Supplementary Figure S1: (A) Schematic representation of the Jarid2 Flox/Flox
|
|
|
- Gwen Carter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure S1: (A) Schematic representation of the Flox/Flox locus and the strategy used to visualize the wt and the Flox/Flox mrna by PCR from cdna. An example of the genotyping strategy is reported. (B) As a control of homogenous recombination throughout all keratin- 14 positive cells in the epidermis, mice were kept in a ROSA6- YFP background. Scale bar: 100 µm. (C) RT- PCR showing deletion of in keratinocytes isolated from cko mice compared to control keratinocytes. Amplification of Keratin- 14 was used as a control. Quantitative RT- qpcr with the same primers shows that the level of is undetectable in the conditional KO mice. Expression of HPRT- I was used for normalizing the data. Data are presented as mean + S.E.M. (D) Western- Blot showing the expression of in keratinocytes isolated from wt and cko newborn mice. Total H3 was used for normalization. Supplementary Figure S: The expression of (mrna) is the same in basal (α6 bright ) and suprabasal (α6 dim ) keratinocytes isolated from the epidermis of E16.5 and E18.5 embryos. CD31, CD140a and CD45 antibodies (Lin- ) were used to exclude the non epidermal lineages from the preparation. One representative FACS- sorting is presented. Data are presented as mean + S.T.D.V. of the RT- qpcr. N=9 mice for E18.5, N=6 for E16.5 embryos. Supplementary Figure S3: mrna levels were downregulated during differentiation in primary human keratinocytes (P*<0.05, P**<0.01). Primary human keratinocytes, isolated from foreskin, were sorted based on their surface levels of α6- integrin, and levels were assessed by RT- qpcr. Involucrin and α6- integrin levels were used as a control. Primers for HPRT- I were used for
2 normalization. The sorting strategy used for this experiment is reported on the left. N=4. Data are presented as average + S.E.M. P value<5. Supplementary Figure S4. is required for the ectopic activation of bulge stem cells and their progeny upon TPA treatment: (A) The response to TPA treatment was delayed in cko. The epidermis of TPA- treated cko animals displayed a thicker cornified layer than control littermates (left panel; scale bar: 100 mm). The middle panel shows an increased expression of the loricrin (red fluorescence) in TPA- treated cko mice compared to controls. Keratin- 14 is marked as green fluorescence. Scale bar: 5 µm. Wholemount staining for Ki67 in TPA- treated tails reveals a reduction in the number of proliferative cells in the bulge and bulb. Scale bars: 100 µm and 5 µm, respectively. N=7. Supplementary Figure S5: (A) Expression of (mrna) is lower in differentiated keratinocytes than in basal progenitors isolated from the epidermis of P8 mice. Cells were FACS- sorted on the basis of bright and dim expression of the surface markers α6- integrin. Non- epidermal contaminants were excluded using Lineage- antibodies (CD31, CD45, CD140a). (B) The epidermis of cko P8 mice show increased expression of differentiation genes and p16. Data are presented as average + S.T.D.V. N=6 wt, 4 cko.
3 Mejetta_Suppl1 Exon3 Exon4 335 bp 335 bp K14wt 150 bp DAPI YFP DAPI YFP ck O S1D) K14 Relative mrna level t wt KO Total H3 ck O K14Cre t w cdna Ja rid Ja rid 3 KO mrna Genomic DNA S1C) K14CreRosa6/YFP-Flox/Flox wt mrna 150bp Flox/Flox wt/wt Flox/Flox S1B) w Exon 5 LoxP Ja r id LoxP Ja r id S1A)
4 Mejetta_Suppl Lineage- E18.5 α6low α6bright E16.5 Relative mrna levels 1, 0,9 0,3 Loricrin Loricrin 0 α6low α6bright Bright E18.5 Relative mrna levels α6low α6bright
5 Mejetta_Suppl3 Relative mrna levels 1, 0,9 0,3 ** * 1, 0,9 0, Involucrin α6bright α6dim α6low
6 cko + TPA DAPIKi67 wt +TPA wt +TPA S4B) cko + TPA cko + TPA wt +TPA S4A) S4C) DAPIKi67 Mejetta_FigS4 DAPIK14Loricrin DAPIK14Loricrin
7 1, α6low α6bright 1, 1,6,0 1, Loricrin P8 mice Lineage cko wt p16 0,5,0,5 3,0 0,5,0,5 3,0 0,5,0,5 3,0 Keratin1 Keratin10 Lce1c Lce1c 0,5,0,5 3,0 Mejetta_FigS5 S5A) S5B)
8 Table1 Genotyping PCR Fw Primer Rev Primer Flox GCGGTAAATGGTGAGTTGAAA ACAGACTGACACACCTTCC K14 wt CAAATGTTGCTTGCTTGTCTGGTG GTCAGTCGAGTGCACAGTTT Cre Tg GTCCATGTCCTTCCTGAAGC TTCCTCAGGAGTGTTCTTCGC Table Mouse qpcr Fw Primer Rev Primer K14 AGCGGCAAGAGTGAGATTTCT CCTCCAGGTTATTCTCCAGGG K1 GACACCACAACCCGGACCCAAAACTTAG ATACTGGGCCTTGACTTCCGAGATGATG K10 GGAGGGTAAAATCAAGGAGTGGTA TCAATCTGCAGCAGCACGTT Loricrin TCACTCATCTTCCCTGGTGCTT GTCTTTCCACAACCCACAGGA Involucrin GTCCGGTTCTCCAATTCGTGTTT GCAATTGGAAGAGAAGCAGCATCAG Lce1a GAGGTGCCCAAGGATCTTGTAC CCAGGCTACAGCAGGAAGACAC Lce1c AGATCTCAAACATTCTATGCAGAGGAA TCACAAAATACTGAAGAAGAAAGGGATT Lce1d GACTGCTGCTGATCTCAATGAGAA TGCAGAAACTTTCCCTGAAGATTTC Lce1l CATGAAGGCTTCAGACAAGCAAT TTGGAATCACAGAAGGAGATGAGAC Lce1m AGCATTGACTGAAGACCTGCAA GCAAAGCCAATGCATCTCAGA Crct1 ACTGCACTTTGATGTTCAGAAACTTC CAGGAGGCCTGTTTTGAACACT Filaggrin GGAGGCATGGTGGAACTGA TGTTTATCTTTTCCCTCACTTCTACATC a6-integrin TGCAGAGGGCGAACAGAAC GCACACGTCACCACTTTGC CD34 AAGGCTGGGTGAAGACCCTTA TGAATGGCCGTTTCTGGAAGT Ki67 AGGAGGAACCAACCAAGGACAGTT TTTCTCTGTGCTGTGGGCTCTTCT GGTGCAGGTACAAACAGTGCCAAA GTGGTGGTTGGGTTTGGTTTCCTT Jmj AGGCCTTGCCGGGAGCCTGAA AGCAAAGGCTCCACTATCTTC Pum1 AGGCGTTAGCATGGTGGAGTA TCCATCAAACGTACCCTTGTTC HPRT-I TCAGTCAACGGGGGACATAAA GGGGCTGTACTGCTTAACCAG Human qpcr Fw Primer Rev Primer a6-integrin CTAGTGGCTATTCTCGCTGGG CGTTCCACTTTGTGATCCACTG Involucrin GACTGCTGTAAAGGGACTGCC CATTCCCAGTTGCTCATCTCTC Filaggrin GAGAGGCGATCTGAGTCTGC CTGCCACGTGACTGTATTCC GGTCAGAAGAACGGGTGGTA TTACCAAGGAGCCCATTCAC Pum1 CGGTCGTCCTGAGGATAAAA CGTACGTGAGGCGTGAGTAA HPRT-I TGGACAGGACTGAACGTCTTG CCAGCAGGTCAGCAAAGAATT Table3 CHIp qpcr Fw Primer Rev Primer Olig TGCTTATTACAGACCGAGCCAAC CTAAATCCTAGCCACTTTGGAGAAGT Neurg1 CCGGGTCGTACGGACAGTAA TCGGTGAGGAAGCTGCACA Neurog CAGATCTGATTGTTTTCTTGGTGGTATA GCGTGGTTGTCTGTCAGTCAGT HoxB13 TCTGGAAAGCAGCGTTTGC CTTAGTGATAAACTTGTTGGCTGCA Actin-B CCGTAAAGACCTCTATGCCAACAC GCTAGGAGCCAGAGCAGTAATCTC p16 Promoter GATGGAGCCCGGACTACAGAA CTGTTTCAACGCCCAGCTCTC K14 AGGAGGGATCTGATCGGGAGT AGAGCTGCTCAGGTGTGTTAGAAAA K1 CTCAGTATATAAGGGCACGGCACT GACTCATGATGCCTTAGAGAGAGGT
9 K10 AGCAAAGCCTAGCACCTGTGA GCTGCTGGAGCTGTATAGAACAGAC Loricrin CAGAGCAGGACAAGAGTATAAAACACA GCCCACACTTACCTGAAGCAC Lce1a GAGGTGCCCAAGGATCTTGTAC CCTTCCCCCAACACTTCCAT Lce1i TCCTGGAGGTAAGGGCAGAGA CAAGGCTGTGGCTAGTTATTGTCA Lce1m AGCATTGACTGAAGACCTGCAA GCAAAGCCAATGCATCTCAGA Lce3b AAAGCATCCTCAGACACGGACTT CCTATTGCACTTATGTCTGGATTTCTGT Crct1 TCTGCCTAGCAGGTGTCAAGTTC GCTACATTCTGGCTGCATCCTACT Filaggrin TCCCTTTTACAGGTGCATACACAC CCTCCTTATCACTGGTTGAGTATTGTT Sprrf TCTTTGAAAGGCCATATACCTCAGC GTTCTGGTGCCCTGAGAAACC Sprrh TGGTTCCAAACTCTGAGCAAGTGTA CCTGTATATCAAGAGAGGGCATCAGAT
Supplementary Figure 1. Wnt10a mutation causes aberrant molar tooth development and formation of an ectopic M4 molar. (a,b) Smaller molar teeth with
 Supplementary Figure 1. Wnt10a mutation causes aberrant molar tooth development and formation of an ectopic M4 molar. (a,b) Smaller molar teeth with blunted cusp formation, and presence of an ectopic molar
Supplementary Figure 1. Wnt10a mutation causes aberrant molar tooth development and formation of an ectopic M4 molar. (a,b) Smaller molar teeth with blunted cusp formation, and presence of an ectopic molar
(a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of Diaph3 ko mice. (a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for different regions of Diaph3 mrna from WT, heterozygote
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of Diaph3 ko mice. (a) Scheme depicting the strategy used to generate the ko and conditional alleles. (b) RT-PCR for different regions of Diaph3 mrna from WT, heterozygote
(A-B) P2ry14 expression was assessed by (A) genotyping (upper arrow: WT; lower
 Supplementary Figures S1. (A-B) P2ry14 expression was assessed by (A) genotyping (upper arrow: ; lower arrow: KO) and (B) q-pcr analysis with Lin- cells, The white vertical line in panel A indicates that
Supplementary Figures S1. (A-B) P2ry14 expression was assessed by (A) genotyping (upper arrow: ; lower arrow: KO) and (B) q-pcr analysis with Lin- cells, The white vertical line in panel A indicates that
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Identification of new regulators of MuSC by a proteome-based shrna screen. (a) FACS plots of GFP + and GFP - cells from Pax7 ICN -Z/EG (upper panel) and
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Identification of new regulators of MuSC by a proteome-based shrna screen. (a) FACS plots of GFP + and GFP - cells from Pax7 ICN -Z/EG (upper panel) and
DRG Pituitary Cerebral Cortex
 Liver Spinal cord Pons Atg5 -/- Atg5 +/+ DRG Pituitary Cerebral Cortex WT KO Supplementary Figure S1 Ubiquitin-positive IBs accumulate in Atg5 -/- tissues. Atg5 -/- neonatal tissues were fixed and decalcified.
Liver Spinal cord Pons Atg5 -/- Atg5 +/+ DRG Pituitary Cerebral Cortex WT KO Supplementary Figure S1 Ubiquitin-positive IBs accumulate in Atg5 -/- tissues. Atg5 -/- neonatal tissues were fixed and decalcified.
At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Generation of TSPOΔ/Δ murine embryonic fibroblasts Embryos were harvested from 13.5-day pregnant TSPOfl/fl mice. After dissection to eviscerate and remove the
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Generation of TSPOΔ/Δ murine embryonic fibroblasts Embryos were harvested from 13.5-day pregnant TSPOfl/fl mice. After dissection to eviscerate and remove the
Revised: RG-RV2 by Fukuhara et al.
 Supplemental Figure 1 The generation of Spns2 conditional knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the wild type Spns2 locus (Spns2 + ), the targeted allele, the floxed allele (Spns2 f ) and the
Supplemental Figure 1 The generation of Spns2 conditional knockout mice. (A) Schematic representation of the wild type Spns2 locus (Spns2 + ), the targeted allele, the floxed allele (Spns2 f ) and the
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.4166
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/9/eaat5401/dc1 Supplementary Materials for GLK-IKKβ signaling induces dimerization and translocation of the AhR-RORγt complex in IL-17A induction and autoimmune
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/9/eaat5401/dc1 Supplementary Materials for GLK-IKKβ signaling induces dimerization and translocation of the AhR-RORγt complex in IL-17A induction and autoimmune
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Construction of lnckdm2b RFP reporter and lnckdm2b-knockout mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Construction of lnckdm2b RFP reporter and lnckdm2b-knockout mice. (a) ILC3s (Lin CD45 lo CD90 hi ) were isolated from small intestines, followed by immunofluorescence staining. LncKdm2b
Supplementary Figure 1 Construction of lnckdm2b RFP reporter and lnckdm2b-knockout mice. (a) ILC3s (Lin CD45 lo CD90 hi ) were isolated from small intestines, followed by immunofluorescence staining. LncKdm2b
Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified
 Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified by primers used for mrna expression analysis. Gray
Supplementary Figure 1. jmj30-2 and jmj32-1 produce null mutants. (a) Schematic drawing of JMJ30 and JMJ32 genome structure showing regions amplified by primers used for mrna expression analysis. Gray
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05574 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Results Additional Materials and Methods Analysis of epidermal wholemounts and sections: Tail epidermis. The patterned organisation of tail
doi: 10.1038/nature05574 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Results Additional Materials and Methods Analysis of epidermal wholemounts and sections: Tail epidermis. The patterned organisation of tail
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous gene tagging to study subcellular localization and chromatin binding. a, b, Schematic of experimental set-up to endogenously tag RNAi factors using the CRISPR Cas9 technology,
Supplementary Figure 1 Endogenous gene tagging to study subcellular localization and chromatin binding. a, b, Schematic of experimental set-up to endogenously tag RNAi factors using the CRISPR Cas9 technology,
Supplementary Figure 1: Analysis of monocyte subsets and lineage relationships. (a) Gating strategy for definition of MDP and cmop populations in BM
 Supplementary Figure 1: Analysis of monocyte subsets and lineage relationships. (a) Gating strategy for definition of MDP and cmop populations in BM of Cx3cr1 GFP/+ mice related to Fig. 1a. MDP was defined
Supplementary Figure 1: Analysis of monocyte subsets and lineage relationships. (a) Gating strategy for definition of MDP and cmop populations in BM of Cx3cr1 GFP/+ mice related to Fig. 1a. MDP was defined
Generation of App knock-in mice reveals deletion mutations protective against Alzheimer s. disease-like pathology. Nagata et al.
 Generation of App knock-in mice reveals deletion mutations protective against Alzheimer s disease-like pathology Nagata et al. Supplementary Fig 1. Previous App knock-in model did not show Aβ accumulation
Generation of App knock-in mice reveals deletion mutations protective against Alzheimer s disease-like pathology Nagata et al. Supplementary Fig 1. Previous App knock-in model did not show Aβ accumulation
Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Supplemental Materials. Matrix Proteases Contribute to Progression of Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Mice and Humans
 Supplemental Materials Matrix Proteases Contribute to Progression of Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Mice and Humans Madhusudhan Budatha, Shayzreen Roshanravan, Qian Zheng, Cecilia Weislander, Shelby L. Chapman,
Supplemental Materials Matrix Proteases Contribute to Progression of Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Mice and Humans Madhusudhan Budatha, Shayzreen Roshanravan, Qian Zheng, Cecilia Weislander, Shelby L. Chapman,
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.2548
 Supplementary Table 1: Genotypes of offspring and embryos from matings of Pmm2 WT/F118L mice with Pmm2 WT/R137H mice total events Pmm2 WT/WT Pmm2 WT/R137H Pmm2 WT/F118L Pmm2 R137H/F118L offspring 117 (100%)
Supplementary Table 1: Genotypes of offspring and embryos from matings of Pmm2 WT/F118L mice with Pmm2 WT/R137H mice total events Pmm2 WT/WT Pmm2 WT/R137H Pmm2 WT/F118L Pmm2 R137H/F118L offspring 117 (100%)
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Supplemental Information Itemized List Materials and Methods, Related to Supplemental Figures S5A-C and S6. Supplemental Figure S1, Related to Figures 1 and 2. Supplemental Figure S2, Related to Figure
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Fig. S1. Specificity of perilipin antibody in SAT compared to various organs. (A) Images of SAT at E18.5 stained with perilipin and CD31 antibody. Scale bars: 100 μm. SAT stained
Supplementary Figures Fig. S1. Specificity of perilipin antibody in SAT compared to various organs. (A) Images of SAT at E18.5 stained with perilipin and CD31 antibody. Scale bars: 100 μm. SAT stained
Supplemental Figure 1 (Figure S1), related to Figure 1 Figure S1 provides evidence to demonstrate Nfatc1Cre is a mouse line that directed gene
 Developmental Cell, Volume 25 Supplemental Information Brg1 Governs a Positive Feedback Circuit in the Hair Follicle for Tissue Regeneration and Repair Yiqin Xiong, Wei Li, Ching Shang, Richard M. Chen,
Developmental Cell, Volume 25 Supplemental Information Brg1 Governs a Positive Feedback Circuit in the Hair Follicle for Tissue Regeneration and Repair Yiqin Xiong, Wei Li, Ching Shang, Richard M. Chen,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3164 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of effective Gnas deletion and epithelial thickness. a, Representative genotyping in mice treated or not with tamoxifen to show Gnas deletion. To
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3164 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of effective Gnas deletion and epithelial thickness. a, Representative genotyping in mice treated or not with tamoxifen to show Gnas deletion. To
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary figures and supplementary tables. File name: Peer review file Description:
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary figures and supplementary tables. File name: Peer review file Description: Supplementary Figure 1. dcas9-mq1 fusion protein induces de novo
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary figures and supplementary tables. File name: Peer review file Description: Supplementary Figure 1. dcas9-mq1 fusion protein induces de novo
Supplemental Material
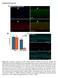 Supplemental Material Figure S1.(A) Immuno-staining of freshly isolated Myf5-Cre:ROSA-YFP fiber (B) Satellite cell enumeration in WT and cko mice from resting hind limb muscles. Bulk hind limb muscles
Supplemental Material Figure S1.(A) Immuno-staining of freshly isolated Myf5-Cre:ROSA-YFP fiber (B) Satellite cell enumeration in WT and cko mice from resting hind limb muscles. Bulk hind limb muscles
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS. -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells. - Two methods to produce transgenic animals:
 TRANSGENIC ANIMALS -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection - random insertion 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated gene
TRANSGENIC ANIMALS -transient transfection of cells -stable transfection of cells - Two methods to produce transgenic animals: 1- DNA microinjection - random insertion 2- embryonic stem cell-mediated gene
Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably expressing shrna sequences against TRF2 were examined by western blotting. shcon, shrna
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. The tetracycline-inducible CRISPR system. A) Hela cells stably expressing shrna sequences against TRF2 were examined by western blotting. shcon, shrna
A novel tool for monitoring endogenous alpha-synuclein transcription by NanoLuciferase
 A novel tool for monitoring endogenous alpha-synuclein transcription by NanoLuciferase tag insertion at the 3 end using CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing technique Sambuddha Basu 1, 3, Levi Adams 1, 3, Subhrangshu
A novel tool for monitoring endogenous alpha-synuclein transcription by NanoLuciferase tag insertion at the 3 end using CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing technique Sambuddha Basu 1, 3, Levi Adams 1, 3, Subhrangshu
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information MicroRNA-212/132 family is required for epithelial stromal interactions necessary for mouse mammary gland development Ahmet Ucar, Vida Vafaizadeh, Hubertus Jarry, Jan Fiedler,
Supplementary Information MicroRNA-212/132 family is required for epithelial stromal interactions necessary for mouse mammary gland development Ahmet Ucar, Vida Vafaizadeh, Hubertus Jarry, Jan Fiedler,
The RRPA knock-in allele was generated by homologous recombination in TC1 ES cells.
 Supplemental Materials Materials & Methods Generation of RRPA and RAPA Knock-in Mice The RRPA knock-in allele was generated by homologous recombination in TC1 ES cells. Targeted ES clones in which the
Supplemental Materials Materials & Methods Generation of RRPA and RAPA Knock-in Mice The RRPA knock-in allele was generated by homologous recombination in TC1 ES cells. Targeted ES clones in which the
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of B2M -/- ESCs. Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.3860
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of B2M -/- ESCs. (a) Maps of the B2M alleles in cells with the indicated B2M genotypes. Probes and restriction enzymes used in Southern blots are indicated (H, Hind III;
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of B2M -/- ESCs. (a) Maps of the B2M alleles in cells with the indicated B2M genotypes. Probes and restriction enzymes used in Southern blots are indicated (H, Hind III;
MeCP2. MeCP2/α-tubulin. GFP mir1-1 mir132
 Conservation Figure S1. Schematic showing 3 UTR (top; thick black line), mir132 MRE (arrow) and nucleotide sequence conservation (vertical black lines; http://genome.ucsc.edu). a GFP mir1-1 mir132 b GFP
Conservation Figure S1. Schematic showing 3 UTR (top; thick black line), mir132 MRE (arrow) and nucleotide sequence conservation (vertical black lines; http://genome.ucsc.edu). a GFP mir1-1 mir132 b GFP
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/ncb3575 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of key reagents and assays a, top, IHC with antibody recognizing specifically
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/ncb3575 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of key reagents and assays a, top, IHC with antibody recognizing specifically
Table S1. Oligonucleotide primer sequences
 Table S1. Oligonucleotide primer sequences Primer Name DNA Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Description CD19c CD19d Cre7 Sfpi1lox1 Sfpi1lox2 Sfpi1lox3 5 -AACCAGTCAACACCCTTCC-3 5 -CCAGACTAGATACAGACCAG-3 5 -TCAGCTACACCAGAGACGG-3
Table S1. Oligonucleotide primer sequences Primer Name DNA Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Description CD19c CD19d Cre7 Sfpi1lox1 Sfpi1lox2 Sfpi1lox3 5 -AACCAGTCAACACCCTTCC-3 5 -CCAGACTAGATACAGACCAG-3 5 -TCAGCTACACCAGAGACGG-3
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Taylor et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201403021/dc1 Figure S1. Representative images of Cav 1a -YFP mutants with and without LMB treatment.
Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Taylor et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201403021/dc1 Figure S1. Representative images of Cav 1a -YFP mutants with and without LMB treatment.
 Figure S1. Generation of HspA4 -/- mice. (A) Structures of the wild-type (Wt) HspA4 -/- allele, targeting vector and targeted allele are shown together with the relevant restriction sites. The filled rectangles
Figure S1. Generation of HspA4 -/- mice. (A) Structures of the wild-type (Wt) HspA4 -/- allele, targeting vector and targeted allele are shown together with the relevant restriction sites. The filled rectangles
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic and results of screening the combinatorial antibody library for Sox2 replacement activity. A single batch of MEFs were plated and transduced with doxycycline inducible
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic and results of screening the combinatorial antibody library for Sox2 replacement activity. A single batch of MEFs were plated and transduced with doxycycline inducible
monoclonal antibody. (a) The specificity of the anti-rhbdd1 monoclonal antibody was examined in
 Supplementary information Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1 Determination of the s pecificity of in-house anti-rhbdd1 mouse monoclonal antibody. (a) The specificity of the anti-rhbdd1 monoclonal
Supplementary information Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1 Determination of the s pecificity of in-house anti-rhbdd1 mouse monoclonal antibody. (a) The specificity of the anti-rhbdd1 monoclonal
Rapid differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into functional motor neurons by
 Supplementary Information Rapid differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into functional motor neurons by mrnas encoding transcription factors Sravan Kumar Goparaju, Kazuhisa Kohda, Keiji Ibata,
Supplementary Information Rapid differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into functional motor neurons by mrnas encoding transcription factors Sravan Kumar Goparaju, Kazuhisa Kohda, Keiji Ibata,
Supplementary Data. Generation and Characterization of Mixl1- Inducible Embryonic Stem Cells Under the Control of Oct3/4 Promoter or CAG Promoter
 Supplementary Data Generation and Characterization of Mixl1- Inducible Embryonic Stem Cells Under the Control of Oct3/4 Promoter or CAG Promoter We first introduced an expression unit composed of a tetresponse
Supplementary Data Generation and Characterization of Mixl1- Inducible Embryonic Stem Cells Under the Control of Oct3/4 Promoter or CAG Promoter We first introduced an expression unit composed of a tetresponse
Pei et al. Supplementary Figure S1
 Pei et al. Supplementary Figure S1 C H-CUL9: + + + + + Myc-ROC1: - - + + + U2OS/pcDN3 U2OS/H-CUL9 U2OS/ + H-CUL9 IP: -H -myc input -H -myc 1 2 3 4 5 H-CUL9 Myc-ROC1 -H -H -H -H H-CUL9: wt RR myc-roc1:
Pei et al. Supplementary Figure S1 C H-CUL9: + + + + + Myc-ROC1: - - + + + U2OS/pcDN3 U2OS/H-CUL9 U2OS/ + H-CUL9 IP: -H -myc input -H -myc 1 2 3 4 5 H-CUL9 Myc-ROC1 -H -H -H -H H-CUL9: wt RR myc-roc1:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION MATERIALS AND METHODS I. Generation of mutant mice Both mutant mouse lines were generated using B6N;B6N-Snap29 tm1a(eucomm)wtsi heterozygous knock-in mice (Snap29 fl/wt ) derived
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION MATERIALS AND METHODS I. Generation of mutant mice Both mutant mouse lines were generated using B6N;B6N-Snap29 tm1a(eucomm)wtsi heterozygous knock-in mice (Snap29 fl/wt ) derived
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. (A) UCSC Genome Browser view of region immediately downstream of the NEUROG3 start codon. All candidate grna target sites which meet the G(N 19 )NGG constraint are aligned to illustrate
Supplementary Figure 1. (A) UCSC Genome Browser view of region immediately downstream of the NEUROG3 start codon. All candidate grna target sites which meet the G(N 19 )NGG constraint are aligned to illustrate
Detection of Histone Modifications at Specific Gene Loci in Single Cells in Histological Sections
 Detection of Histone Modifications at Specific Gene Loci in Single Cells in Histological Sections Delphine Gomez; Laura L Shankman; Anh T Nguyen; Gary K Owens. Supplementary Figures 1-13 Supplementary
Detection of Histone Modifications at Specific Gene Loci in Single Cells in Histological Sections Delphine Gomez; Laura L Shankman; Anh T Nguyen; Gary K Owens. Supplementary Figures 1-13 Supplementary
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Ihh interacts preferentially with its upstream neighboring gene Nhej1. Genes are indicated by gray lines, and Ihh and Nhej1 are highlighted in blue. 4C seq performed in E14.5 limbs
Supplementary Figure 1 Ihh interacts preferentially with its upstream neighboring gene Nhej1. Genes are indicated by gray lines, and Ihh and Nhej1 are highlighted in blue. 4C seq performed in E14.5 limbs
SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector
 SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector Richard J. Wall 1,#, Magali Roques 1,+, Nicholas J. Katris
SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector Richard J. Wall 1,#, Magali Roques 1,+, Nicholas J. Katris
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/85/ra48/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The VDAC2-BAK Rheostat Controls Thymocyte Survival Decheng Ren, Hyungjin Kim, Ho-Chou Tu, Todd D. Westergard, Jill K.
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/85/ra48/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The VDAC2-BAK Rheostat Controls Thymocyte Survival Decheng Ren, Hyungjin Kim, Ho-Chou Tu, Todd D. Westergard, Jill K.
Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic representation of mouse lines Pax6 fl/fl and mrx-cre used in this study. (A) To generate Pax6 fl/ fl
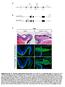 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic representation of mouse lines Pax6 fl/fl and mrx-cre used in this study. (A) To generate Pax6 fl/ fl, loxp sites flanking exons 3-6 (red arrowheads) were introduced into
Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic representation of mouse lines Pax6 fl/fl and mrx-cre used in this study. (A) To generate Pax6 fl/ fl, loxp sites flanking exons 3-6 (red arrowheads) were introduced into
Flow cytometry Stained cells were analyzed and sorted by SORP FACS Aria (BD Biosciences).
 Mice C57BL/6-Ly5.1 or -Ly5.2 congenic mice were used for LSK transduction and competitive repopulation assays. Animal care was in accordance with the guidelines of Keio University for animal and recombinant
Mice C57BL/6-Ly5.1 or -Ly5.2 congenic mice were used for LSK transduction and competitive repopulation assays. Animal care was in accordance with the guidelines of Keio University for animal and recombinant
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3240 Supplementary Figure 1 GBM cell lines display similar levels of p100 to p52 processing but respond differentially to TWEAK-induced TERT expression according to TERT promoter mutation
Supplementary Figure 1. Adipogenic protein expression in WT and KO MEFs after 7 days of adipogenic differentiation.
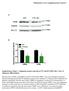 Merkestein et al. Supplementary Figure 1 A PLIN WT FTO KO 72 kda FABP4 17 kda HSC70 72 kda B Supplementary Figure 1. Adipogenic protein expression in WT and KO MEFs after 7 days of adipogenic differentiation.
Merkestein et al. Supplementary Figure 1 A PLIN WT FTO KO 72 kda FABP4 17 kda HSC70 72 kda B Supplementary Figure 1. Adipogenic protein expression in WT and KO MEFs after 7 days of adipogenic differentiation.
Spermatazoa. Sertoli cells. Morc1 WT adult. Morc1 KO adult. Morc1 WT P14.5. Morc1 KO P14.5. Germ cells. Germ cells. Spermatids.
 a. Spermatazoa Sertoli cells Morc1 WT adult c. Morc1 KO adult Morc1 WT P1.5 Morc1 KO P1.5 Morc1 WT adult Morc1 KO adult Germ cells Germ cells Spermatids Spermatozoa Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation
a. Spermatazoa Sertoli cells Morc1 WT adult c. Morc1 KO adult Morc1 WT P1.5 Morc1 KO P1.5 Morc1 WT adult Morc1 KO adult Germ cells Germ cells Spermatids Spermatozoa Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation
WT Day 90 after injections
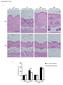 Supplementary Figure 1 a Day 1 after injections Day 9 after injections Klf5 +/- Day 1 after injections Klf5 +/- Day 9 after injections BLM PBS b Day 1 after injections Dermal thickness (μm) 3 1 Day 9 after
Supplementary Figure 1 a Day 1 after injections Day 9 after injections Klf5 +/- Day 1 after injections Klf5 +/- Day 9 after injections BLM PBS b Day 1 after injections Dermal thickness (μm) 3 1 Day 9 after
A Low salt diet. C Low salt diet + mf4-31c1 3. D High salt diet + mf4-31c1 3. B High salt diet
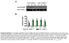 A Low salt diet GV [AU]:. [mmhg]: 0..... 09 9 7 B High salt diet GV [AU]:. [mmhg]: 7 8...0. 7.8 8.. 0 8 7 C Low salt diet + mf-c GV [AU]:. [mmhg]:.0.9 8.7.7. 7 8 0 D High salt diet + mf-c E Lymph capillary
A Low salt diet GV [AU]:. [mmhg]: 0..... 09 9 7 B High salt diet GV [AU]:. [mmhg]: 7 8...0. 7.8 8.. 0 8 7 C Low salt diet + mf-c GV [AU]:. [mmhg]:.0.9 8.7.7. 7 8 0 D High salt diet + mf-c E Lymph capillary
Regulation of axonal and dendritic growth by the extracellular calcium-sensing
 Regulation of axonal and dendritic growth by the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR). Thomas N. Vizard, Gerard W. O Keeffe, Humberto Gutierrez, Claudine H. Kos, Daniela Riccardi, Alun M. Davies
Regulation of axonal and dendritic growth by the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR). Thomas N. Vizard, Gerard W. O Keeffe, Humberto Gutierrez, Claudine H. Kos, Daniela Riccardi, Alun M. Davies
Supplementary Figure 1. Expressions of stem cell markers decreased in TRCs on 2D plastic. TRCs were cultured on plastic for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days,
 Supplementary Figure 1. Expressions of stem cell markers decreased in TRCs on 2D plastic. TRCs were cultured on plastic for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days, respectively, and their mrnas were quantified by real time
Supplementary Figure 1. Expressions of stem cell markers decreased in TRCs on 2D plastic. TRCs were cultured on plastic for 1, 3, 5, or 7 days, respectively, and their mrnas were quantified by real time
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12119 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND LEGENDS pre-let-7a- 1 +14U pre-let-7a- 1 Ddx3x Dhx30 Dis3l2 Elavl1 Ggt5 Hnrnph 2 Osbpl5 Puf60 Rnpc3 Rpl7 Sf3b3 Sf3b4 Tia1 Triobp U2af1 U2af2 1 6 2 4 3
doi:10.1038/nature12119 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND LEGENDS pre-let-7a- 1 +14U pre-let-7a- 1 Ddx3x Dhx30 Dis3l2 Elavl1 Ggt5 Hnrnph 2 Osbpl5 Puf60 Rnpc3 Rpl7 Sf3b3 Sf3b4 Tia1 Triobp U2af1 U2af2 1 6 2 4 3
Supplementary Data. Flvcr1a TCTAAGGCCCAGTAGGACCC GGCCTCAACTGCCTGGGAGC AGAGGGCAACCTCGGTGTCC
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Materials and Methods Measurement of reactive oxygen species accumulation in fresh intestinal rings Accumulation of reactive oxygen species in fresh intestinal rings was
Supplementary Data Supplementary Materials and Methods Measurement of reactive oxygen species accumulation in fresh intestinal rings Accumulation of reactive oxygen species in fresh intestinal rings was
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. ZBTB20 expression in the developing DRG. ZBTB20 expression in the developing DRG was detected by immunohistochemistry using anti-zbtb20 antibody 9A10 on
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. ZBTB20 expression in the developing DRG. ZBTB20 expression in the developing DRG was detected by immunohistochemistry using anti-zbtb20 antibody 9A10 on
Figure S1. Figure S2. Figure S3 HB Anti-FSP27 (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab. Anti-GST-FSP27(45-127) Ab.
 / 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
/ 36B4 mrna ratio Figure S1 * 2. 1.6 1.2.8 *.4 control TNFα BRL49653 Figure S2 Su bw AT p iw Anti- (COOH-terminal peptide) Ab Blot : Anti-GST-(45-127) Ab β-actin Figure S3 HB2 HW AT BA T Figure S4 A TAG
Biology Open (2015): doi: /bio : Supplementary information
 Fig. S1. Verification of optimal conditions for the generation of LIF-dependent inscs Representative images (from five repeat experiments) of human primary fibroblasts undergoing reprogramming for 21 days
Fig. S1. Verification of optimal conditions for the generation of LIF-dependent inscs Representative images (from five repeat experiments) of human primary fibroblasts undergoing reprogramming for 21 days
Summary MicroRNAs (mirnas) are genomically encoded small RNAs used by organisms to regulate the expression of proteins generated from messenger RNA
 Summary MicroRNAs (mirnas) are genomically encoded small RNAs used by organisms to regulate the expression of proteins generated from messenger RNA transcripts. The in vivo requirement of specific mirnas
Summary MicroRNAs (mirnas) are genomically encoded small RNAs used by organisms to regulate the expression of proteins generated from messenger RNA transcripts. The in vivo requirement of specific mirnas
Myofibroblasts in kidney fibrosis. LeBleu et al.
 Origin and Function of Myofibroblasts in Kidney Fibrosis Valerie S. LeBleu, Gangadhar Taduri, Joyce O Connell, Yingqi Teng, Vesselina G. Cooke, Craig Woda, Hikaru Sugimoto and Raghu Kalluri Supplementary
Origin and Function of Myofibroblasts in Kidney Fibrosis Valerie S. LeBleu, Gangadhar Taduri, Joyce O Connell, Yingqi Teng, Vesselina G. Cooke, Craig Woda, Hikaru Sugimoto and Raghu Kalluri Supplementary
a Lamtor1 (gene) b Lamtor1 (mrna) c WT Lamtor1 Lamtor1 flox Lamtor2 A.U. p = LysM-Cre Lamtor3 Lamtor4 Lamtor5 BMDMs: Φ WT Φ KO β-actin WT BMDMs
 a Lamtor (gene) b Lamtor (mrna) c BMDMs: Φ WT Φ KO Lamtor flox 8 bp LysM-Cre 93 bp..5 p =.4 WT BMDMs: Φ WT Φ KO Lamtor (protein) BMDMs: Φ WT Φ KO Lamtor 8 kda Lamtor 4 kda Lamtor3 4 kda Lamtor4 kda Lamtor5.5
a Lamtor (gene) b Lamtor (mrna) c BMDMs: Φ WT Φ KO Lamtor flox 8 bp LysM-Cre 93 bp..5 p =.4 WT BMDMs: Φ WT Φ KO Lamtor (protein) BMDMs: Φ WT Φ KO Lamtor 8 kda Lamtor 4 kda Lamtor3 4 kda Lamtor4 kda Lamtor5.5
Table S1. Primers used in the study
 Table S1. Primers used in the study Primer name Application Sequence I1F16 Genotyping GGCAAGTGAGTGAGTGCCTA I1R11 Genotyping CCCACTCGTATTGACGCTCT V19 Genotyping GGGTCTCAAAGTCAGGGTCA D18Mit184-F Genotyping
Table S1. Primers used in the study Primer name Application Sequence I1F16 Genotyping GGCAAGTGAGTGAGTGCCTA I1R11 Genotyping CCCACTCGTATTGACGCTCT V19 Genotyping GGGTCTCAAAGTCAGGGTCA D18Mit184-F Genotyping
Supplementary Figure 1 Muscle dystrophic phenotype is absent at P6 in PKO mice. (a) Size
 Supplementary Figure 1 Muscle dystrophic phenotype is absent at P6 in PKO mice. (a) Size comparison of the P6 control and PKO mice. (b) H&E staining of hind-limb muscles from control and PKO mice at P6.
Supplementary Figure 1 Muscle dystrophic phenotype is absent at P6 in PKO mice. (a) Size comparison of the P6 control and PKO mice. (b) H&E staining of hind-limb muscles from control and PKO mice at P6.
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3494
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
Supplementary Figure 1 Pol structure-function analysis (a) Inactivating polymerase and helicase mutations do not alter the stability of Pol. Flag epitopes were introduced using CRISPR/Cas9 gene targeting
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS
 TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Wnt7b Is an Important Intrinsic Regulator of Hair Follicle Stem Cell Homeostasis and Hair Follicle Cycling EVE KANDYBA, a,b KRZYSZTOF KOBIELAK a,b Key Words. Hair follicle stem
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Wnt7b Is an Important Intrinsic Regulator of Hair Follicle Stem Cell Homeostasis and Hair Follicle Cycling EVE KANDYBA, a,b KRZYSZTOF KOBIELAK a,b Key Words. Hair follicle stem
administration of tamoxifen. Bars show mean ± s.e.m (n=10-11). P-value was determined by
 Supplementary Figure 1. Chimerism of CD45.2 + GFP + cells at 1 month post transplantation No significant changes were detected in chimerism of CD45.2 + GFP + cells between recipient mice repopulated with
Supplementary Figure 1. Chimerism of CD45.2 + GFP + cells at 1 month post transplantation No significant changes were detected in chimerism of CD45.2 + GFP + cells between recipient mice repopulated with
Positive selection gates for the collection of LRCs or nonlrcs had to be drawn based on the location and
 Determining positive selection gates for LRCs and nonlrcs Positive selection gates for the collection of LRCs or nonlrcs had to be drawn based on the location and shape of the Gaussian distributions. For
Determining positive selection gates for LRCs and nonlrcs Positive selection gates for the collection of LRCs or nonlrcs had to be drawn based on the location and shape of the Gaussian distributions. For
Supplementary Figure Legends
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 gene targeting strategy for disruption of chicken gene, related to Figure 1 (f)-(i). (a) The locus and the targeting constructs showing HpaI restriction sites. The
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 gene targeting strategy for disruption of chicken gene, related to Figure 1 (f)-(i). (a) The locus and the targeting constructs showing HpaI restriction sites. The
PrimePCR Assay Validation Report
 Gene Information Gene Name keratin 5 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID KRT5 Human The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the keratin
Gene Information Gene Name keratin 5 Gene Symbol Organism Gene Summary Gene Aliases RefSeq Accession No. UniGene ID Ensembl Gene ID KRT5 Human The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the keratin
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Zranb1 gene targeting.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Zranb1 gene targeting. (a) Schematic picture of Zranb1 gene targeting using an FRT-LoxP vector, showing the first 6 exons of Zranb1 gene (exons 7-9 are not shown). Targeted mice
Supplementary Figure 1 Zranb1 gene targeting. (a) Schematic picture of Zranb1 gene targeting using an FRT-LoxP vector, showing the first 6 exons of Zranb1 gene (exons 7-9 are not shown). Targeted mice
The cell-cycle regulator c-myc is essential for the formation and maintenance of germinal centers
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The cell-cycle regulator c-myc is essential for the formation and maintenance of germinal centers Dinis Pedro Calado 1,2, Yoshiteru Sasaki 3, Susana A Godinho 4, Alex Pellerin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The cell-cycle regulator c-myc is essential for the formation and maintenance of germinal centers Dinis Pedro Calado 1,2, Yoshiteru Sasaki 3, Susana A Godinho 4, Alex Pellerin
Flowcytometry-based purity analysis of peritoneal macrophage culture.
 Liao et al., KLF4 regulates macrophage polarization Revision of Manuscript 45444-RG- Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S Flowcytometry-based purity analysis of peritoneal macrophage culture. Thioglycollate
Liao et al., KLF4 regulates macrophage polarization Revision of Manuscript 45444-RG- Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S Flowcytometry-based purity analysis of peritoneal macrophage culture. Thioglycollate
Alternative Cleavage and Polyadenylation of RNA
 Developmental Cell 18 Supplemental Information The Spen Family Protein FPA Controls Alternative Cleavage and Polyadenylation of RNA Csaba Hornyik, Lionel C. Terzi, and Gordon G. Simpson Figure S1, related
Developmental Cell 18 Supplemental Information The Spen Family Protein FPA Controls Alternative Cleavage and Polyadenylation of RNA Csaba Hornyik, Lionel C. Terzi, and Gordon G. Simpson Figure S1, related
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Defective T and B cell lineage development in the absence of 53BP1. a, Average number of thymocytes in WT, 53BP1 /, p53 /, 53BP1 / / p53, Nbs1 tr735 and 53BP1 / Nbs1 tr735 mice
Supplementary Figure 1. Defective T and B cell lineage development in the absence of 53BP1. a, Average number of thymocytes in WT, 53BP1 /, p53 /, 53BP1 / / p53, Nbs1 tr735 and 53BP1 / Nbs1 tr735 mice
The non-muscle-myosin-ii heavy chain Myh9 mediates colitis-induced epithelium injury by restricting Lgr5+ stem cells
 Supplementary Information The non-muscle-myosin-ii heavy chain Myh9 mediates colitis-induced epithelium injury by restricting Lgr5+ stem cells Bing Zhao 1,3, Zhen Qi 1,3, Yehua Li 1,3, Chongkai Wang 2,
Supplementary Information The non-muscle-myosin-ii heavy chain Myh9 mediates colitis-induced epithelium injury by restricting Lgr5+ stem cells Bing Zhao 1,3, Zhen Qi 1,3, Yehua Li 1,3, Chongkai Wang 2,
Supplemental data. Zhao et al. (2009). The Wuschel-related homeobox gene WOX11 is required to activate shoot-borne crown root development in rice.
 Supplemental data. Zhao et al. (2009). The Wuschel-related homeobox gene WOX11 is required to activate shoot-borne crown root development in rice. A B Supplemental Figure 1. Expression of WOX11p-GUS WOX11-GFP
Supplemental data. Zhao et al. (2009). The Wuschel-related homeobox gene WOX11 is required to activate shoot-borne crown root development in rice. A B Supplemental Figure 1. Expression of WOX11p-GUS WOX11-GFP
We designed the targeting vector in such a way that the first exon was flanked by two LoxP sites and
 Mice We designed the targeting vector in such a way that the first exon was flanked by two LoxP sites and an Frt flanked neo cassette (Fig. S1A). Targeted BA1 (C57BL/6 129/SvEv) hybrid embryonic stem cells
Mice We designed the targeting vector in such a way that the first exon was flanked by two LoxP sites and an Frt flanked neo cassette (Fig. S1A). Targeted BA1 (C57BL/6 129/SvEv) hybrid embryonic stem cells
Supplementary Figure 1 An overview of pirna biogenesis during fetal mouse reprogramming. (a) (b)
 Supplementary Figure 1 An overview of pirna biogenesis during fetal mouse reprogramming. (a) A schematic overview of the production and amplification of a single pirna from a transposon transcript. The
Supplementary Figure 1 An overview of pirna biogenesis during fetal mouse reprogramming. (a) A schematic overview of the production and amplification of a single pirna from a transposon transcript. The
Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss Yunjong Lee, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Joo-Ho Shin, Yun-Il Lee, Han Seok Ko, Debbie Swing,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Parthanatos mediates AIMP2-activated age-dependent dopaminergic neuronal loss Yunjong Lee, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Joo-Ho Shin, Yun-Il Lee, Han Seok Ko, Debbie Swing,
Supplementary Table S1
 Primers used in RT-qPCR, ChIP and Bisulphite-Sequencing. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR primers Supplementary Table S1 gene Forward primer sequence Reverse primer sequence Product TRAIL CAACTCCGTCAGCTCGTTAGAAAG
Primers used in RT-qPCR, ChIP and Bisulphite-Sequencing. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR primers Supplementary Table S1 gene Forward primer sequence Reverse primer sequence Product TRAIL CAACTCCGTCAGCTCGTTAGAAAG
Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of sirna in PC3 and H1299 cells PC3 (a) and H1299 (b) cells were transfected with sirna oligonucleotides
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of sirna in PC3 and H1299 cells PC3 (a) and H1299 (b) cells were transfected with sirna oligonucleotides targeting RCP (SMARTPool (RCP) or two individual oligos (RCP#1
Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of sirna in PC3 and H1299 cells PC3 (a) and H1299 (b) cells were transfected with sirna oligonucleotides targeting RCP (SMARTPool (RCP) or two individual oligos (RCP#1
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/3/146/ra80/dc1 Supplementary Materials for DNMT1 Stability Is Regulated by Proteins Coordinating Deubiquitination and Acetylation-Driven Ubiquitination Zhanwen
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/3/146/ra80/dc1 Supplementary Materials for DNMT1 Stability Is Regulated by Proteins Coordinating Deubiquitination and Acetylation-Driven Ubiquitination Zhanwen
University of Dundee. Published in: Scientific Reports. DOI: /srep Publication date: 2016
 University of Dundee SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector Wall, Richard J.; Roques, Magali; Katris,
University of Dundee SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector Wall, Richard J.; Roques, Magali; Katris,
Figure S1. Schematic of myeloid lineage reporter mouse model used in this study.
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Schematic of myeloid lineage reporter mouse model used in this study. (A) The Lyzs-Cre mouse was crossed with Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(eyfp)cos/ J mice to label cells expressing
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Schematic of myeloid lineage reporter mouse model used in this study. (A) The Lyzs-Cre mouse was crossed with Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(eyfp)cos/ J mice to label cells expressing
Supplementary Figure 1. Xbp1 deficiency does not alter hematopoietic cellularity.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Xbp1 deficiency does not alter hematopoietic cellularity. Absolute number of leukocytes obtained from bone marrow (BM, 2 tibias and 2 femurs per mouse) of Xbp1 f/f and Xbp1 Vav1
Supplementary Figure 1 Xbp1 deficiency does not alter hematopoietic cellularity. Absolute number of leukocytes obtained from bone marrow (BM, 2 tibias and 2 femurs per mouse) of Xbp1 f/f and Xbp1 Vav1
Supplementary Figure 1. Mouse genetic models used for identification of Axin2-
 Supplementary Figure 1. Mouse genetic models used for identification of Axin2- expressing cells and their derivatives. Schematic representations illustrate genetic cell labeling strategies to identify
Supplementary Figure 1. Mouse genetic models used for identification of Axin2- expressing cells and their derivatives. Schematic representations illustrate genetic cell labeling strategies to identify
A population of Nestin expressing progenitors in the cerebellum exhibits increased tumorigenicity
 A population of Nestin expressing progenitors in the cerebellum exhibits increased tumorigenicity Peng Li 1,2, Fang Du 1, Larra W. Yuelling 1, Tiffany Lin 3, Renata E. Muradimova 1, Rossella Tricarico
A population of Nestin expressing progenitors in the cerebellum exhibits increased tumorigenicity Peng Li 1,2, Fang Du 1, Larra W. Yuelling 1, Tiffany Lin 3, Renata E. Muradimova 1, Rossella Tricarico
Supplementary Information. Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish
 Supplementary Information Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish Hagen R. Witzel 1, Sirisha Cheedipudi 1, Rui Gao 1, Didier Y.R. Stainier 2 and Gergana D. Dobreva 1,3* 1 Origin
Supplementary Information Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish Hagen R. Witzel 1, Sirisha Cheedipudi 1, Rui Gao 1, Didier Y.R. Stainier 2 and Gergana D. Dobreva 1,3* 1 Origin
embryos. Asterisk represents loss of or reduced expression. Brackets represent
 Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1. tfec expression is highly enriched in tail endothelial cells (A- B) ISH of tfec at 15 and 16hpf in WT embryos. (C- D) ISH of tfec at 36 and 38hpf in WT embryos.
Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1. tfec expression is highly enriched in tail endothelial cells (A- B) ISH of tfec at 15 and 16hpf in WT embryos. (C- D) ISH of tfec at 36 and 38hpf in WT embryos.
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 PPAR-γ is dispensable for the development of tissue macrophages in the heart, kidneys, lamina propria and white adipose tissue. Plots show the expression of F4/80 and CD11b (a) or
Supplementary Figure 1 PPAR-γ is dispensable for the development of tissue macrophages in the heart, kidneys, lamina propria and white adipose tissue. Plots show the expression of F4/80 and CD11b (a) or
ASPP1 Fw GGTTGGGAATCCACGTGTTG ASPP1 Rv GCCATATCTTGGAGCTCTGAGAG
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids: the following plasmids were used in the supplementary data: pwzl-myc- Lats2 (Aylon et al, 2006), pretrosuper-vector and pretrosuper-shp53 (generous gift of
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids: the following plasmids were used in the supplementary data: pwzl-myc- Lats2 (Aylon et al, 2006), pretrosuper-vector and pretrosuper-shp53 (generous gift of
of NOBOX. Supplemental Figure S1F shows the staining profile of LHX8 antibody (Abcam, ab41519), which is a
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS LHX8 Staining During the course of this work, it came to our attention that the NOBOX antibody used in this study had been discontinued. There are a number of other nuclear
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS LHX8 Staining During the course of this work, it came to our attention that the NOBOX antibody used in this study had been discontinued. There are a number of other nuclear
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype and genotype of cultured and transplanted S1 KCST (A) Brightfield and mcherry fluorescence images of the spheres
 Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype and genotype of cultured and transplanted S1 KCST (A) Brightfield and mcherry fluorescence images of the spheres generated from the CD133-positive cells infected with
Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotype and genotype of cultured and transplanted S1 KCST (A) Brightfield and mcherry fluorescence images of the spheres generated from the CD133-positive cells infected with
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of migg1-yf mice. (A) Targeting strategy. Upper panel: schematic organization of the murine ɣ1 immunoglobulin
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of migg1-yf mice. (A) Targeting strategy. Upper panel: schematic organization of the murine ɣ1 immunoglobulin locus. The EcoRI restriction site between exons M1 and M2
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation of migg1-yf mice. (A) Targeting strategy. Upper panel: schematic organization of the murine ɣ1 immunoglobulin locus. The EcoRI restriction site between exons M1 and M2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
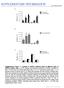 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12474 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of mtdna mutation loads in different types of mtdna mutator mice. a, PCR, cloning, and sequencing analysis of mtdna mutations
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12474 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of mtdna mutation loads in different types of mtdna mutator mice. a, PCR, cloning, and sequencing analysis of mtdna mutations
Supplementary Figures and Figure legends
 Supplementary Figures and Figure legends 3 Supplementary Figure 1. Conditional targeting construct for the murine Satb1 locus with a modified FLEX switch. Schematic of the wild type Satb1 locus; the conditional
Supplementary Figures and Figure legends 3 Supplementary Figure 1. Conditional targeting construct for the murine Satb1 locus with a modified FLEX switch. Schematic of the wild type Satb1 locus; the conditional
amplify the conditional allele (2-lox) and recombined allele (1-lox) following tamoxifen
 Supplementary data Supplementary Table 1. Real-time PCR primer sequences Supplementary Fig. 1. (A) Genomic map of the Vhl (2-lox) conditional allele. Numbered boxes represent exon 1, which is targeted
Supplementary data Supplementary Table 1. Real-time PCR primer sequences Supplementary Fig. 1. (A) Genomic map of the Vhl (2-lox) conditional allele. Numbered boxes represent exon 1, which is targeted
