Variation detection based on second generation sequencing data. Xin LIU Department of Science and Technology, BGI
|
|
|
- Brandon Boone
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Variation detection based on second generation sequencing data Xin LIU Department of Science and Technology, BGI
2 Outline Summary of sequencing techniques Data quality assessing and filtering Mapping the short reads Detection of SNPs Detection of SVs Detection of CNVs 2
3 Sequencing technologies Illumina SOLiD 454 PacBio Sanger Complete Genomics Helicos Ion Torrent Oxford Nanopore 3
4 Illumina sequencing 4
5 Ion Torrent sequencing 5
6 Sequencing techniques Quail, M. A., M. Smith, et al. (2012). "A tale of three next generation sequencing platforms: comparison of Ion Torrent, Pacific Biosciences and Illumina MiSeq sequencers." BMC Genomics 13:
7 Flowchart of sequencing analysis Sequencing data De novo assembly Resequencing Whole genome assembly Regional/partial assembly Whole genome resequencing Target region resequencing RAD/GBS Nielsen, R., J. S. Paul, et al. (2011). "Genotype and SNP calling from next-generation sequencing data." Nat Rev Genet 12(6):
8 Different genomic variations Genome size Karyotypes DNA sequences Chromosome rearrangements Structural variations Indels SNPs 8
9 Detection of variations 9
10 Beginning, mapping/alignment Find the sequenced read s placement in reference genome Calculate the coverage and depth distribution of the sequenced reads Sequencing quality evaluation Important for variation detection 10
11 Previous mapping tools Needleman-Wunsch Global alignment algorithm An example: align COELACANTH and PELICAN Scoring scheme: +1 if letters match, -1 for mismatches, -1 for gaps COELACANTH P-ELICAN-- Smith-Waterman Modified to do local alignment BLAST Three heuristic layers: seeding, extension, and evaluation Seeding identify where to start alignment Extension extending alignment from seeds Evaluation Determine which alignments 11 are statistically significant
12 SOAP Differences between traditional and next-generation sequencing technology reads length data capacity Algorithm change to meet the data characteristics of the sequencing technology traditional aligner: global or local alignment; scoring matrix; dynamic programming and trace-back Next-Gen aligner: Indexing & Bitwise operation Does blastall/blat still work? Short Oligonucleotide Alignment/Analysis Package 12
13 Index the genome 13
14 Algorithm of SOAP Comparing to BLAST, BLAT, short reads aligner applied looking-up method. Index of the reference were made in order to help the process of looking-up. Seed were first looked up by using index and then sequences were extended. Reference Index Reads 14
15 Features of SOAP Fast and efficient Mode of pair-end mapping Permit gaps within alignments Trim of reads permitted 15
16 Algorithm of SOAP2 Indexing Split read into parts, which used to anchor the exact matching region in the reference, excluding much of the unwanted region. 2way-BWT (Burrows-Wheeler transform) provide a excellent solution for the computing complexity Memory effective (~7G memory need for 3G genome). Fast indexing (2 minutes to finish 1M 35bp single end alignment). Thread Parallel Computing Make fully use of process and save time. Bitwise operation Encode each base into 2 binary bits, and use exclusive-or to check if two bases are the same. 16
17 Flowchart of mapping Pre-build index files Reference Branching Limited (Mismatches) BWT Reference Suffix Array Common Prefixes Hash Search queries 17
18 BWA Burrows-Wheeler Alignment tool (BWA), the read alignment package that is based on backward search with Burrows Wheeler Transform (BWT); Allowing mismatches and gaps; BWA is faster than MAQ, while achieving similar accuracy; BWA outputs alignment in the SAM format Variant calling can be achieved by SAMtools software package 18
19 CPU time and RAM 19
20 Sensitivity of mapping 20
21 Correctness of mapping 21
22 Alignment with insertion 22
23 Summary of mapping Short reads mapping need specific aligners Many aligners are available and there are different features. No best aligner exists, and most of them are acceptable. Mapping is important in variation detection. 23
24 Importance of SNPs Well-studied variation Better representing demographic history Method of detection is relatively mature Provides more information for follow-up studies Detect SNPs in individuals Detect SNPs in population 24
25 SOAPsnp to detect SNPs SOAPsnp was developed for consensus calling and SNP detection based on the Solexa sequencing technology. SOAPsnp takes Bayes s theorem as statistic model for SNP calling, it considers: Sequencing quality Likelihood calculation based on observed data Experiment factors Prior probability Alignment uniqueness and accuracy Using dbsnp as prior probability 25
26 SOAPsnp 26
27 Sequencing errors SNP identification can be inferred by counting mismatch numbers. But, sequencing quality is important for distinguishing sequencing error from SNP, especially for Solexa sequencing. 27
28 Statistic model D: is the observed data in alignment. Prior(g): prior probability of a given genotypes P(D x): conditional probability to get the observed data D of a given genotype Diploid Ti contain 10 types: AA,CC,GG,TT,AC,AG,AT,CG,CT,GT; P((Base,quality) Ti) = P((Base,quality) Ti1) /2 + P((Base,quality) Ti2) /2 P(D Ti) = P((Base, quality) Ti) 28
29 Filtering SNPs By comparing the reference allele and the consensus genotype with maximum Bayesian likelihood, decisions of SNP status are made. But this is only the candidate SNPs, the accuracy is not reliable, especially when the mapped reads depth is low. In addition, we used some other measures to get confident SNPs, such as the minimum supporting reads number for each allele, exclude SNP predictions on repeat regions, and the rank-sum test for heterozygous SNP. 29
30 Other software to identify SNPs MAQ provides modules to identify SNPs. Error rates were calculated at each position thus SNPs were identified. Samtools, using sam/bam files, identifies SNPs in individual or populations. 30
31 Detect SNPs at different depth In population studies, sequencing depth of each individual is always low. Then, how can we detect SNPs? 31
32 Detect SNPs in population Sequencing in population Several individuals sequenced Sequencing depth of each individual is relatively low (0.1-20X). Total depth is high, several hundred times. 32
33 Detect SNPs in population Sequencing depth Genome coverage ratio Identified SNP ratio Low (1-3X) 50%-80% 30%-50% Middle (6-10X) High (20-40X) 90%-99% 70%-90% 99.9%~100 % 95%-99% Study purpose Rough population survey, infer population structure, phylogeny, and selection. Whole population sequencing, suitable for further applications, such as molecular inbreeding, and functional genomics. Complete map (de novo assembly) for each subspecies, line, or individual, suitable for all kinds of future applications. 33
34 GLFmulti To detect SNPs in population (applied in silkworm paper) Mapping Using SOAP to align sequences from each individual to the reference. SOAPsnp Using SOAPsnp to determine the likelihood of genotypes at each position in each individual. GLFmulti Integrate the likelihood of each individual at each position, then apply MLE to estimate the allele frequency. 34
35 GLFmulti Frequency at each site with the maximum likelihood is given. Copy number, sequencing depth, quality score and minor allele count are integrated into one score. 35
36 GLFmulti SNPs were confidential, but SNPs at low frequency were underestimated. 35% 30% 25% 20% 15% 10% 5% 0%
37 To detect SNPs in population (applied in Tibetan paper) realsfs Mapping Using SOAP to align sequences from each individual to the reference. SOAPsnp Using SOAPsnp to determine the likelihood of genotypes at each position in each individual. realsfs Calculate the likelihood of allele frequency at each position. 37
38 realsfs 1. Likelihood of different allele frequency Individual1 P0 P1 P Individual2 P0*P0(2) P1*P0(2)+P0*P 1(2) P2*P0(2)+P0*P2(0)+P1 *P1(2) P1*P2(2)+P2*P 1(0) P2*P2( 2) Prior probability of different allele frequency. 35% 30% 25% 20% 15% 10% 5% 0%
39 realsfs Detect SNPs at low depth of each individual (lowest 0.4X depth). Relatively higher false positive ratio. 39
40 Other software to detect SNPs GATK: a widely used software/pipeline to detect variations, especially for human population ( ex.php/main_page) SHORE: a pipeline used in 1000 genome project of Arabidopsis ( e/index.php?title=shore_documentation) 40
41 GATK 41
42 SHORE SHORE is a data analysis and management application for short DNA/RNA reads produced by the various contemporary sequencing platforms. SHORE is designed to support different sequencing applications including genomic re-sequencing, ChIP- Seq, mrna-seq, srna-seq and BS-seq. SHORE was developed for applications in Arabidopsis thaliana but has been successfully used with other genomes, including human, mouse, D. melanogaster, C. elegans, maize and several bacterial genomes. 42
43 Summary of SNP detection Different methods can be applied in SNP detection in single individual. The main problem to cope with is the sequencing errors which would result in false positive. The variation calling would also depend a lot on the mapping result. Experimental validation is necessary. Detect SNPs in individual require higher depth. Detect SNPs in population can detect SNPs at lower individual depth. Statistic method is usually applied in SNP calling to prevent influence of sequencing errors. Different statistic models show different detection power. 43
44 Detection of indels After mapping, if the mapping permits gaps, those alignments with gaps can be the candidate for indels. In SOAPindel sequencing quality and mapping result were combined to deduce the probability of being an indel. 44
45 Detection of indel by SOAPindel Reference Mapped reads Homozygous deletion Heterozygous deletion Homozygous insertion Heterozygous insertion 45
46 Other methods to detect indels Dindel: program for calling small indels from short-read sequence data Extracts all indels from the read-alignments in the BAM file Candidate InDels grouped into windows For each window, Dindel will generate candidate haplotypes from the candidate indels and realign Interpreting the output from Dindel 46
47 Detection of SVs Mainly there are three kinds of methods to detect structural variations: Local de novo assembly Pair end mapping Split reads The SV detection based on assembly is believed to be more accurate. 47
48 Local de novo assembly 1. Assemble pair-end reads into scaffold. 2. Align the scaffold to reference genome.
49 Workflow of SOAPsv: SOAPsv
50 Complex structure variants can be detected: Output format: (#Type, scaffold, start, end, refchr, start, end, length, sequence) Reference: Li, Y., Zheng, H., Luo, R., Wu, H., Zhu, H., Li, R.,... & Wang, J. (2011). Structural variation in two human genomes mapped at single-nucleotide resolution by whole genome de novo assembly. Nature biotechnology, 29(8),
51 Pair end mapping 1. Map the reads to the reference genome. 2. Detect structure variants by discordant reads.
52 Workflow of BreakDancer: BreakDancer
53 Performance of BreakDancer Output format: (#chromosome, position, orientation, chromosome, position, orientation, type, length, score ) Reference: Chen, K., Wallis, J. W., McLellan, M. D., Larson, D. E., Kalicki, J. M., Pohl, C. S.,... & Mardis, E. R. (2009). BreakDancer: an algorithm for high-resolution mapping of genomic structural variation. Nature methods, 6(9),
54 Split reads 1. Map the reads to reference genome. 2. Select those paired reads that mapped with indels or of which only one end can be mapped. 3. Uses the mapped reads to determine the anchor point on the reference genome and the direction of the unmapped reads.
55 Workflow of Pindel: Pindel
56 SLINEs and LINEs can be detected by Pindel: Output format: (#index, type, length, insertion length, chrid, border of event, range of unclear breakpoint, support number) Reference: Ye, K., Schulz, M. H., Long, Q., Apweiler, R., & Ning, Z. (2009). Pindel: a pattern growth approach to detect break points of large deletions and medium sized insertions from paired-end short reads. Bioinformatics,25(21),
57 Comparison Tools SOAPsv BreakDancer Pindel Main detectable length range 1 bp-50 kbp >10bp 1bp-30kbp Detectable SV types Insertions Yes Yes Yes Deletions Yes Yes Yes Inversions Yes Yes Yes Complex Yes Yes No Precision of breakpoints Single base A short ambiguous range Single base Genotypes of SV events False-positive rate in simulated data Yes No Yes 1.20% % <2% False-negative rate in simulated data 9.60% 26 32% ~20% *Reference: Li, Y., Zheng, H., Luo, R., Wu, H., Zhu, H., Li, R.,... & Wang, J. (2011). Structural variation in two human genomes mapped at single-nucleotide resolution by whole genome de novo assembly. Nature biotechnology, 29(8), (Table2)
58 The CNV detection Depth of Coverage (DOC): Number of reads in a region Uniform depth distribution Biased for GC etc. Paired End Mapping (PEM): Proper pairing when mapping Limit by insert sizes Inversions/Translocations Split Reads (SR) The unaligned reads Pinpoint the location of CNV Assembly based (AS) Zhao et al. BMC Bioinformatics 2013, 14(Suppl 11):S1 58
59 Summary of CNV detect tools 59
60 Software to detect CNV CNVer 60
61 Notes about CNV detection Repeat regions would have great impact. Mapping depth should be carefully inspected especially when the pair-end mapping was done. It is always difficult to give the actual copy numbers. 61
62 Summary of variation detection Different models are available in SNP calling of a single individual, and good methods should take care of both sequencing and mapping quality. Indels can be easily detected by interpreting the gapped alignment, and the accuracy do depend greatly on the mapping. Using assembly to find SVs is more accurate in practice than using pair-end information. Depth of coverage was applied in CNV detection. 62
63
Illumina (Solexa) Throughput: 4 Tbp in one run (5 days) Cheapest sequencing technology. Mismatch errors dominate. Cost: ~$1000 per human genme
 Illumina (Solexa) Current market leader Based on sequencing by synthesis Current read length 100-150bp Paired-end easy, longer matepairs harder Error ~0.1% Mismatch errors dominate Throughput: 4 Tbp in
Illumina (Solexa) Current market leader Based on sequencing by synthesis Current read length 100-150bp Paired-end easy, longer matepairs harder Error ~0.1% Mismatch errors dominate Throughput: 4 Tbp in
SNP calling and VCF format
 SNP calling and VCF format Laurent Falquet, Oct 12 SNP? What is this? A type of genetic variation, among others: Family of Single Nucleotide Aberrations Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Single Nucleotide
SNP calling and VCF format Laurent Falquet, Oct 12 SNP? What is this? A type of genetic variation, among others: Family of Single Nucleotide Aberrations Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Single Nucleotide
Alignment methods. Martijn Vermaat Department of Human Genetics Center for Human and Clinical Genetics
 Alignment methods Martijn Vermaat Department of Human Genetics Center for Human and Clinical Genetics Alignment methods Sequence alignment Assembly vs alignment Alignment methods Common issues Platform
Alignment methods Martijn Vermaat Department of Human Genetics Center for Human and Clinical Genetics Alignment methods Sequence alignment Assembly vs alignment Alignment methods Common issues Platform
Read Mapping and Variant Calling. Johannes Starlinger
 Read Mapping and Variant Calling Johannes Starlinger Application Scenario: Personalized Cancer Therapy Different mutations require different therapy Collins, Meredith A., and Marina Pasca di Magliano.
Read Mapping and Variant Calling Johannes Starlinger Application Scenario: Personalized Cancer Therapy Different mutations require different therapy Collins, Meredith A., and Marina Pasca di Magliano.
Variant Detection in Next Generation Sequencing Data. John Osborne Sept 14, 2012
 + Variant Detection in Next Generation Sequencing Data John Osborne Sept 14, 2012 + Overview My Bias Talk slanted towards analyzing whole genomes using Illumina paired end reads with open source tools
+ Variant Detection in Next Generation Sequencing Data John Osborne Sept 14, 2012 + Overview My Bias Talk slanted towards analyzing whole genomes using Illumina paired end reads with open source tools
Next-Generation Sequencing. Technologies
 Next-Generation Next-Generation Sequencing Technologies Sequencing Technologies Nicholas E. Navin, Ph.D. MD Anderson Cancer Center Dept. Genetics Dept. Bioinformatics Introduction to Bioinformatics GS011062
Next-Generation Next-Generation Sequencing Technologies Sequencing Technologies Nicholas E. Navin, Ph.D. MD Anderson Cancer Center Dept. Genetics Dept. Bioinformatics Introduction to Bioinformatics GS011062
Accelerate High Throughput Analysis for Genome Sequencing with GPU
 Accelerate High Throughput Analysis for Genome Sequencing with GPU ATIP - A*CRC Workshop on Accelerator Technologies in High Performance Computing May 7-10, 2012 Singapore BingQiang WANG, Head of Scalable
Accelerate High Throughput Analysis for Genome Sequencing with GPU ATIP - A*CRC Workshop on Accelerator Technologies in High Performance Computing May 7-10, 2012 Singapore BingQiang WANG, Head of Scalable
Variant calling in NGS experiments
 Variant calling in NGS experiments Jorge Jiménez jjimeneza@cipf.es BIER CIBERER Genomics Department Centro de Investigacion Principe Felipe (CIPF) (Valencia, Spain) 1 Index 1. NGS workflow 2. Variant calling
Variant calling in NGS experiments Jorge Jiménez jjimeneza@cipf.es BIER CIBERER Genomics Department Centro de Investigacion Principe Felipe (CIPF) (Valencia, Spain) 1 Index 1. NGS workflow 2. Variant calling
Genomic DNA ASSEMBLY BY REMAPPING. Course overview
 ASSEMBLY BY REMAPPING Laurent Falquet, The Bioinformatics Unravelling Group, UNIFR & SIB MA/MER @ UniFr Group Leader @ SIB Course overview Genomic DNA PacBio Illumina methylation de novo remapping Annotation
ASSEMBLY BY REMAPPING Laurent Falquet, The Bioinformatics Unravelling Group, UNIFR & SIB MA/MER @ UniFr Group Leader @ SIB Course overview Genomic DNA PacBio Illumina methylation de novo remapping Annotation
Ecole de Bioinforma(que AVIESAN Roscoff 2014 GALAXY INITIATION. A. Lermine U900 Ins(tut Curie, INSERM, Mines ParisTech
 GALAXY INITIATION A. Lermine U900 Ins(tut Curie, INSERM, Mines ParisTech How does Next- Gen sequencing work? DNA fragmentation Size selection and clonal amplification Massive parallel sequencing ACCGTTTGCCG
GALAXY INITIATION A. Lermine U900 Ins(tut Curie, INSERM, Mines ParisTech How does Next- Gen sequencing work? DNA fragmentation Size selection and clonal amplification Massive parallel sequencing ACCGTTTGCCG
Why can GBS be complicated? Tools for filtering, error correction and imputation.
 Why can GBS be complicated? Tools for filtering, error correction and imputation. Edward Buckler USDA-ARS Cornell University http://www.maizegenetics.net Many Organisms Are Diverse Humans are at the lower
Why can GBS be complicated? Tools for filtering, error correction and imputation. Edward Buckler USDA-ARS Cornell University http://www.maizegenetics.net Many Organisms Are Diverse Humans are at the lower
Sequence Assembly and Alignment. Jim Noonan Department of Genetics
 Sequence Assembly and Alignment Jim Noonan Department of Genetics james.noonan@yale.edu www.yale.edu/noonanlab The assembly problem >>10 9 sequencing reads 36 bp - 1 kb 3 Gb Outline Basic concepts in genome
Sequence Assembly and Alignment Jim Noonan Department of Genetics james.noonan@yale.edu www.yale.edu/noonanlab The assembly problem >>10 9 sequencing reads 36 bp - 1 kb 3 Gb Outline Basic concepts in genome
Next Generation Sequencing: An Overview
 Next Generation Sequencing: An Overview Cavan Reilly November 13, 2017 Table of contents Next generation sequencing NGS and microarrays Study design Quality assessment Burrows Wheeler transform Next generation
Next Generation Sequencing: An Overview Cavan Reilly November 13, 2017 Table of contents Next generation sequencing NGS and microarrays Study design Quality assessment Burrows Wheeler transform Next generation
Alignment. J Fass UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Wednesday December 17, 2014
 Alignment J Fass UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Wednesday December 17, 2014 From reads to molecules Why align? Individual A Individual B ATGATAGCATCGTCGGGTGTCTGCTCAATAATAGTGCCGTATCATGCTGGTGTTATAATCGCCGCATGACATGATCAATGG
Alignment J Fass UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Wednesday December 17, 2014 From reads to molecules Why align? Individual A Individual B ATGATAGCATCGTCGGGTGTCTGCTCAATAATAGTGCCGTATCATGCTGGTGTTATAATCGCCGCATGACATGATCAATGG
Assembly of Ariolimax dolichophallus using SOAPdenovo2
 Assembly of Ariolimax dolichophallus using SOAPdenovo2 Charles Markello, Thomas Matthew, and Nedda Saremi Image taken from Banana Slug Genome Project, S. Weber SOAPdenovo Assembly Tool Short Oligonucleotide
Assembly of Ariolimax dolichophallus using SOAPdenovo2 Charles Markello, Thomas Matthew, and Nedda Saremi Image taken from Banana Slug Genome Project, S. Weber SOAPdenovo Assembly Tool Short Oligonucleotide
Gap Filling for a Human MHC Haplotype Sequence
 American Journal of Life Sciences 2016; 4(6): 146-151 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajls doi: 10.11648/j.ajls.20160406.12 ISSN: 2328-5702 (Print); ISSN: 2328-5737 (Online) Gap Filling for a Human
American Journal of Life Sciences 2016; 4(6): 146-151 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajls doi: 10.11648/j.ajls.20160406.12 ISSN: 2328-5702 (Print); ISSN: 2328-5737 (Online) Gap Filling for a Human
Bioinformatics small variants Data Analysis. Guidelines. genomescan.nl
 Next Generation Sequencing Bioinformatics small variants Data Analysis Guidelines genomescan.nl GenomeScan s Guidelines for Small Variant Analysis on NGS Data Using our own proprietary data analysis pipelines
Next Generation Sequencing Bioinformatics small variants Data Analysis Guidelines genomescan.nl GenomeScan s Guidelines for Small Variant Analysis on NGS Data Using our own proprietary data analysis pipelines
Outline. General principles of clonal sequencing Analysis principles Applications CNV analysis Genome architecture
 The use of new sequencing technologies for genome analysis Chris Mattocks National Genetics Reference Laboratory (Wessex) NGRL (Wessex) 2008 Outline General principles of clonal sequencing Analysis principles
The use of new sequencing technologies for genome analysis Chris Mattocks National Genetics Reference Laboratory (Wessex) NGRL (Wessex) 2008 Outline General principles of clonal sequencing Analysis principles
ALGORITHMS IN BIO INFORMATICS. Chapman & Hall/CRC Mathematical and Computational Biology Series A PRACTICAL INTRODUCTION. CRC Press WING-KIN SUNG
 Chapman & Hall/CRC Mathematical and Computational Biology Series ALGORITHMS IN BIO INFORMATICS A PRACTICAL INTRODUCTION WING-KIN SUNG CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press
Chapman & Hall/CRC Mathematical and Computational Biology Series ALGORITHMS IN BIO INFORMATICS A PRACTICAL INTRODUCTION WING-KIN SUNG CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press
Next Generation Sequencing. Jeroen Van Houdt - Leuven 13/10/2017
 Next Generation Sequencing Jeroen Van Houdt - Leuven 13/10/2017 Landmarks in DNA sequencing 1953 Discovery of DNA double helix structure 1977 A Maxam and W Gilbert "DNA seq by chemical degradation" F Sanger"DNA
Next Generation Sequencing Jeroen Van Houdt - Leuven 13/10/2017 Landmarks in DNA sequencing 1953 Discovery of DNA double helix structure 1977 A Maxam and W Gilbert "DNA seq by chemical degradation" F Sanger"DNA
HLA and Next Generation Sequencing it s all about the Data
 HLA and Next Generation Sequencing it s all about the Data John Ord, NHSBT Colindale and University of Cambridge BSHI Annual Conference Manchester September 2014 Introduction In 2003 the first full public
HLA and Next Generation Sequencing it s all about the Data John Ord, NHSBT Colindale and University of Cambridge BSHI Annual Conference Manchester September 2014 Introduction In 2003 the first full public
LUMPY: A probabilistic framework for structural variant discovery
 LUMPY: A probabilistic framework for structural variant discovery Ryan M Layer 1, Aaron R Quinlan* 1,2,3,4 and Ira M Hall* 2,4 1 Department of Computer Science 2 Department of Biochemistry and Molecular
LUMPY: A probabilistic framework for structural variant discovery Ryan M Layer 1, Aaron R Quinlan* 1,2,3,4 and Ira M Hall* 2,4 1 Department of Computer Science 2 Department of Biochemistry and Molecular
Data Analysis with CASAVA v1.8 and the MiSeq Reporter
 Data Analysis with CASAVA v1.8 and the MiSeq Reporter Eric Smith, PhD Bioinformatics Scientist September 15 th, 2011 2010 Illumina, Inc. All rights reserved. Illumina, illuminadx, Solexa, Making Sense
Data Analysis with CASAVA v1.8 and the MiSeq Reporter Eric Smith, PhD Bioinformatics Scientist September 15 th, 2011 2010 Illumina, Inc. All rights reserved. Illumina, illuminadx, Solexa, Making Sense
L3: Short Read Alignment to a Reference Genome
 L3: Short Read Alignment to a Reference Genome Shamith Samarajiwa CRUK Autumn School in Bioinformatics Cambridge, September 2017 Where to get help! http://seqanswers.com http://www.biostars.org http://www.bioconductor.org/help/mailing-list
L3: Short Read Alignment to a Reference Genome Shamith Samarajiwa CRUK Autumn School in Bioinformatics Cambridge, September 2017 Where to get help! http://seqanswers.com http://www.biostars.org http://www.bioconductor.org/help/mailing-list
Germline variant calling and joint genotyping
 talks Germline variant calling and joint genotyping Applying the joint discovery workflow with HaplotypeCaller + GenotypeGVCFs You are here in the GATK Best PracDces workflow for germline variant discovery
talks Germline variant calling and joint genotyping Applying the joint discovery workflow with HaplotypeCaller + GenotypeGVCFs You are here in the GATK Best PracDces workflow for germline variant discovery
Sequencing technologies. Jose Blanca COMAV institute bioinf.comav.upv.es
 Sequencing technologies Jose Blanca COMAV institute bioinf.comav.upv.es Outline Sequencing technologies: Sanger 2nd generation sequencing: 3er generation sequencing: 454 Illumina SOLiD Ion Torrent PacBio
Sequencing technologies Jose Blanca COMAV institute bioinf.comav.upv.es Outline Sequencing technologies: Sanger 2nd generation sequencing: 3er generation sequencing: 454 Illumina SOLiD Ion Torrent PacBio
Next Generation Sequencing: Data analysis for genetic profiling
 Next Generation Sequencing: Data analysis for genetic profiling Raed Samara, Ph.D. Global Product Manager Raed.Samara@QIAGEN.com Welcome to the NGS webinar series - 2015 NGS Technology Webinar 1 NGS: Introduction
Next Generation Sequencing: Data analysis for genetic profiling Raed Samara, Ph.D. Global Product Manager Raed.Samara@QIAGEN.com Welcome to the NGS webinar series - 2015 NGS Technology Webinar 1 NGS: Introduction
Sequencing technologies. Jose Blanca COMAV institute bioinf.comav.upv.es
 Sequencing technologies Jose Blanca COMAV institute bioinf.comav.upv.es Outline Sequencing technologies: Sanger 2nd generation sequencing: 3er generation sequencing: 454 Illumina SOLiD Ion Torrent PacBio
Sequencing technologies Jose Blanca COMAV institute bioinf.comav.upv.es Outline Sequencing technologies: Sanger 2nd generation sequencing: 3er generation sequencing: 454 Illumina SOLiD Ion Torrent PacBio
Next Generation Sequencing Lecture Saarbrücken, 19. March Sequencing Platforms
 Next Generation Sequencing Lecture Saarbrücken, 19. March 2012 Sequencing Platforms Contents Introduction Sequencing Workflow Platforms Roche 454 ABI SOLiD Illumina Genome Anlayzer / HiSeq Problems Quality
Next Generation Sequencing Lecture Saarbrücken, 19. March 2012 Sequencing Platforms Contents Introduction Sequencing Workflow Platforms Roche 454 ABI SOLiD Illumina Genome Anlayzer / HiSeq Problems Quality
Tangram: a comprehensive toolbox for mobile element insertion detection
 Wu et al. BMC Genomics 2014, 15:795 METHODOLOGY ARTICLE Open Access Tangram: a comprehensive toolbox for mobile element insertion detection Jiantao Wu 1,Wan-PingLee 1, Alistair Ward 1, Jerilyn A Walker
Wu et al. BMC Genomics 2014, 15:795 METHODOLOGY ARTICLE Open Access Tangram: a comprehensive toolbox for mobile element insertion detection Jiantao Wu 1,Wan-PingLee 1, Alistair Ward 1, Jerilyn A Walker
Analysis of Structural Variants using 3 rd generation Sequencing
 Analysis of Structural Variants using 3 rd generation Sequencing Michael Schatz January 12, 2016 Bioinformatics / PAG XXIV @mike_schatz / #PAGXXIV Analysis of Structural Variants using 3 rd generation
Analysis of Structural Variants using 3 rd generation Sequencing Michael Schatz January 12, 2016 Bioinformatics / PAG XXIV @mike_schatz / #PAGXXIV Analysis of Structural Variants using 3 rd generation
Third Generation Sequencing
 Third Generation Sequencing By Mohammad Hasan Samiee Aref Medical Genetics Laboratory of Dr. Zeinali History of DNA sequencing 1953 : Discovery of DNA structure by Watson and Crick 1973 : First sequence
Third Generation Sequencing By Mohammad Hasan Samiee Aref Medical Genetics Laboratory of Dr. Zeinali History of DNA sequencing 1953 : Discovery of DNA structure by Watson and Crick 1973 : First sequence
Mapping of Next Generation Sequencing Data
 Mapping of Next Generation Sequencing Data Agnes Hotz-Wagenblatt Bioinformatik (HUSAR) Next Generation Sequencers Next (or 3 rd ) generation sequencers came onto the scene in the early 2000 s General characteristics
Mapping of Next Generation Sequencing Data Agnes Hotz-Wagenblatt Bioinformatik (HUSAR) Next Generation Sequencers Next (or 3 rd ) generation sequencers came onto the scene in the early 2000 s General characteristics
Sanger vs Next-Gen Sequencing
 Tools and Algorithms in Bioinformatics GCBA815/MCGB815/BMI815, Fall 2017 Week-8: Next-Gen Sequencing RNA-seq Data Analysis Babu Guda, Ph.D. Professor, Genetics, Cell Biology & Anatomy Director, Bioinformatics
Tools and Algorithms in Bioinformatics GCBA815/MCGB815/BMI815, Fall 2017 Week-8: Next-Gen Sequencing RNA-seq Data Analysis Babu Guda, Ph.D. Professor, Genetics, Cell Biology & Anatomy Director, Bioinformatics
Introduction to Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
 Introduction to Next eneration Sequencing (NS) Simon Rasmussen Assistant Professor enter for Biological Sequence analysis Technical University of Denmark 2012 Today 9.00-9.45: Introduction to NS, How it
Introduction to Next eneration Sequencing (NS) Simon Rasmussen Assistant Professor enter for Biological Sequence analysis Technical University of Denmark 2012 Today 9.00-9.45: Introduction to NS, How it
Barcode Sequence Alignment and Statistical Analysis (Barcas) tool
 Barcode Sequence Alignment and Statistical Analysis (Barcas) tool 2016.10.05 Mun, Jihyeob and Kim, Seon-Young Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology Barcode-Sequencing Ø Genome-wide screening
Barcode Sequence Alignment and Statistical Analysis (Barcas) tool 2016.10.05 Mun, Jihyeob and Kim, Seon-Young Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology Barcode-Sequencing Ø Genome-wide screening
COPE: An accurate k-mer based pair-end reads connection tool to facilitate genome assembly
 Bioinformatics Advance Access published October 8, 2012 COPE: An accurate k-mer based pair-end reads connection tool to facilitate genome assembly Binghang Liu 1,2,, Jianying Yuan 2,, Siu-Ming Yiu 1,3,
Bioinformatics Advance Access published October 8, 2012 COPE: An accurate k-mer based pair-end reads connection tool to facilitate genome assembly Binghang Liu 1,2,, Jianying Yuan 2,, Siu-Ming Yiu 1,3,
Ultrasequencing: Methods and Applications of the New Generation Sequencing Platforms
 Ultrasequencing: Methods and Applications of the New Generation Sequencing Platforms Laura Moya Andérico Master in Advanced Genetics Genomics Class December 16 th, 2015 Brief Overview First-generation
Ultrasequencing: Methods and Applications of the New Generation Sequencing Platforms Laura Moya Andérico Master in Advanced Genetics Genomics Class December 16 th, 2015 Brief Overview First-generation
Analysing genomes and transcriptomes using Illumina sequencing
 Analysing genomes and transcriptomes using Illumina uencing Dr. Heinz Himmelbauer Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) Ultrauencing Unit Barcelona The Sequencing Revolution High-Throughput Sequencing 2000
Analysing genomes and transcriptomes using Illumina uencing Dr. Heinz Himmelbauer Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) Ultrauencing Unit Barcelona The Sequencing Revolution High-Throughput Sequencing 2000
Introduction to Bioinformatics and Gene Expression Technologies
 Introduction to Bioinformatics and Gene Expression Technologies Utah State University Fall 2017 Statistical Bioinformatics (Biomedical Big Data) Notes 1 1 Vocabulary Gene: hereditary DNA sequence at a
Introduction to Bioinformatics and Gene Expression Technologies Utah State University Fall 2017 Statistical Bioinformatics (Biomedical Big Data) Notes 1 1 Vocabulary Gene: hereditary DNA sequence at a
High Throughput Sequencing Technologies. UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Monday 15 June 2015
 High Throughput Sequencing Technologies UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Monday 15 June 2015 Sequencing Explosion www.genome.gov/sequencingcosts http://t.co/ka5cvghdqo Sequencing Explosion 2011 PacBio
High Throughput Sequencing Technologies UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Monday 15 June 2015 Sequencing Explosion www.genome.gov/sequencingcosts http://t.co/ka5cvghdqo Sequencing Explosion 2011 PacBio
NOW GENERATION SEQUENCING. Monday, December 5, 11
 NOW GENERATION SEQUENCING 1 SEQUENCING TIMELINE 1953: Structure of DNA 1975: Sanger method for sequencing 1985: Human Genome Sequencing Project begins 1990s: Clinical sequencing begins 1998: NHGRI $1000
NOW GENERATION SEQUENCING 1 SEQUENCING TIMELINE 1953: Structure of DNA 1975: Sanger method for sequencing 1985: Human Genome Sequencing Project begins 1990s: Clinical sequencing begins 1998: NHGRI $1000
Personal Genomics Platform White Paper Last Updated November 15, Executive Summary
 Executive Summary Helix is a personal genomics platform company with a simple but powerful mission: to empower every person to improve their life through DNA. Our platform includes saliva sample collection,
Executive Summary Helix is a personal genomics platform company with a simple but powerful mission: to empower every person to improve their life through DNA. Our platform includes saliva sample collection,
Next Gen Sequencing. Expansion of sequencing technology. Contents
 Next Gen Sequencing Contents 1 Expansion of sequencing technology 2 The Next Generation of Sequencing: High-Throughput Technologies 3 High Throughput Sequencing Applied to Genome Sequencing (TEDed CC BY-NC-ND
Next Gen Sequencing Contents 1 Expansion of sequencing technology 2 The Next Generation of Sequencing: High-Throughput Technologies 3 High Throughput Sequencing Applied to Genome Sequencing (TEDed CC BY-NC-ND
Opportunities offered by new sequencing technologies
 Opportunities offered by new sequencing technologies Pierre Taberlet Laboratoire d'ecologie Alpine CNRS UMR 5553 Université Joseph Fourier, Grenoble, France Nature Biotechnology, October 2008: special
Opportunities offered by new sequencing technologies Pierre Taberlet Laboratoire d'ecologie Alpine CNRS UMR 5553 Université Joseph Fourier, Grenoble, France Nature Biotechnology, October 2008: special
Sequence assembly. Jose Blanca COMAV institute bioinf.comav.upv.es
 Sequence assembly Jose Blanca COMAV institute bioinf.comav.upv.es Sequencing project Unknown sequence { experimental evidence result read 1 read 4 read 2 read 5 read 3 read 6 read 7 Computational requirements
Sequence assembly Jose Blanca COMAV institute bioinf.comav.upv.es Sequencing project Unknown sequence { experimental evidence result read 1 read 4 read 2 read 5 read 3 read 6 read 7 Computational requirements
BST227 Introduction to Statistical Genetics. Lecture 8: Variant calling from high-throughput sequencing data
 BST227 Introduction to Statistical Genetics Lecture 8: Variant calling from high-throughput sequencing data 1 PC recap typical genome Differs from the reference genome at 4-5 million sites ~85% SNPs ~15%
BST227 Introduction to Statistical Genetics Lecture 8: Variant calling from high-throughput sequencing data 1 PC recap typical genome Differs from the reference genome at 4-5 million sites ~85% SNPs ~15%
Next Generation Sequencing Technologies. Some slides are modified from Robi Mitra s lecture notes
 Next Generation Sequencing Technologies Some slides are modified from Robi Mitra s lecture notes What will you do to understand a disease? What will you do to understand a disease? Genotype Phenotype Hypothesis
Next Generation Sequencing Technologies Some slides are modified from Robi Mitra s lecture notes What will you do to understand a disease? What will you do to understand a disease? Genotype Phenotype Hypothesis
Mate-pair library data improves genome assembly
 De Novo Sequencing on the Ion Torrent PGM APPLICATION NOTE Mate-pair library data improves genome assembly Highly accurate PGM data allows for de Novo Sequencing and Assembly For a draft assembly, generate
De Novo Sequencing on the Ion Torrent PGM APPLICATION NOTE Mate-pair library data improves genome assembly Highly accurate PGM data allows for de Novo Sequencing and Assembly For a draft assembly, generate
RNA-Sequencing analysis
 RNA-Sequencing analysis Markus Kreuz 25. 04. 2012 Institut für Medizinische Informatik, Statistik und Epidemiologie Content: Biological background Overview transcriptomics RNA-Seq RNA-Seq technology Challenges
RNA-Sequencing analysis Markus Kreuz 25. 04. 2012 Institut für Medizinische Informatik, Statistik und Epidemiologie Content: Biological background Overview transcriptomics RNA-Seq RNA-Seq technology Challenges
Bioinformatics Advice on Experimental Design
 Bioinformatics Advice on Experimental Design Where do I start? Please refer to the following guide to better plan your experiments for good statistical analysis, best suited for your research needs. Statistics
Bioinformatics Advice on Experimental Design Where do I start? Please refer to the following guide to better plan your experiments for good statistical analysis, best suited for your research needs. Statistics
Genome Sequencing. I: Methods. MMG 835, SPRING 2016 Eukaryotic Molecular Genetics. George I. Mias
 Genome Sequencing I: Methods MMG 835, SPRING 2016 Eukaryotic Molecular Genetics George I. Mias Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology gmias@msu.edu Sequencing Methods Cost of Sequencing Wetterstrand
Genome Sequencing I: Methods MMG 835, SPRING 2016 Eukaryotic Molecular Genetics George I. Mias Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology gmias@msu.edu Sequencing Methods Cost of Sequencing Wetterstrand
Introduction to RNA sequencing
 Introduction to RNA sequencing Bioinformatics perspective Olga Dethlefsen NBIS, National Bioinformatics Infrastructure Sweden November 2017 Olga (NBIS) RNA-seq November 2017 1 / 49 Outline Why sequence
Introduction to RNA sequencing Bioinformatics perspective Olga Dethlefsen NBIS, National Bioinformatics Infrastructure Sweden November 2017 Olga (NBIS) RNA-seq November 2017 1 / 49 Outline Why sequence
DNA-Sequencing. Technologies & Devices. Matthias Platzer. Genome Analysis Leibniz Institute on Aging - Fritz Lipmann Institute (FLI)
 DNA-Sequencing Technologies & Devices Matthias Platzer Genome Analysis Leibniz Institute on Aging - Fritz Lipmann Institute (FLI) Genome analysis DNA sequencing platforms ABI 3730xl 4/2004 & 6/2006 1 Mb/day,
DNA-Sequencing Technologies & Devices Matthias Platzer Genome Analysis Leibniz Institute on Aging - Fritz Lipmann Institute (FLI) Genome analysis DNA sequencing platforms ABI 3730xl 4/2004 & 6/2006 1 Mb/day,
Mapping strategies for sequence reads
 Mapping strategies for sequence reads Ernest Turro University of Cambridge 21 Oct 2013 Quantification A basic aim in genomics is working out the contents of a biological sample. 1. What distinct elements
Mapping strategies for sequence reads Ernest Turro University of Cambridge 21 Oct 2013 Quantification A basic aim in genomics is working out the contents of a biological sample. 1. What distinct elements
DNA-Sequencing. Technologies & Devices. Matthias Platzer. Genome Analysis Leibniz Institute on Aging - Fritz Lipmann Institute (FLI)
 DNA-Sequencing Technologies & Devices Matthias Platzer Genome Analysis Leibniz Institute on Aging - Fritz Lipmann Institute (FLI) Genome analysis DNA sequencing platforms ABI 3730xl 4/2004 & 6/2006 1 Mb/day,
DNA-Sequencing Technologies & Devices Matthias Platzer Genome Analysis Leibniz Institute on Aging - Fritz Lipmann Institute (FLI) Genome analysis DNA sequencing platforms ABI 3730xl 4/2004 & 6/2006 1 Mb/day,
Research school methods seminar Genomics and Transcriptomics
 Research school methods seminar Genomics and Transcriptomics Stephan Klee 19.11.2014 2 3 4 5 Genetics, Genomics what are we talking about? Genetics and Genomics Study of genes Role of genes in inheritence
Research school methods seminar Genomics and Transcriptomics Stephan Klee 19.11.2014 2 3 4 5 Genetics, Genomics what are we talking about? Genetics and Genomics Study of genes Role of genes in inheritence
Course Presentation. Ignacio Medina Presentation
 Course Index Introduction Agenda Analysis pipeline Some considerations Introduction Who we are Teachers: Marta Bleda: Computational Biologist and Data Analyst at Department of Medicine, Addenbrooke's Hospital
Course Index Introduction Agenda Analysis pipeline Some considerations Introduction Who we are Teachers: Marta Bleda: Computational Biologist and Data Analyst at Department of Medicine, Addenbrooke's Hospital
De Novo Assembly of High-throughput Short Read Sequences
 De Novo Assembly of High-throughput Short Read Sequences Chuming Chen Center for Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (CBCB) University of Delaware NECC Third Skate Genome Annotation Workshop May 23,
De Novo Assembly of High-throughput Short Read Sequences Chuming Chen Center for Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (CBCB) University of Delaware NECC Third Skate Genome Annotation Workshop May 23,
CNV and variant detection for human genome resequencing data - for biomedical researchers (II)
 CNV and variant detection for human genome resequencing data - for biomedical researchers (II) Chuan-Kun Liu 劉傳崑 Senior Maneger National Center for Genome Medican bioit@ncgm.sinica.edu.tw Abstract Common
CNV and variant detection for human genome resequencing data - for biomedical researchers (II) Chuan-Kun Liu 劉傳崑 Senior Maneger National Center for Genome Medican bioit@ncgm.sinica.edu.tw Abstract Common
The Sentieon Genomics Tools A fast and accurate solution to variant calling from next-generation sequence data
 The Sentieon Genomics Tools A fast and accurate solution to variant calling from next-generation sequence data Donald Freed 1*, Rafael Aldana 1, Jessica A. Weber 2, Jeremy S. Edwards 3,4,5 1 Sentieon Inc,
The Sentieon Genomics Tools A fast and accurate solution to variant calling from next-generation sequence data Donald Freed 1*, Rafael Aldana 1, Jessica A. Weber 2, Jeremy S. Edwards 3,4,5 1 Sentieon Inc,
RNA-Seq Software, Tools, and Workflows
 RNA-Seq Software, Tools, and Workflows Monica Britton, Ph.D. Sr. Bioinformatics Analyst September 1, 2016 Some mrna-seq Applications Differential gene expression analysis Transcriptional profiling Assumption:
RNA-Seq Software, Tools, and Workflows Monica Britton, Ph.D. Sr. Bioinformatics Analyst September 1, 2016 Some mrna-seq Applications Differential gene expression analysis Transcriptional profiling Assumption:
Runs of Homozygosity Analysis Tutorial
 Runs of Homozygosity Analysis Tutorial Release 8.7.0 Golden Helix, Inc. March 22, 2017 Contents 1. Overview of the Project 2 2. Identify Runs of Homozygosity 6 Illustrative Example...............................................
Runs of Homozygosity Analysis Tutorial Release 8.7.0 Golden Helix, Inc. March 22, 2017 Contents 1. Overview of the Project 2 2. Identify Runs of Homozygosity 6 Illustrative Example...............................................
Jenny Gu, PhD Strategic Business Development Manager, PacBio
 IDT and PacBio joint presentation Characterizing Alzheimer s Disease candidate genes and transcripts with targeted, long-read, single-molecule sequencing Jenny Gu, PhD Strategic Business Development Manager,
IDT and PacBio joint presentation Characterizing Alzheimer s Disease candidate genes and transcripts with targeted, long-read, single-molecule sequencing Jenny Gu, PhD Strategic Business Development Manager,
BIOINFORMATICS. Lacking alignments? The next-generation sequencing mapper segemehl revisited
 BIOINFORMATICS Vol. 00 no. 00 2014 Pages 1 7 Lacking alignments? The next-generation sequencing mapper segemehl revisited Christian Otto 1,2, Peter F. Stadler 2 8, Steve Hoffmann 1,2 1 Transcriptome Bioinformatics
BIOINFORMATICS Vol. 00 no. 00 2014 Pages 1 7 Lacking alignments? The next-generation sequencing mapper segemehl revisited Christian Otto 1,2, Peter F. Stadler 2 8, Steve Hoffmann 1,2 1 Transcriptome Bioinformatics
Introduction to transcriptome analysis using High Throughput Sequencing technologies. D. Puthier 2012
 Introduction to transcriptome analysis using High Throughput Sequencing technologies D. Puthier 2012 A typical RNA-Seq experiment Library construction Protocol variations Fragmentation methods RNA: nebulization,
Introduction to transcriptome analysis using High Throughput Sequencing technologies D. Puthier 2012 A typical RNA-Seq experiment Library construction Protocol variations Fragmentation methods RNA: nebulization,
Complementary Technologies for Precision Genetic Analysis
 Complementary NGS, CGH and Workflow Featured Publication Zhu, J. et al. Duplication of C7orf58, WNT16 and FAM3C in an obese female with a t(7;22)(q32.1;q11.2) chromosomal translocation and clinical features
Complementary NGS, CGH and Workflow Featured Publication Zhu, J. et al. Duplication of C7orf58, WNT16 and FAM3C in an obese female with a t(7;22)(q32.1;q11.2) chromosomal translocation and clinical features
The Sentieon Genomic Tools Improved Best Practices Pipelines for Analysis of Germline and Tumor-Normal Samples
 The Sentieon Genomic Tools Improved Best Practices Pipelines for Analysis of Germline and Tumor-Normal Samples Andreas Scherer, Ph.D. President and CEO Dr. Donald Freed, Bioinformatics Scientist, Sentieon
The Sentieon Genomic Tools Improved Best Practices Pipelines for Analysis of Germline and Tumor-Normal Samples Andreas Scherer, Ph.D. President and CEO Dr. Donald Freed, Bioinformatics Scientist, Sentieon
Next Generation Sequence Analysis and Computational Genomics Using Graphical Pipeline Workflows
 Genes 2012, 3, 545-575; doi:10.3390/genes3030545 Article OPEN ACCESS genes ISSN 2073-4425 www.mdpi.com/journal/genes Next Generation Sequence Analysis and Computational Genomics Using Graphical Pipeline
Genes 2012, 3, 545-575; doi:10.3390/genes3030545 Article OPEN ACCESS genes ISSN 2073-4425 www.mdpi.com/journal/genes Next Generation Sequence Analysis and Computational Genomics Using Graphical Pipeline
High Throughput Sequencing Technologies. J Fass UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Monday June 16, 2014
 High Throughput Sequencing Technologies J Fass UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Monday June 16, 2014 Sequencing Explosion www.genome.gov/sequencingcosts http://t.co/ka5cvghdqo Sequencing Explosion
High Throughput Sequencing Technologies J Fass UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Monday June 16, 2014 Sequencing Explosion www.genome.gov/sequencingcosts http://t.co/ka5cvghdqo Sequencing Explosion
What is Bioinformatics? Bioinformatics is the application of computational techniques to the discovery of knowledge from biological databases.
 What is Bioinformatics? Bioinformatics is the application of computational techniques to the discovery of knowledge from biological databases. Bioinformatics is the marriage of molecular biology with computer
What is Bioinformatics? Bioinformatics is the application of computational techniques to the discovery of knowledge from biological databases. Bioinformatics is the marriage of molecular biology with computer
Fundamentals of Next-Generation Sequencing: Technologies and Applications
 Fundamentals of Next-Generation Sequencing: Technologies and Applications Society for Hematopathology European Association for Haematopathology 2017 Workshop Eric Duncavage, MD Washington University in
Fundamentals of Next-Generation Sequencing: Technologies and Applications Society for Hematopathology European Association for Haematopathology 2017 Workshop Eric Duncavage, MD Washington University in
Oral Cleft Targeted Sequencing Project
 Oral Cleft Targeted Sequencing Project Oral Cleft Group January, 2013 Contents I Quality Control 3 1 Summary of Multi-Family vcf File, Jan. 11, 2013 3 2 Analysis Group Quality Control (Proposed Protocol)
Oral Cleft Targeted Sequencing Project Oral Cleft Group January, 2013 Contents I Quality Control 3 1 Summary of Multi-Family vcf File, Jan. 11, 2013 3 2 Analysis Group Quality Control (Proposed Protocol)
arxiv: v1 [q-bio.gn] 25 Nov 2015
![arxiv: v1 [q-bio.gn] 25 Nov 2015 arxiv: v1 [q-bio.gn] 25 Nov 2015](/thumbs/76/73490664.jpg) MetaScope - Fast and accurate identification of microbes in metagenomic sequencing data Benjamin Buchfink 1, Daniel H. Huson 1,2 & Chao Xie 2,3 arxiv:1511.08753v1 [q-bio.gn] 25 Nov 2015 1 Department of
MetaScope - Fast and accurate identification of microbes in metagenomic sequencing data Benjamin Buchfink 1, Daniel H. Huson 1,2 & Chao Xie 2,3 arxiv:1511.08753v1 [q-bio.gn] 25 Nov 2015 1 Department of
Welcome to the NGS webinar series
 Welcome to the NGS webinar series Webinar 1 NGS: Introduction to technology, and applications NGS Technology Webinar 2 Targeted NGS for Cancer Research NGS in cancer Webinar 3 NGS: Data analysis for genetic
Welcome to the NGS webinar series Webinar 1 NGS: Introduction to technology, and applications NGS Technology Webinar 2 Targeted NGS for Cancer Research NGS in cancer Webinar 3 NGS: Data analysis for genetic
Whole Transcriptome Analysis of Illumina RNA- Seq Data. Ryan Peters Field Application Specialist
 Whole Transcriptome Analysis of Illumina RNA- Seq Data Ryan Peters Field Application Specialist Partek GS in your NGS Pipeline Your Start-to-Finish Solution for Analysis of Next Generation Sequencing Data
Whole Transcriptome Analysis of Illumina RNA- Seq Data Ryan Peters Field Application Specialist Partek GS in your NGS Pipeline Your Start-to-Finish Solution for Analysis of Next Generation Sequencing Data
Introductie en Toepassingen van Next-Generation Sequencing in de Klinische Virologie. Sander van Boheemen Medical Microbiology
 Introductie en Toepassingen van Next-Generation Sequencing in de Klinische Virologie Sander van Boheemen Medical Microbiology Next-generation sequencing Next-generation sequencing (NGS), also known as
Introductie en Toepassingen van Next-Generation Sequencing in de Klinische Virologie Sander van Boheemen Medical Microbiology Next-generation sequencing Next-generation sequencing (NGS), also known as
Introduction to Bioinformatics
 Introduction to Bioinformatics Richard Corbett Canada s Michael Smith Genome Sciences Centre Vancouver, British Columbia June 28, 2017 Our mandate is to advance knowledge about cancer and other diseases
Introduction to Bioinformatics Richard Corbett Canada s Michael Smith Genome Sciences Centre Vancouver, British Columbia June 28, 2017 Our mandate is to advance knowledge about cancer and other diseases
The String Alignment Problem. Comparative Sequence Sizes. The String Alignment Problem. The String Alignment Problem.
 Dec-82 Oct-84 Aug-86 Jun-88 Apr-90 Feb-92 Nov-93 Sep-95 Jul-97 May-99 Mar-01 Jan-03 Nov-04 Sep-06 Jul-08 May-10 Mar-12 Growth of GenBank 160,000,000,000 180,000,000 Introduction to Bioinformatics Iosif
Dec-82 Oct-84 Aug-86 Jun-88 Apr-90 Feb-92 Nov-93 Sep-95 Jul-97 May-99 Mar-01 Jan-03 Nov-04 Sep-06 Jul-08 May-10 Mar-12 Growth of GenBank 160,000,000,000 180,000,000 Introduction to Bioinformatics Iosif
De novo whole genome assembly
 De novo whole genome assembly Lecture 1 Qi Sun Bioinformatics Facility Cornell University Data generation Sequencing Platforms Short reads: Illumina Long reads: PacBio; Oxford Nanopore Contiging/Scaffolding
De novo whole genome assembly Lecture 1 Qi Sun Bioinformatics Facility Cornell University Data generation Sequencing Platforms Short reads: Illumina Long reads: PacBio; Oxford Nanopore Contiging/Scaffolding
Custom TaqMan Assays DESIGN AND ORDERING GUIDE. For SNP Genotyping and Gene Expression Assays. Publication Number Revision G
 Custom TaqMan Assays DESIGN AND ORDERING GUIDE For SNP Genotyping and Gene Expression Assays Publication Number 4367671 Revision G For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Manufacturer:
Custom TaqMan Assays DESIGN AND ORDERING GUIDE For SNP Genotyping and Gene Expression Assays Publication Number 4367671 Revision G For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Manufacturer:
Biochemistry 412. New Strategies, Technologies, & Applications For DNA Sequencing. 12 February 2008
 Biochemistry 412 New Strategies, Technologies, & Applications For DNA Sequencing 12 February 2008 Note: Scale is wrong!! (at least for sequences) 10 6 In 1980, the sequencing cost per finished bp $1.00
Biochemistry 412 New Strategies, Technologies, & Applications For DNA Sequencing 12 February 2008 Note: Scale is wrong!! (at least for sequences) 10 6 In 1980, the sequencing cost per finished bp $1.00
Theory and Application of Multiple Sequence Alignments
 Theory and Application of Multiple Sequence Alignments a.k.a What is a Multiple Sequence Alignment, How to Make One, and What to Do With It Brett Pickett, PhD History Structure of DNA discovered (1953)
Theory and Application of Multiple Sequence Alignments a.k.a What is a Multiple Sequence Alignment, How to Make One, and What to Do With It Brett Pickett, PhD History Structure of DNA discovered (1953)
Supplementary Material for Extremely low-coverage whole genome sequencing in South Asians captures population genomics information
 Supplementary Material for Extremely low-coverage whole genome sequencing in South Asians captures population genomics information Navin Rustagi, Anbo Zhou, W. Scott Watkins, Erika Gedvilaite, Shuoguo
Supplementary Material for Extremely low-coverage whole genome sequencing in South Asians captures population genomics information Navin Rustagi, Anbo Zhou, W. Scott Watkins, Erika Gedvilaite, Shuoguo
Creation of a PAM matrix
 Rationale for substitution matrices Substitution matrices are a way of keeping track of the structural, physical and chemical properties of the amino acids in proteins, in such a fashion that less detrimental
Rationale for substitution matrices Substitution matrices are a way of keeping track of the structural, physical and chemical properties of the amino acids in proteins, in such a fashion that less detrimental
SNP detection for massively parallel whole-genome resequencing
 Resource SNP detection for massively parallel whole-genome resequencing Ruiqiang Li, 1,2,3 Yingrui Li, 1,3 Xiaodong Fang, 1 Huanming Yang, 1 Jian Wang, 1 Karsten Kristiansen, 1,2 and Jun Wang 1,2,4 1 Beijing
Resource SNP detection for massively parallel whole-genome resequencing Ruiqiang Li, 1,2,3 Yingrui Li, 1,3 Xiaodong Fang, 1 Huanming Yang, 1 Jian Wang, 1 Karsten Kristiansen, 1,2 and Jun Wang 1,2,4 1 Beijing
Sequencing Theory. Brett E. Pickett, Ph.D. J. Craig Venter Institute
 Sequencing Theory Brett E. Pickett, Ph.D. J. Craig Venter Institute Applications of Genomics and Bioinformatics to Infectious Diseases GABRIEL Network Agenda Sequencing Instruments Sanger Illumina Ion
Sequencing Theory Brett E. Pickett, Ph.D. J. Craig Venter Institute Applications of Genomics and Bioinformatics to Infectious Diseases GABRIEL Network Agenda Sequencing Instruments Sanger Illumina Ion
How much sequencing do I need? Emily Crisovan Genomics Core
 How much sequencing do I need? Emily Crisovan Genomics Core How much sequencing? Three questions: 1. How much sequence is required for good experimental design? 2. What type of sequencing run is best?
How much sequencing do I need? Emily Crisovan Genomics Core How much sequencing? Three questions: 1. How much sequence is required for good experimental design? 2. What type of sequencing run is best?
H3A - Genome-Wide Association testing SOP
 H3A - Genome-Wide Association testing SOP Introduction File format Strand errors Sample quality control Marker quality control Batch effects Population stratification Association testing Replication Meta
H3A - Genome-Wide Association testing SOP Introduction File format Strand errors Sample quality control Marker quality control Batch effects Population stratification Association testing Replication Meta
Exploring structural variation in the tomato genome with JBrowse
 Exploring structural variation in the tomato genome with JBrowse Richard Finkers, Wageningen UR Plant Breeding Richard.Finkers@wur.nl; @rfinkers Version 1.0, December 2013 This work is licensed under the
Exploring structural variation in the tomato genome with JBrowse Richard Finkers, Wageningen UR Plant Breeding Richard.Finkers@wur.nl; @rfinkers Version 1.0, December 2013 This work is licensed under the
Create a Planned Run. Using the Ion AmpliSeq Pharmacogenomics Research Panel Plugin USER BULLETIN. Publication Number MAN Revision A.
 USER BULLETIN Create a Planned Run Using the Ion AmpliSeq Pharmacogenomics Research Panel Plugin Publication Number MAN0013730 Revision A.0 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
USER BULLETIN Create a Planned Run Using the Ion AmpliSeq Pharmacogenomics Research Panel Plugin Publication Number MAN0013730 Revision A.0 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Bioinformatics for High Throughput Sequencing
 Bioinformatics for High Throughput Sequencing Eric Rivals LIRMM & IBC, Montpellier http://www.lirmm.fr/~rivals http://www.lirmm.fr/~rivals 1 / High Throughput Sequencing or Next Generation Sequencing High
Bioinformatics for High Throughput Sequencing Eric Rivals LIRMM & IBC, Montpellier http://www.lirmm.fr/~rivals http://www.lirmm.fr/~rivals 1 / High Throughput Sequencing or Next Generation Sequencing High
Incorporating Molecular ID Technology. Accel-NGS 2S MID Indexing Kits
 Incorporating Molecular ID Technology Accel-NGS 2S MID Indexing Kits Molecular Identifiers (MIDs) MIDs are indices used to label unique library molecules MIDs can assess duplicate molecules in sequencing
Incorporating Molecular ID Technology Accel-NGS 2S MID Indexing Kits Molecular Identifiers (MIDs) MIDs are indices used to label unique library molecules MIDs can assess duplicate molecules in sequencing
Identifying copy number alterations and genotype with Control-FREEC
 Identifying copy number alterations and genotype with Control-FREEC Valentina Boeva contact: freec@curie.fr Most approaches for predicting copy number alterations (CNAs) require you to have whole exomesequencing
Identifying copy number alterations and genotype with Control-FREEC Valentina Boeva contact: freec@curie.fr Most approaches for predicting copy number alterations (CNAs) require you to have whole exomesequencing
Next Generation Sequencing Technologies
 Next Generation Sequencing Technologies What is first generation? Sanger Sequencing DNA Polymerase Base-adding reaction +H + http://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/organic_chemistry/organic_chemistry_with_a_biological_emphasis/chapter_10%3a_phosphoryl_transfer_reactions/section_10.4%3a_phosphate_diesters
Next Generation Sequencing Technologies What is first generation? Sanger Sequencing DNA Polymerase Base-adding reaction +H + http://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/organic_chemistry/organic_chemistry_with_a_biological_emphasis/chapter_10%3a_phosphoryl_transfer_reactions/section_10.4%3a_phosphate_diesters
Analysing 454 amplicon resequencing experiments using the modular and database oriented Variant Identification Pipeline
 SOFTWARE Software Analysing 454 amplicon resequencing experiments using the modular and database oriented Variant Identification Pipeline Open Access Joachim M De Schrijver* 1, Kim De Leeneer 2, Steve
SOFTWARE Software Analysing 454 amplicon resequencing experiments using the modular and database oriented Variant Identification Pipeline Open Access Joachim M De Schrijver* 1, Kim De Leeneer 2, Steve
QIAGEN s NGS Solutions for Biomarkers NGS & Bioinformatics team QIAGEN (Suzhou) Translational Medicine Co.,Ltd
 QIAGEN s NGS Solutions for Biomarkers NGS & Bioinformatics team QIAGEN (Suzhou) Translational Medicine Co.,Ltd 1 Our current NGS & Bioinformatics Platform 2 Our NGS workflow and applications 3 QIAGEN s
QIAGEN s NGS Solutions for Biomarkers NGS & Bioinformatics team QIAGEN (Suzhou) Translational Medicine Co.,Ltd 1 Our current NGS & Bioinformatics Platform 2 Our NGS workflow and applications 3 QIAGEN s
Human genome sequence
 NGS: the basics Human genome sequence June 26th 2000: official announcement of the completion of the draft of the human genome sequence (truly finished in 2004) Francis Collins Craig Venter HGP: 3 billion
NGS: the basics Human genome sequence June 26th 2000: official announcement of the completion of the draft of the human genome sequence (truly finished in 2004) Francis Collins Craig Venter HGP: 3 billion
Introductory Next Gen Workshop
 Introductory Next Gen Workshop http://www.illumina.ucr.edu/ http://www.genomics.ucr.edu/ Workshop Objectives Workshop aimed at those who are new to Illumina sequencing and will provide: - a basic overview
Introductory Next Gen Workshop http://www.illumina.ucr.edu/ http://www.genomics.ucr.edu/ Workshop Objectives Workshop aimed at those who are new to Illumina sequencing and will provide: - a basic overview
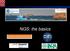
Midterm 1 Results. Midterm 1 Akey/ Fields Median Number of Students. Exam Score
 Midterm 1 Results 10 Midterm 1 Akey/ Fields Median - 69 8 Number of Students 6 4 2 0 21 26 31 36 41 46 51 56 61 66 71 76 81 86 91 96 101 Exam Score Quick review of where we left off Parental type: the
Midterm 1 Results 10 Midterm 1 Akey/ Fields Median - 69 8 Number of Students 6 4 2 0 21 26 31 36 41 46 51 56 61 66 71 76 81 86 91 96 101 Exam Score Quick review of where we left off Parental type: the
