Ensemble refinement shows conformational flexibility in crystal structures of human complement factor D
|
|
|
- Melvin Berry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Information for Ensemble refinement shows conformational flexibility in crystal structures of human complement factor D Federico Forneris a,b, B. Tom Burnley a,b,c and Piet Gros a * a Crystal and Structural Chemistry, Bijvoet Center for Biomolecular Research, Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Utrecht University, Padualaan 8, Utrecht, 3584CH, The Netherlands b These authors contributed equally c Present Address: Scientific Computing Department, STFC, Research Complex at Harwell, Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Didcot, Oxon OX11 0QX, UK. * Correspondence p.gros@uu.nl, phone: , fax: List of Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S1 Structural features of complement Factor D and thrombin. Supplementary Figure S2 Electron density for the catalytic site of FD R202A (R218A) mutant at 1.8-Å resolution. Supplementary Figure S3 Improvement of electron density in disordered exosite regions after ER. Supplementary Figure S4 Real-space cross-correlation for the 10 ensembles and B factor plots obtained from ER of FD and thrombin structures. Supplementary Figure S5 Biophysical analysis of FD mutants. Supplementary Figure S6 ER of crystal structures of FD in complex with an antibody fragment. 1
2 Supplementary Figure S1 Structural features of complement Factor D and thrombin. (a) Cartoon representation of wild-type FD (PDB ID 1DSU, chain A is displayed). The side chains of the residues involved in the catalytic triad His-Asp-Ser, and those of the Arg202-Asp177 (Arg218-Asp189) selfinhibitory lock are shown as sticks. The four loops defining the exosite are highlighted in orange, and the self-inhibitory loop is shown in green. (b) Cartoon representation of wild-type, Na + -bound thrombin (PDB ID 3U69). The side chains of residues of the catalytic triad are shown as sticks, with residue numbering following standard serine protease conventions. The sodium ion is shown as a purple sphere. Several loops involved in ligand binding and with implications in thrombin allosteric regulation are labeled and highlighted with colors. The missing residues of the -loop, not visible in this structure because of disorder, are represented by a dashed line. (c) Zoomed-in view of the catalytic site of wild-type thrombin, showing the canonical arrangement of the His-Asp-Ser catalytic triad. (d) Superposition of the FD (orange) and thrombin (blue) structures, showing the overlap of FD s exosite with the Na + binding site of thrombin. Residues of the catalytic triad are shown as sticks. 2
3 Supplementary Figure S2 Refined electron density map for the Asp-His-Ser catalytic triad of FD R202A (R218A) mutant at 1.8-Å resolution after phenix.refine in the two copies observed in the asymmetric unit (shown as (a) and (b), respectively). Residues are shown as orange sticks. The contour levels for the electron density maps are mFo-DFm, blue) and ±3.00 mfo-dfm, green and red) 3
4 Supplementary Figure S3 ER shows electron density improvement in disordered exosite regions. Comparison of electron densities of refined FD R202A (R218A) structures in the exosite region at equivalent electron density levels after conventional refinement and ER. (a) Conventional refinement structure and mf o -DF m map contoured at ±0.31 Å/e 3 (±2.44 σ). (b) Conventional structure with ensemble map contoured at ±0.31 Å/e 3 (±3.00 σ). (c) Ensemble structure and ensemble map contoured as in (b). 4
5 Supplementary Figure S4 Real-space cross-correlation for the 10 ensembles (Branden & Alwyn Jones, 1990). In addition, B-factor as obtained from single-structure refinement of FD and thrombin structures are shown by dotted lines. (a) wild-type FD (original PDB ID 1DSU, 2 chains in the ASU). (b) FD mutant R202A (R128A) (original PDB ID 4CBN, 2 chains in the ASU). (c) wild-type, Na + - bound thrombin (original PDB ID 3U69); the dashed gray line indicates the separation between thrombin light and heavy chains. Regions with low real-space correlation correspond to flexible loops as indicated by the high B-factors. 5
6 Supplementary Figure S5 Biophysical analysis of FD mutants. (a) Circular dichroism measurements; (b) evaluation of thermal stability using thermofluor The calculated T m values are for FD wild-type, R202A and R106A mutants are 62.8 C, 63.4 C, and 63.8 C, respectively; (c) measurement of thermal-dependent aggregation propensity (left) and unfolding monitored using intrinsic fluorescence (right). The calculated T m values are for FD wild-type, R202A (R218A) and R106A (R121A) mutants are 56.5 C, 54.9 C, and 55.0 C, respectively. Shown are traces for wildtype FD (black), mutant R202A (R218A) (dark grey) and control mutant R106A (R121A) (light grey). 6
7 Supplementary Figure S6 ER of crystal structures of FD in complex with an antibody fragment. From top to bottom, the two copies of the FD-Fab complex observed in each structure originally deposited in the PDB with accession codes 4D9Q (top) and 4D9R (bottom) (Katschke et al., 2012) are displayed. On the left, the overall FD-Fab complexes are represented as ribbons, with models colored by rmsf from blue, through green, to red. On the right, details are shown for the Asp-His-Ser catalytic triad in each copy of the FD molecule. 7
Suppl. Figure 1: RCC1 sequence and sequence alignments. (a) Amino acid
 Supplementary Figures Suppl. Figure 1: RCC1 sequence and sequence alignments. (a) Amino acid sequence of Drosophila RCC1. Same colors are for Figure 1 with sequence of β-wedge that interacts with Ran in
Supplementary Figures Suppl. Figure 1: RCC1 sequence and sequence alignments. (a) Amino acid sequence of Drosophila RCC1. Same colors are for Figure 1 with sequence of β-wedge that interacts with Ran in
X-ray structures of fructosyl peptide oxidases revealing residues responsible for gating oxygen access in the oxidative half reaction
 X-ray structures of fructosyl peptide oxidases revealing residues responsible for gating oxygen access in the oxidative half reaction Tomohisa Shimasaki 1, Hiromi Yoshida 2, Shigehiro Kamitori 2 & Koji
X-ray structures of fructosyl peptide oxidases revealing residues responsible for gating oxygen access in the oxidative half reaction Tomohisa Shimasaki 1, Hiromi Yoshida 2, Shigehiro Kamitori 2 & Koji
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3428
 Supplementary Figure 1 Biochemical characterization of the monou and oligou activity switch of TUT4(7). (a) Mouse TUT4 and human TUT7 were assayed for monou and Lin28-dependent oligou addition activities
Supplementary Figure 1 Biochemical characterization of the monou and oligou activity switch of TUT4(7). (a) Mouse TUT4 and human TUT7 were assayed for monou and Lin28-dependent oligou addition activities
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.2548
 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure of GltPhout. (a) Stereo view of a slice through a single GltPhout protomer shown in stick representation along with 2Fo-Fc and anomalous difference electron maps. The
Supplementary Figure 1. Structure of GltPhout. (a) Stereo view of a slice through a single GltPhout protomer shown in stick representation along with 2Fo-Fc and anomalous difference electron maps. The
Molecular design principles underlying β-strand swapping. in the adhesive dimerization of cadherins
 Supplementary information for: Molecular design principles underlying β-strand swapping in the adhesive dimerization of cadherins Jeremie Vendome 1,2,3,5, Shoshana Posy 1,2,3,5,6, Xiangshu Jin, 1,3 Fabiana
Supplementary information for: Molecular design principles underlying β-strand swapping in the adhesive dimerization of cadherins Jeremie Vendome 1,2,3,5, Shoshana Posy 1,2,3,5,6, Xiangshu Jin, 1,3 Fabiana
Supplementary Fig. 1. Initial electron density maps for the NOX-D20:mC5a complex obtained after SAD-phasing. (a) Initial experimental electron
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Initial electron density maps for the NOX-D20:mC5a complex obtained after SAD-phasing. (a) Initial experimental electron density map obtained after SAD-phasing and density modification
Supplementary Fig. 1. Initial electron density maps for the NOX-D20:mC5a complex obtained after SAD-phasing. (a) Initial experimental electron density map obtained after SAD-phasing and density modification
Specificity: Induced Fit
 Specificity: Induced Fit Conformational changes may occur upon ligand binding (Daniel Koshland in 1958) This adaptation is called the induced fit Induced fit allows for tighter binding of the ligand Induced
Specificity: Induced Fit Conformational changes may occur upon ligand binding (Daniel Koshland in 1958) This adaptation is called the induced fit Induced fit allows for tighter binding of the ligand Induced
Figure S1. Electron density around the LH1 ligand in streptavidin (chain B of the crystal structure). (A) The 2mFo-DFc map contoured at 1 σ.
 A B C D Figure S1. Electron density around the L1 ligand in streptavidin (chain B of the crystal structure). (A) The 2mFo-DFc map contoured at 1 σ. (B) The mfo-dfc map with negative (red) and positive
A B C D Figure S1. Electron density around the L1 ligand in streptavidin (chain B of the crystal structure). (A) The 2mFo-DFc map contoured at 1 σ. (B) The mfo-dfc map with negative (red) and positive
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures 1-8
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figures 1-8 Supplementary Figure 1. TFAM residues contacting the DNA minor groove (A) TFAM contacts on nonspecific DNA. Leu58, Ile81, Asn163, Pro178, and Leu182
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figures 1-8 Supplementary Figure 1. TFAM residues contacting the DNA minor groove (A) TFAM contacts on nonspecific DNA. Leu58, Ile81, Asn163, Pro178, and Leu182
Colchicine. Colchicine. a b c d e
 α1-tub Colchicine Laulimalide RB3 β1-tub Vinblastine α2-tub Taxol Colchicine β2-tub Maytansine a b c d e Supplementary Figure 1 Structures of microtubule and tubulin (a)the cartoon of head to tail arrangement
α1-tub Colchicine Laulimalide RB3 β1-tub Vinblastine α2-tub Taxol Colchicine β2-tub Maytansine a b c d e Supplementary Figure 1 Structures of microtubule and tubulin (a)the cartoon of head to tail arrangement
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Model quality of C3b-miniFH-FI and C3b-miniFH crystal structures and overall structure comparisons. (a) Overall 2DF o -mf c electron density contoured at 1.0 for C3b-miniFH-FI (left)
Supplementary Figure 1 Model quality of C3b-miniFH-FI and C3b-miniFH crystal structures and overall structure comparisons. (a) Overall 2DF o -mf c electron density contoured at 1.0 for C3b-miniFH-FI (left)
Supplementary Information Titles
 Supplementary Information Titles Please list each supplementary item and its title or caption, in the order shown below. Note that we do NOT copy edit or otherwise change supplementary information, and
Supplementary Information Titles Please list each supplementary item and its title or caption, in the order shown below. Note that we do NOT copy edit or otherwise change supplementary information, and
Acceleration of protein folding by four orders of magnitude through a single amino acid substitution
 Acceleration of protein folding by four orders of magnitude through a single amino acid substitution Daniel J. A. Roderer 1, Martin A. Schärer 1, Marina Rubini 2 * and Rudi Glockshuber 1 AUTHOR ADDRESS
Acceleration of protein folding by four orders of magnitude through a single amino acid substitution Daniel J. A. Roderer 1, Martin A. Schärer 1, Marina Rubini 2 * and Rudi Glockshuber 1 AUTHOR ADDRESS
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
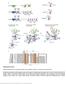 Supplementary Figure 1 Domain architecture and conformational states of the decapping complex, as revealed by structural studies. (a) Domain organization of Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sp) and Saccharomyces
Supplementary Figure 1 Domain architecture and conformational states of the decapping complex, as revealed by structural studies. (a) Domain organization of Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sp) and Saccharomyces
Supplementatry Fig 1. Domain structure, biophysical characterisation and electron microscopy of a TD. (a) XTACC3/Maskin and XMAP215/chTOG domain
 Supplementatry Fig 1. Domain structure, biophysical characterisation and electron microscopy of a TD. (a) XTACC3/Maskin and XMAP215/chTOG domain architecture. Various C-terminal fragments were cloned and
Supplementatry Fig 1. Domain structure, biophysical characterisation and electron microscopy of a TD. (a) XTACC3/Maskin and XMAP215/chTOG domain architecture. Various C-terminal fragments were cloned and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figures. Supplementary Figure 1 a. Page 1 of 30. Nature Chemical Biology: doi: /nchembio.2528
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figures Supplementary Figure 1 a b c Page 1 of 0 11 Supplementary Figure 1: Biochemical characterisation and binding validation of the reversible USP inhibitor 1. a, Biochemical
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figures Supplementary Figure 1 a b c Page 1 of 0 11 Supplementary Figure 1: Biochemical characterisation and binding validation of the reversible USP inhibitor 1. a, Biochemical
Supplementary Information. Structural basis for duplex RNA recognition and cleavage by A.
 Supplementary Information Structural asis for duplex RNA recognition and cleavage y A. fulgidus C3PO Eneida arizotto 1, Edward D Lowe 1 & James S Parker 1 1 Department of Biochemistry University of Oxford
Supplementary Information Structural asis for duplex RNA recognition and cleavage y A. fulgidus C3PO Eneida arizotto 1, Edward D Lowe 1 & James S Parker 1 1 Department of Biochemistry University of Oxford
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Multiple sequence alignments of four Swi2/Snf2 subfamily proteins, ScChd1, SsoRad54 and the RNA helicase Vasa. The sequence alignments of the Swi2/Snf2 subfamily proteins, ScChd1
Supplementary Figure 1 Multiple sequence alignments of four Swi2/Snf2 subfamily proteins, ScChd1, SsoRad54 and the RNA helicase Vasa. The sequence alignments of the Swi2/Snf2 subfamily proteins, ScChd1
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 2 Supplementary Figure 1: Sequence alignment of HsHSD17B8 and HsCBR4 of with KAR orthologs. The secondary structure elements as calculated by DSSP and residue numbers are displayed
Supplementary Figure 1 2 Supplementary Figure 1: Sequence alignment of HsHSD17B8 and HsCBR4 of with KAR orthologs. The secondary structure elements as calculated by DSSP and residue numbers are displayed
Supplemental Information Molecular Cell, Volume 41
 Supplemental Information Molecular Cell, Volume 41 Molecular Mechanisms for the RNA-Dependent ATPase Activity of Upf1 and Its Regulation by Upf2 Sutapa Chakrabarti, Uma Jayachandran, Fabien Bonneau, Francesca
Supplemental Information Molecular Cell, Volume 41 Molecular Mechanisms for the RNA-Dependent ATPase Activity of Upf1 and Its Regulation by Upf2 Sutapa Chakrabarti, Uma Jayachandran, Fabien Bonneau, Francesca
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/11/e1601625/dc1 Supplementary Materials for A molecular mechanism of chaperone-client recognition This PDF file includes: Lichun He, Timothy Sharpe, Adam Mazur,
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/11/e1601625/dc1 Supplementary Materials for A molecular mechanism of chaperone-client recognition This PDF file includes: Lichun He, Timothy Sharpe, Adam Mazur,
Conformational changes in IgE contribute to its. uniquely slow dissociation rate from receptor FcεRI
 Conformational changes in IgE contribute to its uniquely slow dissociation rate from receptor FcεRI M.D. Holdom, A.M. Davies, J.E. Nettleship, S.C. Bagby, B. Dhaliwal, E. Girardi, J. Hunt, H.J. Gould,
Conformational changes in IgE contribute to its uniquely slow dissociation rate from receptor FcεRI M.D. Holdom, A.M. Davies, J.E. Nettleship, S.C. Bagby, B. Dhaliwal, E. Girardi, J. Hunt, H.J. Gould,
Structure and Function of the First Full-Length Murein Peptide Ligase (Mpl) Cell Wall Recycling Protein
 Paper Presentation PLoS ONE 2011 Structure and Function of the First Full-Length Murein Peptide Ligase (Mpl) Cell Wall Recycling Protein Debanu Das, Mireille Herve, Julie Feuerhelm, etc. and Dominique
Paper Presentation PLoS ONE 2011 Structure and Function of the First Full-Length Murein Peptide Ligase (Mpl) Cell Wall Recycling Protein Debanu Das, Mireille Herve, Julie Feuerhelm, etc. and Dominique
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.2307
 A novel locally-closed conformation of a bacterial pentameric proton-gated ion channel Marie S. Prevost*, Ludovic Sauguet*, Hugues Nury, Catherine Van Renterghem, Christèle Huon, Frederic Poitevin, Marc
A novel locally-closed conformation of a bacterial pentameric proton-gated ion channel Marie S. Prevost*, Ludovic Sauguet*, Hugues Nury, Catherine Van Renterghem, Christèle Huon, Frederic Poitevin, Marc
has only one nucleotide, U20, between G19 and A21, while trna Glu CUC has two
 SPPLEMENTRY INFORMTION doi:1.138/nature9411 Supplementary Discussion The structural characteristics of trn Gln G in comparison to trn Glu 16 in trn Gln G is directed towards the G19 56 pair, or the outer
SPPLEMENTRY INFORMTION doi:1.138/nature9411 Supplementary Discussion The structural characteristics of trn Gln G in comparison to trn Glu 16 in trn Gln G is directed towards the G19 56 pair, or the outer
The molecular basis of lysine 48 ubiquitin chain synthesis by Ube2K
 Supplementary Information The molecular basis of lysine 48 ubiquitin chain synthesis by Adam J. Middleton, Catherine L. Day* Department of Biochemistry, Otago School of Medical Sciences, University of
Supplementary Information The molecular basis of lysine 48 ubiquitin chain synthesis by Adam J. Middleton, Catherine L. Day* Department of Biochemistry, Otago School of Medical Sciences, University of
Supplementary Table 1. DNA sequence synthesized to express the Zika virus NS5 protein.
 Supplementary Table 1. DNA sequence synthesized to express the Zika virus NS5 protein. MR766 NS5 sequence 1 ACAGAGAACAGATTGGTGGTGGAGGTGGGACGGGAGAGACTCTGGGAGAGAAGTGGAAAG 61 CTCGTCTGAATCAGATGTCGGCCCTGGAGTTCTACTCTTATAAAAAGTCAGGTATCACTG
Supplementary Table 1. DNA sequence synthesized to express the Zika virus NS5 protein. MR766 NS5 sequence 1 ACAGAGAACAGATTGGTGGTGGAGGTGGGACGGGAGAGACTCTGGGAGAGAAGTGGAAAG 61 CTCGTCTGAATCAGATGTCGGCCCTGGAGTTCTACTCTTATAAAAAGTCAGGTATCACTG
Structural basis of a novel PD-L1 nanobody for immune checkpoint blockade
 Structural basis of a novel PD-L1 nanobody for immune checkpoint blockade Supplementary Materials Supplementary methods Table S1-S Figure S1-S 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 Supplementary Methods Competitive
Structural basis of a novel PD-L1 nanobody for immune checkpoint blockade Supplementary Materials Supplementary methods Table S1-S Figure S1-S 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 Supplementary Methods Competitive
Supplementary Online Material. Structural mimicry in transcription regulation of human RNA polymerase II by the. DNA helicase RECQL5
 Supplementary Online Material Structural mimicry in transcription regulation of human RNA polymerase II by the DNA helicase RECQL5 Susanne A. Kassube, Martin Jinek, Jie Fang, Susan Tsutakawa and Eva Nogales
Supplementary Online Material Structural mimicry in transcription regulation of human RNA polymerase II by the DNA helicase RECQL5 Susanne A. Kassube, Martin Jinek, Jie Fang, Susan Tsutakawa and Eva Nogales
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Rescuing the Rescuer: On the Protein Complex between the Human Mitochondrial Acyl Carrier Protein and ISD11 María Georgina Herrera, María Florencia Pignataro, Martín Ezequiel Noguera,
Supplementary Material Rescuing the Rescuer: On the Protein Complex between the Human Mitochondrial Acyl Carrier Protein and ISD11 María Georgina Herrera, María Florencia Pignataro, Martín Ezequiel Noguera,
Supplementary Information for. Structure of human tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase-2 reveals the mechanism of protein tyrosine sulfation reaction
 Supplementary Information for Structure of human tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase-2 reveals the mechanism of protein tyrosine sulfation reaction Takamasa Teramoto, Yukari Fujikawa, Yoshirou Kawaguchi, Katsuhisa
Supplementary Information for Structure of human tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase-2 reveals the mechanism of protein tyrosine sulfation reaction Takamasa Teramoto, Yukari Fujikawa, Yoshirou Kawaguchi, Katsuhisa
Visualization of codon-dependent conformational rearrangements during translation termination
 Supplementary information for: Visualization of codon-dependent conformational rearrangements during translation termination Shan L. He 1 and Rachel Green 1 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department
Supplementary information for: Visualization of codon-dependent conformational rearrangements during translation termination Shan L. He 1 and Rachel Green 1 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department
doi: /nature09408 Figure S1
 doi:10.1038/nature09408 A Figure S1 www.nature.com/nature 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 Primary sequence, and structure of NorM VC. A. Amino acid sequence alignment of NorM VC with selected
doi:10.1038/nature09408 A Figure S1 www.nature.com/nature 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 Primary sequence, and structure of NorM VC. A. Amino acid sequence alignment of NorM VC with selected
Homology Modelling. Thomas Holberg Blicher NNF Center for Protein Research University of Copenhagen
 Homology Modelling Thomas Holberg Blicher NNF Center for Protein Research University of Copenhagen Why are Protein Structures so Interesting? They provide a detailed picture of interesting biological features,
Homology Modelling Thomas Holberg Blicher NNF Center for Protein Research University of Copenhagen Why are Protein Structures so Interesting? They provide a detailed picture of interesting biological features,
Comparative Modeling Part 1. Jaroslaw Pillardy Computational Biology Service Unit Cornell Theory Center
 Comparative Modeling Part 1 Jaroslaw Pillardy Computational Biology Service Unit Cornell Theory Center Function is the most important feature of a protein Function is related to structure Structure is
Comparative Modeling Part 1 Jaroslaw Pillardy Computational Biology Service Unit Cornell Theory Center Function is the most important feature of a protein Function is related to structure Structure is
Structure and Possible Mechanism of the CcbJ Methyltransferase from Streptomyces caelestis
 Supplemental material to accompany Structure and Possible Mechanism of the CcbJ Methyltransferase from Streptomyces caelestis Jacob Bauer, a Gabriela Ondrovičová, a Lucie Najmanová, b Vladimír Pevala,
Supplemental material to accompany Structure and Possible Mechanism of the CcbJ Methyltransferase from Streptomyces caelestis Jacob Bauer, a Gabriela Ondrovičová, a Lucie Najmanová, b Vladimír Pevala,
Supporting Information Contents
 Supporting Information Choy Theng Loh, Kiyoshi Ozawa, Kellie L. Tuck, Nicholas Barlow, Thomas Huber, Gottfried Otting, and Bim Graham Lanthanide tags for site-specific ligation to an unnatural amino acid
Supporting Information Choy Theng Loh, Kiyoshi Ozawa, Kellie L. Tuck, Nicholas Barlow, Thomas Huber, Gottfried Otting, and Bim Graham Lanthanide tags for site-specific ligation to an unnatural amino acid
Supplemental Online Material
 Supplemental Online Material Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1. A) Crosslinking efficiencies of 5 -biotin tagged oligonucleotides screened with the FASTDXL method 1. Reactive and nonreactive cysteine
Supplemental Online Material Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1. A) Crosslinking efficiencies of 5 -biotin tagged oligonucleotides screened with the FASTDXL method 1. Reactive and nonreactive cysteine
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
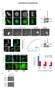 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1: Function of MICAL1 and dmical in cytokinesis (a) HeLa transfected with GFP- MICAL1 (green) were stained with Aurora B (red). Scale bars, 10 µm. (b) Western
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1: Function of MICAL1 and dmical in cytokinesis (a) HeLa transfected with GFP- MICAL1 (green) were stained with Aurora B (red). Scale bars, 10 µm. (b) Western
Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than. SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with
 Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with concentration of 800nM) were incubated with 1mM dgtp for the indicated
Supplementary Fig. S1. SAMHD1c has a more potent dntpase activity than SAMHD1c. Purified recombinant SAMHD1c and SAMHD1c proteins (with concentration of 800nM) were incubated with 1mM dgtp for the indicated
RNP purification, components and activity.
 Supplementary Figure 1 RNP purification, components and activity. (a) Intein-mediated RNP production and purification. The Ll.LtrB intron RNA (red) (Exons E1 and E2 in green) and associated intron encoded
Supplementary Figure 1 RNP purification, components and activity. (a) Intein-mediated RNP production and purification. The Ll.LtrB intron RNA (red) (Exons E1 and E2 in green) and associated intron encoded
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/5/eaas9098/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Kinetic and structural comparison of a protein s cotranslational folding and refolding pathways Avi J. Samelson, Eric
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/5/eaas9098/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Kinetic and structural comparison of a protein s cotranslational folding and refolding pathways Avi J. Samelson, Eric
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Unraveling the effects of amino acid substitutions
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Unraveling the effects of amino acid substitutions
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 This supplementary information is an extension of the letter with the same title and includes further discussion on the comparison of our designed Fe B Mb (computer model and crystal structure) with the
This supplementary information is an extension of the letter with the same title and includes further discussion on the comparison of our designed Fe B Mb (computer model and crystal structure) with the
HEK293T. Fig. 1 in the
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Zinc uptake assay of hzip4 and hzip4-δecd transiently expressed in HEK293T cells. The results of one representative e experiment are shown in Fig. 1 in
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Zinc uptake assay of hzip4 and hzip4-δecd transiently expressed in HEK293T cells. The results of one representative e experiment are shown in Fig. 1 in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature10258 Supplementary Figure 1 Reconstitution of the CENP-A nucleosome with recombinant human histones H2A, H2B, H4, and CENP-A. a, Purified recombinant human
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature10258 Supplementary Figure 1 Reconstitution of the CENP-A nucleosome with recombinant human histones H2A, H2B, H4, and CENP-A. a, Purified recombinant human
Localized Higher Order Structures of mabs and ADCs Investigated by MS-based Protein Footprinting
 Localized Higher Order Structures of s and ADCs Investigated by MS-based Protein Footprinting Lucy Pan, John Valliere-Douglass and Oscar Salas-Solano 6 th International Symposium on the Higher Order Structure
Localized Higher Order Structures of s and ADCs Investigated by MS-based Protein Footprinting Lucy Pan, John Valliere-Douglass and Oscar Salas-Solano 6 th International Symposium on the Higher Order Structure
Figure S1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The distribution of chlorophyll containing complexes eluted from DEAE-cellulose column in a sucrose gradient tube Six pigment-containing bands were resolved and identified as: B1,
Supplementary Figure 1 The distribution of chlorophyll containing complexes eluted from DEAE-cellulose column in a sucrose gradient tube Six pigment-containing bands were resolved and identified as: B1,
Supplementary materials for Structure of an open clamp type II topoisomerase-dna complex provides a mechanism for DNA capture and transport
 Supplementary materials for Structure of an open clamp type II topoisomerase-dna complex provides a mechanism for DNA capture and transport Ivan Laponogov 1,2, Dennis A. Veselkov 1, Isabelle M-T. Crevel
Supplementary materials for Structure of an open clamp type II topoisomerase-dna complex provides a mechanism for DNA capture and transport Ivan Laponogov 1,2, Dennis A. Veselkov 1, Isabelle M-T. Crevel
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06147 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 The genomic and domain structure of Dscam. The Dscam gene comprises 24 exons, encoding a signal peptide (SP), 10 IgSF domains, 6 fibronectin
doi: 10.1038/nature06147 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 The genomic and domain structure of Dscam. The Dscam gene comprises 24 exons, encoding a signal peptide (SP), 10 IgSF domains, 6 fibronectin
Supplementary Figure 1 Two distinct conformational states of the HNH domain in crystal structures. a
 Supplementary Figure 1 Two distinct conformational states of the HNH domain in crystal structures. a HNH-state 1 in PDB 4OO8, in which the distance from the C atom of the HNH catalytic residue 840 to the
Supplementary Figure 1 Two distinct conformational states of the HNH domain in crystal structures. a HNH-state 1 in PDB 4OO8, in which the distance from the C atom of the HNH catalytic residue 840 to the
Supplementary Table 1: List of CH3 domain interface residues in the first chain (A) and
 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1: List of CH3 domain interface residues in the first chain (A) and their side chain contacting residues in the second chain (B) a Interface Res. in Contacting
Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1: List of CH3 domain interface residues in the first chain (A) and their side chain contacting residues in the second chain (B) a Interface Res. in Contacting
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Assessment of quaternary structure of soluble RSV F proteins. Soluble variants of F proteins from A2 and B1 RSV strains were expressed in HEK293 cells. The cell culture supernatants
Supplementary Figure 1. Assessment of quaternary structure of soluble RSV F proteins. Soluble variants of F proteins from A2 and B1 RSV strains were expressed in HEK293 cells. The cell culture supernatants
Supplementary Figure 1. Electron microscopy of gb-698glyco/1g2 Fab complex. a)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Electron microscopy of gb-698glyco/1g2 Fab complex. a) Representative images of 2D class averages of gb-698glyc bound to 1G2 Fab. Top views of the complex were underrepresented
Supplementary Figure 1. Electron microscopy of gb-698glyco/1g2 Fab complex. a) Representative images of 2D class averages of gb-698glyc bound to 1G2 Fab. Top views of the complex were underrepresented
Homology Modelling. Thomas Holberg Blicher NNF Center for Protein Research University of Copenhagen
 Homology Modelling Thomas Holberg Blicher NNF Center for Protein Research University of Copenhagen Why are Protein Structures so Interesting? They provide a detailed picture of interesting biological features,
Homology Modelling Thomas Holberg Blicher NNF Center for Protein Research University of Copenhagen Why are Protein Structures so Interesting? They provide a detailed picture of interesting biological features,
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3018
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of genetic complementation assay in Bmal1 / Per2 Luc fibroblasts. (a) Only Bmal1, not Bmal2, rescues circadian rhythms from cells. Cells expressing various Bmal constructs
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of genetic complementation assay in Bmal1 / Per2 Luc fibroblasts. (a) Only Bmal1, not Bmal2, rescues circadian rhythms from cells. Cells expressing various Bmal constructs
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Determinants of laminin polymerization revealed. by the structure of the α5 chain amino-terminal region
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Determinants of laminin polymerization revealed by the structure of the α5 chain amino-terminal region Sadaf-Ahmahni Hussain 1, Federico Carafoli 1 & Erhard Hohenester 1 1 Department
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Determinants of laminin polymerization revealed by the structure of the α5 chain amino-terminal region Sadaf-Ahmahni Hussain 1, Federico Carafoli 1 & Erhard Hohenester 1 1 Department
Supplementary Note 1. Enzymatic properties of the purified Syn BVR
 Supplementary Note 1. Enzymatic properties of the purified Syn BVR The expression vector pet15b-syn bvr allowed us to routinely prepare 15 mg of electrophoretically homogenous Syn BVR from 2.5 L of TB-medium
Supplementary Note 1. Enzymatic properties of the purified Syn BVR The expression vector pet15b-syn bvr allowed us to routinely prepare 15 mg of electrophoretically homogenous Syn BVR from 2.5 L of TB-medium
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Structure of a tyrosyl-trna synthetase splicing factor bound to a group I intron RNA Paul J. Paukstelis 1, Jui-Hui Chen 2, Elaine Chase 2, Alan M. Lambowitz 1,*, and Barbara L. Golden 2,*,. 1 Institute
Structure of a tyrosyl-trna synthetase splicing factor bound to a group I intron RNA Paul J. Paukstelis 1, Jui-Hui Chen 2, Elaine Chase 2, Alan M. Lambowitz 1,*, and Barbara L. Golden 2,*,. 1 Institute
Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of HSA mutants to hfcrn. (a) The levels of titrated amounts of HSA
 Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of HSA mutants to hfcrn. (a) The levels of titrated amounts of HSA variants (5.0-0.002 μg/ml) directly coated in the wells at ph 6.0 were controlled using a horseradish
Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of HSA mutants to hfcrn. (a) The levels of titrated amounts of HSA variants (5.0-0.002 μg/ml) directly coated in the wells at ph 6.0 were controlled using a horseradish
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS. Figure S1: Homology alignment of DDR2 amino acid sequence. Shown are
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1: Homology alignment of DDR2 amino acid sequence. Shown are the amino acid sequences of human DDR2, mouse DDR2 and the closest homologs in zebrafish and C. Elegans.
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1: Homology alignment of DDR2 amino acid sequence. Shown are the amino acid sequences of human DDR2, mouse DDR2 and the closest homologs in zebrafish and C. Elegans.
Protein-Protein Interactions I
 Biochemistry 412 Protein-Protein Interactions I March 23, 2007 Macromolecular Recognition by Proteins Protein folding is a process governed by intramolecular recognition. Protein-protein association is
Biochemistry 412 Protein-Protein Interactions I March 23, 2007 Macromolecular Recognition by Proteins Protein folding is a process governed by intramolecular recognition. Protein-protein association is
Molecular BioSystems PAPER
 Molecular BioSystems Cite this: Mol. BioSyst., 2012, 8, 2680 2691 www.rsc.org/molecularbiosystems Dynamic Article Links PAPER Functional annotation of the mesophilic-like character of mutants in a cold-adapted
Molecular BioSystems Cite this: Mol. BioSyst., 2012, 8, 2680 2691 www.rsc.org/molecularbiosystems Dynamic Article Links PAPER Functional annotation of the mesophilic-like character of mutants in a cold-adapted
The distinct Z-DNA binding mode of a PKR-like protein kinase containing Z-DNA
 The distinct Z-DNA binding mode of a PKR-like protein kinase containing Z-DNA binding domain (PKZ) Doyoun Kim 1, Jeonghwan Hur 1, Kwangsoo Park 1, Sangsu Bae 2,3, Donghyuk Shin 4, Sung Chul Ha 5, Hye-Yeon
The distinct Z-DNA binding mode of a PKR-like protein kinase containing Z-DNA binding domain (PKZ) Doyoun Kim 1, Jeonghwan Hur 1, Kwangsoo Park 1, Sangsu Bae 2,3, Donghyuk Shin 4, Sung Chul Ha 5, Hye-Yeon
Prediction of Protein-Protein Binding Sites and Epitope Mapping. Copyright 2017 Chemical Computing Group ULC All Rights Reserved.
 Prediction of Protein-Protein Binding Sites and Epitope Mapping Epitope Mapping Antibodies interact with antigens at epitopes Epitope is collection residues on antigen Continuous (sequence) or non-continuous
Prediction of Protein-Protein Binding Sites and Epitope Mapping Epitope Mapping Antibodies interact with antigens at epitopes Epitope is collection residues on antigen Continuous (sequence) or non-continuous
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Reengineering Protein Interfaces Yields Copper-Inducible Ferritin Cage Assembly
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Reengineering Protein Interfaces Yields Copper-Inducible Ferritin Cage Assembly Dustin J. E. Huard, Kathleen M. Kane and F. Akif Tezcan* Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Reengineering Protein Interfaces Yields Copper-Inducible Ferritin Cage Assembly Dustin J. E. Huard, Kathleen M. Kane and F. Akif Tezcan* Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry,
Supplementary Figures:
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1. Crystal structure of ligand 4 drawn with 50% thermal ellipsoid probability. Hydrogens are omitted for clarity. Zinc atoms are dark blue; sulfur, yellow; phosphorus,
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1. Crystal structure of ligand 4 drawn with 50% thermal ellipsoid probability. Hydrogens are omitted for clarity. Zinc atoms are dark blue; sulfur, yellow; phosphorus,
Allosteric Effects of the Oncogenic RasQ61L Mutant on Raf-RBD
 Article Allosteric Effects of the Oncogenic RasQ61L Mutant on Raf-RBD Highlights d Crystal structures of HRas and HRasQ61L have been solved in complex with Raf-RBD Authors Susan K. Fetics, Hugo Guterres,...,
Article Allosteric Effects of the Oncogenic RasQ61L Mutant on Raf-RBD Highlights d Crystal structures of HRas and HRasQ61L have been solved in complex with Raf-RBD Authors Susan K. Fetics, Hugo Guterres,...,
Site-specific time-resolved FRET reveals local variations in the unfolding mechanism in an apparently two-state protein unfolding transition
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2017 Supplementary information for Site-specific time-resolved FRET reveals local variations
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2017 Supplementary information for Site-specific time-resolved FRET reveals local variations
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Mechanism for signal-induced opening of the DNA box. a, An atomic model of the DNA box held closed by locks (orange and blue) that are double helices formed by two short strands
Supplementary Figure 1. Mechanism for signal-induced opening of the DNA box. a, An atomic model of the DNA box held closed by locks (orange and blue) that are double helices formed by two short strands
Clamping down on pathogenic bacteria how to shut down a key DNA polymerase complex
 Clamping down on pathogenic bacteria how to shut down a key DNA polymerase complex Bacterial DNA-replication machinery Pathogenic bacteria that are resistant to the current armoury of antibiotics are an
Clamping down on pathogenic bacteria how to shut down a key DNA polymerase complex Bacterial DNA-replication machinery Pathogenic bacteria that are resistant to the current armoury of antibiotics are an
Molecular basis for allosteric specificity regulation in class Ia ribonucleotide reductase from Escherichia coli
 Molecular basis for allosteric specificity regulation in class Ia ribonucleotide reductase from Escherichia coli The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Molecular basis for allosteric specificity regulation in class Ia ribonucleotide reductase from Escherichia coli The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.2996
 Supplementary Figure 1 Negative-stain EM of native cytoplasmic dynein. (a) A representative micrograph of negatively stained dynein, with the flexible dimeric molecules circled in white. (b) Reference-free
Supplementary Figure 1 Negative-stain EM of native cytoplasmic dynein. (a) A representative micrograph of negatively stained dynein, with the flexible dimeric molecules circled in white. (b) Reference-free
Supporting Information Defined Bilayer Interactions of DNA Nanopores Revealed with a Nuclease-Based Nanoprobe Strategy
 Supporting Information Defined Bilayer Interactions of DNA Nanopores Revealed with a Nuclease-Based Nanoprobe Strategy Jonathan R. Burns* & Stefan Howorka* 1 Contents 1. Design of DNA nanopores... 3 1.1.
Supporting Information Defined Bilayer Interactions of DNA Nanopores Revealed with a Nuclease-Based Nanoprobe Strategy Jonathan R. Burns* & Stefan Howorka* 1 Contents 1. Design of DNA nanopores... 3 1.1.
BMB/Bi/Ch 170 Fall 2017 Problem Set 1: Proteins I
 BMB/Bi/Ch 170 Fall 2017 Problem Set 1: Proteins I Please use ray-tracing feature for all the images you are submitting. Use either the Ray button on the right side of the command window in PyMOL or variations
BMB/Bi/Ch 170 Fall 2017 Problem Set 1: Proteins I Please use ray-tracing feature for all the images you are submitting. Use either the Ray button on the right side of the command window in PyMOL or variations
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Location of the mab 6F10 epitope in capsids.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Location of the mab 6F10 epitope in capsids. The epitope of monoclonal antibody, mab 6F10, was mapped to residues A862 H880 of the HSV-1 major capsid protein VP5 by immunoblotting
Supplementary Figure 1 Location of the mab 6F10 epitope in capsids. The epitope of monoclonal antibody, mab 6F10, was mapped to residues A862 H880 of the HSV-1 major capsid protein VP5 by immunoblotting
The Skap-hom Dimerization and PH Domains Comprise
 Molecular Cell, Volume 32 Supplemental Data The Skap-hom Dimerization and PH Domains Comprise a 3 -Phosphoinositide-Gated Molecular Switch Kenneth D. Swanson, Yong Tang, Derek F. Ceccarelli, Florence Poy,
Molecular Cell, Volume 32 Supplemental Data The Skap-hom Dimerization and PH Domains Comprise a 3 -Phosphoinositide-Gated Molecular Switch Kenneth D. Swanson, Yong Tang, Derek F. Ceccarelli, Florence Poy,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11726 Supplementary Figure 1 SRP RNA constructs used in single molecule experiments. a, Secondary structure of wildtype E. coli SRP RNA, which forms an elongated hairpin structure capped
doi:10.1038/nature11726 Supplementary Figure 1 SRP RNA constructs used in single molecule experiments. a, Secondary structure of wildtype E. coli SRP RNA, which forms an elongated hairpin structure capped
Supplementary Figure 1. Two activation pathways and four conformations of β 2 integrins. KIM127 (red) can specifically detect
 Supplementary Figure 1 Two activation pathways and four conformations of β 2 integrins. KIM127 (red) can specifically detect integrin extension (E + ) and mab24 (green) can specifically detect headpiece-opening
Supplementary Figure 1 Two activation pathways and four conformations of β 2 integrins. KIM127 (red) can specifically detect integrin extension (E + ) and mab24 (green) can specifically detect headpiece-opening
Examination I PHRM 836 Biochemistry for Pharmaceutical Sciences II September 29, 2015
 Examination I PHRM 836 Biochemistry for Pharmaceutical Sciences II September 29, 2015 PHRM 836 Exam I - 1 Name: Instructions 1. Check your exam to make certain that it has 9 pages including this cover
Examination I PHRM 836 Biochemistry for Pharmaceutical Sciences II September 29, 2015 PHRM 836 Exam I - 1 Name: Instructions 1. Check your exam to make certain that it has 9 pages including this cover
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.1805 Visualization and Selective Chemical Targeting of RNA G-quadruplex Structures in the Cytoplasm of Human Cells Giulia Biffi 1, Marco Di Antonio 2, David Tannahill 1 and Shankar Balasubramanian
DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.1805 Visualization and Selective Chemical Targeting of RNA G-quadruplex Structures in the Cytoplasm of Human Cells Giulia Biffi 1, Marco Di Antonio 2, David Tannahill 1 and Shankar Balasubramanian
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Activation and Reduction of Carbon Dioxide by Nitrogenase Iron Proteins Johannes G. Rebelein, Martin T. Stiebritz, Chi Chung Lee, Yilin Hu* Department of Molecular Biology and
Supplementary Information Activation and Reduction of Carbon Dioxide by Nitrogenase Iron Proteins Johannes G. Rebelein, Martin T. Stiebritz, Chi Chung Lee, Yilin Hu* Department of Molecular Biology and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10963 Supplementary Table 1 Data collection, phasing and refinement statistics. Crystal Native Derivative-1 (OsO 4 ) Derivative-2 (Orange-Pt) Data collection Space group C2 C2 C2 Cell
doi:10.1038/nature10963 Supplementary Table 1 Data collection, phasing and refinement statistics. Crystal Native Derivative-1 (OsO 4 ) Derivative-2 (Orange-Pt) Data collection Space group C2 C2 C2 Cell
Diversity in DNA recognition by p53 revealed by crystal structures with Hoogsteen base pairs
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Diversity in DNA recognition by p53 revealed by crystal structures with Hoogsteen base pairs Malka Kitayner 1, 3, Haim Rozenberg 1, 3, Remo Rohs 2, 3, Oded Suad 1, Dov Rabinovich
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Diversity in DNA recognition by p53 revealed by crystal structures with Hoogsteen base pairs Malka Kitayner 1, 3, Haim Rozenberg 1, 3, Remo Rohs 2, 3, Oded Suad 1, Dov Rabinovich
Antibody-Antigen recognition. Structural Biology Weekend Seminar Annegret Kramer
 Antibody-Antigen recognition Structural Biology Weekend Seminar 10.07.2005 Annegret Kramer Contents Function and structure of antibodies Features of antibody-antigen interfaces Examples of antibody-antigen
Antibody-Antigen recognition Structural Biology Weekend Seminar 10.07.2005 Annegret Kramer Contents Function and structure of antibodies Features of antibody-antigen interfaces Examples of antibody-antigen
Supplementary Information. Single-molecule analysis reveals multi-state folding of a guanine. riboswitch
 Supplementary Information Single-molecule analysis reveals multi-state folding of a guanine riboswitch Vishnu Chandra 1,4,#, Zain Hannan 1,5,#, Huizhong Xu 2,# and Maumita Mandal 1,2,3,6* Department of
Supplementary Information Single-molecule analysis reveals multi-state folding of a guanine riboswitch Vishnu Chandra 1,4,#, Zain Hannan 1,5,#, Huizhong Xu 2,# and Maumita Mandal 1,2,3,6* Department of
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL BIOCHEMICAL AND STRUCTURAL STUDIES ON THE M. TUBERCULOSIS O 6 -METHYLGUANINE METHYLTRANSFERASE AND MUTATED VARIANTS
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL BIOCHEMICAL AND STRUCTURAL STUDIES ON THE M. TUBERCULOSIS O 6 -METHYLGUANINE METHYLTRANSFERASE AND MUTATED VARIANTS Riccardo Miggiano 1, Valentina Casazza 1, Silvia Garavaglia 1,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL BIOCHEMICAL AND STRUCTURAL STUDIES ON THE M. TUBERCULOSIS O 6 -METHYLGUANINE METHYLTRANSFERASE AND MUTATED VARIANTS Riccardo Miggiano 1, Valentina Casazza 1, Silvia Garavaglia 1,
Supplemental Information. Single-Molecule Imaging Reveals How. Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 Initiates DNA Break Repair
 Molecular Cell, Volume 67 Supplemental Information Single-Molecule Imaging Reveals How Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 Initiates DNA Break Repair Logan R. Myler, Ignacio F. Gallardo, Michael M. Soniat, Rajashree A. Deshpande,
Molecular Cell, Volume 67 Supplemental Information Single-Molecule Imaging Reveals How Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 Initiates DNA Break Repair Logan R. Myler, Ignacio F. Gallardo, Michael M. Soniat, Rajashree A. Deshpande,
Dr. R. Sankar, BSE 631 (2018)
 Pauling, Corey and Branson Diffraction of DNA http://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/dna-is-a-structure-that-encodes-biological-6493050 In short, stereochemistry is important in determining which helices
Pauling, Corey and Branson Diffraction of DNA http://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/dna-is-a-structure-that-encodes-biological-6493050 In short, stereochemistry is important in determining which helices
Supplementary Figure 1. Botrocetin induces binding of human VWF to human
 Supplementary Figure 1: Supplementary Figure 1. Botrocetin induces binding of human VWF to human platelets in the absence of elevated shear and induces platelet agglutination as detected by flow cytometry.
Supplementary Figure 1: Supplementary Figure 1. Botrocetin induces binding of human VWF to human platelets in the absence of elevated shear and induces platelet agglutination as detected by flow cytometry.
Supplementary Figure 1. Antibody-induced cargo release studied by native PAGE. A clear band corresponding to the cargo strand (lane 1) is visible.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Antibody-induced cargo release studied by native PAGE. A clear band corresponding to the cargo strand (lane 1) is visible. Because SYBR Gold is less sensitive to single stranded
Supplementary Figure 1. Antibody-induced cargo release studied by native PAGE. A clear band corresponding to the cargo strand (lane 1) is visible. Because SYBR Gold is less sensitive to single stranded
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Linkage preference of USP30 and USP domain architecture.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Linkage preference of USP30 and USP domain architecture. a, Catalytic efficiencies determined from Coomassie-stained gel-based kinetics for all eight diub linkages (see Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1 Linkage preference of USP30 and USP domain architecture. a, Catalytic efficiencies determined from Coomassie-stained gel-based kinetics for all eight diub linkages (see Supplementary
Supplementary material 1: DNA tracing
 Supplementary material 1: DNA tracing Figure S1:Typical AFM image showing DNA molecules relaxed when deposited with Mg 2+ DNA molecules that appear to have a higher or larger end (indicated by a red arrow
Supplementary material 1: DNA tracing Figure S1:Typical AFM image showing DNA molecules relaxed when deposited with Mg 2+ DNA molecules that appear to have a higher or larger end (indicated by a red arrow
DNA/Protein Binding, Molecular Docking and in Vitro Anti-cancer Activity of some Thioether-Dipyrrinato Complexes
 DNA/Protein Binding, Molecular Docking and in Vitro Anti-cancer Activity of some Thioether-Dipyrrinato Complexes Rakesh Kumar Gupta, Gunjan Sharma, ξ Rampal Pandey, Amit Kumar, Biplob Koch, ξ Pei- Zhou
DNA/Protein Binding, Molecular Docking and in Vitro Anti-cancer Activity of some Thioether-Dipyrrinato Complexes Rakesh Kumar Gupta, Gunjan Sharma, ξ Rampal Pandey, Amit Kumar, Biplob Koch, ξ Pei- Zhou
Site-directed Mutagenesis
 Site-directed Mutagenesis Applications Subtilisin (Met à Ala mutation resistant to oxidation) Fluorescent proteins Protein structure-function Substrate trapping mutants Identify regulatory regions/sequences
Site-directed Mutagenesis Applications Subtilisin (Met à Ala mutation resistant to oxidation) Fluorescent proteins Protein structure-function Substrate trapping mutants Identify regulatory regions/sequences
Supplementary Material. for. A Tool Set to Map Allosteric Networks through the NMR Chemical Shift Covariance Analysis
 Supplementary Material for A Tool Set to Map Allosteric Networks through the NMR Chemical Shift Covariance Analysis Stephen Boulton 1, Madoka Akimoto 2, Rajeevan Selvaratnam 2, Amir Bashiri 2 and Giuseppe
Supplementary Material for A Tool Set to Map Allosteric Networks through the NMR Chemical Shift Covariance Analysis Stephen Boulton 1, Madoka Akimoto 2, Rajeevan Selvaratnam 2, Amir Bashiri 2 and Giuseppe
A hybrid structural approach to analyze ligand binding by the 5-HT4. receptor
 Supplement A hybrid structural approach to analyze ligand binding by the 5-HT4 receptor Pius S. Padayatti 1**, Liwen Wang 2**, Sayan Gupta 3, Tivadar Orban 4, Wenyu Sun 1, David Salom 1, Steve Jordan 5,
Supplement A hybrid structural approach to analyze ligand binding by the 5-HT4 receptor Pius S. Padayatti 1**, Liwen Wang 2**, Sayan Gupta 3, Tivadar Orban 4, Wenyu Sun 1, David Salom 1, Steve Jordan 5,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 A biomimetic DNA-based channel for the ligand-controlled transport of charged molecular cargo across a biological membrane Jonathan R. Burns, Astrid Seifert, Niels Fertig, Stefan Howorka NATURE NANOTECHNOLOGY
A biomimetic DNA-based channel for the ligand-controlled transport of charged molecular cargo across a biological membrane Jonathan R. Burns, Astrid Seifert, Niels Fertig, Stefan Howorka NATURE NANOTECHNOLOGY
nanodsf 2bind: Your service provider for biophysical characterization of proteins Precisely revealing protein folding and stability
 nanodsf Precisely revealing protein folding and stability 2bind: Your service provider for biophysical characterization of proteins This booklet was written and designed by 2bind 08 2015 Any reproduction
nanodsf Precisely revealing protein folding and stability 2bind: Your service provider for biophysical characterization of proteins This booklet was written and designed by 2bind 08 2015 Any reproduction
What s New in Discovery Studio 2.5.5
 What s New in Discovery Studio 2.5.5 Discovery Studio takes modeling and simulations to the next level. It brings together the power of validated science on a customizable platform for drug discovery research.
What s New in Discovery Studio 2.5.5 Discovery Studio takes modeling and simulations to the next level. It brings together the power of validated science on a customizable platform for drug discovery research.
