaaa Zn8 Zn6 Clamp head SS_ SS_ SS_ aaaaaaaaaa------b aaaa-aaaaaaaaa aaaaa ----AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA AAAA--AAAAAAAAA-AAAAAAAAAAAA---AAAA--AAAA Aaaa bBBBBb aaaAA * drd3-1 SS_ SS_ SS_ AAAAAAAaaa-aaa bBb bBBb aaaAAAAAAAAA AAAAA-----BBBBB BBBBBB AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA AAaaa-----aaa bBBBb bb aaaAAAAAAAAAAAAAA B Clamp core Lid SS_ SS_ SS_ AAAAAaaa-----aaaAAAAAAAAAAAaaa aaaAaaa bb AAAA----AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA AAAAAAAA-----BBB-----BB Aaaa aaaAAAAAAAAAAAAaaa aaaAAAaaa-----bb b C Rudder Switch 2 SS_ SS_ SS_ bbbbb aaaaaaaa---aaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaa BBBBB AAAAAAA-----B----AAAAAAAAAA BBB ----bbbb b---aaaaa-----bbb-aaaaaaaaaaa bbbb-----bbaa * drd3-4 Active site Dock
2 D E F Interaction Rpb8 Interaction Rpb9 Interaction Rpb9 Metal A A Active site Pore 1 Funnel N drd3-3 * drd3-7 --aaaaaa bbbbbb----bbbb bbbbbb-----bbbb B----BBB------BBBBBBB----BBBB BBBBBB------BB aa bbbbbb----bbbb bbbbb------bb bbbb----aaaaaaaaaaaa-----b bbbb---bbbbbbbbb aaaaaaaaaaaa --BBBB----AAAAAAAAAAAA-----B BBBB--AAAAAAAAAA AAAAAAAAAAA aaaaaaaaaaa-----bb bbbbbb-aaaaaaaa------aaaaaaaaaaaaa bb--bbbbbbb bbbb---bbb B--BBBBBBBB BBBBB----BBBBB bbbbbbb bbbbb---bbbbbb- --b bbbbbb------aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa----bbb aaaaa-aaaaaaaa AAA------ABBAAABB----AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA---BB bbb------bbbbbbb---aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa---bbbb AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAaaa aaaAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAaaa AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA AAAAAAAAAA-AAAAA aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa bbbbb aaaaaaaaaaa AAAAA----BBBBB------AAAAAAAAAAAAA aa bbbbb bbbbbbbb SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_
3 G Bridge Interaction Rpb5 Interaction Rpb6 Interaction Rpb9 Cleft Foot Cleft Jaw R drd bbb aaaaaaaa------bbb aaaaaaaaaaaa--bbb----bbbb BBB AAAAAAAA-----AAAAAAAA----AAAAAAAAAA--BBBBB---BB bbb---b-----aaaaaaaa------bbbbbb----aaaaaaaaaaa---bbb----bb--- --bbbbbb BBBBBBB BBBBB AAAAAAAA- --bbbbbbb aaaaa aaaaaaaaa--aaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaa AAAAAAAAAAAAAAaaa bBBBb-aaaAAAAAAAaaa aaaAAAAAaaa---bBB b------aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa---aaaaaaaa-aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa-----abbaaaa aaaaaaa bbbbbbbb------aaa---aa AAAAAAA----AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA a------aaaaa----bbbb----bb-----aaaaaaa bbbbbb aaaaa aaaaa------bbbbbbbbbbbbb------bb bbb------a -AAAAAA BBBBBBB-----BBBBB BBAAAAA AAAAaaa-bBBBBBBb--bBBBb-----bBBBb--aaaAAaaa bBBBbaaaAA SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_
4 SS_ SS_ SS_ aaaa-----bbbbb bbbbbb---- AA AAAAAAAAAA AAAAA BBBBBB----- AAaaa--aaaAAAAAaaa bBBBBb-----bBBBBBBb * drd3-8 * drd3-6 SS_ SS_ SS_ bbb----aaaaaaaaa---b------bbbbbbb bbbbbbb-----aa --BBBAAAAAA----AAA BBBBBB B BBBBB A aaaaaaaaaaa-----b------bbbbbb----bbb * drd3-9 * drd3-5 Interaction Rpb9/Rpb2 Cleft SS_ SS_ SS_ aaaaa aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa------aaaaaaa AAAAAAAA----A AAAAAAA--AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA-----AAAAAAAA -bbbbb-----bbbbb bbb----b-aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaa Interaction Rpb5 SS_ SS_ SS_ Aaaa---bBBBBb-aaaAAAaaa------aaaAAAaaa-aaaAAAAaaa bBBBb A BBB------BB AAAAAAA---AAAAAAAAAA BBBBBB AAAaaa---bBBBBb bBb----aaaAAAAAAaaa bBb H Switch1 Clamp core Switch5 SS_ SS_ SS_ ----bbbbbb BBBBBB bbbbbbaaaaaa Interaction Rpb6 Linker Acidic region SS_ SS_ SS_ bbbbb AAABBBBBBBBB----BBB AAA CTD
5 CTD heptapeptide repeat" AAAA SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SS_ SPT5 motif
6 SS_ SS_ SS_ aaaaaaaa---bb aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa------aaa -----BB AAA-AAAAAAAA--AAAAAAAA-AAAAAAAAAAA SS_ SS_ SS_ DCL motif SS_ SS_ SS_ aa----aaaaaaaa bbbbb bbbbbbbb aaaaaa---aaa -----AAAAAAAAAA BBBBBB BBBBBBB AAAAAAAAAAAA- a----aaaaaaaa AAAAAAAAAAAA SS_ SS_ SS_ 1905 SS_ SS_ SS_ Supplementary Figure 2 Kanno et al.
7 Supplementary Figure 2: Sequence comparisons. Comparisons of amino acid sequences and predicted secondary structures of Arabidopsis NRPD1b, NRPD1a, and yeast Rpb1. The alignment shows a comparison of NRPD1B and NRPD1A in the context of RPB1 from yeast, a closely related homologue RNA polymerase with a well-characterized 3D structure 1. Secondary structure elements have been predicted using jnet 2 and are shown in the rows above the sequences with A/B delineating core alpha helix and beta sheet motifs, and a/b denoting terminal alpha helix and beta sheet areas. The secondary structure predictions have been used to facilitate sequence alignment by Clustal-X 3. Only minor manual corrections were made to the alignment. Box shading by BOXSHADE 3.33c ( The annotation from the 3D structure of RPB1 has been transferred to the aligment manually and is shown beneath the sequences to provide a functional context. Black bars marked A to H denote highly conserved regions showing homology of the yeast RPB1 with human RPB1 and the E. coli RNA polymerase ß' subunit 1. The RPS-BLAST motifs shown in Fig. 3B correspond to the following amino acid intervals: Rpb1-1 (13-250); Rpb1-3 ( ); Rpb1-4 ( ); Rpb1-5 ( ); RpoC (13-815). Only two of the nrpd1b/drd3 mutations identified in this study result in an amino acid exchange: drd3-3 results from substitution of the conserved aspartic acid in position 451 of the metal binding region of the active site by asparagine, whereas drd3-2 results from substitution of the highly conserved glycine at position 776 in the bridge region by arginine. The other seven point mutations introduce premature stop codons within the N-terminal half of NRPD1b. These might lead to the synthesis of truncated proteins that are unable to interact with other proteins or that fail to appropriately bind the DNA substrate of NPRD1b. 1. Cramer P, Bushnell DA and Kornberg RD. (2001) Structural basis of transcription: RNA polymerase II at 2.8 angstrom resolution. Science 292: Cuff J.A. and Barton G.J. (2000) Application of multiple sequence alignment profiles to improve protein secondary structure prediction. Proteins 40: Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F and Higgins DG. (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 25:
IBFT- Account Number Formats
 IBFT- Account Number Formats Allied Bank Please enter Allied Bank Account Number by following the layout below: Total Digits of Account Number: 13 or 20 Digits Format Example: BBBBAAAAAAAAA or BBBBAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
IBFT- Account Number Formats Allied Bank Please enter Allied Bank Account Number by following the layout below: Total Digits of Account Number: 13 or 20 Digits Format Example: BBBBAAAAAAAAA or BBBBAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA
Hmwk # 8 : DNA-Binding Proteins : Part II
 The purpose of this exercise is : Hmwk # 8 : DNA-Binding Proteins : Part II 1). to examine the case of a tandem head-to-tail homodimer binding to DNA 2). to view a Zn finger motif 3). to consider the case
The purpose of this exercise is : Hmwk # 8 : DNA-Binding Proteins : Part II 1). to examine the case of a tandem head-to-tail homodimer binding to DNA 2). to view a Zn finger motif 3). to consider the case
Lecture 11. Initiation of RNA Pol II transcription. Transcription Initiation Complex
 Lecture 11 *Eukaryotic Transcription Gene Organization RNA Processing 5 cap 3 polyadenylation splicing Translation Initiation of RNA Pol II transcription Consensus sequence of promoter TATA Transcription
Lecture 11 *Eukaryotic Transcription Gene Organization RNA Processing 5 cap 3 polyadenylation splicing Translation Initiation of RNA Pol II transcription Consensus sequence of promoter TATA Transcription
Supplementary Online Material. Structural mimicry in transcription regulation of human RNA polymerase II by the. DNA helicase RECQL5
 Supplementary Online Material Structural mimicry in transcription regulation of human RNA polymerase II by the DNA helicase RECQL5 Susanne A. Kassube, Martin Jinek, Jie Fang, Susan Tsutakawa and Eva Nogales
Supplementary Online Material Structural mimicry in transcription regulation of human RNA polymerase II by the DNA helicase RECQL5 Susanne A. Kassube, Martin Jinek, Jie Fang, Susan Tsutakawa and Eva Nogales
6.C: Students will explain the purpose and process of transcription and translation using models of DNA and RNA
 6.C: Students will explain the purpose and process of transcription and translation using models of DNA and RNA DNA mrna Protein DNA is found in the nucleus, but making a protein occurs at the ribosome
6.C: Students will explain the purpose and process of transcription and translation using models of DNA and RNA DNA mrna Protein DNA is found in the nucleus, but making a protein occurs at the ribosome
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Construction of a sensitive TetR mediated auxotrophic off-switch.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Construction of a sensitive TetR mediated auxotrophic off-switch. A Production of the Tet repressor in yeast when conjugated to either the LexA4 or LexA8 promoter DNA binding sequences.
Supplementary Figure 1 Construction of a sensitive TetR mediated auxotrophic off-switch. A Production of the Tet repressor in yeast when conjugated to either the LexA4 or LexA8 promoter DNA binding sequences.
DNA is the MASTER PLAN. RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan
 Sec. 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Roles of DNA and RNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 1 RNA uses the information from DNA to make proteins Differs from DNA: 1. Ribose
Sec. 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Roles of DNA and RNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 1 RNA uses the information from DNA to make proteins Differs from DNA: 1. Ribose
Chapter 14: From DNA to Protein
 Chapter 14: From DNA to Protein Steps from DNA to Proteins Same two steps produce all proteins: 1) DNA is transcribed to form RNA Occurs in the nucleus RNA moves into cytoplasm 2) RNA is translated in
Chapter 14: From DNA to Protein Steps from DNA to Proteins Same two steps produce all proteins: 1) DNA is transcribed to form RNA Occurs in the nucleus RNA moves into cytoplasm 2) RNA is translated in
Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis
 Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis 1. Describe how genetic information is transcribed into sequences of bases in RNA molecules and is finally translated into sequences of amino
Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis 1. Describe how genetic information is transcribed into sequences of bases in RNA molecules and is finally translated into sequences of amino
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II.
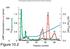 Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
produces an RNA copy of the coding region of a gene
 1. Transcription Gene Expression The expression of a gene into a protein occurs by: 1) Transcription of a gene into RNA produces an RNA copy of the coding region of a gene the RNA transcript may be the
1. Transcription Gene Expression The expression of a gene into a protein occurs by: 1) Transcription of a gene into RNA produces an RNA copy of the coding region of a gene the RNA transcript may be the
Regulation of gene expression. (Lehninger pg )
 Regulation of gene expression (Lehninger pg. 1072-1085) Today s lecture Gene expression Constitutive, inducible, repressible genes Specificity factors, activators, repressors Negative and positive gene
Regulation of gene expression (Lehninger pg. 1072-1085) Today s lecture Gene expression Constitutive, inducible, repressible genes Specificity factors, activators, repressors Negative and positive gene
DNA, RNA, and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
 DNA, RNA, and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA DNA contains genes, sequences of nucleotide bases The genes code for polypeptides (proteins) Proteins are used to build cells and do much of the work inside cells
DNA, RNA, and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA DNA contains genes, sequences of nucleotide bases The genes code for polypeptides (proteins) Proteins are used to build cells and do much of the work inside cells
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature21393 SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT SpMED Immuno-purification and subunit localization Wild-type and subunit deletion mutant SpMEDs (Extended Data Table 1) were immunopurified through TAP-tagged
doi:10.1038/nature21393 SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT SpMED Immuno-purification and subunit localization Wild-type and subunit deletion mutant SpMEDs (Extended Data Table 1) were immunopurified through TAP-tagged
After processing: a short primer on RNA export from the nucleus
 After processing: a short primer on RNA export from the nucleus The nascent (primary) transcript in the nucleus is decorated with RNA-binding proteins to form mrnps These decorations facility mrna identification,
After processing: a short primer on RNA export from the nucleus The nascent (primary) transcript in the nucleus is decorated with RNA-binding proteins to form mrnps These decorations facility mrna identification,
Secondary structure of hvps4b (above) and sequence alignments of VPS4 proteins from
 Supplemental Figure 1. Secondary structure of hvps4b (above) and sequence alignments of VPS4 proteins from different species as well as four other representative members of the meiotic clade of AAA ATPases.
Supplemental Figure 1. Secondary structure of hvps4b (above) and sequence alignments of VPS4 proteins from different species as well as four other representative members of the meiotic clade of AAA ATPases.
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. copyright cmassengale
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA and Genes 2 Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 3 RNA Differs from DNA RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 4 Other
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA and Genes 2 Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 3 RNA Differs from DNA RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 4 Other
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00
 Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00 The general problem RG Clerc March 2, 2016 RNA Transcription
Transcription Regulation And Gene Expression in Eukaryotes FS 2016 Graduate Course G2 P Matthias and RG Clerc Pharmazentrum Hörsaal 2 16h15-18h00 The general problem RG Clerc March 2, 2016 RNA Transcription
Soybean Microarrays. An Introduction. By Steve Clough. November Common Microarray platforms
 Soybean Microarrays Microarray construction An Introduction By Steve Clough November 2005 Common Microarray platforms cdna: spotted collection of PCR products from different cdna clones, each representing
Soybean Microarrays Microarray construction An Introduction By Steve Clough November 2005 Common Microarray platforms cdna: spotted collection of PCR products from different cdna clones, each representing
The Structure of Proteins The Structure of Proteins. How Proteins are Made: Genetic Transcription, Translation, and Regulation
 How Proteins are Made: Genetic, Translation, and Regulation PLAY The Structure of Proteins 14.1 The Structure of Proteins Proteins - polymer amino acids - monomers Linked together with peptide bonds A
How Proteins are Made: Genetic, Translation, and Regulation PLAY The Structure of Proteins 14.1 The Structure of Proteins Proteins - polymer amino acids - monomers Linked together with peptide bonds A
DNA RNA PROTEIN. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted
 DNA RNA PROTEIN Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted DNA Molecule of heredity Contains all the genetic info our cells inherit Determines
DNA RNA PROTEIN Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted DNA Molecule of heredity Contains all the genetic info our cells inherit Determines
Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins
 PHRM 836 September 22, 2015 Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins Devlin Chapter 8.8-9 u General description of transcription factors (TFs) u Sequence-specific interactions between DNA
PHRM 836 September 22, 2015 Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins Devlin Chapter 8.8-9 u General description of transcription factors (TFs) u Sequence-specific interactions between DNA
The Beery Twins Story and Sepiapterin Reductase
 The Beery Twins Story and Sepiapterin Reductase Sepiapterin reductase (SPR) is an enzyme that makes tetrahydrobiopterin an important cofactor used by other enzymes to make the neurotransmitters dopamine
The Beery Twins Story and Sepiapterin Reductase Sepiapterin reductase (SPR) is an enzyme that makes tetrahydrobiopterin an important cofactor used by other enzymes to make the neurotransmitters dopamine
Identifying Regulatory Regions using Multiple Sequence Alignments
 Identifying Regulatory Regions using Multiple Sequence Alignments Prerequisites: BLAST Exercise: Detecting and Interpreting Genetic Homology. Resources: ClustalW is available at http://www.ebi.ac.uk/tools/clustalw2/index.html
Identifying Regulatory Regions using Multiple Sequence Alignments Prerequisites: BLAST Exercise: Detecting and Interpreting Genetic Homology. Resources: ClustalW is available at http://www.ebi.ac.uk/tools/clustalw2/index.html
STRUCTURAL BIOLOGY. α/β structures Closed barrels Open twisted sheets Horseshoe folds
 STRUCTURAL BIOLOGY α/β structures Closed barrels Open twisted sheets Horseshoe folds The α/β domains Most frequent domain structures are α/β domains: A central parallel or mixed β sheet Surrounded by α
STRUCTURAL BIOLOGY α/β structures Closed barrels Open twisted sheets Horseshoe folds The α/β domains Most frequent domain structures are α/β domains: A central parallel or mixed β sheet Surrounded by α
Protein Synthesis Review Bi 12 /25
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Protein Synthesis Review Bi 12 /25 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A certain gene codes for a polypeptide that is
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Protein Synthesis Review Bi 12 /25 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A certain gene codes for a polypeptide that is
Protein Synthesis ~Biology AP~
 Protein Synthesis ~Biology AP~ A Meridian Study Guide by David Guan, Jennifer Zheng [Edited by Lei Gong] Introduction: - DNA and RNA are essential for life because they code for enzymes, which regulate
Protein Synthesis ~Biology AP~ A Meridian Study Guide by David Guan, Jennifer Zheng [Edited by Lei Gong] Introduction: - DNA and RNA are essential for life because they code for enzymes, which regulate
Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation
 Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are the workhorses but contain no information THUS Information in DNA must
Chapter 10: Gene Expression and Regulation Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are the workhorses but contain no information THUS Information in DNA must
Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: cloning the genes
 Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: cloning the genes Objectives: To test the validity of the ABC model for floral organ identity we will: 1. Use the model to make predictions concerning the phenotype
Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: cloning the genes Objectives: To test the validity of the ABC model for floral organ identity we will: 1. Use the model to make predictions concerning the phenotype
Advanced Algorithms and Models for Computational Biology
 10-810 Advanced Algorithms and Models for Computational Biology Ziv Bar-Joseph zivbj@cs.cmu.edu WeH 4107 Eric Xing epxing@cs.cmu.edu WeH 4127 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~epxing/class/10810-06/ Topics Introduction
10-810 Advanced Algorithms and Models for Computational Biology Ziv Bar-Joseph zivbj@cs.cmu.edu WeH 4107 Eric Xing epxing@cs.cmu.edu WeH 4127 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~epxing/class/10810-06/ Topics Introduction
1. The diagram below shows an error in the transcription of a DNA template to messenger RNA (mrna).
 1. The diagram below shows an error in the transcription of a DNA template to messenger RNA (mrna). Which statement best describes the error shown in the diagram? (A) The mrna strand contains the uracil
1. The diagram below shows an error in the transcription of a DNA template to messenger RNA (mrna). Which statement best describes the error shown in the diagram? (A) The mrna strand contains the uracil
Chapter 17. From Gene to Protein
 Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein One Gene One Enzyme Hypothesis Archibald Garrod 1 st to suggest that genes dictate phenotypes through enzymes that catalyze specific chemical reactions ; alkaptonuria Beadle
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein One Gene One Enzyme Hypothesis Archibald Garrod 1 st to suggest that genes dictate phenotypes through enzymes that catalyze specific chemical reactions ; alkaptonuria Beadle
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW. Overview of Biomolecules. Chapter 13 Protein Synthesis
 BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 13 Protein Synthesis 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Are You Getting It?? Which properties are characteristic of the normal genetic code? (multiple answers) a) A
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 13 Protein Synthesis 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Are You Getting It?? Which properties are characteristic of the normal genetic code? (multiple answers) a) A
FROM GENE TO PROTEIN. One Gene One Enzyme Hypothesis 3/12/2013. Basic Principles of Transcription & Translation
 One Gene One Enzyme Hypothesis FROM GENE TO PROTEIN C H A P T E R 1 7 Archibald Garrod 1 st to suggest that genes dictate phenotypes through enzymes that catalyze specific chemical reactions ; alkaptonuria
One Gene One Enzyme Hypothesis FROM GENE TO PROTEIN C H A P T E R 1 7 Archibald Garrod 1 st to suggest that genes dictate phenotypes through enzymes that catalyze specific chemical reactions ; alkaptonuria
The Structure of RNA. The Central Dogma
 12-3 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis The Structure of RNA The Central Dogma Phenotype A gene is a SEQUENCE of DNA that codes for a protein (or functional RNA). Phenotype is the individual s observable trait
12-3 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis The Structure of RNA The Central Dogma Phenotype A gene is a SEQUENCE of DNA that codes for a protein (or functional RNA). Phenotype is the individual s observable trait
Supplementary Note 1. Enzymatic properties of the purified Syn BVR
 Supplementary Note 1. Enzymatic properties of the purified Syn BVR The expression vector pet15b-syn bvr allowed us to routinely prepare 15 mg of electrophoretically homogenous Syn BVR from 2.5 L of TB-medium
Supplementary Note 1. Enzymatic properties of the purified Syn BVR The expression vector pet15b-syn bvr allowed us to routinely prepare 15 mg of electrophoretically homogenous Syn BVR from 2.5 L of TB-medium
Protein Synthesis. DNA to RNA to Protein
 Protein Synthesis DNA to RNA to Protein From Genes to Proteins Processing the information contained in DNA into proteins involves a sequence of events known as gene expression and results in protein synthesis.
Protein Synthesis DNA to RNA to Protein From Genes to Proteins Processing the information contained in DNA into proteins involves a sequence of events known as gene expression and results in protein synthesis.
Name Date Class. The Central Dogma of Biology
 Concept Mapping The Central Dogma of Biology Complete the events chain showing the events that occur as DNA codes for RNA, which guides the synthesis of proteins, the central dogma of biology. These terms
Concept Mapping The Central Dogma of Biology Complete the events chain showing the events that occur as DNA codes for RNA, which guides the synthesis of proteins, the central dogma of biology. These terms
Introduction to Cellular Biology and Bioinformatics. Farzaneh Salari
 Introduction to Cellular Biology and Bioinformatics Farzaneh Salari Outline Bioinformatics Cellular Biology A Bioinformatics Problem What is bioinformatics? Computer Science Statistics Bioinformatics Mathematics...
Introduction to Cellular Biology and Bioinformatics Farzaneh Salari Outline Bioinformatics Cellular Biology A Bioinformatics Problem What is bioinformatics? Computer Science Statistics Bioinformatics Mathematics...
Aaditya Khatri. Abstract
 Abstract In this project, Chimp-chunk 2-7 was annotated. Chimp-chunk 2-7 is an 80 kb region on chromosome 5 of the chimpanzee genome. Analysis with the Mapviewer function using the NCBI non-redundant database
Abstract In this project, Chimp-chunk 2-7 was annotated. Chimp-chunk 2-7 is an 80 kb region on chromosome 5 of the chimpanzee genome. Analysis with the Mapviewer function using the NCBI non-redundant database
Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: cloning the genes
 Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: cloning the genes Objectives: To test the validity of the ABC model for floral organ identity we will: 1. Use the model to make predictions concerning the phenotype
Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: cloning the genes Objectives: To test the validity of the ABC model for floral organ identity we will: 1. Use the model to make predictions concerning the phenotype
Name: Family: Date: Monday/Tuesday, March 9,
 Name: Family: Date: Monday/Tuesday, March 9,10 2015 Select the best answer for each question: Part 1: Multiple Choice (2 points each) 1. Protein Synthesis involves which two processes? a. DNA Replication
Name: Family: Date: Monday/Tuesday, March 9,10 2015 Select the best answer for each question: Part 1: Multiple Choice (2 points each) 1. Protein Synthesis involves which two processes? a. DNA Replication
Structural Perspective on Mutations Affecting the Function of Multisubunit RNA Polymerases
 MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, Mar. 2006, p. 12 36 Vol. 70, No. 1 1092-2172/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/mmbr.70.1.12 36.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, Mar. 2006, p. 12 36 Vol. 70, No. 1 1092-2172/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/mmbr.70.1.12 36.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Structural Perspective on Mutations Affecting the Function of Multisubunit RNA Polymerases
 MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, Mar. 2006, p. 12 36 Vol. 70, No. 1 1092-2172/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/mmbr.70.1.12 36.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, Mar. 2006, p. 12 36 Vol. 70, No. 1 1092-2172/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/mmbr.70.1.12 36.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
DNA Structure DNA Nucleotide 3 Parts: 1. Phosphate Group 2. Sugar 3. Nitrogen Base
 DNA,, RNA,, AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid Enables cells to have different forms and perform different functions Primary functions of DNA: Store and transmit genetic information that tells
DNA,, RNA,, AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid Enables cells to have different forms and perform different functions Primary functions of DNA: Store and transmit genetic information that tells
Section 14.1 Structure of ribonucleic acid
 Section 14.1 Structure of ribonucleic acid The genetic code Sections of DNA are transcribed onto a single stranded molecule called RNA There are two types of RNA One type copies the genetic code and transfers
Section 14.1 Structure of ribonucleic acid The genetic code Sections of DNA are transcribed onto a single stranded molecule called RNA There are two types of RNA One type copies the genetic code and transfers
Representation in Supervised Machine Learning Application to Biological Problems
 Representation in Supervised Machine Learning Application to Biological Problems Frank Lab Howard Hughes Medical Institute & Columbia University 2010 Robert Howard Langlois Hughes Medical Institute What
Representation in Supervised Machine Learning Application to Biological Problems Frank Lab Howard Hughes Medical Institute & Columbia University 2010 Robert Howard Langlois Hughes Medical Institute What
CHapter 14. From DNA to Protein
 CHapter 14 From DNA to Protein How? DNA to RNA to Protein to Trait Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA: carries protein code or transcript 2. Ribosomal RNA: part of ribosomes 3. Transfer RNA: delivers amino
CHapter 14 From DNA to Protein How? DNA to RNA to Protein to Trait Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA: carries protein code or transcript 2. Ribosomal RNA: part of ribosomes 3. Transfer RNA: delivers amino
Biochemistry 111. Carl Parker x A Braun
 Biochemistry 111 Carl Parker x6368 101A Braun csp@caltech.edu Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Requires a DNA Template Synthesizes RNA in a 5 to 3 direction Requires ribonucleoside
Biochemistry 111 Carl Parker x6368 101A Braun csp@caltech.edu Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Requires a DNA Template Synthesizes RNA in a 5 to 3 direction Requires ribonucleoside
Proteins and Protein Synthesis body structures, hormones, enzymes & antibodies amino acids sequence number DNA chemical code codon 'initiator'
 Proteins and Protein Synthesis - Proteins : large complex molecules that make up body structures, hormones, enzymes & antibodies : are composed of subunits called amino acids : there are 20 different amino
Proteins and Protein Synthesis - Proteins : large complex molecules that make up body structures, hormones, enzymes & antibodies : are composed of subunits called amino acids : there are 20 different amino
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. copyright cmassengale
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA and Genes 2 Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 3 RNA Differs from DNA RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 4 Other
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA and Genes 2 Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 3 RNA Differs from DNA RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 4 Other
Basic concepts of molecular biology
 Basic concepts of molecular biology Gabriella Trucco Email: gabriella.trucco@unimi.it Life The main actors in the chemistry of life are molecules called proteins nucleic acids Proteins: many different
Basic concepts of molecular biology Gabriella Trucco Email: gabriella.trucco@unimi.it Life The main actors in the chemistry of life are molecules called proteins nucleic acids Proteins: many different
BIOLOGY. Monday 14 Mar 2016
 BIOLOGY Monday 14 Mar 2016 Entry Task List the terms that were mentioned last week in the video. Translation, Transcription, Messenger RNA (mrna), codon, Ribosomal RNA (rrna), Polypeptide, etc. Agenda
BIOLOGY Monday 14 Mar 2016 Entry Task List the terms that were mentioned last week in the video. Translation, Transcription, Messenger RNA (mrna), codon, Ribosomal RNA (rrna), Polypeptide, etc. Agenda
Neurospora mutants. Beadle & Tatum: Neurospora molds. Mutant A: Mutant B: HOW? Neurospora mutants
 Chapter 10: Central Dogma Gene Expression and Regulation Mutant A: Neurospora mutants Mutant B: Not made Not made Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are
Chapter 10: Central Dogma Gene Expression and Regulation Mutant A: Neurospora mutants Mutant B: Not made Not made Fact 1: DNA contains information but is unable to carry out actions Fact 2: Proteins are
Ch. 10 Notes DNA: Transcription and Translation
 Ch. 10 Notes DNA: Transcription and Translation GOALS Compare the structure of RNA with that of DNA Summarize the process of transcription Relate the role of codons to the sequence of amino acids that
Ch. 10 Notes DNA: Transcription and Translation GOALS Compare the structure of RNA with that of DNA Summarize the process of transcription Relate the role of codons to the sequence of amino acids that
Thebiotutor.com A2 Biology OCR Unit F215: Control, genomes and environment Module 1.1 Cellular control Answers
 Thebiotutor.com A2 Biology OCR Unit F215: Control, genomes and environment Module 1.1 Cellular control Answers Andy Todd 1 1. 1 ref to operon; 2 normally repressor substance bound to operator; 3 prevents
Thebiotutor.com A2 Biology OCR Unit F215: Control, genomes and environment Module 1.1 Cellular control Answers Andy Todd 1 1. 1 ref to operon; 2 normally repressor substance bound to operator; 3 prevents
Bundle 5 Test Review
 Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
DNA & Protein Synthesis #21
 Name: Period: Date: Living Environment Lab DNA & Protein Synthesis #21 Introduction Of all the molecules that is in the body, DNA is perhaps the most important. DNA or dioxiribosenucleic acid is important
Name: Period: Date: Living Environment Lab DNA & Protein Synthesis #21 Introduction Of all the molecules that is in the body, DNA is perhaps the most important. DNA or dioxiribosenucleic acid is important
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Higher Level
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Higher Level Lesson Objectives At the end of this lesson you should be able to 1. Outline the steps in protein synthesis 2. Understand DNA contains the code for protein 3. Understand
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Higher Level Lesson Objectives At the end of this lesson you should be able to 1. Outline the steps in protein synthesis 2. Understand DNA contains the code for protein 3. Understand
Transcription is the first stage of gene expression
 Transcription is the first stage of gene expression RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and hooks together the RNA nucleotides The RNA is complementary to the
Transcription is the first stage of gene expression RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and hooks together the RNA nucleotides The RNA is complementary to the
3. The following sequence is destined to be translated into a protein: However, a mutation occurs that results in the molecule being altered to:
 1. Please identify the molecule below: 5 -ACTCGATTACGATACGA-3ʼ a) DNA b) mrna c) trna d) rrna e) It cannot be determined 2. If a complimentary strand of RNA were made to the molecule in question 1, what
1. Please identify the molecule below: 5 -ACTCGATTACGATACGA-3ʼ a) DNA b) mrna c) trna d) rrna e) It cannot be determined 2. If a complimentary strand of RNA were made to the molecule in question 1, what
Name. Student ID. Midterm 2, Biology 2020, Kropf 2004
 Midterm 2, Biology 2020, Kropf 2004 1 1. RNA vs DNA (5 pts) The table below compares DNA and RNA. Fill in the open boxes, being complete and specific Compare: DNA RNA Pyrimidines C,T C,U Purines 3-D structure
Midterm 2, Biology 2020, Kropf 2004 1 1. RNA vs DNA (5 pts) The table below compares DNA and RNA. Fill in the open boxes, being complete and specific Compare: DNA RNA Pyrimidines C,T C,U Purines 3-D structure
Supplemental Figure legends Figure S1. (A) (B) (C) (D) Figure S2. Figure S3. (A-E) Figure S4. Figure S5. (A, C, E, G, I) (B, D, F, H, Figure S6.
 Supplemental Figure legends Figure S1. Map-based cloning and complementation testing for ZOP1. (A) ZOP1 was mapped to a ~273-kb interval on Chromosome 1. In the interval, a single-nucleotide G to A substitution
Supplemental Figure legends Figure S1. Map-based cloning and complementation testing for ZOP1. (A) ZOP1 was mapped to a ~273-kb interval on Chromosome 1. In the interval, a single-nucleotide G to A substitution
Videos. Lesson Overview. Fermentation
 Lesson Overview Fermentation Videos Bozeman Transcription and Translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Drawing transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/6yqplgnjr4q Objectives 29a) I can contrast
Lesson Overview Fermentation Videos Bozeman Transcription and Translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Drawing transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/6yqplgnjr4q Objectives 29a) I can contrast
Introduction to Bioinformatics Online Course: IBT
 Introduction to Bioinformatics Online Course: IBT Multiple Sequence Alignment Building Multiple Sequence Alignment Lec5: Interpreting your MSA Using Logos Using Logos - Logos are a terrific way to generate
Introduction to Bioinformatics Online Course: IBT Multiple Sequence Alignment Building Multiple Sequence Alignment Lec5: Interpreting your MSA Using Logos Using Logos - Logos are a terrific way to generate
Hello! Outline. Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis. In all living cells, DNA molecules are the storehouses of information. 6.
 Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis In all living cells, DNA molecules are the storehouses of information Hello! Outline u 1. Key concepts u 2. Central Dogma u 3. RNA Types u 4. RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis In all living cells, DNA molecules are the storehouses of information Hello! Outline u 1. Key concepts u 2. Central Dogma u 3. RNA Types u 4. RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
DNA REPLICATION REVIEW
 Biology Ms. Ye DNA REPLICATION REVIEW 1. Number the steps of DNA replication the correct order (1, 2, 3): Name Date Block Daughter strands are formed using complementary base pairing DNA unwinds The DNA
Biology Ms. Ye DNA REPLICATION REVIEW 1. Number the steps of DNA replication the correct order (1, 2, 3): Name Date Block Daughter strands are formed using complementary base pairing DNA unwinds The DNA
Chapter 4: How Cells Work
 Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: l l l l l Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription:
Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: l l l l l Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription:
Chapter 4: How Cells Work
 Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription: Sending the
Chapter 4: How Cells Work David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: Introduction : Central Dogma DNA Replication: Preserving and Propagating DNA Transcription: Sending the
Chapter 8. Microbial Genetics. Lectures prepared by Christine L. Case. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 8 Microbial Genetics Lectures prepared by Christine L. Case Structure and Function of Genetic Material Learning Objectives 8-1 Define genetics, genome, chromosome, gene, genetic code, genotype,
Chapter 8 Microbial Genetics Lectures prepared by Christine L. Case Structure and Function of Genetic Material Learning Objectives 8-1 Define genetics, genome, chromosome, gene, genetic code, genotype,
Chapter 11. Gene Expression and Regulation. Lectures by Gregory Ahearn. University of North Florida. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc..
 Chapter 11 Gene Expression and Regulation Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.. 11.1 How Is The Information In DNA Used In A Cell? Most genes contain
Chapter 11 Gene Expression and Regulation Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.. 11.1 How Is The Information In DNA Used In A Cell? Most genes contain
MOLECULAR GENETICS PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #2 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1 GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 2 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #2 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1 GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 2 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Unit 1. DNA and the Genome
 Unit 1 DNA and the Genome Gene Expression Key Area 3 Vocabulary 1: Transcription Translation Phenotype RNA (mrna, trna, rrna) Codon Anticodon Ribosome RNA polymerase RNA splicing Introns Extrons Gene Expression
Unit 1 DNA and the Genome Gene Expression Key Area 3 Vocabulary 1: Transcription Translation Phenotype RNA (mrna, trna, rrna) Codon Anticodon Ribosome RNA polymerase RNA splicing Introns Extrons Gene Expression
Supplemental Figure 1 A
 Supplemental Figure 1 A Supplemental Data. Han et al. (2016). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.15.00997 BamHI -1616 bp SINE repeats SalI ATG SacI +1653 bp HindIII LB HYG p35s pfwa LUC Tnos RB pfwa-bamhi-f: CGGGATCCCGCCTTTCTCTTCCTCATCTGC
Supplemental Figure 1 A Supplemental Data. Han et al. (2016). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.15.00997 BamHI -1616 bp SINE repeats SalI ATG SacI +1653 bp HindIII LB HYG p35s pfwa LUC Tnos RB pfwa-bamhi-f: CGGGATCCCGCCTTTCTCTTCCTCATCTGC
Sequence Alignments. Week 3
 Sequence Alignments Week 3 Independent Project Gene Due: 9/25 (Monday--must be submitted by email) Rough Draft Due: 11/13 (hard copy due at the beginning of class, and emailed to me) Final Version Due:
Sequence Alignments Week 3 Independent Project Gene Due: 9/25 (Monday--must be submitted by email) Rough Draft Due: 11/13 (hard copy due at the beginning of class, and emailed to me) Final Version Due:
Protein Synthesis. Lab Exercise 12. Introduction. Contents. Objectives
 Lab Exercise Protein Synthesis Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Overview of Process 2 Activity.2 Transcription 2 Activity.3 Translation 3 Resutls Section 4 Introduction Having information
Lab Exercise Protein Synthesis Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Overview of Process 2 Activity.2 Transcription 2 Activity.3 Translation 3 Resutls Section 4 Introduction Having information
C. Incorrect! Threonine is an amino acid, not a nucleotide base.
 MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 05: RNA and Protein Biosynthesis Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following bases are only found in RNA? Question #01 (A) Ribose. (B) Uracil. (C) Threonine. (D) Adenine.
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 05: RNA and Protein Biosynthesis Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following bases are only found in RNA? Question #01 (A) Ribose. (B) Uracil. (C) Threonine. (D) Adenine.
Text Reference, Campbell v.8, chapter 17 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
 AP BIOLOGY Text Reference, Campbell v.8, chapter 17 ACTIVITY 1.22 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW PROTEIN SYNTHESIS TRANSCRIPTION PROTEIN SYNTHESIS TRANSLATION
AP BIOLOGY Text Reference, Campbell v.8, chapter 17 ACTIVITY 1.22 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW PROTEIN SYNTHESIS TRANSCRIPTION PROTEIN SYNTHESIS TRANSLATION
Chapter 13. From DNA to Protein
 Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Alpha-helices, beta-sheets and U-turns within a protein are stabilized by (hint: two words).
 1 Quiz1 Q1 2011 Alpha-helices, beta-sheets and U-turns within a protein are stabilized by (hint: two words) Value Correct Answer 1 noncovalent interactions 100% Equals hydrogen bonds (100%) Equals H-bonds
1 Quiz1 Q1 2011 Alpha-helices, beta-sheets and U-turns within a protein are stabilized by (hint: two words) Value Correct Answer 1 noncovalent interactions 100% Equals hydrogen bonds (100%) Equals H-bonds
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription. RNA polymerases
 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
Videos. Bozeman Transcription and Translation: Drawing transcription and translation:
 Videos Bozeman Transcription and Translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Drawing transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/6yqplgnjr4q Objectives 29a) I can contrast RNA and DNA. 29b) I can explain
Videos Bozeman Transcription and Translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Drawing transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/6yqplgnjr4q Objectives 29a) I can contrast RNA and DNA. 29b) I can explain
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process.
 Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Resources. How to Use This Presentation. Chapter 10. Objectives. Table of Contents. Griffith s Discovery of Transformation. Griffith s Experiments
 How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
Chapter 12. DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION
 Chapter 12 DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis WARM UP What are proteins? Where do they come from? From DNA to RNA to Protein DNA in our cells carry the instructions for making
Chapter 12 DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis WARM UP What are proteins? Where do they come from? From DNA to RNA to Protein DNA in our cells carry the instructions for making
Chimp Sequence Annotation: Region 2_3
 Chimp Sequence Annotation: Region 2_3 Jeff Howenstein March 30, 2007 BIO434W Genomics 1 Introduction We received region 2_3 of the ChimpChunk sequence, and the first step we performed was to run RepeatMasker
Chimp Sequence Annotation: Region 2_3 Jeff Howenstein March 30, 2007 BIO434W Genomics 1 Introduction We received region 2_3 of the ChimpChunk sequence, and the first step we performed was to run RepeatMasker
Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription
 Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription Cis-acting sequences Distance-independent cis-acting elements Dissecting regulatory elements Transcription factors Overview transcriptional regulation Transcription
Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription Cis-acting sequences Distance-independent cis-acting elements Dissecting regulatory elements Transcription factors Overview transcriptional regulation Transcription
The dialkylglycine decarboxylase repressor DgdR. Functional aspects and relation to other LysR proteins
 11/29/2011 1 The dialkylglycine decarboxylase repressor DgdR. Functional aspects and relation to other LysR proteins 1. Dialkylglycine amino acids 2. In vivo and in vitro studies on the DgdR repressor
11/29/2011 1 The dialkylglycine decarboxylase repressor DgdR. Functional aspects and relation to other LysR proteins 1. Dialkylglycine amino acids 2. In vivo and in vitro studies on the DgdR repressor
Protein Synthesis
 HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
Lecture Summary: Regulation of transcription. General mechanisms-what are the major regulatory points?
 BCH 401G Lecture 37 Andres Lecture Summary: Regulation of transcription. General mechanisms-what are the major regulatory points? RNA processing: Capping, polyadenylation, splicing. Why process mammalian
BCH 401G Lecture 37 Andres Lecture Summary: Regulation of transcription. General mechanisms-what are the major regulatory points? RNA processing: Capping, polyadenylation, splicing. Why process mammalian
Section 10.3 Outline 10.3 How Is the Base Sequence of a Messenger RNA Molecule Translated into Protein?
 Section 10.3 Outline 10.3 How Is the Base Sequence of a Messenger RNA Molecule Translated into Protein? Messenger RNA Carries Information for Protein Synthesis from the DNA to Ribosomes Ribosomes Consist
Section 10.3 Outline 10.3 How Is the Base Sequence of a Messenger RNA Molecule Translated into Protein? Messenger RNA Carries Information for Protein Synthesis from the DNA to Ribosomes Ribosomes Consist
Key Area 1.3: Gene Expression
 Key Area 1.3: Gene Expression RNA There is a second type of nucleic acid in the cell, called RNA. RNA plays a vital role in the production of protein from the code in the DNA. What is gene expression?
Key Area 1.3: Gene Expression RNA There is a second type of nucleic acid in the cell, called RNA. RNA plays a vital role in the production of protein from the code in the DNA. What is gene expression?
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
Lecture for Wednesday. Dr. Prince BIOL 1408
 Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) and Mycobacterium smegmatis (Msmeg) contain two ε (dnaq) exonuclease homologs.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) and Mycobacterium smegmatis (Msmeg) contain two ε (dnaq) exonuclease homologs. (a) Sequence alignment of the ε-exonuclease homologs from four different
Supplementary Figure 1 Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) and Mycobacterium smegmatis (Msmeg) contain two ε (dnaq) exonuclease homologs. (a) Sequence alignment of the ε-exonuclease homologs from four different
Introduction to Bioinformatics Online Course: IBT
 Introduction to Bioinformatics Online Course: IBT Multiple Sequence Alignment Building Multiple Sequence Alignment Lec6:Interpreting Your Multiple Sequence Alignment Interpreting Your Multiple Sequence
Introduction to Bioinformatics Online Course: IBT Multiple Sequence Alignment Building Multiple Sequence Alignment Lec6:Interpreting Your Multiple Sequence Alignment Interpreting Your Multiple Sequence
Big Idea 3C Basic Review
 Big Idea 3C Basic Review 1. A gene is a. A sequence of DNA that codes for a protein. b. A sequence of amino acids that codes for a protein. c. A sequence of codons that code for nucleic acids. d. The end
Big Idea 3C Basic Review 1. A gene is a. A sequence of DNA that codes for a protein. b. A sequence of amino acids that codes for a protein. c. A sequence of codons that code for nucleic acids. d. The end
Lecture 1. Basic Definitions and Nucleic Acids. Basic Definitions you should already know
 Lecture 1. Basic Definitions and Nucleic Acids Basic Definitions you should already know apple DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid apple RNA: Ribonucleic Acid apple mrna: messenger RNA: contains the genetic information(coding
Lecture 1. Basic Definitions and Nucleic Acids Basic Definitions you should already know apple DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid apple RNA: Ribonucleic Acid apple mrna: messenger RNA: contains the genetic information(coding
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW. Overview of Biomolecules. Chapter 12 Transcription
 BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 12 Transcription 2 3 4 5 Are You Getting It?? Which are general characteristics of transcription? (multiple answers) a) An entire DNA molecule is transcribed
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 12 Transcription 2 3 4 5 Are You Getting It?? Which are general characteristics of transcription? (multiple answers) a) An entire DNA molecule is transcribed
Protein Structure Analysis
 BINF 731 Protein Structure Analysis http://binf.gmu.edu/vaisman/binf731/ Secondary Structure: Computational Problems Secondary structure characterization Secondary structure assignment Secondary structure
BINF 731 Protein Structure Analysis http://binf.gmu.edu/vaisman/binf731/ Secondary Structure: Computational Problems Secondary structure characterization Secondary structure assignment Secondary structure
