Purification of RNA from populations of hescs and bulk purified RNA.
|
|
|
- Maximillian Banks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure 1 Purification of RNA from populations of hescs and bulk purified RNA. (a) Schematic of the experiment comparing a modified RNA harvesting protocol to standard RNA purification protocol using live or fixed, stained and sorted H1 hes populations. Live or fixed and permeabilized cells were stained with DAPI, and RNA was harvested using either the Qiagen microrneasy Kit (RLT), or using a modified fixed cell method with protease lysis and reverse crosslinking (PLRC). (b) Representative Bioanalyzer traces showing column purified total RNA from 10,000, 1,000, and 100 live or fixed, permeabilized and DAPI-stained H1 hescs with or without reverse-crosslinking (Fixed and Live, respectively). Samples were diluted or concentrated so 66 cell equivalents were loaded per lane. (c) Comparison of gene expression between RNeasy columns and dt25 bead RNA purification techniques by qrt-pcr. Input samples were Human Brain Total RNA (white) and fixed H1 hescs (gray). Data are from 5-6 biological replicates in at least 5 independent experiments, genes were only assessed if they we present in at least 3 samples.
2
3 Supplementary Figure 2 Evaluation of FRISCR with single H1 hescs. Live or fixed single sorted H1 hescs were prepared by standard Triton-X100 lysis (TL) or FRISCR, and sequenced after making SmartSeq2 cdna libraries. (a) Bar plot shows read-mapping percentages for each cell. Single-cell libraries were sequenced to a moderate depth (7.0M reads +/- 0.9M). 100% is all barcoded reads independent of mapping. (b) Bar plot showing mean +/- SD of total cdna yield amplified per cell using SmartSeq2. Numbers of single-cell samples are indicated on bars. Data is from two biological replicates except for Empty (water only) and ERCC only controls which are from one biological replicate. Analysis carried out in (c,e-i) is on libraries subsampled to 5 million reads. (c) Number of unique genes detected by RNA-Seq per cell with TPM > 0. (d) RPKM values of ERCC synthetic RNAs spiked-in at the time of cell collection. Data is the average value of each ERCC RNA for all single cells per experimental preparation. RPKM only takes into account ERCC mapped reads, and the mean slope and Rsq values are shown. All conditions show strong linearity. (e) Percentage of times an ERCC RNA molecule was detected in a sample. Each curve is fitted to the data points and assumes a Poisson distribution of ERCC molecules. The black line indicates the % detection if recovery is 100% and dilution follows Poisson statistics. To detect a species 50% of the time, RNA must be present at ~3.8, ~4.1, ~6.8, and ~6.1 copies for Live/TL, Fixed/TL, Live/FRISCR, and Fixed/FRISCR samples respectively. Color scheme and sample numbers apply to panels e-i. (f) Mutation rate in the singlecell gene expression data. (g) Normalized average read counts per experimental preparation are shown across the percentile predicted transcript length (3 to 5 ). Solid line represents the average and shading is the SD. Note Fixed/FRISCR prepared cells show more 3 bias than Live/TL or Live/FRISCR cells with longer transcripts. (h) Boxplot showing the fraction of genes detected out of all annotated genes for the given GC bin (bottom plot) with TPM > 0. (i) Boxplot showing the fraction of genes expressed out of all annotated genes from the indicated chromosome with TPM > 0. All boxplots show the median as a central line, the second and third quartiles as boxes, the whiskers extend to the highest/lowest value within the 1.5 interquartile range, and data points outside the range are indicated as dots.
4 Supplementary Figure 3 Table of genes differentially expressed in hescs between experimental conditions. Differential expression is based on DESeq. Tables show significantly differentially expressed genes (Padj < 0.01) from single cell comparisons between Live/TL versus Live/FRISCR samples, Live/TL versus Fixed/FRISCR samples, and Live/FRISCR versus Fixed/FRISCR. Non protein-coding, Histone, rrna genes are indicated, as well as genes previously shown to undergo differential polyadenylation 20. Fixed/TL comparisons are not show because the number of differentially expressed genes detected were too high to present in the summary table.
5 Supplementary Figure 4 Gating strategy for prospective isolation and profiling of human cortical progenitor cells. (a) Representative images of the entire gating strategy for the isolation of the SP and SPE cells. Top row: cells are gated for morphology, then single cells, and lastly for the presence of DAPI. Note only cells in the G 0 -G 1 phase of the cell cycle were sorted. Bottom row: Progenitors were first identified by high expression of SOX2 and PAX6, and then by the presence (orange) or absence (blue) of EOMES. Bottom right: Projection of
6 progenitor populations on all cells gated by the strategy on the top row and stained for EOMES and DCX show that SP and SPE progenitors are negative for DCX. (b) Representative SP and SPE cells were irrespective of cell cycle phase. SP and SPE were subsequently evaluated for DAPI fluorescence. Quantitation of cells in S- G 2 -M from three independent prenatal tissues (between 14 and 19 PCW) showed a significant 2-fold difference between SP and SPE cells.* = P < 0.05, homoscedastic t-test.
7
8 Supplementary Figure 5 Single-cell transcriptional analysis of human cortical progenitors. (a) Table of primary human tissues used in this manuscript describing their use in specific experiments: ICC (immunocytochemistry), and FACS indicates flow cytometry for quantitation of population frequency and nuclear content. (b) Representative Bioanalyzer traces show cdna amplification curves of SP and SPE single cells. (c) Bar plot shows read-mapping percentages for each primary cell prepared by FRISCR. Single-cell libraries were sequenced at low depth on a MiSeq. 100% is all barcoded reads independent of mapping. (d) Scatter plots of all SP and SPE cells sequenced on the MiSeq from four primary tissues showing number of mapped reads versus the % mapping to mrna. Red dashed lines indicate the lower limits for secondary analysis steps. For (e-g) only cells with >10,000 mapped reads, >20% mrna mapping, and presence of GAPDH are included (n = 157 SP and n = 29 SPE cells). (e) Barplot for SP and SPE cells show number of unique genes detected at each TPM threshold. Barplot is Mean±SD. (f) Principal component analysis of SP and SPE cells based on the genes with variance beyond technical noise. (g) Spearman correlation between cells based on ERCCs reads only (left), all genes (middle), and high variability genes (right). Color bars from heat maps are indicated below.
9
10 Supplementary Figure 6 Human cortical progenitors prepared by FRISCR show hallmarks of RGs and IPCs, but not of other cell types. (a) Data from fixed SP and SPE cells were compared to existing previously published data generated from live prenatal human neural cells by hierarchical clustering. Clustering was based on the common 482 of the top 500 genes contributing to the first principal component that was identified in a previous study 21. This clustering robustly categorizes cells by cell type despite the two data sets differing by sample age, sample donor, dissociation, cell capture, cdna amplification, and use of live or fixed cells. NPCs are neural precursor cells generated from hescs 21. Lower color bar annotations were based on annotation from the earlier study 21. (b) Gene expression analysis of markers of other brain cell types. SP and SPE cells have only sparse expression of non-progenitor cell type markers.
11 Supplementary Figure 7 Heat maps of genes that comprise each of the five WGCNA modules. Heat map colors show expression of a given gene normalized between cells. Red indicates high expression, blue indicates low expression. Color bars are indicated, and clustering was derived from Fig. 5b.
12
13 Supplementary Figure 8 Heat map of genes from all five WGCNA modules and differential expression between cell clusters. Cells are arranged by hierarchical clustering. Red indicates high expression, blue indicates low expression. Cell clustering was maintained as in Fig. 5b, and color bars are indicated. Nearly every cluster includes cells from each tissue (except B), and clusters are not driven by library read statistics.
14 Supplementary Figure 9 Validation that modules 2 and 3 are enriched in non-overlapping sets of RG progenitors. (a) FACS analysis of SP and SPE cells stained with EOMES and isotype (top) or CYR61 (bottom). Only cells staining for with a higher intensity than the isotype control (non-specific primary antibody) are considered positive for CYR61. Frequencies of events in quadrant gates are indicated (right). Data are from one brain representative of five brains analyzed in two independent experiments. (b) Grayscale (left) micrographs of entire cortical depth showing DAPI, SOX2, and the vrg-enriched protein JUN, or org-enriched protein F3, and (right) merged micrographs of only the germinal zone showing co-staining of SOX2 (magenta), with JUN or F3 (green). Tissue is 16 PCW cortex, scales are 100 µm, and images are stitched montages. Abbreviations are: marginal zone (MZ), cortical plate (CP), subplate/intermediate zone (SP/IZ), outer subventricular zone (osz), inner subventricular zone (isz), and ventricular zone (VZ).
15
16 Supplementary Figure 10 Mapping RG modules to human and nonhuman primate atlas data. (a) Heatmaps illustrating enrichment of module eigengene expression in each brain of the BrainSpan Atlas of the Developing Human Brain data. Regions with high correlation to a given eigengene are red, while poor correlation is blue. (b) Heatmaps showing expression of genes in each brain of the BrainSpan Atlas of the Developing Human Brain 11 identified because they were differentially expressed between cell clusters C and D (orgs) verses cluster E (vrgs) from the FRISCR-prepared single cells (Fig. 5d), and were differentially expressed between osz and VZ regions of 21 PCW human tissues. Common progenitor markers are included at the top of the heatmap for reference. (c) Expression of HOPX in macaque though development. Plot shows expression of HOPX in the visual cortex (V1) of the NIH Blueprint Non-Human Primate Atlas. Each column shows different ages from embryonic day 40 (E40), through 48 months after birth (48M). Rows are microdissected regions. Red indicates high expression. Abbreviations for prenatal time points are: marginal zone (MZ), outer cortical plate (ocp), inner cortical plate (icp), subplate (SP), intermediate zone (IZ), outer subventricular zone (isz), inner subventricular zone (isz), and VZ (ventricular zone). Abbreviations for postnatal time points are: Layer 1-6 (L1-L6), and white matter (WM). Expression of HOPX is initiated in V1 at E70, when the osz is formed, and while first detected in the entire germinal zone, is subsequently enriched in the osz.
17
18 Supplementary Figure 11 Characterization of human HOPX + cortical RG cells. (a) Grayscale (left) micrographs of the entire cortical depth showing DAPI, SOX2, and HOPX, and merged (right) micrographs showing co-staining of SOX2 (magenta) and HOPX (green). Tissue is 19 (top), and 15 (bottom) PCW cortex, scales are 100 µm. 19 PCW tissue appears in Fig. 6d, and is shown here with single color images. Insets of the osz (i, ii, and iv) and the VZ (iii, v) are shown to right. Note substantial overlap of HOPX and SOX2 staining in the osz (i, ii, and iv), some overlap in the 15PCW VZ (v), and no overlap in the 19 PCW VZ (iii). Abbreviations are: marginal zone (MZ), cortical plate (CP), subplate/intermediate zone (SP/IZ), outer subventricular zone (osz), inner subventricular zone (isz), and VZ (ventricular zone). (b) osz region of 16 PCW cortex stained by HOPX (green) and SOX2 (magenta). Note multiple SOX2 +, HOPX + cells in this field exhibit basal processes (arrowhead), but not apical processes (arrow). Scale is 100 µm. (c) Grayscale and merged micrographs of a representative region of osz stained for SOX2, HOPX, and Ki67. White arrows are SOX2 +, HOPX -, Ki67 + cells and arrowheads are SOX2 +, HOPX +, Ki67 + cells. Scale is 20 µm.
19 Supplementary Figure 12
20 Overlap of RG subtype markers. (a) Venn diagram showing the percentage overlap of SOX2 and PAX6 antigen expression in the VZ, isz, osz, and Subplate/Cortical Plate (SP/CP). Data are mean percentages +/- SD. Note nearly all SOX2 + PAX6 - cells reside outside of the germinal zone, and 99% of cells in the osz and VZ that express SOX2 also express PAX6. Data are from three brains between 15 and 18 PCW, at least three fields from each region of each brain were quantified by manual counting. (b) Venn diagram showing the percentage overlap of SOX2, HOPX, and EOMES in the osz; and (c) SOX2, HOPX, EOMES, and ANXA1 in the VZ/iSVZ. Data are mean +/- SD from four brains between 15 and 18 PCW, at least three fields from the indicated brain region of each brain were quantified by manual counting. (d-e) Representative confocal micrographs co-stained for SOX2, EOMES, HOPX, and ANXA1 of the osz (d) and VZ/iSVZ (e) from which quantitation in the above Venn diagrams were derived. Tissue is H PCW and scale bar is 20 µm.
21
22 Supplementary Figure 13 HOPX is expressed in both lateral and medial cortical regions. (a) Micrograph of a 16 PCW tissue section showing both medial and lateral regions of the cortex co- labeled by HOPX, SOX2, and DAPI. HOPX is notably enriched in the osz of both medial and lateral cortical regions. Medial cortex was assigned by the observation of the medial-derived hippocampus in serial sections. (b) Analysis of HOPX expression in each brain of the BrainSpan Atlas of the Developing Human Brain shows no enrichment in medial regions (red) of the cortex in any brain or germinal zone. The cortical regional abbreviations are: frontal polar (fp), dorsolateral (dl), ventrolateral (vl), orbital (or), motor cortex (m1), somatosensory cortex (s1), dorsomedial parietal cortex (dm-p), posterosuperior (dorsal) (pd), posteroinferior (ventral) (pv), medial temporal (mt), lateral temporal (lt), superolateral (sl), inferolateral (il), parahippocampal (ph), primary visual (v1), dorsomedial occipital (dm-o), ventromedial (vm), midlateral (ml), dorsomedial frontal (dm-f), and midinferior (tf).
Fixed single-cell transcriptomic characterization of human radial glial diversity
 Fixed single-cell transcriptomic characterization of human radial glial diversity Elliot R Thomsen,4, John K Mich,4, Zizhen Yao,4, Rebecca D Hodge, Adele M Doyle, Sumin Jang, Soraya I Shehata, Angelique
Fixed single-cell transcriptomic characterization of human radial glial diversity Elliot R Thomsen,4, John K Mich,4, Zizhen Yao,4, Rebecca D Hodge, Adele M Doyle, Sumin Jang, Soraya I Shehata, Angelique
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. sndrop-seq overview.
 Supplementary Figure 1 sndrop-seq overview. A. sndrop-seq method showing modifications needed to process nuclei, including bovine serum albumin (BSA) coating and droplet heating to ensure complete nuclear
Supplementary Figure 1 sndrop-seq overview. A. sndrop-seq method showing modifications needed to process nuclei, including bovine serum albumin (BSA) coating and droplet heating to ensure complete nuclear
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
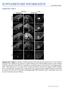 doi:10.1038/nature11094 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Analysis of GFP expression in P0 wild type and mutant ( E1-4) Fezf2-Gfp BAC transgenic mice. Epifluorescent images of sagittal forebrain
doi:10.1038/nature11094 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Analysis of GFP expression in P0 wild type and mutant ( E1-4) Fezf2-Gfp BAC transgenic mice. Epifluorescent images of sagittal forebrain
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Multiplet rate and sensitivity of the GemCode single cell platform from scrna-seq of 50:50 mixing of 293Ts and 3T3s. (a) Inferred multiplet rate as a function
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Multiplet rate and sensitivity of the GemCode single cell platform from scrna-seq of 50:50 mixing of 293Ts and 3T3s. (a) Inferred multiplet rate as a function
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Workflow for multimodal analysis using sc-gem on a programmable microfluidic device (Fluidigm). 1) Cells are captured and lysed, 2) RNA from lysed single cell is reverse-transcribed
Supplementary Figure 1 Workflow for multimodal analysis using sc-gem on a programmable microfluidic device (Fluidigm). 1) Cells are captured and lysed, 2) RNA from lysed single cell is reverse-transcribed
Full-length single-cell RNA-seq applied to a viral human. cancer: Applications to HPV expression and splicing analysis. Supplementary Information
 Full-length single-cell RNA-seq applied to a viral human cancer: Applications to HPV expression and splicing analysis in HeLa S3 cells Liang Wu 1, Xiaolong Zhang 1,2, Zhikun Zhao 1,3,4, Ling Wang 5, Bo
Full-length single-cell RNA-seq applied to a viral human cancer: Applications to HPV expression and splicing analysis in HeLa S3 cells Liang Wu 1, Xiaolong Zhang 1,2, Zhikun Zhao 1,3,4, Ling Wang 5, Bo
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3694
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Bhlhe41 and Bhlhe40 in B cell development and mature B cell subsets. (a) Scatter plot showing differential expression of genes between splenic B-1a cells and follicular
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Bhlhe41 and Bhlhe40 in B cell development and mature B cell subsets. (a) Scatter plot showing differential expression of genes between splenic B-1a cells and follicular
of NOBOX. Supplemental Figure S1F shows the staining profile of LHX8 antibody (Abcam, ab41519), which is a
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS LHX8 Staining During the course of this work, it came to our attention that the NOBOX antibody used in this study had been discontinued. There are a number of other nuclear
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS LHX8 Staining During the course of this work, it came to our attention that the NOBOX antibody used in this study had been discontinued. There are a number of other nuclear
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Rarefaction Analysis and Sampling. a, Rarefaction plots show the expected levels of coverage for different subsamples of sequencing libraries for repertoires of clone size of at
Supplementary Figure 1 Rarefaction Analysis and Sampling. a, Rarefaction plots show the expected levels of coverage for different subsamples of sequencing libraries for repertoires of clone size of at
TECH NOTE SMARTer T-cell receptor profiling in single cells
 TECH NOTE SMARTer T-cell receptor profiling in single cells Flexible workflow: Illumina-ready libraries from FACS or manually sorted single cells Ease of use: Optimized indexing allows for pooling 96 cells
TECH NOTE SMARTer T-cell receptor profiling in single cells Flexible workflow: Illumina-ready libraries from FACS or manually sorted single cells Ease of use: Optimized indexing allows for pooling 96 cells
with different microfluidic device parameters. Distribution of number of transcripts (y-axis) detected across nuclei, ranked in decreasing
 Supplementary Figure 1 DroNc-seq benchmarking experiments. (a) Overview of DroNc-seq. (b) CAD schema of DroNc-seq microfluidic device. (c) Comparison of library complexity from experiments with different
Supplementary Figure 1 DroNc-seq benchmarking experiments. (a) Overview of DroNc-seq. (b) CAD schema of DroNc-seq microfluidic device. (c) Comparison of library complexity from experiments with different
initial single-cell analysis, with a pragmatic focus on surface markers with the highest potential for
 Supplementary Figure 1: Summary of the exclusionary approach to surface marker selection for initial single-cell analysis, with a pragmatic focus on surface markers with the highest potential for protein
Supplementary Figure 1: Summary of the exclusionary approach to surface marker selection for initial single-cell analysis, with a pragmatic focus on surface markers with the highest potential for protein
Novel methods for RNA and DNA- Seq analysis using SMART Technology. Andrew Farmer, D. Phil. Vice President, R&D Clontech Laboratories, Inc.
 Novel methods for RNA and DNA- Seq analysis using SMART Technology Andrew Farmer, D. Phil. Vice President, R&D Clontech Laboratories, Inc. Agenda Enabling Single Cell RNA-Seq using SMART Technology SMART
Novel methods for RNA and DNA- Seq analysis using SMART Technology Andrew Farmer, D. Phil. Vice President, R&D Clontech Laboratories, Inc. Agenda Enabling Single Cell RNA-Seq using SMART Technology SMART
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 CITE-seq library preparation. (a) Illustration of the DNA-barcoded antibodies used in CITE-seq. (b) Antibody-oligonucleotide complexes appear as a high-molecular-weight smear when
Supplementary Figure 1 CITE-seq library preparation. (a) Illustration of the DNA-barcoded antibodies used in CITE-seq. (b) Antibody-oligonucleotide complexes appear as a high-molecular-weight smear when
Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured
 Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured in 90-Pa 3D fibrin gels for 5 days in the presence
Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured in 90-Pa 3D fibrin gels for 5 days in the presence
Supplementary Data. Supplementary Materials and Methods Twenty-cell gene expression profiling. Stem cell transcriptome analysis
 Supplementary Data The Supplementary Data includes Supplementary Materials and Methods, and Figures (Supplementary Figs. S1 S10). Supplementary Materials and Methods Twenty-cell gene expression profiling
Supplementary Data The Supplementary Data includes Supplementary Materials and Methods, and Figures (Supplementary Figs. S1 S10). Supplementary Materials and Methods Twenty-cell gene expression profiling
Measuring gene expression
 Measuring gene expression Grundlagen der Bioinformatik SS2018 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v8gh404a3gg Agenda Organization Gene expression Background Technologies FISH Nanostring Microarrays RNA-seq
Measuring gene expression Grundlagen der Bioinformatik SS2018 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v8gh404a3gg Agenda Organization Gene expression Background Technologies FISH Nanostring Microarrays RNA-seq
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2015 Figure S1 Confirmation of Sca-1 CD34 stain specificity using isotypematched control antibodies. Skeletal muscle preparations were stained and gated as described in the text (Hoechst
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2015 Figure S1 Confirmation of Sca-1 CD34 stain specificity using isotypematched control antibodies. Skeletal muscle preparations were stained and gated as described in the text (Hoechst
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Diffusion of MCF-7 and 3T3 cells. (a) High-resolution image (40x): DAPI and Cy5-CellTracker TM stained MCF-7 cells. (b) Corresponding high-resolution (40x)
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Diffusion of MCF-7 and 3T3 cells. (a) High-resolution image (40x): DAPI and Cy5-CellTracker TM stained MCF-7 cells. (b) Corresponding high-resolution (40x)
Supplementary Data. Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells Mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (ipscs) were cultured
Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells Mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (ipscs) were cultured
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.4396
 Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of technical replicate consistency between and across the standard ATAC-seq method, DNase-seq, and Omni-ATAC. (a) Heatmap-based representation of ATAC-seq quality control
Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of technical replicate consistency between and across the standard ATAC-seq method, DNase-seq, and Omni-ATAC. (a) Heatmap-based representation of ATAC-seq quality control
Throughput cells cells. Methodology Full transcript or end-counting end-counting. Chemistry SMARTer V SMARTer V. Run time hours.
 PN 101-0984 A1 DATASHEET C1 mrna Sequencing Rapidly characterize heterogeneity, identify critical cell populations. Individual cells are unique they differ by size, protein levels, and expressed mrna transcripts.
PN 101-0984 A1 DATASHEET C1 mrna Sequencing Rapidly characterize heterogeneity, identify critical cell populations. Individual cells are unique they differ by size, protein levels, and expressed mrna transcripts.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a before amputation regeneration regenerated limb DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS developmental origin: lateral plate mesoderm presomitic mesoderm
a before amputation regeneration regenerated limb DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS developmental origin: lateral plate mesoderm presomitic mesoderm
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION ARTICLE NUMBER: 16206 DOI: 10.1038/NMICROBIOL.2016.206 Single cell RNA seq ties macrophage polarization to growth rate of intracellular
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION ARTICLE NUMBER: 16206 DOI: 10.1038/NMICROBIOL.2016.206 Single cell RNA seq ties macrophage polarization to growth rate of intracellular
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Table S1. Overview of samples used for sequencing, and the number of sequences obtained from each sample. Visit 1 is day 0, Visit 2 is day 7, Visit 3 is day 28, and Visit 4 is day
Supporting Information Table S1. Overview of samples used for sequencing, and the number of sequences obtained from each sample. Visit 1 is day 0, Visit 2 is day 7, Visit 3 is day 28, and Visit 4 is day
Next Generation Sequencing
 Next Generation Sequencing Complete Report Catalogue # and Service: IR16001 rrna depletion (human, mouse, or rat) IR11081 Total RNA Sequencing (80 million reads, 2x75 bp PE) Xxxxxxx - xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Next Generation Sequencing Complete Report Catalogue # and Service: IR16001 rrna depletion (human, mouse, or rat) IR11081 Total RNA Sequencing (80 million reads, 2x75 bp PE) Xxxxxxx - xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
(a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of Diaph3 ko mice. (a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for different regions of Diaph3 mrna from WT, heterozygote
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of Diaph3 ko mice. (a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for different regions of Diaph3 mrna from WT, heterozygote
Supplementary Information for Single-cell sequencing of the small-rna transcriptome
 Supplementary Information for Single-cell sequencing of the small-rna transcriptome Omid R. Faridani 1,6,*, Ilgar Abdullayev 1,2,6, Michael Hagemann-Jensen 1,3, John P. Schell 4, Fredrik Lanner 4,5 and
Supplementary Information for Single-cell sequencing of the small-rna transcriptome Omid R. Faridani 1,6,*, Ilgar Abdullayev 1,2,6, Michael Hagemann-Jensen 1,3, John P. Schell 4, Fredrik Lanner 4,5 and
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Retention of RNA with LabelX.
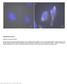 Supplementary Figure 1 Retention of RNA with LabelX. (a) Epi-fluorescence image of single molecule FISH (smfish) against GAPDH on HeLa cells expanded without LabelX treatment. (b) Epi-fluorescence image
Supplementary Figure 1 Retention of RNA with LabelX. (a) Epi-fluorescence image of single molecule FISH (smfish) against GAPDH on HeLa cells expanded without LabelX treatment. (b) Epi-fluorescence image
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Optimization of Patch-seq protocol.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Optimization of Patch-seq protocol. Pilot experiments were carried out to test the effect of various protocol modifications on cdna yield, including addition of RNase inhibitor to
Supplementary Figure 1 Optimization of Patch-seq protocol. Pilot experiments were carried out to test the effect of various protocol modifications on cdna yield, including addition of RNase inhibitor to
Result Tables The Result Table, which indicates chromosomal positions and annotated gene names, promoter regions and CpG islands, is the best way for
 Result Tables The Result Table, which indicates chromosomal positions and annotated gene names, promoter regions and CpG islands, is the best way for you to discover methylation changes at specific genomic
Result Tables The Result Table, which indicates chromosomal positions and annotated gene names, promoter regions and CpG islands, is the best way for you to discover methylation changes at specific genomic
Supplemental Figure 1.
 Supplemental Data. Charron et al. Dynamic landscapes of four histone modifications during de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell (2009). 10.1105/tpc.109.066845 Supplemental Figure 1. Immunodetection
Supplemental Data. Charron et al. Dynamic landscapes of four histone modifications during de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell (2009). 10.1105/tpc.109.066845 Supplemental Figure 1. Immunodetection
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of Hi-C/CHi-C dynamics and enhancer identification. (a) Scatterplot of Hi-C read counts supporting contacts between domain boundaries. Contacts enclosing domains
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of Hi-C/CHi-C dynamics and enhancer identification. (a) Scatterplot of Hi-C read counts supporting contacts between domain boundaries. Contacts enclosing domains
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic and results of screening the combinatorial antibody library for Sox2 replacement activity. A single batch of MEFs were plated and transduced with doxycycline inducible
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic and results of screening the combinatorial antibody library for Sox2 replacement activity. A single batch of MEFs were plated and transduced with doxycycline inducible
Supplementary Figure 1. Serial deletion mutants of BLITz.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Serial deletion mutants of BLITz. (a) Design of TEVseq insertion into J -helix. C-terminal end of J -helix was serially deleted and replaced by TEVseq. TEV cleavage site is labeled
Supplementary Figure 1 Serial deletion mutants of BLITz. (a) Design of TEVseq insertion into J -helix. C-terminal end of J -helix was serially deleted and replaced by TEVseq. TEV cleavage site is labeled
Figure S1: NUN preparation yields nascent, unadenylated RNA with a different profile from Total RNA.
 Summary of Supplemental Information Figure S1: NUN preparation yields nascent, unadenylated RNA with a different profile from Total RNA. Figure S2: rrna removal procedure is effective for clearing out
Summary of Supplemental Information Figure S1: NUN preparation yields nascent, unadenylated RNA with a different profile from Total RNA. Figure S2: rrna removal procedure is effective for clearing out
GENESDEV/2007/ Supplementary Figure 1 Elkabetz et al.,
 GENESDEV/2007/089581 Supplementary Figure 1 Elkabetz et al., GENESDEV/2007/089581 Supplementary Figure 2 Elkabetz et al., GENESDEV/2007/089581 Supplementary Figure 3 Elkabetz et al., GENESDEV/2007/089581
GENESDEV/2007/089581 Supplementary Figure 1 Elkabetz et al., GENESDEV/2007/089581 Supplementary Figure 2 Elkabetz et al., GENESDEV/2007/089581 Supplementary Figure 3 Elkabetz et al., GENESDEV/2007/089581
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Pilot CrY2H-seq experiments to confirm strain and plasmid functionality.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pilot CrY2H-seq experiments to confirm strain and plasmid functionality. (a) RT-PCR on HIS3 positive diploid cell lysate containing known interaction partners AT3G62420 (bzip53)
Supplementary Figure 1 Pilot CrY2H-seq experiments to confirm strain and plasmid functionality. (a) RT-PCR on HIS3 positive diploid cell lysate containing known interaction partners AT3G62420 (bzip53)
Gene expression analysis. Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 5. Gene expression analysis
 Gene expression analysis Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 5 Gene expression analysis From EST clusters to spotted cdna microarrays Long vs. short oligonucleotide microarrays vs. RT-PCR Methods
Gene expression analysis Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 5 Gene expression analysis From EST clusters to spotted cdna microarrays Long vs. short oligonucleotide microarrays vs. RT-PCR Methods
Development 142: doi: /dev : Supplementary Material
 Development 142: doi:1.42/dev.11687: Supplementary Material Figure S1 - Relative expression of lineage markers in single ES cell and cardiomyocyte by real-time quantitative PCR analysis. Single ES cell
Development 142: doi:1.42/dev.11687: Supplementary Material Figure S1 - Relative expression of lineage markers in single ES cell and cardiomyocyte by real-time quantitative PCR analysis. Single ES cell
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Integrative Biology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Table S1. Definition of quantitative cellular features
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Integrative Biology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Table S1. Definition of quantitative cellular features
Supplemental Data. Farmer et al. (2010) Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Amino acid sequence comparison of RAD23 proteins. Identical and similar residues are shown in the black and gray boxes, respectively. Dots denote gaps. The sequence of plant Ub is
Supplemental Figure 1. Amino acid sequence comparison of RAD23 proteins. Identical and similar residues are shown in the black and gray boxes, respectively. Dots denote gaps. The sequence of plant Ub is
reverse transcription! RT 1! RT 2! RT 3!
 Supplementary Figure! Entire workflow repeated 3 times! mirna! stock! -fold dilution series! to yield - copies! per µl in PCR reaction! reverse transcription! RT! pre-pcr! mastermix!!!! 3!!! 3! ddpcr!
Supplementary Figure! Entire workflow repeated 3 times! mirna! stock! -fold dilution series! to yield - copies! per µl in PCR reaction! reverse transcription! RT! pre-pcr! mastermix!!!! 3!!! 3! ddpcr!
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1 shrna mediated knockdown of ZRSR2 in K562 and 293T cells. (a) ZRSR2 transcript levels in stably transduced K562 cells were determined using qrt-pcr. GAPDH was
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1 shrna mediated knockdown of ZRSR2 in K562 and 293T cells. (a) ZRSR2 transcript levels in stably transduced K562 cells were determined using qrt-pcr. GAPDH was
Supplementary Fig. 5
 Supplementary Fig. 5 Supplemental Figures legends Supplementary Figure 1 (A) Additional dot plots from CyTOF analysis from untreated group. (B) Gating strategy for assessment of CD11c + NK cells frequency
Supplementary Fig. 5 Supplemental Figures legends Supplementary Figure 1 (A) Additional dot plots from CyTOF analysis from untreated group. (B) Gating strategy for assessment of CD11c + NK cells frequency
PART I. Single-cell transcriptome analysis. Challenges in single-cell RNA sequencing. Laser capture microdissection FACS. Picking single cells
 Single-cell transcriptome analysis Sten Linnarsson Assistant Professor Molecular Neurobiology Unit Karolinska Institutet PART I Namn Efternamn 2 Challenges in single-cell RNA sequencing Picking single
Single-cell transcriptome analysis Sten Linnarsson Assistant Professor Molecular Neurobiology Unit Karolinska Institutet PART I Namn Efternamn 2 Challenges in single-cell RNA sequencing Picking single
EPIGENTEK. EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit. Base Catalog # P-2002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE
 EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity of
EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2002 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity of
Notch1 (forward: 5 -TGCCTGTGCACACCATTCTGC-3, reverse: Notch2 (forward: 5 -ATGCACCATGACATCGTTCG-3, reverse:
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Methods. RT-PCR. For mouse ES cells, the primers used were: Notch1 (forward: 5 -TGCCTGTGCACACCATTCTGC-3, reverse: 5 -CAATCAGAGATGTTGGAATGC-3 ) 1, Notch2 (forward:
Supplementary Information Supplementary Methods. RT-PCR. For mouse ES cells, the primers used were: Notch1 (forward: 5 -TGCCTGTGCACACCATTCTGC-3, reverse: 5 -CAATCAGAGATGTTGGAATGC-3 ) 1, Notch2 (forward:
Technical Review. Real time PCR
 Technical Review Real time PCR Normal PCR: Analyze with agarose gel Normal PCR vs Real time PCR Real-time PCR, also known as quantitative PCR (qpcr) or kinetic PCR Key feature: Used to amplify and simultaneously
Technical Review Real time PCR Normal PCR: Analyze with agarose gel Normal PCR vs Real time PCR Real-time PCR, also known as quantitative PCR (qpcr) or kinetic PCR Key feature: Used to amplify and simultaneously
Increased transcription detection with the NEBNext Single Cell/Low Input RNA Library Prep Kit
 be INSPIRED drive DISCOVERY stay GENUINE TECHNICAL NOTE Increased transcription detection with the NEBNext Single Cell/Low Input RNA Library Prep Kit Highly sensitive, robust generation of high quality
be INSPIRED drive DISCOVERY stay GENUINE TECHNICAL NOTE Increased transcription detection with the NEBNext Single Cell/Low Input RNA Library Prep Kit Highly sensitive, robust generation of high quality
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Quartz-Seq2: a high-throughput single-cell RNA-sequencing method that effectively uses limited sequence reads
 Sasagawa et al. Genome Biology (218) 19:29 https://doi.org/1.1186/s1359-18-147-3 METHOD Quartz-Seq2: a high-throughput single-cell RNA-sequencing method that effectively uses limited sequence reads Yohei
Sasagawa et al. Genome Biology (218) 19:29 https://doi.org/1.1186/s1359-18-147-3 METHOD Quartz-Seq2: a high-throughput single-cell RNA-sequencing method that effectively uses limited sequence reads Yohei
Parts of a standard FastQC report
 FastQC FastQC, written by Simon Andrews of Babraham Bioinformatics, is a very popular tool used to provide an overview of basic quality control metrics for raw next generation sequencing data. There are
FastQC FastQC, written by Simon Andrews of Babraham Bioinformatics, is a very popular tool used to provide an overview of basic quality control metrics for raw next generation sequencing data. There are
Introduction to Microarray Analysis
 Introduction to Microarray Analysis Methods Course: Gene Expression Data Analysis -Day One Rainer Spang Microarrays Highly parallel measurement devices for gene expression levels 1. How does the microarray
Introduction to Microarray Analysis Methods Course: Gene Expression Data Analysis -Day One Rainer Spang Microarrays Highly parallel measurement devices for gene expression levels 1. How does the microarray
Supplementary Figure 1. Botrocetin induces binding of human VWF to human
 Supplementary Figure 1: Supplementary Figure 1. Botrocetin induces binding of human VWF to human platelets in the absence of elevated shear and induces platelet agglutination as detected by flow cytometry.
Supplementary Figure 1: Supplementary Figure 1. Botrocetin induces binding of human VWF to human platelets in the absence of elevated shear and induces platelet agglutination as detected by flow cytometry.
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Fig. S1. Specificity of perilipin antibody in SAT compared to various organs. (A) Images of SAT at E18.5 stained with perilipin and CD31 antibody. Scale bars: 100 μm. SAT stained
Supplementary Figures Fig. S1. Specificity of perilipin antibody in SAT compared to various organs. (A) Images of SAT at E18.5 stained with perilipin and CD31 antibody. Scale bars: 100 μm. SAT stained
Mapping long-range promoter contacts in human cells with high-resolution capture Hi-C
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 47, 598 606 (2015) Mapping long-range promoter contacts in human cells with high-resolution capture Hi-C Borbala Mifsud, Filipe Tavares-Cadete, Alice N Young, Robert Sugar,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 47, 598 606 (2015) Mapping long-range promoter contacts in human cells with high-resolution capture Hi-C Borbala Mifsud, Filipe Tavares-Cadete, Alice N Young, Robert Sugar,
(A-B) P2ry14 expression was assessed by (A) genotyping (upper arrow: WT; lower
 Supplementary Figures S1. (A-B) P2ry14 expression was assessed by (A) genotyping (upper arrow: ; lower arrow: KO) and (B) q-pcr analysis with Lin- cells, The white vertical line in panel A indicates that
Supplementary Figures S1. (A-B) P2ry14 expression was assessed by (A) genotyping (upper arrow: ; lower arrow: KO) and (B) q-pcr analysis with Lin- cells, The white vertical line in panel A indicates that
Supplementary Information to: Genome-wide Real-time in vivo Transcriptional Dynamics During Plasmodium falciparum. Blood-stage Development
 Supplementary Information to: Genome-wide Real-time in vivo Transcriptional Dynamics During Plasmodium falciparum Blood-stage Development Painter et al. 1 of 8 Supplementary Figure 1: Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Information to: Genome-wide Real-time in vivo Transcriptional Dynamics During Plasmodium falciparum Blood-stage Development Painter et al. 1 of 8 Supplementary Figure 1: Supplementary Figure
Data and Metadata Models Recommendations Version 1.2 Developed by the IHEC Metadata Standards Workgroup
 Data and Metadata Models Recommendations Version 1.2 Developed by the IHEC Metadata Standards Workgroup 1. Introduction The data produced by IHEC is illustrated in Figure 1. Figure 1. The space of epigenomic
Data and Metadata Models Recommendations Version 1.2 Developed by the IHEC Metadata Standards Workgroup 1. Introduction The data produced by IHEC is illustrated in Figure 1. Figure 1. The space of epigenomic
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization and high expression of Lnc-β-Catm in liver CSCs. (a) Heatmap of differently expressed lncrnas in Liver CSCs (CD13 + CD133 + ) and non-cscs (CD13 - CD133 - ) according
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization and high expression of Lnc-β-Catm in liver CSCs. (a) Heatmap of differently expressed lncrnas in Liver CSCs (CD13 + CD133 + ) and non-cscs (CD13 - CD133 - ) according
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Table of contents: Pages: Supplementary Methods 2-3 Supplementary Figure 1 4 Supplementary Figure 2 5 Supplementary Figure 3 6 Supplementary Figure 4 7 Supplementary Figure 5
Supplementary Information Table of contents: Pages: Supplementary Methods 2-3 Supplementary Figure 1 4 Supplementary Figure 2 5 Supplementary Figure 3 6 Supplementary Figure 4 7 Supplementary Figure 5
Supplemental Table/Figure Legends
 MiR-26a is required for skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration in mice Bijan K. Dey, Jeffrey Gagan, Zhen Yan #, Anindya Dutta Supplemental Table/Figure Legends Suppl. Table 1: Effect of overexpression
MiR-26a is required for skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration in mice Bijan K. Dey, Jeffrey Gagan, Zhen Yan #, Anindya Dutta Supplemental Table/Figure Legends Suppl. Table 1: Effect of overexpression
Development of quantitative targeted RNA-seq methodology for use in differential gene expression
 Development of quantitative targeted RNA-seq methodology for use in differential gene expression Dr. Jens Winter, Market Development Group Biological Biological Research Content EMEA QIAGEN Universal Workflows
Development of quantitative targeted RNA-seq methodology for use in differential gene expression Dr. Jens Winter, Market Development Group Biological Biological Research Content EMEA QIAGEN Universal Workflows
TECH NOTE Pushing the Limit: A Complete Solution for Generating Stranded RNA Seq Libraries from Picogram Inputs of Total Mammalian RNA
 TECH NOTE Pushing the Limit: A Complete Solution for Generating Stranded RNA Seq Libraries from Picogram Inputs of Total Mammalian RNA Stranded, Illumina ready library construction in
TECH NOTE Pushing the Limit: A Complete Solution for Generating Stranded RNA Seq Libraries from Picogram Inputs of Total Mammalian RNA Stranded, Illumina ready library construction in
Experimental Design. Dr. Matthew L. Settles. Genome Center University of California, Davis
 Experimental Design Dr. Matthew L. Settles Genome Center University of California, Davis settles@ucdavis.edu What is Differential Expression Differential expression analysis means taking normalized sequencing
Experimental Design Dr. Matthew L. Settles Genome Center University of California, Davis settles@ucdavis.edu What is Differential Expression Differential expression analysis means taking normalized sequencing
Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Ali Mortazavi, Brian A Williams, Kenneth McCue, Lorian Schaeffer & Barbara Wold
 Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq Ali Mortazavi, Brian A Williams, Kenneth McCue, Lorian Schaeffer & Barbara Wold Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1 RNA shatter
Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq Ali Mortazavi, Brian A Williams, Kenneth McCue, Lorian Schaeffer & Barbara Wold Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1 RNA shatter
SMARTer Ultra Low RNA Kit for Illumina Sequencing Two powerful technologies combine to enable sequencing with ultra-low levels of RNA
 SMARTer Ultra Low RNA Kit for Illumina Sequencing Two powerful technologies combine to enable sequencing with ultra-low levels of RNA The most sensitive cdna synthesis technology, combined with next-generation
SMARTer Ultra Low RNA Kit for Illumina Sequencing Two powerful technologies combine to enable sequencing with ultra-low levels of RNA The most sensitive cdna synthesis technology, combined with next-generation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
Polaris and Callisto: Advances in Cellular Biology. Jordan Moore Senior Field Applications Specialist
 Polaris and Callisto: Advances in Cellular Biology Jordan Moore Senior Field Applications Specialist Single-Cell Biology Number of cells The population average is a lie average Transcripts per cell Gene
Polaris and Callisto: Advances in Cellular Biology Jordan Moore Senior Field Applications Specialist Single-Cell Biology Number of cells The population average is a lie average Transcripts per cell Gene
Institut Curie RPPA platform: User Policy and Agreement
 Institut Curie RPPA platform: User Policy and Agreement 1. Technology... 2 2. Samples... 2 2.1. Number of samples... 2 2.2. Sample lysis... 2 2.3. Amount of material... 3 3. Antibodies:... 3 3.1. Antibody
Institut Curie RPPA platform: User Policy and Agreement 1. Technology... 2 2. Samples... 2 2.1. Number of samples... 2 2.2. Sample lysis... 2 2.3. Amount of material... 3 3. Antibodies:... 3 3.1. Antibody
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12119 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND LEGENDS pre-let-7a- 1 +14U pre-let-7a- 1 Ddx3x Dhx30 Dis3l2 Elavl1 Ggt5 Hnrnph 2 Osbpl5 Puf60 Rnpc3 Rpl7 Sf3b3 Sf3b4 Tia1 Triobp U2af1 U2af2 1 6 2 4 3
doi:10.1038/nature12119 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND LEGENDS pre-let-7a- 1 +14U pre-let-7a- 1 Ddx3x Dhx30 Dis3l2 Elavl1 Ggt5 Hnrnph 2 Osbpl5 Puf60 Rnpc3 Rpl7 Sf3b3 Sf3b4 Tia1 Triobp U2af1 U2af2 1 6 2 4 3
Supplementary Figure 1. Western analysis of p-smad1/5/8 of differentiated hescs.
 kda 65 45 45 35 Supplementary Figure 1. Western analysis of p-smad1/5/8 of differentiated hescs. H9 hescs were differentiated with or without BMP4+BMP8A and cell lysates were collected for Western analysis
kda 65 45 45 35 Supplementary Figure 1. Western analysis of p-smad1/5/8 of differentiated hescs. H9 hescs were differentiated with or without BMP4+BMP8A and cell lysates were collected for Western analysis
Integrated Omics Study Delineates the Dynamics of Lipid Droplets in Rhodococcus Opacus PD630
 School of Natural Sciences and Mathematics 2013-10-22 Integrated Omics Study Delineates the Dynamics of Lipid Droplets in Rhodococcus Opacus PD630 UTD AUTHOR(S): Michael Qiwei Zhang 2013 The Authors This
School of Natural Sciences and Mathematics 2013-10-22 Integrated Omics Study Delineates the Dynamics of Lipid Droplets in Rhodococcus Opacus PD630 UTD AUTHOR(S): Michael Qiwei Zhang 2013 The Authors This
QUANTITATIVE RT-PCR PROTOCOL (SYBR Green I) (Last Revised: April, 2007)
 QUANTITATIVE RT-PCR PROTOCOL (SYBR Green I) (Last Revised: April, 007) Please contact Center for Plant Genomics (CPG) facility manager Hailing Jin (hljin@iastate.edu) regarding questions or corrections.
QUANTITATIVE RT-PCR PROTOCOL (SYBR Green I) (Last Revised: April, 007) Please contact Center for Plant Genomics (CPG) facility manager Hailing Jin (hljin@iastate.edu) regarding questions or corrections.
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. DMS-MaPseq data are highly reproducible at elevated DMS concentrations.
 Supplementary Figure 1 DMS-MaPseq data are highly reproducible at elevated DMS concentrations. a, Correlation of Gini index for 202 yeast mrna regions with 15x coverage at 2.5% or 5% v/v DMS concentrations
Supplementary Figure 1 DMS-MaPseq data are highly reproducible at elevated DMS concentrations. a, Correlation of Gini index for 202 yeast mrna regions with 15x coverage at 2.5% or 5% v/v DMS concentrations
Measuring gene expression (Microarrays) Ulf Leser
 Measuring gene expression (Microarrays) Ulf Leser This Lecture Gene expression Microarrays Idea Technologies Problems Quality control Normalization Analysis next week! 2 http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/molecules/transcribe/
Measuring gene expression (Microarrays) Ulf Leser This Lecture Gene expression Microarrays Idea Technologies Problems Quality control Normalization Analysis next week! 2 http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/molecules/transcribe/
DIFFERENT BRAIN REGIONS ARE INFECTED WITH FUNGI IN ALZHEIMER S DISEASE
 DIFFERENT BRAIN REGIONS ARE INFECTED WITH FUNGI IN ALZHEIMER S DISEASE Diana Pisa 1, Ruth Alonso 1, Alberto Rábano 2, Izaskun Rodal 2 and Luis Carrasco 1* 1 Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa. c/nicolás
DIFFERENT BRAIN REGIONS ARE INFECTED WITH FUNGI IN ALZHEIMER S DISEASE Diana Pisa 1, Ruth Alonso 1, Alberto Rábano 2, Izaskun Rodal 2 and Luis Carrasco 1* 1 Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa. c/nicolás
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous gene tagging to study subcellular localization and chromatin binding. a, b, Schematic of experimental set-up to endogenously tag RNAi factors using the CRISPR Cas9 technology,
Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous gene tagging to study subcellular localization and chromatin binding. a, b, Schematic of experimental set-up to endogenously tag RNAi factors using the CRISPR Cas9 technology,
Single-cell analysis reveals the continuum of human lympho-myeloid progenitor cells
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-017-0001-2 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Single-cell analysis reveals the continuum of human lympho-myeloid progenitor
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-017-0001-2 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Single-cell analysis reveals the continuum of human lympho-myeloid progenitor
INSTITUT CURIE RPPA PLATFORM: USER POLICY AND AGREEMENT
 INSTITUT CURIE RPPA PLATFORM: USER POLICY AND AGREEMENT CONTACT: TRANSFERT.RPPA@CURIE.FR Last updated: 17/01/2018 1 CONTENT 1. Technology... 2 2. Samples... 3 2.1. Number of samples... 3 2.2. Sample lysis...
INSTITUT CURIE RPPA PLATFORM: USER POLICY AND AGREEMENT CONTACT: TRANSFERT.RPPA@CURIE.FR Last updated: 17/01/2018 1 CONTENT 1. Technology... 2 2. Samples... 3 2.1. Number of samples... 3 2.2. Sample lysis...
Figure S1. Phenotypic characterization of AND-1_WASKO cell lines. AND- 1_WASKO_C1.1 (WASKO_C1.1) and AND-1_WASKO_C1.2 (WASKO_C1.
 LEGENDS TO SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Phenotypic characterization of AND-1_WASKO cell lines. AND- 1_WASKO_C1.1 (WASKO_C1.1) and AND-1_WASKO_C1.2 (WASKO_C1.2) were stained with the antibodies oct3/4
LEGENDS TO SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Phenotypic characterization of AND-1_WASKO cell lines. AND- 1_WASKO_C1.1 (WASKO_C1.1) and AND-1_WASKO_C1.2 (WASKO_C1.2) were stained with the antibodies oct3/4
High-quality stranded RNA-seq libraries from single cells using the SMART-Seq Stranded Kit Product highlights:
 TECH NOTE High-quality stranded RNA-seq libraries from single cells using the SMART-Seq Stranded Kit Product highlights: Simple workflow starts directly from 1 1,000 cells or 10 pg 10 ng total RNA to generate
TECH NOTE High-quality stranded RNA-seq libraries from single cells using the SMART-Seq Stranded Kit Product highlights: Simple workflow starts directly from 1 1,000 cells or 10 pg 10 ng total RNA to generate
Supplemental Figure 1 A
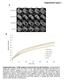 Supplemental Figure A prebleach postbleach 2 min 6 min 3 min mh2a.-gfp mh2a.2-gfp mh2a2-gfp GFP-H2A..9 Relative Intensity.8.7.6.5 mh2a. GFP n=8.4 mh2a.2 GFP n=4.3 mh2a2 GFP n=2.2 GFP H2A n=24. GFP n=7.
Supplemental Figure A prebleach postbleach 2 min 6 min 3 min mh2a.-gfp mh2a.2-gfp mh2a2-gfp GFP-H2A..9 Relative Intensity.8.7.6.5 mh2a. GFP n=8.4 mh2a.2 GFP n=4.3 mh2a2 GFP n=2.2 GFP H2A n=24. GFP n=7.
Introduction into single-cell RNA-seq. Kersti Jääger 19/02/2014
 Introduction into single-cell RNA-seq Kersti Jääger 19/02/2014 Cell is the smallest functional unit of life Nucleus.ATGC.UACG. A Cell KLTSH. The complexity of biology How many cell types? How many cells?
Introduction into single-cell RNA-seq Kersti Jääger 19/02/2014 Cell is the smallest functional unit of life Nucleus.ATGC.UACG. A Cell KLTSH. The complexity of biology How many cell types? How many cells?
EPIGENTEK. EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit. Base Catalog # P-2003 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE
 EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2003 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity
EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit Base Catalog # P-2003 PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE The EpiQuik Tissue Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Kit is suitable for combining the specificity
Roche Molecular Biochemicals Technical Note No. LC 12/2000
 Roche Molecular Biochemicals Technical Note No. LC 12/2000 LightCycler Absolute Quantification with External Standards and an Internal Control 1. General Introduction Purpose of this Note Overview of Method
Roche Molecular Biochemicals Technical Note No. LC 12/2000 LightCycler Absolute Quantification with External Standards and an Internal Control 1. General Introduction Purpose of this Note Overview of Method
Figure legends for supplement
 Figure legends for supplement Supplemental Figure 1 Characterization of purified and recombinant proteins Relevant fractions related the final stage of the purification protocol(bingham et al., 1998; Toba
Figure legends for supplement Supplemental Figure 1 Characterization of purified and recombinant proteins Relevant fractions related the final stage of the purification protocol(bingham et al., 1998; Toba
Echo-Enhanced SMART-Seq v4 for RNA Sequencing
 Echo-Enhanced SMART-Seq v4 for RNA Sequencing Jefferson Lai, Anna Lehto, John Lesnick and Carl Jarman Labcyte Inc. INTRODUCTION As the cost of sequencing has continued to decline by orders of magnitude
Echo-Enhanced SMART-Seq v4 for RNA Sequencing Jefferson Lai, Anna Lehto, John Lesnick and Carl Jarman Labcyte Inc. INTRODUCTION As the cost of sequencing has continued to decline by orders of magnitude
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. (A) UCSC Genome Browser view of region immediately downstream of the NEUROG3 start codon. All candidate grna target sites which meet the G(N 19 )NGG constraint are aligned to illustrate
Supplementary Figure 1. (A) UCSC Genome Browser view of region immediately downstream of the NEUROG3 start codon. All candidate grna target sites which meet the G(N 19 )NGG constraint are aligned to illustrate
T-iPSC. Gra-iPSC. B-iPSC. TTF-iPSC. Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.1667
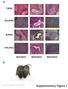 a T-iPSC Gra-iPSC B-iPSC TTF-iPSC Ectoderm Endoderm Mesoderm b Nature Biotechnology: doi:.38/nbt.667 Supplementary Figure Klf4 transgene expression Oct4 transgene expression.7 Fold GAPDH.6.5.4.3 Fold GAPDH
a T-iPSC Gra-iPSC B-iPSC TTF-iPSC Ectoderm Endoderm Mesoderm b Nature Biotechnology: doi:.38/nbt.667 Supplementary Figure Klf4 transgene expression Oct4 transgene expression.7 Fold GAPDH.6.5.4.3 Fold GAPDH
Assay Name: HPC proliferation measurement using Ki-67 cellular marker
 Assay Name: HPC proliferation measurement using Ki-67 cellular marker Assay ID: Celigo_02_0014 Table of Contents Experiment: HPC proliferation measurement using Ki-67 cellular marker... 2 Celigo Setup...2
Assay Name: HPC proliferation measurement using Ki-67 cellular marker Assay ID: Celigo_02_0014 Table of Contents Experiment: HPC proliferation measurement using Ki-67 cellular marker... 2 Celigo Setup...2
Supplementary Figure 1. Expressions of stem cell markers decreased in TRCs on 2D plastic. TRCs were cultured on plastic for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days,
 Supplementary Figure 1. Expressions of stem cell markers decreased in TRCs on 2D plastic. TRCs were cultured on plastic for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days, respectively, and their mrnas were quantified by real time
Supplementary Figure 1. Expressions of stem cell markers decreased in TRCs on 2D plastic. TRCs were cultured on plastic for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days, respectively, and their mrnas were quantified by real time
Positive selection gates for the collection of LRCs or nonlrcs had to be drawn based on the location and
 Determining positive selection gates for LRCs and nonlrcs Positive selection gates for the collection of LRCs or nonlrcs had to be drawn based on the location and shape of the Gaussian distributions. For
Determining positive selection gates for LRCs and nonlrcs Positive selection gates for the collection of LRCs or nonlrcs had to be drawn based on the location and shape of the Gaussian distributions. For
Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Immunodetection of full-length XA21 and the XA21 C-terminal cleavage product. Total protein extracted from Kitaake wild type and rice plants carrying
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 COMSOL simulation demonstrating flow characteristics in hydrodynamic trap structures. (a) Flow field within the hydrodynamic traps before
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 COMSOL simulation demonstrating flow characteristics in hydrodynamic trap structures. (a) Flow field within the hydrodynamic traps before
Single-Molecule Imaging Reveals Dynamics of CREB Transcription Factor Bound to Its Target Sequence
 Supplementary Information Single-Molecule Imaging Reveals Dynamics of CREB Transcription Factor Bound to Its Target Sequence Noriyuki Sugo, Masatoshi Morimatsu, Yoshiyuki Arai, Yoshinori Kousoku, Aya Ohkuni,
Supplementary Information Single-Molecule Imaging Reveals Dynamics of CREB Transcription Factor Bound to Its Target Sequence Noriyuki Sugo, Masatoshi Morimatsu, Yoshiyuki Arai, Yoshinori Kousoku, Aya Ohkuni,
Chemical hijacking of auxin signaling with an engineered auxin-tir1
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Chemical hijacking of auxin signaling with an engineered auxin-tir1 pair Naoyuki Uchida 1,2*, Koji Takahashi 2*, Rie Iwasaki 1, Ryotaro Yamada 2, Masahiko Yoshimura 2, Takaho
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Chemical hijacking of auxin signaling with an engineered auxin-tir1 pair Naoyuki Uchida 1,2*, Koji Takahashi 2*, Rie Iwasaki 1, Ryotaro Yamada 2, Masahiko Yoshimura 2, Takaho
V3 differential gene expression analysis
 differential gene expression analysis - What is measured by microarrays? - Microarray normalization - Differential gene expression (DE) analysis based on microarray data - Detection of outliers - RNAseq
differential gene expression analysis - What is measured by microarrays? - Microarray normalization - Differential gene expression (DE) analysis based on microarray data - Detection of outliers - RNAseq
