SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
|
|
|
- Earl Davidson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 doi: /nature11094 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Analysis of GFP expression in P0 wild type and mutant ( E1-4) Fezf2-Gfp BAC transgenic mice. Epifluorescent images of sagittal forebrain and coronal midbrain sections. In the wildtype Fezf2-Gfp transgenic brain, GFP was expressed in pyramidal neurons of neocortical L5 and hippocampus. GFP + corticofugal axons were present in the striatum (arrowheads) and the pons (dashed outline). Deletion of E1-3 from the BAC transgene ( E1-3) did not alter the expression pattern of GFP. Deletion of E4 ( E4), in contrast, led to the loss of neocortical and hippocampal GFP expression. GFP + corticofugal axons were also lost. Scale bars represent 200 µm. 1
2 Supplementary Figure 2: Analysis of GFP expression in E10.5 and E12.5 wild type and E4 mutant Fezf2-Gfp transgenic mice. Whole-mount brains revealed that deletion of E4 from the BAC transgene led to decreased GFP expression in E10.5 neocortex (Ncx) ventricular zone and loss of GFP expression in E12.5 Ncx. Ventral-medial GFP expression was preserved at E10.5 and
3 Supplementary Figure 3: Analysis of molecular alterations in cortical laminar identity in cortex-specific Fezf2 mutant and E4 deletion mutant. Sections of the P0 neocortex were immunostained with the antibodies against proteins indicated on the left. The expression pattern of CUX1, a marker of L2-4 neurons, was not affected by cortical deletion of Fezf2 (Fezf2 fl/f ;Emx1-Cre) or deletion of E4 (E4 -/- ). In contrast, immunostaining for BCL11B, a marker of subcortically-projecting L5 neurons and, to a lesser extent, L6 neurons, was dramatically reduced in both Fezf2 and E4-null mice. Weakly BCL11B-immunopositive neurons were present in L6 but some were dispersed to the upper layers. The expression of ZFPM2, a marker of L6 and subplate neurons, was also reduced and only observed in the deep portion of L6 and subplate in both Fezf2 and E4-null mice. Scale bar represents 200 µm. 3
4 Supplementary Figure 4: Heatmap matrix of pairwise Pearson correlation of spatio-temporal expression dynamics of human FEZF2 and 18 SOX genes in multiple regions of the developing and adult human brain 45. Gene expression data were generated using exon arrays and retrieved from database or from NCBI GEO with the accession number GSE FEZF2 expression is selectively and highly correlated (correlation coefficient 0.8) with SOX5 and the three members of the SoxC family (SOX4, SOX11, and SOX12), but not with other SOX genes (correlation coefficient ranging from -0.8 to 0.5). 4
5 Supplementary Figure 5: The expression patterns of Fezf2, Sox5, and members of the SoxC family during mouse embryonic development. In situ hybridization of the E14.5 mouse brain showed that the mrna patterns of Sox4 and Sox11, but not Sox12, significantly overlapped with those of Fezf2 and Sox5 in the cortical plate (CP). MZ, marginal zone; SP, subplate; IZ, intermediate zone; SVZ, subventricular zone; VZ, ventricular zone. Images were obtained from the Genepaint database ( 5
6 Supplementary Figure 6: Analysis of species-dependence in Sox11 activation of E4F2 between mouse and zebrafish using a luciferase assay. Sox11 significantly transactivated mouse (Mo), but not zebrafish (Ze), E4F2 sequence (P = 2.1x10-6, n = 4, one-tailed Student s t-test). Supplementary Figure 7: Whole-mount brains of P0 Sox4 and Sox11 single and double conditional knockout mice (cko and cdko, respectively). Cortical single deletion of Sox4 or Sox11 did not alter gross morphology of the cerebral cortex. The sizes of the Sox4;Sox11 cdko cerebral hemispheres and olfactory bulbs were reduced. 6
7 Supplementary Figure 8: Analysis of cortex-specific Sox4 and Sox11 single conditional knockout mice. P6 sagittal and coronal sections through the pons were immunostained for PRKCG, a marker of the CS neurons and axons. CS axons (arrowheads in a sagittal plane and dashed outline in a coronal plane) projected normally to the pons in single mutants of Sox4 (Sox4 fl/fl ;Sox11 fl/+ ; Emx1-Cre) or Sox11 (Sox4 fl/+ ;Sox11 fl/fl ; Emx1-Cre). Scale bar represents 200 µm. 7
8 Supplementary Figure 9: Analysis of cortical axons in cortex-specific Sox4 and Sox11 single and double knockout mice using a transgenic reporter mouse. Mice doubly transgenic for Emx1-Cre and CAG-Cat-Gfp express GFP in all cortical projection neurons and their axons, including the CS tract. P0 sagittal and coronal sections through the pons revealed normal CS axons projecting to the pons (arrowheads in a sagittal plane and dashed outline in a coronal plane) in single conditional mutants of Sox4 (Sox4 fl/fl ;Sox11 fl/+ ;Emx1- Cre) or Sox11 (Sox4 fl/+ ;Sox11 fl/fl ;Emx1-Cre). In Sox4 and Sox11 double conditional mutants (Sox4 fl/fl ;Sox11 fl/fl ; Emx1-Cre), CS axons were severely diminished. Scale bar represents 100 µm. 8
9 Supplementary Figure 10: Analysis of apoptosis marker expression in cortex-specific Sox4 and Sox11 double conditional knockout mice. a, Coronal sections of the P0 neocortex were immunostained for activated CASP3. b, The expression of activated CASP3 was slightly increased in both retrosplenial cortex/subiculum and dorsolateral fronto-parietal neocortex of cortex-specific Sox4 and Sox11 double conditional knockout mice (Sox4 fl/fl ;Sox11 fl/fl ; Emx1-Cre). 9
10 Supplementary Figure 11: Analysis of laminar defects in cortex-specific Sox4 and Sox11 single and double conditional knockout mice. Sections of the P0 neocortex were immunostained with antibodies against proteins indicated on the left. The expression and distribution of the examined markers were unaltered in the cortex-specific Sox4 (Sox4 fl/fl ;Sox11 fl/+ ;Emx1-Cre) or Sox11 (Sox4 fl/+ ;Sox11 fl/fl ;Emx1-Cre) knockout mice. In the Sox4 and Sox11 double mutants (Sox4 fl/fl ;Sox11 fl/fl ; Emx1-Cre), the distribution of neurons expressing CUX1 was shifted towards deep parts of the neocortex, where as the distribution of neurons expressing BCL11B (CTIP2) or ZFPM2 (FOG2) were shifted more superficially. Y axis: bin number, X axis: percentage of immunopositive cells in a bin. Scale bar represents 50 µm. 10
11 Supplementary Figure 12: Analysis of RELN expression in Sox4, Sox11 double mutants and E4 mutant. Sections of the P0 neocortex were immunostained for RELN (red), which is normally expressed in the Cajal-Retzius neurons of the layer (L) 1/marginal zone (MZ) in wild-type and E4 mutant (E4 -/- ). RELNexpression is absent from the marginal zone (MZ) of cortex-specific Sox4 and Sox11 double mutants (Sox4 fl/fl Sox11 fl/fl ; Emx1-Cre). Supplementary Figure 13: Analysis of evolutionary conservation of Fezf2 coding sequence and SOXbinding sites within the E4 element in craniates. a, Dendrogram of Fezf2 coding sequence aligned using ClustalW and drawn using TreeView. b, Analysis of SOX binding sites SB1-3 using TRANSFAC algorithm. Blue type indicates predicted functional binding site whereas black type indicates non-predicted sites. Red type indicates substitutions incompatible with predicted binding. Deletions (-) are also indicated. 11
12 Supplementary Table 1 Primers for the generation of BAC transgenic mutant constructs Primer name Sequence E1 A-arm Forward 5 - ATCTTGCTTTTTGCCTTAT -3 Reverse 5 - CAACAGTGTCAAGAATGCT -3 E1 B-arm Forward 5 - TGTTCTCAACAGAGCAGCT -3 Reverse 5 - TCCCAATTGCTGGGATTAG -3 E2 A-arm Forward 5 - TGTAGCCAGGTATACACT -3 Reverse 5 - TCCCAGTTATTTAACTTG -3 E2 B-arm Forward 5 - TATCTGCCTCAGGCTGAAG -3 Reverse 5 - TTCCAGGTATCGCACAGT -3 E3 A-arm Forward 5 - CTGGCACACAACAACATGC -3 Reverse 5 - TTTATTTTCCCAGGACAC -3 E3 B-arm Forward 5 - GAGGTAGTTCTGCTTTGT -3 Reverse 5 - TAATATCAGTTCACCTGC -3 E4 A-arm Forward 5 - CCAAAGCCACAGCCTTGTAC -3 Reverse 5 - TTTACCGCCTGCTCACCTGA -3 E4 B-arm Forward 5 - TGAAAAGCAGGCTCTCCAC -3 Reverse 5 - CCAAGCCAAGTGTGAAC -3 E4 enhancer primers Primer name Sequence E1 Forward 5 - ggactagt GAGAGACCGCCTAG -3 Reverse 5 - ggactagt TGTTGAGAACAACT - 3 E2 Forward 5 - ggactagt GCTTAACTCCTGCTC - 3 Reverse 5 - ggactagt GGGGGTGGGGCGGTG - 3 E3 Forward 5 - ggactagt AATAAATTTGGAGG - 3 Reverse 5 - ggactagt TCTCTCTCTCTCTCTCCCAT - 3 E4 Forward 5 - ggactagt TGGGCTGGAGGGAG - 3 Reverse 5 - ggactagt TCTACTTTTCTAAC - 3 E4F1 Forward 5 - gaagatct TGGGCTGGAGGGAG - 3 Reverse 5 - ggggtacc TCTCGCTGTGTTTTG - 3 E4F2 Forward 5 - gaagatct AAGATTAACTGGAC - 3 Reverse 5 - ggggtacc ATCTGAAGCTATCC - 3 E4F3 Forward 5 - gaagatct TTTTTTTAAAAAGAG - 3 Reverse 5 - ggggtacc GCTCATTAACTCCC - 3 E4F4 Forward 5 - gaagatct AGCTGACAAACTAC - 3 Reverse 5 - ggggtacc TGGCCTGTTGGGTTC - 3 Human, chimp, Forward 5 - gaagatct AAGATTAAATGGACAAAAGC - 3 macaque-e4f2 Reverse 5 - ggggtacc ATCTGAAGCTATCCTGTTAA - 3 Chick-E4F2 Forward 5 - gaagatct CTCTGAAGCTATCCTGTTAA - 3 Reverse 5 - ggggtacc GAGATTAAATGGACAAAAGC - 3 Xenopus-E4F2 Forward 5 - gaagatct AAGATTAAATGGACAAAAGT - 3 Reverse 5 - ggggtacc ATCTGAGGCTATCCTGTTAA - 3 Zebrafish-E4F2 Forward 5 - gaagatct GATTATAGGGACAAGAGCGCAT - 3 Reverse 5 - ggggtacc TGCTGACGCTACCCCCGTTA
13 MoE4F2 -m1 MoE4F2 -m2 MoE4F2 -m3 ZeE4F2- m1 ZeE4F2- m2 ZeE4F2- m3 Forward 5 - gatctaagattaactggacaaaagcgtagtaatgaactgtcaacagcgggg CCATCCACAGAACCAGCATCACTCAAGAACTCGGCATTTACAGGCAACAAA GGATTGTCTGGGACAGGAAGAAAAGACGACCTAGACTTT TGTTTAGTCAAC ACAATTGATTACAAATGAGAGATTAACAGGATAGCTTCAGATggtac -3 Reverse 5 - catctgaagctatcctgttaatctctcatttgtaatcaattgtgttgactaa ACAAAAGTCTAGGTCGTCTTTTCTTCCTGTCCCAGACAATCCTTTGTTGCCTGT AAATGCCGAGTTCTTGAGTGATGCTGGTTCTGTGGATGGCCCCGCTGTTGACA GTTCATTACTACGCTTTTGTCCAGTTAATCTTa -3 Forward 5 -gatctaagattaactggacaaaagcgtagtaatgaactgtcaacaatcgggc CATCCACAGAACCAGCATCACTCAAGAACTCGGCATTTACAGGCAACAAAGG CCCCGTCTGGGACAGGAAGAAAAGACGACCTAGACTTTTGTTTAGTCAACAC AATTGATTACAAATGAGAGATTAACAGGATAGCTTCAGATggtac -3 Reverse 5 - catctgaagctatcctgttaatctctcatttgtaatcaattgtgttgactaa ACAAAAGTCTAGGTCGTCTTTTCTTCCTGTCCCAGACGGGGCCTTTGTTGCCT GTAAATGCCGAGTTCTTGAGTGATGCTGGTTCTGTGGATGGCCCGATTGTTGA CAGTTCATTACTACGCTTTTGTCCAGTTAATCTTa -3 Forward 5 - gatctaagattaactggacaaaagcgtagtaatgaactgtcaacaatcgggc CATCCACAGAACCAGCATCACTCAAGAACTCGGCATTTACAGGCAACAAAGG ATTGTCTGGGACAGGAAGAAAAGACGACCTAGACTTTTGTTTGGTCAACACA ATTGATTACAAATGAGAGATTAACAGGATAGCTTCAGATggtac -3 Reverse 5 - catctgaagctatcctgttaatctctcatttgtaatcaattgtgttgaccaa ACAAAAGTCTAGGTCGTCTTTTCTTCCTGTCCCAGACAATCCTTTGTTGCCTGT AAATGCCGAGTTCTTGAGTGATGCTGGTTCTGTGGATGGCCCGATTGTTGACA GTTCATTACTACGCTTTTGTCCAGTTAATCTTa -3 Forward 5 -gatctgggattatagggacaagagcgcattaatgaactgtcaacaatcgaga GCATGTACACGACAGAGATCAGCCGAAATTGAGGCATTTACAAGCGACAAAA GCCCCGACTGAGACAGGAAGAAAAAAAGAGCTAGACTTTTGTTTGGTCAACT CAATTGATTGTAAATGGAAGATTAACGGGGGTAGCGTCAGCAggtac -3 Reverse 5 - ctgctgacgctacccccgttaatcttccatttacaatcaattgagttgacc AAACAAAAGTCTAGCTCTTTTTTTCTTCCTGTCTCAGTCGGGGCTTTTGTCGCT TGTAAATGCCTCAATTTCGGCTGATCTCTGTCGTGTACATGCTCTCGATTGTTG ACAGTTCATTAATGCGCTCTTGTCCCTATAATCCCa -3 Forward 5 -gatctgggattatagggacaagagcgcattaatgaactgtcaacagcggaga GCATGTACACGACAGAGATCAGCCGAAATTGAGGCATTTACAAGCGACAAAA GATTGACTGAGACAGGAAGAAAAAAAGAGCTAGACTTTTGTTTGGTCAACTC AATTGATTGTAAATGGAAGATTAACGGGGGTAGCGTCAGCAggtac -3 Reverse 5 - ctgctgacgctacccccgttaatcttccatttacaatcaattgagttgacc AAACAAAAGTCTAGCTCTTTTTTTCTTCCTGTCTCAGTCAATCTTTTGTCGCTT GTAAATGCCTCAATTTCGGCTGATCTCTGTCGTGTACATGCTCTCCGCTGTTG ACAGTTCATTAATGCGCTCTTGTCCCTATAATCCCa -3 Forward 5 -gatctgggattatagggacaagagcgcattaatgaactgtcaacagcggaga GCATGTACACGACAGAGATCAGCCGAAATTGAGGCATTTACAAGCGACAAAA GCCCCGACTGAGACAGGAAGAAAAAAAGAGCTAGACTTTTGTTTAGTCAACT CAATTGATTGTAAATGGAAGATTAACGGGGGTAGCGTCAGCAggtac -3 Reverse 5 - ctgctgacgctacccccgttaatcttccatttacaatcaattgagttgacta AACAAAAGTCTAGCTCTTTTTTTCTTCCTGTCTCAGTCGGGGCTTTTGTCGCTT GTAAATGCCTCAATTTCGGCTGATCTCTGTCGTGTACATGCTCTCCGCTGTTG ACAGTTCATTAATGCGCTCTTGTCCCTATAATCCCa
14 qrt-pcr primers Fezf2 Forward 5 - ACACCGGAGCTAGACCGTTT -3 Reverse 5 - TCCCTTTTTGGTGAAAGCCT -3 Sox4 Forward 5 - CGTCTACAAGGTGCGGACTC -3 Reverse 5 - CGCGCTTCACTTTCTTGT -3 Sox11 Forward 5 - GCCGGCTCTACTACAGCTTC -3 Reverse 5 - GCTGGATGAGGAGGTGGAC -3 Gapdh Forward 5 - GATCAACACGTACCAGTGCAA -3 Reverse 5 - TGCCTCGATGGACAGATAGA -3 Oligonucleotide sequence for EMSA SB2-wt Forward aaaaaacaaaggattgtctgggacaggaagaaaaga Reverse aaaatcttttcttcctgtcccagacaatcctttgtt SB2-mut Forward aaaaaacaaaggcccctctgggacaggaagaaaaga Reverse aaaatcttttcttcctgtcccagaggggcctttgtt 14
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Kwan et al. 10.1073/pnas.0806791105 SI Text Plasmid Constructs. For Sox5 expression, the full-length Sox5 cdna (BC110478) was inserted into pcagen. Luciferase reporter plasmids were
Supporting Information Kwan et al. 10.1073/pnas.0806791105 SI Text Plasmid Constructs. For Sox5 expression, the full-length Sox5 cdna (BC110478) was inserted into pcagen. Luciferase reporter plasmids were
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of inducible BICD2 knock-out mice. A) The mouse BICD2 locus and gene targeting constructs. To generate an inducible Bicd2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of inducible BICD2 knock-out mice. A) The mouse BICD2 locus and gene targeting constructs. To generate an inducible Bicd2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
DOI:.38/ncb327 a b Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP isoform IP: GFP IP: -GFP IP: GFP Sequence coverage (%) 4 3 2 IP: -GFP IP: GFP 33 52 58 isoform 2 33 49 47 IP: Control IP: Peptide Sequence Start
Purification of RNA from populations of hescs and bulk purified RNA.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Purification of RNA from populations of hescs and bulk purified RNA. (a) Schematic of the experiment comparing a modified RNA harvesting protocol to standard RNA purification protocol
Supplementary Figure 1 Purification of RNA from populations of hescs and bulk purified RNA. (a) Schematic of the experiment comparing a modified RNA harvesting protocol to standard RNA purification protocol
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Nowakowski et al. 10.1073/pnas.1219385110 SI Materials and Methods Primary Antibodies. Primary antibodies used in this study were raised against BrdU (rat, 1:50; Abcam), cleaved
Supporting Information Nowakowski et al. 10.1073/pnas.1219385110 SI Materials and Methods Primary Antibodies. Primary antibodies used in this study were raised against BrdU (rat, 1:50; Abcam), cleaved
Supplementary Information. Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish
 Supplementary Information Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish Hagen R. Witzel 1, Sirisha Cheedipudi 1, Rui Gao 1, Didier Y.R. Stainier 2 and Gergana D. Dobreva 1,3* 1 Origin
Supplementary Information Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish Hagen R. Witzel 1, Sirisha Cheedipudi 1, Rui Gao 1, Didier Y.R. Stainier 2 and Gergana D. Dobreva 1,3* 1 Origin
(a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of Diaph3 ko mice. (a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for different regions of Diaph3 mrna from WT, heterozygote
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of Diaph3 ko mice. (a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for different regions of Diaph3 mrna from WT, heterozygote
Satb2 Is a Postmitotic Determinant for Upper-Layer Neuron Specification in the Neocortex
 Article Satb2 Is a Postmitotic Determinant for Upper-Layer Neuron Specification in the Neocortex Olga Britanova, 1,3,8 Camino de Juan Romero, 1,2,8 Amanda Cheung, 4 Kenneth Y. Kwan, 5 Manuela Schwark,
Article Satb2 Is a Postmitotic Determinant for Upper-Layer Neuron Specification in the Neocortex Olga Britanova, 1,3,8 Camino de Juan Romero, 1,2,8 Amanda Cheung, 4 Kenneth Y. Kwan, 5 Manuela Schwark,
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Ihh interacts preferentially with its upstream neighboring gene Nhej1. Genes are indicated by gray lines, and Ihh and Nhej1 are highlighted in blue. 4C seq performed in E14.5 limbs
Supplementary Figure 1 Ihh interacts preferentially with its upstream neighboring gene Nhej1. Genes are indicated by gray lines, and Ihh and Nhej1 are highlighted in blue. 4C seq performed in E14.5 limbs
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of RNF8, HERC2 and NEURL4 in the cerebellum and knockdown of RNF8 by RNAi (a) Lysates of the cerebellum from rat
 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of RNF8, HERC2 and NEURL4 in the cerebellum and knockdown of RNF8 by RNAi (a) Lysates of the cerebellum from rat pups at P6, P14, P22, P30 and adult (A) rats were subjected
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of RNF8, HERC2 and NEURL4 in the cerebellum and knockdown of RNF8 by RNAi (a) Lysates of the cerebellum from rat pups at P6, P14, P22, P30 and adult (A) rats were subjected
Revised: RG-RV2 by Fukuhara et al.
 Supplemental Figure 1 The generation of Spns2 conditional knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the wild type Spns2 locus (Spns2 + ), the targeted allele, the floxed allele (Spns2 f ) and the
Supplemental Figure 1 The generation of Spns2 conditional knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the wild type Spns2 locus (Spns2 + ), the targeted allele, the floxed allele (Spns2 f ) and the
Supplementary Figure 1. APP cleavage assay. HEK293 cells were transfected with various
 Supplementary Figure 1. APP cleavage assay. HEK293 cells were transfected with various GST-tagged N-terminal truncated APP fragments including GST-APP full-length (FL), APP (123-695), APP (189-695), or
Supplementary Figure 1. APP cleavage assay. HEK293 cells were transfected with various GST-tagged N-terminal truncated APP fragments including GST-APP full-length (FL), APP (123-695), APP (189-695), or
Supplementary Figure 1. Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings.
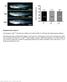 Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
Supplementary Figure 1 Homozygous rag2 E450fs mutants are healthy and viable similar to wild-type and heterozygous siblings. (left) Representative bright-field images of wild type (wt), heterozygous (het)
Supplemental Figure S1. PGRN Binding to Sortilin.
 1 Neuron, volume 68 Supplemental Data Sortilin-Mediated Endocytosis Determines Levels of the Frontotemporal Dementia Protein, Progranulin Fenghua Hu, Thihan Padukkavidana, Christian B. Vægter, Owen A.
1 Neuron, volume 68 Supplemental Data Sortilin-Mediated Endocytosis Determines Levels of the Frontotemporal Dementia Protein, Progranulin Fenghua Hu, Thihan Padukkavidana, Christian B. Vægter, Owen A.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fujii et al. 10.1073/pnas.1217563110 A Human Cen chromosome 4q ART3 NUP54 SCARB2 FAM47E CCDC8 Tel B Bac clones RP11-54D17 RP11-628A4 Exon 1 2 34 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 5 3 PCR region
Supporting Information Fujii et al. 10.1073/pnas.1217563110 A Human Cen chromosome 4q ART3 NUP54 SCARB2 FAM47E CCDC8 Tel B Bac clones RP11-54D17 RP11-628A4 Exon 1 2 34 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 5 3 PCR region
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.4166
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature22047 Supplementary discussion Overall developmental timeline and brain regionalization in human whole-brain organoids We first defined the timeline of generation of broadly-defined cell
doi:10.1038/nature22047 Supplementary discussion Overall developmental timeline and brain regionalization in human whole-brain organoids We first defined the timeline of generation of broadly-defined cell
- Supplementary Information -
 TRIM32 dependent transcription in adult neural progenitor cells regulates neuronal differentiation. - Supplementary Information - Anna-Lena Hillje 1, 2#, Maria Angeliki S. Pavlou 1, 2#, Elisabeth Beckmann
TRIM32 dependent transcription in adult neural progenitor cells regulates neuronal differentiation. - Supplementary Information - Anna-Lena Hillje 1, 2#, Maria Angeliki S. Pavlou 1, 2#, Elisabeth Beckmann
Sall1 regulates cortical neurogenesis and laminar fate specification in mice: implications for neural abnormalities in Townes-Brocks syndrome
 Disease Models & Mechanisms 5, 351-365 (2012) doi:10.1242/dmm.002873 and laminar fate specification in mice: implications for neural abnormalities in Townes-Brocks syndrome Susan J. Harrison 1,2, *, Ryuichi
Disease Models & Mechanisms 5, 351-365 (2012) doi:10.1242/dmm.002873 and laminar fate specification in mice: implications for neural abnormalities in Townes-Brocks syndrome Susan J. Harrison 1,2, *, Ryuichi
DRG Pituitary Cerebral Cortex
 Liver Spinal cord Pons Atg5 -/- Atg5 +/+ DRG Pituitary Cerebral Cortex WT KO Supplementary Figure S1 Ubiquitin-positive IBs accumulate in Atg5 -/- tissues. Atg5 -/- neonatal tissues were fixed and decalcified.
Liver Spinal cord Pons Atg5 -/- Atg5 +/+ DRG Pituitary Cerebral Cortex WT KO Supplementary Figure S1 Ubiquitin-positive IBs accumulate in Atg5 -/- tissues. Atg5 -/- neonatal tissues were fixed and decalcified.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12119 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND LEGENDS pre-let-7a- 1 +14U pre-let-7a- 1 Ddx3x Dhx30 Dis3l2 Elavl1 Ggt5 Hnrnph 2 Osbpl5 Puf60 Rnpc3 Rpl7 Sf3b3 Sf3b4 Tia1 Triobp U2af1 U2af2 1 6 2 4 3
doi:10.1038/nature12119 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND LEGENDS pre-let-7a- 1 +14U pre-let-7a- 1 Ddx3x Dhx30 Dis3l2 Elavl1 Ggt5 Hnrnph 2 Osbpl5 Puf60 Rnpc3 Rpl7 Sf3b3 Sf3b4 Tia1 Triobp U2af1 U2af2 1 6 2 4 3
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
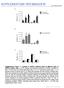 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12474 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of mtdna mutation loads in different types of mtdna mutator mice. a, PCR, cloning, and sequencing analysis of mtdna mutations
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12474 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of mtdna mutation loads in different types of mtdna mutator mice. a, PCR, cloning, and sequencing analysis of mtdna mutations
Supplemental Figure 1 Human REEP family of proteins can be divided into two distinct subfamilies. Residues (single letter amino acid code) identical
 Supplemental Figure Human REEP family of proteins can be divided into two distinct subfamilies. Residues (single letter amino acid code) identical in all six REEPs are highlighted in green. Additional
Supplemental Figure Human REEP family of proteins can be divided into two distinct subfamilies. Residues (single letter amino acid code) identical in all six REEPs are highlighted in green. Additional
GM130 Is Required for Compartmental Organization of Dendritic Golgi Outposts
 Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information GM130 Is Required for Compartmental Organization of Dendritic Golgi Outposts Wei Zhou, Jin Chang, Xin Wang, Masha G. Savelieff, Yinyin Zhao, Shanshan
Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information GM130 Is Required for Compartmental Organization of Dendritic Golgi Outposts Wei Zhou, Jin Chang, Xin Wang, Masha G. Savelieff, Yinyin Zhao, Shanshan
Zbtb20 modulates the sequential generation of neuronal layers in developing cortex
 Tonchev et al. Molecular Brain (2016) 9:65 DOI 10.1186/s13041-016-0242-2 RESEARCH Open Access Zbtb20 modulates the sequential generation of neuronal layers in developing cortex Anton B. Tonchev 1,2,3*,
Tonchev et al. Molecular Brain (2016) 9:65 DOI 10.1186/s13041-016-0242-2 RESEARCH Open Access Zbtb20 modulates the sequential generation of neuronal layers in developing cortex Anton B. Tonchev 1,2,3*,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. lev-9 mutants are resistant to levamisole. The levamisole dose-response curves indicate that lev-9 mutants are partially resistant to levamisole similar to lev-10(kr26) mutants. unc-29(x29)
Figure S1. lev-9 mutants are resistant to levamisole. The levamisole dose-response curves indicate that lev-9 mutants are partially resistant to levamisole similar to lev-10(kr26) mutants. unc-29(x29)
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. ChIP-seq genome browser views of BRM occupancy at previously identified BRM targets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ChIP-seq genome browser views of BRM occupancy at previously identified BRM targets. Gene structures are shown underneath each panel. Supplementary Figure 2 pref6::ref6-gfp complements
Supplementary Figure 1 ChIP-seq genome browser views of BRM occupancy at previously identified BRM targets. Gene structures are shown underneath each panel. Supplementary Figure 2 pref6::ref6-gfp complements
Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss Yunjong Lee, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Joo-Ho Shin, Yun-Il Lee, Han Seok Ko, Debbie Swing,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss Yunjong Lee, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Joo-Ho Shin, Yun-Il Lee, Han Seok Ko, Debbie Swing,
Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic representation of mouse lines Pax6 fl/fl and mrx-cre used in this study. (A) To generate Pax6 fl/ fl
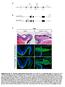 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic representation of mouse lines Pax6 fl/fl and mrx-cre used in this study. (A) To generate Pax6 fl/ fl, loxp sites flanking exons 3-6 (red arrowheads) were introduced into
Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic representation of mouse lines Pax6 fl/fl and mrx-cre used in this study. (A) To generate Pax6 fl/ fl, loxp sites flanking exons 3-6 (red arrowheads) were introduced into
Generation of App knock-in mice reveals deletion mutations protective against Alzheimer s. disease-like pathology. Nagata et al.
 Generation of App knock-in mice reveals deletion mutations protective against Alzheimer s disease-like pathology Nagata et al. Supplementary Fig 1. Previous App knock-in model did not show Aβ accumulation
Generation of App knock-in mice reveals deletion mutations protective against Alzheimer s disease-like pathology Nagata et al. Supplementary Fig 1. Previous App knock-in model did not show Aβ accumulation
Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cell (hesc) Derived Pyramidal Neurons
 University of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Honors Scholar Theses Honors Scholar Program Spring 5-10-2009 Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cell (hesc) Derived Pyramidal Neurons Eagan Jacqueline
University of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Honors Scholar Theses Honors Scholar Program Spring 5-10-2009 Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cell (hesc) Derived Pyramidal Neurons Eagan Jacqueline
Supplementary Table, Figures and Videos
 Supplementary Table, Figures and Videos Table S1. Oligonucleotides used for different approaches. (A) RT-qPCR study. (B) qpcr study after ChIP assay. (C) Probes used for EMSA. Figure S1. Notch activation
Supplementary Table, Figures and Videos Table S1. Oligonucleotides used for different approaches. (A) RT-qPCR study. (B) qpcr study after ChIP assay. (C) Probes used for EMSA. Figure S1. Notch activation
SeeDB: a simple and morphology-preserving optical clearing agent for neuronal circuit reconstruction
 Nature Neuroscience Supplementary Information SeeDB: a simple and morphology-preserving optical clearing agent for neuronal circuit reconstruction Meng-Tsen Ke, Satoshi Fujimoto, and Takeshi Imai. Correspondence
Nature Neuroscience Supplementary Information SeeDB: a simple and morphology-preserving optical clearing agent for neuronal circuit reconstruction Meng-Tsen Ke, Satoshi Fujimoto, and Takeshi Imai. Correspondence
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4169
 Supplementary Fig.1. EC-specific deletion of Ccm3 by Cdh5-CreERT2. a. mt/mg reporter mice were bred with Cdh5CreERT2 deleter mice followed by tamoxifen feeding from P1 to P3. mg expression was specifically
Supplementary Fig.1. EC-specific deletion of Ccm3 by Cdh5-CreERT2. a. mt/mg reporter mice were bred with Cdh5CreERT2 deleter mice followed by tamoxifen feeding from P1 to P3. mg expression was specifically
(A) Schematic depicting morphology of cholinergic DA and DB motor neurons in an L1
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS Supplemental Figure 1 Figure S1. Expression of the non-alpha nachr subunit ACR-2. (A) Schematic depicting morphology of cholinergic DA and DB motor neurons in an L1 animal. Wide-field
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS Supplemental Figure 1 Figure S1. Expression of the non-alpha nachr subunit ACR-2. (A) Schematic depicting morphology of cholinergic DA and DB motor neurons in an L1 animal. Wide-field
Supplemental Figure 1: Podocyte specific knockdown of Klf4 in Podocin-Cre Klf4 flox/flox mice was confirmed. (A) Primary glomerular epithelial cells
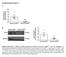 Supplemental Figure 1: Podocyte specific knockdown of Klf4 in Podocin-Cre Klf4 flox/flox mice was confirmed. (A) Primary glomerular epithelial cells were isolated from 10-week old Podocin-Cre Klf4 flox/flox
Supplemental Figure 1: Podocyte specific knockdown of Klf4 in Podocin-Cre Klf4 flox/flox mice was confirmed. (A) Primary glomerular epithelial cells were isolated from 10-week old Podocin-Cre Klf4 flox/flox
Supplementary Figure S1. Alterations in Fzr1( / );Nestin-Cre brains. (a) P10 Cdh1-deficient brains display low levels of Myelin basic protein (MBP)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Alterations in Fzr1( / );Nestin-Cre brains. (a) P10 Cdh1-deficient brains display low levels of Myelin basic protein (MBP) in the cortex (area 1 as defined in Fig. 2a), and corpus
Supplementary Figure S1. Alterations in Fzr1( / );Nestin-Cre brains. (a) P10 Cdh1-deficient brains display low levels of Myelin basic protein (MBP) in the cortex (area 1 as defined in Fig. 2a), and corpus
b number of motif occurrences
 supplementary information DOI: 1.138/ncb194 a b number of motif occurrences number of motif occurrences number of motif occurrences I II III IV V X TTGGTCAGTGCA 3 8 23 4 13 239 TTGGTCAGTGCT 7 5 8 1 3 83
supplementary information DOI: 1.138/ncb194 a b number of motif occurrences number of motif occurrences number of motif occurrences I II III IV V X TTGGTCAGTGCA 3 8 23 4 13 239 TTGGTCAGTGCT 7 5 8 1 3 83
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10810 Supplementary Fig. 1: Mutation of the loqs gene leads to shortened lifespan and adult-onset brain degeneration. a. Northern blot of control and loqs f00791 mutant flies. loqs f00791
doi:10.1038/nature10810 Supplementary Fig. 1: Mutation of the loqs gene leads to shortened lifespan and adult-onset brain degeneration. a. Northern blot of control and loqs f00791 mutant flies. loqs f00791
Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 )
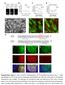 Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 ) homologous recombination arm (left) and of the right (3 )
Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 ) homologous recombination arm (left) and of the right (3 )
Control of cortex development by ULK4, a rare risk gene for mental disorders including schizophrenia
 Control of cortex development by ULK4, a rare risk gene for mental disorders including schizophrenia Bing Lang, Lei Zhang, Guanyu Jiang, Ling Hu, Wei Lan, Lei Zhao, Irene Hunter, Michal Pruski, Ning-Ning
Control of cortex development by ULK4, a rare risk gene for mental disorders including schizophrenia Bing Lang, Lei Zhang, Guanyu Jiang, Ling Hu, Wei Lan, Lei Zhao, Irene Hunter, Michal Pruski, Ning-Ning
Supplementary Figure 1. α-synuclein is truncated in PD and LBD brains. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.
 Supplementary Figure 1 α-synuclein is truncated in PD and LBD brains. (a) Specificity of anti-n103 antibody. Anti-N103 antibody was coated on an ELISA plate and different concentrations of full-length
Supplementary Figure 1 α-synuclein is truncated in PD and LBD brains. (a) Specificity of anti-n103 antibody. Anti-N103 antibody was coated on an ELISA plate and different concentrations of full-length
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/310/5753/1487/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Stem Cell Self-Renewal Controlled by Chromatin Remodeling Factors Rongwen Xi and Ting Xie* *To whom correspondence should
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/310/5753/1487/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Stem Cell Self-Renewal Controlled by Chromatin Remodeling Factors Rongwen Xi and Ting Xie* *To whom correspondence should
To assess the localization of Citrine fusion proteins, we performed antibody staining to
 Trinh et al 1 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL FlipTraps recapitulate endogenous protein localization To assess the localization of Citrine fusion proteins, we performed antibody staining to compare the expression
Trinh et al 1 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL FlipTraps recapitulate endogenous protein localization To assess the localization of Citrine fusion proteins, we performed antibody staining to compare the expression
Supplementary Information Cyclin Y inhibits plasticity-induced AMPA receptor exocytosis and LTP
 Supplementary Information Cyclin Y inhibits plasticity-induced AMPA receptor exocytosis and LTP Eunsil Cho, Dong-Hyun Kim, Young-Na Hur, Daniel J. Whitcomb, Philip Regan, Jung-Hwa Hong, Hanna Kim, Young
Supplementary Information Cyclin Y inhibits plasticity-induced AMPA receptor exocytosis and LTP Eunsil Cho, Dong-Hyun Kim, Young-Na Hur, Daniel J. Whitcomb, Philip Regan, Jung-Hwa Hong, Hanna Kim, Young
GFP CCD2 GFP IP:GFP
 D1 D2 1 75 95 148 178 492 GFP CCD1 CCD2 CCD2 GFP D1 D2 GFP D1 D2 Beclin 1 IB:GFP IP:GFP Supplementary Figure 1: Mapping domains required for binding to HEK293T cells are transfected with EGFP-tagged mutant
D1 D2 1 75 95 148 178 492 GFP CCD1 CCD2 CCD2 GFP D1 D2 GFP D1 D2 Beclin 1 IB:GFP IP:GFP Supplementary Figure 1: Mapping domains required for binding to HEK293T cells are transfected with EGFP-tagged mutant
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information MicroRNA-212/132 family is required for epithelial stromal interactions necessary for mouse mammary gland development Ahmet Ucar, Vida Vafaizadeh, Hubertus Jarry, Jan Fiedler,
Supplementary Information MicroRNA-212/132 family is required for epithelial stromal interactions necessary for mouse mammary gland development Ahmet Ucar, Vida Vafaizadeh, Hubertus Jarry, Jan Fiedler,
 Figure S1. Generation of HspA4 -/- mice. (A) Structures of the wild-type (Wt) HspA4 -/- allele, targeting vector and targeted allele are shown together with the relevant restriction sites. The filled rectangles
Figure S1. Generation of HspA4 -/- mice. (A) Structures of the wild-type (Wt) HspA4 -/- allele, targeting vector and targeted allele are shown together with the relevant restriction sites. The filled rectangles
Supplementary Figure 1 Phosphorylated tau accumulates in Nrf2 (-/-) mice. Hippocampal tissues obtained from Nrf2 (-/-) (10 months old, 4 male; 2
 Supplementary Figure 1 Phosphorylated tau accumulates in Nrf2 (-/-) mice. Hippocampal tissues obtained from Nrf2 (-/-) (10 months old, 4 male; 2 female) or wild-type (5 months old, 1 male; 11 months old,
Supplementary Figure 1 Phosphorylated tau accumulates in Nrf2 (-/-) mice. Hippocampal tissues obtained from Nrf2 (-/-) (10 months old, 4 male; 2 female) or wild-type (5 months old, 1 male; 11 months old,
Supplementary Figure 1. Expressions of stem cell markers decreased in TRCs on 2D plastic. TRCs were cultured on plastic for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days,
 Supplementary Figure 1. Expressions of stem cell markers decreased in TRCs on 2D plastic. TRCs were cultured on plastic for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days, respectively, and their mrnas were quantified by real time
Supplementary Figure 1. Expressions of stem cell markers decreased in TRCs on 2D plastic. TRCs were cultured on plastic for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days, respectively, and their mrnas were quantified by real time
Supplemental Figure 1 (Figure S1), related to Figure 1 Figure S1 provides evidence to demonstrate Nfatc1Cre is a mouse line that directed gene
 Developmental Cell, Volume 25 Supplemental Information Brg1 Governs a Positive Feedback Circuit in the Hair Follicle for Tissue Regeneration and Repair Yiqin Xiong, Wei Li, Ching Shang, Richard M. Chen,
Developmental Cell, Volume 25 Supplemental Information Brg1 Governs a Positive Feedback Circuit in the Hair Follicle for Tissue Regeneration and Repair Yiqin Xiong, Wei Li, Ching Shang, Richard M. Chen,
Peter Dy, Weihuan Wang, Pallavi Bhattaram, Qiuqing Wang, Lai Wang, R. Tracy Ballock, and Véronique Lefebvre
 Developmental Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Sox9 Directs Hypertrophic Maturation and Blocks Osteoblast Differentiation of Growth Plate Chondrocytes Peter Dy, Weihuan Wang, Pallavi Bhattaram,
Developmental Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Sox9 Directs Hypertrophic Maturation and Blocks Osteoblast Differentiation of Growth Plate Chondrocytes Peter Dy, Weihuan Wang, Pallavi Bhattaram,
Optimizing Cas9 and sgrna concentrations for increasing mutation efficiency. Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.3360
 Supplementary Figure 1 Optimizing Cas9 and sgrna concentrations for increasing mutation efficiency. (a) Wild-type, 2-dpf slc24a5 b1 embryos and a series of slc24a5 CRISPR-injected embryos; anterior is
Supplementary Figure 1 Optimizing Cas9 and sgrna concentrations for increasing mutation efficiency. (a) Wild-type, 2-dpf slc24a5 b1 embryos and a series of slc24a5 CRISPR-injected embryos; anterior is
Supplementary Figure 1. TSA (10 nmol/l), non-class-selective HDAC inhibitor, potentiates
 Supplementary Figure 1. TSA (10 nmol/l), non-class-selective HDAC inhibitor, potentiates vascular calcification (VC). (a) Von Kossa staining shows that TSA potentiated the Pi-induced VC. Scale bar, 100
Supplementary Figure 1. TSA (10 nmol/l), non-class-selective HDAC inhibitor, potentiates vascular calcification (VC). (a) Von Kossa staining shows that TSA potentiated the Pi-induced VC. Scale bar, 100
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure S1. Generation of a synaptobrevin2-mrfp knock-in mouse. (a) Targeting strategy of Syb2-mRFP knock-in mouse leaving the synaptobrevin2 gene locus intact except
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure S1. Generation of a synaptobrevin2-mrfp knock-in mouse. (a) Targeting strategy of Syb2-mRFP knock-in mouse leaving the synaptobrevin2 gene locus intact except
Regulation of axonal and dendritic growth by the extracellular calcium-sensing
 Regulation of axonal and dendritic growth by the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR). Thomas N. Vizard, Gerard W. O Keeffe, Humberto Gutierrez, Claudine H. Kos, Daniela Riccardi, Alun M. Davies
Regulation of axonal and dendritic growth by the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR). Thomas N. Vizard, Gerard W. O Keeffe, Humberto Gutierrez, Claudine H. Kos, Daniela Riccardi, Alun M. Davies
MeCP2. MeCP2/α-tubulin. GFP mir1-1 mir132
 Conservation Figure S1. Schematic showing 3 UTR (top; thick black line), mir132 MRE (arrow) and nucleotide sequence conservation (vertical black lines; http://genome.ucsc.edu). a GFP mir1-1 mir132 b GFP
Conservation Figure S1. Schematic showing 3 UTR (top; thick black line), mir132 MRE (arrow) and nucleotide sequence conservation (vertical black lines; http://genome.ucsc.edu). a GFP mir1-1 mir132 b GFP
Supplementary Figure 1 A
 Supplementary Figure A B M. mullata p53, 3 UTR Luciferase activity (%) mir-5b 8 Le et al. Supplementary Information NC-DP - + - - - - - NC-DP - - + - - - - NC-DP3 - - - + - - - 5b-DP - - - - + + + NC-AS
Supplementary Figure A B M. mullata p53, 3 UTR Luciferase activity (%) mir-5b 8 Le et al. Supplementary Information NC-DP - + - - - - - NC-DP - - + - - - - NC-DP3 - - - + - - - 5b-DP - - - - + + + NC-AS
Tcf7L2 is essential for neurogenesis in the developing mouse neocortex
 Chodelkova et al. Neural Development (2018) 13:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13064-018-0107-8 SHORT REPORT Tcf7L2 is essential for neurogenesis in the developing mouse neocortex Olga Chodelkova 1, Jan Masek
Chodelkova et al. Neural Development (2018) 13:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13064-018-0107-8 SHORT REPORT Tcf7L2 is essential for neurogenesis in the developing mouse neocortex Olga Chodelkova 1, Jan Masek
Supplementary Figure 1. Mouse genetic models used for identification of Axin2-
 Supplementary Figure 1. Mouse genetic models used for identification of Axin2- expressing cells and their derivatives. Schematic representations illustrate genetic cell labeling strategies to identify
Supplementary Figure 1. Mouse genetic models used for identification of Axin2- expressing cells and their derivatives. Schematic representations illustrate genetic cell labeling strategies to identify
Regulation of transcription by the MLL2 complex and MLL complex-associated AKAP95
 Supplementary Information Regulation of transcription by the complex and MLL complex-associated Hao Jiang, Xiangdong Lu, Miho Shimada, Yali Dou, Zhanyun Tang, and Robert G. Roeder Input HeLa NE IP lot:
Supplementary Information Regulation of transcription by the complex and MLL complex-associated Hao Jiang, Xiangdong Lu, Miho Shimada, Yali Dou, Zhanyun Tang, and Robert G. Roeder Input HeLa NE IP lot:
Supplementary Figure 1. Wnt10a mutation causes aberrant molar tooth development and formation of an ectopic M4 molar. (a,b) Smaller molar teeth with
 Supplementary Figure 1. Wnt10a mutation causes aberrant molar tooth development and formation of an ectopic M4 molar. (a,b) Smaller molar teeth with blunted cusp formation, and presence of an ectopic molar
Supplementary Figure 1. Wnt10a mutation causes aberrant molar tooth development and formation of an ectopic M4 molar. (a,b) Smaller molar teeth with blunted cusp formation, and presence of an ectopic molar
Supplement Figure S1:
 Supplement Figure S1: A, Sequence of Xcadherin-11 Morpholino 1 (Xcad-11MO) and 2 (Xcad-11 MO2) and control morpholino in comparison to the Xcadherin-11 sequence. The Xcad-11MO binding sequence spans the
Supplement Figure S1: A, Sequence of Xcadherin-11 Morpholino 1 (Xcad-11MO) and 2 (Xcad-11 MO2) and control morpholino in comparison to the Xcadherin-11 sequence. The Xcad-11MO binding sequence spans the
A Novel Role for Dbx1-Derived Cajal-Retzius Cells in Early Regionalization of the Cerebral Cortical Neuroepithelium
 A Novel Role for Dbx1-Derived Cajal-Retzius Cells in Early Regionalization of the Cerebral Cortical Neuroepithelium Amélie Griveau 1, Ugo Borello 1., Frédéric Causeret 1., Fadel Tissir 2, Nicole Boggetto
A Novel Role for Dbx1-Derived Cajal-Retzius Cells in Early Regionalization of the Cerebral Cortical Neuroepithelium Amélie Griveau 1, Ugo Borello 1., Frédéric Causeret 1., Fadel Tissir 2, Nicole Boggetto
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Defective T and B cell lineage development in the absence of 53BP1. a, Average number of thymocytes in WT, 53BP1 /, p53 /, 53BP1 / / p53, Nbs1 tr735 and 53BP1 / Nbs1 tr735 mice
Supplementary Figure 1. Defective T and B cell lineage development in the absence of 53BP1. a, Average number of thymocytes in WT, 53BP1 /, p53 /, 53BP1 / / p53, Nbs1 tr735 and 53BP1 / Nbs1 tr735 mice
Fig Hypoxia causes growth retardation and developmental delay. (A) Morphology of wildtype zebrafish embryos at 48 hours post fertilization
 FIGURES AND TABLES Fig. 1-1. Hypoxia causes growth retardation and developmental delay. (A) Morphology of wildtype zebrafish embryos at 48 hours post fertilization (hpf) after 24 h of normoxia or hypoxia
FIGURES AND TABLES Fig. 1-1. Hypoxia causes growth retardation and developmental delay. (A) Morphology of wildtype zebrafish embryos at 48 hours post fertilization (hpf) after 24 h of normoxia or hypoxia
A population of Nestin expressing progenitors in the cerebellum exhibits increased tumorigenicity
 A population of Nestin expressing progenitors in the cerebellum exhibits increased tumorigenicity Peng Li 1,2, Fang Du 1, Larra W. Yuelling 1, Tiffany Lin 3, Renata E. Muradimova 1, Rossella Tricarico
A population of Nestin expressing progenitors in the cerebellum exhibits increased tumorigenicity Peng Li 1,2, Fang Du 1, Larra W. Yuelling 1, Tiffany Lin 3, Renata E. Muradimova 1, Rossella Tricarico
Supplemental Data. Cui et al. (2012). Plant Cell /tpc a b c d. Stem UBC32 ACTIN
 A Root Stem Leaf Flower Silique Senescence leaf B a b c d UBC32 ACTIN C * Supplemental Figure 1. Expression Pattern and Protein Sequence of UBC32 Homologues in Yeast, Human, and Arabidopsis. (A) Expression
A Root Stem Leaf Flower Silique Senescence leaf B a b c d UBC32 ACTIN C * Supplemental Figure 1. Expression Pattern and Protein Sequence of UBC32 Homologues in Yeast, Human, and Arabidopsis. (A) Expression
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09937 a Name Position Primersets 1a 1b 2 3 4 b2 Phenotype Genotype b Primerset 1a D T C R I E 10000 8000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 800 Donor (D)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09937 a Name Position Primersets 1a 1b 2 3 4 b2 Phenotype Genotype b Primerset 1a D T C R I E 10000 8000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 800 Donor (D)
8Br-cAMP was purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO). Silencer Negative Control sirna #1 and
 1 Supplemental information 2 3 Materials and Methods 4 Reagents and animals 5 8Br-cAMP was purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO). Silencer Negative Control sirna #1 and 6 Silencer Select Pre-designed sirna
1 Supplemental information 2 3 Materials and Methods 4 Reagents and animals 5 8Br-cAMP was purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO). Silencer Negative Control sirna #1 and 6 Silencer Select Pre-designed sirna
Distinct Temporal Requirements for the Homeobox Gene Gsx2 in Specifying Striatal and Olfactory Bulb Neuronal Fates
 Article Distinct Temporal Requirements for the Homeobox Gene Gsx2 in Specifying Striatal and Olfactory Bulb al Fates Ronald R. Waclaw, 1,2 Bei Wang, 1,2,3 Zhenglei Pei, 1 Lisa A. Ehrman, 1 and Kenneth
Article Distinct Temporal Requirements for the Homeobox Gene Gsx2 in Specifying Striatal and Olfactory Bulb al Fates Ronald R. Waclaw, 1,2 Bei Wang, 1,2,3 Zhenglei Pei, 1 Lisa A. Ehrman, 1 and Kenneth
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature08267 Figure S: Karyotype analysis of ips cell line One hundred individual chromosomal spreads were counted for each of the ips samples. Shown here is an spread at passage 5, predominantly
doi:.38/nature08267 Figure S: Karyotype analysis of ips cell line One hundred individual chromosomal spreads were counted for each of the ips samples. Shown here is an spread at passage 5, predominantly
amplification of the 5 flanking region of CAT1 with a tail for the geneticin resistance gene cassette fusion CAT1-3F
 Supplementary materials Table S1. Primer list. Primer Sequence a (5-3 ) Description CAT1-5F CAT1-5R ATACGGATAAGGAAGCGATAGCAGCA gcacaggtacacttgtttagagagcgatccggattttaagtgaacg amplification of the 5 flanking
Supplementary materials Table S1. Primer list. Primer Sequence a (5-3 ) Description CAT1-5F CAT1-5R ATACGGATAAGGAAGCGATAGCAGCA gcacaggtacacttgtttagagagcgatccggattttaagtgaacg amplification of the 5 flanking
Supplemental Data. Li et al. (2015). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1: Characterization of asr3 T-DNA knockout lines and complementation transgenic lines. (A) The scheme of At2G33550 (ASR3) with gray boxes indicating exons and dash
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1: Characterization of asr3 T-DNA knockout lines and complementation transgenic lines. (A) The scheme of At2G33550 (ASR3) with gray boxes indicating exons and dash
Introducing new DNA into the genome requires cloning the donor sequence, delivery of the cloned DNA into the cell, and integration into the genome.
 Key Terms Chapter 32: Genetic Engineering Cloning describes propagation of a DNA sequence by incorporating it into a hybrid construct that can be replicated in a host cell. A cloning vector is a plasmid
Key Terms Chapter 32: Genetic Engineering Cloning describes propagation of a DNA sequence by incorporating it into a hybrid construct that can be replicated in a host cell. A cloning vector is a plasmid
WT Day 90 after injections
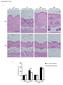 Supplementary Figure 1 a Day 1 after injections Day 9 after injections Klf5 +/- Day 1 after injections Klf5 +/- Day 9 after injections BLM PBS b Day 1 after injections Dermal thickness (μm) 3 1 Day 9 after
Supplementary Figure 1 a Day 1 after injections Day 9 after injections Klf5 +/- Day 1 after injections Klf5 +/- Day 9 after injections BLM PBS b Day 1 after injections Dermal thickness (μm) 3 1 Day 9 after
Supplementary Fig. 1 Generation and genotyping of ThPOK / mice
 Supplementary Fig. 1 Generation and genotyping of ThPOK / mice (a). The strategy used to target the ThPOK locus is schematically depicted. A targeting construct was generated by inserting a loxp site (filled
Supplementary Fig. 1 Generation and genotyping of ThPOK / mice (a). The strategy used to target the ThPOK locus is schematically depicted. A targeting construct was generated by inserting a loxp site (filled
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06293 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION a Testing the incompatibility of Lox2272 and LoxP Construct Expected Lox2272 promoter (CMV) c Testing the incompatibility of LoxN with Lox2272 and LoxP
doi: 10.1038/nature06293 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION a Testing the incompatibility of Lox2272 and LoxP Construct Expected Lox2272 promoter (CMV) c Testing the incompatibility of LoxN with Lox2272 and LoxP
Cell proliferation was measured with Cell Counting Kit-8 (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan).
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Supplemental Materials and Methods Cell proliferation assay Cell proliferation was measured with Cell Counting Kit-8 (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan). GCs were plated at 96-well
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Supplemental Materials and Methods Cell proliferation assay Cell proliferation was measured with Cell Counting Kit-8 (Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan). GCs were plated at 96-well
Development 142: doi: /dev : Supplementary Material
 Development 142: doi:1.42/dev.11687: Supplementary Material Figure S1 - Relative expression of lineage markers in single ES cell and cardiomyocyte by real-time quantitative PCR analysis. Single ES cell
Development 142: doi:1.42/dev.11687: Supplementary Material Figure S1 - Relative expression of lineage markers in single ES cell and cardiomyocyte by real-time quantitative PCR analysis. Single ES cell
Supplementary Table 1. Primers used to construct full-length or various truncated mutants of ISG12b2.
 Supplementary Table 1. Primers used to construct full-length or various truncated mutants of ISG12b2. Construct name ISG12b2 (No tag) HA-ISG12b2 (N-HA) ISG12b2-HA (C-HA; FL-HA) 94-283-HA (FL-GFP) 93-GFP
Supplementary Table 1. Primers used to construct full-length or various truncated mutants of ISG12b2. Construct name ISG12b2 (No tag) HA-ISG12b2 (N-HA) ISG12b2-HA (C-HA; FL-HA) 94-283-HA (FL-GFP) 93-GFP
Table S1. Primers used in the study
 Table S1. Primers used in the study Primer name Application Sequence I1F16 Genotyping GGCAAGTGAGTGAGTGCCTA I1R11 Genotyping CCCACTCGTATTGACGCTCT V19 Genotyping GGGTCTCAAAGTCAGGGTCA D18Mit184-F Genotyping
Table S1. Primers used in the study Primer name Application Sequence I1F16 Genotyping GGCAAGTGAGTGAGTGCCTA I1R11 Genotyping CCCACTCGTATTGACGCTCT V19 Genotyping GGGTCTCAAAGTCAGGGTCA D18Mit184-F Genotyping
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3494
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
with different microfluidic device parameters. Distribution of number of transcripts (y-axis) detected across nuclei, ranked in decreasing
 Supplementary Figure 1 DroNc-seq benchmarking experiments. (a) Overview of DroNc-seq. (b) CAD schema of DroNc-seq microfluidic device. (c) Comparison of library complexity from experiments with different
Supplementary Figure 1 DroNc-seq benchmarking experiments. (a) Overview of DroNc-seq. (b) CAD schema of DroNc-seq microfluidic device. (c) Comparison of library complexity from experiments with different
Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured
 Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured in 90-Pa 3D fibrin gels for 5 days in the presence
Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured in 90-Pa 3D fibrin gels for 5 days in the presence
A Simple Method for 3D Analysis of Immunolabeled Axonal Tracts in a Transparent Nervous System
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information A Simple Method for 3D Analysis of Immunolabeled Axonal Tracts in a Transparent Nervous System Morgane Belle, David Godefroy, Chloé Dominici, Céline Heitz-Marchaland,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information A Simple Method for 3D Analysis of Immunolabeled Axonal Tracts in a Transparent Nervous System Morgane Belle, David Godefroy, Chloé Dominici, Céline Heitz-Marchaland,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11500 Figure S1: The sector in the PDZ domain family. Sectors are defined as groups of statistically coevolving amino acid positions in a protein family and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11500 Figure S1: The sector in the PDZ domain family. Sectors are defined as groups of statistically coevolving amino acid positions in a protein family and
i-stop codon positions in the mcherry gene
 Supplementary Figure 1 i-stop codon positions in the mcherry gene The grnas (green) that can potentially generate stop codons from Trp (63 th and 98 th aa, upper panel) and Gln (47 th and 114 th aa, bottom
Supplementary Figure 1 i-stop codon positions in the mcherry gene The grnas (green) that can potentially generate stop codons from Trp (63 th and 98 th aa, upper panel) and Gln (47 th and 114 th aa, bottom
a previous report, Lee and colleagues showed that Oct4 and Sox2 bind to DXPas34 and Xite
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9496 a 1 Relative RNA levels D12 female ES cells 24h Control sirna 24h sirna Oct4 5 b,4 Oct4 Xist (wt) Xist (mut) Tsix 3' (wt) Tsix 5' (wt) Beads Oct4,2 c,2 Xist
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9496 a 1 Relative RNA levels D12 female ES cells 24h Control sirna 24h sirna Oct4 5 b,4 Oct4 Xist (wt) Xist (mut) Tsix 3' (wt) Tsix 5' (wt) Beads Oct4,2 c,2 Xist
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3164 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of effective Gnas deletion and epithelial thickness. a, Representative genotyping in mice treated or not with tamoxifen to show Gnas deletion. To
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3164 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of effective Gnas deletion and epithelial thickness. a, Representative genotyping in mice treated or not with tamoxifen to show Gnas deletion. To
Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably expressing shrna sequences against TRF2 were examined by western blotting. shcon, shrna
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably expressing shrna sequences against TRF2 were examined by western blotting. shcon, shrna
Supplementary Fig. 1
 a FL (1-2266) NL (1-1190) CL (1191-2266) HA-ICE1: - HA-ICE1: - - - FLAG-ICE2: + + + + FLAG-ELL: + + + + + + IP: anti-ha FLAG-ICE2 HA-ICE1-FL HA-ICE1-NL HA-ICE1-CL FLAG-ICE2 b IP: anti-ha FL (1-2266) NL
a FL (1-2266) NL (1-1190) CL (1191-2266) HA-ICE1: - HA-ICE1: - - - FLAG-ICE2: + + + + FLAG-ELL: + + + + + + IP: anti-ha FLAG-ICE2 HA-ICE1-FL HA-ICE1-NL HA-ICE1-CL FLAG-ICE2 b IP: anti-ha FL (1-2266) NL
Fig. S1. Clustering analysis of expression array and ChIP-PCR assay in the ARF3 locus. (A) Typical examples of the transgenic plants used for
 Fig. S1. Clustering analysis of expression array and ChIP-PCR assay in the ARF3 locus. (A) Typical examples of the transgenic plants used for ChIP-chip and ChIP-PCR assays. The presence of pas1:t7:as1
Fig. S1. Clustering analysis of expression array and ChIP-PCR assay in the ARF3 locus. (A) Typical examples of the transgenic plants used for ChIP-chip and ChIP-PCR assays. The presence of pas1:t7:as1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary figure 1: List of primers/oligonucleotides used in this study. 1 Supplementary figure 2: Sequences and mirna-targets of i) mcherry expresses in transgenic fish used
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary figure 1: List of primers/oligonucleotides used in this study. 1 Supplementary figure 2: Sequences and mirna-targets of i) mcherry expresses in transgenic fish used
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a before amputation regeneration regenerated limb DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS developmental origin: lateral plate mesoderm presomitic mesoderm
a before amputation regeneration regenerated limb DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS developmental origin: lateral plate mesoderm presomitic mesoderm
Table S1. Oligonucleotide primer sequences
 Table S1. Oligonucleotide primer sequences Primer Name DNA Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Description CD19c CD19d Cre7 Sfpi1lox1 Sfpi1lox2 Sfpi1lox3 5 -AACCAGTCAACACCCTTCC-3 5 -CCAGACTAGATACAGACCAG-3 5 -TCAGCTACACCAGAGACGG-3
Table S1. Oligonucleotide primer sequences Primer Name DNA Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Description CD19c CD19d Cre7 Sfpi1lox1 Sfpi1lox2 Sfpi1lox3 5 -AACCAGTCAACACCCTTCC-3 5 -CCAGACTAGATACAGACCAG-3 5 -TCAGCTACACCAGAGACGG-3
Supplemental Fig. 1. Mcr alleles show defects in tracheal tube size and luminal protein accumulation. (A-F) Confocal projections of living stage 15
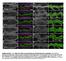 Supplemental Fig. 1. Mcr alleles show defects in tracheal tube size and luminal protein accumulation. (A-F) Confocal projections of living stage 15 embryos expressing GFP and Verm-RFP in tracheal cells
Supplemental Fig. 1. Mcr alleles show defects in tracheal tube size and luminal protein accumulation. (A-F) Confocal projections of living stage 15 embryos expressing GFP and Verm-RFP in tracheal cells
Figure S1 Correlation in size of analogous introns in mouse and teleost Piccolo genes. Mouse intron size was plotted against teleost intron size for t
 Figure S1 Correlation in size of analogous introns in mouse and teleost Piccolo genes. Mouse intron size was plotted against teleost intron size for the pcloa genes of zebrafish, green spotted puffer (listed
Figure S1 Correlation in size of analogous introns in mouse and teleost Piccolo genes. Mouse intron size was plotted against teleost intron size for the pcloa genes of zebrafish, green spotted puffer (listed
