i-stop codon positions in the mcherry gene
|
|
|
- Dwayne Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure 1 i-stop codon positions in the mcherry gene The grnas (green) that can potentially generate stop codons from Trp (63 th and 98 th aa, upper panel) and Gln (47 th and 114 th aa, bottom panel) are shown. Potential Cytosines (or guanines) that may generate stop codons are red and corresponding inverted Thymines (or Adenines ) are blue labeled.
2 Supplementary Figure 2 Expressing WT-Cas9 and BE3 complex in HEK293T cells (a) Schematics of WT-Cas9 and BE3 complex expression vectors. (b) Western blot demonstrates the expression levels of WT-Cas9 and BE3 proteins after transient transfection of indicated plasmid concentrations. Protein levels were detected using the HA antibody which is fused to the C termini of both protein.
3 Supplementary Figure 3 BE3 activity is abolished when the catalytic activity of rat Apobec1 is double mutated (a) Proline (P) at 29 and glutamic acid(e) at 181 were mutated into phenylalanine(f) and Glutamine (Q) respectively by using site directed mutagenesis. Sanger sequencing analyses show mutated nucleotide by red color for both loci and altered codon is underlined. (b) Mutant BE3 lost its activity for the silencing of mcherry signal in the presence of sgrna 3 and sgrna4 with respect to the wild type BE3. Dot plot shows flow cytometry measured percent of mcherry-negative cells upon guiding BE3(wild type) or BE3(double mutant) by sgrna3 and 4.
4 Supplementary Figure 4 Effects of synonymous mutation for gene KO (a) Sequence of the sgrna which produces synonymous mutation in the presence of BE3 complex. There are two potential C s in the first eight nucleotides of protospacer. Red nucleotides show the target C s and blue nucleotides demonstrate the edited bases. Yellow color highlights the PAM region. (b) Control sgrna and synonymous sgrna are used in the presence of WT-Cas9 and BE3 complex. Dot plot shows flow cytometry measured percent of mcherry-negative cells upon guiding WT-Cas9 or BE3.Each dot represents separate experiments. P-value is calculated with unpaired t-test (***<0.001). (c)flow cytometry analysis showing percent mcherry negative cells in low copy number cell line in the presence of WT-Cas9 and BE3. X-axis denotes mcherry signal and Y-axis demonstrates the cell number. (d) Sanger sequencing represents the nucleotide change in the Asp codon. While red codons show the wild type Asp codon in mcherry gene, blue codons represent the Asp codon after the synonymous mutation. Yellow indicates the PAM region and underlined sequence represents the sgrna (left panel). Right panel shows sanger sequencing chromatographs of the nucleotide sequence for control and clone#6 with the edited base (*) sign shows perfect 100 % match.
5 Supplementary Figure 5
6 Sanger sequencing analysis of C to T (or G to A) conversion in Trp codon (a) mcherry target sequence was cloned from mcherry population cells transfected with sgrna3 and BE3. 4/9 colonies have induced stop codon (i-stop, shown by blue) at the location of Trp (63 th aa) (b) Sanger DNA sequencing profiles illustrate edited nucleotides following BE3 and sgrna3 transfection. Sanger sequencing color code is only used for Trp codon nucleotides. Arrows indicate the 4 th and 8 th positions of the sgrna guiding sequence distal to PAM. (c) Sanger sequencing analysis of genetic changes induced by BE3 and WT- Cas9. mcherry target sequence was cloned from low copy mcherry cells following transfection with sgrna4 in the presence of WT-Cas9 or BE3. 4/10 colonies have i-stop codons (shown by blue) at the location of Trp (98 th aa) for BE3 transfection. There was no further C to T conversion or any other base changes in 50 bp flanking regions of sgrna4 target site. On the other hand, WT-Cas9 introduced deletions (shown by gray dashes) in the 3/10 colonies shown in the bottom panel. sgrna target sequences are underlined on the mcherry gene and complementary bases of PAM region on the coding strand were highlighted with yellow. Trp and i- stop codons are highlighted with red and blue respectively. Any other substitutions are labeled by brown. (*) sign shows perfect 100 % match.
7 Supplementary Figure 6 Identification of the copy numbers in single cell colonies from mcherry population cells Relative mcherry copy number levels were quantified in real time-pcr by using the GAPDH primer as a control genomic region. Clone #4, #6 and #12 were used as low, medium and high mcherry copy number cell lines, respectively.
8 Supplementary Figure 7 Comparative analysis of KO efficiency of WT-Cas9 and BE3 mediated CRISPR-STOP approach (a) Dot plot shows flow cytometry measured percent of mcherry-negative cells upon guiding WT-Cas9 or BE3 by four separate sgrnas for four mcherry-targeting sgrnas following WT-Cas9 or BE3 transfection in low and high copy number cell lines. Each dot represents seperate experiments. The black lines on each bar in the dot plots show the mean of three or more replicates. P-value is calculated with unpaired t-test (*<0.05;**<0.01). (b) Flow cytometry analysis showing percent mcherry-negative cells. X-axis denotes mcherry signal and Y- axis demonstrates the cell number. Top two rows are showing the flow analysis for mix population of mcherry cells, middle two rows show the same analysis in low copy mcherry cells and bottom two rows show the rate of silencing in high copy mcherry cells. (c) mcherry-knock out cells (yellow arrows) are shown in the merged images of fluorescence microscopy. sgrna3 was used in the presence of BE3 in the low copy mcherry cell line.
9 Supplementary Figure 8 WT-Cas9 has more deleterious effects compared to the BE3 when targeted to a high copy number loci (a)dot plot summarizes the flow cytometry analysis of the normalized AnnexinV staining levels in low, medium and high copy number cells expressing sgrna3 with WT-Cas9 or BE3. Each dot represents separate experiments. The black lines on each bar in the dot plots show the mean of three or more replicates. P-value is calculated with unpaired t-test (*<0.05). (b) Flow cytometry profiles are showing DAPI and AnnexinV-FITC staining. SgRNA3 and sgrna4 were transfected to high copy mcherry cells together with WT-Cas9 or BE3. Apoptotic cells are stained by AnnexinV-FITC. Of note, cells in the center of each population, which were shown by yellow or red dots, shifted right in the WT-Cas9 treatment. Numbers in each quarter demonstrates the percent cell number. (c) Flow histogram shows AnnexinV staining levels in high copy number mcherry cells upon guiding WT-Cas9 and BE3 with control and mcherry targeting sgrna #3.
10 Supplementary Figure 9 Phospho-H2Ax staining shows WT-Cas9 and BE3 induced levels of DNA damage SgRNA3 and sgrna4 were transfected to high copy mcherry cells together with WT-Cas9 or BE3.Scale bar represents 5 µm.
11 Supplementary Figure 10 CRISPR-STOP mediated gene silencing in endogenous loci. (a, b) Green bars under exons of each gene denote the positions of sgrnas for EHMT2 (a) and LMNB2 (b) in the upper panel. Western blot analyses of protein levels after transient transfection of the indicated sgrnas are shown on the left sides of the bottom panel. Right sites of the bottom panel show the control protein expression of alpha-tubulin. Numbers on the left site of the images indicate the sizes of the protein marker.
12 Supplementary Figure 11 Comparative analysis of KO efficiency of WT-Cas9 and BE3 mediated gene silencing in endogenous LMNB2 loci X-axis shows the BL1-mClover signal intensity and y-axis demonstrates the cell number in the flow cytometry analysis. Numbers on the bars show the percentage mclover(-) and mclover(+) cell numbers for each treatment. Top panel shows the distribution of HCT-116 control cells (no mclover). WT-Cas9 and BE3 transfected cells are shown by the middle two and bottom two panels, respectively. Numbers (#1 thru #8) show the LMNB2 sgrna numbers.
13 Supplementary Figure 12 Characteristics of CRISPR-STOP library (a) Bar plots shows the total numbers of unique sgrnas that target the four codons in the human exome. (b) The percentages of sgrnas with different oligonucleotide stretches are shown for both the CRISPR-STOP and GeCKOv2 libraries. Only 0.9% of the sgrnas contain 6-mer or above for i-stop, and 0.6% for GeCKOv2. (c) GC content of the sgrnas in the CRISPR-STOP and GeCKOv2 libraries is shown. Densities of GC content between the two libraries are comparable, with the mean for i-stop slightly higher due to the specific codons targeted. (d) Nucleotide compositions at each position of the 20 base pairs of the sgrnas were compared between the CRISPR-STOP and GeCKOv2 libraries. In general, the four nucleotides are equally distributed at each position. As expected, the distribution is skewed slightly between the 4th to 8th positions of the sgrnas in the CRISPR-STOP library due to the specific codons targeted. (e) The schematic outline of the CRISPR-STOP mediated knockout screening with a library containing 27 sgrnas in HEK293T cells.
14 Supplementary Table 1 (List of oligos for sgrna) Used in mini Lib Names Sequence yes mcherry-gln(47)+pam cacccagaccgccaagctgaagg mcherry-sg1(f) caccgacccagaccgccaagctga mcherry-sg1(r) aaactcagcttggcggtctgggtc yes mcherry-gln(114)+pam gacccaggactcctccctgcagg mcherry-sg2(f) caccgacccaggactcctccctgc mcherry-sg2(r) aaacgcagggaggagtcctgggtc yes mcherry-trp(63)+pam tgtcccaggcgaagggcaggggg mcherry-sg3(f) caccggtcccaggcgaagggcagg mcherry-sg3(r) aaaccctgcccttcgcctgggacc yes mcherry-trp(98)+pam gctcccacttgaagccctcgggg mcherry-sg4(f) caccgctcccacttgaagccctcg mcherry-sg4(r) aaaccgagggcttcaagtgggagc yes EHMT2-Gln(145)+PAM ctgtccagagtttggctatgagg EHMT2(G9a)-sg1(F) caccgtgtccagagtttggctatg EHMT2(G9a)-sg1(R) aaaccatagccaaactctggacac yes EHMT2-Gln(297)+PAM tgaacaactaagtgaagaggagg EHMT2(G9a)-sg2(F) caccggaacaactaagtgaagagg EHMT2(G9a)-sg2(R) aaaccctcttcacttagttgttcc yes EZH2-Gln(328)+PAM accacagtgttaccagcatttgg EZH2-sg1(F) caccgccacagtgttaccagcatt EZH2-sg1(R) aaacaatgctggtaacactgtggc yes EZH2-Gln(559)+PAM gaaggtcaaaaccgctttccggg EZH2-sg2(F) caccgaaggtcaaaaccgctttcc EZH2-sg2(R) aaacggaaagcggttttgaccttc yes EZH2-Trp(113)+PAM ggagaccaagaatacattatggg EZH2-sg3(F) caccggagaccaagaatacattat EZH2-sg3(R) aaacataatgtattcttggtctcc yes HPRT1-Arg(51)+PAM tcttgctcgagatgtgatgaagg HPRT1-sg1(F) caccgcttgctcgagatgtgatga HPRT1-sg1(R) aaactcatcacatctcgagcaagc yes HPRT1-Gln(144)+PAM aatgcagactttgctttccttgg HPRT1-sg2(F) caccgatgcagactttgctttcct HPRT1-sg2(R) aaacaggaaagcaaagtctgcatc yes HPRT1-Gln(152)+PAM caggcagtataatccaaagatgg HPRT1-sg3(F) caccgaggcagtataatccaaaga HPRT1-sg3(R) aaactctttggattatactgcctc yes puro-trp(76)+pam cgtggtccagaccgccaccgcgg puro-sg1(f) caccggtggtccagaccgccaccg puro-sg1(r) aaaccggtggcggtctggaccacc
15 yes puro-gln(106))+pam gccgcgcagcaacagatggaagg puro-sg2(f) caccgccgcgcagcaacagatgga puro-sg2(r) aaactccatctgttgctgcgcggc yes puro-gln(108)+pam gcaacagatggaaggcctcctgg puro-sg3(f) caccgcaacagatggaaggcctcc puro-sg3(r) aaacggaggccttccatctgttgc yes puro-trp(123)+pam aggaaccacgcgggctccttggg puro-sg4(f) caccgggaaccacgcgggctcctt puro-sg4(r) aaacaaggagcccgcgtggttccc yes Lib_Cont-Sg_1F caccgagaaggatggaaattagaa Lib_Cont-Sg_1R aaacttctaatttccatccttctc yes Lib_Cont-Sg_2F caccgccccgccgccctcccctcc Lib_Cont-Sg_2R aaacggaggggagggcggcggggc yes Lib_Cont-Sg_3F caccgaagaaagaggaatagtagc Lib_Cont-Sg_3R aaacgctactattcctctttcttc yes Lib_Cont-Sg_4F caccgagaagtggggagccattgg Lib_Cont-Sg_4R aaacccaatggctccccacttctc yes Lib_Cont-Sg_5F caccggaagaaaaaaatgtctacg Lib_Cont-Sg_5R aaaccgtagacatttttttcttcc LMNB2-Arg(16)+PAM gccgcgagccgccgccaccatgg LMNB2-sg1F caccgccgcgagccgccgccacca LMNB2-sg1R aaactggtggcggcggctcgcggc LMNB2-Gln(146)+PAM ggtggcccagggccgtgtgaagg LMNB2-sg2F caccggtggcccagggccgtgtga LMNB2-sg2R aaactcacacggccctgggccacc LMNB2-Gln(295)+PAM ctctgaccagaacgacaaggcgg LMNB2-sg3F caccgtctgaccagaacgacaagg LMNB2-sg3R aaacccttgtcgttctggtcagac LMNB2-Gln(213)+PAM ccgctgccagagcctgcaggagg LMNB2-sg4F caccgcgctgccagagcctgcagg LMNB2-sg4R aaaccctgcaggctctggcagcgc LMNB2-Gln(183)+PAM cgggcccagctggccaaggtagg LMNB2-sg5F caccggggcccagctggccaaggt LMNB2-sg5R aaacaccttggccagctgggcccc LMNB2-Gln(466,467)+PAM gcccagcaggcctcggcctcggg LMNB2-sg6F caccgcccagcaggcctcggcctc LMNB2-sg6R aaacgaggccgaggcctgctgggc LMNB2-Gln(487)+PAM tgtgcagctcaagaacaactcgg LMNB2-sg7F caccggtgcagctcaagaacaact LMNB2-sg7R aaacagttgttcttgagctgcacc LMNB2-Gln(506)+PAM gaggcaggtcttggagggggagg LMNB2-sg8F caccgaggcaggtcttggaggggg LMNB2-sg8R aaacccccctccaagacctgcctc
16 cont-sg(f) cont-sg(r) caccgggtcttcgagaagacctgt aaacacaggtcttctcgaagaccc
17 Supplementary Table 2 (Primers for library preparation) Primer Name lib-outf lib-outr lib-in-f-index10 lib-in-f-index11 lib-in-f-index12 lib-in-f-index18 lib-in-f-index21 Sequence (6-bp barcode sequences are shown by small letter in the Lib-IN-For primer) cagggacagcagagatccag cggagccaattcccactcc CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCtagcttTTTCTTGGGTAGTTTGCAGTTTT CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCggctacTTTCTTGGGTAGTTTGCAGTTTT CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCcttgtaTTTCTTGGGTAGTTTGCAGTTTT CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCgtccgcTTTCTTGGGTAGTTTGCAGTTTT CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCgtttcgTTTCTTGGGTAGTTTGCAGTTTT lib-in-f-index4 lib-in-f-index5 lib-in-f-index6 lib-in-f-index22 lib-in-f-index27 lib-in-rev illmn-seqp illmn-indexp CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCtgaccaTTTCTTGGGTAGTTTGCAGTTTT CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCacagtgTTTCTTGGGTAGTTTGCAGTTTT CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCgccaatTTTCTTGGGTAGTTTGCAGTTTT CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCcgtacgTTTCTTGGGTAGTTTGCAGTTTT CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATCattcctTTTCTTGGGTAGTTTGCAGTTTT AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACCGACTCGGTGCCACTTTT CGGTGCCACTTTTTCAAGTTGATAACGGACTAGCCTTATTTTAACTTGCTATTTCTAGCTCTAAAAC TTTCAAGTTACGGTAAGCATATGATAGTCCATTTTAAAACATAATTTTAAAACTGCAAACTACCCAAGAAA
CRISPR RNA-guided activation of endogenous human genes
 CRISPR RNA-guided activation of endogenous human genes Morgan L Maeder, Samantha J Linder, Vincent M Cascio, Yanfang Fu, Quan H Ho, J Keith Joung Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of VEGF activation induced
CRISPR RNA-guided activation of endogenous human genes Morgan L Maeder, Samantha J Linder, Vincent M Cascio, Yanfang Fu, Quan H Ho, J Keith Joung Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of VEGF activation induced
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.4166
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Genome-wide genetic screening with chemically-mutagenized haploid embryonic stem cells
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Supplementary Information Genome-wide genetic screening with chemically-mutagenized haploid embryonic stem cells Josep V. Forment 1,2, Mareike Herzog
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Supplementary Information Genome-wide genetic screening with chemically-mutagenized haploid embryonic stem cells Josep V. Forment 1,2, Mareike Herzog
Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
A novel tool for monitoring endogenous alpha-synuclein transcription by NanoLuciferase
 A novel tool for monitoring endogenous alpha-synuclein transcription by NanoLuciferase tag insertion at the 3 end using CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing technique Sambuddha Basu 1, 3, Levi Adams 1, 3, Subhrangshu
A novel tool for monitoring endogenous alpha-synuclein transcription by NanoLuciferase tag insertion at the 3 end using CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing technique Sambuddha Basu 1, 3, Levi Adams 1, 3, Subhrangshu
Some types of Mutagenesis
 Mutagenesis What Is a Mutation? Genetic information is encoded by the sequence of the nucleotide bases in DNA of the gene. The four nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine
Mutagenesis What Is a Mutation? Genetic information is encoded by the sequence of the nucleotide bases in DNA of the gene. The four nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary figures and supplementary tables. File name: Peer review file Description:
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary figures and supplementary tables. File name: Peer review file Description: Supplementary Figure 1. dcas9-mq1 fusion protein induces de novo
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary figures and supplementary tables. File name: Peer review file Description: Supplementary Figure 1. dcas9-mq1 fusion protein induces de novo
Donor DNA Utilization during Gene Targeting with Zinc- finger Nucleases
 Donor DNA Utilization during Gene Targeting with Zinc- finger Nucleases Kelly J. Beumer, Jonathan K. Trautman, Kusumika Mukherjee and Dana Carroll Department of Biochemistry University of Utah School of
Donor DNA Utilization during Gene Targeting with Zinc- finger Nucleases Kelly J. Beumer, Jonathan K. Trautman, Kusumika Mukherjee and Dana Carroll Department of Biochemistry University of Utah School of
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3494
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Super-resolution imaging of fluorescently labeled, endogenous RNA Polymerase II in living cells with CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing Won-Ki Cho 1, Namrata Jayanth 1, Susan Mullen
Supplementary Information Super-resolution imaging of fluorescently labeled, endogenous RNA Polymerase II in living cells with CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing Won-Ki Cho 1, Namrata Jayanth 1, Susan Mullen
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Gene replacements and insertions in rice by intron targeting using CRISPR Cas9 Table of Contents Supplementary Figure 1. sgrna-induced targeted mutations in the OsEPSPS gene in rice protoplasts. Supplementary
Gene replacements and insertions in rice by intron targeting using CRISPR Cas9 Table of Contents Supplementary Figure 1. sgrna-induced targeted mutations in the OsEPSPS gene in rice protoplasts. Supplementary
Surrogate reporter-based enrichment of cells containing RNA-guided Cas9 nucleaseinduced
 Supplementary Data Surrogate reporter-based enrichment of cells containing RNA-guided Cas9 nucleaseinduced mutations Suresh Ramakrishna 1, Seung Woo Cho 2, Sojung Kim 2, Myungjae Song 1, Ramu Gopalappa
Supplementary Data Surrogate reporter-based enrichment of cells containing RNA-guided Cas9 nucleaseinduced mutations Suresh Ramakrishna 1, Seung Woo Cho 2, Sojung Kim 2, Myungjae Song 1, Ramu Gopalappa
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Product purity of cytosine base editing for the wheat genomic loci tested. Product distributions and indels frequencies at four representative wheat genomic DNA sites in wheat protoplasts
Supplementary Figure 1 Product purity of cytosine base editing for the wheat genomic loci tested. Product distributions and indels frequencies at four representative wheat genomic DNA sites in wheat protoplasts
Supplementary Figure 1 Activities of ABEs using extended sgrnas in HEK293T cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activities of ABEs using extended sgrnas in HEK293T cells. Base editing efficiencies of ABEs with extended sgrnas at Site 18 (a), Site 19 (b), the HBB-E2 site (c), and the HBB-E3
Supplementary Figure 1 Activities of ABEs using extended sgrnas in HEK293T cells. Base editing efficiencies of ABEs with extended sgrnas at Site 18 (a), Site 19 (b), the HBB-E2 site (c), and the HBB-E3
Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably expressing shrna sequences against TRF2 were examined by western blotting. shcon, shrna
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably expressing shrna sequences against TRF2 were examined by western blotting. shcon, shrna
Allele-specific locus binding and genome editing by CRISPR at the
 Supplementary Information Allele-specific locus binding and genome editing by CRISPR at the p6ink4a locus Toshitsugu Fujita, Miyuki Yuno, and Hodaka Fujii Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Information Allele-specific locus binding and genome editing by CRISPR at the p6ink4a locus Toshitsugu Fujita, Miyuki Yuno, and Hodaka Fujii Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure
CRISPR-STOP: Gene silencing through base editing-induced nonsense mutations
 Online Protocols: CRISPR-STOP: Gene silencing through base editing-induced nonsense mutations Cem Kuscu 1, Mahmut Parlak 1, Turan Tufan 1, Jiekun Yang 1, Karol Szlachta 1, Xiaolong Wei 1, Rashad Mammadov
Online Protocols: CRISPR-STOP: Gene silencing through base editing-induced nonsense mutations Cem Kuscu 1, Mahmut Parlak 1, Turan Tufan 1, Jiekun Yang 1, Karol Szlachta 1, Xiaolong Wei 1, Rashad Mammadov
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1 shrna mediated knockdown of ZRSR2 in K562 and 293T cells. (a) ZRSR2 transcript levels in stably transduced K562 cells were determined using qrt-pcr. GAPDH was
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1 shrna mediated knockdown of ZRSR2 in K562 and 293T cells. (a) ZRSR2 transcript levels in stably transduced K562 cells were determined using qrt-pcr. GAPDH was
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Over-expression of CD300f in NIH3T3 cells enhances their capacity to phagocytize AC. (a) NIH3T3 cells were stably transduced by EV, CD300f WT or CD300f
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Over-expression of CD300f in NIH3T3 cells enhances their capacity to phagocytize AC. (a) NIH3T3 cells were stably transduced by EV, CD300f WT or CD300f
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. In vitro validation of OTC sgrnas and donor template.
 Supplementary Figure 1 In vitro validation of OTC sgrnas and donor template. (a) In vitro validation of sgrnas targeted to OTC in the MC57G mouse cell line by transient transfection followed by 4-day puromycin
Supplementary Figure 1 In vitro validation of OTC sgrnas and donor template. (a) In vitro validation of sgrnas targeted to OTC in the MC57G mouse cell line by transient transfection followed by 4-day puromycin
Generation of App knock-in mice reveals deletion mutations protective against Alzheimer s. disease-like pathology. Nagata et al.
 Generation of App knock-in mice reveals deletion mutations protective against Alzheimer s disease-like pathology Nagata et al. Supplementary Fig 1. Previous App knock-in model did not show Aβ accumulation
Generation of App knock-in mice reveals deletion mutations protective against Alzheimer s disease-like pathology Nagata et al. Supplementary Fig 1. Previous App knock-in model did not show Aβ accumulation
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous gene tagging to study subcellular localization and chromatin binding. a, b, Schematic of experimental set-up to endogenously tag RNAi factors using the CRISPR Cas9 technology,
Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous gene tagging to study subcellular localization and chromatin binding. a, b, Schematic of experimental set-up to endogenously tag RNAi factors using the CRISPR Cas9 technology,
Functional analysis reveals that RBM10 mutations. contribute to lung adenocarcinoma pathogenesis by. deregulating splicing
 Supplementary Information Functional analysis reveals that RBM10 mutations contribute to lung adenocarcinoma pathogenesis by deregulating splicing Jiawei Zhao 1,+, Yue Sun 2,3,+, Yin Huang 6, Fan Song
Supplementary Information Functional analysis reveals that RBM10 mutations contribute to lung adenocarcinoma pathogenesis by deregulating splicing Jiawei Zhao 1,+, Yue Sun 2,3,+, Yin Huang 6, Fan Song
(a) Immunoblotting to show the migration position of Flag-tagged MAVS
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of six MAVS isoforms. (a) Immunoblotting to show the migration position of Flag-tagged MAVS isoforms. HEK293T Mavs -/- cells were transfected with constructs expressing
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of six MAVS isoforms. (a) Immunoblotting to show the migration position of Flag-tagged MAVS isoforms. HEK293T Mavs -/- cells were transfected with constructs expressing
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Genome-scale engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with single nucleotide precision Zehua Bao, 1 Mohammad HamediRad, 2 Pu Xue, 2 Han Xiao, 1,7 Ipek Tasan, 3 Ran Chao, 2 Jing
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Genome-scale engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with single nucleotide precision Zehua Bao, 1 Mohammad HamediRad, 2 Pu Xue, 2 Han Xiao, 1,7 Ipek Tasan, 3 Ran Chao, 2 Jing
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Negative selection analysis of sgrnas targeting all Brd4 exons comparing day 2 to day 10 time points. Systematic evaluation of 64 Brd4 sgrnas in negative selection experiments, targeting
Supplementary Figure 1 Negative selection analysis of sgrnas targeting all Brd4 exons comparing day 2 to day 10 time points. Systematic evaluation of 64 Brd4 sgrnas in negative selection experiments, targeting
Soyeong Jun 1, 3, Hyeonseob Lim 1, 3, Hoon Jang 1, Wookjae Lee 1, Jinwoo Ahn 1, Ji Hyun Lee 2,*, Duhee Bang 1,* Korea
 Straightforward Delivery of Linearized Double-stranded DNA Encoding sgrna and Donor DNA for the Generation of Single Nucleotide Variants Based on the CRISPR/Cas9 System Soyeong Jun 1, 3, Hyeonseob Lim
Straightforward Delivery of Linearized Double-stranded DNA Encoding sgrna and Donor DNA for the Generation of Single Nucleotide Variants Based on the CRISPR/Cas9 System Soyeong Jun 1, 3, Hyeonseob Lim
Supplementary Information Targeting fidelity of adenine and cytosine base editors in mouse embryos
 Supplementary Information ing fidelity of adenine and cytosine base s in mouse embryos Lee et al. a P = 1.012e-14 b Frequency (%) 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% CB AB On-target Bystander Proximal Indels Frequency
Supplementary Information ing fidelity of adenine and cytosine base s in mouse embryos Lee et al. a P = 1.012e-14 b Frequency (%) 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% CB AB On-target Bystander Proximal Indels Frequency
Supplementary Figure 1: sgrna library generation and the length of sgrnas for the functional screen. (a) A diagram of the retroviral vector for sgrna
 Supplementary Figure 1: sgrna library generation and the length of sgrnas for the functional screen. (a) A diagram of the retroviral vector for sgrna expression. It contains a U6-promoter-driven sgrna
Supplementary Figure 1: sgrna library generation and the length of sgrnas for the functional screen. (a) A diagram of the retroviral vector for sgrna expression. It contains a U6-promoter-driven sgrna
Incorporating SeqStudio Genetic Analyzer and Sanger sequencing into genome editing workflows
 Incorporating SeqStudio Genetic Analyzer and Sanger sequencing into genome editing workflows Stephen Jackson, Ph.D 27 May 2017 The world leader in serving science Key Applications for Genome Editing Research
Incorporating SeqStudio Genetic Analyzer and Sanger sequencing into genome editing workflows Stephen Jackson, Ph.D 27 May 2017 The world leader in serving science Key Applications for Genome Editing Research
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of B2M -/- ESCs. Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.3860
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of B2M -/- ESCs. (a) Maps of the B2M alleles in cells with the indicated B2M genotypes. Probes and restriction enzymes used in Southern blots are indicated (H, Hind III;
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of B2M -/- ESCs. (a) Maps of the B2M alleles in cells with the indicated B2M genotypes. Probes and restriction enzymes used in Southern blots are indicated (H, Hind III;
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.4198
 Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of DNA methylation on the base editing efficiency induced by BE3. (a) DNMT3-induced DNA methylation leads to the decreased base editing efficiency induced by BE3. Top panels,
Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of DNA methylation on the base editing efficiency induced by BE3. (a) DNMT3-induced DNA methylation leads to the decreased base editing efficiency induced by BE3. Top panels,
Revised: RG-RV2 by Fukuhara et al.
 Supplemental Figure 1 The generation of Spns2 conditional knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the wild type Spns2 locus (Spns2 + ), the targeted allele, the floxed allele (Spns2 f ) and the
Supplemental Figure 1 The generation of Spns2 conditional knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the wild type Spns2 locus (Spns2 + ), the targeted allele, the floxed allele (Spns2 f ) and the
BIO 101 : The genetic code and the central dogma
 BIO 101 : The genetic code and the central dogma NAME Objectives The purpose of this exploration is to... 1. design experiments to decipher the genetic code; 2. visualize the process of protein synthesis;
BIO 101 : The genetic code and the central dogma NAME Objectives The purpose of this exploration is to... 1. design experiments to decipher the genetic code; 2. visualize the process of protein synthesis;
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS
 SUPPLEMENL MERILS Eh-seq: RISPR epitope tagging hip-seq of DN-binding proteins Daniel Savic, E. hristopher Partridge, Kimberly M. Newberry, Sophia. Smith, Sarah K. Meadows, rian S. Roberts, Mark Mackiewicz,
SUPPLEMENL MERILS Eh-seq: RISPR epitope tagging hip-seq of DN-binding proteins Daniel Savic, E. hristopher Partridge, Kimberly M. Newberry, Sophia. Smith, Sarah K. Meadows, rian S. Roberts, Mark Mackiewicz,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental schema for the identification of circular RNAs in six normal tissues and seven cancerous tissues. Supplementary Fiure 2 Comparison of human circrnas
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental schema for the identification of circular RNAs in six normal tissues and seven cancerous tissues. Supplementary Fiure 2 Comparison of human circrnas
Improving CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Knockout with a Validated Guide RNA Algorithm
 Improving CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Knockout with a Validated Guide RNA Algorithm Anja Smith Director R&D Dharmacon, part of GE Healthcare Imagination at work crrna:tracrrna program Cas9 nuclease Active crrna is
Improving CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Knockout with a Validated Guide RNA Algorithm Anja Smith Director R&D Dharmacon, part of GE Healthcare Imagination at work crrna:tracrrna program Cas9 nuclease Active crrna is
Supplementary Information. Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish
 Supplementary Information Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish Hagen R. Witzel 1, Sirisha Cheedipudi 1, Rui Gao 1, Didier Y.R. Stainier 2 and Gergana D. Dobreva 1,3* 1 Origin
Supplementary Information Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish Hagen R. Witzel 1, Sirisha Cheedipudi 1, Rui Gao 1, Didier Y.R. Stainier 2 and Gergana D. Dobreva 1,3* 1 Origin
Supplementary Materials for
 www.advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/7/e1500454/dc1 Supplementary Materials for CRISPR-Cas9 delivery to hard-to-transfect cells via membrane deformation Xin Han, Zongbin Liu, Myeong chan Jo,
www.advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/7/e1500454/dc1 Supplementary Materials for CRISPR-Cas9 delivery to hard-to-transfect cells via membrane deformation Xin Han, Zongbin Liu, Myeong chan Jo,
SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector
 SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector Richard J. Wall 1,#, Magali Roques 1,+, Nicholas J. Katris
SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector Richard J. Wall 1,#, Magali Roques 1,+, Nicholas J. Katris
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Amplification of HEV ORF1, ORF2 and ORF3 genome regions Total RNA was extracted from 200 µl EDTA plasma using Cobas AmpliPrep total nucleic acid isolation kit (Roche,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Amplification of HEV ORF1, ORF2 and ORF3 genome regions Total RNA was extracted from 200 µl EDTA plasma using Cobas AmpliPrep total nucleic acid isolation kit (Roche,
domain. Bottom panel: hybrid surface/ribbon structure (PDB ID: 4UN3) of SpCas9 in complex with sgrna and target DNA. The REC3
 Supplementary Figure 1 Yeast screening for high-specificity SpCas9 variants (a) Top panel: scheme of SpCas9 domains. The REC3 domain is part of the recognition lobe. BH: bridge helix. PI: PAM-interacting
Supplementary Figure 1 Yeast screening for high-specificity SpCas9 variants (a) Top panel: scheme of SpCas9 domains. The REC3 domain is part of the recognition lobe. BH: bridge helix. PI: PAM-interacting
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype and genotype of cultured and transplanted S1 KCST (A) Brightfield and mcherry fluorescence images of the spheres
 Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype and genotype of cultured and transplanted S1 KCST (A) Brightfield and mcherry fluorescence images of the spheres generated from the CD133-positive cells infected with
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype and genotype of cultured and transplanted S1 KCST (A) Brightfield and mcherry fluorescence images of the spheres generated from the CD133-positive cells infected with
Isolation of single-base genome-edited human ips cells without
 Nature Methods Isolation of single-base genome-edited human ips cells without antibiotic selection Yuichiro Miyaoka, Amanda H. Chan, Luke M. Judge, Jennie Yoo, Miller Huang, Trieu D. Nguyen, Paweena P.
Nature Methods Isolation of single-base genome-edited human ips cells without antibiotic selection Yuichiro Miyaoka, Amanda H. Chan, Luke M. Judge, Jennie Yoo, Miller Huang, Trieu D. Nguyen, Paweena P.
Zhang et al., RepID facilitates replication Initiation. Supplemental Information:
 Supplemental Information: a b 1 Supplementary Figure 1 (a) DNA sequence of all the oligonucleotides used in this study. Only one strand is shown. The unshaded nucleotide sequences show changes from the
Supplemental Information: a b 1 Supplementary Figure 1 (a) DNA sequence of all the oligonucleotides used in this study. Only one strand is shown. The unshaded nucleotide sequences show changes from the
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/9/eaat5401/dc1 Supplementary Materials for GLK-IKKβ signaling induces dimerization and translocation of the AhR-RORγt complex in IL-17A induction and autoimmune
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/9/eaat5401/dc1 Supplementary Materials for GLK-IKKβ signaling induces dimerization and translocation of the AhR-RORγt complex in IL-17A induction and autoimmune
Supplementary Figure 1. Supporting data for Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supporting data for Figure 1 (A) Schematic of BLI assay used to measure dissociation. 5 monobiotinylated substrate DNA (identical to λ1, Figure 2) is associated with streptavidin-coated
Supplementary Figure 1 Supporting data for Figure 1 (A) Schematic of BLI assay used to measure dissociation. 5 monobiotinylated substrate DNA (identical to λ1, Figure 2) is associated with streptavidin-coated
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.4199
 Supplementary Figure 1 Base editing activities of engineered A3A-BE3 variants with mutations designed to disrupt non-specific interactions with substrate ssdna. Graphs illustrating the frequencies of C
Supplementary Figure 1 Base editing activities of engineered A3A-BE3 variants with mutations designed to disrupt non-specific interactions with substrate ssdna. Graphs illustrating the frequencies of C
CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing: Transfection Methods
 CRISPR/ Genome Editing: Transfection Methods For over 20 years Mirus Bio has developed and manufactured high performance transfection products and technologies. That expertise is now being applied to the
CRISPR/ Genome Editing: Transfection Methods For over 20 years Mirus Bio has developed and manufactured high performance transfection products and technologies. That expertise is now being applied to the
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. ChIP-seq genome browser views of BRM occupancy at previously identified BRM targets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ChIP-seq genome browser views of BRM occupancy at previously identified BRM targets. Gene structures are shown underneath each panel. Supplementary Figure 2 pref6::ref6-gfp complements
Supplementary Figure 1 ChIP-seq genome browser views of BRM occupancy at previously identified BRM targets. Gene structures are shown underneath each panel. Supplementary Figure 2 pref6::ref6-gfp complements
Supplementary Information. Optimization of the production of knock-in alleles by CRISPR/Cas9 microinjection into the mouse zygote
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures S1 to S5 and Tables S1 to S3. Optimization of the production of knock-in alleles by CRISPR/Cas9 microinjection into the mouse zygote Aurélien Raveux, Sandrine
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures S1 to S5 and Tables S1 to S3. Optimization of the production of knock-in alleles by CRISPR/Cas9 microinjection into the mouse zygote Aurélien Raveux, Sandrine
Supplementary Figures Montero et al._supplementary Figure 1
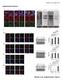 Montero et al_suppl. Info 1 Supplementary Figures Montero et al._supplementary Figure 1 Montero et al_suppl. Info 2 Supplementary Figure 1. Transcripts arising from the structurally conserved subtelomeres
Montero et al_suppl. Info 1 Supplementary Figures Montero et al._supplementary Figure 1 Montero et al_suppl. Info 2 Supplementary Figure 1. Transcripts arising from the structurally conserved subtelomeres
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3259 A Ismail et al. Supplementary Figure 1 B 60000 45000 SSC 30000 15000 Live cells 0 0 15000 30000 45000 60000 FSC- PARR 60000 45000 PARR Width 30000 FSC- 15000 Single cells 0 0 15000
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3259 A Ismail et al. Supplementary Figure 1 B 60000 45000 SSC 30000 15000 Live cells 0 0 15000 30000 45000 60000 FSC- PARR 60000 45000 PARR Width 30000 FSC- 15000 Single cells 0 0 15000
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or
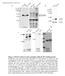 Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
Figure 1: TDP-43 is subject to lysine acetylation within the RNA-binding domain a) QBI-293 cells were transfected with TDP-43 in the presence or absence of the acetyltransferase CBP and acetylated TDP-43
ENGR 213 Bioengineering Fundamentals April 25, A very coarse introduction to bioinformatics
 A very coarse introduction to bioinformatics In this exercise, you will get a quick primer on how DNA is used to manufacture proteins. You will learn a little bit about how the building blocks of these
A very coarse introduction to bioinformatics In this exercise, you will get a quick primer on how DNA is used to manufacture proteins. You will learn a little bit about how the building blocks of these
Supplementary Figure 1 An overview of pirna biogenesis during fetal mouse reprogramming. (a) (b)
 Supplementary Figure 1 An overview of pirna biogenesis during fetal mouse reprogramming. (a) A schematic overview of the production and amplification of a single pirna from a transposon transcript. The
Supplementary Figure 1 An overview of pirna biogenesis during fetal mouse reprogramming. (a) A schematic overview of the production and amplification of a single pirna from a transposon transcript. The
Basic concepts of molecular biology
 Basic concepts of molecular biology Gabriella Trucco Email: gabriella.trucco@unimi.it What is life made of? 1665: Robert Hooke discovered that organisms are composed of individual compartments called cells
Basic concepts of molecular biology Gabriella Trucco Email: gabriella.trucco@unimi.it What is life made of? 1665: Robert Hooke discovered that organisms are composed of individual compartments called cells
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
Supplementary Fig. 1 Proteomic analysis of ATR-interacting proteins. ATR, ARID1A and
 Supplementary Figure Legend: Supplementary Fig. 1 Proteomic analysis of ATR-interacting proteins. ATR, ARID1A and ATRIP protein peptides identified from our mass spectrum analysis were shown. Supplementary
Supplementary Figure Legend: Supplementary Fig. 1 Proteomic analysis of ATR-interacting proteins. ATR, ARID1A and ATRIP protein peptides identified from our mass spectrum analysis were shown. Supplementary
(A-B) P2ry14 expression was assessed by (A) genotyping (upper arrow: WT; lower
 Supplementary Figures S1. (A-B) P2ry14 expression was assessed by (A) genotyping (upper arrow: ; lower arrow: KO) and (B) q-pcr analysis with Lin- cells, The white vertical line in panel A indicates that
Supplementary Figures S1. (A-B) P2ry14 expression was assessed by (A) genotyping (upper arrow: ; lower arrow: KO) and (B) q-pcr analysis with Lin- cells, The white vertical line in panel A indicates that
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/3/146/ra80/dc1 Supplementary Materials for DNMT1 Stability Is Regulated by Proteins Coordinating Deubiquitination and Acetylation-Driven Ubiquitination Zhanwen
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/3/146/ra80/dc1 Supplementary Materials for DNMT1 Stability Is Regulated by Proteins Coordinating Deubiquitination and Acetylation-Driven Ubiquitination Zhanwen
Basic concepts of molecular biology
 Basic concepts of molecular biology Gabriella Trucco Email: gabriella.trucco@unimi.it Life The main actors in the chemistry of life are molecules called proteins nucleic acids Proteins: many different
Basic concepts of molecular biology Gabriella Trucco Email: gabriella.trucco@unimi.it Life The main actors in the chemistry of life are molecules called proteins nucleic acids Proteins: many different
Transfection of CRISPR/Cas9 Nuclease NLS ribonucleoprotein (RNP) into adherent mammalian cells using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX
 Transfection of CRISPR/Cas9 Nuclease NLS ribonucleoprotein (RNP) into adherent mammalian cells using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX INTRODUCTION The CRISPR/Cas genome editing system consists of a single guide RNA
Transfection of CRISPR/Cas9 Nuclease NLS ribonucleoprotein (RNP) into adherent mammalian cells using Lipofectamine RNAiMAX INTRODUCTION The CRISPR/Cas genome editing system consists of a single guide RNA
A Guide to CRISPR/Cas9
 Genome editing and beyond freepik A Guide to CRISPR/Cas9 The latest advance in genomic DNA editing is the Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat (CRISPR)/Cas9 system. This simple-touse
Genome editing and beyond freepik A Guide to CRISPR/Cas9 The latest advance in genomic DNA editing is the Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat (CRISPR)/Cas9 system. This simple-touse
Supplementary Figure 1. CRISPR/Cas9-induced targeted mutations in TaGASR7, TaDEP1, TaNAC2, TaPIN1, TaLOX2 and TaGW2 genes in wheat protoplasts.
 Supplementary Figure 1. CRISPR/Cas9-induced targeted mutations in TaGASR7, TaDEP1, TaNAC2, TaPIN1, TaLOX2 and TaGW2 genes in wheat protoplasts. Lanes 1 and 2: digested CRISPR/Cas9-transformed protoplasts;
Supplementary Figure 1. CRISPR/Cas9-induced targeted mutations in TaGASR7, TaDEP1, TaNAC2, TaPIN1, TaLOX2 and TaGW2 genes in wheat protoplasts. Lanes 1 and 2: digested CRISPR/Cas9-transformed protoplasts;
Somatic Primary pirna Biogenesis Driven by cis-acting RNA Elements and Trans-Acting Yb
 Cell Reports Supplemental Information Somatic Primary pirna Biogenesis Driven by cis-acting RNA Elements and Trans-Acting Yb Hirotsugu Ishizu, Yuka W. Iwasaki, Shigeki Hirakata, Haruka Ozaki, Wataru Iwasaki,
Cell Reports Supplemental Information Somatic Primary pirna Biogenesis Driven by cis-acting RNA Elements and Trans-Acting Yb Hirotsugu Ishizu, Yuka W. Iwasaki, Shigeki Hirakata, Haruka Ozaki, Wataru Iwasaki,
Introduction to CRISPR/Cas9 Background DNA Cleavage and Repair (NHEJ and HDR) Alternative Cas9 Variants Delivery of Cas9 and sgrna Library Products
 Introduction to CRISPR/Cas9 Background DNA Cleavage and Repair (NHEJ and HDR) Alternative Cas9 Variants Delivery of Cas9 and sgrna Library Products which one is right for you? CRISPR Workflow abm s Toolbox
Introduction to CRISPR/Cas9 Background DNA Cleavage and Repair (NHEJ and HDR) Alternative Cas9 Variants Delivery of Cas9 and sgrna Library Products which one is right for you? CRISPR Workflow abm s Toolbox
University of Dundee. Published in: Scientific Reports. DOI: /srep Publication date: 2016
 University of Dundee SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector Wall, Richard J.; Roques, Magali; Katris,
University of Dundee SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector Wall, Richard J.; Roques, Magali; Katris,
Applications of Cas9 nickases for genome engineering
 application note genome editing Applications of Cas9 nickases for genome engineering Shuqi Yan, Mollie Schubert, Maureen Young, Brian Wang Integrated DNA Technologies, 17 Commercial Park, Coralville, IA,
application note genome editing Applications of Cas9 nickases for genome engineering Shuqi Yan, Mollie Schubert, Maureen Young, Brian Wang Integrated DNA Technologies, 17 Commercial Park, Coralville, IA,
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Methods Supplementary Discussion Supplementary Figure 1 Calculated frequencies of embryo cells bearing bi-allelic alterations. Targeted indel mutations induced by
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Methods Supplementary Discussion Supplementary Figure 1 Calculated frequencies of embryo cells bearing bi-allelic alterations. Targeted indel mutations induced by
Optimizing Cas9 and sgrna concentrations for increasing mutation efficiency. Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.3360
 Supplementary Figure 1 Optimizing Cas9 and sgrna concentrations for increasing mutation efficiency. (a) Wild-type, 2-dpf slc24a5 b1 embryos and a series of slc24a5 CRISPR-injected embryos; anterior is
Supplementary Figure 1 Optimizing Cas9 and sgrna concentrations for increasing mutation efficiency. (a) Wild-type, 2-dpf slc24a5 b1 embryos and a series of slc24a5 CRISPR-injected embryos; anterior is
Engineering splicing factors with designed specificities
 nature methods Engineering splicing factors with designed specificities Yang Wang, Cheom-Gil Cheong, Traci M Tanaka Hall & Zefeng Wang Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary
nature methods Engineering splicing factors with designed specificities Yang Wang, Cheom-Gil Cheong, Traci M Tanaka Hall & Zefeng Wang Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Ca 2+ /calmodulin Regulates Salicylic Acid-mediated Plant Immunity Liqun Du, Gul S. Ali, Kayla A. Simons, Jingguo Hou, Tianbao Yang, A.S.N. Reddy and B. W. Poovaiah * *To whom correspondence should be
Ca 2+ /calmodulin Regulates Salicylic Acid-mediated Plant Immunity Liqun Du, Gul S. Ali, Kayla A. Simons, Jingguo Hou, Tianbao Yang, A.S.N. Reddy and B. W. Poovaiah * *To whom correspondence should be
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Construction of a sensitive TetR mediated auxotrophic off-switch.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Construction of a sensitive TetR mediated auxotrophic off-switch. A Production of the Tet repressor in yeast when conjugated to either the LexA4 or LexA8 promoter DNA binding sequences.
Supplementary Figure 1 Construction of a sensitive TetR mediated auxotrophic off-switch. A Production of the Tet repressor in yeast when conjugated to either the LexA4 or LexA8 promoter DNA binding sequences.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 AS-NMD modulates FLM-dependent thermosensory flowering response in Arabidopsis NATURE PLANTS www.nature.com/natureplants 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Genomic sequence of FLM along with the splice sites. Sequencing
AS-NMD modulates FLM-dependent thermosensory flowering response in Arabidopsis NATURE PLANTS www.nature.com/natureplants 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Genomic sequence of FLM along with the splice sites. Sequencing
CRISPR-dCas9 mediated TET1 targeting for selective DNA demethylation at BRCA1 promoter
 CRISPR-dCas9 mediated TET1 targeting for selective DNA demethylation at BRCA1 promoter SUPPLEMENTARY DATA See Supplementary Sequence File: 1 Supplementary Figure S1: The total protein was extracted from
CRISPR-dCas9 mediated TET1 targeting for selective DNA demethylation at BRCA1 promoter SUPPLEMENTARY DATA See Supplementary Sequence File: 1 Supplementary Figure S1: The total protein was extracted from
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. DMS-MaPseq data are highly reproducible at elevated DMS concentrations.
 Supplementary Figure 1 DMS-MaPseq data are highly reproducible at elevated DMS concentrations. a, Correlation of Gini index for 202 yeast mrna regions with 15x coverage at 2.5% or 5% v/v DMS concentrations
Supplementary Figure 1 DMS-MaPseq data are highly reproducible at elevated DMS concentrations. a, Correlation of Gini index for 202 yeast mrna regions with 15x coverage at 2.5% or 5% v/v DMS concentrations
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Reverse transcribed Quantitative PCR. Total RNA was isolated from bone marrow derived macrophages using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), DNase-treated (Promega RQ1), and reverse transcribed
Supplementary Methods Reverse transcribed Quantitative PCR. Total RNA was isolated from bone marrow derived macrophages using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), DNase-treated (Promega RQ1), and reverse transcribed
monoclonal antibody. (a) The specificity of the anti-rhbdd1 monoclonal antibody was examined in
 Supplementary information Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1 Determination of the s pecificity of in-house anti-rhbdd1 mouse monoclonal antibody. (a) The specificity of the anti-rhbdd1 monoclonal
Supplementary information Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1 Determination of the s pecificity of in-house anti-rhbdd1 mouse monoclonal antibody. (a) The specificity of the anti-rhbdd1 monoclonal
Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of sirna in PC3 and H1299 cells PC3 (a) and H1299 (b) cells were transfected with sirna oligonucleotides
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of sirna in PC3 and H1299 cells PC3 (a) and H1299 (b) cells were transfected with sirna oligonucleotides targeting RCP (SMARTPool (RCP) or two individual oligos (RCP#1
Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of sirna in PC3 and H1299 cells PC3 (a) and H1299 (b) cells were transfected with sirna oligonucleotides targeting RCP (SMARTPool (RCP) or two individual oligos (RCP#1
Lentiviral CRISPR guild RNA Cloning Kit for constructing CRISPR targeting grna lentivectors
 Lentiviral CRISPR guild RNA Cloning Kit for constructing CRISPR targeting grna lentivectors Cat# Product Name Amount Application grna-h1-gb grna-h1-gp grna-h1-rb grna-h1-rp grna-h1-puro grna-h1-bsd grna-u6-gb
Lentiviral CRISPR guild RNA Cloning Kit for constructing CRISPR targeting grna lentivectors Cat# Product Name Amount Application grna-h1-gb grna-h1-gp grna-h1-rb grna-h1-rp grna-h1-puro grna-h1-bsd grna-u6-gb
Supplemental Data. Na Xu et al. (2016). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. The weak fluorescence phenotype is not caused by the mutation in At3g60240. (A) A mutation mapped to the gene At3g60240. Map-based cloning strategy was used to map the mutated site
Supplemental Figure 1. The weak fluorescence phenotype is not caused by the mutation in At3g60240. (A) A mutation mapped to the gene At3g60240. Map-based cloning strategy was used to map the mutated site
Chapter 6 - Molecular Genetic Techniques
 Chapter 6 - Molecular Genetic Techniques Two objects of molecular & genetic technologies For analysis For generation Molecular genetic technologies! For analysis DNA gel electrophoresis Southern blotting
Chapter 6 - Molecular Genetic Techniques Two objects of molecular & genetic technologies For analysis For generation Molecular genetic technologies! For analysis DNA gel electrophoresis Southern blotting
Supplementary Figure 1
 number of cells, normalized number of cells, normalized number of cells, normalized Supplementary Figure CD CD53 Cd3e fluorescence intensity fluorescence intensity fluorescence intensity Supplementary
number of cells, normalized number of cells, normalized number of cells, normalized Supplementary Figure CD CD53 Cd3e fluorescence intensity fluorescence intensity fluorescence intensity Supplementary
Pooled CRISPR guide RNA libraries for functional genomics screening: Do you know what s in your library?
 Pooled CRISPR guide RNA libraries for functional genomics screening: Do you know what s in your library? Peter Sheffield R&D Scientific Program Director Agilent Technologies INTRODUCTION CRISPR: A Programmable
Pooled CRISPR guide RNA libraries for functional genomics screening: Do you know what s in your library? Peter Sheffield R&D Scientific Program Director Agilent Technologies INTRODUCTION CRISPR: A Programmable
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information This Supplementary Information file contains the following contents: Supplementary Methods, Supplementary Discussion, Supplementary Figures (S1~S9), Supplementary Tables (1~3)
Supplementary Information This Supplementary Information file contains the following contents: Supplementary Methods, Supplementary Discussion, Supplementary Figures (S1~S9), Supplementary Tables (1~3)
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Synthetic annealed poly(ra):poly(dt) hybrid induces type I interferon response. a) Bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) were transfected with or without
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Synthetic annealed poly(ra):poly(dt) hybrid induces type I interferon response. a) Bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDM) were transfected with or without
Inhibition of HSV-1 Replication by Gene Editing Strategy. Running Title: Targeting HSV-1 Infection by CRISPR/Cas9
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS 2/4/16 Inhibition of HSV-1 Replication by Gene Editing Strategy Running Title: Targeting HSV-1 Infection by CRISPR/Cas9 Pamela C. Roehm 1,2,3*, Masoud Shekarabi 1, Hassen Wollebo
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS 2/4/16 Inhibition of HSV-1 Replication by Gene Editing Strategy Running Title: Targeting HSV-1 Infection by CRISPR/Cas9 Pamela C. Roehm 1,2,3*, Masoud Shekarabi 1, Hassen Wollebo
ASPP1 Fw GGTTGGGAATCCACGTGTTG ASPP1 Rv GCCATATCTTGGAGCTCTGAGAG
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids: the following plasmids were used in the supplementary data: pwzl-myc- Lats2 (Aylon et al, 2006), pretrosuper-vector and pretrosuper-shp53 (generous gift of
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids: the following plasmids were used in the supplementary data: pwzl-myc- Lats2 (Aylon et al, 2006), pretrosuper-vector and pretrosuper-shp53 (generous gift of
DNA Replication: Paper Clip Activity
 DNA Replication: Paper Clip Activity Name Hour: Date: Quick Review: Each DNA molecule has a unique structure that makes it different from other DNA molecules (Remember A chromosome is condensed DNA and
DNA Replication: Paper Clip Activity Name Hour: Date: Quick Review: Each DNA molecule has a unique structure that makes it different from other DNA molecules (Remember A chromosome is condensed DNA and
Computational Biology I LSM5191
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 Lecture 5 Notes: Genetic manipulation & Molecular Biology techniques Broad Overview of: Enzymatic tools in Molecular Biology Gel electrophoresis Restriction mapping DNA
Computational Biology I LSM5191 Lecture 5 Notes: Genetic manipulation & Molecular Biology techniques Broad Overview of: Enzymatic tools in Molecular Biology Gel electrophoresis Restriction mapping DNA
Molecular Genetics Techniques. BIT 220 Chapter 20
 Molecular Genetics Techniques BIT 220 Chapter 20 What is Cloning? Recombinant DNA technologies 1. Producing Recombinant DNA molecule Incorporate gene of interest into plasmid (cloning vector) 2. Recombinant
Molecular Genetics Techniques BIT 220 Chapter 20 What is Cloning? Recombinant DNA technologies 1. Producing Recombinant DNA molecule Incorporate gene of interest into plasmid (cloning vector) 2. Recombinant
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS. -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells. - Two methods to produce transgenic animals:
 TRANSGENIC ANIMALS -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection - random insertion 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated gene
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection - random insertion 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated gene
BSCI410-Liu/Spring 06 Exam #1 Feb. 23, 06
 Your Name: Your UID# 1. (20 points) Match following mutations with corresponding mutagens (X-RAY, Ds transposon excision, UV, EMS, Proflavin) a) Thymidine dimmers b) Breakage of DNA backbone c) Frameshift
Your Name: Your UID# 1. (20 points) Match following mutations with corresponding mutagens (X-RAY, Ds transposon excision, UV, EMS, Proflavin) a) Thymidine dimmers b) Breakage of DNA backbone c) Frameshift
Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 )
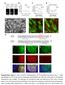 Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 ) homologous recombination arm (left) and of the right (3 )
Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 ) homologous recombination arm (left) and of the right (3 )
Suppl. Table S1. Characteristics of DHS regions analyzed by bisulfite sequencing. No. CpGs analyzed in the amplicon. Genomic location specificity
 Suppl. Table S1. Characteristics of DHS regions analyzed by bisulfite sequencing. DHS/GRE Genomic location Tissue specificity DHS type CpG density (per 100 bp) No. CpGs analyzed in the amplicon CpG within
Suppl. Table S1. Characteristics of DHS regions analyzed by bisulfite sequencing. DHS/GRE Genomic location Tissue specificity DHS type CpG density (per 100 bp) No. CpGs analyzed in the amplicon CpG within
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Sox2 localizes in neutrophils of mouse spleen. (a) Microscopy analysis of Sox2 and MPO in wild-type mouse spleen. Nucl, nucleus. (b) Immunohistochemistry staining of Sox2 and MPO
Supplementary Figure 1 Sox2 localizes in neutrophils of mouse spleen. (a) Microscopy analysis of Sox2 and MPO in wild-type mouse spleen. Nucl, nucleus. (b) Immunohistochemistry staining of Sox2 and MPO
Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured
 Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured in 90-Pa 3D fibrin gels for 5 days in the presence
Supplementary Figure 1. Soft fibrin gels promote growth and organized mesodermal differentiation. Representative images of single OGTR1 ESCs cultured in 90-Pa 3D fibrin gels for 5 days in the presence
Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic structure of TRAIP and RAP80. The prey line below TRAIP indicates bait and the two lines above RAP80 highlight the
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic structure of TRAIP and RAP80. The prey line below TRAIP indicates bait and the two lines above RAP80 highlight the prey clones identified in the yeast two hybrid screen.
Supplementary Fig. 1. Schematic structure of TRAIP and RAP80. The prey line below TRAIP indicates bait and the two lines above RAP80 highlight the prey clones identified in the yeast two hybrid screen.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Park et al. 10.1073/pnas.1410555111 5 -TCAAGTCCATCTACATGGCC-3 5 -CAGCTGCCCGGCTACTACTA-3 5 -TGCAGCTGCCCGGCTACTAC-3 5 -AAGCTGGACATCACCTCCCA-3 5 -TGACAGGAACACCTACAAGT-3 5 -AAGGCACCTTTCTGTCTCCA-3
Supporting Information Park et al. 10.1073/pnas.1410555111 5 -TCAAGTCCATCTACATGGCC-3 5 -CAGCTGCCCGGCTACTACTA-3 5 -TGCAGCTGCCCGGCTACTAC-3 5 -AAGCTGGACATCACCTCCCA-3 5 -TGACAGGAACACCTACAAGT-3 5 -AAGGCACCTTTCTGTCTCCA-3
