Materials Science. Imperfections in Solids CHAPTER 5: IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS. Types of Imperfections
|
|
|
- Lisa Griffin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 In the Name of God Materials Science CHAPTER 5: IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What are the solidification mechanisms? What types of defects arise in solids? Can the number and type of defects be varied and controlled? Dr Mohammad Heidari-Rarani How do defects affect material properties? Are defects undesirable? Chapter 5-1 Chapter 5-2 Types of Imperfections There is no such thing as a perfect crystal. What are these imperfections? Why are they important? Many of the important properties of materials are due to the presence of imperfections. Vacancy atoms Interstitial atoms Substitutional atoms Dislocations Grain Boundaries Point defects Line defects Area defects Chapter 5-3 Chapter 5-4 ١
2 Point Defects in Metals Vacancies: -vacant atomic sites in a structure. distortion of planes Self-Interstitials: -"extra" atoms positioned between atomic sites. distortion of planes Vacancy selfinterstitial Chapter 5-5 Equilibrium concentration varies with temperature! No. of defects No. of potential defect sites Each lattice site is a potential vacancy site Equilibrium Concentration: Point Defects Activation energy N v N = exp Q v kt Temperature Boltzmann's constant (1.38 x J/atom-K) (8.62 x 10-5 ev/atom-k) Chapter 5-6 Nv N Measuring Activation Energy We can get Q v from an experiment. Measure this... exponential dependence! T defect concentration N v N = exp Q v kt Replot it... Nv ln N slope -Qv /k 1/T Chapter 5-7 Estimating Vacancy Concentration Find the equil. # of vacancies in 1 m 3 of Cu at 1000 C. Given: ρ = 8.4 g/cm 3 A Cu = 63.5 g/mol Q v = 0.9 ev/atom N A = 6.02 x atoms/mol 0.9 ev/atom N v N = exp Q v kt = 2.7 x K 8.62 x 10-5 ev/atom-k N For 1 m 3, N = ρ x A x 1 m 3 = 8.0 x sites A Cu Answer: Nv = (2.7 x 10-4 )(8.0 x ) sites = 2.2 x vacancies Chapter 5-8 ٢
3 Point Defects in Ceramics (i) Vacancies -- vacancies exist in ceramics for both cations and anions Interstitials -- interstitials exist for cations -- interstitials are not normally observed for anions because anions are large relative to the interstitial sites Anion Vacancy Cation Interstitial Cation Vacancy Adapted from Fig. 5.2, Callister & Rethwisch 3e. (Fig. 5.2 is from W.G. Moffatt, G.W. Pearsall, and J. Wulff, The Structure and Properties of Materials, Vol. 1, Structure, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., p. 78.) Chapter 5-9 Point Defects in Ceramics (ii) Frenkel Defect -- a cation vacancy-cation interstitial pair. Shottky Defect -- a paired set of cation and anion vacancies. Shottky Defect: Adapted from Fig. 5.3, Callister & Rethwisch 3e. (Fig. 5.3 is from W.G. Moffatt, G.W. Pearsall, and J. Wulff, The Structure and Properties of Materials, Vol. 1, Structure, John Wiley and Sons, Inc., p. 78.) Frenkel Defect Equilibrium concentration of defects e Q D /kt Chapter 5-10 Stoichiometry Imperfections in Metals (i) Two outcomes if impurity (B) added to host (A): Solid solution of B in A (i.e., random dist. of point defects) OR Substitutional solid soln. (e.g., Cu in Ni) Interstitial solid soln. (e.g., C in Fe) Solid solution of B in A plus particles of a new phase (usually for a larger amount of B) Second phase particle -- different composition -- often different structure. Chapter 5-11 Chapter 5-12 ٣
4 Imperfections in Metals (ii) Conditions for substitutional solid solution (S.S.) W. Hume Rothery rule 1. r (atomic radius) < 15% 2. Proximity in periodic table i.e., similar electronegativities 3. Same crystal structure for pure metals 4. Valency All else being equal, a metal will have a greater tendency to dissolve a metal of higher valency than one of lower valency Imperfections in Metals (iii) Application of Hume Rothery rules Solid Solutions 1. Would you predict more Al or Ag to dissolve in Zn? 2. More Zn or Al in Cu? Element Atomic Crystal Electro- Valence Radius Structure nega- (nm) tivity Cu FCC C H O Ag FCC Al FCC Co HCP Cr BCC Fe BCC Ni FCC Pd FCC Zn HCP Table on p. 159, Callister & Rethwisch 3e. Chapter 5-13 Chapter 5-14 Imperfections in Ceramics Electroneutrality (charge balance) must be maintained when impurities are present Na + Cl - Ex: NaCl Substitutional cation impurity Ca 2+ Na + cation vacancy Dislocations: are line defects, slip between crystal planes result when dislocations move, produce permanent (plastic) deformation. Schematic of Zinc (HCP): before deformation Line Defects after tensile elongation Na + Ca 2+ without impurity Ca 2+ impurity with impurity Substitutional anion impurity O 2- anion vacancy slip steps without impurity Cl - Cl - O 2- impurity with impurity Chapter 5-15 Chapter 5-16
5 Linear Defects (Dislocations) Are one-dimensional defects around which atoms are misaligned Edge dislocation: extra half-plane of atoms inserted in a crystal structure b perpendicular ( ) to dislocation line Screw dislocation: spiral planar ramp resulting from shear deformation b parallel ( ) to dislocation line Edge Dislocation Burger s vector, b: measure of lattice distortion Fig. 5.8, Callister & Rethwisch 3e. Chapter 5-17 Chapter 5-18 Screw Dislocation Screw Dislocation Edge, Screw, and Mixed Dislocations Mixed Dislocation line Burgers vector b (a) Adapted from Fig. 5.9, Callister & Rethwisch 3e. b (b) Adapted from Fig. 5.10, Callister & Rethwisch 3e. Edge Screw Chapter 5-19 Chapter 5-20
6 Dislocations are visible in electron micrographs Fig. 5.11, Callister & Rethwisch 3e. Chapter 5-21 Dislocations & Crystal Structures Structure: close-packed planes & directions are preferred. close-packed plane (bottom) close-packed plane (top) Comparison among crystal structures: FCC: many close-packed planes/directions; HCP: only one plane, 3 directions; BCC: none Specimens that were tensile tested. tensile direction view onto two close-packed planes. close-packed directions Mg (HCP) Al (FCC) Chapter 5-22 Planar Defects in Solids Solidification- result of casting of molten material 2 steps Nuclei form Nuclei grow to form crystals grain structure Start with a molten material all liquid nuclei crystals growing grain structure liquid Adapted from Fig (b), Callister & Rethwisch 3e. Crystals grow until they meet each other Chapter 5-23 c03f35 Chapter 5 -
7 Polycrystalline Materials Planar Defects in Solids Grain Boundaries regions between crystals transition from lattice of one region to that of the other slightly disordered low density in grain boundaries high mobility high diffusivity high chemical reactivity Adapted from Fig. 5.12, Callister & Rethwisch 3e. Chapter 5-25 One case is a twin boundary (plane) Essentially a reflection of atom positions across the twin plane. Adapted from Fig. 5.14, Callister & Rethwisch 3e. Stacking faults For FCC metals an error in ABCABC packing sequence Ex: ABCABABC Chapter 5-26 ٧
ISSUES TO ADDRESS...
 Chapter 5: IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS School of Mechanical Engineering Choi, Hae-Jin Materials Science - Prof. Choi, Hae-Jin Chapter 4-1 ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What are the solidification mechanisms? What types
Chapter 5: IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS School of Mechanical Engineering Choi, Hae-Jin Materials Science - Prof. Choi, Hae-Jin Chapter 4-1 ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What are the solidification mechanisms? What types
12/10/09. Chapter 4: Imperfections in Solids. Imperfections in Solids. Polycrystalline Materials ISSUES TO ADDRESS...
 Chapter 4: ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What are the solidification mechanisms? What types of defects arise in solids? Can the number and type of defects be varied and controlled? How do defects affect material
Chapter 4: ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What are the solidification mechanisms? What types of defects arise in solids? Can the number and type of defects be varied and controlled? How do defects affect material
Physics of Materials: Defects in Solids. Dr. Anurag Srivastava. Indian Institute of Information Technology and Manegement, Gwalior
 : Defects in Solids Dr. Anurag Srivastava Atal Bihari Vajpayee Indian Institute of Information Technology and Manegement, Gwalior What you have learnt so far? Properties of Materials affected by defects
: Defects in Solids Dr. Anurag Srivastava Atal Bihari Vajpayee Indian Institute of Information Technology and Manegement, Gwalior What you have learnt so far? Properties of Materials affected by defects
Point coordinates. x z
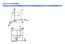 Point coordinates c z 111 a 000 b y x z 2c b y Point coordinates z y Algorithm 1. Vector repositioned (if necessary) to pass through origin. 2. Read off projections in terms of unit cell dimensions a,
Point coordinates c z 111 a 000 b y x z 2c b y Point coordinates z y Algorithm 1. Vector repositioned (if necessary) to pass through origin. 2. Read off projections in terms of unit cell dimensions a,
Point coordinates. Point coordinates for unit cell center are. Point coordinates for unit cell corner are 111
 Point coordinates c z 111 Point coordinates for unit cell center are a/2, b/2, c/2 ½ ½ ½ Point coordinates for unit cell corner are 111 x a z 000 b 2c y Translation: integer multiple of lattice constants
Point coordinates c z 111 Point coordinates for unit cell center are a/2, b/2, c/2 ½ ½ ½ Point coordinates for unit cell corner are 111 x a z 000 b 2c y Translation: integer multiple of lattice constants
Chapter 5. Imperfections in Solids
 Chapter 5 Imperfections in Solids Chapter 5 2D Defects and Introduction to Diffusion Imperfections in Solids Issues to Address... What types of defects arise in solids? Can the number and type of defects
Chapter 5 Imperfections in Solids Chapter 5 2D Defects and Introduction to Diffusion Imperfections in Solids Issues to Address... What types of defects arise in solids? Can the number and type of defects
Chapter 4: Imperfections (Defects) in Solids
 Chapter 4: Imperfections (Defects) in Solids ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What types of defects exist in solids? How do defects affect material properties? Can the number and type of defects be varied and controlled?
Chapter 4: Imperfections (Defects) in Solids ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What types of defects exist in solids? How do defects affect material properties? Can the number and type of defects be varied and controlled?
TOPIC 2. STRUCTURE OF MATERIALS III
 Universidad Carlos III de Madrid www.uc3m.es MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TOPIC 2. STRUCTURE OF MATERIALS III Topic 2.3: Crystalline defects. Solid solutions. 1 PERFECT AND IMPERFECT CRYSTALS Perfect
Universidad Carlos III de Madrid www.uc3m.es MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TOPIC 2. STRUCTURE OF MATERIALS III Topic 2.3: Crystalline defects. Solid solutions. 1 PERFECT AND IMPERFECT CRYSTALS Perfect
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 4: Imperfections in Solids. Dr. Coates
 Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR000 Chapter 4: Imperfections in Solids Dr. Coates Learning Objectives 1. Describe both vacancy and self interstitial defects. Calculate the equilibrium number
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR000 Chapter 4: Imperfections in Solids Dr. Coates Learning Objectives 1. Describe both vacancy and self interstitial defects. Calculate the equilibrium number
Imperfections, Defects and Diffusion
 Imperfections, Defects and Diffusion Lattice Defects Week5 Material Sciences and Engineering MatE271 1 Goals for the Unit I. Recognize various imperfections in crystals (Chapter 4) - Point imperfections
Imperfections, Defects and Diffusion Lattice Defects Week5 Material Sciences and Engineering MatE271 1 Goals for the Unit I. Recognize various imperfections in crystals (Chapter 4) - Point imperfections
Defect in crystals. Primer in Materials Science Spring
 Defect in crystals Primer in Materials Science Spring 2017 11.05.2017 1 Introduction The arrangement of the atoms in all materials contains imperfections which have profound effect on the behavior of the
Defect in crystals Primer in Materials Science Spring 2017 11.05.2017 1 Introduction The arrangement of the atoms in all materials contains imperfections which have profound effect on the behavior of the
Chapter 12: Structures & Properties of Ceramics
 Chapter 12: Structures & Properties of Ceramics ISSUES TO ADDRESS... Review of structures for ceramics How are impurities accommodated in the ceramic lattice? In what ways are ceramic phase diagrams similar
Chapter 12: Structures & Properties of Ceramics ISSUES TO ADDRESS... Review of structures for ceramics How are impurities accommodated in the ceramic lattice? In what ways are ceramic phase diagrams similar
ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What types of defects arise in solids? Can the number and type of defects be varied and controlled?
 CHAPTER 4: IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What types of defects arise in solids? Can the number and type of defects be varied and controlled? How do defects affect material properties? Are
CHAPTER 4: IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS ISSUES TO ADDRESS... What types of defects arise in solids? Can the number and type of defects be varied and controlled? How do defects affect material properties? Are
Chapter 7: Dislocations and strengthening mechanisms
 Chapter 7: Dislocations and strengthening mechanisms Introduction Basic concepts Characteristics of dislocations Slip systems Slip in single crystals Plastic deformation of polycrystalline materials Plastically
Chapter 7: Dislocations and strengthening mechanisms Introduction Basic concepts Characteristics of dislocations Slip systems Slip in single crystals Plastic deformation of polycrystalline materials Plastically
Dept.of BME Materials Science Dr.Jenan S.Kashan 1st semester 2nd level. Imperfections in Solids
 Why are defects important? Imperfections in Solids Defects have a profound impact on the various properties of materials: Production of advanced semiconductor devices require not only a rather perfect
Why are defects important? Imperfections in Solids Defects have a profound impact on the various properties of materials: Production of advanced semiconductor devices require not only a rather perfect
Point Defects. Vacancies are the most important form. Vacancies Self-interstitials
 Grain Boundaries 1 Point Defects 2 Point Defects A Point Defect is a crystalline defect associated with one or, at most, several atomic sites. These are defects at a single atom position. Vacancies Self-interstitials
Grain Boundaries 1 Point Defects 2 Point Defects A Point Defect is a crystalline defect associated with one or, at most, several atomic sites. These are defects at a single atom position. Vacancies Self-interstitials
CHAPTER 6 OUTLINE. DIFFUSION and IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS
 CHAPTER 6 DIFFUSION and IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS OUTLINE 1. TYPES OF DIFFUSIONS 1.1. Interdiffusion 1.2. Selfdiffusion 1.3.Diffusion mechanisms 1.4.Examples 2. TYPES OF IMPERFECTIONS 2.1.Point Defects 2.2.Line
CHAPTER 6 DIFFUSION and IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS OUTLINE 1. TYPES OF DIFFUSIONS 1.1. Interdiffusion 1.2. Selfdiffusion 1.3.Diffusion mechanisms 1.4.Examples 2. TYPES OF IMPERFECTIONS 2.1.Point Defects 2.2.Line
 Defects in solids http://www.bath.ac.uk/podcast/powerpoint/inaugural_lecture_250407.pdf http://www.materials.ac.uk/elearning/matter/crystallography/indexingdirectionsandplanes/indexing-of-hexagonal-systems.html
Defects in solids http://www.bath.ac.uk/podcast/powerpoint/inaugural_lecture_250407.pdf http://www.materials.ac.uk/elearning/matter/crystallography/indexingdirectionsandplanes/indexing-of-hexagonal-systems.html
Learning Objectives. Chapter Outline. Solidification of Metals. Solidification of Metals
 Learning Objectives Study the principles of solidification as they apply to pure metals. Examine the mechanisms by which solidification occurs. - Chapter Outline Importance of Solidification Nucleation
Learning Objectives Study the principles of solidification as they apply to pure metals. Examine the mechanisms by which solidification occurs. - Chapter Outline Importance of Solidification Nucleation
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS ev /atom = exp. kt ( =
 CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for copper at its melting temperature of 1084 C (1357 K). Assume
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for copper at its melting temperature of 1084 C (1357 K). Assume
Dr. Ali Abadi Chapter Three: Crystal Imperfection Materials Properties
 Dr. Ali Abadi Chapter Three: Crystal Imperfection Materials Properties A perfect crystal, with every atom of the same type in the correct position, does not exist. There always exist crystalline defects,
Dr. Ali Abadi Chapter Three: Crystal Imperfection Materials Properties A perfect crystal, with every atom of the same type in the correct position, does not exist. There always exist crystalline defects,
Defects and Diffusion
 Defects and Diffusion Goals for the Unit Recognize various imperfections in crystals Point imperfections Impurities Line, surface and bulk imperfections Define various diffusion mechanisms Identify factors
Defects and Diffusion Goals for the Unit Recognize various imperfections in crystals Point imperfections Impurities Line, surface and bulk imperfections Define various diffusion mechanisms Identify factors
Single vs Polycrystals
 WEEK FIVE This week, we will Learn theoretical strength of single crystals Learn metallic crystal structures Learn critical resolved shear stress Slip by dislocation movement Single vs Polycrystals Polycrystals
WEEK FIVE This week, we will Learn theoretical strength of single crystals Learn metallic crystal structures Learn critical resolved shear stress Slip by dislocation movement Single vs Polycrystals Polycrystals
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS
 CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for copper at its melting temperature of 1084 C (1357 K). Assume
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Vacancies and Self-Interstitials 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for copper at its melting temperature of 1084 C (1357 K). Assume
Point Defects in Metals
 CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Point Defects in Metals 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for lead at its melting temperature of 327 C (600 K). Assume an energy
CHAPTER 5 IMPERFECTIONS IN SOLIDS PROBLEM SOLUTIONS Point Defects in Metals 5.1 Calculate the fraction of atom sites that are vacant for lead at its melting temperature of 327 C (600 K). Assume an energy
Imperfections in Solids. Imperfections in Solids. Point Defects. Types of Imperfections
 Imperfections in Solids In this topic we will try to answer the following questions: What types of defects arise in solids? Are these defects undesirable? How do defects affect material properties? Can
Imperfections in Solids In this topic we will try to answer the following questions: What types of defects arise in solids? Are these defects undesirable? How do defects affect material properties? Can
Ex: NaCl. Ironically Bonded Solid
 Ex: NaCl. Ironically Bonded Solid Lecture 2 THE STRUCTURE OF CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS 3.2 FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS SOLIDS AMORPHOUS CRYSTALLINE Atoms in an amorphous Atoms in a crystalline solid solid are arranged
Ex: NaCl. Ironically Bonded Solid Lecture 2 THE STRUCTURE OF CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS 3.2 FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS SOLIDS AMORPHOUS CRYSTALLINE Atoms in an amorphous Atoms in a crystalline solid solid are arranged
IMPERFECTIONSFOR BENEFIT. Sub-topics. Point defects Linear defects dislocations Plastic deformation through dislocations motion Surface
 IMPERFECTIONSFOR BENEFIT Sub-topics 1 Point defects Linear defects dislocations Plastic deformation through dislocations motion Surface IDEAL STRENGTH Ideally, the strength of a material is the force necessary
IMPERFECTIONSFOR BENEFIT Sub-topics 1 Point defects Linear defects dislocations Plastic deformation through dislocations motion Surface IDEAL STRENGTH Ideally, the strength of a material is the force necessary
Impurities in Solids. Crystal Electro- Element R% Structure negativity Valence
 4-4 Impurities in Solids 4.4 In this problem we are asked to cite which of the elements listed form with Ni the three possible solid solution types. For complete substitutional solubility the following
4-4 Impurities in Solids 4.4 In this problem we are asked to cite which of the elements listed form with Ni the three possible solid solution types. For complete substitutional solubility the following
MSE 170 Midterm review
 MSE 170 Midterm review Exam date: 11/2/2008 Mon, lecture time Place: Here! Close book, notes and no collaborations A sheet of letter-sized paper with double-sided notes is allowed Material on the exam
MSE 170 Midterm review Exam date: 11/2/2008 Mon, lecture time Place: Here! Close book, notes and no collaborations A sheet of letter-sized paper with double-sided notes is allowed Material on the exam
Order in materials. Making Solid Stuff. Primary Bonds Summary. How do they arrange themselves? Results from atomic bonding. What are they?
 Making Solid Stuff Primary Bonds Summary What are they? Results from atomic bonding So the atoms bond together! Order in materials No long range order to atoms Gases little or no interaction between components
Making Solid Stuff Primary Bonds Summary What are they? Results from atomic bonding So the atoms bond together! Order in materials No long range order to atoms Gases little or no interaction between components
Module 10. Crystal Defects in Metals I. Lecture 10. Crystal Defects in Metals I
 Module 10 Crystal Defects in Metals I Lecture 10 Crystal Defects in Metals I 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Introduction Keywords:
Module 10 Crystal Defects in Metals I Lecture 10 Crystal Defects in Metals I 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Introduction Keywords:
3. Solidification & Crystalline Imperfections
 3. Solidification & Crystalline Imperfections solidification (casting process) of metals divided into two steps (1) nucleation formation of stable nuclei in the melt (2) growth of nuclei into crystals
3. Solidification & Crystalline Imperfections solidification (casting process) of metals divided into two steps (1) nucleation formation of stable nuclei in the melt (2) growth of nuclei into crystals
Crystal Defects. Perfect crystal - every atom of the same type in the correct equilibrium position (does not exist at T > 0 K)
 Crystal Defects Perfect crystal - every atom of the same type in the correct equilibrium position (does not exist at T > 0 K) Real crystal - all crystals have some imperfections - defects, most atoms are
Crystal Defects Perfect crystal - every atom of the same type in the correct equilibrium position (does not exist at T > 0 K) Real crystal - all crystals have some imperfections - defects, most atoms are
Imperfections in the Atomic and Ionic Arrangements
 Objectives Introduce the three basic types of imperfections: point defects, line defects (or dislocations), and surface defects. Explore the nature and effects of different types of defects. Outline Point
Objectives Introduce the three basic types of imperfections: point defects, line defects (or dislocations), and surface defects. Explore the nature and effects of different types of defects. Outline Point
Stacking Oranges. Packing atoms together Long Range Order. What controls the nearest number of atoms? Hard Sphere Model. Hard Sphere Model.
 { Stacking atoms together Crystal Structure Stacking Oranges Packing atoms together Long Range Order Crystalline materials... atoms pack in periodic, 3D arrays typical of: -metals -many ceramics -some
{ Stacking atoms together Crystal Structure Stacking Oranges Packing atoms together Long Range Order Crystalline materials... atoms pack in periodic, 3D arrays typical of: -metals -many ceramics -some
Homework #4 PROBLEM SOLUTIONS
 Homework #4 PROBLEM SOLUTIONS 4.2 Determination of the number of vacancies per cubic meter in gold at 900 C (1173 K) requires the utilization of Equations (4.1) and (4.2) as follows: N V N exp Q V kt N
Homework #4 PROBLEM SOLUTIONS 4.2 Determination of the number of vacancies per cubic meter in gold at 900 C (1173 K) requires the utilization of Equations (4.1) and (4.2) as follows: N V N exp Q V kt N
Chapter Outline Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms. Introduction
 Chapter Outline Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms What is happening in material during plastic deformation? Dislocations and Plastic Deformation Motion of dislocations in response to stress Slip
Chapter Outline Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms What is happening in material during plastic deformation? Dislocations and Plastic Deformation Motion of dislocations in response to stress Slip
Imperfections: Good or Bad? Structural imperfections (defects) Compositional imperfections (impurities)
 Imperfections: Good or Bad? Structural imperfections (defects) Compositional imperfections (impurities) 1 Structural Imperfections A perfect crystal has the lowest internal energy E Above absolute zero
Imperfections: Good or Bad? Structural imperfections (defects) Compositional imperfections (impurities) 1 Structural Imperfections A perfect crystal has the lowest internal energy E Above absolute zero
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE, MECHANICAL BEHAVIOUR & FAILURE OF MATERIALS
 MODULE ONE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE, MECHANICAL BEHAVIOUR & FAILURE OF MATERIALS CRYSTAL STRUCTURE Metallic crystal structures; BCC, FCC and HCP Coordination number and Atomic Packing Factor (APF) Crystal imperfections:
MODULE ONE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE, MECHANICAL BEHAVIOUR & FAILURE OF MATERIALS CRYSTAL STRUCTURE Metallic crystal structures; BCC, FCC and HCP Coordination number and Atomic Packing Factor (APF) Crystal imperfections:
Material Science. Prof. Satish V. Kailas Associate Professor Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore India
 Material Science Prof. Satish V. Kailas Associate Professor Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 India Chapter 3. Imperfections in Solids Learning objectives:
Material Science Prof. Satish V. Kailas Associate Professor Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 India Chapter 3. Imperfections in Solids Learning objectives:
INGE Engineering Materials. Chapter 3 (cont.)
 Some techniques used: Chapter 3 (cont.) This section will address the question how do we determine the crystal structure of a solid sample? Electron microscopy (by direct and indirect observations) Scanning
Some techniques used: Chapter 3 (cont.) This section will address the question how do we determine the crystal structure of a solid sample? Electron microscopy (by direct and indirect observations) Scanning
Imperfections in atomic arrangements
 MME131: Lecture 9 Imperfections in atomic arrangements Part 2: 1D 3D Defects A. K. M. B. Rashid Professor, Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Today s Topics Classifications and characteristics of 1D 3D defects
MME131: Lecture 9 Imperfections in atomic arrangements Part 2: 1D 3D Defects A. K. M. B. Rashid Professor, Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Today s Topics Classifications and characteristics of 1D 3D defects
Chapter 7 Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms. Dr. Feras Fraige
 Chapter 7 Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms Dr. Feras Fraige Chapter Outline Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms What is happening in material during plastic deformation? Dislocations and
Chapter 7 Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms Dr. Feras Fraige Chapter Outline Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms What is happening in material during plastic deformation? Dislocations and
Student Name: ID Number:
 Student Name: ID Number: DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CONCORDIA UNIVERSITY MATERIALS SCIENCE - MECH 1/ - Sections T & X MIDTERM 003 Instructors: Dr. M.Pugh & Dr. M.Medraj Time Allowed: one (1)
Student Name: ID Number: DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING CONCORDIA UNIVERSITY MATERIALS SCIENCE - MECH 1/ - Sections T & X MIDTERM 003 Instructors: Dr. M.Pugh & Dr. M.Medraj Time Allowed: one (1)
Why are dislocations observed primarily in metals CHAPTER 8: DEFORMATION AND STRENGTHENING MECHANISMS
 Why are dislocations observed primarily in metals CHAPTER 8: and alloys? DEFORMATION AND STRENGTHENING MECHANISMS How are strength and dislocation motion related? How do we manipulate properties? Strengthening
Why are dislocations observed primarily in metals CHAPTER 8: and alloys? DEFORMATION AND STRENGTHENING MECHANISMS How are strength and dislocation motion related? How do we manipulate properties? Strengthening
(a) Would you expect the element P to be a donor or an acceptor defect in Si?
 MSE 200A Survey of Materials Science Fall, 2008 Problem Set No. 2 Problem 1: At high temperature Fe has the fcc structure (called austenite or γ-iron). Would you expect to find C atoms in the octahedral
MSE 200A Survey of Materials Science Fall, 2008 Problem Set No. 2 Problem 1: At high temperature Fe has the fcc structure (called austenite or γ-iron). Would you expect to find C atoms in the octahedral
Dislocations & Materials Classes. Dislocation Motion. Dislocation Motion. Lectures 9 and 10
 Lectures 9 and 10 Chapter 7: Dislocations & Strengthening Mechanisms Dislocations & Materials Classes Metals: Disl. motion easier. -non-directional bonding -close-packed directions for slip. electron cloud
Lectures 9 and 10 Chapter 7: Dislocations & Strengthening Mechanisms Dislocations & Materials Classes Metals: Disl. motion easier. -non-directional bonding -close-packed directions for slip. electron cloud
4-Crystal Defects & Strengthening
 4-Crystal Defects & Strengthening A perfect crystal, with every atom of the same type in the correct position, does not exist. The crystalline defects are not always bad! Adding alloying elements to a
4-Crystal Defects & Strengthening A perfect crystal, with every atom of the same type in the correct position, does not exist. The crystalline defects are not always bad! Adding alloying elements to a
Chapter 9: Dislocations & Strengthening Mechanisms. Why are the number of dislocations present greatest in metals?
 Chapter 9: Dislocations & Strengthening Mechanisms ISSUES TO ADDRESS... Why are the number of dislocations present greatest in metals? How are strength and dislocation motion related? Why does heating
Chapter 9: Dislocations & Strengthening Mechanisms ISSUES TO ADDRESS... Why are the number of dislocations present greatest in metals? How are strength and dislocation motion related? Why does heating
Chapter Outline How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids?
 Chapter Outline How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids? Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures Face-centered cubic Body-centered cubic Hexagonal close-packed Close packed
Chapter Outline How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids? Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures Face-centered cubic Body-centered cubic Hexagonal close-packed Close packed
From sand to silicon wafer
 From sand to silicon wafer 25% of Earth surface is silicon Metallurgical grade silicon (MGS) Electronic grade silicon (EGS) Polycrystalline silicon (polysilicon) Single crystal Czochralski drawing Single
From sand to silicon wafer 25% of Earth surface is silicon Metallurgical grade silicon (MGS) Electronic grade silicon (EGS) Polycrystalline silicon (polysilicon) Single crystal Czochralski drawing Single
Chapter Outline. How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids?
 Chapter Outline How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids? Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures! Face-centered cubic! Body-centered cubic! Hexagonal close-packed Close packed
Chapter Outline How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids? Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures! Face-centered cubic! Body-centered cubic! Hexagonal close-packed Close packed
Materials and their structures
 Materials and their structures 2.1 Introduction: The ability of materials to undergo forming by different techniques is dependent on their structure and properties. Behavior of materials depends on their
Materials and their structures 2.1 Introduction: The ability of materials to undergo forming by different techniques is dependent on their structure and properties. Behavior of materials depends on their
Lecture # 11. Line defects (1D) / Dislocations
 Lecture # 11 - Line defects (1-D) / Dislocations - Planer defects (2D) - Volume Defects - Burgers vector - Slip - Slip Systems in FCC crystals - Slip systems in HCP - Slip systems in BCC References: 1-
Lecture # 11 - Line defects (1-D) / Dislocations - Planer defects (2D) - Volume Defects - Burgers vector - Slip - Slip Systems in FCC crystals - Slip systems in HCP - Slip systems in BCC References: 1-
N = N A Al A Al. = ( atoms /mol)(2.62 g /cm 3 ) g /mol. ln N v = ln N Q v kt. = kt ln v. Q v
 4.3 alculate the activation energy for vacancy formation in aluminum, given that the equilibrium number of vacancies at 500 (773 K) is 7.57 10 23 m -3. The atomic weight and density (at 500 ) for aluminum
4.3 alculate the activation energy for vacancy formation in aluminum, given that the equilibrium number of vacancies at 500 (773 K) is 7.57 10 23 m -3. The atomic weight and density (at 500 ) for aluminum
Strengthening Mechanisms
 ME 254: Materials Engineering Chapter 7: Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms 1 st Semester 1435-1436 (Fall 2014) Dr. Hamad F. Alharbi, harbihf@ksu.edu.sa November 18, 2014 Outline DISLOCATIONS AND
ME 254: Materials Engineering Chapter 7: Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms 1 st Semester 1435-1436 (Fall 2014) Dr. Hamad F. Alharbi, harbihf@ksu.edu.sa November 18, 2014 Outline DISLOCATIONS AND
Chapter 8. Deformation and Strengthening Mechanisms
 Chapter 8 Deformation and Strengthening Mechanisms Chapter 8 Deformation Deformation and Strengthening Issues to Address... Why are dislocations observed primarily in metals and alloys? How are strength
Chapter 8 Deformation and Strengthening Mechanisms Chapter 8 Deformation Deformation and Strengthening Issues to Address... Why are dislocations observed primarily in metals and alloys? How are strength
3, MSE 791 Mechanical Properties of Nanostructured Materials
 3, MSE 791 Mechanical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Module 3: Fundamental Physics and Materials Design Lecture 1 1. What is strain (work) hardening? What is the mechanism for strain hardening?
3, MSE 791 Mechanical Properties of Nanostructured Materials Module 3: Fundamental Physics and Materials Design Lecture 1 1. What is strain (work) hardening? What is the mechanism for strain hardening?
Solid. Imperfection in solids. Examples of Imperfections #2. Examples of Imperfections #1. Solid
 Solid Imperfection in solids By E-mail: Patama.V@chula.ac.th Solid State of materials Rigid Strong bonding ionic, van der aals, metal bonding normally has crystal structure Examples of Imperfections #
Solid Imperfection in solids By E-mail: Patama.V@chula.ac.th Solid State of materials Rigid Strong bonding ionic, van der aals, metal bonding normally has crystal structure Examples of Imperfections #
Engineering 45: Properties of Materials Final Exam May 9, 2012 Name: Student ID number:
 Engineering 45: Properties of Materials Final Exam May 9, 2012 Name: Student ID number: Instructions: Answer all questions and show your work. You will not receive partial credit unless you show your work.
Engineering 45: Properties of Materials Final Exam May 9, 2012 Name: Student ID number: Instructions: Answer all questions and show your work. You will not receive partial credit unless you show your work.
NPTEL COURSE ADVANCED CERAMICS FOR STRATEGIC APPLICATIONS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 NPTEL COURSE ADVANCED CERAMICS FOR STRATEGIC APPLICATIONS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Q1: What do you understand by Ceramics? Ans: Ceramics are a group of chemical compounds, either simple (consisting of only
NPTEL COURSE ADVANCED CERAMICS FOR STRATEGIC APPLICATIONS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Q1: What do you understand by Ceramics? Ans: Ceramics are a group of chemical compounds, either simple (consisting of only
CHAPTER 5: DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS
 CHAPTER 5: DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How does diffusion occur? Why is it an important part of processing? How can the rate of diffusion be predicted for some simple cases? How does diffusion
CHAPTER 5: DIFFUSION IN SOLIDS ISSUES TO ADDRESS... How does diffusion occur? Why is it an important part of processing? How can the rate of diffusion be predicted for some simple cases? How does diffusion
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 7: Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms. Dr. Coates
 Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 7: Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms Dr. Coates An edge dislocation moves in response to an applied shear stress dislocation motion 7.1 Introduction
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 7: Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms Dr. Coates An edge dislocation moves in response to an applied shear stress dislocation motion 7.1 Introduction
Dislocations and Plastic Deformation
 Dislocations and Plastic Deformation Edge and screw are the two fundamental dislocation types. In an edge dislocation, localized lattice distortion exists along the end of an extra half-plane of atoms,
Dislocations and Plastic Deformation Edge and screw are the two fundamental dislocation types. In an edge dislocation, localized lattice distortion exists along the end of an extra half-plane of atoms,
Lecture 3: Description crystal structures / Defects
 Lecture 3: Description crystal structures / Defects Coordination Close packed structures Cubic close packing Hexagonal close packing Metallic structures Ionic structures with interstitial sites Important
Lecture 3: Description crystal structures / Defects Coordination Close packed structures Cubic close packing Hexagonal close packing Metallic structures Ionic structures with interstitial sites Important
Chapter 2. Ans: e (<100nm size materials are called nanomaterials)
 Chapter 2 1. Materials science and engineering include (s) the study of: (a) metals (b) polymers (c) ceramics (d) composites (e) nanomaterials (f) all of the above Ans: f 2. Which one of the following
Chapter 2 1. Materials science and engineering include (s) the study of: (a) metals (b) polymers (c) ceramics (d) composites (e) nanomaterials (f) all of the above Ans: f 2. Which one of the following
Planar Defects in Materials. Planar Defects in Materials
 Classification of Defects in Solids: Planar defects: Stacking faults o {311} defects in Si o Inversion domain boundaries o Antiphase boundaries (e.g., super dislocations): analogous to partials but in
Classification of Defects in Solids: Planar defects: Stacking faults o {311} defects in Si o Inversion domain boundaries o Antiphase boundaries (e.g., super dislocations): analogous to partials but in
9/16/ :30 PM. Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, Ph.D., PE
 Chapter 3 The structure of crystalline solids 1 Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, Ph.D., PE 2 Home Work Assignments HW 1 2, 7, 12, 17, 22, 29, 34, 39, 44, 48, 53, 58, 63 Due Sunday 17/9/2015 3 Why study the structure
Chapter 3 The structure of crystalline solids 1 Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, Ph.D., PE 2 Home Work Assignments HW 1 2, 7, 12, 17, 22, 29, 34, 39, 44, 48, 53, 58, 63 Due Sunday 17/9/2015 3 Why study the structure
ASE324: Aerospace Materials Laboratory
 ASE324: Aerospace Materials Laboratory Instructor: Rui Huang Dept of Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics The University of Texas at Austin Fall 2003 Lecture 3 September 4, 2003 Iron and Steels
ASE324: Aerospace Materials Laboratory Instructor: Rui Huang Dept of Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics The University of Texas at Austin Fall 2003 Lecture 3 September 4, 2003 Iron and Steels
Lecture # 11 References:
 Lecture # 11 - Line defects (1-D) / Dislocations - Planer defects (2D) - Volume Defects - Burgers vector - Slip - Slip Systems in FCC crystals - Slip systems in HCP - Slip systems in BCC Dr.Haydar Al-Ethari
Lecture # 11 - Line defects (1-D) / Dislocations - Planer defects (2D) - Volume Defects - Burgers vector - Slip - Slip Systems in FCC crystals - Slip systems in HCP - Slip systems in BCC Dr.Haydar Al-Ethari
MSE 351 Engineering Ceramics I
 Kwame Nkrumah University of Science & Technology, Kumasi, Ghana MSE 351 Engineering Ceramics I Ing. Anthony Andrews (PhD) Department of Materials Engineering Faculty of Mechanical and Chemical Engineering
Kwame Nkrumah University of Science & Technology, Kumasi, Ghana MSE 351 Engineering Ceramics I Ing. Anthony Andrews (PhD) Department of Materials Engineering Faculty of Mechanical and Chemical Engineering
Mechanisms of Diffusion II. Ionic Crystals L5 11/3/03-1-
 Mechanisms of Diffusion II. Ionic Crystals 3.05 L5 11/3/03-1- Charges on point imperfections Point imperfections in ionic crystals are generally electrically charged. 3.05 L5 11/3/03 - (a) Unit cell in
Mechanisms of Diffusion II. Ionic Crystals 3.05 L5 11/3/03-1- Charges on point imperfections Point imperfections in ionic crystals are generally electrically charged. 3.05 L5 11/3/03 - (a) Unit cell in
Two marks questions and answers. 1. what is a Crystal? (or) What are crystalline materials? Give examples
 UNIT V CRYSTAL PHYSICS PART-A Two marks questions and answers 1. what is a Crystal? (or) What are crystalline materials? Give examples Crystalline solids (or) Crystals are those in which the constituent
UNIT V CRYSTAL PHYSICS PART-A Two marks questions and answers 1. what is a Crystal? (or) What are crystalline materials? Give examples Crystalline solids (or) Crystals are those in which the constituent
Chapter 1. The Structure of Metals. Body Centered Cubic (BCC) Structures
 Chapter 1 The Structure of Metals Body Centered Cubic (BCC) Structures Figure 1. The body-centered cubic (bcc) crystal structure: (a) hard-ball model; (b) unit cell; and (c) single crystal with many unit
Chapter 1 The Structure of Metals Body Centered Cubic (BCC) Structures Figure 1. The body-centered cubic (bcc) crystal structure: (a) hard-ball model; (b) unit cell; and (c) single crystal with many unit
Chapter 8: Deformation & Strengthening Mechanisms. School of Mechanical Engineering Choi, Hae-Jin ISSUES TO ADDRESS
 Chapter 8: Deformation & Strengthening Mechanisms School of Mechanical Engineering Choi, Hae-Jin Materials Science - Prof. Choi, Hae-Jin Chapter 8-1 ISSUES TO ADDRESS Why are the number of dislocations
Chapter 8: Deformation & Strengthening Mechanisms School of Mechanical Engineering Choi, Hae-Jin Materials Science - Prof. Choi, Hae-Jin Chapter 8-1 ISSUES TO ADDRESS Why are the number of dislocations
atoms = 1.66 x g/amu
 CHAPTER 2 Q1- How many grams are there in a one amu of a material? A1- In order to determine the number of grams in one amu of material, appropriate manipulation of the amu/atom, g/mol, and atom/mol relationships
CHAPTER 2 Q1- How many grams are there in a one amu of a material? A1- In order to determine the number of grams in one amu of material, appropriate manipulation of the amu/atom, g/mol, and atom/mol relationships
Module #8. Defects in Crystalline Materials. READING LIST DIETER: Ch. 4, Pages
 HOMEWORK From Dieter 4-6 Module #8 Defects in Crystalline Materials READING LIST DIETER: Ch. 4, Pages 103-114 Ch. 4, Pages 103-117 in Meyers & Chawla, 1 st ed. Ch. 1, Pages 1-26 in Argon Property Structure,
HOMEWORK From Dieter 4-6 Module #8 Defects in Crystalline Materials READING LIST DIETER: Ch. 4, Pages 103-114 Ch. 4, Pages 103-117 in Meyers & Chawla, 1 st ed. Ch. 1, Pages 1-26 in Argon Property Structure,
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids. Dr. Coates
 Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids Dr. Coates Learning Objectives I 1. Describe difference in atomic/molecular structure between crystalline/noncrystalline
Introduction to Engineering Materials ENGR2000 Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids Dr. Coates Learning Objectives I 1. Describe difference in atomic/molecular structure between crystalline/noncrystalline
Movement of edge and screw dislocations
 Movement of edge and screw dislocations Formation of a step on the surface of a crystal by motion of (a) n edge dislocation: the dislocation line moves in the direction of the applied shear stress τ. (b)
Movement of edge and screw dislocations Formation of a step on the surface of a crystal by motion of (a) n edge dislocation: the dislocation line moves in the direction of the applied shear stress τ. (b)
9/29/2014 8:52 PM. Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 1 Chapter 3 The structure of crystalline solids 2 Home Work Assignments HW 1 2, 7, 12, 17, 22, 29, 34, 39, 44, 48, 53, 58, 63 Due Sunday 12/10/2014 Quiz # 1 will be held on Monday 13/10/2014 at 11:00 am
1 Chapter 3 The structure of crystalline solids 2 Home Work Assignments HW 1 2, 7, 12, 17, 22, 29, 34, 39, 44, 48, 53, 58, 63 Due Sunday 12/10/2014 Quiz # 1 will be held on Monday 13/10/2014 at 11:00 am
3.40 Sketch within a cubic unit cell the following planes: (a) (01 1 ) (b) (112 ) (c) (102 ) (d) (13 1) Solution
 3.40 Sketch within a cubic unit cell the following planes: (a) (01 1 ) (b) (11 ) (c) (10 ) (d) (13 1) The planes called for are plotted in the cubic unit cells shown below. 3.41 Determine the Miller indices
3.40 Sketch within a cubic unit cell the following planes: (a) (01 1 ) (b) (11 ) (c) (10 ) (d) (13 1) The planes called for are plotted in the cubic unit cells shown below. 3.41 Determine the Miller indices
9/28/2013 9:26 PM. Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 3 The structure of crystalline solids 1 2 Why study the structure of crystalline solids? Properties of some materials are directly related to their crystal structure. Significant property differences
Chapter 3 The structure of crystalline solids 1 2 Why study the structure of crystalline solids? Properties of some materials are directly related to their crystal structure. Significant property differences
NATURE OF METALS AND ALLOYS
 NATURE OF METALS AND ALLOYS Chapter 4 NATURE OF METALS AND ALLOYS Instructor: Office: MEC 325, Tel.: 973-642-7455 E-mail: samardzi@njit.edu Link to ME 215: http://mechanical.njit.edu/students/merequired.php
NATURE OF METALS AND ALLOYS Chapter 4 NATURE OF METALS AND ALLOYS Instructor: Office: MEC 325, Tel.: 973-642-7455 E-mail: samardzi@njit.edu Link to ME 215: http://mechanical.njit.edu/students/merequired.php
3. Anisotropic blurring by dislocations
 Dynamical Simulation of EBSD Patterns of Imperfect Crystals 1 G. Nolze 1, A. Winkelmann 2 1 Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (BAM), Berlin, Germany 2 Max-Planck- Institute of Microstructure
Dynamical Simulation of EBSD Patterns of Imperfect Crystals 1 G. Nolze 1, A. Winkelmann 2 1 Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (BAM), Berlin, Germany 2 Max-Planck- Institute of Microstructure
Module-6. Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms
 Module-6 Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms Contents 1) Dislocations & Plastic deformation and Mechanisms of plastic deformation in metals 2) Strengthening mechanisms in metals 3) Recovery, Recrystallization
Module-6 Dislocations and Strengthening Mechanisms Contents 1) Dislocations & Plastic deformation and Mechanisms of plastic deformation in metals 2) Strengthening mechanisms in metals 3) Recovery, Recrystallization
E45 Midterm 01 Fall 2007! By the 0.2% offset method (shown on plot), YS = 500 MPa
 1.!Mechanical Properties (20 points) Refer to the following stress-strain plot derived from a standard uniaxial tensile test of a high performance titanium alloy to answer the following questions. Show
1.!Mechanical Properties (20 points) Refer to the following stress-strain plot derived from a standard uniaxial tensile test of a high performance titanium alloy to answer the following questions. Show
N = N A ρ Pb A Pb. = ln N Q v kt. 지난문제. Below are shown three different crystallographic planes for a unit cell of some hypothetical metal.
 지난문제. Below are shown three different crystallographic planes for a unit cell of some hypothetical metal. The circles represent atoms: (a) To what crystal system does the unit cell belong? (b) What would
지난문제. Below are shown three different crystallographic planes for a unit cell of some hypothetical metal. The circles represent atoms: (a) To what crystal system does the unit cell belong? (b) What would
Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures! Face-centered cubic! Body-centered cubic! Hexagonal close-packed Close packed
 Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures! Face-centered cubic! Body-centered cubic! Hexagonal close-packed Close packed crystal structures Density computations Crystal structure
Fundamental concepts and language Unit cells Crystal structures! Face-centered cubic! Body-centered cubic! Hexagonal close-packed Close packed crystal structures Density computations Crystal structure
STRENGTHENING MECHANISM IN METALS
 Background Knowledge Yield Strength STRENGTHENING MECHANISM IN METALS Metals yield when dislocations start to move (slip). Yield means permanently change shape. Slip Systems Slip plane: the plane on which
Background Knowledge Yield Strength STRENGTHENING MECHANISM IN METALS Metals yield when dislocations start to move (slip). Yield means permanently change shape. Slip Systems Slip plane: the plane on which
Engineering materials
 1 Engineering materials Lecture 2 Imperfections and defects Response of materials to stress 2 Crystalline Imperfections (4.4) No crystal is perfect. Imperfections affect mechanical properties, chemical
1 Engineering materials Lecture 2 Imperfections and defects Response of materials to stress 2 Crystalline Imperfections (4.4) No crystal is perfect. Imperfections affect mechanical properties, chemical
Chapter 3 Structure of Crystalline Solids
 Chapter 3 Structure of Crystalline Solids Crystal Structures Points, Directions, and Planes Linear and Planar Densities X-ray Diffraction How do atoms assemble into solid structures? (for now, focus on
Chapter 3 Structure of Crystalline Solids Crystal Structures Points, Directions, and Planes Linear and Planar Densities X-ray Diffraction How do atoms assemble into solid structures? (for now, focus on
Structure of silica glasses (Chapter 12)
 Questions and Problems 97 Glass Ceramics (Structure) heat-treated so as to become crystalline in nature. The following concept map notes this relationship: Structure of noncrystalline solids (Chapter 3)
Questions and Problems 97 Glass Ceramics (Structure) heat-treated so as to become crystalline in nature. The following concept map notes this relationship: Structure of noncrystalline solids (Chapter 3)
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE TERMS
 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE TERMS crystalline material - a material in which atoms, ions, or molecules are situated in a periodic 3-dimensional array over large atomic distances (all metals, many ceramic materials,
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE TERMS crystalline material - a material in which atoms, ions, or molecules are situated in a periodic 3-dimensional array over large atomic distances (all metals, many ceramic materials,
Strengthening Mechanisms. Today s Topics
 MME 131: Lecture 17 Strengthening Mechanisms Prof. A.K.M.B. Rashid Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Today s Topics Strengthening strategies: Grain strengthening Solid solution strengthening Work hardening
MME 131: Lecture 17 Strengthening Mechanisms Prof. A.K.M.B. Rashid Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Today s Topics Strengthening strategies: Grain strengthening Solid solution strengthening Work hardening
Fundamentals of Plastic Deformation of Metals
 We have finished chapters 1 5 of Callister s book. Now we will discuss chapter 10 of Callister s book Fundamentals of Plastic Deformation of Metals Chapter 10 of Callister s book 1 Elastic Deformation
We have finished chapters 1 5 of Callister s book. Now we will discuss chapter 10 of Callister s book Fundamentals of Plastic Deformation of Metals Chapter 10 of Callister s book 1 Elastic Deformation
Chapter 4. Introduction to Dislocations
 Chapter 4 Introduction to Dislocations The discrepancy between the theoretical and observed yield stresses of crystals Dislocations The Burgers vector Vector notation for dislocations Dislocations in the
Chapter 4 Introduction to Dislocations The discrepancy between the theoretical and observed yield stresses of crystals Dislocations The Burgers vector Vector notation for dislocations Dislocations in the
HOMEWORK 6. solutions
 HOMEWORK 6. SCI 1410: materials science & solid state chemistry solutions Textbook Problems: Imperfections in Solids 1. Askeland 4-67. Why is most gold or siler jewelry made out of gold or siler alloyed
HOMEWORK 6. SCI 1410: materials science & solid state chemistry solutions Textbook Problems: Imperfections in Solids 1. Askeland 4-67. Why is most gold or siler jewelry made out of gold or siler alloyed
Polymorphism. Learning Objectives On completion of this topic you will be able to understand:
 Introduction Do you know the difference between α-quartz, β-quartz? Or why does quartz have these different forms? Certain chemical elements, can exist in two or more different forms. For example, iron
Introduction Do you know the difference between α-quartz, β-quartz? Or why does quartz have these different forms? Certain chemical elements, can exist in two or more different forms. For example, iron
Introduction to Materials Science
 EPMA Powder Metallurgy Summer School 27 June 1 July 2016 Valencia, Spain Introduction to Materials Science Prof. Alberto Molinari University of Trento, Italy Some of the figures used in this presentation
EPMA Powder Metallurgy Summer School 27 June 1 July 2016 Valencia, Spain Introduction to Materials Science Prof. Alberto Molinari University of Trento, Italy Some of the figures used in this presentation
