SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
|
|
|
- Roderick Norman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Table 1. For each experiment the table shows the number of images analyzed, resolution obtained, preparation method used for EM observation, characteristics of the microscope on which the data was collected and the range of defocus values used. Number Experiments of images TFIID-Rap Resolution Holo-TFIID Complex Preparation method Negative stain Microscope, emitter, voltage Philips CM120, LaB6, 120kV Defocus range (um) TFIID-TFIIA- DNA Holo-TFIID Complex TFIID-TFIIA- Rap1-DNA Unstained Cryo-EM FEI Tecnai F20 FEG, 200kV Holo-TFIID Complex I Unstained Cryo-EM FEI Polara, FEG, 300kV Complex II
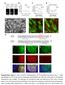
2 Supplementary Figure 1. a, Field of negatively stained TFIID-Rap1 complexes. Arrows show selected TFIID-complexes. Bar represents 100 nm b, Class average images and corresponding reprojection images of the final 3-D model of the Rap1- TFIID complex. c, Angular distribution of the images used for the final reconstruction. 2
3 Supplementary Figure 2. a, Field of cryo TFIID-TFIIA-DNA complexes observed by cryo EM. Arrows show selected complexes. Bar represents 100 nm. b, Class average images and corresponding reprojection images from the final TFIID-TFIIA-DNA structure. c, Angular distribution of the images used for the final reconstruction. 3
4 Supplementary Figure 3. a. Field of cryo TFIID-TFIIA-Rap1-DNA complexes. Arrows show selected complexes. Bar represents 100 nm. b. Class average images and corresponding reprojection images from the final TFIID-TFIIA-DNA complexes. c. Angular distributions of the images used for the final reconstructions. 4
5 Supplementary Figure 4. Resolution curves for each calculated 3-D model. The criterion used to estimate the resolution corresponds to the intersection point of the half bit curve with the Fourier Shell Correlation (FSC) curve, which was obtained by comparing two distinct reconstructions calculated after splitting the data set in two (Van Heel and Schatz, 2005). The values obtained are reported in Supplementary Table 1. a b c 5
6 a b 6
7 c d Supplementary Figure 5. Density difference maps. The electron density map of each complex was normalized and the corresponding holo-tfiid, which was obtained in the same experimental conditions, was subtracted. For each complex, two different views 7
8 same experimental conditions, was subtracted. For each complex, two different views are shown in the upper and lower row. The first panel of each row represents a 3-D view of the complex, the second panel shows the difference map superimposed to the map of the complex. The positive and negative differences are thresholded at 3σ and represented in red and in meshed blue respectively. The third panel represents the corresponding 3-D view of the holo-tfiid reference model used to calculate the difference. 8
9 Supplementary Figure 6. Assessment of the sorting procedure. a. Fourier-Shell correlation curves before and after sorting of the TFIID-TFIIA-Rap1-DNA dataset. Black line shows the Fourier-shell correlation of the reconstructed structure before sorting. The resolution of Complex I (yellow line) and II (magenta line) are higher, showing that the sorting procedure improved dataset homogeneity. Moreover, the Fourier-Shell correlation between Complex I and II is significantly lower than the value obtained for 9
10 each complex alone indicating that the differences between Complex I and II are significant (Liu et al. 2008). b. Local Multivariate Statistical Analysis (Klaholz et al., 2004) was performed on the non-sorted images to assess whether the key features of complex I (a large B-lobe) and of complex II (a bridge of density between C1 and B- lobes) can be revealed prior to sorting. All images corresponding to a particular TFIID view in which these features are clearly visible were extracted for Complex I (upper left panel) and Complex II (lower left panel). The intensity variations of these images were analysed within a mask (white ellipse) containing the characteristic features (arrows). After partitioning, class average images were obtained representing both holo TFIID (central panels) and the TFIID complexes show the key features (right panels, arrows). This experiment shows that the key features that define Complexes I and II can be revealed prior sorting and thus constitute a prominent variation within the masked area. c. In order to verify that these key features are revealed even if all the images variations are analyzed and not only those occurring within the restricted mask, the same experiment was performed using a large mask encompassing all pixels of the image. The same results were obtained indicating that the key features that define complexes I and II constitute a prominent variation within the whole image. 10
11 Supplementary Figure 7. Immunolocalization of the C-terminus of Taf2. a b c d e a. Specificity of anti-taf2p C-terminal antibody. Purified TFIID (50 and 100 ng amounts; see ref 5) was fractionated by SDS-PAGE, electro-transferred to Immobilon membrane and paired, equivalent strips containing either 50 and 100 ng of TFIID were excised from the membrane. Membranes were blocked and then incubated with a 1/8000 dilution of antigen peptide affinity-purified anti-taf2 IgG derived from the serum of a rabbit (#366) immunized with a carrier-conjugated peptide composing Taf2 amino acids Incubation of the two identical sets of blots was conducted either in the presence of Taf2 C-terminal antigen peptide ( 1342 KVEKQIVKPKVTSKQ 1356 ; C- terminal, blot left), or an unrelated peptide derived from the N-terminus of Taf2 ( 3 SKNATPRAIVSESST 19 ; Unrelated, blot right) present at a calculated 200-fold molar excess (peptide:total IgG) of competitor peptides. Note that both the antigen and 11
12 unrelated peptide had an N-terminal cysteine residue added (not shown). Inclusion of antigen peptide, but not unrelated peptide, effectively blocked antibody binding to Taf2 indicating that the anti-taf2 C-terminal antibody was specific. b. Sensitivity of anti-taf2 C-terminal antibody. TFIID-containing blots generated as described above were incubated with affinity purified anti-taf2 IgG at three dilutions as shown (1:2000; 1:4000; 1:8000). Immunoreactive Taf2 was detected by chemiluminescence; robust signals were detected at all three dilutions indicating high sensitivity. c-e. Immunomapping of C-terminal domain of Taf2 in the TFIID complex. A five-fold molar excess of the antibody was incubated for 20 min on ice with purified TFIID. Images from negative stained immune complexes were collected on a Philips CM120 microscope equipped with a LaB 6 cathode and operating at 120kV. Images were recorded on a CCD camera at a nominal magnification 45,000x. Boxed molecular images were aligned against references projected from a negatively stained TFIID reference structure and clustered into classes corresponding to different views. (c) Class average images in which the TFIID-bound antibody is visible (d) Same views outlined by equidensity contour levels. (e) Corresponding orientation of the 3-D reference model showing that the C-terminus of Taf2 is located in lobe D. The arrows indicate the bound antibody. 12
13 Supplementary Figure 8. Schematic representation of the two DNA fragments used in this study to form the TFIID containing complexes. a, Ad2 MLP promoter fragment; location of five tandem copies of a consensus 17 bp yeast Gal4 binding site, TATA element at -30 relative to the transcription start(initiation) site, TSS shown. Nucleotide sequence numbering relative to the shown TSS. b, Chimeric UAS RAP1 -PGK1 promoter fragment; location of the RPS8A enhancer, containing two tandem Rap1 binding sites, single functional PGK1 TATA box and TSS indicated. Note that the nucleotide coordinates shown are relative to the TSS of this chimeric construct, not those of the natural PGK1 or RPS8A genes. 13
14 Supplementary Figure 9. a. Schematic depiction of the RPS1A promoter fragment used in this supplementary study with indications of the distances between Rap1 binding sites and the TATA like elements (Bendjennat and Weil, 2008). b. Measured loop sizes formed upon incubation of TFIID, TFIIA and Rap1 with the RPS1A promoter fragment. The histogram shows two peaks at 72 and 46 nm, which correlates with the expected sizes of the loops. c. Images showing visible DNA ends (arrows) protruding from the Rap1- TFIID complex after loop formation. 14
15 a b c d Supplementary Figure 10. Image analysis of isolated, negatively stained Rap1 molecules. Purified yeast Rap1 was adsorbed on a carbon coated EM grid and negatively stained according to the sandwich method in which a second 10nm thick carbon film is deposited on top in order to obtain a more homogeneous staining. Images were recorded in low dose conditions using a Philips CM120 electron microscope equipped with a LaB6 cathode and operating at 100 kv. Boxed particles were processed using the IMAGIC software package and the first 3-D model was built using the angular reconstruction method (Van Heel 1987). a. Average views of negatively stained Rap1 molecules. b. Reprojections of the 3-D model of Rap1 15
16 using the angular reconstruction method (Van Heel 1987). a. Average views of negatively stained Rap1 molecules. b. Reprojections of the 3-D model of Rap1 corresponding to the views shown in (a). c. Three-dimensional envelope of the negatively stained Rap1 molecule. The structure of Rap1 shows a 2 lobed horseshoe shape structure. d. The 3-D envelope of Rap1 can be fitted into the additional density found on both sides of lobe B in TFIID-TFIIA-Rap1-DNA Complex II. The size and twolobed organization of Rap1 is similar to the additional density. The bar represents 59 nm in (a) and (b), 6 nm in (c) and 10 nm in (d). 16
17 Supplementary Figure 11. TFIIA point mutations affecting interaction with various activators. The atomic structure of TFIIA (Toa1, dark grey; Toa2, light grey), TBP (ochre), TATA DNA (dark green) and of the Rap1 DNA Binding Domain (dark red) were fitted into the additional density found in the TFIID-TFIIA-Rap1-DNA Complex II. TFIIA mutations that affect activation without interfering with TBP binding are highlighted in its structure (Ozer et al. 1996). Activation was tested with the following activators: Gal4-AH, Gal4-CTF, AP-1, Gal4-VP16 and Zta. The yeast equivalent of TFIIA mutations affecting interaction with all of these activators (Y10A and F71A) are colored red, those influencing only Zta interaction are depicted pink and a mutation that has no effect on Zta binding while abolishing interactions with all other activators are colored green. In yellow a triple mutation toa1-25 is depicted (K255A, R257A and K259A), which is defective for in vitro pol II transcription (Kang et al. 1995). 17
18 Supplementary Figure 12. TFIIA mutants affect DNA loop formation. Three TFIIA mutants were tested for DNA binding efficiency and loop formation within the TFIID- Rap1-TFIIA-DNA complex. The Toa2 mutants Y10A (human equivalent Y6A), F71A (human equivalent F67A) (Ozer et al. 1996) and toa1-25 (Kang et al. 1995) were reported to still bind TBP while being deficient in activated Pol II transcription. DNA 18
19 reported to still bind TBP while being deficient in activated Pol II transcription. DNA binding efficiency and loop formation was measured after platinum shadowing of the nucleoprotein complexes as described in the extended Material and Methods section. All DNA binding experiments were performed on the RPS1A promoter fragment with a TFIID: Rap1: TFIIA: DNA molar ratio of 1:5:5:10 for a. Table showing the proportion of TFIID molecules bound to DNA (DNA binding efficiency) and frequency of DNA loop formation of the TFIID-Rap1-DNA complex in the absence or presence of either wild type or mutant TFIIA. The data shows that the TFIID-Rap1 complex binds less efficiently to DNA in the absence (55%) than in the presence (83%) of wild type TFIIA. The DNA binding efficiency is only slightly restored using the mutant versions of TFIIA (around 65% for all mutants tested). DNA loop formation decreases from 36% to 19% when TFIIA is omitted. TFIIA containing the Toa1-25 and Toa2 F71A variant proteins behave similarly and show intermediate looping frequency, while Y10A is strongly impaired in loop formation. b. Histograms showing the size of the loops formed upon incubation of TFIID, Rap1, DNA without TFIIA (2) and in the presence of the wild type (1) or mutant (3 toa1-25; 4 Toa2-F71A; 5 Toa2-Y10A) TFIIA. All versions of TFIIA shows similar loop size distribution pattern with peaks corresponding to the distances between the Rap1 binding sites and the TA-rich regions on the RPS1A promoter (see Supplementary Figure 9), whereas these peaks disappear in the absence of TFIIA. 19
20 Supplementary references Bendjennat M, Weil P.A. (2008) The transcriptional repressor activator protein Rap1p is a direct regulator of TATA-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 283, Kang JJ, Auble DT, Ranish JA, Hahn S. (1995) Analysis of the yeast transcription factor TFIIA: distinct functional regions and a polymerase II-specific role in basal and activated transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 15: Klaholz BP, Myasnikov AG, Van Heel M. (2004) Visualization of release factor 3 on the ribosome during termination of protein synthesis. Nature 427, Liu WL, Coleman RA, Grob P, King DS, Florens L, Washburn MP, Geles KG, Yang JL, Ramey V, Nogales E, Tjian R. Structural changes in TAF4b-TFIID correlate with promoter selectivity. Mol. Cell 29, Ozer J, Bolden AH, Lieberman PM. (1996) Transcription factor IIA mutations show activator-specific defects and reveal a IIA function distinct from stimulation of TBP-DNA binding. J Biol Chem. 271, Van Heel M. (1987) Angular reconstitution: a posteriori assignment of projection directions for 3D reconstruction. Ultramicroscopy. 21, Van Heel M, Schatz M. (2005) Fourier shell correlation threshold criteria. J Struct Biol. 151,
Supplementary Online Material. Structural mimicry in transcription regulation of human RNA polymerase II by the. DNA helicase RECQL5
 Supplementary Online Material Structural mimicry in transcription regulation of human RNA polymerase II by the DNA helicase RECQL5 Susanne A. Kassube, Martin Jinek, Jie Fang, Susan Tsutakawa and Eva Nogales
Supplementary Online Material Structural mimicry in transcription regulation of human RNA polymerase II by the DNA helicase RECQL5 Susanne A. Kassube, Martin Jinek, Jie Fang, Susan Tsutakawa and Eva Nogales
Complex Transcription Machinery
 Complex Transcription Machinery Subunits of the Basal Txn Apparatus Stepwise Assembly of the Pre-initiation Complex Interplay of Activators, Co-regulators and RNA Polymerase at the Promoter Divide and
Complex Transcription Machinery Subunits of the Basal Txn Apparatus Stepwise Assembly of the Pre-initiation Complex Interplay of Activators, Co-regulators and RNA Polymerase at the Promoter Divide and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06147 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 The genomic and domain structure of Dscam. The Dscam gene comprises 24 exons, encoding a signal peptide (SP), 10 IgSF domains, 6 fibronectin
doi: 10.1038/nature06147 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 The genomic and domain structure of Dscam. The Dscam gene comprises 24 exons, encoding a signal peptide (SP), 10 IgSF domains, 6 fibronectin
Supplementary Figure 1 Two distinct conformational states of the HNH domain in crystal structures. a
 Supplementary Figure 1 Two distinct conformational states of the HNH domain in crystal structures. a HNH-state 1 in PDB 4OO8, in which the distance from the C atom of the HNH catalytic residue 840 to the
Supplementary Figure 1 Two distinct conformational states of the HNH domain in crystal structures. a HNH-state 1 in PDB 4OO8, in which the distance from the C atom of the HNH catalytic residue 840 to the
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Location of the mab 6F10 epitope in capsids.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Location of the mab 6F10 epitope in capsids. The epitope of monoclonal antibody, mab 6F10, was mapped to residues A862 H880 of the HSV-1 major capsid protein VP5 by immunoblotting
Supplementary Figure 1 Location of the mab 6F10 epitope in capsids. The epitope of monoclonal antibody, mab 6F10, was mapped to residues A862 H880 of the HSV-1 major capsid protein VP5 by immunoblotting
Electrophoresis and transfer
 Electrophoresis and transfer Electrophoresis Cation = positively charged ion, it moves toward the cathode (-) Anion = negatively charged ion, it moves toward the anode (+) Amphoteric substance = can have
Electrophoresis and transfer Electrophoresis Cation = positively charged ion, it moves toward the cathode (-) Anion = negatively charged ion, it moves toward the anode (+) Amphoteric substance = can have
Transcription Gene regulation
 Transcription Gene regulation The machine that transcribes a gene is composed of perhaps 50 proteins, including RNA polymerase, the enzyme that converts DNA code into RNA code. A crew of transcription
Transcription Gene regulation The machine that transcribes a gene is composed of perhaps 50 proteins, including RNA polymerase, the enzyme that converts DNA code into RNA code. A crew of transcription
Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription
 Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription Cis-acting sequences Distance-independent cis-acting elements Dissecting regulatory elements Transcription factors Overview transcriptional regulation Transcription
Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription Cis-acting sequences Distance-independent cis-acting elements Dissecting regulatory elements Transcription factors Overview transcriptional regulation Transcription
1 24 C63 C β- β-
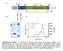 M40 Signal leaved RS1 Domain 59 110 142 Discoidin Domain 223 1 24 63 219 224 + - β- β- M M e e O O H H His 6 -Tag 250 150 100 75 50 37 * 25 20 Supplementary Figure 1 Purification of wild-type retinoschisin.
M40 Signal leaved RS1 Domain 59 110 142 Discoidin Domain 223 1 24 63 219 224 + - β- β- M M e e O O H H His 6 -Tag 250 150 100 75 50 37 * 25 20 Supplementary Figure 1 Purification of wild-type retinoschisin.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1: Suv39h1, but not Suv39h2, promotes HP1α sumoylation in vivo. In vivo HP1α sumoylation assay. Top: experimental scheme. Middle: we
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1: Suv39h1, but not Suv39h2, promotes HP1α sumoylation in vivo. In vivo HP1α sumoylation assay. Top: experimental scheme. Middle: we
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Impaired ITS2 processing results in mislocalization of foot-factors to the cytoplasm. (a) Schematic representation of ITS2 processing. The endonuclease Las1 initiates ITS2 processing
Supplementary Figure 1 Impaired ITS2 processing results in mislocalization of foot-factors to the cytoplasm. (a) Schematic representation of ITS2 processing. The endonuclease Las1 initiates ITS2 processing
Suppl. Figure 1: RCC1 sequence and sequence alignments. (a) Amino acid
 Supplementary Figures Suppl. Figure 1: RCC1 sequence and sequence alignments. (a) Amino acid sequence of Drosophila RCC1. Same colors are for Figure 1 with sequence of β-wedge that interacts with Ran in
Supplementary Figures Suppl. Figure 1: RCC1 sequence and sequence alignments. (a) Amino acid sequence of Drosophila RCC1. Same colors are for Figure 1 with sequence of β-wedge that interacts with Ran in
Supplementary Table 1: Antigenic regions/sites on Ebola-GP identified using GFPDL*
 Supplementary Table 1: Antigenic regions/sites on Ebola-GP identified using GFPDL* Site AA Sequence 3x10 6 3x10 6 20x10 6 20x10 6 100x10 6 100x10 6 Post-1 st Post-2 nd Post-1 st Post-2 nd Post-1 st Post-2
Supplementary Table 1: Antigenic regions/sites on Ebola-GP identified using GFPDL* Site AA Sequence 3x10 6 3x10 6 20x10 6 20x10 6 100x10 6 100x10 6 Post-1 st Post-2 nd Post-1 st Post-2 nd Post-1 st Post-2
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II.
 Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
Chromatographic Separation of the three forms of RNA Polymerase II. α-amanitin α-amanitin bound to Pol II Function of the three enzymes. Yeast Pol II. RNA Polymerase Subunit Structures 10-7 Subunit structure.
Supplemental Figure 1 Kam et al., 2017
 nti-zikv IgG response (OD 450 nm) % Infectivity (Relative to virus only) 3 2 1 2 0 1 0 0 8 0 6 0 1-H1L1 2F-H1L3 SIgN-3C SIgN-3C-LL 1 4 0 2 0 0 1-H1L1 2F-H1L3 SIgN-3C SIgN-3C -LL 0 0.1 1 1 0 1 0 0 [b],
nti-zikv IgG response (OD 450 nm) % Infectivity (Relative to virus only) 3 2 1 2 0 1 0 0 8 0 6 0 1-H1L1 2F-H1L3 SIgN-3C SIgN-3C-LL 1 4 0 2 0 0 1-H1L1 2F-H1L3 SIgN-3C SIgN-3C -LL 0 0.1 1 1 0 1 0 0 [b],
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #1 March 12, 2002
 Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #1 March 12, 2002 Name KEY SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number.
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #1 March 12, 2002 Name KEY SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number.
Rat IGF-1 ELISA Kit (rigf-1-elisa)
 Rat IGF-1 ELISA Kit (rigf-1-elisa) Cat. No. EK0377 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also known as somatomedin C, is a polypeptide protein hormone similar
Rat IGF-1 ELISA Kit (rigf-1-elisa) Cat. No. EK0377 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also known as somatomedin C, is a polypeptide protein hormone similar
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12119 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND LEGENDS pre-let-7a- 1 +14U pre-let-7a- 1 Ddx3x Dhx30 Dis3l2 Elavl1 Ggt5 Hnrnph 2 Osbpl5 Puf60 Rnpc3 Rpl7 Sf3b3 Sf3b4 Tia1 Triobp U2af1 U2af2 1 6 2 4 3
doi:10.1038/nature12119 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND LEGENDS pre-let-7a- 1 +14U pre-let-7a- 1 Ddx3x Dhx30 Dis3l2 Elavl1 Ggt5 Hnrnph 2 Osbpl5 Puf60 Rnpc3 Rpl7 Sf3b3 Sf3b4 Tia1 Triobp U2af1 U2af2 1 6 2 4 3
Recruitment of Grb2 to surface IgG and IgE provides antigen receptor-intrinsic costimulation to class-switched B cells
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Recruitment of Grb2 to surface IgG and IgE provides antigen receptor-intrinsic costimulation to class-switched B cells Niklas Engels, Lars Morten König, Christina Heemann, Johannes
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Recruitment of Grb2 to surface IgG and IgE provides antigen receptor-intrinsic costimulation to class-switched B cells Niklas Engels, Lars Morten König, Christina Heemann, Johannes
Structural basis of a novel PD-L1 nanobody for immune checkpoint blockade
 Structural basis of a novel PD-L1 nanobody for immune checkpoint blockade Supplementary Materials Supplementary methods Table S1-S Figure S1-S 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 Supplementary Methods Competitive
Structural basis of a novel PD-L1 nanobody for immune checkpoint blockade Supplementary Materials Supplementary methods Table S1-S Figure S1-S 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 Supplementary Methods Competitive
human Cdc45 Figure 1c. (c)
 1 Details of the refined crystallographic model of human Cdc45 and comparison of its active-site region with that of bacterial RecJ. (a) Stereo view of a representative example of the final 2F o -F c electron
1 Details of the refined crystallographic model of human Cdc45 and comparison of its active-site region with that of bacterial RecJ. (a) Stereo view of a representative example of the final 2F o -F c electron
For quantitative detection of mouse IGF-1 in serum, body fluids, tissue lysates or cell culture supernatants.
 Mouse IGF-1 ELISA Kit (migf-1-elisa) Cat. No. EK0378 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also known as somatomedin C, is a polypeptide protein hormone similar
Mouse IGF-1 ELISA Kit (migf-1-elisa) Cat. No. EK0378 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also known as somatomedin C, is a polypeptide protein hormone similar
RNP purification, components and activity.
 Supplementary Figure 1 RNP purification, components and activity. (a) Intein-mediated RNP production and purification. The Ll.LtrB intron RNA (red) (Exons E1 and E2 in green) and associated intron encoded
Supplementary Figure 1 RNP purification, components and activity. (a) Intein-mediated RNP production and purification. The Ll.LtrB intron RNA (red) (Exons E1 and E2 in green) and associated intron encoded
HEK293T. Fig. 1 in the
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Zinc uptake assay of hzip4 and hzip4-δecd transiently expressed in HEK293T cells. The results of one representative e experiment are shown in Fig. 1 in
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Zinc uptake assay of hzip4 and hzip4-δecd transiently expressed in HEK293T cells. The results of one representative e experiment are shown in Fig. 1 in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Results Construct purification and coupling. Two A1-GP1bα ReaLiSM constructs, with and without cysteine residues near the N and C-termini (Fig. S2a), were expressed and purified by Ni affinity chromatography
Results Construct purification and coupling. Two A1-GP1bα ReaLiSM constructs, with and without cysteine residues near the N and C-termini (Fig. S2a), were expressed and purified by Ni affinity chromatography
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or
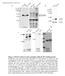 Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature21393 SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT SpMED Immuno-purification and subunit localization Wild-type and subunit deletion mutant SpMEDs (Extended Data Table 1) were immunopurified through TAP-tagged
doi:10.1038/nature21393 SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT SpMED Immuno-purification and subunit localization Wild-type and subunit deletion mutant SpMEDs (Extended Data Table 1) were immunopurified through TAP-tagged
Supplementary Figure 1 PZA inhibits root hair formation as well as cell elongation in the maturation zone of eto1-2 roots. (A) The PI staining of the
 Supplementary Figure 1 PZA inhibits root hair formation as well as cell elongation in the maturation zone of eto1-2 roots. (A) The PI staining of the roots of three-day-old etiolated seedlings of Col-0
Supplementary Figure 1 PZA inhibits root hair formation as well as cell elongation in the maturation zone of eto1-2 roots. (A) The PI staining of the roots of three-day-old etiolated seedlings of Col-0
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Rahmeh et al. 1.173/pnas.1914719 SI Materials and Methods Protein Expression and Purification. was expressed in Sf1 cells with an N-terminal 6xHis tag and purified by Ni- nitrilotriacetic
Supporting Information Rahmeh et al. 1.173/pnas.1914719 SI Materials and Methods Protein Expression and Purification. was expressed in Sf1 cells with an N-terminal 6xHis tag and purified by Ni- nitrilotriacetic
Transcription in Eukaryotes
 Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11500 Figure S1: The sector in the PDZ domain family. Sectors are defined as groups of statistically coevolving amino acid positions in a protein family and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11500 Figure S1: The sector in the PDZ domain family. Sectors are defined as groups of statistically coevolving amino acid positions in a protein family and
Molecular design principles underlying β-strand swapping. in the adhesive dimerization of cadherins
 Supplementary information for: Molecular design principles underlying β-strand swapping in the adhesive dimerization of cadherins Jeremie Vendome 1,2,3,5, Shoshana Posy 1,2,3,5,6, Xiangshu Jin, 1,3 Fabiana
Supplementary information for: Molecular design principles underlying β-strand swapping in the adhesive dimerization of cadherins Jeremie Vendome 1,2,3,5, Shoshana Posy 1,2,3,5,6, Xiangshu Jin, 1,3 Fabiana
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Mechanism for signal-induced opening of the DNA box. a, An atomic model of the DNA box held closed by locks (orange and blue) that are double helices formed by two short strands
Supplementary Figure 1. Mechanism for signal-induced opening of the DNA box. a, An atomic model of the DNA box held closed by locks (orange and blue) that are double helices formed by two short strands
Minicollagen cysteine-rich domains encode distinct modes of. Anja Tursch, Davide Mercadante, Jutta Tennigkeit, Frauke Gräter and Suat
 Supplementary Figure S1. Conformational dynamics of partially reduced CRDs. (A) Root mean square deviation (RMSD) and (B) radius of gyration (R G ) distributions for the N-CRD (green) and C-CRD (red) domains,
Supplementary Figure S1. Conformational dynamics of partially reduced CRDs. (A) Root mean square deviation (RMSD) and (B) radius of gyration (R G ) distributions for the N-CRD (green) and C-CRD (red) domains,
Supplementary Figure 1 Telomerase RNA fragments used in single-molecule FRET experiments. A pseudoknot fragment (nts ) labeled at position U42
 Supplementary Figure 1 Telomerase RNA fragments used in single-molecule FRET experiments. A pseudoknot fragment (nts 32-195) labeled at position U42 with Cy3 (green circle) was constructed by a two piece
Supplementary Figure 1 Telomerase RNA fragments used in single-molecule FRET experiments. A pseudoknot fragment (nts 32-195) labeled at position U42 with Cy3 (green circle) was constructed by a two piece
Solutions to 7.02 Quiz II 10/27/05
 Solutions to 7.02 Quiz II 10/27/05 Class Average = 83 Standard Deviation = 9 Range Grade % 87-100 A 43 74-86 B 39 55-73 C 17 > 54 D 1 Question 1 (56 points) While studying deep sea bacteria, you discover
Solutions to 7.02 Quiz II 10/27/05 Class Average = 83 Standard Deviation = 9 Range Grade % 87-100 A 43 74-86 B 39 55-73 C 17 > 54 D 1 Question 1 (56 points) While studying deep sea bacteria, you discover
Coleman et al., Supplementary Figure 1
 Coleman et al., Supplementary Figure 1 BrdU Merge G1 Early S Mid S Supplementary Figure 1. Sequential destruction of CRL4 Cdt2 targets during the G1/S transition. HCT116 cells were synchronized by sequential
Coleman et al., Supplementary Figure 1 BrdU Merge G1 Early S Mid S Supplementary Figure 1. Sequential destruction of CRL4 Cdt2 targets during the G1/S transition. HCT116 cells were synchronized by sequential
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription. RNA polymerases
 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Transcription RNA polymerases RNA Polymerases A. E. coli RNA polymerase 1. core enzyme = ββ'(α)2 has catalytic activity but cannot recognize start site of transcription ~500,000
Supplementary Figure 1. Two activation pathways and four conformations of β 2 integrins. KIM127 (red) can specifically detect
 Supplementary Figure 1 Two activation pathways and four conformations of β 2 integrins. KIM127 (red) can specifically detect integrin extension (E + ) and mab24 (green) can specifically detect headpiece-opening
Supplementary Figure 1 Two activation pathways and four conformations of β 2 integrins. KIM127 (red) can specifically detect integrin extension (E + ) and mab24 (green) can specifically detect headpiece-opening
Supplementatry Fig 1. Domain structure, biophysical characterisation and electron microscopy of a TD. (a) XTACC3/Maskin and XMAP215/chTOG domain
 Supplementatry Fig 1. Domain structure, biophysical characterisation and electron microscopy of a TD. (a) XTACC3/Maskin and XMAP215/chTOG domain architecture. Various C-terminal fragments were cloned and
Supplementatry Fig 1. Domain structure, biophysical characterisation and electron microscopy of a TD. (a) XTACC3/Maskin and XMAP215/chTOG domain architecture. Various C-terminal fragments were cloned and
Figure S6. Detection of anti-gfp antibodies in anti-dna and normal plasma without competition DNA--9
 Supplementary Information Ultrasensitive antibody detection by agglutination-pcr (ADAP) Cheng-ting Tsai 1 *, Peter V. Robinson 1 *, Carole A. Spencer 2 and Carolyn R. Bertozzi 3,4ǂ Department of 1 Chemistry,
Supplementary Information Ultrasensitive antibody detection by agglutination-pcr (ADAP) Cheng-ting Tsai 1 *, Peter V. Robinson 1 *, Carole A. Spencer 2 and Carolyn R. Bertozzi 3,4ǂ Department of 1 Chemistry,
Eukaryotic Transcription
 Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
Supplementary Table 1. DNA sequence synthesized to express the Zika virus NS5 protein.
 Supplementary Table 1. DNA sequence synthesized to express the Zika virus NS5 protein. MR766 NS5 sequence 1 ACAGAGAACAGATTGGTGGTGGAGGTGGGACGGGAGAGACTCTGGGAGAGAAGTGGAAAG 61 CTCGTCTGAATCAGATGTCGGCCCTGGAGTTCTACTCTTATAAAAAGTCAGGTATCACTG
Supplementary Table 1. DNA sequence synthesized to express the Zika virus NS5 protein. MR766 NS5 sequence 1 ACAGAGAACAGATTGGTGGTGGAGGTGGGACGGGAGAGACTCTGGGAGAGAAGTGGAAAG 61 CTCGTCTGAATCAGATGTCGGCCCTGGAGTTCTACTCTTATAAAAAGTCAGGTATCACTG
Supplementary Fig. 1. Initial electron density maps for the NOX-D20:mC5a complex obtained after SAD-phasing. (a) Initial experimental electron
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Initial electron density maps for the NOX-D20:mC5a complex obtained after SAD-phasing. (a) Initial experimental electron density map obtained after SAD-phasing and density modification
Supplementary Fig. 1. Initial electron density maps for the NOX-D20:mC5a complex obtained after SAD-phasing. (a) Initial experimental electron density map obtained after SAD-phasing and density modification
The molecular basis of lysine 48 ubiquitin chain synthesis by Ube2K
 Supplementary Information The molecular basis of lysine 48 ubiquitin chain synthesis by Adam J. Middleton, Catherine L. Day* Department of Biochemistry, Otago School of Medical Sciences, University of
Supplementary Information The molecular basis of lysine 48 ubiquitin chain synthesis by Adam J. Middleton, Catherine L. Day* Department of Biochemistry, Otago School of Medical Sciences, University of
Conformation of the Mineralocorticoid Receptor N- terminal Domain: Evidence for Induced and Stable Structure
 ME-10-0005 Conformation of the Mineralocorticoid Receptor N- terminal Domain: Evidence for Induced and Stable Structure Katharina Fischer 1, Sharon M. Kelly 2, Kate Watt 1, Nicholas C. Price 2 and Iain
ME-10-0005 Conformation of the Mineralocorticoid Receptor N- terminal Domain: Evidence for Induced and Stable Structure Katharina Fischer 1, Sharon M. Kelly 2, Kate Watt 1, Nicholas C. Price 2 and Iain
Reduced structural flexibility for exonuclease deficient DNA polymerase III mutant
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2018 Reduced structural flexibility for exonuclease deficient DNA polymerase III mutant
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2018 Reduced structural flexibility for exonuclease deficient DNA polymerase III mutant
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Molecular basis of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase II activity Elisabeth Lehmann, Florian Brueckner, and Patrick Cramer Gene Center Munich and Center for integrated Protein Science CiPS M, Department of Chemistry
Molecular basis of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase II activity Elisabeth Lehmann, Florian Brueckner, and Patrick Cramer Gene Center Munich and Center for integrated Protein Science CiPS M, Department of Chemistry
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1. Crystallographic statistics CRM1-SNUPN complex Space group P6 4 22 a=b=250.4, c=190.4 Data collection statistics: CRM1-selenomethionine SNUPN MAD data Peak Inflection Remote Native
Supplementary Table 1. Crystallographic statistics CRM1-SNUPN complex Space group P6 4 22 a=b=250.4, c=190.4 Data collection statistics: CRM1-selenomethionine SNUPN MAD data Peak Inflection Remote Native
Figure S1. Verification of ihog Mutation by Protein Immunoblotting Figure S2. Verification of ihog and boi
 Figure S1. Verification of ihog Mutation by Protein Immunoblotting Extracts from S2R+ cells, embryos, and adults were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with anti-ihog antibody. The Ihog
Figure S1. Verification of ihog Mutation by Protein Immunoblotting Extracts from S2R+ cells, embryos, and adults were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with anti-ihog antibody. The Ihog
PDIP46 (DNA polymerase δ interacting protein 46) is an activating factor for human DNA polymerase δ
 PDIP46 (DNA polymerase δ interacting protein 46) is an activating factor for human DNA polymerase δ Supplementary Material Figure S1. PDIP46 is associated with Pol isolated by immunoaffinity chromatography.
PDIP46 (DNA polymerase δ interacting protein 46) is an activating factor for human DNA polymerase δ Supplementary Material Figure S1. PDIP46 is associated with Pol isolated by immunoaffinity chromatography.
However, only a fraction of these genes are transcribed in an individual cell at any given time.
 All cells in an organism contain the same set of genes. However, only a fraction of these genes are transcribed in an individual cell at any given time. It is the pattern of gene expression that determines
All cells in an organism contain the same set of genes. However, only a fraction of these genes are transcribed in an individual cell at any given time. It is the pattern of gene expression that determines
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3428
 Supplementary Figure 1 Biochemical characterization of the monou and oligou activity switch of TUT4(7). (a) Mouse TUT4 and human TUT7 were assayed for monou and Lin28-dependent oligou addition activities
Supplementary Figure 1 Biochemical characterization of the monou and oligou activity switch of TUT4(7). (a) Mouse TUT4 and human TUT7 were assayed for monou and Lin28-dependent oligou addition activities
Supplementary Fig. 1
 a FL (1-2266) NL (1-1190) CL (1191-2266) HA-ICE1: - HA-ICE1: - - - FLAG-ICE2: + + + + FLAG-ELL: + + + + + + IP: anti-ha FLAG-ICE2 HA-ICE1-FL HA-ICE1-NL HA-ICE1-CL FLAG-ICE2 b IP: anti-ha FL (1-2266) NL
a FL (1-2266) NL (1-1190) CL (1191-2266) HA-ICE1: - HA-ICE1: - - - FLAG-ICE2: + + + + FLAG-ELL: + + + + + + IP: anti-ha FLAG-ICE2 HA-ICE1-FL HA-ICE1-NL HA-ICE1-CL FLAG-ICE2 b IP: anti-ha FL (1-2266) NL
Supplementary Figure 1. Serial deletion mutants of BLITz.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Serial deletion mutants of BLITz. (a) Design of TEVseq insertion into J -helix. C-terminal end of J -helix was serially deleted and replaced by TEVseq. TEV cleavage site is labeled
Supplementary Figure 1 Serial deletion mutants of BLITz. (a) Design of TEVseq insertion into J -helix. C-terminal end of J -helix was serially deleted and replaced by TEVseq. TEV cleavage site is labeled
Colchicine. Colchicine. a b c d e
 α1-tub Colchicine Laulimalide RB3 β1-tub Vinblastine α2-tub Taxol Colchicine β2-tub Maytansine a b c d e Supplementary Figure 1 Structures of microtubule and tubulin (a)the cartoon of head to tail arrangement
α1-tub Colchicine Laulimalide RB3 β1-tub Vinblastine α2-tub Taxol Colchicine β2-tub Maytansine a b c d e Supplementary Figure 1 Structures of microtubule and tubulin (a)the cartoon of head to tail arrangement
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary figures and supplementary tables. File name: Peer review file Description:
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary figures and supplementary tables. File name: Peer review file Description: Supplementary Figure 1. dcas9-mq1 fusion protein induces de novo
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary figures and supplementary tables. File name: Peer review file Description: Supplementary Figure 1. dcas9-mq1 fusion protein induces de novo
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
M1 - Biochemistry. Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I
 M1 - Biochemistry Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I PH Ratz, PhD (Resources: Lehninger et al., 5th ed., Chapters 8, 24 & 26) 1 Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I Learning Objectives: 1.
M1 - Biochemistry Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I PH Ratz, PhD (Resources: Lehninger et al., 5th ed., Chapters 8, 24 & 26) 1 Nucleic Acid Structure II/Transcription I Learning Objectives: 1.
Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than. SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with
 Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with concentration of 800nM) were incubated with 1mM dgtp for the indicated
Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with concentration of 800nM) were incubated with 1mM dgtp for the indicated
TITLE: Restoration of Wild-Type Activity to Mutant p53 in Prostate Cancer: A Novel Therapeutic Approach
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0109 TITLE: Restoration of Wild-Type Activity to Mutant p53 in Prostate Cancer: A Novel Therapeutic Approach PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: James Manfredi, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0109 TITLE: Restoration of Wild-Type Activity to Mutant p53 in Prostate Cancer: A Novel Therapeutic Approach PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: James Manfredi, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
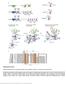 Supplementary Figure 1 Domain architecture and conformational states of the decapping complex, as revealed by structural studies. (a) Domain organization of Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sp) and Saccharomyces
Supplementary Figure 1 Domain architecture and conformational states of the decapping complex, as revealed by structural studies. (a) Domain organization of Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sp) and Saccharomyces
BIO 101 : The genetic code and the central dogma
 BIO 101 : The genetic code and the central dogma NAME Objectives The purpose of this exploration is to... 1. design experiments to decipher the genetic code; 2. visualize the process of protein synthesis;
BIO 101 : The genetic code and the central dogma NAME Objectives The purpose of this exploration is to... 1. design experiments to decipher the genetic code; 2. visualize the process of protein synthesis;
Supplementary Figure 1. Electron microscopy of gb-698glyco/1g2 Fab complex. a)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Electron microscopy of gb-698glyco/1g2 Fab complex. a) Representative images of 2D class averages of gb-698glyc bound to 1G2 Fab. Top views of the complex were underrepresented
Supplementary Figure 1. Electron microscopy of gb-698glyco/1g2 Fab complex. a) Representative images of 2D class averages of gb-698glyc bound to 1G2 Fab. Top views of the complex were underrepresented
Supplementary Figure 1. Botrocetin induces binding of human VWF to human
 Supplementary Figure 1: Supplementary Figure 1. Botrocetin induces binding of human VWF to human platelets in the absence of elevated shear and induces platelet agglutination as detected by flow cytometry.
Supplementary Figure 1: Supplementary Figure 1. Botrocetin induces binding of human VWF to human platelets in the absence of elevated shear and induces platelet agglutination as detected by flow cytometry.
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Study of mgtl translation in vitro. (A) Detection of 5 LR RNA using wild-type and anti-sd (91-95) substituted templates in a transcription-translation
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Study of mgtl translation in vitro. (A) Detection of 5 LR RNA using wild-type and anti-sd (91-95) substituted templates in a transcription-translation
Stargazin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through adaptor protein. complexes during long term depression
 Supplementary Information Stargazin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through adaptor protein complexes during long term depression Shinji Matsuda, Wataru Kakegawa, Timotheus Budisantoso, Toshihiro Nomura,
Supplementary Information Stargazin regulates AMPA receptor trafficking through adaptor protein complexes during long term depression Shinji Matsuda, Wataru Kakegawa, Timotheus Budisantoso, Toshihiro Nomura,
JCB. Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY. Hong et al.,
 Supplemental material JCB Hong et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201412127/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Analysis of purified proteins by SDS-PAGE and pull-down assays. (A) Coomassie-stained
Supplemental material JCB Hong et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201412127/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Analysis of purified proteins by SDS-PAGE and pull-down assays. (A) Coomassie-stained
Supplementary Information for. Regulation of Rev1 by the Fanconi Anemia Core Complex
 Supplementary Information for Regulation of Rev1 by the Fanconi Anemia Core Complex Hyungjin Kim, Kailin Yang, Donniphat Dejsuphong, Alan D. D Andrea* *Corresponding Author: Alan D. D Andrea, M.D. Alan_dandrea@dfci.harvard.edu
Supplementary Information for Regulation of Rev1 by the Fanconi Anemia Core Complex Hyungjin Kim, Kailin Yang, Donniphat Dejsuphong, Alan D. D Andrea* *Corresponding Author: Alan D. D Andrea, M.D. Alan_dandrea@dfci.harvard.edu
S156AT168AY175A (AAA) were purified as GST-fusion proteins and incubated with GSTfused
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Supplemental Materials Supplemental Figure S1 (a) Phenotype of the wild type and grik1-2 grik2-1 plants after 8 days in darkness.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 Supplemental Materials Supplemental Figure S1 (a) Phenotype of the wild type and grik1-2 grik2-1 plants after 8 days in darkness.
Figure S1 is related to Figure 1B, showing more details of outer segment of
 Supplemental Information Supplementary Figure legends and Figures Figure S1. Electron microscopic images in Sema4A +/+ and Sema4A / retinas Figure S1 is related to Figure 1B, showing more details of outer
Supplemental Information Supplementary Figure legends and Figures Figure S1. Electron microscopic images in Sema4A +/+ and Sema4A / retinas Figure S1 is related to Figure 1B, showing more details of outer
fibrils, however, oligomeric structures and amorphous protein aggregates were
 Supplementary Figure 1: Effect of equimolar EGCG on αs and Aβ aggregate formation. A D B E αs C F Figure S1: (A-C) Analysis of EGCG treated αs (1 µm) aggregation reactions by EM. A 1:1 molar ratio of EGCG
Supplementary Figure 1: Effect of equimolar EGCG on αs and Aβ aggregate formation. A D B E αs C F Figure S1: (A-C) Analysis of EGCG treated αs (1 µm) aggregation reactions by EM. A 1:1 molar ratio of EGCG
Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of HSA mutants to hfcrn. (a) The levels of titrated amounts of HSA
 Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of HSA mutants to hfcrn. (a) The levels of titrated amounts of HSA variants (5.0-0.002 μg/ml) directly coated in the wells at ph 6.0 were controlled using a horseradish
Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of HSA mutants to hfcrn. (a) The levels of titrated amounts of HSA variants (5.0-0.002 μg/ml) directly coated in the wells at ph 6.0 were controlled using a horseradish
Discovery and Humanization of Novel High Affinity Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies to Human IL-17A
 Discovery and Humanization of Novel High Affinity Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies to Human IL-17A Contacts: Marty Simonetti martysimonetti@gmail.com Kirby Alton kirby.alton@abeomecorp.com Rick Shimkets
Discovery and Humanization of Novel High Affinity Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies to Human IL-17A Contacts: Marty Simonetti martysimonetti@gmail.com Kirby Alton kirby.alton@abeomecorp.com Rick Shimkets
Conformational changes in IgE contribute to its. uniquely slow dissociation rate from receptor FcεRI
 Conformational changes in IgE contribute to its uniquely slow dissociation rate from receptor FcεRI M.D. Holdom, A.M. Davies, J.E. Nettleship, S.C. Bagby, B. Dhaliwal, E. Girardi, J. Hunt, H.J. Gould,
Conformational changes in IgE contribute to its uniquely slow dissociation rate from receptor FcεRI M.D. Holdom, A.M. Davies, J.E. Nettleship, S.C. Bagby, B. Dhaliwal, E. Girardi, J. Hunt, H.J. Gould,
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Origin use and efficiency are similar among WT, rrm3, pif1-m2, and pif1-m2; rrm3 strains. A. Analysis of fork progression around confirmed and likely origins (from cerevisiae.oridb.org).
Supplementary Figure 1 Origin use and efficiency are similar among WT, rrm3, pif1-m2, and pif1-m2; rrm3 strains. A. Analysis of fork progression around confirmed and likely origins (from cerevisiae.oridb.org).
Rat Laminin ELISA Kit (rlaminin-elisa)
 Rat Laminin ELISA Kit (rlaminin-elisa) Cat. No. EK0435 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Laminin is a large basement membrane glycoprotein composed of three subunits designated the A, B1,
Rat Laminin ELISA Kit (rlaminin-elisa) Cat. No. EK0435 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Laminin is a large basement membrane glycoprotein composed of three subunits designated the A, B1,
WT R72A DS91AA R116A T121A WT W36A F109A WT D91A S92A D169A Q170A
 R72A DS91AA R116A T121A W36A F109A D91A S92A D169A Q170A (Kb) 10 8 6 5 4 3 2 1 0.75 0.5 0.25 Supplementary Fig. 1. Effects of Candida EST3 mutations on telomere lengths. Telomeres from successive streaks
R72A DS91AA R116A T121A W36A F109A D91A S92A D169A Q170A (Kb) 10 8 6 5 4 3 2 1 0.75 0.5 0.25 Supplementary Fig. 1. Effects of Candida EST3 mutations on telomere lengths. Telomeres from successive streaks
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Cell-free translation is more variable than transcription Fabio Chizzolini, Michele Forlin, Noël Yeh Martín, Giuliano Berloffa, Dario Cecchi, and Sheref S. Mansy Deposited DNA sequences
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Cell-free translation is more variable than transcription Fabio Chizzolini, Michele Forlin, Noël Yeh Martín, Giuliano Berloffa, Dario Cecchi, and Sheref S. Mansy Deposited DNA sequences
Immunological Applications. Chapter 8: Background
 Immunological Applications Chapter 8: Background The Immune System Types of Immunity Innate The natural immunity present at birth Acquired A specific response to foreign substances. Some cells remember
Immunological Applications Chapter 8: Background The Immune System Types of Immunity Innate The natural immunity present at birth Acquired A specific response to foreign substances. Some cells remember
Supplemental Figure 1.
 Supplemental Data. Charron et al. Dynamic landscapes of four histone modifications during de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell (2009). 10.1105/tpc.109.066845 Supplemental Figure 1. Immunodetection
Supplemental Data. Charron et al. Dynamic landscapes of four histone modifications during de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell (2009). 10.1105/tpc.109.066845 Supplemental Figure 1. Immunodetection
Proteomics 6/4/2009 WESTERN BLOT ANALYSIS
 SDS-PAGE (PolyAcrylamide Gel Electrophoresis) Proteomics WESTERN BLOT ANALYSIS Presented by: Nuvee Prapasarakul Veterinary Microbiology Chulalongkorn University Proteomics has been said to be the next
SDS-PAGE (PolyAcrylamide Gel Electrophoresis) Proteomics WESTERN BLOT ANALYSIS Presented by: Nuvee Prapasarakul Veterinary Microbiology Chulalongkorn University Proteomics has been said to be the next
Prior to structural analysis by EM we characterised recombinant Geminin for its DNA
 Supplementary Data Functional characterisation of recombinant human Geminin Prior to structural analysis by EM we characterised recombinant Geminin for its DNA replication inhibition activity in the cell-free
Supplementary Data Functional characterisation of recombinant human Geminin Prior to structural analysis by EM we characterised recombinant Geminin for its DNA replication inhibition activity in the cell-free
Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 )
 Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 ) homologous recombination arm (left) and of the right (3 )
Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 ) homologous recombination arm (left) and of the right (3 )
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures 1-8
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figures 1-8 Supplementary Figure 1. TFAM residues contacting the DNA minor groove (A) TFAM contacts on nonspecific DNA. Leu58, Ile81, Asn163, Pro178, and Leu182
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figures 1-8 Supplementary Figure 1. TFAM residues contacting the DNA minor groove (A) TFAM contacts on nonspecific DNA. Leu58, Ile81, Asn163, Pro178, and Leu182
Supplementary Fig. 1 Identification of Nedd4 as an IRS-2-associated protein in camp-treated FRTL-5 cells.
 Supplementary Fig. 1 Supplementary Fig. 1 Identification of Nedd4 as an IRS-2-associated protein in camp-treated FRTL-5 cells. (a) FRTL-5 cells were treated with 1 mm dibutyryl camp for 24 h, and the lysates
Supplementary Fig. 1 Supplementary Fig. 1 Identification of Nedd4 as an IRS-2-associated protein in camp-treated FRTL-5 cells. (a) FRTL-5 cells were treated with 1 mm dibutyryl camp for 24 h, and the lysates
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Schematics of SAM, dcas9-suntag and dcas9-vpr.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematics of SAM, dcas9-suntag and dcas9-vpr. (a) Schematics of SAM. SAM consists of two chimeric proteins, dcas9 fused with VP64 and MS2-coat protein fused with p65 and HSF1 activator
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematics of SAM, dcas9-suntag and dcas9-vpr. (a) Schematics of SAM. SAM consists of two chimeric proteins, dcas9 fused with VP64 and MS2-coat protein fused with p65 and HSF1 activator
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.2996
 Supplementary Figure 1 Negative-stain EM of native cytoplasmic dynein. (a) A representative micrograph of negatively stained dynein, with the flexible dimeric molecules circled in white. (b) Reference-free
Supplementary Figure 1 Negative-stain EM of native cytoplasmic dynein. (a) A representative micrograph of negatively stained dynein, with the flexible dimeric molecules circled in white. (b) Reference-free
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells
 Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3018
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of genetic complementation assay in Bmal1 / Per2 Luc fibroblasts. (a) Only Bmal1, not Bmal2, rescues circadian rhythms from cells. Cells expressing various Bmal constructs
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of genetic complementation assay in Bmal1 / Per2 Luc fibroblasts. (a) Only Bmal1, not Bmal2, rescues circadian rhythms from cells. Cells expressing various Bmal constructs
IgG1 (Human) ELISA Kit
 IgG1 (Human) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA1730 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General
IgG1 (Human) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA1730 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General
Supplementary Table 1: List of CH3 domain interface residues in the first chain (A) and
 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1: List of CH3 domain interface residues in the first chain (A) and their side chain contacting residues in the second chain (B) a Interface Res. in Contacting
Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1: List of CH3 domain interface residues in the first chain (A) and their side chain contacting residues in the second chain (B) a Interface Res. in Contacting
This is the author's accepted version of the manuscript.
 This is the author's accepted version of the manuscript. The definitive version is published in Nature Communications Online Edition: 2015/4/16 (Japan time), doi:10.1038/ncomms7780. The final version published
This is the author's accepted version of the manuscript. The definitive version is published in Nature Communications Online Edition: 2015/4/16 (Japan time), doi:10.1038/ncomms7780. The final version published
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.10 TRANSCRIPTION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF TRANSCRIPTION Transcription is the process of using DNA as a template to RNA RNA polymerase is the enzyme that transcribes DNA - There are many different types
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF TRANSCRIPTION Transcription is the process of using DNA as a template to RNA RNA polymerase is the enzyme that transcribes DNA - There are many different types
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of migg1-yf mice. (A) Targeting strategy. Upper panel: schematic organization of the murine ɣ1 immunoglobulin
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of migg1-yf mice. (A) Targeting strategy. Upper panel: schematic organization of the murine ɣ1 immunoglobulin locus. The EcoRI restriction site between exons M1 and M2
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of migg1-yf mice. (A) Targeting strategy. Upper panel: schematic organization of the murine ɣ1 immunoglobulin locus. The EcoRI restriction site between exons M1 and M2
ALP (alkaline phosphatase) calibrators were analyzed manually in microtiter plates to find the linearity range by following this protocol:
 Exam Mol 3008 May 2009 Subject 1 (15p) ALP (alkaline phosphatase) calibrators were analyzed manually in microtiter plates to find the linearity range by following this protocol: Reaction solutions: 50
Exam Mol 3008 May 2009 Subject 1 (15p) ALP (alkaline phosphatase) calibrators were analyzed manually in microtiter plates to find the linearity range by following this protocol: Reaction solutions: 50
Different Upstream Activators Stimulate Transcription Through Distinct Coactivator Complexes
 Supplemental Material for Different Upstream Activators Stimulate Transcription Through Distinct Coactivator Complexes Dong-ki Lee, Soyoun Kim, and John T. Lis Due to be published as a Research Communication
Supplemental Material for Different Upstream Activators Stimulate Transcription Through Distinct Coactivator Complexes Dong-ki Lee, Soyoun Kim, and John T. Lis Due to be published as a Research Communication
Module 2 overview SPRING BREAK
 1 Module 2 overview lecture lab 1. Introduction to the module 1. Start-up protein eng. 2. Rational protein design 2. Site-directed mutagenesis 3. Fluorescence and sensors 3. DNA amplification 4. Protein
1 Module 2 overview lecture lab 1. Introduction to the module 1. Start-up protein eng. 2. Rational protein design 2. Site-directed mutagenesis 3. Fluorescence and sensors 3. DNA amplification 4. Protein
Supplemental Information. Plk1/Polo Phosphorylates Sas-4 at the Onset. of Mitosis for an Efficient Recruitment
 Cell Reports, Volume 25 Supplemental Information Plk1/Polo Phosphorylates Sas-4 at the Onset of Mitosis for an Efficient Recruitment of Pericentriolar Material to Centrosomes Anand Ramani, Aruljothi Mariappan,
Cell Reports, Volume 25 Supplemental Information Plk1/Polo Phosphorylates Sas-4 at the Onset of Mitosis for an Efficient Recruitment of Pericentriolar Material to Centrosomes Anand Ramani, Aruljothi Mariappan,
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Table of Content: Supplementary Results... 2 Supplementary Figure S1: Experimental validation of AP-MS results by coimmunprecipitation Western blot analysis.... 3 Supplementary
Supplementary information Table of Content: Supplementary Results... 2 Supplementary Figure S1: Experimental validation of AP-MS results by coimmunprecipitation Western blot analysis.... 3 Supplementary
