fga phenotypes were also analyzed in the tracheal system, the organ responsible for
|
|
|
- Ann Richards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT Tracheal defects fga phenotypes were also analyzed in the tracheal system, the organ responsible for oxygen delivery in the fly. In fga homozygous mutant alleles, we observed defects in tracheal liquid absorption apparent at the onset of the 1 st larval instar (Fig S2), when the luminal fluid secreted by tracheal cells should normally be cleared and replaced by air (Manning & Krasnow, 1993). The penetrance of tracheal Air Filling Defects (AFD) was different for each of the fga alleles (Fig S2G) and broadly correlated with the extent of Sima protein accumulation in normoxia (Fig 1B, in the main text). To test if the accumulation of Sima protein observed in fga mutants might be the cause of AFD, we used a series of GAL4 drivers to direct Sima overexpression to the tracheal system. Overexpression of Sima in all tracheal cells caused AFD, with phenotypes essentially indistinguishable from the ones observed in fga mutants (Fig S2C). When Sima ectopic expression was specifically induced in particular tracheal cell types, such as fusion or terminal cells, AFD were restricted to these cells (Fig S2D,E), indicating that the effect is cell-autonomous. In order to better visualize the cells forming liquid-filled tracheal tubes, a membrane-tagged EGFP was co-expressed together with Sima. As shown in figure S2E, terminal cells in this situation looked normal, indicating that overexpression of Sima did not affect the basic shape of these cells. Analysis of the tracheal system of double homozygous larvae revealed that AFD did not develop, these individuals being phenotypically normal (Fig S2F). Taken together these results strongly suggest that AFD in fga mutants are due to over-accumulation of Sima protein in tracheal cells. The mechanism by which over-accumulation of Sima provoke AFD is unclear; as
2 tracheal development relies on other bhlh-pas proteins such as Trachealess (Wilk et al, 1996), over-accumulation of Sima in the tracheae may cause either over-expression of endogenous tracheal genes or a dominant negative effect over the common bhlh-pas partner subunit, Tango (Sonnenfeld et al, 1997). As an additional observation, tracheal terminal branches, that were shown to sprout in response to environmental oxygen levels (Jarecki et al, 1999), looked normal in early 1 st instar larvae (not shown), suggesting that initial formation of terminal branches does not depend on Sima at early developmental stages. SUPPLEMENTARY REFERENCES Jarecki J, Johnson E, Krasnow MA (1999) Oxygen regulation of airway branching in Drosophila is mediated by branchless FGF. Cell 99: Manning G & Krasnow MA (1993) Development of the Drosophila Tracheal System. In: Bate M & Martinez Arias A (eds), The Development of Drosophila melanogaster pp Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. Sonnenfeld M, Ward M, Nystrom G, Mosher J, Stahl S, Crews S (1997) The Drosophila tango gene encodes a bhlh-pas protein that is orthologous to mammalian Arnt and controls CNS midline and tracheal development. Development 124: Wilk R, Weizman I, Shilo BZ (1996) trachealess encodes a bhlh-pas protein that is an inducer of tracheal cell fates in Drosophila. Genes Dev 10: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure S1- Effect of Sima accumulation in different endoreplicative tissues. In endoreplicative tissues, the DNA content correlates with cell size and thus, smaller nuclei correspond to smaller cells (see Fig 3E in the main text for an example). To assess the role of Sima in cell growth, the flip-out technique was used to direct the expression Sima to random cells that could be recognized because they simultaneously expressed GFP. Cells were analyzed in different endoreplicative tissues such as the fat body, salivary glands and proventriculus; 71% of the nuclei of Sima-expressing cells
3 (arrows) were clearly smaller than control nuclei from neighboring GFP-negative cells (N>70). Scale bar, 50µm. Supplementary Figure S2.- sima loss-of-function reverts tracheal phenotypes in fga mutants. (A) In wild type 1 st instar larvae, dorsal tracheal trunks (arrows) are filled with air; in fga 1 mutants (B) or in individuals overexpressing Sima through a btl-gal4 driver in the tracheae (C), defects in tracheal liquid clearance can be observed. Whereas air filled tubes can be visualized by bright field microscopy (A), liquid filled tubes are barely visible (B-D). Specific expression of Sima in tracheal terminal cells through a Term-Gal4 driver caused liquid clearance defects specifically in these cells (arrow in D), indicating that the effect is cell autonomous. (E) Simultaneous expression of GFP in terminal cells shows that liquid-filled tracheal branches are intact. (F) Normal liquid clearance was fully restored in double homozygous mutant larvae (arrows). (G) Air filling is normal in 100% of wild type individuals but impaired with different penetrance in homozygotes for the different fga alleles or in individuals overexpressing Sima in the tracheae. In double homozygotes, air-filling defects do not occur (N>120). Supplementary Figure S3. Defects in wing and ovary development of double-mutant adults. (A) double mutants exhibit defects in the distal part of the wing 56/59). (B) females are sterile and display aberrant ovaries that do not develop beyond stage 4-6 of oogenesis; vitellogenic oocytes were never observed in double mutant females (7/7).
4 GFP Dapi Dapi salivary glands proventriculus fat body Supplementary Figure S1.- Effect of Sima accumulation in different endoreplicative tissues
5 A B C D control brightfield E fga - fluorescence F btl-sima Term-Sima Term-Sima fga - sima - G 100% 99 % of larvae exhibiting liquid filled tracheae 75% 50% 25% % wt 0 fga 9 fga fga 64 fga 1 btl-sima 0 Supplementary Figure S2.- sima loss-of-function reverts tracheal phenotypes in fga mutants.
6 A B wild type wild type Supplementary Figure S3. Defects in wings and ovaries of double-mutant adults
Supplemental Fig. 1. Mcr alleles show defects in tracheal tube size and luminal protein accumulation. (A-F) Confocal projections of living stage 15
 Supplemental Fig. 1. Mcr alleles show defects in tracheal tube size and luminal protein accumulation. (A-F) Confocal projections of living stage 15 embryos expressing GFP and Verm-RFP in tracheal cells
Supplemental Fig. 1. Mcr alleles show defects in tracheal tube size and luminal protein accumulation. (A-F) Confocal projections of living stage 15 embryos expressing GFP and Verm-RFP in tracheal cells
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
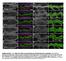
 Normalized dorsal trunk length (µm) Normalized dorsal trunk length (TC1-5) (µm) DOI: 1.138/ncb2467 a b c d btl>src64 Src42, btl>src64 e Src64 f g h DT Src64 DT Midgut Src64 Midgut i Src64 Atpα j k l DT
Normalized dorsal trunk length (µm) Normalized dorsal trunk length (TC1-5) (µm) DOI: 1.138/ncb2467 a b c d btl>src64 Src42, btl>src64 e Src64 f g h DT Src64 DT Midgut Src64 Midgut i Src64 Atpα j k l DT
Trasposable elements: Uses of P elements Problem set B at the end
 Trasposable elements: Uses of P elements Problem set B at the end P-elements have revolutionized the way Drosophila geneticists conduct their research. Here, we will discuss just a few of the approaches
Trasposable elements: Uses of P elements Problem set B at the end P-elements have revolutionized the way Drosophila geneticists conduct their research. Here, we will discuss just a few of the approaches
Sol narae (Sona) is a Drosophila ADAMTS involved in Wg signaling
 Sol narae (Sona) is a Drosophila ADAMTS involved in Wg signaling Go-Woon Kim, Jong-Hoon Won, Ok-Kyung Lee, Sang-Soo Lee, Jeong-Hoon Han, Orkhon Tsogtbaatar, Sujin Nam, Yeon Kim, and Kyung-Ok Cho* Supplementary
Sol narae (Sona) is a Drosophila ADAMTS involved in Wg signaling Go-Woon Kim, Jong-Hoon Won, Ok-Kyung Lee, Sang-Soo Lee, Jeong-Hoon Han, Orkhon Tsogtbaatar, Sujin Nam, Yeon Kim, and Kyung-Ok Cho* Supplementary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2806 Supplemental Material: Figure S1 Wnt4 PCP phenotypes are not mediated through canonical Wnt signaling. (a-a ) Illustration of wg, dwnt4 and dwnt6 expression patterns in wing (a) and
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2806 Supplemental Material: Figure S1 Wnt4 PCP phenotypes are not mediated through canonical Wnt signaling. (a-a ) Illustration of wg, dwnt4 and dwnt6 expression patterns in wing (a) and
A novel stop codon readthrough mechanism produces functional Headcase protein in Drosophila trachea
 EMBO reports A novel stop codon readthrough mechanism produces functional Headcase protein in Drosophila trachea Pär Steneberg & Christos Samakovlis + Umeå Center for Molecular Pathogenesis, Umeå University,
EMBO reports A novel stop codon readthrough mechanism produces functional Headcase protein in Drosophila trachea Pär Steneberg & Christos Samakovlis + Umeå Center for Molecular Pathogenesis, Umeå University,
Mesodermal repression of single-minded in Drosophila embryo is mediated by a cluster of Snail-binding sites proximal to the early promoter
 BMB Reports Mesodermal repression of single-minded in Drosophila embryo is mediated by a cluster of Snail-binding sites proximal to the early promoter Kye Won Park 1 & Joung-Woo Hong 2, * 1 Department
BMB Reports Mesodermal repression of single-minded in Drosophila embryo is mediated by a cluster of Snail-binding sites proximal to the early promoter Kye Won Park 1 & Joung-Woo Hong 2, * 1 Department
a) Stock 4: 126 flies total: 120 are P[w+]: 64 are CyO; 56 are TM3; all are females. 132 are w-: 68 are CyO; 64 are TM3; all are males.
![a) Stock 4: 126 flies total: 120 are P[w+]: 64 are CyO; 56 are TM3; all are females. 132 are w-: 68 are CyO; 64 are TM3; all are males. a) Stock 4: 126 flies total: 120 are P[w+]: 64 are CyO; 56 are TM3; all are females. 132 are w-: 68 are CyO; 64 are TM3; all are males.](/thumbs/88/116538069.jpg) Drosophila Problem Set 2012 1) You have created P element transformants of a construct that contains the mini-white gene, which confers an orange eye color in a homozygous white mutant background. For
Drosophila Problem Set 2012 1) You have created P element transformants of a construct that contains the mini-white gene, which confers an orange eye color in a homozygous white mutant background. For
Genetic control of epithelial tube size in the Drosophila tracheal system
 Development 127, 3271-3282 (2000) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV7811 3271 Genetic control of epithelial tube size in the Drosophila tracheal system Greg J. Beitel*
Development 127, 3271-3282 (2000) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV7811 3271 Genetic control of epithelial tube size in the Drosophila tracheal system Greg J. Beitel*
a) Stock 4: 252 flies total: 120 are P[w+]: 64 are CyO; 56 are TM3; all are females. 132 are w-: 68 are CyO; 64 are TM3; all are males.
![a) Stock 4: 252 flies total: 120 are P[w+]: 64 are CyO; 56 are TM3; all are females. 132 are w-: 68 are CyO; 64 are TM3; all are males. a) Stock 4: 252 flies total: 120 are P[w+]: 64 are CyO; 56 are TM3; all are females. 132 are w-: 68 are CyO; 64 are TM3; all are males.](/thumbs/91/106088469.jpg) Drosophila Problem Set 2018 1) You have created P element transformants of a construct that contains the mini-white gene, which confers an orange eye color in a homozygous white mutant background. For
Drosophila Problem Set 2018 1) You have created P element transformants of a construct that contains the mini-white gene, which confers an orange eye color in a homozygous white mutant background. For
Lecture 20: Drosophila melanogaster
 Lecture 20: Drosophila melanogaster Model organisms Polytene chromosome Life cycle P elements and transformation Embryogenesis Read textbook: 732-744; Fig. 20.4; 20.10; 20.15-26 www.mhhe.com/hartwell3
Lecture 20: Drosophila melanogaster Model organisms Polytene chromosome Life cycle P elements and transformation Embryogenesis Read textbook: 732-744; Fig. 20.4; 20.10; 20.15-26 www.mhhe.com/hartwell3
Blocking endocycle apoptosis page 1. Table S1: Relative abundance of mrna levels in the endocycling salivary gland versus mitotic
 Blocking endocycle apoptosis page 1 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Table S1: Relative abundance of mrna levels in the endocycling salivary gland versus mitotic cycling brain-disc. Gene E/M 1 E rr /M rr E rr /E M rr
Blocking endocycle apoptosis page 1 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Table S1: Relative abundance of mrna levels in the endocycling salivary gland versus mitotic cycling brain-disc. Gene E/M 1 E rr /M rr E rr /E M rr
SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL
 SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL MATERIAL AND METHODS Fly stocks All Drosophila stocks were grown at 25 C on yeast-containing corn meal/molasses medium. The nanos (nos) alleles nos 18 and nos 53 have been previously
SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL MATERIAL AND METHODS Fly stocks All Drosophila stocks were grown at 25 C on yeast-containing corn meal/molasses medium. The nanos (nos) alleles nos 18 and nos 53 have been previously
Lecture 8: Transgenic Model Systems and RNAi
 Lecture 8: Transgenic Model Systems and RNAi I. Model systems 1. Caenorhabditis elegans Caenorhabditis elegans is a microscopic (~1 mm) nematode (roundworm) that normally lives in soil. It has become one
Lecture 8: Transgenic Model Systems and RNAi I. Model systems 1. Caenorhabditis elegans Caenorhabditis elegans is a microscopic (~1 mm) nematode (roundworm) that normally lives in soil. It has become one
New Tool for Late Stage Visualization of Oskar Protein in Drosophila melanogaster. Oocytes. Kathleen Harnois. Supervised by Paul Macdonald
 New Tool for Late Stage Visualization of Oskar Protein in Drosophila melanogaster Oocytes Kathleen Harnois Supervised by Paul Macdonald Institute of Cellular and Molecular Biology, The University of Texas
New Tool for Late Stage Visualization of Oskar Protein in Drosophila melanogaster Oocytes Kathleen Harnois Supervised by Paul Macdonald Institute of Cellular and Molecular Biology, The University of Texas
GM130 Is Required for Compartmental Organization of Dendritic Golgi Outposts
 Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information GM130 Is Required for Compartmental Organization of Dendritic Golgi Outposts Wei Zhou, Jin Chang, Xin Wang, Masha G. Savelieff, Yinyin Zhao, Shanshan
Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information GM130 Is Required for Compartmental Organization of Dendritic Golgi Outposts Wei Zhou, Jin Chang, Xin Wang, Masha G. Savelieff, Yinyin Zhao, Shanshan
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/310/5753/1487/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Stem Cell Self-Renewal Controlled by Chromatin Remodeling Factors Rongwen Xi and Ting Xie* *To whom correspondence should
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/310/5753/1487/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Stem Cell Self-Renewal Controlled by Chromatin Remodeling Factors Rongwen Xi and Ting Xie* *To whom correspondence should
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10810 Supplementary Fig. 1: Mutation of the loqs gene leads to shortened lifespan and adult-onset brain degeneration. a. Northern blot of control and loqs f00791 mutant flies. loqs f00791
doi:10.1038/nature10810 Supplementary Fig. 1: Mutation of the loqs gene leads to shortened lifespan and adult-onset brain degeneration. a. Northern blot of control and loqs f00791 mutant flies. loqs f00791
Supplemental Information. Boundary Formation through a Direct. Threshold-Based Readout. of Mobile Small RNA Gradients
 Developmental Cell, Volume 43 Supplemental Information Boundary Formation through a Direct Threshold-Based Readout of Mobile Small RNA Gradients Damianos S. Skopelitis, Anna H. Benkovics, Aman Y. Husbands,
Developmental Cell, Volume 43 Supplemental Information Boundary Formation through a Direct Threshold-Based Readout of Mobile Small RNA Gradients Damianos S. Skopelitis, Anna H. Benkovics, Aman Y. Husbands,
The Archipelago Ubiquitin Ligase Subunit Acts in Target Tissue to Restrict Tracheal Terminal Cell Branching and Hypoxic-Induced Gene Expression
 The Archipelago Ubiquitin Ligase Subunit Acts in Target Tissue to Restrict Tracheal Terminal Cell Branching and Hypoxic-Induced Gene Expression Nathan T. Mortimer, Emory University Kenneth H Moberg, Emory
The Archipelago Ubiquitin Ligase Subunit Acts in Target Tissue to Restrict Tracheal Terminal Cell Branching and Hypoxic-Induced Gene Expression Nathan T. Mortimer, Emory University Kenneth H Moberg, Emory
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06721 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 The distribution of hatx-1[82q] in Cos7 cells. Cos7 cells are co-transfected with hatx-1[82q]-gfp (green)
doi: 10.1038/nature06721 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 The distribution of hatx-1[82q] in Cos7 cells. Cos7 cells are co-transfected with hatx-1[82q]-gfp (green)
Supplemental Data. Hachez et al. Plant Cell (2014) /tpc Suppl. Figure 1A
 Suppl. Figure 1A Suppl. Figure 1B Supplemental Figure 1: Results of the commercial screening of interactants using split ubiquitin technique. (A) Isolated preys (192) using the bait construct pbt3-n- as
Suppl. Figure 1A Suppl. Figure 1B Supplemental Figure 1: Results of the commercial screening of interactants using split ubiquitin technique. (A) Isolated preys (192) using the bait construct pbt3-n- as
To investigate the heredity of the WFP gene, we selected plants that were homozygous
 Supplementary information Supplementary Note ST-12 WFP allele is semi-dominant To investigate the heredity of the WFP gene, we selected plants that were homozygous for chromosome 1 of Nipponbare and heterozygous
Supplementary information Supplementary Note ST-12 WFP allele is semi-dominant To investigate the heredity of the WFP gene, we selected plants that were homozygous for chromosome 1 of Nipponbare and heterozygous
Aminoacid change in chromophore. PIN3::PIN3-GFP GFP S65 (no change) (5.9) (Kneen et al., 1998)
 Supplemental Table. Table S1. Fluorophore characteristics of used fluorescent proteins, Related to Figure 2 and 3. Transgenic line Fluprescent marker Aminoacid change in chromophore pk(a) Ref. PIN3::PIN3-GFP
Supplemental Table. Table S1. Fluorophore characteristics of used fluorescent proteins, Related to Figure 2 and 3. Transgenic line Fluprescent marker Aminoacid change in chromophore pk(a) Ref. PIN3::PIN3-GFP
Methanol fixation allows better visualization of Kal7. To compare methods for
 Supplementary Data Methanol fixation allows better visualization of Kal7. To compare methods for visualizing Kal7 in dendrites, mature cultures of dissociated hippocampal neurons (DIV21) were fixed with
Supplementary Data Methanol fixation allows better visualization of Kal7. To compare methods for visualizing Kal7 in dendrites, mature cultures of dissociated hippocampal neurons (DIV21) were fixed with
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3374 Supplementary Figure 1 staccato mutations affect a late step of the tube fusion process. (a) Immunostaining of stage 15 embryos labeled with anti- Dys (green in merge) and a probe
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3374 Supplementary Figure 1 staccato mutations affect a late step of the tube fusion process. (a) Immunostaining of stage 15 embryos labeled with anti- Dys (green in merge) and a probe
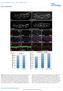
Figure S1. Figure S2. Figure S3 HB Anti-FSP27 (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab. Anti-GST-FSP27(45-127) Ab.
 / 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
/ 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
Supplementary Methods
 Caussinus and Gonzalez Supplementary Methods Mitotic clones Clones of NBs homozygous for numb 03235, mira ZZ176, pros 17 or apkc k06403 were generated by FLP/FRT mediated mitotic recombination (1). As
Caussinus and Gonzalez Supplementary Methods Mitotic clones Clones of NBs homozygous for numb 03235, mira ZZ176, pros 17 or apkc k06403 were generated by FLP/FRT mediated mitotic recombination (1). As
Structural and functional analysis of the mir-282 microrna gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Ágnes Bujna
 Structural and functional analysis of the mir-282 microrna gene of Drosophila melanogaster Ph.D. thesis Ágnes Bujna Supervisor: Dr. Miklós Erdélyi University of Szeged, PhD School of Biological Sciences
Structural and functional analysis of the mir-282 microrna gene of Drosophila melanogaster Ph.D. thesis Ágnes Bujna Supervisor: Dr. Miklós Erdélyi University of Szeged, PhD School of Biological Sciences
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Willecke et al. 1.173/pnas.852115 A A' clones A'' A''' ' GFP clones ' fj- clones D D' Diap1 fj- clones Fig. S1. oundaries of and activity induce Hippo target genes. Third instar
Supporting Information Willecke et al. 1.173/pnas.852115 A A' clones A'' A''' ' GFP clones ' fj- clones D D' Diap1 fj- clones Fig. S1. oundaries of and activity induce Hippo target genes. Third instar
Flybow genetic multicolor cell labeling for neural circuit analysis in Drosophila melanogaster
 Nature Methods Flybow genetic multicolor cell labeling for neural circuit analysis in Drosophila melanogaster Dafni Hadjieconomou, Shay Rotkopf, Cyrille Alexandre, Donald M Bell, Barry J Dickson & Iris
Nature Methods Flybow genetic multicolor cell labeling for neural circuit analysis in Drosophila melanogaster Dafni Hadjieconomou, Shay Rotkopf, Cyrille Alexandre, Donald M Bell, Barry J Dickson & Iris
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 b Supplementary Figure 1. Analysis of Vkg-Dpp interactions. a, In vitro pulldown showing binding of Dpp-HA to the GST-VkgC fusion protein. No interaction is detected between denatured Dpp-HA and GST-Vkg.
b Supplementary Figure 1. Analysis of Vkg-Dpp interactions. a, In vitro pulldown showing binding of Dpp-HA to the GST-VkgC fusion protein. No interaction is detected between denatured Dpp-HA and GST-Vkg.
BIOSCI 0351: GENETICS LABORATORY COURSE INFORMATION- SPRING TERM 2016
 BioSci 0351, Spring, 2016 BIOSCI 0351: GENETICS LABORATORY COURSE INFORMATION- SPRING TERM 2016 GENERAL INFORMATION Time: Location: INSTRUCTORS: Office hours: Phone Numbers: Email: Mondays, 8:30AM 12:20PM
BioSci 0351, Spring, 2016 BIOSCI 0351: GENETICS LABORATORY COURSE INFORMATION- SPRING TERM 2016 GENERAL INFORMATION Time: Location: INSTRUCTORS: Office hours: Phone Numbers: Email: Mondays, 8:30AM 12:20PM
Supplementary Information. The flowering gene SINGLE FLOWER TRUSS drives heterosis for yield in tomato
 Supplementary Information The flowering gene SINGLE FLOWER TRUSS drives heterosis for yield in tomato Uri Krieger 1, Zachary B. Lippman 2 *, and Dani Zamir 1 * 1. The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Faculty
Supplementary Information The flowering gene SINGLE FLOWER TRUSS drives heterosis for yield in tomato Uri Krieger 1, Zachary B. Lippman 2 *, and Dani Zamir 1 * 1. The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Faculty
At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.4166
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information ER-localized auxin transporter PIN8 regulates auxin homeostasis and male gametophyte development in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figures a 8 6 4 2 Absolute Expression b Absolute Expression
Supplementary Information ER-localized auxin transporter PIN8 regulates auxin homeostasis and male gametophyte development in Arabidopsis Supplemental Figures a 8 6 4 2 Absolute Expression b Absolute Expression
No, because expression of the P elements and hence transposase in suppressed in the F1.
 Problem set B 1. A wild-type ry+ (rosy) gene was introduced into a ry mutant using P element-mediated gene transformation, and a strain containing a stable ry+ gene was established. If a transformed male
Problem set B 1. A wild-type ry+ (rosy) gene was introduced into a ry mutant using P element-mediated gene transformation, and a strain containing a stable ry+ gene was established. If a transformed male
From the Deportment of Biology, Essex University
 /. Embryol. exp. Morph. Vol. 47, pp. 111-120, 1978 \ \ \ Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited 1978 Genetic analysis of vitellogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: the identification of
/. Embryol. exp. Morph. Vol. 47, pp. 111-120, 1978 \ \ \ Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited 1978 Genetic analysis of vitellogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: the identification of
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods MARCM-based forward genetic screen We used ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS) to mutagenize flies carrying FRT 2A and FRT 82B transgenes, which are sites for the FLP-mediated recombination
Supplementary Methods MARCM-based forward genetic screen We used ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS) to mutagenize flies carrying FRT 2A and FRT 82B transgenes, which are sites for the FLP-mediated recombination
Disengaging the Smc3/kleisin interface releases cohesin from Drosophila chromosomes during interphase and mitosis
 Manuscript EMBO-2012-83126 Disengaging the Smc3/kleisin interface releases cohesin from Drosophila chromosomes during interphase and mitosis Christian S. Eichinger, Alexander Kurze, Raquel A. Oliveira,
Manuscript EMBO-2012-83126 Disengaging the Smc3/kleisin interface releases cohesin from Drosophila chromosomes during interphase and mitosis Christian S. Eichinger, Alexander Kurze, Raquel A. Oliveira,
Figure S1a. The modular dcas9 fusion system works efficiently to suppress and activate endogenous gene expression in C. elegans
 Figure S1a. The modular dcas9 fusion system works efficiently to suppress and activate endogenous gene expression in C. elegans A, a normal wild-type hermaphrodite N2 is shown. B, a dpy-5-supressed F1
Figure S1a. The modular dcas9 fusion system works efficiently to suppress and activate endogenous gene expression in C. elegans A, a normal wild-type hermaphrodite N2 is shown. B, a dpy-5-supressed F1
A subclass of HSP70s regulate development and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 Journal of Plant Research A subclass of HSP70s regulate development and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana Linna Leng 1 Qianqian Liang
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 Journal of Plant Research A subclass of HSP70s regulate development and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana Linna Leng 1 Qianqian Liang
KDD Cup Task 1 Information Extraction from Biomedical Articles
 Information Extraction from Biomedical Articles Sub title here Sub title here System Description June / July 2002 The Task: Curate or Not-Curate Build a system for automatic analysis of scientific papers
Information Extraction from Biomedical Articles Sub title here Sub title here System Description June / July 2002 The Task: Curate or Not-Curate Build a system for automatic analysis of scientific papers
Development of Eye Colors in Drosophila: Fat Bodies and Malpighian Tubes as Sources of Diffusible Substances. G. W. Beadle
 Development of Eye Colors in Drosophila: Fat Bodies and Malpighian Tubes as Sources of Diffusible Substances G. W. Beadle PNAS 1937;23;146-152 doi:10.1073/pnas.23.3.146 This information is current as of
Development of Eye Colors in Drosophila: Fat Bodies and Malpighian Tubes as Sources of Diffusible Substances G. W. Beadle PNAS 1937;23;146-152 doi:10.1073/pnas.23.3.146 This information is current as of
Fig. S1. Endocytosis of extracellular cargo does not depend on dia. (A) To visualize endocytosis, fluorescently labelled wheat germ agglutinin
 Fig. S1. Endocytosis of extracellular cargo does not depend on dia. (A) To visualize endocytosis, fluorescently labelled wheat germ agglutinin (WGA-Alexa555) was injected into the extracellular perivitteline
Fig. S1. Endocytosis of extracellular cargo does not depend on dia. (A) To visualize endocytosis, fluorescently labelled wheat germ agglutinin (WGA-Alexa555) was injected into the extracellular perivitteline
Fig. S1. Inhibition of Rh1 accumulation on the rhabdomere membrane in CG13089 PIG-U mutants. (A) Late pupae with dark wings were put into 0.
 Fig. S1. Inhibition of Rh1 accumulation on the rhabdomere membrane in CG13089 PIG-U mutants. (A) Late pupae with dark wings were put into 0.2% agar after the pupal case was partially removed. Two fluorescent
Fig. S1. Inhibition of Rh1 accumulation on the rhabdomere membrane in CG13089 PIG-U mutants. (A) Late pupae with dark wings were put into 0.2% agar after the pupal case was partially removed. Two fluorescent
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information MED18 interaction with distinct transcription factors regulates plant immunity, flowering time and responses to hormones Supplementary Figure 1. Diagram showing T-DNA insertion
Supplementary Information MED18 interaction with distinct transcription factors regulates plant immunity, flowering time and responses to hormones Supplementary Figure 1. Diagram showing T-DNA insertion
Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
The bhlh-pas protein Spineless is necessary for the diversification of dendrite morphology of Drosophila dendritic arborization neurons
 The bhlh-pas protein Spineless is necessary for the diversification of dendrite morphology of Drosophila dendritic arborization neurons Michael D. Kim, Lily Yeh Jan, and Yuh Nung Jan 1 Howard Hughes Medical
The bhlh-pas protein Spineless is necessary for the diversification of dendrite morphology of Drosophila dendritic arborization neurons Michael D. Kim, Lily Yeh Jan, and Yuh Nung Jan 1 Howard Hughes Medical
Creating mosaics in Drosophila
 Int. J. Dev. Biol. 42: 243-247 (1998) Creating mosaics in Drosophila NORBERT PERRIMON* Department of Genetics, Harvard Medical School, Boston,USA ABSTRACT The ability to create mosaic animals allows the
Int. J. Dev. Biol. 42: 243-247 (1998) Creating mosaics in Drosophila NORBERT PERRIMON* Department of Genetics, Harvard Medical School, Boston,USA ABSTRACT The ability to create mosaic animals allows the
Drosophila, Genetics, Behavior, and Optogenetics. David Deitcher BioNB 4910
 Drosophila, Genetics, Behavior, and Optogenetics David Deitcher BioNB 4910 Seymour Benzer Father of Drosophila Behavior Mutant Behaviors Identified by Benzer and Others Many of these mutants encode genes
Drosophila, Genetics, Behavior, and Optogenetics David Deitcher BioNB 4910 Seymour Benzer Father of Drosophila Behavior Mutant Behaviors Identified by Benzer and Others Many of these mutants encode genes
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary information $ /%0123! ' $'%& 4,5% =5*7"5 /%0123 26,7/ 0123 & * '()*+,,-,' / 0'(1*+2-,-- / 0,3405$6$000000000 doi:101038/nature12106 ' $'%& ' $'%& ' $'%& " 4,5% =5*7"5%
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary information $ /%0123! ' $'%& 4,5% =5*7"5 /%0123 26,7/ 0123 & * '()*+,,-,' / 0'(1*+2-,-- / 0,3405$6$000000000 doi:101038/nature12106 ' $'%& ' $'%& ' $'%& " 4,5% =5*7"5%
Lecture 20: Drosophila embryogenesis
 Lecture 20: Drosophila embryogenesis Mitotic recombination/clonal analyses Embrygenesis Four classes of genes: Maternal genes Gap genes Pair-rule genes Segment polarity genes Homeotic genes Read 140-141;
Lecture 20: Drosophila embryogenesis Mitotic recombination/clonal analyses Embrygenesis Four classes of genes: Maternal genes Gap genes Pair-rule genes Segment polarity genes Homeotic genes Read 140-141;
Characterization of a novel gene involved in border cell migration
 Characterization of a novel gene involved in border cell migration Wei-Hao Li, He-Yen Chou and Li-Mei Pai Graduate Institute of Basic Medical Science Chang-Gung University, Tao-Yuan, Taiwan, R.O.C. Abstract
Characterization of a novel gene involved in border cell migration Wei-Hao Li, He-Yen Chou and Li-Mei Pai Graduate Institute of Basic Medical Science Chang-Gung University, Tao-Yuan, Taiwan, R.O.C. Abstract
(a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of Diaph3 ko mice. (a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for different regions of Diaph3 mrna from WT, heterozygote
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of Diaph3 ko mice. (a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for different regions of Diaph3 mrna from WT, heterozygote
Fig. S1. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of AtHD-ZIP IV family. A phylogenetic tree was constructed using Bayesian analysis with Markov Chain Monte
 Fig. S1. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of AtHD-ZIP IV family. A phylogenetic tree was constructed using Bayesian analysis with Markov Chain Monte Carlo algorithm for one million generations to obtain
Fig. S1. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of AtHD-ZIP IV family. A phylogenetic tree was constructed using Bayesian analysis with Markov Chain Monte Carlo algorithm for one million generations to obtain
The Role of Star in the Production of an Activated Ligand for the EGF Receptor Signaling Pathway
 Developmental Biology 205, 254 259 (1999) Article ID dbio.1998.9119, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on The Role of Star in the Production of an Activated Ligand for the EGF Receptor Signaling
Developmental Biology 205, 254 259 (1999) Article ID dbio.1998.9119, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on The Role of Star in the Production of an Activated Ligand for the EGF Receptor Signaling
Fig. S1. CrgA intracellular levels in M. tuberculosis. Ten and twenty micrograms of
 Supplementary data Fig. S1. CrgA intracellular levels in M. tuberculosis. Ten and twenty micrograms of cell free protein lysates from WT M. tuberculosis (Rv) together with various known concentrations
Supplementary data Fig. S1. CrgA intracellular levels in M. tuberculosis. Ten and twenty micrograms of cell free protein lysates from WT M. tuberculosis (Rv) together with various known concentrations
Methods and Materials
 SUMMARY OF PH.D. THESIS Molecular biological and genetic study of the sumoylation of Drosophila melanogaster p53 Pardi Norbert Supervisor: Dr. Boros Imre Doctoral School of Biology University of Szeged
SUMMARY OF PH.D. THESIS Molecular biological and genetic study of the sumoylation of Drosophila melanogaster p53 Pardi Norbert Supervisor: Dr. Boros Imre Doctoral School of Biology University of Szeged
embryos. Asterisk represents loss of or reduced expression. Brackets represent
 Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1. tfec expression is highly enriched in tail endothelial cells (A- B) ISH of tfec at 15 and 16hpf in WT embryos. (C- D) ISH of tfec at 36 and 38hpf in WT embryos.
Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1. tfec expression is highly enriched in tail endothelial cells (A- B) ISH of tfec at 15 and 16hpf in WT embryos. (C- D) ISH of tfec at 36 and 38hpf in WT embryos.
Supplemental Material: Rev1 promotes replication through UV lesions in conjunction with DNA
 Supplemental Material: Rev1 promotes replication through UV lesions in conjunction with DNA polymerases,, and, but not with DNA polymerase Jung-Hoon Yoon, Jeseong Park, Juan Conde, Maki Wakamiya, Louise
Supplemental Material: Rev1 promotes replication through UV lesions in conjunction with DNA polymerases,, and, but not with DNA polymerase Jung-Hoon Yoon, Jeseong Park, Juan Conde, Maki Wakamiya, Louise
BISC403 Genetic and Evolutionary Biology Spring, Summary of requirements for Exam 2 (to be given on March 24) plus exam 2 from Fall, 2010.
 BISC403 Genetic and Evolutionary Biology Spring, 2011 March 17, 2011 Summary of requirements for Exam 2 (to be given on March 24) plus exam 2 from Fall, 2010. The primary responsibility is for any topic
BISC403 Genetic and Evolutionary Biology Spring, 2011 March 17, 2011 Summary of requirements for Exam 2 (to be given on March 24) plus exam 2 from Fall, 2010. The primary responsibility is for any topic
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Lu et al. 10.1073/pnas.1106801108 Fig. S1. Analysis of spatial localization of mrnas coding for 23 zebrafish Wnt genes by whole mount in situ hybridization to identify those present
Supporting Information Lu et al. 10.1073/pnas.1106801108 Fig. S1. Analysis of spatial localization of mrnas coding for 23 zebrafish Wnt genes by whole mount in situ hybridization to identify those present
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. lev-9 mutants are resistant to levamisole. The levamisole dose-response curves indicate that lev-9 mutants are partially resistant to levamisole similar to lev-10(kr26) mutants. unc-29(x29)
Figure S1. lev-9 mutants are resistant to levamisole. The levamisole dose-response curves indicate that lev-9 mutants are partially resistant to levamisole similar to lev-10(kr26) mutants. unc-29(x29)
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/332/6034/1210/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Interaction Between Notch and Hif-α in Development and Survival of Drosophila Blood Cells Tina Mukherjee, William Sang
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/332/6034/1210/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Interaction Between Notch and Hif-α in Development and Survival of Drosophila Blood Cells Tina Mukherjee, William Sang
Sperm cells are passive cargo of the pollen tube in plant fertilization
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 3 ARTICLE NUMBER: 17079 Sperm cells are passive cargo of the pollen tube in plant fertilization Jun Zhang 1, Qingpei
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 3 ARTICLE NUMBER: 17079 Sperm cells are passive cargo of the pollen tube in plant fertilization Jun Zhang 1, Qingpei
Live-cell visualization of excitation energy dynamics in chloroplast thylakoid structures
 Supplementary Information Live-cell visualization of excitation energy dynamics in chloroplast thylakoid structures Masakazu Iwai, Makio Yokono, Kazuo Kurokawa, Akira Ichihara & Akihiko Nakano Supplementary
Supplementary Information Live-cell visualization of excitation energy dynamics in chloroplast thylakoid structures Masakazu Iwai, Makio Yokono, Kazuo Kurokawa, Akira Ichihara & Akihiko Nakano Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1. Drawing of spinal cord open-book preparations and DiI tracing. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.3893
 Supplementary Figure 1 Drawing of spinal cord open-book preparations and DiI tracing. Supplementary Figure 2 In ovo electroporation of dominant-negative PlexinA1 in commissural neurons induces midline
Supplementary Figure 1 Drawing of spinal cord open-book preparations and DiI tracing. Supplementary Figure 2 In ovo electroporation of dominant-negative PlexinA1 in commissural neurons induces midline
Diverse modes of Drosophila tracheal fusion cell transcriptional regulation
 MECHANISMS OF DEVELOPMENT 127 (2010) 265 280 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/modo Diverse modes of Drosophila tracheal fusion cell transcriptional regulation
MECHANISMS OF DEVELOPMENT 127 (2010) 265 280 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/modo Diverse modes of Drosophila tracheal fusion cell transcriptional regulation
Supplementary Information. c d e
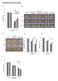 Supplementary Information a b c d e f Supplementary Figure 1. atabcg30, atabcg31, and atabcg40 mutant seeds germinate faster than the wild type on ½ MS medium supplemented with ABA (a and d-f) Germination
Supplementary Information a b c d e f Supplementary Figure 1. atabcg30, atabcg31, and atabcg40 mutant seeds germinate faster than the wild type on ½ MS medium supplemented with ABA (a and d-f) Germination
species- Mus musculus Engineering the mouse genome David Ornitz
 species- Mus musculus Engineering the mouse genome David Ornitz How do we analyze gene function in mice? Gene addition (transgenic approach) Permits GOF, DN and knockdown experiments Ectopic (spatial or
species- Mus musculus Engineering the mouse genome David Ornitz How do we analyze gene function in mice? Gene addition (transgenic approach) Permits GOF, DN and knockdown experiments Ectopic (spatial or
Lecture Three: Genes and Inheritance
 Lecture Three: Genes and Inheritance As we already know, the smallest, most basic unit of life is the CELL. Define: Prokaryotic a cell with no membrane-bounded organelles or nucleus Eukaryotic - a cell
Lecture Three: Genes and Inheritance As we already know, the smallest, most basic unit of life is the CELL. Define: Prokaryotic a cell with no membrane-bounded organelles or nucleus Eukaryotic - a cell
A Comparison of Midline and Tracheal Gene Regulation during Drosophila Development
 A Comparison of Midline and Tracheal Gene Regulation during Drosophila Development Sarah K. R. Long 1, Eric Fulkerson 1, Rebecca Breese 1, Giovanna Hernandez 1, Cara Davis 1, Mark A. Melton 2, Rachana
A Comparison of Midline and Tracheal Gene Regulation during Drosophila Development Sarah K. R. Long 1, Eric Fulkerson 1, Rebecca Breese 1, Giovanna Hernandez 1, Cara Davis 1, Mark A. Melton 2, Rachana
Developmental Biology
 Developmental Biology 318 (2008) 247 257 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Larval cells become imaginal cells under
Developmental Biology 318 (2008) 247 257 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Larval cells become imaginal cells under
To assess the localization of Citrine fusion proteins, we performed antibody staining to
 Trinh et al 1 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL FlipTraps recapitulate endogenous protein localization To assess the localization of Citrine fusion proteins, we performed antibody staining to compare the expression
Trinh et al 1 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL FlipTraps recapitulate endogenous protein localization To assess the localization of Citrine fusion proteins, we performed antibody staining to compare the expression
(A) Schematic depicting morphology of cholinergic DA and DB motor neurons in an L1
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS Supplemental Figure 1 Figure S1. Expression of the non-alpha nachr subunit ACR-2. (A) Schematic depicting morphology of cholinergic DA and DB motor neurons in an L1 animal. Wide-field
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS Supplemental Figure 1 Figure S1. Expression of the non-alpha nachr subunit ACR-2. (A) Schematic depicting morphology of cholinergic DA and DB motor neurons in an L1 animal. Wide-field
Drosophila Distal-less and Rotund Bind a Single Enhancer Ensuring Reliable and Robust bric-a-brac2 Expression in Distinct Limb Morphogenetic Fields
 Drosophila Distal-less and Rotund Bind a Single Enhancer Ensuring Reliable and Robust bric-a-brac2 Expression in Distinct Limb Morphogenetic Fields Aissette Baanannou 1, Luis Humberto Mojica-Vazquez 1,
Drosophila Distal-less and Rotund Bind a Single Enhancer Ensuring Reliable and Robust bric-a-brac2 Expression in Distinct Limb Morphogenetic Fields Aissette Baanannou 1, Luis Humberto Mojica-Vazquez 1,
Name: Genetics - Fall 2004 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Professor Chris Kaiser Professor Gerry Fink Professor Leona Samson
 7.03 - Genetics - Fall 2004 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Professor Chris Kaiser Professor Gerry Fink Professor Leona Samson 1 1. You are studying three autosomal recessive mutations in the fruit
7.03 - Genetics - Fall 2004 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Professor Chris Kaiser Professor Gerry Fink Professor Leona Samson 1 1. You are studying three autosomal recessive mutations in the fruit
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Legends for Supplementary Tables. Supplementary Table 1. An excel file containing primary screen data. Worksheet 1, Normalized quantification data from a duplicated screen: valid
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Legends for Supplementary Tables. Supplementary Table 1. An excel file containing primary screen data. Worksheet 1, Normalized quantification data from a duplicated screen: valid
Mouse Engineering Technology. Musculoskeletal Research Center 2016 Summer Educational Series David M. Ornitz Department of Developmental Biology
 Mouse Engineering Technology Musculoskeletal Research Center 2016 Summer Educational Series David M. Ornitz Department of Developmental Biology Core service and new technologies Mouse ES core Discussions
Mouse Engineering Technology Musculoskeletal Research Center 2016 Summer Educational Series David M. Ornitz Department of Developmental Biology Core service and new technologies Mouse ES core Discussions
Supplemental Data. Borg et al. Plant Cell (2014) /tpc
 Supplementary Figure 1 - Alignment of selected angiosperm DAZ1 and DAZ2 homologs Multiple sequence alignment of selected DAZ1 and DAZ2 homologs. A consensus sequence built using default parameters is shown
Supplementary Figure 1 - Alignment of selected angiosperm DAZ1 and DAZ2 homologs Multiple sequence alignment of selected DAZ1 and DAZ2 homologs. A consensus sequence built using default parameters is shown
BRANCHED epithelial tubes are the structural and
 Copyright Ó 2007 by the Genetics Society of America DOI: 10.1534/genetics.107.074088 A Clonal Genetic Screen for Mutants Causing Defects in Larval Tracheal Morphogenesis in Drosophila Magdalena M. Baer,
Copyright Ó 2007 by the Genetics Society of America DOI: 10.1534/genetics.107.074088 A Clonal Genetic Screen for Mutants Causing Defects in Larval Tracheal Morphogenesis in Drosophila Magdalena M. Baer,
Practice Problems 5. Location of LSA-GFP fluorescence
 Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 5 1. Soluble proteins that are normally secreted from the cell into the extracellular environment must go through a series of steps referred to as the secretory pathway.
Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 5 1. Soluble proteins that are normally secreted from the cell into the extracellular environment must go through a series of steps referred to as the secretory pathway.
Supplementary Figure 1 a
 3 min PMA 45 min PMA AnnexinV-FITC Supplementary Figure 1 5 min PMA 15 min PMA a 9 min PMA 12 min PMA 5 min FGF7 15 min FGF7 3 min FGF7 6 min FGF7 9 min FGF7 12 min FGF7 5 min control 3 min control 6 min
3 min PMA 45 min PMA AnnexinV-FITC Supplementary Figure 1 5 min PMA 15 min PMA a 9 min PMA 12 min PMA 5 min FGF7 15 min FGF7 3 min FGF7 6 min FGF7 9 min FGF7 12 min FGF7 5 min control 3 min control 6 min
R-loops cause replication impairment and genome instability during meiosis
 Manuscript EMBOR-2012-35976 R-loops cause replication impairment and genome instability during meiosis Maikel Castellano-Pozo, Tatiana Garcia-Muse and Andres Aguilera Corresponding author: Andres Aguilera,
Manuscript EMBOR-2012-35976 R-loops cause replication impairment and genome instability during meiosis Maikel Castellano-Pozo, Tatiana Garcia-Muse and Andres Aguilera Corresponding author: Andres Aguilera,
b number of motif occurrences
 supplementary information DOI: 1.138/ncb194 a b number of motif occurrences number of motif occurrences number of motif occurrences I II III IV V X TTGGTCAGTGCA 3 8 23 4 13 239 TTGGTCAGTGCT 7 5 8 1 3 83
supplementary information DOI: 1.138/ncb194 a b number of motif occurrences number of motif occurrences number of motif occurrences I II III IV V X TTGGTCAGTGCA 3 8 23 4 13 239 TTGGTCAGTGCT 7 5 8 1 3 83
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Kunduri et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405020/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Subcellular localization and interactions of PAPLA1.
Supplemental material Kunduri et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405020/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Subcellular localization and interactions of PAPLA1.
(phosphatase tensin) domain is shown in dark gray, the FH1 domain in black, and the
 Supplemental Figure 1. Predicted Domain Organization of the AFH14 Protein. (A) Schematic representation of the predicted domain organization of AFH14. The PTEN (phosphatase tensin) domain is shown in dark
Supplemental Figure 1. Predicted Domain Organization of the AFH14 Protein. (A) Schematic representation of the predicted domain organization of AFH14. The PTEN (phosphatase tensin) domain is shown in dark
Temporal regulation of h'n-14 by the antagonistic action of two other heterochronic genes, h'n-4 and lin-28
 Temporal regulation of h'n-14 by the antagonistic action of two other heterochronic genes, h'n-4 and lin-28 Prema Arasu, Bruce Wightman, and Gary Ruvkun Department of Molecular Biology, Massachusetts General
Temporal regulation of h'n-14 by the antagonistic action of two other heterochronic genes, h'n-4 and lin-28 Prema Arasu, Bruce Wightman, and Gary Ruvkun Department of Molecular Biology, Massachusetts General
FINDING THE PAIN GENE How do geneticists connect a specific gene with a specific phenotype?
 FINDING THE PAIN GENE How do geneticists connect a specific gene with a specific phenotype? 1 Linkage & Recombination HUH? What? Why? Who cares? How? Multiple choice question. Each colored line represents
FINDING THE PAIN GENE How do geneticists connect a specific gene with a specific phenotype? 1 Linkage & Recombination HUH? What? Why? Who cares? How? Multiple choice question. Each colored line represents
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 2. Supplememtary Note 2, Wehr et al., Monitoring Regulated Protein-Protein Interactions Using Split-TEV 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 2 A recombinase reporter system for permanent reporter activation We made use of the Cre-loxP recombinase system for a maximal amplification and complete kinetic uncoupling within single
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 2 A recombinase reporter system for permanent reporter activation We made use of the Cre-loxP recombinase system for a maximal amplification and complete kinetic uncoupling within single
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Ihh interacts preferentially with its upstream neighboring gene Nhej1. Genes are indicated by gray lines, and Ihh and Nhej1 are highlighted in blue. 4C seq performed in E14.5 limbs
Supplementary Figure 1 Ihh interacts preferentially with its upstream neighboring gene Nhej1. Genes are indicated by gray lines, and Ihh and Nhej1 are highlighted in blue. 4C seq performed in E14.5 limbs
KEY Reproductive cloning Therapeutic cloning
 1. (20 pts) Define Reproductive and Therapeutic cloning. Make sure your descriptions clearly distinguish the critical differences between them. Describe an example of each. Reproductive cloning refers
1. (20 pts) Define Reproductive and Therapeutic cloning. Make sure your descriptions clearly distinguish the critical differences between them. Describe an example of each. Reproductive cloning refers
DRG Pituitary Cerebral Cortex
 Liver Spinal cord Pons Atg5 -/- Atg5 +/+ DRG Pituitary Cerebral Cortex WT KO Supplementary Figure S1 Ubiquitin-positive IBs accumulate in Atg5 -/- tissues. Atg5 -/- neonatal tissues were fixed and decalcified.
Liver Spinal cord Pons Atg5 -/- Atg5 +/+ DRG Pituitary Cerebral Cortex WT KO Supplementary Figure S1 Ubiquitin-positive IBs accumulate in Atg5 -/- tissues. Atg5 -/- neonatal tissues were fixed and decalcified.
Supplementary Figure 1. Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings.
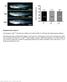 Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table.
 Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
Supplementary Table 1. The Q-PCR primer sequence is summarized in the following table. Name Sequence (5-3 ) Application Flag-u ggactacaaggacgacgatgac Shared upstream primer for all the amplifications of
Matters arising Minitest Pick up from your TA after class Answer key posted next week Re-grade requests in writing to Anne Paul by next Friday, please
 Matters arising Minitest Pick up from your TA after class Answer key posted next week Re-grade requests in writing to Anne Paul by next Friday, please Mini-survey just before break 25 20 Minitest 1 - Winter
Matters arising Minitest Pick up from your TA after class Answer key posted next week Re-grade requests in writing to Anne Paul by next Friday, please Mini-survey just before break 25 20 Minitest 1 - Winter
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Supplementary figures Figure S1 Level of mycdet1 protein in DET1 OE-1, OE-2 and OE-3 transgenic lines. Total protein extract from wild type Col0, det1-1 mutant and DET1 OE lines
Supplementary information Supplementary figures Figure S1 Level of mycdet1 protein in DET1 OE-1, OE-2 and OE-3 transgenic lines. Total protein extract from wild type Col0, det1-1 mutant and DET1 OE lines
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
