CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 11: Transcription, Translation and The Genetic Code
|
|
|
- Percival Bishop
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 11: Transcription, Translation and The Genetic Code No. 1 of Three types of RNA comprise the structural and functional core for protein synthesis, serving as a template for translation, and transporting amino acid, respectively (in that order), are, and. (A) mrna, trna and rrna (B) rrna, trna, and mrna (C) trna, mrna and rrna (D) trna, rrna and mrna (E) rrna, mrna and trna mrna is not a structural component for ribosome. trna is not a template - wrong order. The trna and rrna order is wrong. The order is all wrong. E. Correct! Three major types of RNA are mrna, which is the template for protein synthesis; trna, which carries amino acids to the protein synthesizing sites; and rrna, which is the structural component for ribosome, the protein synthesis core structure. It is important to understand the function of each class of RNA. (E)rRNA, mrna and trna
2 No. 2 of Which mrna codes for the following polypeptide? Met-arg-ser-leu-glu (A) 3'-AUGCGUAGCUUGGAGUGA -5 (B) 3'-AGUGAGGUUCGAUGCGUA-5 (C) 5 -AUGCGUAGCUUGGAGUGG-3 (D) 5 -AUGCGUAGCUUGGACUGA-3 (E) 5 -AUGAGUAGCUUGGACUGA-3 This mrna, when reading from 5 to 3 direction, codes for Ser-Glu-Val-Arg-Cys- Val. B. Correct! Again, this mrna needs to be read from 5 end to 3 end, which codes for Met-Arg- Ser-Leu-Glu. This one code for Met-Arg-Ser-Leu-Glu-Trp, extra amino acid at the C-terminus. This mrna codes for Met-Arg-Ser-Leu-Asp, one amino acid difference. This mrna also codes for Met-Ser-Ser-Leu-Asp, two amino acids different. The key to solve this problem is to understand that mrna is always read from the 5 end to 3 end. (B)3'-AGUGAGGUUCGAUGCGUA-5
3 No. 3 of With what mrna codon would the trna in the diagram below be able to form a codon-anticodon base-pairing interaction? (A) 5'-AUG -3 (B) 3'-GUA-5 (C) 3 -CAU-5 (D) 3 -UCA-5 (E) 3 -AUG-5 The anticodon for 5'-AUG-3 should be 5 -CAU-3, according to base-paring antiparallel principle. It is the opposite direction. The anticodon for this one is 5 CAU 3 ; again, it is the opposite direction. This sequence is identical to the sequence in choice A. The anticodon for this is 5 GUA 3, which wouldn t match the one in the trna. The anticodon for this is 5 AGU3, which also wouldn t match the one in trna. E. Correct! The anticodon for this is 5 UAC3, matching the one on trna. Key point: the codon-anticodon base-pairing also follows the antiparallel complementary rule. (E)3 -AUG-5
4 No. 4 of A messenger RNA is 336 nucleotides long, including the initiator and termination codons. The number of amino acids in the protein translated from this mrna is. (A) 1015 (B) 630 (C) 335 (D) 111 (E) 110 Three nucleotides code for one amino acid, a peptide with 1015 aa would have an mrna at least 1015x3=3045 nt. Same as A, a peptide with 630 aa needs an mrna at least 630x3=1890 nt. Same as a, the mrna would be 335 x 3 = 1015 nt. D. Correct! An mrna of 336 nt codes for amino acid 336/3 1 = 111 amino acid. Minus one is due to the stop codon, which does not encode any amino acid. The initiation codon stays on; it doesn t get cleaved from the mature peptide and, therefore, the correct number is 111 aa. A point to make here is that, in cells, the real mrna is usually longer than just the coding sequence because it includes a 5 end untranslated region and a 3 end untranslated region, both of which play an important role in regulating the mrna activity. (D) 111
5 No. 5 of A synthetic mrna of repeating sequence 5'-CACACACACACACACAC... is used for a cell-free protein synthesizing system, like the one used by Niremberg. If we assume that protein synthesis can begin without the need for an initiator codon, what product or products would you expect to occur after protein synthesis (refer to the codon table in problem number 2)? (A) One protein, consisting of a single amino acid. (B) Three proteins, each consisting of a different, single amino acid. (C) Two proteins, each with an alternating sequence of two different amino acids. (D) One protein, with an alternating sequence of three different amino acids. (E) One protein, with an alternating sequence of two different amino acids. If this mrna is read in 5 to 3 direction with triplet codons, it is read as 5 CAC- ACA-CAC-ACA-CAC-ACA. The resulting amino acid sequence is His-Thr-His-Thr- His-Thr Even if the protein synthesis does not start from the first nucleotide, say, the second one, then the codon would be ACA-CAC-ACA-CAC- still it codes for a peptide alternating for his and Thr. C. Correct! If the reading starts from nt #1, it codes for His-Thr-His-Thr.; if the reading starts from the second nt, then the peptide is Thr-His-Thr-His. Since it is not defined where the synthesis may start, there are two possible peptides, as demonstrated in C. It has two proteins. The key to solving the tetrad analysis problem is to understand the triplet codon characteristics. (C)Two proteins, each with an alternating sequence of two different amino acids.
6 No. 6 of Which of the following statements about the anatomy of trna is correct? (A) trna is an L-shaped molecule, with a codon on its codon arm. (B) The 3ʹ end has an attachment site, which carries the appropriate base to the growing polypeptide chain. (C) The 3ʹ end has an amino acid attachment site, which carries the appropriate amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain. (D) The trna molecule has only 2 arms: T and D arms. (E) The 5ʹ end is an alternative amino acid binding site. trna has an anticodon on its anticodon arm. The 3ʹ end has an amino acid attachment site, which carries the appropriate amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain. C. Correct! The 3ʹ end has an amino acid attachment site, which carries the appropriate amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain. The trna molecule has 3 arms: T, D, and an anticodon arm. The 5ʹ end is the phosphate terminus; only the 3 activated sites can carry amino acids. RNA is normally single-stranded, which can have a diverse form of secondary structures other than duplex. trna carries an amino acid for incorporation into the polypeptide chain. trna has a cloverleaf secondary structure. The anti-codon loop of trna complements the codon loop of mrna. Each single chain has between 73 and 93 ribonucleotides. 3 CCA terminus is part of the amino acid acceptor stem. The 5 end is the phosphate terminus. trna does have some modified nucleosides indicated by a *. (C)The 3ʹ end has an amino acid attachment site, which carries the appropriate amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain.
7 No. 7 of The transcription process. (A) Creates an exact copy of the DNA, known as cdna. (B) Creates an RNA molecule based on a DNA template. (C) Involves an elongation step, in which the RNA polymerase complex assembles at the promoter. (D) Ends or terminates when the DNA polymerase reaches the very end of the DNA template. (E) Includes two steps: elongation and termination. The transcription process creates an RNA molecule based on a DNA template. B. Correct! The transcription process creates an RNA molecule based on a DNA template. During elongation, RNA polymerase catalyzes the elongation of the RNA, while the DNA is unwound this occurs after binding and initiation. Transcription ends in response to a termination signal, then the transcription complex disassembles. Transcription involves three steps: initiation, then elongation, and finally termination at the stop signal. The transcription process has 3 steps: Initiation: RNA polymerase complex assembles at promoter and initiates transcription. Elongation: RNA polymerase catalyzes the elongation of the RNA, while the DNA template is unwound and rewound. Termination: transcription complex responds to specific termination signals and disassembles. (B)Creates an RNA molecule based on a DNA template.
8 No. 8 of Which of the following statements about RNA processing is true? (A) The precursor to mrna is called hnrna, which stands for heterogeneous nuclear RNA. (B) The precursor to mrna is called snrna, which stands for small nuclear RNA. (C) The precursor RNA molecule contains both introns and exons; the exons will be spliced out during the processing. (D) The remaining steps are 5ʹ-capping and 5ʹ-polyadenylation. (E) The remaining steps are 3ʹ capping and 3ʹ polyadenylation. A. Correct! The precursor to mrna is called hnrna, which stands for heterogeneous nuclear RNA. The precursor to mrna is called hnrna, which stands for heterogeneous nuclear RNA. The introns will be spliced out during processing, leaving the exons behind. The remaining steps are 5ʹ-capping and 3ʹ-polyadenylation. The remaining steps are 5ʹ-capping and 3ʹ-polyadenylation. hnrna is originally transcribed RNA in the nucleus. 1. Exist in nucleus 2. Precursor of mature mrna 3. Very short half life 4. Containing extra non-coding sequence (intron sequence) (A)The precursor to mrna is called hnrna, which stands for heterogeneous nuclear RNA.
9 No. 9 of Which of the following statements about wobble and the genetic code is correct? (A) There are 61 amino acid codons, approximately 40 trna molecules for 20 amino acids. (B) There are 41 amino acid codons, approximately 30 trna molecules for 20 amino acids. (C) Codons that encode the same amino acid are different in the first 2 bases. (D) Wobble in the 3 rd position of the mrna codon prevents more than one codon for an amino acid. (E) Wobble in the 3 rd position of the anticodon prevents more than one codon for an amino acid. A. Correct! There are 61 amino acid codons, approximately 40 trna molecules for 20 amino acids. There are 61 amino acid codons, approximately 40 trna molecules for 20 amino acids. Codons that encode the same amino acid usually only differ in their 3rd base. Wobble in the 3rd position of the mrna codon allows multiple codons for the same amino acid. Wobble in the 3rd position of the mrna codon allows multiple codons for the same amino acid. There are 61 amino acid coding codons and about 40 trna molecules for 20 amino acids. Codons that encode the same amino acid often differ only by their third base. The binding of the third base is less stringent than the other two. Because of this wobble, one trna can pair with multiple mrna codons. (A)There are 61 amino acid codons, approximately 40 trna molecules for 20 amino acids.
10 No. 10 of Protein biosynthesis. (A) Includes 3 main phases: initiation, peptide elongation, and protein folding. (B) Initiation in bacteria involves the 80S and 50S ribosomal subunits. (C) Initiation in eukaryotes involves the 40S and 60S subunits. (D) Is dependent on the enzyme aminoacyl transfer DNA synthetase, which links the amino acid to the trna molecule. (E) Involves the formation of a growing polypeptide chain, in which amino acids are connected to one another with hydrogen and covalent bonds. Protein biosynthesis includes 3 main phases: initiation, peptide elongation, and termination. Protein biosynthesis initiation in bacteria involves the 30S and 50S ribosomal subunits. C. Correct! Protein biosynthesis initiation in eukaryotes involves the 40S and 60S subunits. Protein biosynthesis is dependent on the enzyme aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetase, which links the amino acid to the trna molecule. Protein biosynthesis involves the formation of a growing polypeptide chain, in which amino acids are connected to one another with peptide bonds. Ribosome is made up of several smaller proteins and is responsible for protein synthesis. It brings together the mrna, trna and rrna molecules and catalyzes the synthesis of the protein. The ribosome is the molecular machine that coordinates the charged trnas, mrna and protein that culminates in protein synthesis. Anticodon is a sequence of three nucleotides in a trna molecule that is complementary (matches) a three nucleotide codon in an mrna molecule. Protein is a polymer that is made by linking amino acids together by the peptide bond. A peptide bond is a chemical bond between the carbonyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of a second amino acid. (C)Initiation in eukaryotes involves the 40S and 60S subunits.
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 08: Transcription, Translation and the Genetic Code
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 08: Transcription, Translation and the Genetic Code Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about how genes function is correct? Question #1 (A)
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 08: Transcription, Translation and the Genetic Code Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about how genes function is correct? Question #1 (A)
Replication, Transcription, and Translation
 Replication, Transcription, and Translation Information Flow from DNA to Protein The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Replication is the copying of DNA in the course of cell division. Transcription is
Replication, Transcription, and Translation Information Flow from DNA to Protein The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Replication is the copying of DNA in the course of cell division. Transcription is
Gene function at the level of traits Gene function at the molecular level
 Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function at the molecular level Two levels tied together since the molecular level affects the structure and function of cells which determines
Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function at the molecular level Two levels tied together since the molecular level affects the structure and function of cells which determines
Protein Synthesis. DNA to RNA to Protein
 Protein Synthesis DNA to RNA to Protein From Genes to Proteins Processing the information contained in DNA into proteins involves a sequence of events known as gene expression and results in protein synthesis.
Protein Synthesis DNA to RNA to Protein From Genes to Proteins Processing the information contained in DNA into proteins involves a sequence of events known as gene expression and results in protein synthesis.
Transcription steps. Transcription steps. Eukaryote RNA processing
 Transcription steps Initiation at 5 end of gene binding of RNA polymerase to promoter unwinding of DNA Elongation addition of nucleotides to 3 end rules of base pairing requires Mg 2+ energy from NTP substrates
Transcription steps Initiation at 5 end of gene binding of RNA polymerase to promoter unwinding of DNA Elongation addition of nucleotides to 3 end rules of base pairing requires Mg 2+ energy from NTP substrates
Key Area 1.3: Gene Expression
 Key Area 1.3: Gene Expression RNA There is a second type of nucleic acid in the cell, called RNA. RNA plays a vital role in the production of protein from the code in the DNA. What is gene expression?
Key Area 1.3: Gene Expression RNA There is a second type of nucleic acid in the cell, called RNA. RNA plays a vital role in the production of protein from the code in the DNA. What is gene expression?
CH 17 :From Gene to Protein
 CH 17 :From Gene to Protein Defining a gene gene gene Defining a gene is problematic because one gene can code for several protein products, some genes code only for RNA, two genes can overlap, and there
CH 17 :From Gene to Protein Defining a gene gene gene Defining a gene is problematic because one gene can code for several protein products, some genes code only for RNA, two genes can overlap, and there
A. Incorrect! This feature does help with it suitability as genetic material.
 College Biology - Problem Drill 08: Gene Structures and Functions No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the statements below is NOT true in explaining why DNA is a suitable genetic material? #01 (A) Its double helix
College Biology - Problem Drill 08: Gene Structures and Functions No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the statements below is NOT true in explaining why DNA is a suitable genetic material? #01 (A) Its double helix
Lecture for Wednesday. Dr. Prince BIOL 1408
 Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Higher Level
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Higher Level Lesson Objectives At the end of this lesson you should be able to 1. Outline the steps in protein synthesis 2. Understand DNA contains the code for protein 3. Understand
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Higher Level Lesson Objectives At the end of this lesson you should be able to 1. Outline the steps in protein synthesis 2. Understand DNA contains the code for protein 3. Understand
DNA is the MASTER PLAN. RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan
 Sec. 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Roles of DNA and RNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 1 RNA uses the information from DNA to make proteins Differs from DNA: 1. Ribose
Sec. 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Roles of DNA and RNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 1 RNA uses the information from DNA to make proteins Differs from DNA: 1. Ribose
Genes and How They Work. Chapter 15
 Genes and How They Work Chapter 15 The Nature of Genes They proposed the one gene one enzyme hypothesis. Today we know this as the one gene one polypeptide hypothesis. 2 The Nature of Genes The central
Genes and How They Work Chapter 15 The Nature of Genes They proposed the one gene one enzyme hypothesis. Today we know this as the one gene one polypeptide hypothesis. 2 The Nature of Genes The central
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr.
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
The Nature of Genes. The Nature of Genes. Genes and How They Work. Chapter 15/16
 Genes and How They Work Chapter 15/16 The Nature of Genes Beadle and Tatum proposed the one gene one enzyme hypothesis. Today we know this as the one gene one polypeptide hypothesis. 2 The Nature of Genes
Genes and How They Work Chapter 15/16 The Nature of Genes Beadle and Tatum proposed the one gene one enzyme hypothesis. Today we know this as the one gene one polypeptide hypothesis. 2 The Nature of Genes
Biology. Biology. Slide 1 of 39. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology Biology 1 of 39 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis 2 of 39 Essential Question What is transcription and translation and how do they take place? 3 of 39 12 3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Genes are coded
Biology Biology 1 of 39 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis 2 of 39 Essential Question What is transcription and translation and how do they take place? 3 of 39 12 3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Genes are coded
Biology. Biology. Slide 1 of 39. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology Biology 1 of 39 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis 2 of 39 12 3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins. Genetic messages can be decoded by
Biology Biology 1 of 39 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis 2 of 39 12 3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins. Genetic messages can be decoded by
Chapter 12: Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Biology Textbook Notes Chapter 12: Molecular Biology of the Gene p. 214-219 The Genetic Material (12.1) - Genetic Material must: 1. Be able to store information that pertains to the development, structure,
Biology Textbook Notes Chapter 12: Molecular Biology of the Gene p. 214-219 The Genetic Material (12.1) - Genetic Material must: 1. Be able to store information that pertains to the development, structure,
Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of..
 Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code
 Lecture 28-29 Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code Central dogma of molecular biology During transcription, the information in a DNA sequence (a gene) is copied into a
Lecture 28-29 Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code Central dogma of molecular biology During transcription, the information in a DNA sequence (a gene) is copied into a
RNA : functional role
 RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. copyright cmassengale
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA and Genes 2 Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 3 RNA Differs from DNA RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 4 Other
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA and Genes 2 Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 3 RNA Differs from DNA RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 4 Other
Fig Ch 17: From Gene to Protein
 Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
Translation BIT 220 Chapter 13
 Translation BIT 220 Chapter 13 Making protein from mrna Most genes encode for proteins -some make RNA as end product Proteins -Monomer Amino Acid 20 amino acids -peptides -polypeptides -Structure of Amino
Translation BIT 220 Chapter 13 Making protein from mrna Most genes encode for proteins -some make RNA as end product Proteins -Monomer Amino Acid 20 amino acids -peptides -polypeptides -Structure of Amino
Chapter 14: From DNA to Protein
 Chapter 14: From DNA to Protein Steps from DNA to Proteins Same two steps produce all proteins: 1) DNA is transcribed to form RNA Occurs in the nucleus RNA moves into cytoplasm 2) RNA is translated in
Chapter 14: From DNA to Protein Steps from DNA to Proteins Same two steps produce all proteins: 1) DNA is transcribed to form RNA Occurs in the nucleus RNA moves into cytoplasm 2) RNA is translated in
Hello! Outline. Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis. In all living cells, DNA molecules are the storehouses of information. 6.
 Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis In all living cells, DNA molecules are the storehouses of information Hello! Outline u 1. Key concepts u 2. Central Dogma u 3. RNA Types u 4. RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis In all living cells, DNA molecules are the storehouses of information Hello! Outline u 1. Key concepts u 2. Central Dogma u 3. RNA Types u 4. RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
Unit 1: DNA and the Genome. Sub-Topic (1.3) Gene Expression
 Unit 1: DNA and the Genome Sub-Topic (1.3) Gene Expression Unit 1: DNA and the Genome Sub-Topic (1.3) Gene Expression On completion of this subtopic I will be able to State the meanings of the terms genotype,
Unit 1: DNA and the Genome Sub-Topic (1.3) Gene Expression Unit 1: DNA and the Genome Sub-Topic (1.3) Gene Expression On completion of this subtopic I will be able to State the meanings of the terms genotype,
1. DNA, RNA structure. 2. DNA replication. 3. Transcription, translation
 1. DNA, RNA structure 2. DNA replication 3. Transcription, translation DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides DNA is a nucleic acid, made of long chains of nucleotides Nucleotide Phosphate group Nitrogenous
1. DNA, RNA structure 2. DNA replication 3. Transcription, translation DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides DNA is a nucleic acid, made of long chains of nucleotides Nucleotide Phosphate group Nitrogenous
From RNA To Protein
 From RNA To Protein 22-11-2016 Introduction mrna Processing heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnrna) RNA that comprises transcripts of nuclear genes made by RNA polymerase II; it has a wide size distribution
From RNA To Protein 22-11-2016 Introduction mrna Processing heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnrna) RNA that comprises transcripts of nuclear genes made by RNA polymerase II; it has a wide size distribution
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.17 - GENE EXPRESSION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: GENES Beadle and Tatum develop the one gene one enzyme hypothesis through their work with Neurospora (bread mold). This idea was later revised as the one gene one polypeptide
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: GENES Beadle and Tatum develop the one gene one enzyme hypothesis through their work with Neurospora (bread mold). This idea was later revised as the one gene one polypeptide
Chapter 13. From DNA to Protein
 Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Regulation of bacterial gene expression
 Regulation of bacterial gene expression Gene Expression Gene Expression: RNA and protein synthesis DNA ----------> RNA ----------> Protein transcription translation! DNA replication only occurs in cells
Regulation of bacterial gene expression Gene Expression Gene Expression: RNA and protein synthesis DNA ----------> RNA ----------> Protein transcription translation! DNA replication only occurs in cells
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins. The Central Dogma
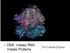 DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
Ch. 10 From DNA to Protein. AP Biology
 Ch. 10 From DNA to Protein Protein Synthesis Metabolism and Gene Expression n Inheritance of metabolic diseases suggests that genes coded for enzymes n Diseases (phenotypes) caused by non-functional gene
Ch. 10 From DNA to Protein Protein Synthesis Metabolism and Gene Expression n Inheritance of metabolic diseases suggests that genes coded for enzymes n Diseases (phenotypes) caused by non-functional gene
DNA, RNA, and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
 DNA, RNA, and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA DNA contains genes, sequences of nucleotide bases The genes code for polypeptides (proteins) Proteins are used to build cells and do much of the work inside cells
DNA, RNA, and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA DNA contains genes, sequences of nucleotide bases The genes code for polypeptides (proteins) Proteins are used to build cells and do much of the work inside cells
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch 17 Practice Questions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Garrod hypothesized that "inborn errors of metabolism" such as alkaptonuria
Ch 17 Practice Questions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Garrod hypothesized that "inborn errors of metabolism" such as alkaptonuria
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW. Overview of Biomolecules. Chapter 13 Protein Synthesis
 BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 13 Protein Synthesis 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Are You Getting It?? Which properties are characteristic of the normal genetic code? (multiple answers) a) A
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 13 Protein Synthesis 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Are You Getting It?? Which properties are characteristic of the normal genetic code? (multiple answers) a) A
I. Gene Expression Figure 1: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
 I. Gene Expression Figure 1: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Central Dogma: Gene Expression: RNA Structure RNA nucleotides contain the pentose sugar Ribose instead of deoxyribose. Contain the bases
I. Gene Expression Figure 1: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Central Dogma: Gene Expression: RNA Structure RNA nucleotides contain the pentose sugar Ribose instead of deoxyribose. Contain the bases
From Gene to Protein. How Genes Work
 From Gene to Protein How Genes Work 2007-2008 The Central Dogma Flow of genetic information in a cell How do we move information from DNA to proteins? DNA RNA protein replication phenotype You! Step 1:
From Gene to Protein How Genes Work 2007-2008 The Central Dogma Flow of genetic information in a cell How do we move information from DNA to proteins? DNA RNA protein replication phenotype You! Step 1:
Chapter 17. From Gene to Protein
 Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein Overview: The Flow of Genetic Information The information content of DNA is in the form of specific sequences of nucleotides The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein Overview: The Flow of Genetic Information The information content of DNA is in the form of specific sequences of nucleotides The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific
From Gene to Protein
 8.2 Structure of DNA From Gene to Protein deoxyribonucleic acid - (DNA) - the ultimate source of all information in a cell This information is used by the cell to produce the protein molecules which are
8.2 Structure of DNA From Gene to Protein deoxyribonucleic acid - (DNA) - the ultimate source of all information in a cell This information is used by the cell to produce the protein molecules which are
Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis
 Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis 1. Describe how genetic information is transcribed into sequences of bases in RNA molecules and is finally translated into sequences of amino
Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis 1. Describe how genetic information is transcribed into sequences of bases in RNA molecules and is finally translated into sequences of amino
RNA, & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. 7 th Grade, Week 4, Day 1 Monday, July 15, 2013
 RNA, & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 7 th Grade, Week 4, Day 1 Monday, July 15, 2013 The Central Dogma RNA vs. DNA Ribonucleic Acid RNA is required for translation of genetic information stored in DNA into protein
RNA, & PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 7 th Grade, Week 4, Day 1 Monday, July 15, 2013 The Central Dogma RNA vs. DNA Ribonucleic Acid RNA is required for translation of genetic information stored in DNA into protein
The Nature of Genes. The Nature of Genes. The Nature of Genes. The Nature of Genes. The Nature of Genes. The Genetic Code. Genes and How They Work
 Genes and How They Work Chapter 15 Early ideas to explain how genes work came from studying human diseases. Archibald Garrod studied alkaptonuria, 1902 Garrod recognized that the disease is inherited via
Genes and How They Work Chapter 15 Early ideas to explain how genes work came from studying human diseases. Archibald Garrod studied alkaptonuria, 1902 Garrod recognized that the disease is inherited via
7.2 Protein Synthesis. From DNA to Protein Animation
 7.2 Protein Synthesis From DNA to Protein Animation Proteins Why are proteins so important? They break down your food They build up muscles They send signals through your brain that control your body They
7.2 Protein Synthesis From DNA to Protein Animation Proteins Why are proteins so important? They break down your food They build up muscles They send signals through your brain that control your body They
The Structure of RNA. The Central Dogma
 12-3 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis The Structure of RNA The Central Dogma Phenotype A gene is a SEQUENCE of DNA that codes for a protein (or functional RNA). Phenotype is the individual s observable trait
12-3 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis The Structure of RNA The Central Dogma Phenotype A gene is a SEQUENCE of DNA that codes for a protein (or functional RNA). Phenotype is the individual s observable trait
DNA Replication and Repair
 DNA Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif Overview of DNA Replication SWYK CNs 1, 2, 30 Explain how specific base pairing enables existing DNA strands
DNA Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif Overview of DNA Replication SWYK CNs 1, 2, 30 Explain how specific base pairing enables existing DNA strands
Molecular Genetics. The flow of genetic information from DNA. DNA Replication. Two kinds of nucleic acids in cells: DNA and RNA.
 Molecular Genetics DNA Replication Two kinds of nucleic acids in cells: DNA and RNA. DNA function 1: DNA transmits genetic information from parents to offspring. DNA function 2: DNA controls the functions
Molecular Genetics DNA Replication Two kinds of nucleic acids in cells: DNA and RNA. DNA function 1: DNA transmits genetic information from parents to offspring. DNA function 2: DNA controls the functions
Biology 3201 Genetics Unit #5
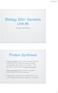 Biology 3201 Genetics Unit #5 Protein Synthesis Protein Synthesis Protein synthesis: this is the process whereby instructions from DNA are used to create polypeptides that make up a protein. This process
Biology 3201 Genetics Unit #5 Protein Synthesis Protein Synthesis Protein synthesis: this is the process whereby instructions from DNA are used to create polypeptides that make up a protein. This process
MOLECULAR GENETICS PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #2 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1 GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 2 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #2 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1 GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 2 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
DNA Model Stations. For the following activity, you will use the following DNA sequence.
 Name: DNA Model Stations DNA Replication In this lesson, you will learn how a copy of DNA is replicated for each cell. You will model a 2D representation of DNA replication using the foam nucleotide pieces.
Name: DNA Model Stations DNA Replication In this lesson, you will learn how a copy of DNA is replicated for each cell. You will model a 2D representation of DNA replication using the foam nucleotide pieces.
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. copyright cmassengale
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA and Genes 2 Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 3 RNA Differs from DNA RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 4 Other
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA and Genes 2 Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 3 RNA Differs from DNA RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 4 Other
Transcription in Eukaryotes
 Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
The Central Dogma. DNA makes RNA makes Proteins
 The Central Dogma DNA makes RNA makes Proteins TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION OF
The Central Dogma DNA makes RNA makes Proteins TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION OF
Nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ribonucleic acid (RNA) nucleotide
 Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Analyzed Fungi Neurospora crassa mutants. Mutants were UNABLE to grow without Arginine (an amino acid) Other biochemical experiments indicated:
 From Gene to Protein Beadle and Tatum Analyzed Fungi Neurospora crassa mutants Mutants were UNABLE to grow without Arginine (an amino acid) Other biochemical experiments indicated: Precursor Ornithine
From Gene to Protein Beadle and Tatum Analyzed Fungi Neurospora crassa mutants Mutants were UNABLE to grow without Arginine (an amino acid) Other biochemical experiments indicated: Precursor Ornithine
NCEA Level 2 Biology (91159) 2017 page 1 of 6. Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence
 NCEA Level 2 Biology (91159) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of gene expression (91159) Assessment Criteria with Merit with Excellence Demonstrate understanding
NCEA Level 2 Biology (91159) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of gene expression (91159) Assessment Criteria with Merit with Excellence Demonstrate understanding
DNA Function: Information Transmission
 DNA Function: Information Transmission DNA is called the code of life. What does it code for? *the information ( code ) to make proteins! Why are proteins so important? Nearly every function of a living
DNA Function: Information Transmission DNA is called the code of life. What does it code for? *the information ( code ) to make proteins! Why are proteins so important? Nearly every function of a living
Transcription is the first stage of gene expression
 Transcription is the first stage of gene expression RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and hooks together the RNA nucleotides The RNA is complementary to the
Transcription is the first stage of gene expression RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and hooks together the RNA nucleotides The RNA is complementary to the
IB BIO I Replication/Transcription/Translation Van Roekel/Madden. Name Date Period. D. It separates DNA strands. (Total 1 mark)
 Name Date Period 1. What is the function of helicase? A. It forms bonds between DNA nucleotides. B. It adds new nucleotides to the DNA helix. C. It forms the DNA helix. D. It separates DNA strands. 2.
Name Date Period 1. What is the function of helicase? A. It forms bonds between DNA nucleotides. B. It adds new nucleotides to the DNA helix. C. It forms the DNA helix. D. It separates DNA strands. 2.
From Gene to Protein transcription, messenger RNA (mrna) translation, RNA processing triplet code, template strand, codons,
 From Gene to Protein I. Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes
From Gene to Protein I. Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes
Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene For Next Week Lab -Hand in questions from 4 and 5 by TUES in my mailbox (Biology Office) -Do questions for Lab 6 for next week -Lab practical next week Lecture Read
Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene For Next Week Lab -Hand in questions from 4 and 5 by TUES in my mailbox (Biology Office) -Do questions for Lab 6 for next week -Lab practical next week Lecture Read
Big Idea 3C Basic Review
 Big Idea 3C Basic Review 1. A gene is a. A sequence of DNA that codes for a protein. b. A sequence of amino acids that codes for a protein. c. A sequence of codons that code for nucleic acids. d. The end
Big Idea 3C Basic Review 1. A gene is a. A sequence of DNA that codes for a protein. b. A sequence of amino acids that codes for a protein. c. A sequence of codons that code for nucleic acids. d. The end
CHapter 14. From DNA to Protein
 CHapter 14 From DNA to Protein How? DNA to RNA to Protein to Trait Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA: carries protein code or transcript 2. Ribosomal RNA: part of ribosomes 3. Transfer RNA: delivers amino
CHapter 14 From DNA to Protein How? DNA to RNA to Protein to Trait Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA: carries protein code or transcript 2. Ribosomal RNA: part of ribosomes 3. Transfer RNA: delivers amino
From DNA to Protein. Chapter 14
 From DNA to Protein Chapter 14 What do genes code for? How does DNA code for cells & bodies? How are cells and bodies made from the instructions in DNA? DNA proteins cells bodies The Central Dogma Flow
From DNA to Protein Chapter 14 What do genes code for? How does DNA code for cells & bodies? How are cells and bodies made from the instructions in DNA? DNA proteins cells bodies The Central Dogma Flow
Bio11 Announcements. Ch 21: DNA Biology and Technology. DNA Functions. DNA and RNA Structure. How do DNA and RNA differ? What are genes?
 Bio11 Announcements TODAY Genetics (review) and quiz (CP #4) Structure and function of DNA Extra credit due today Next week in lab: Case study presentations Following week: Lab Quiz 2 Ch 21: DNA Biology
Bio11 Announcements TODAY Genetics (review) and quiz (CP #4) Structure and function of DNA Extra credit due today Next week in lab: Case study presentations Following week: Lab Quiz 2 Ch 21: DNA Biology
Degenerate Code. Translation. trna. The Code is Degenerate trna / Proofreading Ribosomes Translation Mechanism
 Translation The Code is Degenerate trna / Proofreading Ribosomes Translation Mechanism Degenerate Code There are 64 possible codon triplets There are 20 naturally-encoding amino acids Several codons specify
Translation The Code is Degenerate trna / Proofreading Ribosomes Translation Mechanism Degenerate Code There are 64 possible codon triplets There are 20 naturally-encoding amino acids Several codons specify
NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM. Omidiwura, B.R.O
 NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM Omidiwura, B.R.O Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid
NUCLEIC ACID METABOLISM Omidiwura, B.R.O Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid
produces an RNA copy of the coding region of a gene
 1. Transcription Gene Expression The expression of a gene into a protein occurs by: 1) Transcription of a gene into RNA produces an RNA copy of the coding region of a gene the RNA transcript may be the
1. Transcription Gene Expression The expression of a gene into a protein occurs by: 1) Transcription of a gene into RNA produces an RNA copy of the coding region of a gene the RNA transcript may be the
RNA: Transcription and Triplet Code
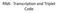 RNA: Transcription and Triplet Code There are Five Kinds of RNA, All of Which are Templated from DNA. The first type of RNA is trna. The "t" stands for "transfer". This RNA is the RNA that transfers amino
RNA: Transcription and Triplet Code There are Five Kinds of RNA, All of Which are Templated from DNA. The first type of RNA is trna. The "t" stands for "transfer". This RNA is the RNA that transfers amino
Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins. From DNA to RNA
 From DNA to RNA Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins I. After the discovery of the structure of DNA, the major question remaining was how does the stored in the 4 letter code of DNA direct the and of
From DNA to RNA Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins I. After the discovery of the structure of DNA, the major question remaining was how does the stored in the 4 letter code of DNA direct the and of
Text Reference, Campbell v.8, chapter 17 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
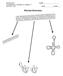 AP BIOLOGY Text Reference, Campbell v.8, chapter 17 ACTIVITY 1.22 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW PROTEIN SYNTHESIS TRANSCRIPTION PROTEIN SYNTHESIS TRANSLATION
AP BIOLOGY Text Reference, Campbell v.8, chapter 17 ACTIVITY 1.22 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW PROTEIN SYNTHESIS TRANSCRIPTION PROTEIN SYNTHESIS TRANSLATION
From Gene to Protein
 Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
8/21/2014. From Gene to Protein
 From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
Unit 1. DNA and the Genome
 Unit 1 DNA and the Genome Gene Expression Key Area 3 Vocabulary 1: Transcription Translation Phenotype RNA (mrna, trna, rrna) Codon Anticodon Ribosome RNA polymerase RNA splicing Introns Extrons Gene Expression
Unit 1 DNA and the Genome Gene Expression Key Area 3 Vocabulary 1: Transcription Translation Phenotype RNA (mrna, trna, rrna) Codon Anticodon Ribosome RNA polymerase RNA splicing Introns Extrons Gene Expression
Problem Set Unit The base ratios in the DNA and RNA for an onion (Allium cepa) are given below.
 Problem Set Unit 3 Name 1. Which molecule is found in both DNA and RNA? A. Ribose B. Uracil C. Phosphate D. Amino acid 2. Which molecules form the nucleotide marked in the diagram? A. phosphate, deoxyribose
Problem Set Unit 3 Name 1. Which molecule is found in both DNA and RNA? A. Ribose B. Uracil C. Phosphate D. Amino acid 2. Which molecules form the nucleotide marked in the diagram? A. phosphate, deoxyribose
Chapter 17. From Gene to Protein. AP Biology
 Chapter 17. From Gene to Protein Metabolism teaches us about genes Metabolic defects studying metabolic diseases suggested that genes specified proteins alkaptonuria (black urine from alkapton) PKU (phenylketonuria)
Chapter 17. From Gene to Protein Metabolism teaches us about genes Metabolic defects studying metabolic diseases suggested that genes specified proteins alkaptonuria (black urine from alkapton) PKU (phenylketonuria)
Protein Synthesis ~Biology AP~
 Protein Synthesis ~Biology AP~ A Meridian Study Guide by David Guan, Jennifer Zheng [Edited by Lei Gong] Introduction: - DNA and RNA are essential for life because they code for enzymes, which regulate
Protein Synthesis ~Biology AP~ A Meridian Study Guide by David Guan, Jennifer Zheng [Edited by Lei Gong] Introduction: - DNA and RNA are essential for life because they code for enzymes, which regulate
Transcription. The sugar molecule found in RNA is ribose, rather than the deoxyribose found in DNA.
 Transcription RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a key intermediary between a DNA sequence and a polypeptide. RNA is an informational polynucleotide similar to DNA, but it differs from DNA in three ways: RNA generally
Transcription RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a key intermediary between a DNA sequence and a polypeptide. RNA is an informational polynucleotide similar to DNA, but it differs from DNA in three ways: RNA generally
Chapter 17. From Gene to Protein
 Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein One Gene One Enzyme Hypothesis Archibald Garrod 1 st to suggest that genes dictate phenotypes through enzymes that catalyze specific chemical reactions ; alkaptonuria Beadle
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein One Gene One Enzyme Hypothesis Archibald Garrod 1 st to suggest that genes dictate phenotypes through enzymes that catalyze specific chemical reactions ; alkaptonuria Beadle
Daily Agenda. Warm Up: Review. Translation Notes Protein Synthesis Practice. Redos
 Daily Agenda Warm Up: Review Translation Notes Protein Synthesis Practice Redos 1. What is DNA Replication? 2. Where does DNA Replication take place? 3. Replicate this strand of DNA into complimentary
Daily Agenda Warm Up: Review Translation Notes Protein Synthesis Practice Redos 1. What is DNA Replication? 2. Where does DNA Replication take place? 3. Replicate this strand of DNA into complimentary
6.C: Students will explain the purpose and process of transcription and translation using models of DNA and RNA
 6.C: Students will explain the purpose and process of transcription and translation using models of DNA and RNA DNA mrna Protein DNA is found in the nucleus, but making a protein occurs at the ribosome
6.C: Students will explain the purpose and process of transcription and translation using models of DNA and RNA DNA mrna Protein DNA is found in the nucleus, but making a protein occurs at the ribosome
Bundle 6 Test Review
 Bundle 6 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? Deoxyribonucleic
Bundle 6 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? Deoxyribonucleic
FROM GENE TO PROTEIN. One Gene One Enzyme Hypothesis 3/12/2013. Basic Principles of Transcription & Translation
 One Gene One Enzyme Hypothesis FROM GENE TO PROTEIN C H A P T E R 1 7 Archibald Garrod 1 st to suggest that genes dictate phenotypes through enzymes that catalyze specific chemical reactions ; alkaptonuria
One Gene One Enzyme Hypothesis FROM GENE TO PROTEIN C H A P T E R 1 7 Archibald Garrod 1 st to suggest that genes dictate phenotypes through enzymes that catalyze specific chemical reactions ; alkaptonuria
Bioinformatics. ONE Introduction to Biology. Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Biology/CS 123A Fall 2012
 Bioinformatics ONE Introduction to Biology Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Biology/CS 123A Fall 2012 Biology Review DNA RNA Proteins Central Dogma Transcription Translation
Bioinformatics ONE Introduction to Biology Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Biology/CS 123A Fall 2012 Biology Review DNA RNA Proteins Central Dogma Transcription Translation
GENE EXPRESSION AT THE MOLECULAR LEVEL. Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 GENE EXPRESSION AT THE MOLECULAR LEVEL Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function
GENE EXPRESSION AT THE MOLECULAR LEVEL Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function
From Gene to Protein. Chapter 17. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Q. No. 1. How can RNA be distinguished from DNA?
 Frequently asked questions (FAQS): Q. No. 1. How can RNA be distinguished from DNA? Ans. RNA and DNA are both nucleic acids, but differ in three main ways. First, unlike DNA which is generally double-stranded,
Frequently asked questions (FAQS): Q. No. 1. How can RNA be distinguished from DNA? Ans. RNA and DNA are both nucleic acids, but differ in three main ways. First, unlike DNA which is generally double-stranded,
BEADLE & TATUM EXPERIMENT
 FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE OBJECTIVES What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? How Does Information Flow from Genes to Proteins? How Is the Information Content in
FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE OBJECTIVES What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? How Does Information Flow from Genes to Proteins? How Is the Information Content in
Videos. Lesson Overview. Fermentation
 Lesson Overview Fermentation Videos Bozeman Transcription and Translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Drawing transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/6yqplgnjr4q Objectives 29a) I can contrast
Lesson Overview Fermentation Videos Bozeman Transcription and Translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Drawing transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/6yqplgnjr4q Objectives 29a) I can contrast
Fermentation. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview 13.1 RNA
 13.1 RNA THINK ABOUT IT DNA is the genetic material of cells. The sequence of nucleotide bases in the strands of DNA carries some sort of code. In order for that code to work, the cell must be able to
13.1 RNA THINK ABOUT IT DNA is the genetic material of cells. The sequence of nucleotide bases in the strands of DNA carries some sort of code. In order for that code to work, the cell must be able to
Flow of Genetic Information
 Flow of Genetic Information Transcription and Translation Links to the Next Generation Standards Scientific and Engineering Practices: Asking Questions (for science) and Defining Problems (for engineering)
Flow of Genetic Information Transcription and Translation Links to the Next Generation Standards Scientific and Engineering Practices: Asking Questions (for science) and Defining Problems (for engineering)
The Structure of Proteins The Structure of Proteins. How Proteins are Made: Genetic Transcription, Translation, and Regulation
 How Proteins are Made: Genetic, Translation, and Regulation PLAY The Structure of Proteins 14.1 The Structure of Proteins Proteins - polymer amino acids - monomers Linked together with peptide bonds A
How Proteins are Made: Genetic, Translation, and Regulation PLAY The Structure of Proteins 14.1 The Structure of Proteins Proteins - polymer amino acids - monomers Linked together with peptide bonds A
Chapter Twelve Protein Synthesis: Translation of the Genetic Message
 Mary K. Campbell Shawn O. Farrell international.cengage.com/ Chapter Twelve Protein Synthesis: Translation of the Genetic Message Paul D. Adams University of Arkansas 1 Translating the Genetic Message
Mary K. Campbell Shawn O. Farrell international.cengage.com/ Chapter Twelve Protein Synthesis: Translation of the Genetic Message Paul D. Adams University of Arkansas 1 Translating the Genetic Message
SCBC203 Gene Expression. Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science PR318
 SCBC203 Gene Expression Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science PR318 Rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th 1 Gene Expression Gene expression is a process where by the genetic
SCBC203 Gene Expression Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science PR318 Rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th 1 Gene Expression Gene expression is a process where by the genetic
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
 Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein The Flow of Genetic Information The information content of DNA is in the form of specific sequences of nucleotides The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein The Flow of Genetic Information The information content of DNA is in the form of specific sequences of nucleotides The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits
Year Morgan and fellow researchers found that chromosomes contained DNA, RNA, and protein.
 DNA Year 1920 Morgan and fellow researchers found that chromosomes contained DNA, RNA, and protein. Which one actually carries the genetic information? The stuff that gets passed on from generation
DNA Year 1920 Morgan and fellow researchers found that chromosomes contained DNA, RNA, and protein. Which one actually carries the genetic information? The stuff that gets passed on from generation
Information Readout: Transcription and Post-transcriptional Processing Translation
 Information Readout: Transcription and Post-transcriptional Processing Translation Copyright 2013 Pearson Canada Inc. 27-1 DNA as the Template for RNA Synthesis Enzymology of RNA Synthesis: RNA Polymerase
Information Readout: Transcription and Post-transcriptional Processing Translation Copyright 2013 Pearson Canada Inc. 27-1 DNA as the Template for RNA Synthesis Enzymology of RNA Synthesis: RNA Polymerase
Transcription and Translation. DANILO V. ROGAYAN JR. Faculty, Department of Natural Sciences
 Transcription and Translation DANILO V. ROGAYAN JR. Faculty, Department of Natural Sciences Protein Structure Made up of amino acids Polypeptide- string of amino acids 20 amino acids are arranged in different
Transcription and Translation DANILO V. ROGAYAN JR. Faculty, Department of Natural Sciences Protein Structure Made up of amino acids Polypeptide- string of amino acids 20 amino acids are arranged in different
DNA. Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses.
 Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
Is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses. Genetic information is encoded as a sequence of nucleotides (guanine,
