SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
|
|
|
- Magnus Shields
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Conserved arginines on the rim of Hfq catalyze base pair formation and exchange Subrata Panja and Sarah A. Woodson T.C. Jenkins Department of Biophysics, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD 21218, USA Table S1: Oligoribonucleotides and molecular beacons used in this study. Beacon rmbd FAM-CCAGGGCACUUAAAAAAUUCGCCUGG-C6-NH-DABCYL 3 rmbdss 5 6-FAM-GGUCCCCCACUCGACUCACCACCGGACC-C6-NH-DABCYL 3 RNA D16 cd16 Oligo CA Oligo CU A18 U6 5 CGAAUUUUUUAAGUGC 5 GCACUUAAAAAAUUCG 5 GUGGUCAGUCGAGUGGAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA 5 GUGGUCAGUCGAGUGGUUUUUU 5 AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA 5 UUUUUU These RNAs were previously reported in (Hopkins et al. 2009; Panja and Woodson 2012b).
2 Figure S1 Figure S1: Multiple sequence alignment of Hfq protein. Alignment of 384 bacterial Hfq sequences (top bars) with Clustal Omega shows that the basic patch on the rim of Hfq is highly conserved. Arginine at position 16 is invariant within the curated sequences used to create the multiple sequence alignment (*). The one exception is S. aureus, which has a lysine at position 16. Position 17 is typically lysine or arginine, position 18 is glutamate, while position 19 is least conserved within this region. The consensus sequence for the arginine patch is RKER (black bars). Sequences from select organisms in which Hfq s function has been characterized are shown below the alignment results for comparison.
3 Figure S2 Figure S2: Activation of rpos expression. Cells were grown on MacConkey / lactose agar with % arabinose overnight at 37 C. Red color indicates up-regulation of rpos::lacz expression in the presence of Hfq and ArcZ srna; white color indicates a lack of srnadependent activation.
4 Fig S3: Fig S3: Stability of Hfq hexamer. Over-expressed and purified E. coli Hfq (wt) and other mutant Hfq proteins (50 µm) were analyzed by semi-native PAGE as previously described (Panja & Woodson, 2012a) and stained with Coomassie blue. a. Comparison of WT and S23W Hfq on 15% polyacrylamide. b. Rim mutants on 4-20% polyacrylamide. Bands migrating at 11 kda, 66 kda and 132 kda correspond to the Hfq monomer, hexamer and dodecamer, respectively.
5 Figure S4 Figure S4: Reduced binding of Hfq:R16A to rpos mrna and srnas. Native gel electrophoresis of each RNAs with WT Hfq (top) or Hfq:R16A (middle). (a) rpos323, (b) DsrA, (c) RprA, (d) ArcZ56. Bands assigned to the free RNA (R, D, Rp and A, respectively) and to complexes with one or more Hfq hexamers are indicated to the left of each gel. In part a, the rightmost lane contains only rpos323. Binding constants were obtained by fitting the fraction of R-H complex to a two state binding model (black = wt, red = R16A). For rpos323, DsrA, RprA, we summed the counts in all shifted complexes. For ArcZ56, the fraction bound was based on the disappearance of free RNA, as its Hfq complexes are not well resolved (Soper et al., 2010).
6 Figure S5 Figure S5: Hfq:R16A is defective in RNA annealing. Binding kinetics of rpos srna complexes at 30 C was measured using radiolabeled rpos323 and 200 nm srna (DsrA/RprA/ArcZ56). First row, no Hfq (first row); second row, 1 µm WT Hfq; third row, 1 µm Hfq:R16A. Control reactions with rpos323 only, rpos323 plus srna, rpos323 plus 1 µm Hfq and all three components were incubated 2 h at 30 C before loading on the gel. R, free rpos323; R H, rpos-hfq compex; R D, rpos-dsra complex, R D H, ternary complex. Complexes of RprA (Rp) and ArcZ (A) were labeled analogously. Lower panel, progress curves for forming binary ( Hfq) and ternary (+Hfq) complexes (grey, no Hfq; black, WT Hfq; red, Hfq:R16A; blue, R16K; cyan, R19A; magenta, TM), were fitted to rate equations to obtain observed rate constants (Materials and Methods).
7 Figure S6 Figure S6: Fluorescence anisotropy measurements of Hfq binding. (a) Hfq binding was measured by fluorescence anisotropy. (b) 5 nm D16-FAM equilibrated in TNK buffer was titrated with Hfq (nm monomer) at 30 C. The increase in anisotropy was measured by exciting the sample at 490 nm and recording the polarization of emission intensity at 515 nm as previously described (Hopkins et al. 2009). The binding isotherm was fit to a cooperative (Hill) model. The fit parameters were: R16A, K d = 239 nm and n = 1.4; TM, K d = 105 nm and n = Only one transition is observed because the R16A mutation blocks hexamer association (Panja and Woodson 2012a). (c) Binding of ra18-fam to WT, R16A and TM Hfq as above. The fit parameters were: WT, K d = 80 nm and n = 1.7; R16A, K d = 14 nm and n = 0.7; TM, K d = 101 nm and n = 3.
8 Figure S7 (a) (b) (c) Figure S7: A positively charged rim is required for strand exchange. (a) The rate of strand exchange was measured by challenging 50 nm rmb-d16 D16 RNA complex with 50 nm cd16 RNA in TNK buffer at 30 C. (b) Release of the beacon upon exchange with cd16 RNA decreases the fluorescence emission. (c) Observed rates depended on the amino acid at position 16 and 19, with only WT Hfq exhibiting significant strand exchange activity. Error bars indicate the standard deviation from the mean of 5 trials.
9 Figure S8 Figure S8: Hfq:R16A binds RNA slowly and dissociates slowly from the ternary complex. (a-c) FRET assay for Hfq binding. (a) 50 nm D16-FAM RNA (red) was mixed with 0.5 µm Cy3-labeled Hfq monomer. The decrease in FAM emission due to FRET was detected using a 515 nm cut-off filter. (b) WT Hfq binds with two kinetic phases and the data were fit to a double exponential (k obs = 37 s -1 and 0.2 s -1 ). (c) Hfq:R16A displays only the slow phase of binding, and data were fit to a single exponential over 10 s (k obs = 0.62 s -1 ). (d-f) FRET assay for Hfq release. (d) 100 nm D16-FAM (red) was pre-mixed with 0.5 µm Hfq-Cy3, and the D16- FAM Hfq-Cy3 complex challenged with 100 nm complementary cd16 RNA (green line). Release of base paired D16 cd16 causes a loss of FRET. (e) For WT Hfq, release of dsrna resulted in a rapid loss of FRET and increase in FAM emission. (f) There was little change in FRET signal for Hfq:R16A, indicating no net release of D16-cD16 double helix. (g-i) To observe turnover of the ternary complex, cd16 RNA (100 nm) was pre-mixed with 0.5 µm Hfq-Cy3, and challenged with 100 nm complementary D16-FAM RNA. (h) For WT Hfq, binding of D16- FAM to the cd16 Hfq-Cy3 complex resulted in initial decrease in FAM emission (high FRET). Subsequent release of WT Hfq from the ternary complex was manifest as increased emission (low FRET). (i) For Hfq:R16A, we did not observe any signal corresponding to release of R16A Hfq within 10 s. The observed rate constant of the signal decay was 0.35 sec -1, which corresponds to the binding rate of Hfq:R16A in part c. Data in (e) and (h) taken from Hopkins et al. (2011).
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Multiple sequence alignments of four Swi2/Snf2 subfamily proteins, ScChd1, SsoRad54 and the RNA helicase Vasa. The sequence alignments of the Swi2/Snf2 subfamily proteins, ScChd1
Supplementary Figure 1 Multiple sequence alignments of four Swi2/Snf2 subfamily proteins, ScChd1, SsoRad54 and the RNA helicase Vasa. The sequence alignments of the Swi2/Snf2 subfamily proteins, ScChd1
Viral RNAi suppressor reversibly binds sirna to. outcompete Dicer and RISC via multiple-turnover
 Supplementary Data Viral RNAi suppressor reversibly binds sirna to outcompete Dicer and RISC via multiple-turnover Renata A. Rawlings 1,2, Vishalakshi Krishnan 2 and Nils G. Walter 2 * 1 Biophysics and
Supplementary Data Viral RNAi suppressor reversibly binds sirna to outcompete Dicer and RISC via multiple-turnover Renata A. Rawlings 1,2, Vishalakshi Krishnan 2 and Nils G. Walter 2 * 1 Biophysics and
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Minimal mechanistic model of sirna-dependent target RNA slicing by recombinant human Argonaute2 protein Andrea Deerberg*, Sarah Willkomm* and Tobias Restle Institute of Molecular
Supplementary Information Minimal mechanistic model of sirna-dependent target RNA slicing by recombinant human Argonaute2 protein Andrea Deerberg*, Sarah Willkomm* and Tobias Restle Institute of Molecular
Masayoshi Honda, Jeehae Park, Robert A. Pugh, Taekjip Ha, and Maria Spies
 Molecular Cell, Volume 35 Supplemental Data Single-Molecule Analysis Reveals Differential Effect of ssdna-binding Proteins on DNA Translocation by XPD Helicase Masayoshi Honda, Jeehae Park, Robert A. Pugh,
Molecular Cell, Volume 35 Supplemental Data Single-Molecule Analysis Reveals Differential Effect of ssdna-binding Proteins on DNA Translocation by XPD Helicase Masayoshi Honda, Jeehae Park, Robert A. Pugh,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature08627 Supplementary Figure 1. DNA sequences used to construct nucleosomes in this work. a, DNA sequences containing the 601 positioning sequence (blue)24 with a PstI restriction site
doi: 10.1038/nature08627 Supplementary Figure 1. DNA sequences used to construct nucleosomes in this work. a, DNA sequences containing the 601 positioning sequence (blue)24 with a PstI restriction site
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures 1-8
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figures 1-8 Supplementary Figure 1. TFAM residues contacting the DNA minor groove (A) TFAM contacts on nonspecific DNA. Leu58, Ile81, Asn163, Pro178, and Leu182
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figures 1-8 Supplementary Figure 1. TFAM residues contacting the DNA minor groove (A) TFAM contacts on nonspecific DNA. Leu58, Ile81, Asn163, Pro178, and Leu182
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Materials and Methods Circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. Far ultraviolet (UV) CD spectra of apo- and holo- CaM and the CaM mutants were recorded on a Jasco J-715 spectropolarimeter
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Materials and Methods Circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy. Far ultraviolet (UV) CD spectra of apo- and holo- CaM and the CaM mutants were recorded on a Jasco J-715 spectropolarimeter
The molecular basis of lysine 48 ubiquitin chain synthesis by Ube2K
 Supplementary Information The molecular basis of lysine 48 ubiquitin chain synthesis by Adam J. Middleton, Catherine L. Day* Department of Biochemistry, Otago School of Medical Sciences, University of
Supplementary Information The molecular basis of lysine 48 ubiquitin chain synthesis by Adam J. Middleton, Catherine L. Day* Department of Biochemistry, Otago School of Medical Sciences, University of
University of Bristol - Explore Bristol Research
 Butterer, A., Pernstich, C., Smith, R. M., Sobott, F., Szczelkun, M. D., & Tóth, J. (2014). Type III restriction endonucleases are heterotrimeric: comprising one helicase-nuclease subunit and a dimeric
Butterer, A., Pernstich, C., Smith, R. M., Sobott, F., Szczelkun, M. D., & Tóth, J. (2014). Type III restriction endonucleases are heterotrimeric: comprising one helicase-nuclease subunit and a dimeric
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL BIOCHEMICAL AND STRUCTURAL STUDIES ON THE M. TUBERCULOSIS O 6 -METHYLGUANINE METHYLTRANSFERASE AND MUTATED VARIANTS
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL BIOCHEMICAL AND STRUCTURAL STUDIES ON THE M. TUBERCULOSIS O 6 -METHYLGUANINE METHYLTRANSFERASE AND MUTATED VARIANTS Riccardo Miggiano 1, Valentina Casazza 1, Silvia Garavaglia 1,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL BIOCHEMICAL AND STRUCTURAL STUDIES ON THE M. TUBERCULOSIS O 6 -METHYLGUANINE METHYLTRANSFERASE AND MUTATED VARIANTS Riccardo Miggiano 1, Valentina Casazza 1, Silvia Garavaglia 1,
Supplementary Figure 1. FRET probe labeling locations in the Cas9-RNA-DNA complex.
 Supplementary Figure 1. FRET probe labeling locations in the Cas9-RNA-DNA complex. (a) Cy3 and Cy5 labeling locations shown in the crystal structure of Cas9-RNA bound to a cognate DNA target (PDB ID: 4UN3)
Supplementary Figure 1. FRET probe labeling locations in the Cas9-RNA-DNA complex. (a) Cy3 and Cy5 labeling locations shown in the crystal structure of Cas9-RNA bound to a cognate DNA target (PDB ID: 4UN3)
Functional activity of fluorescence-labeled ribosome complexes used in this study, as determined by the time-resolved puromycin assay.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Functional activity of fluorescence-labeled ribosome complexes used in this study, as determined by the time-resolved puromycin assay. Closed circles, unlabeled PRE complex; open
Supplementary Figure 1 Functional activity of fluorescence-labeled ribosome complexes used in this study, as determined by the time-resolved puromycin assay. Closed circles, unlabeled PRE complex; open
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Results Construct purification and coupling. Two A1-GP1bα ReaLiSM constructs, with and without cysteine residues near the N and C-termini (Fig. S2a), were expressed and purified by Ni affinity chromatography
Results Construct purification and coupling. Two A1-GP1bα ReaLiSM constructs, with and without cysteine residues near the N and C-termini (Fig. S2a), were expressed and purified by Ni affinity chromatography
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Koh et al. 10.1073/pnas.1212917110 SI Materials and Methods Protein Purification. N-terminal His 6 -Dicer was purified as previously described with several modifications (1). After
Supporting Information Koh et al. 10.1073/pnas.1212917110 SI Materials and Methods Protein Purification. N-terminal His 6 -Dicer was purified as previously described with several modifications (1). After
Visualization of codon-dependent conformational rearrangements during translation termination
 Supplementary information for: Visualization of codon-dependent conformational rearrangements during translation termination Shan L. He 1 and Rachel Green 1 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department
Supplementary information for: Visualization of codon-dependent conformational rearrangements during translation termination Shan L. He 1 and Rachel Green 1 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department
Bacterial trans-encoded small regulatory RNAs (srnas)
 This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial purposes. pubs.acs.org/biochemistry
This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial purposes. pubs.acs.org/biochemistry
Oligonucleotides were purchased from Eurogentec, purified by denaturing gel electrophoresis
 SUPPLEMENRY INFORMION Purification of probes and Oligonucleotides sequence Oligonucleotides were purchased from Eurogentec, purified by denaturing gel electrophoresis and recovered by electroelution. Labelling
SUPPLEMENRY INFORMION Purification of probes and Oligonucleotides sequence Oligonucleotides were purchased from Eurogentec, purified by denaturing gel electrophoresis and recovered by electroelution. Labelling
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany RNA ligands that distinguish metabolite-induced conformations in the TPP riboswitch Günter Mayer, Marie-Sophie L. Raddatz, Julia D. Grunwald,
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany RNA ligands that distinguish metabolite-induced conformations in the TPP riboswitch Günter Mayer, Marie-Sophie L. Raddatz, Julia D. Grunwald,
Supplementary Figure 1. Antibody-induced cargo release studied by native PAGE. A clear band corresponding to the cargo strand (lane 1) is visible.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Antibody-induced cargo release studied by native PAGE. A clear band corresponding to the cargo strand (lane 1) is visible. Because SYBR Gold is less sensitive to single stranded
Supplementary Figure 1. Antibody-induced cargo release studied by native PAGE. A clear band corresponding to the cargo strand (lane 1) is visible. Because SYBR Gold is less sensitive to single stranded
Supplementary Materials. Signal recognition particle binds to translating ribosomes before emergence of a signal anchor sequence
 Supplementary Materials Signal recognition particle binds to translating ribosomes before emergence of a signal anchor sequence Evan Mercier, Wolf Holtkamp, Marina V. Rodnina, Wolfgang Wintermeyer* Department
Supplementary Materials Signal recognition particle binds to translating ribosomes before emergence of a signal anchor sequence Evan Mercier, Wolf Holtkamp, Marina V. Rodnina, Wolfgang Wintermeyer* Department
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06147 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 The genomic and domain structure of Dscam. The Dscam gene comprises 24 exons, encoding a signal peptide (SP), 10 IgSF domains, 6 fibronectin
doi: 10.1038/nature06147 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 The genomic and domain structure of Dscam. The Dscam gene comprises 24 exons, encoding a signal peptide (SP), 10 IgSF domains, 6 fibronectin
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) and Mycobacterium smegmatis (Msmeg) contain two ε (dnaq) exonuclease homologs.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) and Mycobacterium smegmatis (Msmeg) contain two ε (dnaq) exonuclease homologs. (a) Sequence alignment of the ε-exonuclease homologs from four different
Supplementary Figure 1 Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) and Mycobacterium smegmatis (Msmeg) contain two ε (dnaq) exonuclease homologs. (a) Sequence alignment of the ε-exonuclease homologs from four different
Supplementary information. for the paper:
 Supplementary information for the paper: Screening for protein-protein interactions using Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) and fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) Anca Margineanu 1*,
Supplementary information for the paper: Screening for protein-protein interactions using Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) and fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) Anca Margineanu 1*,
Supplementary Information for
 Supplementary Information for Conformational landscapes of DNA polymerase I and mutator derivatives establish fidelity checkpoints for nucleotide insertion Hohlbein et al. 1 Supplementary Figure S1. Wt
Supplementary Information for Conformational landscapes of DNA polymerase I and mutator derivatives establish fidelity checkpoints for nucleotide insertion Hohlbein et al. 1 Supplementary Figure S1. Wt
Conformation of the Mineralocorticoid Receptor N- terminal Domain: Evidence for Induced and Stable Structure
 ME-10-0005 Conformation of the Mineralocorticoid Receptor N- terminal Domain: Evidence for Induced and Stable Structure Katharina Fischer 1, Sharon M. Kelly 2, Kate Watt 1, Nicholas C. Price 2 and Iain
ME-10-0005 Conformation of the Mineralocorticoid Receptor N- terminal Domain: Evidence for Induced and Stable Structure Katharina Fischer 1, Sharon M. Kelly 2, Kate Watt 1, Nicholas C. Price 2 and Iain
Supplementary Note 1. Enzymatic properties of the purified Syn BVR
 Supplementary Note 1. Enzymatic properties of the purified Syn BVR The expression vector pet15b-syn bvr allowed us to routinely prepare 15 mg of electrophoretically homogenous Syn BVR from 2.5 L of TB-medium
Supplementary Note 1. Enzymatic properties of the purified Syn BVR The expression vector pet15b-syn bvr allowed us to routinely prepare 15 mg of electrophoretically homogenous Syn BVR from 2.5 L of TB-medium
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Reengineering Protein Interfaces Yields Copper-Inducible Ferritin Cage Assembly
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Reengineering Protein Interfaces Yields Copper-Inducible Ferritin Cage Assembly Dustin J. E. Huard, Kathleen M. Kane and F. Akif Tezcan* Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Reengineering Protein Interfaces Yields Copper-Inducible Ferritin Cage Assembly Dustin J. E. Huard, Kathleen M. Kane and F. Akif Tezcan* Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry,
DNA supercoiling, a critical signal regulating the basal expression of the lac operon in Escherichia coli
 Supplementary Information DNA supercoiling, a critical signal regulating the basal expression of the lac operon in Escherichia coli Geraldine Fulcrand 1,2, Samantha Dages 1,2, Xiaoduo Zhi 1,2, Prem Chapagain
Supplementary Information DNA supercoiling, a critical signal regulating the basal expression of the lac operon in Escherichia coli Geraldine Fulcrand 1,2, Samantha Dages 1,2, Xiaoduo Zhi 1,2, Prem Chapagain
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3494
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
Supplementary Materials. for. array reveals biophysical and evolutionary landscapes
 Supplementary Materials for Quantitative analysis of RNA- protein interactions on a massively parallel array reveals biophysical and evolutionary landscapes Jason D. Buenrostro 1,2,4, Carlos L. Araya 1,4,
Supplementary Materials for Quantitative analysis of RNA- protein interactions on a massively parallel array reveals biophysical and evolutionary landscapes Jason D. Buenrostro 1,2,4, Carlos L. Araya 1,4,
Advanced Protein Electrophoresis. Advanced Protein Electrophoresis. Learning Objective. Proteomics ; Molecular & cell Biology
 Electrophoresis is a powerful technique for finer protein separation and visualization of separated proteins. It is based on the principle of migration of charged proteins in an electric field. Electrophoretic
Electrophoresis is a powerful technique for finer protein separation and visualization of separated proteins. It is based on the principle of migration of charged proteins in an electric field. Electrophoretic
Supplementary Online Material. Structural mimicry in transcription regulation of human RNA polymerase II by the. DNA helicase RECQL5
 Supplementary Online Material Structural mimicry in transcription regulation of human RNA polymerase II by the DNA helicase RECQL5 Susanne A. Kassube, Martin Jinek, Jie Fang, Susan Tsutakawa and Eva Nogales
Supplementary Online Material Structural mimicry in transcription regulation of human RNA polymerase II by the DNA helicase RECQL5 Susanne A. Kassube, Martin Jinek, Jie Fang, Susan Tsutakawa and Eva Nogales
Coleman et al., Supplementary Figure 1
 Coleman et al., Supplementary Figure 1 BrdU Merge G1 Early S Mid S Supplementary Figure 1. Sequential destruction of CRL4 Cdt2 targets during the G1/S transition. HCT116 cells were synchronized by sequential
Coleman et al., Supplementary Figure 1 BrdU Merge G1 Early S Mid S Supplementary Figure 1. Sequential destruction of CRL4 Cdt2 targets during the G1/S transition. HCT116 cells were synchronized by sequential
Supporting Information for: DNA-based delivery vehicles: ph-controlled disassembly and cargo release by Jung-Won Keum and Harry Bermudez
 Supporting Information for: DNA-based delivery vehicles: ph-controlled disassembly and cargo release by Jung-Won Keum and Harry Bermudez DNA sequences Strand Sequence 1- GGGTTAGGGTTAGGGTTAGGGAGGGTTAGGGTTAGGGTTAGGGAGGGTTAGGGTTAGGGTTAGGG
Supporting Information for: DNA-based delivery vehicles: ph-controlled disassembly and cargo release by Jung-Won Keum and Harry Bermudez DNA sequences Strand Sequence 1- GGGTTAGGGTTAGGGTTAGGGAGGGTTAGGGTTAGGGTTAGGGAGGGTTAGGGTTAGGGTTAGGG
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 A biomimetic DNA-based channel for the ligand-controlled transport of charged molecular cargo across a biological membrane Jonathan R. Burns, Astrid Seifert, Niels Fertig, Stefan Howorka NATURE NANOTECHNOLOGY
A biomimetic DNA-based channel for the ligand-controlled transport of charged molecular cargo across a biological membrane Jonathan R. Burns, Astrid Seifert, Niels Fertig, Stefan Howorka NATURE NANOTECHNOLOGY
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Amplified Visualization of Protein-Specific Glycosylation in Zebrafish via Proximity-Induced Hybridization Chain Reaction Jingying Li, Shuya Liu, Liqin Sun, Wei Li,
Electronic Supplementary Information Amplified Visualization of Protein-Specific Glycosylation in Zebrafish via Proximity-Induced Hybridization Chain Reaction Jingying Li, Shuya Liu, Liqin Sun, Wei Li,
PDIP46 (DNA polymerase δ interacting protein 46) is an activating factor for human DNA polymerase δ
 PDIP46 (DNA polymerase δ interacting protein 46) is an activating factor for human DNA polymerase δ Supplementary Material Figure S1. PDIP46 is associated with Pol isolated by immunoaffinity chromatography.
PDIP46 (DNA polymerase δ interacting protein 46) is an activating factor for human DNA polymerase δ Supplementary Material Figure S1. PDIP46 is associated with Pol isolated by immunoaffinity chromatography.
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2014. Supporting Information for Small, DOI: 10.1002/smll.201303558 Ultraspecific and Highly Sensitive Nucleic Acid Detection by Integrating
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2014. Supporting Information for Small, DOI: 10.1002/smll.201303558 Ultraspecific and Highly Sensitive Nucleic Acid Detection by Integrating
Supplementary Figure 1: Two modes of low concentration of BsSMC on a DNA (a) Protein staining (left) and fluorescent imaging of Cy3 (right) confirm
 Supplementary Figure 1: Two modes of low concentration of BsSMC on a DNA (a) Protein staining (left) and fluorescent imaging of Cy3 (right) confirm that BsSMC was labeled with Cy3 NHS-Ester. In each panel,
Supplementary Figure 1: Two modes of low concentration of BsSMC on a DNA (a) Protein staining (left) and fluorescent imaging of Cy3 (right) confirm that BsSMC was labeled with Cy3 NHS-Ester. In each panel,
Supplementary Information
 1 upplementary Information Membrane targeting mechanism of Rab GTPases elucidated by semisynthetic prenylated protein probes Yao-Wen Wu*,, Lena K. esterlin, Kui-Thong Tan, erbert Waldmann, Kirill Alexandrov
1 upplementary Information Membrane targeting mechanism of Rab GTPases elucidated by semisynthetic prenylated protein probes Yao-Wen Wu*,, Lena K. esterlin, Kui-Thong Tan, erbert Waldmann, Kirill Alexandrov
Hossain_Supplemental Figure 1
 Hossain_Supplemental Figure 1 GFP-PACT GFP-PACT Motif I GFP-PACT Motif II A. MG132 (1µM) GFP Tubulin GFP-PACT Pericentrin GFP-PACT GFP-PACT Pericentrin Fig. S1. Expression and localization of Orc1 PACT
Hossain_Supplemental Figure 1 GFP-PACT GFP-PACT Motif I GFP-PACT Motif II A. MG132 (1µM) GFP Tubulin GFP-PACT Pericentrin GFP-PACT GFP-PACT Pericentrin Fig. S1. Expression and localization of Orc1 PACT
Multiplex PCR. Bruce Applegate, Michael Kane and Sergei Savikhin. Analysis of multiplex PCR reactions. Detect multiple target DNA sequences
 Improved Detection Techniques for Food Borne Pathogens Use of Multi-Plex Detection Platforms Bruce Applegate, Michael Kane and Sergei Savikhin Multiplex PCR Detect multiple target DNA sequences Multiple
Improved Detection Techniques for Food Borne Pathogens Use of Multi-Plex Detection Platforms Bruce Applegate, Michael Kane and Sergei Savikhin Multiplex PCR Detect multiple target DNA sequences Multiple
Supplementary Figure 1. Analysis of replication rates by Pol. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3207
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of replication rates by Pol (a) Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) of Pol -DV binding to template-primer DNA (Fried, M. & Crothers, D.M. Equilibria and kinetics
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of replication rates by Pol (a) Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) of Pol -DV binding to template-primer DNA (Fried, M. & Crothers, D.M. Equilibria and kinetics
3-Input Majority Logic Gate and Multiple Input Logic Circuit Based on DNA Strand Displacement
 Supporting Information for 3-Input Majority Logic Gate and Multiple Input Logic Circuit Based on DNA Strand Displacement Wei Li, Yang Yang, Hao Yan, Yan Liu Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry and
Supporting Information for 3-Input Majority Logic Gate and Multiple Input Logic Circuit Based on DNA Strand Displacement Wei Li, Yang Yang, Hao Yan, Yan Liu Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry and
Mechanism of Transcription Termination by RNA Polymerase III Utilizes a Non-template Strand Sequence-Specific Signal Element
 Molecular Cell Supplemental Information Mechanism of ranscription ermination by RNA Polymerase III Utilizes a Non-template Strand Sequence-Specific Signal Element Aneeshkumar G. Arimbasseri and Richard
Molecular Cell Supplemental Information Mechanism of ranscription ermination by RNA Polymerase III Utilizes a Non-template Strand Sequence-Specific Signal Element Aneeshkumar G. Arimbasseri and Richard
Supplementatry Fig 1. Domain structure, biophysical characterisation and electron microscopy of a TD. (a) XTACC3/Maskin and XMAP215/chTOG domain
 Supplementatry Fig 1. Domain structure, biophysical characterisation and electron microscopy of a TD. (a) XTACC3/Maskin and XMAP215/chTOG domain architecture. Various C-terminal fragments were cloned and
Supplementatry Fig 1. Domain structure, biophysical characterisation and electron microscopy of a TD. (a) XTACC3/Maskin and XMAP215/chTOG domain architecture. Various C-terminal fragments were cloned and
Stopped-Flow Fluorescence Polarisation/Anisotropy
 SX SERIES APPLICATION NOTE Stopped-Flow Fluorescence Polarisation/Anisotropy Abstract: Stopped-flow fluorescence polarisation/anisotropy is a highly useful technique for obtaining valuable kinetic information
SX SERIES APPLICATION NOTE Stopped-Flow Fluorescence Polarisation/Anisotropy Abstract: Stopped-flow fluorescence polarisation/anisotropy is a highly useful technique for obtaining valuable kinetic information
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/11/e1601625/dc1 Supplementary Materials for A molecular mechanism of chaperone-client recognition This PDF file includes: Lichun He, Timothy Sharpe, Adam Mazur,
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/11/e1601625/dc1 Supplementary Materials for A molecular mechanism of chaperone-client recognition This PDF file includes: Lichun He, Timothy Sharpe, Adam Mazur,
Amgen Laboratory Series. Tabs C and E
 Amgen Laboratory Series Tabs C and E Chapter 2A Goals Describe the characteristics of plasmids Explain how plasmids are used in cloning a gene Describe the function of restriction enzymes Explain how to
Amgen Laboratory Series Tabs C and E Chapter 2A Goals Describe the characteristics of plasmids Explain how plasmids are used in cloning a gene Describe the function of restriction enzymes Explain how to
Supporting Information. DNA Tetraplexes-Based Toehold Activation for Controllable DNA Strand Displacement Reactions
 Supporting Information DNA Tetraplexes-Based Toehold Activation for Controllable DNA Strand Displacement Reactions Wei Tang, Huaming Wang, Dingzhong Wang, Yan Zhao, Na Li, and Feng Liu* Beijing National
Supporting Information DNA Tetraplexes-Based Toehold Activation for Controllable DNA Strand Displacement Reactions Wei Tang, Huaming Wang, Dingzhong Wang, Yan Zhao, Na Li, and Feng Liu* Beijing National
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11726 Supplementary Figure 1 SRP RNA constructs used in single molecule experiments. a, Secondary structure of wildtype E. coli SRP RNA, which forms an elongated hairpin structure capped
doi:10.1038/nature11726 Supplementary Figure 1 SRP RNA constructs used in single molecule experiments. a, Secondary structure of wildtype E. coli SRP RNA, which forms an elongated hairpin structure capped
Supplementary Table 1. Oligonucleotide sequences used in the study
 Supplementary Table 1. Oligonucleotide sequences used in the study Oligonucleotides Sequences (5 3 ) Substrate strand Lock -4 Lock -5 Lock -6 Lock -7 Free control DNAzyme DNAzyme strand linked to AuNP
Supplementary Table 1. Oligonucleotide sequences used in the study Oligonucleotides Sequences (5 3 ) Substrate strand Lock -4 Lock -5 Lock -6 Lock -7 Free control DNAzyme DNAzyme strand linked to AuNP
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Mechanism for signal-induced opening of the DNA box. a, An atomic model of the DNA box held closed by locks (orange and blue) that are double helices formed by two short strands
Supplementary Figure 1. Mechanism for signal-induced opening of the DNA box. a, An atomic model of the DNA box held closed by locks (orange and blue) that are double helices formed by two short strands
Molecular Techniques. 3 Goals in Molecular Biology. Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA. Disclaimer Nucleic Acids Proteins
 Molecular Techniques Disclaimer Nucleic Acids Proteins Houpt, CMN, 9-30-11 3 Goals in Molecular Biology Identify All nucleic acids (and proteins) are chemically identical in aggregate - need to identify
Molecular Techniques Disclaimer Nucleic Acids Proteins Houpt, CMN, 9-30-11 3 Goals in Molecular Biology Identify All nucleic acids (and proteins) are chemically identical in aggregate - need to identify
Single-molecule real-time detection of telomerase extension activity
 Supplementary Information Single-molecule real-time detection of telomerase extension activity Helen Hwang 1, Patricia Opresko 2, Sua Myong 1,3,4,5 1. Bioengineering Department, University of Illinois
Supplementary Information Single-molecule real-time detection of telomerase extension activity Helen Hwang 1, Patricia Opresko 2, Sua Myong 1,3,4,5 1. Bioengineering Department, University of Illinois
RNP purification, components and activity.
 Supplementary Figure 1 RNP purification, components and activity. (a) Intein-mediated RNP production and purification. The Ll.LtrB intron RNA (red) (Exons E1 and E2 in green) and associated intron encoded
Supplementary Figure 1 RNP purification, components and activity. (a) Intein-mediated RNP production and purification. The Ll.LtrB intron RNA (red) (Exons E1 and E2 in green) and associated intron encoded
Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription
 Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription Cis-acting sequences Distance-independent cis-acting elements Dissecting regulatory elements Transcription factors Overview transcriptional regulation Transcription
Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription Cis-acting sequences Distance-independent cis-acting elements Dissecting regulatory elements Transcription factors Overview transcriptional regulation Transcription
substrate with ri was incubated with endonuclease V enzymes (25 nm) in buffers with varying ph (7.5-
 Supplementary information Effect of ph, Mg 2+ and Mn 2+ concentrations on endonuclease V activity. (a) Single-stranded RNA substrate with ri was incubated with endonuclease V enzymes (25 nm) in buffers
Supplementary information Effect of ph, Mg 2+ and Mn 2+ concentrations on endonuclease V activity. (a) Single-stranded RNA substrate with ri was incubated with endonuclease V enzymes (25 nm) in buffers
Supplementary Information. Arrays of Individual DNA Molecules on Nanopatterned Substrates
 Supplementary Information Arrays of Individual DNA Molecules on Nanopatterned Substrates Roland Hager, Alma Halilovic, Jonathan R. Burns, Friedrich Schäffler, Stefan Howorka S1 Figure S-1. Characterization
Supplementary Information Arrays of Individual DNA Molecules on Nanopatterned Substrates Roland Hager, Alma Halilovic, Jonathan R. Burns, Friedrich Schäffler, Stefan Howorka S1 Figure S-1. Characterization
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11500 Figure S1: The sector in the PDZ domain family. Sectors are defined as groups of statistically coevolving amino acid positions in a protein family and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11500 Figure S1: The sector in the PDZ domain family. Sectors are defined as groups of statistically coevolving amino acid positions in a protein family and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1. Crystallographic statistics CRM1-SNUPN complex Space group P6 4 22 a=b=250.4, c=190.4 Data collection statistics: CRM1-selenomethionine SNUPN MAD data Peak Inflection Remote Native
Supplementary Table 1. Crystallographic statistics CRM1-SNUPN complex Space group P6 4 22 a=b=250.4, c=190.4 Data collection statistics: CRM1-selenomethionine SNUPN MAD data Peak Inflection Remote Native
Supplementary data. sienigma. F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM. a-p53
 Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
Supplementary data Supplemental Figure 1 A sienigma #2 sienigma sicontrol a-enigma - + ++ - - - - - - + ++ - - - - - - ++ B sienigma F-Enigma F-EnigmaSM a-flag HLK3 cells - - - + ++ + ++ - + - + + - -
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Deng et al. 10.1073/pnas.1515692112 SI Materials and Methods FPLC. All fusion proteins were expressed and purified through a three-step FPLC purification protocol, as described (20),
Supporting Information Deng et al. 10.1073/pnas.1515692112 SI Materials and Methods FPLC. All fusion proteins were expressed and purified through a three-step FPLC purification protocol, as described (20),
Supplemental Figure 1. Ribose-614 cleavage is unaffected by the addition of 10%
 Supplemental Figure 1. Ribose-614 cleavage is unaffected by the addition of 1% complementary strand. Addition of equimolar amounts of the complement greatly lowers cleavage rate and plateau. (A) Cleavage
Supplemental Figure 1. Ribose-614 cleavage is unaffected by the addition of 1% complementary strand. Addition of equimolar amounts of the complement greatly lowers cleavage rate and plateau. (A) Cleavage
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
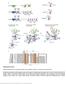 Supplementary Figure 1 Domain architecture and conformational states of the decapping complex, as revealed by structural studies. (a) Domain organization of Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sp) and Saccharomyces
Supplementary Figure 1 Domain architecture and conformational states of the decapping complex, as revealed by structural studies. (a) Domain organization of Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sp) and Saccharomyces
Human endonuclease V is a ribonuclease specific for inosine-containing RNA
 Supplementary Information Human endonuclease V is a ribonuclease specific for inosine-containing RNA Yoko Morita 1, Toshihiro Shibutani 1, Nozomi Nakanishi 1, Kazuko Nishikura 2, Shigenori Iwai 1, Isao
Supplementary Information Human endonuclease V is a ribonuclease specific for inosine-containing RNA Yoko Morita 1, Toshihiro Shibutani 1, Nozomi Nakanishi 1, Kazuko Nishikura 2, Shigenori Iwai 1, Isao
Deep sequencing reveals global patterns of mrna recruitment
 Supplementary information for: Deep sequencing reveals global patterns of mrna recruitment during translation initiation Rong Gao 1#*, Kai Yu 1#, Ju-Kui Nie 1,Teng-Fei Lian 1, Jian-Shi Jin 1, Anders Liljas
Supplementary information for: Deep sequencing reveals global patterns of mrna recruitment during translation initiation Rong Gao 1#*, Kai Yu 1#, Ju-Kui Nie 1,Teng-Fei Lian 1, Jian-Shi Jin 1, Anders Liljas
Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of LRRK1 bind to Grb2.
 Myc- HA-Grb2 Mr(K) 105 IP HA 75 25 105 1-1163 1-595 - + - + - + 1164-1989 Blot Myc HA total lysate 75 25 Myc HA Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of bind to Grb2. COS7 cells were cotransfected
Myc- HA-Grb2 Mr(K) 105 IP HA 75 25 105 1-1163 1-595 - + - + - + 1164-1989 Blot Myc HA total lysate 75 25 Myc HA Supplementary Figure S1. N-terminal fragments of bind to Grb2. COS7 cells were cotransfected
Supplementary Figure 1. Ratiometric fluorescence visualization of DNA cleavage by
 Supplementary Figure 1. Ratiometric fluorescence visualization of DNA cleavage by Cas9:gRNA. (a) A labeled by Cy3 and Cy5 with an inter-probe distance of > 30 bp was tethered to a PEG-coated surface via
Supplementary Figure 1. Ratiometric fluorescence visualization of DNA cleavage by Cas9:gRNA. (a) A labeled by Cy3 and Cy5 with an inter-probe distance of > 30 bp was tethered to a PEG-coated surface via
Supplemental Data. Farmer et al. (2010) Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Amino acid sequence comparison of RAD23 proteins. Identical and similar residues are shown in the black and gray boxes, respectively. Dots denote gaps. The sequence of plant Ub is
Supplemental Figure 1. Amino acid sequence comparison of RAD23 proteins. Identical and similar residues are shown in the black and gray boxes, respectively. Dots denote gaps. The sequence of plant Ub is
A Domain Swapping Study of Nano-Capsule Proteins. Rongli Fan, Aimee L. Boyle, Vee Vee Cheong, See Liang Ng, Brendan P. Orner*
 A Domain Swapping Study of Nano-Capsule Proteins Rongli Fan, Aimee L. Boyle, Vee Vee Cheong, See Liang Ng, Brendan P. Orner* Figure S1. Amino acid sequences of proteins used in this study. Grey shading
A Domain Swapping Study of Nano-Capsule Proteins Rongli Fan, Aimee L. Boyle, Vee Vee Cheong, See Liang Ng, Brendan P. Orner* Figure S1. Amino acid sequences of proteins used in this study. Grey shading
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Purification and biochemical characterization of acid phosphatase-i from seeds of Nelumbo nucifera Sanaullah Khan a*, Shahnaz Asmat c, Sajida Batool a, Mushtaq Ahmed b a Department
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Purification and biochemical characterization of acid phosphatase-i from seeds of Nelumbo nucifera Sanaullah Khan a*, Shahnaz Asmat c, Sajida Batool a, Mushtaq Ahmed b a Department
A quantitative investigation of linker histone interactions with nucleosomes and chromatin
 White et al Supplementary figures and figure legends A quantitative investigation of linker histone interactions with nucleosomes and chromatin 1 Alison E. White, Aaron R. Hieb, and 1 Karolin Luger 1 White
White et al Supplementary figures and figure legends A quantitative investigation of linker histone interactions with nucleosomes and chromatin 1 Alison E. White, Aaron R. Hieb, and 1 Karolin Luger 1 White
Studies of G-quadruplexes formed within self-assembled DNA minicircles
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Studies of G-quadruplexes formed within self-assembled DNA minicircles Beata Klejevskaja, 1,2 Alice
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Studies of G-quadruplexes formed within self-assembled DNA minicircles Beata Klejevskaja, 1,2 Alice
HBV RNA pre-genome encodes specific motifs that mediate interactions with the viral core protein that promote nucleocapsid assembly
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Nikesh Patel *, Simon J. White *, Rebecca F Thompson, Richard Bingham 1, Eva U. Weiß 1, Daniel P. Maskell, Adam Zlotnick 2,
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Nikesh Patel *, Simon J. White *, Rebecca F Thompson, Richard Bingham 1, Eva U. Weiß 1, Daniel P. Maskell, Adam Zlotnick 2,
Supporting Information. Multi-strand Structure Prediction of Nucleic. Acid Assemblies and Design of RNA Switches
 Supporting Information Multi-strand Structure Prediction of Nucleic Acid Assemblies and Design of RNA Switches Eckart Bindewald 1#, Kirill A. Afonin 2,3#, Mathias Viard 1, Paul Zakrevsky 2, Taejin Kim
Supporting Information Multi-strand Structure Prediction of Nucleic Acid Assemblies and Design of RNA Switches Eckart Bindewald 1#, Kirill A. Afonin 2,3#, Mathias Viard 1, Paul Zakrevsky 2, Taejin Kim
DNA polymerase proofreading: active site switching catalyzed by the bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase
 5452 5463 Nucleic Acids Research, 2007, Vol. 35, No. 16 Published online 15 August 2007 doi:10.1093/nar/gkm591 DNA polymerase proofreading: active site switching catalyzed by the bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase
5452 5463 Nucleic Acids Research, 2007, Vol. 35, No. 16 Published online 15 August 2007 doi:10.1093/nar/gkm591 DNA polymerase proofreading: active site switching catalyzed by the bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase
WESTERN BLOT. BCH462- Practical
 WESTERN BLOT BCH462- Practical What is Antigen [Ag]? What is Antibody [Ab]? Immunoassay: is a test that uses the highly specific and selective antigen-antibody reactions forming antibody and antigen complexes
WESTERN BLOT BCH462- Practical What is Antigen [Ag]? What is Antibody [Ab]? Immunoassay: is a test that uses the highly specific and selective antigen-antibody reactions forming antibody and antigen complexes
Supplementary Figure 1 PZA inhibits root hair formation as well as cell elongation in the maturation zone of eto1-2 roots. (A) The PI staining of the
 Supplementary Figure 1 PZA inhibits root hair formation as well as cell elongation in the maturation zone of eto1-2 roots. (A) The PI staining of the roots of three-day-old etiolated seedlings of Col-0
Supplementary Figure 1 PZA inhibits root hair formation as well as cell elongation in the maturation zone of eto1-2 roots. (A) The PI staining of the roots of three-day-old etiolated seedlings of Col-0
Supplemental Information. A Versatile Tool for Live-Cell Imaging. and Super-Resolution Nanoscopy Studies. of HIV-1 Env Distribution and Mobility
 Cell Chemical Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information A Versatile Tool for Live-Cell Imaging and Super-Resolution Nanoscopy Studies of HIV-1 Env Distribution and Mobility Volkan Sakin, Janina Hanne,
Cell Chemical Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information A Versatile Tool for Live-Cell Imaging and Super-Resolution Nanoscopy Studies of HIV-1 Env Distribution and Mobility Volkan Sakin, Janina Hanne,
Supplementary Information. Small Molecule-Induced Domain Swapping as a Mechanism for Controlling Protein Function and Assembly
 Supplementary Information Small Molecule-Induced Domain Swapping as a Mechanism for Controlling Protein Function and Assembly Joshua M. Karchin, Jeung-Hoi Ha, Kevin E. Namitz, Michael S. Cosgrove, and
Supplementary Information Small Molecule-Induced Domain Swapping as a Mechanism for Controlling Protein Function and Assembly Joshua M. Karchin, Jeung-Hoi Ha, Kevin E. Namitz, Michael S. Cosgrove, and
Modulating the Cascade architecture of a minimal Type I-F CRISPR-Cas system
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Modulating the Cascade architecture of a minimal Type I-F CRISPR-Cas system Daniel Gleditzsch 1, Hanna Müller-Esparza 1, Patrick Pausch 2,3, Kundan Sharma 4, Srivatsa Dwarakanath 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Modulating the Cascade architecture of a minimal Type I-F CRISPR-Cas system Daniel Gleditzsch 1, Hanna Müller-Esparza 1, Patrick Pausch 2,3, Kundan Sharma 4, Srivatsa Dwarakanath 1,
Supplementary Results Supplementary Table 1. P1 and P2 enrichment scores for wild-type subtiligase.
 Supplementary Results Supplementary Table 1. P1 and P2 enrichment scores for wild-type subtiligase. Supplementary Table 2. Masses of subtiligase mutants measured by LC-MS. Supplementary Table 2 (cont d).
Supplementary Results Supplementary Table 1. P1 and P2 enrichment scores for wild-type subtiligase. Supplementary Table 2. Masses of subtiligase mutants measured by LC-MS. Supplementary Table 2 (cont d).
Supplementary Materials: A Toolbox of Genetically Encoded FRET-Based Biosensors for Rapid L-Lysine Analysis
 S1 of S9 Supplementary Materials: A Toolbox of Genetically Encoded FRET-Based Biosensors for Rapid L-Lysine Analysis Victoria Steffen, Julia Otten, Susann Engelmann, Andreas Radek, Michael Limberg, Bernd
S1 of S9 Supplementary Materials: A Toolbox of Genetically Encoded FRET-Based Biosensors for Rapid L-Lysine Analysis Victoria Steffen, Julia Otten, Susann Engelmann, Andreas Radek, Michael Limberg, Bernd
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12119 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND LEGENDS pre-let-7a- 1 +14U pre-let-7a- 1 Ddx3x Dhx30 Dis3l2 Elavl1 Ggt5 Hnrnph 2 Osbpl5 Puf60 Rnpc3 Rpl7 Sf3b3 Sf3b4 Tia1 Triobp U2af1 U2af2 1 6 2 4 3
doi:10.1038/nature12119 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND LEGENDS pre-let-7a- 1 +14U pre-let-7a- 1 Ddx3x Dhx30 Dis3l2 Elavl1 Ggt5 Hnrnph 2 Osbpl5 Puf60 Rnpc3 Rpl7 Sf3b3 Sf3b4 Tia1 Triobp U2af1 U2af2 1 6 2 4 3
Notes to accompany the slidecast on theory of SDS PAGE and Western blotting
 S317 Biological science: from genes to species Notes to accompany the slidecast on theory of SDS PAGE and Western blotting SDS PAGE SDS PAGE is a standard technique for determining the molecular size of
S317 Biological science: from genes to species Notes to accompany the slidecast on theory of SDS PAGE and Western blotting SDS PAGE SDS PAGE is a standard technique for determining the molecular size of
Fig. S1. CrgA intracellular levels in M. tuberculosis. Ten and twenty micrograms of
 Supplementary data Fig. S1. CrgA intracellular levels in M. tuberculosis. Ten and twenty micrograms of cell free protein lysates from WT M. tuberculosis (Rv) together with various known concentrations
Supplementary data Fig. S1. CrgA intracellular levels in M. tuberculosis. Ten and twenty micrograms of cell free protein lysates from WT M. tuberculosis (Rv) together with various known concentrations
A Highly Selective Lead Sensor Based on a Classic Lead DNAzyme.
 Supplementary Information Submitted to Chemical Communications A Highly Selective Lead Sensor Based on a Classic Lead DNAzyme. Tian Lan a, Kimberly Furuya b and Yi Lu* b a Department of Biochemistry, b
Supplementary Information Submitted to Chemical Communications A Highly Selective Lead Sensor Based on a Classic Lead DNAzyme. Tian Lan a, Kimberly Furuya b and Yi Lu* b a Department of Biochemistry, b
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2017). Plant Cell /tpc NIP1;2 NIP7;1
 Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (217). Plant Cell 1.115/tpc.16.825 NIP1;1 NIP1;2 NIP2;1 NIP3;1 NIP4;1 NIP5;1 NIP6;1 NIP7;1 Supplemental Figure 1. Distinct Localization of NIPs in Root Epidermal Cells. (Supports
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (217). Plant Cell 1.115/tpc.16.825 NIP1;1 NIP1;2 NIP2;1 NIP3;1 NIP4;1 NIP5;1 NIP6;1 NIP7;1 Supplemental Figure 1. Distinct Localization of NIPs in Root Epidermal Cells. (Supports
Suppl. Figure 1: RCC1 sequence and sequence alignments. (a) Amino acid
 Supplementary Figures Suppl. Figure 1: RCC1 sequence and sequence alignments. (a) Amino acid sequence of Drosophila RCC1. Same colors are for Figure 1 with sequence of β-wedge that interacts with Ran in
Supplementary Figures Suppl. Figure 1: RCC1 sequence and sequence alignments. (a) Amino acid sequence of Drosophila RCC1. Same colors are for Figure 1 with sequence of β-wedge that interacts with Ran in
Product Specifications & Manual
 Product Specifications & Manual Custom Oligo Synthesis, antisense oligos, RNA oligos, chimeric oligos, Fluorescent dye labeled oligos, Molecular Beacons, sirna, phosphonates Affinity Ligands, 2-5 linked
Product Specifications & Manual Custom Oligo Synthesis, antisense oligos, RNA oligos, chimeric oligos, Fluorescent dye labeled oligos, Molecular Beacons, sirna, phosphonates Affinity Ligands, 2-5 linked
Isothermal amplification system based on template-dependent extension
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Isothermal amplification system based on template-dependent extension 1. Experimental Section The molecular beacon (Takara Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Dalian, China)
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Isothermal amplification system based on template-dependent extension 1. Experimental Section The molecular beacon (Takara Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Dalian, China)
Lecture 13: Analysis of 2D gels
 Lecture 13: Analysis of 2D gels A complete proteomic analysis aims at collecting quantitative information about all protein in a sample. A normal 2 Dimensional gel electrophoresis results are analyzed
Lecture 13: Analysis of 2D gels A complete proteomic analysis aims at collecting quantitative information about all protein in a sample. A normal 2 Dimensional gel electrophoresis results are analyzed
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Coupling dttp Hydrolysis with DNA Unwinding by the DNA Helicase of Bacteriophage T7 Satapathy, Ajit K.; Kulczyk, Arkadiusz W.; Ghosh, Sharmistha; van Oijen, Antonius; Richardson,
University of Groningen Coupling dttp Hydrolysis with DNA Unwinding by the DNA Helicase of Bacteriophage T7 Satapathy, Ajit K.; Kulczyk, Arkadiusz W.; Ghosh, Sharmistha; van Oijen, Antonius; Richardson,
RPA-AB RPA-C Supplemental Figure S1: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue after protein purification.
 RPA-AB RPA-C (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Supplemental Figure S: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue after protein purification. (a) RPA; (b) RPA-AB; (c) RPA-CDE; (d) RPA-CDE core; (e) RPA-DE; and (f) RPA-C
RPA-AB RPA-C (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Supplemental Figure S: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue after protein purification. (a) RPA; (b) RPA-AB; (c) RPA-CDE; (d) RPA-CDE core; (e) RPA-DE; and (f) RPA-C
Supplementary Information for. Coordination of multiple enzyme activities by a single PCNA in archaeal Okazaki fragment.
 Supplementary Information for Coordination of multiple enzyme activities by a single PCNA in archaeal Okazaki fragment maturation Thomas R. Beattie and Stephen D. Bell Sir William Dunn School of Pathology,
Supplementary Information for Coordination of multiple enzyme activities by a single PCNA in archaeal Okazaki fragment maturation Thomas R. Beattie and Stephen D. Bell Sir William Dunn School of Pathology,
Kawamata et al., Figure S1
 Kawamata et al., Figure S1 +Lysate Lysate Time (min) ss let-7 1 15 3 6 Duplex A Duplex B 1 15 3 6 1 15 3 6 ss let-7 Duplex A Duplex B Complex I Complex II Complex III Complex IV Complex V Free ighter exposure
Kawamata et al., Figure S1 +Lysate Lysate Time (min) ss let-7 1 15 3 6 Duplex A Duplex B 1 15 3 6 1 15 3 6 ss let-7 Duplex A Duplex B Complex I Complex II Complex III Complex IV Complex V Free ighter exposure
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Tolerance of a knotted near infrared fluorescent protein to random circular permutation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Tolerance of a knotted near infrared fluorescent protein to random circular permutation Naresh Pandey 1,3, Brianna E. Kuypers 2,4, Barbara Nassif 1, Emily E. Thomas 1,3, Razan
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Tolerance of a knotted near infrared fluorescent protein to random circular permutation Naresh Pandey 1,3, Brianna E. Kuypers 2,4, Barbara Nassif 1, Emily E. Thomas 1,3, Razan
JCB. Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY. Hong et al.,
 Supplemental material JCB Hong et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201412127/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Analysis of purified proteins by SDS-PAGE and pull-down assays. (A) Coomassie-stained
Supplemental material JCB Hong et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201412127/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Analysis of purified proteins by SDS-PAGE and pull-down assays. (A) Coomassie-stained
Lecture 22: Questions from Quiz 2 and the Trypsin Digestion Experiment
 Biological Chemistry Laboratory Biology 3515/Chemistry 3515 Spring 2018 Lecture 22: Questions from Quiz 2 and the Trypsin Digestion Experiment 29 March 2018 c David P. Goldenberg University of Utah goldenberg@biology.utah.edu
Biological Chemistry Laboratory Biology 3515/Chemistry 3515 Spring 2018 Lecture 22: Questions from Quiz 2 and the Trypsin Digestion Experiment 29 March 2018 c David P. Goldenberg University of Utah goldenberg@biology.utah.edu
