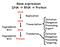
Le proteine regolative variano nei vari tipi cellulari e in funzione degli stimoli ambientali
|
|
|
- Phoebe Sparks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Le proteine regolative variano nei vari tipi cellulari e in funzione degli stimoli ambientali Tipo cellulare 1 Tipo cellulare 2 Tipo cellulare 3
2 DNA-protein Crosslink Lisi Frammentazione Immunopurificazione Identificazione DNA purificato
3 ChIP on chip = Chromatin IP + microarray Different from the arrays for transcriptome analysis : all the genome on the slide!
4 ChIP on chip procedure : a tool to map protein /genome interaction tion IP Reference : WCE Buck and Lieb, 2004
5 1. Cross link and chromatin preparation -Cross link with formaldehyde -Cell lysis -Sonication of the DNA into 1 kb fragments 2. Immunoprecipitation and cross link reversion -Over-night IP with antibodies coupled with magnetic beads -Specific antibodies are required -Reversion of the cross link by heating and agitating IP WCE
6 3. Amplification and labeling of DNA IP WCE -Proteinase and Rnase treatment : to «clean» the DNA -Amplification (PCR ) : random primers or ligation mediated -Labeling : direct or indirect (aadutp) Microarray with the whole genome
7 The results of ChIP on chip experiments Enriched DNA (from IP) Input DNA (from WCE) All the sequences bound by the protein of interest - Global map of the protein fixation - No need to know some of the targets before the experiment - No need to determine the non enriched sequences before the experiment
8 Analysis of the results For one experiment : 1. For each spot (each sequence) the enrichment ratio is determined : IP/WCE 2. Then, the data are normalized : so that the median log2 ratio =0 But one experiment is not enough
9 Representation : Chip vs ChIP on chip Transcriptome microarrays Symetric representation ChIP on chip There is only enrichment of DNA, there is no depletion! Non enriched repressed activated enriched count Log2 ratio
10 Analysis of the results For 4 experiments : At least 4 biological independent experiments are required to obtain significant results. For each sequence, the median of the normalized ratio is calculated Median log2 ratio (4 experiments) Median log2 ratio BUT, the amplitude of the ratios can change dramatically from one experiment to another for the same spot RANK
11 1. What is a rank? Analysis of the results The median rank method The rank of a sequence is the position of this sequence in a list sorted by ratio in descending order. 2. Why the ranks rather than ratios? - To avoid normalization pb - It s easy
12 Analysis of the results The Median rank method Exp 1 Exp 2 Exp 3 Exp 4 log2ratio IP/WCE log2ratio IP/WCE log2ratio IP/WCE log2ratio IP/WCE Normalized log2ratio IP/WCE Normalized log2ratio IP/WCE Normalized log2ratio IP/WCE Normalized log2ratio IP/WCE Rank Rank Rank Rank Median rank
13 Analysis of the results Median percentile rank method Theoretically For real Median IP rank That should give a bimodal distribution that makes the cut-off easier Efficient if more than 4% of the total elements are enriched Loss of amplitude information
14 Transcriptional regulatory networks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Lee TI, Rinaldi NJ, Robert F, Odom DT, Bar-Joseph Z, Gerber GK, Hannett NM, Harbison CT, Thompson CM, Simon I, Zeitlinger J, Jennings EG, Murray HL, Gordon DB, Ren B, Wyrick JJ, Tagne JB, Volkert TL, Fraenkel E, Gifford DK, Young RA. Science 2002 Oct 25;298(5594):763-4
15 1.Profiling the dynamics of TF binding Genome-wide analysis of 84 TF in yeast in many different growing conditions TF1myc TF2myc TF3myc TF4myc TF5myc Highly hyperoxic Elevated temperature Harbison et al 2004
16 1.Profiling the dynamics of TF binding Identification of cis-regulatory elements By merging informations from ChIP on chip, phylogeny and prior knowledge Harbisson et al 2004 New regulatory sequences
17 1.Profiling the dynamics of TF binding Transcriptional regulatory code of an eukaryotic genome Static Dynamics
18 2. Study of the general transcription machinery Recruitment of general transcription machinery is often the end point in a cascade of regulatory events TF ChIP on chip to have a genome-wide view of RNA polymerase (II and III) repartition along the chromosome in different conditions
19 2. Study of the general transcription machinery Genome-wide analysis of RNA Pol II location during stationnary phase (SP) in yeast To survive to harsh conditions, yeast adopt a quiescent state (=GO for mammalian). Transition from and to this state were not well known, at the gene regulation level General shutdown of Pol II transcription has been reported. At what point does this shutdown occur? Are there genes that escape repression? Radonjic et al, 2005
20 2. Study of the general transcription machinery FIRST : Global changing in mrna levels during quiescence exit and entry studied with microarrays Extremely rapid response upon exit from SP (2500 genes upregulated within 6 min) Hypothesis : this extremely rapid response can be explained by the fact that the transcription machinery is maintained on the promoter.
21 2. Study of the general transcription machinery ChIP on chip experiments SP Tap Tag version of Rpb3, a PolII subunit Pol II is located upstream of rapid exit genes during SP Different from the current model : Pol II recruitment is the rate limiting step controled through chromatin remodeling How this selective PolII binding occurs?
22 3. ChIP on chip analysis and chromatin dynamics Transcription occurs only if DNA is accessible! The chromatin components are important regulators of transcription Changes in modification or occupancy affect TF binding
23 3. ChIP on chip analysis and chromatin dynamics To increase accessibility : 1. Nucleosome disruption by remodeling complexes (SWI-SNF) 2. Chemical modifications of nucleosome by histone modifying complexes (HATs, HDACs) TF Genome-wide correlation between chromatine modification and gene activation by using ChIP on chip : detection of enzymes and histones modification
24 3. ChIP on chip analysis and chromatin dynamics Genome-wide studies of histone modifications Systematic ChIP on chip to map 11 different histone acetylation marks in yeast Compared with - each other - gene expression Purpose : correlation between patterns of acetylation and gene activity? Conclusions : Genes that share the same pattern of acetylation are biologicaly related For the future : basis for deciphering complex patterns of histone modification and their downstream effects on gene expression Kurdistani et al, 2004
25 3. ChIP on chip analysis and chromatin dynamics Analysis of histone-modifying proteins location Binding sites of HAT and HDAC both global and gene specific control - recruitment of HAT on active promoters - recruitment of HDAC have a preference for distinct gene classes Roberts et al, 2004
26 3. ChIP on chip analysis and chromatin dynamics Challenges of applying ChIP on chip to chromatin Formaldehyde fixation Epitop accessibility Differential underlying nucleosome occupancy Choice of microarray design
27 3. Chip chip analysis and chromatin dynamics ChIP on chip is not efficient to detect direct modifications of DNA Two microarray-based methods to detect methylations Methylation-sensitive restriction endonucleases high MW fragments are not methylated microarray Treatment CU but CmethCmeth after PCR : CT use of special design oligonucleotide array to quantify the CT changes
28 4. Alternatives to ChIP on chip DAMID The protein of interest is fused to DNA methyl adenine transferase (DAM) ChIP on chip DAM ID Van steensel et al, 2004 Advantage :No specific antibody required, no crosslink Limits : no detection of histone modification
29 4. Alternatives to ChIP on chip Protein Binding Microarray ChIP on chip : in vivo, but, it doesn t give all the potential targets Mukherjee et al Advantages : - No need for specific antibody - No need to find the condition for which the protein of interest is nuclear Limits : -in vitro -Few overlap between ChIP on chip and PBM results
30 Conclusion ChIP on chip is a very powerful tool to explore gene regulation ChIP on chip can also be useful to study the dynamics of replication and recombination ChIP on chip is not restricted to S. cerevisiae Real challenge in the future : - Integrating all these data using bioinformatics - Studying the dynamics of the response to one condition at all the levels TF
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42 Comparative bidimensional transcriptome analysis of SW480 and SW620 cell lines. Provenzani A et al. Carcinogenesis 2006;27: The Author Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org
Genome-Scale Predictions of the Transcription Factor Binding Sites of Cys 2 His 2 Zinc Finger Proteins in Yeast June 17 th, 2005
 Genome-Scale Predictions of the Transcription Factor Binding Sites of Cys 2 His 2 Zinc Finger Proteins in Yeast June 17 th, 2005 John Brothers II 1,3 and Panayiotis V. Benos 1,2 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics
Genome-Scale Predictions of the Transcription Factor Binding Sites of Cys 2 His 2 Zinc Finger Proteins in Yeast June 17 th, 2005 John Brothers II 1,3 and Panayiotis V. Benos 1,2 1 Bioengineering and Bioinformatics
Chapter 17 Lecture. Concepts of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Chapter 17 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Chapter Contents 17.1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Can Occur at Any of the Steps Leading from DNA to Protein
Chapter 17 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Chapter Contents 17.1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Can Occur at Any of the Steps Leading from DNA to Protein
Lecture 22 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes III
 Lecture 22 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes III In the last three lectures we have thought a lot about analyzing a regulatory system in S. cerevisiae, namely Gal regulation that involved a hand full of genes.
Lecture 22 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes III In the last three lectures we have thought a lot about analyzing a regulatory system in S. cerevisiae, namely Gal regulation that involved a hand full of genes.
Applied Bioinformatics - Lecture 16: Transcriptomics
 Applied Bioinformatics - Lecture 16: Transcriptomics David Hendrix Oregon State University Feb 15th 2016 Transcriptomics High-throughput Sequencing (deep sequencing) High-throughput sequencing (also
Applied Bioinformatics - Lecture 16: Transcriptomics David Hendrix Oregon State University Feb 15th 2016 Transcriptomics High-throughput Sequencing (deep sequencing) High-throughput sequencing (also
7.03, 2006, Lecture 23 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes IV
 1 Fall 2006 7.03 7.03, 2006, Lecture 23 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes IV In the last three lectures we have thought a lot about analyzing a regulatory system in S. cerevisiae, namely Gal regulation that
1 Fall 2006 7.03 7.03, 2006, Lecture 23 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes IV In the last three lectures we have thought a lot about analyzing a regulatory system in S. cerevisiae, namely Gal regulation that
7.05, 2005, Lecture 23 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes IV
 7.05, 2005, Lecture 23 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes IV In the last three lectures we have thought a lot about analyzing a regulatory system in S. cerevisiae, namely Gal regulation that involved a hand
7.05, 2005, Lecture 23 Eukaryotic Genes and Genomes IV In the last three lectures we have thought a lot about analyzing a regulatory system in S. cerevisiae, namely Gal regulation that involved a hand
Name Genotype Reference
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Table 1 S. cerevisiae strains. Name Genotype Reference RMY200 UKY403 W303-1a MATa ade2-101 (och) his3 200 lys2-801 (amp) trp1 901 ura3-52 hht1,hhf1::leu2 hht2,hhf2::his3
Supplemental Data Supplemental Table 1 S. cerevisiae strains. Name Genotype Reference RMY200 UKY403 W303-1a MATa ade2-101 (och) his3 200 lys2-801 (amp) trp1 901 ura3-52 hht1,hhf1::leu2 hht2,hhf2::his3
Gene expression analysis. Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 5. Gene expression analysis
 Gene expression analysis Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 5 Gene expression analysis From EST clusters to spotted cdna microarrays Long vs. short oligonucleotide microarrays vs. RT-PCR Methods
Gene expression analysis Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 5 Gene expression analysis From EST clusters to spotted cdna microarrays Long vs. short oligonucleotide microarrays vs. RT-PCR Methods
Chromatin and Transcription
 Chromatin and Transcription Chromatin Structure Chromatin Represses Transcription Nucleosome Positioning Histone Acetylation Chromatin Remodeling Histone Methylation CHIP Analysis Chromatin and Elongation
Chromatin and Transcription Chromatin Structure Chromatin Represses Transcription Nucleosome Positioning Histone Acetylation Chromatin Remodeling Histone Methylation CHIP Analysis Chromatin and Elongation
EPIGENTEK. EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit. Base Catalog # P-2002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE
 EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity of
EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity of
ChampionChIP Quick, High Throughput Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay System
 ChampionChIP Quick, High Throughput Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay System Liyan Pang, Ph.D. Application Scientist 1 Topics to be Covered Introduction What is ChIP-qPCR? Challenges Facing Biological
ChampionChIP Quick, High Throughput Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay System Liyan Pang, Ph.D. Application Scientist 1 Topics to be Covered Introduction What is ChIP-qPCR? Challenges Facing Biological
A new framework for identifying combinatorial regulation of. transcription factors: a case study of the yeast cell cycle
 A new framework for identifying combinatorial regulation of transcription factors: a case study of the yeast cell cycle Junbai Wang 1 * 1. Department of Biological Sciences, Columbia University, 1212 Amsterdam
A new framework for identifying combinatorial regulation of transcription factors: a case study of the yeast cell cycle Junbai Wang 1 * 1. Department of Biological Sciences, Columbia University, 1212 Amsterdam
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
Exam 2 BIO200, Winter 2012
 Exam 2 BIO200, Winter 2012 Name: Multiple Choice Questions: Circle the one best answer for each question. (2 points each) 1. The 5 cap structure is often described as a backwards G. What makes this nucleotide
Exam 2 BIO200, Winter 2012 Name: Multiple Choice Questions: Circle the one best answer for each question. (2 points each) 1. The 5 cap structure is often described as a backwards G. What makes this nucleotide
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers
 Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that usually extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated the (#1) of transcription
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that usually extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated the (#1) of transcription
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Functional Genomics Overview RORY STARK PRINCIPAL BIOINFORMATICS ANALYST CRUK CAMBRIDGE INSTITUTE 18 SEPTEMBER 2017
 Functional Genomics Overview RORY STARK PRINCIPAL BIOINFORMATICS ANALYST CRUK CAMBRIDGE INSTITUTE 18 SEPTEMBER 2017 Agenda What is Functional Genomics? RNA Transcription/Gene Expression Measuring Gene
Functional Genomics Overview RORY STARK PRINCIPAL BIOINFORMATICS ANALYST CRUK CAMBRIDGE INSTITUTE 18 SEPTEMBER 2017 Agenda What is Functional Genomics? RNA Transcription/Gene Expression Measuring Gene
2/10/17. Contents. Applications of HMMs in Epigenomics
 2/10/17 I529: Machine Learning in Bioinformatics (Spring 2017) Contents Applications of HMMs in Epigenomics Yuzhen Ye School of Informatics and Computing Indiana University, Bloomington Spring 2017 Background:
2/10/17 I529: Machine Learning in Bioinformatics (Spring 2017) Contents Applications of HMMs in Epigenomics Yuzhen Ye School of Informatics and Computing Indiana University, Bloomington Spring 2017 Background:
Chapter 1. from genomics to proteomics Ⅱ
 Proteomics Chapter 1. from genomics to proteomics Ⅱ 1 Functional genomics Functional genomics: study of relations of genomics to biological functions at systems level However, it cannot explain any more
Proteomics Chapter 1. from genomics to proteomics Ⅱ 1 Functional genomics Functional genomics: study of relations of genomics to biological functions at systems level However, it cannot explain any more
Supplemental Figure 1.
 Supplemental Data. Charron et al. Dynamic landscapes of four histone modifications during de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell (2009). 10.1105/tpc.109.066845 Supplemental Figure 1. Immunodetection
Supplemental Data. Charron et al. Dynamic landscapes of four histone modifications during de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell (2009). 10.1105/tpc.109.066845 Supplemental Figure 1. Immunodetection
LABORATORY FUNDAMENTALS IN BIOLOGICAL ENGINEERING. Leona Samson. MODULE 2 EXPRESSION ENGINEERING Lecture # 3.
 20.109 LABORATORY FUNDAMENTALS IN BIOLOGICAL ENGINEERING MODULE 2 EXPRESSION ENGINEERING Lecture # 3 Leona Samson March 31 st 2009 Snapshot of the next four weeks We will eliminate the expression of various
20.109 LABORATORY FUNDAMENTALS IN BIOLOGICAL ENGINEERING MODULE 2 EXPRESSION ENGINEERING Lecture # 3 Leona Samson March 31 st 2009 Snapshot of the next four weeks We will eliminate the expression of various
Epigenetics in. Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chapter 4 2/4/14
 Epigenetics in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Chapter 4 2/4/14 The budding yeast - Saccharomyces cerevisiae The fission yeast - Schizosaccharomyces pombe The budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the fission
Epigenetics in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Chapter 4 2/4/14 The budding yeast - Saccharomyces cerevisiae The fission yeast - Schizosaccharomyces pombe The budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the fission
ChIP-seq/Functional Genomics/Epigenomics. CBSU/3CPG/CVG Next-Gen Sequencing Workshop. Josh Waterfall. March 31, 2010
 ChIP-seq/Functional Genomics/Epigenomics CBSU/3CPG/CVG Next-Gen Sequencing Workshop Josh Waterfall March 31, 2010 Outline Introduction to ChIP-seq Control data sets Peak/enriched region identification
ChIP-seq/Functional Genomics/Epigenomics CBSU/3CPG/CVG Next-Gen Sequencing Workshop Josh Waterfall March 31, 2010 Outline Introduction to ChIP-seq Control data sets Peak/enriched region identification
Like use other ChIP kits, before handle ChIP assay please choose a good antibody suitable for precipitation the crosslinked protein / DNA complexes.
 ChIP Assay Kit Cat:RK20100 Like use other ChIP kits, before handle ChIP assay please choose a good antibody suitable for precipitation the crosslinked protein / DNA complexes. Manufactured by Global Headquarters
ChIP Assay Kit Cat:RK20100 Like use other ChIP kits, before handle ChIP assay please choose a good antibody suitable for precipitation the crosslinked protein / DNA complexes. Manufactured by Global Headquarters
Measuring Protein-DNA interactions
 Measuring Protein-DNA interactions How is Biological Complexity Achieved? Mediated by Transcription Factors (TFs) 2 Transcription Factors are genetic switches 3 Regulation of Gene Expression by Transcription
Measuring Protein-DNA interactions How is Biological Complexity Achieved? Mediated by Transcription Factors (TFs) 2 Transcription Factors are genetic switches 3 Regulation of Gene Expression by Transcription
Why does this matter?
 Background Why does this matter? Better understanding of how the nucleosome affects transcription Important for understanding the nucleosome s role in gene expression Treats each component and region of
Background Why does this matter? Better understanding of how the nucleosome affects transcription Important for understanding the nucleosome s role in gene expression Treats each component and region of
EPIGENTEK. EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit. Base Catalog # P-2003 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE
 EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2003 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity
EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2003 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity
The Biotechnology Toolbox
 Chapter 15 The Biotechnology Toolbox Cutting and Pasting DNA Cutting DNA Restriction endonuclease or restriction enzymes Cellular protection mechanism for infected foreign DNA Recognition and cutting specific
Chapter 15 The Biotechnology Toolbox Cutting and Pasting DNA Cutting DNA Restriction endonuclease or restriction enzymes Cellular protection mechanism for infected foreign DNA Recognition and cutting specific
Chapter 19 Genetic Regulation of the Eukaryotic Genome. A. Bergeron AP Biology PCHS
 Chapter 19 Genetic Regulation of the Eukaryotic Genome A. Bergeron AP Biology PCHS 2 Do Now - Eukaryotic Transcription Regulation The diagram below shows five genes (with their enhancers) from the genome
Chapter 19 Genetic Regulation of the Eukaryotic Genome A. Bergeron AP Biology PCHS 2 Do Now - Eukaryotic Transcription Regulation The diagram below shows five genes (with their enhancers) from the genome
THE ANALYSIS OF CHROMATIN CONDENSATION STATE AND TRANSCRIPTIONAL ACTIVITY USING DNA MICROARRAYS 1. INTRODUCTION
 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL INFORMATICS & TECHNOLOGIES Vol.6/2003, ISSN 1642-6037 Piotr WIDŁAK *, Krzysztof FUJAREWICZ ** DNA microarrays, chromatin, transcription THE ANALYSIS OF CHROMATIN CONDENSATION STATE AND
JOURNAL OF MEDICAL INFORMATICS & TECHNOLOGIES Vol.6/2003, ISSN 1642-6037 Piotr WIDŁAK *, Krzysztof FUJAREWICZ ** DNA microarrays, chromatin, transcription THE ANALYSIS OF CHROMATIN CONDENSATION STATE AND
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #1 March 12, 2002
 Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #1 March 12, 2002 Name KEY SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number.
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #1 March 12, 2002 Name KEY SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number.
ECS 234: Genomic Data Integration ECS 234
 : Genomic Data Integration Heterogeneous Data Integration DNA Sequence Microarray Proteomics >gi 12004594 gb AF217406.1 Saccharomyces cerevisiae uridine nucleosidase (URH1) gene, complete cds ATGGAATCTGCTGATTTTTTTACCTCACGAAACTTATTAAAACAGATAATTTCCCTCATCTGCAAGGTTG
: Genomic Data Integration Heterogeneous Data Integration DNA Sequence Microarray Proteomics >gi 12004594 gb AF217406.1 Saccharomyces cerevisiae uridine nucleosidase (URH1) gene, complete cds ATGGAATCTGCTGATTTTTTTACCTCACGAAACTTATTAAAACAGATAATTTCCCTCATCTGCAAGGTTG
Gene expression DNA RNA. Protein DNA. Replication. Initiation Elongation Processing Export. DNA RNA Protein. Transcription. Degradation.
 Gene expression DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA Degradation RNA Degradation Protein Replication Transcription Translation Initiation Elongation Processing Export Initiation Elongation Processing Targeting Chapter
Gene expression DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA Degradation RNA Degradation Protein Replication Transcription Translation Initiation Elongation Processing Export Initiation Elongation Processing Targeting Chapter
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Table of contents: Pages: Supplementary Methods 2-3 Supplementary Figure 1 4 Supplementary Figure 2 5 Supplementary Figure 3 6 Supplementary Figure 4 7 Supplementary Figure 5
Supplementary Information Table of contents: Pages: Supplementary Methods 2-3 Supplementary Figure 1 4 Supplementary Figure 2 5 Supplementary Figure 3 6 Supplementary Figure 4 7 Supplementary Figure 5
Expressed genes profiling (Microarrays) Overview Of Gene Expression Control Profiling Of Expressed Genes
 Expressed genes profiling (Microarrays) Overview Of Gene Expression Control Profiling Of Expressed Genes Genes can be regulated at many levels Usually, gene regulation, are referring to transcriptional
Expressed genes profiling (Microarrays) Overview Of Gene Expression Control Profiling Of Expressed Genes Genes can be regulated at many levels Usually, gene regulation, are referring to transcriptional
Nucleosome Positioning and Organization Advanced Topics in Computa8onal Genomics
 Nucleosome Positioning and Organization 02-715 Advanced Topics in Computa8onal Genomics Nucleosome Core Nucleosome Core and Linker 147 bp DNA wrapping around nucleosome core Varying lengths of linkers
Nucleosome Positioning and Organization 02-715 Advanced Topics in Computa8onal Genomics Nucleosome Core Nucleosome Core and Linker 147 bp DNA wrapping around nucleosome core Varying lengths of linkers
Control of Eukaryotic Genes. AP Biology
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
Chromatin immunoprecipitation: five steps to great results
 Chromatin immunoprecipitation: five steps to great results Introduction The discovery and use of antibodies in life science research has been critical to many advancements across applications, including
Chromatin immunoprecipitation: five steps to great results Introduction The discovery and use of antibodies in life science research has been critical to many advancements across applications, including
Reading Lecture 8: Lecture 9: Lecture 8. DNA Libraries. Definition Types Construction
 Lecture 8 Reading Lecture 8: 96-110 Lecture 9: 111-120 DNA Libraries Definition Types Construction 142 DNA Libraries A DNA library is a collection of clones of genomic fragments or cdnas from a certain
Lecture 8 Reading Lecture 8: 96-110 Lecture 9: 111-120 DNA Libraries Definition Types Construction 142 DNA Libraries A DNA library is a collection of clones of genomic fragments or cdnas from a certain
Characterizing DNA binding sites high throughput approaches Biol4230 Tues, April 24, 2018 Bill Pearson Pinn 6-057
 Characterizing DNA binding sites high throughput approaches Biol4230 Tues, April 24, 2018 Bill Pearson wrp@virginia.edu 4-2818 Pinn 6-057 Reviewing sites: affinity and specificity representation binding
Characterizing DNA binding sites high throughput approaches Biol4230 Tues, April 24, 2018 Bill Pearson wrp@virginia.edu 4-2818 Pinn 6-057 Reviewing sites: affinity and specificity representation binding
Introduction to genome biology
 Introduction to genome biology Lisa Stubbs Deep transcritpomes for traditional model species from ENCODE (and modencode) Deep RNA-seq and chromatin analysis on 147 human cell types, as well as tissues,
Introduction to genome biology Lisa Stubbs Deep transcritpomes for traditional model species from ENCODE (and modencode) Deep RNA-seq and chromatin analysis on 147 human cell types, as well as tissues,
Motivation From Protein to Gene
 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 2003-4 Topic B Recombinant DNA -principles and tools Construct a library - what for, how Major techniques +principles Bioinformatics - in brief Chapter 7 (MCB) 1 Motivation From Protein
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 2003-4 Topic B Recombinant DNA -principles and tools Construct a library - what for, how Major techniques +principles Bioinformatics - in brief Chapter 7 (MCB) 1 Motivation From Protein
Microarrays: since we use probes we obviously must know the sequences we are looking at!
 These background are needed: 1. - Basic Molecular Biology & Genetics DNA replication Transcription Post-transcriptional RNA processing Translation Post-translational protein modification Gene expression
These background are needed: 1. - Basic Molecular Biology & Genetics DNA replication Transcription Post-transcriptional RNA processing Translation Post-translational protein modification Gene expression
H3K36me3 polyclonal antibody
 H3K36me3 polyclonal antibody Cat. No. C15410192 Type: Polyclonal ChIP-grade/ChIP-seq grade Source: Rabbit Lot #: A1845P Size: 50 µg/32 µl Concentration: 1.6 μg/μl Specificity: Human, mouse, Arabidopsis,
H3K36me3 polyclonal antibody Cat. No. C15410192 Type: Polyclonal ChIP-grade/ChIP-seq grade Source: Rabbit Lot #: A1845P Size: 50 µg/32 µl Concentration: 1.6 μg/μl Specificity: Human, mouse, Arabidopsis,
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. ChIP-seq genome browser views of BRM occupancy at previously identified BRM targets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ChIP-seq genome browser views of BRM occupancy at previously identified BRM targets. Gene structures are shown underneath each panel. Supplementary Figure 2 pref6::ref6-gfp complements
Supplementary Figure 1 ChIP-seq genome browser views of BRM occupancy at previously identified BRM targets. Gene structures are shown underneath each panel. Supplementary Figure 2 pref6::ref6-gfp complements
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 9: Nuclear Genome Organization: Chromosome Structure, Chromatin, DNA Packaging, Mitosis Gary Peter
 Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 9: Nuclear Genome Organization: Chromosome Structure, Chromatin, DNA Packaging, Mitosis Gary Peter 9/16/2008 1 Learning Objectives 1. List and explain how DNA
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 9: Nuclear Genome Organization: Chromosome Structure, Chromatin, DNA Packaging, Mitosis Gary Peter 9/16/2008 1 Learning Objectives 1. List and explain how DNA
Supplementary Figure 2
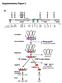 Supplementary Figure 2 a SBS-C1 SBS-C2 SBS-C3 SBS-C4 SBS-C5 SBS-C6 SBS-C7 SBS-C8 SBS-C9 LCR CNS-1 CNS-2 Il5 Rad50 Il13 Il4 Kif3a Sept8 0 50 100 150 200kb Sau3AI 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
Supplementary Figure 2 a SBS-C1 SBS-C2 SBS-C3 SBS-C4 SBS-C5 SBS-C6 SBS-C7 SBS-C8 SBS-C9 LCR CNS-1 CNS-2 Il5 Rad50 Il13 Il4 Kif3a Sept8 0 50 100 150 200kb Sau3AI 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives)
 Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Compare and contrast chromatin and chromosome: composition, proteins involved and level of packing. Explain the structure and function of
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Compare and contrast chromatin and chromosome: composition, proteins involved and level of packing. Explain the structure and function of
Understanding transcriptional regulation by integrative analysis of transcription factor binding data
 Understanding transcriptional regulation by integrative analysis of transcription factor binding data Cheng et al. 2012 Shu Yang Feb. 21, 2013 1 / 26 Introduction 2 / 26 DNA-binding Proteins sequence-specific
Understanding transcriptional regulation by integrative analysis of transcription factor binding data Cheng et al. 2012 Shu Yang Feb. 21, 2013 1 / 26 Introduction 2 / 26 DNA-binding Proteins sequence-specific
Introduction to ChIP Seq data analyses. Acknowledgement: slides taken from Dr. H
 Introduction to ChIP Seq data analyses Acknowledgement: slides taken from Dr. H Wu @Emory ChIP seq: Chromatin ImmunoPrecipitation it ti + sequencing Same biological motivation as ChIP chip: measure specific
Introduction to ChIP Seq data analyses Acknowledgement: slides taken from Dr. H Wu @Emory ChIP seq: Chromatin ImmunoPrecipitation it ti + sequencing Same biological motivation as ChIP chip: measure specific
WORKSHOP. Transcriptional circuitry and the regulatory conformation of the genome. Ofir Hakim Faculty of Life Sciences
 WORKSHOP Transcriptional circuitry and the regulatory conformation of the genome Ofir Hakim Faculty of Life Sciences Chromosome conformation capture (3C) Most GR Binding Sites Are Distant From Regulated
WORKSHOP Transcriptional circuitry and the regulatory conformation of the genome Ofir Hakim Faculty of Life Sciences Chromosome conformation capture (3C) Most GR Binding Sites Are Distant From Regulated
Selected Techniques Part I
 1 Selected Techniques Part I Gel Electrophoresis Can be both qualitative and quantitative Qualitative About what size is the fragment? How many fragments are present? Is there in insert or not? Quantitative
1 Selected Techniques Part I Gel Electrophoresis Can be both qualitative and quantitative Qualitative About what size is the fragment? How many fragments are present? Is there in insert or not? Quantitative
Supplemental Data. Noncoding Transcription by RNA Polymerase Pol IVb/Pol V Mediates Transcriptional Silencing of Overlapping and Adjacent Genes
 Cell, Volume 135 Supplemental Data Noncoding Transcription by RNA Polymerase Pol IVb/Pol V Mediates Transcriptional Silencing of Overlapping and Adjacent Genes Andrzej T. Wierzbicki, Jeremy R. Haag, and
Cell, Volume 135 Supplemental Data Noncoding Transcription by RNA Polymerase Pol IVb/Pol V Mediates Transcriptional Silencing of Overlapping and Adjacent Genes Andrzej T. Wierzbicki, Jeremy R. Haag, and
Bioinformatics of Transcriptional Regulation
 Bioinformatics of Transcriptional Regulation Carl Herrmann IPMB & DKFZ c.herrmann@dkfz.de Wechselwirkung von Maßnahmen und Auswirkungen Einflussmöglichkeiten in einem Dialog From genes to active compounds
Bioinformatics of Transcriptional Regulation Carl Herrmann IPMB & DKFZ c.herrmann@dkfz.de Wechselwirkung von Maßnahmen und Auswirkungen Einflussmöglichkeiten in einem Dialog From genes to active compounds
Section C: The Control of Gene Expression
 Section C: The Control of Gene Expression 1. Each cell of a multicellular eukaryote expresses only a small fraction of its genes 2. The control of gene expression can occur at any step in the pathway from
Section C: The Control of Gene Expression 1. Each cell of a multicellular eukaryote expresses only a small fraction of its genes 2. The control of gene expression can occur at any step in the pathway from
The role of erna in chromatin looping
 The role of erna in chromatin looping Introduction Enhancers are cis-acting DNA regulatory elements that activate transcription of target genes 1,2. It is estimated that 400 000 to >1 million alleged enhancers
The role of erna in chromatin looping Introduction Enhancers are cis-acting DNA regulatory elements that activate transcription of target genes 1,2. It is estimated that 400 000 to >1 million alleged enhancers
ChIP DNA Clean & Concentrator Catalog Nos. D5201 & D5205
 Page 0 INSTRUCTION MANUAL ChIP DNA Clean & Concentrator Catalog Nos. D5201 & D5205 Highlights Quick (2 minute) recovery of ultra-pure DNA from chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays, cell lysates,
Page 0 INSTRUCTION MANUAL ChIP DNA Clean & Concentrator Catalog Nos. D5201 & D5205 Highlights Quick (2 minute) recovery of ultra-pure DNA from chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays, cell lysates,
Charles Girardot, Furlong Lab. MACS, CisGenome, SISSRs and other peak calling algorithms: differences and practical use
 Charles Girardot, Furlong Lab MACS, CisGenome, SISSRs and other peak calling algorithms: differences and practical use ChIP-Seq signal properties Only 5 ends of ChIPed fragments are sequenced Shifted read
Charles Girardot, Furlong Lab MACS, CisGenome, SISSRs and other peak calling algorithms: differences and practical use ChIP-Seq signal properties Only 5 ends of ChIPed fragments are sequenced Shifted read
EpiQuik Methyl-CpG Binding Domain Protein 2 ChIP Kit
 EpiQuik Methyl-CpG Binding Domain Protein 2 ChIP Kit Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Methyl-CpG Binding Domain Protein 2 ChIP Kit is suitable for combining the
EpiQuik Methyl-CpG Binding Domain Protein 2 ChIP Kit Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Methyl-CpG Binding Domain Protein 2 ChIP Kit is suitable for combining the
Computing with large data sets
 Computing with large data sets Richard Bonneau, spring 2009 Lecture 14 (week 8): genomics 1 Central dogma Gene expression DNA RNA Protein v22.0480: computing with data, Richard Bonneau Lecture 14 places
Computing with large data sets Richard Bonneau, spring 2009 Lecture 14 (week 8): genomics 1 Central dogma Gene expression DNA RNA Protein v22.0480: computing with data, Richard Bonneau Lecture 14 places
Tissue Acetyl-Histone H4 ChIP Kit
 Tissue Acetyl-Histone H4 ChIP Kit Catalog Number KA0672 48 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Tissue Acetyl-Histone H4 ChIP Kit Catalog Number KA0672 48 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Genes - DNA - Chromosome. Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology
 Genes - DNA - Chromosome Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology DNA Cellular DNA contains genes and intragenic regions both of which may
Genes - DNA - Chromosome Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology DNA Cellular DNA contains genes and intragenic regions both of which may
Control of Eukaryotic Genes
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes 2007-2008 The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Control of Eukaryotic Genes 2007-2008 The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
DNA:CHROMATIN INTERACTIONS
 DNA:CHROMATIN INTERACTIONS Exploring transcription factor binding and the epigenomic landscape Chris Seward Introductions Cell and Developmental Biology PhD Candidate in Dr. Lisa Stubbs Laboratory Currently
DNA:CHROMATIN INTERACTIONS Exploring transcription factor binding and the epigenomic landscape Chris Seward Introductions Cell and Developmental Biology PhD Candidate in Dr. Lisa Stubbs Laboratory Currently
ChIP grade antibodies: selection and validation. Rachel Imoberdorf, PhD Senior Development Scientist
 ChIP grade antibodies: selection and validation Rachel Imoberdorf, PhD Senior Development Scientist Introduction Antibody selection Antibody validation ChIP at www.abcam.com Introduction Chromatin Immunoprecipitation
ChIP grade antibodies: selection and validation Rachel Imoberdorf, PhD Senior Development Scientist Introduction Antibody selection Antibody validation ChIP at www.abcam.com Introduction Chromatin Immunoprecipitation
Genes found in the genome include protein-coding genes and non-coding RNA genes. Which nucleotide is not normally found in non-coding RNA genes?
 Midterm Q Genes found in the genome include protein-coding genes and non-coding RNA genes Which nucleotide is not normally found in non-coding RNA genes? G T 3 A 4 C 5 U 00% Midterm Q Which of the following
Midterm Q Genes found in the genome include protein-coding genes and non-coding RNA genes Which nucleotide is not normally found in non-coding RNA genes? G T 3 A 4 C 5 U 00% Midterm Q Which of the following
Control of Eukaryotic Genes. AP Biology
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
1. Cross-linking and cell harvesting
 ChIP is a powerful tool that allows the specific matching of proteins or histone modifications to regions of the genome. Chromatin is isolated and antibodies to the antigen of interest are used to determine
ChIP is a powerful tool that allows the specific matching of proteins or histone modifications to regions of the genome. Chromatin is isolated and antibodies to the antigen of interest are used to determine
ChIP. November 21, 2017
 ChIP November 21, 2017 functional signals: is DNA enough? what is the smallest number of letters used by a written language? DNA is only one part of the functional genome DNA is heavily bound by proteins,
ChIP November 21, 2017 functional signals: is DNA enough? what is the smallest number of letters used by a written language? DNA is only one part of the functional genome DNA is heavily bound by proteins,
Analysis of Microarray Data
 Analysis of Microarray Data Lecture 3: Visualization and Functional Analysis George Bell, Ph.D. Senior Bioinformatics Scientist Bioinformatics and Research Computing Whitehead Institute Outline Review
Analysis of Microarray Data Lecture 3: Visualization and Functional Analysis George Bell, Ph.D. Senior Bioinformatics Scientist Bioinformatics and Research Computing Whitehead Institute Outline Review
(c) 2014 Dr. Alice Heicklen & Dr. Deborah Mowshowitz, Columbia University, New York, NY. Last update 02/26/ :57 PM
 C2006/F2402 '14 OUTLINE OF LECTURE #11 (c) 2014 Dr. Alice Heicklen & Dr. Deborah Mowshowitz, Columbia University, New York, NY. Last update 02/26/2014 12:57 PM Handouts: 10C -- Typical Eukaryotic Gene,
C2006/F2402 '14 OUTLINE OF LECTURE #11 (c) 2014 Dr. Alice Heicklen & Dr. Deborah Mowshowitz, Columbia University, New York, NY. Last update 02/26/2014 12:57 PM Handouts: 10C -- Typical Eukaryotic Gene,
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 7 - GENE EXPRESSION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION BASICS Gene expression is the process through which cells selectively to express some genes and not others Every cell in an organism is a clone
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION BASICS Gene expression is the process through which cells selectively to express some genes and not others Every cell in an organism is a clone
ab ChIP Kit Magnetic One-Step
 ab156907 ChIP Kit Magnetic One-Step Instructions for Use For selective enrichment of a chromatin fraction containing specific DNA sequences in a high throughput format using chromatin isolated from various
ab156907 ChIP Kit Magnetic One-Step Instructions for Use For selective enrichment of a chromatin fraction containing specific DNA sequences in a high throughput format using chromatin isolated from various
A more efficient, sensitive and robust method of chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
 A more efficient, sensitive and robust method of chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) ADVANCEMENTS IN EPIGENETICS Introducing ChIP and Chromatrap Chromatrap is a more efficient, sensitive and robust method
A more efficient, sensitive and robust method of chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) ADVANCEMENTS IN EPIGENETICS Introducing ChIP and Chromatrap Chromatrap is a more efficient, sensitive and robust method
Epigenetic genome control by RNAi and transposon-derived proteins
 Epigenetic genome control by RNAi and transposon-derived proteins Shiv Grewal Center for Cancer Research, NCI National Institutes of Health, Bethesda Transposons and their remnants constitute a significant
Epigenetic genome control by RNAi and transposon-derived proteins Shiv Grewal Center for Cancer Research, NCI National Institutes of Health, Bethesda Transposons and their remnants constitute a significant
Introduction to genome biology
 Introduction to genome biology Lisa Stubbs We ve found most genes; but what about the rest of the genome? Genome size* 12 Mb 95 Mb 170 Mb 1500 Mb 2700 Mb 3200 Mb #coding genes ~7000 ~20000 ~14000 ~26000
Introduction to genome biology Lisa Stubbs We ve found most genes; but what about the rest of the genome? Genome size* 12 Mb 95 Mb 170 Mb 1500 Mb 2700 Mb 3200 Mb #coding genes ~7000 ~20000 ~14000 ~26000
How DNA Is Packed In The Cell: Chromosomes, Genes, Nucleosomes
 Summer Course in Biophysics June 5, 2014 How DNA Is Packed In The Cell: Chromosomes, Genes, Nucleosomes Brian D. Strahl Department of Biochemistry & Biophysics UNC-School of Medicine Outline I. Chromatin
Summer Course in Biophysics June 5, 2014 How DNA Is Packed In The Cell: Chromosomes, Genes, Nucleosomes Brian D. Strahl Department of Biochemistry & Biophysics UNC-School of Medicine Outline I. Chromatin
Non-coding Function & Variation, MPRAs II. Mike White Bio /5/18
 Non-coding Function & Variation, MPRAs II Mike White Bio 5488 3/5/18 MPRA Review Problem 1: Where does your CRE DNA come from? DNA synthesis Genomic fragments Targeted regulome capture Problem 2: How do
Non-coding Function & Variation, MPRAs II Mike White Bio 5488 3/5/18 MPRA Review Problem 1: Where does your CRE DNA come from? DNA synthesis Genomic fragments Targeted regulome capture Problem 2: How do
Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes
 Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes Concepts, Strategies, and Techniques Michael Carey Stephen T. Smale COLD SPRING HARBOR LABORATORY PRESS NEW YORK 2000 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 0-87969-537-4
Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes Concepts, Strategies, and Techniques Michael Carey Stephen T. Smale COLD SPRING HARBOR LABORATORY PRESS NEW YORK 2000 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 0-87969-537-4
rev. 05/31/12 Box 2 contains the following buffers/reagents:
 Store at RT, 4 C, and 20 C #9002 SimpleChIP Enzymatic Chromatin IP Kit (Agarose Beads) 3 n 1 Kit (30 Immunoprecipitations) For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. rev. 05/31/12 Orders
Store at RT, 4 C, and 20 C #9002 SimpleChIP Enzymatic Chromatin IP Kit (Agarose Beads) 3 n 1 Kit (30 Immunoprecipitations) For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. rev. 05/31/12 Orders
Gene Expression Technology
 Gene Expression Technology Bing Zhang Department of Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University bing.zhang@vanderbilt.edu Gene expression Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene
Gene Expression Technology Bing Zhang Department of Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University bing.zhang@vanderbilt.edu Gene expression Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene
M Keramatipour 2. M Keramatipour 1. M Keramatipour 4. M Keramatipour 3. M Keramatipour 5. M Keramatipour
 Molecular Cloning Methods Mohammad Keramatipour MD, PhD keramatipour@tums.ac.ir Outline DNA recombinant technology DNA cloning co Cell based PCR PCR-based Some application of DNA cloning Genomic libraries
Molecular Cloning Methods Mohammad Keramatipour MD, PhD keramatipour@tums.ac.ir Outline DNA recombinant technology DNA cloning co Cell based PCR PCR-based Some application of DNA cloning Genomic libraries
Chapter 13. The Nucleus. The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus".
 Chapter 13 The Nucleus The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus". Fig.13.1. The EM of the Nucleus of a Eukaryotic Cell 13.1. The Nuclear Envelope
Chapter 13 The Nucleus The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus". Fig.13.1. The EM of the Nucleus of a Eukaryotic Cell 13.1. The Nuclear Envelope
Einführung in die Genetik
 Einführung in die Genetik Prof. Dr. Kay Schneitz (EBio Pflanzen) http://plantdev.bio.wzw.tum.de schneitz@wzw.tum.de Prof. Dr. Claus Schwechheimer (PlaSysBiol) http://wzw.tum.de/sysbiol claus.schwechheimer@wzw.tum.de
Einführung in die Genetik Prof. Dr. Kay Schneitz (EBio Pflanzen) http://plantdev.bio.wzw.tum.de schneitz@wzw.tum.de Prof. Dr. Claus Schwechheimer (PlaSysBiol) http://wzw.tum.de/sysbiol claus.schwechheimer@wzw.tum.de
APPLICATION NOTE. Abstract. Introduction
 From minuscule amounts to magnificent results: reliable ChIP-seq data from 1, cells with the True MicroChIP and the MicroPlex Library Preparation kits Abstract Diagenode has developed groundbreaking solutions
From minuscule amounts to magnificent results: reliable ChIP-seq data from 1, cells with the True MicroChIP and the MicroPlex Library Preparation kits Abstract Diagenode has developed groundbreaking solutions
Chapter 18. Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 2007-2008 Control of Prokaryotic (Bacterial) Genes 2007- Bacterial metabolism Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment STOP GO if they have
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 2007-2008 Control of Prokaryotic (Bacterial) Genes 2007- Bacterial metabolism Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment STOP GO if they have
ChIP-seq analysis 2/28/2018
 ChIP-seq analysis 2/28/2018 Acknowledgements Much of the content of this lecture is from: Furey (2012) ChIP-seq and beyond Park (2009) ChIP-seq advantages + challenges Landt et al. (2012) ChIP-seq guidelines
ChIP-seq analysis 2/28/2018 Acknowledgements Much of the content of this lecture is from: Furey (2012) ChIP-seq and beyond Park (2009) ChIP-seq advantages + challenges Landt et al. (2012) ChIP-seq guidelines
HPV E6 oncoprotein targets histone methyltransferases for modulating specific. Chih-Hung Hsu, Kai-Lin Peng, Hua-Ci Jhang, Chia-Hui Lin, Shwu-Yuan Wu,
 1 HPV E oncoprotein targets histone methyltransferases for modulating specific gene transcription 3 5 Chih-Hung Hsu, Kai-Lin Peng, Hua-Ci Jhang, Chia-Hui Lin, Shwu-Yuan Wu, Cheng-Ming Chiang, Sheng-Chung
1 HPV E oncoprotein targets histone methyltransferases for modulating specific gene transcription 3 5 Chih-Hung Hsu, Kai-Lin Peng, Hua-Ci Jhang, Chia-Hui Lin, Shwu-Yuan Wu, Cheng-Ming Chiang, Sheng-Chung
Intracellular receptors specify complex patterns of gene expression that are cell and gene
 SUPPLEMENTAL RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Some HPr-1AR ARE-containing Genes Are Unresponsive to Androgen Intracellular receptors specify complex patterns of gene expression that are cell and gene specific. For
SUPPLEMENTAL RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Some HPr-1AR ARE-containing Genes Are Unresponsive to Androgen Intracellular receptors specify complex patterns of gene expression that are cell and gene specific. For
Supplementary Fig. 1
 a FL (1-2266) NL (1-1190) CL (1191-2266) HA-ICE1: - HA-ICE1: - - - FLAG-ICE2: + + + + FLAG-ELL: + + + + + + IP: anti-ha FLAG-ICE2 HA-ICE1-FL HA-ICE1-NL HA-ICE1-CL FLAG-ICE2 b IP: anti-ha FL (1-2266) NL
a FL (1-2266) NL (1-1190) CL (1191-2266) HA-ICE1: - HA-ICE1: - - - FLAG-ICE2: + + + + FLAG-ELL: + + + + + + IP: anti-ha FLAG-ICE2 HA-ICE1-FL HA-ICE1-NL HA-ICE1-CL FLAG-ICE2 b IP: anti-ha FL (1-2266) NL
Wednesday, November 22, 17. Exons and Introns
 Exons and Introns Introns and Exons Exons: coded regions of DNA that get transcribed and translated into proteins make up 5% of the genome Introns and Exons Introns: non-coded regions of DNA Must be removed
Exons and Introns Introns and Exons Exons: coded regions of DNA that get transcribed and translated into proteins make up 5% of the genome Introns and Exons Introns: non-coded regions of DNA Must be removed
DIAMANTINA INSTITUTE for Cancer, Immunology and Metabolic Medicine
 DIAMANTINA INSTITUTE for Cancer, Immunology and Metabolic Medicine Defining MYB Transcriptional Network by Genome-wide Chromatin Occupancy Profiling (ChIP-Seq) 2010 E.Glazov, L. Zhao Transcription Factors:
DIAMANTINA INSTITUTE for Cancer, Immunology and Metabolic Medicine Defining MYB Transcriptional Network by Genome-wide Chromatin Occupancy Profiling (ChIP-Seq) 2010 E.Glazov, L. Zhao Transcription Factors:
Methods of Biomaterials Testing Lesson 3-5. Biochemical Methods - Molecular Biology -
 Methods of Biomaterials Testing Lesson 3-5 Biochemical Methods - Molecular Biology - Chromosomes in the Cell Nucleus DNA in the Chromosome Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) DNA has double-helix structure The
Methods of Biomaterials Testing Lesson 3-5 Biochemical Methods - Molecular Biology - Chromosomes in the Cell Nucleus DNA in the Chromosome Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) DNA has double-helix structure The
From reads to results: differential. Alicia Oshlack Head of Bioinformatics
 From reads to results: differential expression analysis with ihrna seq Alicia Oshlack Head of Bioinformatics Murdoch Childrens Research Institute Benefits and opportunities ii of RNA seq All transcripts
From reads to results: differential expression analysis with ihrna seq Alicia Oshlack Head of Bioinformatics Murdoch Childrens Research Institute Benefits and opportunities ii of RNA seq All transcripts
Control of Eukaryotic Genes. AP Biology
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
Control of Eukaryotic Genes The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? Evolution
EPIGENTEK. ChromaFlash Chromatin Extraction Kit. Base Catalog # P-2001 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE KIT CONTENTS
 ChromaFlash Chromatin Extraction Kit Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE Uses: The ChromaFlash Chromatin Extraction Kit is suitable for isolating chromatin or DNA-protein complex
ChromaFlash Chromatin Extraction Kit Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE Uses: The ChromaFlash Chromatin Extraction Kit is suitable for isolating chromatin or DNA-protein complex
ChIP-seq data analysis with Chipster. Eija Korpelainen CSC IT Center for Science, Finland
 ChIP-seq data analysis with Chipster Eija Korpelainen CSC IT Center for Science, Finland chipster@csc.fi What will I learn? Short introduction to ChIP-seq Analyzing ChIP-seq data Central concepts Analysis
ChIP-seq data analysis with Chipster Eija Korpelainen CSC IT Center for Science, Finland chipster@csc.fi What will I learn? Short introduction to ChIP-seq Analyzing ChIP-seq data Central concepts Analysis
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes 2007-2008 The BIG Questions n How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? n How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Control of Eukaryotic Genes 2007-2008 The BIG Questions n How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? n How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Design. Construction. Characterization
 Design Construction Characterization DNA mrna (messenger) A C C transcription translation C A C protein His A T G C T A C G Plasmids replicon copy number incompatibility selection marker origin of replication
Design Construction Characterization DNA mrna (messenger) A C C transcription translation C A C protein His A T G C T A C G Plasmids replicon copy number incompatibility selection marker origin of replication
The Nucleus, DNA and Chromatin Structure
 The Nucleus, DNA and Chromatin Structure Size of the human genom: The diploid human genome contains approximately 6 billion base pairs of DNA packaged into 23 chromosome pairs. Each diploid cell therefore
The Nucleus, DNA and Chromatin Structure Size of the human genom: The diploid human genome contains approximately 6 billion base pairs of DNA packaged into 23 chromosome pairs. Each diploid cell therefore
