Page 18 of 165 AGRICULTURE
|
|
|
- Erik Marshall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Page 17 of 165 D. CAPABILITY APPROACH : associated with Prof. Amartya Sen. Access to education and health facilities. INTERNATIONAL COMPARISIONS Size of the country and per-capita income are not directly related to human development. Like SRILANKA AND TRINIDAD HAVE HIGHER HDI THAN INDIA THEY ARE DIVIDED INTO THREE GROUPS HIGH -ABOVE 0.8 :57 COUNTRIES MEDIUM :88 COUNTRIES LOW - BELOW 0.5 :32 COUNTRIES COUNTRIES WITH HIGH INDEX VALUE: NORWAY, ICELAND, AUSTRALIA education and health care are priorities for the government. COUNTRIES WITH MEDIUM INDEX: it consists of large group, emerged after second world war, adopting people oriented policies. COUNTRIES WITH LOW INDEX VALUE: large number of these countries are very small. political turmoil, social instability, civil war, high incidence of diseases. CHAPTER-5 PRIMARY ACTIVITIES HUNITING AND GATHERING 1. Depend on their immediate environment 2. Depend on animals they hunted and edible plants which they gathered 3.Primitive societies depend on hunting and gathering, fishing. 4. oldest occupation, practiced in harsh climatic conditions 5. depend on animals, for food, shelter, clothing 6. small capital, low level of technology, 7. practiced in High latitude areas such as Eurasia, Southern Chile. Low latitude such as Amazon, Congo, S.E. Asian countries 8. in modern market some gathering is done such as leaves, bark nuts, fabric rubber, balata, gums and resins. PASTORALISM NOMEDIC HERDING: o herders depend on animals for food, transport, and shelter and clothing. o Keep on moving from one place to another along with their animals. o Each nomadic community occupies a well identified territory o Variety of animals are kept indifferent regions o Sahara& Asiatic deserts: sheep, goat,& camel o Tibet: yak,andes: llamas, arctic region: Reindeer REGIONS: 1 CORE REGIONS EXTENDING FROM ATLANTIC COAST OF N.AFRICA THROUGH
2 Page 18 of 165 ARABIAN PENINSULA TO CENTRAL CHINA 2.SECOND REGION EXTENDS IN TUNDR REGION OF EURASIA 3. THIRD REGION IS FOUND IN S.W AFRICA AND MADAGASCAR TRANSHUMANCE: SEASONAL MOVEMENT OF PEOPLE ALONG WITH THEIR HERDS TO MOUNTAINS IN SUMMER AND TO PLAINS IN WINTER. Ex. Gujjars, Bakarwals, Gaddis& Bhotias in Himalayas The number of pastoral nomads is decreasing due to 1. Imposition of political boundaries 2. New settlement plans by different countries COMMERCIAL LIVE STOCK REARING 1.It is more organized 2. Capital intensive 3.practised in permanent ranches 4.larger areas and divided in to parcels 5Animals are moved from one parcel to another 6.Number of animals are kept based on capacity of the pasture 7.Animals are sheep, cattle, goats and horses and products are meat, wool, hides and skin 8.Practiced in New Zealand, Australia Argentina Uruguay and USA AGRICULTURE TYPES OF AGRICULTURE SUBSISTENCE AGRICULTURE a. primitive subsistence agriculture b. intensive subsistence agriculture primitive subsistence agriculture: 1. Also called shifting cultivation/ slash and burn agriculture 2.practicved by tribes in topics 3. land holdings are small 4.do not use fertilizers 5. Change the land frequently 6.after 5 yeas they come back again. 7. It is called JHUMING in N.E. INDIA, MILPA in South America, LADANG in Malaysia INTENSIVE SUBSISTENCE AGRICULTURE: 1. Found in density populated areas 2.there are two types A.INTENSIVE SUBSISTENCE AGRICULTURE DOMINATED BY WET PADDY CULTIVATION a. dominated by rice crop, b. land holdings are very small
3 Page 19 of 165 c. family labor is used d. less use of machine e. manual labor is used f. Farm yard manure is used g. Yield per unit is high but per labor is low B.INTENSIVE SUBSISTENCE AGRICULTURE DOMINATED BY OTHER CROPS. a. depend on climate, soil, relief other crops are cultivated. b. mainly practiced in SE ASIA. C. wheat, barley, soya bean, sorghum are cultivated d. in India wheat is grown in western parts of Ganga plain e. millets are grown in western parts of south India f. irrigation is used g. Europeans introduced Plantation agriculture PLANTATION AGRICULTURE 1. Introduced by Europeans 2. Found in tropics 3. Important crops are tea, coffee, cocoa, rubber, cotton, oil palm, sugarcane,banana, &pine apples 4. Large estates, capital, managerial, technical support 5. Scientific methods of cultivation 6. Single crop specialization, 7. Cheap labour 8. Good system of transport 9. Export oriented 10. (a)the French established cocoa and coffee in west Africa (b)the British setup tea gardens In India and Sri Lanka Rubber plantation in Malaysia, sugarcane and banana In west indies (C) Spanish and Americans introduced coconut and sugar cane in Philippines (d) Dutch started sugarcane in Indonesia (e) coffee Fazandas are managed by British in Brazil EXTENSIVE COMMERCIAL GRAIN CULTIVATION 1. Practiced in semiarid land of mid latitudes 2. Whet is the main crop 3. Corn, barley oats and rye are grown 4. Large land holdings 5. Machines are used 6. Low yield per acre but high yield per person 7. Practiced in prairies, pampas, veldts, down, Canterbury plains. DAIRY FARMING 1. Most advanced and efficient type of animal rearing
4 Page 20 of Highly capital intensive 3. Animal shed, storage facilities, mulching machines are used 4. Special emphasis is laid on breeding health care 5. Highly labour intensive 6. No off season 7. Practiced nearby urban areas and industries 8. Development of transportation, refrigeration pasteurization have increased the marketing MEDITERRANEAN AGRICULTURE 1. Highly specialized commercial agriculture 2. Practiced in the countries around Mediterranean sea also central Chile, SW Africa,SW Australia& California 3. It is an important supplier of citrus fruits 4. VITICULTURE is specialized in this region 5. Best quality wine is produced from grapes 6. Low quality grapes are used for raisins, and currants 7. Olives and figs are also grown 8. Fruits and vegetable are grown in winter which are great demand in Europe MARKET GARDENING AND HORTICULTURE 1. Vegetable, fruits and flowers are grown 2. Small farms, located nearby urban areas 3. Good transportation is required 4. Labor and capital intensive 5. Use of irrigation, HYV seeds, fertilizers & pesticides are used 6. Green houses and artificial heating is used in cold regions 7. Practiced in NW Europe, NE USA & Mediterranean regions 8. Netherlands is famous in growing tulips flower 9. The regions where vegetable are grown is called TRUCK FARMING FACTORY FARMING 1.Factory farming is also practiced in NW Europe 2.It consists of poultry farming livestock rearing 3.They are fed on factory feedstuff and carefully supervised against diseases 4.Heavy capital investments 5.Veterinary services, heating and lightning is provided 6. Breed selection and scientific breeding is important feature COPERATIVE FARMING 1. A group of farmers form a society 2. Pool their resources to get more profit 3. Individual farms remain intact
5 Page 21 of Farming is a matter of cooperative initiative 5. Societies help farmers in getting agriculture inputs 6. Sell the products at the most favorable terms 7. Help in processing products at cheaper rates 8. Practiced in Denmark, Netherlands, Belgium, Sweden & Italy COLLECTIVE FARMING 1. Social owner ship for means of production and labour 2. It is also called as KOLKHOZ 3. It was introduced in erstwhile USSR 4. Farmers pool their resources like land livestock labour 5. A small land is allowed to retain of their own to grow their own crops 6. Yearly targets are fixed by the government 7. Government fixes the product rates 8. Excess produce is distributed among the farmers 9. The farmers are to pay taxes for their own land 10. Members are paid according to their nature of the work 11. Exceptional work is rewarded by the government MINING 1. There are stages of minerals copper age, bronze age, iron age 2. Actual development is started with the industrialization FACTORS AFFECTION MINING ACTIVITY 1. Physical factors such as size, grade, and mode of occurrence of mineral 2. Economic factors such as demand for mineral, technology available, capital, labor, and transportation METHODS OF MINING 1. Depend on mode of occurrence of mineral there are two types of mining A. SURFACE /OPENCAST MINING 1. Easiest, and cheapest mining 2. Occur close to the surface 3. Low safety precautions 4. Large and quick output B. UNDERGROUND/SHAFT MINING 1. Vertical shafts to be sunk 2. Minerals are extracted and sent to surface 3. It requires specialized drills, lifts, haulage vehicles,ventilation systems 4. This method is risky poisonous gases, fires, floods and caving leads to accidents 5. It requires large investment 6. Developed countries are showing less interest but developing countries are more interest due to large labor availability
6 Page 22 of 165 CHAPTER-6 SECONDARY ACTIVITIES GIST : MANUFACATURING, CHARACTERISTICS OF MODERN LARGE SCALE MANUFACTURING, CLASSIFICATION OF INDUSTRIES GENERAL: 1. secondary activities add value to natural resources by transforming raw materials into valuable products 2.Manufacturing: a. Involves a full array of production from handicrafts to molding iron and steel and stamping out plastic toys to assembling delicate computer components or space vehicles b. Application of power c. mass production d. identical products e. specialized labour f. standardized commodities CHARACTERISTICS OF MODERN LARGE SCALE MANUFACTURING 1. Specialization of skills/ methods of production 2. Mechanization 3. Technical innovation 4. Organizational structure and stratification 5. Uneven geographic distribution 6. Access to market 7. Access to raw material 8. Access to labour supply 9. Access to sources of energy 10. Access to transportation& communication skills 11. Government policy 12. Link to industries CLASSIFICATION OF INDUSTRIES A. BASED ON SIZE 1. COTTATGE / HOUSE HOLD 2. SMALL SCALE 3. LARGE SCALE B. BASED ON INPUT/RAW MATERIAL 1. AGROBASED 2. MINERAL BASED 3.CHEMICAL BASED 4. FOREST BASED 5ANIMAL BASED C. BASED ON OUTPUT/PRODUCT 1. BASIC INDUSTRIE 2. CONSUMER INDUSTRIES D. BASED ON OWNERSHIP 1. PUBSIC SECTOR 2. PRIVATE SECTOR 3. JOINT SECTOR TRADITIONAL LAREGE SCALE INDUSTRIAL REGIONS
7 Page 23 of HIGH PROPORTIONOF EMPLOYMENT 2. HIGH DENSITY OF HOUSING 3. POOR SERVICES INFERIOR QUALITY 4. POLLUTION, WASTE HEAPS 5. UNEMPLOYMENT, EMIGRATION DERELICT LAND AREAS RUHR COAL FIELD GERMANY 1. One of the major industrial area 2. Coal, iron, steel are bases for the economy 3. Demand for coal declined so industry shrinking 4. Ruhr region is producing 80% of steel production 5. Problems of industrial waste and pollution 6. New industries emerged in the place of old industries such as car assembly new chemical industry, universities. CONCEPT OF HIGH TECHNOLOGY INDUSTRY 1. Latest generation manufacturing unit 2. Application of R&D unit 3. Professional workers(white collar) share large group 4. Highly skilled specialists (blue collar) also working 5. Robotics are used in assembly line 6. Computer Aided Design is used 7. Electronic controls 8. Neatly spaced, low modern dispersed office plant and lab buildings 9. Planned business parks for high-tech industries 10. Regionally concentrated, self sustained highly specialized techno-poles 11. Silicon valley in San Francisco and silicon forest near Seattle are techno poles IRON AND STEEL INDUSTRIE 1. Base for other industries so it is called basic industry 2. Provide raw material to other industries 3. Also called heavy industry 4. Use bulky material 5. Produce heavy material RAW MATERIALS A. COAL B.LIME STONE C COKE D.IRONORE E. MANGANESE FEATURES 1. Located nearby raw material or Near the ports 2. Mini steel industries are located near by markets 3. Located nearby integrated steel plants for scrap DISTRIBUTION 1. Most complex and capital intensive industry a. North America: USA North Appalachian region: PITTISBURG, Great lake region: CHICOGO, GARRY, ERIE, CLEVELAND LORAIN BUFALLO, DULUTH
8 Page 24 of 165 Atlantic region SPARRPWS POINT AND MORRISVILLE b. Europe UK - Birmingham, &Sheffield Germany: Duisburg, Dortmund Dusseldorf Essen France: Le Creosote St.Ettienne Russia: Moscow, St. Petersburg. Lipetsk Tula Asia: Nagasaki, Tokyo Yokoma of Japan Shanghai, Tangshan and Wuhan in China Jamshedpur, Kulti Burnpur Durgapur Roukela Bhilai Bokaro Salem Vizak of India COTTON TEXTILE INDUSTRY THREE SUB SECTORS 1. handloom provide more labour employment, semi skilled workers, small capital, spinning weaving and finishing of fabrics are important functions Power loom Machines are used, less labour intensive, volume of production increases Mill sector: highly capital intensive produces cloth in bulk Distribution: INDIA CHINA USA PAKISTAN UZBEKISTAN EGYPT Egypt produces half of the world cotton UK NW EUROPE JAPAN produce textiles by importing raw material from other countries Industry facing stiff competition with synthetic fiber Now it is declining trend due to technology It is shifted to less developed countries
9 Page 25 of 165 CHAPTER-7 TERTIARY AND QUATERNARY ACTIVITIES GENERAL FEATURES 1.large number work in tertiary sector and medium number work in secondary sector 2. they include both production and exchange 3. production includes provision of service 4.output is indirectly measured in terms of wages and salaries 5. exchange involves trade transport and communication 6. provide commercial output service 7. specialized skills are involved TYPES OF TERTIARY ACTIVITIES SERVICE SECTOR SERVICE SECTOR TERTIARY QUATERNARY QUINARY TRADE & COMMERCE TRANSPORT COMMUNICATION SERVICES WHOLE SALE RETAIL ROAD RAIL WATER AIR URBAN SUPPLY HOUSE RURAL MANDIS URBAN RURAL INLAND OCEANIC PASSENGER CARGO PERIODIC MARKETS CHAIN STORES MAIL ORDER CONVENIENT SHOPPING PDS TELEPHONE INTERNET
10 Page 26 of 165 COMMUNICATION MEANS OF TRANSPORT TELE- COMMUNIC ATION AUDIOVISUAL TELEPHONE FILMS RADIO TV PRINT LANDLINE MOBILE NEWS MAGAZINE SERVICES BANKING INSURANCE REAL ESTATE PERRSONAL PRIVATE GOVT. NGO QUATERNARY INFORMATION BASED R&D BASED QUINARY SPECIALIST DECISION MAKERS CONSULTANT POLICY FORMULATORS
11 Page 27 of 165 SOME SELECTED EXAMPLES Tourism : tourist regions, factors affecting tourism: demand, transport TOURIST ATTRACTIONS: climate, landscape history and art, culture and economy Empowered workers, QUATERNARY ACTIVITIES 1. Collection production and dissemination of information,. 2.Production of information, 3.Research and development, 4.specialized knowledge, 5.technical skills, 6.administrative competence. QUINARY ACTIVITIES The highest level of decision makers, policy makers, Outsourcing Large no. of call centers in India and China opened Advantages Cheap, availability of skilled persons, English language communication skills, out migrating countries. It includes 1. Knowledge processing outsourcing 2. Home shoring 3. Business process outsourcing 3. Availability of high skilled workers ex. E- learning, business research intellectual property legal profession and banking sector MEDICAL SERVICES FOR OVERSEAS PATIENTS I INDIA 1. India is leading country in medical tourism 2. World class hospitals are located in India 3. Abundant benefits for the developing countries 4. It is cheap for developed countries 5. Advantages for patients 6. Developed transport in India DIGITAL DIVIDE 1. Availability of information and communication technology 2. It is uneven in the world 3. It depends on the government policy 4. Developed countries provide but developing countries still to provide the ICT to their people
CHAPTER 4 : AGRICULTURE
 I. ECONOMIC ACTIVITIES:- ITL Public School Social Science Hand Out (2017-18) Class VIII Subject: Geography Instructions For each questions value points are given from the content. Frame the sentences of
I. ECONOMIC ACTIVITIES:- ITL Public School Social Science Hand Out (2017-18) Class VIII Subject: Geography Instructions For each questions value points are given from the content. Frame the sentences of
Agricultural Regions
 Agricultural Regions Derwent Wittlesey s 11 Agricultural Regions Images: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:agricultural_map_by_whittlesey,_d.s.png Agriculture in the Developing World 5 types Poorer
Agricultural Regions Derwent Wittlesey s 11 Agricultural Regions Images: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:agricultural_map_by_whittlesey,_d.s.png Agriculture in the Developing World 5 types Poorer
Chapter 9: Economic Geography, Agriculture and Primary Activities
 Chapter 9: Economic Geography, Agriculture and Primary Activities Oil tanker indicating increasing economic interdependence Categories of Activities Primary Activities: related to harvesting or extracting
Chapter 9: Economic Geography, Agriculture and Primary Activities Oil tanker indicating increasing economic interdependence Categories of Activities Primary Activities: related to harvesting or extracting
CHAPTER 10: AGRICULTURE. An Introduction to Human Geography. The Cultural Landscape: 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 CHAPTER 10: AGRICULTURE The Cultural Landscape: An Introduction to Human Geography Pg 308 How much of the population in less developed countries are farmers? Where are 97% of the world s farmers located?
CHAPTER 10: AGRICULTURE The Cultural Landscape: An Introduction to Human Geography Pg 308 How much of the population in less developed countries are farmers? Where are 97% of the world s farmers located?
Agriculture and Rural Land Use. Unit 5
 Agriculture and Rural Land Use Unit 5 Agriculture Raising of animals or growing of crops to obtain food for consumption or sale History of Agriculture Hunting and gathering Nomads Agricultural Revolution
Agriculture and Rural Land Use Unit 5 Agriculture Raising of animals or growing of crops to obtain food for consumption or sale History of Agriculture Hunting and gathering Nomads Agricultural Revolution
Agriculture. Key Issue Three: Where are agricultural regions in more developed countries?
 Agriculture Key Issue Three: Where are agricultural regions in more developed countries? Key Issue 3: Agriculture in Developed Countries Mixed crop and livestock systems Dairy farming Grain farming Livestock
Agriculture Key Issue Three: Where are agricultural regions in more developed countries? Key Issue 3: Agriculture in Developed Countries Mixed crop and livestock systems Dairy farming Grain farming Livestock
Agricultural Regions
 Agricultural Regions The following map displays a more specific representation of agricultural regions. It shows (through numbers) when other types of agriculture are practiced within a region where another
Agricultural Regions The following map displays a more specific representation of agricultural regions. It shows (through numbers) when other types of agriculture are practiced within a region where another
6th Grade Geography 2nd Nine Weeks Test
 6th Grade Geography 2nd Nine Weeks Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 The fertile soil and flat lands of the Midwest help make it the
6th Grade Geography 2nd Nine Weeks Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 The fertile soil and flat lands of the Midwest help make it the
Unit 3. The primary sector
 Unit 3. The primary sector - Economic activities devoted to obtaining resources directly from nature. Agrarian space - Agrarian space: land where agrarian activities are undertaken - Rural space: non urban
Unit 3. The primary sector - Economic activities devoted to obtaining resources directly from nature. Agrarian space - Agrarian space: land where agrarian activities are undertaken - Rural space: non urban
AP Human Geography: Agriculture
 AP Human Geography: Agriculture History LDCS MDCS Regions Visuals 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 5 5 History- 1 Which of the following is NOT an agricultural hearth? A) Southwest
AP Human Geography: Agriculture History LDCS MDCS Regions Visuals 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 5 5 History- 1 Which of the following is NOT an agricultural hearth? A) Southwest
Agriculture. Word Origin The word agriculture is derived from Latin words ager or agri meaning soil and culture meaning, cultivation.
 Word Origin The word agriculture is derived from Latin words ager or agri meaning soil and culture meaning, cultivation. Gurpreet, Madho and Tina were walking through the village where they saw a farmer
Word Origin The word agriculture is derived from Latin words ager or agri meaning soil and culture meaning, cultivation. Gurpreet, Madho and Tina were walking through the village where they saw a farmer
FOREI ~CTS for Illinois Citizen,~~ 6'75
 FOREI ~CTS for Illinois Citizen,~~ 6'75 THE FOREIGN TRADE of the United States is a 40 billion dollar business. It involves every major industry and affects every family in the nation. Since foreign trade
FOREI ~CTS for Illinois Citizen,~~ 6'75 THE FOREIGN TRADE of the United States is a 40 billion dollar business. It involves every major industry and affects every family in the nation. Since foreign trade
Unit 6 Energy, mining and industry.
 Unit 6 Energy, mining and industry. In the last unit we learnt about agriculture, livestock breeding and fishing, activities that provides us with food and raw materials to the industry. In this unit we
Unit 6 Energy, mining and industry. In the last unit we learnt about agriculture, livestock breeding and fishing, activities that provides us with food and raw materials to the industry. In this unit we
Economic Review. South African Agriculture. of the DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE, FORESTRY AND FISHERIES
 Economic Review of the South African Agriculture 2018 DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE, FORESTRY AND FISHERIES Compiled by the Directorate: Statistics and Economic Analysis, Private Bag X246, PRETORIA 0001 Published
Economic Review of the South African Agriculture 2018 DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE, FORESTRY AND FISHERIES Compiled by the Directorate: Statistics and Economic Analysis, Private Bag X246, PRETORIA 0001 Published
11.F. Taiwan. Hsing-Chun Lin, Lin-Chun Chung and Ruey-Wan Liou. References
 11.F Taiwan Hsing-Chun Lin, Lin-Chun Chung and Ruey-Wan Liou This documentation outlines the main procedure followed by the Directorate-General of Budget, Accounting and Statistics (DGBAS), Executive Yuan,
11.F Taiwan Hsing-Chun Lin, Lin-Chun Chung and Ruey-Wan Liou This documentation outlines the main procedure followed by the Directorate-General of Budget, Accounting and Statistics (DGBAS), Executive Yuan,
The Cultural Landscape by Rubenstein Chapter 10: Agriculture
 Key Issue 1: Where Did Agriculture Originate? Pages 346-351 ***Always keep your key term packet out whenever you take notes from Rubenstein. As the terms come up in the text, think through the significance
Key Issue 1: Where Did Agriculture Originate? Pages 346-351 ***Always keep your key term packet out whenever you take notes from Rubenstein. As the terms come up in the text, think through the significance
agriculture, forestry & fisheries Department: Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries REPUBLIC OF SOUTH AFRICA
 2014 agriculture, forestry & fisheries Department: Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries REPUBLIC OF SOUTH AFRICA Economic Review of the South African Agriculture 2014 DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE, FORESTRY
2014 agriculture, forestry & fisheries Department: Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries REPUBLIC OF SOUTH AFRICA Economic Review of the South African Agriculture 2014 DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE, FORESTRY
Interpreting Maps, Charts, and Graphs
 Interpreting Maps, Charts, and Graphs Crop Hearths (pg. 348) # s 1-5 1. The map of crop hearths indicates that a. coconuts, pigeonpeas, maize, and tomatoes were first domesticated in Southeast Asia. b.
Interpreting Maps, Charts, and Graphs Crop Hearths (pg. 348) # s 1-5 1. The map of crop hearths indicates that a. coconuts, pigeonpeas, maize, and tomatoes were first domesticated in Southeast Asia. b.
Chapter 23 Test on South Asia
 Name Score Chapter 23 Test on South Asia Part 1 - Multiple Choice (26 pts.) Read the following statements carefully. Select and circle the most correct choice from among the choices provided. 1. The northern
Name Score Chapter 23 Test on South Asia Part 1 - Multiple Choice (26 pts.) Read the following statements carefully. Select and circle the most correct choice from among the choices provided. 1. The northern
Industry and Trade: Test Review- Answer Key
 Industry and Trade: Test Review- Answer Key Definitions: Industry Primary Industry Secondary Industry Tertiary Industry Quaternary Industry Import/Export Labour Force Location Factor Incentive Branch Plant
Industry and Trade: Test Review- Answer Key Definitions: Industry Primary Industry Secondary Industry Tertiary Industry Quaternary Industry Import/Export Labour Force Location Factor Incentive Branch Plant
The Economy. Chapter 28, Section 1 (Pages ) Economic Activities (page 699) APEC
 Chapter 28, Section 1 (Pages 698 703) The Economy The countries of East Asia are experiencing rapid economic changes as they emerge from the Asian financial crisis of the 1990s and adjust to a global economy.
Chapter 28, Section 1 (Pages 698 703) The Economy The countries of East Asia are experiencing rapid economic changes as they emerge from the Asian financial crisis of the 1990s and adjust to a global economy.
Grade 7 Practice Test for State Geography CRT 2007
 Grade 7 Practice Test for State Geography CRT 2007 PASS 1.2 Sample Test Items: Depth of Knowledge: 2 Correct Answer: C Compared to the rest of Australia, the climate of Tasmania is A warmer. B drier. C
Grade 7 Practice Test for State Geography CRT 2007 PASS 1.2 Sample Test Items: Depth of Knowledge: 2 Correct Answer: C Compared to the rest of Australia, the climate of Tasmania is A warmer. B drier. C
Essential Knowledge. Neolithic agricultural revolution, hearth, domestication, Fertile Crescent. Diffusion, Columbian Exchange, globalization
 A. The development of agriculture led to widespread alteration of the natural environment. Identify major centers of domestication of plants and animals and patterns of diffusion in the first (Neolithic)
A. The development of agriculture led to widespread alteration of the natural environment. Identify major centers of domestication of plants and animals and patterns of diffusion in the first (Neolithic)
UNIT 4: Primary Sector
 Y3 GEOGRAPHY Session 1 UNIT 4: Primary Sector Learning objective: 1 To tell the importance of the Primary sector Starter: guess (next slide) Importance of the Primary Sector 1. It employs. of the total
Y3 GEOGRAPHY Session 1 UNIT 4: Primary Sector Learning objective: 1 To tell the importance of the Primary sector Starter: guess (next slide) Importance of the Primary Sector 1. It employs. of the total
Key Issue 1: Where Did Agriculture Originate?
 Revised 2018 NAME: PERIOD: Rubenstein: The Cultural Landscape (12 th edition) Chapter Nine Food and Agriculture (pages 306 thru 347) This is the primary means by which you will be taking notes this year
Revised 2018 NAME: PERIOD: Rubenstein: The Cultural Landscape (12 th edition) Chapter Nine Food and Agriculture (pages 306 thru 347) This is the primary means by which you will be taking notes this year
Chapter 10. Agriculture
 Chapter 10 Agriculture Key Issue #1 Where Did Agriculture Originate? Agricultural Origins & Regions Origins of agriculture Hunters and gatherers Invention of agriculture Location of agricultural hearths
Chapter 10 Agriculture Key Issue #1 Where Did Agriculture Originate? Agricultural Origins & Regions Origins of agriculture Hunters and gatherers Invention of agriculture Location of agricultural hearths
Unit V Test: Development and Agricultural and Rural Land Use
 Unit V Test: Development and Agricultural and Rural Land Use Multiple Choice: Select the best answer and mark it on your scantron. You may write on the test (1 point each). 1. The core-periphery model
Unit V Test: Development and Agricultural and Rural Land Use Multiple Choice: Select the best answer and mark it on your scantron. You may write on the test (1 point each). 1. The core-periphery model
The 11 regions are divided between 5 developing countries and 6 that are. Mixed crop and Livestock. Dairy. Grain. Mediterranean.
 Key Issue 3: Where Is Agriculture Distributed? Pages 356-373 Let s talk about Agriculture in LDCs! Haven t you heard of dependency theory? What would a white man know about LDCs?! Shut up and push this
Key Issue 3: Where Is Agriculture Distributed? Pages 356-373 Let s talk about Agriculture in LDCs! Haven t you heard of dependency theory? What would a white man know about LDCs?! Shut up and push this
AP HUMAN GEOGRAPHY UNIT 2 Textbook Chapter 11
 AP HUMAN GEOGRAPHY UNIT 2 Textbook Chapter 11 Agriculture The purposeful tending of crops and raising of livestock in order to produce food and fiber. Hunting and Gathering Before agriculture humans were
AP HUMAN GEOGRAPHY UNIT 2 Textbook Chapter 11 Agriculture The purposeful tending of crops and raising of livestock in order to produce food and fiber. Hunting and Gathering Before agriculture humans were
6. Base your answer to question on the quotation below and on your knowledge of social studies.
 1. During which period did the domestication of animals and growing of crops first occur? A) Iron Age B) Paleolithic Period C) Neolithic Revolution D) Scientific Revolution 2. Where does the archaeological
1. During which period did the domestication of animals and growing of crops first occur? A) Iron Age B) Paleolithic Period C) Neolithic Revolution D) Scientific Revolution 2. Where does the archaeological
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved.
 Study Island Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 04/02/2014 Generated By: Cheryl Shelton Title: Grade 6 - Geography Japan is a small island nation with few natural resources.
Study Island Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 04/02/2014 Generated By: Cheryl Shelton Title: Grade 6 - Geography Japan is a small island nation with few natural resources.
Minimum Core Data Set
 Global Strategy IMPROVING AGRICULTURAL AND RURAL STATISTICS IN ASIA PACIFIC Minimum Core Data Set Regional Office for the Asia-Pacific Regional Action Plan to Improve Agricultural and Rural Statistics
Global Strategy IMPROVING AGRICULTURAL AND RURAL STATISTICS IN ASIA PACIFIC Minimum Core Data Set Regional Office for the Asia-Pacific Regional Action Plan to Improve Agricultural and Rural Statistics
APHUG Chapter 10: Agriculture p.306
 APHUG Chapter 10: Agriculture p.306 P a g e 1 KI 1 4 Name Key Issues 1: Where Did Agriculture Originate? 2: Where Are Agricultural Regions in LDCs? 3: Where Are Agricultural Regions in MDCs? 4: Why Do
APHUG Chapter 10: Agriculture p.306 P a g e 1 KI 1 4 Name Key Issues 1: Where Did Agriculture Originate? 2: Where Are Agricultural Regions in LDCs? 3: Where Are Agricultural Regions in MDCs? 4: Why Do
Chapter 10: Agriculture
 Chapter 10: Agriculture Introduction and Case Study (p. 326-328) 1. What is the typical human like? 2. Why does farming vary from place to place? 3. Case Study: Describe the difference between wheat farming
Chapter 10: Agriculture Introduction and Case Study (p. 326-328) 1. What is the typical human like? 2. Why does farming vary from place to place? 3. Case Study: Describe the difference between wheat farming
Key Issue 1: Where Did Agriculture Originate?
 Due Thursday, October 23 rd, 2014 Name: Period: Key Issue 1: Where Did Agriculture Originate? Pages 346-351 1. Define agriculture: 2. Define crop: 3. What are the characteristics of a hunter-gatherer society?
Due Thursday, October 23 rd, 2014 Name: Period: Key Issue 1: Where Did Agriculture Originate? Pages 346-351 1. Define agriculture: 2. Define crop: 3. What are the characteristics of a hunter-gatherer society?
The Beginning of Agriculture
 The Beginning of Agriculture Many Neolithic settlements were located in the Fertile Crescent, where the land was fertile. Here, people built towns such as Jericho, Catal Hoyuk, and Jarmo. Complex hunter-gatherer
The Beginning of Agriculture Many Neolithic settlements were located in the Fertile Crescent, where the land was fertile. Here, people built towns such as Jericho, Catal Hoyuk, and Jarmo. Complex hunter-gatherer
Principles of Cultural Geography
 Agriculture Agriculture: Terms Agriculture is the deliberate modification of the Earth s surface through cultivation of plants and rearing of animals to obtain sustenance or economic gain. Cultivate means
Agriculture Agriculture: Terms Agriculture is the deliberate modification of the Earth s surface through cultivation of plants and rearing of animals to obtain sustenance or economic gain. Cultivate means
OVERVIEW OF THE ROLE OF THE PRIVATE SECTOR IN WEST AFRICA DEVELOPMENT AGENDA. 1st ECOWAS Japan Business Forum October, 2015 Tokyo. Japan.
 OVERVIEW OF THE ROLE OF THE PRIVATE SECTOR 1st ECOWAS Japan Business Forum. 28 29 October, 2015 Tokyo. Japan. IN WEST AFRICA DEVELOPMENT AGENDA Kalilou Traore Commissioner Industry and Private Sector Promotion
OVERVIEW OF THE ROLE OF THE PRIVATE SECTOR 1st ECOWAS Japan Business Forum. 28 29 October, 2015 Tokyo. Japan. IN WEST AFRICA DEVELOPMENT AGENDA Kalilou Traore Commissioner Industry and Private Sector Promotion
not to be republished NCERT Secondary Activities Unit-III Chapter-6
 Unit-III Chapter-6 Secondary Activities All economic activities namely primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary, revolve around obtaining and utilising resources necessary for survival. Secondary activities
Unit-III Chapter-6 Secondary Activities All economic activities namely primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary, revolve around obtaining and utilising resources necessary for survival. Secondary activities
The Industrial Revolution Section 1
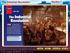 Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Main Idea A New Kind of Revolution In the 1700s conditions in Great Britain led to the rapid growth
Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Main Idea A New Kind of Revolution In the 1700s conditions in Great Britain led to the rapid growth
Key Issue 1: Where Did Agriculture Originate?
 Key Issue 1: Where Did Agriculture Originate? Pages 308-311 ***Always keep your key term packet out whenever you take notes from Rubenstein. As the terms come up in the text, think through the significance
Key Issue 1: Where Did Agriculture Originate? Pages 308-311 ***Always keep your key term packet out whenever you take notes from Rubenstein. As the terms come up in the text, think through the significance
Unit: Agriculture. Class 7 Geography Project
 Unit: Agriculture Class 7 Geography Project Introduction More than two thirds of the population of Pakistan lives in rural areas, and about 68% are directly or indirectly engaged in agriculture. It constitutes
Unit: Agriculture Class 7 Geography Project Introduction More than two thirds of the population of Pakistan lives in rural areas, and about 68% are directly or indirectly engaged in agriculture. It constitutes
Unit 4. The secondary sector 1. The secondary sector - Industry is the activity that transforms raw materials into manufactured products.
 Unit 4. The secondary sector 1. The secondary sector - Industry is the activity that transforms raw materials into manufactured products. Industry requires raw materials, energy sources (provide the force)
Unit 4. The secondary sector 1. The secondary sector - Industry is the activity that transforms raw materials into manufactured products. Industry requires raw materials, energy sources (provide the force)
Chapter 13. Europe Today
 Chapter 13 Europe Today Chapter Objectives Examine recent economic changes in Europe as they relate to industry, agriculture, transportation, and communications. Discuss the impact of industrialization
Chapter 13 Europe Today Chapter Objectives Examine recent economic changes in Europe as they relate to industry, agriculture, transportation, and communications. Discuss the impact of industrialization
! Ural Mountains. Please SAVE and PRINT the document file transferred to you when you logged in to help you take notes during class. !
 Europe s Climate and Environment Teacher: Mrs. Moody Class begins at: 10:05 Learning Targets: I I CAN describe the major environmental concerns facing Europe today. While you wait: Work on your USA Test
Europe s Climate and Environment Teacher: Mrs. Moody Class begins at: 10:05 Learning Targets: I I CAN describe the major environmental concerns facing Europe today. While you wait: Work on your USA Test
Global Strategy. Session 1.2: Minimum Set of Core Data Items. Module 1: Sampling in the Context of the Global Minimum Set of Core Data Items
 Global Strategy IMPROVING AGRICULTURAL AND RURAL STATISTICS IN ASIA PACIFIC Module 1: Sampling in the Context of the Global Minimum Set of Core Data Items Session 1.2: Minimum Set of Core Data Items 13
Global Strategy IMPROVING AGRICULTURAL AND RURAL STATISTICS IN ASIA PACIFIC Module 1: Sampling in the Context of the Global Minimum Set of Core Data Items Session 1.2: Minimum Set of Core Data Items 13
Agriculture Assignment #1: Von Thünen s Model. 1. City Center/Market. 2. Truck Farming/Dairy. 3. Forests. 4. Field Crops no fallow
 Agriculture Assignment #1: Von Thünen s Model Explain the location of each zone in the model 1. City Center/Market 2. Truck Farming/Dairy 3. Forests 4. Field Crops no fallow Limitations to using Von Thünen
Agriculture Assignment #1: Von Thünen s Model Explain the location of each zone in the model 1. City Center/Market 2. Truck Farming/Dairy 3. Forests 4. Field Crops no fallow Limitations to using Von Thünen
Name that Sector. By Marsha Masters Economics Arkansas
 Name that Sector By Marsha Masters Economics Arkansas Lesson Description Every country is known by many features and characteristics including its geographical location, its people, its government, its
Name that Sector By Marsha Masters Economics Arkansas Lesson Description Every country is known by many features and characteristics including its geographical location, its people, its government, its
ITL PUBLIC SCHOOL. Pre-SA2 ( ) Social Science Handout Class VIII Subject: Geography
 ITL PUBLIC SCHOOL Pre-SA2 (2016-2017) Social Science Handout Class VIII Subject: Geography Instructions: For 1 mark questions write one line and underline the key word. For 3 mark questions give three
ITL PUBLIC SCHOOL Pre-SA2 (2016-2017) Social Science Handout Class VIII Subject: Geography Instructions: For 1 mark questions write one line and underline the key word. For 3 mark questions give three
THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
 THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION 1700-1900 WHAT IS THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION? The Industrial Revolution refers to the time period when there was a huge increase of machine-made goods Images of Industrialization
THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION 1700-1900 WHAT IS THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION? The Industrial Revolution refers to the time period when there was a huge increase of machine-made goods Images of Industrialization
Instructor Manual for the Cultural Landscape: An Introduction to Human Geography, 10e
 Chapter 11: Industry Chapter Outline Introduction. Geographers are interested in studying industry because the choice of location of an industry is fundamentally about spatial relationships among raw materials,
Chapter 11: Industry Chapter Outline Introduction. Geographers are interested in studying industry because the choice of location of an industry is fundamentally about spatial relationships among raw materials,
1. Can you name a major North American city not on a river or with access to an ocean?? Where is the clothing you are wearing made? (check!
 1. Can you name a major North American city not on a river or with access to an ocean?? Where is the clothing you are wearing made? (check!) Agenda Weekend Recap Vocab Quiz KI 1-2 due today Ppt on Industry
1. Can you name a major North American city not on a river or with access to an ocean?? Where is the clothing you are wearing made? (check!) Agenda Weekend Recap Vocab Quiz KI 1-2 due today Ppt on Industry
Introduction. Production/Consumption
 European Union Rice (EU 27) Introduction The European Union, abbreviated as EU, is an economic and political union of 27 European countries. The EU was established on 1 November 1993 by the Treaty on European
European Union Rice (EU 27) Introduction The European Union, abbreviated as EU, is an economic and political union of 27 European countries. The EU was established on 1 November 1993 by the Treaty on European
Marking Scheme Set II CLASS XII SUBJECT- GEOGRAPHY (029) VALUE POINTS AND ANSWER KEY
 Marking Scheme Set II CLASS XII SUBJECT- GEOGRAPHY (029) 2015-2016 TIME ALLOWED- 3 HRS. MAXIMUM MARKS-70 VALUE POINTS AND ANSWER KEY 1. People migrate from one place to another in search of better living
Marking Scheme Set II CLASS XII SUBJECT- GEOGRAPHY (029) 2015-2016 TIME ALLOWED- 3 HRS. MAXIMUM MARKS-70 VALUE POINTS AND ANSWER KEY 1. People migrate from one place to another in search of better living
Economic Geography. Indicators of Development. Indicators of Development 1/9/2012. Economic Geography
 Economic Geography Economic Geography Chapter 10 The study of how people earn a living, how livelihood systems vary by area, and how economic activities are spatially interrelated and linked Livelihood
Economic Geography Economic Geography Chapter 10 The study of how people earn a living, how livelihood systems vary by area, and how economic activities are spatially interrelated and linked Livelihood
IMPACTS OF NATIONAL AGROFOOD POLICY TOWARDS AGRICULTURE SECTOR IN MALAYSIA
 IMPACTS OF NATIONAL AGROFOOD POLICY TOWARDS AGRICULTURE SECTOR IN MALAYSIA Rozhan Abu Dardak Director General Office, MARDI Head Quarters, Persiaran MARDI-UPM 43400 Serdang. E-mail: rozhan@mardi.gov.my
IMPACTS OF NATIONAL AGROFOOD POLICY TOWARDS AGRICULTURE SECTOR IN MALAYSIA Rozhan Abu Dardak Director General Office, MARDI Head Quarters, Persiaran MARDI-UPM 43400 Serdang. E-mail: rozhan@mardi.gov.my
National 4/5 Geography Rural Change
 National 4/5 Geography Rural Change Summary Notes and Past Paper Questions 1 National 4/5 Geography Rural Change By the end of this unit you will: 1. Be able to explain key terms in farming 2. Be able
National 4/5 Geography Rural Change Summary Notes and Past Paper Questions 1 National 4/5 Geography Rural Change By the end of this unit you will: 1. Be able to explain key terms in farming 2. Be able
Early Agricultural Regions AGRICULTURE 2. Climate and Agriculture. Map of Agriculture. Areas of Naturally Fertile Soil 4/20/2015.
 GEOG 247 Cultural Geography Early Agricultural Regions AGRICULTURE 2 Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College CUNY AFG 2015 What accounts for this distribution? 2 World Climates Köppen Climate Classification
GEOG 247 Cultural Geography Early Agricultural Regions AGRICULTURE 2 Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College CUNY AFG 2015 What accounts for this distribution? 2 World Climates Köppen Climate Classification
CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE 3: WHY DO INDUSTRIES HAVE DIFFERENT DISTRIBUTIONS?
 CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE 3: WHY DO INDUSTRIES HAVE DIFFERENT DISTRIBUTIONS? INDUSTRIAL LOCATION Situation factors Location near inputs Location near markets Transport choices Site factors Land Labor Capital
CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE 3: WHY DO INDUSTRIES HAVE DIFFERENT DISTRIBUTIONS? INDUSTRIAL LOCATION Situation factors Location near inputs Location near markets Transport choices Site factors Land Labor Capital
FOOD, NUTRITION AND FOOD SECURITY
 ECONOMIC INDICATORS FOOD, NUTRITION AND FOOD SECURITY Per capita food supply Quantity [kcal/capita/day] 1996 2001 2006 Food Aid shipments Quantity [1000 t] Prevalence of undernutrition Prevalence [%] Food
ECONOMIC INDICATORS FOOD, NUTRITION AND FOOD SECURITY Per capita food supply Quantity [kcal/capita/day] 1996 2001 2006 Food Aid shipments Quantity [1000 t] Prevalence of undernutrition Prevalence [%] Food
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore DOMESTICATIO N For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore DOMESTICATIO N For the complete encyclopedic entry with media resources,
B2B MATCH-MAKING EVENT AGRO-PROCESSING & LIGHT MANUFACTURING. Company Profile - Africa
 PIGA - Partnership for Investment and Growth in Africa B2B MATCH-MAKING EVENT AGRO-PROCESSING & LIGHT MANUFACTURING PART I: COMPANY GENERAL INFORMATION CONTACT DETAILS Name of company Physical address,
PIGA - Partnership for Investment and Growth in Africa B2B MATCH-MAKING EVENT AGRO-PROCESSING & LIGHT MANUFACTURING PART I: COMPANY GENERAL INFORMATION CONTACT DETAILS Name of company Physical address,
4/21/2009. Chapter 7. What Is Adaptation? People Adapt
 Chapter 7 Patterns of Subsistence What Is Adaptation? Adaptation refers to beneficial adjustments of organisms to their environment. This process leads to changes in the organisms and impacts their environment.
Chapter 7 Patterns of Subsistence What Is Adaptation? Adaptation refers to beneficial adjustments of organisms to their environment. This process leads to changes in the organisms and impacts their environment.
The Industrial Revolution Section 1
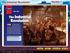 Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Main Idea A New Kind of Revolution In the 1700s conditions in Great Britain led to the rapid growth
Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Main Idea A New Kind of Revolution In the 1700s conditions in Great Britain led to the rapid growth
Trading in Agricultural Products: Past Future Opportunities The African Perspective
 Trading in Agricultural Products: Past Future Opportunities The African Perspective Miriam W. Oiro Omolo, Ph.D. Director of Programmes The African Policy Research Institute Outline 1. Introduction 2. World
Trading in Agricultural Products: Past Future Opportunities The African Perspective Miriam W. Oiro Omolo, Ph.D. Director of Programmes The African Policy Research Institute Outline 1. Introduction 2. World
U.S. Agricultural Trade: Trends, Composition, Direction, and Policy
 U.S. Agricultural Trade: Trends, Composition, Direction, and Policy Charles E. Hanrahan Senior Specialist in Agricultural Policy Carol Canada Information Research Specialist Beverly A. Banks Acquisitions
U.S. Agricultural Trade: Trends, Composition, Direction, and Policy Charles E. Hanrahan Senior Specialist in Agricultural Policy Carol Canada Information Research Specialist Beverly A. Banks Acquisitions
Chapter 11 Industry and Energy
 Chapter 11 Industry and Energy Industry and Energy: Key Issues 1. Where Is Industry Distributed? 2. Why Are Situation and Site Factors Important? 3. Why Do Industries Face Resource Challenges? 4. Why Are
Chapter 11 Industry and Energy Industry and Energy: Key Issues 1. Where Is Industry Distributed? 2. Why Are Situation and Site Factors Important? 3. Why Do Industries Face Resource Challenges? 4. Why Are
MT EDUCARE LTD. GEOGRAPHY Agro-Based Industries and Industries in India STEP UP ANSWER SHEET SUBJECT :
 ICSE X MT EDUCARE LTD. SUBJECT : GEOGRAPHY Agro-Based Industries and Industries in India STEP UP ANSWER SHEET Agro-Based Industries A.1. (a) Two large sugar producing states are : In North-Uttar Pradesh
ICSE X MT EDUCARE LTD. SUBJECT : GEOGRAPHY Agro-Based Industries and Industries in India STEP UP ANSWER SHEET Agro-Based Industries A.1. (a) Two large sugar producing states are : In North-Uttar Pradesh
The Industrial Revolution Section 1
 Preview A New Kind of Revolution Starting Points Map: Resources of Great Britain Main Idea / Reading Focus A Revolution in Great Britain A Revolution in Textiles Steam Powers the Revolution Faces of History:
Preview A New Kind of Revolution Starting Points Map: Resources of Great Britain Main Idea / Reading Focus A Revolution in Great Britain A Revolution in Textiles Steam Powers the Revolution Faces of History:
Steps to Civilization. Paleolithic Age Farming Revolution Permanent settlements Division of labor Specialization of labor Technology Trade Cities
 Paleolithic Age Farming Revolution Permanent settlements Division of labor Specialization of labor Technology Trade Cities Paleolithic Age nomadic hunters and gatherers clan groups: 15-20 clan leader
Paleolithic Age Farming Revolution Permanent settlements Division of labor Specialization of labor Technology Trade Cities Paleolithic Age nomadic hunters and gatherers clan groups: 15-20 clan leader
Minimum Core Data Set
 Minimum Core Data Set Dalip Singh Statistician Regional Office for the Asia-Pacific Regional Action Plan to Improve Agricultural and Rural Statistics 1 Background The Global Strategy describes three pillars
Minimum Core Data Set Dalip Singh Statistician Regional Office for the Asia-Pacific Regional Action Plan to Improve Agricultural and Rural Statistics 1 Background The Global Strategy describes three pillars
Agriculture in the DDR & South Asian Positions
 Agriculture in the DDR & South Asian Positions Anura Herath Country Programme Officer Sri Lanka International Fund for Agriculture Development (IFAD) Sri Lankan position Are we really trying to take advantage
Agriculture in the DDR & South Asian Positions Anura Herath Country Programme Officer Sri Lanka International Fund for Agriculture Development (IFAD) Sri Lankan position Are we really trying to take advantage
Chapter 10. Latin America Today
 Chapter 10 Latin America Today Chapter Objectives Discuss aspects of the Latin American economy and how geography affects transportation and communications. Explain how Latin America s forest resources
Chapter 10 Latin America Today Chapter Objectives Discuss aspects of the Latin American economy and how geography affects transportation and communications. Explain how Latin America s forest resources
Unit 2 The Primary Sector
 Unit 2 The Primary Sector INDEX 1. Introduction... 2 1.1. What is Primary Sector?... 2 1.2. What are agriculture, livestock farming, forestry and fishing?... 2 1.3. Distribution of agriculture in the world....
Unit 2 The Primary Sector INDEX 1. Introduction... 2 1.1. What is Primary Sector?... 2 1.2. What are agriculture, livestock farming, forestry and fishing?... 2 1.3. Distribution of agriculture in the world....
KEY CONCEPT 1.2 THE NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION AND EARLY AGRICULTURAL SOCIETIES
 KEY CONCEPT 1.2 THE NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION AND EARLY AGRICULTURAL SOCIETIES Beginning about 10,000 years ago, the Neolithic Revolution led to the development of new and more complex economic and social systems.
KEY CONCEPT 1.2 THE NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION AND EARLY AGRICULTURAL SOCIETIES Beginning about 10,000 years ago, the Neolithic Revolution led to the development of new and more complex economic and social systems.
Colusa County Department of Agriculture Crop Report. Harry A. Krug Agricultural Commissioner
 Colusa County Department of Agriculture 2001 Crop Report Harry A. Krug Agricultural Commissioner The 2001 Colusa County Crop Report is dedicated to Robert E. Herkert in memory of his untimely passing on
Colusa County Department of Agriculture 2001 Crop Report Harry A. Krug Agricultural Commissioner The 2001 Colusa County Crop Report is dedicated to Robert E. Herkert in memory of his untimely passing on
China. Li Shantong and He Janus Data Source. 2. Sector Classification
 China Li Shantong and He Janus 1 1. Data Source The source of the initial input-output (I-O) table for China is "Input-Output Table of China - 2002 from the Department of National Economy Accounting, State
China Li Shantong and He Janus 1 1. Data Source The source of the initial input-output (I-O) table for China is "Input-Output Table of China - 2002 from the Department of National Economy Accounting, State
The Economy. Chapter 25, Section 1 (Pages ) Economic Activities (page 629) Obstacles
 Chapter 25, Section 1 (Pages 628 633) The Economy Economic growth has occurred in different ways and at different rates in the countries of South Asia, but increased trade has helped the region s countries
Chapter 25, Section 1 (Pages 628 633) The Economy Economic growth has occurred in different ways and at different rates in the countries of South Asia, but increased trade has helped the region s countries
Before agriculture humans hunted and gathered. Groups of related families united in bands. They traveled frequently following animal herds.
 Before agriculture humans hunted and gathered. Groups of related families united in bands. They traveled frequently following animal herds. What is this called? Women collected roots, berries, and nuts,
Before agriculture humans hunted and gathered. Groups of related families united in bands. They traveled frequently following animal herds. What is this called? Women collected roots, berries, and nuts,
The Industrial Revolution ( )
 Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain in the 1750s? Objective: Explain the causes of Industrial Revolution in Great Britain. The Industrial Revolution (1750-1850) The Industrial Revolution
Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain in the 1750s? Objective: Explain the causes of Industrial Revolution in Great Britain. The Industrial Revolution (1750-1850) The Industrial Revolution
Chapter 11 Industry and Energy
 Chapter 11 Lecture Chapter 11 Industry and Energy Tim Scharks Green River College Industry and Energy: Key Issues 1. Where Is Industry Distributed? 2. Why Are Situation and Site Factors Important? 3. Why
Chapter 11 Lecture Chapter 11 Industry and Energy Tim Scharks Green River College Industry and Energy: Key Issues 1. Where Is Industry Distributed? 2. Why Are Situation and Site Factors Important? 3. Why
Ch. 1 Prehistory Test
 Name: Date: 1. In which order did the occupations listed below most likely develop in human history? (A) farmers (B) traders (C) nomadic herders (D) hunters and gatherers A. A,B,C,D B. B,D,A,C C. C,A,B,D
Name: Date: 1. In which order did the occupations listed below most likely develop in human history? (A) farmers (B) traders (C) nomadic herders (D) hunters and gatherers A. A,B,C,D B. B,D,A,C C. C,A,B,D
Rubenstein Chapter 10: Food and Agriculture Guided Reading Questions
 Name: Key Issue #1 Rubenstein Chapter 10: Food and Agriculture Guided Reading Questions 1. What does cultivate mean? 2. What percentage of people in less developed countries are farmers? 3. What percentage
Name: Key Issue #1 Rubenstein Chapter 10: Food and Agriculture Guided Reading Questions 1. What does cultivate mean? 2. What percentage of people in less developed countries are farmers? 3. What percentage
Asia. Economic Geography
 Asia Economic Geography Agriculture in Asia v Many countries in Asia have arable land that is good for farming. v Tropical crops are grown in countries with tropical climate zones. v Rice is the most important
Asia Economic Geography Agriculture in Asia v Many countries in Asia have arable land that is good for farming. v Tropical crops are grown in countries with tropical climate zones. v Rice is the most important
Water Policy Assessment in a Computable General Equilibrium Setting: Morocco, Mexico, Turkey, South Africa
 Water Policy Assessment in a Computable General Equilibrium Setting: Morocco, Mexico, Turkey, South Africa Terry Roe University of Minnesota Material taken from the working papers, and Journal Articles
Water Policy Assessment in a Computable General Equilibrium Setting: Morocco, Mexico, Turkey, South Africa Terry Roe University of Minnesota Material taken from the working papers, and Journal Articles
AP Human Geography Unit V. Agricultural and Rural Land Use. Multiple Choice Questions
 AP Human Geography Unit V. Agricultural and Rural Land Use Multiple Choice Questions 1. The modern definition of agriculture includes A) animal husbandry and shifting cultivation. B) vegetative and seed
AP Human Geography Unit V. Agricultural and Rural Land Use Multiple Choice Questions 1. The modern definition of agriculture includes A) animal husbandry and shifting cultivation. B) vegetative and seed
Agricultural. eg1ons. Climate and Agriculture. Climate Conditions and Agricultural Production
 Agricultural eg1ons II Without agriculture it is not possible to have a cit50 stock market, banks, university, church or army. Agriculture is the foundation of civilization and any stable economy. -Allan
Agricultural eg1ons II Without agriculture it is not possible to have a cit50 stock market, banks, university, church or army. Agriculture is the foundation of civilization and any stable economy. -Allan
Statistics Overview. Vancouver Fraser Port Authority
 Statistics Overview Vancouver Fraser Port Authority 2017 Table of contents Overview 1 Foreign vessel traffic 2 Cargo summary by sector 2 Bulk sector 3 Container units and TEUs 4 Container sector 5 Breakbulk
Statistics Overview Vancouver Fraser Port Authority 2017 Table of contents Overview 1 Foreign vessel traffic 2 Cargo summary by sector 2 Bulk sector 3 Container units and TEUs 4 Container sector 5 Breakbulk
The dynamics of global food and agribusiness
 Welcome to the world of Rabobank! The dynamics of global food and agribusiness Adrie Zwanenberg NUFFIELD Global Head F&A Research 20 February 2006 2 The world of Rabobank Food & agribusiness: a global
Welcome to the world of Rabobank! The dynamics of global food and agribusiness Adrie Zwanenberg NUFFIELD Global Head F&A Research 20 February 2006 2 The world of Rabobank Food & agribusiness: a global
Overview of Global Strategy Minimum Core Data Set requirements
 Global Strategy IMPROVING AGRICULTURAL AND RURAL STATISTICS IN ASIA PACIFIC Overview of Global Strategy Minimum Core Data Set requirements Allan Nicholls, Regional Coordinator Workshop on Statistical Capacity
Global Strategy IMPROVING AGRICULTURAL AND RURAL STATISTICS IN ASIA PACIFIC Overview of Global Strategy Minimum Core Data Set requirements Allan Nicholls, Regional Coordinator Workshop on Statistical Capacity
CHAPTER 8. Agriculture and the Malaysian Economy
 CHAPTER 8 Agriculture and the Malaysian Economy 8.1 Contribution of agriculture to the gross domestic product (GDP) Agriculture is part of the primary sector in the Malaysian economy which contributes
CHAPTER 8 Agriculture and the Malaysian Economy 8.1 Contribution of agriculture to the gross domestic product (GDP) Agriculture is part of the primary sector in the Malaysian economy which contributes
Key Issue 1: Where Is Industry Distributed?
 Key Issue 1: Where Is Industry Distributed? Pages 395-397 ***Always keep your key term packet out whenever you take notes from Rubenstein. As the terms come up in the text, think through the significance
Key Issue 1: Where Is Industry Distributed? Pages 395-397 ***Always keep your key term packet out whenever you take notes from Rubenstein. As the terms come up in the text, think through the significance
CHILE. Sectoral Activities Department. Community, Social & Personal Services. Fig. 1: Employment by Major Economic Activity ('000s),
 CHILE 7,000 6,000 5,000 Fig. 1: Employment by Major Economic Activity ('000s), 2000-2008 Agriculture, Hunting, Forestry and Fishing Mining and Quarrying Community, Social & The community, social and personal
CHILE 7,000 6,000 5,000 Fig. 1: Employment by Major Economic Activity ('000s), 2000-2008 Agriculture, Hunting, Forestry and Fishing Mining and Quarrying Community, Social & The community, social and personal
Chapter 10: Agriculture. Key Issue #1 & #2
 Chapter 10: Agriculture Key Issue #1 & #2 KEY ISSUE #1 Where Did Agriculture Originate? Before Agriculture Began long before recorded history! Agriculture: deliberate modification of Earth s surface through
Chapter 10: Agriculture Key Issue #1 & #2 KEY ISSUE #1 Where Did Agriculture Originate? Before Agriculture Began long before recorded history! Agriculture: deliberate modification of Earth s surface through
8.1 Agricultural Landscapes and Production Methods.
 AP Human Geography Kuby: Agricultural Landscapes NAME: HOUR: Agricultural Landscapes and Production Methods DIRECTIONS: Click on the website listed below. Under Computerized Chapter Activities please select
AP Human Geography Kuby: Agricultural Landscapes NAME: HOUR: Agricultural Landscapes and Production Methods DIRECTIONS: Click on the website listed below. Under Computerized Chapter Activities please select
Prospects and challenges of agricultural trade between China and Latin America: analysis of problems and opportunities from the Chinese perspective
 Prospects and challenges of agricultural trade between China and Latin America: analysis of problems and opportunities from the Chinese perspective Li Xiande Institute of Agricultural Economics and Development,
Prospects and challenges of agricultural trade between China and Latin America: analysis of problems and opportunities from the Chinese perspective Li Xiande Institute of Agricultural Economics and Development,
Bio-Based Eco Industrial Clustering in Dambulla Sri Lanka
 Bio-Based Eco Industrial Clustering in Dambulla Sri Lanka Gemunu Herath and Uditha Ratnayake Department of Civil Engineering University of Peradeniya Sri Lanka Gemunu 1 Country Profile Sri Lanka Population
Bio-Based Eco Industrial Clustering in Dambulla Sri Lanka Gemunu Herath and Uditha Ratnayake Department of Civil Engineering University of Peradeniya Sri Lanka Gemunu 1 Country Profile Sri Lanka Population
World Agricultural Outlook Board Interagency Commodity Estimates Committee Forecasts. Lockup Briefing June 11, 2014
 World Agricultural Outlook Board Interagency Commodity Estimates Committee Forecasts Lockup Briefing World Wheat Production Country or Region 2014/15 Million Tons World 714.0 701.6 0.7-1.7 United States
World Agricultural Outlook Board Interagency Commodity Estimates Committee Forecasts Lockup Briefing World Wheat Production Country or Region 2014/15 Million Tons World 714.0 701.6 0.7-1.7 United States
