Wesley T. Barber, Wei Zhang, Hlaing Win, Kranthi K. Varala, Jane E. Dorweiler, Matthew E. Hudson and Stephen P. Moose
|
|
|
- Archibald Dixon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Repeat associated small RNAs vary among parents and following hybridization in maize Wesley T. Barber, Wei Zhang, Hlaing Win, Kranthi K. Varala, Jane E. Dorweiler, Matthew E. Hudson and Stephen P. Moose Abstract Small RNAs (srnas) are hypothesized to contribute to hybrid vigor because they maintain genome integrity, contribute to genetic diversity, and control gene expression. We used Illumina sequencing to assess how srna populations vary between two maize inbred lines (, ) and their hybrid. We sampled srnas from the seedling shoot apex and the developing ear, two rapidly growing tissues that program the greater growth of maize hybrids. We found that parental differences in sirnas primarily originate from repeat regions. Although the maize genome contains greater number and complexity of repeats compared to Arabidopsis or rice, we confirmed that like these simpler plant genomes, 24-nt sirnas whose abundance differs between maize parents also show a trend of downregulation following hybridization. Surprisingly, hybrid vigor is fully maintained when 24-nt sirnas are globally reduced by mutation of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase2 (RDR2) encoded by modifier of paramutation1 (mop1). We also discovered that 21-22nt sirnas derived from a number of distinct retrotransposon families differentially accumulate between and as well as their hybrid. We found that significant variation exists for nt sirna accumulation for these families among a larger set of diverse maize inbred lines. Thus, maize possesses a novel source of genetic variation for regulating both transposons and genes at a genomic scale, which may contribute to its high degree of observed heterosis.
2 Repeat associated small RNAs vary among parents and following hybridization in maize Wesley T. Barber Matthew E. Hudson Stephen P. Moose 48 th Annual Illinois Corn Breeders School March 5, 2012
3 Outline Heterosis/hybrid vigor srnas 22-nt vs. 24-nt srnas Behavior of srnas following hybridization Variation in srnas between inbred lines What to learn from this talk the maize genome provides a significant opportunity for inbred lines to vary for srnas srnas are a source for genetic variation at the epigenetic and post-transcriptional levels
4 Hybrid vigor phenotype Offspring perform better than their parents Greater cell proliferation in the hybrid x (right) is taller than one of its parents, (left).
5 Genetic principles of hybrid vigor Multiple mechanisms Genetic variation between parents Variation in regulatory genes = large effects? Altered genetic states in hybrids Additivity is an altered state Genomics uncovers more ways for how parents may vary Phenotypic value parent a parent b Stupar et al hybrid axb
6 Non-additive possibilities from genes behaving additively Inbred 1 Inbred 2 F1 Hybrid = regulatory gene = proteins Possibility for something new in hybrid (non-additivity) even from factors behaving additively
7 srnas regulate crop phenotypes Soybean seed coat color Tuteja et al Flowering time, biomass in maize Lauter et al. 2005
8 srnas are major regulators of the genome Genetically encoded mirna sirna Aberrant transcript 1 sirna rasirnas RDR Antisense transcripts natsirna DCL Cleaved transcript tasirna 2 sirna RDR AGO AGO AGO CH3 CH3 CH3 rrna srna primed 2 sirna RDR Small interfering RNAs (sirnas) regulate genes and repeats RDR enzymes Maintain genome integrity 21/22-nt sirnas posttranscriptional 24-nt sirnas transcriptional DNA methylation Target cleavage Translational inhibition
9 How do srnas behave following hybridization in maize? Shoot apex (tips) at 11 DAS srna sequencing from,, and their hybrids Compared abundances (reads per million) of individual srnas and blocks of srnas between the genotypes sampled actively growing tissues that program greater growth of hybrids Ear at V12 growth stage Emerged Leaf Leaf primordia SAM Sampled tissue
10 Differences between parents and hybrids result from and passing on divergent sirna populations % of nt sirnas Shoot apex x x 0.1% 0.2% 0.4% 1% 2% 1% 0.1% 20% 19% 1% 51% 1% 1% 1% 0.2% Ear 10% 2% 4% 50% 15% 17% 3% x Genotypes x x
11 Parental differences in nt sirnas are inherited at levels below mid-parent in the ear A. Shoot apex Log2 (F1/mp) B. Ear 5 Log2 (F1/mp) > 4x > 8x > 4x > 8x Increasing parental fold-change 24-nt sirnas reduced in Arabidopsis, rice, wheat hybrids/polyploids Connected to epigenetic and gene expression changes (Groszman et al. 2011) Transgressive phenotypes of tomato RILs are influenced by sirnas (Shivaprasad et al. 2011)
12 MOP1 (RDR2) provides unique system to test importance of 24-nt sirnas to hybrid vigor Parent 1 - wild type - mop1-1 X Parent 2 - wild type - mop1-1 Nobuta et al Reciprocal hybrids Do the mutant hybrids still show as much heterosis as wild type hybrids?
13 Loss of MOP1 reduces 24-nt sirnas and height and delays flowering for each genotype Relative Expression ( Ct) Wild type mop nt sirna-1 x 24-nt sirna-4 x wt mop1-1 wt mop1-1 x wt x mop1-1 x wt x mop1-1 Height (cm) 50% anther (days)
14 Loss of MOP1 does not suppress hybrid vigor for x Wild type x mop1-1 mutant x
15 MOP1 mutant hybrids show the same degree of heterosis as wild type hybrids Ratio of trait in hybrids relative to inbreds * ** *** x mut x wt x mut x wt * p-value p-value p-value ** ** *** *** * 0 plant height days to silk days to shed cob weight stover biomass Agronomic trait
16 Conclusions on how srnas vary following hybridization Hybridization doesn t cause global changes to srna populations or core components of srna biogenesis MOP1 result questions the functional significance of 24-nt sirnas to hybrid vigor 24-nt sirnas may play a bigger role in other processes (inbreeding?)
17 Differences in nt sirnas between and primarily originate from repeat regions gene Genomic feature repeat within gene within ±1000-bp of gene repeat within ±1000- bp of gene repeat gene repeat within gene within ±1000-bp of gene repeat within ±1000- bp of gene repeat Repeats = DNA transposons, MITEs, helitrons, retrotransposons All 22-nt 24-nt >8X 22-nt 24-nt Shoot apex Developing ear Low High Number of sirna regions Majority of genomic intervals annotated as high copy retrotransposon families
18 Parental differences in retrotransposon sirna activity are driven by 21/22-nt sirnas, not 24-nt sirnas * * * * * cinful zeon rire1 giepum grande ji misfit huck1 milt opie Total Abundance x Shoot apex x x 21-nt 22-nt 24-nt sirna length Total Abundance Developing ear x x * Indicates that for the length of sirna investigated, and were found to significantly differ in their abundance of sirnas in the same direction in both tissues (χ 2 test, Bonferroni corrected p-value 0.01). x 21-nt 22-nt 24-nt sirna length Abundance (rpm) Low High
19 Retrotransposon derived sirnas and cellular proliferation Retrotransposon derived sirnas in human stem cells may regulate DNA repair, cell cycle control and chromatin (Wang et al. 2011) Active retrotransposons in pollen cells are dealt with at posttranscriptional level Slotkin et al seedling shoot apex x polyprotein LTR-retro RNA Degraded RNA 21,22-nt sirna
20 Relative expression ( Ct) Combining divergent 21/22-nt rasirna cinful populations in the hybrid doesn t lead to greater silencing Cinful expression in seedling shoot apex x 3 leaves emerged x 4 leaves emerged x 5 leaves emerged What are retrotransposon derived sirnas doing in proliferating tissues? Regulate themselves? Regulate genes? (Ohtsu et al. 2007) Recent evidence for gene regulation found in Arabidopsis (McCue et al. 2011)
21 Current work: How do rasirnas vary among a diverse set of inbred lines in maize? Characterizing 21/22-nt rasirna across diverse maize germplasm combined with genetic tests of hybrid performance Determining if genes are targeted by rasirnas Investigating inheritance/stability of rasirnas Genetic Material 36 inbred lines, 22 NAM founders 10 PVP lines IHP1 ILP1 From Liu et al PH207 Iodent LH82 PHZ51 Unrelated PHG35 PHG84 Oh07/Midland LH123Ht PHG47 Oh43 Lancaster Stiff Stalk LH1 Stiff Stalk PHG39 Maiz Amargo PHJ40 Stiff Stalk
22 Are heterotic subgroups defined by specific patterns of 21/22-nt rasirna activities? PH207 Iodent LH82 PHZ51 Unrelated PHG35 PHG84 Oh07/Midland LH123Ht PHG47 Oh43 PH nt Oh43-21-nt - 21-nt - 21-nt Lancaster PH nt LH1 PHG39 PHJ40 Stiff Stalk Stiff Stalk Maiz Amargo Stiff Stalk Oh43-22-nt - 22-nt - 22-nt cinful dagaf giepum grande ji machiavelli opie rire1
23 Conclusions for parental variation in sirnas Studies in Arabidopsis, rice, and wheat did not find significant variation for 21/22- nt sirnas derived from retrotransposons Heterosis cannot be compared across genera because the relative degree of genetic differences varies (East, 1936) Related to the high degree of heterosis observed in the species? Nobuta et al. 2008
24 Take home messages The maize genome provides a significant opportunity for inbred lines to vary for srnas 21/22-nt rasirnas from retrotransposons may allow inbred lines to differ in their posttranscriptional regulation of repeat elements and genes at a genomic scale srnas are a source for genetic variation at the epigenetic and post-transcriptional levels Could this genomics information be useful to guide breeding strategies?
25 Acknowledgements National Science Foundation Heterosis Challenge Grant Pioneer Hi-Bred Bob Seifert Honorary Plant Breeding Fellowship Moose Lab Qing Li Wei Zhang Hudson Lab Kranthi Varala Wendy Win Ying Li Jane Dorweiler EBI/Miscanthus Magdy Albady Chris Austin
Gene Discovery of Nitrogen Utilization in Maize Yuhe Liu, Devin Nichols, Stephen Moose Department of Crop Sciences, University of Illinois
 Gene Discovery of Nitrogen Utilization in Maize Yuhe Liu, Devin Nichols, Stephen Moose Department of Crop Sciences, University of Illinois Nitrogen utilization in cereal crops such as maize significantly
Gene Discovery of Nitrogen Utilization in Maize Yuhe Liu, Devin Nichols, Stephen Moose Department of Crop Sciences, University of Illinois Nitrogen utilization in cereal crops such as maize significantly
Advances in Genetics Lesson 5
 Advances in Genetics Lesson 5 May 16 6:43 PM How can organisms be produced with desired traits? May 16 6:44 PM 1 I. How can organisms be produced with desired traits A. With advance in genetics, DNA evidence
Advances in Genetics Lesson 5 May 16 6:43 PM How can organisms be produced with desired traits? May 16 6:44 PM 1 I. How can organisms be produced with desired traits A. With advance in genetics, DNA evidence
Advances in Genetics #101
 Questions: Five study Questions EQ1: What are 3 ways of producing organisms with desired traits? EQ2: What are 2 applications of DNA technology in human genetics? Like your fingerprints, your DNA is different
Questions: Five study Questions EQ1: What are 3 ways of producing organisms with desired traits? EQ2: What are 2 applications of DNA technology in human genetics? Like your fingerprints, your DNA is different
Unit 3: Sustainability and Interdependence
 Unit 3: Sustainability and Interdependence Sub-topic 3.2 Plant and Animal Breeding Page 1 of 17 On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to: understand that plant and animal breeding involves the
Unit 3: Sustainability and Interdependence Sub-topic 3.2 Plant and Animal Breeding Page 1 of 17 On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to: understand that plant and animal breeding involves the
Identifying Genes Underlying QTLs
 Identifying Genes Underlying QTLs Reading: Frary, A. et al. 2000. fw2.2: A quantitative trait locus key to the evolution of tomato fruit size. Science 289:85-87. Paran, I. and D. Zamir. 2003. Quantitative
Identifying Genes Underlying QTLs Reading: Frary, A. et al. 2000. fw2.2: A quantitative trait locus key to the evolution of tomato fruit size. Science 289:85-87. Paran, I. and D. Zamir. 2003. Quantitative
Marker types. Potato Association of America Frederiction August 9, Allen Van Deynze
 Marker types Potato Association of America Frederiction August 9, 2009 Allen Van Deynze Use of DNA Markers in Breeding Germplasm Analysis Fingerprinting of germplasm Arrangement of diversity (clustering,
Marker types Potato Association of America Frederiction August 9, 2009 Allen Van Deynze Use of DNA Markers in Breeding Germplasm Analysis Fingerprinting of germplasm Arrangement of diversity (clustering,
Module 1 Principles of plant breeding
 Covered topics, Distance Learning course Plant Breeding M1-M5 V2.0 Dr. Jan-Kees Goud, Wageningen University & Research The five main modules consist of the following content: Module 1 Principles of plant
Covered topics, Distance Learning course Plant Breeding M1-M5 V2.0 Dr. Jan-Kees Goud, Wageningen University & Research The five main modules consist of the following content: Module 1 Principles of plant
srnas of Plants Function o Transcriptional silencing o Posttranscriptional gene silencing
 srnas of Plants Small, Non-coding RNAs of Plants Regulatory RNAs that act through gene silencing Two classes of small RNAs (srnas) o microrna (mirnas) Encoded by mirna genes in the genome o small interfering
srnas of Plants Small, Non-coding RNAs of Plants Regulatory RNAs that act through gene silencing Two classes of small RNAs (srnas) o microrna (mirnas) Encoded by mirna genes in the genome o small interfering
Supplementary Information. The flowering gene SINGLE FLOWER TRUSS drives heterosis for yield in tomato
 Supplementary Information The flowering gene SINGLE FLOWER TRUSS drives heterosis for yield in tomato Uri Krieger 1, Zachary B. Lippman 2 *, and Dani Zamir 1 * 1. The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Faculty
Supplementary Information The flowering gene SINGLE FLOWER TRUSS drives heterosis for yield in tomato Uri Krieger 1, Zachary B. Lippman 2 *, and Dani Zamir 1 * 1. The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Faculty
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Materials and Methods Transgenic Plant Materials and DNA Constructs. VEX1::H2B-GFP, ACA3::H2B-GFP, KRP6::H2B-GFP, KRP6::mock21ts-GFP, KRP6::TE21ts- GFP and KRP6::miR161ts-GFP constructs were generated
Materials and Methods Transgenic Plant Materials and DNA Constructs. VEX1::H2B-GFP, ACA3::H2B-GFP, KRP6::H2B-GFP, KRP6::mock21ts-GFP, KRP6::TE21ts- GFP and KRP6::miR161ts-GFP constructs were generated
There are four major types of introns. Group I introns, found in some rrna genes, are self-splicing: they can catalyze their own removal.
 1 2 Continuous genes - Intron: Many eukaryotic genes contain coding regions called exons and noncoding regions called intervening sequences or introns. The average human gene contains from eight to nine
1 2 Continuous genes - Intron: Many eukaryotic genes contain coding regions called exons and noncoding regions called intervening sequences or introns. The average human gene contains from eight to nine
Supplemental data. Li et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc/114/133140
 MET (CG) CMT (CHG / CHH) DRM (CHH / CG / CHG) Supplemental Figure 1. Phylogenetic Tree of DNA Methyltransferases in Maize and Arabidopsis. Maize genes are indicated by red dots. The DNA methylation sequence
MET (CG) CMT (CHG / CHH) DRM (CHH / CG / CHG) Supplemental Figure 1. Phylogenetic Tree of DNA Methyltransferases in Maize and Arabidopsis. Maize genes are indicated by red dots. The DNA methylation sequence
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 7 - GENE EXPRESSION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION BASICS Gene expression is the process through which cells selectively to express some genes and not others Every cell in an organism is a clone
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION BASICS Gene expression is the process through which cells selectively to express some genes and not others Every cell in an organism is a clone
The biology of naturally occurring insertions
 The biology of naturally occurring insertions Justin Vaughn, PhD Soybean Breeding and Molecular Genetics Laboratory University of Georgia, Athens 14 April 2014 Paris, France Titan Lane Valencia Morrell
The biology of naturally occurring insertions Justin Vaughn, PhD Soybean Breeding and Molecular Genetics Laboratory University of Georgia, Athens 14 April 2014 Paris, France Titan Lane Valencia Morrell
Conservation and divergence of transcriptomic and epigenomic variation in maize hybrids
 RESEARCH PAPER Open Access Conservation and divergence of transcriptomic and epigenomic variation in maize hybrids Guangming He 1*, Beibei Chen 2,3, Xuncheng Wang 4, Xueyong Li 2,5, Jigang Li 1,2, Hang
RESEARCH PAPER Open Access Conservation and divergence of transcriptomic and epigenomic variation in maize hybrids Guangming He 1*, Beibei Chen 2,3, Xuncheng Wang 4, Xueyong Li 2,5, Jigang Li 1,2, Hang
SolCAP. Executive Commitee : David Douches Walter De Jong Robin Buell David Francis Alexandra Stone Lukas Mueller AllenVan Deynze
 SolCAP Solanaceae Coordinated Agricultural Project Supported by the National Research Initiative Plant Genome Program of USDA CSREES for the Improvement of Potato and Tomato Executive Commitee : David
SolCAP Solanaceae Coordinated Agricultural Project Supported by the National Research Initiative Plant Genome Program of USDA CSREES for the Improvement of Potato and Tomato Executive Commitee : David
Development of Early Maturing GEM lines with Value Added Traits: Moving U.S. Corn Belt GEM Germplasm Northward
 Development of Early Maturing GEM lines with Value Added Traits: Moving U.S. Corn Belt GEM Germplasm Northward Marcelo J. Carena Department of Plant Sciences, North Dakota State University (NDSU) I am
Development of Early Maturing GEM lines with Value Added Traits: Moving U.S. Corn Belt GEM Germplasm Northward Marcelo J. Carena Department of Plant Sciences, North Dakota State University (NDSU) I am
Characterizing the Novel Roles of Small RNA-directed DNA Methylation in the Epigenetic Regulation of Athila Family Retrotransposons
 1 Characterizing the Novel Roles of Small RNA-directed DNA Methylation in the Epigenetic Regulation of Athila Family Retrotransposons Honors Research Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the requirements
1 Characterizing the Novel Roles of Small RNA-directed DNA Methylation in the Epigenetic Regulation of Athila Family Retrotransposons Honors Research Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the requirements
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives)
 Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Compare and contrast chromatin and chromosome: composition, proteins involved and level of packing. Explain the structure and function of
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Compare and contrast chromatin and chromosome: composition, proteins involved and level of packing. Explain the structure and function of
ARGONAUTE 6 bridges transposable element mrnaderived. sirnas to the establishment of DNA methylation
 Manuscript EMBO-2014-89499 ARGONAUTE 6 bridges transposable element mrnaderived sirnas to the establishment of DNA methylation Andrea D. McCue, Kaushik Panda, Saivageethi Nuthikattu, Sarah G. Choudury,
Manuscript EMBO-2014-89499 ARGONAUTE 6 bridges transposable element mrnaderived sirnas to the establishment of DNA methylation Andrea D. McCue, Kaushik Panda, Saivageethi Nuthikattu, Sarah G. Choudury,
Chapter 18. Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 2007-2008 Control of Prokaryotic (Bacterial) Genes 2007- Bacterial metabolism Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment STOP GO if they have
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 2007-2008 Control of Prokaryotic (Bacterial) Genes 2007- Bacterial metabolism Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment STOP GO if they have
AP Biology. The BIG Questions. Chapter 19. Prokaryote vs. eukaryote genome. Prokaryote vs. eukaryote genome. Why turn genes on & off?
 The BIG Questions Chapter 19. Control of Eukaryotic Genome How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
The BIG Questions Chapter 19. Control of Eukaryotic Genome How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Pattern Formation via Small RNA Mobility SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE 1 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION. Daniel H. Chitwood et al.
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Pattern Formation via Small RNA Mobility Daniel H. Chitwood et al. SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE 1 Supplemental Figure 1. The ARF3 promoter drives expression throughout leaves. (A, B) Expression
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Pattern Formation via Small RNA Mobility Daniel H. Chitwood et al. SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE 1 Supplemental Figure 1. The ARF3 promoter drives expression throughout leaves. (A, B) Expression
Chapter 11: Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter Review 1. It has long been known that there is probably a genetic link for alcoholism. Researchers studying rats have begun to elucidate this link. Briefly describe the genetic mechanism found
Chapter Review 1. It has long been known that there is probably a genetic link for alcoholism. Researchers studying rats have begun to elucidate this link. Briefly describe the genetic mechanism found
Genetics & The Work of Mendel
 Genetics & The Work of Mendel 2011-2012 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas used experimental method
Genetics & The Work of Mendel 2011-2012 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas used experimental method
Mapping and Mapping Populations
 Mapping and Mapping Populations Types of mapping populations F 2 o Two F 1 individuals are intermated Backcross o Cross of a recurrent parent to a F 1 Recombinant Inbred Lines (RILs; F 2 -derived lines)
Mapping and Mapping Populations Types of mapping populations F 2 o Two F 1 individuals are intermated Backcross o Cross of a recurrent parent to a F 1 Recombinant Inbred Lines (RILs; F 2 -derived lines)
3. A form of a gene that is only expressed in the absence of a dominant alternative is:
 Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Robeson Assessment: 9_12 Agriculture AU71 - Biotech and Agrisci Rsch I Test 3 Description: Obj 12 - Simple Mendelian Genetics Form: 501 1. The genotype of an organism
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Robeson Assessment: 9_12 Agriculture AU71 - Biotech and Agrisci Rsch I Test 3 Description: Obj 12 - Simple Mendelian Genetics Form: 501 1. The genotype of an organism
What is Epigenetics? Watch the video
 EPIGENETICS What is Epigenetics? The study of environmental factors on gene expression in DNA. The molecule is called methylation controls when genes are turned on. Methylation turns off genes. Acetylation
EPIGENETICS What is Epigenetics? The study of environmental factors on gene expression in DNA. The molecule is called methylation controls when genes are turned on. Methylation turns off genes. Acetylation
Developing New GM Products and Detection Methods
 Developing New GM Products and Detection Methods Dave Grothaus Monsanto Company Slides Thanks to: International Life Sciences Institute Crop Life International Indus try Colleagues Hope Hart - Syngenta
Developing New GM Products and Detection Methods Dave Grothaus Monsanto Company Slides Thanks to: International Life Sciences Institute Crop Life International Indus try Colleagues Hope Hart - Syngenta
Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. A. Fire et al. (1998) Nature Vol 391:
 Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans A. Fire et al. (1998) Nature Vol 391: 806-810 1 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Objective 3. Results 4. Mechanism 5.
Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans A. Fire et al. (1998) Nature Vol 391: 806-810 1 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Objective 3. Results 4. Mechanism 5.
ENDOGENOUS SHORT INTERFERING RNAS THAT SILENCE CHALCONE SYNTHASE RESULT IN PIGMENT PATTERN FORMATION ON SOYBEAN SEED COATS YOUNG B.
 ENDOGENOUS SHORT INTERFERING RNAS THAT SILENCE CHALCONE SYNTHASE RESULT IN PIGMENT PATTERN FORMATION ON SOYBEAN SEED COATS BY YOUNG B. CHO THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
ENDOGENOUS SHORT INTERFERING RNAS THAT SILENCE CHALCONE SYNTHASE RESULT IN PIGMENT PATTERN FORMATION ON SOYBEAN SEED COATS BY YOUNG B. CHO THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for
Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms
 Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms No. 1 of 10 1. The mouse gene knockout is based on. (A) Homologous recombination (B) Site-specific recombination
Genetics - Problem Drill 19: Dissection of Gene Function: Mutational Analysis of Model Organisms No. 1 of 10 1. The mouse gene knockout is based on. (A) Homologous recombination (B) Site-specific recombination
DEPARTMENT OF PLANT BREEDING AND GENETICS
 DEPARTMENT OF PLANT BREEDING AND GENETICS Course No. PBG 511 (Principles of Genetics and Cell Biology ) Cr. Hr. 3(2+1) Teacher Dr. D.K.Gothwal 16 5.10.15 Extra chromosomal inheritance 17 6.10.15 Concepts
DEPARTMENT OF PLANT BREEDING AND GENETICS Course No. PBG 511 (Principles of Genetics and Cell Biology ) Cr. Hr. 3(2+1) Teacher Dr. D.K.Gothwal 16 5.10.15 Extra chromosomal inheritance 17 6.10.15 Concepts
New Plant Breeding Techniques Group 3 Transgenic construct driven breeding
 WORKSHOP COMPERATIVE SITUATION OF NEW PLANT BREEDING TECHNIQUES 12-13 SEPTEMBER 2011 SEVILLE, SPAIN 1 New Plant Breeding Techniques Group 3 Transgenic construct driven breeding Maria Lusser Joint Research
WORKSHOP COMPERATIVE SITUATION OF NEW PLANT BREEDING TECHNIQUES 12-13 SEPTEMBER 2011 SEVILLE, SPAIN 1 New Plant Breeding Techniques Group 3 Transgenic construct driven breeding Maria Lusser Joint Research
Evaluation of Advanced GEM Lines for Multiple Insect Resistance and Fumonisin Concentration
 Evaluation of Advanced GEM Lines for Multiple Insect Resistance and Fumonisin Concentration Martin Bohn University of Illinois, Urbana, Illinois PROJECT DESCRIPTION The overall objective of this project
Evaluation of Advanced GEM Lines for Multiple Insect Resistance and Fumonisin Concentration Martin Bohn University of Illinois, Urbana, Illinois PROJECT DESCRIPTION The overall objective of this project
HIGH-QUALITY ASSEMBLY OF THE DURUM WHEAT GENOME CV. SVEVO
 HIGH-QUALITY ASSEMBLY OF THE DURUM WHEAT GENOME CV. SVEVO Luigi Cattivelli, The International Durum Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium 31/01/2017 1 Durum wheat Durum wheat with a total production of about
HIGH-QUALITY ASSEMBLY OF THE DURUM WHEAT GENOME CV. SVEVO Luigi Cattivelli, The International Durum Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium 31/01/2017 1 Durum wheat Durum wheat with a total production of about
BICD100 Midterm (10/27/10) KEY
 BICD100 Midterm (10/27/10) KEY 1. Variation in tail length is characteristic of some dog breeds, such as Pembroke Welsh Corgis, which sometimes show a bob tail (short tail) phenotype (see illustration
BICD100 Midterm (10/27/10) KEY 1. Variation in tail length is characteristic of some dog breeds, such as Pembroke Welsh Corgis, which sometimes show a bob tail (short tail) phenotype (see illustration
Chapter 1 Molecular Genetic Approaches to Maize Improvement an Introduction
 Chapter 1 Molecular Genetic Approaches to Maize Improvement an Introduction Robert T. Fraley In the following chapters prominent scientists will discuss the recent genetic improvements in maize that have
Chapter 1 Molecular Genetic Approaches to Maize Improvement an Introduction Robert T. Fraley In the following chapters prominent scientists will discuss the recent genetic improvements in maize that have
RNA Structure and the Versatility of RNA. Mitesh Shrestha
 RNA Structure and the Versatility of RNA Mitesh Shrestha Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Nitrogenous Bases (Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine) Ribose Sugar Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Phosphate Group RNA world Hypothesis
RNA Structure and the Versatility of RNA Mitesh Shrestha Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Nitrogenous Bases (Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine) Ribose Sugar Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Phosphate Group RNA world Hypothesis
DICER-LIKE2 Plays a Primary Role in Transitive Silencing of Transgenes in Arabidopsis
 DICER-LIKE2 Plays a Primary Role in Transitive Silencing of Transgenes in Arabidopsis Sizolwenkosi Mlotshwa 1, Gail J. Pruss 1, Angela Peragine 2, Matthew W. Endres 1, Junjie Li 3, Xuemei Chen 3, R. Scott
DICER-LIKE2 Plays a Primary Role in Transitive Silencing of Transgenes in Arabidopsis Sizolwenkosi Mlotshwa 1, Gail J. Pruss 1, Angela Peragine 2, Matthew W. Endres 1, Junjie Li 3, Xuemei Chen 3, R. Scott
Chapter 19. Control of Eukaryotic Genome. AP Biology
 Chapter 19. Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Chapter 19. Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions?
Characterization of mature maize (Zea mays L.) root system architecture and complexity in a diverse set of Ex PVP inbreds and hybrids
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1187-0 RESEARCH Open Access Characterization of mature maize (Zea mays L.) root system architecture and complexity in a diverse set of Ex PVP inbreds and hybrids Andrew L Hauck 1,
DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1187-0 RESEARCH Open Access Characterization of mature maize (Zea mays L.) root system architecture and complexity in a diverse set of Ex PVP inbreds and hybrids Andrew L Hauck 1,
UNIT MOLECULAR GENETICS AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
 UNIT MOLECULAR GENETICS AND BIOTECHNOLOGY Standard B-4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the molecular basis of heredity. B-4.1-4,8,9 Effective June 2008 All Indicators in Standard B-4
UNIT MOLECULAR GENETICS AND BIOTECHNOLOGY Standard B-4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the molecular basis of heredity. B-4.1-4,8,9 Effective June 2008 All Indicators in Standard B-4
Epigenetic control of tomato fruit development. Key Laboratories of Molecular Epigenetics of MOE, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, China
 Epigenetic control of tomato fruit development Silin Zhong 1,2*,, Zhangjun Fei 1,3,*,, Yun-Ru Chen 1, Yi Zheng 1, Mingyun Huang 1, Julia Vrebalov 1, Ryan McQuinn 1, Nigel Gapper 1, Bao Liu 2, Jenny Xiang
Epigenetic control of tomato fruit development Silin Zhong 1,2*,, Zhangjun Fei 1,3,*,, Yun-Ru Chen 1, Yi Zheng 1, Mingyun Huang 1, Julia Vrebalov 1, Ryan McQuinn 1, Nigel Gapper 1, Bao Liu 2, Jenny Xiang
3. Protein(s)or polypeptide(s): a. are a chain of amino acids b. is a rare molecule in an organism
 2018 Iowa FFA Ag Biotechnology CDE General Knowledge Exam 1. A plant breeder makes a cross between two plants that are both the genotype Aa (Aa X Aa). How many different genotypes with respect to the A,a
2018 Iowa FFA Ag Biotechnology CDE General Knowledge Exam 1. A plant breeder makes a cross between two plants that are both the genotype Aa (Aa X Aa). How many different genotypes with respect to the A,a
Heterosis and Inbreeding Depression for Grain Yield and Yield Contributing Characters in Quality Protein Maize.
 AGRICULTURAL COMMUNICATIONS, 24, 2(): 8-6. Heterosis and Inbreeding Depression for Grain Yield and Yield Contributing Characters in Quality Protein Maize. RASHMI JAIN AND DINESH NARAYAN BHARADWAJ* Department
AGRICULTURAL COMMUNICATIONS, 24, 2(): 8-6. Heterosis and Inbreeding Depression for Grain Yield and Yield Contributing Characters in Quality Protein Maize. RASHMI JAIN AND DINESH NARAYAN BHARADWAJ* Department
Basic Concepts and History of Genetic Engineering. Mitesh Shrestha
 Basic Concepts and History of Genetic Engineering Mitesh Shrestha Genetic Engineering AKA gene manipulation, gene cloning, recombinant DNA technology, genetic modification, and the new genetics. A technique
Basic Concepts and History of Genetic Engineering Mitesh Shrestha Genetic Engineering AKA gene manipulation, gene cloning, recombinant DNA technology, genetic modification, and the new genetics. A technique
Supplemental Figure legends Figure S1. (A) (B) (C) (D) Figure S2. Figure S3. (A-E) Figure S4. Figure S5. (A, C, E, G, I) (B, D, F, H, Figure S6.
 Supplemental Figure legends Figure S1. Map-based cloning and complementation testing for ZOP1. (A) ZOP1 was mapped to a ~273-kb interval on Chromosome 1. In the interval, a single-nucleotide G to A substitution
Supplemental Figure legends Figure S1. Map-based cloning and complementation testing for ZOP1. (A) ZOP1 was mapped to a ~273-kb interval on Chromosome 1. In the interval, a single-nucleotide G to A substitution
Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley
The Plant Cell, March 2013, American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved.
 Epigenetics (TTPB4) Teaching Guide Overview Epigenetic modifications of DNA and chromatin affect the activity of genes and transposons. Epigenetic controls affect processes as diverse as time-of-flowering,
Epigenetics (TTPB4) Teaching Guide Overview Epigenetic modifications of DNA and chromatin affect the activity of genes and transposons. Epigenetic controls affect processes as diverse as time-of-flowering,
REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. II. Eukaryotes
 REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS II. Eukaryotes Complexities of eukaryotic gene expression! Several steps needed for synthesis of mrna! Separation in space of transcription and translation! Compartmentation
REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS II. Eukaryotes Complexities of eukaryotic gene expression! Several steps needed for synthesis of mrna! Separation in space of transcription and translation! Compartmentation
6/256 1/256 0/256 1/256 2/256 7/256 10/256. At3g06290 (SAC3B)
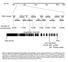 Chr.III M 5M 1M 15M 2M 23M BAC clones F22F7 F1A16 F24F17 F24P17 T8E24 F17A9 F21O3 F17A17 F18C1 F2O1 F28L1 F5E6 F3E22 T1B9 MLP3 Number of recombinants 6/256 1/256 /256 1/256 2/256 7/256 1/256 At3g629 (SAC3B)
Chr.III M 5M 1M 15M 2M 23M BAC clones F22F7 F1A16 F24F17 F24P17 T8E24 F17A9 F21O3 F17A17 F18C1 F2O1 F28L1 F5E6 F3E22 T1B9 MLP3 Number of recombinants 6/256 1/256 /256 1/256 2/256 7/256 1/256 At3g629 (SAC3B)
Relating Silk Emergence at Pollination to Kernel Set at Harvest
 Relating Silk Emergence at Pollination to Kernel Set at Harvest Summary Maximum kernel set and grain yield occur when pollen shed coincides with rapid silk growth. Silks attached near the base of the ear
Relating Silk Emergence at Pollination to Kernel Set at Harvest Summary Maximum kernel set and grain yield occur when pollen shed coincides with rapid silk growth. Silks attached near the base of the ear
Expressed genes profiling (Microarrays) Overview Of Gene Expression Control Profiling Of Expressed Genes
 Expressed genes profiling (Microarrays) Overview Of Gene Expression Control Profiling Of Expressed Genes Genes can be regulated at many levels Usually, gene regulation, are referring to transcriptional
Expressed genes profiling (Microarrays) Overview Of Gene Expression Control Profiling Of Expressed Genes Genes can be regulated at many levels Usually, gene regulation, are referring to transcriptional
Genetics & The Work of Mendel
 Genetics & The Work of Mendel He studied at the University of Vienna from 1851 to 1853 where he was influenced by a physicist who encouraged experimentation and the application of mathematics to science
Genetics & The Work of Mendel He studied at the University of Vienna from 1851 to 1853 where he was influenced by a physicist who encouraged experimentation and the application of mathematics to science
Iowa State FFA Biotechnology CDE Comprehensive Knowledge Test
 Iowa State FFA Biotechnology CDE Comprehensive Knowledge Test - 2017 - Name Chapter 1. What is the name of the technique that allows geneticists to observe DNA fragments from a DNA sample and compare them
Iowa State FFA Biotechnology CDE Comprehensive Knowledge Test - 2017 - Name Chapter 1. What is the name of the technique that allows geneticists to observe DNA fragments from a DNA sample and compare them
Applying Genotyping by Sequencing (GBS) to Corn Genetics and Breeding. Peter Bradbury USDA/Cornell University
 Applying Genotyping by Sequencing (GBS) to Corn Genetics and Breeding Peter Bradbury USDA/Cornell University Genotyping by sequencing (GBS) makes use of high through-put, short-read sequencing to provide
Applying Genotyping by Sequencing (GBS) to Corn Genetics and Breeding Peter Bradbury USDA/Cornell University Genotyping by sequencing (GBS) makes use of high through-put, short-read sequencing to provide
Chapter 19 Genetic Regulation of the Eukaryotic Genome. A. Bergeron AP Biology PCHS
 Chapter 19 Genetic Regulation of the Eukaryotic Genome A. Bergeron AP Biology PCHS 2 Do Now - Eukaryotic Transcription Regulation The diagram below shows five genes (with their enhancers) from the genome
Chapter 19 Genetic Regulation of the Eukaryotic Genome A. Bergeron AP Biology PCHS 2 Do Now - Eukaryotic Transcription Regulation The diagram below shows five genes (with their enhancers) from the genome
Watson BM Gene Capitolo 11
 Watson BM Gene Capitolo 11 Le proteine della trasposizione ? target-site primed reverse transcription Watson et al., BIOLOGIA MOLECOLARE DEL GENE, Zanichelli editore S.p.A. Trimeric structure for an
Watson BM Gene Capitolo 11 Le proteine della trasposizione ? target-site primed reverse transcription Watson et al., BIOLOGIA MOLECOLARE DEL GENE, Zanichelli editore S.p.A. Trimeric structure for an
THE EFFECT OF SHOOT MATURATION ON TOTAL BIOMASS PRODUCTION IN MAIZE RAWIKARN PULAM THESIS
 THE EFFECT OF SHOOT MATURATION ON TOTAL BIOMASS PRODUCTION IN MAIZE BY RAWIKARN PULAM THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Crop Sciences in
THE EFFECT OF SHOOT MATURATION ON TOTAL BIOMASS PRODUCTION IN MAIZE BY RAWIKARN PULAM THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Crop Sciences in
MARKER-ASSISTED EVALUATION AND IMPROVEMENT OF MAIZE
 MARKER-ASSISTED EVALUATION AND IMPROVEMENT OF MAIZE Charles W. Stuber Department of Genetics North Carolina State University Raleigh, North Carolina 27695-7614 Q INTRODUCTION Plant and animal breeders
MARKER-ASSISTED EVALUATION AND IMPROVEMENT OF MAIZE Charles W. Stuber Department of Genetics North Carolina State University Raleigh, North Carolina 27695-7614 Q INTRODUCTION Plant and animal breeders
Herculex RW Insect Protection
 Herculex RW Insect Protection (OECD Unique Identifier: DAS-59122-7) Active Ingredients: Bacillus thuringiensis Cry34Ab1 protein and the genetic material (PHP17662 T-DNA) necessary for its production in
Herculex RW Insect Protection (OECD Unique Identifier: DAS-59122-7) Active Ingredients: Bacillus thuringiensis Cry34Ab1 protein and the genetic material (PHP17662 T-DNA) necessary for its production in
Biology 163 Laboratory in Genetics Midterm 2, Nov. 14, Honor Pledge: I have neither given nor received any unauthorized help on this exam:
 1 Biology 163 Laboratory in Genetics Midterm 2, Nov. 14, 2005 Honor Pledge: I have neither given nor received any unauthorized help on this exam: Name Printed: ignature: 1. Normally you need to cross two
1 Biology 163 Laboratory in Genetics Midterm 2, Nov. 14, 2005 Honor Pledge: I have neither given nor received any unauthorized help on this exam: Name Printed: ignature: 1. Normally you need to cross two
What Can the Epigenome Teach Us About Cellular States and Diseases?
 What Can the Epigenome Teach Us About Cellular States and Diseases? (a computer scientist s view) Luca Pinello Outline Epigenetic: the code over the code What can we learn from epigenomic data? Resources
What Can the Epigenome Teach Us About Cellular States and Diseases? (a computer scientist s view) Luca Pinello Outline Epigenetic: the code over the code What can we learn from epigenomic data? Resources
Technical tips Session 4
 Technical tips Session 4 Biotinylation assay: Streptavidin is a small bacterial protein that binds with high affinity to the vitamin biotin. This streptavidin-biotin combination can be used to link molecules
Technical tips Session 4 Biotinylation assay: Streptavidin is a small bacterial protein that binds with high affinity to the vitamin biotin. This streptavidin-biotin combination can be used to link molecules
Learning Objectives. Define RNA interference. Define basic terminology. Describe molecular mechanism. Define VSP and relevance
 Learning Objectives Define RNA interference Define basic terminology Describe molecular mechanism Define VSP and relevance Describe role of RNAi in antigenic variation A Nobel Way to Regulate Gene Expression
Learning Objectives Define RNA interference Define basic terminology Describe molecular mechanism Define VSP and relevance Describe role of RNAi in antigenic variation A Nobel Way to Regulate Gene Expression
Gene Editing in Cereals. Emma Wallington
 Gene Editing in Cereals Emma Wallington emma.wallington@niab.com NIAB Group NIAB established in 1919 by charitable donations for the improvement of crops.. with higher.. genetic quality A charitable company
Gene Editing in Cereals Emma Wallington emma.wallington@niab.com NIAB Group NIAB established in 1919 by charitable donations for the improvement of crops.. with higher.. genetic quality A charitable company
Genetics Test. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Genetics Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 41. Situations in which one allele for a gene is not completely dominant over another allele
Genetics Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 41. Situations in which one allele for a gene is not completely dominant over another allele
Lecture 2-3: Using Mutants to study Biological processes
 Lecture 2-3: Using Mutants to study Biological processes Objectives: 1. Why use mutants? 2. How are mutants isolated? 3. What important genetic analyses must be done immediately after a genetic screen
Lecture 2-3: Using Mutants to study Biological processes Objectives: 1. Why use mutants? 2. How are mutants isolated? 3. What important genetic analyses must be done immediately after a genetic screen
Ch. 14 Mendel and the Gene Idea
 Ch. 14 Mendel and the Gene Idea 2006-2007 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas used experimental method
Ch. 14 Mendel and the Gene Idea 2006-2007 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas used experimental method
Dent corn (Zea mays L.) is a major field crop in the United
 RESEARCH Genetic Composition of Contemporary U.S. Commercial Dent Corn Germplasm Mark A. Mikel* ABSTRACT Germplasm of contemporary U.S. dent corn (Zea mays L.) is predominately from proprietary programs.
RESEARCH Genetic Composition of Contemporary U.S. Commercial Dent Corn Germplasm Mark A. Mikel* ABSTRACT Germplasm of contemporary U.S. dent corn (Zea mays L.) is predominately from proprietary programs.
Maize breeders decide which combination of traits and environments is needed to breed for both inbreds and hybrids. A trait controlled by genes that
 Preface Plant breeding is a science of evolution. The scientific basis of plant breeding started in the 1900s. The rediscovery of Mendelian genetics and the development of the statistical concepts of randomization
Preface Plant breeding is a science of evolution. The scientific basis of plant breeding started in the 1900s. The rediscovery of Mendelian genetics and the development of the statistical concepts of randomization
The Major Function Of Rna Is To Carry Out The Genetic Instructions For Protein Synthesis
 The Major Function Of Rna Is To Carry Out The Genetic Instructions For Protein Synthesis For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that Leder and Nirenberg were able
The Major Function Of Rna Is To Carry Out The Genetic Instructions For Protein Synthesis For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that Leder and Nirenberg were able
Stalking the Genetic Basis of a Trait
 OVERVIEW This activity supplements the short film Popped Secret: The Mysterious Origin of Corn. It focuses on the tb1 gene, whose expression is related to phenotypic changes associated with the evolution
OVERVIEW This activity supplements the short film Popped Secret: The Mysterious Origin of Corn. It focuses on the tb1 gene, whose expression is related to phenotypic changes associated with the evolution
Microbials. Impact on agriculture and the seed industry. Marcus Meadows-Smith. BioConsortia, Inc.
 Microbials Impact on agriculture and the seed industry Marcus Meadows-Smith BioConsortia, Inc. Seed Central, UC Davis, 9 February 2017 Agenda 1) Introduction to Microbials - Marcus Meadows-Smith, CEO,
Microbials Impact on agriculture and the seed industry Marcus Meadows-Smith BioConsortia, Inc. Seed Central, UC Davis, 9 February 2017 Agenda 1) Introduction to Microbials - Marcus Meadows-Smith, CEO,
EVALUATION OF ADDITIVE AND NONADDITIVE GENETIC VARIATION IN ELITE MAIZE GERMPLASM FOR ROOT, SHOOT, AND EAR CHARACTERISTICS ANDREW HAUCK DISSERTATION
 EVALUATION OF ADDITIVE AND NONADDITIVE GENETIC VARIATION IN ELITE MAIZE GERMPLASM FOR ROOT, SHOOT, AND EAR CHARACTERISTICS BY ANDREW HAUCK DISSERTATION Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements
EVALUATION OF ADDITIVE AND NONADDITIVE GENETIC VARIATION IN ELITE MAIZE GERMPLASM FOR ROOT, SHOOT, AND EAR CHARACTERISTICS BY ANDREW HAUCK DISSERTATION Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements
Plants Fight it out Intrinsic defence mechanism The magic world of Gene silencing
 I LOVE YOU Plants Fight it out Intrinsic defence mechanism The magic world of Gene silencing Over expression of Chalcone synthase gene to get Purple Petunias Napoli, Lemieux & Jorgensen,1990 Desired Effect
I LOVE YOU Plants Fight it out Intrinsic defence mechanism The magic world of Gene silencing Over expression of Chalcone synthase gene to get Purple Petunias Napoli, Lemieux & Jorgensen,1990 Desired Effect
This is DUE: Tuesday, March 1, 2011 Come prepared to share your findings with your group.
 Biology 160 NAME: Reading Guide 12: Population Dynamics, Humans, Part II This is DUE: Tuesday, March 1, 2011 Come prepared to share your findings with your group. *As before, please turn in only the Critical
Biology 160 NAME: Reading Guide 12: Population Dynamics, Humans, Part II This is DUE: Tuesday, March 1, 2011 Come prepared to share your findings with your group. *As before, please turn in only the Critical
Advanced Plant Technology Program Vocabulary
 Advanced Plant Technology Program Vocabulary A Below you ll find a list of words (and their simplified definitions) that our researchers use on a daily basis. Abiotic stress (noun): Stress brought on by
Advanced Plant Technology Program Vocabulary A Below you ll find a list of words (and their simplified definitions) that our researchers use on a daily basis. Abiotic stress (noun): Stress brought on by
Gene Expression and Heritable Phenotype. CBS520 Eric Nabity
 Gene Expression and Heritable Phenotype CBS520 Eric Nabity DNA is Just the Beginning DNA was determined to be the genetic material, and the structure was identified as a (double stranded) double helix.
Gene Expression and Heritable Phenotype CBS520 Eric Nabity DNA is Just the Beginning DNA was determined to be the genetic material, and the structure was identified as a (double stranded) double helix.
CHAPTER 14 Genetics and Propagation
 CHAPTER 14 Genetics and Propagation BASIC GENETIC CONCEPTS IN PLANT SCIENCE The plants we cultivate for our survival and pleasure all originated from wild plants. However, most of our domesticated plants
CHAPTER 14 Genetics and Propagation BASIC GENETIC CONCEPTS IN PLANT SCIENCE The plants we cultivate for our survival and pleasure all originated from wild plants. However, most of our domesticated plants
DNA REPLICATION & BIOTECHNOLOGY Biology Study Review
 DNA REPLICATION & BIOTECHNOLOGY Biology Study Review DNA DNA is found in, in the nucleus. It controls cellular activity by regulating the production of, which includes It is a very long molecule made up
DNA REPLICATION & BIOTECHNOLOGY Biology Study Review DNA DNA is found in, in the nucleus. It controls cellular activity by regulating the production of, which includes It is a very long molecule made up
Stalking the Genetic Basis of a Trait
 INTRODUCTION The short film Popped Secret: The Mysterious Origin of Corn describes how the evolution of corn was mostly a mystery until George Beadle proposed a bold new hypothesis in 1939: corn evolved
INTRODUCTION The short film Popped Secret: The Mysterious Origin of Corn describes how the evolution of corn was mostly a mystery until George Beadle proposed a bold new hypothesis in 1939: corn evolved
Applicazioni biotecnologiche
 Applicazioni biotecnologiche Analisi forense Sintesi di proteine ricombinanti Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Polymorphism (more fully genetic polymorphism) refers to the simultaneous occurrence
Applicazioni biotecnologiche Analisi forense Sintesi di proteine ricombinanti Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) Polymorphism (more fully genetic polymorphism) refers to the simultaneous occurrence
Cassava. Monitoring transcriptional changes in cassava infected with South African cassava mosaic using next-generation sequencing 4/19/2013
 Monitoring transcriptional changes in cassava infected with South African cassava mosaic using next-generation sequencing Farhahna Allie University of the Witwatersrand Plant Biotechnology Laboratory ACGT
Monitoring transcriptional changes in cassava infected with South African cassava mosaic using next-generation sequencing Farhahna Allie University of the Witwatersrand Plant Biotechnology Laboratory ACGT
Lecture 1. Basic Definitions and Nucleic Acids. Basic Definitions you should already know
 Lecture 1. Basic Definitions and Nucleic Acids Basic Definitions you should already know apple DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid apple RNA: Ribonucleic Acid apple mrna: messenger RNA: contains the genetic information(coding
Lecture 1. Basic Definitions and Nucleic Acids Basic Definitions you should already know apple DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid apple RNA: Ribonucleic Acid apple mrna: messenger RNA: contains the genetic information(coding
Chapter 13 - Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 13 - Regulation of Gene Expression 1. Describe the typical components of an operon in an E. coli (prokaryotic) cell. (p. 238-239) a. regulator gene - b. promoter - c. operator - d. structural gene
Chapter 13 - Regulation of Gene Expression 1. Describe the typical components of an operon in an E. coli (prokaryotic) cell. (p. 238-239) a. regulator gene - b. promoter - c. operator - d. structural gene
Association Mapping in Wheat: Issues and Trends
 Association Mapping in Wheat: Issues and Trends Dr. Pawan L. Kulwal Mahatma Phule Agricultural University, Rahuri-413 722 (MS), India Contents Status of AM studies in wheat Comparison with other important
Association Mapping in Wheat: Issues and Trends Dr. Pawan L. Kulwal Mahatma Phule Agricultural University, Rahuri-413 722 (MS), India Contents Status of AM studies in wheat Comparison with other important
PLANT BREEDING FOR YIELD IMPROVEMENT
 PLANT BREEDING FOR YIELD IMPROVEMENT A Challenging Future World population increasing by 160,000 every day 7 billion currently, rising to 9.3 billion by 2050 UN estimates global food production must: Increase
PLANT BREEDING FOR YIELD IMPROVEMENT A Challenging Future World population increasing by 160,000 every day 7 billion currently, rising to 9.3 billion by 2050 UN estimates global food production must: Increase
Research Advances in the Development of Transgenic and Gene Edited Products in Sri Lanka
 Research Advances in the Development of Transgenic and Gene Edited Products in Sri Lanka Dr. Pradeepa C.G. Bandaranayake Director, Agricultural Biotechnology Centre Faculty of Agriculture University of
Research Advances in the Development of Transgenic and Gene Edited Products in Sri Lanka Dr. Pradeepa C.G. Bandaranayake Director, Agricultural Biotechnology Centre Faculty of Agriculture University of
Plant Genome Modification Technologies and Applications Amitabh Mohanty DuPont Pioneer
 Plant Genome Modification Technologies and Applications Amitabh Mohanty DuPont Pioneer International Conference on New Plant Breeding Molecular Technologies Technology Development And Regulation, Oct 9-,
Plant Genome Modification Technologies and Applications Amitabh Mohanty DuPont Pioneer International Conference on New Plant Breeding Molecular Technologies Technology Development And Regulation, Oct 9-,
Lecture 3 Mutagens and Mutagenesis. 1. Mutagens A. Physical and Chemical mutagens B. Transposons and retrotransposons C. T-DNA
 Lecture 3 Mutagens and Mutagenesis 1. Mutagens A. Physical and Chemical mutagens B. Transposons and retrotransposons C. T-DNA 2. Mutagenesis A. Screen B. Selection C. Lethal mutations Read: 508-514 Figs:
Lecture 3 Mutagens and Mutagenesis 1. Mutagens A. Physical and Chemical mutagens B. Transposons and retrotransposons C. T-DNA 2. Mutagenesis A. Screen B. Selection C. Lethal mutations Read: 508-514 Figs:
I.1 The Principle: Identification and Application of Molecular Markers
 I.1 The Principle: Identification and Application of Molecular Markers P. Langridge and K. Chalmers 1 1 Introduction Plant breeding is based around the identification and utilisation of genetic variation.
I.1 The Principle: Identification and Application of Molecular Markers P. Langridge and K. Chalmers 1 1 Introduction Plant breeding is based around the identification and utilisation of genetic variation.
RNAi minilecture and Using Genetics to Explore Complex Biological Processes
 RNAi minilecture and Using Genetics to Explore Complex Biological Processes 2 American Worm People Win Nobel for RNA Work New York Times Oct. 2, 2006 The 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was
RNAi minilecture and Using Genetics to Explore Complex Biological Processes 2 American Worm People Win Nobel for RNA Work New York Times Oct. 2, 2006 The 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was
Genetics and Biotechnology. Section 1. Applied Genetics
 Section 1 Applied Genetics Selective Breeding! The process by which desired traits of certain plants and animals are selected and passed on to their future generations is called selective breeding. Section
Section 1 Applied Genetics Selective Breeding! The process by which desired traits of certain plants and animals are selected and passed on to their future generations is called selective breeding. Section
Department of Genetics
 Department of Genetics Program Specific Outcomes (PSO) Program- MSc. Genetics (404) The course prepares students for pursuing further research and teaching. Key features: Students have high success rate
Department of Genetics Program Specific Outcomes (PSO) Program- MSc. Genetics (404) The course prepares students for pursuing further research and teaching. Key features: Students have high success rate
Genetics Transcription Translation Replication
 Genetics Transcription Translation Replication 1. Which statement best describes the relationship between an allele and a gene? A. An allele is a variation of a gene that can be expressed as a phenotype.
Genetics Transcription Translation Replication 1. Which statement best describes the relationship between an allele and a gene? A. An allele is a variation of a gene that can be expressed as a phenotype.
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins. The Central Dogma
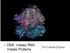 DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
Name Class Date. Practice Test
 Name Class Date 12 DNA Practice Test Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. What do bacteriophages infect? a. mice. c. viruses.
Name Class Date 12 DNA Practice Test Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. What do bacteriophages infect? a. mice. c. viruses.
Fundamentals of Genetics. 4. Name the 7 characteristics, giving both dominant and recessive forms of the pea plants, in Mendel s experiments.
 Fundamentals of Genetics 1. What scientist is responsible for our study of heredity? 2. Define heredity. 3. What plant did Mendel use for his hereditary experiments? 4. Name the 7 characteristics, giving
Fundamentals of Genetics 1. What scientist is responsible for our study of heredity? 2. Define heredity. 3. What plant did Mendel use for his hereditary experiments? 4. Name the 7 characteristics, giving
