Energy Waste. Major Energy Wasters. Chapter 16: Renewable Energy APES
|
|
|
- Jonah Ward
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 16: Renewable Energy APES Energy Waste Energy Conservation - decrease in energy use based on reducing unnecessary waste of energy Energy Efficiency - measure of how much work can be gained from each unit of energy 84% of all commercial energy used in the U.S. is wasted. 41% is unavoidable because of degradation (2nd Law of Thermodynamics). 43% is unnecessary waste because of inefficiency. Energy waste in the U.S. costs about $570,000 per minute. Reducing energy waste quickest, cleanest, and often the cheapest way to provide more energy, reduce pollution and environmental degradation, slow global warming, and increase economic and national security. 2 Major Energy Wasters Incandescent lightbulbs - use only 5-10% of the energy it draws to produce light (90-95% wasted as heat) Internal Combustion Engine - wastes 94% of energy in its fuel Nuclear Power Plant - wastes 83% of energy in nuclear fuel (92% when entire nuclear fuel cycle is included) Coal-fired Power Plant - wastes 66% of energy from coal (75-80% if energy to access and transport coal is included) 3
2 Industry Industry accounts for 30% of world energy consumption (38% for U.S.) Cogeneration (Combined Heat and Power) - producing heat and electricity from the same fuel source This can increase energy efficiency from 30-40% to up to 80%. It also emits one third less CO 2. Energy-wasting electric motors - only run at full speed. Replacing could save the equivalent of 150 coal power plants of energy. Recycling - It takes 75% less energy to produce steel from recycled than from virgin ore. Cement industry could cut energy use by 42%. Lighting - from incandescent to fluorescent and LED 4 The Grid and Industry The Grid wastes huge amounts of energy. Converting to a digitally controlled network could save $100 billion a year. Dow Chemical is on track to cut its energy consumption in half by Their energy savings will equal the amount used by the entire nation of New Zealand. These energy efficiency improvements cost Dow $1 billion dollars, but have saved about $5 billion already 5 Transportation Accounts for two-thirds of U.S. oil consumption, and is a major cause of air pollution and CO2 emissions. 6
3 CAFE Standards Corporate Average Fuel Economy Government mandated standards for fuel efficiency fuel efficiency rose sharply Since 1985, average fuel efficiency for new vehicles has decreased by about 21 mpg Government did not increase standards after 1985 SUVs and trucks became more popular 7 U.S. Average Fuel Economy Fig International Standards Europe, Japan, China, and Canada have much higher fuel efficiency standards than the U.S. The U.S. raised CAFE standards to 35 mpg by 2020, but that will still keep them well below other countries Fig
4 Fuel Efficient Vehicles Should be at least 35 mpg Ex. Toyota Prius (46 mpg) Fuel efficient cars are only 1% of new vehicle sales True cost of gas could be estimated at $16 per gallon when all factors are taken in to consideration Government does not incentivize fuel efficiency through subsidies and tax breaks. Ex. Small business could buy a $50,000 Hummer and get a $25,000 tax deduction. Buying a $22,000 hybrid would only provide a $3,100 tax deduction. 10 Fuel Efficient Future Superefficient and Ultralight cars that could get mpg Conventional Hybird - invented in 1900 by Ferdinand Porsche, improved by Japanese automakers Up to 46 mpg and 65% less CO2 emissions Plug-in Hybrid - hybrid with a more powerful battery that can be plugged into a standard outlet to recharge Up to 100 mpg for standard drivers Up to 1,000 mpg for those who only make trips less than 40 miles between recharges 11 Hybrid Vehicles Fig Replacing the U.S. fleet would cut U.S. oil consumption by 70-90% (eliminate need for foreign oil imports) and reduce CO 2 emissions by 27% If the vehicles were recharged by wind, solar, or hydropower CO 2 emissions would drop by 80-90% 12
5 Diesel Energy efficient diesel - 30% more fuel efficient, 20% less CO2 Diesel fuel can be made from coal, plant material, and cooking oil Hybrid-electric diesel cars would be more efficient than gasoline hybrids Fuel Cells Twice as efficient as internal combustion engines Use hydrogen gas as a fuel to produce electricity with no carbon dioxide emissions 13 Green Architecture Better architecture and energy saving building practices could save 30-40% of global energy Green architecture takes advantage of: natural lighting, passive solar heating, geothermal heat pumps, cogeneration, solar hot water heaters, natural ventilation, recycled building materials, energy efficient lighting, rainwater collection, efficient water use 14 Superinsulation When a house is so heavily insulated and airtight that heat from direct sunlight, appliances, and human bodies can warm it with little or no use of a heating system. Air-to-air heat exchangers prevents indoor air pollution Costs 5% more to build (this cost is made up within 5 years). Can save $50, ,000 over a 40 year period Superinsulated houses in Sweden use 90% less energy than similar American homes 15
6 Straw Bale Houses Type of superinsulated house Made by stacking compact bales of straw (renewable resource) then covering the outside with plaster 16 Green Building Certifications U.S. Green Building Council s - Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) Accredited more than 25,000 buildings Four levels: Certified, Silver, Gold, and Platinum 17 Existing Buildings Insulate and plug leaks - up to one third of all heated air escapes Energy-efficient windows Other heating and cooling losses Heat houses more effectively - passive solar heating, geothermal heat pumps Heat water more efficiently - solar water heaters, tankless water heater Energy efficient appliances Energy efficient lighting 18
7 Passive Solar Heating Absorbs and stores heat from the sun directly within a well-insulated structure without the need for pumps or fans to distribute Fig Active Solar Heating Absorbs energy from the sun by pumping heatabsorbing fluid (such as water) through collectors on the roof 20 Solar Thermal System Transform energy from the sun into high-temperature thermal energy which can be used to heat water and produce steam and generate electricity Central Receiver System - mirrors (heliostats) track the sun and focus sunlight on a central heat collection tower (power tower) Sunlight can also be focused on oil filled pipes These systems have high costs, low energy yields, and few sustainable sites 21
8 Solar Cookers Small scale Focuses and and concentrates sunlight to cook food Cost only $2-10 to build Zero pollution way to cook 22 Photovoltaic (PV) Cells Often called solar cells Thin wafers of purified silicon with trace amounts of metals that allows them to focus as semiconductors to produce electricity Can be connected to the grid (earn money back from power company) or to batteries (store energy) Safe, quiet, little maintenance, produce no pollution, last as long as a commercial power plant Good tool for developing countries not connected to an electrical grid 23 Small and Large Scale Fig Largest Solar Energy Producers Germany, Japan, and China Fig
9 Fig Cost of Solar Energy Costs are expected to go down as mass production begins 26 Future of Solar Currently 0.2% of electricity, but if tax breaks and other subsidies are used, it could eventually provide 16% by Can now print cells like printing a newspaper (flexible, light) at half the cost of rigid panels Could become most widely used form of energy within two decades Pg. S67 27
10 Future of Solar Estimates are that if solar cells are put on just 4% of the world s desert, it could supply the entire world with energy Solar industry could become one of the world s largest Germany (even though it is cloudy and rainy) is the world s largest producer of solar energy. Huge governmental investment 28 Hydropower Relies on the water cycle (Indirect from of solar energy) Most common means of production is to build a dam and create a reservoir Third cheapest way to produce energy (when environmental costs are considered) Global warming could have an impact on this Micro-hydropower - small and placed in stream (low cost, almost zero environmental impact) 29 Ocean Tides and Waves Turbines placed in tidal zones to harness the power of the tides Chains of floating steel tubes can be installed along coasts with continuous waves that get energy from up and down motion (In Portugal this produces enough electricity for 15,000 homes) 30
11 Wind Power Indirect form of solar energy (difference in heating between equator and poles combined with Earth s rotation) Today s turbines can generate 20 times more energy than those produced in the 1980s 2nd fastest growing source of energy Germany hopes to get 30% of its electricity from wind by 2030 Capturing only one-fifth of the wind energy at the world s best sites would generate more than seven times the amount of electricity currently used in the world 31 Offshore Wind Farms Wind speeds are often stronger and steadier over water Installation costs are higher Critics site visual pollution Cape Cod, Massachusetts Lake Michigan 32 Wind Energy Challenges Locations with greatest wind potential are often located far away from heavily populated areas (need to expand the current grid system) If winds die down, it requires a back up energy source. Could store wind energy with plug-in hybrids or passing it through water to make hydrogen fuel cells Could store it in the form of compressed air. 33
12 Wind Energy Challenges Does occasionally result in the death of birds (40,000 bird a year) but other sources like windows, buildings, and electrical transmission towers kill over 1 billion birds a year Perceived as noisy and ugly Farmers can earn $3,000-$10,000 per turbine per year 34 Biomass Plant materials and animal wastes that can be directly burned or converted into gas or liquid biofuels Supplies 10% of world s energy (35% in developing countries and 95% in poor countries) Wood chips and waste can be burned to produce electricity and heating systems (half of the heating in Sweden, 80% of downtown St. Paul, Minnesota) Wood is renewable as long as it is not harvested faster than it is grown (choose fast growing plants/trees) Can also use waste materials from crop harvests 35 Biodiesel and Ethanol Produced from plants and plant waste Reduces dependence on imported oil Crops not used faster than they are replenished (no net increase in carbon dioxide emissions) Can be distributed through existing networks Problems: Decreases biodiversity (monocultures), soil degradation (erosion, nutrient leaching), raise food prices 36
13 Is Biodiesel the Answer? Vegetable oil from soybeans, sunflowers, etc. Type of plant used impacts how much biodiesel can be produced 40% more efficient than conventional gasoline engines Could produce 10% of U.S. diesel fuel needs 37 Is Ethanol the Answer? Made through distillation of sugars from sugarcane, corn, and switchgrass Gasohol % ethanol with gasoline can be burned in conventional engines E85-85% ethanol (flex-fuel) Brazil is the 2nd largest ethanol producer (behind U.S.) 45% of Brazil s vehicles run on ethanol Saved $50 billion in oil costs since 1970s (10 times investment in ethanol 38 Is Ethanol the Answer? In the U.S., ethanol is made from corn Huge government subsidies Net energy is only units per unit of fossil fuel May increase climate change because of huge amounts of nitrogen fertilizers used to produce corn (greenhouse gas nitrous oxide) 39
14 Geothermal Heat stored in soil, underground rocks, and fluids Used to heat and cool buildings as well as produce electricity Estimated that using 1% of the heat in the upper 5km of Earth s crust could provide 250 times more energy than oil and natural gas reserves 40 Geothermal Heat Pump Loop of pipes In winter extracts heat from ground In summer deposits heat in ground Fig Hydrothermal Reservoirs Iceland has done this for decades Drill wells into reservoirs to extract steam and hot water which is used to heat buildings and produce electricity Cool water is pumped back to be reheated U.S. is the largest producer of geothermal energy (mostly in California, Nevada, Utah, and Hawaii) Releases one-sixth as much carbon dioxide as a natural gas power plant 42
15 Fig Hydrogen Fuel cells that combine hydrogen gas and oxygen to produce electricity and emit water Would eliminate air pollution problems and reduce climate change (produces no carbon dioxide) 43 Problems with Hydrogen Hydrogen is chemically locked up in water and organic compounds - takes energy to separate it (net energy yield will always be negative) Fuel cells are very expensive Produces no carbon dioxide directly, but the energy to separate hydrogen uses conventional energy sources Pure hydrogen and pure oxygen are explosive 44 Energy Transition Need to: improve efficiency, use a mix of renewable energy resources, and include environmental costs into market prices Supply-side (hard-path) - finding more nonrenewable resources Demand-side (soft-path) - reducing energy waste and depending on a mix of renewable resources Make a shift from centralized macropower systems to smaller, decentralized micropower systems 45
16 Governmental Controls To ensure a sustainable future: Keep prices of selected energy resources low to encourage use Currently R &D (2007) $159 million for solar energy, $303 million for nuclear energy, and $427 million for coal Keep prices high for selected resources to discourage use Emphasize consumer education Inform about incentives and advantages 46 Californian Model Very powerful/influential (On its own, it would be the world s 6th largest economy.) Uses less energy per person than any other U.S. state. Average U.S. citizen uses 12,000 kwh of energy per day Californians use less than 7,000 kwh (save $800 per person) Higher electricity rates (promotes energy efficiency) California has decreased carbon dioxide emissions by 30% 47
Chapter 16. Energy efficiency and renewable energy
 Chapter 16 Energy efficiency and renewable energy Energy efficiency Measure of how much work we can get from each unit of energy we use Improving in US but far behind Europe and Japan 43% is unnecessarily
Chapter 16 Energy efficiency and renewable energy Energy efficiency Measure of how much work we can get from each unit of energy we use Improving in US but far behind Europe and Japan 43% is unnecessarily
February 19, Chapter 17: Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy
 Chapter 17: Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Energy conservation - reducing or eliminating unnecessary waste of energy Energy efficiency - one way to conserve by using less to accomplish same task
Chapter 17: Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Energy conservation - reducing or eliminating unnecessary waste of energy Energy efficiency - one way to conserve by using less to accomplish same task
RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES
 RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES State of Renewable Energy Only 6% of energy used in U.S.; 18% of world s energy use Why so low, if most renewable energies are environmentally friendly and potentially limitless?
RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES State of Renewable Energy Only 6% of energy used in U.S.; 18% of world s energy use Why so low, if most renewable energies are environmentally friendly and potentially limitless?
Renewable Energy Alternatives
 Renewable Energy Alternatives Reasons for Alternative Energy Fossil fuels won t last forever Renewable unlikely to run out Decrease air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions Less dependent on other nations
Renewable Energy Alternatives Reasons for Alternative Energy Fossil fuels won t last forever Renewable unlikely to run out Decrease air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions Less dependent on other nations
4. If the Earth is to continue to use oil its current rate, what must happen for us to sustain this rate?
 CHAPTER 15 Nonrenewable Energy Core Case Study: How Long Will Supplies of Conventional Oil Last? Oil supplies about of the world s energy. When do geologist predict that oil reserves will be 80% depleted?
CHAPTER 15 Nonrenewable Energy Core Case Study: How Long Will Supplies of Conventional Oil Last? Oil supplies about of the world s energy. When do geologist predict that oil reserves will be 80% depleted?
Chapter 13 Renewable Energy and Conservation
 Chapter 13 Renewable Energy and Conservation Overview of Chapter 13 Direct Solar Energy Indirect Solar Energy Wind Biomass Hydropower Geothermal Tidal High and Low Technology Energy Solutions Direct Solar
Chapter 13 Renewable Energy and Conservation Overview of Chapter 13 Direct Solar Energy Indirect Solar Energy Wind Biomass Hydropower Geothermal Tidal High and Low Technology Energy Solutions Direct Solar
Chapter 13 Renewable Energy and Conservation
 Chapter 13 Renewable Energy and Conservation Overview of Chapter 13 Direct Solar Energy Indirect Solar Energy Wind Biomass Hydropower Geothermal Tidal High and Low Technology Energy Solution Direct Solar
Chapter 13 Renewable Energy and Conservation Overview of Chapter 13 Direct Solar Energy Indirect Solar Energy Wind Biomass Hydropower Geothermal Tidal High and Low Technology Energy Solution Direct Solar
General Energy Use & Conservation Measures
 General Energy Use & Conservation Measures What is Energy? The ability to do work (create motion or change matter) Ways to Measure Energy Joule (J) BTU British Thermal Unit amount of energy needed to heat
General Energy Use & Conservation Measures What is Energy? The ability to do work (create motion or change matter) Ways to Measure Energy Joule (J) BTU British Thermal Unit amount of energy needed to heat
Chapter 17 Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy. It s A Small World After All
 Outline Reducing energy waste and improving energy efficiency A. Energy efficiency is a measure of the useful energy produced compared to the energy that is converted to low-quality heat energy. 1. Energy
Outline Reducing energy waste and improving energy efficiency A. Energy efficiency is a measure of the useful energy produced compared to the energy that is converted to low-quality heat energy. 1. Energy
ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE
 Advanced Placement ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE Renewable Energy STUDENT 2014 Renewable Energy The worldwide demand for energy has soared. Human population is increasing exponentially with the emergence of large
Advanced Placement ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE Renewable Energy STUDENT 2014 Renewable Energy The worldwide demand for energy has soared. Human population is increasing exponentially with the emergence of large
Chapter 18 Renewable Energy
 Chapter 18 Renewable Energy MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Habitat loss, soil erosion, and air pollution are disadvantages of which renewable energy source? a. solar c. biomass fuel b. wind d. moving water C DIF:
Chapter 18 Renewable Energy MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Habitat loss, soil erosion, and air pollution are disadvantages of which renewable energy source? a. solar c. biomass fuel b. wind d. moving water C DIF:
Renewable Energy Today
 Chapter 18 Renewable Energy Today Renewable Energy energy from a source that is constantly being reformed. Many governments are planning to increase their use of renewable energy resources. This will reduce
Chapter 18 Renewable Energy Today Renewable Energy energy from a source that is constantly being reformed. Many governments are planning to increase their use of renewable energy resources. This will reduce
Would / Does tidal power work? How does it work? In what ways is tidal power an improvement on wind and solar power?
 APES Chapter 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability Intro: Energy from the Moon? Would / Does tidal power work? How does it work? In what ways is tidal power an improvement on wind and solar power? What are
APES Chapter 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability Intro: Energy from the Moon? Would / Does tidal power work? How does it work? In what ways is tidal power an improvement on wind and solar power? What are
Ch. 16 Overview Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy
 Name Forensic Science Hour Date Ch. 16 Overview Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy Core Case Study 1. What is the Rocky Mountain Institute (RMI)? 2. How much energy is supplied by solar energy : Hot
Name Forensic Science Hour Date Ch. 16 Overview Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy Core Case Study 1. What is the Rocky Mountain Institute (RMI)? 2. How much energy is supplied by solar energy : Hot
Section 1: Renewable Energy Today
 Section 1: Renewable Energy Today Preview Bellringer Objectives Renewable Energy Solar Energy-Power from the Sun Passive Solar Heating Active Solar Heating Photovoltaic Cells Section 1: Renewable Energy
Section 1: Renewable Energy Today Preview Bellringer Objectives Renewable Energy Solar Energy-Power from the Sun Passive Solar Heating Active Solar Heating Photovoltaic Cells Section 1: Renewable Energy
Chapter 14 area strip mining contour strip mining high-grade ore low-grade ore mineral mineral resource mountaintop removal open-pit mining
 Vocabulary: Directions: Review key vocabulary, words may appear in quizzes and/or tests. You are not required to write the definitions but are encouraged to review them online Chapter 14 area strip mining
Vocabulary: Directions: Review key vocabulary, words may appear in quizzes and/or tests. You are not required to write the definitions but are encouraged to review them online Chapter 14 area strip mining
Chapter 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability. Monday, February 26, 18
 Chapter 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability Module 37 Conservation, Efficiency, and Renewable Energy After reading this module you should be able to describe strategies to conserve energy and increase energy
Chapter 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability Module 37 Conservation, Efficiency, and Renewable Energy After reading this module you should be able to describe strategies to conserve energy and increase energy
Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy Resources
 Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy Resources Discuss with your table partner: What is the difference between energy conservation and energy efficiency? Give an example of each. Improving the percentage
Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy Resources Discuss with your table partner: What is the difference between energy conservation and energy efficiency? Give an example of each. Improving the percentage
Chapter 17. Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy REDUCING ENERGY WASTE AND IMPROVING ENERGY EFFICIENCY
 Chapter 17 Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy REDUCING ENERGY WASTE AND IMPROVING ENERGY EFFICIENCY Flow of commercial energy through the U.S. economy. 84% of all commercial energy used in the U.S.
Chapter 17 Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy REDUCING ENERGY WASTE AND IMPROVING ENERGY EFFICIENCY Flow of commercial energy through the U.S. economy. 84% of all commercial energy used in the U.S.
Period 26 Solutions: Using Energy Wisely
 Period 26 Solutions: Using Energy Wisely Activity 26.1: Comparison of Energy Sources for Generating Electricity 1) Comparison of energy sources a) Fill in the table below to describe the advantages and
Period 26 Solutions: Using Energy Wisely Activity 26.1: Comparison of Energy Sources for Generating Electricity 1) Comparison of energy sources a) Fill in the table below to describe the advantages and
Renewable Energy Resources
 Visualizing Environmental Science Renewable Energy Resources Chapter 18 Chapter 7 [chapter opener image] Copyright Reducing Heat Loss Two strategies to decrease reliance on fossil fuels Developing alternative
Visualizing Environmental Science Renewable Energy Resources Chapter 18 Chapter 7 [chapter opener image] Copyright Reducing Heat Loss Two strategies to decrease reliance on fossil fuels Developing alternative
Achieving Energy Sustainability. Renewable Energy 2/23/2015. February 23, 2015 Mr. Alvarez
 Achieving Energy Sustainability February 23, 2015 Mr. Alvarez Renewable Energy Renewable Energy- can be rapidly regenerated, and some can never be depleted, no matter how much of them we use. Potentially
Achieving Energy Sustainability February 23, 2015 Mr. Alvarez Renewable Energy Renewable Energy- can be rapidly regenerated, and some can never be depleted, no matter how much of them we use. Potentially
Energy and Global Issues
 Energy and Global Issues Chemical reactions Reactions that release heat are exothermic Reactions that absorb heat from surroundings are endothermic The energy involved in chemical reactions is measured
Energy and Global Issues Chemical reactions Reactions that release heat are exothermic Reactions that absorb heat from surroundings are endothermic The energy involved in chemical reactions is measured
RENEWABLE ENERGY IN THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST
 RENEWABLE ENERGY IN THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST Renewable energy comes from natural sources that are continually and sustainably replenished such as the sun, the flow of water, or other natural processes. By
RENEWABLE ENERGY IN THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST Renewable energy comes from natural sources that are continually and sustainably replenished such as the sun, the flow of water, or other natural processes. By
Biomass. Coal. 10 Intermediate Energy Infobook Activities. Description of biomass: Renewable or nonrenewable: Description of photosynthesis:
 Biomass Description of biomass: Description of photosynthesis: Ways we turn biomass into energy we can use: Who uses biomass and for what purposes: Effect of using biomass on the environment: Important
Biomass Description of biomass: Description of photosynthesis: Ways we turn biomass into energy we can use: Who uses biomass and for what purposes: Effect of using biomass on the environment: Important
Reliant on fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas)
 Reliant on fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) Those will not last forever, need to have a back up plan Using fossil fuels creates greenhouse gases, which impact climate change Renewable energy is better
Reliant on fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) Those will not last forever, need to have a back up plan Using fossil fuels creates greenhouse gases, which impact climate change Renewable energy is better
2. What is cyanide heap leaching? What are some environmental impacts of using it?
 Name: UNIT 7 (Ch 14, 15 & 16) Reading Questions Chapter 14 Geology and Nonrenewable Resources Core Case Study: Environmental Effects of Gold Mining 1. Where does most mining waste end up? How much is often
Name: UNIT 7 (Ch 14, 15 & 16) Reading Questions Chapter 14 Geology and Nonrenewable Resources Core Case Study: Environmental Effects of Gold Mining 1. Where does most mining waste end up? How much is often
Environmental Science Sixth Edition
 Environmental Science Sixth Edition Daniel B. Botkin Edward A. Keller 978--47-499-7 CHAPTER 19 Alternative Energy and the Environment Introduction Fossil Fuels supply about 9% of energy All others are
Environmental Science Sixth Edition Daniel B. Botkin Edward A. Keller 978--47-499-7 CHAPTER 19 Alternative Energy and the Environment Introduction Fossil Fuels supply about 9% of energy All others are
Solar panels The Fizzics Organisation
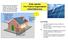 Most solar panels installed on houses in the last few years convert the energy of sunlight directly into electrical energy. These are photovoltaic cells. Solar panels 3 This electricity can be used around
Most solar panels installed on houses in the last few years convert the energy of sunlight directly into electrical energy. These are photovoltaic cells. Solar panels 3 This electricity can be used around
CHAPTER - 14 SOURCES OF ENERGY
 CHAPTER - 14 SOURCES OF ENERGY PREPARED BY NIKHIL V JONES 1) Characteristics of a good source of fuel :- i) It should have a high energy output per unit mass or volume. ii) It should be easily available.
CHAPTER - 14 SOURCES OF ENERGY PREPARED BY NIKHIL V JONES 1) Characteristics of a good source of fuel :- i) It should have a high energy output per unit mass or volume. ii) It should be easily available.
NONRENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES
 1 2 3 4 5 6 ENERGY Chapter 13 NONRENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES Two primary categories of nonrenewable energy resources are fossil fuels and nuclear fuels. Fossil fuels are derived from biological material;
1 2 3 4 5 6 ENERGY Chapter 13 NONRENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES Two primary categories of nonrenewable energy resources are fossil fuels and nuclear fuels. Fossil fuels are derived from biological material;
Biology 112 Introduction to Ecology. QUIZZAM Energy. Chapter Number 10
 Chapter Number 10 1. Which of the following is a true statement regarding sustainable building design? 1. Construction costs are usually less than traditional building practices. 2. There are currently
Chapter Number 10 1. Which of the following is a true statement regarding sustainable building design? 1. Construction costs are usually less than traditional building practices. 2. There are currently
Alternative Fuels, How to improve air quality
 Alternative Fuels, How to improve air quality 1 1 1 1 1 1 Introduction Nearly one-fifth of pollution in the USA is caused by cars and trucks. Fossil fuel-powered transportation is the primary contributor
Alternative Fuels, How to improve air quality 1 1 1 1 1 1 Introduction Nearly one-fifth of pollution in the USA is caused by cars and trucks. Fossil fuel-powered transportation is the primary contributor
Natural Resources. Renewable Energy Resources. Renewable Energy Resources
 Natural Resources Renewable Energy Resources What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Natural Resources Renewable Energy Resources What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Overview of renewable energy
 Overview of renewable energy Outline What is renewable energy? Renewable energy sources Renewable energy technologies: - Characteristics - Uses What is renewable energy? Energy that doesn t run out! Energy
Overview of renewable energy Outline What is renewable energy? Renewable energy sources Renewable energy technologies: - Characteristics - Uses What is renewable energy? Energy that doesn t run out! Energy
Name Date Class. How do fuels provide energy? What are the three major fossil fuels? Why are fossil fuels considered nonrenewable resources?
 Chapter 12 Energy and Material Resources Section 1 Summary Fossil Fuels How do fuels provide energy? What are the three major fossil fuels? Why are fossil fuels considered nonrenewable resources? A fuel
Chapter 12 Energy and Material Resources Section 1 Summary Fossil Fuels How do fuels provide energy? What are the three major fossil fuels? Why are fossil fuels considered nonrenewable resources? A fuel
Alternate Energy Sources, part II
 Alternate Energy Sources, part II FIGURE V01_T1: Bird kills from commercial wind turbines Tidal Power Rise and fall of water used to move turbines, producing electricity Clean energy no water or air pollution
Alternate Energy Sources, part II FIGURE V01_T1: Bird kills from commercial wind turbines Tidal Power Rise and fall of water used to move turbines, producing electricity Clean energy no water or air pollution
Name Class Date. Conventional Energy Resources
 Energy Resources SECTION 25.1 Conventional Energy Resources In your textbook, read about energy resources on Earth. For each statement below, write true or false. 1. The Sun is the ultimate source of most
Energy Resources SECTION 25.1 Conventional Energy Resources In your textbook, read about energy resources on Earth. For each statement below, write true or false. 1. The Sun is the ultimate source of most
Lesson Plan Time Requirements: Objectives: Materials: Methods: Lesson Information: Clean, Green Power (Target: Grades 1-4)
 Lesson Plan 050106 Clean, Green Power (Target: Grades 1-4) Time Requirements: 1. 30-minutes during science or reading time Objectives: 1. Create awareness for alternative energies 2. Create awareness for
Lesson Plan 050106 Clean, Green Power (Target: Grades 1-4) Time Requirements: 1. 30-minutes during science or reading time Objectives: 1. Create awareness for alternative energies 2. Create awareness for
Chapter: Conserving Resources
 Table of Contents Chapter: Conserving Resources Section 1: Resources Section 2: Pollution Section 3: The Three Rs of Conservation *Problems related to the use of Fossil Fuels Limited availability Pollution
Table of Contents Chapter: Conserving Resources Section 1: Resources Section 2: Pollution Section 3: The Three Rs of Conservation *Problems related to the use of Fossil Fuels Limited availability Pollution
Natural Resources. Mr. Dvorin Muir Middle School
 Natural Resources Mr. Dvorin Muir Middle School NONRENEWABLE AND RENEWABLE RESOURCES HMMMM... What do you think nonrenewable resources are? Break it down... Nonrenewable? Resource? NONRENEWABLE RESOURCES
Natural Resources Mr. Dvorin Muir Middle School NONRENEWABLE AND RENEWABLE RESOURCES HMMMM... What do you think nonrenewable resources are? Break it down... Nonrenewable? Resource? NONRENEWABLE RESOURCES
Environmental Resources: Renewable & Non-Renewable Resources & Energy
 Directions: Fill in the blanks. Renewable Resources & Energy Segment 1. Renewable Resources Are significant resources which can be replenished and reused to reduce negative environmental Are used as a
Directions: Fill in the blanks. Renewable Resources & Energy Segment 1. Renewable Resources Are significant resources which can be replenished and reused to reduce negative environmental Are used as a
Chapter 16 ALTERNATIVE ENERGY AND THE ENVIRONMENT
 Case Study: Using Wind Power in New Ways for an Old Application Use of traditional wind power to propel cargo vessels had been pretty much abandoned due to expense and difficulty maintaining equipment
Case Study: Using Wind Power in New Ways for an Old Application Use of traditional wind power to propel cargo vessels had been pretty much abandoned due to expense and difficulty maintaining equipment
CREATIVE SPACES INFORMATION PACK THREE SUSTAINABLE DESIGN
 SUSTAINABLE DESIGN The information contained in this presentation is for general information purposes only and it is intended that there will be strictly no commercial gain from its production. The content
SUSTAINABLE DESIGN The information contained in this presentation is for general information purposes only and it is intended that there will be strictly no commercial gain from its production. The content
CREATIVE SPACES 2013 INFORMATION PACK THREE SUSTAINABLE DESIGN
 SUSTAINABLE DESIGN The information contained in this presentation is for general information purposes only and it is intended that there will be strictly no commercial gain from its production. The content
SUSTAINABLE DESIGN The information contained in this presentation is for general information purposes only and it is intended that there will be strictly no commercial gain from its production. The content
Ch 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability
 Ch 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability Module 38 Biomass and Water Module 39 Solar, Wind, Geothermal, and Hydrogen 4/16/18 Variation in Solar Radiation Potential Active Solar Energy captured from sunlight
Ch 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability Module 38 Biomass and Water Module 39 Solar, Wind, Geothermal, and Hydrogen 4/16/18 Variation in Solar Radiation Potential Active Solar Energy captured from sunlight
Fuel Information Sheet
 Wood (Biomass) Maine has 17 million acres of forest. Wood is a renewable energy source; we can grow more trees and manage forested areas. Wood must be transported to where it is used. Wood requires storage
Wood (Biomass) Maine has 17 million acres of forest. Wood is a renewable energy source; we can grow more trees and manage forested areas. Wood must be transported to where it is used. Wood requires storage
Chapter: Energy and Energy Resources
 Table of Contents Chapter: Energy and Energy Resources Section 1: What is energy? Section 2: Energy Transformations Section 3: Sources of Energy 1 What is energy? The Nature of Energy When an object has
Table of Contents Chapter: Energy and Energy Resources Section 1: What is energy? Section 2: Energy Transformations Section 3: Sources of Energy 1 What is energy? The Nature of Energy When an object has
Earth s Energy Resources: GeothermaL
 Earth s Energy Resources: GeothermaL Geothermal energy comes from heat deep under the ground. This energy is produced in the core of the Earth. The heat from the core can melt rock into magma. The magma
Earth s Energy Resources: GeothermaL Geothermal energy comes from heat deep under the ground. This energy is produced in the core of the Earth. The heat from the core can melt rock into magma. The magma
Ch 21. New Renewable Energy Alternatives. Part 2: Environmental Issues and the Search for Solutions
 Ch 21 New Renewable Energy Alternatives Part 2: Environmental Issues and the Search for Solutions PowerPoint Slides prepared by Jay Withgott and Heidi Marcum Copyright 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
Ch 21 New Renewable Energy Alternatives Part 2: Environmental Issues and the Search for Solutions PowerPoint Slides prepared by Jay Withgott and Heidi Marcum Copyright 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
Readings for the assignment: Renewables assignment: Questions. Amory Lovins. Environmental Issues & Problems ENV 150 Guillaume Mauger
 Environmental Issues & Problems ENV 150 Guillaume Mauger Today: Renewable Energy Assignment: Research your Renewable Energy topic: - Hydrokinetic: Waves - Hydrokinetic: Tidal Power - Hydroelectric - Passive
Environmental Issues & Problems ENV 150 Guillaume Mauger Today: Renewable Energy Assignment: Research your Renewable Energy topic: - Hydrokinetic: Waves - Hydrokinetic: Tidal Power - Hydroelectric - Passive
RENEWABLE ENERGY RESOURCES
 RENEWABLE ENERGY RESOURCES Energy Efficiency Energy efficiency the amount of useful energy produced compared to the amount wasted as heat (2 nd Law of Thermodynamics); built into the device or system,
RENEWABLE ENERGY RESOURCES Energy Efficiency Energy efficiency the amount of useful energy produced compared to the amount wasted as heat (2 nd Law of Thermodynamics); built into the device or system,
Renewable Energy Sources. Lesson Plan: NRES F1-2
 Renewable Energy Sources Lesson Plan: NRES F1-2 1 Anticipated Problems 1. What are renewable energy sources? 2. What are advantages and disadvantages of renewable energy sources? 2 Terms biomass biopower
Renewable Energy Sources Lesson Plan: NRES F1-2 1 Anticipated Problems 1. What are renewable energy sources? 2. What are advantages and disadvantages of renewable energy sources? 2 Terms biomass biopower
3/26/2015. Renewable Energy Alternatives. Chapter 16. Renewable energy sources. New renewables provide little energy. Alternatives to fossil fuels
 Chapter 16 Renewable energy sources Essential Environment: The Science Behind the Stories 4th Edition Withgott/Laposata 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Renewable Energy Alternatives Lecture Presentations
Chapter 16 Renewable energy sources Essential Environment: The Science Behind the Stories 4th Edition Withgott/Laposata 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Renewable Energy Alternatives Lecture Presentations
SCI181 exam 2 test #3 Page 1
 SI181 exam 2 test #3 Page 1 Name: ate: 1 Which of the following would most reduce current U.S. reliance on foreign oil imports? Switching to energy-efficient lightbulbs ontinuing to raise the fuel efficiency
SI181 exam 2 test #3 Page 1 Name: ate: 1 Which of the following would most reduce current U.S. reliance on foreign oil imports? Switching to energy-efficient lightbulbs ontinuing to raise the fuel efficiency
SCI181 exam 2 test #2 Page 1
 SI181 exam 2 test #2 Page 1 Name: ate: 1 Which of the following sectors is most heavily dependent on oil? Industrial Residential Transportation ommercial 2 One way to reduce energy use is to find more
SI181 exam 2 test #2 Page 1 Name: ate: 1 Which of the following sectors is most heavily dependent on oil? Industrial Residential Transportation ommercial 2 One way to reduce energy use is to find more
Energy Resources. Nonrenewable Energy Resources. Fossil Fuels
 Energy Resources Renewable resources are resources that can be replaced within a human life span or as they are used. Nonrenewable resources are resources that exist in limited amounts and cannot be replaced
Energy Resources Renewable resources are resources that can be replaced within a human life span or as they are used. Nonrenewable resources are resources that exist in limited amounts and cannot be replaced
By Mark Z. Jacobson Stanford University November 11, 2016
 Repowering 100% of all Energy in the United States and the World for 100% of the People at Low Cost With Clean and Renewable Wind, Water, and Sunlight (WWS) By Mark Z. Jacobson Stanford University November
Repowering 100% of all Energy in the United States and the World for 100% of the People at Low Cost With Clean and Renewable Wind, Water, and Sunlight (WWS) By Mark Z. Jacobson Stanford University November
Chapter 13. Achieving Energy Sustainability
 Chapter 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability Energy from the Moon Tidal energy Moon power Capture energy in moving water Clean source of energy Efficient source of energy Roosevelt Island First commercial
Chapter 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability Energy from the Moon Tidal energy Moon power Capture energy in moving water Clean source of energy Efficient source of energy Roosevelt Island First commercial
FUTURE WITH RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES
 FUTURE WITH RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES Electronics Heat Transportation Computers Food Preparation Communication And Many More Fossil Fuels Oil Coal Natural Gas Main types of renewable energy Solar energy
FUTURE WITH RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES Electronics Heat Transportation Computers Food Preparation Communication And Many More Fossil Fuels Oil Coal Natural Gas Main types of renewable energy Solar energy
Chapter 16. Renewable Energy Alternatives. Lecture Presentations prepared by Reggie Cobb Nash Community College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Renewable Energy Alternatives Lecture Presentations prepared by Reggie Cobb Nash Community College This lecture will help you understand: Reasons for seeking alternative fuels Major sources
Chapter 16 Renewable Energy Alternatives Lecture Presentations prepared by Reggie Cobb Nash Community College This lecture will help you understand: Reasons for seeking alternative fuels Major sources
Chapter 16: Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy
 Chapter 16: Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy Energy Units Power = Energy/Time = Work/Time: watts Energy = Power x Time: watt-hour kwh = kilowatt-hour (10 3 ) MWh = megawatt-hours (10 6 ) GWh = gigawatt-hours
Chapter 16: Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy Energy Units Power = Energy/Time = Work/Time: watts Energy = Power x Time: watt-hour kwh = kilowatt-hour (10 3 ) MWh = megawatt-hours (10 6 ) GWh = gigawatt-hours
Exploring Energy Science Texts for Close Reading
 Science Texts for Close Reading Solar Energy Solar energy is a way to harness sunlight for heating or electricity. There are different ways to convert sunlight into usable energy. Concentrated solar power
Science Texts for Close Reading Solar Energy Solar energy is a way to harness sunlight for heating or electricity. There are different ways to convert sunlight into usable energy. Concentrated solar power
Where will our energy come from? Ch. 16. All from the Sun
 Where will our energy come from? Ch. 16 All from the Sun A problem: Dependence on imported oil Cost to the economy: 350 billion dollars per year (2011 prices) Transferred to foreign (hostile) oil producers,
Where will our energy come from? Ch. 16 All from the Sun A problem: Dependence on imported oil Cost to the economy: 350 billion dollars per year (2011 prices) Transferred to foreign (hostile) oil producers,
RENEWABLE SOURCES OF ENERGY. Ajay Kumar Jakhar
 RENEWABLE SOURCES OF ENERGY Ajay Kumar Jakhar Renewable energy is energy that comes from resources which are continually replenished such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves and geothermal heat. In
RENEWABLE SOURCES OF ENERGY Ajay Kumar Jakhar Renewable energy is energy that comes from resources which are continually replenished such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves and geothermal heat. In
SOLAR ENERGY INTRODUCTION:
 INTRODUCTION: SOLAR ENERGY Solar energy is energy that comes from the sun. Every day the sun radiates an enormous amount of energy. The sun radiates more energy in one second than people have used since
INTRODUCTION: SOLAR ENERGY Solar energy is energy that comes from the sun. Every day the sun radiates an enormous amount of energy. The sun radiates more energy in one second than people have used since
Section 1. Electricity and Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 7 Earth s Natural Resources Section 1 Electricity and Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Compare energy resources used to generate electricity in the United
Chapter 7 Earth s Natural Resources Section 1 Electricity and Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Compare energy resources used to generate electricity in the United
What Are Our Alternatives, If Fossil Fuels Are a Problem?
 What Are Our Alternatives, If Fossil Fuels Are a Problem? George W. Bush has given us one reason why we need to make changes Unstable foreign oil supply. Al Gore has given us another reason Climate change.
What Are Our Alternatives, If Fossil Fuels Are a Problem? George W. Bush has given us one reason why we need to make changes Unstable foreign oil supply. Al Gore has given us another reason Climate change.
Student Guidebook Energy Workshops
 2017-18 Student Guidebook Energy Workshops Name School Energy Sources Boards Use the Energy Source Boards to connect the box on the right with the box on the left that finishes the sentence correctly.
2017-18 Student Guidebook Energy Workshops Name School Energy Sources Boards Use the Energy Source Boards to connect the box on the right with the box on the left that finishes the sentence correctly.
16.3 Electric generators and transformers
 ElEctromagnEts and InductIon Chapter 16 16.3 Electric generators and transformers Motors transform electrical energy into mechanical energy. Electric generators do the opposite. They transform mechanical
ElEctromagnEts and InductIon Chapter 16 16.3 Electric generators and transformers Motors transform electrical energy into mechanical energy. Electric generators do the opposite. They transform mechanical
Chapter 16: Energy: Some Basics
 Chapter 16: Energy: Some Basics Energy Crisis in Ancient Greece and Rome Greeks and Romans used wood to heat there homes. As local supplies ran out had to bring it in from farther away. Eventually both
Chapter 16: Energy: Some Basics Energy Crisis in Ancient Greece and Rome Greeks and Romans used wood to heat there homes. As local supplies ran out had to bring it in from farther away. Eventually both
Chapter 10 - Energy Conservation
 Chapter 10 - Energy Conservation Introduction... 211 Wind, Solar, and Geothermal Energy... 211 Incentives... 212 Building Considerations... 213 Examples of Energy Conservation in Berks County.. 213 Energy
Chapter 10 - Energy Conservation Introduction... 211 Wind, Solar, and Geothermal Energy... 211 Incentives... 212 Building Considerations... 213 Examples of Energy Conservation in Berks County.. 213 Energy
Energy Source Uses. Biomass
 Energy Source Uses Biomass Uses: produce heat to manufacture products, candles, fireplaces, and campfires, woodstoves, fireplaces, and campfires, ethanol and gasohol for vehicles, waste to energy and co
Energy Source Uses Biomass Uses: produce heat to manufacture products, candles, fireplaces, and campfires, woodstoves, fireplaces, and campfires, ethanol and gasohol for vehicles, waste to energy and co
batteries, 7, 14, 16, 17, 22 ethanol, fuel cells, 14, 15 gasoline, conservation, 21, 22 consumption, 4, 5, 21 hydrogen, 12 15
 pollutants (n.) dirt or debris in the air or on the ground (p. 5) radiant (adj.) brightly shining (p. 7) renewable a supply of something that can be resource (n.) replaced; a source of energy that is not
pollutants (n.) dirt or debris in the air or on the ground (p. 5) radiant (adj.) brightly shining (p. 7) renewable a supply of something that can be resource (n.) replaced; a source of energy that is not
Introduction to Energy Topics
 Introduction to Energy Topics Energy Path 2018 Thomas Cleary, M.Engr. Energy Units of Measurement The unit of energy: Joule (SI system). British Thermal Unit BTU (U.S. Customary system) 1British Thermal
Introduction to Energy Topics Energy Path 2018 Thomas Cleary, M.Engr. Energy Units of Measurement The unit of energy: Joule (SI system). British Thermal Unit BTU (U.S. Customary system) 1British Thermal
Chapter: Conserving Resources
 Table of Contents Chapter: Conserving Resources Section 1: Resources Section 2: Pollution Section 3: The Three Rs of Conservation Chapter 19 Section 1- Natural Resources What are fossil fuels? *Fossil
Table of Contents Chapter: Conserving Resources Section 1: Resources Section 2: Pollution Section 3: The Three Rs of Conservation Chapter 19 Section 1- Natural Resources What are fossil fuels? *Fossil
Curriculum Connections for re- energy.ca
 Curriculum Connections for re- energy.ca Science, Grades 6 to 12 Alberta & Northwest Territories SCIENCE 7 Heat and Temperature Overall apply an understanding of heat and temperature in interpreting natural
Curriculum Connections for re- energy.ca Science, Grades 6 to 12 Alberta & Northwest Territories SCIENCE 7 Heat and Temperature Overall apply an understanding of heat and temperature in interpreting natural
The Bright Prospects of Renewable Energy
 The Bright Prospects of Renewable Energy George Philippidis, Ph.D. Associate Professor Patel College of Global Sustainability University of South Florida (USF) Contact information: gphilippidis@usf.edu
The Bright Prospects of Renewable Energy George Philippidis, Ph.D. Associate Professor Patel College of Global Sustainability University of South Florida (USF) Contact information: gphilippidis@usf.edu
Explain how energy is conserved within a closed system. Explain the law of conservation of energy.
 Section 3 Conservation of Energy Objectives Explain how energy is conserved within a closed system. Explain the law of conservation of energy. Give examples of how thermal energy is always a result of
Section 3 Conservation of Energy Objectives Explain how energy is conserved within a closed system. Explain the law of conservation of energy. Give examples of how thermal energy is always a result of
8. Confusion About Renewable Energy. Gail Tverberg Energy Economics and Analysis Modeling
 8. Confusion About Renewable Energy Gail Tverberg Energy Economics and Analysis Modeling We get free energy from the sun! Physicists describe the situation as a thermodynamically open system! Humans, animals,
8. Confusion About Renewable Energy Gail Tverberg Energy Economics and Analysis Modeling We get free energy from the sun! Physicists describe the situation as a thermodynamically open system! Humans, animals,
THE ALTERNATIVE GENERATION Emerging technologies for renewable energy sources
 Community Research EUROPEAN COMMISSION THE ALTERNATIVE GENERATION Emerging technologies for renewable energy sources T he introduction of renewable energy sources will diversify European energy supply
Community Research EUROPEAN COMMISSION THE ALTERNATIVE GENERATION Emerging technologies for renewable energy sources T he introduction of renewable energy sources will diversify European energy supply
ENERGY 1: RESOURCES. Ppt. by Robin D. Seamon
 ENERGY 1: RESOURCES Ppt. by Robin D. Seamon Types of Energy Energy: the ability to do work (joules) (amt. of E to lift an apple 1m) Energy comes in many forms. FORMS of ENERGY: Thermal energy: energy from
ENERGY 1: RESOURCES Ppt. by Robin D. Seamon Types of Energy Energy: the ability to do work (joules) (amt. of E to lift an apple 1m) Energy comes in many forms. FORMS of ENERGY: Thermal energy: energy from
10 Energy Consumption. Copyright 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
 10 Energy Consumption Copyright Overview of Chapter 10 Energy Consumption and Policy Energy Efficiency and Conservation Electricity, Hydrogen and Energy Storage Energy Policy Energy and Climate Change
10 Energy Consumption Copyright Overview of Chapter 10 Energy Consumption and Policy Energy Efficiency and Conservation Electricity, Hydrogen and Energy Storage Energy Policy Energy and Climate Change
Power Technologies. Question. Answer. Energy is the ability to do work or change the system. Answer. Question. What are the various sources of energy?
 What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work or change the system. What are the various sources of energy? Fossil fuels Oil (Petroleum) Propane Natural gas Coal Alternative fuels Nuclear Wind Solar
What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work or change the system. What are the various sources of energy? Fossil fuels Oil (Petroleum) Propane Natural gas Coal Alternative fuels Nuclear Wind Solar
Alternative Fuels. Reduce our dependence on the fossil fuels.
 Alternative Fuels Reduce our dependence on the fossil fuels. News Article http://news.nationalgeographic.com/ne ws/2009/09/090904-farm-energy.html Alternatives to Fossil Fuels 80% of our energy comes from
Alternative Fuels Reduce our dependence on the fossil fuels. News Article http://news.nationalgeographic.com/ne ws/2009/09/090904-farm-energy.html Alternatives to Fossil Fuels 80% of our energy comes from
2010 Culver Media, LLC 1
 Alternating current Also known as AC power, alternating current is electricity that reverses direction within a circuit. The electricity we use in our homes does this 120 times per second. Appliances Devices
Alternating current Also known as AC power, alternating current is electricity that reverses direction within a circuit. The electricity we use in our homes does this 120 times per second. Appliances Devices
Renewable & Low Carbon Technologies
 Services and Utilities Renewable & Low Carbon Technologies An overview Recommended Reading BSRIA Illustrated Guide to Renewable Technologies. What do we mean by renewable technologies? Generating electricity
Services and Utilities Renewable & Low Carbon Technologies An overview Recommended Reading BSRIA Illustrated Guide to Renewable Technologies. What do we mean by renewable technologies? Generating electricity
Renewable vs. Non-Renewable Energy
 Renewable vs. Non-Renewable Energy In today s society, we are heavily reliant on electrical energy to complete a lot of the work that we do. It seems to be the most functional form of energy and the most
Renewable vs. Non-Renewable Energy In today s society, we are heavily reliant on electrical energy to complete a lot of the work that we do. It seems to be the most functional form of energy and the most
Chapter 21 Environment: The Science behind the Stories 4th Edition Withgott/Brennan
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 21 Environment: The Science behind the Stories 4th Edition Withgott/Brennan This lecture will help you understand: The major sources of renewable energy Solar energy Wind energy
Lecture Outlines Chapter 21 Environment: The Science behind the Stories 4th Edition Withgott/Brennan This lecture will help you understand: The major sources of renewable energy Solar energy Wind energy
WORK Potential Kinetic
 Energy What is energy? - Ability to do WORK - The transfer of energy is work, power is the rate at which energy is transferred. - There are many forms of energy (chemical, mechanical, nuclear, thermal,
Energy What is energy? - Ability to do WORK - The transfer of energy is work, power is the rate at which energy is transferred. - There are many forms of energy (chemical, mechanical, nuclear, thermal,
Alternative Energy. 1. Solar 2. Biofuels (biomass) 3. Nuclear. 4. Fuel Cells 5. Wind 6. Hydroelectric 7. Geothermal 8. Tidal (wave power)
 Alternative Energy 1. Solar 2. Biofuels (biomass) 3. Nuclear a. Fusion b. Fission 4. Fuel Cells 5. Wind 6. Hydroelectric 7. Geothermal 8. Tidal (wave power) Solar Energy Solar energy uses energy from the
Alternative Energy 1. Solar 2. Biofuels (biomass) 3. Nuclear a. Fusion b. Fission 4. Fuel Cells 5. Wind 6. Hydroelectric 7. Geothermal 8. Tidal (wave power) Solar Energy Solar energy uses energy from the
3. Forms when pre-existing rock is changed due to high temperatures, pressure, or chemicals.
 Unit 4 ENERGY Practice Quiz 1. The North American and Eurasian plates are moving apart from one another and creating the Mid-Atlantic ridge. This is an example of what type of plate boundary? (A) Convergent
Unit 4 ENERGY Practice Quiz 1. The North American and Eurasian plates are moving apart from one another and creating the Mid-Atlantic ridge. This is an example of what type of plate boundary? (A) Convergent
1) Fact, Advantage, or Disadvantage? 2) How we use Our Energy Sources Solar Energy. How Do We Use Our Energy Sources?
 1) Fact, Advantage, or Disadvantage? 2) How we use Our Energy Sources Solar Energy 3) Graphs (homework??) 4) Study for test on Monday!!! How Do We Use Our Energy Sources? Biomass Coal Geothermal Hydropower
1) Fact, Advantage, or Disadvantage? 2) How we use Our Energy Sources Solar Energy 3) Graphs (homework??) 4) Study for test on Monday!!! How Do We Use Our Energy Sources? Biomass Coal Geothermal Hydropower
4th Grade. Energy and Natural Resources.
 1 4th Grade Energy and Natural Resources 2015 11 18 www.njctl.org 2 Energy and Natural Resources Human Energy Use Click on the topic to go to that section Renewable Energy Non Renewable Energy Environmental
1 4th Grade Energy and Natural Resources 2015 11 18 www.njctl.org 2 Energy and Natural Resources Human Energy Use Click on the topic to go to that section Renewable Energy Non Renewable Energy Environmental
- renewable - cheap - no pollution. - expensive equipment - no energy on cloudy or rainy days
 Alternative Energy Solar Power The heat from the sun can be used to heat water for use in pools and stoves. Solar power can also be used to make electricity. In California's Mojave Desert, there are huge
Alternative Energy Solar Power The heat from the sun can be used to heat water for use in pools and stoves. Solar power can also be used to make electricity. In California's Mojave Desert, there are huge
Environmental Science 101 Energy. Fall Learning Objectives: Reading Assignment:
 1 Environmental Science 101 Energy Fall 2012 Lecture Outline: 9. RENEWABLE ENERGY RESOURCES WIND AND SOLAR A. Solar Energy B. Wind Energy Terms You Should Know: Passive solar system Active solar system
1 Environmental Science 101 Energy Fall 2012 Lecture Outline: 9. RENEWABLE ENERGY RESOURCES WIND AND SOLAR A. Solar Energy B. Wind Energy Terms You Should Know: Passive solar system Active solar system
Ch 16 BIOL 101. Iceland. aims to convert to an economy based completely on renewable energy. excellent sources of geothermal energy and hydropower
 Ch 16 BIOL 101 Iceland aims to convert to an economy based completely on renewable energy excellent sources of geothermal energy and hydropower It also uses imported fossil fuels weak link in their economy
Ch 16 BIOL 101 Iceland aims to convert to an economy based completely on renewable energy excellent sources of geothermal energy and hydropower It also uses imported fossil fuels weak link in their economy
ENERGY FORMS & CONVERSION
 1 ENERGY FORMS & CONVERSION 1.1 Energy sources and forms 1.2 Energy conversion 1.3 Energy storage and conservation Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: Knowledge, Understanding and Application
1 ENERGY FORMS & CONVERSION 1.1 Energy sources and forms 1.2 Energy conversion 1.3 Energy storage and conservation Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: Knowledge, Understanding and Application
Mitigation Strategies for Atmospheric Carbon. Clarence Lehman Department of Ecology, Evolution, and Behavior October 14, 2008
 Mitigation Strategies for Atmospheric Carbon Clarence Lehman Department of Ecology, Evolution, and Behavior October 14, 2008 Outline 1. What needs mitigation? 2. How did we get where we are? 3. How will
Mitigation Strategies for Atmospheric Carbon Clarence Lehman Department of Ecology, Evolution, and Behavior October 14, 2008 Outline 1. What needs mitigation? 2. How did we get where we are? 3. How will
