Nucleosome Positioning and Organization Advanced Topics in Computa8onal Genomics
|
|
|
- Regina Morgan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nucleosome Positioning and Organization Advanced Topics in Computa8onal Genomics
2 Nucleosome Core
3 Nucleosome Core and Linker 147 bp DNA wrapping around nucleosome core Varying lengths of linkers between adjacent cores Linker
4 Nucleosome Positions Nucleosome posi8ons are non- random and conserved across the similar cell types Nucleosome posi8oning affects gene regula8on The binding of other proteins affect the posi8ons of nucleosomes Dynamic nature of nucleosome posi8oning influenced by the dynamic gene regula8on Sta8c nature of nucleosome posi8oning influenced by DNA sequence
5 Dynamic Nucleosomes Kine8c measurements show the DNA in an isolated nucleosome is surprisingly dynamic, rapidly uncoiling and then rewrapping around its nucleosome core. This way, most of nucleosome- bound DNA sequence is accessible to other DNA- binding proteins
6 Dynamic Nucleosomes DNA in an isolated nucleosome unwraps around four 8mes per second, remaining exposed for milliseconds before the DNA re- wraps around the nucleosome Allows for other DNA- binding proteins to access the DNA for transcrip8on, DNA replica8on, etc.
7 Dynamic Nucleosomes: Chromatin Remodeling Complex Nucleosome sliding ATP- dependent chroma8n remodeling complexes bind to nucleosome core proteins and DNA that wraps around it, and use the energy of ATP hydrolysis to move DNA rela8ve to the core.
8 Dynamic Nucleosomes: Chromatin Remodeling Complex Chroma8n remodeling complex replacing histone proteins with other variants
9 Dynamic Nucleosomes: Chromatin Remodeling Complex Chroma8n remodeling complex (with histone chaperones) replacing/removing histone proteins with other variants
10 Dynamic Nucleosomes: Chromatin Remodeling Complex As genes are turned on and off, chroma8n remodeling complex are brought to specific regions of DNA to locally influence chroma8n structure Certain chroma8n structure can be inherited during cell division
11 Dynamic Nucleosomes: Chromatin Remodeling with Code Reader-Writer Complex Spreading chroma8n changes Gene regulatory protein recruits a code- writer enzyme, which modifies the histone code The code- writer recruits code- reader, which then again recruits code- writer. Reader and writer should recognize the same code Barrier DNA sequence for blocking the long- range spreading
12 Dynamic Nucleosomes: Chromatin Remodeling Complex Spreading wave of chroma8n condensa8on to form a long range heterochroma8n
13 Nucleosomes and Chromatin Structure H3 variant histone, called CENP- A replaces H3 in centromeric DNA sequences
14 Definitions of Terminology Nucleosome posi8ons: the nucleosome start/center/end posi8ons of the 147bp sequence wrapped around a nucleosome Nucleosome configura8on a set of non- overlapping nucleosome posi8ons on a single DNA molecule of defined length. if a base pair is in state 1, then both the preceding and following 146 base pairs (bp) must be 0
15 Definitions of Terminology Nucleosome organiza8on: a probability distribu8on over nucleosome configura8ons P: nucleosome organiza8on C: a set of nucleosome configura8ons P(c): the probability of a nucleosome configura8on c
16 Definitions of Terminology Nucleosome occupancy: the sum of the probabili8es of the configura8ons in which the base pair is covered by a nucleosome Occ(x): the occupancy at basepair x C: nucleosome configura8on P(c): nucleosome organiza8on
17 Illustration of Different Terminology
18 Definitions of Terminology Nucleosome posi8oning: the degree to which the posi8ons of individual nucleosomes vary across the different configura8ons of a nucleosome organiza8on. a perfectly posi8oned nucleosome is one that adopts the same posi8on across all measured configura8ons 30% posi8oning? Absolute vs. condi8onal posi8oning
19 Definitions of Terminology Absolute nucleosome posi8oning at basepair x: the probability of a nucleosome star8ng at basepair x Absolute nucleosome posi8oning does not uniquely determine nucleosome organiza8on Condi8onal nucleosome posi8oning at basepair x: the absolute posi8oning at basepair x divided by the probability that a nucleosome starts anywhere within a larger region centered on x the probability that a nucleosome starts at x given that a nucleosome starts somewhere between x - 73 and x + 73
20 Illustration of Different Terminology
21 Experimental Technology for Measuring Nucleosome Organization Diges8on of chroma8n by micrococcal nuclease (MNase), an endonuclease that preferen8ally cuts linker DNA rather than DNA wrapped around a nucleosome highly digested DNA: depleted of nucleosomes under- digested DNA: rela8vely protected by nucleosomes Measure the diges8ng paeern with microarray or sequencing of the nucleosome- protected DNA segments Occ(x): occupancy at base pair x r i : read counts at basepair i
22 Experimental Technology for Measuring Nucleosome Organization Challenges Bias introduced by MNase s preference of TA/AT dinucleo8de as its cleavage site Cannot obtain the nucleosome posi8on at a single nucleo8de resolu8on Naked DNA as a control, but linker DNA is TA/AT rich, reducing the u8lity of naked DNA as a control Experiment is performed not on a single cell, but on a popula8on of cells We get to measure only the average of the dynamically changing nucleosome posi8ons
23 Experimental Technology for Measuring Nucleosome Organization Challenges In vitro and in vivo nucleosome posi8ons are different With low coverage in sequencing, it is difficult to obtain a reliable map of nucleosome posi8ons. Currently, 2 nucleosome read starts per base pair in a yeast in vivo map nucleosome read starts in yeast in vitro map 0.07 nucleosome read starts in human in vivo map
24 Experimental Technology for Measuring Nucleosome Organization Robustness of nucleosome map: Are the two independently generated nucleosome maps highly correlated?
25 Yeast Genome-Scale Nucleosome Map Map of posi8ons of 2278 nucleosomes over 482 kilobases of Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA, including almost all of chromosome III and 223 addi8onal regulatory regions Most of the nucleosome were well posi8oned A nucleosome free region of ~200bp in the Pol II promoters Nucleosome free regions had evolu8onarily conserved sequences Most TF binding mo8fs were nucleosome free regions
26 Yeast Genome-Scale Nucleosome Map Nucleosome- free regions common in TF binding sites. Microarray data for nucleosome posi8ons Inferred nucleosome posi8ons with boxes for a TF binding mo8f DNA Sequence conserva8on score
27 Yeast Genome-Scale Nucleosome Map Nucleosome- free regions common in TF binding sites. Microarray data for nucleosome posi8ons Inferred nucleosome posi8ons with boxes for a TF binding mo8f DNA Sequence conserva8on score
28 Yeast Genome-Scale Nucleosome Map Func8onal transcrip8on factor binding mo8fs are more accessible than unbound mo8fs
29 Nucleosome Maps DNA sequence is significantly predic8ve of nucleosome organiza8on in vitro and in vivo discussion on Wednesday!
30 Summary Dynamic nature of nucleosome posi8oning Sta8c nature of nucleosome posi8oning Challenges in measuring nucleosome occupancy
31 Reference Genome- Scale Iden8fica8on of Nucleosome Posi8ons in S. cerevisiae. Science 2005, 309:30. Contribu8on of histone sequence preferences to nucleosome organiza8on: proposed defini8ons and methology. Genome Biology 2010.
Decoding Chromatin States with Epigenome Data Advanced Topics in Computa8onal Genomics
 Decoding Chromatin States with Epigenome Data 02-715 Advanced Topics in Computa8onal Genomics HMMs for Decoding Chromatin States Epigene8c modifica8ons of the genome have been associated with Establishing
Decoding Chromatin States with Epigenome Data 02-715 Advanced Topics in Computa8onal Genomics HMMs for Decoding Chromatin States Epigene8c modifica8ons of the genome have been associated with Establishing
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 9: Nuclear Genome Organization: Chromosome Structure, Chromatin, DNA Packaging, Mitosis Gary Peter
 Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 9: Nuclear Genome Organization: Chromosome Structure, Chromatin, DNA Packaging, Mitosis Gary Peter 9/16/2008 1 Learning Objectives 1. List and explain how DNA
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 9: Nuclear Genome Organization: Chromosome Structure, Chromatin, DNA Packaging, Mitosis Gary Peter 9/16/2008 1 Learning Objectives 1. List and explain how DNA
DNA, Genes and their Regula4on. Me#e Voldby Larsen PhD, Assistant Professor
 DNA, Genes and their Regula4on Me#e Voldby Larsen PhD, Assistant Professor Learning Objecer this talk, you should be able to Account for the structure of DNA and RNA including their similari
DNA, Genes and their Regula4on Me#e Voldby Larsen PhD, Assistant Professor Learning Objecer this talk, you should be able to Account for the structure of DNA and RNA including their similari
Le proteine regolative variano nei vari tipi cellulari e in funzione degli stimoli ambientali
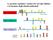 Le proteine regolative variano nei vari tipi cellulari e in funzione degli stimoli ambientali Tipo cellulare 1 Tipo cellulare 2 Tipo cellulare 3 DNA-protein Crosslink Lisi Frammentazione Immunopurificazione
Le proteine regolative variano nei vari tipi cellulari e in funzione degli stimoli ambientali Tipo cellulare 1 Tipo cellulare 2 Tipo cellulare 3 DNA-protein Crosslink Lisi Frammentazione Immunopurificazione
Nucleosome Positioning in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
 MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, June 2011, p. 301 320 Vol. 75, No. 2 1092-2172/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/mmbr.00046-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Nucleosome
MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, June 2011, p. 301 320 Vol. 75, No. 2 1092-2172/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/mmbr.00046-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Nucleosome
Chromatin Structure. a basic discussion of protein-nucleic acid binding
 Chromatin Structure 1 Chromatin DNA packaging g First a basic discussion of protein-nucleic acid binding Questions to answer: How do proteins bind DNA / RNA? How do proteins recognize a specific nucleic
Chromatin Structure 1 Chromatin DNA packaging g First a basic discussion of protein-nucleic acid binding Questions to answer: How do proteins bind DNA / RNA? How do proteins recognize a specific nucleic
Y1 Biology 131 Syllabus - Academic Year
 Y1 Biology 131 Syllabus - Academic Year 2016-2017 Monday 28/11/2016 DNA Packaging Week 11 Tuesday 29/11/2016 Regulation of gene expression Wednesday 22/9/2014 Cell cycle Sunday 4/12/2016 Tutorial Monday
Y1 Biology 131 Syllabus - Academic Year 2016-2017 Monday 28/11/2016 DNA Packaging Week 11 Tuesday 29/11/2016 Regulation of gene expression Wednesday 22/9/2014 Cell cycle Sunday 4/12/2016 Tutorial Monday
Chromatin. Structure and modification of chromatin. Chromatin domains
 Chromatin Structure and modification of chromatin Chromatin domains 2 DNA consensus 5 3 3 DNA DNA 4 RNA 5 ss RNA forms secondary structures with ds hairpins ds forms 6 of nucleic acids Form coiling bp/turn
Chromatin Structure and modification of chromatin Chromatin domains 2 DNA consensus 5 3 3 DNA DNA 4 RNA 5 ss RNA forms secondary structures with ds hairpins ds forms 6 of nucleic acids Form coiling bp/turn
Mechanisms of Transcription. School of Life Science Shandong University
 Mechanisms of Transcription School of Life Science Shandong University Ch 12: Mechanisms of Transcription 1. RNA polymerase and the transcription cycle 2. The transcription cycle in bacteria 3. Transcription
Mechanisms of Transcription School of Life Science Shandong University Ch 12: Mechanisms of Transcription 1. RNA polymerase and the transcription cycle 2. The transcription cycle in bacteria 3. Transcription
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3175
 Supplementary Figure 1 Medium- and low-fret groups probably representing varying positions on the DNA show similar changes between H3 and CENP-A nucleosomes with and without CENP-C CD, as does the high-fret
Supplementary Figure 1 Medium- and low-fret groups probably representing varying positions on the DNA show similar changes between H3 and CENP-A nucleosomes with and without CENP-C CD, as does the high-fret
Chapter 13. The Nucleus. The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus".
 Chapter 13 The Nucleus The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus". Fig.13.1. The EM of the Nucleus of a Eukaryotic Cell 13.1. The Nuclear Envelope
Chapter 13 The Nucleus The nucleus is the hallmark of eukaryotic cells; the very term eukaryotic means having a "true nucleus". Fig.13.1. The EM of the Nucleus of a Eukaryotic Cell 13.1. The Nuclear Envelope
Genes - DNA - Chromosome. Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology
 Genes - DNA - Chromosome Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology DNA Cellular DNA contains genes and intragenic regions both of which may
Genes - DNA - Chromosome Chutima Talabnin Ph.D. School of Biochemistry,Institute of Science, Suranaree University of Technology DNA Cellular DNA contains genes and intragenic regions both of which may
Chapter 5 DNA and Chromosomes
 Chapter 5 DNA and Chromosomes DNA as the genetic material Heat-killed bacteria can transform living cells S Smooth R Rough Fred Griffith, 1920 DNA is the genetic material Oswald Avery Colin MacLeod Maclyn
Chapter 5 DNA and Chromosomes DNA as the genetic material Heat-killed bacteria can transform living cells S Smooth R Rough Fred Griffith, 1920 DNA is the genetic material Oswald Avery Colin MacLeod Maclyn
1. Mitosis = growth, repair, asexual reproduc4on
 Places Muta4ons get passed on: Cell Reproduc4on: 2 types of cell reproduc4on: 1. Mitosis = growth, repair, asexual reproduc4on Photocopy machine Growth/Repair Passed on in the same body 2. Meiosis = sexual
Places Muta4ons get passed on: Cell Reproduc4on: 2 types of cell reproduc4on: 1. Mitosis = growth, repair, asexual reproduc4on Photocopy machine Growth/Repair Passed on in the same body 2. Meiosis = sexual
Epigenetics in. Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chapter 4 2/4/14
 Epigenetics in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Chapter 4 2/4/14 The budding yeast - Saccharomyces cerevisiae The fission yeast - Schizosaccharomyces pombe The budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the fission
Epigenetics in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Chapter 4 2/4/14 The budding yeast - Saccharomyces cerevisiae The fission yeast - Schizosaccharomyces pombe The budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the fission
BIOINFORMATICS. NORMAL: accurate nucleosome positioning using a modified Gaussian mixture model
 BIOINFORMATICS Vol. 28 ISMB 2012, pages i242 i249 doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bts206 : accurate nucleosome positioning using a modified Gaussian mixture model Anton Polishko 1,, Nadia Ponts 2,3, Karine
BIOINFORMATICS Vol. 28 ISMB 2012, pages i242 i249 doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bts206 : accurate nucleosome positioning using a modified Gaussian mixture model Anton Polishko 1,, Nadia Ponts 2,3, Karine
Sequence Analysis Lab Protocol
 Sequence Analysis Lab Protocol You will need this handout of instructions The sequence of your plasmid from the ABI The Accession number for Lambda DNA J02459 The Accession number for puc 18 is L09136
Sequence Analysis Lab Protocol You will need this handout of instructions The sequence of your plasmid from the ABI The Accession number for Lambda DNA J02459 The Accession number for puc 18 is L09136
Learning a Weighted Sequence Model of the Nucleosome Core and Linker Yields More Accurate Predictions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Homo sapiens
 Learning a Weighted Sequence Model of the Nucleosome Core and Linker Yields More Accurate Predictions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Homo sapiens Sheila M. Reynolds 1, Jeff A. Bilmes 1,2, William Stafford
Learning a Weighted Sequence Model of the Nucleosome Core and Linker Yields More Accurate Predictions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Homo sapiens Sheila M. Reynolds 1, Jeff A. Bilmes 1,2, William Stafford
Functional Genomics Overview RORY STARK PRINCIPAL BIOINFORMATICS ANALYST CRUK CAMBRIDGE INSTITUTE 18 SEPTEMBER 2017
 Functional Genomics Overview RORY STARK PRINCIPAL BIOINFORMATICS ANALYST CRUK CAMBRIDGE INSTITUTE 18 SEPTEMBER 2017 Agenda What is Functional Genomics? RNA Transcription/Gene Expression Measuring Gene
Functional Genomics Overview RORY STARK PRINCIPAL BIOINFORMATICS ANALYST CRUK CAMBRIDGE INSTITUTE 18 SEPTEMBER 2017 Agenda What is Functional Genomics? RNA Transcription/Gene Expression Measuring Gene
Serial Analysis of Gene Expression
 Serial Analysis of Gene Expression Cloning of Tissue-Specific Genes Using SAGE and a Novel Computational Substraction Approach. Genomic (2001) Hung-Jui Shih Outline of Presentation SAGE EST Article TPE
Serial Analysis of Gene Expression Cloning of Tissue-Specific Genes Using SAGE and a Novel Computational Substraction Approach. Genomic (2001) Hung-Jui Shih Outline of Presentation SAGE EST Article TPE
Identifying and mitigating bias in next-generation sequencing methods for chromatin biology
 STUDY DESIGNS Identifying and mitigating bias in next-generation sequencing methods for chromatin biology Clifford A. Meyer and X. Shirley Liu Abstract Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies have
STUDY DESIGNS Identifying and mitigating bias in next-generation sequencing methods for chromatin biology Clifford A. Meyer and X. Shirley Liu Abstract Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies have
Analysis of Nucleosome Isolation and Recovery: From In Silico Invitrosomes to In Vivo Nucleosomes
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2016-12-01 Analysis of Nucleosome Isolation and Recovery: From In Silico Invitrosomes to In Vivo Nucleosomes Collin Brendan Skousen
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2016-12-01 Analysis of Nucleosome Isolation and Recovery: From In Silico Invitrosomes to In Vivo Nucleosomes Collin Brendan Skousen
Lecture 21: Epigenetics Nurture or Nature? Chromatin DNA methylation Histone Code Twin study X-chromosome inactivation Environemnt and epigenetics
 Lecture 21: Epigenetics Nurture or Nature? Chromatin DNA methylation Histone Code Twin study X-chromosome inactivation Environemnt and epigenetics Epigenetics represents the science for the studying heritable
Lecture 21: Epigenetics Nurture or Nature? Chromatin DNA methylation Histone Code Twin study X-chromosome inactivation Environemnt and epigenetics Epigenetics represents the science for the studying heritable
Midterm 1 Results. Midterm 1 Akey/ Fields Median Number of Students. Exam Score
 Midterm 1 Results 10 Midterm 1 Akey/ Fields Median - 69 8 Number of Students 6 4 2 0 21 26 31 36 41 46 51 56 61 66 71 76 81 86 91 96 101 Exam Score Quick review of where we left off Parental type: the
Midterm 1 Results 10 Midterm 1 Akey/ Fields Median - 69 8 Number of Students 6 4 2 0 21 26 31 36 41 46 51 56 61 66 71 76 81 86 91 96 101 Exam Score Quick review of where we left off Parental type: the
Recombinant DNA Technology
 Recombinant DNA Technology Common General Cloning Strategy Target DNA from donor organism extracted, cut with restriction endonuclease and ligated into a cloning vector cut with compatible restriction
Recombinant DNA Technology Common General Cloning Strategy Target DNA from donor organism extracted, cut with restriction endonuclease and ligated into a cloning vector cut with compatible restriction
Research supervisors Thermal Fluctuation Spectroscopy
 Synopsis of thesis titled Thermal Fluctuation Spectroscopy and its application in the study of Biomolecules K. S. Nagapriya Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore - 560012, INDIA.
Synopsis of thesis titled Thermal Fluctuation Spectroscopy and its application in the study of Biomolecules K. S. Nagapriya Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore - 560012, INDIA.
Site specific recombina(on applica(ons
 Replica(on: Replica(on of eucaryo(c linear chromosomes Nucleosomes as obstacles during replica(on Replica(on of chromosome ends (telomeres) DNA repair Homologous recombina(on in DNA repair for exchange
Replica(on: Replica(on of eucaryo(c linear chromosomes Nucleosomes as obstacles during replica(on Replica(on of chromosome ends (telomeres) DNA repair Homologous recombina(on in DNA repair for exchange
Synthetic Biology for
 Synthetic Biology for Plasmids and DNA Digestion Plasmids Plasmids are small DNA molecules that are separate from chromosomal DNA They are most commonly found as double stranded, circular DNA Typical plasmids
Synthetic Biology for Plasmids and DNA Digestion Plasmids Plasmids are small DNA molecules that are separate from chromosomal DNA They are most commonly found as double stranded, circular DNA Typical plasmids
 The replication of DNA Kornberg 1957 Meselson and Stahl 1958 Cairns 1963 Okazaki 1968 DNA Replication The driving force for DNA synthesis. The addition of a nucleotide to a growing polynucleotide
The replication of DNA Kornberg 1957 Meselson and Stahl 1958 Cairns 1963 Okazaki 1968 DNA Replication The driving force for DNA synthesis. The addition of a nucleotide to a growing polynucleotide
DNA Replication in Eukaryotes
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44517 1 DNA Replication in Eukaryotes OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m44517 1 DNA Replication in Eukaryotes OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
Structure of nucleic acids II Biochemistry 302. January 20, 2006
 Structure of nucleic acids II Biochemistry 302 January 20, 2006 Intrinsic structural flexibility of RNA antiparallel A-form Fig. 4.19 High Temp Denaturants In vivo conditions Base stacking w/o base pairing/h-bonds
Structure of nucleic acids II Biochemistry 302 January 20, 2006 Intrinsic structural flexibility of RNA antiparallel A-form Fig. 4.19 High Temp Denaturants In vivo conditions Base stacking w/o base pairing/h-bonds
PPAR-γ - Peroxisome proliferator-ac4vated receptor gamma
 PPAR-γ - Peroxisome proliferator-ac4vated receptor gamma PPAR-γ - Peroxisome proliferator-ac4vated receptor gamma C/EBPalpha - CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha C/EBPα contains: - a func)onally related
PPAR-γ - Peroxisome proliferator-ac4vated receptor gamma PPAR-γ - Peroxisome proliferator-ac4vated receptor gamma C/EBPalpha - CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha C/EBPα contains: - a func)onally related
Nucleosomes: Structure and Function
 Nucleosomes: Structure and Function Karolin Luger, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado, USA The structure of the nucleosome core particle, the basic repeating unit in eukaryotic chromatin,
Nucleosomes: Structure and Function Karolin Luger, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado, USA The structure of the nucleosome core particle, the basic repeating unit in eukaryotic chromatin,
Post- sequencing quality evalua2on. or what to do when you get your reads from the sequencer
 Post- sequencing quality evalua2on or what to do when you get your reads from the sequencer The fastq file contains informa2on about sequence and quality Read Iden(fier Sequence Quality Sources of Library
Post- sequencing quality evalua2on or what to do when you get your reads from the sequencer The fastq file contains informa2on about sequence and quality Read Iden(fier Sequence Quality Sources of Library
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription. RNA polymerases
 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
Genome Sequence Assembly
 Genome Sequence Assembly Learning Goals: Introduce the field of bioinformatics Familiarize the student with performing sequence alignments Understand the assembly process in genome sequencing Introduction:
Genome Sequence Assembly Learning Goals: Introduce the field of bioinformatics Familiarize the student with performing sequence alignments Understand the assembly process in genome sequencing Introduction:
Chromatin assembly kit
 Chromatin assembly kit Cat. No. C01030001 (20 rxns) Version 1 I 09.15 Contacts DIAGENODE HEADQUARTERS Diagenode s.a. BELGIUM EUROPE LIEGE SCIENCE PARK Rue Bois Saint-Jean, 3 4102 Seraing - Belgium Tel:
Chromatin assembly kit Cat. No. C01030001 (20 rxns) Version 1 I 09.15 Contacts DIAGENODE HEADQUARTERS Diagenode s.a. BELGIUM EUROPE LIEGE SCIENCE PARK Rue Bois Saint-Jean, 3 4102 Seraing - Belgium Tel:
Chromatin and Transcription
 Chromatin and Transcription Chromatin Structure Chromatin Represses Transcription Nucleosome Positioning Histone Acetylation Chromatin Remodeling Histone Methylation CHIP Analysis Chromatin and Elongation
Chromatin and Transcription Chromatin Structure Chromatin Represses Transcription Nucleosome Positioning Histone Acetylation Chromatin Remodeling Histone Methylation CHIP Analysis Chromatin and Elongation
WORKSHOP. Transcriptional circuitry and the regulatory conformation of the genome. Ofir Hakim Faculty of Life Sciences
 WORKSHOP Transcriptional circuitry and the regulatory conformation of the genome Ofir Hakim Faculty of Life Sciences Chromosome conformation capture (3C) Most GR Binding Sites Are Distant From Regulated
WORKSHOP Transcriptional circuitry and the regulatory conformation of the genome Ofir Hakim Faculty of Life Sciences Chromosome conformation capture (3C) Most GR Binding Sites Are Distant From Regulated
Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription
 Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription Epigenetics 2014 by Nigel Atkinson The University of Texas at Austin From Weaver 4th edition and Armstrong 1st edition What is the point? DNA is not
Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription Epigenetics 2014 by Nigel Atkinson The University of Texas at Austin From Weaver 4th edition and Armstrong 1st edition What is the point? DNA is not
DNA replication: Enzymes link the aligned nucleotides by phosphodiester bonds to form a continuous strand.
 DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
MCDB 1041 Class 21 Splicing and Gene Expression
 MCDB 1041 Class 21 Splicing and Gene Expression Learning Goals Describe the role of introns and exons Interpret the possible outcomes of alternative splicing Relate the generation of protein from DNA to
MCDB 1041 Class 21 Splicing and Gene Expression Learning Goals Describe the role of introns and exons Interpret the possible outcomes of alternative splicing Relate the generation of protein from DNA to
DNA Transcription. Dr Aliwaini
 DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes. Dr. Syahril Abdullah Medical Genetics Laboratory
 Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes Dr. Syahril Abdullah Medical Genetics Laboratory syahril@medic.upm.edu.my Lecture Outline 1. The Genome 2. Overview of Gene Control 3. Cellular Differentiation in Higher Eukaryotes
Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes Dr. Syahril Abdullah Medical Genetics Laboratory syahril@medic.upm.edu.my Lecture Outline 1. The Genome 2. Overview of Gene Control 3. Cellular Differentiation in Higher Eukaryotes
Initiation of Replication. This section will begin with a brief discussion of chromosomal DNA sequences that sponsor the initiation of replication.
 Initiation of Replication This section will begin with a brief discussion of chromosomal DNA sequences that sponsor the initiation of replication. Replicons and origins of replication The unit of DNA replication
Initiation of Replication This section will begin with a brief discussion of chromosomal DNA sequences that sponsor the initiation of replication. Replicons and origins of replication The unit of DNA replication
Structure of nucleic acids II Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm January 21, 2005
 Structure of nucleic acids II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 21, 2005 http://biochem.uvm.edu/courses/kelm/302 User: student PW: nucleicacid Secondary structure of RNAs antiparallel A-form Fig. 4.19
Structure of nucleic acids II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 21, 2005 http://biochem.uvm.edu/courses/kelm/302 User: student PW: nucleicacid Secondary structure of RNAs antiparallel A-form Fig. 4.19
Bioinformatics of Transcriptional Regulation
 Bioinformatics of Transcriptional Regulation Carl Herrmann IPMB & DKFZ c.herrmann@dkfz.de Wechselwirkung von Maßnahmen und Auswirkungen Einflussmöglichkeiten in einem Dialog From genes to active compounds
Bioinformatics of Transcriptional Regulation Carl Herrmann IPMB & DKFZ c.herrmann@dkfz.de Wechselwirkung von Maßnahmen und Auswirkungen Einflussmöglichkeiten in einem Dialog From genes to active compounds
A RSC/Nucleosome Complex Determines Chromatin Architecture and Facilitates Activator Binding
 A RSC/Nucleosome Complex Determines Chromatin Architecture and Facilitates Activator Binding Monique Floer, 1,3 Xin Wang, 1,3 Vidya Prabhu, 1 Georgina Berrozpe, 1 Santosh Narayan, 1 Dan Spagna, 1 David
A RSC/Nucleosome Complex Determines Chromatin Architecture and Facilitates Activator Binding Monique Floer, 1,3 Xin Wang, 1,3 Vidya Prabhu, 1 Georgina Berrozpe, 1 Santosh Narayan, 1 Dan Spagna, 1 David
Eukaryotic Transcription
 Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. II. Eukaryotes
 REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS II. Eukaryotes Complexities of eukaryotic gene expression! Several steps needed for synthesis of mrna! Separation in space of transcription and translation! Compartmentation
REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS II. Eukaryotes Complexities of eukaryotic gene expression! Several steps needed for synthesis of mrna! Separation in space of transcription and translation! Compartmentation
Functional Genomics II
 Functional Genomics II Jay Hesselberth PhD University of Colorado SOM Biochemistry & Molecular Genetics jay.hesselberth@gmail.com Outline Tues, May. Definition. Yeast genome 3. Gene-centric resources and
Functional Genomics II Jay Hesselberth PhD University of Colorado SOM Biochemistry & Molecular Genetics jay.hesselberth@gmail.com Outline Tues, May. Definition. Yeast genome 3. Gene-centric resources and
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Control of Eukaryotic Genes 2007-2008 The BIG Questions n How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? n How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Control of Eukaryotic Genes 2007-2008 The BIG Questions n How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? n How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Genome Architecture Structural Subdivisons
 Lecture 4 Hierarchical Organization of the Genome by John R. Finnerty Genome Architecture Structural Subdivisons 1. Nucleotide : monomer building block of DNA 2. DNA : polymer string of nucleotides 3.
Lecture 4 Hierarchical Organization of the Genome by John R. Finnerty Genome Architecture Structural Subdivisons 1. Nucleotide : monomer building block of DNA 2. DNA : polymer string of nucleotides 3.
Triplet Expansion Diseases Modes of Gene<c Inheritance Sex Linkage Color Blindness Discuss Katherine Moser, WSJ aracle, on facing HunAngton Disease.
 9/8/17 Week 3 Genetic Disease Detection Reviewing Gene Expression Triplet Expansion Diseases Modes of Gene
9/8/17 Week 3 Genetic Disease Detection Reviewing Gene Expression Triplet Expansion Diseases Modes of Gene
Wednesday, November 22, 17. Exons and Introns
 Exons and Introns Introns and Exons Exons: coded regions of DNA that get transcribed and translated into proteins make up 5% of the genome Introns and Exons Introns: non-coded regions of DNA Must be removed
Exons and Introns Introns and Exons Exons: coded regions of DNA that get transcribed and translated into proteins make up 5% of the genome Introns and Exons Introns: non-coded regions of DNA Must be removed
Terminology: chromosome; gene; allele; proteins; enzymes
 Title Workshop on genetic disease and gene therapy Authors Danielle Higham (BSc Genetics), Dr. Maggy Fostier Contact Maggy.fostier@manchester.ac.uk Target level KS4 science, GCSE (or A-level) Publication
Title Workshop on genetic disease and gene therapy Authors Danielle Higham (BSc Genetics), Dr. Maggy Fostier Contact Maggy.fostier@manchester.ac.uk Target level KS4 science, GCSE (or A-level) Publication
Genetics Lecture 21 Recombinant DNA
 Genetics Lecture 21 Recombinant DNA Recombinant DNA In 1971, a paper published by Kathleen Danna and Daniel Nathans marked the beginning of the recombinant DNA era. The paper described the isolation of
Genetics Lecture 21 Recombinant DNA Recombinant DNA In 1971, a paper published by Kathleen Danna and Daniel Nathans marked the beginning of the recombinant DNA era. The paper described the isolation of
Biology 201 (Genetics) Exam #3 120 points 20 November Read the question carefully before answering. Think before you write.
 Name KEY Section Biology 201 (Genetics) Exam #3 120 points 20 November 2006 Read the question carefully before answering. Think before you write. You will have up to 50 minutes to take this exam. After
Name KEY Section Biology 201 (Genetics) Exam #3 120 points 20 November 2006 Read the question carefully before answering. Think before you write. You will have up to 50 minutes to take this exam. After
What controls nucleosome positions?
 Review What controls nucleosome positions? Eran Segal 1 and Jonathan Widom 2,3 1 Department of Computer Science and Applied Mathematics, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, 76100, Israel 2 Department
Review What controls nucleosome positions? Eran Segal 1 and Jonathan Widom 2,3 1 Department of Computer Science and Applied Mathematics, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, 76100, Israel 2 Department
MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: I 32 II 33 III 24 IV 30 V
 MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 32 II 33 III 24 IV 30 V 31 150 Please write your name/student ID number on each of the following five pages. This exam must be written
MIDTERM I NAME: Student ID Number: Question Maximum Points Your Points I 32 II 33 III 24 IV 30 V 31 150 Please write your name/student ID number on each of the following five pages. This exam must be written
Fig. 16-7a. 5 end Hydrogen bond 3 end. 1 nm. 3.4 nm nm
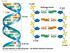 Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
A genomic code for nucleosome positioning
 doi:10.1038/nature04979 A genomic code for nucleosome positioning Eran Segal 1, Yvonne Fondufe-Mittendorf 2, Lingyi Chen 2, AnnChristine Thåström 2, Yair Field 1, Irene K. Moore 2, Ji-Ping Z. Wang 3 &
doi:10.1038/nature04979 A genomic code for nucleosome positioning Eran Segal 1, Yvonne Fondufe-Mittendorf 2, Lingyi Chen 2, AnnChristine Thåström 2, Yair Field 1, Irene K. Moore 2, Ji-Ping Z. Wang 3 &
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids
 Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Epigenetics. Medical studies in English, Lecture # 12,
 Epigenetics Medical studies in English, 2018. Lecture # 12, Epigenetics Regulation of gene activity in eukaryotes Correlation of chromatin structure with transcription stably heritable phenotype resulting
Epigenetics Medical studies in English, 2018. Lecture # 12, Epigenetics Regulation of gene activity in eukaryotes Correlation of chromatin structure with transcription stably heritable phenotype resulting
Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes
 Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes Concepts, Strategies, and Techniques Michael Carey Stephen T. Smale COLD SPRING HARBOR LABORATORY PRESS NEW YORK 2000 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 0-87969-537-4
Transcriptional Regulation in Eukaryotes Concepts, Strategies, and Techniques Michael Carey Stephen T. Smale COLD SPRING HARBOR LABORATORY PRESS NEW YORK 2000 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 0-87969-537-4
Subtracting the sequence bias from partially digested MNase seq data reveals a general contribution of TFIIS to nucleosome positioning
 Gutiérrez et al. Epigenetics & Chromatin (217) 1:58 https://doi.org/1.1186/s1372-17-165-x Epigenetics & Chromatin METHODOLOGY Open Access Subtracting the sequence bias from partially digested MNase seq
Gutiérrez et al. Epigenetics & Chromatin (217) 1:58 https://doi.org/1.1186/s1372-17-165-x Epigenetics & Chromatin METHODOLOGY Open Access Subtracting the sequence bias from partially digested MNase seq
A Link between ORC-Origin Binding Mechanisms and Origin Activation Time Revealed in Budding Yeast
 A Link between ORC-Origin Binding Mechanisms and Origin Activation Time Revealed in Budding Yeast Timothy Hoggard 1,2, Erika Shor 1, Carolin A. Müller 3, Conrad A. Nieduszynski 3 *, Catherine A. Fox 1,2
A Link between ORC-Origin Binding Mechanisms and Origin Activation Time Revealed in Budding Yeast Timothy Hoggard 1,2, Erika Shor 1, Carolin A. Müller 3, Conrad A. Nieduszynski 3 *, Catherine A. Fox 1,2
DNA: The Genetic Material. Chapter 10
 DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 10 DNA as the Genetic Material DNA was first extracted from nuclei in 1870 named nuclein after their source. Chemical analysis determined that DNA was a weak acid rich
DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 10 DNA as the Genetic Material DNA was first extracted from nuclei in 1870 named nuclein after their source. Chemical analysis determined that DNA was a weak acid rich
Methods xxx (2013) xxx xxx. Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Methods. journal homepage:
 Methods xxx (2013) xxx xxx Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Methods journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ymeth Taking into account nucleosomes for predicting gene expression Vladimir
Methods xxx (2013) xxx xxx Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Methods journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ymeth Taking into account nucleosomes for predicting gene expression Vladimir
Controlling DNA. Ethical guidelines for the use of DNA technology. Module Type: Discussion, literature review, and debate
 Ethical guidelines for the use of DNA technology Author: Tara Cornelisse, Ph.D. Candidate, Environmental Studies, University of California Santa Cruz. Field-tested with: 11 th -12 th grade students in
Ethical guidelines for the use of DNA technology Author: Tara Cornelisse, Ph.D. Candidate, Environmental Studies, University of California Santa Cruz. Field-tested with: 11 th -12 th grade students in
Exploring genomic databases: Practical session "
 Exploring genomic databases: Practical session Work through the following practical exercises on your own. The objective of these exercises is to become familiar with the information available in each
Exploring genomic databases: Practical session Work through the following practical exercises on your own. The objective of these exercises is to become familiar with the information available in each
Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins
 PHRM 836 September 22, 2015 Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins Devlin Chapter 8.8-9 u General description of transcription factors (TFs) u Sequence-specific interactions between DNA
PHRM 836 September 22, 2015 Structure/function relationship in DNA-binding proteins Devlin Chapter 8.8-9 u General description of transcription factors (TFs) u Sequence-specific interactions between DNA
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression. 1. Gene Regulation in Bacteria 2. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes 3. Gene Regulation & Cancer
 Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression 1. Gene Regulation in Bacteria 2. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes 3. Gene Regulation & Cancer Gene Regulation Gene regulation refers to all aspects of controlling
Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression 1. Gene Regulation in Bacteria 2. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes 3. Gene Regulation & Cancer Gene Regulation Gene regulation refers to all aspects of controlling
By the end of this lecture you should be able to explain: Some of the principles underlying the statistical analysis of QTLs
 (3) QTL and GWAS methods By the end of this lecture you should be able to explain: Some of the principles underlying the statistical analysis of QTLs Under what conditions particular methods are suitable
(3) QTL and GWAS methods By the end of this lecture you should be able to explain: Some of the principles underlying the statistical analysis of QTLs Under what conditions particular methods are suitable
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Origin use and efficiency are similar among WT, rrm3, pif1-m2, and pif1-m2; rrm3 strains. A. Analysis of fork progression around confirmed and likely origins (from cerevisiae.oridb.org).
Supplementary Figure 1 Origin use and efficiency are similar among WT, rrm3, pif1-m2, and pif1-m2; rrm3 strains. A. Analysis of fork progression around confirmed and likely origins (from cerevisiae.oridb.org).
M Keramatipour 2. M Keramatipour 1. M Keramatipour 4. M Keramatipour 3. M Keramatipour 5. M Keramatipour
 Molecular Cloning Methods Mohammad Keramatipour MD, PhD keramatipour@tums.ac.ir Outline DNA recombinant technology DNA cloning co Cell based PCR PCR-based Some application of DNA cloning Genomic libraries
Molecular Cloning Methods Mohammad Keramatipour MD, PhD keramatipour@tums.ac.ir Outline DNA recombinant technology DNA cloning co Cell based PCR PCR-based Some application of DNA cloning Genomic libraries
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 12 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes WORKING WITH THE FIGURES 1. In Figure 12-4, certain mutations decrease the relative transcription rate of the -globin gene. Where are these mutations located,
12 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes WORKING WITH THE FIGURES 1. In Figure 12-4, certain mutations decrease the relative transcription rate of the -globin gene. Where are these mutations located,
Do engineered ips and ES cells have similar molecular signatures?
 Do engineered ips and ES cells have similar molecular signatures? Comparing expression and epigenetics in stem cells George Bell, Ph.D. Bioinformatics and Research Computing 2012 Spring Lecture Series
Do engineered ips and ES cells have similar molecular signatures? Comparing expression and epigenetics in stem cells George Bell, Ph.D. Bioinformatics and Research Computing 2012 Spring Lecture Series
Gene Expression and Heritable Phenotype. CBS520 Eric Nabity
 Gene Expression and Heritable Phenotype CBS520 Eric Nabity DNA is Just the Beginning DNA was determined to be the genetic material, and the structure was identified as a (double stranded) double helix.
Gene Expression and Heritable Phenotype CBS520 Eric Nabity DNA is Just the Beginning DNA was determined to be the genetic material, and the structure was identified as a (double stranded) double helix.
Announcements. Coffee! Evalua,on. Dr. Yoshiki Sasai, R.I.P.
 Announcements Coffee! Evalua,on. Dr. Yoshiki Sasai, R.I.P. Sequencing considerations Three basic problems Resequencing, coun,ng, and assembly. A. B. C. 1. Resequencing analysis We know a reference genome,
Announcements Coffee! Evalua,on. Dr. Yoshiki Sasai, R.I.P. Sequencing considerations Three basic problems Resequencing, coun,ng, and assembly. A. B. C. 1. Resequencing analysis We know a reference genome,
Introduction to genome biology
 Introduction to genome biology Lisa Stubbs We ve found most genes; but what about the rest of the genome? Genome size* 12 Mb 95 Mb 170 Mb 1500 Mb 2700 Mb 3200 Mb #coding genes ~7000 ~20000 ~14000 ~26000
Introduction to genome biology Lisa Stubbs We ve found most genes; but what about the rest of the genome? Genome size* 12 Mb 95 Mb 170 Mb 1500 Mb 2700 Mb 3200 Mb #coding genes ~7000 ~20000 ~14000 ~26000
Nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ribonucleic acid (RNA) nucleotide
 Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra
 Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Chapter 3. DNA Replication & The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 3 DNA Replication & The Cell Cycle DNA Replication and the Cell Cycle Before cells divide, they must duplicate their DNA // the genetic material DNA is organized into strands called chromosomes
Chapter 3 DNA Replication & The Cell Cycle DNA Replication and the Cell Cycle Before cells divide, they must duplicate their DNA // the genetic material DNA is organized into strands called chromosomes
Machine learning applications in genomics: practical issues & challenges. Yuzhen Ye School of Informatics and Computing, Indiana University
 Machine learning applications in genomics: practical issues & challenges Yuzhen Ye School of Informatics and Computing, Indiana University Reference Machine learning applications in genetics and genomics
Machine learning applications in genomics: practical issues & challenges Yuzhen Ye School of Informatics and Computing, Indiana University Reference Machine learning applications in genetics and genomics
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302. Bob Kelm January 26, 2005
 DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 26, 2005 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
DNA Replication II Biochemistry 302 Bob Kelm January 26, 2005 Following in Dad s footsteps Original A. Kornberg E. coli DNA Pol I is a lousy replicative enzyme. 400 molecules/cell but ~2 replication forks/cell
NUCLEUS. Fig. 2. Various stages in the condensation of chromatin
 NUCLEUS Animal cells contain DNA in nucleus (contains ~ 98% of cell DNA) and mitochondrion. Both compartments are surrounded by an envelope (double membrane). Nuclear DNA represents some linear molecules
NUCLEUS Animal cells contain DNA in nucleus (contains ~ 98% of cell DNA) and mitochondrion. Both compartments are surrounded by an envelope (double membrane). Nuclear DNA represents some linear molecules
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE SLIDES
 CHAPTER 13 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies
 CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies Recombinant DNA Artificially created DNA that combines sequences that do not occur together in the nature Basis of much of the modern molecular biology Molecular cloning of genes
CHAPTER 9 DNA Technologies Recombinant DNA Artificially created DNA that combines sequences that do not occur together in the nature Basis of much of the modern molecular biology Molecular cloning of genes
EUKARYOTIC GENE CONTROL
 EUKARYOTIC GENE CONTROL THE BIG QUESTIONS How are genes turned on and off? How do cells with the same DNA/ genes differentiate to perform completely different and specialized functions? GENE EXPRESSION
EUKARYOTIC GENE CONTROL THE BIG QUESTIONS How are genes turned on and off? How do cells with the same DNA/ genes differentiate to perform completely different and specialized functions? GENE EXPRESSION
T and B cell gene rearrangement October 17, Ram Savan
 T and B cell gene rearrangement October 17, 2016 Ram Savan savanram@uw.edu 441 Lecture #9 Slide 1 of 28 Three lectures on antigen receptors Part 1 (Last Friday): Structural features of the BCR and TCR
T and B cell gene rearrangement October 17, 2016 Ram Savan savanram@uw.edu 441 Lecture #9 Slide 1 of 28 Three lectures on antigen receptors Part 1 (Last Friday): Structural features of the BCR and TCR
Exam 2 BIO200, Winter 2012
 Exam 2 BIO200, Winter 2012 Name: Multiple Choice Questions: Circle the one best answer for each question. (2 points each) 1. The 5 cap structure is often described as a backwards G. What makes this nucleotide
Exam 2 BIO200, Winter 2012 Name: Multiple Choice Questions: Circle the one best answer for each question. (2 points each) 1. The 5 cap structure is often described as a backwards G. What makes this nucleotide
GENE REGULATION slide shows by Kim Foglia modified Slides with blue edges are Kim s
 GENE REGULATION slide shows by Kim Foglia modified Slides with blue edges are Kim s 2007-2008 Bacterial metabolism Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment STOP GO if they have
GENE REGULATION slide shows by Kim Foglia modified Slides with blue edges are Kim s 2007-2008 Bacterial metabolism Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment STOP GO if they have
Computational Biology I LSM5191
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 Lecture 5 Notes: Genetic manipulation & Molecular Biology techniques Broad Overview of: Enzymatic tools in Molecular Biology Gel electrophoresis Restriction mapping DNA
Computational Biology I LSM5191 Lecture 5 Notes: Genetic manipulation & Molecular Biology techniques Broad Overview of: Enzymatic tools in Molecular Biology Gel electrophoresis Restriction mapping DNA
Regulation of Gene Expression
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 15 Regulation of Gene Expression Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 15 Regulation of Gene Expression Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers
 Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that usually extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated the (#1) of transcription
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that usually extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated the (#1) of transcription
