Food Webs K.Selph, OCN 621 Spring 2010
|
|
|
- Beverley Anthony
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Food Webs
2 Relatively few species (discounting the controversy over the number of microbes) Yet: 1) High diversity in terms of trophic mode, e.g., herbivory, carnivory, mixotrophy, omnivory 2) Trophic level changes with developmental phase (egg to adult) within a species 3) Prey selection based on size, but not necessarily at a ratio of 1:10, especially for raptorial/direct interception consumers 4) Behaviors lead to niche partitioning, even though environment relatively uniform, e.g., diel vertical migration Given this background, how would we expect food webs to look?
3 Integrating Classical and Microbial Loop Food Webs carnivores/omnivores already mentioned in class and see Landry 2002 paper on-line modified from Lalli & Parsons 1997
4 Comparison of food web structures oligotrophic eutrophic Lalli & Parsons 1997
5 Humans (7-10) Whales/porpoises/ birds (6-9) NW Atlantic Food Web Squid (5-8) Bigger fish (4-7) Small fish (4-6) Ctenophores/ Chaetognaths (3-5) Copepods (2-4*) Phytoplankton (1) Link, 2002
6 Trophic Transfer Efficiency TTE (or Trophic Yield) = Amount of production at trophic level (X+1) relative to production at trophic level X -- Usually thought to be lower than GGE, because of other modes of death (e.g., viral lysis, natural death...) -- Because of losses to metabolism/egestion at each step, longer food chains result in less yield to the top predator How to apply to actual food chain? Overall Food Chain Efficiency = TTE(2)*TTE(3)*TTE(4)*TTE(n) Kaiser et al. 2005
7 How does biomass change over a seasonal cycle and what does it mean?
8 Spring blooms biomass, not production This is the general view of three of the ocean ecosystems on the planet...
9 Historical Observations of Seasonal Cycles Using net tows, catch diatoms, large dinoflagellates and zooplankton From these catches, infer food web relations and seasonal cycles Did use in situ chlorophyll measurements around the world s seas to generate maps (note: didn t have large scale, synoptic maps such as we have today with satellites)
10 1) Phytoplankton low through the winter: light limited, nutrients sufficient deep winter mixing North Atlantic Bloom 2) Spring Bloom reduced winds, stratification near surface increased light, nutrients sufficient 3) Summer: Low phyto biomass grazers consume the phytoplankton nutrients depleted and not renewed
11 End of North Atlantic Bloom 4) Fall: Second bloom Fewer grazers: non-feeding stage Intermittent storms Inject nutrients, but still stratified Light sufficient 5) Early winter: Storm mixing Re-supply of nutrients to surface Set for next Spring Bloom In places where phytoplankton cycles are strongly different (most of the rest of the world s oceans!), they are usually discussed in contrast to the spring bloom cycle.
12 An ecosystem change? Jellyfish in the North Atlantic Hot topic -- Hydrobiologia special issue in 2009 Usual top predator: Cod or other fish species Observation: Jellyfish increasing in frequency in North Sea Data from Continuous Plankton Recorder (towed monthly behind merchant ships at 6.5 m -- records presence/absence of nematocysts) Attrill et al. 2007
13 Bad years for herring = good years for jellyfish? Data set from a 15 year survey ( ), with jellyfish as by-catch herring recruitment jellyfish abundance Lynam et al. 2005
14 Why? Natural Environmental Variability (NAO) and/or effect of overfishing Jellyfish (medusoid Scyphozoa) eat larval herring and also compete with them for their zooplankton prey Adult finfish and jellyfish also compete for prey Reduced larval herring stocks, and therefore adult herring, further allow jellyfish to outcompete them Attrill et al. 2007
15 Subarctic Pacific - HNLC region Objective: to test the Major Grazer Hypothesis (1980) Experimental goal: Can mesozooplankton grazers control phytoplankton stocks? Miller et al L & O 36:
16 Observations Seasonal blooms do not occur -- Canadian weathership at Station P (50 N, 145 W) Occupied station from 1950s until mid-1981 This is in contrast to the North Atlantic -- chlorophyll levels >1 mg/m 3 every year 1970
17 Characteristics of Subarctic Ecosystems deep winter mixing in Atlantic, but a permanent halocline in the Pacific low summer nitrate in Atlantic, but still high in summer in Pacific N. Pacific N. Atlantic
18 Plankton Phytoplankton concentration low & nearly constant year round despite excess nutrients (nitrate) & physical conditions favoring a seasonal bloom. Seasonal signal in phytoplankton production, but not abundance Phytoplankton dominated by tiny species, similar to tropics, not large forms associated with high nitrate
19 Seasonal migration of Neocalanus plumchrus Zooplankton dominated by large species, Neocalanus (4-5 mm) C-5, adult female C-2, C-3, C-4 C-1 nauplius egg Zooplankton biomass peaks in summer: leads to historical hypothesis that phytoplankton controlled by grazing by large copepods. Images from: and Miller et al. 1984
20 Control Capabilities of Neocalanus Could consume cells 2-30 µm, but food limited at ambient concentrations Could keep phytoplankton in check at an abundance of 1 copepod/liter Without them present, phytoplankton did bloom But: not present in sufficient density to control blooms (only ~0.2/L) Another role: to consume smaller grazers... Left: Rate estimates from bottle expts. Right: Experiments in 60-L microcosms Landry & Lehner-Fournier 1988
21 Role of Protists Landry et al. 1993
22 Subarctic Pacific Ecosystem 1) Major grazers were not eating enough phytoplankton to provide for their own growth -- omnivores, eating phagotrophic protists 2) Too few mesozooplankton to keep phytoplankton in check 3) Microzooplankton grazing provides the top-down control on the system 4) First project to start to explore Fe-limitation to phytoplankton growth -- we know from subsequent studies that Fe-limitation alone is not sufficient to explain the system, need grazing regulation, too
23 Upwelling Zones Continental Shelf Ecosystem Classical coastal upwelling regions of eastern boundary currents and other coasts. Narrow shelf, river effluent influences minor. Primary producers: diatoms Primary herbivores: copepods, anchovies and/or sardines tornado.sfsu.edu
24 Small (<5 µm) Phytoplankton in Upwelling Zones Despite dominance of diatoms in upwelling zones -- smaller phytoplankton are present, too Sherr et al. 2005
25 Distribution of Small vs. Large Phytoplankton in Oregon Upwelling System Near Shore, relatively few small (<5 µm) phytoplankton -- mostly diatoms onshore offshore Offshore, phytoplankton biomass dominated by small cells Sherr et al. 2005
26 Food Webs in Chilean Upwelling System copepod copepod Biomass dominated by diatoms Copepods and appendicularians have high clearance rates on microzooplankton, too -- omnivory appendicularian Vargas & Gonzalez 2004
27 More than one pathway for export flux... Clearance rates show optimum prey size Appendicularians -- consumers and responsible for passive particle scavenging A. Alldredge Vargas & Gonzalez 2004
28 SubTropical Ecosystems DSR II 1996 Vol 43 DSR II 2001 Vol 48 DSR II 2006 Brix et al. Vol 53: HOT Site: N, 158 W BATS Site: N, W 1988 to present
29 HOT -- Primary Production summer usually sees the highest phytoplankton biomass/production D. Karl 1999 Ecosystems 2:
30 BATS -- Primary Production Spring bloom (not summer like HOTS) Steinberg et al DSR II, 48,
31 Data Comparison
32 Ecosystem Structure in Gyres Multi-level, start out with small primary producers (picoplankton)... how many trophic levels?
33 Trophic Cascades Microbial loop organisms the most important (recycling system) Size fractionation experiments suggest several trophic levels smaller than 20 µm
34 Mesozooplankton Biomass, HOT site Timing of maximum is the most puzzling: In the summer, when the water column is the most stratified (as opposed to the spring, after winter mixing) Coincides with blooms of N 2 fixers, such as Trichodesmium
35
36 HOT/BATS MesoZP comparison Roman et al. 2002, DSR II, 49:
37
38 Why the difference? Don t know for sure, but... Salps and sarcodines at BATS -- not quantified well with net tows (grazers and mixotrophs) Mesoscale eddies at BATS leading to episodic nutrient enrichments -- uncoupling of 1 producers and consumers L. Madin, WHOI
39 On the relationships between primary, net community, and export production in subtropical gyres, 2006, Deep-Sea Res. II, 53: , Holger Brix, Nicolas Gruber, David M. Karl and Nicholas R. Bates Export POC/Net Primary Production If ratio high, then export pathway ecosystem (larger phytoplankton) If ratio low, then regeneration ecosystem (microbial loop organisms dominate) Switch between these states by addition of increased nutrients 10 year data set at HOTS and BATS: BATS: Export pathway in Spring, Regeneration Pathway in Summer, Fall HOTS: Regeneration pathway all year round
40 Aside: Modern Primary Production Measurements vs. Historical Subtropical Gyres: mg C/m 2 /d (~ g C/m 2 /y) historical: <100 g C/m 2 /y Note that fisheries oceanographers still use the lower numbers, along with lower estimates of trophic levels leading to fish -- the combined effect of these opposing trends may luckily end up with fisheries yields that aren t too far off...
41 Polar Ecosystems: Arctic vs. Antarctic Max (end of winter) Min (~Fall) - Size (15 mill km 2 vs. 36 mill km 2 ) -Arctic Sea Ice only 2-fold annually, whereas it is 5-fold lower in the Southern Ocean over that period - Sea surrounded by Land vs. Land surrounded by Sea, so ability to exchange with other regions very different Kaiser, textbook
42 Arctic vs. Southern Ocean -- very different - 1/3 of Arctic Ocean is shelf seas ( 100 m), mean depth 1800 m - Continental shelves of Antarctica very narrow, with pack ice zone over deep ocean basins ( m deep) - Arctic affected by freshwater flows from surrounding rivers and their contents (high productivity in coastal/upwelling areas, but short-lived) - Southern Ocean fairly isolated from land (HNLC area) -- high productivity in areas affected by shelf sediments, otherwise Fe-limited and fairly low
43 Arctic Ocean Ice effect on Bloom Timing e.g., bloom relatively late in year as ice needs to melt Results in short growing season (tied to light) Zooplankton: grow slowly, have short feeding season, rest at depth over winter May take two-three years to complete growth cycle e.g., Calanus glacialis & C. hyperboreus
44 Arctic UNEP/GRID-Arendal Pelagic Food Web rge/index.php?url=11214
45 Antarctic: Southern Ocean Krill as a Keystone Species Kaiser, Box 11.3
46 Antarctic Sea Ice Community Kaiser, Fig. 11.8
47 Krill Swarms under the Sea Ice Kaiser, Box 11.3
48 Krill vs. Salps Changing Ecosystem -- may be due to decline in sea ice Since 1926, decline in krill populations (38-75%) and an increase in salps (>66%) krill need sea ice algae nutrition prior to spawning & for juvenile stages in winter and feed on Spring bloom phytoplankton salps can survive in warmer water and at lower phytoplankton concentrations and do not feed on sea ice Atkinson et al. 2004
49 Summary: Why are marine ecosystems so different? Why does the North Atlantic bloom so dramatically? Why doesn t the North Pacific? Why aren t there ever blooms in the vast open ocean regions? Extraordinarily Simplistic Answer All systems have microbial organisms, as well as the larger phytoplankton and consumers, but physical processes force the system towards dominance of one ecosystem over another.
50 Dominant Pathways are determined by physical processes Small cells are more efficient in competing for low N (high surface area:volume) General size hierarchy of consumers based on energetic considerations, i.e., for like organisms, reduced size and biomass of prey makes the environment more suitable for smaller consumers Energetic reasons why small primary consumers are favored in oligotrophic open ocean systems (subtropical gyres): reduced [phyto] I declines for given F max decreased phyto size F max declines for consumer of given size increased T C higher I is required for maintenance or to sustain a given level of growth
51 Diatoms : dynamic component in the food web Diatoms are responsive to high nutrient conditions and can escape control of grazers. In the absence of external energy to stimulate diatom blooms, a eutrophic system shifts to oligotrophic system -seasonally, e.g., spring to summer in temperate systems -spatially, e.g., distance from upwelling source Diatoms decrease in relative abundance from: Eutrophic Systems Oligotrophic Systems High Latitude Low Latitude Spring Season Summer Season Upwelling Source Distance from Upwelling
52 Low Energy Stable Systems Low energy Lack of nutrient re-supply Low nutrients (oligotrophic) Small Phytoplankton (high surface:volume ratio) Long food chains (small consumers at base) Relatively stable system (high recycling)
53 High energy (storm activity, eddy action, upwelling, etc.) High Energy Unstable Systems High nutrients (eutrophic) Large Phytoplankton (small, too) Composite Spring Picture Mean Chlorophyll (µg/l) at the surface Short food chain (dynamic) (superimposed on stable long food chain) Unstable (dynamic) system (High new production)
54
Includes the coastal zone and the pelagic zone, the realm of the oceanographer. I. Ocean Circulation
 Includes the coastal zone and the pelagic zone, the realm of the oceanographer I. Ocean Circulation II. Water Column Production A. Coastal Oceans B. Open Oceans E. Micronutrients F. Harmful Algal Blooms
Includes the coastal zone and the pelagic zone, the realm of the oceanographer I. Ocean Circulation II. Water Column Production A. Coastal Oceans B. Open Oceans E. Micronutrients F. Harmful Algal Blooms
Patterns of Productivity
 Phytoplankton Zooplankton Nutrients Patterns of Productivity There is a large Spring Bloom in the North Atlantic (temperate latitudes remember the Gulf Stream!) What is a bloom? Analogy to terrestrial
Phytoplankton Zooplankton Nutrients Patterns of Productivity There is a large Spring Bloom in the North Atlantic (temperate latitudes remember the Gulf Stream!) What is a bloom? Analogy to terrestrial
4/28/2013. Transmission of Light in Seawater. Color in the Ocean Color of ocean ranges from deep blue to yellow-green Factors Turbidity from runoff
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer Chapter summary in haiku form Primary produce Sunlight and phytoplankton Ocean is garden Chapter Overview Productivity
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 CHAPTER 13 Biological Productivity and Energy Transfer Chapter summary in haiku form Primary produce Sunlight and phytoplankton Ocean is garden Chapter Overview Productivity
State of phytoplankton and. zooplankton in the Estuary and northwestern Gulf of St. Lawrence during Summary. DFO Science
 Fisheries and Oceans Canada Science Pêches et Océans Canada Sciences DFO Science Laurentian Region Stock Status Report C4-18 (2) State of phytoplankton and zooplankton in the Estuary and northwestern Gulf
Fisheries and Oceans Canada Science Pêches et Océans Canada Sciences DFO Science Laurentian Region Stock Status Report C4-18 (2) State of phytoplankton and zooplankton in the Estuary and northwestern Gulf
Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Ling TONG Qisheng TANG
 Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Ling TONG Qisheng TANG Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, CAFS Both environmental and human factors affect the bioproducts in
Impacts of global warming on bio-products of marine and coastal system Ling TONG Qisheng TANG Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, CAFS Both environmental and human factors affect the bioproducts in
Marine Processes and Ecology
 T-TH 10:00-11:45 Discussion Sections TH 12:30-13:40 Textbook: Charlie Miller, Biological Oceanography Others listed in the syllabus (optional) Textbooks available at the Science Library: Oceanography:
T-TH 10:00-11:45 Discussion Sections TH 12:30-13:40 Textbook: Charlie Miller, Biological Oceanography Others listed in the syllabus (optional) Textbooks available at the Science Library: Oceanography:
Patterns of Productivity
 Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of autotrophic biomass Secondary Production - the production of heterotrophic biomass Production vs Biomass Biomass
Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of autotrophic biomass Secondary Production - the production of heterotrophic biomass Production vs Biomass Biomass
Continued from Lecture 20a
 IV. Primary Production (p.p.) Continued from Lecture 20a C. Biomass & Productivity 1. Biomass = mass of organic matter (in grams) a. Gross primary production = total amount of organic material synthesized
IV. Primary Production (p.p.) Continued from Lecture 20a C. Biomass & Productivity 1. Biomass = mass of organic matter (in grams) a. Gross primary production = total amount of organic material synthesized
Denitrification 2/11/2011. Energy to be gained in oxidation. Oxidized N. Reduced N
 Oxidized N Energy to be gained in oxidation Reduced N (Sarmiento & Gruber, 2006) Denitrification The reduction of NO 3 and NO 2 to N 2 during heterotrophic respiration of organic matter. Occurs predominately
Oxidized N Energy to be gained in oxidation Reduced N (Sarmiento & Gruber, 2006) Denitrification The reduction of NO 3 and NO 2 to N 2 during heterotrophic respiration of organic matter. Occurs predominately
Production vs Biomass
 Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 5 Production vs Biomass Biomass = amount of carbon per unit area (= standing stock * C/cell) Units (e.g.): g C m -2 Primary Production = amount of carbon
Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 5 Production vs Biomass Biomass = amount of carbon per unit area (= standing stock * C/cell) Units (e.g.): g C m -2 Primary Production = amount of carbon
The Open Ocean. College of Marine Sciences, Shanghai Ocean University
 The Open Ocean Regions of the Open Sea Beyond the shallow coastal seas over the continental shelves (neritic zone) lies the open ocean (oceanic zone). The photic zone is the layer that receives enough
The Open Ocean Regions of the Open Sea Beyond the shallow coastal seas over the continental shelves (neritic zone) lies the open ocean (oceanic zone). The photic zone is the layer that receives enough
Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability
 Why should we care about productivity? Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability Photosynthetic activity in oceans created current O 2 -rich atmosphere Plankton form ocean sediments & fossil
Why should we care about productivity? Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability Photosynthetic activity in oceans created current O 2 -rich atmosphere Plankton form ocean sediments & fossil
Aquatic respiration and ocean metabolism
 Aquatic respiration and ocean metabolism Remember what life is all about: Energy (ATP) Reducing power (NADPH) Nutrients (C, N, P, S, Fe, etc., etc.) Photosynthetic organisms use sunlight, H 2 O, and dissolved
Aquatic respiration and ocean metabolism Remember what life is all about: Energy (ATP) Reducing power (NADPH) Nutrients (C, N, P, S, Fe, etc., etc.) Photosynthetic organisms use sunlight, H 2 O, and dissolved
Primary Production in the Ocean
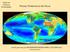 Primary Production in the Ocean A global composite of sea surface chlorophyll concentration Oligotrophic gyre (LNLC) Seasonal Phytoplankton blooms Coastal Upwelling High-nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC)
Primary Production in the Ocean A global composite of sea surface chlorophyll concentration Oligotrophic gyre (LNLC) Seasonal Phytoplankton blooms Coastal Upwelling High-nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC)
High Latitude Environment
 9. Habitats: High Latitude Ecosystems High Latitude Environments Seasonal Processes Sea ice Food Fall Reproduction Bentho-pelagic coupling Food Weds Climate Change Effects Dr Rhian G. Waller 26th April
9. Habitats: High Latitude Ecosystems High Latitude Environments Seasonal Processes Sea ice Food Fall Reproduction Bentho-pelagic coupling Food Weds Climate Change Effects Dr Rhian G. Waller 26th April
Operational oceanography and the ecosystem approach
 Operational oceanography and the ecosystem approach Einar Svendsen with input from many others PICES ASC, Victoria BC 02 November, 2007 Operational Vision Deliver operational information of the marine
Operational oceanography and the ecosystem approach Einar Svendsen with input from many others PICES ASC, Victoria BC 02 November, 2007 Operational Vision Deliver operational information of the marine
SUNLIGHT & OCEAN ZONATION
 PLANKTON, PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY, AND BIOGEOCHEMISTRY EPSS 15 Fall 2017 LAB #7 SUNLIGHT & OCEAN ZONATION Sunlight is critical to the distribution of oceanic life The base of the food chain (phytoplankton)
PLANKTON, PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY, AND BIOGEOCHEMISTRY EPSS 15 Fall 2017 LAB #7 SUNLIGHT & OCEAN ZONATION Sunlight is critical to the distribution of oceanic life The base of the food chain (phytoplankton)
Primary Production in the Ocean
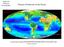 Primary Production in the Ocean A global composite of sea surface chlorophyll concentration Oligotrophic gyre (LNLC) Seasonal Phytoplankton blooms Coastal Upwelling High-nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC)
Primary Production in the Ocean A global composite of sea surface chlorophyll concentration Oligotrophic gyre (LNLC) Seasonal Phytoplankton blooms Coastal Upwelling High-nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC)
microzooplankton ( µm, e.g. ciliates); mesozooplankton (200 µm-20 mm, e.g. calanoid copepods); macrozooplankton (2-20 cm, e.g.
 Zooplankton Classifications Size: Life history: microzooplankton (20-200 µm, e.g. ciliates); mesozooplankton (200 µm-20 mm, e.g. calanoid copepods); macrozooplankton (2-20 cm, e.g. ctenophores) holoplankton
Zooplankton Classifications Size: Life history: microzooplankton (20-200 µm, e.g. ciliates); mesozooplankton (200 µm-20 mm, e.g. calanoid copepods); macrozooplankton (2-20 cm, e.g. ctenophores) holoplankton
Zooplankton variability in the Balearic Sea and its relation to North Atlantic climate : A boundary area in the Western Mediterranean.
 Effects of climate change on the world s oceans Symp.: Gijon 18-23, 28 Workshop 1: Zooplankton and climate: response modes and linkages among regions, regimes and trophic levels Zooplankton variability
Effects of climate change on the world s oceans Symp.: Gijon 18-23, 28 Workshop 1: Zooplankton and climate: response modes and linkages among regions, regimes and trophic levels Zooplankton variability
Southern Ocean productivity control and feedback
 Southern Ocean productivity control and feedback Resource M1 Source: NASA/GFSC Composite satellite image of phytoplankton abundance between 1978 and 1986. False colours code for low (blues and purples)
Southern Ocean productivity control and feedback Resource M1 Source: NASA/GFSC Composite satellite image of phytoplankton abundance between 1978 and 1986. False colours code for low (blues and purples)
Satellite data show that phytoplankton biomass and growth generally decline as the
 Oceanography Plankton in a warmer world Scott C. Doney Satellite data show that phytoplankton biomass and growth generally decline as the oceans surface waters warm up. Is this trend, seen over the past
Oceanography Plankton in a warmer world Scott C. Doney Satellite data show that phytoplankton biomass and growth generally decline as the oceans surface waters warm up. Is this trend, seen over the past
Climate Change and Trophic Mismatches between Plankton Blooms and Fish Phenology
 Climate Change and Trophic Mismatches between Plankton Blooms and Fish Phenology Rebecca G. Asch (Princeton) Co-authors: Charles A. Stock (NOAA GFDL) Jorge L. Sarmiento (Princeton) July 28, 2016 Phenology
Climate Change and Trophic Mismatches between Plankton Blooms and Fish Phenology Rebecca G. Asch (Princeton) Co-authors: Charles A. Stock (NOAA GFDL) Jorge L. Sarmiento (Princeton) July 28, 2016 Phenology
Stable versus unstable planktonic food webs in oceans
 Stable versus unstable planktonic food webs in oceans L. Legendre 1, F. Rassoulzadegan 2 1 Département de biologie, Université Laval, Québec, QC G1K 7P4, Canada 2 Station Zoologique, BP 28, F-06230 Villefranche-sur-Mer,
Stable versus unstable planktonic food webs in oceans L. Legendre 1, F. Rassoulzadegan 2 1 Département de biologie, Université Laval, Québec, QC G1K 7P4, Canada 2 Station Zoologique, BP 28, F-06230 Villefranche-sur-Mer,
Chapter VI. Primary and Secondary Production rate in the Arabian Sea. Using Remote Sensing. 6.1 Introduction Results and Discussion
 Primary and Secondary Production rate in the Arabian Sea Using Remote Sensing 6.1 Introduction 6.2. Results and Discussion 6.2.1 Primary production 6.2.2 Secondary production CHAPTER VI Primary and Secondary
Primary and Secondary Production rate in the Arabian Sea Using Remote Sensing 6.1 Introduction 6.2. Results and Discussion 6.2.1 Primary production 6.2.2 Secondary production CHAPTER VI Primary and Secondary
Oceans 11 Marine Food Web 12/3/ th Trophic Level. 3rd Trophic Level. 2nd Trophic Level. 1st Trophic Level
 Food Web Assignment Marine Ecosystems Name: Section: An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in which there are interactions between living and non-living things. From earlier in your science career,
Food Web Assignment Marine Ecosystems Name: Section: An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in which there are interactions between living and non-living things. From earlier in your science career,
Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic Sea Basin
 The BACC Author Team Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic Sea Basin 4u Springer Contents Preface The BACC Author Team Acknowledgements V VII XIII 1 Introduction and Summary 1 1.1 The BACC Approach
The BACC Author Team Assessment of Climate Change for the Baltic Sea Basin 4u Springer Contents Preface The BACC Author Team Acknowledgements V VII XIII 1 Introduction and Summary 1 1.1 The BACC Approach
Investigating Alternate Trophic Pathways through Gelatinous Zooplankton and Planktivorous Fishes in an Upwelling Ecosystem Using End-to-End Models
 Interdisciplinary Studies on Environmental Chemistry Marine Environmental Modeling & Analysis, Eds., K. Omori, X. Guo, N. Yoshie, N. Fujii, I. C. Handoh, A. Isobe and S. Tanabe, pp. 57 63. by TERRAPUB,
Interdisciplinary Studies on Environmental Chemistry Marine Environmental Modeling & Analysis, Eds., K. Omori, X. Guo, N. Yoshie, N. Fujii, I. C. Handoh, A. Isobe and S. Tanabe, pp. 57 63. by TERRAPUB,
California Current Ecosystem Plankton Food Web
 TEACHER PAGES What role do plankton play in the food web? California Current Ecosystem Plankton Food Web and the Beth Simmons Education and Outreach Coordinator, CCE LTER, Scripps Institution of Oceanography,
TEACHER PAGES What role do plankton play in the food web? California Current Ecosystem Plankton Food Web and the Beth Simmons Education and Outreach Coordinator, CCE LTER, Scripps Institution of Oceanography,
Southern Ocean food web research &
 Southern Ocean food web research & Southern Ocean Sentinel Andrew Constable Antarctic Climate & Ecosystems Cooperative Research Centre & Australian Antarctic Division Thanks to many involved in ACE, AAD,
Southern Ocean food web research & Southern Ocean Sentinel Andrew Constable Antarctic Climate & Ecosystems Cooperative Research Centre & Australian Antarctic Division Thanks to many involved in ACE, AAD,
Dead-Zones and Coastal Eutrophication: Case- Study of Chesapeake Bay W. M. Kemp University of Maryland CES Horn Point Laboratory Cambridge, MD
 Dead-Zones and Coastal Eutrophication: Case- Study of Chesapeake Bay W. M. Kemp University of Maryland CES Horn Point Laboratory Cambridge, MD Presentation to COSEE Trends Orientation at UMCES HPL 4 August
Dead-Zones and Coastal Eutrophication: Case- Study of Chesapeake Bay W. M. Kemp University of Maryland CES Horn Point Laboratory Cambridge, MD Presentation to COSEE Trends Orientation at UMCES HPL 4 August
The euphausiids Euphausia pacifica and Thysanoessa spinifera in the coastal upwelling zone off the Oregon Coast, USA
 The euphausiids Euphausia pacifica and Thysanoessa spinifera in the coastal upwelling zone off the Oregon Coast, USA Euphausia pacifica Thysanoessa spinifera C. Tracy Shaw, Leah R. Feinberg, Jennifer Fisher,
The euphausiids Euphausia pacifica and Thysanoessa spinifera in the coastal upwelling zone off the Oregon Coast, USA Euphausia pacifica Thysanoessa spinifera C. Tracy Shaw, Leah R. Feinberg, Jennifer Fisher,
Classification of systems. Aquatic Ecosystems. Lakes 9/9/2013. Chapter 25
 Aquatic Ecosystems Chapter 25 Classification of systems Aquatic systems classified by physical environment Salinity most important Marine divided broadly into coastal and open water Freshwater divided
Aquatic Ecosystems Chapter 25 Classification of systems Aquatic systems classified by physical environment Salinity most important Marine divided broadly into coastal and open water Freshwater divided
10 Productivity and Food Webs in the Sea. Notes for Marine Biology: Function, Biodiversity, Ecology By Jeffrey S. Levinton
 10 Productivity and Food Webs in the Sea Notes for Marine Biology: Function, Biodiversity, Ecology By Jeffrey S. Levinton Microbial Loop 2 Larger consumers Microbial loop DOC & POC Viruses Bacteria Herbivores
10 Productivity and Food Webs in the Sea Notes for Marine Biology: Function, Biodiversity, Ecology By Jeffrey S. Levinton Microbial Loop 2 Larger consumers Microbial loop DOC & POC Viruses Bacteria Herbivores
Examine annual or seasonal scale changes in
 Primary production approach 5: Estimate Net community production based on in situ variations in oxygen, nutrients, carbon, or biomass (often chlorophyll) Examine annual or seasonal scale changes in O 2,
Primary production approach 5: Estimate Net community production based on in situ variations in oxygen, nutrients, carbon, or biomass (often chlorophyll) Examine annual or seasonal scale changes in O 2,
25 years of Hawaii Ocean Time-series carbon flux determinations: Insights into productivity, export, and nutrient supply in the oligotrophic ocean
 25 years of Hawaii Ocean Time-series carbon flux determinations: Insights into productivity, export, and nutrient supply in the oligotrophic ocean MATTHEW CHURCH, ROBERT BIDIGARE, JOHN DORE, DAVID KARL,
25 years of Hawaii Ocean Time-series carbon flux determinations: Insights into productivity, export, and nutrient supply in the oligotrophic ocean MATTHEW CHURCH, ROBERT BIDIGARE, JOHN DORE, DAVID KARL,
Life in Water. Chapter 3
 Life in Water Chapter 3 Outline Hydrologic Cycle Oceans Shallow Marine Waters Marine Shores Estuaries, Salt Marshes, and Mangrove Forests Rivers and Streams Lakes 2 The Hydrologic Cycle Over 71% of the
Life in Water Chapter 3 Outline Hydrologic Cycle Oceans Shallow Marine Waters Marine Shores Estuaries, Salt Marshes, and Mangrove Forests Rivers and Streams Lakes 2 The Hydrologic Cycle Over 71% of the
Gary Fahnenstiel RECENT CHANGES IN PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY AND PHYTOPLANKTON DYNAMICS
 RECENT CHANGES IN PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY AND PHYTOPLANKTON DYNAMICS Gary Fahnenstiel Great Lakes Research Center Michigan Tech Research Institute Michigan Technological University And Water Center Graham
RECENT CHANGES IN PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY AND PHYTOPLANKTON DYNAMICS Gary Fahnenstiel Great Lakes Research Center Michigan Tech Research Institute Michigan Technological University And Water Center Graham
Climate and the ecosystem approach to research and management
 Climate and the ecosystem approach to research and management Einar Svendsen with input from many others Nordic Climate Fish Conference, Norway, Solstrand 19-21 Jan., 2011 Our Task: Research for better
Climate and the ecosystem approach to research and management Einar Svendsen with input from many others Nordic Climate Fish Conference, Norway, Solstrand 19-21 Jan., 2011 Our Task: Research for better
Illustrations/B.Harmon
 Illustrations/B.Harmon An underwater earthquake causes a tsunami to wash over a penguin nesting beach. reproduction Melting glaciers in Antarctica reduce the distance the female emperor penguin has to
Illustrations/B.Harmon An underwater earthquake causes a tsunami to wash over a penguin nesting beach. reproduction Melting glaciers in Antarctica reduce the distance the female emperor penguin has to
Trophic Interactions
 Trophic Cascading Trophic Interactions Trophic Interactions Trophic Interactions Control of Primary Production Only about one-half of the variation in primary production among lakes worldwide can be explained
Trophic Cascading Trophic Interactions Trophic Interactions Trophic Interactions Control of Primary Production Only about one-half of the variation in primary production among lakes worldwide can be explained
Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake
 Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake Fig. 6.6 Recall: Current ocean is gaining Carbon.. OCEAN Reservoir size: 38000 Flux in: 90 Flux out: 88+0.2=88.2 90-88.2 = 1.8 Pg/yr OCEAN is gaining 1.8 Pg/yr Sum of the
Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake Fig. 6.6 Recall: Current ocean is gaining Carbon.. OCEAN Reservoir size: 38000 Flux in: 90 Flux out: 88+0.2=88.2 90-88.2 = 1.8 Pg/yr OCEAN is gaining 1.8 Pg/yr Sum of the
15.1 Life in the Earth System. KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems.
 15.1 Life in the Earth System KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is the portion of Earth that is inhabited by life. The
15.1 Life in the Earth System KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is the portion of Earth that is inhabited by life. The
Global Ocean Ecosystems Dynamics and Climate Change
 A Component of the U.S. Global Change Research Program Global Ocean Ecosystems Dynamics and Climate Change A Long Range Science Plan 1995-2005 U.S. Global Ocean Ecosystems Dynamics Report Number 12 April
A Component of the U.S. Global Change Research Program Global Ocean Ecosystems Dynamics and Climate Change A Long Range Science Plan 1995-2005 U.S. Global Ocean Ecosystems Dynamics Report Number 12 April
Changes in coastal environment and mass occurrence of jellyfish in Tokyo Bay. Haruto ISHII. (Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology)
 Changes in coastal environment and mass occurrence of jellyfish in Tokyo Bay Haruto ISHII (Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology) Ecosystem in hyper eutrophicated bay High concentrations of
Changes in coastal environment and mass occurrence of jellyfish in Tokyo Bay Haruto ISHII (Tokyo University of Marine Science and Technology) Ecosystem in hyper eutrophicated bay High concentrations of
SUMMARY OF THE COPERNICUS MARINE ENVIRONMENT MONITORING SERVICE OCEAN STATE REPORT 2016
 SUMMARY OF THE COPERNICUS MARINE ENVIRONMENT MONITORING SERVICE OCEAN STATE REPORT 2016 C O P E RNICUS M ARINE E NVIRO N MEN T M ONIT ORING SE R VICE OCEAN STATE REPORT No.1, 2016 Journal of Operational
SUMMARY OF THE COPERNICUS MARINE ENVIRONMENT MONITORING SERVICE OCEAN STATE REPORT 2016 C O P E RNICUS M ARINE E NVIRO N MEN T M ONIT ORING SE R VICE OCEAN STATE REPORT No.1, 2016 Journal of Operational
Interpreting Lake Data
 Interpreting Lake Data Indiana Clean Lakes Program The Indiana Clean Lakes Program was created in 1989 as a program within the Indiana Department of Environmental Management's (IDEM) Office of Water Management.
Interpreting Lake Data Indiana Clean Lakes Program The Indiana Clean Lakes Program was created in 1989 as a program within the Indiana Department of Environmental Management's (IDEM) Office of Water Management.
MONDAY, 27 FEBRUARY 2017
 MONDAY, 27 FEBRUARY 2017 Room 301 B 302 A/B 304 A/B 305 A/B 306 A 306 B 308 A/B 199 168 258 162 150 168 194 9:00-9:50 9:50 - MORNING PLENARY - Marcia McNutt - 9:00 to 9:50 Session# 71 96 12 9 34 58 65
MONDAY, 27 FEBRUARY 2017 Room 301 B 302 A/B 304 A/B 305 A/B 306 A 306 B 308 A/B 199 168 258 162 150 168 194 9:00-9:50 9:50 - MORNING PLENARY - Marcia McNutt - 9:00 to 9:50 Session# 71 96 12 9 34 58 65
Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater
 Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater or saltwater. The two sets of communities interact and are joined by the water cycle. Gravity eventually returns all fresh water
Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater or saltwater. The two sets of communities interact and are joined by the water cycle. Gravity eventually returns all fresh water
2009/2010 Water Column Overview, Red Tide Update, and Bay Eutrophication Model 2010 Results. OMSAP Meeting June 30, 2011.
 29/21 Water Column Overview, Red Tide Update, and Bay Eutrophication Model 21 Results OMSAP Meeting June 3, 211 Scott Libby Contributions from D. Anderson, D. Borkman, C.S. Chen, R. Geyer, and C. Oviatt
29/21 Water Column Overview, Red Tide Update, and Bay Eutrophication Model 21 Results OMSAP Meeting June 3, 211 Scott Libby Contributions from D. Anderson, D. Borkman, C.S. Chen, R. Geyer, and C. Oviatt
RESPONSE OF PHYTOPLANKTON AND OCEAN BIOGEOCHEMISTRY IN A WARMING WORLD
 RESPONSE OF PHYTOPLANKTON AND OCEAN BIOGEOCHEMISTRY IN A WARMING WORLD Jeffery Scott, Michael Follows Massachusetts Institute of Technology Program in Atmospheres, Oceans and Climate INTRODUCTION: Marine
RESPONSE OF PHYTOPLANKTON AND OCEAN BIOGEOCHEMISTRY IN A WARMING WORLD Jeffery Scott, Michael Follows Massachusetts Institute of Technology Program in Atmospheres, Oceans and Climate INTRODUCTION: Marine
STOCK ASSESSMENT OF WITCH FLOUNDER (GLYPTOCEPHALUS CYNOGLOSSUS) IN NAFO SUBDIVISION 3PS
 Canadian Science Advisory Secretariat Newfoundland and Labrador Region Science Advisory Report 2018/011 STOCK ASSESSMENT OF WITCH FLOUNDER (GLYPTOCEPHALUS CYNOGLOSSUS) IN NAFO SUBDIVISION 3PS Image: Witch
Canadian Science Advisory Secretariat Newfoundland and Labrador Region Science Advisory Report 2018/011 STOCK ASSESSMENT OF WITCH FLOUNDER (GLYPTOCEPHALUS CYNOGLOSSUS) IN NAFO SUBDIVISION 3PS Image: Witch
Chapter Concepts LIFE IN WATER. The Hydrologic Cycle. The Hydrologic Cycle
 Chapter Concepts Chapter 3 LIFE IN WATER The hydrologic cycle exchanges water among reservoirs The biology of aquatic environments corresponds broadly to variations in physical factors such as light, temperature,
Chapter Concepts Chapter 3 LIFE IN WATER The hydrologic cycle exchanges water among reservoirs The biology of aquatic environments corresponds broadly to variations in physical factors such as light, temperature,
Food Chains, Food Webs, and Bioaccumulation Background
 Food Chains, Food Webs, and Bioaccumulation Background Introduction Every living organism needs energy to sustain life. Organisms within a community depend on one another for food to create energy. This
Food Chains, Food Webs, and Bioaccumulation Background Introduction Every living organism needs energy to sustain life. Organisms within a community depend on one another for food to create energy. This
Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book)
 Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p.87-89 (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book) Term Definition Weather Day-to-day condition of earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place
Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p.87-89 (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book) Term Definition Weather Day-to-day condition of earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place
Part I: Salish Sea Introduction. Review:
 Part I: Salish Sea Introduction Review: The Salish Sea The Salish Sea was formed about 20,000 years ago during the last ice age by the carving action of glaciers. There are 3 major parts of the Salish
Part I: Salish Sea Introduction Review: The Salish Sea The Salish Sea was formed about 20,000 years ago during the last ice age by the carving action of glaciers. There are 3 major parts of the Salish
Ecosystem Status Assessment in Korea
 Ecosystem Status Assessment in Korea Sinjae Yoo Indicators of Status and Change within North Pacific Marine Ecosystems: A FUTURE Workshop Honolulu, 2011.04.26-28 Purpose To introduce monitoring and assessment
Ecosystem Status Assessment in Korea Sinjae Yoo Indicators of Status and Change within North Pacific Marine Ecosystems: A FUTURE Workshop Honolulu, 2011.04.26-28 Purpose To introduce monitoring and assessment
RIVER SEDIMENTS AND COASTAL FISH PRODUCTION: WHAT ABOUT THE MEKONG?
 people Ÿ science Ÿ environment Ÿ partners! RIVER SEDIMENTS AND COASTAL FISH PRODUCTION: WHAT ABOUT THE MEKONG? Eric BARAN Eric GUERIN Project A Climate Resilient Mekong: Maintaining the Flows that Nourish
people Ÿ science Ÿ environment Ÿ partners! RIVER SEDIMENTS AND COASTAL FISH PRODUCTION: WHAT ABOUT THE MEKONG? Eric BARAN Eric GUERIN Project A Climate Resilient Mekong: Maintaining the Flows that Nourish
Chapter 6. Aquatic Biodiversity. Chapter Overview Questions
 Chapter 6 Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter Overview Questions Ø What are the basic types of aquatic life zones and what factors influence the kinds of life they contain? Ø What are the major types of saltwater
Chapter 6 Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter Overview Questions Ø What are the basic types of aquatic life zones and what factors influence the kinds of life they contain? Ø What are the major types of saltwater
Trace Metal Iron (Fe), an important element to measure at sea. Dr. Thato Nicholas Mtshali
 Trace Metal Iron (Fe), an important element to measure at sea Dr. Thato Nicholas Mtshali Southern Atlantic Ocean and Antarctic Seminar (Cape Town): 5 December 2017 A CSIR-led multidisciplinary and multi-institutional
Trace Metal Iron (Fe), an important element to measure at sea Dr. Thato Nicholas Mtshali Southern Atlantic Ocean and Antarctic Seminar (Cape Town): 5 December 2017 A CSIR-led multidisciplinary and multi-institutional
Ecology. Limiting factors. Introduction to Marine Ecology. Ecological communities and ecosystems
 Introduction to Marine Ecology Physical limiting factors light, temperature, salinity, nutrients, gases variation within the ocean: depth and geography Marine habitats: where to make a living Marine feeding
Introduction to Marine Ecology Physical limiting factors light, temperature, salinity, nutrients, gases variation within the ocean: depth and geography Marine habitats: where to make a living Marine feeding
Coastal studies in Long Term Ecological Research. Dan Reed Santa Barbara Coastal LTER
 Coastal studies in Long Term Ecological Research Dan Reed Santa Barbara Coastal LTER NSF s Long Term Ecological Research Program 24 sites representing a diverse array of biomes Major focus of research
Coastal studies in Long Term Ecological Research Dan Reed Santa Barbara Coastal LTER NSF s Long Term Ecological Research Program 24 sites representing a diverse array of biomes Major focus of research
Spatial Distribution of the Winter Nutrient Pool
 Spatial Distribution of the Winter Nutrient Pool Author: Philip Axe, Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute Key message Good news: DIN concentrations remain below those observed in the 1990s,
Spatial Distribution of the Winter Nutrient Pool Author: Philip Axe, Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute Key message Good news: DIN concentrations remain below those observed in the 1990s,
Food for thought Antarctic Food Web. Photo credit: Will Reid
 Food for thought Antarctic Food Web Photo credit: Will Reid Notes for teachers: Food for thought is an interactive food webs game, designed to give pupils an appreciation for the fact that every organism
Food for thought Antarctic Food Web Photo credit: Will Reid Notes for teachers: Food for thought is an interactive food webs game, designed to give pupils an appreciation for the fact that every organism
BIOMES. Living World
 BIOMES Living World Biomes Biomes are large regions of the world with distinctive climate, wildlife and vegetation. They are divided by terrestrial (land) or aquatic biomes. Terrestrial Biomes Terrestrial
BIOMES Living World Biomes Biomes are large regions of the world with distinctive climate, wildlife and vegetation. They are divided by terrestrial (land) or aquatic biomes. Terrestrial Biomes Terrestrial
Why is the Benthos Important? OR Pre- and Post- Salt Pond Restoration Assessment of Benthic Communities in South San Francisco Bay
 Why is the Benthos Important? OR Pre- and Post- Salt Pond Restoration Assessment of Benthic Communities in South San Francisco Bay Jan Thompson and Francis Parchaso Menlo Park, USGS Benthic communities
Why is the Benthos Important? OR Pre- and Post- Salt Pond Restoration Assessment of Benthic Communities in South San Francisco Bay Jan Thompson and Francis Parchaso Menlo Park, USGS Benthic communities
Climate Change, Global Warming & Ocean Biology. Doug Capone May 2008
 Climate Change, Global Warming & Ocean Biology Doug Capone May 2008 Disclaimer: I m a Microbial Ecologist not a Climate Dynamicist IPCC 4 th Assessment And I d rather have a bottle in front of me than
Climate Change, Global Warming & Ocean Biology Doug Capone May 2008 Disclaimer: I m a Microbial Ecologist not a Climate Dynamicist IPCC 4 th Assessment And I d rather have a bottle in front of me than
Seasonal Anoxia over the Western Indian Continental Shelf
 Seasonal Anoxia over the Western Indian Continental Shelf S.W.A. Naqvi, Hema Naik, A.K. Pratihary, M. Gauns, Witty D Souza, Gayatree Narvenkar, D.A. Jayakumar, M.S. Shailaja & P.V. Narvekar National Institute
Seasonal Anoxia over the Western Indian Continental Shelf S.W.A. Naqvi, Hema Naik, A.K. Pratihary, M. Gauns, Witty D Souza, Gayatree Narvenkar, D.A. Jayakumar, M.S. Shailaja & P.V. Narvekar National Institute
How will biogeochemical processes in the ocean respond to surface warming? Anja Engel Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research (AWI)
 How will biogeochemical processes in the ocean respond to surface warming? Anja Engel Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research (AWI) The Naked Earth The Discovery of Global Warming Air traps
How will biogeochemical processes in the ocean respond to surface warming? Anja Engel Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research (AWI) The Naked Earth The Discovery of Global Warming Air traps
Causes of Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia
 Causes of Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Nancy N. Rabalais 1 R. Eugene Turner 2 1 Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium 2 Louisiana State University Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research, Coastal Ocean
Causes of Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Nancy N. Rabalais 1 R. Eugene Turner 2 1 Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium 2 Louisiana State University Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research, Coastal Ocean
Total Budget for FY2006-FY2008: 92,332,000Yen (FY2008; 28,019,000Yen) Silica Deficiency, Diatom, Autonomous Sinking, Nutritions Export, Jellyfish
 D-061-E-1 D-061 Study on the Ecological Deterioration of East Asian Marginal Seas due to the Anthropogenic Change in the Effluent Nutrient Ratio of N: P: Si (Abstract of the Final Report) Contact person
D-061-E-1 D-061 Study on the Ecological Deterioration of East Asian Marginal Seas due to the Anthropogenic Change in the Effluent Nutrient Ratio of N: P: Si (Abstract of the Final Report) Contact person
Sara Cregeen, Mike Zubkov National Oceanography Centre Southampton, Southampton, UK
 ATLANTIC MERIDINIONAL TRANSECT CRUISE 24: ZOOPLANKTON ECOLOGY Erica Goetze, Michelle Jungbluth Department of Oceanography, University of Hawaii at Manoa, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA. egoetze@hawaii.edu, mjjungb@hawaii.edu
ATLANTIC MERIDINIONAL TRANSECT CRUISE 24: ZOOPLANKTON ECOLOGY Erica Goetze, Michelle Jungbluth Department of Oceanography, University of Hawaii at Manoa, Honolulu, HI 96822, USA. egoetze@hawaii.edu, mjjungb@hawaii.edu
Keystone Biology Remediation B4: Ecology
 Keystone Biology Remediation B4: Ecology Assessment Anchors: to describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e. organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere) (B.4.1.1) to describe
Keystone Biology Remediation B4: Ecology Assessment Anchors: to describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e. organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere) (B.4.1.1) to describe
1. All the interconnected feeding relationships in an ecosystem make up a food. a. Interaction b. Chain c. Network d. Web
 Ecology Unit Test DO NOT WRITE ON TEST!!! Take a deep breath, take your time, and make sure you understand exactly what the question is asking you. For true/false, fill in the correct bubble ( A for true
Ecology Unit Test DO NOT WRITE ON TEST!!! Take a deep breath, take your time, and make sure you understand exactly what the question is asking you. For true/false, fill in the correct bubble ( A for true
CHAPTER 55: Community Ecology
 CHAPTER 55: Community Ecology 1) How is co-evolution significant in community ecology? 2) What is meant by the trophic structure of a community? 3) What does a food web show that isn t indicated by a food
CHAPTER 55: Community Ecology 1) How is co-evolution significant in community ecology? 2) What is meant by the trophic structure of a community? 3) What does a food web show that isn t indicated by a food
K r i l l. Investigating behavior. Antarctica harbors one of the most extreme yet productive ecosystems on Earth.
 K r i l l Investigating behavior of Critical to the survival of birds, mammals, penguins and whales a group of tiny crustaceans collectively known as Antarctic krill are at the heart of the polar marine
K r i l l Investigating behavior of Critical to the survival of birds, mammals, penguins and whales a group of tiny crustaceans collectively known as Antarctic krill are at the heart of the polar marine
Name: Section: Biology 101L Laboratory 8: Ecology and Food Webs (Exercise and homework adapted from Bio Food webs of Western Oregon University)
 Biology 101L Laboratory 8: Ecology and Food Webs (Exercise and homework adapted from Bio 101-6 Food webs of Western Oregon University) Objectives (1) You will explore some of the key trophic relationships
Biology 101L Laboratory 8: Ecology and Food Webs (Exercise and homework adapted from Bio 101-6 Food webs of Western Oregon University) Objectives (1) You will explore some of the key trophic relationships
A biological contribution to partial pressure of CO 2 in the western Arctic Ocean and Bering Sea
 A biological contribution to partial pressure of CO 2 in the western Arctic Ocean and Bering Sea *Futsuki, R. 1, T. Hirawake 2, A. Fujiwara 2,3, T. Kikuchi 4, S. Nishino 4, D. Sasano 5,6, M. Ishii 5,6,
A biological contribution to partial pressure of CO 2 in the western Arctic Ocean and Bering Sea *Futsuki, R. 1, T. Hirawake 2, A. Fujiwara 2,3, T. Kikuchi 4, S. Nishino 4, D. Sasano 5,6, M. Ishii 5,6,
What factors affect life in aquatic ecosystems?
 Aquatic Ecosystems: Notes Outline Today s Objective: Students will explain that different types of organisms exist within aquatic systems due to chemistry, geography, light, depth, salinity, and/or temperature.
Aquatic Ecosystems: Notes Outline Today s Objective: Students will explain that different types of organisms exist within aquatic systems due to chemistry, geography, light, depth, salinity, and/or temperature.
Gas Guzzlers. Biological Pump
 Gas Guzzlers Biological Pump Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter 8 Coral Reefs Open Ocean Deep Sea Marine equivalent of tropical rain forests Habitats for one-fourth of all marine species Coral polyps, which
Gas Guzzlers Biological Pump Aquatic Biodiversity Chapter 8 Coral Reefs Open Ocean Deep Sea Marine equivalent of tropical rain forests Habitats for one-fourth of all marine species Coral polyps, which
Ecosystem refers to the organism which live in a particular area, the relationship between them, and their physical environment.
 Ecosystem refers to the organism which live in a particular area, the relationship between them, and their physical environment. Ecosystem have two components: Biocenosis: is the set of living being in
Ecosystem refers to the organism which live in a particular area, the relationship between them, and their physical environment. Ecosystem have two components: Biocenosis: is the set of living being in
What is Ecology? Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
 ECOLOGY What is Ecology? The scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings Factors involved in ecology Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
ECOLOGY What is Ecology? The scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings Factors involved in ecology Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
Part 3. Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling
 OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (11.03.11) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) Part 3. Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling Lecture Outline 1. Models of Carbon in the Ocean 2. Nutrient Cycling in the Ocean Atmospheric-Ocean
OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (11.03.11) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) Part 3. Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling Lecture Outline 1. Models of Carbon in the Ocean 2. Nutrient Cycling in the Ocean Atmospheric-Ocean
What is ECOLOGY? The study of the biotic and abiotic factors in an environment and their interactions.
 Ecology What is ECOLOGY? The study of the biotic and abiotic factors in an environment and their interactions. Biotic Factors Living things in the environment. Animals Plants Fungi Protists Bacteria Abiotic
Ecology What is ECOLOGY? The study of the biotic and abiotic factors in an environment and their interactions. Biotic Factors Living things in the environment. Animals Plants Fungi Protists Bacteria Abiotic
Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion: Potential Environmental Impacts and Fisheries
 Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion: Potential Environmental Impacts and Fisheries Christina M Comfort, M.Sc. Candidate University of Hawaii at Manoa Department of Oceanography Hawaii Natural Energy Institute
Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion: Potential Environmental Impacts and Fisheries Christina M Comfort, M.Sc. Candidate University of Hawaii at Manoa Department of Oceanography Hawaii Natural Energy Institute
AP Environmental Science
 AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
AP Environmental Science Types of aquatic life zones MARINE Estuaries coral reefs mangrove swamps neritic zone pelagic zone FRESHWATER lakes and ponds streams and rivers wetlands Distribution of aquatic
A sense of place N, W LNLC region two layered system. < 50m mixed layer ~125 m euphotic zone/nutricline. Station ALOHA (1988 onwards)
 STATION ALOHA 1. Introduction to the region 2. Types of blooms (enhanced biomass/growth emphasis on the mixed layer) 3. Drivers of variability 4. Beyond biomass towards productivity angelicque white, oregon
STATION ALOHA 1. Introduction to the region 2. Types of blooms (enhanced biomass/growth emphasis on the mixed layer) 3. Drivers of variability 4. Beyond biomass towards productivity angelicque white, oregon
Climate Change & the Chesapeake TS3 workgroup chapter. European MedSeA
 Climate Change & the Chesapeake TS3 workgroup chapter European MedSeA 21 ST CENTURY CLIMATE CHANGE AND SUBMERGED AQUATIC VEGETATION IN THE CHESAPEAKE BAY The 20 th century story: nutrient pollution, eutrophication,
Climate Change & the Chesapeake TS3 workgroup chapter European MedSeA 21 ST CENTURY CLIMATE CHANGE AND SUBMERGED AQUATIC VEGETATION IN THE CHESAPEAKE BAY The 20 th century story: nutrient pollution, eutrophication,
CHAPTER. Evolution and Community Ecology
 CHAPTER 5 Evolution and Community Ecology Lesson 5.3 Ecological Communities https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gu2ezaisvqu The sun provides the energy for almost all of the ecological communities and species
CHAPTER 5 Evolution and Community Ecology Lesson 5.3 Ecological Communities https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gu2ezaisvqu The sun provides the energy for almost all of the ecological communities and species
Marine Ecology of the Arctic
 Marine Ecology of the Arctic Connectivity, change, and resilience Arny Blanchard Institute of Marine Science University of Alaska Fairbanks Oceanography 2015 Philadelphia, PE, June 22, 2015 Alaska s Arctic
Marine Ecology of the Arctic Connectivity, change, and resilience Arny Blanchard Institute of Marine Science University of Alaska Fairbanks Oceanography 2015 Philadelphia, PE, June 22, 2015 Alaska s Arctic
Assessment of climate change impacts on marine ecosystems in East Antarctica: outcomes of a research collaboration between Australia & Japan
 Assessment of climate change impacts on marine ecosystems in East Antarctica: outcomes of a research collaboration between Australia & Japan So Kawaguchi 12, Mitsuo Fukuchi 3 Andrew Constable 12 and Anthony
Assessment of climate change impacts on marine ecosystems in East Antarctica: outcomes of a research collaboration between Australia & Japan So Kawaguchi 12, Mitsuo Fukuchi 3 Andrew Constable 12 and Anthony
Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary. Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP)
 Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP) Introduction: A key theme of the ongoing DCERP program is monitoring
Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP) Introduction: A key theme of the ongoing DCERP program is monitoring
Ponds: Careful of the Fish!
 Ponds: Careful of the Fish! Dr. Chuck Cichra Extension Fisheries Specialist University of Florida / IFAS SFRC - Program of Fisheries & Aquatic Sciences All Plants Need Water, Light, and Nutrients Aquatic
Ponds: Careful of the Fish! Dr. Chuck Cichra Extension Fisheries Specialist University of Florida / IFAS SFRC - Program of Fisheries & Aquatic Sciences All Plants Need Water, Light, and Nutrients Aquatic
5.2. Monitoring the plankton community
 5.2. Monitoring the plankton community by Knutsen t. 5.2.1. Nutrients and chlorophyll a Nutrients and chlorophyll a are sampled at all stations, using a CTD water bottle rosette sampler. Nutrients samples
5.2. Monitoring the plankton community by Knutsen t. 5.2.1. Nutrients and chlorophyll a Nutrients and chlorophyll a are sampled at all stations, using a CTD water bottle rosette sampler. Nutrients samples
Coral Reefs- A Challenging Ecosystem for Human Societies* B. Salvat Originally published in Global Environmental Change, 1992, vol. 2, pp.
 Coral Reefs- A Challenging Ecosystem for Human Societies* B. Salvat Originally published in Global Environmental Change, 1992, vol. 2, pp. 12-18 18 Presented by: Amy Dewees & Melissa Parente What is coral?
Coral Reefs- A Challenging Ecosystem for Human Societies* B. Salvat Originally published in Global Environmental Change, 1992, vol. 2, pp. 12-18 18 Presented by: Amy Dewees & Melissa Parente What is coral?
DOC and major carbon reservoirs and fluxes
 The Composition and cycling of Dissolved organic matter-i Review of DOC distribution Review of radiocarbon in DOC Sources of DOC Seasonal cycling of DOC above the permanent thermocline Composition of DOC
The Composition and cycling of Dissolved organic matter-i Review of DOC distribution Review of radiocarbon in DOC Sources of DOC Seasonal cycling of DOC above the permanent thermocline Composition of DOC
Developing and optimizing a coordinated Salish Sea zooplankton monitoring program
 Western Washington University Western CEDAR Salish Sea Ecosystem Conference 2014 Salish Sea Ecosystem Conference (Seattle) May 1st, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM Developing and optimizing a coordinated Salish Sea
Western Washington University Western CEDAR Salish Sea Ecosystem Conference 2014 Salish Sea Ecosystem Conference (Seattle) May 1st, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM Developing and optimizing a coordinated Salish Sea
STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems
 Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems TEK 8.11D: Recognize human dependence on ocean systems and explain how human activities such as runoff, artificial
Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems TEK 8.11D: Recognize human dependence on ocean systems and explain how human activities such as runoff, artificial
Ecosystem consists of the organism which live in a particular area, the relationship between them, and their physical environment.
 Ecosystem consists of the organism which live in a particular area, the relationship between them, and their physical environment. An ecosystem can be terrestrial (on land) or aquatic (in water) An ecosystem
Ecosystem consists of the organism which live in a particular area, the relationship between them, and their physical environment. An ecosystem can be terrestrial (on land) or aquatic (in water) An ecosystem
