Concepts and methods in genome assembly and annotation
|
|
|
- Tobias Ellis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BCM-2002 Concepts and methods in genome assembly and annotation B. Franz LANG, Département de Biochimie Bureau: H Courrier électronique:
2 Outline 1. What is genome assembly? 2. What is genome annotation? 3. Annotating protein coding genes and introns 4. Prediction of RNA genes
3 1. What is genome assembly? Stitching together the native genome sequence (the basis for genome annotation), as well as the genome architecture, from sequence reads. These may be several tens up to thousands of nucleotides in size. Long reads or paired-end reads of long fragments are required for resolving repeat regions. Result: contigs of assembled reads that allow calculation of a coverage level. An average coverage of >10 is required for decent genome assemblies.
4 Genome assembly at a higher level Genomes may be made from DNA or RNA (double- or single-stranded) An organism may have several genomes (foremost eukaryotes) Genomes may consist of more than one physical unit (chromosomes) Chromosomes may be linear, circular, directly repeated several times and linear (e.g., product of rolling circle replication, appears as circularmapping in sequence assembly!) Circular-mapping concatamers
5 How genome assembly of real (dirty) data works Given sequence read information (Sanger, Illumina, PacBio ) an algorithmic approach is required to: Combine reads with overlapping sequence into a genome sequence: Overlap-join procedures (slow, but sequence error/variation may be taken into account). It allows use of error-prone sequencing technologies like 454, but may introduce errors in the assembly (it does with 454 data; e.g., frame-shifts). Examples of software Phrap, Consed, Newbler, Mira. Eulerian algorithms based on graphs. Very fast, but require reads without sequence error or variation; drops reads that do not fit, up to a certain defined level. Therefore, an important feature is monitoring of the sequence coverage across contigs. Works with short sequences; these have to be highest quality. Huge datasets such as those produced by Illumina can be processed. Examples of software - Velvet, SOAPdenovo, Abyss, Allpath.
6 Graph algorithms for assembly (a) Sequence, (b) Traditional assembly, walk through Hamiltonian cycle. Variant in (c), after split of reads into short k-mers. (d) Modern de Bruijn graph finding sequence more quickly via Eulerian cycle. P. Compeau, P. Pevzner & G. Tesler (2011) NATURE BIOTECHNOLOGY 2 9:
7 How genome assembly of real (dirty) data works Given sequence read information (Sanger, Illumina, PacBio ) an algorithmic approach is required to: Discard information from contaminating DNA, primers and adapters If low level, sequence coverage cut-off values will resolve the issue Resolve repeat regions of all kinds that constitute assembly conflicts Mobile genetic elements and other short repeated DNA segments Segmental genome duplication Diploid, aneuploid genomes with sequence differences in allels ( snips ) Whole genome duplication followed by genetic drift of one copy or its partial loss. Requires sequence from large DNA fragments, chromosome size mapping, other physical or biological genome information
8 How genome assembly of real data works Resolve chromosome architecture (multiple genomes and chromosomes, linear, circular, or circular-mapping concatamers) An issue that usually needs manual input of an expert who has additional information
9
10 2. What is genome annotation? Finding and precise positional prediction of all genes, other genetic elements, insertion elements and repeats, on a given genome sequence Species may contain more than one genome (e.g., nuclear, mitochondrial, chloroplast, virus/phage, plasmid ) The genetic code and gene expression signals may differ from one genome to another - needs info on gene expression at the RNA and protein level Genes may be contiguous, or disrupted by introns, as well as discontinuous (trans-spliced or in pieces). Based on comparative gene/intron predictions (gene models, bioinformatics inference); information on transcript and protein sequence and other biological facts usually required List of features at the sequence level (e.g., GenBank submission file) Genetic maps
11 What is genome annotation? COMMENT Complete mitochondrial genome. FEATURES Location/Qualifiers source /organism="glomus irregulare" /organelle="mitochondrion" /mol_type="genomic DNA" /strain="daom " /type="genomic" gene /gene="rnl" rrna join( , , , , , , ) /gene="rnl" /product="large subunit ribosomal RNA" exon /gene="rnl" /number=1 intron /gene="rnl" /note="group IA3" /number=1 exon /gene="rnl" /number=2 intron /gene="rnl" /note="group IA3" /number=2 gene /gene="orf202 CDS /gene="orf202" /codon_start=1 /transl_table=4 /product="hypothetical protein" /translation="mkspnpqpalssiqreilvggllgdlsiyrakvthnarlyvqqg SVHKEYLNHLYSVFQNLCSSEPKWSLSLDKRSNTTYETLRFNSRSLPCFNYYRDVFYP EGVKIVPANIGELLTARGLAYWSMDDGYKDRGNFRLATQSFSRNDVLLLIKLLKDNFS LDCSLNTVKSTQYRIYVRANSMVQFRALVSPYFHPSMLYKLQ" exon /gene="rnl" /number=3 intron /gene="rnl" /note="group IB" /number=3 and so on Continued to the right Example: Partial GenBank annotation of a mitochondrial genome (rrna gene with introns and a predicted protein coding sequence) 11
12 What is genome annotation? Example: Genetic maps of two mitochondrial genomes 12
13 Effect of completeness, sequencing error, and assembly artifacts on genome annotation Incomplete genome assembly ( draft genome ) annotation of genes and genetic elements somewhat incomplete still works for gene identification, expression studies and comparisons Systematic sequence error (technology-specific) 454, number of nucleotides in homopolymer sequences incorrect causes difficulties in genome assembly at these sites, and potentially severe frameshifting in protein coding genes Sanger, difficulties to resolve snap-back structures; termination and/or slippage at long homopolymers - same as above but less severe Illumina, uncertain sequence at certain sequence motifs such as GGCNN seems to be less with latest technology. Error prediction and correction is possible. Ion Torrent, Pacific Biosciences overall error rate high, may to some degree be corrected by using very deep coverage (fails if polymorphic sites/snips are of interest; errors and snips are hard to distinguish)
14
15 3. Annotation of protein coding genes and introns First, one needs to know, or infer, the genetic code Translate Open Reading Frames (ORFs) that are not interrupted by a stop codon and that start with a know initiation codon (ATG, GTG ) ORFs may be given a functional identity, by sequence comparison to known genes. Protein sequence data can be used to confirm factual translation and identification of the genetic code.
16 3. Annotation of protein coding genes and introns Transcription data for the gene region as well as the presence of regulatory elements help to confirm the prediction (in case of bacteria, ribosomal binding site at 5 ; terminator sequence at 3 ; upstream promoters ); If these genes contain introns, exons may be identified in two ways By comparing the gene region with transcript sequences (do not contain introns) Inference of exon-intron structure based on sequence similarities of exons, intron features such as conserved splice site motifs, as well as any other feature that is known to define a gene in a given group of organisms. Gene models and intron models.
17 3. Annotation of protein coding genes and introns If genes contain introns, exon/intron boundaries (nucleus, eukaryotes) may be identified by conserved splice site motifs (intron models). For other intron types, use respective models.
18 3. Annotation of protein coding genes and introns M Yandell and D. Ence (2012) NATURE REVIEWS GENETICS 13: 329
19 3. Annotation of protein coding genes and introns M Yandell and D. Ence (2012) NATURE REVIEWS GENETICS 13: 329
20
21 4. Prediction of RNA genes a comparison of RNAmotif with ERPIN Features of structured RNAs: primary sequence conservation secondary structure tertiary interactions site-wise conservation is variable follow examples from catalytic introns and RNase P RNA
22 Secondary structure model of domain V of mitochondrial group II introns. The consensus structure is based on the compilation of 520 mitochondrial introns. Positional sequence conservation: R = A,G; Y = C,U; K = U,G; M = A,C; N = A,G,C,U; with prevalent nucleotides or nucleotide combinations color-coded red, 99%; magenta, 95%; blue, 80%; and green, 60%. Lower case nucleotides are alternatives that occur at frequencies of at least 10%. A few recurrent insertions of up to three nucleotides are indicated with arrows. Note that in some introns the conserved GAAA tetraloop motif (shaded grey) that interacts with a conserved structural motif in domain I is absent, that the size of the loop may vary by a few nucleotides, and that the number of base pairs in its connected helical region might be reduced.
23 Mitochondrial RNase P RNA is highly conserved in pairing P4, the reactive centre of the molecule, with respect to its bacterial counterparts. The two primary sequence motifs (red) are sufficient to identify > 50% of known homologs. However, when considering all known mitochondrial P- RNAs, the nucleotide variance (number of false positives) becomes too high for searches see following series of secondary structure models.
24 Modeling mitochondrial RNase P RNA structures has been difficult, due to their derived structures and high A+T content. Less derived mitochondrial P-RNAs have served as a starting point for RNA structure predictions.
25 By using phylogenetic-comparative principles, highly derived mitochondrial rnpb sequences were identified, leaving for most part P4 (the catalytic centre) as the universally conserved principle.
26 How to search most effectively for mitochondrial RNase P RNAs? Method 1: conserved primary sequence (using regular sequence expressions)
27 Mitochondrial primary consensus sequence most conservation is close to P4 P4 helical interaction
28 Corresponding regular expression: [AT]G[GA]NAA[GA]T[TC][ATC][GT][GA] A[CT][AU]NAAN[ATC][TC][AC][GAT][GT][CT]TTA[GAT] Apparently, primary sequence conservation is weak, just ~50% of currently known sequences are found with this information.
29 How to search most effectively for mitochondrial RNase P RNAs? Method 2: Use both conserved primary sequence plus secondary structure, united in a structural profile that is translated into an RNAmotif descriptor
30 Structured sequence profile including P4 helical region (using more sequences than in the primary sequence example)
31 Translation of this complex structural motif into an RNAmotif descriptor parms ### finds mt RNase P RNAs wc +=gu; ### permits global GU descr ss(len=20) ### 20 flanking nucleotides ss(len=5, seq="[gat][at]g[gat]a$") ### ss 5' to structure h5(len=3, seq="a[ga][ga]",mispair=1,ends='mm') ### P4-1 ss(len=1,seq="t$") ### T bulge h5(len=5,seq="[tc][atc][gat][gat].$",mispair=2,ends='mm') ### P4-2 ss(minlen=50, maxlen=1000,seq="[ac]c[atc].[ga]a$") ### P4 loop h3 (seq="[atc][atc][atc][gat][gt]$") ### P4-1' h3 (seq="[gtc][tc]t$") ### P4-2' ss(len=1,seq="a") ### universal A ss(len=20) ### 20 flanking nt It finds four false positives in a collection of 9 mtdnas with RNase P RNA, and misses one solution: lack of both sensitivity and specificity.
32 How to search most effectively for mitochondrial RNase P RNAs? Method 3: Use both conserved primary sequence plus secondary structure, united in a training set with all known sequences aligned, plus a corresponding structural line: to be used for ERPIN searches.
33 Translate the structural alignment into the ERPIN format however, it is a bit cryptic
34 The GDE editor comes to help, with color coding, coupled to a tool that translates the alignment into ERPIN format
35 ERPIN then calculates RNA primary and secondary structure profiles from the sequence alignment that are matched to the target sequence. Probabilistic search taking into account nucleotide frequencies. Much of the algorithm s efficiency stems from the use of userdefined, precisely delimited structural elements that can be searched individually or in combination, and by the option to use a defined search order ( search strategy ).
36 The ERPIN output of results is a bit cryptic, so we may use tools (RNAweasel) to compacts the results Note the E-values, the probability that a given structural motif occurs by chance in a target database of given size and nucleotide composition. Values of 1e-2 and smaller can be already considered safe matches, although solutions close to 1e+1 might also be considered. Results are much superior to RNAmotif, no suspected false positives, more promising matches.
37 RNAweasel functions Public webserver Export of ERPIN format from GDE Automatic alignment of ERPIN results Normalization of training set sequences to increase the sensitivity of searches Reiterative mode of search A recent, even more powerful probabilistic approach covariance/hmm like inferences with Infernal (Sean Eddy development, to be watched)
38 How much structural conservation is required for meaningful ERPIN searches? Example: T-stem plus T-loop of trnas, to find matches with E-value better than 5e-2 Results: few if any false positives even in large datasets
39 This is it, folks!
Section 10.3 Outline 10.3 How Is the Base Sequence of a Messenger RNA Molecule Translated into Protein?
 Section 10.3 Outline 10.3 How Is the Base Sequence of a Messenger RNA Molecule Translated into Protein? Messenger RNA Carries Information for Protein Synthesis from the DNA to Ribosomes Ribosomes Consist
Section 10.3 Outline 10.3 How Is the Base Sequence of a Messenger RNA Molecule Translated into Protein? Messenger RNA Carries Information for Protein Synthesis from the DNA to Ribosomes Ribosomes Consist
Themes: RNA and RNA Processing. Messenger RNA (mrna) What is a gene? RNA is very versatile! RNA-RNA interactions are very important!
 Themes: RNA is very versatile! RNA and RNA Processing Chapter 14 RNA-RNA interactions are very important! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have many important differences. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries genetic
Themes: RNA is very versatile! RNA and RNA Processing Chapter 14 RNA-RNA interactions are very important! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have many important differences. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries genetic
Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of..
 Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Gene Expression: Transcription
 Gene Expression: Transcription The majority of genes are expressed as the proteins they encode. The process occurs in two steps: Transcription = DNA RNA Translation = RNA protein Taken together, they make
Gene Expression: Transcription The majority of genes are expressed as the proteins they encode. The process occurs in two steps: Transcription = DNA RNA Translation = RNA protein Taken together, they make
Lecture for Wednesday. Dr. Prince BIOL 1408
 Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
CH 17 :From Gene to Protein
 CH 17 :From Gene to Protein Defining a gene gene gene Defining a gene is problematic because one gene can code for several protein products, some genes code only for RNA, two genes can overlap, and there
CH 17 :From Gene to Protein Defining a gene gene gene Defining a gene is problematic because one gene can code for several protein products, some genes code only for RNA, two genes can overlap, and there
8/21/2014. From Gene to Protein
 From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION
 M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION Chapter 7 Microbial Genetics Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, University of Tennessee, Knoxville The Structure and Replication
M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION Chapter 7 Microbial Genetics Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, University of Tennessee, Knoxville The Structure and Replication
DNA Function: Information Transmission
 DNA Function: Information Transmission DNA is called the code of life. What does it code for? *the information ( code ) to make proteins! Why are proteins so important? Nearly every function of a living
DNA Function: Information Transmission DNA is called the code of life. What does it code for? *the information ( code ) to make proteins! Why are proteins so important? Nearly every function of a living
Chapter 13. From DNA to Protein
 Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
Fig Ch 17: From Gene to Protein
 Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Ch. 10 Notes DNA: Transcription and Translation
 Ch. 10 Notes DNA: Transcription and Translation GOALS Compare the structure of RNA with that of DNA Summarize the process of transcription Relate the role of codons to the sequence of amino acids that
Ch. 10 Notes DNA: Transcription and Translation GOALS Compare the structure of RNA with that of DNA Summarize the process of transcription Relate the role of codons to the sequence of amino acids that
Mate-pair library data improves genome assembly
 De Novo Sequencing on the Ion Torrent PGM APPLICATION NOTE Mate-pair library data improves genome assembly Highly accurate PGM data allows for de Novo Sequencing and Assembly For a draft assembly, generate
De Novo Sequencing on the Ion Torrent PGM APPLICATION NOTE Mate-pair library data improves genome assembly Highly accurate PGM data allows for de Novo Sequencing and Assembly For a draft assembly, generate
Mapping strategies for sequence reads
 Mapping strategies for sequence reads Ernest Turro University of Cambridge 21 Oct 2013 Quantification A basic aim in genomics is working out the contents of a biological sample. 1. What distinct elements
Mapping strategies for sequence reads Ernest Turro University of Cambridge 21 Oct 2013 Quantification A basic aim in genomics is working out the contents of a biological sample. 1. What distinct elements
Big Idea 3C Basic Review
 Big Idea 3C Basic Review 1. A gene is a. A sequence of DNA that codes for a protein. b. A sequence of amino acids that codes for a protein. c. A sequence of codons that code for nucleic acids. d. The end
Big Idea 3C Basic Review 1. A gene is a. A sequence of DNA that codes for a protein. b. A sequence of amino acids that codes for a protein. c. A sequence of codons that code for nucleic acids. d. The end
DNA RNA PROTEIN. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted
 DNA RNA PROTEIN Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted DNA Molecule of heredity Contains all the genetic info our cells inherit Determines
DNA RNA PROTEIN Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted DNA Molecule of heredity Contains all the genetic info our cells inherit Determines
Gene Identification in silico
 Gene Identification in silico Nita Parekh, IIIT Hyderabad Presented at National Seminar on Bioinformatics and Functional Genomics, at Bioinformatics centre, Pondicherry University, Feb 15 17, 2006. Introduction
Gene Identification in silico Nita Parekh, IIIT Hyderabad Presented at National Seminar on Bioinformatics and Functional Genomics, at Bioinformatics centre, Pondicherry University, Feb 15 17, 2006. Introduction
Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10
 Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10 1. Which of the following is NOT needed for DNA replication? A. nucleotides B. ribosomes C. Enzymes (like polymerases) D. DNA E. all of the above are needed 2 The information
Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10 1. Which of the following is NOT needed for DNA replication? A. nucleotides B. ribosomes C. Enzymes (like polymerases) D. DNA E. all of the above are needed 2 The information
The Genetic Code and Transcription. Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot
 The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot TRANSCRIPTION Copy SAME language DNA to RNA Nucleic Acid to Nucleic Acid TRANSLATION Copy DIFFERENT language RNA to Amino
The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot TRANSCRIPTION Copy SAME language DNA to RNA Nucleic Acid to Nucleic Acid TRANSLATION Copy DIFFERENT language RNA to Amino
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr.
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
MODULE 1: INTRODUCTION TO THE GENOME BROWSER: WHAT IS A GENE?
 MODULE 1: INTRODUCTION TO THE GENOME BROWSER: WHAT IS A GENE? Lesson Plan: Title Introduction to the Genome Browser: what is a gene? JOYCE STAMM Objectives Demonstrate basic skills in using the UCSC Genome
MODULE 1: INTRODUCTION TO THE GENOME BROWSER: WHAT IS A GENE? Lesson Plan: Title Introduction to the Genome Browser: what is a gene? JOYCE STAMM Objectives Demonstrate basic skills in using the UCSC Genome
Hello! Outline. Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis. In all living cells, DNA molecules are the storehouses of information. 6.
 Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis In all living cells, DNA molecules are the storehouses of information Hello! Outline u 1. Key concepts u 2. Central Dogma u 3. RNA Types u 4. RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis In all living cells, DNA molecules are the storehouses of information Hello! Outline u 1. Key concepts u 2. Central Dogma u 3. RNA Types u 4. RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
Chromosomes. Chromosomes. Genes. Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce
 Chromosomes Chromosomes Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce Genes Segments of DNA that specify how to build a protein genes may specify more than one
Chromosomes Chromosomes Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce Genes Segments of DNA that specify how to build a protein genes may specify more than one
Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene For Next Week Lab -Hand in questions from 4 and 5 by TUES in my mailbox (Biology Office) -Do questions for Lab 6 for next week -Lab practical next week Lecture Read
Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene For Next Week Lab -Hand in questions from 4 and 5 by TUES in my mailbox (Biology Office) -Do questions for Lab 6 for next week -Lab practical next week Lecture Read
DNA is the genetic material. DNA structure. Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test
 DNA is the genetic material Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test Dr. Amy Rogers Bio 139 General Microbiology Hereditary information is carried by DNA Griffith/Avery
DNA is the genetic material Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test Dr. Amy Rogers Bio 139 General Microbiology Hereditary information is carried by DNA Griffith/Avery
Chapter 10 - Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Bio 100 - Molecular Genetics 1 A. Bacterial Transformation Chapter 10 - Molecular Biology of the Gene Researchers found that they could transfer an inherited characteristic (e.g. the ability to cause pneumonia),
Bio 100 - Molecular Genetics 1 A. Bacterial Transformation Chapter 10 - Molecular Biology of the Gene Researchers found that they could transfer an inherited characteristic (e.g. the ability to cause pneumonia),
Gene Expression - Transcription
 DNA Gene Expression - Transcription Genes are expressed as encoded proteins in a 2 step process: transcription + translation Central dogma of biology: DNA RNA protein Transcription: copy DNA strand making
DNA Gene Expression - Transcription Genes are expressed as encoded proteins in a 2 step process: transcription + translation Central dogma of biology: DNA RNA protein Transcription: copy DNA strand making
Protein Synthesis & Gene Expression
 DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictates the order of amino acids that
DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictates the order of amino acids that
Wednesday, November 22, 17. Exons and Introns
 Exons and Introns Introns and Exons Exons: coded regions of DNA that get transcribed and translated into proteins make up 5% of the genome Introns and Exons Introns: non-coded regions of DNA Must be removed
Exons and Introns Introns and Exons Exons: coded regions of DNA that get transcribed and translated into proteins make up 5% of the genome Introns and Exons Introns: non-coded regions of DNA Must be removed
BIOL 300 Foundations of Biology Summer 2017 Telleen Lecture Outline
 BIOL 300 Foundations of Biology Summer 2017 Telleen Lecture Outline RNA, the Genetic Code, Proteins I. How RNA differs from DNA A. The sugar ribose replaces deoxyribose. The presence of the oxygen on the
BIOL 300 Foundations of Biology Summer 2017 Telleen Lecture Outline RNA, the Genetic Code, Proteins I. How RNA differs from DNA A. The sugar ribose replaces deoxyribose. The presence of the oxygen on the
Sequence assembly. Jose Blanca COMAV institute bioinf.comav.upv.es
 Sequence assembly Jose Blanca COMAV institute bioinf.comav.upv.es Sequencing project Unknown sequence { experimental evidence result read 1 read 4 read 2 read 5 read 3 read 6 read 7 Computational requirements
Sequence assembly Jose Blanca COMAV institute bioinf.comav.upv.es Sequencing project Unknown sequence { experimental evidence result read 1 read 4 read 2 read 5 read 3 read 6 read 7 Computational requirements
Genome annotation. Erwin Datema (2011) Sandra Smit (2012, 2013)
 Genome annotation Erwin Datema (2011) Sandra Smit (2012, 2013) Genome annotation AGACAAAGATCCGCTAAATTAAATCTGGACTTCACATATTGAAGTGATATCACACGTTTCTCTAAT AATCTCCTCACAATATTATGTTTGGGATGAACTTGTCGTGATTTGCCATTGTAGCAATCACTTGAA
Genome annotation Erwin Datema (2011) Sandra Smit (2012, 2013) Genome annotation AGACAAAGATCCGCTAAATTAAATCTGGACTTCACATATTGAAGTGATATCACACGTTTCTCTAAT AATCTCCTCACAATATTATGTTTGGGATGAACTTGTCGTGATTTGCCATTGTAGCAATCACTTGAA
De novo genome assembly with next generation sequencing data!! "
 De novo genome assembly with next generation sequencing data!! " Jianbin Wang" HMGP 7620 (CPBS 7620, and BMGN 7620)" Genomics lectures" 2/7/12" Outline" The need for de novo genome assembly! The nature
De novo genome assembly with next generation sequencing data!! " Jianbin Wang" HMGP 7620 (CPBS 7620, and BMGN 7620)" Genomics lectures" 2/7/12" Outline" The need for de novo genome assembly! The nature
Bacterial Genome Annotation
 Bacterial Genome Annotation Bacterial Genome Annotation For an annotation you want to predict from the sequence, all of... protein-coding genes their stop-start the resulting protein the function the control
Bacterial Genome Annotation Bacterial Genome Annotation For an annotation you want to predict from the sequence, all of... protein-coding genes their stop-start the resulting protein the function the control
Prokaryotic Transcription
 Prokaryotic Transcription Transcription Basics DNA is the genetic material Nucleic acid Capable of self-replication and synthesis of RNA RNA is the middle man Nucleic acid Structure and base sequence are
Prokaryotic Transcription Transcription Basics DNA is the genetic material Nucleic acid Capable of self-replication and synthesis of RNA RNA is the middle man Nucleic acid Structure and base sequence are
Eukaryotic Gene Structure
 Eukaryotic Gene Structure Terminology Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Gene Basic physical and
Eukaryotic Gene Structure Terminology Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Gene Basic physical and
Transcription in Eukaryotes
 Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
RNA-Seq analysis workshop
 RNA-Seq analysis workshop Zhangjun Fei Boyce Thompson Institute for Plant Research USDA Robert W. Holley Center for Agriculture and Health Cornell University Outline Background of RNA-Seq Application of
RNA-Seq analysis workshop Zhangjun Fei Boyce Thompson Institute for Plant Research USDA Robert W. Holley Center for Agriculture and Health Cornell University Outline Background of RNA-Seq Application of
Molecular Genetics Quiz #1 SBI4U K T/I A C TOTAL
 Name: Molecular Genetics Quiz #1 SBI4U K T/I A C TOTAL Part A: Multiple Choice (15 marks) Circle the letter of choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. One mark for each correct
Name: Molecular Genetics Quiz #1 SBI4U K T/I A C TOTAL Part A: Multiple Choice (15 marks) Circle the letter of choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. One mark for each correct
RNA Genomics. BME 110: CompBio Tools Todd Lowe May 14, 2010
 RNA Genomics BME 110: CompBio Tools Todd Lowe May 14, 2010 Admin WebCT quiz on Tuesday cover reading, using Jalview & Pfam Homework #3 assigned today due next Friday (8 days) In Genomes, Two Types of Genes
RNA Genomics BME 110: CompBio Tools Todd Lowe May 14, 2010 Admin WebCT quiz on Tuesday cover reading, using Jalview & Pfam Homework #3 assigned today due next Friday (8 days) In Genomes, Two Types of Genes
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA
 Chapter 8: DNA and RNA Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 8-1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins Proteins play
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 8-1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins Proteins play
Contact us for more information and a quotation
 GenePool Information Sheet #1 Installed Sequencing Technologies in the GenePool The GenePool offers sequencing service on three platforms: Sanger (dideoxy) sequencing on ABI 3730 instruments Illumina SOLEXA
GenePool Information Sheet #1 Installed Sequencing Technologies in the GenePool The GenePool offers sequencing service on three platforms: Sanger (dideoxy) sequencing on ABI 3730 instruments Illumina SOLEXA
From Gene to Protein transcription, messenger RNA (mrna) translation, RNA processing triplet code, template strand, codons,
 From Gene to Protein I. Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes
From Gene to Protein I. Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes
Protein Synthesis. DNA to RNA to Protein
 Protein Synthesis DNA to RNA to Protein From Genes to Proteins Processing the information contained in DNA into proteins involves a sequence of events known as gene expression and results in protein synthesis.
Protein Synthesis DNA to RNA to Protein From Genes to Proteins Processing the information contained in DNA into proteins involves a sequence of events known as gene expression and results in protein synthesis.
Chapter 12. DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION
 Chapter 12 DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis WARM UP What are proteins? Where do they come from? From DNA to RNA to Protein DNA in our cells carry the instructions for making
Chapter 12 DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis WARM UP What are proteins? Where do they come from? From DNA to RNA to Protein DNA in our cells carry the instructions for making
Analysis of Biological Sequences SPH
 Analysis of Biological Sequences SPH 140.638 swheelan@jhmi.edu nuts and bolts meet Tuesdays & Thursdays, 3:30-4:50 no exam; grade derived from 3-4 homework assignments plus a final project (open book,
Analysis of Biological Sequences SPH 140.638 swheelan@jhmi.edu nuts and bolts meet Tuesdays & Thursdays, 3:30-4:50 no exam; grade derived from 3-4 homework assignments plus a final project (open book,
DNA/RNA STUDY GUIDE. Match the following scientists with their accomplishments in discovering DNA using the statement in the box below.
 Name: Period: Date: DNA/RNA STUDY GUIDE Part A: DNA History Match the following scientists with their accomplishments in discovering DNA using the statement in the box below. Used a technique called x-ray
Name: Period: Date: DNA/RNA STUDY GUIDE Part A: DNA History Match the following scientists with their accomplishments in discovering DNA using the statement in the box below. Used a technique called x-ray
BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST DNA to PROTEIN & BIOTECHNOLOGY
 Biology Multiple Choice 016074 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST DNA to PROTEIN & BIOTECHNOLOGY Test Code: 016074 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested
Biology Multiple Choice 016074 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST DNA to PROTEIN & BIOTECHNOLOGY Test Code: 016074 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested
DNA Replication and Repair
 DNA Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif Overview of DNA Replication SWYK CNs 1, 2, 30 Explain how specific base pairing enables existing DNA strands
DNA Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif Overview of DNA Replication SWYK CNs 1, 2, 30 Explain how specific base pairing enables existing DNA strands
From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype
 12 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype 12.1 What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? The gene-enzyme relationship is one-gene, one-polypeptide relationship. Example: In hemoglobin, each
12 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype 12.1 What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? The gene-enzyme relationship is one-gene, one-polypeptide relationship. Example: In hemoglobin, each
Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis
 Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis 1. Describe how genetic information is transcribed into sequences of bases in RNA molecules and is finally translated into sequences of amino
Gene Expression Transcription/Translation Protein Synthesis 1. Describe how genetic information is transcribed into sequences of bases in RNA molecules and is finally translated into sequences of amino
Microbial Genetics. Chapter 8
 Microbial Genetics Chapter 8 Structure and Function of Genetic Material Genome A cell s genetic information Chromosome Structures containing DNA that physically carry hereditary information Gene Segments
Microbial Genetics Chapter 8 Structure and Function of Genetic Material Genome A cell s genetic information Chromosome Structures containing DNA that physically carry hereditary information Gene Segments
produces an RNA copy of the coding region of a gene
 1. Transcription Gene Expression The expression of a gene into a protein occurs by: 1) Transcription of a gene into RNA produces an RNA copy of the coding region of a gene the RNA transcript may be the
1. Transcription Gene Expression The expression of a gene into a protein occurs by: 1) Transcription of a gene into RNA produces an RNA copy of the coding region of a gene the RNA transcript may be the
Genes found in the genome include protein-coding genes and non-coding RNA genes. Which nucleotide is not normally found in non-coding RNA genes?
 Midterm Q Genes found in the genome include protein-coding genes and non-coding RNA genes Which nucleotide is not normally found in non-coding RNA genes? G T 3 A 4 C 5 U 00% Midterm Q Which of the following
Midterm Q Genes found in the genome include protein-coding genes and non-coding RNA genes Which nucleotide is not normally found in non-coding RNA genes? G T 3 A 4 C 5 U 00% Midterm Q Which of the following
 Genome Annotation Genome annotation What is the function of each part of the genome? Where are the genes? What is the mrna sequence (transcription, splicing) What is the protein sequence? What does
Genome Annotation Genome annotation What is the function of each part of the genome? Where are the genes? What is the mrna sequence (transcription, splicing) What is the protein sequence? What does
DNA Model Stations. For the following activity, you will use the following DNA sequence.
 Name: DNA Model Stations DNA Replication In this lesson, you will learn how a copy of DNA is replicated for each cell. You will model a 2D representation of DNA replication using the foam nucleotide pieces.
Name: DNA Model Stations DNA Replication In this lesson, you will learn how a copy of DNA is replicated for each cell. You will model a 2D representation of DNA replication using the foam nucleotide pieces.
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes
 Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 3, 2004 Eukaryotic Gene Structure eukaryotic genomes are considerably more complex than those of prokaryotes eukaryotic cells have organelles
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 3, 2004 Eukaryotic Gene Structure eukaryotic genomes are considerably more complex than those of prokaryotes eukaryotic cells have organelles
MOLECULAR GENETICS PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #2 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1 GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 2 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #2 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1 GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 2 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins. The Central Dogma
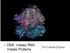 DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA
 TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 2 2/20/15
 Name: TRASK Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 2 2/20/15 Answer each of the following short and longer answer questions in the space provided; circle the BEST answer or answers for each multiple choice question
Name: TRASK Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 2 2/20/15 Answer each of the following short and longer answer questions in the space provided; circle the BEST answer or answers for each multiple choice question
Protein Synthesis
 HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes
 Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes 1.1 Division and Differentiation in Human Cells I can state that cellular differentiation is the process by which a cell develops more
Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes 1.1 Division and Differentiation in Human Cells I can state that cellular differentiation is the process by which a cell develops more
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. copyright cmassengale
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA and Genes 2 Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 3 RNA Differs from DNA RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 4 Other
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA and Genes 2 Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 3 RNA Differs from DNA RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 4 Other
Transcription. DNA to RNA
 Transcription from DNA to RNA The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology replication DNA RNA Protein transcription translation Why call it transcription and translation? transcription is such a direct copy
Transcription from DNA to RNA The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology replication DNA RNA Protein transcription translation Why call it transcription and translation? transcription is such a direct copy
Unit 1 Human cells. 1. Division and differentiation in human cells
 Unit 1 Human cells 1. Division and differentiation in human cells Stem cells Describe the process of differentiation. Explain how differentiation is brought about with reference to genes. Name the two
Unit 1 Human cells 1. Division and differentiation in human cells Stem cells Describe the process of differentiation. Explain how differentiation is brought about with reference to genes. Name the two
Nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ribonucleic acid (RNA) nucleotide
 Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
DNA and RNA. Chapter 12
 DNA and RNA Chapter 12 History of DNA Late 1800 s scientists discovered that DNA is in the nucleus of the cell 1902 Walter Sutton proposed that hereditary material resided in the chromosomes in the nucleus
DNA and RNA Chapter 12 History of DNA Late 1800 s scientists discovered that DNA is in the nucleus of the cell 1902 Walter Sutton proposed that hereditary material resided in the chromosomes in the nucleus
Introduction to RNA-Seq. David Wood Winter School in Mathematics and Computational Biology July 1, 2013
 Introduction to RNA-Seq David Wood Winter School in Mathematics and Computational Biology July 1, 2013 Abundance RNA is... Diverse Dynamic Central DNA rrna Epigenetics trna RNA mrna Time Protein Abundance
Introduction to RNA-Seq David Wood Winter School in Mathematics and Computational Biology July 1, 2013 Abundance RNA is... Diverse Dynamic Central DNA rrna Epigenetics trna RNA mrna Time Protein Abundance
RNA folding & ncrna discovery
 I519 Introduction to Bioinformatics RNA folding & ncrna discovery Yuzhen Ye (yye@indiana.edu) School of Informatics & Computing, IUB Contents Non-coding RNAs and their functions RNA structures RNA folding
I519 Introduction to Bioinformatics RNA folding & ncrna discovery Yuzhen Ye (yye@indiana.edu) School of Informatics & Computing, IUB Contents Non-coding RNAs and their functions RNA structures RNA folding
Chapter 17. From Gene to Protein. AP Biology
 Chapter 17. From Gene to Protein Metabolism teaches us about genes Metabolic defects studying metabolic diseases suggested that genes specified proteins alkaptonuria (black urine from alkapton) PKU (phenylketonuria)
Chapter 17. From Gene to Protein Metabolism teaches us about genes Metabolic defects studying metabolic diseases suggested that genes specified proteins alkaptonuria (black urine from alkapton) PKU (phenylketonuria)
Chapter 14 Active Reading Guide From Gene to Protein
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 14 Active Reading Guide From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 14 Active Reading Guide From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single
7.2 Protein Synthesis. From DNA to Protein Animation
 7.2 Protein Synthesis From DNA to Protein Animation Proteins Why are proteins so important? They break down your food They build up muscles They send signals through your brain that control your body They
7.2 Protein Synthesis From DNA to Protein Animation Proteins Why are proteins so important? They break down your food They build up muscles They send signals through your brain that control your body They
Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein
 Name Period This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours to truly master
Name Period This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours to truly master
DNA/RNA STUDY GUIDE. Match the following scientists with their accomplishments in discovering DNA using the statement in the box below.
 Name: Period: Date: DNA/RNA STUDY GUIDE Part A: DNA History Match the following scientists with their accomplishments in discovering DNA using the statement in the box below. Used a technique called x-ray
Name: Period: Date: DNA/RNA STUDY GUIDE Part A: DNA History Match the following scientists with their accomplishments in discovering DNA using the statement in the box below. Used a technique called x-ray
Gene function at the level of traits Gene function at the molecular level
 Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function at the molecular level Two levels tied together since the molecular level affects the structure and function of cells which determines
Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function at the molecular level Two levels tied together since the molecular level affects the structure and function of cells which determines
Unit 6: Molecular Genetics & DNA Technology Guided Reading Questions (100 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Unit 6: Molecular Genetics
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Unit 6: Molecular Genetics
KEY CONCEPT DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. Found live S with R bacteria and injected
 Section 1: Identifying DNA as the Genetic Material KEY CONCEPT DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. VOCABULARY bacteriophage MAIN IDEA: Griffith finds a transforming
Section 1: Identifying DNA as the Genetic Material KEY CONCEPT DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. VOCABULARY bacteriophage MAIN IDEA: Griffith finds a transforming
Chapter 8 From DNA to Proteins. Chapter 8 From DNA to Proteins
 KEY CONCEPT Section 1 DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. Griffith finds a transforming principle. Griffith experimented with the bacteria that cause pneumonia.
KEY CONCEPT Section 1 DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. Griffith finds a transforming principle. Griffith experimented with the bacteria that cause pneumonia.
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells
 Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
NUCLEIC ACIDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
 NUCLEIC ACIDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA Cell Nucleus Chromosomes is a coiled double helix carrying hereditary information of the cell Contains the instructions for making from 20 different amino acids
NUCLEIC ACIDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA Cell Nucleus Chromosomes is a coiled double helix carrying hereditary information of the cell Contains the instructions for making from 20 different amino acids
CHAPTER 21 LECTURE SLIDES
 CHAPTER 21 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
CHAPTER 21 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
Nucleic acids and protein synthesis
 THE FUNCTIONS OF DNA Nucleic acids and protein synthesis The full name of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. Every nucleotide has the same sugar molecule and phosphate group, but each nucleotide contains one
THE FUNCTIONS OF DNA Nucleic acids and protein synthesis The full name of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. Every nucleotide has the same sugar molecule and phosphate group, but each nucleotide contains one
Bio11 Announcements. Ch 21: DNA Biology and Technology. DNA Functions. DNA and RNA Structure. How do DNA and RNA differ? What are genes?
 Bio11 Announcements TODAY Genetics (review) and quiz (CP #4) Structure and function of DNA Extra credit due today Next week in lab: Case study presentations Following week: Lab Quiz 2 Ch 21: DNA Biology
Bio11 Announcements TODAY Genetics (review) and quiz (CP #4) Structure and function of DNA Extra credit due today Next week in lab: Case study presentations Following week: Lab Quiz 2 Ch 21: DNA Biology
Chapter 12 Packet DNA 1. What did Griffith conclude from his experiment? 2. Describe the process of transformation.
 Chapter 12 Packet DNA and RNA Name Period California State Standards covered by this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions
Chapter 12 Packet DNA and RNA Name Period California State Standards covered by this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions
Bundle 5 Test Review
 Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES-
 DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES- THE COMPONENTS AND STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA is made up of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of three basic components:, called deoxyribose in DNA In DNA, there
DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES- THE COMPONENTS AND STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA is made up of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of three basic components:, called deoxyribose in DNA In DNA, there
Single Nucleotide Variant Analysis. H3ABioNet May 14, 2014
 Single Nucleotide Variant Analysis H3ABioNet May 14, 2014 Outline What are SNPs and SNVs? How do we identify them? How do we call them? SAMTools GATK VCF File Format Let s call variants! Single Nucleotide
Single Nucleotide Variant Analysis H3ABioNet May 14, 2014 Outline What are SNPs and SNVs? How do we identify them? How do we call them? SAMTools GATK VCF File Format Let s call variants! Single Nucleotide
2. From the first paragraph in this section, find three ways in which RNA differs from DNA.
 Name Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein Begin reading at page 328 Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours
Name Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein Begin reading at page 328 Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours
Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Algorithms in Bioinformatics Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University San José, California, USA khuri@cs.sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Outline Central Dogma of Molecular
Algorithms in Bioinformatics Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University San José, California, USA khuri@cs.sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Outline Central Dogma of Molecular
RNA does not adopt the classic B-DNA helix conformation when it forms a self-complementary double helix
 Reason: RNA has ribose sugar ring, with a hydroxyl group (OH) If RNA in B-from conformation there would be unfavorable steric contact between the hydroxyl group, base, and phosphate backbone. RNA structure
Reason: RNA has ribose sugar ring, with a hydroxyl group (OH) If RNA in B-from conformation there would be unfavorable steric contact between the hydroxyl group, base, and phosphate backbone. RNA structure
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN. Section C: The Synthesis of Protein
 CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section C: The Synthesis of Protein 1. Translation is the RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide: a closer look 2. Signal peptides target some eukaryotic polypeptides to
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section C: The Synthesis of Protein 1. Translation is the RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide: a closer look 2. Signal peptides target some eukaryotic polypeptides to
RNA : functional role
 RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
AP Biology
 Chapter 17. From Gene to Protein Metabolism teaches us about genes Metabolic defects studying metabolic diseases suggested that genes specified proteins alkaptonuria (black urine from alkapton) PKU (phenylketonuria)
Chapter 17. From Gene to Protein Metabolism teaches us about genes Metabolic defects studying metabolic diseases suggested that genes specified proteins alkaptonuria (black urine from alkapton) PKU (phenylketonuria)
Analytics Behind Genomic Testing
 A Quick Guide to the Analytics Behind Genomic Testing Elaine Gee, PhD Director, Bioinformatics ARUP Laboratories 1 Learning Objectives Catalogue various types of bioinformatics analyses that support clinical
A Quick Guide to the Analytics Behind Genomic Testing Elaine Gee, PhD Director, Bioinformatics ARUP Laboratories 1 Learning Objectives Catalogue various types of bioinformatics analyses that support clinical
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. copyright cmassengale
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA and Genes 2 Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 3 RNA Differs from DNA RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 4 Other
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA and Genes 2 Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 3 RNA Differs from DNA RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 4 Other
Adv Biology: DNA and RNA Study Guide
 Adv Biology: DNA and RNA Study Guide Chapter 12 Vocabulary -Notes What experiments led up to the discovery of DNA being the hereditary material? o The discovery that DNA is the genetic code involved many
Adv Biology: DNA and RNA Study Guide Chapter 12 Vocabulary -Notes What experiments led up to the discovery of DNA being the hereditary material? o The discovery that DNA is the genetic code involved many
