La Molécula de AND y los Procesos de Transcripción y Traducción
|
|
|
- Hugo Hensley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 La Molécula de ND y los Procesos de Transcripción y Traducción MSP 21-Superior Enero-Mayo-2017 Prof. Tacher
2 Objetivos Describir la estructura de la molécula de DN Establecer la importancia del código genético. Describir los procesos de transcripción y traducción de la molécula de DN. Establecer las consecuencias de las mutaciones en el DN.
3 Estándar: Estructura y Niveles de Organización de la Materia Indicadores Relevantes: ES.B.B1.EM.3 : Explica, utilizando evidencia cienti fica, de co mo la estructura del DN determina la estructura de las protei nas que llevan a cabo las funciones esenciales de la vida por medio de sistemas de ce lulas especializadas. ES.B.B3.EM.1: Formula preguntas para aclarar las relaciones del rol del DN y de los cromosomas en la codificacio n de las instrucciones para las variaciones de las caracteri sticas que pasan de una generacio n a otra.
4 Estándar: onservación y ambio Indicadores Relevantes: ES.B.B3..1:Formula y defiende una afirmacio n basada en evidencia, de que las variaciones gene ticas y hereditarias pueden resultar de: (1) nueva combinacio n gene tica mediante el proceso de meiosis, (2) errores viables pueden ocurrir durante la replicacio n del DN y/o (3) las mutaciones a causa de los factores ambientales. El e nfasis esta en el uso de datos para apoyar argumentos sobre las diferentes formas en que pueden ocurrir las mutaciones.
5 Figure 1
6 Figure 2 (a) Rosalind Franklin (b) Franklin s X-ray diffraction photograph of DN
7 Figure 3 Sugar phosphate backbone end Nitrogenous bases Thymine (T) denine () ytosine () end DN nucleotide Guanine (G)
8 Figure 4 G G G G end Hydrogen bond T end T 3.4 nm G G G T 1 nm T G G G G T T T T 0.34 nm end end (a) Key features of DN structure (b) Partial chemical structure (c) Space-filling model
9 Figure 5 G G G G T 3.4 nm G G T 1 nm T G G G T T T 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DN structure
10 Figure 6 end Hydrogen bond end T G G T end (b) Partial chemical structure end
11 Figure 7 DN double helix (2 nm in diameter) Nucleosome (10 nm in diameter) 30-nm fiber hromatid (700 nm) Loops Scaffold Histones Histone tail H1 300-nm fiber Replicated chromosome (1,400 nm)
12 Figure 8 DN double helix (2 nm in diameter) Nucleosome (10 nm in diameter) Histones Histone tail H1
13 Figure 9 hromatid (700 nm) 30-nm fiber Loops Scaffold 300-nm fiber Replicated chromosome (1,400 nm)
14 De Gen a Proteína (Procesos de Transcripción y Traducción)
15 Figure 10
16 Fig 11
17 Fig.12
18 Fig.13
19 Figure 15a Nuclear envelope TRNSRIPTION DN Pre-mRN (b) Eukaryotic cell
20 Figure 15-b Nuclear envelope TRNSRIPTION DN RN PROESSING Pre-mRN mrn (b) Eukaryotic cell
21 Figure 15-c Nuclear envelope TRNSRIPTION DN RN PROESSING Pre-mRN mrn TRNSLTION Ribosome Polypeptide (b) Eukaryotic cell
22 Fig. 15-d DN molecule Gene 1 Gene 2 Gene 3 DN template strand TRNSRIPTION mrn odon TRNSLTION Protein mino acid
23 Fig 16: Lista de minoácidos
24 First mrn base ( end of codon) Third mrn base ( end of codon) Figure 17 Second mrn base U G U UUU UU UU UUG Phe Leu UU U U UG Ser UU U U UG Tyr Stop Stop UGU UG UG UGG ys Stop Trp U G UU U U UG Leu U G Pro U G His Gln GU G G GG rg U G UU U U UG IIe Met or start U G Thr U G sn Lys GU G G GG Ser rg U G G GUU GU GU GUG Val GU G G GG la GU G G GG sp Glu GGU GG GG GGG Gly U G
25 Figure 18-a Promoter Transcription unit 1 Initiation Start point RN polymerase Unwound DN RN Template strand of DN transcript
26 Figure 18-b Promoter Transcription unit 1 Initiation Start point RN polymerase 2 Elongation Unwound DN Rewound DN RN transcript RN Template strand of DN transcript Direction of transcription ( downstream )
27 Figure 18-c Promoter Transcription unit 1 Initiation Start point RN polymerase 2 3 Elongation Termination Unwound DN Rewound DN RN transcript RN Template strand of DN transcript ompleted RN transcript Direction of transcription ( downstream )
28 Figure 19 DN T T T T T T T TT box Promoter Transcription factors Start point Nontemplate strand Template strand 1 eukaryotic promoter 2 Several transcription factors bind to DN. RN polymerase II Transcription factors 3 Transcription initiation complex forms. Transcription initiation complex RN transcript
29 Figure 20 RN polymerase Nontemplate strand of DN RN nucleotides T end U T G G T T Newly made RN Direction of transcription Template strand of DN
30 Promoter Transcription unit 1 Initiation Start point RN polymerase 2 3 Elongation Termination Unwound DN Rewound DN RN transcript RN Template strand of DN transcript ompleted RN transcript Direction of transcription ( downstream )
31 Figure 21 modified guanine nucleotide added to the end G P Protein-coding segment P P U adenine nucleotides added to the end Polyadenylation signal Start Stop ap UTR UTR Poly- tail codon codon
32 Figure 22 Pre-mRN ap Intron mrn Intron Introns cut out and exons spliced together Poly- tail ap UTR oding segment Poly- tail UTR U
33 Fig. 23-a RN transcript (pre-mrn) Exon 1 Intron Exon 2 Protein snrn snrnps Other proteins
34 Fig. 23-b RN transcript (pre-mrn) Exon 1 Intron Exon 2 Protein snrn snrnps Other proteins Spliceosome
35 Fig. 23-c RN transcript (pre-mrn) Exon 1 Intron Exon 2 Protein snrn snrnps Spliceosome Other proteins Spliceosome components mrn Exon 1 Exon 2 ut-out intron
36 Práctica de Transcripción
37 Práctica de Transcripción
38 Práctica de Transcripción 1 DN T T T RNm U G G U U U
39 Práctica de Transcripción 2 DN G T G G RNm
40 Práctica de Transcripción 2 DN G T G G RNm G G G U U
41 Proceso de Traducción De RNm a Proteína
42 Fig 24-a Molécula de RNt
43 Figure 24-b Polypeptide mino acids Ribosome trn with amino acid attached Gly U G G U U U G G trn nticodon mrn odons
44 Figure 25 P site (Peptidyl-tRN binding site) E site (Exit site) mrn binding site Exit tunnel site (minoacyltrn binding site) E P Large subunit Small subunit (b) Schematic model showing binding sites
45 Figure 26 U U G P site Large ribosomal subunit Initiator trn mrn GTP Start codon Small mrn binding site ribosomal subunit 1 Small ribosomal subunit binds to mrn. 2 P i GDP E Translation initiation complex Large ribosomal subunit completes the initiation complex.
46 Figure 27-a mino end of polypeptide 1 odon recognition mrn E P site site GTP GDP P i E P
47 Figure 27-b mino end of polypeptide 1 odon recognition mrn E P site site GTP GDP P i E P 2 Peptide bond formation E P
48 Figure 27-c mino end of polypeptide 1 odon recognition Ribosome ready for next aminoacyl trn mrn E P site site GTP GDP P i E E P P 3 Translocation GDP P i GTP 2 Peptide bond formation E P
49 Figure 28-a Release factor 1 Stop codon (UG, U, or UG) Ribosome reaches a stop codon on mrn.
50 Figure 28-b Release factor Free polypeptide Stop codon (UG, U, or UG) 1 Ribosome reaches a stop codon on mrn. 2 Release factor promotes hydrolysis.
51 Figure 28-c Release factor Free polypeptide 1 Stop codon (UG, U, or UG) Ribosome reaches a stop codon on mrn. 2 GTP 2 Release factor 3 promotes hydrolysis. 2 GDP P i Ribosomal subunits and other components dissociate.
52 Figure 29 Growing polypeptides ompleted polypeptide Incoming ribosomal subunits Start of mrn ( end) End of mrn ( end) (a) Several ribosomes simultaneously translating one mrn molecule Ribosomes mrn (b) large polyribosome in a bacterial cell (TEM) 0.1 m
53 Figure 30 TRNSRIPTION DN RN transcript RN PROESSING YTOPLSM Exon NULEUS RN polymerase RN transcript (pre-mrn) Intron mino acid trn minoacyl-trn synthetase MINO ID TIVTION mrn E P Ribosomal subunits minoacyl (charged) trn TRNSLTION E U G G U U U U G nticodon Ribosome odon
54 Figure 31-a Nucleus Rough ER Smooth ER Plasma membrane
55 Figure 31-b Nucleus Rough ER Smooth ER cis Golgi trans Golgi Plasma membrane
56 Figure 31-c Nucleus Rough ER Smooth ER cis Golgi trans Golgi Plasma membrane
57 Práctica de traducción
58 Práctica de traducción
59 Práctica
60 Práctica
61 Figure 32 Wild-type hemoglobin Sickle-cell hemoglobin Wild-type hemoglobin DN T G G Mutant hemoglobin DN G T G mrn G G mrn G U G Normal hemoglobin Glu Sickle-cell hemoglobin Val
62 Figure 33
63 Figure 34 T T Met DN template strand T mrn Protein mino end (a) Nucleotide-pair substitution Lys Phe Gly T T G T T T G G T T T G G T U G G U U U G G U Met T T T T T G G T T T G G T T U G G U U U G G U U Stop Silent (no effect on amino acid sequence) T T T G T T T G G T T T G T U G G U U U G U Met Missense Lys T T U instead of U G G Met Nonsense instead of T Phe Ser T G T T G T G T T T G G T U U U U G G U U Stop instead of G U instead of T instead of instead of G Stop Wild type Lys Phe T T T Gly Met Stop arboxyl end (b) Nucleotide-pair insertion or deletion Extra T T G T T G T G T T T G G T U G U G U U U G G U U T T G T T T G G T T G G T U G G U U G G G U Met Met Extra U Stop Frameshift causing immediate nonsense (1 nucleotide-pair insertion) T T Lys Phe U Leu G Gly la Frameshift causing extensive missense (1 nucleotide-pair deletion) T G T T T G G T G missing missing missing missing U G U U U G G U T T Stop No frameshift, but one amino acid missing (3 nucleotide-pair deletion) T
64 Figure 34-a Wild type DN template strand mrn Protein mino end T T T G T T T G G T T T G G T U G G U U U G G U Met Lys Phe Gly Stop arboxyl end Nucleotide-pair substitution: silent instead of G T T T T T T G G T T T G G T T Met Lys Phe Gly U instead of U G G U U U G G U U Stop
65 Figure 34-b Wild type DN template strand mrn Protein mino end T T T G T T T G G T T T G G T U G G U U U G G U Met Lys Phe Gly Stop arboxyl end Nucleotide-pair substitution: missense Met Lys T instead of T T T T G T T T G G T T T G T instead of G U G G U U U G U Phe Ser Stop
66 Figure 34-c Wild type DN template strand mrn Protein mino end T T T G T T T G G T T T G G T U G G U U U G G U Met Lys Phe Gly Stop arboxyl end Nucleotide-pair substitution: nonsense instead of T T T G T T T G T G T T T G G T U instead of U G U G U U U G G U Met Stop
67 Figure 34-d Wild type DN template strand mrn Protein mino end T T T G T T T G G T T T G G T U G G U U U G G U Met Lys Phe Gly Stop arboxyl end Nucleotide-pair insertion: frameshift causing immediate nonsense Extra T T T G T T T G T G T T T G G T Met Extra U U G U G U U U G G U Stop
68 Figure 34-e Wild type DN template strand mrn Protein mino end T T T G T T T G G T T T G G T U G G U U U G G U Met Lys Phe Gly Stop arboxyl end Nucleotide-pair deletion: frameshift causing extensive missense U missing T T T G T T T G G T T G G T missing U G G U U G G U Met Lys Leu la
BIOLOGY. Chapter 15 Genes & Proteins
 BIOLOGY Chapter 15 Genes & Proteins CMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 17 Protein Synthesis 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Fig. 17-1 Figure 17.1a n albino racoon Condition
BIOLOGY Chapter 15 Genes & Proteins CMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 17 Protein Synthesis 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Fig. 17-1 Figure 17.1a n albino racoon Condition
1. Overview of Gene Expression
 Chapter 17: From Gene to 1. Overview of Gene Expression 2. Transcription 3. The Genetic Code 4. Translation 5. Mutations 1. Overview of Gene Expression Chapter Reading pp. 334-337 How are Genes related
Chapter 17: From Gene to 1. Overview of Gene Expression 2. Transcription 3. The Genetic Code 4. Translation 5. Mutations 1. Overview of Gene Expression Chapter Reading pp. 334-337 How are Genes related
14 Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein
 CMPBELL BIOLOY IN FOCS rry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 14 ene Expression: From ene to Protein Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Flow of enetic Information
CMPBELL BIOLOY IN FOCS rry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 14 ene Expression: From ene to Protein Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Flow of enetic Information
Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein
 hapter 17 ene Expression: From ene to Protein Dr. Wendy Sera Houston ommunity ollege Biology 1406 The Flow of enetic Information The information content of genes is in the specific sequences of nucleotides
hapter 17 ene Expression: From ene to Protein Dr. Wendy Sera Houston ommunity ollege Biology 1406 The Flow of enetic Information The information content of genes is in the specific sequences of nucleotides
From Gene to Phenotype- part 3. Lecture Outline 11/9/05. The genetic code. Translation: overview
 DN mrn From ene to Phenotype- part 3 TRNSRIPTION DN 1 RN is transcribed from a DN template. 5 RN RN transcript polymerase RN PROESSIN Exon 2 In eukaryotes, the RN transcript RN transcript (premrn) is spliced
DN mrn From ene to Phenotype- part 3 TRNSRIPTION DN 1 RN is transcribed from a DN template. 5 RN RN transcript polymerase RN PROESSIN Exon 2 In eukaryotes, the RN transcript RN transcript (premrn) is spliced
CH 17 :From Gene to Protein
 CH 17 :From Gene to Protein Defining a gene gene gene Defining a gene is problematic because one gene can code for several protein products, some genes code only for RNA, two genes can overlap, and there
CH 17 :From Gene to Protein Defining a gene gene gene Defining a gene is problematic because one gene can code for several protein products, some genes code only for RNA, two genes can overlap, and there
Lecture for Wednesday. Dr. Prince BIOL 1408
 Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
1. DNA, RNA structure. 2. DNA replication. 3. Transcription, translation
 1. DNA, RNA structure 2. DNA replication 3. Transcription, translation DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides DNA is a nucleic acid, made of long chains of nucleotides Nucleotide Phosphate group Nitrogenous
1. DNA, RNA structure 2. DNA replication 3. Transcription, translation DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides DNA is a nucleic acid, made of long chains of nucleotides Nucleotide Phosphate group Nitrogenous
Gene Expression Translation U C A G A G
 Why? ene Expression Translation How do cells synthesize polypeptides and convert them to functional proteins? The message in your DN of who you are and how your body works is carried out by cells through
Why? ene Expression Translation How do cells synthesize polypeptides and convert them to functional proteins? The message in your DN of who you are and how your body works is carried out by cells through
From Gene to Protein. Chapter 17. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene For Next Week Lab -Hand in questions from 4 and 5 by TUES in my mailbox (Biology Office) -Do questions for Lab 6 for next week -Lab practical next week Lecture Read
Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene For Next Week Lab -Hand in questions from 4 and 5 by TUES in my mailbox (Biology Office) -Do questions for Lab 6 for next week -Lab practical next week Lecture Read
Molecular Biology: DNA, gene, chromosome and genome (Learning Objectives)
 Molecular Biology: DN, gene, chromosome and genome (Learning bjectives) Nucleic acid structure and composition ompare and contrast the structure of DN and RN: features they share and how do they differ?
Molecular Biology: DN, gene, chromosome and genome (Learning bjectives) Nucleic acid structure and composition ompare and contrast the structure of DN and RN: features they share and how do they differ?
Fig Ch 17: From Gene to Protein
 Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Outline. Gene Expression. One Gene One Enzyme Hypothesis. 1. Central Dogma DNA RNA Protein
 ene Expression: RN and Synthesis ene Expression RN synthesis synthesis enetic ode Outline Splicing enes Introns and Exons omparison of ene Expression in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes ene Expression 1. entral
ene Expression: RN and Synthesis ene Expression RN synthesis synthesis enetic ode Outline Splicing enes Introns and Exons omparison of ene Expression in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes ene Expression 1. entral
From Gene to Protein transcription, messenger RNA (mrna) translation, RNA processing triplet code, template strand, codons,
 From Gene to Protein I. Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes
From Gene to Protein I. Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes
CH_12_molecular_genetics_DNA_RNA_protein.notebook. February 08, DNA : The Genetic Material
 Oswald very Identified the molecule that transformed the R strain into the S strain DN : The Genetic Material * fter Mendel, scientists knew that some kind of genetic material was located on chromosomes.
Oswald very Identified the molecule that transformed the R strain into the S strain DN : The Genetic Material * fter Mendel, scientists knew that some kind of genetic material was located on chromosomes.
8/21/2014. From Gene to Protein
 From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of..
 Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
From Gene to Protein. How Genes Work (Ch. 17)
 From Gene to Protein How Genes Work (Ch. 17) What do genes code for? How does DNA code for cells & bodies? how are cells and bodies made from the instructions in DNA DNA proteins cells bodies The Central
From Gene to Protein How Genes Work (Ch. 17) What do genes code for? How does DNA code for cells & bodies? how are cells and bodies made from the instructions in DNA DNA proteins cells bodies The Central
IOWA End-of-Course Assessment Programs. Released Items BIOLOGY. Copyright 2010 by The University of Iowa.
 IOW End-of-ourse ssessment Programs Released Items opyright 2010 by The University of Iowa. IOLOGY First mrn base 1 ased on the table, which of the following sequences in a template N strand would be transcribed
IOW End-of-ourse ssessment Programs Released Items opyright 2010 by The University of Iowa. IOLOGY First mrn base 1 ased on the table, which of the following sequences in a template N strand would be transcribed
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch 17 Practice Questions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Garrod hypothesized that "inborn errors of metabolism" such as alkaptonuria
Ch 17 Practice Questions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Garrod hypothesized that "inborn errors of metabolism" such as alkaptonuria
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN. Section C: The Synthesis of Protein
 CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section C: The Synthesis of Protein 1. Translation is the RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide: a closer look 2. Signal peptides target some eukaryotic polypeptides to
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section C: The Synthesis of Protein 1. Translation is the RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide: a closer look 2. Signal peptides target some eukaryotic polypeptides to
GENE EXPRESSION AT THE MOLECULAR LEVEL. Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 GENE EXPRESSION AT THE MOLECULAR LEVEL Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function
GENE EXPRESSION AT THE MOLECULAR LEVEL Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function
DNA Function: Information Transmission
 DNA Function: Information Transmission DNA is called the code of life. What does it code for? *the information ( code ) to make proteins! Why are proteins so important? Nearly every function of a living
DNA Function: Information Transmission DNA is called the code of life. What does it code for? *the information ( code ) to make proteins! Why are proteins so important? Nearly every function of a living
BIOLOGY. Gene Expression. Gene to Protein. Protein Synthesis Overview. The process in which the information coded in DNA is used to make proteins
 17 CAMPBLL BIOLOGY TNTH DITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Gene to Protein Gene xpression The process in which the information coded in is used to make proteins A gene is the part of the
17 CAMPBLL BIOLOGY TNTH DITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Gene to Protein Gene xpression The process in which the information coded in is used to make proteins A gene is the part of the
Honors Research in Molecular Genetics Part 1
 Third Base Honors Research in Molecular enetics Part 1 ll bout ene Expression How do cells synthesize polypeptides and convert them to functional proteins? The message in your DN of who you are and how
Third Base Honors Research in Molecular enetics Part 1 ll bout ene Expression How do cells synthesize polypeptides and convert them to functional proteins? The message in your DN of who you are and how
MOLECULAR GENETICS PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #2 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1 GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 2 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #2 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1 GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 2 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA
 Chapter 8: DNA and RNA Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 8-1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins Proteins play
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 8-1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins Proteins play
DNA. Empty protein shell Phage. Radioactivity in liquid. Pellet. 3 Centrifuge the mixture so bacteria form a pellet at the bottom of the test tube.
 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY: RELICATION, TRANSCITION, AND TRANSLATION Honors Biology 0 IMORTANT EXERIMENTS Frederick Griffith Described a transforming factor that could be transferred into a bacterial cell rocess
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY: RELICATION, TRANSCITION, AND TRANSLATION Honors Biology 0 IMORTANT EXERIMENTS Frederick Griffith Described a transforming factor that could be transferred into a bacterial cell rocess
Chapter 9. Microbial Genetics. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 9 Microbial Genetics Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9.1 Introduction to Genetics and Genes: Unlocking the Secrets of Heredity Genetics
Chapter 9 Microbial Genetics Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9.1 Introduction to Genetics and Genes: Unlocking the Secrets of Heredity Genetics
Problem Set Unit The base ratios in the DNA and RNA for an onion (Allium cepa) are given below.
 Problem Set Unit 3 Name 1. Which molecule is found in both DNA and RNA? A. Ribose B. Uracil C. Phosphate D. Amino acid 2. Which molecules form the nucleotide marked in the diagram? A. phosphate, deoxyribose
Problem Set Unit 3 Name 1. Which molecule is found in both DNA and RNA? A. Ribose B. Uracil C. Phosphate D. Amino acid 2. Which molecules form the nucleotide marked in the diagram? A. phosphate, deoxyribose
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr.
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
Molecular Genetics Quiz #1 SBI4U K T/I A C TOTAL
 Name: Molecular Genetics Quiz #1 SBI4U K T/I A C TOTAL Part A: Multiple Choice (15 marks) Circle the letter of choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. One mark for each correct
Name: Molecular Genetics Quiz #1 SBI4U K T/I A C TOTAL Part A: Multiple Choice (15 marks) Circle the letter of choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. One mark for each correct
DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES-
 DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES- THE COMPONENTS AND STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA is made up of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of three basic components:, called deoxyribose in DNA In DNA, there
DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES- THE COMPONENTS AND STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA is made up of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of three basic components:, called deoxyribose in DNA In DNA, there
Bio11 Announcements. Ch 21: DNA Biology and Technology. DNA Functions. DNA and RNA Structure. How do DNA and RNA differ? What are genes?
 Bio11 Announcements TODAY Genetics (review) and quiz (CP #4) Structure and function of DNA Extra credit due today Next week in lab: Case study presentations Following week: Lab Quiz 2 Ch 21: DNA Biology
Bio11 Announcements TODAY Genetics (review) and quiz (CP #4) Structure and function of DNA Extra credit due today Next week in lab: Case study presentations Following week: Lab Quiz 2 Ch 21: DNA Biology
Chapter 13. From DNA to Protein
 Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Chapter 10. The Structure and Function of DNA. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 10 The Structure and Function of DNA PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey,
Chapter 10 The Structure and Function of DNA PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey,
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process.
 Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Hello! Outline. Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis. In all living cells, DNA molecules are the storehouses of information. 6.
 Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis In all living cells, DNA molecules are the storehouses of information Hello! Outline u 1. Key concepts u 2. Central Dogma u 3. RNA Types u 4. RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis In all living cells, DNA molecules are the storehouses of information Hello! Outline u 1. Key concepts u 2. Central Dogma u 3. RNA Types u 4. RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
Protein Synthesis & Gene Expression
 DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictates the order of amino acids that
DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictates the order of amino acids that
From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype
 12 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype 12.1 What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? The gene-enzyme relationship is one-gene, one-polypeptide relationship. Example: In hemoglobin, each
12 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype 12.1 What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? The gene-enzyme relationship is one-gene, one-polypeptide relationship. Example: In hemoglobin, each
This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section:
 DN 11 Syllabus hecklist This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section: 11.1 DN DN occurs bound to proteins in chromosomes in the nucs and as unbound DN in the mitochondria.
DN 11 Syllabus hecklist This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section: 11.1 DN DN occurs bound to proteins in chromosomes in the nucs and as unbound DN in the mitochondria.
Bundle 5 Test Review
 Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
DNA and RNA. Chapter 12
 DNA and RNA Chapter 12 Warm Up Exercise Test Corrections Make sure to indicate your new answer and provide an explanation for why this is the correct answer. Do this with a red pen in the margins of your
DNA and RNA Chapter 12 Warm Up Exercise Test Corrections Make sure to indicate your new answer and provide an explanation for why this is the correct answer. Do this with a red pen in the margins of your
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins. The Central Dogma
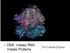 DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
Big Idea 3C Basic Review
 Big Idea 3C Basic Review 1. A gene is a. A sequence of DNA that codes for a protein. b. A sequence of amino acids that codes for a protein. c. A sequence of codons that code for nucleic acids. d. The end
Big Idea 3C Basic Review 1. A gene is a. A sequence of DNA that codes for a protein. b. A sequence of amino acids that codes for a protein. c. A sequence of codons that code for nucleic acids. d. The end
Chapter 8 From DNA to Proteins. Chapter 8 From DNA to Proteins
 KEY CONCEPT Section 1 DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. Griffith finds a transforming principle. Griffith experimented with the bacteria that cause pneumonia.
KEY CONCEPT Section 1 DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. Griffith finds a transforming principle. Griffith experimented with the bacteria that cause pneumonia.
Key Concept Translation converts an mrna message into a polypeptide, or protein.
 8.5 Translation VOBLRY translation codon stop codon start codon anticodon Key oncept Translation converts an mrn message into a polypeptide, or protein. MIN IDES mino acids are coded by mrn base sequences.
8.5 Translation VOBLRY translation codon stop codon start codon anticodon Key oncept Translation converts an mrn message into a polypeptide, or protein. MIN IDES mino acids are coded by mrn base sequences.
Chapter 2 - DNA MC [37 marks]
![Chapter 2 - DNA MC [37 marks] Chapter 2 - DNA MC [37 marks]](/thumbs/74/71041787.jpg) Chapter 2 - N MC [37 marks] 1. The image shows a N nucleotide. Which correctly identifies the parts labelled I and II? C 2. Which model represents transcription? 3. Which sequence represents the order
Chapter 2 - N MC [37 marks] 1. The image shows a N nucleotide. Which correctly identifies the parts labelled I and II? C 2. Which model represents transcription? 3. Which sequence represents the order
Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein
 Name Period This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours to truly master
Name Period This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours to truly master
Section 10.3 Outline 10.3 How Is the Base Sequence of a Messenger RNA Molecule Translated into Protein?
 Section 10.3 Outline 10.3 How Is the Base Sequence of a Messenger RNA Molecule Translated into Protein? Messenger RNA Carries Information for Protein Synthesis from the DNA to Ribosomes Ribosomes Consist
Section 10.3 Outline 10.3 How Is the Base Sequence of a Messenger RNA Molecule Translated into Protein? Messenger RNA Carries Information for Protein Synthesis from the DNA to Ribosomes Ribosomes Consist
DNA and Protein Synthesis Practice. C. protein D. carbohydrate 7. Which of the following best describes how DNA and RNA are similar?
 N and Protein Synthesis Practice Name: ate: 1. The discovery of which of the following has most directly led to advances in the identification of suspects in criminal investigations and in the identification
N and Protein Synthesis Practice Name: ate: 1. The discovery of which of the following has most directly led to advances in the identification of suspects in criminal investigations and in the identification
Nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ribonucleic acid (RNA) nucleotide
 Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction There are two types of nucleic acids: - deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) These
7.013 Problem Set 3 FRIDAY October 8th, 2004
 MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert. Weinberg, Dr. laudette ardel Name: T: 7.013 Problem Set 3 FRIDY October 8th, 2004 Problem
MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert. Weinberg, Dr. laudette ardel Name: T: 7.013 Problem Set 3 FRIDY October 8th, 2004 Problem
Chapter 14 Active Reading Guide From Gene to Protein
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 14 Active Reading Guide From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 14 Active Reading Guide From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single
Genes and How They Work. Chapter 15
 Genes and How They Work Chapter 15 1 The Nature of Genes Early ideas to explain how genes work came from studying human diseases Archibald Garrod 1902 Recognized that alkaptonuria (black urine disease)
Genes and How They Work Chapter 15 1 The Nature of Genes Early ideas to explain how genes work came from studying human diseases Archibald Garrod 1902 Recognized that alkaptonuria (black urine disease)
Degenerate Code. Translation. trna. The Code is Degenerate trna / Proofreading Ribosomes Translation Mechanism
 Translation The Code is Degenerate trna / Proofreading Ribosomes Translation Mechanism Degenerate Code There are 64 possible codon triplets There are 20 naturally-encoding amino acids Several codons specify
Translation The Code is Degenerate trna / Proofreading Ribosomes Translation Mechanism Degenerate Code There are 64 possible codon triplets There are 20 naturally-encoding amino acids Several codons specify
Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein
 Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect
Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect
Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Molecular Biology of the Gene : where the genetic information is stored, blueprint for making proteins. RNA: Always involved in protein synthesis Macromolecules (polymers!) Monomers (units): nucleotides
Molecular Biology of the Gene : where the genetic information is stored, blueprint for making proteins. RNA: Always involved in protein synthesis Macromolecules (polymers!) Monomers (units): nucleotides
DNA.notebook March 08, DNA Overview
 DNA Overview Deoxyribonucleic Acid, or DNA, must be able to do 2 things: 1) give instructions for building and maintaining cells. 2) be copied each time a cell divides. DNA is made of subunits called nucleotides
DNA Overview Deoxyribonucleic Acid, or DNA, must be able to do 2 things: 1) give instructions for building and maintaining cells. 2) be copied each time a cell divides. DNA is made of subunits called nucleotides
7.014 Quiz II Handout
 7.014 Quiz II Handout Quiz II: Wednesday, March 17 12:05-12:55 54-100 **This will be a closed book exam** Quiz Review Session: Friday, March 12 7:00-9:00 pm room 54-100 Open Tutoring Session: Tuesday,
7.014 Quiz II Handout Quiz II: Wednesday, March 17 12:05-12:55 54-100 **This will be a closed book exam** Quiz Review Session: Friday, March 12 7:00-9:00 pm room 54-100 Open Tutoring Session: Tuesday,
Nucleic acids and protein synthesis
 THE FUNCTIONS OF DNA Nucleic acids and protein synthesis The full name of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. Every nucleotide has the same sugar molecule and phosphate group, but each nucleotide contains one
THE FUNCTIONS OF DNA Nucleic acids and protein synthesis The full name of DNA is deoxyribonucleic acid. Every nucleotide has the same sugar molecule and phosphate group, but each nucleotide contains one
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Division ve. High School Making s From ene to Protein How enes Work Organelles nucleus ribosomes endoplasmic reticulum (ER) olgi apparatus vesicles small nuclear pore ribosomal mrn large ribosomal cytoplasm
Division ve. High School Making s From ene to Protein How enes Work Organelles nucleus ribosomes endoplasmic reticulum (ER) olgi apparatus vesicles small nuclear pore ribosomal mrn large ribosomal cytoplasm
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells
 Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
DNA Replication and Repair
 DNA Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif Overview of DNA Replication SWYK CNs 1, 2, 30 Explain how specific base pairing enables existing DNA strands
DNA Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif Overview of DNA Replication SWYK CNs 1, 2, 30 Explain how specific base pairing enables existing DNA strands
Protein Synthesis Notes
 Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Section A: The Connection Between Genes and Proteins
 CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section A: The Connection Between Genes and Proteins 1. The study of metabolic defects provided evidence that genes specify proteins 2. Transcription and translation are
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section A: The Connection Between Genes and Proteins 1. The study of metabolic defects provided evidence that genes specify proteins 2. Transcription and translation are
C. Incorrect! Threonine is an amino acid, not a nucleotide base.
 MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 05: RNA and Protein Biosynthesis Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following bases are only found in RNA? Question #01 (A) Ribose. (B) Uracil. (C) Threonine. (D) Adenine.
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 05: RNA and Protein Biosynthesis Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following bases are only found in RNA? Question #01 (A) Ribose. (B) Uracil. (C) Threonine. (D) Adenine.
AP2013-DNAPacket-II. Use the list of choices below for the following questions:
 Class: Date: AP2013-DNAPacket-II Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the list of choices below for the following questions: I. helicase II.
Class: Date: AP2013-DNAPacket-II Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the list of choices below for the following questions: I. helicase II.
Topic 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Topic 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene Sabotage Inside Our Cells Viruses are invaders that sabotage our cells Viruses have genetic material surrounded by a protein coat and, in some cases, a membranous
Topic 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene Sabotage Inside Our Cells Viruses are invaders that sabotage our cells Viruses have genetic material surrounded by a protein coat and, in some cases, a membranous
DNA. translation. base pairing rules for DNA Replication. thymine. cytosine. amino acids. The building blocks of proteins are?
 2 strands, has the 5-carbon sugar deoxyribose, and has the nitrogen base Thymine. The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? DNA translation Adenine pairs with Thymine, Thymine
2 strands, has the 5-carbon sugar deoxyribose, and has the nitrogen base Thymine. The actual process of assembling the proteins on the ribosome is called? DNA translation Adenine pairs with Thymine, Thymine
RNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Chapter 13
 RNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Chapter 13 DNA Double stranded Thymine Sugar is RNA Single stranded Uracil Sugar is Ribose Deoxyribose Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries copies of instructions from
RNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Chapter 13 DNA Double stranded Thymine Sugar is RNA Single stranded Uracil Sugar is Ribose Deoxyribose Types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries copies of instructions from
Protein Synthesis
 HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
Biology. DNA Replication. Slide 1 / 111 Slide 2 / 111. Slide 4 / 111. Slide 3 / 111. Slide 5 / 111. Slide 6 / 111. Genes. Genes Unit Topics.
 Slide 1 / 111 Slide 2 / 111 iology Genes www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 111 Vocabulary lick on each word below to go to the definition. P site 3' end polymerase chain reaction 5' end parent strand site promoter
Slide 1 / 111 Slide 2 / 111 iology Genes www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 111 Vocabulary lick on each word below to go to the definition. P site 3' end polymerase chain reaction 5' end parent strand site promoter
AP BIOLOGY RNA, DNA, & Proteins Chapters 16 & 17 Review
 AP BIOLOGY RNA, DNA, & Proteins Chapters 16 & 17 Review Enzyme that adds nucleotide subunits to an RNA primer during replication DNA polymerase III Another name for protein synthesis translation Sugar
AP BIOLOGY RNA, DNA, & Proteins Chapters 16 & 17 Review Enzyme that adds nucleotide subunits to an RNA primer during replication DNA polymerase III Another name for protein synthesis translation Sugar
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Chapter 17 Genes to Proteins Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The following questions refer to Figure 17.1, a simple metabolic
Exam Chapter 17 Genes to Proteins Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The following questions refer to Figure 17.1, a simple metabolic
A Zero-Knowledge Based Introduction to Biology
 A Zero-Knowledge Based Introduction to Biology Konstantinos (Gus) Katsiapis 25 Sep 2009 Thanks to Cory McLean and George Asimenos Cells: Building Blocks of Life cell, membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondrion
A Zero-Knowledge Based Introduction to Biology Konstantinos (Gus) Katsiapis 25 Sep 2009 Thanks to Cory McLean and George Asimenos Cells: Building Blocks of Life cell, membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondrion
Matakuliah Genetika (BIO612206) Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Lampung. Priyambodo, M.Sc. staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo
 Matakuliah Genetika (BIO612206) Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Lampung Priyambodo, M.Sc. staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Prokariotik Eukariotik staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Regulasi ekspresi gen pada
Matakuliah Genetika (BIO612206) Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Lampung Priyambodo, M.Sc. staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Prokariotik Eukariotik staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Regulasi ekspresi gen pada
DNA & Protein Synthesis UNIT D & E
 DNA & Protein Synthesis UNIT D & E How this Unit is broken down Chapter 10.1 10.3 The structure of the genetic material Chapter 10.4 & 10.5 DNA replication Chapter 10.6 10.15 The flow of genetic information
DNA & Protein Synthesis UNIT D & E How this Unit is broken down Chapter 10.1 10.3 The structure of the genetic material Chapter 10.4 & 10.5 DNA replication Chapter 10.6 10.15 The flow of genetic information
Flow of Genetic Information
 Flow of Genetic Information Transcription and Translation Links to the Next Generation Standards Scientific and Engineering Practices: Asking Questions (for science) and Defining Problems (for engineering)
Flow of Genetic Information Transcription and Translation Links to the Next Generation Standards Scientific and Engineering Practices: Asking Questions (for science) and Defining Problems (for engineering)
12 1 DNA. Slide 1 of 37. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall:
 12 1 DNA 1 of 37 http://www.biologyjunction.com/powerpoints_dragonfly_book_prent.htm 12 1 DNA Griffith and Transformation Griffith and Transformation In 1928, Fredrick Griffith was trying to learn how
12 1 DNA 1 of 37 http://www.biologyjunction.com/powerpoints_dragonfly_book_prent.htm 12 1 DNA Griffith and Transformation Griffith and Transformation In 1928, Fredrick Griffith was trying to learn how
Frederick Griffith: Transformation Conclusion: bacteria could give other bacteria heritable traits, even after they were dead.
 Frederick Griffith: Transformation 1928 Conclusion: bacteria could give other bacteria heritable traits, even after they were dead. 1 Avery, McCarty & MacLeod: Griffiths Refined (1944) Refined Griffith's
Frederick Griffith: Transformation 1928 Conclusion: bacteria could give other bacteria heritable traits, even after they were dead. 1 Avery, McCarty & MacLeod: Griffiths Refined (1944) Refined Griffith's
RNA: Transcription and Triplet Code
 RNA: Transcription and Triplet Code There are Five Kinds of RNA, All of Which are Templated from DNA. The first type of RNA is trna. The "t" stands for "transfer". This RNA is the RNA that transfers amino
RNA: Transcription and Triplet Code There are Five Kinds of RNA, All of Which are Templated from DNA. The first type of RNA is trna. The "t" stands for "transfer". This RNA is the RNA that transfers amino
Bioinformatics. ONE Introduction to Biology. Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Biology/CS 123A Fall 2012
 Bioinformatics ONE Introduction to Biology Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Biology/CS 123A Fall 2012 Biology Review DNA RNA Proteins Central Dogma Transcription Translation
Bioinformatics ONE Introduction to Biology Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Biology/CS 123A Fall 2012 Biology Review DNA RNA Proteins Central Dogma Transcription Translation
Nucleic Acids: Structure and Function
 ucleic Acids: Structure and Function Components of ucleotides The building blocks (monomers) of the nucleic acids are called nucleotides. ucleotides are made up of: phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar, and
ucleic Acids: Structure and Function Components of ucleotides The building blocks (monomers) of the nucleic acids are called nucleotides. ucleotides are made up of: phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar, and
Ch Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Ch. 12 - Molecular Biology of the Gene AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER GUIDE 1. In the middle of the unraveling the mysteries of DNA, researchers knew that genetic material must be able to. It must be stable so it
Ch. 12 - Molecular Biology of the Gene AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER GUIDE 1. In the middle of the unraveling the mysteries of DNA, researchers knew that genetic material must be able to. It must be stable so it
Biomolecules: lecture 6
 Biomolecules: lecture 6 - to learn the basics on how DNA serves to make RNA = transcription - to learn how the genetic code instructs protein synthesis - to learn the basics on how proteins are synthesized
Biomolecules: lecture 6 - to learn the basics on how DNA serves to make RNA = transcription - to learn how the genetic code instructs protein synthesis - to learn the basics on how proteins are synthesized
How can something so small cause problems so large?
 How can something so small cause problems so large? Objectives Identify the structural components of DNA and relate to its function Create and ask questions about a model of DNA DNA is made of genes. Gene
How can something so small cause problems so large? Objectives Identify the structural components of DNA and relate to its function Create and ask questions about a model of DNA DNA is made of genes. Gene
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
 Review Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Protein synthesis requires two steps: transcription and translation. DNA contains codes Three bases in DNA code
Review Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Protein synthesis requires two steps: transcription and translation. DNA contains codes Three bases in DNA code
BIO303, Genetics Study Guide II for Spring 2007 Semester
 BIO303, Genetics Study Guide II for Spring 2007 Semester 1 Questions from F05 1. Tryptophan (Trp) is encoded by the codon UGG. Suppose that a cell was treated with high levels of 5- Bromouracil such that
BIO303, Genetics Study Guide II for Spring 2007 Semester 1 Questions from F05 1. Tryptophan (Trp) is encoded by the codon UGG. Suppose that a cell was treated with high levels of 5- Bromouracil such that
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
Lecture Overview. Overview of the Genetic Information. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Protein Synthesis Lecture 6
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Protein Synthesis Lecture 6 Lecture Overview The Genetic Information Structure of DNA/RNA DNA Replication Overview of protein synthesis
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Protein Synthesis Lecture 6 Lecture Overview The Genetic Information Structure of DNA/RNA DNA Replication Overview of protein synthesis
DNA Structure and Protein synthesis
 DNA Structure and Protein synthesis What is DNA? DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid Chromosomes are made of DNA It carries genetic information: controls the activities of cells by providing instructions for making
DNA Structure and Protein synthesis What is DNA? DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid Chromosomes are made of DNA It carries genetic information: controls the activities of cells by providing instructions for making
Adv Biology: DNA and RNA Study Guide
 Adv Biology: DNA and RNA Study Guide Chapter 12 Vocabulary -Notes What experiments led up to the discovery of DNA being the hereditary material? o The discovery that DNA is the genetic code involved many
Adv Biology: DNA and RNA Study Guide Chapter 12 Vocabulary -Notes What experiments led up to the discovery of DNA being the hereditary material? o The discovery that DNA is the genetic code involved many
2. From the first paragraph in this section, find three ways in which RNA differs from DNA.
 Name Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein Begin reading at page 328 Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours
Name Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein Begin reading at page 328 Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours
BEADLE & TATUM EXPERIMENT
 FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE OBJECTIVES What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? How Does Information Flow from Genes to Proteins? How Is the Information Content in
FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE OBJECTIVES What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? How Does Information Flow from Genes to Proteins? How Is the Information Content in
DNA/RNA STUDY GUIDE. Match the following scientists with their accomplishments in discovering DNA using the statement in the box below.
 Name: Period: Date: DNA/RNA STUDY GUIDE Part A: DNA History Match the following scientists with their accomplishments in discovering DNA using the statement in the box below. Used a technique called x-ray
Name: Period: Date: DNA/RNA STUDY GUIDE Part A: DNA History Match the following scientists with their accomplishments in discovering DNA using the statement in the box below. Used a technique called x-ray
DNA RNA PROTEIN. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted
 DNA RNA PROTEIN Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted DNA Molecule of heredity Contains all the genetic info our cells inherit Determines
DNA RNA PROTEIN Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted DNA Molecule of heredity Contains all the genetic info our cells inherit Determines
